User login
A plane crash interrupts a doctor’s vacation
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Emergencies happen anywhere, anytime – and sometimes physicians find themselves in situations where they are the only ones who can help. “Is There a Doctor in the House?” is a new series telling these stories.
When the plane crashed, I was asleep. I had arrived the evening before with my wife and three sons at a house on Kezar Lake on the Maine–New Hampshire border. I jumped out of bed and ran downstairs. My kids had been watching a float plane circling and gliding along the lake. It had crashed into the water and flipped upside down. My oldest brother-in-law jumped into his ski boat and we sped out to the scene.
All we can see are the plane’s pontoons. The rest is underwater. A woman has already surfaced, screaming. I dive in.
I find the woman’s husband and 3-year-old son struggling to get free from the plane through the smashed windshield. They manage to get to the surface. The pilot is dead, impaled through the chest by the left wing strut.
The big problem: A little girl, whom I would learn later is named Lauren, remained trapped. The water is murky but I can see her, a 5- or 6-year-old girl with this long hair, strapped in upside down and unconscious.
The mom and I dive down over and over, pulling and ripping at the door. We cannot get it open. Finally, I’m able to bend the door open enough where I can reach in, but I can’t undo the seatbelt. In my mind, I’m debating, should I try and go through the front windshield? I’m getting really tired, I can tell there’s fuel in the water, and I don’t want to drown in the plane. So I pop up to the surface and yell, “Does anyone have a knife?”
My brother-in-law shoots back to shore in the boat, screaming, “Get a knife!” My niece gets in the boat with one. I’m standing on the pontoon, and my niece is in the front of the boat calling, “Uncle Todd! Uncle Todd!” and she throws the knife. It goes way over my head. I can’t even jump for it, it’s so high.
I have to get the knife. So, I dive into the water to try and find it. Somehow, the black knife has landed on the white wing, 4 or 5 feet under the water. Pure luck. It could have sunk down a hundred feet into the lake. I grab the knife and hand it to the mom, Beth. She’s able to cut the seatbelt, and we both pull Lauren to the surface.
I lay her out on the pontoon. She has no pulse and her pupils are fixed and dilated. Her mom is yelling, “She’s dead, isn’t she?” I start CPR. My skin and eyes are burning from the airplane fuel in the water. I get her breathing, and her heart comes back very quickly. Lauren starts to vomit and I’m trying to keep her airway clear. She’s breathing spontaneously and she has a pulse, so I decide it’s time to move her to shore.
We pull the boat up to the dock and Lauren’s now having anoxic seizures. Her brain has been without oxygen, and now she’s getting perfused again. We get her to shore and lay her on the lawn. I’m still doing mouth-to-mouth, but she’s seizing like crazy, and I don’t have any way to control that. Beth is crying and wants to hold her daughter gently while I’m working.
Someone had called 911, and finally this dude shows up with an ambulance, and it’s like something out of World War II. All he has is an oxygen tank, but the mask is old and cracked. It’s too big for Lauren, but it sort of fits me, so I’m sucking in oxygen and blowing it into the girl’s mouth. I’m doing whatever I can, but I don’t have an IV to start. I have no fluids. I got nothing.
As it happens, I’d done my emergency medicine training at Maine Medical Center, so I tell someone to call them and get a Life Flight chopper. We have to drive somewhere where the chopper can land, so we take the ambulance to the parking lot of the closest store called the Wicked Good Store. That’s a common thing in Maine. Everything is “wicked good.”
The whole town is there by that point. The chopper arrives. The ambulance doors pop open and a woman says, “Todd?” And I say, “Heather?”
Heather is an emergency flight nurse whom I’d trained with many years ago. There’s immediate trust. She has all the right equipment. We put in breathing tubes and IVs. We stop Lauren from seizing. The kid is soon stable.
There is only one extra seat in the chopper, so I tell Beth to go. They take off.
Suddenly, I begin to doubt my decision. Lauren had been underwater for 15 minutes at minimum. I know how long that is. Did I do the right thing? Did I resuscitate a brain-dead child? I didn’t think about it at the time, but if that patient had come to me in the emergency department, I’m honestly not sure what I would have done.
So, I go home. And I don’t get a call. The FAA and sheriff arrive to take statements from us. I don’t hear from anyone.
The next day I start calling. No one will tell me anything, so I finally get to one of the pediatric ICU attendings who had trained me. He says Lauren literally woke up and said, “I have to go pee.” And that was it. She was 100% normal. I couldn’t believe it.
Here’s a theory: In kids, there’s something called the glottic reflex. I think her glottic reflex went off as soon as she hit the water, which basically closed her airway. So when she passed out, she could never get enough water in her lungs and still had enough air in there to keep her alive. Later, I got a call from her uncle. He could barely get the words out because he was in tears. He said Lauren was doing beautifully.
Three days later, I drove to Lauren’s house with my wife and kids. I had her read to me. I watched her play on the jungle gym for motor function. All sorts of stuff. She was totally normal.
Beth told us that the night before the accident, her mother had given the women in her family what she called a “miracle bracelet,” a bracelet that is supposed to give you one miracle in your life. Beth said she had the bracelet on her wrist the day of the accident, and now it’s gone. “Saving Lauren’s life was my miracle,” she said.
Funny thing: For 20 years, I ran all the EMS, police, fire, ambulance, in Boulder, Colo., where I live. I wrote all the protocols, and I would never advise any of my paramedics to dive into jet fuel to save someone. That was risky. But at the time, it was totally automatic. I think it taught me not to give up in certain situations, because you really don’t know.
Dr. Dorfman is an emergency medicine physician in Boulder, Colo., and medical director at Cedalion Health.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is there a doctor on the plane? Tips for providing in-flight assistance
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.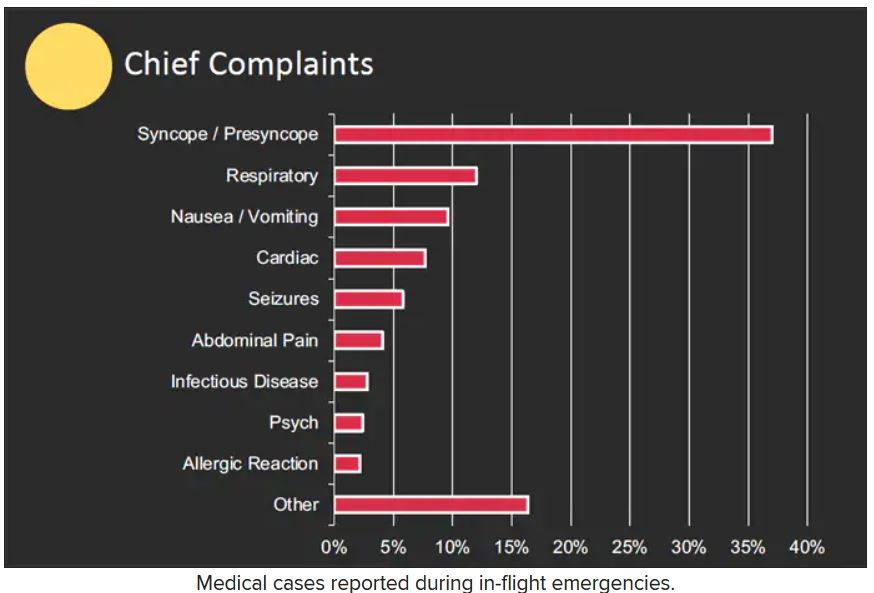
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In most cases, passengers on an airline flight are representative of the general population, which means that anyone could have an emergency at any time.
as determined on the basis of in-flight medical emergencies that resulted in calls to a physician-directed medical communications center, said Amy Faith Ho, MD, MPH of Integrative Emergency Services, Dallas–Fort Worth, in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians.
The study authors reviewed records of 11,920 in-flight medical emergencies between Jan. 1, 2008, and Oct. 31, 2010. The data showed that physician passengers provided medical assistance in nearly half of in-flight emergencies (48.1%) and that flights were diverted because of the emergency in 7.3% of cases.
The majority of the in-flight emergencies involved syncope or presyncope (37.4% of cases), followed by respiratory symptoms (12.1%) and nausea or vomiting (9.5%), according to the study.
When a physician is faced with an in-flight emergency, the medical team includes the physician himself, medical ground control, and the flight attendants, said Dr. Ho. Requirements may vary among airlines, but all flight attendants will be trained in cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) or basic life support, as well as use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs).
Physician call centers (medical ground control) can provide additional assistance remotely, she said.
The in-flight medical bag
Tools in a physician’s in-flight toolbox start with the first-aid kit. Airplanes also have an emergency medical kit (EMK), an oxygen tank, and an AED.
The minimum EMK contents are mandated by the Federal Aviation Administration, said Dr. Ho. The standard equipment includes a stethoscope, a sphygmomanometer, and three sizes of oropharyngeal airways. Other items include self-inflating manual resuscitation devices and CPR masks in thee sizes, alcohol sponges, gloves, adhesive tape, scissors, a tourniquet, as well as saline solution, needles, syringes, and an intravenous administration set consisting of tubing and two Y connectors.
An EMK also should contain the following medications: nonnarcotic analgesic tablets, antihistamine tablets, an injectable antihistamine, atropine, aspirin tablets, a bronchodilator, and epinephrine (both 1:1000; 1 injectable cc and 1:10,000; two injectable cc). Nitroglycerin tablets and 5 cc of 20 mg/mL injectable cardiac lidocaine are part of the mandated kit as well, according to Dr. Ho.
Some airlines carry additional supplies on all their flights, said Dr. Ho. Notably, American Airlines and British Airways carry EpiPens for adults and children, as well as opioid reversal medication (naloxone) and glucose for managing low blood sugar. American Airlines and Delta stock antiemetics, and Delta also carries naloxone. British Airways is unique in stocking additional cardiac medications, both oral and injectable.
How to handle an in-flight emergency
Physicians should always carry a copy of their medical license when traveling for documentation by the airline if they assist in a medical emergency during a flight, Dr. Ho emphasized. “Staff” personnel should be used. These include the flight attendants, medical ground control, and other passengers who might have useful skills, such as nursing, the ability to perform CPR, or therapy/counseling to calm a frightened patient. If needed, “crowdsource additional supplies from passengers,” such as a glucometer or pulse oximeter.
Legal lessons
Physicians are not obligated to assist during an in-flight medical emergency, said Dr. Ho. Legal jurisdiction can vary. In the United States, a bystander who assists in an emergency is generally protected by Good Samaritan laws; for international airlines, the laws may vary; those where the airline is based usually apply.
The Aviation Medical Assistance Act, passed in 1998, protects individuals from being sued for negligence while providing medical assistance, “unless the individual, while rendering such assistance, is guilty of gross negligence of willful misconduct,” Dr. Ho noted. The Aviation Medical Assistance Act also protects the airline itself “if the carrier in good faith believes that the passenger is a medically qualified individual.”
Dr. Ho disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ACEP 2022
Is opioid abuse leading to pediatric head trauma?
As a physician in the heart of the opioid epidemic, Pavirthra R. Ellison, MD, has watched for years as her patients have lost parents to overdoses. More than 1,400 adults in West Virginia, where she practices, died of opioid abuse in 2021 alone, government statistics show.
The grim toll made Ellison wonder: What was happening to children in the state? The answer, according to a new study, is not reassuring.
Ellison and her colleagues have found a troubling link between a surge in critical head and neck injuries among youth in West Virginia and a spike in positive tests for opioids and benzodiazepines among children who arrive at emergency departments in the state. They don’t think the pattern is a coincidence.
“What we found was really kind of scary,” said Dr. Ellison, a professor of anesthesiology and pediatrics at West Virginia University, Morgantown. “Children in this region often get exposure to these drugs early on.”
A region in crisis
According to a 2020 report from the Department of Health & Human Services, about 9.9 million Americans abused prescription opioids in 2018. That same year, almost 47,000 died following an overdose of the painkillers. In 2017, Appalachian counties experienced a death rate from opioid overdoses that was 72% higher than that of the rest of the country.
Dr. Ellison and associates who presented their findings recently at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, examined rates of pediatric trauma injuries, injury severity, and results of drug screenings throughout West Virginia between 2009 and 2019.
The study included 4,538 children and adolescents younger than 18 years who had been treated for head and neck trauma. The youth were divided into two groups: 3,356 who were treated from 2009 to 2016, and 1,182 who were treated between 2017 and 2019.
The incidence of critical head injuries increased from 3.7% in the period 2009-2016 to 7.2% in the period 2017-2019 (P = .007). The incidence of serious neck injuries increased from 12.2% to 27.1% (P = .007) during that period, according to the researchers. The number of days that these patients spent on ventilators more than doubled, from 3.1 to 6.3 (P < .001), they reported.
At the same time, the rate of positive urine drug tests rose sharply, from 0.8% to 1.8% (P < .001) for benzodiazepines and from 1% to 4.9% for opioids (P < .001).
Drug testing of children hospitalized for trauma rose more than threefold, from 6.9% to 23.2% (P < .001). Dr. Ellison’s group was unable to match positive drug screens with patients who came in with injuries.
Dr. Ellison said her research “warrants further evaluation of current policies and protocols targeting substance use in children and adolescents.” To that end, her team is planning to conduct a prospective study in mid 2023 to further illuminate the trends.
“I hope early next year we can put together a group of physicians, pediatric general surgeons, neurosurgeons, and anesthesiologists,” she said. “I want to look at what we can do to reduce the severity of injury.”
She also wants to reach the population that these findings directly affect.
“The next step that we are currently working on is community awareness of the issue,” Dr. Ellison said. “Our trauma institute is partnering with middle school and high school kids to create material to raise awareness.”
Rural Appalachia faces several other endemic problems that affect the health and well-being of children and families, including limited access to health care, poverty, and minimal community support, according to Dr. Ellison. Children and teens in the region who live with parents who abuse opioids are more likely to experience family conflict, mental health challenges, legal troubles, and negative health effects, including physical trauma.
A call to action
Toufic Jildeh, MD, assistant professor of orthopedics, Michigan State University Health Care, East Lansing, who has studied ways to reduce opioid use among surgery patients, called the new findings “alarming.”
After reviewing the study, Dr. Jildeh said that in his opinion, the results support standardized drug testing of children, particularly in the context of severe trauma.
Bruce Bassi, MD, an addiction psychiatrist and owner of TelepsychHealth, a private, online psychiatric practice, agreed. “The main take-home message is that drug screening should be the standard of care for pediatric patients in this region, because it changes the management of those individuals,” Dr. Bassi said.
But identifying these patients is just the first step. “We should continue to educate and raise awareness, not only in the health care system,” Dr. Bassi said. “We also need to let parents know that the possibility of children obtaining access to medications is high.”
The study was independently supported. Dr. Ellison and Dr. Jildeh reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bassi owns a private psychiatry practice called Telepsychhealth but has no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a physician in the heart of the opioid epidemic, Pavirthra R. Ellison, MD, has watched for years as her patients have lost parents to overdoses. More than 1,400 adults in West Virginia, where she practices, died of opioid abuse in 2021 alone, government statistics show.
The grim toll made Ellison wonder: What was happening to children in the state? The answer, according to a new study, is not reassuring.
Ellison and her colleagues have found a troubling link between a surge in critical head and neck injuries among youth in West Virginia and a spike in positive tests for opioids and benzodiazepines among children who arrive at emergency departments in the state. They don’t think the pattern is a coincidence.
“What we found was really kind of scary,” said Dr. Ellison, a professor of anesthesiology and pediatrics at West Virginia University, Morgantown. “Children in this region often get exposure to these drugs early on.”
A region in crisis
According to a 2020 report from the Department of Health & Human Services, about 9.9 million Americans abused prescription opioids in 2018. That same year, almost 47,000 died following an overdose of the painkillers. In 2017, Appalachian counties experienced a death rate from opioid overdoses that was 72% higher than that of the rest of the country.
Dr. Ellison and associates who presented their findings recently at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, examined rates of pediatric trauma injuries, injury severity, and results of drug screenings throughout West Virginia between 2009 and 2019.
The study included 4,538 children and adolescents younger than 18 years who had been treated for head and neck trauma. The youth were divided into two groups: 3,356 who were treated from 2009 to 2016, and 1,182 who were treated between 2017 and 2019.
The incidence of critical head injuries increased from 3.7% in the period 2009-2016 to 7.2% in the period 2017-2019 (P = .007). The incidence of serious neck injuries increased from 12.2% to 27.1% (P = .007) during that period, according to the researchers. The number of days that these patients spent on ventilators more than doubled, from 3.1 to 6.3 (P < .001), they reported.
At the same time, the rate of positive urine drug tests rose sharply, from 0.8% to 1.8% (P < .001) for benzodiazepines and from 1% to 4.9% for opioids (P < .001).
Drug testing of children hospitalized for trauma rose more than threefold, from 6.9% to 23.2% (P < .001). Dr. Ellison’s group was unable to match positive drug screens with patients who came in with injuries.
Dr. Ellison said her research “warrants further evaluation of current policies and protocols targeting substance use in children and adolescents.” To that end, her team is planning to conduct a prospective study in mid 2023 to further illuminate the trends.
“I hope early next year we can put together a group of physicians, pediatric general surgeons, neurosurgeons, and anesthesiologists,” she said. “I want to look at what we can do to reduce the severity of injury.”
She also wants to reach the population that these findings directly affect.
“The next step that we are currently working on is community awareness of the issue,” Dr. Ellison said. “Our trauma institute is partnering with middle school and high school kids to create material to raise awareness.”
Rural Appalachia faces several other endemic problems that affect the health and well-being of children and families, including limited access to health care, poverty, and minimal community support, according to Dr. Ellison. Children and teens in the region who live with parents who abuse opioids are more likely to experience family conflict, mental health challenges, legal troubles, and negative health effects, including physical trauma.
A call to action
Toufic Jildeh, MD, assistant professor of orthopedics, Michigan State University Health Care, East Lansing, who has studied ways to reduce opioid use among surgery patients, called the new findings “alarming.”
After reviewing the study, Dr. Jildeh said that in his opinion, the results support standardized drug testing of children, particularly in the context of severe trauma.
Bruce Bassi, MD, an addiction psychiatrist and owner of TelepsychHealth, a private, online psychiatric practice, agreed. “The main take-home message is that drug screening should be the standard of care for pediatric patients in this region, because it changes the management of those individuals,” Dr. Bassi said.
But identifying these patients is just the first step. “We should continue to educate and raise awareness, not only in the health care system,” Dr. Bassi said. “We also need to let parents know that the possibility of children obtaining access to medications is high.”
The study was independently supported. Dr. Ellison and Dr. Jildeh reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bassi owns a private psychiatry practice called Telepsychhealth but has no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a physician in the heart of the opioid epidemic, Pavirthra R. Ellison, MD, has watched for years as her patients have lost parents to overdoses. More than 1,400 adults in West Virginia, where she practices, died of opioid abuse in 2021 alone, government statistics show.
The grim toll made Ellison wonder: What was happening to children in the state? The answer, according to a new study, is not reassuring.
Ellison and her colleagues have found a troubling link between a surge in critical head and neck injuries among youth in West Virginia and a spike in positive tests for opioids and benzodiazepines among children who arrive at emergency departments in the state. They don’t think the pattern is a coincidence.
“What we found was really kind of scary,” said Dr. Ellison, a professor of anesthesiology and pediatrics at West Virginia University, Morgantown. “Children in this region often get exposure to these drugs early on.”
A region in crisis
According to a 2020 report from the Department of Health & Human Services, about 9.9 million Americans abused prescription opioids in 2018. That same year, almost 47,000 died following an overdose of the painkillers. In 2017, Appalachian counties experienced a death rate from opioid overdoses that was 72% higher than that of the rest of the country.
Dr. Ellison and associates who presented their findings recently at the 2022 annual meeting of the American Society of Anesthesiologists, examined rates of pediatric trauma injuries, injury severity, and results of drug screenings throughout West Virginia between 2009 and 2019.
The study included 4,538 children and adolescents younger than 18 years who had been treated for head and neck trauma. The youth were divided into two groups: 3,356 who were treated from 2009 to 2016, and 1,182 who were treated between 2017 and 2019.
The incidence of critical head injuries increased from 3.7% in the period 2009-2016 to 7.2% in the period 2017-2019 (P = .007). The incidence of serious neck injuries increased from 12.2% to 27.1% (P = .007) during that period, according to the researchers. The number of days that these patients spent on ventilators more than doubled, from 3.1 to 6.3 (P < .001), they reported.
At the same time, the rate of positive urine drug tests rose sharply, from 0.8% to 1.8% (P < .001) for benzodiazepines and from 1% to 4.9% for opioids (P < .001).
Drug testing of children hospitalized for trauma rose more than threefold, from 6.9% to 23.2% (P < .001). Dr. Ellison’s group was unable to match positive drug screens with patients who came in with injuries.
Dr. Ellison said her research “warrants further evaluation of current policies and protocols targeting substance use in children and adolescents.” To that end, her team is planning to conduct a prospective study in mid 2023 to further illuminate the trends.
“I hope early next year we can put together a group of physicians, pediatric general surgeons, neurosurgeons, and anesthesiologists,” she said. “I want to look at what we can do to reduce the severity of injury.”
She also wants to reach the population that these findings directly affect.
“The next step that we are currently working on is community awareness of the issue,” Dr. Ellison said. “Our trauma institute is partnering with middle school and high school kids to create material to raise awareness.”
Rural Appalachia faces several other endemic problems that affect the health and well-being of children and families, including limited access to health care, poverty, and minimal community support, according to Dr. Ellison. Children and teens in the region who live with parents who abuse opioids are more likely to experience family conflict, mental health challenges, legal troubles, and negative health effects, including physical trauma.
A call to action
Toufic Jildeh, MD, assistant professor of orthopedics, Michigan State University Health Care, East Lansing, who has studied ways to reduce opioid use among surgery patients, called the new findings “alarming.”
After reviewing the study, Dr. Jildeh said that in his opinion, the results support standardized drug testing of children, particularly in the context of severe trauma.
Bruce Bassi, MD, an addiction psychiatrist and owner of TelepsychHealth, a private, online psychiatric practice, agreed. “The main take-home message is that drug screening should be the standard of care for pediatric patients in this region, because it changes the management of those individuals,” Dr. Bassi said.
But identifying these patients is just the first step. “We should continue to educate and raise awareness, not only in the health care system,” Dr. Bassi said. “We also need to let parents know that the possibility of children obtaining access to medications is high.”
The study was independently supported. Dr. Ellison and Dr. Jildeh reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bassi owns a private psychiatry practice called Telepsychhealth but has no other relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Lucid dying’: EEG backs near-death experience during CPR
“These recalled experiences and brain wave changes may be the first signs of the so-called ‘near-death’ experience, and we have captured them for the first time in a large study,” lead investigator Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, with NYU Langone Health, said in a news release.
Identifying measurable electrical signs of lucid and heightened brain activity during CPR, coupled with stories of recalled near-death experiences, suggests that the human sense of self and consciousness, much like other biological body functions, may not stop completely around the time of death, Dr. Parnia added.
He presented the findings Nov. 6 at a resuscitation science symposium at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The AWARE II study
“For years, some people in cardiac arrest have reported being lucid, often with a heightened sense of consciousness, while seemingly unconscious and on the brink of death,” Dr. Parnia noted in an interview.
“Yet, no one’s ever be able to prove it and a lot of people have dismissed these experiences, thinking it’s all just a trick on the brain,” Dr. Parnia said.
In a first-of-its-kind study, Dr. Parnia and colleagues examined consciousness and its underlying electrocortical biomarkers during CPR for in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA).
They incorporated independent audiovisual testing of awareness with continuous real-time EEG and cerebral oxygenation (rSO2) monitoring into CPR.
Only 53 of the 567 IHCA patients survived (9.3%). Among the 28 (52.8%) IHCA survivors who completed interviews, 11 (39.3%) reported unique, lucid experiences during resuscitation.
These experiences included a perception of separation from one’s body, observing events without pain or distress, and an awareness and meaningful evaluation of life, including of their actions, intentions, and thoughts toward others.
“These lucid experiences of death are not hallucinations or delusions. They cannot be considered a trick of a disordered or dying brain, but rather a unique human experience that emerges on the brink of death,” Dr. Parnia said.
And what’s “fascinating,” he added, is that despite marked cerebral ischemia (mean regional oxygen saturation [rSO2] 43%), near-normal/physiologic EEG activity (gamma, delta, theta, alpha, and beta rhythms) consistent with consciousness and a possible resumption of a network-level of cognitive and neuronal activity emerged for as long as 35-60 minutes into CPR.
Some of these brain waves normally occur when people are conscious and performing higher mental functions, including thinking, memory retrieval, and conscious perception, he said.
‘Seismic shift’ in understanding of death
This is the first time such biomarkers of consciousness have been identified during cardiac arrest and CPR, Dr. Parnia said.
He said further study is needed to more precisely define biomarkers of what is considered to be clinical consciousness and the recalled experience of death, and to monitor the long-term psychological effects of resuscitation after cardiac arrest.
“Our understanding of death has gone through a seismic shift in the last few years,” he said.
“The biological discoveries around death and the postmortem period are completely different to the social conventions that we have about death. That is, we perceive of death as being the end, but actually what we’re finding is that brain cells don’t die immediately. They die very slowly over many hours of time,” Dr. Parnia noted.
Reached for comment, Ajmal Zemmar, MD, PhD, of University of Louisville (Ky.), noted that several studies, including this one, “challenge the traditional way that we think of death – that when the heart stops beating that’s when we die.”
The observation that during cardiac arrest and CPR, the brain waves are still normal for up to an hour is “fairly remarkable,” Dr. Zemmar told this news organization.
“However, whether there is conscious perception or not is very hard to answer,” he cautioned.
“This type of research tries to bridge the objective EEG recordings with the subjective description you get from the patient, but it’s hard to know when conscious perception stops,” he said.
Funding and support for the study were provided by NYU Langone Health, The John Templeton Foundation, and the UK Resuscitation Council, and National Institutes for Health Research. Dr. Parnia and Dr. Zemmar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“These recalled experiences and brain wave changes may be the first signs of the so-called ‘near-death’ experience, and we have captured them for the first time in a large study,” lead investigator Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, with NYU Langone Health, said in a news release.
Identifying measurable electrical signs of lucid and heightened brain activity during CPR, coupled with stories of recalled near-death experiences, suggests that the human sense of self and consciousness, much like other biological body functions, may not stop completely around the time of death, Dr. Parnia added.
He presented the findings Nov. 6 at a resuscitation science symposium at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The AWARE II study
“For years, some people in cardiac arrest have reported being lucid, often with a heightened sense of consciousness, while seemingly unconscious and on the brink of death,” Dr. Parnia noted in an interview.
“Yet, no one’s ever be able to prove it and a lot of people have dismissed these experiences, thinking it’s all just a trick on the brain,” Dr. Parnia said.
In a first-of-its-kind study, Dr. Parnia and colleagues examined consciousness and its underlying electrocortical biomarkers during CPR for in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA).
They incorporated independent audiovisual testing of awareness with continuous real-time EEG and cerebral oxygenation (rSO2) monitoring into CPR.
Only 53 of the 567 IHCA patients survived (9.3%). Among the 28 (52.8%) IHCA survivors who completed interviews, 11 (39.3%) reported unique, lucid experiences during resuscitation.
These experiences included a perception of separation from one’s body, observing events without pain or distress, and an awareness and meaningful evaluation of life, including of their actions, intentions, and thoughts toward others.
“These lucid experiences of death are not hallucinations or delusions. They cannot be considered a trick of a disordered or dying brain, but rather a unique human experience that emerges on the brink of death,” Dr. Parnia said.
And what’s “fascinating,” he added, is that despite marked cerebral ischemia (mean regional oxygen saturation [rSO2] 43%), near-normal/physiologic EEG activity (gamma, delta, theta, alpha, and beta rhythms) consistent with consciousness and a possible resumption of a network-level of cognitive and neuronal activity emerged for as long as 35-60 minutes into CPR.
Some of these brain waves normally occur when people are conscious and performing higher mental functions, including thinking, memory retrieval, and conscious perception, he said.
‘Seismic shift’ in understanding of death
This is the first time such biomarkers of consciousness have been identified during cardiac arrest and CPR, Dr. Parnia said.
He said further study is needed to more precisely define biomarkers of what is considered to be clinical consciousness and the recalled experience of death, and to monitor the long-term psychological effects of resuscitation after cardiac arrest.
“Our understanding of death has gone through a seismic shift in the last few years,” he said.
“The biological discoveries around death and the postmortem period are completely different to the social conventions that we have about death. That is, we perceive of death as being the end, but actually what we’re finding is that brain cells don’t die immediately. They die very slowly over many hours of time,” Dr. Parnia noted.
Reached for comment, Ajmal Zemmar, MD, PhD, of University of Louisville (Ky.), noted that several studies, including this one, “challenge the traditional way that we think of death – that when the heart stops beating that’s when we die.”
The observation that during cardiac arrest and CPR, the brain waves are still normal for up to an hour is “fairly remarkable,” Dr. Zemmar told this news organization.
“However, whether there is conscious perception or not is very hard to answer,” he cautioned.
“This type of research tries to bridge the objective EEG recordings with the subjective description you get from the patient, but it’s hard to know when conscious perception stops,” he said.
Funding and support for the study were provided by NYU Langone Health, The John Templeton Foundation, and the UK Resuscitation Council, and National Institutes for Health Research. Dr. Parnia and Dr. Zemmar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“These recalled experiences and brain wave changes may be the first signs of the so-called ‘near-death’ experience, and we have captured them for the first time in a large study,” lead investigator Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, with NYU Langone Health, said in a news release.
Identifying measurable electrical signs of lucid and heightened brain activity during CPR, coupled with stories of recalled near-death experiences, suggests that the human sense of self and consciousness, much like other biological body functions, may not stop completely around the time of death, Dr. Parnia added.
He presented the findings Nov. 6 at a resuscitation science symposium at the American Heart Association scientific sessions.
The AWARE II study
“For years, some people in cardiac arrest have reported being lucid, often with a heightened sense of consciousness, while seemingly unconscious and on the brink of death,” Dr. Parnia noted in an interview.
“Yet, no one’s ever be able to prove it and a lot of people have dismissed these experiences, thinking it’s all just a trick on the brain,” Dr. Parnia said.
In a first-of-its-kind study, Dr. Parnia and colleagues examined consciousness and its underlying electrocortical biomarkers during CPR for in-hospital cardiac arrest (IHCA).
They incorporated independent audiovisual testing of awareness with continuous real-time EEG and cerebral oxygenation (rSO2) monitoring into CPR.
Only 53 of the 567 IHCA patients survived (9.3%). Among the 28 (52.8%) IHCA survivors who completed interviews, 11 (39.3%) reported unique, lucid experiences during resuscitation.
These experiences included a perception of separation from one’s body, observing events without pain or distress, and an awareness and meaningful evaluation of life, including of their actions, intentions, and thoughts toward others.
“These lucid experiences of death are not hallucinations or delusions. They cannot be considered a trick of a disordered or dying brain, but rather a unique human experience that emerges on the brink of death,” Dr. Parnia said.
And what’s “fascinating,” he added, is that despite marked cerebral ischemia (mean regional oxygen saturation [rSO2] 43%), near-normal/physiologic EEG activity (gamma, delta, theta, alpha, and beta rhythms) consistent with consciousness and a possible resumption of a network-level of cognitive and neuronal activity emerged for as long as 35-60 minutes into CPR.
Some of these brain waves normally occur when people are conscious and performing higher mental functions, including thinking, memory retrieval, and conscious perception, he said.
‘Seismic shift’ in understanding of death
This is the first time such biomarkers of consciousness have been identified during cardiac arrest and CPR, Dr. Parnia said.
He said further study is needed to more precisely define biomarkers of what is considered to be clinical consciousness and the recalled experience of death, and to monitor the long-term psychological effects of resuscitation after cardiac arrest.
“Our understanding of death has gone through a seismic shift in the last few years,” he said.
“The biological discoveries around death and the postmortem period are completely different to the social conventions that we have about death. That is, we perceive of death as being the end, but actually what we’re finding is that brain cells don’t die immediately. They die very slowly over many hours of time,” Dr. Parnia noted.
Reached for comment, Ajmal Zemmar, MD, PhD, of University of Louisville (Ky.), noted that several studies, including this one, “challenge the traditional way that we think of death – that when the heart stops beating that’s when we die.”
The observation that during cardiac arrest and CPR, the brain waves are still normal for up to an hour is “fairly remarkable,” Dr. Zemmar told this news organization.
“However, whether there is conscious perception or not is very hard to answer,” he cautioned.
“This type of research tries to bridge the objective EEG recordings with the subjective description you get from the patient, but it’s hard to know when conscious perception stops,” he said.
Funding and support for the study were provided by NYU Langone Health, The John Templeton Foundation, and the UK Resuscitation Council, and National Institutes for Health Research. Dr. Parnia and Dr. Zemmar reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AHA 2022
Sexual assault–related visits to the ED are on the rise
Data from the Federal Bureau of Investigation show an increase in reported rapes and sexual assaults (SAs) since 2006, and studies of victims show an increased risk of conditions such as suicidal ideation, PTSD, depression, substance use, and chronic conditions, write Emily L. Vogt of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
However, trends and disparities in ED use by adults seeking care following SA have not been explored, they said.
For a study that was published in JAMA Network Open, researchers reviewed data from the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS), a large, nationally representative database managed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The dataset consisted of 120 million to 143 million weighted ED visits reported annually from 2006 through 2016. The study population included adults aged 18-65 years who had made an ED visit that was recorded in the NEDS and that was coded as an SA. SA was defined using ICD-9 codes until the fourth quarter of 2015, at which time ICD-10 codes came into use.
Overall, the number of SA-related ED visits increased by 1,533.0% during the study period, from 3,607 in 2006 to 55,296 in 2019. The average annual percentage change was 23.0% (P < .001). The greatest increase occurred from 2015 to 2016, when annual visits increased from 17,709 to 47,732. This increase likely reflected the updated ICD-10 codes, in which there are categories for suspected adult rape, confirmed adult rape, and adult forced sexual exploitation, the researchers note.
Patients presenting to the ED after an SA were mainly women (91.5%). Individuals aged 18-25 years accounted for nearly half of the presentations. Individuals in the lowest and second-lowest income quartiles also were overrepresented.
Despite the increased presentation to EDs, admission rates for SA decreased, from 12.6% to 4.3%, the researchers note. Patients who were older and were insured through Medicaid were more likely to be admitted than persons of other demographic groups.
The researchers also found that increases in ED presentations outpaced increases in SA reports to law enforcement. They compared the ED trends with FBI-reported rapes/SAs from 2015 to 2019 and found increases of 7% and 22% during the times of ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes, respectively. However, in 2019, the number of SA survivors who sought ED care remained below the number who reported to law enforcement (55,296 vs. 139,815, as determined on the basis of revised SA definitions).
“Although the association between increased coding specificity and documentation of SA is still unclear, ICD-10 likely contributed to increased ED documentation of SA,” but the data show steady increases that are independent of the coding change, the researchers write.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for multiple representations of patients, coding errors associated with the NEDS database, and the reliance on voluntary reports in the NEDS and FBI datasets, the researchers note. The results were strengthened by the large, diverse sample size and by the inclusion of hospital admissions and crime data for comparison, they say.
“As few as 21% of survivors seek medical care after SA, meaning that the survivors captured in this study represent a fraction of total SA-related care need,” the researchers write. “Our finding that most SA ED visits are by young, female, and low-income survivors can inform policy changes to better support these individuals,” which could include the development of outpatient and longitudinal care settings to better serve these populations, they conclude.
Better understanding not only of the trends underlying SA reporting but also of the demographics of survivors who seek treatment and evaluation after SA is vital, said Robert Glatter, MD, in an interview.
“Being able to better understand how social and societal movements affect a patient’s comfort in reporting an SA is vital in tracking the numbers of people who seek care in the ED,” said Dr. Glatter, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital at Northwell Health, New York, and also of Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.
Dr. Glatter said he was not surprised by the significant increase in sexual assault presentations, especially in light of increased awareness and the influence of the #MeToo movement and other social justice movements over the past decade.
“While I believe that victims of sexual violence may now feel more empowered to report an assault, the volume of SA that go unreported remains a serious public health issue and concern” in the United States and globally, he emphasized.
A key message from the current study is that there is a need for investment in “compassionate and comprehensive care for all survivors of SA,” Dr. Glatter said. “This includes recognition of the extensive mental health consequences of SA that can lead to not only depression, PTSD, and anxiety but also to suicidal ideation and suicide. The longer-term medical effects become life altering, permeating families and future generations,” he emphasized.
“As a society, we must also place a strong emphasis on caring for all SA survivors, but particularly those who come from economically or socially disadvantaged backgrounds who are uninsured or underinsured,” Dr. Glatter said. Issues of race, gender identity, and sexual identity among SA survivors also must be taken into consideration, he added.
“We need to better understand how our health care system can provide more nuanced follow-up care and reporting for survivors in outpatient settings. … Making access easier, while ensuring confidentiality, will allow more survivors of SA to seek treatment and care,” he said. “We also need to understand how using forensic nurses in this capacity, and beyond the ED, can better serve minority and racially diverse communities” and to increase the recruitment and training of such specialized nurses to care for SA victims, Dr. Glatter noted.
The study was supported by internal funding from the University of Michigan and the department of obstetrics and gynecology. Corresponding author Erica C. Marsh, MD, has received personal fees from Myovant Sciences and Pfizer unrelated to the current study. Dr. Glatter has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Data from the Federal Bureau of Investigation show an increase in reported rapes and sexual assaults (SAs) since 2006, and studies of victims show an increased risk of conditions such as suicidal ideation, PTSD, depression, substance use, and chronic conditions, write Emily L. Vogt of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
However, trends and disparities in ED use by adults seeking care following SA have not been explored, they said.
For a study that was published in JAMA Network Open, researchers reviewed data from the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS), a large, nationally representative database managed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The dataset consisted of 120 million to 143 million weighted ED visits reported annually from 2006 through 2016. The study population included adults aged 18-65 years who had made an ED visit that was recorded in the NEDS and that was coded as an SA. SA was defined using ICD-9 codes until the fourth quarter of 2015, at which time ICD-10 codes came into use.
Overall, the number of SA-related ED visits increased by 1,533.0% during the study period, from 3,607 in 2006 to 55,296 in 2019. The average annual percentage change was 23.0% (P < .001). The greatest increase occurred from 2015 to 2016, when annual visits increased from 17,709 to 47,732. This increase likely reflected the updated ICD-10 codes, in which there are categories for suspected adult rape, confirmed adult rape, and adult forced sexual exploitation, the researchers note.
Patients presenting to the ED after an SA were mainly women (91.5%). Individuals aged 18-25 years accounted for nearly half of the presentations. Individuals in the lowest and second-lowest income quartiles also were overrepresented.
Despite the increased presentation to EDs, admission rates for SA decreased, from 12.6% to 4.3%, the researchers note. Patients who were older and were insured through Medicaid were more likely to be admitted than persons of other demographic groups.
The researchers also found that increases in ED presentations outpaced increases in SA reports to law enforcement. They compared the ED trends with FBI-reported rapes/SAs from 2015 to 2019 and found increases of 7% and 22% during the times of ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes, respectively. However, in 2019, the number of SA survivors who sought ED care remained below the number who reported to law enforcement (55,296 vs. 139,815, as determined on the basis of revised SA definitions).
“Although the association between increased coding specificity and documentation of SA is still unclear, ICD-10 likely contributed to increased ED documentation of SA,” but the data show steady increases that are independent of the coding change, the researchers write.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for multiple representations of patients, coding errors associated with the NEDS database, and the reliance on voluntary reports in the NEDS and FBI datasets, the researchers note. The results were strengthened by the large, diverse sample size and by the inclusion of hospital admissions and crime data for comparison, they say.
“As few as 21% of survivors seek medical care after SA, meaning that the survivors captured in this study represent a fraction of total SA-related care need,” the researchers write. “Our finding that most SA ED visits are by young, female, and low-income survivors can inform policy changes to better support these individuals,” which could include the development of outpatient and longitudinal care settings to better serve these populations, they conclude.
Better understanding not only of the trends underlying SA reporting but also of the demographics of survivors who seek treatment and evaluation after SA is vital, said Robert Glatter, MD, in an interview.
“Being able to better understand how social and societal movements affect a patient’s comfort in reporting an SA is vital in tracking the numbers of people who seek care in the ED,” said Dr. Glatter, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital at Northwell Health, New York, and also of Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.
Dr. Glatter said he was not surprised by the significant increase in sexual assault presentations, especially in light of increased awareness and the influence of the #MeToo movement and other social justice movements over the past decade.
“While I believe that victims of sexual violence may now feel more empowered to report an assault, the volume of SA that go unreported remains a serious public health issue and concern” in the United States and globally, he emphasized.
A key message from the current study is that there is a need for investment in “compassionate and comprehensive care for all survivors of SA,” Dr. Glatter said. “This includes recognition of the extensive mental health consequences of SA that can lead to not only depression, PTSD, and anxiety but also to suicidal ideation and suicide. The longer-term medical effects become life altering, permeating families and future generations,” he emphasized.
“As a society, we must also place a strong emphasis on caring for all SA survivors, but particularly those who come from economically or socially disadvantaged backgrounds who are uninsured or underinsured,” Dr. Glatter said. Issues of race, gender identity, and sexual identity among SA survivors also must be taken into consideration, he added.
“We need to better understand how our health care system can provide more nuanced follow-up care and reporting for survivors in outpatient settings. … Making access easier, while ensuring confidentiality, will allow more survivors of SA to seek treatment and care,” he said. “We also need to understand how using forensic nurses in this capacity, and beyond the ED, can better serve minority and racially diverse communities” and to increase the recruitment and training of such specialized nurses to care for SA victims, Dr. Glatter noted.
The study was supported by internal funding from the University of Michigan and the department of obstetrics and gynecology. Corresponding author Erica C. Marsh, MD, has received personal fees from Myovant Sciences and Pfizer unrelated to the current study. Dr. Glatter has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Data from the Federal Bureau of Investigation show an increase in reported rapes and sexual assaults (SAs) since 2006, and studies of victims show an increased risk of conditions such as suicidal ideation, PTSD, depression, substance use, and chronic conditions, write Emily L. Vogt of the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and colleagues.
However, trends and disparities in ED use by adults seeking care following SA have not been explored, they said.
For a study that was published in JAMA Network Open, researchers reviewed data from the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample (NEDS), a large, nationally representative database managed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality. The dataset consisted of 120 million to 143 million weighted ED visits reported annually from 2006 through 2016. The study population included adults aged 18-65 years who had made an ED visit that was recorded in the NEDS and that was coded as an SA. SA was defined using ICD-9 codes until the fourth quarter of 2015, at which time ICD-10 codes came into use.
Overall, the number of SA-related ED visits increased by 1,533.0% during the study period, from 3,607 in 2006 to 55,296 in 2019. The average annual percentage change was 23.0% (P < .001). The greatest increase occurred from 2015 to 2016, when annual visits increased from 17,709 to 47,732. This increase likely reflected the updated ICD-10 codes, in which there are categories for suspected adult rape, confirmed adult rape, and adult forced sexual exploitation, the researchers note.
Patients presenting to the ED after an SA were mainly women (91.5%). Individuals aged 18-25 years accounted for nearly half of the presentations. Individuals in the lowest and second-lowest income quartiles also were overrepresented.
Despite the increased presentation to EDs, admission rates for SA decreased, from 12.6% to 4.3%, the researchers note. Patients who were older and were insured through Medicaid were more likely to be admitted than persons of other demographic groups.
The researchers also found that increases in ED presentations outpaced increases in SA reports to law enforcement. They compared the ED trends with FBI-reported rapes/SAs from 2015 to 2019 and found increases of 7% and 22% during the times of ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes, respectively. However, in 2019, the number of SA survivors who sought ED care remained below the number who reported to law enforcement (55,296 vs. 139,815, as determined on the basis of revised SA definitions).
“Although the association between increased coding specificity and documentation of SA is still unclear, ICD-10 likely contributed to increased ED documentation of SA,” but the data show steady increases that are independent of the coding change, the researchers write.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for multiple representations of patients, coding errors associated with the NEDS database, and the reliance on voluntary reports in the NEDS and FBI datasets, the researchers note. The results were strengthened by the large, diverse sample size and by the inclusion of hospital admissions and crime data for comparison, they say.
“As few as 21% of survivors seek medical care after SA, meaning that the survivors captured in this study represent a fraction of total SA-related care need,” the researchers write. “Our finding that most SA ED visits are by young, female, and low-income survivors can inform policy changes to better support these individuals,” which could include the development of outpatient and longitudinal care settings to better serve these populations, they conclude.
Better understanding not only of the trends underlying SA reporting but also of the demographics of survivors who seek treatment and evaluation after SA is vital, said Robert Glatter, MD, in an interview.
“Being able to better understand how social and societal movements affect a patient’s comfort in reporting an SA is vital in tracking the numbers of people who seek care in the ED,” said Dr. Glatter, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital at Northwell Health, New York, and also of Hofstra University, Hempstead, N.Y.
Dr. Glatter said he was not surprised by the significant increase in sexual assault presentations, especially in light of increased awareness and the influence of the #MeToo movement and other social justice movements over the past decade.
“While I believe that victims of sexual violence may now feel more empowered to report an assault, the volume of SA that go unreported remains a serious public health issue and concern” in the United States and globally, he emphasized.
A key message from the current study is that there is a need for investment in “compassionate and comprehensive care for all survivors of SA,” Dr. Glatter said. “This includes recognition of the extensive mental health consequences of SA that can lead to not only depression, PTSD, and anxiety but also to suicidal ideation and suicide. The longer-term medical effects become life altering, permeating families and future generations,” he emphasized.
“As a society, we must also place a strong emphasis on caring for all SA survivors, but particularly those who come from economically or socially disadvantaged backgrounds who are uninsured or underinsured,” Dr. Glatter said. Issues of race, gender identity, and sexual identity among SA survivors also must be taken into consideration, he added.
“We need to better understand how our health care system can provide more nuanced follow-up care and reporting for survivors in outpatient settings. … Making access easier, while ensuring confidentiality, will allow more survivors of SA to seek treatment and care,” he said. “We also need to understand how using forensic nurses in this capacity, and beyond the ED, can better serve minority and racially diverse communities” and to increase the recruitment and training of such specialized nurses to care for SA victims, Dr. Glatter noted.
The study was supported by internal funding from the University of Michigan and the department of obstetrics and gynecology. Corresponding author Erica C. Marsh, MD, has received personal fees from Myovant Sciences and Pfizer unrelated to the current study. Dr. Glatter has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Are mass shootings contagious?
That’s not just a feeling – it’s a fact.
The devastating shooting on May 24 in Uvalde, Tex., which killed 19 children, two teachers, and injured 17 others, occurred 10 days after a supermarket shooting in Buffalo, N.Y., which resulted in 10 deaths. In 2021, a shooting at a massage parlor in Atlanta, which left eight dead, came less than a week before a shooting at a supermarket in Boulder, Colo., that killed 10. And a 2019 shooting in Dayton, Ohio, on Aug. 4 that killed nine people took place only a day after a Walmart shooting in El Paso, Tex., which claimed 22 lives.
Contagion theory
Researchers argue that the clustering of mass shootings suggests that this type of violence spreads like a virus and should be treated as one.
This theory – called the “contagion effect” – has been examined at length in cases of suicide, especially among teens and young adults. Studies have demonstrated that the majority of adolescents who attempt suicide have previously been exposed to the suicidal behavior of a peer.
In many cases, mass shootings are also suicides, with shooters taking their own lives at the time of the shooting or not long after.
“They have literally and figuratively given up on their life as they know it.” said Joel Dvoskin, PhD, a clinical and forensic psychologist at the University of Arizona, Tucson, and former acting commissioner of mental health for New York state.
According to contagion theory, mass shootings – and the round-the-clock media coverage they generate – lead to even more killings.
A team of researchers at Arizona State University led by Sherry Towers, PhD, analyzed mass shooting data in 2015 to find out whether those events followed a similar pattern. Dr. Towers spent much of her career modeling the spread of infectious diseases, such as influenza, Ebola, and Zika.
Dr. Towers and colleagues discovered that a mass killing tended to give rise to more killings in its immediate aftermath. According to her evaluation of USA Today’s mass shooting database, a second incident was most likely to occur within 13 days of the initial event.
What defines a mass shooting?
The FBI defines a mass shooting as any incident in which four or more people die by gunfire. That definition, however, is not universally accepted. The lack of a standard definition complicates the work of researchers who study contagion theory.
Mother Jones magazine created an open-source database of mass killings that employs a similar definition but that includes only incidents that involve a person shooting indiscriminately in a public place.
With this narrower definition, shootings involving organized crime, robberies, and domestic violence – which make up the vast majority of shootings in which multiple fatalities occur in this country – are excluded. Events such as those that occurred in Sandy Hook or the killings in Highland Park, Ill., this past July would be included.
The Gun Violence Archive categorizes mass shootings as any incident in which four or more people are shot but not necessarily killed, while Everytown for Gun Safety tallies mass shootings that take at least four lives.
James Meindl, PhD, a professor of behavioral analysis at the University of Memphis who studies mass shootings, said parsing the differences between what happened in Uvalde and what happens during a shooting involving organized crime or domestic violence is crucial when thinking about intervention and prevention.
“If you want to intervene, you have to know why the person engaged in this behavior in the first place,” Dr. Meindl said. “The factors that led a person to commit gang violence, the factors in domestic violence, the factors in indiscriminate mass shootings – those are all very different factors that would call for very different interventions.”
So, should mass shootings be treated like an infectious disease?
Rather than using contagion theory, Dr. Meindl said he prefers to view mass shootings through the lens of “generalized imitation,” a psychological concept involving the learned ability to mimic behaviors observed either in person or through the media. Behaviors “are not diseases that can spread on contact.”
Gary Slutkin, MD, is an epidemiologist who pivoted from studying the spread of diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV, and cholera to trying to understand the epidemic of gun violence.
“The more you’re exposed [to violence], the more likely you are to repeat it, just like the more you’re exposed to COVID, the more likely you are to get it and give it to somebody else,” Dr. Slutkin said. And just as people have varying degrees of susceptibility to COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, he argued that some are more susceptible to committing a mass shooting, depending on their level of isolation, personal “grievances, and their need for belonging or credit.”
To Dr. Slutkin, mass shootings, and other forms of violence, should be treated with the standard methods that public health officials would use to stop the spread of a contagious disease: detection and interdiction that would put a stop to potential events. The nonprofit organization that he founded, Cure Violence Global, employs “violence interrupters” to reach out to and engage with community members who might be at risk of being a victim of violence or of committing an act of violence, much as a public health worker would approach epidemic control.
Research conducted on the effects of this method of reducing rates of violence suggests the approach works. In 2017, New York City saw a 63% reduction in gun injuries, according to a study from the John Jay College of Criminal Justice. And after evaluating the effects of this approach in Chicago in 2014, researchers from the University of Illinois and the University of Chicago determined that there was a 19% reduction in shootings in the city.
“The results of stopping an epidemic come really fast,” Dr. Slutkin said. “But getting people to switch gears to the right kind of treatment happens really slowly.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That’s not just a feeling – it’s a fact.
The devastating shooting on May 24 in Uvalde, Tex., which killed 19 children, two teachers, and injured 17 others, occurred 10 days after a supermarket shooting in Buffalo, N.Y., which resulted in 10 deaths. In 2021, a shooting at a massage parlor in Atlanta, which left eight dead, came less than a week before a shooting at a supermarket in Boulder, Colo., that killed 10. And a 2019 shooting in Dayton, Ohio, on Aug. 4 that killed nine people took place only a day after a Walmart shooting in El Paso, Tex., which claimed 22 lives.
Contagion theory
Researchers argue that the clustering of mass shootings suggests that this type of violence spreads like a virus and should be treated as one.
This theory – called the “contagion effect” – has been examined at length in cases of suicide, especially among teens and young adults. Studies have demonstrated that the majority of adolescents who attempt suicide have previously been exposed to the suicidal behavior of a peer.
In many cases, mass shootings are also suicides, with shooters taking their own lives at the time of the shooting or not long after.
“They have literally and figuratively given up on their life as they know it.” said Joel Dvoskin, PhD, a clinical and forensic psychologist at the University of Arizona, Tucson, and former acting commissioner of mental health for New York state.
According to contagion theory, mass shootings – and the round-the-clock media coverage they generate – lead to even more killings.
A team of researchers at Arizona State University led by Sherry Towers, PhD, analyzed mass shooting data in 2015 to find out whether those events followed a similar pattern. Dr. Towers spent much of her career modeling the spread of infectious diseases, such as influenza, Ebola, and Zika.
Dr. Towers and colleagues discovered that a mass killing tended to give rise to more killings in its immediate aftermath. According to her evaluation of USA Today’s mass shooting database, a second incident was most likely to occur within 13 days of the initial event.
What defines a mass shooting?
The FBI defines a mass shooting as any incident in which four or more people die by gunfire. That definition, however, is not universally accepted. The lack of a standard definition complicates the work of researchers who study contagion theory.
Mother Jones magazine created an open-source database of mass killings that employs a similar definition but that includes only incidents that involve a person shooting indiscriminately in a public place.
With this narrower definition, shootings involving organized crime, robberies, and domestic violence – which make up the vast majority of shootings in which multiple fatalities occur in this country – are excluded. Events such as those that occurred in Sandy Hook or the killings in Highland Park, Ill., this past July would be included.
The Gun Violence Archive categorizes mass shootings as any incident in which four or more people are shot but not necessarily killed, while Everytown for Gun Safety tallies mass shootings that take at least four lives.
James Meindl, PhD, a professor of behavioral analysis at the University of Memphis who studies mass shootings, said parsing the differences between what happened in Uvalde and what happens during a shooting involving organized crime or domestic violence is crucial when thinking about intervention and prevention.
“If you want to intervene, you have to know why the person engaged in this behavior in the first place,” Dr. Meindl said. “The factors that led a person to commit gang violence, the factors in domestic violence, the factors in indiscriminate mass shootings – those are all very different factors that would call for very different interventions.”
So, should mass shootings be treated like an infectious disease?
Rather than using contagion theory, Dr. Meindl said he prefers to view mass shootings through the lens of “generalized imitation,” a psychological concept involving the learned ability to mimic behaviors observed either in person or through the media. Behaviors “are not diseases that can spread on contact.”
Gary Slutkin, MD, is an epidemiologist who pivoted from studying the spread of diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV, and cholera to trying to understand the epidemic of gun violence.
“The more you’re exposed [to violence], the more likely you are to repeat it, just like the more you’re exposed to COVID, the more likely you are to get it and give it to somebody else,” Dr. Slutkin said. And just as people have varying degrees of susceptibility to COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, he argued that some are more susceptible to committing a mass shooting, depending on their level of isolation, personal “grievances, and their need for belonging or credit.”
To Dr. Slutkin, mass shootings, and other forms of violence, should be treated with the standard methods that public health officials would use to stop the spread of a contagious disease: detection and interdiction that would put a stop to potential events. The nonprofit organization that he founded, Cure Violence Global, employs “violence interrupters” to reach out to and engage with community members who might be at risk of being a victim of violence or of committing an act of violence, much as a public health worker would approach epidemic control.
Research conducted on the effects of this method of reducing rates of violence suggests the approach works. In 2017, New York City saw a 63% reduction in gun injuries, according to a study from the John Jay College of Criminal Justice. And after evaluating the effects of this approach in Chicago in 2014, researchers from the University of Illinois and the University of Chicago determined that there was a 19% reduction in shootings in the city.
“The results of stopping an epidemic come really fast,” Dr. Slutkin said. “But getting people to switch gears to the right kind of treatment happens really slowly.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
That’s not just a feeling – it’s a fact.
The devastating shooting on May 24 in Uvalde, Tex., which killed 19 children, two teachers, and injured 17 others, occurred 10 days after a supermarket shooting in Buffalo, N.Y., which resulted in 10 deaths. In 2021, a shooting at a massage parlor in Atlanta, which left eight dead, came less than a week before a shooting at a supermarket in Boulder, Colo., that killed 10. And a 2019 shooting in Dayton, Ohio, on Aug. 4 that killed nine people took place only a day after a Walmart shooting in El Paso, Tex., which claimed 22 lives.
Contagion theory
Researchers argue that the clustering of mass shootings suggests that this type of violence spreads like a virus and should be treated as one.
This theory – called the “contagion effect” – has been examined at length in cases of suicide, especially among teens and young adults. Studies have demonstrated that the majority of adolescents who attempt suicide have previously been exposed to the suicidal behavior of a peer.
In many cases, mass shootings are also suicides, with shooters taking their own lives at the time of the shooting or not long after.
“They have literally and figuratively given up on their life as they know it.” said Joel Dvoskin, PhD, a clinical and forensic psychologist at the University of Arizona, Tucson, and former acting commissioner of mental health for New York state.
According to contagion theory, mass shootings – and the round-the-clock media coverage they generate – lead to even more killings.
A team of researchers at Arizona State University led by Sherry Towers, PhD, analyzed mass shooting data in 2015 to find out whether those events followed a similar pattern. Dr. Towers spent much of her career modeling the spread of infectious diseases, such as influenza, Ebola, and Zika.
Dr. Towers and colleagues discovered that a mass killing tended to give rise to more killings in its immediate aftermath. According to her evaluation of USA Today’s mass shooting database, a second incident was most likely to occur within 13 days of the initial event.
What defines a mass shooting?
The FBI defines a mass shooting as any incident in which four or more people die by gunfire. That definition, however, is not universally accepted. The lack of a standard definition complicates the work of researchers who study contagion theory.
Mother Jones magazine created an open-source database of mass killings that employs a similar definition but that includes only incidents that involve a person shooting indiscriminately in a public place.
With this narrower definition, shootings involving organized crime, robberies, and domestic violence – which make up the vast majority of shootings in which multiple fatalities occur in this country – are excluded. Events such as those that occurred in Sandy Hook or the killings in Highland Park, Ill., this past July would be included.
The Gun Violence Archive categorizes mass shootings as any incident in which four or more people are shot but not necessarily killed, while Everytown for Gun Safety tallies mass shootings that take at least four lives.
James Meindl, PhD, a professor of behavioral analysis at the University of Memphis who studies mass shootings, said parsing the differences between what happened in Uvalde and what happens during a shooting involving organized crime or domestic violence is crucial when thinking about intervention and prevention.
“If you want to intervene, you have to know why the person engaged in this behavior in the first place,” Dr. Meindl said. “The factors that led a person to commit gang violence, the factors in domestic violence, the factors in indiscriminate mass shootings – those are all very different factors that would call for very different interventions.”
So, should mass shootings be treated like an infectious disease?
Rather than using contagion theory, Dr. Meindl said he prefers to view mass shootings through the lens of “generalized imitation,” a psychological concept involving the learned ability to mimic behaviors observed either in person or through the media. Behaviors “are not diseases that can spread on contact.”
Gary Slutkin, MD, is an epidemiologist who pivoted from studying the spread of diseases such as tuberculosis, HIV, and cholera to trying to understand the epidemic of gun violence.
“The more you’re exposed [to violence], the more likely you are to repeat it, just like the more you’re exposed to COVID, the more likely you are to get it and give it to somebody else,” Dr. Slutkin said. And just as people have varying degrees of susceptibility to COVID-19 and other infectious diseases, he argued that some are more susceptible to committing a mass shooting, depending on their level of isolation, personal “grievances, and their need for belonging or credit.”
To Dr. Slutkin, mass shootings, and other forms of violence, should be treated with the standard methods that public health officials would use to stop the spread of a contagious disease: detection and interdiction that would put a stop to potential events. The nonprofit organization that he founded, Cure Violence Global, employs “violence interrupters” to reach out to and engage with community members who might be at risk of being a victim of violence or of committing an act of violence, much as a public health worker would approach epidemic control.
Research conducted on the effects of this method of reducing rates of violence suggests the approach works. In 2017, New York City saw a 63% reduction in gun injuries, according to a study from the John Jay College of Criminal Justice. And after evaluating the effects of this approach in Chicago in 2014, researchers from the University of Illinois and the University of Chicago determined that there was a 19% reduction in shootings in the city.
“The results of stopping an epidemic come really fast,” Dr. Slutkin said. “But getting people to switch gears to the right kind of treatment happens really slowly.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Incomplete recovery common 6 months after mild TBI
, new data from the TRACK-TBI study shows.
“Seeing that more than half of the GCS [Glasgow Coma Score] 15, CT-negative TBI cohort in our study were not back to their preinjury baseline at 6 months was surprising and impacts the millions of Americans who suffer from concussions annually,” said lead author Debbie Madhok, MD, with department of emergency medicine, University of California, San Francisco.
“These results highlight the importance of improving care pathways for concussion, particularly from the emergency department,” Dr. Madhok said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
The short- and long-term outcomes in the large group of patients who come into the ED with TBI, a GCS of 15, and without acute intracranial traumatic injury (defined as a negative head CT scan) remain poorly understood, the investigators noted. To investigate further, they evaluated outcomes at 2 weeks and 6 months in 991 of these patients (mean age, 38 years; 64% men) from the TRACK-TBI study.
Among the 751 (76%) participants followed up at 2 weeks after the injury, only 204 (27%) had functional recovery – with a Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended (GOS-E) score of 8. The remaining 547 (73%) had incomplete recovery (GOS-E scores < 8).
Among the 659 patients (66%) followed up at 6 months after the injury, 287 (44%) had functional recovery and 372 (56%) had incomplete recovery.
Most patients who failed to recover completely reported they had not returned to their preinjury life (88%). They described trouble returning to social activities outside the home and disruptions in family relationships and friendships.
The researchers noted that the study population had a high rate of preinjury psychiatric comorbidities, and these patients were more likely to have incomplete recovery than those without psychiatric comorbidities. This aligns with results from previous studies, they added.
The investigators also noted that patients with mild TBI without acute intracranial trauma are typically managed by ED personnel.
“These findings highlight the importance of ED clinicians being aware of the risk of incomplete recovery for patients with a mild TBI (that is, GCS score of 15 and negative head CT scan) and providing accurate education and timely referral information before ED discharge,” they wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Foundation of Emergency Medicine, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the U.S. Department of Defense Traumatic Brain Injury Endpoints Development Initiative. Dr. Madhok has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data from the TRACK-TBI study shows.
“Seeing that more than half of the GCS [Glasgow Coma Score] 15, CT-negative TBI cohort in our study were not back to their preinjury baseline at 6 months was surprising and impacts the millions of Americans who suffer from concussions annually,” said lead author Debbie Madhok, MD, with department of emergency medicine, University of California, San Francisco.
“These results highlight the importance of improving care pathways for concussion, particularly from the emergency department,” Dr. Madhok said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
The short- and long-term outcomes in the large group of patients who come into the ED with TBI, a GCS of 15, and without acute intracranial traumatic injury (defined as a negative head CT scan) remain poorly understood, the investigators noted. To investigate further, they evaluated outcomes at 2 weeks and 6 months in 991 of these patients (mean age, 38 years; 64% men) from the TRACK-TBI study.
Among the 751 (76%) participants followed up at 2 weeks after the injury, only 204 (27%) had functional recovery – with a Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended (GOS-E) score of 8. The remaining 547 (73%) had incomplete recovery (GOS-E scores < 8).
Among the 659 patients (66%) followed up at 6 months after the injury, 287 (44%) had functional recovery and 372 (56%) had incomplete recovery.
Most patients who failed to recover completely reported they had not returned to their preinjury life (88%). They described trouble returning to social activities outside the home and disruptions in family relationships and friendships.
The researchers noted that the study population had a high rate of preinjury psychiatric comorbidities, and these patients were more likely to have incomplete recovery than those without psychiatric comorbidities. This aligns with results from previous studies, they added.
The investigators also noted that patients with mild TBI without acute intracranial trauma are typically managed by ED personnel.
“These findings highlight the importance of ED clinicians being aware of the risk of incomplete recovery for patients with a mild TBI (that is, GCS score of 15 and negative head CT scan) and providing accurate education and timely referral information before ED discharge,” they wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Foundation of Emergency Medicine, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the U.S. Department of Defense Traumatic Brain Injury Endpoints Development Initiative. Dr. Madhok has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new data from the TRACK-TBI study shows.
“Seeing that more than half of the GCS [Glasgow Coma Score] 15, CT-negative TBI cohort in our study were not back to their preinjury baseline at 6 months was surprising and impacts the millions of Americans who suffer from concussions annually,” said lead author Debbie Madhok, MD, with department of emergency medicine, University of California, San Francisco.
“These results highlight the importance of improving care pathways for concussion, particularly from the emergency department,” Dr. Madhok said.
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
The short- and long-term outcomes in the large group of patients who come into the ED with TBI, a GCS of 15, and without acute intracranial traumatic injury (defined as a negative head CT scan) remain poorly understood, the investigators noted. To investigate further, they evaluated outcomes at 2 weeks and 6 months in 991 of these patients (mean age, 38 years; 64% men) from the TRACK-TBI study.
Among the 751 (76%) participants followed up at 2 weeks after the injury, only 204 (27%) had functional recovery – with a Glasgow Outcome Scale-Extended (GOS-E) score of 8. The remaining 547 (73%) had incomplete recovery (GOS-E scores < 8).
Among the 659 patients (66%) followed up at 6 months after the injury, 287 (44%) had functional recovery and 372 (56%) had incomplete recovery.
Most patients who failed to recover completely reported they had not returned to their preinjury life (88%). They described trouble returning to social activities outside the home and disruptions in family relationships and friendships.
The researchers noted that the study population had a high rate of preinjury psychiatric comorbidities, and these patients were more likely to have incomplete recovery than those without psychiatric comorbidities. This aligns with results from previous studies, they added.
The investigators also noted that patients with mild TBI without acute intracranial trauma are typically managed by ED personnel.
“These findings highlight the importance of ED clinicians being aware of the risk of incomplete recovery for patients with a mild TBI (that is, GCS score of 15 and negative head CT scan) and providing accurate education and timely referral information before ED discharge,” they wrote.
The study was funded by grants from the National Foundation of Emergency Medicine, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, and the U.S. Department of Defense Traumatic Brain Injury Endpoints Development Initiative. Dr. Madhok has reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Active shooter drills may be harming children, but doctors offer help
The drills can range from staging lockdowns and sheltering in place to quasi dramas with mock shooters roaming the halls. Although the goals of these training exercises are important, equally important are the potential negative effects of drills on students’ mental health, according to doctors with expertise in pediatrics and mental health.
“Dramatic simulation of an active shooter event at school would be expected to provoke the same stress response as the real thing,” said Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, a pediatrician and psychiatrist, in an interview. “While ensuring their physical safety is very important, we must be intentional about making sure that we are not doing so at the expense of their psychosocial or emotional safety.”
“Children may not be able to differentiate a dramatic drill from a real event,” emphasized Dr. Loper, of the neuropsychiatry and behavioral science departments at the University of South Carolina, Columbia. “The parts of the brain responsible for our flight-fight-or-freeze response would interpret both simulated and real events identically and produce the same neurohormonal stress-response.”
Indeed, a study published in the journal Humanities & Social Sciences Communications suggested children experienced mental health problems related to participating in active shooter drills. In the large study, a team of statisticians from the Georgia Institute of Technology found that students reported a 42% increase in stress and anxiety and a 38.7% increase in depression during the 90 days following active shooter drills, compared with the 90 days before the drills.
The authors of this study, including Mai ElSherief, PhD, drew these conclusions after analyzing 54 million social media posts before and after drills in 114 schools across 33 states. The researchers analyzed the language of the social media posts by teachers, parents, and students and found increased use of the words hope, love, home, school, kids, community, support, and help after the drills. The researchers considered posting with these terms in the aftermath of the drills to be indicative of having high anxiety.
They included examples of how high stress, anxiety, and depression manifested in specific posts from parents in their report. The following is an example of a poster expressing high anxiety and stress: “are we really gonna normalize school shooter drills?! holy sh* there has to be a real way to avoid these tragedies. sh*t like this cannot be normalized. teachers injured after being shot with plastic pellets ‘execution style’ in active shooter drill.”
The authors also shared this post to serve as an example of a person who seems depressed: “and now we are revisiting the trauma on our kids, forcing them to act out school drills monthly. i don’t get why gen x parents buy into this concept wholeheartedly. things need to change.”
The published material did not include posts from students, but the researchers’ analysis of the content of posts overall showed increased concerns for health and increased concerns about death during the period after drills, compared with before drills.
The authors also conducted focus groups in communities in which drills occurred, and many teachers and parents reported anecdotal evidence of children who were nervous long after the drills were over, with some showing extreme reactions such as panic over a standard fire alarm at school. Overall, the results show that school shooter drills can negatively affect school communities over prolonged periods of time, they concluded.
According to a statement from the American Academy of Pediatrics, “there is a need to be cautious about the potential psychological risks and other unintended consequences of directly involving children in live exercises and drills.”
“These risks and consequences are especially a concern when children are deceived and led to believe there is an actual attack and not a drill,” wrote David Schonfeld, MD, the lead author of the statement on Participation of Children and Adolescents in Live Crisis Drills and Exercises, and colleagues.
Managing the fallout
Physicians can help students experiencing mental health problems from these drills, according to doctors interviewed for this piece.
It’s important for providers to know that stress will show up differently in children than in adults, said Chelsea Younghans, MD, a psychiatrist and military officer in Bethesda, Md., in an interview.
“They may see children with headaches, stomach aches, or nonspecific complaints. They may also see children who have not had difficulty with sleep present with nightmares or bed wetting,” she added.
For teens and preteens, validated tools such as the Child PTSD Symptom Scale (CPSS-5) and Child and Adolescent Trauma Screen (CATS) to assess PTSD in youth, may help serve as a starting point for a conversation between providers and their older child population, she noted.
Children who exhibit avoidance or withdrawal behaviors including consistent school refusal, an increase in reassurance-seeking behaviors, or somatic symptoms like vague abdominal pain or headaches that prevent school attendance after participating in a drill, may need more robust mental health services, Dr. Loper noted.
Dr. Schonfeld, who is also director of the National Center for School Crisis and Bereavement at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, called for health care providers to be available to help children process traumatic reactions to these exercises.
Agreeing with Dr. Schonfeld, Dr. Younghans said: “It is vital to debrief with students and staff after drills, making sure that students have a safe space and ample time to speak with trusted staff. As children will undoubtedly have questions and concerns, creating open lines of communication will help alleviate any traumatic effect these drills may have.”
Communicating with various stakeholders
Experts also gave recommendations for how clinicians communicate with leaders in their area’s school districts and other members of their communities about these training exercises.
“For primary care providers, it is important to establish meaningful relationships within your community and patient population as much as possible,” Dr. Younghans said. “Having a good relationship with the local schools and being part of the conversation can help increase school and community awareness on the impact these drills can have on students and staff,” she added.
For those pediatricians or other health care providers who serve as consultants to schools, Dr. Schonfeld advised they ask about policies related to exercises and drills, such as what are the limits to what children might be exposed to in a drill, and what requirements there might be at the local and state level in terms of frequency and what the drills will and will not involve.
He also noted that clinicians should encourage school leaders to consider the fact that kids may have personal histories of trauma that are completely unknown to the school when they design these exercises.
School staff and health care providers should explain the nature and reasons for drills, invite family members to express concerns, and make accommodations if necessary for some children to participate in drills in a more limited way, noted Dr. Schonfeld, who is also clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
“I think health care providers should work with legislators, so that if they require a drill, it must be done in a way that is physically and emotionally safe,” he added.
Executing better drills for students’ mental health
Experts also advised on ways to execute these drills that will be least damaging to students.
The AAP statement on Participation of Children and Adolescents in Live Crisis Drills and Exercises, for example, advocates eliminating high-intensity drills, prohibiting deception in drills, and providing accommodations based on children’s vulnerabilities.
Dr. Schonfeld also emphasized, in an interview, that training for an attack need not be extremely realistic to be effective.
“When you are preparing for a crisis, the drills and exercises are for children to practice and develop mastery over something they don’t know how to do fully yet,” said Dr. Schonfeld.
Citing a suggestion from a 2020 report conducted by Everytown for Gun Safety on keeping schools safe from gun violence, Dr. Younghans said, “Schools should be in clear communication with communities and families regarding when drills will be happening,” and advised ensuring that the explanation of drills is developmentally appropriate to the age of the children participating.
The report also recommends conducting drills that do not simulate an actual incident, combining drills with trauma-informed approaches to address students’ well-being during and for a sustained period after the drills, and tracking data on the efficacy and effects of drills.
Dr. Loper suggested ways that clinicians and parents can help navigate the tricky territory of school safety drills.
In his view, they should not be random or unexpected, and anticipatory guidance should be given regarding any visual or auditory stimuli, such as flashing lights or sirens, alarms, or announcements.
“A preventive approach should be utilized to ensure that any child who is experiencing extreme drill-distress be excused from any future disaster drills to prevent retraumatization,” Dr. Loper said.
Physicians interviewed for this piece also provided tips on how to talk about these events with children in a way that is beneficial to their mental health.
“What we want to do is [have a] calm discussion [with kids] about what we are doing and why we are doing it” and guide them through the movements, Dr. Schonfeld said.
When teaching children how to respond to an emergency, some elements of uncertainty need to be discussed. Children need to anticipate “what you might do if you are not in the classroom if something occurs, such as being in the bathroom, or out at recess,” he continued.
Dr. Younghans recommended that parents and staff schedule time to prepare children for the drill and practice in advance, and that behavioral health providers, counselors, and/or primary care providers should be involved in the planning and execution of the drill.
The Georgia Tech study was supported through a grant from Everytown for Gun Safety.
The study authors and experts interviewed for this piece had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The drills can range from staging lockdowns and sheltering in place to quasi dramas with mock shooters roaming the halls. Although the goals of these training exercises are important, equally important are the potential negative effects of drills on students’ mental health, according to doctors with expertise in pediatrics and mental health.
“Dramatic simulation of an active shooter event at school would be expected to provoke the same stress response as the real thing,” said Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, a pediatrician and psychiatrist, in an interview. “While ensuring their physical safety is very important, we must be intentional about making sure that we are not doing so at the expense of their psychosocial or emotional safety.”
“Children may not be able to differentiate a dramatic drill from a real event,” emphasized Dr. Loper, of the neuropsychiatry and behavioral science departments at the University of South Carolina, Columbia. “The parts of the brain responsible for our flight-fight-or-freeze response would interpret both simulated and real events identically and produce the same neurohormonal stress-response.”
Indeed, a study published in the journal Humanities & Social Sciences Communications suggested children experienced mental health problems related to participating in active shooter drills. In the large study, a team of statisticians from the Georgia Institute of Technology found that students reported a 42% increase in stress and anxiety and a 38.7% increase in depression during the 90 days following active shooter drills, compared with the 90 days before the drills.
The authors of this study, including Mai ElSherief, PhD, drew these conclusions after analyzing 54 million social media posts before and after drills in 114 schools across 33 states. The researchers analyzed the language of the social media posts by teachers, parents, and students and found increased use of the words hope, love, home, school, kids, community, support, and help after the drills. The researchers considered posting with these terms in the aftermath of the drills to be indicative of having high anxiety.
They included examples of how high stress, anxiety, and depression manifested in specific posts from parents in their report. The following is an example of a poster expressing high anxiety and stress: “are we really gonna normalize school shooter drills?! holy sh* there has to be a real way to avoid these tragedies. sh*t like this cannot be normalized. teachers injured after being shot with plastic pellets ‘execution style’ in active shooter drill.”
The authors also shared this post to serve as an example of a person who seems depressed: “and now we are revisiting the trauma on our kids, forcing them to act out school drills monthly. i don’t get why gen x parents buy into this concept wholeheartedly. things need to change.”
The published material did not include posts from students, but the researchers’ analysis of the content of posts overall showed increased concerns for health and increased concerns about death during the period after drills, compared with before drills.
The authors also conducted focus groups in communities in which drills occurred, and many teachers and parents reported anecdotal evidence of children who were nervous long after the drills were over, with some showing extreme reactions such as panic over a standard fire alarm at school. Overall, the results show that school shooter drills can negatively affect school communities over prolonged periods of time, they concluded.
According to a statement from the American Academy of Pediatrics, “there is a need to be cautious about the potential psychological risks and other unintended consequences of directly involving children in live exercises and drills.”
“These risks and consequences are especially a concern when children are deceived and led to believe there is an actual attack and not a drill,” wrote David Schonfeld, MD, the lead author of the statement on Participation of Children and Adolescents in Live Crisis Drills and Exercises, and colleagues.
Managing the fallout
Physicians can help students experiencing mental health problems from these drills, according to doctors interviewed for this piece.
It’s important for providers to know that stress will show up differently in children than in adults, said Chelsea Younghans, MD, a psychiatrist and military officer in Bethesda, Md., in an interview.
“They may see children with headaches, stomach aches, or nonspecific complaints. They may also see children who have not had difficulty with sleep present with nightmares or bed wetting,” she added.
For teens and preteens, validated tools such as the Child PTSD Symptom Scale (CPSS-5) and Child and Adolescent Trauma Screen (CATS) to assess PTSD in youth, may help serve as a starting point for a conversation between providers and their older child population, she noted.
Children who exhibit avoidance or withdrawal behaviors including consistent school refusal, an increase in reassurance-seeking behaviors, or somatic symptoms like vague abdominal pain or headaches that prevent school attendance after participating in a drill, may need more robust mental health services, Dr. Loper noted.
Dr. Schonfeld, who is also director of the National Center for School Crisis and Bereavement at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, called for health care providers to be available to help children process traumatic reactions to these exercises.
Agreeing with Dr. Schonfeld, Dr. Younghans said: “It is vital to debrief with students and staff after drills, making sure that students have a safe space and ample time to speak with trusted staff. As children will undoubtedly have questions and concerns, creating open lines of communication will help alleviate any traumatic effect these drills may have.”
Communicating with various stakeholders
Experts also gave recommendations for how clinicians communicate with leaders in their area’s school districts and other members of their communities about these training exercises.
“For primary care providers, it is important to establish meaningful relationships within your community and patient population as much as possible,” Dr. Younghans said. “Having a good relationship with the local schools and being part of the conversation can help increase school and community awareness on the impact these drills can have on students and staff,” she added.
For those pediatricians or other health care providers who serve as consultants to schools, Dr. Schonfeld advised they ask about policies related to exercises and drills, such as what are the limits to what children might be exposed to in a drill, and what requirements there might be at the local and state level in terms of frequency and what the drills will and will not involve.
He also noted that clinicians should encourage school leaders to consider the fact that kids may have personal histories of trauma that are completely unknown to the school when they design these exercises.
School staff and health care providers should explain the nature and reasons for drills, invite family members to express concerns, and make accommodations if necessary for some children to participate in drills in a more limited way, noted Dr. Schonfeld, who is also clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
“I think health care providers should work with legislators, so that if they require a drill, it must be done in a way that is physically and emotionally safe,” he added.
Executing better drills for students’ mental health
Experts also advised on ways to execute these drills that will be least damaging to students.
The AAP statement on Participation of Children and Adolescents in Live Crisis Drills and Exercises, for example, advocates eliminating high-intensity drills, prohibiting deception in drills, and providing accommodations based on children’s vulnerabilities.
Dr. Schonfeld also emphasized, in an interview, that training for an attack need not be extremely realistic to be effective.
“When you are preparing for a crisis, the drills and exercises are for children to practice and develop mastery over something they don’t know how to do fully yet,” said Dr. Schonfeld.
Citing a suggestion from a 2020 report conducted by Everytown for Gun Safety on keeping schools safe from gun violence, Dr. Younghans said, “Schools should be in clear communication with communities and families regarding when drills will be happening,” and advised ensuring that the explanation of drills is developmentally appropriate to the age of the children participating.
The report also recommends conducting drills that do not simulate an actual incident, combining drills with trauma-informed approaches to address students’ well-being during and for a sustained period after the drills, and tracking data on the efficacy and effects of drills.
Dr. Loper suggested ways that clinicians and parents can help navigate the tricky territory of school safety drills.
In his view, they should not be random or unexpected, and anticipatory guidance should be given regarding any visual or auditory stimuli, such as flashing lights or sirens, alarms, or announcements.
“A preventive approach should be utilized to ensure that any child who is experiencing extreme drill-distress be excused from any future disaster drills to prevent retraumatization,” Dr. Loper said.
Physicians interviewed for this piece also provided tips on how to talk about these events with children in a way that is beneficial to their mental health.
“What we want to do is [have a] calm discussion [with kids] about what we are doing and why we are doing it” and guide them through the movements, Dr. Schonfeld said.
When teaching children how to respond to an emergency, some elements of uncertainty need to be discussed. Children need to anticipate “what you might do if you are not in the classroom if something occurs, such as being in the bathroom, or out at recess,” he continued.
Dr. Younghans recommended that parents and staff schedule time to prepare children for the drill and practice in advance, and that behavioral health providers, counselors, and/or primary care providers should be involved in the planning and execution of the drill.
The Georgia Tech study was supported through a grant from Everytown for Gun Safety.
The study authors and experts interviewed for this piece had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The drills can range from staging lockdowns and sheltering in place to quasi dramas with mock shooters roaming the halls. Although the goals of these training exercises are important, equally important are the potential negative effects of drills on students’ mental health, according to doctors with expertise in pediatrics and mental health.
“Dramatic simulation of an active shooter event at school would be expected to provoke the same stress response as the real thing,” said Peter L. Loper Jr., MD, a pediatrician and psychiatrist, in an interview. “While ensuring their physical safety is very important, we must be intentional about making sure that we are not doing so at the expense of their psychosocial or emotional safety.”
“Children may not be able to differentiate a dramatic drill from a real event,” emphasized Dr. Loper, of the neuropsychiatry and behavioral science departments at the University of South Carolina, Columbia. “The parts of the brain responsible for our flight-fight-or-freeze response would interpret both simulated and real events identically and produce the same neurohormonal stress-response.”
Indeed, a study published in the journal Humanities & Social Sciences Communications suggested children experienced mental health problems related to participating in active shooter drills. In the large study, a team of statisticians from the Georgia Institute of Technology found that students reported a 42% increase in stress and anxiety and a 38.7% increase in depression during the 90 days following active shooter drills, compared with the 90 days before the drills.
The authors of this study, including Mai ElSherief, PhD, drew these conclusions after analyzing 54 million social media posts before and after drills in 114 schools across 33 states. The researchers analyzed the language of the social media posts by teachers, parents, and students and found increased use of the words hope, love, home, school, kids, community, support, and help after the drills. The researchers considered posting with these terms in the aftermath of the drills to be indicative of having high anxiety.
They included examples of how high stress, anxiety, and depression manifested in specific posts from parents in their report. The following is an example of a poster expressing high anxiety and stress: “are we really gonna normalize school shooter drills?! holy sh* there has to be a real way to avoid these tragedies. sh*t like this cannot be normalized. teachers injured after being shot with plastic pellets ‘execution style’ in active shooter drill.”
The authors also shared this post to serve as an example of a person who seems depressed: “and now we are revisiting the trauma on our kids, forcing them to act out school drills monthly. i don’t get why gen x parents buy into this concept wholeheartedly. things need to change.”
The published material did not include posts from students, but the researchers’ analysis of the content of posts overall showed increased concerns for health and increased concerns about death during the period after drills, compared with before drills.
The authors also conducted focus groups in communities in which drills occurred, and many teachers and parents reported anecdotal evidence of children who were nervous long after the drills were over, with some showing extreme reactions such as panic over a standard fire alarm at school. Overall, the results show that school shooter drills can negatively affect school communities over prolonged periods of time, they concluded.
According to a statement from the American Academy of Pediatrics, “there is a need to be cautious about the potential psychological risks and other unintended consequences of directly involving children in live exercises and drills.”
“These risks and consequences are especially a concern when children are deceived and led to believe there is an actual attack and not a drill,” wrote David Schonfeld, MD, the lead author of the statement on Participation of Children and Adolescents in Live Crisis Drills and Exercises, and colleagues.
Managing the fallout
Physicians can help students experiencing mental health problems from these drills, according to doctors interviewed for this piece.
It’s important for providers to know that stress will show up differently in children than in adults, said Chelsea Younghans, MD, a psychiatrist and military officer in Bethesda, Md., in an interview.
“They may see children with headaches, stomach aches, or nonspecific complaints. They may also see children who have not had difficulty with sleep present with nightmares or bed wetting,” she added.
For teens and preteens, validated tools such as the Child PTSD Symptom Scale (CPSS-5) and Child and Adolescent Trauma Screen (CATS) to assess PTSD in youth, may help serve as a starting point for a conversation between providers and their older child population, she noted.
Children who exhibit avoidance or withdrawal behaviors including consistent school refusal, an increase in reassurance-seeking behaviors, or somatic symptoms like vague abdominal pain or headaches that prevent school attendance after participating in a drill, may need more robust mental health services, Dr. Loper noted.
Dr. Schonfeld, who is also director of the National Center for School Crisis and Bereavement at Children’s Hospital Los Angeles, called for health care providers to be available to help children process traumatic reactions to these exercises.
Agreeing with Dr. Schonfeld, Dr. Younghans said: “It is vital to debrief with students and staff after drills, making sure that students have a safe space and ample time to speak with trusted staff. As children will undoubtedly have questions and concerns, creating open lines of communication will help alleviate any traumatic effect these drills may have.”
Communicating with various stakeholders
Experts also gave recommendations for how clinicians communicate with leaders in their area’s school districts and other members of their communities about these training exercises.
“For primary care providers, it is important to establish meaningful relationships within your community and patient population as much as possible,” Dr. Younghans said. “Having a good relationship with the local schools and being part of the conversation can help increase school and community awareness on the impact these drills can have on students and staff,” she added.
For those pediatricians or other health care providers who serve as consultants to schools, Dr. Schonfeld advised they ask about policies related to exercises and drills, such as what are the limits to what children might be exposed to in a drill, and what requirements there might be at the local and state level in terms of frequency and what the drills will and will not involve.
He also noted that clinicians should encourage school leaders to consider the fact that kids may have personal histories of trauma that are completely unknown to the school when they design these exercises.
School staff and health care providers should explain the nature and reasons for drills, invite family members to express concerns, and make accommodations if necessary for some children to participate in drills in a more limited way, noted Dr. Schonfeld, who is also clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
“I think health care providers should work with legislators, so that if they require a drill, it must be done in a way that is physically and emotionally safe,” he added.
Executing better drills for students’ mental health
Experts also advised on ways to execute these drills that will be least damaging to students.
The AAP statement on Participation of Children and Adolescents in Live Crisis Drills and Exercises, for example, advocates eliminating high-intensity drills, prohibiting deception in drills, and providing accommodations based on children’s vulnerabilities.
Dr. Schonfeld also emphasized, in an interview, that training for an attack need not be extremely realistic to be effective.
“When you are preparing for a crisis, the drills and exercises are for children to practice and develop mastery over something they don’t know how to do fully yet,” said Dr. Schonfeld.
Citing a suggestion from a 2020 report conducted by Everytown for Gun Safety on keeping schools safe from gun violence, Dr. Younghans said, “Schools should be in clear communication with communities and families regarding when drills will be happening,” and advised ensuring that the explanation of drills is developmentally appropriate to the age of the children participating.
The report also recommends conducting drills that do not simulate an actual incident, combining drills with trauma-informed approaches to address students’ well-being during and for a sustained period after the drills, and tracking data on the efficacy and effects of drills.
Dr. Loper suggested ways that clinicians and parents can help navigate the tricky territory of school safety drills.
In his view, they should not be random or unexpected, and anticipatory guidance should be given regarding any visual or auditory stimuli, such as flashing lights or sirens, alarms, or announcements.
“A preventive approach should be utilized to ensure that any child who is experiencing extreme drill-distress be excused from any future disaster drills to prevent retraumatization,” Dr. Loper said.
Physicians interviewed for this piece also provided tips on how to talk about these events with children in a way that is beneficial to their mental health.
“What we want to do is [have a] calm discussion [with kids] about what we are doing and why we are doing it” and guide them through the movements, Dr. Schonfeld said.
When teaching children how to respond to an emergency, some elements of uncertainty need to be discussed. Children need to anticipate “what you might do if you are not in the classroom if something occurs, such as being in the bathroom, or out at recess,” he continued.
Dr. Younghans recommended that parents and staff schedule time to prepare children for the drill and practice in advance, and that behavioral health providers, counselors, and/or primary care providers should be involved in the planning and execution of the drill.
The Georgia Tech study was supported through a grant from Everytown for Gun Safety.
The study authors and experts interviewed for this piece had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Sexual assault flagged as a possible psychosis trigger
A new study sheds light on some of the risk factors for the development of psychosis, including the potentially causative role of sexual assault.
Investigators conducted an exposome-wide association analysis on more than 155,000 individuals. Of more than 140 correlates of psychotic experiences that they identified, they narrowed it down to 36 variables, which they further explored using Mendelian randomization analysis.
On the other hand, having experienced a physical violent crime, cannabis use, and prolonged worry after embarrassment showed a pleiotropic association and appeared to be an aftereffect of psychotic experience.
“From a public health perspective, we need more investment in comprehensive strategies to prevent traumatic experiences at the population level to decrease the burden of psychosis,” senior author Sinan Gülöksüz, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and neuropsychiatry, Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
“From a clinical perspective, clinicians should be aware of the harmful influence of traumatic experiences on mental health and address this through interventions such as trauma-informed care,” he said.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Disentangling’ cause and effect
“Previous research has shown associations between psychosis and a few environmental factors, such as substance use, urbanicity, pregnancy complications, and traumatic experiences, but research has so far investigated only a few specific environmental factors by singling them out in individual studies,” Dr. Gülöksüz said.
“Yet, environment is a much more complex and interactive network that includes many factors shaping our health – where we live, what we eat, our lifestyle preferences and habits such as exercise and smoking, and our social surrounding,” he continued. “Rarely has it been possible to understand whether these environmental factors have causal roles in developing psychosis.”
To investigate the question, the researchers turned to the UK Biobank, one of the largest population-based datasets in the world. The current study focused on individuals with completed data on mental questionnaires that assessed psychotic experiences (n = 155,247; mean [SD] age, 55.94 [7.74] years; 57% female).
They began by conducting an exposome-wide association study, using logistic regression analyses with psychotic experiences as the outcome and adjusting all analyses for age and sex.
“Initially, we identified many associations between environmental factors and psychotic experiences in this large cohort,” Dr. Gülöksüz reported.
In the final multivariable model, variables associated with psychotic experiences were further analyzed using “genetically informed approaches to probe potential associations.”
The researchers utilized Mendelian randomization (MR) methodology “to disentangle cause and effect in this observational study,” Dr. Gülöksüz said. “This method reduces confounding and reverse causation in observational studies by using genetic variants that have been passed on from generation to generation randomly as instruments.”
MR analysis “has allowed us to assess whether these associations reflect potentially causal influences of environmental factors on psychotic experiences,” he added.
Well-studied and unexplored risk factors
The researchers identified 162 variables associated with psychotic experiences in the discovery dataset and were able to replicate 148. When these 148 variables were subjected to multivariable analyses, 36 were found to be statistically significantly associated with psychotic experiences. Of these variables, 28 had “significant genetic overlap” with psychotic experiences.
When the researchers conducted one-sample MR analyses, they found forward associations with three variables and reverse associations with three variables.
Forward associations were found with ever having experienced sexual assault (odds ratio [OR], 1.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.14-1.52; P = 2.67), and forward associations (with pleiotropy) were found with ever having experienced a physically violent crime and risk-taking behavior (OR, 1.25, 95% CI, 1.11-1.41; P = 3.28 and OR, 1.21, 95% CI, 1.08-1.35; P = 1.34, respectively).
“The allele scores for these 3 variables explained 0.03% to 0.23% variance of the corresponding variable” and the F statistics “ranged from 21.53 to 181.84, indicating that the results did not suffer from a weak-instrument bias,” the authors reported.
The researchers calculated an instrument based on increasing psychotic experiences risk allele scores and found that these scores explained 0.14% variance of psychotic experiences (F statistic, 19.26).
Using that calculation, they found a reverse association with having experienced a physically violent crime (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.13; P = 3.92 × 10-4), cannabis use (OR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.06-1.15; P = 2.64 × 10-6), and worrying too long after embarrassment (OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03-1.10; P = 3.96 × 10-4). They then validated these associations.
The presence of all five correlates was associated with tenfold increased odds of psychotic experiences (OR, 10.63; 95% CI, 8.27-13.65, P = 1.2 × 10-114).
“Associations with psychotic experiences were found with both well-studied and unexplored multiple correlated variables,” the authors stated.
Era of ‘big data’
In a comment, Chirag Patel, PhD, associate professor of biomedical informatics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not involved with the study, said he thought the study was “a nice example of a data-driven and comprehensive study of the environment coupled with attempts to triangulate evidence from genetics, made possible by biobank data.
“To guide public health policies and implementation of prevention strategies for psychosis, we need more systematic analyses and triangulate evidence with genetically informed methods to identify potentially modifiable risk factors in the era of ‘big data,’ ” he said.
“For instance, traumatic experiences contribute to poor mental and physical health, including psychosis,” Dr. Gülöksüz added.
The Kootstra Talent Fellowship, the Ophelia Research Project, and the Vidi Award from the Netherlands Scientific Organization provided funding to individual investigators. Dr. Gülöksüz and coauthors declared no relevant financial conflicts. Dr. Patel served as a reviewer on the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study sheds light on some of the risk factors for the development of psychosis, including the potentially causative role of sexual assault.
Investigators conducted an exposome-wide association analysis on more than 155,000 individuals. Of more than 140 correlates of psychotic experiences that they identified, they narrowed it down to 36 variables, which they further explored using Mendelian randomization analysis.
On the other hand, having experienced a physical violent crime, cannabis use, and prolonged worry after embarrassment showed a pleiotropic association and appeared to be an aftereffect of psychotic experience.
“From a public health perspective, we need more investment in comprehensive strategies to prevent traumatic experiences at the population level to decrease the burden of psychosis,” senior author Sinan Gülöksüz, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and neuropsychiatry, Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
“From a clinical perspective, clinicians should be aware of the harmful influence of traumatic experiences on mental health and address this through interventions such as trauma-informed care,” he said.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Disentangling’ cause and effect
“Previous research has shown associations between psychosis and a few environmental factors, such as substance use, urbanicity, pregnancy complications, and traumatic experiences, but research has so far investigated only a few specific environmental factors by singling them out in individual studies,” Dr. Gülöksüz said.
“Yet, environment is a much more complex and interactive network that includes many factors shaping our health – where we live, what we eat, our lifestyle preferences and habits such as exercise and smoking, and our social surrounding,” he continued. “Rarely has it been possible to understand whether these environmental factors have causal roles in developing psychosis.”
To investigate the question, the researchers turned to the UK Biobank, one of the largest population-based datasets in the world. The current study focused on individuals with completed data on mental questionnaires that assessed psychotic experiences (n = 155,247; mean [SD] age, 55.94 [7.74] years; 57% female).
They began by conducting an exposome-wide association study, using logistic regression analyses with psychotic experiences as the outcome and adjusting all analyses for age and sex.
“Initially, we identified many associations between environmental factors and psychotic experiences in this large cohort,” Dr. Gülöksüz reported.
In the final multivariable model, variables associated with psychotic experiences were further analyzed using “genetically informed approaches to probe potential associations.”
The researchers utilized Mendelian randomization (MR) methodology “to disentangle cause and effect in this observational study,” Dr. Gülöksüz said. “This method reduces confounding and reverse causation in observational studies by using genetic variants that have been passed on from generation to generation randomly as instruments.”
MR analysis “has allowed us to assess whether these associations reflect potentially causal influences of environmental factors on psychotic experiences,” he added.
Well-studied and unexplored risk factors
The researchers identified 162 variables associated with psychotic experiences in the discovery dataset and were able to replicate 148. When these 148 variables were subjected to multivariable analyses, 36 were found to be statistically significantly associated with psychotic experiences. Of these variables, 28 had “significant genetic overlap” with psychotic experiences.
When the researchers conducted one-sample MR analyses, they found forward associations with three variables and reverse associations with three variables.
Forward associations were found with ever having experienced sexual assault (odds ratio [OR], 1.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.14-1.52; P = 2.67), and forward associations (with pleiotropy) were found with ever having experienced a physically violent crime and risk-taking behavior (OR, 1.25, 95% CI, 1.11-1.41; P = 3.28 and OR, 1.21, 95% CI, 1.08-1.35; P = 1.34, respectively).
“The allele scores for these 3 variables explained 0.03% to 0.23% variance of the corresponding variable” and the F statistics “ranged from 21.53 to 181.84, indicating that the results did not suffer from a weak-instrument bias,” the authors reported.
The researchers calculated an instrument based on increasing psychotic experiences risk allele scores and found that these scores explained 0.14% variance of psychotic experiences (F statistic, 19.26).
Using that calculation, they found a reverse association with having experienced a physically violent crime (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.13; P = 3.92 × 10-4), cannabis use (OR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.06-1.15; P = 2.64 × 10-6), and worrying too long after embarrassment (OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03-1.10; P = 3.96 × 10-4). They then validated these associations.
The presence of all five correlates was associated with tenfold increased odds of psychotic experiences (OR, 10.63; 95% CI, 8.27-13.65, P = 1.2 × 10-114).
“Associations with psychotic experiences were found with both well-studied and unexplored multiple correlated variables,” the authors stated.
Era of ‘big data’
In a comment, Chirag Patel, PhD, associate professor of biomedical informatics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not involved with the study, said he thought the study was “a nice example of a data-driven and comprehensive study of the environment coupled with attempts to triangulate evidence from genetics, made possible by biobank data.
“To guide public health policies and implementation of prevention strategies for psychosis, we need more systematic analyses and triangulate evidence with genetically informed methods to identify potentially modifiable risk factors in the era of ‘big data,’ ” he said.
“For instance, traumatic experiences contribute to poor mental and physical health, including psychosis,” Dr. Gülöksüz added.
The Kootstra Talent Fellowship, the Ophelia Research Project, and the Vidi Award from the Netherlands Scientific Organization provided funding to individual investigators. Dr. Gülöksüz and coauthors declared no relevant financial conflicts. Dr. Patel served as a reviewer on the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new study sheds light on some of the risk factors for the development of psychosis, including the potentially causative role of sexual assault.
Investigators conducted an exposome-wide association analysis on more than 155,000 individuals. Of more than 140 correlates of psychotic experiences that they identified, they narrowed it down to 36 variables, which they further explored using Mendelian randomization analysis.
On the other hand, having experienced a physical violent crime, cannabis use, and prolonged worry after embarrassment showed a pleiotropic association and appeared to be an aftereffect of psychotic experience.
“From a public health perspective, we need more investment in comprehensive strategies to prevent traumatic experiences at the population level to decrease the burden of psychosis,” senior author Sinan Gülöksüz, MD, PhD, associate professor in the department of psychiatry and neuropsychiatry, Maastricht University Medical Center, the Netherlands, said in an interview.
“From a clinical perspective, clinicians should be aware of the harmful influence of traumatic experiences on mental health and address this through interventions such as trauma-informed care,” he said.
The study was published online in JAMA Psychiatry.
‘Disentangling’ cause and effect
“Previous research has shown associations between psychosis and a few environmental factors, such as substance use, urbanicity, pregnancy complications, and traumatic experiences, but research has so far investigated only a few specific environmental factors by singling them out in individual studies,” Dr. Gülöksüz said.
“Yet, environment is a much more complex and interactive network that includes many factors shaping our health – where we live, what we eat, our lifestyle preferences and habits such as exercise and smoking, and our social surrounding,” he continued. “Rarely has it been possible to understand whether these environmental factors have causal roles in developing psychosis.”
To investigate the question, the researchers turned to the UK Biobank, one of the largest population-based datasets in the world. The current study focused on individuals with completed data on mental questionnaires that assessed psychotic experiences (n = 155,247; mean [SD] age, 55.94 [7.74] years; 57% female).
They began by conducting an exposome-wide association study, using logistic regression analyses with psychotic experiences as the outcome and adjusting all analyses for age and sex.
“Initially, we identified many associations between environmental factors and psychotic experiences in this large cohort,” Dr. Gülöksüz reported.
In the final multivariable model, variables associated with psychotic experiences were further analyzed using “genetically informed approaches to probe potential associations.”
The researchers utilized Mendelian randomization (MR) methodology “to disentangle cause and effect in this observational study,” Dr. Gülöksüz said. “This method reduces confounding and reverse causation in observational studies by using genetic variants that have been passed on from generation to generation randomly as instruments.”
MR analysis “has allowed us to assess whether these associations reflect potentially causal influences of environmental factors on psychotic experiences,” he added.
Well-studied and unexplored risk factors
The researchers identified 162 variables associated with psychotic experiences in the discovery dataset and were able to replicate 148. When these 148 variables were subjected to multivariable analyses, 36 were found to be statistically significantly associated with psychotic experiences. Of these variables, 28 had “significant genetic overlap” with psychotic experiences.
When the researchers conducted one-sample MR analyses, they found forward associations with three variables and reverse associations with three variables.
Forward associations were found with ever having experienced sexual assault (odds ratio [OR], 1.32; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.14-1.52; P = 2.67), and forward associations (with pleiotropy) were found with ever having experienced a physically violent crime and risk-taking behavior (OR, 1.25, 95% CI, 1.11-1.41; P = 3.28 and OR, 1.21, 95% CI, 1.08-1.35; P = 1.34, respectively).
“The allele scores for these 3 variables explained 0.03% to 0.23% variance of the corresponding variable” and the F statistics “ranged from 21.53 to 181.84, indicating that the results did not suffer from a weak-instrument bias,” the authors reported.
The researchers calculated an instrument based on increasing psychotic experiences risk allele scores and found that these scores explained 0.14% variance of psychotic experiences (F statistic, 19.26).
Using that calculation, they found a reverse association with having experienced a physically violent crime (OR, 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.13; P = 3.92 × 10-4), cannabis use (OR, 1.11; 95% CI, 1.06-1.15; P = 2.64 × 10-6), and worrying too long after embarrassment (OR, 1.06; 95% CI, 1.03-1.10; P = 3.96 × 10-4). They then validated these associations.
The presence of all five correlates was associated with tenfold increased odds of psychotic experiences (OR, 10.63; 95% CI, 8.27-13.65, P = 1.2 × 10-114).
“Associations with psychotic experiences were found with both well-studied and unexplored multiple correlated variables,” the authors stated.
Era of ‘big data’
In a comment, Chirag Patel, PhD, associate professor of biomedical informatics at Harvard Medical School, Boston, who was not involved with the study, said he thought the study was “a nice example of a data-driven and comprehensive study of the environment coupled with attempts to triangulate evidence from genetics, made possible by biobank data.
“To guide public health policies and implementation of prevention strategies for psychosis, we need more systematic analyses and triangulate evidence with genetically informed methods to identify potentially modifiable risk factors in the era of ‘big data,’ ” he said.
“For instance, traumatic experiences contribute to poor mental and physical health, including psychosis,” Dr. Gülöksüz added.
The Kootstra Talent Fellowship, the Ophelia Research Project, and the Vidi Award from the Netherlands Scientific Organization provided funding to individual investigators. Dr. Gülöksüz and coauthors declared no relevant financial conflicts. Dr. Patel served as a reviewer on the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA PSYCHIATRY
Good news, bad news
“Children’s hospitals saw a more than 25% decline in injury-related emergency room visits during the first year of the pandemic.” There’s a headline that should soothe a nation starved for some good news. It was based on a study published in Pediatrics that reports on data collected in the Pediatric Health Information System between March 2020 and March 2021 using a 3-year period between 2017 and 2020 as a control. How could this not be good news? First, let’s not be too hasty in celebrating the good fortune of all those millions of children spared the pain and anxiety of an emergency department visit.
If you were an administrator of an emergency department attempting to match revenues with expenses, a 25% drop in visits may have hit your bottom line. Office-based pediatricians experienced a similar phenomenon when many parents quickly learned that they could ignore or self-manage minor illnesses and complaints.
A decrease in visits doesn’t necessarily mean that the conditions that drive the traffic flow in your facility have gone away. It may simply be that they are being managed somewhere else. However, it is equally likely that for some reason the pandemic created situations that made the usual illnesses and injuries that flood into emergency departments less likely to occur. And, here, other anecdotal evidence about weight gain and a decline in fitness point to the conclusion that when children are no longer in school, they settle into more sedentary and less injury-generating activities. Injuries from falling off the couch watching television or playing video games alone do occur but certainly with less frequency than the random collisions that are inevitable when scores of classmates are running around on the playground.
So while it may be tempting to view a decline in emergency department visits as a positive statistic, this pandemic should remind us to be careful about how we choose our metrics to measure the health of the community. A decline in injuries in the short term may be masking a more serious erosion in the health of the pediatric population over the long term. At times I worry that as a specialty we are so focused on injury prevention that we lose sight of the fact that being physically active comes with a risk. A risk that we may wish to minimize, but a risk we must accept if we want to encourage the physical activity that we know is so important in the bigger health picture. For example, emergency department visits caused by pedal cycles initially rose 60%, eventually settling into the 25%-30% range leading one to suspect there was a learning or relearning curve.
However, while visits for minor injuries declined 25%, those associated with firearms rose initially 22%, and then 42%, and finally over 35%. These numbers combined with significant increases in visits from suffocation, nonpedal transportation, and suicide intent make it clear that, for most children, being in school is significantly less dangerous than staying at home.
As the pandemic continues to tumble on and we are presented with future questions about whether to keep schools open or closed, I hope the results of this study and others will help school officials and their advisers step back and look beyond the simple metric of case numbers and appreciate that there are benefits to being in school that go far beyond what can be learned in class.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
“Children’s hospitals saw a more than 25% decline in injury-related emergency room visits during the first year of the pandemic.” There’s a headline that should soothe a nation starved for some good news. It was based on a study published in Pediatrics that reports on data collected in the Pediatric Health Information System between March 2020 and March 2021 using a 3-year period between 2017 and 2020 as a control. How could this not be good news? First, let’s not be too hasty in celebrating the good fortune of all those millions of children spared the pain and anxiety of an emergency department visit.
If you were an administrator of an emergency department attempting to match revenues with expenses, a 25% drop in visits may have hit your bottom line. Office-based pediatricians experienced a similar phenomenon when many parents quickly learned that they could ignore or self-manage minor illnesses and complaints.
A decrease in visits doesn’t necessarily mean that the conditions that drive the traffic flow in your facility have gone away. It may simply be that they are being managed somewhere else. However, it is equally likely that for some reason the pandemic created situations that made the usual illnesses and injuries that flood into emergency departments less likely to occur. And, here, other anecdotal evidence about weight gain and a decline in fitness point to the conclusion that when children are no longer in school, they settle into more sedentary and less injury-generating activities. Injuries from falling off the couch watching television or playing video games alone do occur but certainly with less frequency than the random collisions that are inevitable when scores of classmates are running around on the playground.
So while it may be tempting to view a decline in emergency department visits as a positive statistic, this pandemic should remind us to be careful about how we choose our metrics to measure the health of the community. A decline in injuries in the short term may be masking a more serious erosion in the health of the pediatric population over the long term. At times I worry that as a specialty we are so focused on injury prevention that we lose sight of the fact that being physically active comes with a risk. A risk that we may wish to minimize, but a risk we must accept if we want to encourage the physical activity that we know is so important in the bigger health picture. For example, emergency department visits caused by pedal cycles initially rose 60%, eventually settling into the 25%-30% range leading one to suspect there was a learning or relearning curve.
However, while visits for minor injuries declined 25%, those associated with firearms rose initially 22%, and then 42%, and finally over 35%. These numbers combined with significant increases in visits from suffocation, nonpedal transportation, and suicide intent make it clear that, for most children, being in school is significantly less dangerous than staying at home.
As the pandemic continues to tumble on and we are presented with future questions about whether to keep schools open or closed, I hope the results of this study and others will help school officials and their advisers step back and look beyond the simple metric of case numbers and appreciate that there are benefits to being in school that go far beyond what can be learned in class.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
“Children’s hospitals saw a more than 25% decline in injury-related emergency room visits during the first year of the pandemic.” There’s a headline that should soothe a nation starved for some good news. It was based on a study published in Pediatrics that reports on data collected in the Pediatric Health Information System between March 2020 and March 2021 using a 3-year period between 2017 and 2020 as a control. How could this not be good news? First, let’s not be too hasty in celebrating the good fortune of all those millions of children spared the pain and anxiety of an emergency department visit.
If you were an administrator of an emergency department attempting to match revenues with expenses, a 25% drop in visits may have hit your bottom line. Office-based pediatricians experienced a similar phenomenon when many parents quickly learned that they could ignore or self-manage minor illnesses and complaints.
A decrease in visits doesn’t necessarily mean that the conditions that drive the traffic flow in your facility have gone away. It may simply be that they are being managed somewhere else. However, it is equally likely that for some reason the pandemic created situations that made the usual illnesses and injuries that flood into emergency departments less likely to occur. And, here, other anecdotal evidence about weight gain and a decline in fitness point to the conclusion that when children are no longer in school, they settle into more sedentary and less injury-generating activities. Injuries from falling off the couch watching television or playing video games alone do occur but certainly with less frequency than the random collisions that are inevitable when scores of classmates are running around on the playground.
So while it may be tempting to view a decline in emergency department visits as a positive statistic, this pandemic should remind us to be careful about how we choose our metrics to measure the health of the community. A decline in injuries in the short term may be masking a more serious erosion in the health of the pediatric population over the long term. At times I worry that as a specialty we are so focused on injury prevention that we lose sight of the fact that being physically active comes with a risk. A risk that we may wish to minimize, but a risk we must accept if we want to encourage the physical activity that we know is so important in the bigger health picture. For example, emergency department visits caused by pedal cycles initially rose 60%, eventually settling into the 25%-30% range leading one to suspect there was a learning or relearning curve.
However, while visits for minor injuries declined 25%, those associated with firearms rose initially 22%, and then 42%, and finally over 35%. These numbers combined with significant increases in visits from suffocation, nonpedal transportation, and suicide intent make it clear that, for most children, being in school is significantly less dangerous than staying at home.
As the pandemic continues to tumble on and we are presented with future questions about whether to keep schools open or closed, I hope the results of this study and others will help school officials and their advisers step back and look beyond the simple metric of case numbers and appreciate that there are benefits to being in school that go far beyond what can be learned in class.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].






