User login
The Secrets of Optimal Migraine Treatment
Do you use nonpharmacologic approaches to treat your patients living with migraines? Which ones do you prefer?
I always like to start with nonpharmacologic approaches (also termed bio-behavioral approaches) with my patients. I talk to patients about sleep hygiene because if they don't sleep well, they're going to have more headaches. Most of my patients have issues with sleep and rarely feel refreshed in the morning. Most of them have middle insomnia; they wake up between 2 am and 4 am and cannot get back to sleep.
I also talk to my patients about eating properly. If patients don't eat on time or miss a meal, they often get headaches. While timing is probably more critical, what they eat is important also. Poor diet can lead to decreased energy, and patients can become obese. Obesity impacts headache—especially migraine. I am not sure if there are any particularly good or bad foods for migraine patients, but in general, they should eat fewer fatty foods, fewer carbohydrates, more chicken, and fish than red meat, and a lot of fruits, vegetables, salads, nuts, and whole grains. A good trick is to limit the volume of each meal; do not go back for seconds and limit desserts and alcohol.
Exercise is beneficial to decrease headaches, and the converse is even more true. Patients should start with low-impact, brief exercise like short walks and slowly build up to 20 minutes of cardio as tolerated, 3 to 5 times per week. Like poor diet choices, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity and then not doing well with headaches and so on.
What are your goals for treating your patients at the start of a migraine attack?
The goals for treating a migraine attack are to reduce the intensity of the pain quickly and, if possible, make the patient pain-free in ≤2 hours. We also try to reduce their most bothersome symptom, which is usually sensitivity to light or nausea, without causing any adverse effects from the treatment. Possibly as important, we want to get the patient back to functioning at work or at home, so they need no further treatment for that attack.
Unfortunately, many of the medicines we have available do cause adverse events, which are sometimes worse than the headache itself. A patient can't continue to take a medication that causes significant side effects.
It is also critical to stop the headache quickly, as we don't want patients to take the prescribed acute care medicine and then, if they don’t feel like it’s working, proceed to take aspirin and then acetaminophen and then an anti-inflammatory tablet. The more medicine they take, the more likely they'll get medication overuse headache (MOH).
MOH is not a great name, but it does imply that patients are taking one or many medications per week to stop their headaches, not realizing that this can worsen and prolong their headaches rather than helping them. They can also experience adverse events from taking so much medication.
Finally, we want the patients to get rid of a headache so that they do not need to go to an emergency room, and we want to use medication that is cost effective and gets the patient functioning. Some medicines and devices are extremely expensive and not well covered by insurance companies but imagine the patient who takes a new medicine or uses a new device and gets better rapidly. If they hadn't done that, they may have lost a day or 2 of pay from missing work, or they might have gone to work and not done a very effective job because they were feeling miserable and couldn’t think or speak well.
Do you prescribe triptans?
Definitely. The triptans first became available 30 years ago. There are 7 different triptans, and some work better for some patients than others. They come in tablets, injections, and nasal sprays. Sometimes patients need to try 2 or 3 different triptans to see which one is the most effective for them. If a patient has no success with tablets, there's a possibility that an injection or even a nasal spray would be more effective.
There are 2 triptans available as a nasal spray. I happen to like a triptan nasal spray called zolmitriptan, which usually works faster with fewer adverse events than the tablets.
There's also an injection of sumatriptan available, which is the fastest way to get relief from a triptan. Patients usually don't prefer it because it is an injection that they give themselves via an auto injector, and it may hurt and can be a bit complex to administer. There are definitely more adverse events when sumatriptan is given by injection, but because an injection can deliver very fast results that stop the headache reliably, some patients prefer it.
Triptans have been the mainstay treatment to stop an ongoing migraine attack for 30 years. We have always known there is some constriction of blood vessels and triptan-related side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and tingling sensations, so not every patient can take them. The newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) do not constrict blood vessels and have fewer adverse events but cost a lot more if not covered by insurance.
Another newer, nontriptan nasal spray is dihydroergotamine (DHE) mesylate for acute care. It is one of the best medications to use if the patient’s migraine has been going on for 24 hours, as it tends to work well for a long-lasting headache. It also works for a long period, giving the patient a rest before their next attack. A nasal spray works faster than a tablet form, as the medication is absorbed from the nasal mucosa and does not have to make its way through the GI tract, then to the liver for metabolism, and finally, up to the brain before it begins to work. There can be some side effects in the nose such as discomfort or stuffiness, but if it works well, patients usually tolerate it.
There's also a newer class of medicine called ditans. In a recent study, lasmiditan, which comes in a 50-mg and a 100-mg tablet for acute care of migraine, showed no vasoconstrictive effects, suggesting that ditans could be a safe option for patients living with chronic cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. Lasmiditan could be an alternative to triptans when they are contraindicated in patients with blood vessel disease, obesity, high blood pressure or cholesterol levels, or in nonresponsive patients. Lasmiditan does cause some dizziness and drowsiness, so patients cannot drive for 8 hours after taking it. However, it does have good efficacy.
When do you prescribe gepants?
Gepants are small-molecule CGRP receptor blockers. They are tablets that sit on the receptor, preventing the CGRP from docking on the receptor and increasing the headache during a migraine attack. There are 2 gepants that can be used to stop a headache that is just starting or in progress: ubrogepant and rimegepant.
Ubrogepant is a regular tablet that is available in 50-mg or 100-mg strengths. If the first dose does not make a patient pain free, a second dose is recommended about 2 hours later. Rimegepant is a meltaway tablet and only comes in a 75-mg strength. It should be taken early in the attack, and usually the patient does not need further treatment that day. If they do, they need to switch to another treatment, as rimegepant should not be repeated that day. Rimegepant may be used for both acute care and prevention. It is the only tablet that can be used for both.
Both drugs have been shown to provide pain freedom for about 20% of patients at 2 hours, which is statistically better than the patients that received the placebo. These drugs generally don’t cause many adverse events but can cause a little nausea or drowsiness in some patients. Ubrogepant has a few contraindications; patients on certain medications such as antibiotics or antifungals cannot take it. If a patient is not doing well on a triptan or should not be given a drug that constricts blood vessels, I often switch them to one of these gepants (if covered by insurance). Both drugs have a plan to let the patient try them at a low cost.
How are the gepants used acutely?
Gepants are used just like a triptan. As soon as the patient has a migraine headache starting, they take either ubrogepant or rimegepant as quickly as possible. Some patients say they feel the gepant begin to work within an hour or less, and some patients say it doesn't work at all, so I have them try the other gepant.
Gepants are probably a better option than triptans if the patient is >40 years because triptans can constrict blood vessels. Older patients, and certainly those who have any kind of cardiac or cerebral blood vessel issues or even peripheral blood vessel disease, should not be given triptans.
When do you consider using preventive treatment in migraine?
If a patient has ≥4 moderate-to-severe headache days a month, or fewer with severe disability, or does not respond to acute care medications or those drugs are contraindicated, I consider giving them preventive therapy for migraine. The goal is to decrease the number of migraine days per month and to decrease the intensity, duration, and disability of the attacks.
Which gepants can you use for prevention of migraine?
I discussed rimegepant as an acute care medication, but the same 75-mg meltaway tablet given every other day works preventively to decrease the number of headaches. I like it, as it has few adverse events—<3% of patients experience nausea and abdominal pain—and it can also be used to stop a headache on days the patient did not take a tablet.
Atogepant is a newer, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved gepant taken once daily by mouth for prevention of migraine, and it works to decrease headache days per month. It has more side effects than the other gepants, including constipation, drowsiness, and nausea. If a patient does not have many adverse events while taking it, it is a good migraine preventive.
How do you feel about monoclonal antibodies that bind to CGRP or its receptor for migraine preventive treatment?
Before the gepants became available, 4 different pharmaceutical companies were making monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that bind to either CGRP or its receptor. This class of medication can be quite effective for most patients needing migraine prevention, as these medications last for a long time if the patient keeps taking it.
Antibodies, when injected, continue to work for 1 to 3 months, making them perfect for migraine prevention, but they must be given either by the patient using an autoinjector with a tiny needle or by intravenous (IV) infusion in a hospital or office. They tend to be quite effective and have few adverse events.
The first one to come out was erenumab, then frenanezumab, and galcanezumab. The newest one is eptinezumab, given by IV infusion over 30 minutes. Erenumab is the only mAb that sits on the receptor to prevent the CGRP from docking on the receptor, and it's the only one that seems to cause adverse events such as constipation and increased blood pressure in some patients. Eptinezumab is the only drug in this category given by IV infusion; patients must come to the office to receive the injection every 3 months. Even though eptinezumab is a powerful drug, I find that patients generally don't like coming in for IV treatment. I reserve it for when a patient has failed several other preventive treatments. The other 3 drugs (erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab) are subcutaneous injections that the patient can self-administer at home. Fremanezumab can be taken once a month or once every 3 months, depending on the dose prescribed.
What migraine devices do you like to prescribe?
The device that I tend to have my patients use is called Nerivio®; it has been cleared by the FDA for acute treatment of migraine in patients ≥12 years. An article was just published in the journal Headache on its use in prevention of migraine. The company expects the FDA to clear it very soon for prevention when used for 45 minutes every other day.
Nerivio® is an electrical stimulator that is placed on the upper arm like a blood pressure cuff. It is battery-powered and links to an app on a smartphone. I have my patients turn it up slowly to a higher gain, and when they feel a slight discomfort, they lower down until they do not feel it. That's where I recommend that they keep it for 45 minutes of treatment, starting at the beginning of a migraine attack.
Nerivio® also has a behavioral medicine program incorporated into the smartphone app that lasts for 25 minutes. While the patient is receiving the 45 minutes of electrical stimulation, they are also being guided through relaxation techniques to help ease the headache. The company has done a controlled study comparing the efficacy of Nerivio® with and without the behavioral treatment and found that the 2 together are more effective than Nerivio® alone.
The early double-blind studies of this device, as sent to the FDA for clearance, have excellent efficacy data with very few adverse events. Thus, it is used by many patients. The company has arranged a lower cost for the first month of treatment so a patient can see whether the device is effective.
There's also a device called Relivion®, which is worn like a tiara on the head to stimulate 4 nerves above the eyebrows that are part of the trigeminal system and 2 in the back of the head that affect the occipital nerves.
One of the earliest devices to launch is the gammaCore vagal nerve stimulator. It is handheld and controlled by the patient. It is placed on the front and side of the neck in the region of the vagal nerve. For acute care of migraine, the patient stimulates for 2 minutes and then waits several minutes before repeating 2 minutes of treatment. If you want to prescribe it for the prevention of migraine, a patient could do this sequence twice per day. It has been approved for acute care and prevention of migraine and, along with other medication for cluster headaches, it is easy to use and approved for almost any kind of headache. Unfortunately, it is extremely expensive for patients and is not covered well by insurance unless the patient is a veteran or goes to a Veterans Health Administration hospital for care.
There are a few other devices that also work for migraine. Most electrical stimulation devices are costly, but we do hope that insurance companies will begin to cover them soon. Most devices cause few adverse events, have few contraindications, and will be used more as they become more affordable.
Can you summarize migraine treatment for us in one paragraph?
No, but I will try. We have many acute care treatments for migraine that are effective. Some, such as the triptans, do constrict blood vessels, and certain patients should not be taking medications that affect blood vessels. Some medications cause certain side effects or take too long to work, and we have other options for those patients. If a patient has ≥4 headache days per month or fewer associated with a lot of disability, we need to consider prevention. We have older preventives such as beta blockers and epilepsy medications, which are less expensive and can work but usually have many side effects. Now we have 4 mAbs that bind to CGRP or its receptor, which work well for a month or more with few adverse events. We also have 2 oral gepants for prevention. When you add in several devices, I have so many options for my patients today that I am a lucky neurologist, and my patients are even luckier!
Do you use nonpharmacologic approaches to treat your patients living with migraines? Which ones do you prefer?
I always like to start with nonpharmacologic approaches (also termed bio-behavioral approaches) with my patients. I talk to patients about sleep hygiene because if they don't sleep well, they're going to have more headaches. Most of my patients have issues with sleep and rarely feel refreshed in the morning. Most of them have middle insomnia; they wake up between 2 am and 4 am and cannot get back to sleep.
I also talk to my patients about eating properly. If patients don't eat on time or miss a meal, they often get headaches. While timing is probably more critical, what they eat is important also. Poor diet can lead to decreased energy, and patients can become obese. Obesity impacts headache—especially migraine. I am not sure if there are any particularly good or bad foods for migraine patients, but in general, they should eat fewer fatty foods, fewer carbohydrates, more chicken, and fish than red meat, and a lot of fruits, vegetables, salads, nuts, and whole grains. A good trick is to limit the volume of each meal; do not go back for seconds and limit desserts and alcohol.
Exercise is beneficial to decrease headaches, and the converse is even more true. Patients should start with low-impact, brief exercise like short walks and slowly build up to 20 minutes of cardio as tolerated, 3 to 5 times per week. Like poor diet choices, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity and then not doing well with headaches and so on.
What are your goals for treating your patients at the start of a migraine attack?
The goals for treating a migraine attack are to reduce the intensity of the pain quickly and, if possible, make the patient pain-free in ≤2 hours. We also try to reduce their most bothersome symptom, which is usually sensitivity to light or nausea, without causing any adverse effects from the treatment. Possibly as important, we want to get the patient back to functioning at work or at home, so they need no further treatment for that attack.
Unfortunately, many of the medicines we have available do cause adverse events, which are sometimes worse than the headache itself. A patient can't continue to take a medication that causes significant side effects.
It is also critical to stop the headache quickly, as we don't want patients to take the prescribed acute care medicine and then, if they don’t feel like it’s working, proceed to take aspirin and then acetaminophen and then an anti-inflammatory tablet. The more medicine they take, the more likely they'll get medication overuse headache (MOH).
MOH is not a great name, but it does imply that patients are taking one or many medications per week to stop their headaches, not realizing that this can worsen and prolong their headaches rather than helping them. They can also experience adverse events from taking so much medication.
Finally, we want the patients to get rid of a headache so that they do not need to go to an emergency room, and we want to use medication that is cost effective and gets the patient functioning. Some medicines and devices are extremely expensive and not well covered by insurance companies but imagine the patient who takes a new medicine or uses a new device and gets better rapidly. If they hadn't done that, they may have lost a day or 2 of pay from missing work, or they might have gone to work and not done a very effective job because they were feeling miserable and couldn’t think or speak well.
Do you prescribe triptans?
Definitely. The triptans first became available 30 years ago. There are 7 different triptans, and some work better for some patients than others. They come in tablets, injections, and nasal sprays. Sometimes patients need to try 2 or 3 different triptans to see which one is the most effective for them. If a patient has no success with tablets, there's a possibility that an injection or even a nasal spray would be more effective.
There are 2 triptans available as a nasal spray. I happen to like a triptan nasal spray called zolmitriptan, which usually works faster with fewer adverse events than the tablets.
There's also an injection of sumatriptan available, which is the fastest way to get relief from a triptan. Patients usually don't prefer it because it is an injection that they give themselves via an auto injector, and it may hurt and can be a bit complex to administer. There are definitely more adverse events when sumatriptan is given by injection, but because an injection can deliver very fast results that stop the headache reliably, some patients prefer it.
Triptans have been the mainstay treatment to stop an ongoing migraine attack for 30 years. We have always known there is some constriction of blood vessels and triptan-related side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and tingling sensations, so not every patient can take them. The newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) do not constrict blood vessels and have fewer adverse events but cost a lot more if not covered by insurance.
Another newer, nontriptan nasal spray is dihydroergotamine (DHE) mesylate for acute care. It is one of the best medications to use if the patient’s migraine has been going on for 24 hours, as it tends to work well for a long-lasting headache. It also works for a long period, giving the patient a rest before their next attack. A nasal spray works faster than a tablet form, as the medication is absorbed from the nasal mucosa and does not have to make its way through the GI tract, then to the liver for metabolism, and finally, up to the brain before it begins to work. There can be some side effects in the nose such as discomfort or stuffiness, but if it works well, patients usually tolerate it.
There's also a newer class of medicine called ditans. In a recent study, lasmiditan, which comes in a 50-mg and a 100-mg tablet for acute care of migraine, showed no vasoconstrictive effects, suggesting that ditans could be a safe option for patients living with chronic cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. Lasmiditan could be an alternative to triptans when they are contraindicated in patients with blood vessel disease, obesity, high blood pressure or cholesterol levels, or in nonresponsive patients. Lasmiditan does cause some dizziness and drowsiness, so patients cannot drive for 8 hours after taking it. However, it does have good efficacy.
When do you prescribe gepants?
Gepants are small-molecule CGRP receptor blockers. They are tablets that sit on the receptor, preventing the CGRP from docking on the receptor and increasing the headache during a migraine attack. There are 2 gepants that can be used to stop a headache that is just starting or in progress: ubrogepant and rimegepant.
Ubrogepant is a regular tablet that is available in 50-mg or 100-mg strengths. If the first dose does not make a patient pain free, a second dose is recommended about 2 hours later. Rimegepant is a meltaway tablet and only comes in a 75-mg strength. It should be taken early in the attack, and usually the patient does not need further treatment that day. If they do, they need to switch to another treatment, as rimegepant should not be repeated that day. Rimegepant may be used for both acute care and prevention. It is the only tablet that can be used for both.
Both drugs have been shown to provide pain freedom for about 20% of patients at 2 hours, which is statistically better than the patients that received the placebo. These drugs generally don’t cause many adverse events but can cause a little nausea or drowsiness in some patients. Ubrogepant has a few contraindications; patients on certain medications such as antibiotics or antifungals cannot take it. If a patient is not doing well on a triptan or should not be given a drug that constricts blood vessels, I often switch them to one of these gepants (if covered by insurance). Both drugs have a plan to let the patient try them at a low cost.
How are the gepants used acutely?
Gepants are used just like a triptan. As soon as the patient has a migraine headache starting, they take either ubrogepant or rimegepant as quickly as possible. Some patients say they feel the gepant begin to work within an hour or less, and some patients say it doesn't work at all, so I have them try the other gepant.
Gepants are probably a better option than triptans if the patient is >40 years because triptans can constrict blood vessels. Older patients, and certainly those who have any kind of cardiac or cerebral blood vessel issues or even peripheral blood vessel disease, should not be given triptans.
When do you consider using preventive treatment in migraine?
If a patient has ≥4 moderate-to-severe headache days a month, or fewer with severe disability, or does not respond to acute care medications or those drugs are contraindicated, I consider giving them preventive therapy for migraine. The goal is to decrease the number of migraine days per month and to decrease the intensity, duration, and disability of the attacks.
Which gepants can you use for prevention of migraine?
I discussed rimegepant as an acute care medication, but the same 75-mg meltaway tablet given every other day works preventively to decrease the number of headaches. I like it, as it has few adverse events—<3% of patients experience nausea and abdominal pain—and it can also be used to stop a headache on days the patient did not take a tablet.
Atogepant is a newer, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved gepant taken once daily by mouth for prevention of migraine, and it works to decrease headache days per month. It has more side effects than the other gepants, including constipation, drowsiness, and nausea. If a patient does not have many adverse events while taking it, it is a good migraine preventive.
How do you feel about monoclonal antibodies that bind to CGRP or its receptor for migraine preventive treatment?
Before the gepants became available, 4 different pharmaceutical companies were making monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that bind to either CGRP or its receptor. This class of medication can be quite effective for most patients needing migraine prevention, as these medications last for a long time if the patient keeps taking it.
Antibodies, when injected, continue to work for 1 to 3 months, making them perfect for migraine prevention, but they must be given either by the patient using an autoinjector with a tiny needle or by intravenous (IV) infusion in a hospital or office. They tend to be quite effective and have few adverse events.
The first one to come out was erenumab, then frenanezumab, and galcanezumab. The newest one is eptinezumab, given by IV infusion over 30 minutes. Erenumab is the only mAb that sits on the receptor to prevent the CGRP from docking on the receptor, and it's the only one that seems to cause adverse events such as constipation and increased blood pressure in some patients. Eptinezumab is the only drug in this category given by IV infusion; patients must come to the office to receive the injection every 3 months. Even though eptinezumab is a powerful drug, I find that patients generally don't like coming in for IV treatment. I reserve it for when a patient has failed several other preventive treatments. The other 3 drugs (erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab) are subcutaneous injections that the patient can self-administer at home. Fremanezumab can be taken once a month or once every 3 months, depending on the dose prescribed.
What migraine devices do you like to prescribe?
The device that I tend to have my patients use is called Nerivio®; it has been cleared by the FDA for acute treatment of migraine in patients ≥12 years. An article was just published in the journal Headache on its use in prevention of migraine. The company expects the FDA to clear it very soon for prevention when used for 45 minutes every other day.
Nerivio® is an electrical stimulator that is placed on the upper arm like a blood pressure cuff. It is battery-powered and links to an app on a smartphone. I have my patients turn it up slowly to a higher gain, and when they feel a slight discomfort, they lower down until they do not feel it. That's where I recommend that they keep it for 45 minutes of treatment, starting at the beginning of a migraine attack.
Nerivio® also has a behavioral medicine program incorporated into the smartphone app that lasts for 25 minutes. While the patient is receiving the 45 minutes of electrical stimulation, they are also being guided through relaxation techniques to help ease the headache. The company has done a controlled study comparing the efficacy of Nerivio® with and without the behavioral treatment and found that the 2 together are more effective than Nerivio® alone.
The early double-blind studies of this device, as sent to the FDA for clearance, have excellent efficacy data with very few adverse events. Thus, it is used by many patients. The company has arranged a lower cost for the first month of treatment so a patient can see whether the device is effective.
There's also a device called Relivion®, which is worn like a tiara on the head to stimulate 4 nerves above the eyebrows that are part of the trigeminal system and 2 in the back of the head that affect the occipital nerves.
One of the earliest devices to launch is the gammaCore vagal nerve stimulator. It is handheld and controlled by the patient. It is placed on the front and side of the neck in the region of the vagal nerve. For acute care of migraine, the patient stimulates for 2 minutes and then waits several minutes before repeating 2 minutes of treatment. If you want to prescribe it for the prevention of migraine, a patient could do this sequence twice per day. It has been approved for acute care and prevention of migraine and, along with other medication for cluster headaches, it is easy to use and approved for almost any kind of headache. Unfortunately, it is extremely expensive for patients and is not covered well by insurance unless the patient is a veteran or goes to a Veterans Health Administration hospital for care.
There are a few other devices that also work for migraine. Most electrical stimulation devices are costly, but we do hope that insurance companies will begin to cover them soon. Most devices cause few adverse events, have few contraindications, and will be used more as they become more affordable.
Can you summarize migraine treatment for us in one paragraph?
No, but I will try. We have many acute care treatments for migraine that are effective. Some, such as the triptans, do constrict blood vessels, and certain patients should not be taking medications that affect blood vessels. Some medications cause certain side effects or take too long to work, and we have other options for those patients. If a patient has ≥4 headache days per month or fewer associated with a lot of disability, we need to consider prevention. We have older preventives such as beta blockers and epilepsy medications, which are less expensive and can work but usually have many side effects. Now we have 4 mAbs that bind to CGRP or its receptor, which work well for a month or more with few adverse events. We also have 2 oral gepants for prevention. When you add in several devices, I have so many options for my patients today that I am a lucky neurologist, and my patients are even luckier!
Do you use nonpharmacologic approaches to treat your patients living with migraines? Which ones do you prefer?
I always like to start with nonpharmacologic approaches (also termed bio-behavioral approaches) with my patients. I talk to patients about sleep hygiene because if they don't sleep well, they're going to have more headaches. Most of my patients have issues with sleep and rarely feel refreshed in the morning. Most of them have middle insomnia; they wake up between 2 am and 4 am and cannot get back to sleep.
I also talk to my patients about eating properly. If patients don't eat on time or miss a meal, they often get headaches. While timing is probably more critical, what they eat is important also. Poor diet can lead to decreased energy, and patients can become obese. Obesity impacts headache—especially migraine. I am not sure if there are any particularly good or bad foods for migraine patients, but in general, they should eat fewer fatty foods, fewer carbohydrates, more chicken, and fish than red meat, and a lot of fruits, vegetables, salads, nuts, and whole grains. A good trick is to limit the volume of each meal; do not go back for seconds and limit desserts and alcohol.
Exercise is beneficial to decrease headaches, and the converse is even more true. Patients should start with low-impact, brief exercise like short walks and slowly build up to 20 minutes of cardio as tolerated, 3 to 5 times per week. Like poor diet choices, a sedentary lifestyle can lead to obesity and then not doing well with headaches and so on.
What are your goals for treating your patients at the start of a migraine attack?
The goals for treating a migraine attack are to reduce the intensity of the pain quickly and, if possible, make the patient pain-free in ≤2 hours. We also try to reduce their most bothersome symptom, which is usually sensitivity to light or nausea, without causing any adverse effects from the treatment. Possibly as important, we want to get the patient back to functioning at work or at home, so they need no further treatment for that attack.
Unfortunately, many of the medicines we have available do cause adverse events, which are sometimes worse than the headache itself. A patient can't continue to take a medication that causes significant side effects.
It is also critical to stop the headache quickly, as we don't want patients to take the prescribed acute care medicine and then, if they don’t feel like it’s working, proceed to take aspirin and then acetaminophen and then an anti-inflammatory tablet. The more medicine they take, the more likely they'll get medication overuse headache (MOH).
MOH is not a great name, but it does imply that patients are taking one or many medications per week to stop their headaches, not realizing that this can worsen and prolong their headaches rather than helping them. They can also experience adverse events from taking so much medication.
Finally, we want the patients to get rid of a headache so that they do not need to go to an emergency room, and we want to use medication that is cost effective and gets the patient functioning. Some medicines and devices are extremely expensive and not well covered by insurance companies but imagine the patient who takes a new medicine or uses a new device and gets better rapidly. If they hadn't done that, they may have lost a day or 2 of pay from missing work, or they might have gone to work and not done a very effective job because they were feeling miserable and couldn’t think or speak well.
Do you prescribe triptans?
Definitely. The triptans first became available 30 years ago. There are 7 different triptans, and some work better for some patients than others. They come in tablets, injections, and nasal sprays. Sometimes patients need to try 2 or 3 different triptans to see which one is the most effective for them. If a patient has no success with tablets, there's a possibility that an injection or even a nasal spray would be more effective.
There are 2 triptans available as a nasal spray. I happen to like a triptan nasal spray called zolmitriptan, which usually works faster with fewer adverse events than the tablets.
There's also an injection of sumatriptan available, which is the fastest way to get relief from a triptan. Patients usually don't prefer it because it is an injection that they give themselves via an auto injector, and it may hurt and can be a bit complex to administer. There are definitely more adverse events when sumatriptan is given by injection, but because an injection can deliver very fast results that stop the headache reliably, some patients prefer it.
Triptans have been the mainstay treatment to stop an ongoing migraine attack for 30 years. We have always known there is some constriction of blood vessels and triptan-related side effects such as dizziness, drowsiness, and tingling sensations, so not every patient can take them. The newer medications that block calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) do not constrict blood vessels and have fewer adverse events but cost a lot more if not covered by insurance.
Another newer, nontriptan nasal spray is dihydroergotamine (DHE) mesylate for acute care. It is one of the best medications to use if the patient’s migraine has been going on for 24 hours, as it tends to work well for a long-lasting headache. It also works for a long period, giving the patient a rest before their next attack. A nasal spray works faster than a tablet form, as the medication is absorbed from the nasal mucosa and does not have to make its way through the GI tract, then to the liver for metabolism, and finally, up to the brain before it begins to work. There can be some side effects in the nose such as discomfort or stuffiness, but if it works well, patients usually tolerate it.
There's also a newer class of medicine called ditans. In a recent study, lasmiditan, which comes in a 50-mg and a 100-mg tablet for acute care of migraine, showed no vasoconstrictive effects, suggesting that ditans could be a safe option for patients living with chronic cardio- and cerebrovascular disease. Lasmiditan could be an alternative to triptans when they are contraindicated in patients with blood vessel disease, obesity, high blood pressure or cholesterol levels, or in nonresponsive patients. Lasmiditan does cause some dizziness and drowsiness, so patients cannot drive for 8 hours after taking it. However, it does have good efficacy.
When do you prescribe gepants?
Gepants are small-molecule CGRP receptor blockers. They are tablets that sit on the receptor, preventing the CGRP from docking on the receptor and increasing the headache during a migraine attack. There are 2 gepants that can be used to stop a headache that is just starting or in progress: ubrogepant and rimegepant.
Ubrogepant is a regular tablet that is available in 50-mg or 100-mg strengths. If the first dose does not make a patient pain free, a second dose is recommended about 2 hours later. Rimegepant is a meltaway tablet and only comes in a 75-mg strength. It should be taken early in the attack, and usually the patient does not need further treatment that day. If they do, they need to switch to another treatment, as rimegepant should not be repeated that day. Rimegepant may be used for both acute care and prevention. It is the only tablet that can be used for both.
Both drugs have been shown to provide pain freedom for about 20% of patients at 2 hours, which is statistically better than the patients that received the placebo. These drugs generally don’t cause many adverse events but can cause a little nausea or drowsiness in some patients. Ubrogepant has a few contraindications; patients on certain medications such as antibiotics or antifungals cannot take it. If a patient is not doing well on a triptan or should not be given a drug that constricts blood vessels, I often switch them to one of these gepants (if covered by insurance). Both drugs have a plan to let the patient try them at a low cost.
How are the gepants used acutely?
Gepants are used just like a triptan. As soon as the patient has a migraine headache starting, they take either ubrogepant or rimegepant as quickly as possible. Some patients say they feel the gepant begin to work within an hour or less, and some patients say it doesn't work at all, so I have them try the other gepant.
Gepants are probably a better option than triptans if the patient is >40 years because triptans can constrict blood vessels. Older patients, and certainly those who have any kind of cardiac or cerebral blood vessel issues or even peripheral blood vessel disease, should not be given triptans.
When do you consider using preventive treatment in migraine?
If a patient has ≥4 moderate-to-severe headache days a month, or fewer with severe disability, or does not respond to acute care medications or those drugs are contraindicated, I consider giving them preventive therapy for migraine. The goal is to decrease the number of migraine days per month and to decrease the intensity, duration, and disability of the attacks.
Which gepants can you use for prevention of migraine?
I discussed rimegepant as an acute care medication, but the same 75-mg meltaway tablet given every other day works preventively to decrease the number of headaches. I like it, as it has few adverse events—<3% of patients experience nausea and abdominal pain—and it can also be used to stop a headache on days the patient did not take a tablet.
Atogepant is a newer, US Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved gepant taken once daily by mouth for prevention of migraine, and it works to decrease headache days per month. It has more side effects than the other gepants, including constipation, drowsiness, and nausea. If a patient does not have many adverse events while taking it, it is a good migraine preventive.
How do you feel about monoclonal antibodies that bind to CGRP or its receptor for migraine preventive treatment?
Before the gepants became available, 4 different pharmaceutical companies were making monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) that bind to either CGRP or its receptor. This class of medication can be quite effective for most patients needing migraine prevention, as these medications last for a long time if the patient keeps taking it.
Antibodies, when injected, continue to work for 1 to 3 months, making them perfect for migraine prevention, but they must be given either by the patient using an autoinjector with a tiny needle or by intravenous (IV) infusion in a hospital or office. They tend to be quite effective and have few adverse events.
The first one to come out was erenumab, then frenanezumab, and galcanezumab. The newest one is eptinezumab, given by IV infusion over 30 minutes. Erenumab is the only mAb that sits on the receptor to prevent the CGRP from docking on the receptor, and it's the only one that seems to cause adverse events such as constipation and increased blood pressure in some patients. Eptinezumab is the only drug in this category given by IV infusion; patients must come to the office to receive the injection every 3 months. Even though eptinezumab is a powerful drug, I find that patients generally don't like coming in for IV treatment. I reserve it for when a patient has failed several other preventive treatments. The other 3 drugs (erenumab, fremanezumab, galcanezumab) are subcutaneous injections that the patient can self-administer at home. Fremanezumab can be taken once a month or once every 3 months, depending on the dose prescribed.
What migraine devices do you like to prescribe?
The device that I tend to have my patients use is called Nerivio®; it has been cleared by the FDA for acute treatment of migraine in patients ≥12 years. An article was just published in the journal Headache on its use in prevention of migraine. The company expects the FDA to clear it very soon for prevention when used for 45 minutes every other day.
Nerivio® is an electrical stimulator that is placed on the upper arm like a blood pressure cuff. It is battery-powered and links to an app on a smartphone. I have my patients turn it up slowly to a higher gain, and when they feel a slight discomfort, they lower down until they do not feel it. That's where I recommend that they keep it for 45 minutes of treatment, starting at the beginning of a migraine attack.
Nerivio® also has a behavioral medicine program incorporated into the smartphone app that lasts for 25 minutes. While the patient is receiving the 45 minutes of electrical stimulation, they are also being guided through relaxation techniques to help ease the headache. The company has done a controlled study comparing the efficacy of Nerivio® with and without the behavioral treatment and found that the 2 together are more effective than Nerivio® alone.
The early double-blind studies of this device, as sent to the FDA for clearance, have excellent efficacy data with very few adverse events. Thus, it is used by many patients. The company has arranged a lower cost for the first month of treatment so a patient can see whether the device is effective.
There's also a device called Relivion®, which is worn like a tiara on the head to stimulate 4 nerves above the eyebrows that are part of the trigeminal system and 2 in the back of the head that affect the occipital nerves.
One of the earliest devices to launch is the gammaCore vagal nerve stimulator. It is handheld and controlled by the patient. It is placed on the front and side of the neck in the region of the vagal nerve. For acute care of migraine, the patient stimulates for 2 minutes and then waits several minutes before repeating 2 minutes of treatment. If you want to prescribe it for the prevention of migraine, a patient could do this sequence twice per day. It has been approved for acute care and prevention of migraine and, along with other medication for cluster headaches, it is easy to use and approved for almost any kind of headache. Unfortunately, it is extremely expensive for patients and is not covered well by insurance unless the patient is a veteran or goes to a Veterans Health Administration hospital for care.
There are a few other devices that also work for migraine. Most electrical stimulation devices are costly, but we do hope that insurance companies will begin to cover them soon. Most devices cause few adverse events, have few contraindications, and will be used more as they become more affordable.
Can you summarize migraine treatment for us in one paragraph?
No, but I will try. We have many acute care treatments for migraine that are effective. Some, such as the triptans, do constrict blood vessels, and certain patients should not be taking medications that affect blood vessels. Some medications cause certain side effects or take too long to work, and we have other options for those patients. If a patient has ≥4 headache days per month or fewer associated with a lot of disability, we need to consider prevention. We have older preventives such as beta blockers and epilepsy medications, which are less expensive and can work but usually have many side effects. Now we have 4 mAbs that bind to CGRP or its receptor, which work well for a month or more with few adverse events. We also have 2 oral gepants for prevention. When you add in several devices, I have so many options for my patients today that I am a lucky neurologist, and my patients are even luckier!
Key takeaways from ACP’s new Tx guidelines for adults with major depressive disorder
In January 2023, the American College of Physicians (ACP) published updated recommendations on the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).1 The ACP guidelines address initial treatment of patients in the acute phase of mild and moderate-to-severe MDD. Here’s what the ACP recommends, as well as 6 important takeaways.
Recommendations for initial treatment of those with mild or moderate-to-severe MDD center around cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and second-generation antidepressants (SGA). For patients in the acute phase of mild MDD, the recommendation is for monotherapy with CBT. However, if CBT is not an option due to cost and/or availability of services, the use of an SGA is acceptable.
For patients in the acute phase of moderate-to-severe MDD, either CBT, an SGA, or a combination of both is recommended.
If initial treatment does not work … Up to 70% of patients with moderate-to-severe MDD will not respond to the initial therapy chosen. If a patient does not respond to initial treatment with an SGA, consider 1 of the following:
- Switching to CBT
- Adding on CBT while continuing the SGA
- Changing to a different SGA
- Adding a second pharmacologic agent.
6 key takeaways. The full guideline should be read for a more complete discussion of the many clinical considerations of these treatment options. However, the most important points include:
• Employ shared clinical decision-making and consider the individual characteristics of each patient when making treatment decisions.
• Consider generic options when using an SGA; generic options appear to be as effective as more expensive brand-name products.
• Start with a low-dose SGA and increase gradually to an approved maximum dose before determining there has been no response.
• Monitor frequently for medication adverse effects.
• Monitor the patient for thoughts about self-harm for the first 2 months.
• Continue treatment for 4 to 9 months once remission is achieved.
A word about strength of evidence. While these recommendations are based on an extensive review of the best available evidence, most are based on low-certainty evidence—illustrating the amount of clinical research still needed on this topic. The exceptions are monotherapy with either CBT or SGA for initial treatment of moderate-to-severe MDD, both of which are based on moderate-strength evidence and received a strong recommendation. The panel felt there was insufficient evidence to assess complementary and alternative interventions including exercise and omega-3 fatty acids.
1. Qaseem A, Owens D, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, et al; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments of adults in the acute phase of major depressive disorder: a living clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. Published online January 24, 2023. doi: 10.7326/M22-2056
In January 2023, the American College of Physicians (ACP) published updated recommendations on the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).1 The ACP guidelines address initial treatment of patients in the acute phase of mild and moderate-to-severe MDD. Here’s what the ACP recommends, as well as 6 important takeaways.
Recommendations for initial treatment of those with mild or moderate-to-severe MDD center around cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and second-generation antidepressants (SGA). For patients in the acute phase of mild MDD, the recommendation is for monotherapy with CBT. However, if CBT is not an option due to cost and/or availability of services, the use of an SGA is acceptable.
For patients in the acute phase of moderate-to-severe MDD, either CBT, an SGA, or a combination of both is recommended.
If initial treatment does not work … Up to 70% of patients with moderate-to-severe MDD will not respond to the initial therapy chosen. If a patient does not respond to initial treatment with an SGA, consider 1 of the following:
- Switching to CBT
- Adding on CBT while continuing the SGA
- Changing to a different SGA
- Adding a second pharmacologic agent.
6 key takeaways. The full guideline should be read for a more complete discussion of the many clinical considerations of these treatment options. However, the most important points include:
• Employ shared clinical decision-making and consider the individual characteristics of each patient when making treatment decisions.
• Consider generic options when using an SGA; generic options appear to be as effective as more expensive brand-name products.
• Start with a low-dose SGA and increase gradually to an approved maximum dose before determining there has been no response.
• Monitor frequently for medication adverse effects.
• Monitor the patient for thoughts about self-harm for the first 2 months.
• Continue treatment for 4 to 9 months once remission is achieved.
A word about strength of evidence. While these recommendations are based on an extensive review of the best available evidence, most are based on low-certainty evidence—illustrating the amount of clinical research still needed on this topic. The exceptions are monotherapy with either CBT or SGA for initial treatment of moderate-to-severe MDD, both of which are based on moderate-strength evidence and received a strong recommendation. The panel felt there was insufficient evidence to assess complementary and alternative interventions including exercise and omega-3 fatty acids.
In January 2023, the American College of Physicians (ACP) published updated recommendations on the treatment of adults with major depressive disorder (MDD).1 The ACP guidelines address initial treatment of patients in the acute phase of mild and moderate-to-severe MDD. Here’s what the ACP recommends, as well as 6 important takeaways.
Recommendations for initial treatment of those with mild or moderate-to-severe MDD center around cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) and second-generation antidepressants (SGA). For patients in the acute phase of mild MDD, the recommendation is for monotherapy with CBT. However, if CBT is not an option due to cost and/or availability of services, the use of an SGA is acceptable.
For patients in the acute phase of moderate-to-severe MDD, either CBT, an SGA, or a combination of both is recommended.
If initial treatment does not work … Up to 70% of patients with moderate-to-severe MDD will not respond to the initial therapy chosen. If a patient does not respond to initial treatment with an SGA, consider 1 of the following:
- Switching to CBT
- Adding on CBT while continuing the SGA
- Changing to a different SGA
- Adding a second pharmacologic agent.
6 key takeaways. The full guideline should be read for a more complete discussion of the many clinical considerations of these treatment options. However, the most important points include:
• Employ shared clinical decision-making and consider the individual characteristics of each patient when making treatment decisions.
• Consider generic options when using an SGA; generic options appear to be as effective as more expensive brand-name products.
• Start with a low-dose SGA and increase gradually to an approved maximum dose before determining there has been no response.
• Monitor frequently for medication adverse effects.
• Monitor the patient for thoughts about self-harm for the first 2 months.
• Continue treatment for 4 to 9 months once remission is achieved.
A word about strength of evidence. While these recommendations are based on an extensive review of the best available evidence, most are based on low-certainty evidence—illustrating the amount of clinical research still needed on this topic. The exceptions are monotherapy with either CBT or SGA for initial treatment of moderate-to-severe MDD, both of which are based on moderate-strength evidence and received a strong recommendation. The panel felt there was insufficient evidence to assess complementary and alternative interventions including exercise and omega-3 fatty acids.
1. Qaseem A, Owens D, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, et al; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments of adults in the acute phase of major depressive disorder: a living clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. Published online January 24, 2023. doi: 10.7326/M22-2056
1. Qaseem A, Owens D, Etxeandia-Ikobaltzeta I, et al; Clinical Guidelines Committee of the American College of Physicians. Nonpharmacologic and pharmacologic treatments of adults in the acute phase of major depressive disorder: a living clinical guideline from the American College of Physicians. Ann Intern Med. Published online January 24, 2023. doi: 10.7326/M22-2056
Comment & Controversy
Drospirenone vs norethindrone progestin-only pills. Is there a clear winner?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (FEBRUARY 2022)
Contraception queries
Dr. Barbieri, addressing your editorial on drospirenone and norethindrone pills, can you tell me why there are 4 placebo pills in Slynd? In addition, why did Exeltis choose a 24/4 regimen instead of a continuous regimen? And are there data on bleeding patterns with continuous drospirenone versus 24/4?
Meredith S. Cassidy, MD
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Cassidy for the excellent question! The purpose of the 4 placebo pills in the Slynd (drospirenone 4 mg) 24/4 progestin-only contraceptive is to induce scheduled bleeding and reduce the number of days of unscheduled uterine bleeding. In a study of 858 patients, compared with a continuous progestin-only desogestrel contraceptive, Slynd with 4 placebo pills, was associated with significantly fewer days of unscheduled bleeding, 22 days versus 35 days (P<.0003) over 8 months of contraceptive use.1
The norethindrone progestin-only pill (POP) , which is available in the United States has very weak anti-ovulatory properties. If there were 4 placebo pills in the norethindrone POP, ovulation rates would increase, leading to reduced contraceptive efficacy. In contrast, Slynd with 4 placebo pills has excellent anti-ovulatory efficacy.
Reference
1. Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Bleeding profile of women using a drospirenone-ony 4 mg over nine cycles in comparison with desogestrel 0.075 mg. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231856.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (NOVEMBER 2022)
ERAS for all cesarean deliveries
In Dr. Barbieri’s editorial “Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?”, he and Dr. Schantz-Dunn outline several reasons why the answer is a resounding, “Yes!”
I would suggest that ERAS principles should be used for all cesarean deliveries (CDs), not only scheduled ones. Many components of CD ERAS pathways are equally applicable to scheduled and unscheduled CDs, specifically those components that apply to intraoperative care (antibiotic prophylaxis, skin preparation, surgical technique, uterotonic administration, normothermia, and multimodal anesthesia) and postoperative care (VTE prophylaxis, gum chewing, early oral intake, early ambulation, early removal of bladder catheter, predischarge patient education, scheduled analgesic prophylaxis with acetaminophen, and NSAIDS). Although scheduled CDs have the additional advantage of the pre-hospital components (breastfeeding education, shortened fasting interval, carbohydrate loading, anemia prevention, and physiologic optimization), most of the benefit of ERAS for CD is likely attributable to the intraoperative and postoperative components.
For example, in our CD ERAS program, the median postoperative opioid consumption was reduced from a baseline of more than 100 morphine mg equivalents (MME) in both scheduled CDs (23 MME, interquartile range [IQR], 0-70) and unscheduled CDs (23 MME, IQR, 0-75).1 Remarkably, 29% of patients in the ERAS pathway used no postoperative opioids at all, a testament to the efficacy of neuraxial morphine and postoperative acetaminophen and NSAIDS. In another program, ERAS was associated with decreased postpartum length of stay and reduced direct costs in both scheduled and unscheduled CDs.2
References
- Combs CA, Robinson T, Mekis C, et al. Enhanced recovery after cesarean: impact on postoperative opioid use and length of stay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:237-239.
- Fay EE, Hitti JE, Delgado CM, et al. An enhanced recovery after surgery pathway for cesarean delivery decreases hospital stay and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:349.e1-e9.
C. Andrew Combs, MD, PhD
Sunrise, Florida
Dr. Barbieri responds
I am grateful to Dr. Combs’ advocacy for applying ERAS principles to all CD births, including scheduled and unscheduled operations. Dr. Combs notes that the intraoperative and postoperative components of ERAS can be used for both scheduled and unscheduled CD births. Of particular note is the marked reduction in opioid medication use achieved among Dr. Combs’ patients who were on an ERAS pathway. Hopefully, due to Dr. Combs clinical and research leadership many more patients will benefit from the use of an ERAS pathway.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
ERIN TRACY BRADLEY, MD, MPH, AND MEGAN L. EVANS,MD, MPH (DECEMBER 2022)
ObGyns are not united on this issue
I just finished reading the article by Drs. Bradley and Evans in the December edition of
The unborn seem not to have advocates like Drs. Bradley and Evans. In fact, those who hold pro-life opinions are regularly silenced in publications and on social media. The Facebooks and Twitters of the world tend to hold us in derision when they are not silencing us. There used to be a detente in our field where we each respected the viewpoint of the other, but now it is nonstop advocacy for abortion. Some authors want to accelerate and intensify that advocacy. I suspect that the pro-life views like mine will continue to be silenced. I just want the authors to know that we are not united in this post-Dobbs world. Many of us want appropriate limits on termination. We are not in favor of the unlimited right to abort a fetus up to the moment of delivery.
Steven G. Nelson
Phoenix, Arizona
Drospirenone vs norethindrone progestin-only pills. Is there a clear winner?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (FEBRUARY 2022)
Contraception queries
Dr. Barbieri, addressing your editorial on drospirenone and norethindrone pills, can you tell me why there are 4 placebo pills in Slynd? In addition, why did Exeltis choose a 24/4 regimen instead of a continuous regimen? And are there data on bleeding patterns with continuous drospirenone versus 24/4?
Meredith S. Cassidy, MD
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Cassidy for the excellent question! The purpose of the 4 placebo pills in the Slynd (drospirenone 4 mg) 24/4 progestin-only contraceptive is to induce scheduled bleeding and reduce the number of days of unscheduled uterine bleeding. In a study of 858 patients, compared with a continuous progestin-only desogestrel contraceptive, Slynd with 4 placebo pills, was associated with significantly fewer days of unscheduled bleeding, 22 days versus 35 days (P<.0003) over 8 months of contraceptive use.1
The norethindrone progestin-only pill (POP) , which is available in the United States has very weak anti-ovulatory properties. If there were 4 placebo pills in the norethindrone POP, ovulation rates would increase, leading to reduced contraceptive efficacy. In contrast, Slynd with 4 placebo pills has excellent anti-ovulatory efficacy.
Reference
1. Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Bleeding profile of women using a drospirenone-ony 4 mg over nine cycles in comparison with desogestrel 0.075 mg. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231856.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (NOVEMBER 2022)
ERAS for all cesarean deliveries
In Dr. Barbieri’s editorial “Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?”, he and Dr. Schantz-Dunn outline several reasons why the answer is a resounding, “Yes!”
I would suggest that ERAS principles should be used for all cesarean deliveries (CDs), not only scheduled ones. Many components of CD ERAS pathways are equally applicable to scheduled and unscheduled CDs, specifically those components that apply to intraoperative care (antibiotic prophylaxis, skin preparation, surgical technique, uterotonic administration, normothermia, and multimodal anesthesia) and postoperative care (VTE prophylaxis, gum chewing, early oral intake, early ambulation, early removal of bladder catheter, predischarge patient education, scheduled analgesic prophylaxis with acetaminophen, and NSAIDS). Although scheduled CDs have the additional advantage of the pre-hospital components (breastfeeding education, shortened fasting interval, carbohydrate loading, anemia prevention, and physiologic optimization), most of the benefit of ERAS for CD is likely attributable to the intraoperative and postoperative components.
For example, in our CD ERAS program, the median postoperative opioid consumption was reduced from a baseline of more than 100 morphine mg equivalents (MME) in both scheduled CDs (23 MME, interquartile range [IQR], 0-70) and unscheduled CDs (23 MME, IQR, 0-75).1 Remarkably, 29% of patients in the ERAS pathway used no postoperative opioids at all, a testament to the efficacy of neuraxial morphine and postoperative acetaminophen and NSAIDS. In another program, ERAS was associated with decreased postpartum length of stay and reduced direct costs in both scheduled and unscheduled CDs.2
References
- Combs CA, Robinson T, Mekis C, et al. Enhanced recovery after cesarean: impact on postoperative opioid use and length of stay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:237-239.
- Fay EE, Hitti JE, Delgado CM, et al. An enhanced recovery after surgery pathway for cesarean delivery decreases hospital stay and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:349.e1-e9.
C. Andrew Combs, MD, PhD
Sunrise, Florida
Dr. Barbieri responds
I am grateful to Dr. Combs’ advocacy for applying ERAS principles to all CD births, including scheduled and unscheduled operations. Dr. Combs notes that the intraoperative and postoperative components of ERAS can be used for both scheduled and unscheduled CD births. Of particular note is the marked reduction in opioid medication use achieved among Dr. Combs’ patients who were on an ERAS pathway. Hopefully, due to Dr. Combs clinical and research leadership many more patients will benefit from the use of an ERAS pathway.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
ERIN TRACY BRADLEY, MD, MPH, AND MEGAN L. EVANS,MD, MPH (DECEMBER 2022)
ObGyns are not united on this issue
I just finished reading the article by Drs. Bradley and Evans in the December edition of
The unborn seem not to have advocates like Drs. Bradley and Evans. In fact, those who hold pro-life opinions are regularly silenced in publications and on social media. The Facebooks and Twitters of the world tend to hold us in derision when they are not silencing us. There used to be a detente in our field where we each respected the viewpoint of the other, but now it is nonstop advocacy for abortion. Some authors want to accelerate and intensify that advocacy. I suspect that the pro-life views like mine will continue to be silenced. I just want the authors to know that we are not united in this post-Dobbs world. Many of us want appropriate limits on termination. We are not in favor of the unlimited right to abort a fetus up to the moment of delivery.
Steven G. Nelson
Phoenix, Arizona
Drospirenone vs norethindrone progestin-only pills. Is there a clear winner?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (FEBRUARY 2022)
Contraception queries
Dr. Barbieri, addressing your editorial on drospirenone and norethindrone pills, can you tell me why there are 4 placebo pills in Slynd? In addition, why did Exeltis choose a 24/4 regimen instead of a continuous regimen? And are there data on bleeding patterns with continuous drospirenone versus 24/4?
Meredith S. Cassidy, MD
Colorado Springs, Colorado
Dr. Barbieri responds
I thank Dr. Cassidy for the excellent question! The purpose of the 4 placebo pills in the Slynd (drospirenone 4 mg) 24/4 progestin-only contraceptive is to induce scheduled bleeding and reduce the number of days of unscheduled uterine bleeding. In a study of 858 patients, compared with a continuous progestin-only desogestrel contraceptive, Slynd with 4 placebo pills, was associated with significantly fewer days of unscheduled bleeding, 22 days versus 35 days (P<.0003) over 8 months of contraceptive use.1
The norethindrone progestin-only pill (POP) , which is available in the United States has very weak anti-ovulatory properties. If there were 4 placebo pills in the norethindrone POP, ovulation rates would increase, leading to reduced contraceptive efficacy. In contrast, Slynd with 4 placebo pills has excellent anti-ovulatory efficacy.
Reference
1. Palacios S, Colli E, Regidor PA. Bleeding profile of women using a drospirenone-ony 4 mg over nine cycles in comparison with desogestrel 0.075 mg. PLoS ONE. 2020;15:e0231856.
Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?
ROBERT L. BARBIERI, MD (NOVEMBER 2022)
ERAS for all cesarean deliveries
In Dr. Barbieri’s editorial “Should every scheduled cesarean birth use an Enhanced Recovery After Surgery (ERAS) pathway?”, he and Dr. Schantz-Dunn outline several reasons why the answer is a resounding, “Yes!”
I would suggest that ERAS principles should be used for all cesarean deliveries (CDs), not only scheduled ones. Many components of CD ERAS pathways are equally applicable to scheduled and unscheduled CDs, specifically those components that apply to intraoperative care (antibiotic prophylaxis, skin preparation, surgical technique, uterotonic administration, normothermia, and multimodal anesthesia) and postoperative care (VTE prophylaxis, gum chewing, early oral intake, early ambulation, early removal of bladder catheter, predischarge patient education, scheduled analgesic prophylaxis with acetaminophen, and NSAIDS). Although scheduled CDs have the additional advantage of the pre-hospital components (breastfeeding education, shortened fasting interval, carbohydrate loading, anemia prevention, and physiologic optimization), most of the benefit of ERAS for CD is likely attributable to the intraoperative and postoperative components.
For example, in our CD ERAS program, the median postoperative opioid consumption was reduced from a baseline of more than 100 morphine mg equivalents (MME) in both scheduled CDs (23 MME, interquartile range [IQR], 0-70) and unscheduled CDs (23 MME, IQR, 0-75).1 Remarkably, 29% of patients in the ERAS pathway used no postoperative opioids at all, a testament to the efficacy of neuraxial morphine and postoperative acetaminophen and NSAIDS. In another program, ERAS was associated with decreased postpartum length of stay and reduced direct costs in both scheduled and unscheduled CDs.2
References
- Combs CA, Robinson T, Mekis C, et al. Enhanced recovery after cesarean: impact on postoperative opioid use and length of stay. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2021;224:237-239.
- Fay EE, Hitti JE, Delgado CM, et al. An enhanced recovery after surgery pathway for cesarean delivery decreases hospital stay and cost. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2019;221:349.e1-e9.
C. Andrew Combs, MD, PhD
Sunrise, Florida
Dr. Barbieri responds
I am grateful to Dr. Combs’ advocacy for applying ERAS principles to all CD births, including scheduled and unscheduled operations. Dr. Combs notes that the intraoperative and postoperative components of ERAS can be used for both scheduled and unscheduled CD births. Of particular note is the marked reduction in opioid medication use achieved among Dr. Combs’ patients who were on an ERAS pathway. Hopefully, due to Dr. Combs clinical and research leadership many more patients will benefit from the use of an ERAS pathway.
ObGyns united in a divided post-Dobbs America
ERIN TRACY BRADLEY, MD, MPH, AND MEGAN L. EVANS,MD, MPH (DECEMBER 2022)
ObGyns are not united on this issue
I just finished reading the article by Drs. Bradley and Evans in the December edition of
The unborn seem not to have advocates like Drs. Bradley and Evans. In fact, those who hold pro-life opinions are regularly silenced in publications and on social media. The Facebooks and Twitters of the world tend to hold us in derision when they are not silencing us. There used to be a detente in our field where we each respected the viewpoint of the other, but now it is nonstop advocacy for abortion. Some authors want to accelerate and intensify that advocacy. I suspect that the pro-life views like mine will continue to be silenced. I just want the authors to know that we are not united in this post-Dobbs world. Many of us want appropriate limits on termination. We are not in favor of the unlimited right to abort a fetus up to the moment of delivery.
Steven G. Nelson
Phoenix, Arizona
Addressing OR sustainability: How we can decrease waste and emissions
In 2009, the Lancet called climate change the biggest global health threat of the 21st century, the effects of which will be experienced in our lifetimes.1 Significant amounts of data have demonstrated the negative health effects of heat, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances.2,3 These effects have been seen in every geographic region of the United States, and in multiple organ systems and specialties, including obstetrics, pediatrics, and even cardiopulmonary and bariatric surgery.2-5
Although it does not receive the scrutiny of other industries, the global health care industry accounts for almost double the amount of carbon emissions as global aviation, and the United States accounts for 27% of this footprint despite only having 4% of the world’s population.6 It therefore serves that our own industry is an excellent target for reducing the carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Consider the climate impact of hysterectomy, the second-most common surgery that women undergo. In this article, we will use the example of a 50-year-old woman with fibroids who plans to undergo definitive treatment via total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH).
Climate impact of US health care
Hospital buildings in the United States are energy intensive, consuming 10% of the energy used in commercial buildings every year, accounting for over $8 billion. Operating rooms (ORs) account for a third of this usage.7 Hospitals also use more water than any other type of commercial building, for necessary actions like cooling, sterilization, and laundry.8 Further, US hospitals generate 14,000 tons of waste per day, with a third of this coming from the ORs. Sadly, up to 15% is food waste, as we are not very good about selecting and proportioning healthy food for our staff and inpatients.6
While health care is utility intensive, the majority of emissions are created through the production, transport, and disposal of goods coming through our supply chain.6 Hospitals are significant consumers of single-use objects, the majority of which are petroleum-derived plastics—accounting for an estimated 71% of emissions coming from the health care sector. Supply chain is the second largest expense in health care, but with current shortages, it is estimated to overtake labor costs by this year. The United States is also the largest consumer of pharmaceuticals worldwide, supporting a $20 billion packaging industry,9 which creates a significant amount of waste.
Climate impact of the OR
Although ORs only account for a small portion of hospital square footage, they account for a significant amount of health care’s carbon footprint through high waste production and excessive consumption of single-use items. Just one surgical procedure in a hospital is estimated to produce about the same amount of waste as a typical family of 4 would in an entire week.10 Furthermore, the majority of these single-use items, including sterile packaging, are sorted inappropriately as regulated medical waste (RMW, “biohazardous” or “red bag” waste) (FIGURE 1a). RMW has significant effects on the environment since it must be incinerated or steam autoclaved prior to transport to the landfill, leading to high amounts of air pollution and energy usage.

We all notice the visible impacts of waste in the OR, but other contributors to carbon emissions are invisible. Energy consumption is a huge contributor to the overall carbon footprint of surgery. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning [HVAC] is responsible for 52% of hospital energy needs but accounts for 99% of OR energy consumption.11 Despite the large energy requirements of the ORs, they are largely unoccupied in the evenings and on weekends, and thermostats are not adjusted accordingly.
Anesthetic gases are another powerful contributor to greenhouse gas emissions from the OR. Anesthetic gases alone contribute about 25% of the overall carbon footprint of the OR, and US health care emits 660,000 tons of carbon equivalents from anesthetic gas use per year.12 Desflurane is 1,600 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in its global warming potential followed by isoflurane and sevoflurane;13 this underscores the importance of working with our anesthesia colleagues on the differences between the anesthetic gases they use. Enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations in gynecology already recommend avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases in favor of propofol to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.14
In the context of a patient undergoing a TLH, the estimated carbon footprint in the United States is about 560 kg of CO2 equivalents—roughly the same as driving 1,563 miles in a gas-powered car.
Continue to: Climate impact on our patients...
Climate impact on our patients
The data in obstetrics and gynecology is clear that climate change is affecting patient outcomes, both globally and in our own country. A systematic review of 32 million births found that air pollution and heat exposure were associated with preterm birth and low birth weight, and these effects were seen in all geographic regions across the United States.1 A study of 5.9 million births in California found that patients who lived near coal- and oil-power plants had up to a 27% reduction in preterm births when those power plants closed and air pollution decreased.15 A study in Nature Sustainability on 250,000 pregnancies that ended in missed abortions at 14 weeks or less found the odds ratio of missed abortion increased with the cumulative exposure to air pollution.16 When air pollution was examined in comparison to other factors, neighborhood air pollution better predicted preterm birth, very preterm birth, and small for gestational age more than race, ethnicity, or any other socio-economic factor.17 The effects of air pollution have been demonstrated in other fields as well, including increased mortality after cardiac transplantation with exposure to air pollution,4 and for patients undergoing bariatric surgery who live near major roadways, decreased weight loss, less improvement in hemoglobin A1c, and less change in lipids compared with those with less exposure to roadway pollution.5
Air pollution and heat are not the only factors that influence health. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and single-use plastic polymers, which are used in significant supply in US health care, have been found in human blood,18 intestine, and all portions of the placenta.19 Phthalates, an EDC found in medical use plastics and medications to control delivery, have been associated with increasing fibroid burden in patients undergoing hysterectomy and myomectomy.20 The example case patient with fibroids undergoing TLH may have had her condition worsened by exposure to phthalates.

Specific areas for improvement
There is a huge opportunity for improvement to reduce the total carbon footprint of a TLH.
A lifecycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States concluded that an 80% reduction in carbon emissions could be achieved by minimizing opened materials, using reusable and reprocessed instruments, reducing off-hour energy use in the OR (HVAC setbacks), and avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases.21 The sterilization and re-processing of reusable instruments represented the smallest proportion of carbon emissions from a TLH. Data on patient safety supports these interventions, as current practices have more to do with hospital culture and processes than evidence.
Despite a push to use single-use objects by industry and regulatory agencies in the name of patient safety, data demonstrate that single-use objects are in actuality not safer for patients and may be associated with increased surgical site infections (SSIs). A study from a cancer center in California found that when single-use head covers, shoe covers, and facemasks were eliminated due to supply shortages during the pandemic, SSIs went down by half, despite an increase in surgical volume and an increase in the number of contaminated cases.22 The authors reported an increase in hand hygiene throughout the hospital, which likely contributed to the success of reducing SSIs.
Similarly, a systematic review found no evidence to support single-use instruments over reusable or reprocessed instruments when considering instrument function, ease of use, patient safety, SSIs, or long-term patient outcomes.23 While it may be easy for regulatory agencies to focus on disposing objects as paramount to reducing infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the biggest factors affecting SSIs are appropriate use of prophylactic antibiotics, skin antisepsis, and patient metabolic control.24 Disposing of single-use objects in the name of patient safety will worsen patient health outcomes when considering patient proximity to waste, pollution, and EDCs.
The sterilization process for reusable items is often called out by the medical supply industry as wasteful and energy intensive; however, data refute these claims. A Swedish study researching reusable versus single-use trocars found that a reusable trocar system offers a robust opportunity to reduce both the environmental and financial costs for laparoscopic surgery.25 We can further decrease the environmental impact of reusable instruments by using sets instead of individually packed instruments and packing autoclaves more efficiently. By using rigid sterilization containers, there was an 85% reduction in carbon footprint as compared with the blue wrap system.
Electricity use can be easily reduced across all surgical spaces by performing HVAC setbacks during low occupancy times of day. On nights and weekends, when there are very few surgical cases occurring, one study found that by decreasing the ventilation rate, turning off lights, and performing the minimum temperature control in unused ORs, electricity use was cut in half.11
Waste triage and recycling
Reducing regulated medical waste is another area where hospitals can make a huge impact on carbon emissions and costs with little more than education and process change. Guidelines for regulated medical waste sorting developed out of the HIV epidemic due to the fear of blood products. Although studies show that regulated medical waste is not more infectious than household waste, state departments of public health have kept these guidelines in place for sorting fluid blood and tissue into RMW containers and bags.26 The best hospital performers keep RMW below 10% of the total waste stream, while many ORs send close to 100% of their waste as RMW (FIGURE 1b). ORs can work with nursing and environmental services staff to assess processes and divert waste into recycling and regular waste. Many OR staff are acutely aware of the huge amount of waste produced and want to make a positive impact. Success in this small area often builds momentum to tackle harder sustainability practices throughout the hospital.
Continue to: Removal of EDCs from medical products...
Removal of EDCs from medical products
Single-use medical supplies are not only wasteful but also contain harmful EDCs, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), parabens, perfluoroalkyl substances, and triclosan. Phthalates, for example, account for 30% to 40% of the weight of medical-use plastics, and parabens are ubiquitously found in ultrasound gel.3 Studies looking at exposure to EDCs within the neonatal intensive care unit reveal substantial BPA, phthalate, and paraben levels within biologic samples from premature infants, thought to be above toxicity limits. While we do not know the full extent to which EDCs can affect neonatal development, there is already mounting evidence that EDCs are associated with endocrine, metabolic, and neurodevelopmental disorders throughout our lifespan.3
30-day climate challenge
Although the example case patient undergoing TLH for fibroids will never need care for her fibroids again, the climate impact of her time in the OR represents the most carbon-intensive care she will ever need. Surgery as practiced in the United States today is unsustainable.
In 2021, the Biden administration issued an executive order requiring all federal facilities, including health care facilities and hospitals, to be carbon neutral by 2035. In order to make meaningful changes industry-wide, we should be petitioning lawmakers for stricter environmental regulations in health care, similar to regulations in the manufacturing and airline industries. We recommend a 30-day climate challenge (FIGURE 2) for bringing awareness to your circles of influence. Physicians have an ethical duty to advocate for change at the local, regional, and national level if we want to see a better future for our patients, their children, and even ourselves. Organizations such as Practice Greenhealth, Health Care without Harm, and Citizens’ Climate Lobby can help amplify our voices to reach the right people to implement sweeping policy changes. ●
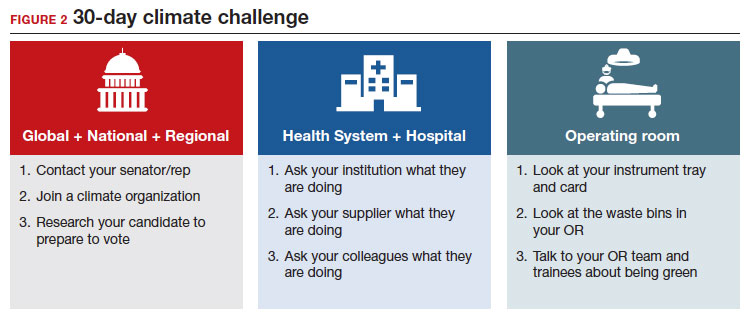
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen et al. Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet. 2009;373:1693-1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1.
- Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, et al. Association of air pollution and heat exposure with preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth in the US: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3. doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.8243.
- Genco M, Anderson-Shaw L, Sargis RM. Unwitting accomplices: endocrine disruptors confounding clinical care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3822–7. doi: 10.1210/cline2. m/dgaa358.
- Al-Kindi SG, Sarode A, Zullo M, et al. Ambient air pollution and mortality after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:3026-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.066.
- Ghosh R, Gauderman WJ, Minor H, et al. Air pollution, weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery: a potential model for study of metabolic effects of environmental exposures. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12210.
- Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Health care without harm climate-smart health care series, Green Paper Number one. September 2019. https://www.noharm.org/
ClimateFootprintReport. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Healthcare Energy End-Use Monitoring. US Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/eere/
buildings/downloads/ healthcare-energy-end-use- monitoring. Accessed December 11, 2022. - 2012 Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey: Water Consumption in Large Buildings Summary. U.S Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/
consumption/commercial/ reports/2012/water. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Belkhir L, Elmeligi A. Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative implact of its major players. J Cleaner Production. 2019;214:185-194. doi: 10.1016 /j.jclearpro.2019.11.204.
- Esaki RK, Macario A. Wastage of Supplies and Drugs in the Operating Room. 2015:8-13.
- MacNeill AJ, et al. The Impact of Surgery on Global Climate: A Carbon Footprinting Study of Operating Theatres in Three Health Systems. Lancet Planet Health.2017;1:e360–367. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30162-6.
- Shoham MA, Baker NM, Peterson ME, et al. The environmental impact of surgery: a systematic review. 2022;172:897-905. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2022.04.010.
- Ryan SM, Nielsen CJ. Global warming potential of inhaled anesthetics: application to clinical use. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:92-98. doi:10.1213/ANE.0B013E3181E058D7.
- Kalogera E, Dowdy SC. Enhanced recovery pathway in gynecologic surgery: improving outcomes through evidence-based medicine. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016;43:551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.006.
- Casey JA, Karasek D, Ogburn EL, et al. Retirements of coal and oil power plants in California: association with reduced preterm birth among populations nearby. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1586-1594. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy110.
- Zhang L, Liu W, Hou K, et al. Air pollution-induced missed abortion risk for pregnancies. Nat Sustain. 2019:1011–1017.
- Benmarhnia T, Huang J, Basu R, et al. Decomposition analysis of Black-White disparities in birth outcomes: the relative contribution of air pollution and social factors in California. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125:107003. doi: 10.1289/EHP490.
- Leslie HA, van Velzen MJM, Brandsma SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107199.
- Ragusa A, Svelato A, Santacroce C, et al. Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int. 2021;146:106274. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274.
- Zota AR, Geller RJ, Calafat AM, et al. Phthalates exposure and uterine fibroid burden among women undergoing surgical treatment for fibroids: a preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 2019;111:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.09.009.
- Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, et al. Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:1779-1786. doi: 10.1021/es504719g.
- Malhotra GK, Tran T, Stewart C, et al. Pandemic operating room supply shortage and surgical site infection: considerations as we emerge from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:571-578. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000087.
- Siu J, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Systematic review of reusable versus disposable laparoscopic instruments: costs and safety. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:28-33. doi:10.1111/ANS.13856.
- Berríos-Torres SI, Umscheid CA, Bratzler DW, et al; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017 [published correction appears in: JAMA Surg. 2017;152:803]. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:784-791. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904.
- Rizan, Chantelle, Lillywhite, et al. Minimising carbon and financial costs of steam sterilisation and packaging of reusable surgical instruments. Br J Surg. 2022;109:200-210. doi:10.1093/BJS/ZNAB406.
- Sustainability Benchmarking Report, 2010. Practice Greenhealth. https://www.practicegreenhealth.org. Accessed December 11, 2022.
In 2009, the Lancet called climate change the biggest global health threat of the 21st century, the effects of which will be experienced in our lifetimes.1 Significant amounts of data have demonstrated the negative health effects of heat, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances.2,3 These effects have been seen in every geographic region of the United States, and in multiple organ systems and specialties, including obstetrics, pediatrics, and even cardiopulmonary and bariatric surgery.2-5
Although it does not receive the scrutiny of other industries, the global health care industry accounts for almost double the amount of carbon emissions as global aviation, and the United States accounts for 27% of this footprint despite only having 4% of the world’s population.6 It therefore serves that our own industry is an excellent target for reducing the carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Consider the climate impact of hysterectomy, the second-most common surgery that women undergo. In this article, we will use the example of a 50-year-old woman with fibroids who plans to undergo definitive treatment via total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH).
Climate impact of US health care
Hospital buildings in the United States are energy intensive, consuming 10% of the energy used in commercial buildings every year, accounting for over $8 billion. Operating rooms (ORs) account for a third of this usage.7 Hospitals also use more water than any other type of commercial building, for necessary actions like cooling, sterilization, and laundry.8 Further, US hospitals generate 14,000 tons of waste per day, with a third of this coming from the ORs. Sadly, up to 15% is food waste, as we are not very good about selecting and proportioning healthy food for our staff and inpatients.6
While health care is utility intensive, the majority of emissions are created through the production, transport, and disposal of goods coming through our supply chain.6 Hospitals are significant consumers of single-use objects, the majority of which are petroleum-derived plastics—accounting for an estimated 71% of emissions coming from the health care sector. Supply chain is the second largest expense in health care, but with current shortages, it is estimated to overtake labor costs by this year. The United States is also the largest consumer of pharmaceuticals worldwide, supporting a $20 billion packaging industry,9 which creates a significant amount of waste.
Climate impact of the OR
Although ORs only account for a small portion of hospital square footage, they account for a significant amount of health care’s carbon footprint through high waste production and excessive consumption of single-use items. Just one surgical procedure in a hospital is estimated to produce about the same amount of waste as a typical family of 4 would in an entire week.10 Furthermore, the majority of these single-use items, including sterile packaging, are sorted inappropriately as regulated medical waste (RMW, “biohazardous” or “red bag” waste) (FIGURE 1a). RMW has significant effects on the environment since it must be incinerated or steam autoclaved prior to transport to the landfill, leading to high amounts of air pollution and energy usage.

We all notice the visible impacts of waste in the OR, but other contributors to carbon emissions are invisible. Energy consumption is a huge contributor to the overall carbon footprint of surgery. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning [HVAC] is responsible for 52% of hospital energy needs but accounts for 99% of OR energy consumption.11 Despite the large energy requirements of the ORs, they are largely unoccupied in the evenings and on weekends, and thermostats are not adjusted accordingly.
Anesthetic gases are another powerful contributor to greenhouse gas emissions from the OR. Anesthetic gases alone contribute about 25% of the overall carbon footprint of the OR, and US health care emits 660,000 tons of carbon equivalents from anesthetic gas use per year.12 Desflurane is 1,600 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in its global warming potential followed by isoflurane and sevoflurane;13 this underscores the importance of working with our anesthesia colleagues on the differences between the anesthetic gases they use. Enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations in gynecology already recommend avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases in favor of propofol to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.14
In the context of a patient undergoing a TLH, the estimated carbon footprint in the United States is about 560 kg of CO2 equivalents—roughly the same as driving 1,563 miles in a gas-powered car.
Continue to: Climate impact on our patients...
Climate impact on our patients
The data in obstetrics and gynecology is clear that climate change is affecting patient outcomes, both globally and in our own country. A systematic review of 32 million births found that air pollution and heat exposure were associated with preterm birth and low birth weight, and these effects were seen in all geographic regions across the United States.1 A study of 5.9 million births in California found that patients who lived near coal- and oil-power plants had up to a 27% reduction in preterm births when those power plants closed and air pollution decreased.15 A study in Nature Sustainability on 250,000 pregnancies that ended in missed abortions at 14 weeks or less found the odds ratio of missed abortion increased with the cumulative exposure to air pollution.16 When air pollution was examined in comparison to other factors, neighborhood air pollution better predicted preterm birth, very preterm birth, and small for gestational age more than race, ethnicity, or any other socio-economic factor.17 The effects of air pollution have been demonstrated in other fields as well, including increased mortality after cardiac transplantation with exposure to air pollution,4 and for patients undergoing bariatric surgery who live near major roadways, decreased weight loss, less improvement in hemoglobin A1c, and less change in lipids compared with those with less exposure to roadway pollution.5
Air pollution and heat are not the only factors that influence health. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and single-use plastic polymers, which are used in significant supply in US health care, have been found in human blood,18 intestine, and all portions of the placenta.19 Phthalates, an EDC found in medical use plastics and medications to control delivery, have been associated with increasing fibroid burden in patients undergoing hysterectomy and myomectomy.20 The example case patient with fibroids undergoing TLH may have had her condition worsened by exposure to phthalates.

Specific areas for improvement
There is a huge opportunity for improvement to reduce the total carbon footprint of a TLH.
A lifecycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States concluded that an 80% reduction in carbon emissions could be achieved by minimizing opened materials, using reusable and reprocessed instruments, reducing off-hour energy use in the OR (HVAC setbacks), and avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases.21 The sterilization and re-processing of reusable instruments represented the smallest proportion of carbon emissions from a TLH. Data on patient safety supports these interventions, as current practices have more to do with hospital culture and processes than evidence.
Despite a push to use single-use objects by industry and regulatory agencies in the name of patient safety, data demonstrate that single-use objects are in actuality not safer for patients and may be associated with increased surgical site infections (SSIs). A study from a cancer center in California found that when single-use head covers, shoe covers, and facemasks were eliminated due to supply shortages during the pandemic, SSIs went down by half, despite an increase in surgical volume and an increase in the number of contaminated cases.22 The authors reported an increase in hand hygiene throughout the hospital, which likely contributed to the success of reducing SSIs.
Similarly, a systematic review found no evidence to support single-use instruments over reusable or reprocessed instruments when considering instrument function, ease of use, patient safety, SSIs, or long-term patient outcomes.23 While it may be easy for regulatory agencies to focus on disposing objects as paramount to reducing infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the biggest factors affecting SSIs are appropriate use of prophylactic antibiotics, skin antisepsis, and patient metabolic control.24 Disposing of single-use objects in the name of patient safety will worsen patient health outcomes when considering patient proximity to waste, pollution, and EDCs.
The sterilization process for reusable items is often called out by the medical supply industry as wasteful and energy intensive; however, data refute these claims. A Swedish study researching reusable versus single-use trocars found that a reusable trocar system offers a robust opportunity to reduce both the environmental and financial costs for laparoscopic surgery.25 We can further decrease the environmental impact of reusable instruments by using sets instead of individually packed instruments and packing autoclaves more efficiently. By using rigid sterilization containers, there was an 85% reduction in carbon footprint as compared with the blue wrap system.
Electricity use can be easily reduced across all surgical spaces by performing HVAC setbacks during low occupancy times of day. On nights and weekends, when there are very few surgical cases occurring, one study found that by decreasing the ventilation rate, turning off lights, and performing the minimum temperature control in unused ORs, electricity use was cut in half.11
Waste triage and recycling
Reducing regulated medical waste is another area where hospitals can make a huge impact on carbon emissions and costs with little more than education and process change. Guidelines for regulated medical waste sorting developed out of the HIV epidemic due to the fear of blood products. Although studies show that regulated medical waste is not more infectious than household waste, state departments of public health have kept these guidelines in place for sorting fluid blood and tissue into RMW containers and bags.26 The best hospital performers keep RMW below 10% of the total waste stream, while many ORs send close to 100% of their waste as RMW (FIGURE 1b). ORs can work with nursing and environmental services staff to assess processes and divert waste into recycling and regular waste. Many OR staff are acutely aware of the huge amount of waste produced and want to make a positive impact. Success in this small area often builds momentum to tackle harder sustainability practices throughout the hospital.
Continue to: Removal of EDCs from medical products...
Removal of EDCs from medical products
Single-use medical supplies are not only wasteful but also contain harmful EDCs, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), parabens, perfluoroalkyl substances, and triclosan. Phthalates, for example, account for 30% to 40% of the weight of medical-use plastics, and parabens are ubiquitously found in ultrasound gel.3 Studies looking at exposure to EDCs within the neonatal intensive care unit reveal substantial BPA, phthalate, and paraben levels within biologic samples from premature infants, thought to be above toxicity limits. While we do not know the full extent to which EDCs can affect neonatal development, there is already mounting evidence that EDCs are associated with endocrine, metabolic, and neurodevelopmental disorders throughout our lifespan.3
30-day climate challenge
Although the example case patient undergoing TLH for fibroids will never need care for her fibroids again, the climate impact of her time in the OR represents the most carbon-intensive care she will ever need. Surgery as practiced in the United States today is unsustainable.
In 2021, the Biden administration issued an executive order requiring all federal facilities, including health care facilities and hospitals, to be carbon neutral by 2035. In order to make meaningful changes industry-wide, we should be petitioning lawmakers for stricter environmental regulations in health care, similar to regulations in the manufacturing and airline industries. We recommend a 30-day climate challenge (FIGURE 2) for bringing awareness to your circles of influence. Physicians have an ethical duty to advocate for change at the local, regional, and national level if we want to see a better future for our patients, their children, and even ourselves. Organizations such as Practice Greenhealth, Health Care without Harm, and Citizens’ Climate Lobby can help amplify our voices to reach the right people to implement sweeping policy changes. ●

In 2009, the Lancet called climate change the biggest global health threat of the 21st century, the effects of which will be experienced in our lifetimes.1 Significant amounts of data have demonstrated the negative health effects of heat, air pollution, and exposure to toxic substances.2,3 These effects have been seen in every geographic region of the United States, and in multiple organ systems and specialties, including obstetrics, pediatrics, and even cardiopulmonary and bariatric surgery.2-5
Although it does not receive the scrutiny of other industries, the global health care industry accounts for almost double the amount of carbon emissions as global aviation, and the United States accounts for 27% of this footprint despite only having 4% of the world’s population.6 It therefore serves that our own industry is an excellent target for reducing the carbon emissions that contribute to climate change. Consider the climate impact of hysterectomy, the second-most common surgery that women undergo. In this article, we will use the example of a 50-year-old woman with fibroids who plans to undergo definitive treatment via total laparoscopic hysterectomy (TLH).
Climate impact of US health care
Hospital buildings in the United States are energy intensive, consuming 10% of the energy used in commercial buildings every year, accounting for over $8 billion. Operating rooms (ORs) account for a third of this usage.7 Hospitals also use more water than any other type of commercial building, for necessary actions like cooling, sterilization, and laundry.8 Further, US hospitals generate 14,000 tons of waste per day, with a third of this coming from the ORs. Sadly, up to 15% is food waste, as we are not very good about selecting and proportioning healthy food for our staff and inpatients.6
While health care is utility intensive, the majority of emissions are created through the production, transport, and disposal of goods coming through our supply chain.6 Hospitals are significant consumers of single-use objects, the majority of which are petroleum-derived plastics—accounting for an estimated 71% of emissions coming from the health care sector. Supply chain is the second largest expense in health care, but with current shortages, it is estimated to overtake labor costs by this year. The United States is also the largest consumer of pharmaceuticals worldwide, supporting a $20 billion packaging industry,9 which creates a significant amount of waste.
Climate impact of the OR
Although ORs only account for a small portion of hospital square footage, they account for a significant amount of health care’s carbon footprint through high waste production and excessive consumption of single-use items. Just one surgical procedure in a hospital is estimated to produce about the same amount of waste as a typical family of 4 would in an entire week.10 Furthermore, the majority of these single-use items, including sterile packaging, are sorted inappropriately as regulated medical waste (RMW, “biohazardous” or “red bag” waste) (FIGURE 1a). RMW has significant effects on the environment since it must be incinerated or steam autoclaved prior to transport to the landfill, leading to high amounts of air pollution and energy usage.

We all notice the visible impacts of waste in the OR, but other contributors to carbon emissions are invisible. Energy consumption is a huge contributor to the overall carbon footprint of surgery. Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning [HVAC] is responsible for 52% of hospital energy needs but accounts for 99% of OR energy consumption.11 Despite the large energy requirements of the ORs, they are largely unoccupied in the evenings and on weekends, and thermostats are not adjusted accordingly.
Anesthetic gases are another powerful contributor to greenhouse gas emissions from the OR. Anesthetic gases alone contribute about 25% of the overall carbon footprint of the OR, and US health care emits 660,000 tons of carbon equivalents from anesthetic gas use per year.12 Desflurane is 1,600 times more potent than carbon dioxide (CO2) in its global warming potential followed by isoflurane and sevoflurane;13 this underscores the importance of working with our anesthesia colleagues on the differences between the anesthetic gases they use. Enhanced recovery after surgery recommendations in gynecology already recommend avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases in favor of propofol to reduce postoperative nausea and vomiting.14
In the context of a patient undergoing a TLH, the estimated carbon footprint in the United States is about 560 kg of CO2 equivalents—roughly the same as driving 1,563 miles in a gas-powered car.
Continue to: Climate impact on our patients...
Climate impact on our patients
The data in obstetrics and gynecology is clear that climate change is affecting patient outcomes, both globally and in our own country. A systematic review of 32 million births found that air pollution and heat exposure were associated with preterm birth and low birth weight, and these effects were seen in all geographic regions across the United States.1 A study of 5.9 million births in California found that patients who lived near coal- and oil-power plants had up to a 27% reduction in preterm births when those power plants closed and air pollution decreased.15 A study in Nature Sustainability on 250,000 pregnancies that ended in missed abortions at 14 weeks or less found the odds ratio of missed abortion increased with the cumulative exposure to air pollution.16 When air pollution was examined in comparison to other factors, neighborhood air pollution better predicted preterm birth, very preterm birth, and small for gestational age more than race, ethnicity, or any other socio-economic factor.17 The effects of air pollution have been demonstrated in other fields as well, including increased mortality after cardiac transplantation with exposure to air pollution,4 and for patients undergoing bariatric surgery who live near major roadways, decreased weight loss, less improvement in hemoglobin A1c, and less change in lipids compared with those with less exposure to roadway pollution.5
Air pollution and heat are not the only factors that influence health. Endocrine disrupting chemicals (EDCs) and single-use plastic polymers, which are used in significant supply in US health care, have been found in human blood,18 intestine, and all portions of the placenta.19 Phthalates, an EDC found in medical use plastics and medications to control delivery, have been associated with increasing fibroid burden in patients undergoing hysterectomy and myomectomy.20 The example case patient with fibroids undergoing TLH may have had her condition worsened by exposure to phthalates.

Specific areas for improvement
There is a huge opportunity for improvement to reduce the total carbon footprint of a TLH.
A lifecycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States concluded that an 80% reduction in carbon emissions could be achieved by minimizing opened materials, using reusable and reprocessed instruments, reducing off-hour energy use in the OR (HVAC setbacks), and avoiding the use of volatile anesthetic gases.21 The sterilization and re-processing of reusable instruments represented the smallest proportion of carbon emissions from a TLH. Data on patient safety supports these interventions, as current practices have more to do with hospital culture and processes than evidence.
Despite a push to use single-use objects by industry and regulatory agencies in the name of patient safety, data demonstrate that single-use objects are in actuality not safer for patients and may be associated with increased surgical site infections (SSIs). A study from a cancer center in California found that when single-use head covers, shoe covers, and facemasks were eliminated due to supply shortages during the pandemic, SSIs went down by half, despite an increase in surgical volume and an increase in the number of contaminated cases.22 The authors reported an increase in hand hygiene throughout the hospital, which likely contributed to the success of reducing SSIs.
Similarly, a systematic review found no evidence to support single-use instruments over reusable or reprocessed instruments when considering instrument function, ease of use, patient safety, SSIs, or long-term patient outcomes.23 While it may be easy for regulatory agencies to focus on disposing objects as paramount to reducing infections, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that the biggest factors affecting SSIs are appropriate use of prophylactic antibiotics, skin antisepsis, and patient metabolic control.24 Disposing of single-use objects in the name of patient safety will worsen patient health outcomes when considering patient proximity to waste, pollution, and EDCs.
The sterilization process for reusable items is often called out by the medical supply industry as wasteful and energy intensive; however, data refute these claims. A Swedish study researching reusable versus single-use trocars found that a reusable trocar system offers a robust opportunity to reduce both the environmental and financial costs for laparoscopic surgery.25 We can further decrease the environmental impact of reusable instruments by using sets instead of individually packed instruments and packing autoclaves more efficiently. By using rigid sterilization containers, there was an 85% reduction in carbon footprint as compared with the blue wrap system.
Electricity use can be easily reduced across all surgical spaces by performing HVAC setbacks during low occupancy times of day. On nights and weekends, when there are very few surgical cases occurring, one study found that by decreasing the ventilation rate, turning off lights, and performing the minimum temperature control in unused ORs, electricity use was cut in half.11
Waste triage and recycling
Reducing regulated medical waste is another area where hospitals can make a huge impact on carbon emissions and costs with little more than education and process change. Guidelines for regulated medical waste sorting developed out of the HIV epidemic due to the fear of blood products. Although studies show that regulated medical waste is not more infectious than household waste, state departments of public health have kept these guidelines in place for sorting fluid blood and tissue into RMW containers and bags.26 The best hospital performers keep RMW below 10% of the total waste stream, while many ORs send close to 100% of their waste as RMW (FIGURE 1b). ORs can work with nursing and environmental services staff to assess processes and divert waste into recycling and regular waste. Many OR staff are acutely aware of the huge amount of waste produced and want to make a positive impact. Success in this small area often builds momentum to tackle harder sustainability practices throughout the hospital.
Continue to: Removal of EDCs from medical products...
Removal of EDCs from medical products
Single-use medical supplies are not only wasteful but also contain harmful EDCs, such as phthalates, bisphenol A (BPA), parabens, perfluoroalkyl substances, and triclosan. Phthalates, for example, account for 30% to 40% of the weight of medical-use plastics, and parabens are ubiquitously found in ultrasound gel.3 Studies looking at exposure to EDCs within the neonatal intensive care unit reveal substantial BPA, phthalate, and paraben levels within biologic samples from premature infants, thought to be above toxicity limits. While we do not know the full extent to which EDCs can affect neonatal development, there is already mounting evidence that EDCs are associated with endocrine, metabolic, and neurodevelopmental disorders throughout our lifespan.3
30-day climate challenge
Although the example case patient undergoing TLH for fibroids will never need care for her fibroids again, the climate impact of her time in the OR represents the most carbon-intensive care she will ever need. Surgery as practiced in the United States today is unsustainable.
In 2021, the Biden administration issued an executive order requiring all federal facilities, including health care facilities and hospitals, to be carbon neutral by 2035. In order to make meaningful changes industry-wide, we should be petitioning lawmakers for stricter environmental regulations in health care, similar to regulations in the manufacturing and airline industries. We recommend a 30-day climate challenge (FIGURE 2) for bringing awareness to your circles of influence. Physicians have an ethical duty to advocate for change at the local, regional, and national level if we want to see a better future for our patients, their children, and even ourselves. Organizations such as Practice Greenhealth, Health Care without Harm, and Citizens’ Climate Lobby can help amplify our voices to reach the right people to implement sweeping policy changes. ●

- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen et al. Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet. 2009;373:1693-1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1.
- Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, et al. Association of air pollution and heat exposure with preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth in the US: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3. doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.8243.
- Genco M, Anderson-Shaw L, Sargis RM. Unwitting accomplices: endocrine disruptors confounding clinical care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3822–7. doi: 10.1210/cline2. m/dgaa358.
- Al-Kindi SG, Sarode A, Zullo M, et al. Ambient air pollution and mortality after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:3026-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.066.
- Ghosh R, Gauderman WJ, Minor H, et al. Air pollution, weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery: a potential model for study of metabolic effects of environmental exposures. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12210.
- Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Health care without harm climate-smart health care series, Green Paper Number one. September 2019. https://www.noharm.org/
ClimateFootprintReport. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Healthcare Energy End-Use Monitoring. US Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/eere/
buildings/downloads/ healthcare-energy-end-use- monitoring. Accessed December 11, 2022. - 2012 Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey: Water Consumption in Large Buildings Summary. U.S Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/
consumption/commercial/ reports/2012/water. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Belkhir L, Elmeligi A. Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative implact of its major players. J Cleaner Production. 2019;214:185-194. doi: 10.1016 /j.jclearpro.2019.11.204.
- Esaki RK, Macario A. Wastage of Supplies and Drugs in the Operating Room. 2015:8-13.
- MacNeill AJ, et al. The Impact of Surgery on Global Climate: A Carbon Footprinting Study of Operating Theatres in Three Health Systems. Lancet Planet Health.2017;1:e360–367. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30162-6.
- Shoham MA, Baker NM, Peterson ME, et al. The environmental impact of surgery: a systematic review. 2022;172:897-905. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2022.04.010.
- Ryan SM, Nielsen CJ. Global warming potential of inhaled anesthetics: application to clinical use. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:92-98. doi:10.1213/ANE.0B013E3181E058D7.
- Kalogera E, Dowdy SC. Enhanced recovery pathway in gynecologic surgery: improving outcomes through evidence-based medicine. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016;43:551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.006.
- Casey JA, Karasek D, Ogburn EL, et al. Retirements of coal and oil power plants in California: association with reduced preterm birth among populations nearby. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1586-1594. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy110.
- Zhang L, Liu W, Hou K, et al. Air pollution-induced missed abortion risk for pregnancies. Nat Sustain. 2019:1011–1017.
- Benmarhnia T, Huang J, Basu R, et al. Decomposition analysis of Black-White disparities in birth outcomes: the relative contribution of air pollution and social factors in California. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125:107003. doi: 10.1289/EHP490.
- Leslie HA, van Velzen MJM, Brandsma SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107199.
- Ragusa A, Svelato A, Santacroce C, et al. Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int. 2021;146:106274. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274.
- Zota AR, Geller RJ, Calafat AM, et al. Phthalates exposure and uterine fibroid burden among women undergoing surgical treatment for fibroids: a preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 2019;111:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.09.009.
- Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, et al. Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:1779-1786. doi: 10.1021/es504719g.
- Malhotra GK, Tran T, Stewart C, et al. Pandemic operating room supply shortage and surgical site infection: considerations as we emerge from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:571-578. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000087.
- Siu J, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Systematic review of reusable versus disposable laparoscopic instruments: costs and safety. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:28-33. doi:10.1111/ANS.13856.
- Berríos-Torres SI, Umscheid CA, Bratzler DW, et al; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017 [published correction appears in: JAMA Surg. 2017;152:803]. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:784-791. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904.
- Rizan, Chantelle, Lillywhite, et al. Minimising carbon and financial costs of steam sterilisation and packaging of reusable surgical instruments. Br J Surg. 2022;109:200-210. doi:10.1093/BJS/ZNAB406.
- Sustainability Benchmarking Report, 2010. Practice Greenhealth. https://www.practicegreenhealth.org. Accessed December 11, 2022.
- Costello A, Abbas M, Allen et al. Managing the health effects of climate change: Lancet and University College London Institute for Global Health Commission. Lancet. 2009;373:1693-1733. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60935-1.
- Bekkar B, Pacheco S, Basu R, et al. Association of air pollution and heat exposure with preterm birth, low birth weight, and stillbirth in the US: a systematic review. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3. doi:10.1001/JAMANETWORKOPEN.2020.8243.
- Genco M, Anderson-Shaw L, Sargis RM. Unwitting accomplices: endocrine disruptors confounding clinical care. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2020;105:e3822–7. doi: 10.1210/cline2. m/dgaa358.
- Al-Kindi SG, Sarode A, Zullo M, et al. Ambient air pollution and mortality after cardiac transplantation. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2019;74:3026-3035. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2019.09.066.
- Ghosh R, Gauderman WJ, Minor H, et al. Air pollution, weight loss and metabolic benefits of bariatric surgery: a potential model for study of metabolic effects of environmental exposures. Pediatr Obes. 2018;13:312-320. doi: 10.1111/ijpo.12210.
- Health Care’s Climate Footprint. Health care without harm climate-smart health care series, Green Paper Number one. September 2019. https://www.noharm.org/
ClimateFootprintReport. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Healthcare Energy End-Use Monitoring. US Department of Energy. https://www.energy.gov/eere/
buildings/downloads/ healthcare-energy-end-use- monitoring. Accessed December 11, 2022. - 2012 Commercial Buildings Energy Consumption Survey: Water Consumption in Large Buildings Summary. U.S Energy Information Administration. https://www.eia.gov/
consumption/commercial/ reports/2012/water. Accessed December 11, 2022. - Belkhir L, Elmeligi A. Carbon footprint of the global pharmaceutical industry and relative implact of its major players. J Cleaner Production. 2019;214:185-194. doi: 10.1016 /j.jclearpro.2019.11.204.
- Esaki RK, Macario A. Wastage of Supplies and Drugs in the Operating Room. 2015:8-13.
- MacNeill AJ, et al. The Impact of Surgery on Global Climate: A Carbon Footprinting Study of Operating Theatres in Three Health Systems. Lancet Planet Health.2017;1:e360–367. doi:10.1016/S2542-5196(17)30162-6.
- Shoham MA, Baker NM, Peterson ME, et al. The environmental impact of surgery: a systematic review. 2022;172:897-905. doi:10.1016/j.surg.2022.04.010.
- Ryan SM, Nielsen CJ. Global warming potential of inhaled anesthetics: application to clinical use. Anesth Analg. 2010;111:92-98. doi:10.1213/ANE.0B013E3181E058D7.
- Kalogera E, Dowdy SC. Enhanced recovery pathway in gynecologic surgery: improving outcomes through evidence-based medicine. Obstet Gynecol Clin North Am. 2016;43:551-573. doi: 10.1016/j.ogc.2016.04.006.
- Casey JA, Karasek D, Ogburn EL, et al. Retirements of coal and oil power plants in California: association with reduced preterm birth among populations nearby. Am J Epidemiol. 2018;187:1586-1594. doi: 10.1093/aje/kwy110.
- Zhang L, Liu W, Hou K, et al. Air pollution-induced missed abortion risk for pregnancies. Nat Sustain. 2019:1011–1017.
- Benmarhnia T, Huang J, Basu R, et al. Decomposition analysis of Black-White disparities in birth outcomes: the relative contribution of air pollution and social factors in California. Environ Health Perspect. 2017;125:107003. doi: 10.1289/EHP490.
- Leslie HA, van Velzen MJM, Brandsma SH, et al. Discovery and quantification of plastic particle pollution in human blood. Environ Int. 2022;163:107199. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107199.
- Ragusa A, Svelato A, Santacroce C, et al. Plasticenta: first evidence of microplastics in human placenta. Environ Int. 2021;146:106274. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2020.106274.
- Zota AR, Geller RJ, Calafat AM, et al. Phthalates exposure and uterine fibroid burden among women undergoing surgical treatment for fibroids: a preliminary study. Fertil Steril. 2019;111:112-121. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2018.09.009.
- Thiel CL, Eckelman M, Guido R, et al. Environmental impacts of surgical procedures: life cycle assessment of hysterectomy in the United States. Environ Sci Technol. 2015;49:1779-1786. doi: 10.1021/es504719g.
- Malhotra GK, Tran T, Stewart C, et al. Pandemic operating room supply shortage and surgical site infection: considerations as we emerge from the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic. J Am Coll Surg. 2022;234:571-578. doi: 10.1097/XCS.0000000000000087.
- Siu J, Hill AG, MacCormick AD. Systematic review of reusable versus disposable laparoscopic instruments: costs and safety. ANZ J Surg. 2017;87:28-33. doi:10.1111/ANS.13856.
- Berríos-Torres SI, Umscheid CA, Bratzler DW, et al; Healthcare Infection Control Practices Advisory Committee. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Guideline for the Prevention of Surgical Site Infection, 2017 [published correction appears in: JAMA Surg. 2017;152:803]. JAMA Surg. 2017;152:784-791. doi: 10.1001/jamasurg.2017.0904.
- Rizan, Chantelle, Lillywhite, et al. Minimising carbon and financial costs of steam sterilisation and packaging of reusable surgical instruments. Br J Surg. 2022;109:200-210. doi:10.1093/BJS/ZNAB406.
- Sustainability Benchmarking Report, 2010. Practice Greenhealth. https://www.practicegreenhealth.org. Accessed December 11, 2022.
Diagnosis to treatment interval: A crucial prognostic factor in newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma
Key clinical point: Diagnosis to treatment interval (DTI; time in days from the diagnosis date to therapy initiation) is strongly associated with poor survival outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: Patients with a short vs long DTI had significantly shorter median overall (7.8 vs 11.8 years) and progression-free (2.5 vs 4.8 years) survival (both log-rank P < .0001). A short vs long DTI was associated with significantly poorer overall (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.57) and progression-free (aHR 1.50) survival (both P < .001).
Study details: This pooled analysis of three large datasets included 1097 patients with newly diagnosed MCL and available DTI data, of which 300 had a short (0-14 days) and 797 had a long (15-60 days) DTI.
Disclosures: One of the datasets, Molecular Epidemiology Resource, was supported by grants from the US National Cancer Institute. Some authors reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Epperla N et al. Impact of diagnosis to treatment interval in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022 (Dec 14). Doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009225
Key clinical point: Diagnosis to treatment interval (DTI; time in days from the diagnosis date to therapy initiation) is strongly associated with poor survival outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: Patients with a short vs long DTI had significantly shorter median overall (7.8 vs 11.8 years) and progression-free (2.5 vs 4.8 years) survival (both log-rank P < .0001). A short vs long DTI was associated with significantly poorer overall (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.57) and progression-free (aHR 1.50) survival (both P < .001).
Study details: This pooled analysis of three large datasets included 1097 patients with newly diagnosed MCL and available DTI data, of which 300 had a short (0-14 days) and 797 had a long (15-60 days) DTI.
Disclosures: One of the datasets, Molecular Epidemiology Resource, was supported by grants from the US National Cancer Institute. Some authors reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Epperla N et al. Impact of diagnosis to treatment interval in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022 (Dec 14). Doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009225
Key clinical point: Diagnosis to treatment interval (DTI; time in days from the diagnosis date to therapy initiation) is strongly associated with poor survival outcomes in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: Patients with a short vs long DTI had significantly shorter median overall (7.8 vs 11.8 years) and progression-free (2.5 vs 4.8 years) survival (both log-rank P < .0001). A short vs long DTI was associated with significantly poorer overall (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.57) and progression-free (aHR 1.50) survival (both P < .001).
Study details: This pooled analysis of three large datasets included 1097 patients with newly diagnosed MCL and available DTI data, of which 300 had a short (0-14 days) and 797 had a long (15-60 days) DTI.
Disclosures: One of the datasets, Molecular Epidemiology Resource, was supported by grants from the US National Cancer Institute. Some authors reported ties with various organizations.
Source: Epperla N et al. Impact of diagnosis to treatment interval in patients with newly diagnosed mantle cell lymphoma. Blood Adv. 2022 (Dec 14). Doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009225
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma: No impact of lenalidomide after R-CHOP on unfavorable prognosis of low NK-cell counts
Key clinical point: Low natural killer (NK) cell counts (NKCC; <100 cells/μL) at diagnosis predict poor outcomes in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and lenalidomide maintenance therapy has no impact on this unfavorable prognosis.
Major finding: Low baseline NKCC were associated with shorter progression-free (hazard ratio [HR] 2.2) and overall (HR 2.8) survival (both P < .001), independently of age-adjusted International Prognostic Index scores, and with a higher risk for progression or relapse (P = .0025). Lenalidomide maintenance therapy did not affect the prognostic value of low NKCC at diagnosis or random assignment (P = .6349).
Study details: This prospective ancillary study of the REMARC trial included 335 elderly patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone who underwent flow cytometric peripheral blood lymphocyte analysis at diagnosis, at random assignment to the lenalidomide or placebo arm, or at 6 months after random assignment.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Celgene.
Source: Beldi-Ferchiou A et al. Lenalidomide maintenance fails to overcome the unfavourable prognosis of low NK-cell counts in rituximab–chemotherapy responsive elderly DLBCL patients: A LYSA group study. Br J Haematol. 2023 (Feb 6). Doi: 10.1111/bjh.18642
Key clinical point: Low natural killer (NK) cell counts (NKCC; <100 cells/μL) at diagnosis predict poor outcomes in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and lenalidomide maintenance therapy has no impact on this unfavorable prognosis.
Major finding: Low baseline NKCC were associated with shorter progression-free (hazard ratio [HR] 2.2) and overall (HR 2.8) survival (both P < .001), independently of age-adjusted International Prognostic Index scores, and with a higher risk for progression or relapse (P = .0025). Lenalidomide maintenance therapy did not affect the prognostic value of low NKCC at diagnosis or random assignment (P = .6349).
Study details: This prospective ancillary study of the REMARC trial included 335 elderly patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone who underwent flow cytometric peripheral blood lymphocyte analysis at diagnosis, at random assignment to the lenalidomide or placebo arm, or at 6 months after random assignment.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Celgene.
Source: Beldi-Ferchiou A et al. Lenalidomide maintenance fails to overcome the unfavourable prognosis of low NK-cell counts in rituximab–chemotherapy responsive elderly DLBCL patients: A LYSA group study. Br J Haematol. 2023 (Feb 6). Doi: 10.1111/bjh.18642
Key clinical point: Low natural killer (NK) cell counts (NKCC; <100 cells/μL) at diagnosis predict poor outcomes in patients with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL), and lenalidomide maintenance therapy has no impact on this unfavorable prognosis.
Major finding: Low baseline NKCC were associated with shorter progression-free (hazard ratio [HR] 2.2) and overall (HR 2.8) survival (both P < .001), independently of age-adjusted International Prognostic Index scores, and with a higher risk for progression or relapse (P = .0025). Lenalidomide maintenance therapy did not affect the prognostic value of low NKCC at diagnosis or random assignment (P = .6349).
Study details: This prospective ancillary study of the REMARC trial included 335 elderly patients with DLBCL treated with rituximab, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone who underwent flow cytometric peripheral blood lymphocyte analysis at diagnosis, at random assignment to the lenalidomide or placebo arm, or at 6 months after random assignment.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Celgene.
Source: Beldi-Ferchiou A et al. Lenalidomide maintenance fails to overcome the unfavourable prognosis of low NK-cell counts in rituximab–chemotherapy responsive elderly DLBCL patients: A LYSA group study. Br J Haematol. 2023 (Feb 6). Doi: 10.1111/bjh.18642
Ibrutinib shows long-term benefits in chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma in RESONATE-2
Key clinical point: Ibrutinib continued to benefit most treatment-naive patients (58%) with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in the RESONATE-2 study for ≥5 years, irrespective of baseline characteristics.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 89.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were not reached; the 7-year PFS and OS rates were 82% and 94%, respectively. Complete response rates increased from 10% at 1 year to 42% at 5 years and 46% at 7 years. No new safety signals were observed.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of 79 treatment-naive patients aged ≥65 years with CLL or SLL who were randomly assigned to receive ibrutinib in the phase 3 RESONATE-2 trial and its extension study and had continued the treatment for ≥5 years.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Pharmacyclics. Two authors declared being employees of, holding stocks in, or having other ownership interests in Pharmacyclics/AbbVie.
Source: Woyach JA et al. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma receiving ibrutinib for ≥5 years in the RESONATE-2 study. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(2):507 (Jan 13). Doi: 10.3390/cancers15020507
Key clinical point: Ibrutinib continued to benefit most treatment-naive patients (58%) with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in the RESONATE-2 study for ≥5 years, irrespective of baseline characteristics.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 89.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were not reached; the 7-year PFS and OS rates were 82% and 94%, respectively. Complete response rates increased from 10% at 1 year to 42% at 5 years and 46% at 7 years. No new safety signals were observed.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of 79 treatment-naive patients aged ≥65 years with CLL or SLL who were randomly assigned to receive ibrutinib in the phase 3 RESONATE-2 trial and its extension study and had continued the treatment for ≥5 years.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Pharmacyclics. Two authors declared being employees of, holding stocks in, or having other ownership interests in Pharmacyclics/AbbVie.
Source: Woyach JA et al. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma receiving ibrutinib for ≥5 years in the RESONATE-2 study. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(2):507 (Jan 13). Doi: 10.3390/cancers15020507
Key clinical point: Ibrutinib continued to benefit most treatment-naive patients (58%) with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL) in the RESONATE-2 study for ≥5 years, irrespective of baseline characteristics.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 89.2 months, the median progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) were not reached; the 7-year PFS and OS rates were 82% and 94%, respectively. Complete response rates increased from 10% at 1 year to 42% at 5 years and 46% at 7 years. No new safety signals were observed.
Study details: This study analyzed the data of 79 treatment-naive patients aged ≥65 years with CLL or SLL who were randomly assigned to receive ibrutinib in the phase 3 RESONATE-2 trial and its extension study and had continued the treatment for ≥5 years.
Disclosures: This study was sponsored by Pharmacyclics LLC, an AbbVie Company. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Pharmacyclics. Two authors declared being employees of, holding stocks in, or having other ownership interests in Pharmacyclics/AbbVie.
Source: Woyach JA et al. Characteristics and clinical outcomes of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma receiving ibrutinib for ≥5 years in the RESONATE-2 study. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(2):507 (Jan 13). Doi: 10.3390/cancers15020507
Relapsed follicular lymphoma: Autologous stem cell transplantation shows long-term curative effects
Key clinical point: Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) leads to high durable remission rates in patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL), with the functional cure rate elucidated by long-term follow-up being >50%.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 12.5 years, the 12-year time-to-progression (TTP), time-to-next-treatment, progression-free survival, and overall survival rates were 57% (95% CI 49%-65%), 61% (95% CI 52%-69%), 51% (95% CI 42%-59%), and 69% (95% CI 60%-76%), respectively. The TTP curve achieved a plateau at 57% starting 9 years after ASCT with no relapses after this timepoint; 10 patients remained alive without recurrence for ≥20 years after ASCT.
Study details: This retrospective multicenter study included 162 adult patients with relapsed FL who underwent ASCT.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared receiving honoraria from various sources.
Source: Puckrin R et al. Long-term follow-up demonstrates curative potential of autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2023 (Jan 10). Doi: 10.1111/bjh.18640
Key clinical point: Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) leads to high durable remission rates in patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL), with the functional cure rate elucidated by long-term follow-up being >50%.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 12.5 years, the 12-year time-to-progression (TTP), time-to-next-treatment, progression-free survival, and overall survival rates were 57% (95% CI 49%-65%), 61% (95% CI 52%-69%), 51% (95% CI 42%-59%), and 69% (95% CI 60%-76%), respectively. The TTP curve achieved a plateau at 57% starting 9 years after ASCT with no relapses after this timepoint; 10 patients remained alive without recurrence for ≥20 years after ASCT.
Study details: This retrospective multicenter study included 162 adult patients with relapsed FL who underwent ASCT.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared receiving honoraria from various sources.
Source: Puckrin R et al. Long-term follow-up demonstrates curative potential of autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2023 (Jan 10). Doi: 10.1111/bjh.18640
Key clinical point: Autologous stem cell transplantation (ASCT) leads to high durable remission rates in patients with relapsed follicular lymphoma (FL), with the functional cure rate elucidated by long-term follow-up being >50%.
Major finding: At a median follow-up of 12.5 years, the 12-year time-to-progression (TTP), time-to-next-treatment, progression-free survival, and overall survival rates were 57% (95% CI 49%-65%), 61% (95% CI 52%-69%), 51% (95% CI 42%-59%), and 69% (95% CI 60%-76%), respectively. The TTP curve achieved a plateau at 57% starting 9 years after ASCT with no relapses after this timepoint; 10 patients remained alive without recurrence for ≥20 years after ASCT.
Study details: This retrospective multicenter study included 162 adult patients with relapsed FL who underwent ASCT.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. Some authors declared receiving honoraria from various sources.
Source: Puckrin R et al. Long-term follow-up demonstrates curative potential of autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed follicular lymphoma. Br J Haematol. 2023 (Jan 10). Doi: 10.1111/bjh.18640
Second-line lisocabtagene maraleucel shows promise in large B-cell lymphoma
Key clinical point: Second-line lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) offers better efficacy over standard of care (SOC; platinum-based immunochemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy+autologous stem cell transplantation [ASCT]) in chemotherapy-sensitive patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) along with a favorable safety profile.
Major finding: After a 17.5-month median follow-up, the liso-cel vs SOC group had significantly improved median event-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.356; 95% CI 0.243-0.522), median progression-free survival (HR 0.400; P < .0001), and complete response rate (74% vs 43%; P < .0001), along with low grade 3 cytokine release syndrome (1%) and neurological event (4%) rates.
Study details: This phase 3 study, TRANSFORM, included 184 adult patients with relapsed/refractory LBCL who were eligible for high-dose chemotherapy+ASCT and were randomly assigned to receive liso-cel (100×106 chimeric antigen receptor-positive T cells) or three cycles of SOC.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Celgene. Three authors declared being employees of Celgene.
Source: Abramson JS et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: Primary analysis of phase 3 TRANSFORM study. Blood. 2022 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1182/blood.2022018730
Key clinical point: Second-line lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) offers better efficacy over standard of care (SOC; platinum-based immunochemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy+autologous stem cell transplantation [ASCT]) in chemotherapy-sensitive patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) along with a favorable safety profile.
Major finding: After a 17.5-month median follow-up, the liso-cel vs SOC group had significantly improved median event-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.356; 95% CI 0.243-0.522), median progression-free survival (HR 0.400; P < .0001), and complete response rate (74% vs 43%; P < .0001), along with low grade 3 cytokine release syndrome (1%) and neurological event (4%) rates.
Study details: This phase 3 study, TRANSFORM, included 184 adult patients with relapsed/refractory LBCL who were eligible for high-dose chemotherapy+ASCT and were randomly assigned to receive liso-cel (100×106 chimeric antigen receptor-positive T cells) or three cycles of SOC.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Celgene. Three authors declared being employees of Celgene.
Source: Abramson JS et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: Primary analysis of phase 3 TRANSFORM study. Blood. 2022 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1182/blood.2022018730
Key clinical point: Second-line lisocabtagene maraleucel (liso-cel) offers better efficacy over standard of care (SOC; platinum-based immunochemotherapy followed by high-dose chemotherapy+autologous stem cell transplantation [ASCT]) in chemotherapy-sensitive patients with relapsed/refractory large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL) along with a favorable safety profile.
Major finding: After a 17.5-month median follow-up, the liso-cel vs SOC group had significantly improved median event-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 0.356; 95% CI 0.243-0.522), median progression-free survival (HR 0.400; P < .0001), and complete response rate (74% vs 43%; P < .0001), along with low grade 3 cytokine release syndrome (1%) and neurological event (4%) rates.
Study details: This phase 3 study, TRANSFORM, included 184 adult patients with relapsed/refractory LBCL who were eligible for high-dose chemotherapy+ASCT and were randomly assigned to receive liso-cel (100×106 chimeric antigen receptor-positive T cells) or three cycles of SOC.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Celgene, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company. Some authors reported ties with various organizations, including Celgene. Three authors declared being employees of Celgene.
Source: Abramson JS et al. Lisocabtagene maraleucel as second-line therapy for large B-cell lymphoma: Primary analysis of phase 3 TRANSFORM study. Blood. 2022 (Dec 21). Doi: 10.1182/blood.2022018730
Mantle cell lymphoma: Real-world benefits of rituximab maintenance after first-line BR/R-CHOP
Key clinical point: Rituximab maintenance (RM) therapy after first-line bendamustine-rituximab (BR) or rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) improved overall survival and disease control in older patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: Patients who did vs did not receive RM therapy had a significantly longer overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.53; 95% CI 0.34-0.82) and approximated progression-free survival (survival or free of second-line therapy; aHR 0.51; 95% CI 0.36-0.72).
Study details: This real-world study included 131 propensity-score matched pairs of autologous stem cell transplant-ineligible patients aged ≥66 years with MCL who did and did not receive RM after first-line treatment with BR or R-CHOP.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any financial support. No information on conflicts of interest was reported.
Source: Di M et al. Treatment patterns and real-world effectiveness of rituximab maintenance in older patients with mantle cell lymphoma: A population-based analysis. Haematologica. 2023 (Jan 19). Doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.282252
Key clinical point: Rituximab maintenance (RM) therapy after first-line bendamustine-rituximab (BR) or rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) improved overall survival and disease control in older patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: Patients who did vs did not receive RM therapy had a significantly longer overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.53; 95% CI 0.34-0.82) and approximated progression-free survival (survival or free of second-line therapy; aHR 0.51; 95% CI 0.36-0.72).
Study details: This real-world study included 131 propensity-score matched pairs of autologous stem cell transplant-ineligible patients aged ≥66 years with MCL who did and did not receive RM after first-line treatment with BR or R-CHOP.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any financial support. No information on conflicts of interest was reported.
Source: Di M et al. Treatment patterns and real-world effectiveness of rituximab maintenance in older patients with mantle cell lymphoma: A population-based analysis. Haematologica. 2023 (Jan 19). Doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.282252
Key clinical point: Rituximab maintenance (RM) therapy after first-line bendamustine-rituximab (BR) or rituximab plus cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin, vincristine, and prednisone (R-CHOP) improved overall survival and disease control in older patients with mantle cell lymphoma (MCL).
Major finding: Patients who did vs did not receive RM therapy had a significantly longer overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 0.53; 95% CI 0.34-0.82) and approximated progression-free survival (survival or free of second-line therapy; aHR 0.51; 95% CI 0.36-0.72).
Study details: This real-world study included 131 propensity-score matched pairs of autologous stem cell transplant-ineligible patients aged ≥66 years with MCL who did and did not receive RM after first-line treatment with BR or R-CHOP.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any financial support. No information on conflicts of interest was reported.
Source: Di M et al. Treatment patterns and real-world effectiveness of rituximab maintenance in older patients with mantle cell lymphoma: A population-based analysis. Haematologica. 2023 (Jan 19). Doi: 10.3324/haematol.2022.282252




