User login
Linking Metabolic Health, Psychiatric Disease, and Oxytocin Levels
African American men with diabetes may be at risk for significantly low levels of oxytocin (OT), according to a study of 92 veterans by researchers from the Jesse Brown Veterans Administration Medical Center in Chicago, Illinois. Research has recently been revealing oxytocin’s role in energy homeostasis; OT derangements have also been implicated in a variety of diseases, including schizophrenia, autism, dysthymia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
The researchers note that their study participants represent a “unique population” of African American male veterans for whom no data on OT levels exist in the literature. The population has a disproportionately high rate of obesity and dysglycemia, as well as high rates of comorbid psychiatric disease.
In the study, urinary oxytocin was higher in men with lower weight, body mass index (BMI), and hemoglobin A1c and better renal function. Men with the highest levels of oxytocin were about 80% less likely to have type 2 diabetes. The researchers say several studies have appeared to show that intranasal OT may reduce reward-driven food intake, and that OT administration may result in weight reduction.
Men with high oxytocin levels were 4 times more likely to be using psychiatric medications. Although there was no difference in psychiatric conditions based on OT levels, the use of psychiatric medications remained significant after adjustment for BMI. The influence of psychiatric medications on oxytocinergic systems is not well understood, the researchers say. However, they add that medication-related improved psychological health outcome might result in OT changes.
Men with high oxytocin levels were also 4 times more likely to be smokers. The researchers note that chronic administration of nicotine seems to upregulate OT receptor binding in regions of the brain involved in stress and emotion regulation, and these neuro-adaptations likely influence nicotine-seeking behavior. Intranasal OT is being investigated for smoking cessation.
African American men with diabetes may be at risk for significantly low levels of oxytocin (OT), according to a study of 92 veterans by researchers from the Jesse Brown Veterans Administration Medical Center in Chicago, Illinois. Research has recently been revealing oxytocin’s role in energy homeostasis; OT derangements have also been implicated in a variety of diseases, including schizophrenia, autism, dysthymia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
The researchers note that their study participants represent a “unique population” of African American male veterans for whom no data on OT levels exist in the literature. The population has a disproportionately high rate of obesity and dysglycemia, as well as high rates of comorbid psychiatric disease.
In the study, urinary oxytocin was higher in men with lower weight, body mass index (BMI), and hemoglobin A1c and better renal function. Men with the highest levels of oxytocin were about 80% less likely to have type 2 diabetes. The researchers say several studies have appeared to show that intranasal OT may reduce reward-driven food intake, and that OT administration may result in weight reduction.
Men with high oxytocin levels were 4 times more likely to be using psychiatric medications. Although there was no difference in psychiatric conditions based on OT levels, the use of psychiatric medications remained significant after adjustment for BMI. The influence of psychiatric medications on oxytocinergic systems is not well understood, the researchers say. However, they add that medication-related improved psychological health outcome might result in OT changes.
Men with high oxytocin levels were also 4 times more likely to be smokers. The researchers note that chronic administration of nicotine seems to upregulate OT receptor binding in regions of the brain involved in stress and emotion regulation, and these neuro-adaptations likely influence nicotine-seeking behavior. Intranasal OT is being investigated for smoking cessation.
African American men with diabetes may be at risk for significantly low levels of oxytocin (OT), according to a study of 92 veterans by researchers from the Jesse Brown Veterans Administration Medical Center in Chicago, Illinois. Research has recently been revealing oxytocin’s role in energy homeostasis; OT derangements have also been implicated in a variety of diseases, including schizophrenia, autism, dysthymia, and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder.
The researchers note that their study participants represent a “unique population” of African American male veterans for whom no data on OT levels exist in the literature. The population has a disproportionately high rate of obesity and dysglycemia, as well as high rates of comorbid psychiatric disease.
In the study, urinary oxytocin was higher in men with lower weight, body mass index (BMI), and hemoglobin A1c and better renal function. Men with the highest levels of oxytocin were about 80% less likely to have type 2 diabetes. The researchers say several studies have appeared to show that intranasal OT may reduce reward-driven food intake, and that OT administration may result in weight reduction.
Men with high oxytocin levels were 4 times more likely to be using psychiatric medications. Although there was no difference in psychiatric conditions based on OT levels, the use of psychiatric medications remained significant after adjustment for BMI. The influence of psychiatric medications on oxytocinergic systems is not well understood, the researchers say. However, they add that medication-related improved psychological health outcome might result in OT changes.
Men with high oxytocin levels were also 4 times more likely to be smokers. The researchers note that chronic administration of nicotine seems to upregulate OT receptor binding in regions of the brain involved in stress and emotion regulation, and these neuro-adaptations likely influence nicotine-seeking behavior. Intranasal OT is being investigated for smoking cessation.
Type 2 diabetes remission: Reducing excess fat in the liver might be the key
LOS ANGELES – More than 20 years ago, Roy Taylor, MD, began working to further understand the pathogenesis of hepatic insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes. It became clear that the main determinant was the amount of fat in the liver.

“If you reduced the amount of fat, the resistance went down,” Dr. Taylor, professor of medicine and metabolism at Newcastle University (England), said at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. “We had a very clear picture of what might be controlling this awful matter of fasting glucose being too high.”
Then, Dr. Taylor read a study from Caterina Guidone, MD, and colleagues in Italy, which found that 1 week after patients with type 2 diabetes underwent gastric bypass surgery, their fasting plasma glucose levels became normal (Diabetes. 2006;55[7]:2025-31). “I was sitting at my desk and I thought, ‘This really changes type 2 diabetes,’ ” Dr. Taylor said. “It set in process a series of thoughts as to what was controlling what.”
This inspired ongoing work that Dr. Taylor termed the “twin-cycle hypothesis,” which postulates that chronic calorie excess leads to accumulation of liver fat, which spills over into the pancreas (Diabetologia. 2008;51[10]:1781-9).
“People with type 2 diabetes have been in positive calorie balance for a number of years,” he said. “That’s going to lead to an excess of fat in the body, and liver fat levels tend to rise with increasing body weight. If a person has normal insulin sensitivity in muscle tissue, then dealing with a meal is quite easy. Some 30 years ago, we showed using MR spectroscopy that you will have stored the carbohydrate from your breakfast in muscle, to the extent of about one-third of your breakfast, and the peak will be about 5 hours after breakfast. If you had your corn flakes at seven in the morning, by noon there will be peak in muscle, nicely stored away. However, if you happen to be insulin resistant in muscle, that doesn’t happen. There’s only one other pathway that the body can use, and that’s lipogenesis. The body can turn this very toxic substance [glucose] into safe storage [fat]. A lot of that happens in the liver. This means that people with insulin resistance tend to build up liver fat more rapidly than others.”
To test the twin-cycle hypothesis, Dr. Taylor and colleagues launched an 8-week study known as Counterpoint, which set out to induce negative calorie balance using a very low–calorie diet – about one-quarter of an average person’s daily food intake – in 11 people with diabetes (Diabetologia. 2011;54[10]:2506-14). The diet included consuming three packets of liquid formula food each day (46.4% carbohydrate, 32.5% protein, and 20.1% fat; plus vitamins, minerals, and trace elements), supplemented with portions of nonstarchy vegetables such that total energy intake was about 700 calories a day.
“On a liquid-formula diet, hunger is not a problem after the first 36 hours,” Dr. Taylor said. “This is one of the best-kept secrets of the obesity field. Our low-calorie diet was designed as something that people would be able to do in real life. We included nonstarchy vegetables to keep the bowels happy. That was important. It also fulfilled another point. People didn’t want just a liquid diet. They missed the sensation of chewing.”
The researchers also developed three-point Dixon MRI to measure pancreas and liver triacylglycerol content. “The pancreas was particularly challenging, and the full resources of the magnetic resonance physics team were needed to crack the technical problems,” he said.
After just 1 week of restricted energy intake, the fasting plasma glucose level normalized in the diabetic group, going from 9.2 to 5.9 mmol/L (P = .003), while insulin suppression of hepatic glucose output improved from 43% to 74 % (P = .003). By week 8, pancreatic triacylglycerol decreased from 8.0% to 1.1% (P = .03), and hepatic triacylglycerol content fell from 12.8% to 2.9% (P = .003).
“Within 7 days, there was a 30% drop in liver fat, and hepatic insulin resistance had disappeared,” Dr. Taylor said. “This is not a significant change – it’s a disappearance. For one individual, the amount of fat in the liver decreased from 36% to 2%. In fact, 2% [fat in the liver] was the average in the whole group. But what was simply amazing was the change in first-phase insulin response. It gradually increased throughout the 8 weeks of the study to become similar to the normal control group. We knew right away that a low-calorie diet would start correcting this central abnormality of type 2 diabetes.”
After the results from Counterpoint were published, Dr. Taylor received a “tsunami” of emails from researchers and from members of the public. “Some of the medical experts said it was a flash in the pan – interesting, but not relevant,” he said. “People with diabetes learned of it by the media, and it was talked about as a crash diet, which is unfortunate. First, it wasn’t a crash diet. This diet has to be very carefully planned, and people need to think about it in advance. They need to talk about it with their nearest and dearest, because it’s the spouse, the partner, the friends who will be supporting the individual through this journey. That’s critically important. People don’t eat as isolated individuals, they often eat as a family. We’re not talking about cure. We’re talking about reversal of the processes underpinning diabetes, with the aim of achieving remission.”
Dr. Taylor created a website devoted to providing information for clinicians and patients about the low-calorie diet and other tips on how to reverse type 2 diabetes. Soon afterward, he started to receive emails from people telling him about their experiences with the diet. “In the comfort of their own kitchens these people had lost the same amount of weight as in our trial subjects – about 33 pounds,” Dr. Taylor said. “Most of them had gotten rid of their type 2 diabetes. This was not something artificial as part of a research project. This was something that real people would do if the motivation was strong enough.”
To find out if the results from the Counterpoint study were sustainable, Dr. Taylor and his associates launched the Counterbalance study in 30 patients with type 2 diabetes who had a positive calorie imbalance and whom the researchers followed for 6 months. The 8-week diet consisted of consuming three packets of liquid formula a day comprising 43.0% carbohydrates, 34.0% protein, and 19.5% fat, as well as up to 240 g of nonstarchy vegetables (Diabetes Care. 2016;39[5]:808-15). “This was followed for a 6-month period of normal eating: Eating whatever foods they liked but in quantities to keep their weight steady,” Dr. Taylor explained. “These people gained no weight over the 6-month follow-up period. They achieved normalization of liver fat, and it remained normal.”
The patients’ hemoglobin A1c levels fell from an average of 7.1% at baseline to less than 6.0%, and stayed at less than 6.0%. Patients who didn’t respond tended to have a longer duration of diabetes. Their beta cells had fallen to a level beyond that capable of recovery. “So the durability of the return to normal metabolic function was not in question, at least up to 6 months,” he said. “This study also gave us the opportunity to look at changes in pancreas fat. Was it likely that the liver fat was driving the pancreas fat? Yes.”
During the weight-loss period, the researchers found that there was the same degree of reduction of pancreas fat in the Counterbalance study as there’d been in the Counterpoint study. “Remarkably, it decreased slightly during the 6 months of follow-up,” Dr. Taylor said. “Those changes were significant. Type 2 diabetes seems to be caused by about a half a gram of fat within the cells of the pancreas.”
To investigate if a very low–calorie diet could be used as a routine treatment for type 2 diabetes, Dr. Taylor collaborated with his colleague, Mike Lean, MD, in launching the randomized controlled Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT) at 49 primary care practices in the United Kingdom (Diabetologia. 2018;61[3]:589-98). In all, 298 patients were randomized to either best-practice diabetes care alone (control arm) or with an additional evidence-based weight-management program (intervention arm). Remission was defined as having a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5% for at least 2 months without receiving glucose-lowering therapy.
At 1 year, 46% of patients in the intervention arm achieved remission, compared with 4% in the control arm (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7[5]:344-55). At 2 years, 36% of patients in the intervention arm achieved remission, compared with 2% in the control arm. “The most common comment from study participants was, ‘I feel 10 years younger,’ ” Dr. Taylor said. “That’s important.”
The percentage of patients who achieved remission was 5% in those who lost less than 11 lb (5 kg), 29% in those who lost between 11 lb and 22 lb (5-10 kg), 60% in those who lost between 22 lb and 33 lb (10-15 kg), and 70% in those who lost 33 lb (15 kg) or more.
The researchers found that 62 patients achieved no remission at 12 or 24 months, 15 achieved remission at 12 but not at 24 months, and 48 achieved remission at 12 and 24 months. “We haven’t got this perfectly right yet,” Dr. Taylor said. “There is more work to do in understanding how to achieve prevention of weight gain, maybe with behavioral interventions and/or other agents such as [glucagonlike peptide–1] agonists. This is the start of a story, not the end of it.”
He and his associates also observed that delivery of fat from the liver to the rest of the body was increased in study participants who relapsed. “What effect did that have on the pancreas fat? The people who continued to be free of diabetes showed a slight fall in pancreatic fat between 5 and 24 months,” Dr. Taylor said. “In sharp contrast, the relapsers had a complete increase. Over the whole period of the study, the relapsers had not changed from baseline. It appears beyond reasonable doubt that excess pancreas fat seems to be driving the beta-cell problem underlying type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Taylor reported that he has received lecture fees from Novartis, Lilly, and Janssen. He has also been an advisory board member for Wilmington Healthcare.
LOS ANGELES – More than 20 years ago, Roy Taylor, MD, began working to further understand the pathogenesis of hepatic insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes. It became clear that the main determinant was the amount of fat in the liver.

“If you reduced the amount of fat, the resistance went down,” Dr. Taylor, professor of medicine and metabolism at Newcastle University (England), said at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. “We had a very clear picture of what might be controlling this awful matter of fasting glucose being too high.”
Then, Dr. Taylor read a study from Caterina Guidone, MD, and colleagues in Italy, which found that 1 week after patients with type 2 diabetes underwent gastric bypass surgery, their fasting plasma glucose levels became normal (Diabetes. 2006;55[7]:2025-31). “I was sitting at my desk and I thought, ‘This really changes type 2 diabetes,’ ” Dr. Taylor said. “It set in process a series of thoughts as to what was controlling what.”
This inspired ongoing work that Dr. Taylor termed the “twin-cycle hypothesis,” which postulates that chronic calorie excess leads to accumulation of liver fat, which spills over into the pancreas (Diabetologia. 2008;51[10]:1781-9).
“People with type 2 diabetes have been in positive calorie balance for a number of years,” he said. “That’s going to lead to an excess of fat in the body, and liver fat levels tend to rise with increasing body weight. If a person has normal insulin sensitivity in muscle tissue, then dealing with a meal is quite easy. Some 30 years ago, we showed using MR spectroscopy that you will have stored the carbohydrate from your breakfast in muscle, to the extent of about one-third of your breakfast, and the peak will be about 5 hours after breakfast. If you had your corn flakes at seven in the morning, by noon there will be peak in muscle, nicely stored away. However, if you happen to be insulin resistant in muscle, that doesn’t happen. There’s only one other pathway that the body can use, and that’s lipogenesis. The body can turn this very toxic substance [glucose] into safe storage [fat]. A lot of that happens in the liver. This means that people with insulin resistance tend to build up liver fat more rapidly than others.”
To test the twin-cycle hypothesis, Dr. Taylor and colleagues launched an 8-week study known as Counterpoint, which set out to induce negative calorie balance using a very low–calorie diet – about one-quarter of an average person’s daily food intake – in 11 people with diabetes (Diabetologia. 2011;54[10]:2506-14). The diet included consuming three packets of liquid formula food each day (46.4% carbohydrate, 32.5% protein, and 20.1% fat; plus vitamins, minerals, and trace elements), supplemented with portions of nonstarchy vegetables such that total energy intake was about 700 calories a day.
“On a liquid-formula diet, hunger is not a problem after the first 36 hours,” Dr. Taylor said. “This is one of the best-kept secrets of the obesity field. Our low-calorie diet was designed as something that people would be able to do in real life. We included nonstarchy vegetables to keep the bowels happy. That was important. It also fulfilled another point. People didn’t want just a liquid diet. They missed the sensation of chewing.”
The researchers also developed three-point Dixon MRI to measure pancreas and liver triacylglycerol content. “The pancreas was particularly challenging, and the full resources of the magnetic resonance physics team were needed to crack the technical problems,” he said.
After just 1 week of restricted energy intake, the fasting plasma glucose level normalized in the diabetic group, going from 9.2 to 5.9 mmol/L (P = .003), while insulin suppression of hepatic glucose output improved from 43% to 74 % (P = .003). By week 8, pancreatic triacylglycerol decreased from 8.0% to 1.1% (P = .03), and hepatic triacylglycerol content fell from 12.8% to 2.9% (P = .003).
“Within 7 days, there was a 30% drop in liver fat, and hepatic insulin resistance had disappeared,” Dr. Taylor said. “This is not a significant change – it’s a disappearance. For one individual, the amount of fat in the liver decreased from 36% to 2%. In fact, 2% [fat in the liver] was the average in the whole group. But what was simply amazing was the change in first-phase insulin response. It gradually increased throughout the 8 weeks of the study to become similar to the normal control group. We knew right away that a low-calorie diet would start correcting this central abnormality of type 2 diabetes.”
After the results from Counterpoint were published, Dr. Taylor received a “tsunami” of emails from researchers and from members of the public. “Some of the medical experts said it was a flash in the pan – interesting, but not relevant,” he said. “People with diabetes learned of it by the media, and it was talked about as a crash diet, which is unfortunate. First, it wasn’t a crash diet. This diet has to be very carefully planned, and people need to think about it in advance. They need to talk about it with their nearest and dearest, because it’s the spouse, the partner, the friends who will be supporting the individual through this journey. That’s critically important. People don’t eat as isolated individuals, they often eat as a family. We’re not talking about cure. We’re talking about reversal of the processes underpinning diabetes, with the aim of achieving remission.”
Dr. Taylor created a website devoted to providing information for clinicians and patients about the low-calorie diet and other tips on how to reverse type 2 diabetes. Soon afterward, he started to receive emails from people telling him about their experiences with the diet. “In the comfort of their own kitchens these people had lost the same amount of weight as in our trial subjects – about 33 pounds,” Dr. Taylor said. “Most of them had gotten rid of their type 2 diabetes. This was not something artificial as part of a research project. This was something that real people would do if the motivation was strong enough.”
To find out if the results from the Counterpoint study were sustainable, Dr. Taylor and his associates launched the Counterbalance study in 30 patients with type 2 diabetes who had a positive calorie imbalance and whom the researchers followed for 6 months. The 8-week diet consisted of consuming three packets of liquid formula a day comprising 43.0% carbohydrates, 34.0% protein, and 19.5% fat, as well as up to 240 g of nonstarchy vegetables (Diabetes Care. 2016;39[5]:808-15). “This was followed for a 6-month period of normal eating: Eating whatever foods they liked but in quantities to keep their weight steady,” Dr. Taylor explained. “These people gained no weight over the 6-month follow-up period. They achieved normalization of liver fat, and it remained normal.”
The patients’ hemoglobin A1c levels fell from an average of 7.1% at baseline to less than 6.0%, and stayed at less than 6.0%. Patients who didn’t respond tended to have a longer duration of diabetes. Their beta cells had fallen to a level beyond that capable of recovery. “So the durability of the return to normal metabolic function was not in question, at least up to 6 months,” he said. “This study also gave us the opportunity to look at changes in pancreas fat. Was it likely that the liver fat was driving the pancreas fat? Yes.”
During the weight-loss period, the researchers found that there was the same degree of reduction of pancreas fat in the Counterbalance study as there’d been in the Counterpoint study. “Remarkably, it decreased slightly during the 6 months of follow-up,” Dr. Taylor said. “Those changes were significant. Type 2 diabetes seems to be caused by about a half a gram of fat within the cells of the pancreas.”
To investigate if a very low–calorie diet could be used as a routine treatment for type 2 diabetes, Dr. Taylor collaborated with his colleague, Mike Lean, MD, in launching the randomized controlled Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT) at 49 primary care practices in the United Kingdom (Diabetologia. 2018;61[3]:589-98). In all, 298 patients were randomized to either best-practice diabetes care alone (control arm) or with an additional evidence-based weight-management program (intervention arm). Remission was defined as having a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5% for at least 2 months without receiving glucose-lowering therapy.
At 1 year, 46% of patients in the intervention arm achieved remission, compared with 4% in the control arm (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7[5]:344-55). At 2 years, 36% of patients in the intervention arm achieved remission, compared with 2% in the control arm. “The most common comment from study participants was, ‘I feel 10 years younger,’ ” Dr. Taylor said. “That’s important.”
The percentage of patients who achieved remission was 5% in those who lost less than 11 lb (5 kg), 29% in those who lost between 11 lb and 22 lb (5-10 kg), 60% in those who lost between 22 lb and 33 lb (10-15 kg), and 70% in those who lost 33 lb (15 kg) or more.
The researchers found that 62 patients achieved no remission at 12 or 24 months, 15 achieved remission at 12 but not at 24 months, and 48 achieved remission at 12 and 24 months. “We haven’t got this perfectly right yet,” Dr. Taylor said. “There is more work to do in understanding how to achieve prevention of weight gain, maybe with behavioral interventions and/or other agents such as [glucagonlike peptide–1] agonists. This is the start of a story, not the end of it.”
He and his associates also observed that delivery of fat from the liver to the rest of the body was increased in study participants who relapsed. “What effect did that have on the pancreas fat? The people who continued to be free of diabetes showed a slight fall in pancreatic fat between 5 and 24 months,” Dr. Taylor said. “In sharp contrast, the relapsers had a complete increase. Over the whole period of the study, the relapsers had not changed from baseline. It appears beyond reasonable doubt that excess pancreas fat seems to be driving the beta-cell problem underlying type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Taylor reported that he has received lecture fees from Novartis, Lilly, and Janssen. He has also been an advisory board member for Wilmington Healthcare.
LOS ANGELES – More than 20 years ago, Roy Taylor, MD, began working to further understand the pathogenesis of hepatic insulin resistance in people with type 2 diabetes. It became clear that the main determinant was the amount of fat in the liver.

“If you reduced the amount of fat, the resistance went down,” Dr. Taylor, professor of medicine and metabolism at Newcastle University (England), said at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. “We had a very clear picture of what might be controlling this awful matter of fasting glucose being too high.”
Then, Dr. Taylor read a study from Caterina Guidone, MD, and colleagues in Italy, which found that 1 week after patients with type 2 diabetes underwent gastric bypass surgery, their fasting plasma glucose levels became normal (Diabetes. 2006;55[7]:2025-31). “I was sitting at my desk and I thought, ‘This really changes type 2 diabetes,’ ” Dr. Taylor said. “It set in process a series of thoughts as to what was controlling what.”
This inspired ongoing work that Dr. Taylor termed the “twin-cycle hypothesis,” which postulates that chronic calorie excess leads to accumulation of liver fat, which spills over into the pancreas (Diabetologia. 2008;51[10]:1781-9).
“People with type 2 diabetes have been in positive calorie balance for a number of years,” he said. “That’s going to lead to an excess of fat in the body, and liver fat levels tend to rise with increasing body weight. If a person has normal insulin sensitivity in muscle tissue, then dealing with a meal is quite easy. Some 30 years ago, we showed using MR spectroscopy that you will have stored the carbohydrate from your breakfast in muscle, to the extent of about one-third of your breakfast, and the peak will be about 5 hours after breakfast. If you had your corn flakes at seven in the morning, by noon there will be peak in muscle, nicely stored away. However, if you happen to be insulin resistant in muscle, that doesn’t happen. There’s only one other pathway that the body can use, and that’s lipogenesis. The body can turn this very toxic substance [glucose] into safe storage [fat]. A lot of that happens in the liver. This means that people with insulin resistance tend to build up liver fat more rapidly than others.”
To test the twin-cycle hypothesis, Dr. Taylor and colleagues launched an 8-week study known as Counterpoint, which set out to induce negative calorie balance using a very low–calorie diet – about one-quarter of an average person’s daily food intake – in 11 people with diabetes (Diabetologia. 2011;54[10]:2506-14). The diet included consuming three packets of liquid formula food each day (46.4% carbohydrate, 32.5% protein, and 20.1% fat; plus vitamins, minerals, and trace elements), supplemented with portions of nonstarchy vegetables such that total energy intake was about 700 calories a day.
“On a liquid-formula diet, hunger is not a problem after the first 36 hours,” Dr. Taylor said. “This is one of the best-kept secrets of the obesity field. Our low-calorie diet was designed as something that people would be able to do in real life. We included nonstarchy vegetables to keep the bowels happy. That was important. It also fulfilled another point. People didn’t want just a liquid diet. They missed the sensation of chewing.”
The researchers also developed three-point Dixon MRI to measure pancreas and liver triacylglycerol content. “The pancreas was particularly challenging, and the full resources of the magnetic resonance physics team were needed to crack the technical problems,” he said.
After just 1 week of restricted energy intake, the fasting plasma glucose level normalized in the diabetic group, going from 9.2 to 5.9 mmol/L (P = .003), while insulin suppression of hepatic glucose output improved from 43% to 74 % (P = .003). By week 8, pancreatic triacylglycerol decreased from 8.0% to 1.1% (P = .03), and hepatic triacylglycerol content fell from 12.8% to 2.9% (P = .003).
“Within 7 days, there was a 30% drop in liver fat, and hepatic insulin resistance had disappeared,” Dr. Taylor said. “This is not a significant change – it’s a disappearance. For one individual, the amount of fat in the liver decreased from 36% to 2%. In fact, 2% [fat in the liver] was the average in the whole group. But what was simply amazing was the change in first-phase insulin response. It gradually increased throughout the 8 weeks of the study to become similar to the normal control group. We knew right away that a low-calorie diet would start correcting this central abnormality of type 2 diabetes.”
After the results from Counterpoint were published, Dr. Taylor received a “tsunami” of emails from researchers and from members of the public. “Some of the medical experts said it was a flash in the pan – interesting, but not relevant,” he said. “People with diabetes learned of it by the media, and it was talked about as a crash diet, which is unfortunate. First, it wasn’t a crash diet. This diet has to be very carefully planned, and people need to think about it in advance. They need to talk about it with their nearest and dearest, because it’s the spouse, the partner, the friends who will be supporting the individual through this journey. That’s critically important. People don’t eat as isolated individuals, they often eat as a family. We’re not talking about cure. We’re talking about reversal of the processes underpinning diabetes, with the aim of achieving remission.”
Dr. Taylor created a website devoted to providing information for clinicians and patients about the low-calorie diet and other tips on how to reverse type 2 diabetes. Soon afterward, he started to receive emails from people telling him about their experiences with the diet. “In the comfort of their own kitchens these people had lost the same amount of weight as in our trial subjects – about 33 pounds,” Dr. Taylor said. “Most of them had gotten rid of their type 2 diabetes. This was not something artificial as part of a research project. This was something that real people would do if the motivation was strong enough.”
To find out if the results from the Counterpoint study were sustainable, Dr. Taylor and his associates launched the Counterbalance study in 30 patients with type 2 diabetes who had a positive calorie imbalance and whom the researchers followed for 6 months. The 8-week diet consisted of consuming three packets of liquid formula a day comprising 43.0% carbohydrates, 34.0% protein, and 19.5% fat, as well as up to 240 g of nonstarchy vegetables (Diabetes Care. 2016;39[5]:808-15). “This was followed for a 6-month period of normal eating: Eating whatever foods they liked but in quantities to keep their weight steady,” Dr. Taylor explained. “These people gained no weight over the 6-month follow-up period. They achieved normalization of liver fat, and it remained normal.”
The patients’ hemoglobin A1c levels fell from an average of 7.1% at baseline to less than 6.0%, and stayed at less than 6.0%. Patients who didn’t respond tended to have a longer duration of diabetes. Their beta cells had fallen to a level beyond that capable of recovery. “So the durability of the return to normal metabolic function was not in question, at least up to 6 months,” he said. “This study also gave us the opportunity to look at changes in pancreas fat. Was it likely that the liver fat was driving the pancreas fat? Yes.”
During the weight-loss period, the researchers found that there was the same degree of reduction of pancreas fat in the Counterbalance study as there’d been in the Counterpoint study. “Remarkably, it decreased slightly during the 6 months of follow-up,” Dr. Taylor said. “Those changes were significant. Type 2 diabetes seems to be caused by about a half a gram of fat within the cells of the pancreas.”
To investigate if a very low–calorie diet could be used as a routine treatment for type 2 diabetes, Dr. Taylor collaborated with his colleague, Mike Lean, MD, in launching the randomized controlled Diabetes Remission Clinical Trial (DiRECT) at 49 primary care practices in the United Kingdom (Diabetologia. 2018;61[3]:589-98). In all, 298 patients were randomized to either best-practice diabetes care alone (control arm) or with an additional evidence-based weight-management program (intervention arm). Remission was defined as having a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5% for at least 2 months without receiving glucose-lowering therapy.
At 1 year, 46% of patients in the intervention arm achieved remission, compared with 4% in the control arm (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019;7[5]:344-55). At 2 years, 36% of patients in the intervention arm achieved remission, compared with 2% in the control arm. “The most common comment from study participants was, ‘I feel 10 years younger,’ ” Dr. Taylor said. “That’s important.”
The percentage of patients who achieved remission was 5% in those who lost less than 11 lb (5 kg), 29% in those who lost between 11 lb and 22 lb (5-10 kg), 60% in those who lost between 22 lb and 33 lb (10-15 kg), and 70% in those who lost 33 lb (15 kg) or more.
The researchers found that 62 patients achieved no remission at 12 or 24 months, 15 achieved remission at 12 but not at 24 months, and 48 achieved remission at 12 and 24 months. “We haven’t got this perfectly right yet,” Dr. Taylor said. “There is more work to do in understanding how to achieve prevention of weight gain, maybe with behavioral interventions and/or other agents such as [glucagonlike peptide–1] agonists. This is the start of a story, not the end of it.”
He and his associates also observed that delivery of fat from the liver to the rest of the body was increased in study participants who relapsed. “What effect did that have on the pancreas fat? The people who continued to be free of diabetes showed a slight fall in pancreatic fat between 5 and 24 months,” Dr. Taylor said. “In sharp contrast, the relapsers had a complete increase. Over the whole period of the study, the relapsers had not changed from baseline. It appears beyond reasonable doubt that excess pancreas fat seems to be driving the beta-cell problem underlying type 2 diabetes.”
Dr. Taylor reported that he has received lecture fees from Novartis, Lilly, and Janssen. He has also been an advisory board member for Wilmington Healthcare.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AACE 2109
Canagliflozin after metabolic surgery may aid weight loss, reduce glucose levels
LOS ANGELES – Patients who took the sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor canagliflozin after undergoing metabolic surgery experienced reductions in blood glucose, body mass index, and truncal body fat, results from a small pilot study have shown.
“We hypothesized that canagliflozin would be a good choice for these patients, because these drugs work independently of insulin,” the study’s principal investigator, Sangeeta R. Kashyap, MD, said in an interview at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. “They help promote weight loss and improve blood pressure. [After] bariatric surgery, patients have an issue with weight regain, and sometimes their diabetes comes back.”
In what she said is the first prospective, randomized, controlled trial of its kind, Dr. Kashyap, an endocrinologist at the Cleveland Clinic, and her colleagues enrolled 11 women and 5 men with type 2 diabetes who had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy to study the effects of canagliflozin on clinical parameters over a period of 6 months. At baseline, the patients’ mean body mass index was 39.2 kg/m2 and their mean hemoglobin A1c level was 7.4%. The researchers used maximum likelihood estimation in a linear mixed-effect model to deduce differences between the treatment and placebo groups. Patients randomized to the study drug were assigned a 6-month course of canagliflozin, starting on 100 mg for 2 weeks titrated up to 300 mg daily.
At 6 months, fasting glucose was significantly reduced in the canagliflozin group, compared with baseline (from 163 to 122 mg/dL; P = .007), but it rose in the placebo group (from 164 to 192 mg/dL), a between-group difference that fell short of statistical significance (P = .12). In addition, C-reactive protein in the treatment group fell from 8.9 mg/L to 3.9 mg/L, but rose from 1.6 mg/L to 4.7 mg/L in the placebo group, a between-group difference that trended toward significance (P = .07).
During the 6-month study period, the mean BMI fell from 39.6 kg/m2 to 38 kg/m2 in the canagliflozin group but increased from 38 to 41 in the placebo group, a between-group difference that reached statistical significance (P = .014). Mean changes in body fat (a reduction of 1.82%), truncal fat (a reduction of 2.67%), and android fat (a reduction of 3%) also reached statistical significance in the treatment group, compared with the placebo group. Reductions in adiponectin, leptin, and high–molecular weight adiponectin did not reach statistical significance.
“I think these drugs have a place in post–bariatric surgery care,” Dr. Kashyap said. “Canagliflozin after metabolic surgery improved weight-loss outcomes and blood sugar levels. It also improved abdominal fat levels, and in this way might even lower cardiovascular disease risk in these patients.”
She acknowledged the study’s small sample size and single-center design as limitations. “It was very difficult to recruit patients for this study,” she said. “Not many patients have recurrent diabetes after bariatric surgery.”
Janssen provided funding to Dr. Kashyap for the trial.
LOS ANGELES – Patients who took the sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor canagliflozin after undergoing metabolic surgery experienced reductions in blood glucose, body mass index, and truncal body fat, results from a small pilot study have shown.
“We hypothesized that canagliflozin would be a good choice for these patients, because these drugs work independently of insulin,” the study’s principal investigator, Sangeeta R. Kashyap, MD, said in an interview at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. “They help promote weight loss and improve blood pressure. [After] bariatric surgery, patients have an issue with weight regain, and sometimes their diabetes comes back.”
In what she said is the first prospective, randomized, controlled trial of its kind, Dr. Kashyap, an endocrinologist at the Cleveland Clinic, and her colleagues enrolled 11 women and 5 men with type 2 diabetes who had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy to study the effects of canagliflozin on clinical parameters over a period of 6 months. At baseline, the patients’ mean body mass index was 39.2 kg/m2 and their mean hemoglobin A1c level was 7.4%. The researchers used maximum likelihood estimation in a linear mixed-effect model to deduce differences between the treatment and placebo groups. Patients randomized to the study drug were assigned a 6-month course of canagliflozin, starting on 100 mg for 2 weeks titrated up to 300 mg daily.
At 6 months, fasting glucose was significantly reduced in the canagliflozin group, compared with baseline (from 163 to 122 mg/dL; P = .007), but it rose in the placebo group (from 164 to 192 mg/dL), a between-group difference that fell short of statistical significance (P = .12). In addition, C-reactive protein in the treatment group fell from 8.9 mg/L to 3.9 mg/L, but rose from 1.6 mg/L to 4.7 mg/L in the placebo group, a between-group difference that trended toward significance (P = .07).
During the 6-month study period, the mean BMI fell from 39.6 kg/m2 to 38 kg/m2 in the canagliflozin group but increased from 38 to 41 in the placebo group, a between-group difference that reached statistical significance (P = .014). Mean changes in body fat (a reduction of 1.82%), truncal fat (a reduction of 2.67%), and android fat (a reduction of 3%) also reached statistical significance in the treatment group, compared with the placebo group. Reductions in adiponectin, leptin, and high–molecular weight adiponectin did not reach statistical significance.
“I think these drugs have a place in post–bariatric surgery care,” Dr. Kashyap said. “Canagliflozin after metabolic surgery improved weight-loss outcomes and blood sugar levels. It also improved abdominal fat levels, and in this way might even lower cardiovascular disease risk in these patients.”
She acknowledged the study’s small sample size and single-center design as limitations. “It was very difficult to recruit patients for this study,” she said. “Not many patients have recurrent diabetes after bariatric surgery.”
Janssen provided funding to Dr. Kashyap for the trial.
LOS ANGELES – Patients who took the sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 inhibitor canagliflozin after undergoing metabolic surgery experienced reductions in blood glucose, body mass index, and truncal body fat, results from a small pilot study have shown.
“We hypothesized that canagliflozin would be a good choice for these patients, because these drugs work independently of insulin,” the study’s principal investigator, Sangeeta R. Kashyap, MD, said in an interview at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists. “They help promote weight loss and improve blood pressure. [After] bariatric surgery, patients have an issue with weight regain, and sometimes their diabetes comes back.”
In what she said is the first prospective, randomized, controlled trial of its kind, Dr. Kashyap, an endocrinologist at the Cleveland Clinic, and her colleagues enrolled 11 women and 5 men with type 2 diabetes who had undergone Roux-en-Y gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy to study the effects of canagliflozin on clinical parameters over a period of 6 months. At baseline, the patients’ mean body mass index was 39.2 kg/m2 and their mean hemoglobin A1c level was 7.4%. The researchers used maximum likelihood estimation in a linear mixed-effect model to deduce differences between the treatment and placebo groups. Patients randomized to the study drug were assigned a 6-month course of canagliflozin, starting on 100 mg for 2 weeks titrated up to 300 mg daily.
At 6 months, fasting glucose was significantly reduced in the canagliflozin group, compared with baseline (from 163 to 122 mg/dL; P = .007), but it rose in the placebo group (from 164 to 192 mg/dL), a between-group difference that fell short of statistical significance (P = .12). In addition, C-reactive protein in the treatment group fell from 8.9 mg/L to 3.9 mg/L, but rose from 1.6 mg/L to 4.7 mg/L in the placebo group, a between-group difference that trended toward significance (P = .07).
During the 6-month study period, the mean BMI fell from 39.6 kg/m2 to 38 kg/m2 in the canagliflozin group but increased from 38 to 41 in the placebo group, a between-group difference that reached statistical significance (P = .014). Mean changes in body fat (a reduction of 1.82%), truncal fat (a reduction of 2.67%), and android fat (a reduction of 3%) also reached statistical significance in the treatment group, compared with the placebo group. Reductions in adiponectin, leptin, and high–molecular weight adiponectin did not reach statistical significance.
“I think these drugs have a place in post–bariatric surgery care,” Dr. Kashyap said. “Canagliflozin after metabolic surgery improved weight-loss outcomes and blood sugar levels. It also improved abdominal fat levels, and in this way might even lower cardiovascular disease risk in these patients.”
She acknowledged the study’s small sample size and single-center design as limitations. “It was very difficult to recruit patients for this study,” she said. “Not many patients have recurrent diabetes after bariatric surgery.”
Janssen provided funding to Dr. Kashyap for the trial.
REPORTING FROM AACE 2019
Mystery hypoglycemia case highlights troublesome diagnosis
LOS ANGELES – The 69-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes had persistent hypoglycemia despite treatment with hydrocortisone, dextrose, and glucagon. Doctors in South Carolina worried about insulinoma and planned to launch an intra-arterial calcium stimulation test. But the medical team wasn’t quite certain it had the correct diagnosis.
Then along came a suspicious nurse who uncovered the truth: The patient had used syringes and vials of insulin socked away in a cosmetics bag. The diagnosis? An unusual, but not entirely rare, case of factitious hypoglycemia. That doesn’t mean her condition was fictional. Instead, it means she created it herself.

In this case, he said, “the challenge with the patient was that she was denying insulin use very firmly,” and her demeanor didn’t suggest she was lying or had a mental illness. “If you saw the lady, you’d believe her.”
The patient presented with glucose levels that were repeatedly less than 40 mg/dL even though medical personnel fed her and gave her glucose. Her insulin level was high.
“The suspicion was that something in her body was producing insulin or she [was] giving herself or someone from her family was injecting her with insulin,” Dr. Aljehani said. “She denied that she was using insulin and said the last time she had used it was about 3 months earlier. Her husband and multiple family members confirmed the story.”
The results of a C-peptide test, however, suggested she was taking insulin herself. But it wasn’t conclusive.
Nurses monitored the patient during her stay of about 2 weeks. “They were keeping a good eye on her all the time, but nobody noticed anything suspicious. Then, probably 2 or 3 days before the discharge, one of the nurses had noted the patient gave her husband a bag. The nurse was able to take a look inside the bag, and she found empty insulin vials and syringes.”
The patient and her husband still denied that she was taking insulin. A psychiatric examination suggested the patient had a dissociative identity disorder and wasn’t aware she was giving herself insulin, he said.
If the patient’s insulin use hadn’t been discovered, Dr. Aljehani said, the next steps could have included more invasive testing and, potentially, removal of the pancreas.
Factitious hypoglycemia has a long history. The first case appeared in 1927, not long after the discovery of insulin, endocrinologist F.J. Service, MD, PhD, an emeritus professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, said in an interview.
Dr. Service, who has written about factitious hypoglycemia, offered these tips about diagnosis and treatment:
- In every patient, he said, do a drug screen for sulfonylureas. “Now that we have multiple classes of diabetes drugs, most of which have a risk for hypoglycemia, one has to have a lab capable of measuring all of them. And that is not easy. It’s not just ‘draw the blood and send to your corner lab.’ ”
- Patients with factitious hypoglycemia don’t tend to have predictable dips in blood sugar during fasting or after meals. Instead, their symptoms are chaotic. “It all depends on when they’re taking [insulin],” he said.
- Patients with factitious hypoglycemia don’t seem ill, but those with insulinomas do. “Patients with insulinomas are totally incapable of living normal lives. They’re incapacitated. Their lives are so disrupted that some of them need ‘babysitters’,” Dr. Service said. If they “get the tumor removed, they are cured. Then they are back to the normal life.”
- Beware that patients may not realize they’re taking a medication that causes factitious hypoglycemia. It’s common, Dr. Service said, for a patient to accidentally take his or her spouse’s medication because of a mix-up.
Ultimately, the goal is to catch factitious hypoglycemia in time. Some physicians haven’t been so fortunate. “They only get to the right answer,” he said, “after the patient has recovered from surgery.”
LOS ANGELES – The 69-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes had persistent hypoglycemia despite treatment with hydrocortisone, dextrose, and glucagon. Doctors in South Carolina worried about insulinoma and planned to launch an intra-arterial calcium stimulation test. But the medical team wasn’t quite certain it had the correct diagnosis.
Then along came a suspicious nurse who uncovered the truth: The patient had used syringes and vials of insulin socked away in a cosmetics bag. The diagnosis? An unusual, but not entirely rare, case of factitious hypoglycemia. That doesn’t mean her condition was fictional. Instead, it means she created it herself.

In this case, he said, “the challenge with the patient was that she was denying insulin use very firmly,” and her demeanor didn’t suggest she was lying or had a mental illness. “If you saw the lady, you’d believe her.”
The patient presented with glucose levels that were repeatedly less than 40 mg/dL even though medical personnel fed her and gave her glucose. Her insulin level was high.
“The suspicion was that something in her body was producing insulin or she [was] giving herself or someone from her family was injecting her with insulin,” Dr. Aljehani said. “She denied that she was using insulin and said the last time she had used it was about 3 months earlier. Her husband and multiple family members confirmed the story.”
The results of a C-peptide test, however, suggested she was taking insulin herself. But it wasn’t conclusive.
Nurses monitored the patient during her stay of about 2 weeks. “They were keeping a good eye on her all the time, but nobody noticed anything suspicious. Then, probably 2 or 3 days before the discharge, one of the nurses had noted the patient gave her husband a bag. The nurse was able to take a look inside the bag, and she found empty insulin vials and syringes.”
The patient and her husband still denied that she was taking insulin. A psychiatric examination suggested the patient had a dissociative identity disorder and wasn’t aware she was giving herself insulin, he said.
If the patient’s insulin use hadn’t been discovered, Dr. Aljehani said, the next steps could have included more invasive testing and, potentially, removal of the pancreas.
Factitious hypoglycemia has a long history. The first case appeared in 1927, not long after the discovery of insulin, endocrinologist F.J. Service, MD, PhD, an emeritus professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, said in an interview.
Dr. Service, who has written about factitious hypoglycemia, offered these tips about diagnosis and treatment:
- In every patient, he said, do a drug screen for sulfonylureas. “Now that we have multiple classes of diabetes drugs, most of which have a risk for hypoglycemia, one has to have a lab capable of measuring all of them. And that is not easy. It’s not just ‘draw the blood and send to your corner lab.’ ”
- Patients with factitious hypoglycemia don’t tend to have predictable dips in blood sugar during fasting or after meals. Instead, their symptoms are chaotic. “It all depends on when they’re taking [insulin],” he said.
- Patients with factitious hypoglycemia don’t seem ill, but those with insulinomas do. “Patients with insulinomas are totally incapable of living normal lives. They’re incapacitated. Their lives are so disrupted that some of them need ‘babysitters’,” Dr. Service said. If they “get the tumor removed, they are cured. Then they are back to the normal life.”
- Beware that patients may not realize they’re taking a medication that causes factitious hypoglycemia. It’s common, Dr. Service said, for a patient to accidentally take his or her spouse’s medication because of a mix-up.
Ultimately, the goal is to catch factitious hypoglycemia in time. Some physicians haven’t been so fortunate. “They only get to the right answer,” he said, “after the patient has recovered from surgery.”
LOS ANGELES – The 69-year-old woman with a history of type 2 diabetes had persistent hypoglycemia despite treatment with hydrocortisone, dextrose, and glucagon. Doctors in South Carolina worried about insulinoma and planned to launch an intra-arterial calcium stimulation test. But the medical team wasn’t quite certain it had the correct diagnosis.
Then along came a suspicious nurse who uncovered the truth: The patient had used syringes and vials of insulin socked away in a cosmetics bag. The diagnosis? An unusual, but not entirely rare, case of factitious hypoglycemia. That doesn’t mean her condition was fictional. Instead, it means she created it herself.

In this case, he said, “the challenge with the patient was that she was denying insulin use very firmly,” and her demeanor didn’t suggest she was lying or had a mental illness. “If you saw the lady, you’d believe her.”
The patient presented with glucose levels that were repeatedly less than 40 mg/dL even though medical personnel fed her and gave her glucose. Her insulin level was high.
“The suspicion was that something in her body was producing insulin or she [was] giving herself or someone from her family was injecting her with insulin,” Dr. Aljehani said. “She denied that she was using insulin and said the last time she had used it was about 3 months earlier. Her husband and multiple family members confirmed the story.”
The results of a C-peptide test, however, suggested she was taking insulin herself. But it wasn’t conclusive.
Nurses monitored the patient during her stay of about 2 weeks. “They were keeping a good eye on her all the time, but nobody noticed anything suspicious. Then, probably 2 or 3 days before the discharge, one of the nurses had noted the patient gave her husband a bag. The nurse was able to take a look inside the bag, and she found empty insulin vials and syringes.”
The patient and her husband still denied that she was taking insulin. A psychiatric examination suggested the patient had a dissociative identity disorder and wasn’t aware she was giving herself insulin, he said.
If the patient’s insulin use hadn’t been discovered, Dr. Aljehani said, the next steps could have included more invasive testing and, potentially, removal of the pancreas.
Factitious hypoglycemia has a long history. The first case appeared in 1927, not long after the discovery of insulin, endocrinologist F.J. Service, MD, PhD, an emeritus professor of medicine at the Mayo Clinic, said in an interview.
Dr. Service, who has written about factitious hypoglycemia, offered these tips about diagnosis and treatment:
- In every patient, he said, do a drug screen for sulfonylureas. “Now that we have multiple classes of diabetes drugs, most of which have a risk for hypoglycemia, one has to have a lab capable of measuring all of them. And that is not easy. It’s not just ‘draw the blood and send to your corner lab.’ ”
- Patients with factitious hypoglycemia don’t tend to have predictable dips in blood sugar during fasting or after meals. Instead, their symptoms are chaotic. “It all depends on when they’re taking [insulin],” he said.
- Patients with factitious hypoglycemia don’t seem ill, but those with insulinomas do. “Patients with insulinomas are totally incapable of living normal lives. They’re incapacitated. Their lives are so disrupted that some of them need ‘babysitters’,” Dr. Service said. If they “get the tumor removed, they are cured. Then they are back to the normal life.”
- Beware that patients may not realize they’re taking a medication that causes factitious hypoglycemia. It’s common, Dr. Service said, for a patient to accidentally take his or her spouse’s medication because of a mix-up.
Ultimately, the goal is to catch factitious hypoglycemia in time. Some physicians haven’t been so fortunate. “They only get to the right answer,” he said, “after the patient has recovered from surgery.”
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM AACE 2019
SGLT2 inhibitors prevent HF hospitalization regardless of baseline LVEF
NEW ORLEANS – based on data from a large real-world patient registry.
“The observed beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure may extend across the range of baseline ejection fractions,” Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, observed at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
This is an important new insight. The major randomized cardiovascular outcome trials that showed lower risks of heart failure hospitalization and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetic patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor, such as EMPA-REG OUTCOME for empagliflozin (Jardiance) and CANVAS for canagliflozin (Invokana), didn’t include information on baseline LVEF. So until now it has been unclear whether the beneficial effects of the SGLT2 inhibitors preventing heart failure hospitalization vary depending upon LVEF, explained Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo.
He presented an analysis drawn from the patient database kept by Maccabi Healthcare Services in Israel. The study included 5,307 patients with type 2 diabetes and an LVEF measurement recorded in their chart at the time they started on either empagliflozin or dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and an equal number of propensity-matched type 2 diabetic controls who started on other glucose-lowering drugs, most commonly an oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor.
During roughly 16,000 person-years of follow-up, 239 deaths occurred. Compared with patients on another glucose-lowering drug, the risk of death from all causes was reduced by 47% among patients who were on an SGLT2 inhibitor and had a baseline LVEF of 50% or greater and by 62% among the 9% of subjects who had a baseline LVEF less than 50%.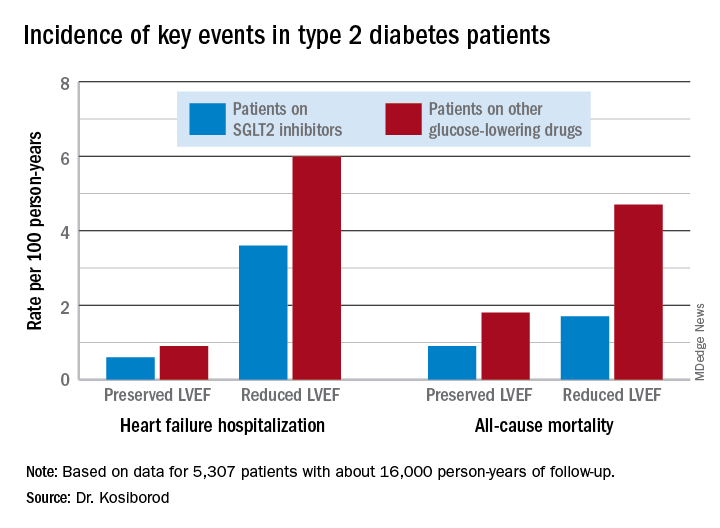
Similarly, the risk of heart failure hospitalization was reduced by 29% in SGLT2 inhibitor users with a preserved LVEF and by 27% if they had a reduced LVEF.
For the composite endpoint of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the risk reductions associated with SGLT2 inhibitor therapy were 45% with preserved and 39% with reduced LVEF.
Session comoderator Prakash C. Deedwania, MD, noted that there are ongoing major randomized trials of various SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with known heart failure, with cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization as primary endpoints. He asked Dr. Kosiborod whether, given that the results of these studies aren’t in yet, he thinks clinicians should be prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors to diabetic or prediabetic patients who don’t have clinical symptoms of heart failure but may have a marker of increased risk, such as an elevated B-type natriuretic peptide.
“At least in my mind, we have more than enough evidence at this point to say that SGLT2 inhibitors are effective in preventing heart failure,” Dr. Kosiborod replied.
“Obviously, if your risk for developing a condition is higher at baseline, then the absolute benefit that you’re going to get from using an agent that’s effective in preventing that event is going to be higher and the number needed to treat is going to be lower. So if you have a patient at high risk for heart failure by whatever risk predictor you’re using and the patient doesn’t yet have heart failure but does have diabetes, which is already a risk factor for heart failure, I think we have pretty solid data now that SGLT2 inhibitors will likely be effective in preventing heart failure in that kind of patient population. But I don’t think we have definitive data at this point to say that the drugs are effective in treating heart failure in people who already have a manifest clinical syndrome of heart failure, which is why we’re doing all these clinical trials now,” he continued.
Dr. Deedwania urged audience members to make the effort to become comfortable in prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors for their patients with type 2 diabetes.
“Many different surveys show that these drugs are not being utilized effectively by cardiologists,” noted Dr. Deedwania, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the heart failure program at the university’s Fresno campus.
“As cardiologists, we may not want to own diabetes, but we at least have to feel that we have the ownership of treating the diabetic patient with cardiovascular disease with appropriate drugs. We don’t need to depend on endocrinologists because if we do these patients may become lost,” he said.
Dr. Kosiborod concurred, citing evidence that diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease are much more likely to see a cardiologist than an endocrinologist in the course of usual care.
“There’s definitely a golden opportunity here to intervene to reduce risk,” he said.
Dr. Kosiborod reported serving as a consultant to roughly a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Kosiborod M. ACC 19, Abstract #1024-07.
NEW ORLEANS – based on data from a large real-world patient registry.
“The observed beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure may extend across the range of baseline ejection fractions,” Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, observed at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
This is an important new insight. The major randomized cardiovascular outcome trials that showed lower risks of heart failure hospitalization and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetic patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor, such as EMPA-REG OUTCOME for empagliflozin (Jardiance) and CANVAS for canagliflozin (Invokana), didn’t include information on baseline LVEF. So until now it has been unclear whether the beneficial effects of the SGLT2 inhibitors preventing heart failure hospitalization vary depending upon LVEF, explained Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo.
He presented an analysis drawn from the patient database kept by Maccabi Healthcare Services in Israel. The study included 5,307 patients with type 2 diabetes and an LVEF measurement recorded in their chart at the time they started on either empagliflozin or dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and an equal number of propensity-matched type 2 diabetic controls who started on other glucose-lowering drugs, most commonly an oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor.
During roughly 16,000 person-years of follow-up, 239 deaths occurred. Compared with patients on another glucose-lowering drug, the risk of death from all causes was reduced by 47% among patients who were on an SGLT2 inhibitor and had a baseline LVEF of 50% or greater and by 62% among the 9% of subjects who had a baseline LVEF less than 50%.
Similarly, the risk of heart failure hospitalization was reduced by 29% in SGLT2 inhibitor users with a preserved LVEF and by 27% if they had a reduced LVEF.
For the composite endpoint of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the risk reductions associated with SGLT2 inhibitor therapy were 45% with preserved and 39% with reduced LVEF.
Session comoderator Prakash C. Deedwania, MD, noted that there are ongoing major randomized trials of various SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with known heart failure, with cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization as primary endpoints. He asked Dr. Kosiborod whether, given that the results of these studies aren’t in yet, he thinks clinicians should be prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors to diabetic or prediabetic patients who don’t have clinical symptoms of heart failure but may have a marker of increased risk, such as an elevated B-type natriuretic peptide.
“At least in my mind, we have more than enough evidence at this point to say that SGLT2 inhibitors are effective in preventing heart failure,” Dr. Kosiborod replied.
“Obviously, if your risk for developing a condition is higher at baseline, then the absolute benefit that you’re going to get from using an agent that’s effective in preventing that event is going to be higher and the number needed to treat is going to be lower. So if you have a patient at high risk for heart failure by whatever risk predictor you’re using and the patient doesn’t yet have heart failure but does have diabetes, which is already a risk factor for heart failure, I think we have pretty solid data now that SGLT2 inhibitors will likely be effective in preventing heart failure in that kind of patient population. But I don’t think we have definitive data at this point to say that the drugs are effective in treating heart failure in people who already have a manifest clinical syndrome of heart failure, which is why we’re doing all these clinical trials now,” he continued.
Dr. Deedwania urged audience members to make the effort to become comfortable in prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors for their patients with type 2 diabetes.
“Many different surveys show that these drugs are not being utilized effectively by cardiologists,” noted Dr. Deedwania, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the heart failure program at the university’s Fresno campus.
“As cardiologists, we may not want to own diabetes, but we at least have to feel that we have the ownership of treating the diabetic patient with cardiovascular disease with appropriate drugs. We don’t need to depend on endocrinologists because if we do these patients may become lost,” he said.
Dr. Kosiborod concurred, citing evidence that diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease are much more likely to see a cardiologist than an endocrinologist in the course of usual care.
“There’s definitely a golden opportunity here to intervene to reduce risk,” he said.
Dr. Kosiborod reported serving as a consultant to roughly a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Kosiborod M. ACC 19, Abstract #1024-07.
NEW ORLEANS – based on data from a large real-world patient registry.
“The observed beneficial effects of SGLT2 inhibitors on heart failure may extend across the range of baseline ejection fractions,” Mikhail Kosiborod, MD, observed at the annual meeting of the American College of Cardiology.
This is an important new insight. The major randomized cardiovascular outcome trials that showed lower risks of heart failure hospitalization and all-cause mortality in type 2 diabetic patients on an SGLT2 inhibitor, such as EMPA-REG OUTCOME for empagliflozin (Jardiance) and CANVAS for canagliflozin (Invokana), didn’t include information on baseline LVEF. So until now it has been unclear whether the beneficial effects of the SGLT2 inhibitors preventing heart failure hospitalization vary depending upon LVEF, explained Dr. Kosiborod, a cardiologist at Saint Luke’s Mid America Heart Institute in Kansas City, Mo.
He presented an analysis drawn from the patient database kept by Maccabi Healthcare Services in Israel. The study included 5,307 patients with type 2 diabetes and an LVEF measurement recorded in their chart at the time they started on either empagliflozin or dapagliflozin (Farxiga) and an equal number of propensity-matched type 2 diabetic controls who started on other glucose-lowering drugs, most commonly an oral dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitor.
During roughly 16,000 person-years of follow-up, 239 deaths occurred. Compared with patients on another glucose-lowering drug, the risk of death from all causes was reduced by 47% among patients who were on an SGLT2 inhibitor and had a baseline LVEF of 50% or greater and by 62% among the 9% of subjects who had a baseline LVEF less than 50%.
Similarly, the risk of heart failure hospitalization was reduced by 29% in SGLT2 inhibitor users with a preserved LVEF and by 27% if they had a reduced LVEF.
For the composite endpoint of heart failure hospitalization or all-cause mortality, the risk reductions associated with SGLT2 inhibitor therapy were 45% with preserved and 39% with reduced LVEF.
Session comoderator Prakash C. Deedwania, MD, noted that there are ongoing major randomized trials of various SGLT2 inhibitors in patients with known heart failure, with cardiovascular death and heart failure hospitalization as primary endpoints. He asked Dr. Kosiborod whether, given that the results of these studies aren’t in yet, he thinks clinicians should be prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors to diabetic or prediabetic patients who don’t have clinical symptoms of heart failure but may have a marker of increased risk, such as an elevated B-type natriuretic peptide.
“At least in my mind, we have more than enough evidence at this point to say that SGLT2 inhibitors are effective in preventing heart failure,” Dr. Kosiborod replied.
“Obviously, if your risk for developing a condition is higher at baseline, then the absolute benefit that you’re going to get from using an agent that’s effective in preventing that event is going to be higher and the number needed to treat is going to be lower. So if you have a patient at high risk for heart failure by whatever risk predictor you’re using and the patient doesn’t yet have heart failure but does have diabetes, which is already a risk factor for heart failure, I think we have pretty solid data now that SGLT2 inhibitors will likely be effective in preventing heart failure in that kind of patient population. But I don’t think we have definitive data at this point to say that the drugs are effective in treating heart failure in people who already have a manifest clinical syndrome of heart failure, which is why we’re doing all these clinical trials now,” he continued.
Dr. Deedwania urged audience members to make the effort to become comfortable in prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors for their patients with type 2 diabetes.
“Many different surveys show that these drugs are not being utilized effectively by cardiologists,” noted Dr. Deedwania, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and director of the heart failure program at the university’s Fresno campus.
“As cardiologists, we may not want to own diabetes, but we at least have to feel that we have the ownership of treating the diabetic patient with cardiovascular disease with appropriate drugs. We don’t need to depend on endocrinologists because if we do these patients may become lost,” he said.
Dr. Kosiborod concurred, citing evidence that diabetic patients with cardiovascular disease are much more likely to see a cardiologist than an endocrinologist in the course of usual care.
“There’s definitely a golden opportunity here to intervene to reduce risk,” he said.
Dr. Kosiborod reported serving as a consultant to roughly a dozen pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Kosiborod M. ACC 19, Abstract #1024-07.
REPORTING FROM ACC 19
Short-term use of CGMs can deliver life-changing data for patients with type 2 diabetes
LOS ANGELES – Cardiology patients can strap on a Holter monitor for a day or two to track their heart activity and get a brief but helpful glimpse at their cardiac health. Could patients with type 2 diabetes benefit by monitoring their blood sugar for a short period? Absolutely, according to an endocrinologist who says he’s had tremendous success with the temporary use of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in appropriate patients.
“There’s an actionable surprise with almost every patient,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, FACP, FACE, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute and clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
The key is to use CGM data to pinpoint glucose spikes and then quickly make adjustments, typically over a period of 2 weeks. “This is about pattern recognition. We can do [CGM] over a week, see what the pattern is, and then try to fix something. Then they come back after the second week or send [the monitor] in, and they have the problem fixed. You have a happy patient and a happy family,” said Dr. Einhorn, who spoke in a presentation at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
He highlighted how CGM data allow patients to track their blood sugar over extended periods of time and detect patterns. The data can uncover hidden hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, he said, and is much more useful to patients than the self-monitoring of glucose levels or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) data.
Reading the patterns, adjusting behavior
Dr. Einhorn discussed several specific cases of patients who had changed their behavior in regard to food or medicine after CGM data disclosed certain blood sugar patterns.
Often, he said, patients say they’re surprised to find their well-being improves after they make adjustments, saying something along the lines of “I didn’t feel badly, but I feel better now.” According to Dr. Einhorn, “You hear that all the time.”
For example, he said, one patient knew his blood sugar occasionally topped 200 mg/dL, but he felt all right and didn’t want to take insulin. CGM monitoring over 6 days showed the patient had continuous glucose levels well over 200 mg/dL, especially at night. The patient accepted insulin, and a few months later his HbA1c dropped from 10.4% to 6.6%, and his blood sugar level stayed near or below the target range of 154 mg/dL.
Dr. Einhorn said the CGM data can reveal a range of problems, including:
- The “breakfast bump” after carbohydrate-heavy breakfasts of cereal, toast, and juice. “Breakfast cereal is diabolical,” he said.
- Hypoglycemia hours after exercise.
- Nocturnal hypoglycemia.
- Hypoglycemia unawareness.
Insurance coverage of the CGM device varies widely, he said, and insurers may not cover it at all in type 2 diabetes or only pay if the patient takes insulin. Fortunately, he said, the devices can be inexpensive.
Temporary use is not for everyone
Dr. Einhorn cautioned that temporary use of CGM is not appropriate for every patient with type 2 diabetes. “There’s absolutely a place for [permanent] monitoring for those people who have to make decisions throughout the day, especially if they are taking insulin,” he said.
And anyone with type 1 diabetes should use CGM on an ongoing basis, he emphasized. “Type 1 is a different world, a different universe,” he said.
He also noted that some patients don’t fare well on CGM, even on a temporary basis. That would include patients who hate to wear devices (possibly out of embarrassment), those who can’t manage to switch over from self-monitoring, and those who can’t manage to understand the data.
Dr. Einhorn disclosed various types of relationships with a number of drug makers, including Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo, Sanofi, Janssen, and others.
LOS ANGELES – Cardiology patients can strap on a Holter monitor for a day or two to track their heart activity and get a brief but helpful glimpse at their cardiac health. Could patients with type 2 diabetes benefit by monitoring their blood sugar for a short period? Absolutely, according to an endocrinologist who says he’s had tremendous success with the temporary use of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in appropriate patients.
“There’s an actionable surprise with almost every patient,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, FACP, FACE, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute and clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
The key is to use CGM data to pinpoint glucose spikes and then quickly make adjustments, typically over a period of 2 weeks. “This is about pattern recognition. We can do [CGM] over a week, see what the pattern is, and then try to fix something. Then they come back after the second week or send [the monitor] in, and they have the problem fixed. You have a happy patient and a happy family,” said Dr. Einhorn, who spoke in a presentation at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
He highlighted how CGM data allow patients to track their blood sugar over extended periods of time and detect patterns. The data can uncover hidden hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, he said, and is much more useful to patients than the self-monitoring of glucose levels or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) data.
Reading the patterns, adjusting behavior
Dr. Einhorn discussed several specific cases of patients who had changed their behavior in regard to food or medicine after CGM data disclosed certain blood sugar patterns.
Often, he said, patients say they’re surprised to find their well-being improves after they make adjustments, saying something along the lines of “I didn’t feel badly, but I feel better now.” According to Dr. Einhorn, “You hear that all the time.”
For example, he said, one patient knew his blood sugar occasionally topped 200 mg/dL, but he felt all right and didn’t want to take insulin. CGM monitoring over 6 days showed the patient had continuous glucose levels well over 200 mg/dL, especially at night. The patient accepted insulin, and a few months later his HbA1c dropped from 10.4% to 6.6%, and his blood sugar level stayed near or below the target range of 154 mg/dL.
Dr. Einhorn said the CGM data can reveal a range of problems, including:
- The “breakfast bump” after carbohydrate-heavy breakfasts of cereal, toast, and juice. “Breakfast cereal is diabolical,” he said.
- Hypoglycemia hours after exercise.
- Nocturnal hypoglycemia.
- Hypoglycemia unawareness.
Insurance coverage of the CGM device varies widely, he said, and insurers may not cover it at all in type 2 diabetes or only pay if the patient takes insulin. Fortunately, he said, the devices can be inexpensive.
Temporary use is not for everyone
Dr. Einhorn cautioned that temporary use of CGM is not appropriate for every patient with type 2 diabetes. “There’s absolutely a place for [permanent] monitoring for those people who have to make decisions throughout the day, especially if they are taking insulin,” he said.
And anyone with type 1 diabetes should use CGM on an ongoing basis, he emphasized. “Type 1 is a different world, a different universe,” he said.
He also noted that some patients don’t fare well on CGM, even on a temporary basis. That would include patients who hate to wear devices (possibly out of embarrassment), those who can’t manage to switch over from self-monitoring, and those who can’t manage to understand the data.
Dr. Einhorn disclosed various types of relationships with a number of drug makers, including Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo, Sanofi, Janssen, and others.
LOS ANGELES – Cardiology patients can strap on a Holter monitor for a day or two to track their heart activity and get a brief but helpful glimpse at their cardiac health. Could patients with type 2 diabetes benefit by monitoring their blood sugar for a short period? Absolutely, according to an endocrinologist who says he’s had tremendous success with the temporary use of continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) in appropriate patients.
“There’s an actionable surprise with almost every patient,” said Daniel Einhorn, MD, FACP, FACE, medical director of Scripps Whittier Diabetes Institute and clinical professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
The key is to use CGM data to pinpoint glucose spikes and then quickly make adjustments, typically over a period of 2 weeks. “This is about pattern recognition. We can do [CGM] over a week, see what the pattern is, and then try to fix something. Then they come back after the second week or send [the monitor] in, and they have the problem fixed. You have a happy patient and a happy family,” said Dr. Einhorn, who spoke in a presentation at the annual scientific and clinical congress of the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists.
He highlighted how CGM data allow patients to track their blood sugar over extended periods of time and detect patterns. The data can uncover hidden hypoglycemia and hyperglycemia, he said, and is much more useful to patients than the self-monitoring of glucose levels or hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) data.
Reading the patterns, adjusting behavior
Dr. Einhorn discussed several specific cases of patients who had changed their behavior in regard to food or medicine after CGM data disclosed certain blood sugar patterns.
Often, he said, patients say they’re surprised to find their well-being improves after they make adjustments, saying something along the lines of “I didn’t feel badly, but I feel better now.” According to Dr. Einhorn, “You hear that all the time.”
For example, he said, one patient knew his blood sugar occasionally topped 200 mg/dL, but he felt all right and didn’t want to take insulin. CGM monitoring over 6 days showed the patient had continuous glucose levels well over 200 mg/dL, especially at night. The patient accepted insulin, and a few months later his HbA1c dropped from 10.4% to 6.6%, and his blood sugar level stayed near or below the target range of 154 mg/dL.
Dr. Einhorn said the CGM data can reveal a range of problems, including:
- The “breakfast bump” after carbohydrate-heavy breakfasts of cereal, toast, and juice. “Breakfast cereal is diabolical,” he said.
- Hypoglycemia hours after exercise.
- Nocturnal hypoglycemia.
- Hypoglycemia unawareness.
Insurance coverage of the CGM device varies widely, he said, and insurers may not cover it at all in type 2 diabetes or only pay if the patient takes insulin. Fortunately, he said, the devices can be inexpensive.
Temporary use is not for everyone
Dr. Einhorn cautioned that temporary use of CGM is not appropriate for every patient with type 2 diabetes. “There’s absolutely a place for [permanent] monitoring for those people who have to make decisions throughout the day, especially if they are taking insulin,” he said.
And anyone with type 1 diabetes should use CGM on an ongoing basis, he emphasized. “Type 1 is a different world, a different universe,” he said.
He also noted that some patients don’t fare well on CGM, even on a temporary basis. That would include patients who hate to wear devices (possibly out of embarrassment), those who can’t manage to switch over from self-monitoring, and those who can’t manage to understand the data.
Dr. Einhorn disclosed various types of relationships with a number of drug makers, including Abbott, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo, Sanofi, Janssen, and others.
REPORTING FROM AACE 2019
AACE 2019: Top takeaways from Yehuda Handelsman and Paul Jellinger
in a video interview at the meeting.
Dr. Handelsman, medical director of the Metabolic Institute of America, in Tarzana, Calif., summarized the top take-home messages from a premeeting symposium he chaired on diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and lipid management in high-risk patients. Dr. Jellinger, professor of clinical medicine on the voluntary faculty at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, looked at management aspects and therapy goals based on a comparison of the lipid guideline from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association with that from the AACE. Other highlights from the symposium included expert analysis of the CREDENCE trial results on canagliflozin for improving renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes, advice on the management of heart failure in diabetes, and recommendations on managing hyperglycemia.
Dr. Jellinger and Dr. Handelsman, who are members of the editorial advisory board of Clinical Endocrinology News, highlighted the emergence of anabolic treatments for osteoporosis, in particular the sclerostin-neutralizing monoclonal antibody, romosozumab. The therapy was recently approved for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and is unique in that it both promotes bone formation and reduces resorption. They also noted the switch away from previous practice to now using an anabolic drug first, then going to an antiresorptive therapy, rather than the other way around.
They discussed the keynote address by social media guru, Kevin Pho, MD; a debate that centered on the merits of the American Diabetes Association’s guideline for treating diabetes versus that from the AACE; a presentation on sustained remission of type 2 diabetes with a very low calorie diet; and a report on encouraging findings with an experimental drug for Graves eye disease.
in a video interview at the meeting.
Dr. Handelsman, medical director of the Metabolic Institute of America, in Tarzana, Calif., summarized the top take-home messages from a premeeting symposium he chaired on diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and lipid management in high-risk patients. Dr. Jellinger, professor of clinical medicine on the voluntary faculty at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, looked at management aspects and therapy goals based on a comparison of the lipid guideline from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association with that from the AACE. Other highlights from the symposium included expert analysis of the CREDENCE trial results on canagliflozin for improving renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes, advice on the management of heart failure in diabetes, and recommendations on managing hyperglycemia.
Dr. Jellinger and Dr. Handelsman, who are members of the editorial advisory board of Clinical Endocrinology News, highlighted the emergence of anabolic treatments for osteoporosis, in particular the sclerostin-neutralizing monoclonal antibody, romosozumab. The therapy was recently approved for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and is unique in that it both promotes bone formation and reduces resorption. They also noted the switch away from previous practice to now using an anabolic drug first, then going to an antiresorptive therapy, rather than the other way around.
They discussed the keynote address by social media guru, Kevin Pho, MD; a debate that centered on the merits of the American Diabetes Association’s guideline for treating diabetes versus that from the AACE; a presentation on sustained remission of type 2 diabetes with a very low calorie diet; and a report on encouraging findings with an experimental drug for Graves eye disease.
in a video interview at the meeting.
Dr. Handelsman, medical director of the Metabolic Institute of America, in Tarzana, Calif., summarized the top take-home messages from a premeeting symposium he chaired on diabetes, cardiovascular disease (CVD), and lipid management in high-risk patients. Dr. Jellinger, professor of clinical medicine on the voluntary faculty at the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, looked at management aspects and therapy goals based on a comparison of the lipid guideline from the American College of Cardiology and the American Heart Association with that from the AACE. Other highlights from the symposium included expert analysis of the CREDENCE trial results on canagliflozin for improving renal outcomes in patients with type 2 diabetes, advice on the management of heart failure in diabetes, and recommendations on managing hyperglycemia.
Dr. Jellinger and Dr. Handelsman, who are members of the editorial advisory board of Clinical Endocrinology News, highlighted the emergence of anabolic treatments for osteoporosis, in particular the sclerostin-neutralizing monoclonal antibody, romosozumab. The therapy was recently approved for the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis and is unique in that it both promotes bone formation and reduces resorption. They also noted the switch away from previous practice to now using an anabolic drug first, then going to an antiresorptive therapy, rather than the other way around.
They discussed the keynote address by social media guru, Kevin Pho, MD; a debate that centered on the merits of the American Diabetes Association’s guideline for treating diabetes versus that from the AACE; a presentation on sustained remission of type 2 diabetes with a very low calorie diet; and a report on encouraging findings with an experimental drug for Graves eye disease.
REPORTING FROM AACE 2019
ERRATUM
A recent letter, “Hypoglycemia in the elderly: Watch for atypical symptoms” (J Fam Pract. 2019;68:116) provided an incomplete list of the letter’s authors. The list should have read: Jan Brož, MD, Jana Urbanová, MD, PhD, Prague, Czech Republic; Brian M. Frier, MD, BSc, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
A recent letter, “Hypoglycemia in the elderly: Watch for atypical symptoms” (J Fam Pract. 2019;68:116) provided an incomplete list of the letter’s authors. The list should have read: Jan Brož, MD, Jana Urbanová, MD, PhD, Prague, Czech Republic; Brian M. Frier, MD, BSc, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
A recent letter, “Hypoglycemia in the elderly: Watch for atypical symptoms” (J Fam Pract. 2019;68:116) provided an incomplete list of the letter’s authors. The list should have read: Jan Brož, MD, Jana Urbanová, MD, PhD, Prague, Czech Republic; Brian M. Frier, MD, BSc, Edinburgh, United Kingdom.
FDA approves Qternmet XR as adjunct therapy for glycemic improvement in type 2 diabetes
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Qternmet XR (dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin) as an oral adjunct therapy to diet and exercise for the improvement of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to AstraZeneca.
FDA approval is based on results from a pair of phase 3 trials that tested different combinations of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes who were also receiving metformin over a 24-week period. In both trials, treatment with dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin decreased hemoglobin A1c by statistically significant amounts, and increased the number of patients with HbA1c levels below 7%
The safety results of Qternmet XR was consistent with each component medication’s known profile.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Qternmet XR (dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin) as an oral adjunct therapy to diet and exercise for the improvement of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to AstraZeneca.
FDA approval is based on results from a pair of phase 3 trials that tested different combinations of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes who were also receiving metformin over a 24-week period. In both trials, treatment with dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin decreased hemoglobin A1c by statistically significant amounts, and increased the number of patients with HbA1c levels below 7%
The safety results of Qternmet XR was consistent with each component medication’s known profile.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved Qternmet XR (dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin) as an oral adjunct therapy to diet and exercise for the improvement of glycemic control in patients with type 2 diabetes, according to AstraZeneca.
FDA approval is based on results from a pair of phase 3 trials that tested different combinations of dapagliflozin and saxagliptin in patients with inadequately controlled type 2 diabetes who were also receiving metformin over a 24-week period. In both trials, treatment with dapagliflozin/saxagliptin/metformin decreased hemoglobin A1c by statistically significant amounts, and increased the number of patients with HbA1c levels below 7%
The safety results of Qternmet XR was consistent with each component medication’s known profile.
Fournier gangrene cases surge in patients using SGLT2 inhibitors
since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a 2018 warning about this rare but serious infection, researchers say.
Health care providers prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors to patients with diabetes should have a high index of suspicion for the signs and symptoms of Fournier gangrene, given its substantial morbidity and mortality, according to Susan J. Bersoff-Matcha, MD, and her colleagues at the FDA.
“Although the risk for [Fournier gangrene] is low, serious infection should be considered and weighed against the benefits of SGLT2 inhibitor therapy,” said Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors in their recent report published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2019 May 6. doi: 10.7326/M19-0085).
In the previous warning, FDA officials said 12 cases of Fournier gangrene in patients taking an SGLT2 inhibitor had been reported to the agency or in medical literature from March 2013, when the first such inhibitor was approved, and May 2018.
In this latest report, a total of 55 Fournier gangrene cases had been reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors from March 2, 2013 through January 31, 2019.
The influx of reports may have been prompted by growing awareness of the safety issue, investigators said, but could also reflect the increasing prevalence of diabetes combined with SGLT2 inhibitor use. The researchers also noted that diabetes is a comorbidity in 32% to 66% of cases of Fournier gangrene.
But the likliehood that diabetes mellitus alone causes Fournier gangrene seems unlikley, given that Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors only found 19 Fournier gangrene cases associated with other classes of antiglycemic agents reported to the FDA or in the literature over a 35-year time frame.
“If Fournier gangrene were associated only with diabetes mellitus and not SGLT2 inhibitors, we would expect far more cases reported with the other antiglycemic agents, considering the 35-year timeframe and the large number of agents,” they said in their report.
Cases were reported for all FDA-approved SGLT2 inhibitors besides ertugliflozin, an agent approved for use in the U.S. in December 2017. The lack of cases reported for this drug could be related to its limited time on the market, the investigators said.
Fournier gangrene, marked by rapidly progressing necrotizing infection of the genitalia, perineum, and perianal region, requires antibiotics and immediate surgery, according to Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and colleagues.
“Serious complications and death are likely if Fournier gangrene is not recognized immediately and surgical intervention is not carried out within the first few hours of diagnosis,” they said in the report.
Of the 55 cases reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, 39 were men and 16 were women, with an average of 9 months from the start of treatment to the event, investigators said.
At least 25 patients required multiple surgeries, including one patient who had 17 trips to the operating room, they said. A total of 8 patients had a fecal diversion procedure, and 4 patients had skin grafting.
Six patients had multiple encounters with a provider before being diagnosed, suggesting that the provider may have not recognized the infection due to its nonspecific symptoms, which include fatigue, fever, and malaise.
“Pain that seems out of proportion to findings on physical examination is a strong clinical indicator of necrotizing fasciitis and may be the most important diagnostic clue,” Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors said in their report.
The incidence of Fournier gangrene in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors can’t be established by these cases reported to the FDA, which are spontaneously provided by health care providers and patients, investigators said.
“We suspect that our numbers underestimate the true burden,” they said in their report.
Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors disclosed no conflicts of interest related to their report.
SOURCE: Bersoff-Matcha SJ, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 May 6. Doi: doi:10.7326/M19-0085.
This article was updated May 9, 2019.
since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a 2018 warning about this rare but serious infection, researchers say.
Health care providers prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors to patients with diabetes should have a high index of suspicion for the signs and symptoms of Fournier gangrene, given its substantial morbidity and mortality, according to Susan J. Bersoff-Matcha, MD, and her colleagues at the FDA.
“Although the risk for [Fournier gangrene] is low, serious infection should be considered and weighed against the benefits of SGLT2 inhibitor therapy,” said Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors in their recent report published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2019 May 6. doi: 10.7326/M19-0085).
In the previous warning, FDA officials said 12 cases of Fournier gangrene in patients taking an SGLT2 inhibitor had been reported to the agency or in medical literature from March 2013, when the first such inhibitor was approved, and May 2018.
In this latest report, a total of 55 Fournier gangrene cases had been reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors from March 2, 2013 through January 31, 2019.
The influx of reports may have been prompted by growing awareness of the safety issue, investigators said, but could also reflect the increasing prevalence of diabetes combined with SGLT2 inhibitor use. The researchers also noted that diabetes is a comorbidity in 32% to 66% of cases of Fournier gangrene.
But the likliehood that diabetes mellitus alone causes Fournier gangrene seems unlikley, given that Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors only found 19 Fournier gangrene cases associated with other classes of antiglycemic agents reported to the FDA or in the literature over a 35-year time frame.
“If Fournier gangrene were associated only with diabetes mellitus and not SGLT2 inhibitors, we would expect far more cases reported with the other antiglycemic agents, considering the 35-year timeframe and the large number of agents,” they said in their report.
Cases were reported for all FDA-approved SGLT2 inhibitors besides ertugliflozin, an agent approved for use in the U.S. in December 2017. The lack of cases reported for this drug could be related to its limited time on the market, the investigators said.
Fournier gangrene, marked by rapidly progressing necrotizing infection of the genitalia, perineum, and perianal region, requires antibiotics and immediate surgery, according to Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and colleagues.
“Serious complications and death are likely if Fournier gangrene is not recognized immediately and surgical intervention is not carried out within the first few hours of diagnosis,” they said in the report.
Of the 55 cases reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, 39 were men and 16 were women, with an average of 9 months from the start of treatment to the event, investigators said.
At least 25 patients required multiple surgeries, including one patient who had 17 trips to the operating room, they said. A total of 8 patients had a fecal diversion procedure, and 4 patients had skin grafting.
Six patients had multiple encounters with a provider before being diagnosed, suggesting that the provider may have not recognized the infection due to its nonspecific symptoms, which include fatigue, fever, and malaise.
“Pain that seems out of proportion to findings on physical examination is a strong clinical indicator of necrotizing fasciitis and may be the most important diagnostic clue,” Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors said in their report.
The incidence of Fournier gangrene in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors can’t be established by these cases reported to the FDA, which are spontaneously provided by health care providers and patients, investigators said.
“We suspect that our numbers underestimate the true burden,” they said in their report.
Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors disclosed no conflicts of interest related to their report.
SOURCE: Bersoff-Matcha SJ, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 May 6. Doi: doi:10.7326/M19-0085.
This article was updated May 9, 2019.
since the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) issued a 2018 warning about this rare but serious infection, researchers say.
Health care providers prescribing SGLT2 inhibitors to patients with diabetes should have a high index of suspicion for the signs and symptoms of Fournier gangrene, given its substantial morbidity and mortality, according to Susan J. Bersoff-Matcha, MD, and her colleagues at the FDA.
“Although the risk for [Fournier gangrene] is low, serious infection should be considered and weighed against the benefits of SGLT2 inhibitor therapy,” said Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors in their recent report published in the Annals of Internal Medicine (2019 May 6. doi: 10.7326/M19-0085).
In the previous warning, FDA officials said 12 cases of Fournier gangrene in patients taking an SGLT2 inhibitor had been reported to the agency or in medical literature from March 2013, when the first such inhibitor was approved, and May 2018.
In this latest report, a total of 55 Fournier gangrene cases had been reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors from March 2, 2013 through January 31, 2019.
The influx of reports may have been prompted by growing awareness of the safety issue, investigators said, but could also reflect the increasing prevalence of diabetes combined with SGLT2 inhibitor use. The researchers also noted that diabetes is a comorbidity in 32% to 66% of cases of Fournier gangrene.
But the likliehood that diabetes mellitus alone causes Fournier gangrene seems unlikley, given that Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors only found 19 Fournier gangrene cases associated with other classes of antiglycemic agents reported to the FDA or in the literature over a 35-year time frame.
“If Fournier gangrene were associated only with diabetes mellitus and not SGLT2 inhibitors, we would expect far more cases reported with the other antiglycemic agents, considering the 35-year timeframe and the large number of agents,” they said in their report.
Cases were reported for all FDA-approved SGLT2 inhibitors besides ertugliflozin, an agent approved for use in the U.S. in December 2017. The lack of cases reported for this drug could be related to its limited time on the market, the investigators said.
Fournier gangrene, marked by rapidly progressing necrotizing infection of the genitalia, perineum, and perianal region, requires antibiotics and immediate surgery, according to Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and colleagues.
“Serious complications and death are likely if Fournier gangrene is not recognized immediately and surgical intervention is not carried out within the first few hours of diagnosis,” they said in the report.
Of the 55 cases reported in patients receiving SGLT2 inhibitors, 39 were men and 16 were women, with an average of 9 months from the start of treatment to the event, investigators said.
At least 25 patients required multiple surgeries, including one patient who had 17 trips to the operating room, they said. A total of 8 patients had a fecal diversion procedure, and 4 patients had skin grafting.
Six patients had multiple encounters with a provider before being diagnosed, suggesting that the provider may have not recognized the infection due to its nonspecific symptoms, which include fatigue, fever, and malaise.
“Pain that seems out of proportion to findings on physical examination is a strong clinical indicator of necrotizing fasciitis and may be the most important diagnostic clue,” Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors said in their report.
The incidence of Fournier gangrene in patients taking SGLT2 inhibitors can’t be established by these cases reported to the FDA, which are spontaneously provided by health care providers and patients, investigators said.
“We suspect that our numbers underestimate the true burden,” they said in their report.
Dr. Bersoff-Matcha and co-authors disclosed no conflicts of interest related to their report.
SOURCE: Bersoff-Matcha SJ, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 May 6. Doi: doi:10.7326/M19-0085.
This article was updated May 9, 2019.
FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Key clinical point: The number of Fournier gangrene cases reported in patients receiving sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) inhibitors has increased in the time since an FDA warning was issued about this rare but potentially serious infection.
Major finding: The previous FDA warning noted 12 reported cases from March 1, 2013 through March 1, 2018. This latest report included a total of 55 cases reported through January 31, 2019.
Study details: A review of spontaneous postmarketing cases of Fournier gangrene reported to the FDA or in the medical literature.
Disclosures: Authors disclosed no conflicts of interest related to the study.
Source: Bersoff-Matcha SJ, et al. Ann Intern Med. 2019 May 6.







