User login
Anticoagulation Hub contains news and clinical review articles for physicians seeking the most up-to-date information on the rapidly evolving treatment options for preventing stroke, acute coronary events, deep vein thrombosis, and pulmonary embolism in at-risk patients. The Anticoagulation Hub is powered by Frontline Medical Communications.
Anticipation runs high for coming megatrials in general cardiology
SAN DIEGO – Preventive cardiovascular medicine will get “a big boost” from ongoing major randomized controlled trials due to report results during the next several years, Dr. Eric D. Peterson predicted at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
He presented an overview of eagerly anticipated clinical trials approaching completion in three of the hottest areas of research in general cardiology: new cardiovascular prevention agents and strategies; innovative health policy initiatives; and optimal antithrombotic regimens across the range of chronic coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, patients with atrial fibrillation who’ve undergone percutaneous coronary intervention, and cerebrovascular disease.
Dr. Peterson is executive director of the Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI), a major player in some of these studies. To gain additional perspective regarding what’s in store, he consulted a who’s who list of eminent American cardiology clinical trialists as to what’s going to be big in 2016-2017 and shortly beyond.
One thing’s clear looking out at the research horizon: Megatrials enrolling tens of thousands of patients to answer key clinical questions are not a thing of the past.
Far from it.
Cardiovascular prevention
Exciting pivotal phase III cardiovascular prevention trials are well underway in the areas of lipid modification, diabetes, and hypertension. In addition, the possible preventive effect of vitamin D and omega-3 free fatty acid supplementation seen in hypothesis-generating epidemiologic studies is finally being put to a definitive test in a 26,000-subject randomized trial known as VITAL (the Vitamin D and omega-3 trial).
Lipids: All eyes are on ongoing pivotal phase III randomized clinical outcome trials of three monoclonal antibodies that inhibit proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9): the 22,500-patient FOURIER trial of evolocumab, which includes 9,000 patients older than 65 years; the 18,000-patient ODYSSEY Outcomes trial of alirocumab; and the SPIRE-1 and SPIRE-2 trials of bococizumab totaling 18,300 patients.
In phase II studies, these agents have generated enormous excitement, because they safely achieve unprecedented LDL lowering, with early hints of improved clinical outcomes beyond what’s achievable with today’s drugs, noted Dr. Peterson, professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
CETP inhibitors: The cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors torcetrapib and dalcetrapib flamed out in clinical trials because of safety concerns and lack of clinical benefit. But pivotal phase III trials of two other CETP inhibitors are well underway: anacetrapib, which is the focus of the 30,000-patient REVEAL trial; and evacetrapib, featured in the 11,000-patient ACCELERATE trial. The CETP inhibitors simultaneously boost HDL while reducing LDL.
Diabetes: The search continues for new drugs that not only enhance diabetes control but also improve cardiovascular outcomes, or at the very least are safe in diabetes patients with coronary disease.
Next up is the nearly 15,000-patient Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS), coordinated by the DCRI and University of Oxford. It’s due to be presented in June at the annual meeting of the American Diabetes Association in Boston. Trials of other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors have shown evidence of an increased risk of heart failure, specifically with saxagliptin in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial and alogliptin in EXAMINE, so a lot is riding on TECOS.
The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists are under study in cardiovascular event-driven randomized clinical trials collectively totaling more than 33,000 patients with type 2 diabetes. The Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering (EXSCEL), also coordinated by the DCRI and University of Oxford, includes 14,000 randomized patients. Other major trials of GLP-1 agonists are ELIXA (lixisenatide), LEADER (liraglutide), and REWIND (dulaglutide).
In addition, ongoing phase III trials of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors with cardiovascular endpoints include the Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study (CANVAS) and a 7,000-patient study of empagliflozin known as EMPA-REG OUTCOME.
Hypertension: The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) is an NIH-funded, randomized trial designed to finally answer a question bothering physicians for years: What’s the right amount of blood pressure lowering?
Nearly 9,400 high-risk patients with clinical or subclinical cardiovascular disease have been randomized to a target systolic blood pressure of less than 120 mm Hg, compared with less than 140 mm Hg. The primary composite endpoint is cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI or stroke, or hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome. Secondary endpoints focus on cognitive impairment, dementia, and rates of progression of chronic kidney disease. Results are expected in 2018.
Vitamin D: The VITAL trial, also sponsored by the NIH, has randomized 25,875 initially healthy men and women to 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 per day or placebo, and further randomized them to 1 g/day of omega-3 fatty acids or placebo. Key endpoints are total cancers, MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death. Results are coming in 2017.
Optimal antithrombotic therapy
Chronic coronary artery disease: It’s remarkable that physicians still don’t know the right dose of aspirin to use, even though the drug has been around since 1897. The answer is finally on the way. It will come from the ADAPTABLE eTrial, the first comparative effectiveness research project funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI).
Twenty thousand U.S. patients with known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and at least one extra risk factor will be randomized to daily aspirin at 81 mg or 325 mg and followed for a maximum of 30 months. The primary efficacy endpoint is all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke. The primary safety endpoint is major bleeding.
This is a groundbreaking innovative study: It’s a 20,000-patient trial budgeted at a mere $10 million – peanuts in the world of megatrials. By comparison, the NIH-funded SPRINT hypertension trial includes less than half as many patients, yet the price tag is $114 million.
The bargain-basement cost of the aspirin trial is possible because follow-up will be via electronic medical records and claims data provided every 3 months by 29 health data networks participating in PCORI’s National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet). The aspirin study is sort of a shakedown cruise for an exciting new cost-effective approach to conducting comparative effectiveness research.
“This study could be a game changer,” Dr. Peterson declared. “Whether you think the research question is important or not, the ability to utilize electronic health records in long-term patient follow-up in randomized trials will be revolutionary in terms of answering key clinical questions cost effectively.”
Peripheral vascular disease: In search of the antithrombotic regimen that optimizes limb salvage while minimizing vascular event rate, the EUCLID trial has randomized 13,500 patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease to ticagrelor at 90 mg BID or clopidogrel at 75 mg/day. Follow-up will be for 18 months, with the primary endpoint a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or ischemic stroke.
Atrial fibrillation patients who undergo coronary stent placement: The 2,100-patient PIONEER AF-PCI study, now recruiting, is evaluating different combinations of rivaroxaban in various dosing regimens coupled with clopidogrel, warfarin, and/or aspirin.
Stroke: The SOCRATES trial is recruiting 9,600 patients with acute ischemic stroke or high-risk transient ischemic attack to be randomized within 24 hours to ticagrelor at 90 mg BID or aspirin at 100 mg/day. As with PIONEER, results from SOCRATES are anticipated next year.
Health policy and implementation
The ARTEMIS study poses the question of whether providing a guideline-directed medication gratis will improve patient adherence and/or clinical outcomes.
Some 9,000 high-cardiovascular-risk patients at 300 sites are being randomized to free ticagrelor or clopidogrel – no copay – for 1 year or to usual care. Outcomes include choice of medication, adherence, and major adverse cardiovascular events.
“If this works, there’s the possibility that insurers can be persuaded to pay for medications and basically give them away as a means of ultimately resulting in better outcomes for patients and lower costs,” Dr. Peterson said.
IMPACT AF is an international quality improvement project aimed at improving the use of oral anticoagulation therapy in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation in Argentina, Brazil, China, India, and Romania. Participating centers will be randomized to receive a provider education and feedback program or not. The primary outcome is a change from baseline through year 1 in the proportion of patients with atrial fibrillation taking an oral anticoagulant.
In summing up the state of research in general cardiology, Dr. Peterson observed, “The way we do trials is changing. The size of the studies is changing. But ultimately, we will find better ways to treat patients, and perhaps we can find better ways to encourage patients to take their medications long term.”
Dr. Peterson reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, Janssen, and Sanofi, and receiving research funding from Eli Lilly and Janssen.
SAN DIEGO – Preventive cardiovascular medicine will get “a big boost” from ongoing major randomized controlled trials due to report results during the next several years, Dr. Eric D. Peterson predicted at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
He presented an overview of eagerly anticipated clinical trials approaching completion in three of the hottest areas of research in general cardiology: new cardiovascular prevention agents and strategies; innovative health policy initiatives; and optimal antithrombotic regimens across the range of chronic coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, patients with atrial fibrillation who’ve undergone percutaneous coronary intervention, and cerebrovascular disease.
Dr. Peterson is executive director of the Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI), a major player in some of these studies. To gain additional perspective regarding what’s in store, he consulted a who’s who list of eminent American cardiology clinical trialists as to what’s going to be big in 2016-2017 and shortly beyond.
One thing’s clear looking out at the research horizon: Megatrials enrolling tens of thousands of patients to answer key clinical questions are not a thing of the past.
Far from it.
Cardiovascular prevention
Exciting pivotal phase III cardiovascular prevention trials are well underway in the areas of lipid modification, diabetes, and hypertension. In addition, the possible preventive effect of vitamin D and omega-3 free fatty acid supplementation seen in hypothesis-generating epidemiologic studies is finally being put to a definitive test in a 26,000-subject randomized trial known as VITAL (the Vitamin D and omega-3 trial).
Lipids: All eyes are on ongoing pivotal phase III randomized clinical outcome trials of three monoclonal antibodies that inhibit proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9): the 22,500-patient FOURIER trial of evolocumab, which includes 9,000 patients older than 65 years; the 18,000-patient ODYSSEY Outcomes trial of alirocumab; and the SPIRE-1 and SPIRE-2 trials of bococizumab totaling 18,300 patients.
In phase II studies, these agents have generated enormous excitement, because they safely achieve unprecedented LDL lowering, with early hints of improved clinical outcomes beyond what’s achievable with today’s drugs, noted Dr. Peterson, professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
CETP inhibitors: The cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors torcetrapib and dalcetrapib flamed out in clinical trials because of safety concerns and lack of clinical benefit. But pivotal phase III trials of two other CETP inhibitors are well underway: anacetrapib, which is the focus of the 30,000-patient REVEAL trial; and evacetrapib, featured in the 11,000-patient ACCELERATE trial. The CETP inhibitors simultaneously boost HDL while reducing LDL.
Diabetes: The search continues for new drugs that not only enhance diabetes control but also improve cardiovascular outcomes, or at the very least are safe in diabetes patients with coronary disease.
Next up is the nearly 15,000-patient Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS), coordinated by the DCRI and University of Oxford. It’s due to be presented in June at the annual meeting of the American Diabetes Association in Boston. Trials of other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors have shown evidence of an increased risk of heart failure, specifically with saxagliptin in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial and alogliptin in EXAMINE, so a lot is riding on TECOS.
The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists are under study in cardiovascular event-driven randomized clinical trials collectively totaling more than 33,000 patients with type 2 diabetes. The Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering (EXSCEL), also coordinated by the DCRI and University of Oxford, includes 14,000 randomized patients. Other major trials of GLP-1 agonists are ELIXA (lixisenatide), LEADER (liraglutide), and REWIND (dulaglutide).
In addition, ongoing phase III trials of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors with cardiovascular endpoints include the Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study (CANVAS) and a 7,000-patient study of empagliflozin known as EMPA-REG OUTCOME.
Hypertension: The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) is an NIH-funded, randomized trial designed to finally answer a question bothering physicians for years: What’s the right amount of blood pressure lowering?
Nearly 9,400 high-risk patients with clinical or subclinical cardiovascular disease have been randomized to a target systolic blood pressure of less than 120 mm Hg, compared with less than 140 mm Hg. The primary composite endpoint is cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI or stroke, or hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome. Secondary endpoints focus on cognitive impairment, dementia, and rates of progression of chronic kidney disease. Results are expected in 2018.
Vitamin D: The VITAL trial, also sponsored by the NIH, has randomized 25,875 initially healthy men and women to 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 per day or placebo, and further randomized them to 1 g/day of omega-3 fatty acids or placebo. Key endpoints are total cancers, MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death. Results are coming in 2017.
Optimal antithrombotic therapy
Chronic coronary artery disease: It’s remarkable that physicians still don’t know the right dose of aspirin to use, even though the drug has been around since 1897. The answer is finally on the way. It will come from the ADAPTABLE eTrial, the first comparative effectiveness research project funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI).
Twenty thousand U.S. patients with known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and at least one extra risk factor will be randomized to daily aspirin at 81 mg or 325 mg and followed for a maximum of 30 months. The primary efficacy endpoint is all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke. The primary safety endpoint is major bleeding.
This is a groundbreaking innovative study: It’s a 20,000-patient trial budgeted at a mere $10 million – peanuts in the world of megatrials. By comparison, the NIH-funded SPRINT hypertension trial includes less than half as many patients, yet the price tag is $114 million.
The bargain-basement cost of the aspirin trial is possible because follow-up will be via electronic medical records and claims data provided every 3 months by 29 health data networks participating in PCORI’s National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet). The aspirin study is sort of a shakedown cruise for an exciting new cost-effective approach to conducting comparative effectiveness research.
“This study could be a game changer,” Dr. Peterson declared. “Whether you think the research question is important or not, the ability to utilize electronic health records in long-term patient follow-up in randomized trials will be revolutionary in terms of answering key clinical questions cost effectively.”
Peripheral vascular disease: In search of the antithrombotic regimen that optimizes limb salvage while minimizing vascular event rate, the EUCLID trial has randomized 13,500 patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease to ticagrelor at 90 mg BID or clopidogrel at 75 mg/day. Follow-up will be for 18 months, with the primary endpoint a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or ischemic stroke.
Atrial fibrillation patients who undergo coronary stent placement: The 2,100-patient PIONEER AF-PCI study, now recruiting, is evaluating different combinations of rivaroxaban in various dosing regimens coupled with clopidogrel, warfarin, and/or aspirin.
Stroke: The SOCRATES trial is recruiting 9,600 patients with acute ischemic stroke or high-risk transient ischemic attack to be randomized within 24 hours to ticagrelor at 90 mg BID or aspirin at 100 mg/day. As with PIONEER, results from SOCRATES are anticipated next year.
Health policy and implementation
The ARTEMIS study poses the question of whether providing a guideline-directed medication gratis will improve patient adherence and/or clinical outcomes.
Some 9,000 high-cardiovascular-risk patients at 300 sites are being randomized to free ticagrelor or clopidogrel – no copay – for 1 year or to usual care. Outcomes include choice of medication, adherence, and major adverse cardiovascular events.
“If this works, there’s the possibility that insurers can be persuaded to pay for medications and basically give them away as a means of ultimately resulting in better outcomes for patients and lower costs,” Dr. Peterson said.
IMPACT AF is an international quality improvement project aimed at improving the use of oral anticoagulation therapy in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation in Argentina, Brazil, China, India, and Romania. Participating centers will be randomized to receive a provider education and feedback program or not. The primary outcome is a change from baseline through year 1 in the proportion of patients with atrial fibrillation taking an oral anticoagulant.
In summing up the state of research in general cardiology, Dr. Peterson observed, “The way we do trials is changing. The size of the studies is changing. But ultimately, we will find better ways to treat patients, and perhaps we can find better ways to encourage patients to take their medications long term.”
Dr. Peterson reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, Janssen, and Sanofi, and receiving research funding from Eli Lilly and Janssen.
SAN DIEGO – Preventive cardiovascular medicine will get “a big boost” from ongoing major randomized controlled trials due to report results during the next several years, Dr. Eric D. Peterson predicted at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
He presented an overview of eagerly anticipated clinical trials approaching completion in three of the hottest areas of research in general cardiology: new cardiovascular prevention agents and strategies; innovative health policy initiatives; and optimal antithrombotic regimens across the range of chronic coronary artery disease, peripheral vascular disease, patients with atrial fibrillation who’ve undergone percutaneous coronary intervention, and cerebrovascular disease.
Dr. Peterson is executive director of the Duke Clinical Research Institute (DCRI), a major player in some of these studies. To gain additional perspective regarding what’s in store, he consulted a who’s who list of eminent American cardiology clinical trialists as to what’s going to be big in 2016-2017 and shortly beyond.
One thing’s clear looking out at the research horizon: Megatrials enrolling tens of thousands of patients to answer key clinical questions are not a thing of the past.
Far from it.
Cardiovascular prevention
Exciting pivotal phase III cardiovascular prevention trials are well underway in the areas of lipid modification, diabetes, and hypertension. In addition, the possible preventive effect of vitamin D and omega-3 free fatty acid supplementation seen in hypothesis-generating epidemiologic studies is finally being put to a definitive test in a 26,000-subject randomized trial known as VITAL (the Vitamin D and omega-3 trial).
Lipids: All eyes are on ongoing pivotal phase III randomized clinical outcome trials of three monoclonal antibodies that inhibit proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin type 9 (PCSK9): the 22,500-patient FOURIER trial of evolocumab, which includes 9,000 patients older than 65 years; the 18,000-patient ODYSSEY Outcomes trial of alirocumab; and the SPIRE-1 and SPIRE-2 trials of bococizumab totaling 18,300 patients.
In phase II studies, these agents have generated enormous excitement, because they safely achieve unprecedented LDL lowering, with early hints of improved clinical outcomes beyond what’s achievable with today’s drugs, noted Dr. Peterson, professor of medicine at Duke University in Durham, N.C.
CETP inhibitors: The cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitors torcetrapib and dalcetrapib flamed out in clinical trials because of safety concerns and lack of clinical benefit. But pivotal phase III trials of two other CETP inhibitors are well underway: anacetrapib, which is the focus of the 30,000-patient REVEAL trial; and evacetrapib, featured in the 11,000-patient ACCELERATE trial. The CETP inhibitors simultaneously boost HDL while reducing LDL.
Diabetes: The search continues for new drugs that not only enhance diabetes control but also improve cardiovascular outcomes, or at the very least are safe in diabetes patients with coronary disease.
Next up is the nearly 15,000-patient Trial Evaluating Cardiovascular Outcomes with Sitagliptin (TECOS), coordinated by the DCRI and University of Oxford. It’s due to be presented in June at the annual meeting of the American Diabetes Association in Boston. Trials of other dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors have shown evidence of an increased risk of heart failure, specifically with saxagliptin in the SAVOR-TIMI 53 trial and alogliptin in EXAMINE, so a lot is riding on TECOS.
The glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonists are under study in cardiovascular event-driven randomized clinical trials collectively totaling more than 33,000 patients with type 2 diabetes. The Exenatide Study of Cardiovascular Event Lowering (EXSCEL), also coordinated by the DCRI and University of Oxford, includes 14,000 randomized patients. Other major trials of GLP-1 agonists are ELIXA (lixisenatide), LEADER (liraglutide), and REWIND (dulaglutide).
In addition, ongoing phase III trials of sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors with cardiovascular endpoints include the Canagliflozin Cardiovascular Assessment Study (CANVAS) and a 7,000-patient study of empagliflozin known as EMPA-REG OUTCOME.
Hypertension: The Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial (SPRINT) is an NIH-funded, randomized trial designed to finally answer a question bothering physicians for years: What’s the right amount of blood pressure lowering?
Nearly 9,400 high-risk patients with clinical or subclinical cardiovascular disease have been randomized to a target systolic blood pressure of less than 120 mm Hg, compared with less than 140 mm Hg. The primary composite endpoint is cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI or stroke, or hospitalization for acute coronary syndrome. Secondary endpoints focus on cognitive impairment, dementia, and rates of progression of chronic kidney disease. Results are expected in 2018.
Vitamin D: The VITAL trial, also sponsored by the NIH, has randomized 25,875 initially healthy men and women to 2,000 IU of vitamin D3 per day or placebo, and further randomized them to 1 g/day of omega-3 fatty acids or placebo. Key endpoints are total cancers, MI, stroke, and cardiovascular death. Results are coming in 2017.
Optimal antithrombotic therapy
Chronic coronary artery disease: It’s remarkable that physicians still don’t know the right dose of aspirin to use, even though the drug has been around since 1897. The answer is finally on the way. It will come from the ADAPTABLE eTrial, the first comparative effectiveness research project funded by the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI).
Twenty thousand U.S. patients with known atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and at least one extra risk factor will be randomized to daily aspirin at 81 mg or 325 mg and followed for a maximum of 30 months. The primary efficacy endpoint is all-cause mortality, nonfatal MI, or nonfatal stroke. The primary safety endpoint is major bleeding.
This is a groundbreaking innovative study: It’s a 20,000-patient trial budgeted at a mere $10 million – peanuts in the world of megatrials. By comparison, the NIH-funded SPRINT hypertension trial includes less than half as many patients, yet the price tag is $114 million.
The bargain-basement cost of the aspirin trial is possible because follow-up will be via electronic medical records and claims data provided every 3 months by 29 health data networks participating in PCORI’s National Patient-Centered Clinical Research Network (PCORnet). The aspirin study is sort of a shakedown cruise for an exciting new cost-effective approach to conducting comparative effectiveness research.
“This study could be a game changer,” Dr. Peterson declared. “Whether you think the research question is important or not, the ability to utilize electronic health records in long-term patient follow-up in randomized trials will be revolutionary in terms of answering key clinical questions cost effectively.”
Peripheral vascular disease: In search of the antithrombotic regimen that optimizes limb salvage while minimizing vascular event rate, the EUCLID trial has randomized 13,500 patients with symptomatic peripheral artery disease to ticagrelor at 90 mg BID or clopidogrel at 75 mg/day. Follow-up will be for 18 months, with the primary endpoint a composite of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, or ischemic stroke.
Atrial fibrillation patients who undergo coronary stent placement: The 2,100-patient PIONEER AF-PCI study, now recruiting, is evaluating different combinations of rivaroxaban in various dosing regimens coupled with clopidogrel, warfarin, and/or aspirin.
Stroke: The SOCRATES trial is recruiting 9,600 patients with acute ischemic stroke or high-risk transient ischemic attack to be randomized within 24 hours to ticagrelor at 90 mg BID or aspirin at 100 mg/day. As with PIONEER, results from SOCRATES are anticipated next year.
Health policy and implementation
The ARTEMIS study poses the question of whether providing a guideline-directed medication gratis will improve patient adherence and/or clinical outcomes.
Some 9,000 high-cardiovascular-risk patients at 300 sites are being randomized to free ticagrelor or clopidogrel – no copay – for 1 year or to usual care. Outcomes include choice of medication, adherence, and major adverse cardiovascular events.
“If this works, there’s the possibility that insurers can be persuaded to pay for medications and basically give them away as a means of ultimately resulting in better outcomes for patients and lower costs,” Dr. Peterson said.
IMPACT AF is an international quality improvement project aimed at improving the use of oral anticoagulation therapy in high-risk patients with atrial fibrillation in Argentina, Brazil, China, India, and Romania. Participating centers will be randomized to receive a provider education and feedback program or not. The primary outcome is a change from baseline through year 1 in the proportion of patients with atrial fibrillation taking an oral anticoagulant.
In summing up the state of research in general cardiology, Dr. Peterson observed, “The way we do trials is changing. The size of the studies is changing. But ultimately, we will find better ways to treat patients, and perhaps we can find better ways to encourage patients to take their medications long term.”
Dr. Peterson reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca Boehringer Ingelheim, Genentech, Janssen, and Sanofi, and receiving research funding from Eli Lilly and Janssen.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC 15
Advanced age no barrier to aggressive heart attack treatment
SAN DIEGO – Patients aged 80 years and older benefit from more invasive early treatment after non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction or unstable angina, the After Eighty Trial showed.
After a median follow-up of 1.5 years, an invasive strategy that included coronary angiography significantly reduced the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction (MI), need for urgent revascularization, stroke, and death from 61% with optimal medical treatment to 41% (risk ratio, 0.48; P value < .00001).
That drop was driven primarily by significantly fewer MIs (17% vs. 30%; RR, 0.50; P = .0003) and urgent revascularizations (2% vs. 11%; RR, 0.19; P = .0001), lead author Dr. Nicolai Tegn reported at the American College of Cardiology/Cardiovascular Research Foundation Innovation in Intervention Summit.
There were no significant differences between the invasive and conservative strategy groups in rates of stroke (3% vs. 6%; RR, 0.61; P = .26) or all-cause death (25% vs. 27%; RR, 0.87; P = .53).
The composite of death and MI, however, significantly favored the invasive group (35% vs. 48%; RR, 0.54; P < .0001), he said during a latebreaking clinical trial session.
After Eighty randomly assigned 457 patients, aged 80 years or older, to either optimal medical therapy with no invasive treatments or coronary angiography at a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) center the day after inclusion, plus optimal medical therapy after about 4-5 hours if PCI was not performed or about 6-18 hours if it was. Of the 225 patients receiving angiography, 48% went on to balloon angioplasty and/or coronary stenting, and 3% had bypass surgery.
Patients 80 years or older account for roughly one-third of all patients with non-STEMI and unstable angina, but they are underrepresented in clinical trials. As a result, the role of an early invasive strategy, and even an invasive strategy at all, in those elderly patients is still a subject of debate, observed Dr. Tegn, a cardiologist from Rikshospitalet, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo.
The study demonstrated that an invasive strategy is superior to a conservative strategy in patients at least 80 years with NSTEMI or unstable angina, he concluded.
After Eighty is a welcome study because of the under-representation of the elderly in clinical trials, Dr. David Kandzari, director of interventional cardiology at the Piedmont Heart Center in Atlanta, said during a press briefing at the meeting. But it raises the challenge of identifying patients in clinical practice with the same qualifying characteristics, he added, given that the study population represents only 10% of the entire screened population,
There was also a fairly high prevalence of patients who angiographically did not have significant coronary artery disease, yet MI and stroke rates were quite considerable.
That said, “the study in other ways reminds us that the coronary anatomy does not know the age of the patient, meaning that the findings of a benefit of an early invasive strategy seem consistent with previous studies we know across the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes,” Dr. Kandzari said.
After Eighty investigators screened 4,187 elderly patients presenting at 17 community hospitals in Norway with non-STEMI or unstable angina, with or without ST-segment depression in ECG, and normal or elevated troponin T or I levels. Patients had to have no chest pain or other ischemic symptoms after medical treatment and mobilization.
In all, 3,730 patients were excluded for life expectancy less than 12 months because of a serious comorbidity; ongoing or recent bleeding; inability to comply with protocol; clinically unstable including ongoing ischemia; refusal to participate; logistic reasons; or other reasons.
The average age was 84.7 years in the invasive group (range 80-93 years) and 84.9 years in the conservative group (range 80-94 years).
Medical treatment during the index admission included 75 mg aspirin in 97% of both the invasive and conservative groups, clopidogrel (85% vs. 82%), ticagrelor (both 5%), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) (43% vs. 50%), beta blocker (83% vs. 85%), statins (90% vs. 85%), loop or thiazide diuretics (41% vs. 33%), calcium channel blocker (20% vs. 21%), nitrates (45% vs. 55%), warfarin (17% vs. 9%), low molecular-weight heparin (both 76% ), and dabigatran in one patient in each group.
Medical therapy at discharge in the invasive and conservative groups was aspirin (both 93%), clopidogrel (both 72%), ticagrelor (both 4%), ACE inhibitor/ARB (52% vs. 54%), beta blockers (both 84%), statins (90% vs. 86%), diuretics (45% vs. 38%), calcium channel blocker (24% vs. 23%), nitrates (34% vs. 48%), warfarin (21% vs. 14%), rivaroxaban (three patients in both groups), and dabigatran (one patient vs. six patients).
There were no differences in bleeding rates between the two groups, Dr. Tegn said. Four major bleeding events were reported in both groups, while 23 patients in the invasive group and 16 patients in the conservative group had minor bleeds.
The Norwegian Health Association sponsored the study. Dr. Tegn reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Kandazari reported research and grant support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronic, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, and minor consulting honoraria from Boston Scientific and Medtronic.
SAN DIEGO – Patients aged 80 years and older benefit from more invasive early treatment after non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction or unstable angina, the After Eighty Trial showed.
After a median follow-up of 1.5 years, an invasive strategy that included coronary angiography significantly reduced the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction (MI), need for urgent revascularization, stroke, and death from 61% with optimal medical treatment to 41% (risk ratio, 0.48; P value < .00001).
That drop was driven primarily by significantly fewer MIs (17% vs. 30%; RR, 0.50; P = .0003) and urgent revascularizations (2% vs. 11%; RR, 0.19; P = .0001), lead author Dr. Nicolai Tegn reported at the American College of Cardiology/Cardiovascular Research Foundation Innovation in Intervention Summit.
There were no significant differences between the invasive and conservative strategy groups in rates of stroke (3% vs. 6%; RR, 0.61; P = .26) or all-cause death (25% vs. 27%; RR, 0.87; P = .53).
The composite of death and MI, however, significantly favored the invasive group (35% vs. 48%; RR, 0.54; P < .0001), he said during a latebreaking clinical trial session.
After Eighty randomly assigned 457 patients, aged 80 years or older, to either optimal medical therapy with no invasive treatments or coronary angiography at a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) center the day after inclusion, plus optimal medical therapy after about 4-5 hours if PCI was not performed or about 6-18 hours if it was. Of the 225 patients receiving angiography, 48% went on to balloon angioplasty and/or coronary stenting, and 3% had bypass surgery.
Patients 80 years or older account for roughly one-third of all patients with non-STEMI and unstable angina, but they are underrepresented in clinical trials. As a result, the role of an early invasive strategy, and even an invasive strategy at all, in those elderly patients is still a subject of debate, observed Dr. Tegn, a cardiologist from Rikshospitalet, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo.
The study demonstrated that an invasive strategy is superior to a conservative strategy in patients at least 80 years with NSTEMI or unstable angina, he concluded.
After Eighty is a welcome study because of the under-representation of the elderly in clinical trials, Dr. David Kandzari, director of interventional cardiology at the Piedmont Heart Center in Atlanta, said during a press briefing at the meeting. But it raises the challenge of identifying patients in clinical practice with the same qualifying characteristics, he added, given that the study population represents only 10% of the entire screened population,
There was also a fairly high prevalence of patients who angiographically did not have significant coronary artery disease, yet MI and stroke rates were quite considerable.
That said, “the study in other ways reminds us that the coronary anatomy does not know the age of the patient, meaning that the findings of a benefit of an early invasive strategy seem consistent with previous studies we know across the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes,” Dr. Kandzari said.
After Eighty investigators screened 4,187 elderly patients presenting at 17 community hospitals in Norway with non-STEMI or unstable angina, with or without ST-segment depression in ECG, and normal or elevated troponin T or I levels. Patients had to have no chest pain or other ischemic symptoms after medical treatment and mobilization.
In all, 3,730 patients were excluded for life expectancy less than 12 months because of a serious comorbidity; ongoing or recent bleeding; inability to comply with protocol; clinically unstable including ongoing ischemia; refusal to participate; logistic reasons; or other reasons.
The average age was 84.7 years in the invasive group (range 80-93 years) and 84.9 years in the conservative group (range 80-94 years).
Medical treatment during the index admission included 75 mg aspirin in 97% of both the invasive and conservative groups, clopidogrel (85% vs. 82%), ticagrelor (both 5%), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) (43% vs. 50%), beta blocker (83% vs. 85%), statins (90% vs. 85%), loop or thiazide diuretics (41% vs. 33%), calcium channel blocker (20% vs. 21%), nitrates (45% vs. 55%), warfarin (17% vs. 9%), low molecular-weight heparin (both 76% ), and dabigatran in one patient in each group.
Medical therapy at discharge in the invasive and conservative groups was aspirin (both 93%), clopidogrel (both 72%), ticagrelor (both 4%), ACE inhibitor/ARB (52% vs. 54%), beta blockers (both 84%), statins (90% vs. 86%), diuretics (45% vs. 38%), calcium channel blocker (24% vs. 23%), nitrates (34% vs. 48%), warfarin (21% vs. 14%), rivaroxaban (three patients in both groups), and dabigatran (one patient vs. six patients).
There were no differences in bleeding rates between the two groups, Dr. Tegn said. Four major bleeding events were reported in both groups, while 23 patients in the invasive group and 16 patients in the conservative group had minor bleeds.
The Norwegian Health Association sponsored the study. Dr. Tegn reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Kandazari reported research and grant support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronic, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, and minor consulting honoraria from Boston Scientific and Medtronic.
SAN DIEGO – Patients aged 80 years and older benefit from more invasive early treatment after non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction or unstable angina, the After Eighty Trial showed.
After a median follow-up of 1.5 years, an invasive strategy that included coronary angiography significantly reduced the primary endpoint of myocardial infarction (MI), need for urgent revascularization, stroke, and death from 61% with optimal medical treatment to 41% (risk ratio, 0.48; P value < .00001).
That drop was driven primarily by significantly fewer MIs (17% vs. 30%; RR, 0.50; P = .0003) and urgent revascularizations (2% vs. 11%; RR, 0.19; P = .0001), lead author Dr. Nicolai Tegn reported at the American College of Cardiology/Cardiovascular Research Foundation Innovation in Intervention Summit.
There were no significant differences between the invasive and conservative strategy groups in rates of stroke (3% vs. 6%; RR, 0.61; P = .26) or all-cause death (25% vs. 27%; RR, 0.87; P = .53).
The composite of death and MI, however, significantly favored the invasive group (35% vs. 48%; RR, 0.54; P < .0001), he said during a latebreaking clinical trial session.
After Eighty randomly assigned 457 patients, aged 80 years or older, to either optimal medical therapy with no invasive treatments or coronary angiography at a percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) center the day after inclusion, plus optimal medical therapy after about 4-5 hours if PCI was not performed or about 6-18 hours if it was. Of the 225 patients receiving angiography, 48% went on to balloon angioplasty and/or coronary stenting, and 3% had bypass surgery.
Patients 80 years or older account for roughly one-third of all patients with non-STEMI and unstable angina, but they are underrepresented in clinical trials. As a result, the role of an early invasive strategy, and even an invasive strategy at all, in those elderly patients is still a subject of debate, observed Dr. Tegn, a cardiologist from Rikshospitalet, Oslo University Hospital, Oslo.
The study demonstrated that an invasive strategy is superior to a conservative strategy in patients at least 80 years with NSTEMI or unstable angina, he concluded.
After Eighty is a welcome study because of the under-representation of the elderly in clinical trials, Dr. David Kandzari, director of interventional cardiology at the Piedmont Heart Center in Atlanta, said during a press briefing at the meeting. But it raises the challenge of identifying patients in clinical practice with the same qualifying characteristics, he added, given that the study population represents only 10% of the entire screened population,
There was also a fairly high prevalence of patients who angiographically did not have significant coronary artery disease, yet MI and stroke rates were quite considerable.
That said, “the study in other ways reminds us that the coronary anatomy does not know the age of the patient, meaning that the findings of a benefit of an early invasive strategy seem consistent with previous studies we know across the management of patients with acute coronary syndromes,” Dr. Kandzari said.
After Eighty investigators screened 4,187 elderly patients presenting at 17 community hospitals in Norway with non-STEMI or unstable angina, with or without ST-segment depression in ECG, and normal or elevated troponin T or I levels. Patients had to have no chest pain or other ischemic symptoms after medical treatment and mobilization.
In all, 3,730 patients were excluded for life expectancy less than 12 months because of a serious comorbidity; ongoing or recent bleeding; inability to comply with protocol; clinically unstable including ongoing ischemia; refusal to participate; logistic reasons; or other reasons.
The average age was 84.7 years in the invasive group (range 80-93 years) and 84.9 years in the conservative group (range 80-94 years).
Medical treatment during the index admission included 75 mg aspirin in 97% of both the invasive and conservative groups, clopidogrel (85% vs. 82%), ticagrelor (both 5%), angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor/angiotensin receptor blockers (ARB) (43% vs. 50%), beta blocker (83% vs. 85%), statins (90% vs. 85%), loop or thiazide diuretics (41% vs. 33%), calcium channel blocker (20% vs. 21%), nitrates (45% vs. 55%), warfarin (17% vs. 9%), low molecular-weight heparin (both 76% ), and dabigatran in one patient in each group.
Medical therapy at discharge in the invasive and conservative groups was aspirin (both 93%), clopidogrel (both 72%), ticagrelor (both 4%), ACE inhibitor/ARB (52% vs. 54%), beta blockers (both 84%), statins (90% vs. 86%), diuretics (45% vs. 38%), calcium channel blocker (24% vs. 23%), nitrates (34% vs. 48%), warfarin (21% vs. 14%), rivaroxaban (three patients in both groups), and dabigatran (one patient vs. six patients).
There were no differences in bleeding rates between the two groups, Dr. Tegn said. Four major bleeding events were reported in both groups, while 23 patients in the invasive group and 16 patients in the conservative group had minor bleeds.
The Norwegian Health Association sponsored the study. Dr. Tegn reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Kandazari reported research and grant support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronic, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, and minor consulting honoraria from Boston Scientific and Medtronic.
AT ACC/CRF i2 SUMMIT
Key clinical point: An early invasive treatment strategy improved most outcomes in patients aged 80 years and older with acute coronary syndromes.
Major finding: Myocardial infarction, need for urgent revascularization, stroke, and death were significantly lower with invasive vs. conservative care (41% vs. 61%; risk ratio, 0.48; P < .00001).
Data source: Randomized study in 457 patients aged 80 years or older with non-STEMI or unstable angina.
Disclosures: The Norwegian Health Association sponsored the study. Dr. Tegn reported nothing to disclose. Dr. Kandzari reported research and grant support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronic, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic, and minor consulting honoraria from Boston Scientific and Medtronic.
For high-risk SVT patients, anticoagulants may be effective option
Anticoagulation may be an effective option for patients with superficial venous thrombosis and are at high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), according to an evidence-based review by Dr. Joseph Raffetto and Dr. Robert Eberhardt.
In particular, they reviewed the results of three clinical trials with a total of nearly 1400 patients: STENOX, STEFLUX, and CALISTO.
Based on their assessment, Dr. Raffetto and Dr. Eberhardt, summarized that surgery and anticoagulants were both acceptable treatments for SVT patients at high risk of VTE, who had severe symptoms, who presented with close proximity to the saphenofemoral junction, or who had recurrence. Anticoagulants seemed to have fewer complications and a lower VTE rate than did surgery. However, treating all SVT patients with anticoagulants is not recommended because of cost concerns.
While anticoagulants do appear to be an effective treatment for SVT, “it is not known if SVT is causative of or an epiphenomenon for VTE. The optimal treatment of SVT is unknown with respect to selection of patient and vein, preferred therapy, and timing and duration of therapy,” the authors cautioned.
Find the full report in the Journal of Vascular Surgery: Venous and Lymphatic Disorders (doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2014.11.005).
Anticoagulation may be an effective option for patients with superficial venous thrombosis and are at high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), according to an evidence-based review by Dr. Joseph Raffetto and Dr. Robert Eberhardt.
In particular, they reviewed the results of three clinical trials with a total of nearly 1400 patients: STENOX, STEFLUX, and CALISTO.
Based on their assessment, Dr. Raffetto and Dr. Eberhardt, summarized that surgery and anticoagulants were both acceptable treatments for SVT patients at high risk of VTE, who had severe symptoms, who presented with close proximity to the saphenofemoral junction, or who had recurrence. Anticoagulants seemed to have fewer complications and a lower VTE rate than did surgery. However, treating all SVT patients with anticoagulants is not recommended because of cost concerns.
While anticoagulants do appear to be an effective treatment for SVT, “it is not known if SVT is causative of or an epiphenomenon for VTE. The optimal treatment of SVT is unknown with respect to selection of patient and vein, preferred therapy, and timing and duration of therapy,” the authors cautioned.
Find the full report in the Journal of Vascular Surgery: Venous and Lymphatic Disorders (doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2014.11.005).
Anticoagulation may be an effective option for patients with superficial venous thrombosis and are at high risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE), according to an evidence-based review by Dr. Joseph Raffetto and Dr. Robert Eberhardt.
In particular, they reviewed the results of three clinical trials with a total of nearly 1400 patients: STENOX, STEFLUX, and CALISTO.
Based on their assessment, Dr. Raffetto and Dr. Eberhardt, summarized that surgery and anticoagulants were both acceptable treatments for SVT patients at high risk of VTE, who had severe symptoms, who presented with close proximity to the saphenofemoral junction, or who had recurrence. Anticoagulants seemed to have fewer complications and a lower VTE rate than did surgery. However, treating all SVT patients with anticoagulants is not recommended because of cost concerns.
While anticoagulants do appear to be an effective treatment for SVT, “it is not known if SVT is causative of or an epiphenomenon for VTE. The optimal treatment of SVT is unknown with respect to selection of patient and vein, preferred therapy, and timing and duration of therapy,” the authors cautioned.
Find the full report in the Journal of Vascular Surgery: Venous and Lymphatic Disorders (doi: 10.1016/j.jvsv.2014.11.005).
Cardiovascular safety evidence for alogliptin reassuring
SAN DIEGO – No adverse interaction occurred between the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor alogliptin and ACE inhibitors in patients with high cardiovascular risk and type 2 diabetes enrolled in the EXAMINE trial.
This is reassuring news that puts to rest concerns that patients on these two classes of medications might experience an increase in cardiovascular events, Dr. Christopher P. Cannon said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
These concerns arose from evidence suggesting the possibility that DPP-4 inhibition in the presence of higher-dose ACE inhibitor therapy might activate the sympathetic nervous system through an increase in substance P, with a resultant elevated risk of serious cardiovascular events.
This hypothesis was tested in a secondary analysis of the EXAMINE (Examination of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Alogliptin Versus Standard of Care) trial. In EXAMINE, 5,380 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of an acute coronary syndrome within the previous 90 days were randomized in a double-blind fashion to oral alogliptin (Nesina) or placebo on top of standard guideline-directed medical therapy for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors. They were prospectively followed for a median of 18 months and a maximum of 40 months.
The primary results of EXAMINE have been reported previously: Among patients with type 2 diabetes and a recent acute coronary syndrome, major adverse cardiovascular events weren’t increased with agoliptin, compared with placebo (N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;369:1327-35). But because of subsequent theoretical safety questions raised about dual therapy with agoliptin and an ACE inhibitor – and in light of the fact that 3,323 participants in EXAMINE were on background ACE inhibitor therapy – the investigators decided to perform this new secondary analysis, according to Dr. Cannon, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The composite primary endpoint comprised of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke occurred in 11.4% of subjects on alogliptin plus an ACE inhibitor, compared with 11.8% of those on placebo plus an ACE inhibitor, 11.2% of patients on alogliptin without an ACE inhibitor, and 11.9% of those not on alogliptin or an ACE inhibitor.
The secondary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 6.8% of patients on alogliptin and an ACE inhibitor, 7.2% of those on placebo plus an ACE inhibitor, 8.5% of subjects on alogliptin but no ACE inhibitor, and 8.0% of those on neither – again, with no significant differences.
The EXAMINE trial was funded by Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Cannon reported serving as a consultant to that company and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
SAN DIEGO – No adverse interaction occurred between the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor alogliptin and ACE inhibitors in patients with high cardiovascular risk and type 2 diabetes enrolled in the EXAMINE trial.
This is reassuring news that puts to rest concerns that patients on these two classes of medications might experience an increase in cardiovascular events, Dr. Christopher P. Cannon said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
These concerns arose from evidence suggesting the possibility that DPP-4 inhibition in the presence of higher-dose ACE inhibitor therapy might activate the sympathetic nervous system through an increase in substance P, with a resultant elevated risk of serious cardiovascular events.
This hypothesis was tested in a secondary analysis of the EXAMINE (Examination of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Alogliptin Versus Standard of Care) trial. In EXAMINE, 5,380 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of an acute coronary syndrome within the previous 90 days were randomized in a double-blind fashion to oral alogliptin (Nesina) or placebo on top of standard guideline-directed medical therapy for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors. They were prospectively followed for a median of 18 months and a maximum of 40 months.
The primary results of EXAMINE have been reported previously: Among patients with type 2 diabetes and a recent acute coronary syndrome, major adverse cardiovascular events weren’t increased with agoliptin, compared with placebo (N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;369:1327-35). But because of subsequent theoretical safety questions raised about dual therapy with agoliptin and an ACE inhibitor – and in light of the fact that 3,323 participants in EXAMINE were on background ACE inhibitor therapy – the investigators decided to perform this new secondary analysis, according to Dr. Cannon, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The composite primary endpoint comprised of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke occurred in 11.4% of subjects on alogliptin plus an ACE inhibitor, compared with 11.8% of those on placebo plus an ACE inhibitor, 11.2% of patients on alogliptin without an ACE inhibitor, and 11.9% of those not on alogliptin or an ACE inhibitor.
The secondary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 6.8% of patients on alogliptin and an ACE inhibitor, 7.2% of those on placebo plus an ACE inhibitor, 8.5% of subjects on alogliptin but no ACE inhibitor, and 8.0% of those on neither – again, with no significant differences.
The EXAMINE trial was funded by Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Cannon reported serving as a consultant to that company and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
SAN DIEGO – No adverse interaction occurred between the dipeptidyl peptidase–4 inhibitor alogliptin and ACE inhibitors in patients with high cardiovascular risk and type 2 diabetes enrolled in the EXAMINE trial.
This is reassuring news that puts to rest concerns that patients on these two classes of medications might experience an increase in cardiovascular events, Dr. Christopher P. Cannon said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
These concerns arose from evidence suggesting the possibility that DPP-4 inhibition in the presence of higher-dose ACE inhibitor therapy might activate the sympathetic nervous system through an increase in substance P, with a resultant elevated risk of serious cardiovascular events.
This hypothesis was tested in a secondary analysis of the EXAMINE (Examination of Cardiovascular Outcomes With Alogliptin Versus Standard of Care) trial. In EXAMINE, 5,380 patients with type 2 diabetes and a history of an acute coronary syndrome within the previous 90 days were randomized in a double-blind fashion to oral alogliptin (Nesina) or placebo on top of standard guideline-directed medical therapy for type 2 diabetes and cardiovascular risk factors. They were prospectively followed for a median of 18 months and a maximum of 40 months.
The primary results of EXAMINE have been reported previously: Among patients with type 2 diabetes and a recent acute coronary syndrome, major adverse cardiovascular events weren’t increased with agoliptin, compared with placebo (N. Engl. J. Med. 2013;369:1327-35). But because of subsequent theoretical safety questions raised about dual therapy with agoliptin and an ACE inhibitor – and in light of the fact that 3,323 participants in EXAMINE were on background ACE inhibitor therapy – the investigators decided to perform this new secondary analysis, according to Dr. Cannon, professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, Boston.
The composite primary endpoint comprised of cardiovascular death, nonfatal MI, and nonfatal stroke occurred in 11.4% of subjects on alogliptin plus an ACE inhibitor, compared with 11.8% of those on placebo plus an ACE inhibitor, 11.2% of patients on alogliptin without an ACE inhibitor, and 11.9% of those not on alogliptin or an ACE inhibitor.
The secondary composite endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure occurred in 6.8% of patients on alogliptin and an ACE inhibitor, 7.2% of those on placebo plus an ACE inhibitor, 8.5% of subjects on alogliptin but no ACE inhibitor, and 8.0% of those on neither – again, with no significant differences.
The EXAMINE trial was funded by Takeda Pharmaceuticals. Dr. Cannon reported serving as a consultant to that company and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
AT ACC 15
Key clinical point: Concomitant use of an ACE inhibitor and alogliptin by patients with type 2 diabetes and high cardiovascular risk isn’t associated with an increase in serious cardiovascular events.
Major finding: Patients on alogliptin and an ACE inhibitor had an 11.4% incidence of cardiovascular death or nonfatal MI or stroke during a median 18 months’ follow-up, while those on an ACE inhibitor plus placebo rather than alogliptin had a statistically similar 11.8% rate.
Data source: A secondary analysis of the 5,380-patient, randomized double-blind EXAMINE trial.
Disclosures: The EXAMINE trial was sponsored by Takeda Pharmaceuticals. The presenter serves as a consultant to Takeda and numerous other pharmaceutical companies.
PE patients with malignancy survived longer if given LMWH instead of oral VKA
Among pulmonary embolism patients with malignancy, post-treatment lengths of survival were higher for those who received long-term low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) than for those who received oral vitamin K agonist (VKA), according to a prospective study.
Of the 92 PE patients with malignancy studied, 56 received long-term LMWH and 36 received oral VKA. The long-term LMWH treatment group had a median survival time of 30 months, which was significantly longer than the 12.5-month median survival time of the VKA treatment group, according to Shuai Zhang and colleagues.
The overall mortality rate for patients with malignancy was 48.9%, and the mortality rates of patients with malignancy treated with LMWH and VKA were 44.4% and 55.4%, respectively. Although a higher percentage of the LMWH treatment group survived than the VKA treatment group, the difference between the groups’ overall survival rates was not significant. However, the median survival time was significantly longer in the LMWH group than the VKA group (30 months vs. 12.5 months; P = .041), with the rate of all-cause death in the first 6 months decreased by long-term therapy with LMWH (19.6% vs. 41.7%; P = .022). In the multivariable Cox regression, long-term LMWH was a protective factor for all-cause death in the first 6 months (hazard ratio, 0.399; P = .022).
PE patients with malignancies could more effectively protect their lives and extend their survival time by using LMWH for at least 3 months instead of oral VKA, the investigators said. “In order to evaluate the impact of extended duration of LMWH on mortality, randomized controlled trials with [a] large sample size need to be designed,” they said.
Find the full study in Thrombosis Research (doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2014.11.015).
Among pulmonary embolism patients with malignancy, post-treatment lengths of survival were higher for those who received long-term low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) than for those who received oral vitamin K agonist (VKA), according to a prospective study.
Of the 92 PE patients with malignancy studied, 56 received long-term LMWH and 36 received oral VKA. The long-term LMWH treatment group had a median survival time of 30 months, which was significantly longer than the 12.5-month median survival time of the VKA treatment group, according to Shuai Zhang and colleagues.
The overall mortality rate for patients with malignancy was 48.9%, and the mortality rates of patients with malignancy treated with LMWH and VKA were 44.4% and 55.4%, respectively. Although a higher percentage of the LMWH treatment group survived than the VKA treatment group, the difference between the groups’ overall survival rates was not significant. However, the median survival time was significantly longer in the LMWH group than the VKA group (30 months vs. 12.5 months; P = .041), with the rate of all-cause death in the first 6 months decreased by long-term therapy with LMWH (19.6% vs. 41.7%; P = .022). In the multivariable Cox regression, long-term LMWH was a protective factor for all-cause death in the first 6 months (hazard ratio, 0.399; P = .022).
PE patients with malignancies could more effectively protect their lives and extend their survival time by using LMWH for at least 3 months instead of oral VKA, the investigators said. “In order to evaluate the impact of extended duration of LMWH on mortality, randomized controlled trials with [a] large sample size need to be designed,” they said.
Find the full study in Thrombosis Research (doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2014.11.015).
Among pulmonary embolism patients with malignancy, post-treatment lengths of survival were higher for those who received long-term low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) than for those who received oral vitamin K agonist (VKA), according to a prospective study.
Of the 92 PE patients with malignancy studied, 56 received long-term LMWH and 36 received oral VKA. The long-term LMWH treatment group had a median survival time of 30 months, which was significantly longer than the 12.5-month median survival time of the VKA treatment group, according to Shuai Zhang and colleagues.
The overall mortality rate for patients with malignancy was 48.9%, and the mortality rates of patients with malignancy treated with LMWH and VKA were 44.4% and 55.4%, respectively. Although a higher percentage of the LMWH treatment group survived than the VKA treatment group, the difference between the groups’ overall survival rates was not significant. However, the median survival time was significantly longer in the LMWH group than the VKA group (30 months vs. 12.5 months; P = .041), with the rate of all-cause death in the first 6 months decreased by long-term therapy with LMWH (19.6% vs. 41.7%; P = .022). In the multivariable Cox regression, long-term LMWH was a protective factor for all-cause death in the first 6 months (hazard ratio, 0.399; P = .022).
PE patients with malignancies could more effectively protect their lives and extend their survival time by using LMWH for at least 3 months instead of oral VKA, the investigators said. “In order to evaluate the impact of extended duration of LMWH on mortality, randomized controlled trials with [a] large sample size need to be designed,” they said.
Find the full study in Thrombosis Research (doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2014.11.015).
Extended anticoagulant therapy reduced risk of VTE recurrence
Apixaban was the safest anticoagulant used for extended treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), according to a network meta-analysis of more than 11.000 patients.
While several anticoagulants significantly reduced the risk of VTE recurrence compared to placebo, only apixaban also did not increase bleeding risk significantly more than placebo. In fact, all active therapies except aspirin increased the risk of composite bleeding by 2-4 times compared to apixaban (2.5 mg), according to Diana M. Sobieraj, Pharm.D., of the University of Connecticut, and her colleagues.
In addition to apixaban (2.5 mg and 5 mg), the other anticoagulants that significantly reduced the risk of VTE recurrence compared to placebo were dabigatran, rivaroxaban, idraparinux, and vitamin K antagonists (VKAs). Of these drugs, idraparinux was least effective and VKAs were most effective at reducing the risk of a recurring VTE,
All of the anticoagulants other than idraparinux significantly reduced VTE risk more than aspirin did, ranging from a 73% reduction, with either apixaban (2.5 mg) or rivaroxaban, to an 80% reduced risk with VKAs.
Whether anticoagulation therapy should be extended for patients with VTE beyond 3 months remains a topic of debate, but results of the analysis “provide additional justification for” doing so, “primarily in patients with unprovoked proximal [VTE] with low to moderate bleeding risk,” the researchers reported.
Find the full study in Thrombosis Research (doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2015.02.032)
Apixaban was the safest anticoagulant used for extended treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), according to a network meta-analysis of more than 11.000 patients.
While several anticoagulants significantly reduced the risk of VTE recurrence compared to placebo, only apixaban also did not increase bleeding risk significantly more than placebo. In fact, all active therapies except aspirin increased the risk of composite bleeding by 2-4 times compared to apixaban (2.5 mg), according to Diana M. Sobieraj, Pharm.D., of the University of Connecticut, and her colleagues.
In addition to apixaban (2.5 mg and 5 mg), the other anticoagulants that significantly reduced the risk of VTE recurrence compared to placebo were dabigatran, rivaroxaban, idraparinux, and vitamin K antagonists (VKAs). Of these drugs, idraparinux was least effective and VKAs were most effective at reducing the risk of a recurring VTE,
All of the anticoagulants other than idraparinux significantly reduced VTE risk more than aspirin did, ranging from a 73% reduction, with either apixaban (2.5 mg) or rivaroxaban, to an 80% reduced risk with VKAs.
Whether anticoagulation therapy should be extended for patients with VTE beyond 3 months remains a topic of debate, but results of the analysis “provide additional justification for” doing so, “primarily in patients with unprovoked proximal [VTE] with low to moderate bleeding risk,” the researchers reported.
Find the full study in Thrombosis Research (doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2015.02.032)
Apixaban was the safest anticoagulant used for extended treatment of venous thromboembolism (VTE), according to a network meta-analysis of more than 11.000 patients.
While several anticoagulants significantly reduced the risk of VTE recurrence compared to placebo, only apixaban also did not increase bleeding risk significantly more than placebo. In fact, all active therapies except aspirin increased the risk of composite bleeding by 2-4 times compared to apixaban (2.5 mg), according to Diana M. Sobieraj, Pharm.D., of the University of Connecticut, and her colleagues.
In addition to apixaban (2.5 mg and 5 mg), the other anticoagulants that significantly reduced the risk of VTE recurrence compared to placebo were dabigatran, rivaroxaban, idraparinux, and vitamin K antagonists (VKAs). Of these drugs, idraparinux was least effective and VKAs were most effective at reducing the risk of a recurring VTE,
All of the anticoagulants other than idraparinux significantly reduced VTE risk more than aspirin did, ranging from a 73% reduction, with either apixaban (2.5 mg) or rivaroxaban, to an 80% reduced risk with VKAs.
Whether anticoagulation therapy should be extended for patients with VTE beyond 3 months remains a topic of debate, but results of the analysis “provide additional justification for” doing so, “primarily in patients with unprovoked proximal [VTE] with low to moderate bleeding risk,” the researchers reported.
Find the full study in Thrombosis Research (doi.org/10.1016/j.thromres.2015.02.032)
VIDEO: Data support switching to transradial PCI access
SAN DIEGO – Cardiologists should switch from transfemoral to transradial access in acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, given the reduced mortality rates associated with the transradial approach in the MATRIX study and other studies, Dr. Cindy L. Grines said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Because U.S. interventionalists are “under the clock” when treating patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction, “many physicians have been unwilling to risk having a difficult transradial case that would take too much time,” explained Dr. Grines, an interventional cardiologist at the Detroit Medical Center.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
For that and other reasons, American interventionalists have been “slow adopters” of the transradial approach, currently using it for about 20% of PCIs, compared with a worldwide rate of about 70%.
It may take instituting incentives to get U.S. cardiologists to change their practice, Dr. Grines suggested in an interview. That could involve increased reimbursement for PCIs done transradially, an increased allowance on acceptable door-to-balloon times for STEMI patients treated transradially, or imposition of new standards for quality assurance that mandate use of transradial in a certain percentage of PCI cases, she said.
The MATRIX study included a second, independent, prespecified analysis that compared outcomes in patients randomized to treatment with two different antithrombin drugs, either bivalirudin (Angiomax) or unfractionated heparin.
That part of the study showed that while treatment with either of the two drugs resulted in no statistically significant difference in the study’s two primary endpoints, treatment with bivalirudin led to statistically significant reductions in all-cause death and cardiovascular death, as well as in major bleeding events, compared with patients treated with unfractionated heparin (Lancet 2015 [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6]).
Although bivalirudin has generally been the more commonly used antithrombin drug in this clinical setting by U.S. interventionalists in recent years, results reported last year from the HEAT-PCI trial (Lancet 2014;384:1849-58) that showed better outcomes with unfractionated heparin have led to reduced use of bivalirudin, Dr. Grines said.
The new results from MATRIX coupled with results from other trials that compared those drugs can make clinicians “more confident about the benefit of bivalirudin,” she said.
Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from the Medicines Company, which markets Angiomax, and from Abbott Vascular, Merck, and the Volcano Group.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
SAN DIEGO – Cardiologists should switch from transfemoral to transradial access in acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, given the reduced mortality rates associated with the transradial approach in the MATRIX study and other studies, Dr. Cindy L. Grines said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Because U.S. interventionalists are “under the clock” when treating patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction, “many physicians have been unwilling to risk having a difficult transradial case that would take too much time,” explained Dr. Grines, an interventional cardiologist at the Detroit Medical Center.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
For that and other reasons, American interventionalists have been “slow adopters” of the transradial approach, currently using it for about 20% of PCIs, compared with a worldwide rate of about 70%.
It may take instituting incentives to get U.S. cardiologists to change their practice, Dr. Grines suggested in an interview. That could involve increased reimbursement for PCIs done transradially, an increased allowance on acceptable door-to-balloon times for STEMI patients treated transradially, or imposition of new standards for quality assurance that mandate use of transradial in a certain percentage of PCI cases, she said.
The MATRIX study included a second, independent, prespecified analysis that compared outcomes in patients randomized to treatment with two different antithrombin drugs, either bivalirudin (Angiomax) or unfractionated heparin.
That part of the study showed that while treatment with either of the two drugs resulted in no statistically significant difference in the study’s two primary endpoints, treatment with bivalirudin led to statistically significant reductions in all-cause death and cardiovascular death, as well as in major bleeding events, compared with patients treated with unfractionated heparin (Lancet 2015 [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6]).
Although bivalirudin has generally been the more commonly used antithrombin drug in this clinical setting by U.S. interventionalists in recent years, results reported last year from the HEAT-PCI trial (Lancet 2014;384:1849-58) that showed better outcomes with unfractionated heparin have led to reduced use of bivalirudin, Dr. Grines said.
The new results from MATRIX coupled with results from other trials that compared those drugs can make clinicians “more confident about the benefit of bivalirudin,” she said.
Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from the Medicines Company, which markets Angiomax, and from Abbott Vascular, Merck, and the Volcano Group.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
SAN DIEGO – Cardiologists should switch from transfemoral to transradial access in acute coronary syndrome patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention, given the reduced mortality rates associated with the transradial approach in the MATRIX study and other studies, Dr. Cindy L. Grines said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
Because U.S. interventionalists are “under the clock” when treating patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction, “many physicians have been unwilling to risk having a difficult transradial case that would take too much time,” explained Dr. Grines, an interventional cardiologist at the Detroit Medical Center.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
For that and other reasons, American interventionalists have been “slow adopters” of the transradial approach, currently using it for about 20% of PCIs, compared with a worldwide rate of about 70%.
It may take instituting incentives to get U.S. cardiologists to change their practice, Dr. Grines suggested in an interview. That could involve increased reimbursement for PCIs done transradially, an increased allowance on acceptable door-to-balloon times for STEMI patients treated transradially, or imposition of new standards for quality assurance that mandate use of transradial in a certain percentage of PCI cases, she said.
The MATRIX study included a second, independent, prespecified analysis that compared outcomes in patients randomized to treatment with two different antithrombin drugs, either bivalirudin (Angiomax) or unfractionated heparin.
That part of the study showed that while treatment with either of the two drugs resulted in no statistically significant difference in the study’s two primary endpoints, treatment with bivalirudin led to statistically significant reductions in all-cause death and cardiovascular death, as well as in major bleeding events, compared with patients treated with unfractionated heparin (Lancet 2015 [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6]).
Although bivalirudin has generally been the more commonly used antithrombin drug in this clinical setting by U.S. interventionalists in recent years, results reported last year from the HEAT-PCI trial (Lancet 2014;384:1849-58) that showed better outcomes with unfractionated heparin have led to reduced use of bivalirudin, Dr. Grines said.
The new results from MATRIX coupled with results from other trials that compared those drugs can make clinicians “more confident about the benefit of bivalirudin,” she said.
Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from the Medicines Company, which markets Angiomax, and from Abbott Vascular, Merck, and the Volcano Group.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ACC 15
Ablation cuts AF recurrence 2.5-fold vs. amiodarone in heart failure
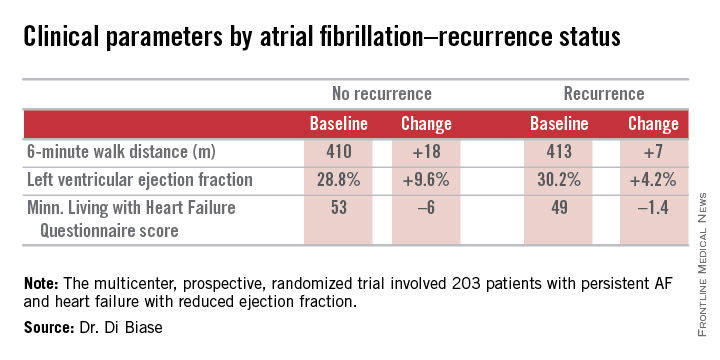
SAN DIEGO – Catheter ablation proved superior to amiodarone for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with systolic heart failure in the randomized AATAC-AF trial.
The rate of the primary study endpoint – freedom from recurrent AF through 26 months of prospective follow-up– was 70% in the catheter ablation group, twice the 34% rate with amiodarone, Dr. Luigi Di Biase reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. After covariate adjustment, the investigators found that recurrence was 2.5 times more likely in the patients treated with amiodarone.
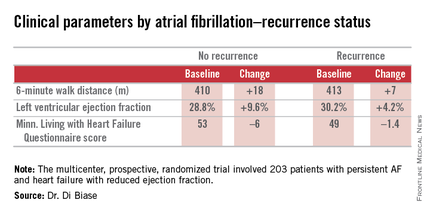
But he added a major caveat: pulmonary vein antrum isolation (PVI) alone was no better than the antiarrhythmic drug. The high overall treatment success rate seen with catheter ablation in the trial was achieved by operators who performed PVI plus some additional form of ablation of their own choosing, such as elimination of non–pulmonary vein triggers, ablation of complex fractionated electrograms, and/or additional linear ablation lesions, according to Dr. Di Biase, head of electrophysiology at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
AATAC-AF (Ablation versus Amiodarone for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure and an Implanted ICD/CRTD) was a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial involving 203 patients with persistent AF and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Patients randomized to ablation had to receive PVI at a minimum; operators could perform additional ablation according to their preference. Twenty percent of patients randomized to ablation received PVI alone; 80% underwent additional posterior wall and non–pulmonary vein trigger ablation. The 26-month rate of freedom from recurrence of AF was 36% in patients who received PVI alone and 79% in those who underwent more extensive ablations. A particular strength of the AATAC study was that all participants had an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and/or cardiac resynchronization therapy device, permitting detection of AF with a much higher degree of accuracy than possible in most AF ablation trials.
Any recurrent AF episodes during the first 3 months of follow-up were excluded from the analysis, regardless of whether patients were in the ablation or amiodarone arms, in accord with the 3-month blanking period that’s standard among electrophysiologists. Patients averaged 1.4 ablation sessions during the first 3 months of the trial.
Regardless of treatment, patients in whom AF did not recur showed significantly greater improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction, exercise capacity, and heart failure–related quality of life.
In addition, all-cause mortality during follow-up was significantly lower in the ablation group: 8%, compared with 18% in patients assigned to amiodarone. Moreover, the rate of hospitalization for arrhythmia or worsening heart failure was 31% in the ablation group versus 57% in patients on amiodarone. The economic implications of this sharp reduction in hospitalizations will be the subject of further study, according to Dr. Di Biase.
Also noteworthy was the finding that seven patients had to discontinue amiodarone due to serious side effects: four because of thyroid toxicity, two for pulmonary toxicity, and one owing to hepatic dysfunction, he continued.
Discussant Dr. Richard I. Fogel, current president of the Heart Rhythm Society, commented that “the 70% arrhythmia-free follow-up was a little surprising to me.”
“That seems a little bit high, particularly in a group with persistent atrial fibrillation,” observed Dr. Fogel, who is chief executive officer at St. Vincent Medical Group, Indianapolis.
Dr. Di Biase attributed the high success rate to two factors: One, only highly experienced operators participated in AATAC, and two, most of them weren’t content to stick to PVI alone.
“If you try to do a more extensive procedure addressing non–pulmonary vein triggers in other areas in the left atrium, the success rate is increased by far,” the electrophysiologist said.
As for a possible mechanism for the mortality benefit seen with ablation, “several studies have shown that in a population with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, atrial fibrillation is an independent predictor of mortality,” Dr. Di Biase said. “So I believe that staying in sinus rhythm may have affected the long-term mortality. If you have a treatment that reduces the amount of time in atrial fibrillation, you may reduce mortality.”
While catheter ablation is an increasingly popular treatment strategy in patients with drug-refractory paroxysmal AF, it has been understudied in the setting of AF and comorbid heart failure. These two conditions are commonly coexistent, and they feed on each other in a destructive way: AF worsens heart failure, and heart failure tends to make AF worse.
AATAC was funded by the participating investigators and institutions without external financial support. Dr. Di Biase reported serving as a consultant to Biosense Webster and St. Jude Medical and serving as a paid speaker for Atricure, Biotronik, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Epi EP.
SAN DIEGO – Catheter ablation proved superior to amiodarone for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with systolic heart failure in the randomized AATAC-AF trial.
The rate of the primary study endpoint – freedom from recurrent AF through 26 months of prospective follow-up– was 70% in the catheter ablation group, twice the 34% rate with amiodarone, Dr. Luigi Di Biase reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. After covariate adjustment, the investigators found that recurrence was 2.5 times more likely in the patients treated with amiodarone.

But he added a major caveat: pulmonary vein antrum isolation (PVI) alone was no better than the antiarrhythmic drug. The high overall treatment success rate seen with catheter ablation in the trial was achieved by operators who performed PVI plus some additional form of ablation of their own choosing, such as elimination of non–pulmonary vein triggers, ablation of complex fractionated electrograms, and/or additional linear ablation lesions, according to Dr. Di Biase, head of electrophysiology at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
AATAC-AF (Ablation versus Amiodarone for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure and an Implanted ICD/CRTD) was a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial involving 203 patients with persistent AF and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Patients randomized to ablation had to receive PVI at a minimum; operators could perform additional ablation according to their preference. Twenty percent of patients randomized to ablation received PVI alone; 80% underwent additional posterior wall and non–pulmonary vein trigger ablation. The 26-month rate of freedom from recurrence of AF was 36% in patients who received PVI alone and 79% in those who underwent more extensive ablations. A particular strength of the AATAC study was that all participants had an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and/or cardiac resynchronization therapy device, permitting detection of AF with a much higher degree of accuracy than possible in most AF ablation trials.
Any recurrent AF episodes during the first 3 months of follow-up were excluded from the analysis, regardless of whether patients were in the ablation or amiodarone arms, in accord with the 3-month blanking period that’s standard among electrophysiologists. Patients averaged 1.4 ablation sessions during the first 3 months of the trial.
Regardless of treatment, patients in whom AF did not recur showed significantly greater improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction, exercise capacity, and heart failure–related quality of life.
In addition, all-cause mortality during follow-up was significantly lower in the ablation group: 8%, compared with 18% in patients assigned to amiodarone. Moreover, the rate of hospitalization for arrhythmia or worsening heart failure was 31% in the ablation group versus 57% in patients on amiodarone. The economic implications of this sharp reduction in hospitalizations will be the subject of further study, according to Dr. Di Biase.
Also noteworthy was the finding that seven patients had to discontinue amiodarone due to serious side effects: four because of thyroid toxicity, two for pulmonary toxicity, and one owing to hepatic dysfunction, he continued.
Discussant Dr. Richard I. Fogel, current president of the Heart Rhythm Society, commented that “the 70% arrhythmia-free follow-up was a little surprising to me.”
“That seems a little bit high, particularly in a group with persistent atrial fibrillation,” observed Dr. Fogel, who is chief executive officer at St. Vincent Medical Group, Indianapolis.
Dr. Di Biase attributed the high success rate to two factors: One, only highly experienced operators participated in AATAC, and two, most of them weren’t content to stick to PVI alone.
“If you try to do a more extensive procedure addressing non–pulmonary vein triggers in other areas in the left atrium, the success rate is increased by far,” the electrophysiologist said.
As for a possible mechanism for the mortality benefit seen with ablation, “several studies have shown that in a population with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, atrial fibrillation is an independent predictor of mortality,” Dr. Di Biase said. “So I believe that staying in sinus rhythm may have affected the long-term mortality. If you have a treatment that reduces the amount of time in atrial fibrillation, you may reduce mortality.”
While catheter ablation is an increasingly popular treatment strategy in patients with drug-refractory paroxysmal AF, it has been understudied in the setting of AF and comorbid heart failure. These two conditions are commonly coexistent, and they feed on each other in a destructive way: AF worsens heart failure, and heart failure tends to make AF worse.
AATAC was funded by the participating investigators and institutions without external financial support. Dr. Di Biase reported serving as a consultant to Biosense Webster and St. Jude Medical and serving as a paid speaker for Atricure, Biotronik, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Epi EP.
SAN DIEGO – Catheter ablation proved superior to amiodarone for treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with systolic heart failure in the randomized AATAC-AF trial.
The rate of the primary study endpoint – freedom from recurrent AF through 26 months of prospective follow-up– was 70% in the catheter ablation group, twice the 34% rate with amiodarone, Dr. Luigi Di Biase reported at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. After covariate adjustment, the investigators found that recurrence was 2.5 times more likely in the patients treated with amiodarone.

But he added a major caveat: pulmonary vein antrum isolation (PVI) alone was no better than the antiarrhythmic drug. The high overall treatment success rate seen with catheter ablation in the trial was achieved by operators who performed PVI plus some additional form of ablation of their own choosing, such as elimination of non–pulmonary vein triggers, ablation of complex fractionated electrograms, and/or additional linear ablation lesions, according to Dr. Di Biase, head of electrophysiology at the Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York.
AATAC-AF (Ablation versus Amiodarone for Treatment of Atrial Fibrillation in Patients with Congestive Heart Failure and an Implanted ICD/CRTD) was a multicenter, prospective, randomized trial involving 203 patients with persistent AF and heart failure with reduced ejection fraction. Patients randomized to ablation had to receive PVI at a minimum; operators could perform additional ablation according to their preference. Twenty percent of patients randomized to ablation received PVI alone; 80% underwent additional posterior wall and non–pulmonary vein trigger ablation. The 26-month rate of freedom from recurrence of AF was 36% in patients who received PVI alone and 79% in those who underwent more extensive ablations. A particular strength of the AATAC study was that all participants had an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator and/or cardiac resynchronization therapy device, permitting detection of AF with a much higher degree of accuracy than possible in most AF ablation trials.
Any recurrent AF episodes during the first 3 months of follow-up were excluded from the analysis, regardless of whether patients were in the ablation or amiodarone arms, in accord with the 3-month blanking period that’s standard among electrophysiologists. Patients averaged 1.4 ablation sessions during the first 3 months of the trial.
Regardless of treatment, patients in whom AF did not recur showed significantly greater improvement in left ventricular ejection fraction, exercise capacity, and heart failure–related quality of life.
In addition, all-cause mortality during follow-up was significantly lower in the ablation group: 8%, compared with 18% in patients assigned to amiodarone. Moreover, the rate of hospitalization for arrhythmia or worsening heart failure was 31% in the ablation group versus 57% in patients on amiodarone. The economic implications of this sharp reduction in hospitalizations will be the subject of further study, according to Dr. Di Biase.
Also noteworthy was the finding that seven patients had to discontinue amiodarone due to serious side effects: four because of thyroid toxicity, two for pulmonary toxicity, and one owing to hepatic dysfunction, he continued.
Discussant Dr. Richard I. Fogel, current president of the Heart Rhythm Society, commented that “the 70% arrhythmia-free follow-up was a little surprising to me.”
“That seems a little bit high, particularly in a group with persistent atrial fibrillation,” observed Dr. Fogel, who is chief executive officer at St. Vincent Medical Group, Indianapolis.
Dr. Di Biase attributed the high success rate to two factors: One, only highly experienced operators participated in AATAC, and two, most of them weren’t content to stick to PVI alone.
“If you try to do a more extensive procedure addressing non–pulmonary vein triggers in other areas in the left atrium, the success rate is increased by far,” the electrophysiologist said.
As for a possible mechanism for the mortality benefit seen with ablation, “several studies have shown that in a population with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, atrial fibrillation is an independent predictor of mortality,” Dr. Di Biase said. “So I believe that staying in sinus rhythm may have affected the long-term mortality. If you have a treatment that reduces the amount of time in atrial fibrillation, you may reduce mortality.”
While catheter ablation is an increasingly popular treatment strategy in patients with drug-refractory paroxysmal AF, it has been understudied in the setting of AF and comorbid heart failure. These two conditions are commonly coexistent, and they feed on each other in a destructive way: AF worsens heart failure, and heart failure tends to make AF worse.
AATAC was funded by the participating investigators and institutions without external financial support. Dr. Di Biase reported serving as a consultant to Biosense Webster and St. Jude Medical and serving as a paid speaker for Atricure, Biotronik, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Epi EP.
AT ACC 15
Key clinical point: Catheter ablation is hands down more effective than amiodarone for the treatment of persistent atrial fibrillation in patients with systolic heart failure.
Major finding: The rate of freedom from recurrent atrial fibrillation during 26 months of follow-up was 70% in patients randomized to catheter ablation, compared with 34% in those assigned to amiodarone.
Data source: The AATAC-AF study was a multicenter, randomized, prospective clinical trial inc 203 patients.
Disclosures: The trial was funded by the participating investigators and institutions without commercial support. Dr. Di Biase reported serving as a consultant to Biosense Webster and St. Jude Medical and serving as a paid speaker for Atricure, Biotronik, Medtronic, Boston Scientific, and Epi EP.
Outcomes worse for lung cancer patients with VTE
Hospitalized lung cancer patients who had venous thromboembolisms had significantly worse outcomes than did other patients, according to a study published in Lung Cancer.
Of the more than 570,000 included lung cancer patient hospitalizations, just over 3.6% also presented with venous thromboembolisms (VTE). Patients with VTE had a longer length of stay (7.15 days vs. 6.05 days), higher inpatient mortality (10.03% vs. 8.69%), greater hospital costs ($43,800 vs. $37,800), and were more likely to have moderate to severe disability after being discharged (55% vs. 49%) than patients who did not have VTE. Blacks were also at a higher risk, comprising 13.07% of the VTE group but only 10.66% of the non-VTE group, reported Dr. Conor Steuer and his associates at Emory University, Atlanta.
The study results “highlight the need for prospective studies to clarify the impact of VTE complications in lung cancer patients and identify effective interventions to improve the poorer outcome observed in this population,” Dr. Steuer and his associates concluded.
Find the full study in Lung Cancer (doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.01.022).
Hospitalized lung cancer patients who had venous thromboembolisms had significantly worse outcomes than did other patients, according to a study published in Lung Cancer.
Of the more than 570,000 included lung cancer patient hospitalizations, just over 3.6% also presented with venous thromboembolisms (VTE). Patients with VTE had a longer length of stay (7.15 days vs. 6.05 days), higher inpatient mortality (10.03% vs. 8.69%), greater hospital costs ($43,800 vs. $37,800), and were more likely to have moderate to severe disability after being discharged (55% vs. 49%) than patients who did not have VTE. Blacks were also at a higher risk, comprising 13.07% of the VTE group but only 10.66% of the non-VTE group, reported Dr. Conor Steuer and his associates at Emory University, Atlanta.
The study results “highlight the need for prospective studies to clarify the impact of VTE complications in lung cancer patients and identify effective interventions to improve the poorer outcome observed in this population,” Dr. Steuer and his associates concluded.
Find the full study in Lung Cancer (doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.01.022).
Hospitalized lung cancer patients who had venous thromboembolisms had significantly worse outcomes than did other patients, according to a study published in Lung Cancer.
Of the more than 570,000 included lung cancer patient hospitalizations, just over 3.6% also presented with venous thromboembolisms (VTE). Patients with VTE had a longer length of stay (7.15 days vs. 6.05 days), higher inpatient mortality (10.03% vs. 8.69%), greater hospital costs ($43,800 vs. $37,800), and were more likely to have moderate to severe disability after being discharged (55% vs. 49%) than patients who did not have VTE. Blacks were also at a higher risk, comprising 13.07% of the VTE group but only 10.66% of the non-VTE group, reported Dr. Conor Steuer and his associates at Emory University, Atlanta.
The study results “highlight the need for prospective studies to clarify the impact of VTE complications in lung cancer patients and identify effective interventions to improve the poorer outcome observed in this population,” Dr. Steuer and his associates concluded.
Find the full study in Lung Cancer (doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.01.022).
Transradial PCI outperforms transfemoral for acute coronary syndromes
SAN DIEGO – The unshakable grip that transfemoral access has held on coronary artery catheterization for the U.S. practice of interventional cardiology may finally loosen with results from an 8,000-patient, multinational controlled trial.
MATRIX showed that transradial access for coronary catheterization of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) produced significantly fewer access-site bleeding events and significantly improved patient survival, compared with transfemoral access.
“Our results, in conjunction with the updated meta-analysis, suggest that the radial approach should become the default access for patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing invasive management,” Dr. Marco Valgimigli said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. “Access site does matter, and a reduction in access-site bleeding complications seems to translate into a mortality benefit,” said Dr. Valgimigli, an interventional cardiologist at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The MATRIX (Minimizing Adverse Haemorrhagic Events by Transradial Access Site and Systemic Implementation of Angiox) trial enrolled 8,404 ACS patients at 78 sites in four European countries: Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the Netherlands. The study randomized patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to catheterization via either the patient’s radial or femoral artery. After 30 days, the combined rate of death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and major bleeding was reduced by an absolute rate of 1.9% among the patients treated with transradial access, a 17% relative risk reduction that was statistically significant for one of the study’s two primary endpoints.
This outcome difference seemed driven primarily by significant reductions in major bleeds and specifically major access-site bleeds, and this led to a statistically significant reduction in all-cause death by 0.6%, a 28% relative risk reduction in 30-day mortality tied to transradial access, Dr. Valgimigli said.
“I think this will be the study that helps change guidelines, to make radial artery access the default approach,” commented Dr. Sanjit S. Jolly, an interventional cardiologist at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont.
“The United States is very behind in the use of transradial access; it’s used in about 20% of coronary PCIs,” noted Dr. Cindy L. Grines, an interventional cardiologist at the Detroit Medical Center. “We need to make a concerted effort in the United States to retrain practitioners to do transradial procedures. This approach is initially more time consuming, involves more radiation exposure, and can be frustrating, so we probably need to incentivize physicians by increasing their reimbursement for transradial PCIs and by making it part of quality assurance programs. Unless we do something like that, transradial use may not change,” Dr. Grines said in an interview.
The significant superiority of transradial over transfemoral access for both patient survival and for one of the study’s primary endpoints contrasted with the neutral result seen in an earlier major study that compared the two access approaches, RIVAL (Radial Versus Femoral Access for Coronary Angiography and Intervention in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes; Lancet 2011;377:1409-20).
Dr. Valgimigli also reported results from a meta-analysis that combined the MATRIX and RIVAL results as well as data from a few additional much smaller trials. This combined analysis, which involved a total of more than 19,000 ACS patients randomized to PCI via one of the two access sites, further confirmed that transradial catheterization linked with statistically significant reductions in death, in major bleeds not associated with coronary artery surgery, and in the combined endpoint of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke, he said. Concurrent with his report at the meeting, the MATRIX results as well as the updated meta-analysis results, appeared in an article published online (Lancet 2015 [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6]).
The MATRIX study used only highly experienced interventionalists who had extensive familiarity with performing PCI using both types of access. They successfully used transradial access in 94% of patients randomized to that approach, but in the other 6% technical difficulties resulted in a crossover to the transfemoral route. Among patients randomized to transfemoral access, 2% required crossover to a transradial procedure.
MATRIX was an investigator-initiated study that received grant support from Terumo and the Medicines Co. Dr. Valgimigli had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Jolly has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, has been a speaker on behalf of St. Jude, and has received research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott Vascular, the Medicines Co., Merck, and the Volcano Group.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
U.S. interventionalists have lagged in adopting transradial access for percutaneous coronary interventions. I reviewed the status within the past year and found that about 17% of all U.S. percutaneous coronary interventions were done by transradial access, and this level jibes with recent results from a survey of U.S. interventionalists.

|
Dr. David E. Kandzari |
American use of transradial access grew markedly over the last decade. Ten years ago, the rate stood at about 3%. But it remains well behind most other countries. Results reported at the ACC meeting from another large international study of coronary interventions in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients showed a 68% worldwide rate of transradial access (N. Engl. J. Med. 2015 [doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415098])
I believe that the MATRIX results will help further fuel change in U.S. practice. Soon, quality assurance programs at many U.S. hospitals may incorporate transradial access as a performance measure.
The accumulated evidence, now including the MATRIX results, supports transradial access as the default approach for vascular access during coronary procedures. However, in some patients transradial access is impossible, especially in some women, in the elderly, and in patients with a high body mass index.
Dr. David E. Kandzari, director of interventional cardiology at the Piedmont Heart Institute in Atlanta, made these comments in an interview. He has been a consultant to Medtronic and Boston Scientific and has received research support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
U.S. interventionalists have lagged in adopting transradial access for percutaneous coronary interventions. I reviewed the status within the past year and found that about 17% of all U.S. percutaneous coronary interventions were done by transradial access, and this level jibes with recent results from a survey of U.S. interventionalists.

|
Dr. David E. Kandzari |
American use of transradial access grew markedly over the last decade. Ten years ago, the rate stood at about 3%. But it remains well behind most other countries. Results reported at the ACC meeting from another large international study of coronary interventions in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients showed a 68% worldwide rate of transradial access (N. Engl. J. Med. 2015 [doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415098])
I believe that the MATRIX results will help further fuel change in U.S. practice. Soon, quality assurance programs at many U.S. hospitals may incorporate transradial access as a performance measure.
The accumulated evidence, now including the MATRIX results, supports transradial access as the default approach for vascular access during coronary procedures. However, in some patients transradial access is impossible, especially in some women, in the elderly, and in patients with a high body mass index.
Dr. David E. Kandzari, director of interventional cardiology at the Piedmont Heart Institute in Atlanta, made these comments in an interview. He has been a consultant to Medtronic and Boston Scientific and has received research support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
U.S. interventionalists have lagged in adopting transradial access for percutaneous coronary interventions. I reviewed the status within the past year and found that about 17% of all U.S. percutaneous coronary interventions were done by transradial access, and this level jibes with recent results from a survey of U.S. interventionalists.

|
Dr. David E. Kandzari |
American use of transradial access grew markedly over the last decade. Ten years ago, the rate stood at about 3%. But it remains well behind most other countries. Results reported at the ACC meeting from another large international study of coronary interventions in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients showed a 68% worldwide rate of transradial access (N. Engl. J. Med. 2015 [doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1415098])
I believe that the MATRIX results will help further fuel change in U.S. practice. Soon, quality assurance programs at many U.S. hospitals may incorporate transradial access as a performance measure.
The accumulated evidence, now including the MATRIX results, supports transradial access as the default approach for vascular access during coronary procedures. However, in some patients transradial access is impossible, especially in some women, in the elderly, and in patients with a high body mass index.
Dr. David E. Kandzari, director of interventional cardiology at the Piedmont Heart Institute in Atlanta, made these comments in an interview. He has been a consultant to Medtronic and Boston Scientific and has received research support from Abbott Vascular, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, and Medtronic.
SAN DIEGO – The unshakable grip that transfemoral access has held on coronary artery catheterization for the U.S. practice of interventional cardiology may finally loosen with results from an 8,000-patient, multinational controlled trial.
MATRIX showed that transradial access for coronary catheterization of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) produced significantly fewer access-site bleeding events and significantly improved patient survival, compared with transfemoral access.
“Our results, in conjunction with the updated meta-analysis, suggest that the radial approach should become the default access for patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing invasive management,” Dr. Marco Valgimigli said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. “Access site does matter, and a reduction in access-site bleeding complications seems to translate into a mortality benefit,” said Dr. Valgimigli, an interventional cardiologist at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The MATRIX (Minimizing Adverse Haemorrhagic Events by Transradial Access Site and Systemic Implementation of Angiox) trial enrolled 8,404 ACS patients at 78 sites in four European countries: Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the Netherlands. The study randomized patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to catheterization via either the patient’s radial or femoral artery. After 30 days, the combined rate of death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and major bleeding was reduced by an absolute rate of 1.9% among the patients treated with transradial access, a 17% relative risk reduction that was statistically significant for one of the study’s two primary endpoints.
This outcome difference seemed driven primarily by significant reductions in major bleeds and specifically major access-site bleeds, and this led to a statistically significant reduction in all-cause death by 0.6%, a 28% relative risk reduction in 30-day mortality tied to transradial access, Dr. Valgimigli said.
“I think this will be the study that helps change guidelines, to make radial artery access the default approach,” commented Dr. Sanjit S. Jolly, an interventional cardiologist at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont.
“The United States is very behind in the use of transradial access; it’s used in about 20% of coronary PCIs,” noted Dr. Cindy L. Grines, an interventional cardiologist at the Detroit Medical Center. “We need to make a concerted effort in the United States to retrain practitioners to do transradial procedures. This approach is initially more time consuming, involves more radiation exposure, and can be frustrating, so we probably need to incentivize physicians by increasing their reimbursement for transradial PCIs and by making it part of quality assurance programs. Unless we do something like that, transradial use may not change,” Dr. Grines said in an interview.
The significant superiority of transradial over transfemoral access for both patient survival and for one of the study’s primary endpoints contrasted with the neutral result seen in an earlier major study that compared the two access approaches, RIVAL (Radial Versus Femoral Access for Coronary Angiography and Intervention in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes; Lancet 2011;377:1409-20).
Dr. Valgimigli also reported results from a meta-analysis that combined the MATRIX and RIVAL results as well as data from a few additional much smaller trials. This combined analysis, which involved a total of more than 19,000 ACS patients randomized to PCI via one of the two access sites, further confirmed that transradial catheterization linked with statistically significant reductions in death, in major bleeds not associated with coronary artery surgery, and in the combined endpoint of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke, he said. Concurrent with his report at the meeting, the MATRIX results as well as the updated meta-analysis results, appeared in an article published online (Lancet 2015 [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6]).
The MATRIX study used only highly experienced interventionalists who had extensive familiarity with performing PCI using both types of access. They successfully used transradial access in 94% of patients randomized to that approach, but in the other 6% technical difficulties resulted in a crossover to the transfemoral route. Among patients randomized to transfemoral access, 2% required crossover to a transradial procedure.
MATRIX was an investigator-initiated study that received grant support from Terumo and the Medicines Co. Dr. Valgimigli had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Jolly has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, has been a speaker on behalf of St. Jude, and has received research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott Vascular, the Medicines Co., Merck, and the Volcano Group.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
SAN DIEGO – The unshakable grip that transfemoral access has held on coronary artery catheterization for the U.S. practice of interventional cardiology may finally loosen with results from an 8,000-patient, multinational controlled trial.
MATRIX showed that transradial access for coronary catheterization of patients with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) produced significantly fewer access-site bleeding events and significantly improved patient survival, compared with transfemoral access.
“Our results, in conjunction with the updated meta-analysis, suggest that the radial approach should become the default access for patients with acute coronary syndrome undergoing invasive management,” Dr. Marco Valgimigli said at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology. “Access site does matter, and a reduction in access-site bleeding complications seems to translate into a mortality benefit,” said Dr. Valgimigli, an interventional cardiologist at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
The MATRIX (Minimizing Adverse Haemorrhagic Events by Transradial Access Site and Systemic Implementation of Angiox) trial enrolled 8,404 ACS patients at 78 sites in four European countries: Italy, Spain, Sweden, and the Netherlands. The study randomized patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to catheterization via either the patient’s radial or femoral artery. After 30 days, the combined rate of death, myocardial infarction, stroke, and major bleeding was reduced by an absolute rate of 1.9% among the patients treated with transradial access, a 17% relative risk reduction that was statistically significant for one of the study’s two primary endpoints.
This outcome difference seemed driven primarily by significant reductions in major bleeds and specifically major access-site bleeds, and this led to a statistically significant reduction in all-cause death by 0.6%, a 28% relative risk reduction in 30-day mortality tied to transradial access, Dr. Valgimigli said.
“I think this will be the study that helps change guidelines, to make radial artery access the default approach,” commented Dr. Sanjit S. Jolly, an interventional cardiologist at McMaster University in Hamilton, Ont.
“The United States is very behind in the use of transradial access; it’s used in about 20% of coronary PCIs,” noted Dr. Cindy L. Grines, an interventional cardiologist at the Detroit Medical Center. “We need to make a concerted effort in the United States to retrain practitioners to do transradial procedures. This approach is initially more time consuming, involves more radiation exposure, and can be frustrating, so we probably need to incentivize physicians by increasing their reimbursement for transradial PCIs and by making it part of quality assurance programs. Unless we do something like that, transradial use may not change,” Dr. Grines said in an interview.
The significant superiority of transradial over transfemoral access for both patient survival and for one of the study’s primary endpoints contrasted with the neutral result seen in an earlier major study that compared the two access approaches, RIVAL (Radial Versus Femoral Access for Coronary Angiography and Intervention in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndromes; Lancet 2011;377:1409-20).
Dr. Valgimigli also reported results from a meta-analysis that combined the MATRIX and RIVAL results as well as data from a few additional much smaller trials. This combined analysis, which involved a total of more than 19,000 ACS patients randomized to PCI via one of the two access sites, further confirmed that transradial catheterization linked with statistically significant reductions in death, in major bleeds not associated with coronary artery surgery, and in the combined endpoint of death, myocardial infarction, and stroke, he said. Concurrent with his report at the meeting, the MATRIX results as well as the updated meta-analysis results, appeared in an article published online (Lancet 2015 [doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60292-6]).
The MATRIX study used only highly experienced interventionalists who had extensive familiarity with performing PCI using both types of access. They successfully used transradial access in 94% of patients randomized to that approach, but in the other 6% technical difficulties resulted in a crossover to the transfemoral route. Among patients randomized to transfemoral access, 2% required crossover to a transradial procedure.
MATRIX was an investigator-initiated study that received grant support from Terumo and the Medicines Co. Dr. Valgimigli had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Jolly has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, has been a speaker on behalf of St. Jude, and has received research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott Vascular, the Medicines Co., Merck, and the Volcano Group.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
AT ACC 15
Key clinical point: ACS patients randomized to transradial access for PCI had significantly better survival at 30 days, compared with those treated via the transfemoral route.
Major finding: Thirty-day all-cause death occurred in 0.6% fewer patients using transradial access, a 28% relative risk reduction.
Data source: MATRIX, a multicenter, randomized controlled trial with 8,404 patients.
Disclosures: MATRIX was an investigator-initiated study that received grant support from Terumo and the Medicines Co. Dr. Valgimigli had no relevant financial disclosures. Dr. Jolly has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, has been a speaker on behalf of St. Jude, and has received research grants from Medtronic. Dr. Grines has been a consultant to and received honoraria from Abbott Vascular, the Medicines Co., Merck, and the Volcano Group.