User login
LIFSCREEN data support broader cancer screening in Li-Fraumeni syndrome
Broader cancer screening of individuals with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS), with or without whole-body magnetic resonance imaging, has a good diagnostic yield and identifies a wide range of cancers, according to a preliminary analysis of the ongoing LIFSCREEN phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Investigators led by Olivier Caron, MD, chair of the oncogenetics committee, department of medical oncology, at the Gustave Roussy University Hospital in Villejuif, France, enrolled in the trial 107 individuals from 75 families carrying a TP53 mutation, a genetic aberration commonly present in LFS that confers heightened risk of a variety of malignancies.
Participants had a median age at baseline of 32.9 years, with a range from 5 to 67 years. Fully 98% had a family history of cancer, and 48% had a personal history of cancer.
The participants were assigned to 5 years of standard screening – annual clinical examination, abdomen and pelvis ultrasound, brain MRI, complete blood cell count, and, for women older than 20 years, breast ultrasound and MRI – or intensive screening, entailing the addition of diffusion whole-body MRI.
At the time of the preliminary analysis, 15 patients had undergone only one round of screening; 35, two rounds; 19, three rounds; 24, four rounds; and 7, five rounds, Dr. Caron and associates reported in a research letter (JAMA Oncol. 2017; Aug 3 doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.1358).
Collectively, this amounted to 226.4 person-years of follow-up.
Screening with either trial strategy (with or without whole-body MRI) led to diagnosis of 23 new primary cancers in 20 patients. Nearly half of the total (12 cancers) were detected at the first round. Patients had a median age of 39.8 at the new cancer diagnosis, with a range from 6 to 70 years.
Of the new cancers, 10 belonged to the core LFS spectrum of breast cancer, sarcoma, and brain tumors. However, the other 13 were outside that spectrum, for example, lung adenocarcinomas, all seen in never or light smokers, and leukemias. Screening also detected three relapses of previous cancers.
Analyses further showed that prior cancer diagnosis was not a reliable marker for risk of new primaries. Although 12 of the patients with a screening-detected new primary had a personal cancer history, 8 did not (P = .22).
“The proportion and diversity of off–core LFS spectrum cancers detected in TP53 mutation carriers as reported by others give growing evidence of a broader LFS spectrum, in agreement with the permissive role of TP53 mutations,” write Dr. Caron and colleagues, who report having no relevant disclosures. “Our observations seem to support recent moves toward broader cancer screening in TP53 mutation carriers.”
The investigators continue to collect data in LIFSCREEN and plan to undertake main analysis later this year. “Our final analysis will help to determine the benefits and drawbacks (mostly related to false-positive test results) of whole-body MRI in TP53 mutation carrier surveillance,” they conclude. “Studies focused on TP53 mutation penetrance, using methods limiting selection bias, are required to refine cancer risks to improve TP53 mutation carrier management.”
Broader cancer screening of individuals with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS), with or without whole-body magnetic resonance imaging, has a good diagnostic yield and identifies a wide range of cancers, according to a preliminary analysis of the ongoing LIFSCREEN phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Investigators led by Olivier Caron, MD, chair of the oncogenetics committee, department of medical oncology, at the Gustave Roussy University Hospital in Villejuif, France, enrolled in the trial 107 individuals from 75 families carrying a TP53 mutation, a genetic aberration commonly present in LFS that confers heightened risk of a variety of malignancies.
Participants had a median age at baseline of 32.9 years, with a range from 5 to 67 years. Fully 98% had a family history of cancer, and 48% had a personal history of cancer.
The participants were assigned to 5 years of standard screening – annual clinical examination, abdomen and pelvis ultrasound, brain MRI, complete blood cell count, and, for women older than 20 years, breast ultrasound and MRI – or intensive screening, entailing the addition of diffusion whole-body MRI.
At the time of the preliminary analysis, 15 patients had undergone only one round of screening; 35, two rounds; 19, three rounds; 24, four rounds; and 7, five rounds, Dr. Caron and associates reported in a research letter (JAMA Oncol. 2017; Aug 3 doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.1358).
Collectively, this amounted to 226.4 person-years of follow-up.
Screening with either trial strategy (with or without whole-body MRI) led to diagnosis of 23 new primary cancers in 20 patients. Nearly half of the total (12 cancers) were detected at the first round. Patients had a median age of 39.8 at the new cancer diagnosis, with a range from 6 to 70 years.
Of the new cancers, 10 belonged to the core LFS spectrum of breast cancer, sarcoma, and brain tumors. However, the other 13 were outside that spectrum, for example, lung adenocarcinomas, all seen in never or light smokers, and leukemias. Screening also detected three relapses of previous cancers.
Analyses further showed that prior cancer diagnosis was not a reliable marker for risk of new primaries. Although 12 of the patients with a screening-detected new primary had a personal cancer history, 8 did not (P = .22).
“The proportion and diversity of off–core LFS spectrum cancers detected in TP53 mutation carriers as reported by others give growing evidence of a broader LFS spectrum, in agreement with the permissive role of TP53 mutations,” write Dr. Caron and colleagues, who report having no relevant disclosures. “Our observations seem to support recent moves toward broader cancer screening in TP53 mutation carriers.”
The investigators continue to collect data in LIFSCREEN and plan to undertake main analysis later this year. “Our final analysis will help to determine the benefits and drawbacks (mostly related to false-positive test results) of whole-body MRI in TP53 mutation carrier surveillance,” they conclude. “Studies focused on TP53 mutation penetrance, using methods limiting selection bias, are required to refine cancer risks to improve TP53 mutation carrier management.”
Broader cancer screening of individuals with Li-Fraumeni syndrome (LFS), with or without whole-body magnetic resonance imaging, has a good diagnostic yield and identifies a wide range of cancers, according to a preliminary analysis of the ongoing LIFSCREEN phase 3, randomized, controlled trial.
Investigators led by Olivier Caron, MD, chair of the oncogenetics committee, department of medical oncology, at the Gustave Roussy University Hospital in Villejuif, France, enrolled in the trial 107 individuals from 75 families carrying a TP53 mutation, a genetic aberration commonly present in LFS that confers heightened risk of a variety of malignancies.
Participants had a median age at baseline of 32.9 years, with a range from 5 to 67 years. Fully 98% had a family history of cancer, and 48% had a personal history of cancer.
The participants were assigned to 5 years of standard screening – annual clinical examination, abdomen and pelvis ultrasound, brain MRI, complete blood cell count, and, for women older than 20 years, breast ultrasound and MRI – or intensive screening, entailing the addition of diffusion whole-body MRI.
At the time of the preliminary analysis, 15 patients had undergone only one round of screening; 35, two rounds; 19, three rounds; 24, four rounds; and 7, five rounds, Dr. Caron and associates reported in a research letter (JAMA Oncol. 2017; Aug 3 doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2017.1358).
Collectively, this amounted to 226.4 person-years of follow-up.
Screening with either trial strategy (with or without whole-body MRI) led to diagnosis of 23 new primary cancers in 20 patients. Nearly half of the total (12 cancers) were detected at the first round. Patients had a median age of 39.8 at the new cancer diagnosis, with a range from 6 to 70 years.
Of the new cancers, 10 belonged to the core LFS spectrum of breast cancer, sarcoma, and brain tumors. However, the other 13 were outside that spectrum, for example, lung adenocarcinomas, all seen in never or light smokers, and leukemias. Screening also detected three relapses of previous cancers.
Analyses further showed that prior cancer diagnosis was not a reliable marker for risk of new primaries. Although 12 of the patients with a screening-detected new primary had a personal cancer history, 8 did not (P = .22).
“The proportion and diversity of off–core LFS spectrum cancers detected in TP53 mutation carriers as reported by others give growing evidence of a broader LFS spectrum, in agreement with the permissive role of TP53 mutations,” write Dr. Caron and colleagues, who report having no relevant disclosures. “Our observations seem to support recent moves toward broader cancer screening in TP53 mutation carriers.”
The investigators continue to collect data in LIFSCREEN and plan to undertake main analysis later this year. “Our final analysis will help to determine the benefits and drawbacks (mostly related to false-positive test results) of whole-body MRI in TP53 mutation carrier surveillance,” they conclude. “Studies focused on TP53 mutation penetrance, using methods limiting selection bias, are required to refine cancer risks to improve TP53 mutation carrier management.”
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point:
Major finding: A total of 23 new primary cancers were diagnosed in 20 patients; more than half were outside the core spectrum of Li-Fraumeni syndrome.
Data source: A preliminary analysis of a phase 3, randomized, controlled trial comparing standard and intensive screening among 107 individuals with Li-Fraumeni syndrome carrying a TP53 mutation (LIFSCREEN trial).
Disclosures: The investigators report having no relevant disclosures. The trial was funded by the French Ligue Contre le Cancer.
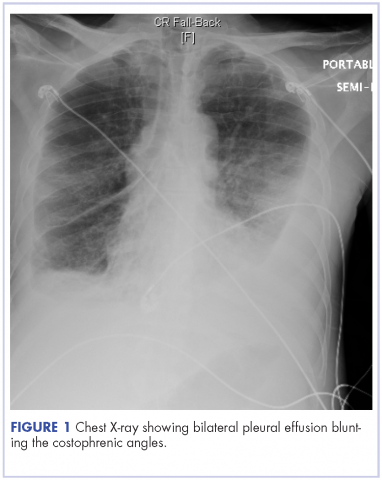
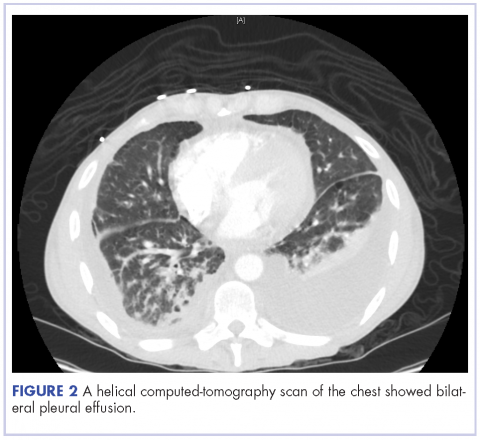
Bilateral chylothorax in an AIDS patient with newly diagnosed Kaposi sarcoma
Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative tumor that is associated with human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8). Mucocutaneous disease is the most common site for manifestation of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, commonly affecting the lower extremities, oral mucosa, face, and genitalia. Pleural effusions can occur in 36%-60% of patients with Kaposi sarcoma, and it has been documented that chylothorax is a rare, but plausible presentation in patients with Kaposi sarcoma.1 We present here a case of bilateral chylothorax in a patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma.
Case presentation and summary
A 52-year-old MSM male with AIDS (CD4, <20 mm3; viral load, 58 copies/ml) presented to the emergency department with complaints of shortness of breath, productive cough, and diarrhea for 2 days prior to presentation. His medical history also included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease, and hyperlipidemia. The patient was not on HAART because of his history of noncompliance. The results of a chest X-ray and computed-tomography (CT) scan showed that the patient had bilateral pleural effusion and a spiculated 14-mm nodule in the left upper lobe.
The patient underwent ultrasound-guided placement of a 12-French left-sided chest catheter, and a milky white fluid was aspirated from the left pleural space. Laboratory analysis of the pleural fluid confirmed an exudate with an elevated triglyceride level of 120 mg/dL (chylous, >110 mg/dL) indicating chylothorax.
On close physical examination, the patient was found to have multiple irregular plaques on the back and lower extremities. As described by dermatology, there was a violaceous indurated plaque on the left axillae, violaceous indurated plaques with superficial scale grouped on the left midlateral back, and hyperpigmented lichenified plaques and papules on bilateral shins, with some with plate-like scale. Two punch biopsies were taken of the skin lesions, which confirmed Kaposi sarcoma, plaque stage from the lesion biopsied on the back, and patch stage from the lesion biopsied in the left axilla. Cytology of the pleural fluid was negative for malignant cells. On review by the radiologist of the CT scan of the chest, there was no indication of gross distention of the thoracic duct. Treatment options were offered to the patient, and the patient was considering options for chemotherapy and home hospice given his advanced disease state at the time of discharge.
Discussion
Chylothorax occurs with a thoracic duct obstruction, which results in leakage of lymphatic fluid into the pleural cavity. The two leading causes of chylothorax are trauma and malignancy, with lymphoma being the most common cause of chylothorax among those with malignancy.2 Chylothorax, however, is a rare but documented complication of Kaposi sarcoma. Marais and colleagues reported the case of a 3-year-old HIV-positive patient with newly diagnosed Kaposi sarcoma who was found to have tumor infiltration in the thoracic duct leading to bilateral chylothorax.3 Maradona and colleagues described a 40-year-old man with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma who was found to have pleural and pericardial Kaposi sarcoma with chylothorax.4 Priest and colleagues wrote about a 32-year-old patient with AIDS with biopsy-proven Kaposi sarcoma who required multiple therapeutic thoracenteses for rapidly recurrent left chylothorax effusions.5
There are two leading discussions as to the pathophysiology of chylothorax that is related to Kaposi sarcoma: chylothorax developing secondary to metastatic disease or the development of chylothorax secondary to primary Kaposi sarcoma arising from the pleural region.6 One case report examined pleural and lung biopsies in a 34-year-old patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma that showed immunohistochemical staining that was suggestive of early-stage Kaposi sarcoma of lymphatic endothelial origin. The authors were attempting to illustrate that Kaposi sarcoma may have a stem-cell origin which can differentiate into lymph cells. Kontantinopoulos and colleagues postulated that in situ Kaposi sarcoma can arise from the lymphatic system with a resultant clinical presentation of chylothorax.7 The more mainstream thought however, is that chylothorax has been found to develop secondary to metastatic disease. The present case, therefore, illustrates an unusual presentation of cytology negative chylothorax in a patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma.
1. Sridar S, Garza EG, Cox J, Rumbak MJ. Serosanguineous pleural effusions in a patient with HIV and Kaposi sarcoma: pleuroscopic findings. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2011;18(4):337-339.
2. Light RW. Chylothorax and pseudochylothorax. In: Light RW, ed. Pleural diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013:412-426.
3. Marais BJ, Pienaar J, Gie RP. Kaposi sarcoma with upper airway obstruction and bilateral chylothoraces. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:926-928.
4. Maradona JA, Carton JA, Asensi V, Rodriguez-Guardado A. AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma with chylothorax and pericardial involvement satisfactorily treated with liposomal doxorubicin. AIDS. 2002;16(5):806.
5. Priest ER, Weiss R. Chylothorax with Kaposi sarcoma. South Med J. 1991;84:806-807.
6. Pantanowitz L, Dezube BJ. Kaposi sarcoma in unusual locations. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:190.
7. Konstantinopoulos PA, Dezube BJ, Pantanowitz L. Morphologic and immunophenotypic evidence of in situ Kaposi sarcoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 2006;30:6:7.
Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative tumor that is associated with human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8). Mucocutaneous disease is the most common site for manifestation of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, commonly affecting the lower extremities, oral mucosa, face, and genitalia. Pleural effusions can occur in 36%-60% of patients with Kaposi sarcoma, and it has been documented that chylothorax is a rare, but plausible presentation in patients with Kaposi sarcoma.1 We present here a case of bilateral chylothorax in a patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma.
Case presentation and summary
A 52-year-old MSM male with AIDS (CD4, <20 mm3; viral load, 58 copies/ml) presented to the emergency department with complaints of shortness of breath, productive cough, and diarrhea for 2 days prior to presentation. His medical history also included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease, and hyperlipidemia. The patient was not on HAART because of his history of noncompliance. The results of a chest X-ray and computed-tomography (CT) scan showed that the patient had bilateral pleural effusion and a spiculated 14-mm nodule in the left upper lobe.
The patient underwent ultrasound-guided placement of a 12-French left-sided chest catheter, and a milky white fluid was aspirated from the left pleural space. Laboratory analysis of the pleural fluid confirmed an exudate with an elevated triglyceride level of 120 mg/dL (chylous, >110 mg/dL) indicating chylothorax.
On close physical examination, the patient was found to have multiple irregular plaques on the back and lower extremities. As described by dermatology, there was a violaceous indurated plaque on the left axillae, violaceous indurated plaques with superficial scale grouped on the left midlateral back, and hyperpigmented lichenified plaques and papules on bilateral shins, with some with plate-like scale. Two punch biopsies were taken of the skin lesions, which confirmed Kaposi sarcoma, plaque stage from the lesion biopsied on the back, and patch stage from the lesion biopsied in the left axilla. Cytology of the pleural fluid was negative for malignant cells. On review by the radiologist of the CT scan of the chest, there was no indication of gross distention of the thoracic duct. Treatment options were offered to the patient, and the patient was considering options for chemotherapy and home hospice given his advanced disease state at the time of discharge.
Discussion
Chylothorax occurs with a thoracic duct obstruction, which results in leakage of lymphatic fluid into the pleural cavity. The two leading causes of chylothorax are trauma and malignancy, with lymphoma being the most common cause of chylothorax among those with malignancy.2 Chylothorax, however, is a rare but documented complication of Kaposi sarcoma. Marais and colleagues reported the case of a 3-year-old HIV-positive patient with newly diagnosed Kaposi sarcoma who was found to have tumor infiltration in the thoracic duct leading to bilateral chylothorax.3 Maradona and colleagues described a 40-year-old man with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma who was found to have pleural and pericardial Kaposi sarcoma with chylothorax.4 Priest and colleagues wrote about a 32-year-old patient with AIDS with biopsy-proven Kaposi sarcoma who required multiple therapeutic thoracenteses for rapidly recurrent left chylothorax effusions.5
There are two leading discussions as to the pathophysiology of chylothorax that is related to Kaposi sarcoma: chylothorax developing secondary to metastatic disease or the development of chylothorax secondary to primary Kaposi sarcoma arising from the pleural region.6 One case report examined pleural and lung biopsies in a 34-year-old patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma that showed immunohistochemical staining that was suggestive of early-stage Kaposi sarcoma of lymphatic endothelial origin. The authors were attempting to illustrate that Kaposi sarcoma may have a stem-cell origin which can differentiate into lymph cells. Kontantinopoulos and colleagues postulated that in situ Kaposi sarcoma can arise from the lymphatic system with a resultant clinical presentation of chylothorax.7 The more mainstream thought however, is that chylothorax has been found to develop secondary to metastatic disease. The present case, therefore, illustrates an unusual presentation of cytology negative chylothorax in a patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma.
Kaposi sarcoma is an angioproliferative tumor that is associated with human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8). Mucocutaneous disease is the most common site for manifestation of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, commonly affecting the lower extremities, oral mucosa, face, and genitalia. Pleural effusions can occur in 36%-60% of patients with Kaposi sarcoma, and it has been documented that chylothorax is a rare, but plausible presentation in patients with Kaposi sarcoma.1 We present here a case of bilateral chylothorax in a patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma.
Case presentation and summary
A 52-year-old MSM male with AIDS (CD4, <20 mm3; viral load, 58 copies/ml) presented to the emergency department with complaints of shortness of breath, productive cough, and diarrhea for 2 days prior to presentation. His medical history also included chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, coronary artery disease, and hyperlipidemia. The patient was not on HAART because of his history of noncompliance. The results of a chest X-ray and computed-tomography (CT) scan showed that the patient had bilateral pleural effusion and a spiculated 14-mm nodule in the left upper lobe.
The patient underwent ultrasound-guided placement of a 12-French left-sided chest catheter, and a milky white fluid was aspirated from the left pleural space. Laboratory analysis of the pleural fluid confirmed an exudate with an elevated triglyceride level of 120 mg/dL (chylous, >110 mg/dL) indicating chylothorax.
On close physical examination, the patient was found to have multiple irregular plaques on the back and lower extremities. As described by dermatology, there was a violaceous indurated plaque on the left axillae, violaceous indurated plaques with superficial scale grouped on the left midlateral back, and hyperpigmented lichenified plaques and papules on bilateral shins, with some with plate-like scale. Two punch biopsies were taken of the skin lesions, which confirmed Kaposi sarcoma, plaque stage from the lesion biopsied on the back, and patch stage from the lesion biopsied in the left axilla. Cytology of the pleural fluid was negative for malignant cells. On review by the radiologist of the CT scan of the chest, there was no indication of gross distention of the thoracic duct. Treatment options were offered to the patient, and the patient was considering options for chemotherapy and home hospice given his advanced disease state at the time of discharge.
Discussion
Chylothorax occurs with a thoracic duct obstruction, which results in leakage of lymphatic fluid into the pleural cavity. The two leading causes of chylothorax are trauma and malignancy, with lymphoma being the most common cause of chylothorax among those with malignancy.2 Chylothorax, however, is a rare but documented complication of Kaposi sarcoma. Marais and colleagues reported the case of a 3-year-old HIV-positive patient with newly diagnosed Kaposi sarcoma who was found to have tumor infiltration in the thoracic duct leading to bilateral chylothorax.3 Maradona and colleagues described a 40-year-old man with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma who was found to have pleural and pericardial Kaposi sarcoma with chylothorax.4 Priest and colleagues wrote about a 32-year-old patient with AIDS with biopsy-proven Kaposi sarcoma who required multiple therapeutic thoracenteses for rapidly recurrent left chylothorax effusions.5
There are two leading discussions as to the pathophysiology of chylothorax that is related to Kaposi sarcoma: chylothorax developing secondary to metastatic disease or the development of chylothorax secondary to primary Kaposi sarcoma arising from the pleural region.6 One case report examined pleural and lung biopsies in a 34-year-old patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma that showed immunohistochemical staining that was suggestive of early-stage Kaposi sarcoma of lymphatic endothelial origin. The authors were attempting to illustrate that Kaposi sarcoma may have a stem-cell origin which can differentiate into lymph cells. Kontantinopoulos and colleagues postulated that in situ Kaposi sarcoma can arise from the lymphatic system with a resultant clinical presentation of chylothorax.7 The more mainstream thought however, is that chylothorax has been found to develop secondary to metastatic disease. The present case, therefore, illustrates an unusual presentation of cytology negative chylothorax in a patient with AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma.
1. Sridar S, Garza EG, Cox J, Rumbak MJ. Serosanguineous pleural effusions in a patient with HIV and Kaposi sarcoma: pleuroscopic findings. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2011;18(4):337-339.
2. Light RW. Chylothorax and pseudochylothorax. In: Light RW, ed. Pleural diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013:412-426.
3. Marais BJ, Pienaar J, Gie RP. Kaposi sarcoma with upper airway obstruction and bilateral chylothoraces. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:926-928.
4. Maradona JA, Carton JA, Asensi V, Rodriguez-Guardado A. AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma with chylothorax and pericardial involvement satisfactorily treated with liposomal doxorubicin. AIDS. 2002;16(5):806.
5. Priest ER, Weiss R. Chylothorax with Kaposi sarcoma. South Med J. 1991;84:806-807.
6. Pantanowitz L, Dezube BJ. Kaposi sarcoma in unusual locations. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:190.
7. Konstantinopoulos PA, Dezube BJ, Pantanowitz L. Morphologic and immunophenotypic evidence of in situ Kaposi sarcoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 2006;30:6:7.
1. Sridar S, Garza EG, Cox J, Rumbak MJ. Serosanguineous pleural effusions in a patient with HIV and Kaposi sarcoma: pleuroscopic findings. J Bronchology Interv Pulmonol. 2011;18(4):337-339.
2. Light RW. Chylothorax and pseudochylothorax. In: Light RW, ed. Pleural diseases. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, 2013:412-426.
3. Marais BJ, Pienaar J, Gie RP. Kaposi sarcoma with upper airway obstruction and bilateral chylothoraces. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2003;22:926-928.
4. Maradona JA, Carton JA, Asensi V, Rodriguez-Guardado A. AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma with chylothorax and pericardial involvement satisfactorily treated with liposomal doxorubicin. AIDS. 2002;16(5):806.
5. Priest ER, Weiss R. Chylothorax with Kaposi sarcoma. South Med J. 1991;84:806-807.
6. Pantanowitz L, Dezube BJ. Kaposi sarcoma in unusual locations. BMC Cancer. 2008;8:190.
7. Konstantinopoulos PA, Dezube BJ, Pantanowitz L. Morphologic and immunophenotypic evidence of in situ Kaposi sarcoma. BMC Clin Pathol. 2006;30:6:7.
Metastatic Kaposi sarcoma with osseous involvement in a patient with AIDS
Kaposi sarcoma is an AIDS-defining illness associated with human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8) co-infection. It was described in 1872 by the Hungarian dermatologist Mortiz Kaposi, and was an isolated and sporadic occurrence before the emergence of HIV infection and AIDS.1 It was first affiliated as an AIDS-associated neoplasm in 1981.1 Kaposi sarcoma is a systemic disease that can present with cutaneous lesions with or without internal involvement. There are four subtypes: Classic, African endemic, AIDS-related (CD4 count, <200), and Kaposi sarcoma in iatrogenically immunosuppressed patients. The disease has the propensity to manifest in the skin and gastro-intestinal and respiratory tracts, and osseous involvement is rarely encountered. We present here the case of an AIDS-positive man with generalized bone pain as a result of metastasis from Kaposi sarcoma. Our discussion includes the epidemiological, clinical, pathological, and radiological facets of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, and the anomaly of osseous involvement.
Case presentation and summary
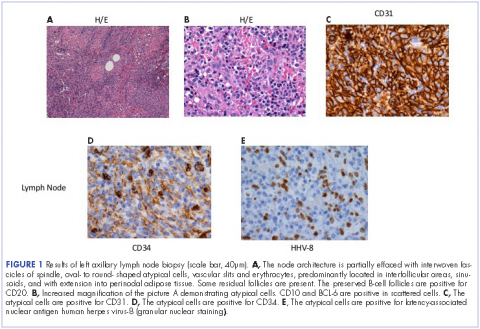
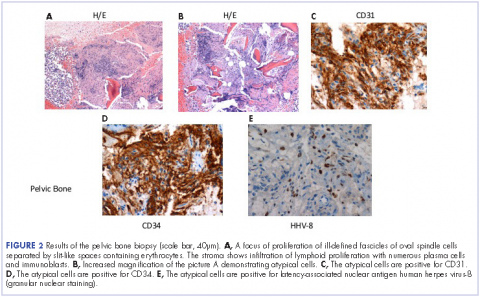
He restarted his previous HAART regimen in March 2016, and was subsequently started on chemotherapy with liposomal doxorubicin (50 mg [20 mg/m2] in 250 ml D5W IV every 2 weeks) because of his extensive disease.2 He completed 6 cycles by June 2016. However, he returned in July 2016 with worsening back pain. A repeat CT scan revealed significant improvement in the disseminated lymphadenopathy, but worsening osseous metastatic disease was seen in the lumbar, thoracic, and pelvic regions. A pelvic lytic lesion biopsy revealed Kaposi sarcoma; pathology showed spindle cells positive for CD34, CD31, and HHV-8 (Figure 2). The patient received palliative radiation to the spine, aiding in pain management and ambulatory dysfunction. He continued with his noncompliance with all medications and outpatient follow-ups, and succumbed to his disease burden.
Discussion
Kaposi sarcoma is a low-grade mesenchymal tumor that involves the blood and lymphatic vessels.3 Its association with AIDS was revealed in the early 1980s at the start of the HIV epidemic in the United States. In 1994, Chang and colleagues discovered the association between Karposi sarcoma and HHV-8 by isolating DNA fragments of HHV in Kaposi sarcoma tumors from AIDS patients.4 The mode of transmission of HHV-8 has not been fully decoded. It has been presumed that adult homosexual contact continues to be an important route of transmission, inferring a common route of infection. In 1990, the overall risk of developing Kaposi sarcoma in AIDS patients was 20,000 times greater than it was in the general population, and 300 times greater than in other immunosuppressed patients.5 This suggests an increase in incidence, in direct relation, with a decrease in the CD4 count.
Kaposi sarcoma can present with a range of clinical features, from negligible cutaneous lesions to a hastily progressing neoplasm. Involvement in the musculoskeletal system is infrequent, but encountered increasingly in the AIDS-related subtype. Moreover, it is recurrently observed in the African population.6 In one of the largest reviews to date exploring Kaposi sarcoma involving the musculoskeletal system, Caponetti and colleagues observed the greatest osseous involvement distinctly in patients with CD4 and T-cell counts below 100 cells/mm3.6
Kaposi sarcoma musculoskeletal involvement, specifically bone, is atypical. If it does occur, it usually manifests as a result of contiguous invasion from an adjacent nonosseous lesion. Caponetti and colleagues that isolated osseous Kaposi sarcoma lesions (with no overlying skin lesion) were found to be more likely to be associated with AIDS in the review by Caponetti and colleagues.6 As in our patient, it is also typically a manifestation of more widely disseminated disease.7
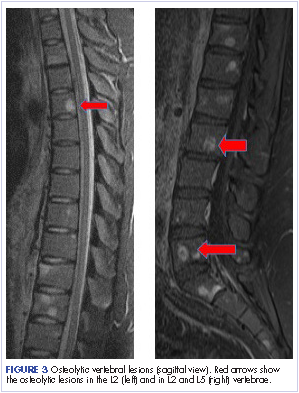
Most of the osseous lytic lesions in AIDS patients are located in the axial skeleton. Radiological features of musculoskeletal Kaposi sarcoma are variable. As observed by Caponetti and colleagues, Kaposi sarcoma lesions can appear as a periosteal reaction, cortical erosions, osteolysis, or osseous destruction, with irregular-shaped cortical erosions being most typical.6 Despite their osteolytic features, Kaposi sarcoma lesions are often not visualized by conventional radiography.6 The preferred imaging for identification of lytic bone changes is CT (Figure 3). Magnetic resonance imaging can also help distinguish marrow abnormalities as well as adjacent soft tissues masses. Radiologically, Kaposi sarcoma osseous lesions have parallel features to bacillary angiomatosis, tuberculosis, or lymphoma.8 Therefore, biopsy of the lesion is essential in establishing the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma.
In theory, there should be clinical improvement in Kaposi sarcoma when immunity is restored. Cancers caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus may eventually also be preventable with vaccines.10
There is rarely bone involvement without the foreshadowing of a poor prognosis. Erroneous patient care may inevitably arise from Kaposi sarcoma in uncharacteristic sites. A differential of Kaposi sarcoma should be included if a patient with AIDS presents with osteolytic lesions on imaging. Biopsying the lesion cements the diagnosis and eliminates the possibility of mimicry conditions such as bacillary angiomatosis, benign vascular lesions, and angiosarcoma. As of today, a HAART regimen remains the standard initial care for patients with Kaposi sarcoma.
1. Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294.
2. Northfelt DW, Dezube BJ, Thommes JA, et al. Pegylated-liposomal doxorubicin versus doxorubicin, bleomycin, and vincristine in the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma: results of a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(7):2445-2451.
3. Restrepo CS, Martinez S, Lemos JA, et al. Imaging manifestations of Kaposi sarcoma. RadioGraphics. 2006;26:1169-1185.
4. Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, et al. Identification of herpes virus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865-1869.
5. Beral V, Peterman TA, Berkelman RL, Jaffe HW. Kaposi sarcoma among persons with AIDS: a sexually transmitted infection? Lancet. 1990;335:123-128.
6. Caponetti G, Dezube BJ, Restrepo CS, Pantanowitz I. Kaposi sarcoma of the musculoskeletal system: a review of 66 patients. Cancer. 2007;109(6):1040-1052.
7. Krishna G, Chitkara RK. Osseous Kaposi sarcoma. JAMA. 2003;286(9):1106.
8. Thanos L, Mylona S, Kalioras V, Pomoni M, Batakis N. Osseous Kaposi sarcoma in an HIV-positive patient. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(4):241-243.
9. Guiholt A, Dupin N, Marcelin AG, et al. Low T-cell response to human herpesvirus 8 in patients with AIDS-related and classic Kaposi sarcoma. J Infect Dis. 2006;194(8):1078-1088.
10. Gopal S, Achenbach CJ, Yanik EL, Dither DP, Eron JJ, Engels EA. Moving forward in HIV-associated cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(9):876-880.
Kaposi sarcoma is an AIDS-defining illness associated with human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8) co-infection. It was described in 1872 by the Hungarian dermatologist Mortiz Kaposi, and was an isolated and sporadic occurrence before the emergence of HIV infection and AIDS.1 It was first affiliated as an AIDS-associated neoplasm in 1981.1 Kaposi sarcoma is a systemic disease that can present with cutaneous lesions with or without internal involvement. There are four subtypes: Classic, African endemic, AIDS-related (CD4 count, <200), and Kaposi sarcoma in iatrogenically immunosuppressed patients. The disease has the propensity to manifest in the skin and gastro-intestinal and respiratory tracts, and osseous involvement is rarely encountered. We present here the case of an AIDS-positive man with generalized bone pain as a result of metastasis from Kaposi sarcoma. Our discussion includes the epidemiological, clinical, pathological, and radiological facets of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, and the anomaly of osseous involvement.
Case presentation and summary
He restarted his previous HAART regimen in March 2016, and was subsequently started on chemotherapy with liposomal doxorubicin (50 mg [20 mg/m2] in 250 ml D5W IV every 2 weeks) because of his extensive disease.2 He completed 6 cycles by June 2016. However, he returned in July 2016 with worsening back pain. A repeat CT scan revealed significant improvement in the disseminated lymphadenopathy, but worsening osseous metastatic disease was seen in the lumbar, thoracic, and pelvic regions. A pelvic lytic lesion biopsy revealed Kaposi sarcoma; pathology showed spindle cells positive for CD34, CD31, and HHV-8 (Figure 2). The patient received palliative radiation to the spine, aiding in pain management and ambulatory dysfunction. He continued with his noncompliance with all medications and outpatient follow-ups, and succumbed to his disease burden.
Discussion
Kaposi sarcoma is a low-grade mesenchymal tumor that involves the blood and lymphatic vessels.3 Its association with AIDS was revealed in the early 1980s at the start of the HIV epidemic in the United States. In 1994, Chang and colleagues discovered the association between Karposi sarcoma and HHV-8 by isolating DNA fragments of HHV in Kaposi sarcoma tumors from AIDS patients.4 The mode of transmission of HHV-8 has not been fully decoded. It has been presumed that adult homosexual contact continues to be an important route of transmission, inferring a common route of infection. In 1990, the overall risk of developing Kaposi sarcoma in AIDS patients was 20,000 times greater than it was in the general population, and 300 times greater than in other immunosuppressed patients.5 This suggests an increase in incidence, in direct relation, with a decrease in the CD4 count.
Kaposi sarcoma can present with a range of clinical features, from negligible cutaneous lesions to a hastily progressing neoplasm. Involvement in the musculoskeletal system is infrequent, but encountered increasingly in the AIDS-related subtype. Moreover, it is recurrently observed in the African population.6 In one of the largest reviews to date exploring Kaposi sarcoma involving the musculoskeletal system, Caponetti and colleagues observed the greatest osseous involvement distinctly in patients with CD4 and T-cell counts below 100 cells/mm3.6
Kaposi sarcoma musculoskeletal involvement, specifically bone, is atypical. If it does occur, it usually manifests as a result of contiguous invasion from an adjacent nonosseous lesion. Caponetti and colleagues that isolated osseous Kaposi sarcoma lesions (with no overlying skin lesion) were found to be more likely to be associated with AIDS in the review by Caponetti and colleagues.6 As in our patient, it is also typically a manifestation of more widely disseminated disease.7
Most of the osseous lytic lesions in AIDS patients are located in the axial skeleton. Radiological features of musculoskeletal Kaposi sarcoma are variable. As observed by Caponetti and colleagues, Kaposi sarcoma lesions can appear as a periosteal reaction, cortical erosions, osteolysis, or osseous destruction, with irregular-shaped cortical erosions being most typical.6 Despite their osteolytic features, Kaposi sarcoma lesions are often not visualized by conventional radiography.6 The preferred imaging for identification of lytic bone changes is CT (Figure 3). Magnetic resonance imaging can also help distinguish marrow abnormalities as well as adjacent soft tissues masses. Radiologically, Kaposi sarcoma osseous lesions have parallel features to bacillary angiomatosis, tuberculosis, or lymphoma.8 Therefore, biopsy of the lesion is essential in establishing the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma.
In theory, there should be clinical improvement in Kaposi sarcoma when immunity is restored. Cancers caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus may eventually also be preventable with vaccines.10
There is rarely bone involvement without the foreshadowing of a poor prognosis. Erroneous patient care may inevitably arise from Kaposi sarcoma in uncharacteristic sites. A differential of Kaposi sarcoma should be included if a patient with AIDS presents with osteolytic lesions on imaging. Biopsying the lesion cements the diagnosis and eliminates the possibility of mimicry conditions such as bacillary angiomatosis, benign vascular lesions, and angiosarcoma. As of today, a HAART regimen remains the standard initial care for patients with Kaposi sarcoma.
Kaposi sarcoma is an AIDS-defining illness associated with human herpes virus-8 (HHV-8) co-infection. It was described in 1872 by the Hungarian dermatologist Mortiz Kaposi, and was an isolated and sporadic occurrence before the emergence of HIV infection and AIDS.1 It was first affiliated as an AIDS-associated neoplasm in 1981.1 Kaposi sarcoma is a systemic disease that can present with cutaneous lesions with or without internal involvement. There are four subtypes: Classic, African endemic, AIDS-related (CD4 count, <200), and Kaposi sarcoma in iatrogenically immunosuppressed patients. The disease has the propensity to manifest in the skin and gastro-intestinal and respiratory tracts, and osseous involvement is rarely encountered. We present here the case of an AIDS-positive man with generalized bone pain as a result of metastasis from Kaposi sarcoma. Our discussion includes the epidemiological, clinical, pathological, and radiological facets of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma, and the anomaly of osseous involvement.
Case presentation and summary
He restarted his previous HAART regimen in March 2016, and was subsequently started on chemotherapy with liposomal doxorubicin (50 mg [20 mg/m2] in 250 ml D5W IV every 2 weeks) because of his extensive disease.2 He completed 6 cycles by June 2016. However, he returned in July 2016 with worsening back pain. A repeat CT scan revealed significant improvement in the disseminated lymphadenopathy, but worsening osseous metastatic disease was seen in the lumbar, thoracic, and pelvic regions. A pelvic lytic lesion biopsy revealed Kaposi sarcoma; pathology showed spindle cells positive for CD34, CD31, and HHV-8 (Figure 2). The patient received palliative radiation to the spine, aiding in pain management and ambulatory dysfunction. He continued with his noncompliance with all medications and outpatient follow-ups, and succumbed to his disease burden.
Discussion
Kaposi sarcoma is a low-grade mesenchymal tumor that involves the blood and lymphatic vessels.3 Its association with AIDS was revealed in the early 1980s at the start of the HIV epidemic in the United States. In 1994, Chang and colleagues discovered the association between Karposi sarcoma and HHV-8 by isolating DNA fragments of HHV in Kaposi sarcoma tumors from AIDS patients.4 The mode of transmission of HHV-8 has not been fully decoded. It has been presumed that adult homosexual contact continues to be an important route of transmission, inferring a common route of infection. In 1990, the overall risk of developing Kaposi sarcoma in AIDS patients was 20,000 times greater than it was in the general population, and 300 times greater than in other immunosuppressed patients.5 This suggests an increase in incidence, in direct relation, with a decrease in the CD4 count.
Kaposi sarcoma can present with a range of clinical features, from negligible cutaneous lesions to a hastily progressing neoplasm. Involvement in the musculoskeletal system is infrequent, but encountered increasingly in the AIDS-related subtype. Moreover, it is recurrently observed in the African population.6 In one of the largest reviews to date exploring Kaposi sarcoma involving the musculoskeletal system, Caponetti and colleagues observed the greatest osseous involvement distinctly in patients with CD4 and T-cell counts below 100 cells/mm3.6
Kaposi sarcoma musculoskeletal involvement, specifically bone, is atypical. If it does occur, it usually manifests as a result of contiguous invasion from an adjacent nonosseous lesion. Caponetti and colleagues that isolated osseous Kaposi sarcoma lesions (with no overlying skin lesion) were found to be more likely to be associated with AIDS in the review by Caponetti and colleagues.6 As in our patient, it is also typically a manifestation of more widely disseminated disease.7
Most of the osseous lytic lesions in AIDS patients are located in the axial skeleton. Radiological features of musculoskeletal Kaposi sarcoma are variable. As observed by Caponetti and colleagues, Kaposi sarcoma lesions can appear as a periosteal reaction, cortical erosions, osteolysis, or osseous destruction, with irregular-shaped cortical erosions being most typical.6 Despite their osteolytic features, Kaposi sarcoma lesions are often not visualized by conventional radiography.6 The preferred imaging for identification of lytic bone changes is CT (Figure 3). Magnetic resonance imaging can also help distinguish marrow abnormalities as well as adjacent soft tissues masses. Radiologically, Kaposi sarcoma osseous lesions have parallel features to bacillary angiomatosis, tuberculosis, or lymphoma.8 Therefore, biopsy of the lesion is essential in establishing the diagnosis of Kaposi sarcoma.
In theory, there should be clinical improvement in Kaposi sarcoma when immunity is restored. Cancers caused by the Epstein-Barr virus and Kaposi sarcoma-associated herpes virus may eventually also be preventable with vaccines.10
There is rarely bone involvement without the foreshadowing of a poor prognosis. Erroneous patient care may inevitably arise from Kaposi sarcoma in uncharacteristic sites. A differential of Kaposi sarcoma should be included if a patient with AIDS presents with osteolytic lesions on imaging. Biopsying the lesion cements the diagnosis and eliminates the possibility of mimicry conditions such as bacillary angiomatosis, benign vascular lesions, and angiosarcoma. As of today, a HAART regimen remains the standard initial care for patients with Kaposi sarcoma.
1. Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294.
2. Northfelt DW, Dezube BJ, Thommes JA, et al. Pegylated-liposomal doxorubicin versus doxorubicin, bleomycin, and vincristine in the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma: results of a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(7):2445-2451.
3. Restrepo CS, Martinez S, Lemos JA, et al. Imaging manifestations of Kaposi sarcoma. RadioGraphics. 2006;26:1169-1185.
4. Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, et al. Identification of herpes virus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865-1869.
5. Beral V, Peterman TA, Berkelman RL, Jaffe HW. Kaposi sarcoma among persons with AIDS: a sexually transmitted infection? Lancet. 1990;335:123-128.
6. Caponetti G, Dezube BJ, Restrepo CS, Pantanowitz I. Kaposi sarcoma of the musculoskeletal system: a review of 66 patients. Cancer. 2007;109(6):1040-1052.
7. Krishna G, Chitkara RK. Osseous Kaposi sarcoma. JAMA. 2003;286(9):1106.
8. Thanos L, Mylona S, Kalioras V, Pomoni M, Batakis N. Osseous Kaposi sarcoma in an HIV-positive patient. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(4):241-243.
9. Guiholt A, Dupin N, Marcelin AG, et al. Low T-cell response to human herpesvirus 8 in patients with AIDS-related and classic Kaposi sarcoma. J Infect Dis. 2006;194(8):1078-1088.
10. Gopal S, Achenbach CJ, Yanik EL, Dither DP, Eron JJ, Engels EA. Moving forward in HIV-associated cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(9):876-880.
1. Radu O, Pantanowitz L. Kaposi sarcoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:289-294.
2. Northfelt DW, Dezube BJ, Thommes JA, et al. Pegylated-liposomal doxorubicin versus doxorubicin, bleomycin, and vincristine in the treatment of AIDS-related Kaposi sarcoma: results of a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol. 1998;16(7):2445-2451.
3. Restrepo CS, Martinez S, Lemos JA, et al. Imaging manifestations of Kaposi sarcoma. RadioGraphics. 2006;26:1169-1185.
4. Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, et al. Identification of herpes virus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865-1869.
5. Beral V, Peterman TA, Berkelman RL, Jaffe HW. Kaposi sarcoma among persons with AIDS: a sexually transmitted infection? Lancet. 1990;335:123-128.
6. Caponetti G, Dezube BJ, Restrepo CS, Pantanowitz I. Kaposi sarcoma of the musculoskeletal system: a review of 66 patients. Cancer. 2007;109(6):1040-1052.
7. Krishna G, Chitkara RK. Osseous Kaposi sarcoma. JAMA. 2003;286(9):1106.
8. Thanos L, Mylona S, Kalioras V, Pomoni M, Batakis N. Osseous Kaposi sarcoma in an HIV-positive patient. Skeletal Radiol. 2004;33(4):241-243.
9. Guiholt A, Dupin N, Marcelin AG, et al. Low T-cell response to human herpesvirus 8 in patients with AIDS-related and classic Kaposi sarcoma. J Infect Dis. 2006;194(8):1078-1088.
10. Gopal S, Achenbach CJ, Yanik EL, Dither DP, Eron JJ, Engels EA. Moving forward in HIV-associated cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2014;32(9):876-880.
TRK inhibitor shows ‘striking’ activity, durability across diverse adult and pediatric cancers
CHICAGO – Larotrectinib, an oral inhibitor of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK), has durable efficacy across diverse adult and pediatric cancers that harbor a genetic aberration known as TRK fusion, finds an analysis of three trials reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Fusion of a TRK gene with an unrelated gene leads to uncontrolled signaling in the TRK pathway, potentially causing tumor growth and addiction to this input, lead author David Hyman, MD, chief of early drug development at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York explained in a press briefing.
Dr. Hyman and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 patients having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer harboring TRK fusions who were treated with larotrectinib in phase I and II trials. Results showed an overall response rate of 76%, and the large majority of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
“I believe these data support larotrectinib as a potential new standard of care for these patients,” he said. “However, I want to emphasize that really recognizing this benefit in the community will require that we test patients more universally for the presence of TRK fusions or other tumor-agnostic biomarkers, such as microsatellite instability.”
On the basis of these promising data, the drug’s manufacturer, Loxo Oncology, plans to submit a New Drug Application to the Food and Drug Administration later this year or early next year. Larotrectinib has already been granted both orphan drug designation (for drugs used to treat rare conditions) and breakthrough therapy designation (for drugs used to treat serious conditions showing greater efficacy than available therapies).
A randomized trial pitting larotrectinib against other therapies is unlikely given the low prevalence of TRK fusions, the lack of treatment options for the fairly heavily pretreated trial patients, and the drug’s impressive performance, according to Dr. Hyman.
“The efficacy is so striking that it really exceeds almost any existing standard of care for solid tumors,” he elaborated. “There is hardly any chemotherapy or targeted therapy that has a response rate or durability that looks like larotrectinib in these patients.”
Expert perspective
The data for larotrectinib “really bring us into a new era where treatment is truly based on mutation, not location,” said Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, a medical oncologist at City of Hope, in Duarte, Calif. “When I was in training, which was not too long ago, it really would have been a pipe dream to think that we could have treated cancers independent of their site of origin. … With the data presented by Dr. Hyman for larotrectinib, we may now be poised to treat many cancers in a manner that is agnostic of their site of origin and that is instead based on molecular criteria.
TRK testing
Several next-generation sequencing–based tests already available clinically can pick up TRK fusions, Dr. Hyman pointed out. “But it is important for the ordering physician to understand whether the tests they are ordering includes fusion detection and, if it’s an option, to select it. Otherwise, they will not find TRK fusions.
“The list price for these tests is in the kind of low thousands of dollars, which equates essentially to a PET scan for the cancer patient,” he noted. In cancers where sequential single-gene testing is already being done as standard of care, there is “minimal” incremental cost of instead using comprehensive testing that would detect TRK fusions.
Oncologists should be aware that obtaining test results can take weeks, Dr. Hyman stressed. “My personal opinion is that this [testing] should be more broadly adopted and should be adopted at a point in the patient’s treatment … [so that they] don’t become too sick, as we see in our own experience as well, and don’t have an opportunity to be treated even when the test results come back positive. So I would generally advocate early testing.”
Study details
For the study, which was funded by Loxo Oncology, the investigators analyzed data from three trials in which patients with advanced TRK fusion–positive solid cancers received larotrectinib (LOXO-101): a phase I trial among 8 adult patients, a phase I/II trial among 12 pediatric patients (SCOUT), and a phase II “basket” trial among 35 adult and adolescent patients (NAVIGATE).
“I want to emphasize that these patients were identified by local testing,” Dr. Hyman noted. “We did not perform central screening to find the TRK fusions, and in fact, 50 different laboratories identified the 55 patients. So this in a sense really represents the real-world identification of these patients.”
In an integrated analysis, the overall rate of confirmed response as assessed by investigators was 76%, with complete response in 12% of patients and partial response in 64%. Two patients had such deep tumor regression that they experienced downstaging enabling them to undergo potentially curative surgery. Efficacy was consistent regardless of tumor type, which TRK gene was affected, and the fusion partner gene.
Median time to response was 1.8 months. “This is actually just a reflection of when the first scan was obtained. But in the clinic, patients reported dramatic improvement of their symptoms within days of beginning therapy,” Dr. Hyman said.
With a median follow-up of 5.8 months, the median duration of response was not yet reached. Fully 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months. Median progression-free survival was likewise not reached; the 12-month rate was 63%.
The leading treatment-emergent adverse events were fatigue (38%), dizziness (27%), nausea (26%), and anemia (26%). “This is an extremely well tolerated therapy with only 13% of patients requiring any form of dose modification and not a single patient discontinuing due to adverse events,” he said.
It is unclear why some patients had apparent primary resistance to larotrectinib, but their TRK fusion test results may have been incorrect, Dr. Hyman speculated. Six patients developed acquired resistance to larotrectinib; five of them were found to have an identical resistance mutation, and two went on to receive and have a response to LOXO-195, a next-generation TRK inhibitor that appears to retain activity in the presence of this mutation (Cancer Discov. 2017 June 3. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0507).
Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology.
CHICAGO – Larotrectinib, an oral inhibitor of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK), has durable efficacy across diverse adult and pediatric cancers that harbor a genetic aberration known as TRK fusion, finds an analysis of three trials reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Fusion of a TRK gene with an unrelated gene leads to uncontrolled signaling in the TRK pathway, potentially causing tumor growth and addiction to this input, lead author David Hyman, MD, chief of early drug development at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York explained in a press briefing.
Dr. Hyman and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 patients having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer harboring TRK fusions who were treated with larotrectinib in phase I and II trials. Results showed an overall response rate of 76%, and the large majority of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
“I believe these data support larotrectinib as a potential new standard of care for these patients,” he said. “However, I want to emphasize that really recognizing this benefit in the community will require that we test patients more universally for the presence of TRK fusions or other tumor-agnostic biomarkers, such as microsatellite instability.”
On the basis of these promising data, the drug’s manufacturer, Loxo Oncology, plans to submit a New Drug Application to the Food and Drug Administration later this year or early next year. Larotrectinib has already been granted both orphan drug designation (for drugs used to treat rare conditions) and breakthrough therapy designation (for drugs used to treat serious conditions showing greater efficacy than available therapies).
A randomized trial pitting larotrectinib against other therapies is unlikely given the low prevalence of TRK fusions, the lack of treatment options for the fairly heavily pretreated trial patients, and the drug’s impressive performance, according to Dr. Hyman.
“The efficacy is so striking that it really exceeds almost any existing standard of care for solid tumors,” he elaborated. “There is hardly any chemotherapy or targeted therapy that has a response rate or durability that looks like larotrectinib in these patients.”
Expert perspective
The data for larotrectinib “really bring us into a new era where treatment is truly based on mutation, not location,” said Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, a medical oncologist at City of Hope, in Duarte, Calif. “When I was in training, which was not too long ago, it really would have been a pipe dream to think that we could have treated cancers independent of their site of origin. … With the data presented by Dr. Hyman for larotrectinib, we may now be poised to treat many cancers in a manner that is agnostic of their site of origin and that is instead based on molecular criteria.
TRK testing
Several next-generation sequencing–based tests already available clinically can pick up TRK fusions, Dr. Hyman pointed out. “But it is important for the ordering physician to understand whether the tests they are ordering includes fusion detection and, if it’s an option, to select it. Otherwise, they will not find TRK fusions.
“The list price for these tests is in the kind of low thousands of dollars, which equates essentially to a PET scan for the cancer patient,” he noted. In cancers where sequential single-gene testing is already being done as standard of care, there is “minimal” incremental cost of instead using comprehensive testing that would detect TRK fusions.
Oncologists should be aware that obtaining test results can take weeks, Dr. Hyman stressed. “My personal opinion is that this [testing] should be more broadly adopted and should be adopted at a point in the patient’s treatment … [so that they] don’t become too sick, as we see in our own experience as well, and don’t have an opportunity to be treated even when the test results come back positive. So I would generally advocate early testing.”
Study details
For the study, which was funded by Loxo Oncology, the investigators analyzed data from three trials in which patients with advanced TRK fusion–positive solid cancers received larotrectinib (LOXO-101): a phase I trial among 8 adult patients, a phase I/II trial among 12 pediatric patients (SCOUT), and a phase II “basket” trial among 35 adult and adolescent patients (NAVIGATE).
“I want to emphasize that these patients were identified by local testing,” Dr. Hyman noted. “We did not perform central screening to find the TRK fusions, and in fact, 50 different laboratories identified the 55 patients. So this in a sense really represents the real-world identification of these patients.”
In an integrated analysis, the overall rate of confirmed response as assessed by investigators was 76%, with complete response in 12% of patients and partial response in 64%. Two patients had such deep tumor regression that they experienced downstaging enabling them to undergo potentially curative surgery. Efficacy was consistent regardless of tumor type, which TRK gene was affected, and the fusion partner gene.
Median time to response was 1.8 months. “This is actually just a reflection of when the first scan was obtained. But in the clinic, patients reported dramatic improvement of their symptoms within days of beginning therapy,” Dr. Hyman said.
With a median follow-up of 5.8 months, the median duration of response was not yet reached. Fully 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months. Median progression-free survival was likewise not reached; the 12-month rate was 63%.
The leading treatment-emergent adverse events were fatigue (38%), dizziness (27%), nausea (26%), and anemia (26%). “This is an extremely well tolerated therapy with only 13% of patients requiring any form of dose modification and not a single patient discontinuing due to adverse events,” he said.
It is unclear why some patients had apparent primary resistance to larotrectinib, but their TRK fusion test results may have been incorrect, Dr. Hyman speculated. Six patients developed acquired resistance to larotrectinib; five of them were found to have an identical resistance mutation, and two went on to receive and have a response to LOXO-195, a next-generation TRK inhibitor that appears to retain activity in the presence of this mutation (Cancer Discov. 2017 June 3. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0507).
Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology.
CHICAGO – Larotrectinib, an oral inhibitor of tropomyosin receptor kinase (TRK), has durable efficacy across diverse adult and pediatric cancers that harbor a genetic aberration known as TRK fusion, finds an analysis of three trials reported at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Fusion of a TRK gene with an unrelated gene leads to uncontrolled signaling in the TRK pathway, potentially causing tumor growth and addiction to this input, lead author David Hyman, MD, chief of early drug development at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York explained in a press briefing.
Dr. Hyman and his colleagues analyzed data from 55 patients having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer harboring TRK fusions who were treated with larotrectinib in phase I and II trials. Results showed an overall response rate of 76%, and the large majority of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
“I believe these data support larotrectinib as a potential new standard of care for these patients,” he said. “However, I want to emphasize that really recognizing this benefit in the community will require that we test patients more universally for the presence of TRK fusions or other tumor-agnostic biomarkers, such as microsatellite instability.”
On the basis of these promising data, the drug’s manufacturer, Loxo Oncology, plans to submit a New Drug Application to the Food and Drug Administration later this year or early next year. Larotrectinib has already been granted both orphan drug designation (for drugs used to treat rare conditions) and breakthrough therapy designation (for drugs used to treat serious conditions showing greater efficacy than available therapies).
A randomized trial pitting larotrectinib against other therapies is unlikely given the low prevalence of TRK fusions, the lack of treatment options for the fairly heavily pretreated trial patients, and the drug’s impressive performance, according to Dr. Hyman.
“The efficacy is so striking that it really exceeds almost any existing standard of care for solid tumors,” he elaborated. “There is hardly any chemotherapy or targeted therapy that has a response rate or durability that looks like larotrectinib in these patients.”
Expert perspective
The data for larotrectinib “really bring us into a new era where treatment is truly based on mutation, not location,” said Sumanta Kumar Pal, MD, a medical oncologist at City of Hope, in Duarte, Calif. “When I was in training, which was not too long ago, it really would have been a pipe dream to think that we could have treated cancers independent of their site of origin. … With the data presented by Dr. Hyman for larotrectinib, we may now be poised to treat many cancers in a manner that is agnostic of their site of origin and that is instead based on molecular criteria.
TRK testing
Several next-generation sequencing–based tests already available clinically can pick up TRK fusions, Dr. Hyman pointed out. “But it is important for the ordering physician to understand whether the tests they are ordering includes fusion detection and, if it’s an option, to select it. Otherwise, they will not find TRK fusions.
“The list price for these tests is in the kind of low thousands of dollars, which equates essentially to a PET scan for the cancer patient,” he noted. In cancers where sequential single-gene testing is already being done as standard of care, there is “minimal” incremental cost of instead using comprehensive testing that would detect TRK fusions.
Oncologists should be aware that obtaining test results can take weeks, Dr. Hyman stressed. “My personal opinion is that this [testing] should be more broadly adopted and should be adopted at a point in the patient’s treatment … [so that they] don’t become too sick, as we see in our own experience as well, and don’t have an opportunity to be treated even when the test results come back positive. So I would generally advocate early testing.”
Study details
For the study, which was funded by Loxo Oncology, the investigators analyzed data from three trials in which patients with advanced TRK fusion–positive solid cancers received larotrectinib (LOXO-101): a phase I trial among 8 adult patients, a phase I/II trial among 12 pediatric patients (SCOUT), and a phase II “basket” trial among 35 adult and adolescent patients (NAVIGATE).
“I want to emphasize that these patients were identified by local testing,” Dr. Hyman noted. “We did not perform central screening to find the TRK fusions, and in fact, 50 different laboratories identified the 55 patients. So this in a sense really represents the real-world identification of these patients.”
In an integrated analysis, the overall rate of confirmed response as assessed by investigators was 76%, with complete response in 12% of patients and partial response in 64%. Two patients had such deep tumor regression that they experienced downstaging enabling them to undergo potentially curative surgery. Efficacy was consistent regardless of tumor type, which TRK gene was affected, and the fusion partner gene.
Median time to response was 1.8 months. “This is actually just a reflection of when the first scan was obtained. But in the clinic, patients reported dramatic improvement of their symptoms within days of beginning therapy,” Dr. Hyman said.
With a median follow-up of 5.8 months, the median duration of response was not yet reached. Fully 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months. Median progression-free survival was likewise not reached; the 12-month rate was 63%.
The leading treatment-emergent adverse events were fatigue (38%), dizziness (27%), nausea (26%), and anemia (26%). “This is an extremely well tolerated therapy with only 13% of patients requiring any form of dose modification and not a single patient discontinuing due to adverse events,” he said.
It is unclear why some patients had apparent primary resistance to larotrectinib, but their TRK fusion test results may have been incorrect, Dr. Hyman speculated. Six patients developed acquired resistance to larotrectinib; five of them were found to have an identical resistance mutation, and two went on to receive and have a response to LOXO-195, a next-generation TRK inhibitor that appears to retain activity in the presence of this mutation (Cancer Discov. 2017 June 3. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0507).
Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology.
AT ASCO 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The overall response rate was 76%, and 79% of responses were still ongoing at 12 months.
Data source: An integrated analysis of phase I and II trials among 55 children and adults having 17 discrete types of advanced cancer with TRK fusions.
Disclosures: Dr. Hyman disclosed that he has a consulting or advisory role with Atara Biotherapeutics, Chugai Pharma, and CytomX Therapeutics, and that he receives research funding from AstraZeneca and Puma Biotechnology. The study was funded by Loxo Oncology.
VIDEO: Routine genomic testing identifies actionable alterations in 52% of tumors
CHICAGO –
Molecular profiling, including genetic sequencing and copy number variation analysis, was performed in 1944 tumors from patients with advanced tumors enrolled in the profiLER study. Of the tumors screened, mutations deemed actionable were identified in 1,004 (52%), with 394 patients having two or more actionable targets, and the remainder having one identified targeted treatment. A molecular targeted treatment was recommended for 676 patients (35% of those tested).
“We showed that the patients who did receive the molecular targeted agents were doing better in terms of overall survival,” said Olivier Tredan, MD, PhD, the study’s lead investigator. Noting that these are trends as the trial was not randomized, he reported that the overall survival (OS) for those receiving targeted treatments was 53.7% at 3 years, compared with 46.1% for those who did not receive targeted treatment. The trend continued out to 5 years, with the OS for the targeted treatment group at 34.8%, compared with 28.1% OS for those who did not receive targeted treatment, he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Many patients either were too sick to receive the recommended treatment or died before they could be treated, Dr. Tredan said in a video interview.
Of the patients who did receive targeted treatment, over 60% received mTOR inhibitors. The next most common therapies were multitarget tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR)–inhibiting/antiangiogenic therapies, received by about one-third of patients. Fewer than one in five patients received any other therapies. Tumor types were colorectal, gynecological, breast, head and neck carcinomas, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
A new randomized clinical study, profiLER 2, is planned. The new study will pit a 315-gene commercial test against the 69-gene test used in profiLER 1, to see whether casting a wider net yields more targets for therapy.
Still, knowing that a treatment might help is useful only if the patient can actually receive the drug, said Dr. Tredan. “What we want is more molecular targeted agent initiation, so we need to have larger screening programs, but we need also to have access to novel targeted agents.”
Dr. Tredan reported financial relationships with Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis.
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
CHICAGO –
Molecular profiling, including genetic sequencing and copy number variation analysis, was performed in 1944 tumors from patients with advanced tumors enrolled in the profiLER study. Of the tumors screened, mutations deemed actionable were identified in 1,004 (52%), with 394 patients having two or more actionable targets, and the remainder having one identified targeted treatment. A molecular targeted treatment was recommended for 676 patients (35% of those tested).
“We showed that the patients who did receive the molecular targeted agents were doing better in terms of overall survival,” said Olivier Tredan, MD, PhD, the study’s lead investigator. Noting that these are trends as the trial was not randomized, he reported that the overall survival (OS) for those receiving targeted treatments was 53.7% at 3 years, compared with 46.1% for those who did not receive targeted treatment. The trend continued out to 5 years, with the OS for the targeted treatment group at 34.8%, compared with 28.1% OS for those who did not receive targeted treatment, he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Many patients either were too sick to receive the recommended treatment or died before they could be treated, Dr. Tredan said in a video interview.
Of the patients who did receive targeted treatment, over 60% received mTOR inhibitors. The next most common therapies were multitarget tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR)–inhibiting/antiangiogenic therapies, received by about one-third of patients. Fewer than one in five patients received any other therapies. Tumor types were colorectal, gynecological, breast, head and neck carcinomas, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
A new randomized clinical study, profiLER 2, is planned. The new study will pit a 315-gene commercial test against the 69-gene test used in profiLER 1, to see whether casting a wider net yields more targets for therapy.
Still, knowing that a treatment might help is useful only if the patient can actually receive the drug, said Dr. Tredan. “What we want is more molecular targeted agent initiation, so we need to have larger screening programs, but we need also to have access to novel targeted agents.”
Dr. Tredan reported financial relationships with Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis.
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
CHICAGO –
Molecular profiling, including genetic sequencing and copy number variation analysis, was performed in 1944 tumors from patients with advanced tumors enrolled in the profiLER study. Of the tumors screened, mutations deemed actionable were identified in 1,004 (52%), with 394 patients having two or more actionable targets, and the remainder having one identified targeted treatment. A molecular targeted treatment was recommended for 676 patients (35% of those tested).
“We showed that the patients who did receive the molecular targeted agents were doing better in terms of overall survival,” said Olivier Tredan, MD, PhD, the study’s lead investigator. Noting that these are trends as the trial was not randomized, he reported that the overall survival (OS) for those receiving targeted treatments was 53.7% at 3 years, compared with 46.1% for those who did not receive targeted treatment. The trend continued out to 5 years, with the OS for the targeted treatment group at 34.8%, compared with 28.1% OS for those who did not receive targeted treatment, he said at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The video associated with this article is no longer available on this site. Please view all of our videos on the MDedge YouTube channel
Many patients either were too sick to receive the recommended treatment or died before they could be treated, Dr. Tredan said in a video interview.
Of the patients who did receive targeted treatment, over 60% received mTOR inhibitors. The next most common therapies were multitarget tyrosine kinase receptor (TKR)–inhibiting/antiangiogenic therapies, received by about one-third of patients. Fewer than one in five patients received any other therapies. Tumor types were colorectal, gynecological, breast, head and neck carcinomas, sarcomas, and brain tumors.
A new randomized clinical study, profiLER 2, is planned. The new study will pit a 315-gene commercial test against the 69-gene test used in profiLER 1, to see whether casting a wider net yields more targets for therapy.
Still, knowing that a treatment might help is useful only if the patient can actually receive the drug, said Dr. Tredan. “What we want is more molecular targeted agent initiation, so we need to have larger screening programs, but we need also to have access to novel targeted agents.”
Dr. Tredan reported financial relationships with Bayer, GlaxoSmithKline, and Novartis.
[email protected]
On Twitter @karioakes
AT ASCO 2017
Fractures in adult osteosarcoma patients presage worse survival
AMSTERDAM – Pathological fractures are prognostic of poor outcomes in adults with osteosarcoma, but not in children with osteosarcoma, investigators have found.
A retrospective review of data on consecutive patients treated over the course of 30 years showed that among patients of all ages, both 5-year and 10-year overall survival (OS) rates were worse among patients who had pathological fractures.
But in an analysis stratified by age, the survival difference attributable to fractures was limited entirely to patients who were 18 or older at the time of an osteosarcoma diagnosis, reported Lisa Kelley, a medical student at the Ludwig-Maximilians Universität in Munich.
“It’s important to understand what are the prognostic factors [in osteosarcoma], and while many of the factors have been thoroughly researched, on pathological fractures the data are still fairly inconclusive due to the results of studies contradicting each other, and also having a relatively small patient number due to the fact that osteosarcoma itself is rare, and the pathological fractures occur only in approximately 10% of cases,” she said at an annual congress sponsored by the European Cancer Organisation.
To get a better handle on possible correlations between pathological fractures and prognosis in patients with central high-grade osteosarcoma, Ms. Kelley and her coauthors collected data on consecutive patients treated for localized or metastatic osteosarcoma of the extremities from 1980 through 2010 at one of the member institutions of the Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group (COSS).
They identified 2,847 patients, of whom 2,193 (77%) were 18 or younger at the time of diagnosis. Of the entire cohort, 321 patients (11.3%) had a pathological fracture either at presentation or soon after diagnosis.
Comparing patients with and without pathological fractures, the investigators found that factors significantly associated with fracture risk included tumor location, especially the humerus (P less than .001), tumors occurring proximally and in a diaphysis (P less than .001), telangiectatic subtype (P less than .001), the presence of primary metastases (P = .025). and tumors comprising more than one-third of the affected bone (P less than .001).
There were no significant differences in the cohort as a whole between patients with or without fractures in either age in years, sex, body-mass index, history of pain or swelling symptoms, local surgical remission at the main tumor site, total surgical remission including metastases, response to chemotherapy, use of adjuvant chemotherapy rather than neoadjuvant, or type of surgery.
Among adult patients only, however, factors associated with pathological fractures included age (P less than .001). BMI (P = .021), tumor site (P less than .001), histologic subtype (P less than .001), primary metastases (P = .011), relative tumor size (P = .047), and total surgical remission (P = .015).
Among pediatric patients, factors associated with fracture risk were (P less than .001 for all unless otherwise specified) age, BMI (P = .018), history or symptoms (P = .001). tumor site, localization within bone, histologic subtype, and relative tumor size.
In univariate analysis, 5-year OS rates were 70.6% for patients without fractures compared with 63.0% for those with fractures, and respective 10-year OS rates were 64.9% vs. 58.1% (P = .007 for both comparisons).
Among pediatric patients, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with and without pathological fractures overlapped. But for adult patients, survival of those with fractures was significantly worse, with 5-year OS of 69.3% with no fractures vs. 45.9% with fractures, and respective 10-year OS rates of 62.1% vs. 36.8% (P less than .001 for both comparisons).
Also in univariate analysis, 5-year and 10-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were significantly lower for patients who experienced pathological fractures.
Finally, in multivariable analysis of overall survival by age group, the investigators found that among adults pathological fracture was associated with a nearly twofold risk for death (hazard ratio [HR] 1.893, P = .013). Other factors were primary metastases (HR 2.486, P = .001), response to chemotherapy (P less than .001) and total surgical remission (P less than .001).
As noted before, pathological fracture among pediatric patients was not associated with worse OS. Factors significantly associated with OS in younger patients were primary metastases (HR 2.187, P less than .001), relative tumor size (HR 1.239, P = .024), response to chemotherapy (HR 2.295, P less than .001), total surgical remission (HR 4.253, P less than .001), and type of surgery (HR 1.282, P = .008).
In contrast, pathological fracture was not associated with EFS among either adult or pediatric patients. Factors significantly associated with EFS in both children and adults were primary metastases and response to chemotherapy. Among pediatric patients only, tumor site and relative tumor size were also associated with EFS.
Ms. Kelley acknowledged that the study was limited by the retrospective design.
She said that exploration of the discrepancies between adult and pediatric patients in regard to the influence of pathological fracture on survival and of the role of pathologic fracture as a negative prognostic factor for OS but not EFS in adults is warranted.
The study was funded by the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung Foundation for cancer research. Ms. Kelley reported having no conflicts of interest.
AMSTERDAM – Pathological fractures are prognostic of poor outcomes in adults with osteosarcoma, but not in children with osteosarcoma, investigators have found.
A retrospective review of data on consecutive patients treated over the course of 30 years showed that among patients of all ages, both 5-year and 10-year overall survival (OS) rates were worse among patients who had pathological fractures.
But in an analysis stratified by age, the survival difference attributable to fractures was limited entirely to patients who were 18 or older at the time of an osteosarcoma diagnosis, reported Lisa Kelley, a medical student at the Ludwig-Maximilians Universität in Munich.
“It’s important to understand what are the prognostic factors [in osteosarcoma], and while many of the factors have been thoroughly researched, on pathological fractures the data are still fairly inconclusive due to the results of studies contradicting each other, and also having a relatively small patient number due to the fact that osteosarcoma itself is rare, and the pathological fractures occur only in approximately 10% of cases,” she said at an annual congress sponsored by the European Cancer Organisation.
To get a better handle on possible correlations between pathological fractures and prognosis in patients with central high-grade osteosarcoma, Ms. Kelley and her coauthors collected data on consecutive patients treated for localized or metastatic osteosarcoma of the extremities from 1980 through 2010 at one of the member institutions of the Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group (COSS).
They identified 2,847 patients, of whom 2,193 (77%) were 18 or younger at the time of diagnosis. Of the entire cohort, 321 patients (11.3%) had a pathological fracture either at presentation or soon after diagnosis.
Comparing patients with and without pathological fractures, the investigators found that factors significantly associated with fracture risk included tumor location, especially the humerus (P less than .001), tumors occurring proximally and in a diaphysis (P less than .001), telangiectatic subtype (P less than .001), the presence of primary metastases (P = .025). and tumors comprising more than one-third of the affected bone (P less than .001).
There were no significant differences in the cohort as a whole between patients with or without fractures in either age in years, sex, body-mass index, history of pain or swelling symptoms, local surgical remission at the main tumor site, total surgical remission including metastases, response to chemotherapy, use of adjuvant chemotherapy rather than neoadjuvant, or type of surgery.
Among adult patients only, however, factors associated with pathological fractures included age (P less than .001). BMI (P = .021), tumor site (P less than .001), histologic subtype (P less than .001), primary metastases (P = .011), relative tumor size (P = .047), and total surgical remission (P = .015).
Among pediatric patients, factors associated with fracture risk were (P less than .001 for all unless otherwise specified) age, BMI (P = .018), history or symptoms (P = .001). tumor site, localization within bone, histologic subtype, and relative tumor size.
In univariate analysis, 5-year OS rates were 70.6% for patients without fractures compared with 63.0% for those with fractures, and respective 10-year OS rates were 64.9% vs. 58.1% (P = .007 for both comparisons).
Among pediatric patients, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with and without pathological fractures overlapped. But for adult patients, survival of those with fractures was significantly worse, with 5-year OS of 69.3% with no fractures vs. 45.9% with fractures, and respective 10-year OS rates of 62.1% vs. 36.8% (P less than .001 for both comparisons).
Also in univariate analysis, 5-year and 10-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were significantly lower for patients who experienced pathological fractures.
Finally, in multivariable analysis of overall survival by age group, the investigators found that among adults pathological fracture was associated with a nearly twofold risk for death (hazard ratio [HR] 1.893, P = .013). Other factors were primary metastases (HR 2.486, P = .001), response to chemotherapy (P less than .001) and total surgical remission (P less than .001).
As noted before, pathological fracture among pediatric patients was not associated with worse OS. Factors significantly associated with OS in younger patients were primary metastases (HR 2.187, P less than .001), relative tumor size (HR 1.239, P = .024), response to chemotherapy (HR 2.295, P less than .001), total surgical remission (HR 4.253, P less than .001), and type of surgery (HR 1.282, P = .008).
In contrast, pathological fracture was not associated with EFS among either adult or pediatric patients. Factors significantly associated with EFS in both children and adults were primary metastases and response to chemotherapy. Among pediatric patients only, tumor site and relative tumor size were also associated with EFS.
Ms. Kelley acknowledged that the study was limited by the retrospective design.
She said that exploration of the discrepancies between adult and pediatric patients in regard to the influence of pathological fracture on survival and of the role of pathologic fracture as a negative prognostic factor for OS but not EFS in adults is warranted.
The study was funded by the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung Foundation for cancer research. Ms. Kelley reported having no conflicts of interest.
AMSTERDAM – Pathological fractures are prognostic of poor outcomes in adults with osteosarcoma, but not in children with osteosarcoma, investigators have found.
A retrospective review of data on consecutive patients treated over the course of 30 years showed that among patients of all ages, both 5-year and 10-year overall survival (OS) rates were worse among patients who had pathological fractures.
But in an analysis stratified by age, the survival difference attributable to fractures was limited entirely to patients who were 18 or older at the time of an osteosarcoma diagnosis, reported Lisa Kelley, a medical student at the Ludwig-Maximilians Universität in Munich.
“It’s important to understand what are the prognostic factors [in osteosarcoma], and while many of the factors have been thoroughly researched, on pathological fractures the data are still fairly inconclusive due to the results of studies contradicting each other, and also having a relatively small patient number due to the fact that osteosarcoma itself is rare, and the pathological fractures occur only in approximately 10% of cases,” she said at an annual congress sponsored by the European Cancer Organisation.
To get a better handle on possible correlations between pathological fractures and prognosis in patients with central high-grade osteosarcoma, Ms. Kelley and her coauthors collected data on consecutive patients treated for localized or metastatic osteosarcoma of the extremities from 1980 through 2010 at one of the member institutions of the Cooperative Osteosarcoma Study Group (COSS).
They identified 2,847 patients, of whom 2,193 (77%) were 18 or younger at the time of diagnosis. Of the entire cohort, 321 patients (11.3%) had a pathological fracture either at presentation or soon after diagnosis.
Comparing patients with and without pathological fractures, the investigators found that factors significantly associated with fracture risk included tumor location, especially the humerus (P less than .001), tumors occurring proximally and in a diaphysis (P less than .001), telangiectatic subtype (P less than .001), the presence of primary metastases (P = .025). and tumors comprising more than one-third of the affected bone (P less than .001).
There were no significant differences in the cohort as a whole between patients with or without fractures in either age in years, sex, body-mass index, history of pain or swelling symptoms, local surgical remission at the main tumor site, total surgical remission including metastases, response to chemotherapy, use of adjuvant chemotherapy rather than neoadjuvant, or type of surgery.
Among adult patients only, however, factors associated with pathological fractures included age (P less than .001). BMI (P = .021), tumor site (P less than .001), histologic subtype (P less than .001), primary metastases (P = .011), relative tumor size (P = .047), and total surgical remission (P = .015).
Among pediatric patients, factors associated with fracture risk were (P less than .001 for all unless otherwise specified) age, BMI (P = .018), history or symptoms (P = .001). tumor site, localization within bone, histologic subtype, and relative tumor size.
In univariate analysis, 5-year OS rates were 70.6% for patients without fractures compared with 63.0% for those with fractures, and respective 10-year OS rates were 64.9% vs. 58.1% (P = .007 for both comparisons).
Among pediatric patients, the Kaplan-Meier survival curves of patients with and without pathological fractures overlapped. But for adult patients, survival of those with fractures was significantly worse, with 5-year OS of 69.3% with no fractures vs. 45.9% with fractures, and respective 10-year OS rates of 62.1% vs. 36.8% (P less than .001 for both comparisons).
Also in univariate analysis, 5-year and 10-year event-free survival (EFS) rates were significantly lower for patients who experienced pathological fractures.
Finally, in multivariable analysis of overall survival by age group, the investigators found that among adults pathological fracture was associated with a nearly twofold risk for death (hazard ratio [HR] 1.893, P = .013). Other factors were primary metastases (HR 2.486, P = .001), response to chemotherapy (P less than .001) and total surgical remission (P less than .001).
As noted before, pathological fracture among pediatric patients was not associated with worse OS. Factors significantly associated with OS in younger patients were primary metastases (HR 2.187, P less than .001), relative tumor size (HR 1.239, P = .024), response to chemotherapy (HR 2.295, P less than .001), total surgical remission (HR 4.253, P less than .001), and type of surgery (HR 1.282, P = .008).
In contrast, pathological fracture was not associated with EFS among either adult or pediatric patients. Factors significantly associated with EFS in both children and adults were primary metastases and response to chemotherapy. Among pediatric patients only, tumor site and relative tumor size were also associated with EFS.
Ms. Kelley acknowledged that the study was limited by the retrospective design.
She said that exploration of the discrepancies between adult and pediatric patients in regard to the influence of pathological fracture on survival and of the role of pathologic fracture as a negative prognostic factor for OS but not EFS in adults is warranted.
The study was funded by the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung Foundation for cancer research. Ms. Kelley reported having no conflicts of interest.
AT ECCO2017
Key clinical point: Pathological fractures are associated with worse survival of adults but not children with osteosarcoma of the extremities.
Major finding: Among adults pathological fracture was associated with a nearly twofold risk for death (hazard ratio, 1.893, P = .013).
Data source: Retrospective review of data on 2,847 consecutive patients with osteosarcoma.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Wilhelm Sander-Stiftung Foundation for cancer research. Ms. Kelley reported having no conflicts of interest.
PD-1, PD-L1 expression in sarcomas is subtype dependent
AMSTERDAM – Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeted against programmed death–1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) show strong activity against several different tumor types, but unfortunately may have only limited efficacy against soft tissue and bone sarcomas, investigators reported.
“We found that the clinical expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 is sarcoma subtype dependent,” said Anke van Erp, a PhD candidate in oncology at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
“The introduction of PD-1 antibodies has led to increased interest in the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 in a large variety of tumor types, and has shown in several of these tumor types that PD-L1 could be associated with a worse prognosis. In addition, treatment with PD-1 antibodies has shown impressive effects in an increasing number of adult tumors. This makes the exploration of PD-1 blockade in sarcoma of interest,” she said.
Additionally, CD8-positive T cells are of interest because they are critical mediators of adaptive immunity, she noted.
Ms. van Erp and colleagues looked at expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and the presence of CD8-positive cells in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor samples from patients with one of six sarcoma subtypes: primary osteosarcoma (48 samples), Ewing sarcoma (32), alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (28), embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (78), synovial sarcoma (23), and desmoplastic small round cell tumors (8).
The samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8-positive cells, and expression levels were then correlated with clinical outcomes.
The investigators classified expression of markers on less than 10% of cells in a sample as negative, 10%-50% as positive, and more than 50% as highly positive.
PD-1 was expressed in lymphocytes in 6% of all samples, and in 19% of all tumors. PD-L1 was expressed in 10%, and CD8-positive cells in 46%.
Only 2% of samples expressed both PD-1 and PD-L1, 11% expressed both PD-1 and CD8-positive T cells, 7% had PD-L1 and CD8, and 2% expressed all three markers.
The highest percentages of PD-1 expression were in lymphocytes from synovial sarcoma samples (17%), and the highest levels of PD-1 were seen in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma samples. However, neither PD-1 nor PD-L1 were detected at significant levels in synovial sarcoma tumor cells, and PD-1 was not detected in tumor cells from alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
“These data show that there is a high difference between the different subtypes, and they highlight the need to really look at PD-1 blockade per individual subtype,” Ms. van Erp said.
For all subtypes combined, the OS was significantly better for patients with PD-L1 positive vs. PD-L1–negative tumors out to 25 years of follow-up (P = .028). Similarly OS was better for patients with PD-L1–positive, CD8-positive tumors, compared with tumors negative for both markers (P = .020).
When they looked at individual sarcoma subtypes, however, they saw significant results only for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, with PD-L1 positivity vs. negativity associated with better OS and EFS out to more than 10.5 years (P = .007 for both). There was also a trend toward better EFS for tumors positive for both PD-L1 and CD8, but this was not significant.
For Ewing sarcoma, PD-1 was found to be expressed on tumor rather than on lymphocytes in 19% of all samples, and PD-1 expression was found to be associated with worse EFS. PD-1 was also found in tumors of all desmoplastic small round cell tumor samples, but this group was too small to determine significance, Ms. van Erp said.
She acknowledged that the study was limited by the use of tissue microarray sampling rather than examination of the whole tumor and its microenvironment. In addition, no functional assays have been performed to determine the clinical relevance of PD-1 expression for either Ewing sarcoma or desmoplastic small round cell tumor cells.
“In this study, we looked at the primary tumors for these subtypes, and as we know that there can be a difference in the pattern of expression between primary tumors and metastatic tumors in sarcoma subtypes, and as sarcoma patients are in great need for new therapeutic options, it would be very interesting to look at the expression of PD-1. PD-L1, and CD8 in these tumor types in metastatic disease,’ she said.
The study was supported by Radboud University; the Princess Maxima Center for Pediatric Oncology in Utrecht, the Netherlands; and the Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust in London. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
AMSTERDAM – Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeted against programmed death–1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) show strong activity against several different tumor types, but unfortunately may have only limited efficacy against soft tissue and bone sarcomas, investigators reported.
“We found that the clinical expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 is sarcoma subtype dependent,” said Anke van Erp, a PhD candidate in oncology at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
“The introduction of PD-1 antibodies has led to increased interest in the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 in a large variety of tumor types, and has shown in several of these tumor types that PD-L1 could be associated with a worse prognosis. In addition, treatment with PD-1 antibodies has shown impressive effects in an increasing number of adult tumors. This makes the exploration of PD-1 blockade in sarcoma of interest,” she said.
Additionally, CD8-positive T cells are of interest because they are critical mediators of adaptive immunity, she noted.
Ms. van Erp and colleagues looked at expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and the presence of CD8-positive cells in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor samples from patients with one of six sarcoma subtypes: primary osteosarcoma (48 samples), Ewing sarcoma (32), alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (28), embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (78), synovial sarcoma (23), and desmoplastic small round cell tumors (8).
The samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8-positive cells, and expression levels were then correlated with clinical outcomes.
The investigators classified expression of markers on less than 10% of cells in a sample as negative, 10%-50% as positive, and more than 50% as highly positive.
PD-1 was expressed in lymphocytes in 6% of all samples, and in 19% of all tumors. PD-L1 was expressed in 10%, and CD8-positive cells in 46%.
Only 2% of samples expressed both PD-1 and PD-L1, 11% expressed both PD-1 and CD8-positive T cells, 7% had PD-L1 and CD8, and 2% expressed all three markers.
The highest percentages of PD-1 expression were in lymphocytes from synovial sarcoma samples (17%), and the highest levels of PD-1 were seen in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma samples. However, neither PD-1 nor PD-L1 were detected at significant levels in synovial sarcoma tumor cells, and PD-1 was not detected in tumor cells from alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
“These data show that there is a high difference between the different subtypes, and they highlight the need to really look at PD-1 blockade per individual subtype,” Ms. van Erp said.
For all subtypes combined, the OS was significantly better for patients with PD-L1 positive vs. PD-L1–negative tumors out to 25 years of follow-up (P = .028). Similarly OS was better for patients with PD-L1–positive, CD8-positive tumors, compared with tumors negative for both markers (P = .020).
When they looked at individual sarcoma subtypes, however, they saw significant results only for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, with PD-L1 positivity vs. negativity associated with better OS and EFS out to more than 10.5 years (P = .007 for both). There was also a trend toward better EFS for tumors positive for both PD-L1 and CD8, but this was not significant.
For Ewing sarcoma, PD-1 was found to be expressed on tumor rather than on lymphocytes in 19% of all samples, and PD-1 expression was found to be associated with worse EFS. PD-1 was also found in tumors of all desmoplastic small round cell tumor samples, but this group was too small to determine significance, Ms. van Erp said.
She acknowledged that the study was limited by the use of tissue microarray sampling rather than examination of the whole tumor and its microenvironment. In addition, no functional assays have been performed to determine the clinical relevance of PD-1 expression for either Ewing sarcoma or desmoplastic small round cell tumor cells.
“In this study, we looked at the primary tumors for these subtypes, and as we know that there can be a difference in the pattern of expression between primary tumors and metastatic tumors in sarcoma subtypes, and as sarcoma patients are in great need for new therapeutic options, it would be very interesting to look at the expression of PD-1. PD-L1, and CD8 in these tumor types in metastatic disease,’ she said.
The study was supported by Radboud University; the Princess Maxima Center for Pediatric Oncology in Utrecht, the Netherlands; and the Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust in London. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
AMSTERDAM – Immune checkpoint inhibitors targeted against programmed death–1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1) show strong activity against several different tumor types, but unfortunately may have only limited efficacy against soft tissue and bone sarcomas, investigators reported.
“We found that the clinical expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 is sarcoma subtype dependent,” said Anke van Erp, a PhD candidate in oncology at Radboud University Medical Center in Nijmegen, the Netherlands.
“The introduction of PD-1 antibodies has led to increased interest in the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 in a large variety of tumor types, and has shown in several of these tumor types that PD-L1 could be associated with a worse prognosis. In addition, treatment with PD-1 antibodies has shown impressive effects in an increasing number of adult tumors. This makes the exploration of PD-1 blockade in sarcoma of interest,” she said.
Additionally, CD8-positive T cells are of interest because they are critical mediators of adaptive immunity, she noted.
Ms. van Erp and colleagues looked at expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and the presence of CD8-positive cells in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tumor samples from patients with one of six sarcoma subtypes: primary osteosarcoma (48 samples), Ewing sarcoma (32), alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma (28), embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma (78), synovial sarcoma (23), and desmoplastic small round cell tumors (8).
The samples were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for the expression of PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8-positive cells, and expression levels were then correlated with clinical outcomes.
The investigators classified expression of markers on less than 10% of cells in a sample as negative, 10%-50% as positive, and more than 50% as highly positive.
PD-1 was expressed in lymphocytes in 6% of all samples, and in 19% of all tumors. PD-L1 was expressed in 10%, and CD8-positive cells in 46%.
Only 2% of samples expressed both PD-1 and PD-L1, 11% expressed both PD-1 and CD8-positive T cells, 7% had PD-L1 and CD8, and 2% expressed all three markers.
The highest percentages of PD-1 expression were in lymphocytes from synovial sarcoma samples (17%), and the highest levels of PD-1 were seen in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma samples. However, neither PD-1 nor PD-L1 were detected at significant levels in synovial sarcoma tumor cells, and PD-1 was not detected in tumor cells from alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
“These data show that there is a high difference between the different subtypes, and they highlight the need to really look at PD-1 blockade per individual subtype,” Ms. van Erp said.
For all subtypes combined, the OS was significantly better for patients with PD-L1 positive vs. PD-L1–negative tumors out to 25 years of follow-up (P = .028). Similarly OS was better for patients with PD-L1–positive, CD8-positive tumors, compared with tumors negative for both markers (P = .020).
When they looked at individual sarcoma subtypes, however, they saw significant results only for alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma, with PD-L1 positivity vs. negativity associated with better OS and EFS out to more than 10.5 years (P = .007 for both). There was also a trend toward better EFS for tumors positive for both PD-L1 and CD8, but this was not significant.
For Ewing sarcoma, PD-1 was found to be expressed on tumor rather than on lymphocytes in 19% of all samples, and PD-1 expression was found to be associated with worse EFS. PD-1 was also found in tumors of all desmoplastic small round cell tumor samples, but this group was too small to determine significance, Ms. van Erp said.
She acknowledged that the study was limited by the use of tissue microarray sampling rather than examination of the whole tumor and its microenvironment. In addition, no functional assays have been performed to determine the clinical relevance of PD-1 expression for either Ewing sarcoma or desmoplastic small round cell tumor cells.
“In this study, we looked at the primary tumors for these subtypes, and as we know that there can be a difference in the pattern of expression between primary tumors and metastatic tumors in sarcoma subtypes, and as sarcoma patients are in great need for new therapeutic options, it would be very interesting to look at the expression of PD-1. PD-L1, and CD8 in these tumor types in metastatic disease,’ she said.
The study was supported by Radboud University; the Princess Maxima Center for Pediatric Oncology in Utrecht, the Netherlands; and the Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust in London. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
AT ECCO2017
Key clinical point: PD-1, PD-L1, and CD8 expression in tumors varies by sarcoma subtype, suggesting that success of PD-1 blockade may be subtype dependent.
Major finding: PD-L1 positivity was associated with better overall and event-free survival only in alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma.
Data source: Retrospective review of tumor samples from patients with one of six sarcoma subtypes.
Disclosures: The study was supported by Radboud University; the Princess Maxima Center for Pediatric Oncology in Utrecht, the Netherlands; and the Institute of Cancer Research and Royal Marsden NHS Foundation Trust in London. The authors reported no conflicts of interest.
Soft Tissue Sarcoma: Diagnosis and Treatment
INTRODUCTION
Soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) are rare adult tumors, with 3.4 new cases per 100,000 persons or 12,310 expected new cases in 2016.1 Sarcomas are a heterogeneous collection of tumors that affect fat, muscle, nerve, nerve sheath, vascular, and connective tissues. There are more than 50 histological subtypes that comprise this diverse category of tumors. Treatment varies by stage, with limb-sparing surgery representing the mainstay of curative-intent treatment. Radiation and chemotherapy may also be considered depending on the size, grade, and location of the tumor. Survival rates have been stagnant until recently, with a disease-specific survival hovering around 65%.1 Given the complexity of these cases, all patients ideally should be evaluated and treated by a multidisciplinary team at an institution with extensive experience treating STS.2
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION
The most common STS subtypes are gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), undifferentiate pleomorphic sarcoma (previously referred to as malignant fibrous histiocytoma), liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, and unclassified sarcoma.3 Liposarcoma is one of the most common subtypes, comprising 20% of all STSs; it is subdivided into well-differentiated/dedifferentiated liposarcomas, myxoid/round cell liposarcomas, and pleomorphic liposarcomas. Well-differentiated liposarcomas tend to occur in the retroperitoneum and limbs, while both myxoid and round cell as well as pleomorphic liposarcomas more commonly originate on the limbs. Histology varies based on subtype and ranges from mature-appearing adipocytes and fibroblasts to undifferentiated cells with minimal lipogenic differentiation.4
Leiomyosarcomas are smooth muscle tumors and are usually located in the retroperitoneum, but have also been associated with peripheral soft tissue and vasculature. Typical histology ranges from well-defined areas of spindle-shaped cells to poorly differentiated anaplastic spindle cells.5,6 Synovial sarcomas are a distinct type of STS that can show epithelial differentiation and account for 5% of adult STSs. The extremities are the most common presenting location (90%).7
Rhabdomyosarcomas are skeletal muscle tumors and are further subdivided into embryonal, alveolar, and pleomorphic subtypes. Embryonal histology ranges from primitive mesenchymal-appearing cells to highly differentiated muscle cells. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma has the worst prognosis of the subtypes and consists of round cells with high nuclear-to-chromatin ratios that form “glandular-like” or “alveolar” spaces.8 Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcomas are composed of rhabdomyoblasts that can affect many different locations, but most commonly present on the lower extremities.9
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) comprises 5% to 10% of all STSs. These tumors are associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), with 25% to 50% of tumors occurring in NF-1 patients. Additionally, most patients have a truncating lesion in the NF1 gene on chromosome 17.10 Anghileri et al in their single institution analysis of 205 patients with MPNSTs found the 2 most common presenting sites were the trunk and extremities. Histologically, these tumors have dense fascicles of spindle cells.10
GISTs are the most common STS of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Previously, GISTs were classified as smooth muscle tumors and were not accounted for in the literature as a separate entity distinct from leiomyomas, leiomyoblastomas, and leiomyosarcomas.11 GISTs are found throughout the GI tract: the most common sites are the stomach (60%) and small intestine (30%). Less common sites include duodenum (4%–5%), esophagus (1%), rectum (1%–2%), and appendix (< 0.2%).12 GISTs can be spindle cell, epithelioid, or mesenchymal tumors. Immunohistochemically, GISTs are KIT (CD117) positive. Other cell markers that are also commonly positive include CD34 (60%–70%) and smooth muscle actin (SMA) (25%).11 The majority of GISTs (80%) have an activating c-KIT gene mutation. The most common mutation site is exon 11, with less common c-KIT gene mutations also occurring at exon 9 or 13. Not all GISTs have KIT mutations. The second most common mutation is the PDGFRA mutation (5%–10% of GISTs).2 A minority of GISTs are negative for both KIT and PDGFRA mutations. These tumors were previously called wild-type, but as the majority have either a succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) loss of function or loss of SDHB protein expression, they are now referred to as SDH-deficient GISTs.2 GISTs vary in aggressiveness from incidental to aggressive. Typically, small intestine and rectal GISTs are more aggressive than gastric GISTs. Both size and mitotic rate help to predict the metastatic potential of the tumor. Tumors less than 2 cm in size and having a mitotic rate of less than 5 per 50 high-power fields (hpf) have the lowest risk of metastases, while tumors greater than 5 cm and with more than 5 mitoses per 50 hpf have the highest rates of metastases.12
Angiosarcomas are rare tumors comprising 4% of all STSs. Although they can occur in any site, the majority are cutaneous and occur most frequently in the head and neck regions. These tumors are either of vascular or lymphatic origin and are comprised of abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. The most useful immunohistochemical markers include von Willebrand factor, CD31, and Ulex europaeus agglutinin 1. The majority of these tumors occur sporadically; however, radiation exposure, chronic lymphedema, and certain toxins including vinyl chloride and thorium dioxide are known risk factors.13
Undifferentiated sarcomas have no specific features and typically consist of primitive mesenchymal cells.
CLINICAL EVALUATION
CASE PRESENTATION
Initial Presentation and History
A 55-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a painless mass in his anterior thigh. The mass has been present for the past 3 months and he believes that it is enlarging. The patient has a history of well-controlled hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His medications include atorvastatin and hydrochlorothiazide. He has no known drug allergies. Family history is notable for diabetes and hypertension. He drinks 4 to 5 alcoholic drinks a week and he is a former smoker. He quit smoking in his 30s and only smoked intermittently prior to quitting. He denies any illicit drug use. He works as a high school principal. Currently, he feels well. His review of systems is otherwise noncontributory.
Physical Examination
On physical exam, he is afebrile with a blood pressure of 132/75 mm Hg, respiratory rate of 10 breaths/min, and oxygen saturation of 99% on room air. He is a well appearing, overweight male. His head and neck exam is unremarkable. Lung exam reveals clear breath sounds, and cardiac exam reveals a regular rate and rhythm. His abdomen is obese, soft, and without hepatosplenomegaly. There is a large, fixed mass on the anterior lateral aspect of his right thigh. He has no appreciable lymphadenopathy. His neurological exam is unremarkable.
• What are risk factors for sarcoma?
There are few known risk factors for sarcoma. Established risks factors include prior radiation therapy, chronic lymphedema, viruses, and genetic cancer syndromes including Li-Fraumeni syndrome, hereditary retinoblastoma, and NF-1. Other environmental exposures include phenoxyacetic acids and chlorophenols.14 The majority of cases are sporadic, with only a minority of patients having one of these known risk factors.15 Up to one third of sarcomas have a specific translocation and are driven by fusion oncogenes (Table 1).
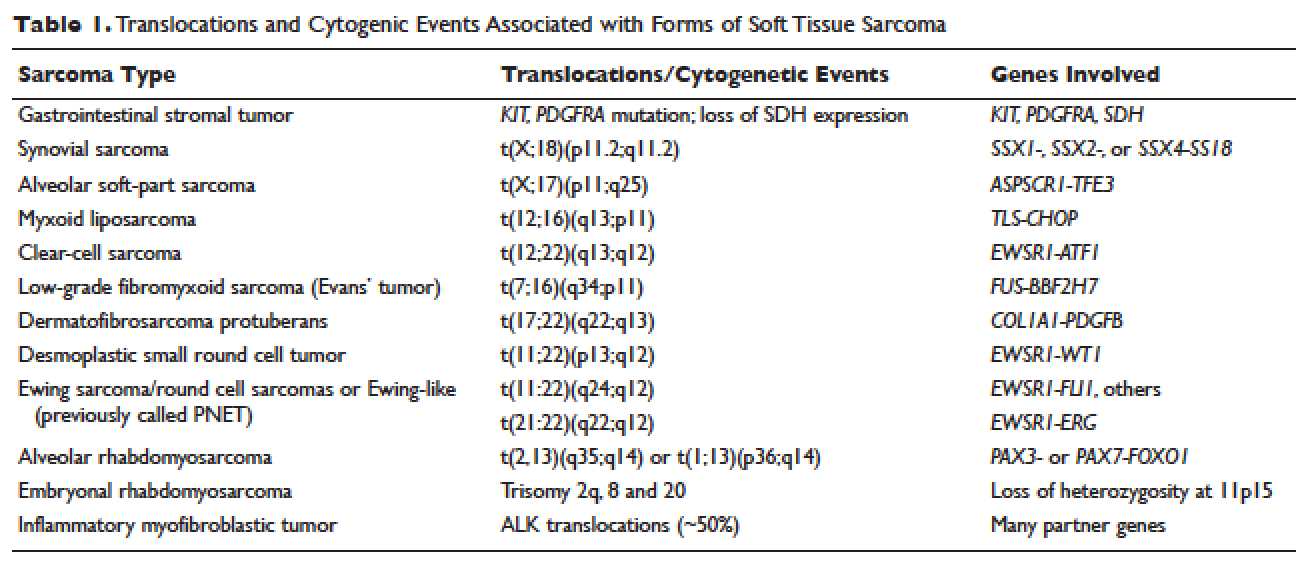
A painless mass is the most typical presenting symptom. Size at presentation varies based on location, with extremity and head and neck locations typically presenting at smaller sizes than retroperitoneal tumors.14 Patients may experience pain and numbness as the mass enlarges and impinges on surrounding structures including nerves and vasculature. The vast majority of patients are without systemic symptoms.
• How is sarcoma staged?
The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system is the most widely used staging system in the United States. The latest AJCC manual was updated in 2010 to include a 3-tiered grading system where the tumor is classified according to tumor size, lymph node involvement, metastases, and grade at time of diagnosis (Table 2 and Table 3). Additionally, tumor depth in relation to deep fascia is also taken into account, with superficial tumors being assigned a designation of “a” and deep tumors a designation of “b.”

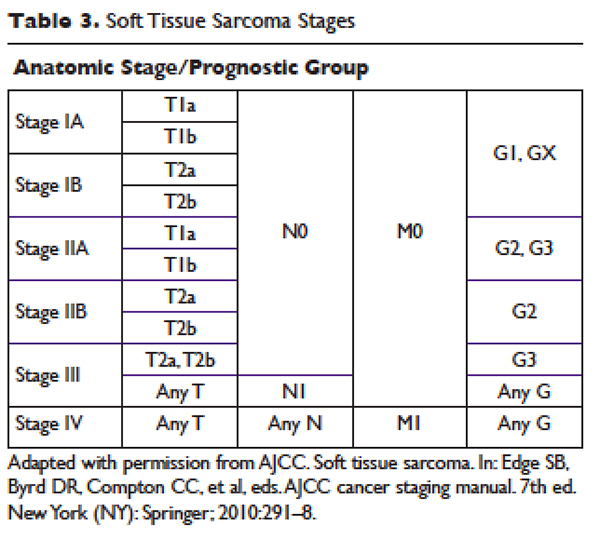
Previously, 2 of the most widely used grading systems were the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group (FNCLCC) systems, both 3-tier grading systems. The main components that determine the NCI grade are the tumor’s histologic type and location and the amount of tumor necrosis. The FNCLCC system evaluation focuses on tumor differentiation, mitotic rate, and amount of tumor necrosis. A study that compared the NCI and FNCLCC grading systems found that FNCLCC was a better predictor of mortality and distant metastasis.16 Previously, the AJCC was a 4-tier grading system, but the 2010 version was updated to the 3-tier FNCLCC grading system. Additionally, the AJCC system has reclassified single lymph node disease as stage III as it confers better survival than metastatic disease.17 It is important that pathology be evaluated by a sarcoma specialist as disagreements with regard to histologic subtype and grade are common.18,19
• What are the most important prognostic factors?
Prognostic factors include grade, size, and presence of metastases at presentation. Best survival is associated with low-grade, small tumors with no metastases at time of diagnosis.14
• What imaging should be considered?
Imaging should be undertaken to help differentiate between benign and malignant lesions. Ideally, it should be undertaken before a biopsy is planned as the imaging can be used to plan biopsy as well as provide invaluable prognostic information. There are several imaging modalities that should be considered during the preliminary work-up and staging of STSs. Conventional imaging includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the original tumor site; computed tomography (CT) to evaluate for pulmonary metastases and, depending on location, liver metastases; and in the case of small, low-grade tumors, chest radiography. MRI is considered the test of choice for soft tissue masses and can help delineate benign masses such as hematomas, lipomas, and hemangiomas from sarcomas.20 It is difficult to compare the accuracy of positron emission tomography (PET)/CT to CT and MRI because most studies have evaluated PET/CT in parallel with CT and MRI.21 Tateishi et al compared the accuracy of conventional imaging, PET/CT, and PET/CT combined with conventional imaging at determining the TNM staging for 117 patients. They found that conventional imaging correctly classified 77% of patients, PET alone correctly classified 70%, PET/CT correctly classified 83%, and PET/CT combined with conventional imaging correctly staged 87%.22
• Which subtypes are most likely to metastasize?
Although the vast majority of sarcomas spread hematogenously, 3 have a propensity to spread lymphogenously: epithelioid sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, and clear-cell sarcoma. Additionally, certain subtypes are more likely to metastasize: leiomyosarcomas, synovial sarcomas, neurogenic sarcomas, rhabdomyosarcomas, and epithelioid sarcomas.23 Sarcomas metastasize to the lungs more frequently than to the liver. The metastatic pattern is defined primarily by sarcoma subtype and site of primary tumor. Sarcomas rarely metastasize to the brain (~1%).
MANAGEMENT
CASE CONTINUED
The patient undergoes an ultrasound to better visualize the mass. Given the heterogeneous character of the mass, he is referred for an MRI to evaluate the mass and a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to evaluate for distant metastases. MRI reveals a 5.1 cm × 4.6 cm heterogeneous mass invading the superficial fascia of the rectus femoris muscle. No suspicious lymph nodes or other masses are identified on imaging. The patient next undergoes an image-guided core needle biopsy. Pathology from that procedure is consistent with a stage III, T2bNxMx, grade 3, dedifferentiated liposarcoma.
• What is the best management approach for this patient?
SURGERY
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for STS. Patients with the best prognosis are those who undergo complete resection with negative surgical margins.24,25 Goal tumor-free margin is 1 to 3 cm.26 Complete resection confers the best long-term survival. Both local and metastatic recurrence is higher in patients with incomplete resection and positive margins.24,25 In a study that analyzed 2084 localized primary STSs, patients with negative margins had a local recurrence rate of 15% versus a rate of 28% in patients with positive margins. This translated into higher 5-year local recurrence-free survival for patients with negative surgical margins (82%) compared to patients with positive margins (65%).27 Another study similarly found that patients with negative margins at referral to their institution who underwent postoperative radiation had high local control rates of 93% (95% confidence interval [CI] 87% to 97%) at 5, 10, and 15 years.26 Although radiation improves local control, neither preoperative or postoperative radiation has been shown to improve progression-free or overall survival.28 Other factors that are associated with risk of recurrence are tumor location, history of previous recurrence, age of patient, histopathology, tumor grade, and tumor size. Approximately 40% to 50% of patients with high-grade tumors (defined as size > 5 cm, deep location, and high grade) will develop distant metastases.29
Zagars et al found that positive or uncertain resection margin had a relative risk of local recurrence of 2.0 (95% CI 1.3 to 3.1; P = 0.002), and presentation with locally recurrent disease (vs new tumor) had a relative risk of local recurrence of 2.0 (95% CI 1.2 to 3.4; P = 0.013).26 Patients with STS of head and neck and deep trunk have higher recurrence rates than those with superficial trunk and extremity STS. A single-institution retrospective review demonstrated that patients with completely resectable retroperitoneal sarcomas have longer median survival (103 months) compared to patients with incompletely resected abdominal sarcomas (18 months).25
Rosenberg and colleagues compared amputation to limb-sparing surgery and radiation.24 Their prospective analysis of 65 patients found no difference in disease-free and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups. The limb-sparing treatment group had higher rates of local recurrence, which was highly correlated with positive surgical margins on pathology.24 Evidence from this and similar studies has resulted in radical amputations being replaced by conservative limb-sparing procedures and radiation therapy. In those found to have positive margins, re-resection is an option for some. Patients who undergo re-resection have higher local control rates than patients with positive margins who do not undergo re-resection. The 5-year control rate for patients who undergo re-resection is 85% (95% CI 80% to 89%) compared to 78% (95% CI 71% to 83%) for those who do not undergo re-resection. Similarly, patients who undergo re-resection have lower rates of metastases at 5, 10, and 15 years as well as higher 5-, 10-, and 15-year disease-free survival rates.26
CASE CONTINUED
The patient is referred for limb-sparing surgery after presentation at a multidisciplinary tumor board. Prior to undergoing resection of the tumor, he is also referred to radiation-oncology to discuss the risks and benefits of combination radiotherapy and surgery as opposed to surgical resection alone.
• What is the evidence for radiation therapy?
RADIATION THERAPY
Radiation therapy is used in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative settings to reduce the risk of local recurrence. There are several options for radiation, including external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), intraoperative radiation, and brachytherapy. A newer strategy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), utilizes 3-dimensional modeling to reduce radiation dosages. Overall there are no differences in overall survival or local recurrence rates between preoperative and postoperative radiation in STS.28
The rationale behind preoperative radiation is that it reduces seeding of tumor cells, especially at the time of surgery.30 Additionally, for EBRT, preoperative radiation has smaller field sizes and lower radiation doses. It can also help to reduce the size of the tumor prior to resection. Intraoperative radiation is often paired with preoperative radiation as a boost dose given only to the area of residual tumor.
Suit et al reviewed patients treated at a single institution with limb-sparing surgery and different radiation strategies. Local control rates between preoperative and postoperative radiation groups were not statistically significant. Local recurrence was linked to grade and size of the tumor in both groups. The authors did note, however, that the preoperative radiation group tended to have larger tumor sizes at baseline compared to the patients who received postoperative radiation.30 A study that compared 190 patients who received preoperative and postoperative EBRT or brachytherapy (primary end point was wound complications, and local control was a secondary end point) showed a trend towards greater local control with preoperative radiation; however, the preoperative radiation group had significantly more wound complications compared to the postoperative radiation group.31
Yang et al found that postoperative EBRT decreases rates of local recurrence compared to surgery alone in high-grade extremity sarcomas.32 However, there were no differences in rates of distant metastases and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups. Similarly, in patients with low-grade sarcoma, there were fewer local recurrences in those who received EBRT and surgery as compared to surgery alone.32 Another study that evaluated 164 patients who received either adjuvant brachytherapy or no further therapy after complete resection found that brachytherapy reduced local recurrence in high-grade sarcomas. No difference in local recurrence rates was found in patients with low-grade sarcomas, nor was a significant difference found in the rates of distant metastases and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups.33 With regards to IMRT, a single institution cohort experience with 41 patients who received IMRT following limb-sparing surgery had similar local control rates when compared to historical controls.34
CASE CONTINUED
After discussion of the risks and benefits of radiation therapy, the patient opts for preoperative radiation prior to resection of his liposarcoma. He receives 50 Gy of EBRT prior to undergoing resection. Resection results in R1 margin consistent with microscopic disease. He receives 16 Gy of EBRT as a boost after recovery from his resection.2
• What is the evidence for neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for stage I tumors?
CHEMOTHERAPY
Localized Sarcoma
For localized sarcoma, limb-sparing resection with or without radiation forms the backbone of treatment. Studies have evaluated chemotherapy in both the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings, with the vast majority of studies evaluating doxorubicin-based chemotherapy regimens in the adjuvant settings. Due to the rare nature of sarcomas, most studies are not sufficiently powered to detect significant benefit from chemotherapy. Several trials evaluating chemotherapy regimens in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings needed to be terminated prematurely due to inadequate enrollment into the study. 35,36
For stage IA (T1a-Tb, N0, M0, low grade) tumors, no additional therapy is recommended after limb-sparing surgery with appropriate surgical margins. For stage IB (T2a-2b, N0, M0, low grade) tumors with insufficient margins, re-resection and radiation therapy should be considered, while for stage IIA (T1a-1b, N0, M0, G2-3) tumors preoperative or postoperative radiation therapy is recommended.2 Studies have not found benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in these low-grade, stage I tumors in terms of progression-free survival and overall survival.37
• At what stage should chemotherapy be considered?
For stage IIb and stage III tumors, surgery and radiation therapy again form the backbone of therapy; however, neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy are also recommended as considerations. Anthracycline-based chemotherapy with either single-agent doxorubicin or doxorubicin and ifosfamide in combination are considered first-line chemotherapy agents in locally advanced STS.2,29,37
Evidence regarding the efficacy of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy regimens in the setting of locally advanced high-grade STS has been mixed. The Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration evaluated 14 trials of doxorubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy and found a trend towards overall survival in the treatment groups that received chemotherapy.37 All trials included in the meta-analysis compared patients with localized resectable soft-tissue sarcomas who were randomized to either adjuvant chemotherapy or no adjuvant chemotherapy after limb-sparing surgery with or without radiation therapy. None of the individual trials showed a significant benefit, and all trials had large confidence intervals; however, the meta-analysis showed significant benefit in the chemotherapy treatment groups with regard to local recurrence, distant recurrence, and progression-free survival. No significant difference in overall survival was found.37 Pervais et al updated the Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration’s 1997 meta-analysis with the inclusion of 4 new trials that evaluated doxorubicin combined with ifosfamide and found that both patients who received doxorubicin-based regimens or doxorubicin with ifosfamide had significant decreases in distant and overall recurrences. Only the trials that utilized doxorubicin and ifosfamide had an improved overall survival that was statistically significant (hazard ratio 0.56 [95% CI 0.36 to 0.85]; P = 0.01).29 Although no significant heterogeneity was found among the trials included in either meta-analysis, a variety of sarcomas were included in each clinical trial evaluated. Given the extremely small number of each sarcoma subtype present in each trial, subgroup analysis is difficult and prone to inaccuracies. As a result, it is not known if certain histological subtypes are more or less responsive to chemotherapy.37–39
One randomized controlled trial evaluated neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk sarcomas defined as tumors greater than 8 cm or grade II/III tumors. This study evaluated doxorubicin and ifosfamide and found no significant difference in disease-free and overall survival in the neoadjuvant therapy group compared to the control group.35 There remains controversy in the literature with regards to adjuvant chemotherapy. Many oncologists offer adjuvant chemotherapy to patients with certain stage III subtypes. Examples of subtypes that may be offered adjuvant therapy include myxoid liposarcomas, synovial sarcomas, and leiomyosarcomas.2 With regards to how many cycles of chemotherapy should be considered, a noninferiority study compared 3 cycles of epirubicin and ifosfamide to 5 cycles of epirubicin and ifosfamide in patients with high-risk locally advanced adult STSs. Three cycles of preoperative epirubicin and ifosfamide was found to be noninferior to 5 cycles with regards to overall survival.38
• What is this patient’s risk for recurrence?
The patient is at intermediate risk for recurrence. Numerous studies have demonstrated that tumor size, grade, and location are the most important factors to determine risk of recurrence, with larger size, higher grades, and deeper locations being associated with higher risk of recurrence. In an analysis of 1041 patients with STS of the extremities, high grade was the most important risk factor for distant metastases.39 The highest risk of recurrence is within the first 2 years. Given that the patient’s initial tumor was located in the extremity, he is more likely to have a distant metastasis as his site of recurrence; individuals with retroperitoneal tumors and visceral tumors are more likely to recur locally.40 For STSs of the extremity, distant metastases determine overall survival, whereas patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas can die from complications of local metastases.41 Once a patient develops distant metastases, the most important prognostic factor is the size of the tumor, with tumors larger than 10 cm having a relative risk of 1.5 (95% CI 1.0 to 2.0).39
• What are the recommendations for surveillance?
Surveillance recommendations are based on the stage of the sarcoma. Stage I tumors are the least likely to recur either locally or distally. As a result, it is recommended that stage I tumors be followed with history and physical exam every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 to 3 years, and then annually after the first 2 to 3 years. Chest x-rays should be considered every 6 to 12 months.2 For stage II–IV tumors, history and physical exam is recommended every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 to 3 years. Chest and distant metastases imaging should also be performed every 3 to 6 months during this time frame. For the next 2 years, history and physical exam and imaging are recommended every 6 months. After the first 4 to 5 years, annual follow-up is recommended.2
A study that followed 141 patients with primary extremity STSs for a median interval of 49 months found that high-grade tumors were most likely to recur during the first 2 years, with 20% of their patients recurring locally and 40% recurring distally. Chest x-rays performed during surveillance follow-up found distant lung metastases in 36 asymptomatic patients and had a positive predictive value of 92%, a negative predictive value of 97%, and a quality-adjusted life-year of $30,000.40,41 No laboratory testing was found to aid in detection of recurrence.
CASE CONTINUED
The patient does well for 1 year. With physical therapy, he regains most of the strength and coordination of the lower extremity. He is followed every 3 months with chest x-rays and a MRI of the thigh for the first year. On his fourth follow-up clinic visit, he describes increased dyspnea on exertion over the previous few weeks and is found to have multiple lung metastases in both lungs on chest x-ray. He undergoes further evaluation for metastases and is not found to have any other metastatic lesions. Bronchoscopy and biopsy of 1 of the lung nodules confirms recurrent dedifferentiated liposarcoma.
• Should this patient undergo metastectomy?
An analysis of 3149 patients with STS treated at Memorial Sloan-Kettering who developed lung metastases found that patients with pulmonary metastases have survival rates of 25%. The most important prognostic factor for survival was complete resection of all metastases.42 For stage IV disease, surgery is used only in certain instances. In instances where tumor is more localized or limited, removal of metastases or metastectomy can play a role in management.2
CASE CONTINUED
Because the patient’s metastases are limited to the lungs, he is referred for metastectomy. He undergoes wedge resection for definitive diagnosis but it is not possible to completely resect all of the metastases. He is thus referred to a medical oncologist to discuss his treatment options.
• What are treatment options for unresectable or metastatic disease?
Metastatic Disease
Unlike local and locally advanced disease, chemotherapy forms the backbone of treatment in stage IV disease. Doxorubicin and olaratumab or doxorubicin and ifosfamide in combination are considered first line in metastatic disease. Response rates for single-agent doxorubicin range from 16% to 27%, while phase 2 and phase 3 studies of doxorubicin and ifosfamide have found response rates ranging from 18% to 36%.43 In addition, the effectiveness of doxorubicin and ifosfamide phase 2 and 3 trials varied. Edmonson et al found a tumor regression rate of 34% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide as compared to 20% for doxorubicin alone.44 In comparison, Santoro et al found a response rate of 21.3% for doxorubicin alone and 25.2% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide.45 Neither study found increased survival benefit for doxorubicin and ifosfamide when compared to doxorubicin alone. In a Cochrane review evaluating randomized trials that compared doxorubicin and combination chemotherapy regimens, response rates varied from 14% for doxorubicin in combination with streptomycin to 34% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide. Most trials did not show a significant benefit for combination therapies when compared to doxorubicin alone.43 Mean survival with doxorubicin or doxorubicin and ifosfamide is 12 months. High rates of recurrence highlight the need for additional chemotherapy regimens.
The newest approved agent is olaratumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and prevents receptor activation. A phase 1-b and phase 2 trial evaluated patients with locally advanced and metastatic STS and randomly assigned them to either olaratumab and doxorubicin or doxorubicin alone.46 Progression-free survival for olaratumab/doxorubicin was 6.6 months (95% CI 4.1 to 8.3) compared to 4.1 months (95% CI 2.8 to 5.4) for doxorubicin alone. The objective response rate was 18.2% (95% CI 9.8 to 29.6) for olaratumab/doxorubicin compared to 7.5% (95% CI 2.5 to 6.6) for doxorubicin alone. Furthermore, the median overall survival for olaratumab plus doxorubicin was 26.5 months (95% CI 20.9 to 31.7) compared to 14.7 months for doxorubicin alone (95% CI 5.5 to 26.0). Impressively, this improved response was notable across histological types. Furthermore, patients who had previously been treated with more than 1 regimen and those who were treatment naïve had similar response rates.46
• What are second-line treatment options?
Doxorubicin has been used in combination with several other agents including dacarbazine (DTIC) as well as DTIC and ifosfamide (MAID). Borden et al evaluated patients with metastatic STS and randomly assigned the patients to either doxorubicin or doxorubicin and DTIC. Combination therapy demonstrated better tumor response than doxorubicin alone: 30% complete or partial response for combination therapy and 18% for doxorubicin alone.47 However, Omura et al
found similar rates of efficacy between doxorubicin and combination doxorubicin and DTIC in women with recurrent or nonresectable uterine sarcomas.48 MAID has never been directly compared in a randomized trial to doxorubicin alone. In a study that compared MAID to doxorubicin and DTIC (AD) in patients with unresectable or metastatic sarcomas, MAID had superior response rates (32% versus 17%), but there was no difference with regards to overall survival (mean survival of 12.5 months).49
Several additional regimens have undergone evaluation in metastatic and recurrent STSs. Gemcitabine has been used both as a single agent and as part of combination therapy in many studies. Studies with gemcitabine in combination with either docetaxel or DTIC have been the most efficacious. In a phase 2 trial, patients with metastatic STS were randomly assigned to either gemcitabine alone or gemcitabine and docetaxel. Combination therapy had a higher response rate (16% versus 8%) and longer overall survival (17.9 months versus 11.5 months) than gemcitabine alone.50 Furthermore, a phase 2 trial of gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with unresectable leiomyosarcoma showed an overall response rate of 56%, with 3 complete and 15 partial responses among the 34 patients enrolled in the study.51
A phase 2 trial randomly assigned patients with unresectable or metastatic STS to either DTIC or combination gemcitabine and DTIC.52 Gemcitabine-DTIC had a superior progression-free survival at 3 months (56% [95% CI 43% to 69%]) as compared to DTIC alone (37% [95% CI 23.5% to 50%]). Furthermore, mean progression-free survival and overall survival were improved in the gemcitabine-DTIC group (4.2 months and 16.8 months) as compared to the DTIC group (2.0 months and 8.2 months).52 DTIC has a single-agent response rate of 16%, but has been shown to be particularly effective in the setting of leiomyosarcomas.49
• Does response to treatment regimens differ by histologic subtype?
The majority of STS trials include many different histologic subtypes. Given the rarity of sarcomas as a whole, many trials have had difficulty recruiting adequate numbers of patients to have sufficient power to definitely determine if the treatment under investigation has clinical benefit. Furthermore, the patients recruited have been heterogeneous with regard to subtype. Many older studies hypothesized that the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents vary based on histologic subtype; however, for most subtypes the number of individuals included in those trials was too low to evaluate efficacy based on subtype.
Some exceptions exist, however. For example, both gemcitabine-DTIC and gemcitabine-docetaxel have been found to be particularly effective in the treatment of leiomyosarcomas.50,52 Additionally, a retrospective study found a 51% overall response rate for patients with myxoid liposarcomas treated with trabectedin.53 Studies of patients with angiosarcoma treated with paclitaxel have demonstrated response rates of 43% and 53%.54,55
• What are the newest approved and investigational agents?
A recently approved agent is trabectedin, a tris tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from ascidians that binds to the minor groove of DNA and causes disruptions in the cell cycle. Samuels et al reported data from a single-arm, open-label expanded access trial that evaluated patients with advanced metastatic sarcomas.56 In this study, patients with liposarcomas and leiomyosarcomas had an objective response rate of 6.9% (95% CI 4.8 to 9.6) as compared to a rate of 5.9% (95% CI 4.4 to 7.8) for all assessable patients. Median survival was 11.9 months for all patients, with improved median survivals for liposarcoma and leiomyosarcomas of 16.2 months (95% CI 14.1 to 19.5) compared to 8.4 months (95% CI 7.1 to 10.7 months) for other subtypes.56
Schöffski et al evaluated eribulin, a chemotherapeutic agent that affects microtubule dynamics, in a phase 2 trial of patients with progressive or high-grade STS with progression on previous chemotherapy. They found a median progression-free survival of 2.6 months (95% CI 1.7 to 6.2) for adipocytic sarcoma, 2.9 months (95% CI 2.4 to 4.6) for leiomyosarcoma, 2.6 months (95% CI 2.3 to 4.3) for synovial sarcoma, and 2.1 months (95% CI 1.4 to 2.9) for other sarcomas.57
Van der Graaf and colleagues randomly assigned patients with metastatic nonadipocytic STS to pazopanib or placebo in a phase 3 trial. Pazopanib is a small-molecule endothelial growth factor inhibitor with activity against vascular endothelial growth factors 1, 2, and 3 as well as platelet-derived growth factors. Median progression-free survival was 4.6 months (95% CI 3.7 to 4.8) with pazopanib compared to 1.6 months (95% CI 0.9 to 1.8) with placebo.58 Adipocytic sarcomas (liposarcomas) were excluded from the trial because phase 2 trials had found a lower rate of progression-free survival (26%) for them compared to other subtypes.
• What are the most common toxicities associated with the approved and investigational chemotherapeutic agents?
Toxicities were seen with each of the regimens studied and were common in the randomized trials, with higher rates of toxicities in the combination chemotherapy regimens. The most common toxicities are myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting. In the doxorubicin trials, the most common toxicities were myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting.44
Ifosfamide both as an individual agent and in combination with doxorubicin has higher rates and higher grades of toxicity than doxorubicin alone. Myelosuppression is the most common toxicity associated with ifosfamide, and the most commonly affected cell line is leukocytes.44 Combination doxorubicin and ifosfamide also had high rates of nausea and vomiting (95%) and alopecia (100%).35
Neutropenia is the most common toxicity associated with gemcitabine and dacarbazine, while their most common nonhematologic toxicities are fatigue and nausea.52,59 Trabectedin’s most common toxicities are nausea (29%), neutropenia (24%), and fatigue (23%). It has also been shown to cause increased alkaline phosphatase (20%) and alanine aminotransferase (19%) levels.56 In a phase 2 study of eribulin, 50% of patients had neutropenia, and other toxicities included fatigue, alopecia, nausea, sensory neuropathy, and thrombocytopenia.57 Pazopanib is generally well tolerated; the most common toxicities are fatigue (65%), diarrhea (58%), nausea (54%), and hypertension (41%).58 Higher rates of neutropenia, mucositis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and transfusion reactions were seen with olaratumab and doxorubicin compared to doxorubicin alone in phase 1b and 2 studies.46
CASE CONCLUSION
Given his poor prognosis with unresectable metastatic undifferentiated liposarcoma, the patient considers a clinical trial prior to undergoing combined therapy with doxorubicin and ifosfamide. He tolerates therapy well with stable disease at 6 months.
CONCLUSION
STSs are a heterogeneous collection of rare tumors. Low-grade, localized tumors have the best prognosis, and patients who undergo complete resection have the best long-term survival. Due to the rarity of STSs, trials often have limited enrollment, and little progress has been made with regards to treatment and survival rates for metastatic and unresectable disease. All patients should be evaluated and treated at specialized sarcoma centers. This case highlights the need for continued research and clinical trials to improve overall survival of patients with sarcoma.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2016. American Cancer Society Web site. www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@research/documents/document/acspc-047079.pdf. Accessed December 20, 2016.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical guidelines in oncology: soft tissue sarcoma. 2016
- Coindre J, Terrier P, Guillou L, et al. Predictive value of grade for metastasis development in the main histologic types of adult soft tissue sarcomas: a study of 1240 patients from the French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group. Cancer 2001;91:1914–26.
- Dei Tos A. Liposarcoma: new entities and evolving concepts. Ann Diagn Pathol 2000;4:252–66.
- Wile AG, Evans HL, Romsdahl MM. Leiomyosarcoma of soft tissue: a clinicopathologic study. Cancer 1981;48:1022–32.
- Hashimoto H, Daimaru Y, Tsuneyoshi M, Enjoji M. Leiomyosarcoma of the external soft tissues. A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopic study. Cancer 1986;57:2077–88
- Fisher C. Synovial sarcoma. Ann Diagn Pathol 1998;2:401–21.
- Newton WA Jr, Gehan EA, Webber BL, et al. Classification of rhabdomyosarcomas and related sarcomas. Pathologic aspects and proposal for a new classification--an Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Cancer 1995;76:1073–85.
- Furlong MA. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: a clinicopathologic study of 38 cases with emphasis on morphologic variants and recent skeletal muscle-specific markers. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:595–603.
- Anghileri M, Miceli R, Fiore M. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: prognostic factors and survival in a series of patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2006;107:1065–74.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors–definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Archive 2001;438:1–12.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol 2006;23:70–83.
- Young RJ, Brown NJ, Reed MW, et al. Angiosarcoma. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:983–91.
- Cormier JN, Pollock RE. Soft tissue sarcomas. CA Cancer J Clin 2004;54:94–109.
- Penel N, Grosjean J, Robin YM, et al. Frequency of certain established risk factors in soft tissue sarcomas in adults: a prospective descriptive study of 658 cases. Sarcoma 2008;2008:459386.
- Guillou L, Coindre JM, Bonichon F, et al. Comparative study of the National Cancer Institute and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group grading systems in a population of 410 adult patients with soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1997;15:350–62.
- Maki RG, Moraco N, Antonescu CR, et al. Toward better soft tissue sarcoma staging: building on American joint committee on cancer staging systems versions 6 and 7. Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:3377–83.
- Shiraki M, Enterline HT, Brooks JJ, et al. Pathologic analysis of advanced adult soft tissue sarcomas, bone sarcomas, and mesotheliomas. The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) experience. Cancer 1989;64:484–90.
- Presant CA, Russell WO, Alexander RW, Fu YS. Soft-tissue and bone sarcoma histopathology peer review: The frequency of disagreement in diagnosis and the need for second pathology opinions. The Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol 1986; 4:1658–61.
- Sundaram M, McLeod RA. MR imaging of tumor and tumorlike lesions of bone and soft tissue. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1990;155:817–24.
- Ioannidis JP, Lau J. 18F-FDG PET for the diagnosis and grading of soft-tissue sarcoma: a meta-analysis. J Nucl Med 2003;44:717–24.
- Tateishi U, Yamaguchi U, Seki K, et al. Bone and soft-tissue sarcoma: preoperative staging with fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT and conventional imaging. Radiology 2007;245:839–47.
- Zagars GK, Ballo MT, Pisters PW, et al. Prognostic factors for patients with localized soft-tissue sarcoma treated with conservation surgery and radiation therapy: an analysis of 1225 patients. Cancer 2003;97:2530–43
- Rosenberg S, Tepper J, Glatstein E, et al. The treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities: prospective randomized evaluations of (1) limb-sparing surgery plus radiation therapy compared with amputation and (2) the role of adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg 1982;196:305–14.
- Lewis J, Leung D, Woodruff J, et al. Retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma: analysis of 500 patients treated and followed at a single institution. Ann Surg 1998;288:355–65.
- Zagars GK, Ballo MT, Pisters PW, et al. Surgical margins and reresection in the management of patients with soft tissue sarcoma using conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Cancer 2003;97:2544–53.
- Stojadinovic A, Leung DH, Hoos A. Analysis of the prognostic significance of microscopic margins in 2,084 localized primary adult soft tisusse sarcomas. Ann Surg 2002;235:424–34.
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomized trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235–41.
- Pervaiz N, Colterjohn N, Farrokhyar F, et al. A systematic meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2008;113:573–81.
- Suit HD, Mankin HJ, Wood WC, Proppe KH. Preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative radiation in the treatment of primary soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer 1985;55:2659–67
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomized trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235–41.
- Yang J, Chang A, Baker A, et al. Randomized prospective study of the benefit of adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 1998;16:197–203.
- Pisters PW, Harrison LB, Leung DH, et al. Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:859–68.
- Alektiar KM, Brennan MF, Healey JH, Singer S. Impact of intensity-modulated radiation therapy on local control in primary soft-tissue sarcoma of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:3440–5.
- Gortzak E, Azzarelli A, Buesa J, et al. A randomized phase II study on neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for ‘high-risk’ adult soft-tissue sarcoma. Eur J Cancer 2001;37:1096–1103.
- Fakhari N, Ebm C, Kostler WJ, et al. Intensified adjuvant IFADIC chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for soft tissue sarcoma: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized feasibility trial. Wein Klin Wochenschr 2010;122:614–9.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy for localised resectable soft-tissue sarcoma of adults: meta-analysis of individual data. Lancet 1997;350:1647–54.
- Gronchi A, Frustaci S, Mercuri M, et al. Short, full-dose adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk adult soft tissue sarcomas: a randomized clinical trial from the Italian Sarcoma Group and the Spanish Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:850–56.
- Pisters PW, Leung DH, Woodruff J. Analysis of prognostic factors in 1,041 patients with localized soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:1679–89.
- Whooley B, Gibbs J, Mooney M. Primary Extremity Sarcoma: What is the Appropriate Follow-up? Annals of Surg Oncol 2000; 7: 9-14.
- Whooley BP, Mooney MN, Gibbs JF, Graybill WG. Effective follow-up strategies in soft tissue sarcoma. Sem Surg Oncol 1999;17:83–87.
- Billingsley KG, Burt ME, Jara E, et al. Pulmonary metastases from soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of patterns of diseases and postmetastasis survival. Ann Surg 1999;229:602–10.
- Bramwell VH, Anderson D, Charette ML; Sarcoma Disease Site Group. Doxorubicin-based chemotherapy for the palliative treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(3):CD003293.
- Edmonson J, Ryan L, Blum R. Randomized comparison of doxorubicin alone versus ifosfamide plus doxorubicin or mitomycin, doxorubicin, and cisplatin against advanced soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1269–75.
- Santoro A, Tursz T, Mouridsen H. Doxorubicin versus CYVADIC versus doxorubicin plus ifosfamide in first-line treatment of advanced soft tissue sarcomas: a randomized study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol 1995;13:1537–45.
- Tap WD, Jones RL, Van Tine B, et al. Olaratumab and doxorubicin versus doxorubicin alone for treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: an open-label phase 1b and randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016;388:488–97.
- Borden EC, Amato DA, Rosenbaum C, et al. Randomized comparison of three adriamycin regimens for metastatic soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1987;5:840–50.
- Omura GA, Major FJ, Blessing JA, et al. A randomized study of adriamycin with and without dimethyl triazenoimidazole carboxamide in advanced uterine sarcomas. Cancer 1983;52:626–32.
- Antman K, Crowley J, Balcerzak SP, et al. An intergroup phase III randomized study of doxorubicin and dacarbazine with or without ifosfamide and mesna in advanced soft tissue and bone sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1276–85.
- Maki R, Wathen K, Patel SR, et al. Randomized phase II study of gemcitabine and docetaxel compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcomas: results of sarcoma alliance for research through collaboration study 002 [corrected]. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2755–63.
- Hensley ML, Maki R, Venkatraman E, et al. Gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with unresectable leiomyosarcoma: results of a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 2002;12:2824–31.
- Garcia-del-Muro X, Lopez-Pousa A, Maurel J, et al. Randomized phase II study comparing gemcitabine plus dacarbazine versus dacarbazine alone in patients with previously treated soft tissue sarcoma: a Spanish Group for Research on Sarcomas study. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:2528–33.
- Grosso F, Jones RL, Demetri GD, et al. Efficacy of trabectedin (ecteinascidin-743) in advanced pretreated myxoid liposarcomas: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol 2007;7:595–602.
- Italiano A, Cioffi A, Penel N, et al. Comparison of doxorubicin and weekly paclitaxel efficacy in metastatic angiosarcomas. Cancer 2012;118:3330–6.
- Penel N, Italiano A, Ray-Coquard I, et al. Metastatic angiosarcomas: doxorubicin-based regimens, weekly paclitaxel and metastasectomy significantly improve outcome. Ann Oncol 2012;23:517–23.
- Samuels BL, Chawla S, Patel S, et al. Clinical outcomes and safety with trabectedin therapy in patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas following failure of prior chemotherapy: results of a worldwide expanded access program study. Ann Oncol 2013;24:1703–9.
- Schöffski P, Ray-Coquard IL, Cioffi A, et al. Activity of eribulin mesylate in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma: a phase 2 study in four independent histolical subtypes. Lancet 2011;11:1045–52.
- Van der Graaf W, Blay JY, Chawla S, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012;379:1879–86.
- Dileo P, Morgan JA, Zahrieh D, et al. Gemcitabine and vinorelbine combination chemotherapy for patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas: results of a phase II trial. Cancer 2007;109:1863–9.
INTRODUCTION
Soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) are rare adult tumors, with 3.4 new cases per 100,000 persons or 12,310 expected new cases in 2016.1 Sarcomas are a heterogeneous collection of tumors that affect fat, muscle, nerve, nerve sheath, vascular, and connective tissues. There are more than 50 histological subtypes that comprise this diverse category of tumors. Treatment varies by stage, with limb-sparing surgery representing the mainstay of curative-intent treatment. Radiation and chemotherapy may also be considered depending on the size, grade, and location of the tumor. Survival rates have been stagnant until recently, with a disease-specific survival hovering around 65%.1 Given the complexity of these cases, all patients ideally should be evaluated and treated by a multidisciplinary team at an institution with extensive experience treating STS.2
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION
The most common STS subtypes are gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), undifferentiate pleomorphic sarcoma (previously referred to as malignant fibrous histiocytoma), liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, and unclassified sarcoma.3 Liposarcoma is one of the most common subtypes, comprising 20% of all STSs; it is subdivided into well-differentiated/dedifferentiated liposarcomas, myxoid/round cell liposarcomas, and pleomorphic liposarcomas. Well-differentiated liposarcomas tend to occur in the retroperitoneum and limbs, while both myxoid and round cell as well as pleomorphic liposarcomas more commonly originate on the limbs. Histology varies based on subtype and ranges from mature-appearing adipocytes and fibroblasts to undifferentiated cells with minimal lipogenic differentiation.4
Leiomyosarcomas are smooth muscle tumors and are usually located in the retroperitoneum, but have also been associated with peripheral soft tissue and vasculature. Typical histology ranges from well-defined areas of spindle-shaped cells to poorly differentiated anaplastic spindle cells.5,6 Synovial sarcomas are a distinct type of STS that can show epithelial differentiation and account for 5% of adult STSs. The extremities are the most common presenting location (90%).7
Rhabdomyosarcomas are skeletal muscle tumors and are further subdivided into embryonal, alveolar, and pleomorphic subtypes. Embryonal histology ranges from primitive mesenchymal-appearing cells to highly differentiated muscle cells. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma has the worst prognosis of the subtypes and consists of round cells with high nuclear-to-chromatin ratios that form “glandular-like” or “alveolar” spaces.8 Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcomas are composed of rhabdomyoblasts that can affect many different locations, but most commonly present on the lower extremities.9
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) comprises 5% to 10% of all STSs. These tumors are associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), with 25% to 50% of tumors occurring in NF-1 patients. Additionally, most patients have a truncating lesion in the NF1 gene on chromosome 17.10 Anghileri et al in their single institution analysis of 205 patients with MPNSTs found the 2 most common presenting sites were the trunk and extremities. Histologically, these tumors have dense fascicles of spindle cells.10
GISTs are the most common STS of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Previously, GISTs were classified as smooth muscle tumors and were not accounted for in the literature as a separate entity distinct from leiomyomas, leiomyoblastomas, and leiomyosarcomas.11 GISTs are found throughout the GI tract: the most common sites are the stomach (60%) and small intestine (30%). Less common sites include duodenum (4%–5%), esophagus (1%), rectum (1%–2%), and appendix (< 0.2%).12 GISTs can be spindle cell, epithelioid, or mesenchymal tumors. Immunohistochemically, GISTs are KIT (CD117) positive. Other cell markers that are also commonly positive include CD34 (60%–70%) and smooth muscle actin (SMA) (25%).11 The majority of GISTs (80%) have an activating c-KIT gene mutation. The most common mutation site is exon 11, with less common c-KIT gene mutations also occurring at exon 9 or 13. Not all GISTs have KIT mutations. The second most common mutation is the PDGFRA mutation (5%–10% of GISTs).2 A minority of GISTs are negative for both KIT and PDGFRA mutations. These tumors were previously called wild-type, but as the majority have either a succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) loss of function or loss of SDHB protein expression, they are now referred to as SDH-deficient GISTs.2 GISTs vary in aggressiveness from incidental to aggressive. Typically, small intestine and rectal GISTs are more aggressive than gastric GISTs. Both size and mitotic rate help to predict the metastatic potential of the tumor. Tumors less than 2 cm in size and having a mitotic rate of less than 5 per 50 high-power fields (hpf) have the lowest risk of metastases, while tumors greater than 5 cm and with more than 5 mitoses per 50 hpf have the highest rates of metastases.12
Angiosarcomas are rare tumors comprising 4% of all STSs. Although they can occur in any site, the majority are cutaneous and occur most frequently in the head and neck regions. These tumors are either of vascular or lymphatic origin and are comprised of abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. The most useful immunohistochemical markers include von Willebrand factor, CD31, and Ulex europaeus agglutinin 1. The majority of these tumors occur sporadically; however, radiation exposure, chronic lymphedema, and certain toxins including vinyl chloride and thorium dioxide are known risk factors.13
Undifferentiated sarcomas have no specific features and typically consist of primitive mesenchymal cells.
CLINICAL EVALUATION
CASE PRESENTATION
Initial Presentation and History
A 55-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a painless mass in his anterior thigh. The mass has been present for the past 3 months and he believes that it is enlarging. The patient has a history of well-controlled hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His medications include atorvastatin and hydrochlorothiazide. He has no known drug allergies. Family history is notable for diabetes and hypertension. He drinks 4 to 5 alcoholic drinks a week and he is a former smoker. He quit smoking in his 30s and only smoked intermittently prior to quitting. He denies any illicit drug use. He works as a high school principal. Currently, he feels well. His review of systems is otherwise noncontributory.
Physical Examination
On physical exam, he is afebrile with a blood pressure of 132/75 mm Hg, respiratory rate of 10 breaths/min, and oxygen saturation of 99% on room air. He is a well appearing, overweight male. His head and neck exam is unremarkable. Lung exam reveals clear breath sounds, and cardiac exam reveals a regular rate and rhythm. His abdomen is obese, soft, and without hepatosplenomegaly. There is a large, fixed mass on the anterior lateral aspect of his right thigh. He has no appreciable lymphadenopathy. His neurological exam is unremarkable.
• What are risk factors for sarcoma?
There are few known risk factors for sarcoma. Established risks factors include prior radiation therapy, chronic lymphedema, viruses, and genetic cancer syndromes including Li-Fraumeni syndrome, hereditary retinoblastoma, and NF-1. Other environmental exposures include phenoxyacetic acids and chlorophenols.14 The majority of cases are sporadic, with only a minority of patients having one of these known risk factors.15 Up to one third of sarcomas have a specific translocation and are driven by fusion oncogenes (Table 1).

A painless mass is the most typical presenting symptom. Size at presentation varies based on location, with extremity and head and neck locations typically presenting at smaller sizes than retroperitoneal tumors.14 Patients may experience pain and numbness as the mass enlarges and impinges on surrounding structures including nerves and vasculature. The vast majority of patients are without systemic symptoms.
• How is sarcoma staged?
The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system is the most widely used staging system in the United States. The latest AJCC manual was updated in 2010 to include a 3-tiered grading system where the tumor is classified according to tumor size, lymph node involvement, metastases, and grade at time of diagnosis (Table 2 and Table 3). Additionally, tumor depth in relation to deep fascia is also taken into account, with superficial tumors being assigned a designation of “a” and deep tumors a designation of “b.”


Previously, 2 of the most widely used grading systems were the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group (FNCLCC) systems, both 3-tier grading systems. The main components that determine the NCI grade are the tumor’s histologic type and location and the amount of tumor necrosis. The FNCLCC system evaluation focuses on tumor differentiation, mitotic rate, and amount of tumor necrosis. A study that compared the NCI and FNCLCC grading systems found that FNCLCC was a better predictor of mortality and distant metastasis.16 Previously, the AJCC was a 4-tier grading system, but the 2010 version was updated to the 3-tier FNCLCC grading system. Additionally, the AJCC system has reclassified single lymph node disease as stage III as it confers better survival than metastatic disease.17 It is important that pathology be evaluated by a sarcoma specialist as disagreements with regard to histologic subtype and grade are common.18,19
• What are the most important prognostic factors?
Prognostic factors include grade, size, and presence of metastases at presentation. Best survival is associated with low-grade, small tumors with no metastases at time of diagnosis.14
• What imaging should be considered?
Imaging should be undertaken to help differentiate between benign and malignant lesions. Ideally, it should be undertaken before a biopsy is planned as the imaging can be used to plan biopsy as well as provide invaluable prognostic information. There are several imaging modalities that should be considered during the preliminary work-up and staging of STSs. Conventional imaging includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the original tumor site; computed tomography (CT) to evaluate for pulmonary metastases and, depending on location, liver metastases; and in the case of small, low-grade tumors, chest radiography. MRI is considered the test of choice for soft tissue masses and can help delineate benign masses such as hematomas, lipomas, and hemangiomas from sarcomas.20 It is difficult to compare the accuracy of positron emission tomography (PET)/CT to CT and MRI because most studies have evaluated PET/CT in parallel with CT and MRI.21 Tateishi et al compared the accuracy of conventional imaging, PET/CT, and PET/CT combined with conventional imaging at determining the TNM staging for 117 patients. They found that conventional imaging correctly classified 77% of patients, PET alone correctly classified 70%, PET/CT correctly classified 83%, and PET/CT combined with conventional imaging correctly staged 87%.22
• Which subtypes are most likely to metastasize?
Although the vast majority of sarcomas spread hematogenously, 3 have a propensity to spread lymphogenously: epithelioid sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, and clear-cell sarcoma. Additionally, certain subtypes are more likely to metastasize: leiomyosarcomas, synovial sarcomas, neurogenic sarcomas, rhabdomyosarcomas, and epithelioid sarcomas.23 Sarcomas metastasize to the lungs more frequently than to the liver. The metastatic pattern is defined primarily by sarcoma subtype and site of primary tumor. Sarcomas rarely metastasize to the brain (~1%).
MANAGEMENT
CASE CONTINUED
The patient undergoes an ultrasound to better visualize the mass. Given the heterogeneous character of the mass, he is referred for an MRI to evaluate the mass and a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to evaluate for distant metastases. MRI reveals a 5.1 cm × 4.6 cm heterogeneous mass invading the superficial fascia of the rectus femoris muscle. No suspicious lymph nodes or other masses are identified on imaging. The patient next undergoes an image-guided core needle biopsy. Pathology from that procedure is consistent with a stage III, T2bNxMx, grade 3, dedifferentiated liposarcoma.
• What is the best management approach for this patient?
SURGERY
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for STS. Patients with the best prognosis are those who undergo complete resection with negative surgical margins.24,25 Goal tumor-free margin is 1 to 3 cm.26 Complete resection confers the best long-term survival. Both local and metastatic recurrence is higher in patients with incomplete resection and positive margins.24,25 In a study that analyzed 2084 localized primary STSs, patients with negative margins had a local recurrence rate of 15% versus a rate of 28% in patients with positive margins. This translated into higher 5-year local recurrence-free survival for patients with negative surgical margins (82%) compared to patients with positive margins (65%).27 Another study similarly found that patients with negative margins at referral to their institution who underwent postoperative radiation had high local control rates of 93% (95% confidence interval [CI] 87% to 97%) at 5, 10, and 15 years.26 Although radiation improves local control, neither preoperative or postoperative radiation has been shown to improve progression-free or overall survival.28 Other factors that are associated with risk of recurrence are tumor location, history of previous recurrence, age of patient, histopathology, tumor grade, and tumor size. Approximately 40% to 50% of patients with high-grade tumors (defined as size > 5 cm, deep location, and high grade) will develop distant metastases.29
Zagars et al found that positive or uncertain resection margin had a relative risk of local recurrence of 2.0 (95% CI 1.3 to 3.1; P = 0.002), and presentation with locally recurrent disease (vs new tumor) had a relative risk of local recurrence of 2.0 (95% CI 1.2 to 3.4; P = 0.013).26 Patients with STS of head and neck and deep trunk have higher recurrence rates than those with superficial trunk and extremity STS. A single-institution retrospective review demonstrated that patients with completely resectable retroperitoneal sarcomas have longer median survival (103 months) compared to patients with incompletely resected abdominal sarcomas (18 months).25
Rosenberg and colleagues compared amputation to limb-sparing surgery and radiation.24 Their prospective analysis of 65 patients found no difference in disease-free and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups. The limb-sparing treatment group had higher rates of local recurrence, which was highly correlated with positive surgical margins on pathology.24 Evidence from this and similar studies has resulted in radical amputations being replaced by conservative limb-sparing procedures and radiation therapy. In those found to have positive margins, re-resection is an option for some. Patients who undergo re-resection have higher local control rates than patients with positive margins who do not undergo re-resection. The 5-year control rate for patients who undergo re-resection is 85% (95% CI 80% to 89%) compared to 78% (95% CI 71% to 83%) for those who do not undergo re-resection. Similarly, patients who undergo re-resection have lower rates of metastases at 5, 10, and 15 years as well as higher 5-, 10-, and 15-year disease-free survival rates.26
CASE CONTINUED
The patient is referred for limb-sparing surgery after presentation at a multidisciplinary tumor board. Prior to undergoing resection of the tumor, he is also referred to radiation-oncology to discuss the risks and benefits of combination radiotherapy and surgery as opposed to surgical resection alone.
• What is the evidence for radiation therapy?
RADIATION THERAPY
Radiation therapy is used in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative settings to reduce the risk of local recurrence. There are several options for radiation, including external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), intraoperative radiation, and brachytherapy. A newer strategy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), utilizes 3-dimensional modeling to reduce radiation dosages. Overall there are no differences in overall survival or local recurrence rates between preoperative and postoperative radiation in STS.28
The rationale behind preoperative radiation is that it reduces seeding of tumor cells, especially at the time of surgery.30 Additionally, for EBRT, preoperative radiation has smaller field sizes and lower radiation doses. It can also help to reduce the size of the tumor prior to resection. Intraoperative radiation is often paired with preoperative radiation as a boost dose given only to the area of residual tumor.
Suit et al reviewed patients treated at a single institution with limb-sparing surgery and different radiation strategies. Local control rates between preoperative and postoperative radiation groups were not statistically significant. Local recurrence was linked to grade and size of the tumor in both groups. The authors did note, however, that the preoperative radiation group tended to have larger tumor sizes at baseline compared to the patients who received postoperative radiation.30 A study that compared 190 patients who received preoperative and postoperative EBRT or brachytherapy (primary end point was wound complications, and local control was a secondary end point) showed a trend towards greater local control with preoperative radiation; however, the preoperative radiation group had significantly more wound complications compared to the postoperative radiation group.31
Yang et al found that postoperative EBRT decreases rates of local recurrence compared to surgery alone in high-grade extremity sarcomas.32 However, there were no differences in rates of distant metastases and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups. Similarly, in patients with low-grade sarcoma, there were fewer local recurrences in those who received EBRT and surgery as compared to surgery alone.32 Another study that evaluated 164 patients who received either adjuvant brachytherapy or no further therapy after complete resection found that brachytherapy reduced local recurrence in high-grade sarcomas. No difference in local recurrence rates was found in patients with low-grade sarcomas, nor was a significant difference found in the rates of distant metastases and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups.33 With regards to IMRT, a single institution cohort experience with 41 patients who received IMRT following limb-sparing surgery had similar local control rates when compared to historical controls.34
CASE CONTINUED
After discussion of the risks and benefits of radiation therapy, the patient opts for preoperative radiation prior to resection of his liposarcoma. He receives 50 Gy of EBRT prior to undergoing resection. Resection results in R1 margin consistent with microscopic disease. He receives 16 Gy of EBRT as a boost after recovery from his resection.2
• What is the evidence for neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for stage I tumors?
CHEMOTHERAPY
Localized Sarcoma
For localized sarcoma, limb-sparing resection with or without radiation forms the backbone of treatment. Studies have evaluated chemotherapy in both the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings, with the vast majority of studies evaluating doxorubicin-based chemotherapy regimens in the adjuvant settings. Due to the rare nature of sarcomas, most studies are not sufficiently powered to detect significant benefit from chemotherapy. Several trials evaluating chemotherapy regimens in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings needed to be terminated prematurely due to inadequate enrollment into the study. 35,36
For stage IA (T1a-Tb, N0, M0, low grade) tumors, no additional therapy is recommended after limb-sparing surgery with appropriate surgical margins. For stage IB (T2a-2b, N0, M0, low grade) tumors with insufficient margins, re-resection and radiation therapy should be considered, while for stage IIA (T1a-1b, N0, M0, G2-3) tumors preoperative or postoperative radiation therapy is recommended.2 Studies have not found benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in these low-grade, stage I tumors in terms of progression-free survival and overall survival.37
• At what stage should chemotherapy be considered?
For stage IIb and stage III tumors, surgery and radiation therapy again form the backbone of therapy; however, neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy are also recommended as considerations. Anthracycline-based chemotherapy with either single-agent doxorubicin or doxorubicin and ifosfamide in combination are considered first-line chemotherapy agents in locally advanced STS.2,29,37
Evidence regarding the efficacy of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy regimens in the setting of locally advanced high-grade STS has been mixed. The Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration evaluated 14 trials of doxorubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy and found a trend towards overall survival in the treatment groups that received chemotherapy.37 All trials included in the meta-analysis compared patients with localized resectable soft-tissue sarcomas who were randomized to either adjuvant chemotherapy or no adjuvant chemotherapy after limb-sparing surgery with or without radiation therapy. None of the individual trials showed a significant benefit, and all trials had large confidence intervals; however, the meta-analysis showed significant benefit in the chemotherapy treatment groups with regard to local recurrence, distant recurrence, and progression-free survival. No significant difference in overall survival was found.37 Pervais et al updated the Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration’s 1997 meta-analysis with the inclusion of 4 new trials that evaluated doxorubicin combined with ifosfamide and found that both patients who received doxorubicin-based regimens or doxorubicin with ifosfamide had significant decreases in distant and overall recurrences. Only the trials that utilized doxorubicin and ifosfamide had an improved overall survival that was statistically significant (hazard ratio 0.56 [95% CI 0.36 to 0.85]; P = 0.01).29 Although no significant heterogeneity was found among the trials included in either meta-analysis, a variety of sarcomas were included in each clinical trial evaluated. Given the extremely small number of each sarcoma subtype present in each trial, subgroup analysis is difficult and prone to inaccuracies. As a result, it is not known if certain histological subtypes are more or less responsive to chemotherapy.37–39
One randomized controlled trial evaluated neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk sarcomas defined as tumors greater than 8 cm or grade II/III tumors. This study evaluated doxorubicin and ifosfamide and found no significant difference in disease-free and overall survival in the neoadjuvant therapy group compared to the control group.35 There remains controversy in the literature with regards to adjuvant chemotherapy. Many oncologists offer adjuvant chemotherapy to patients with certain stage III subtypes. Examples of subtypes that may be offered adjuvant therapy include myxoid liposarcomas, synovial sarcomas, and leiomyosarcomas.2 With regards to how many cycles of chemotherapy should be considered, a noninferiority study compared 3 cycles of epirubicin and ifosfamide to 5 cycles of epirubicin and ifosfamide in patients with high-risk locally advanced adult STSs. Three cycles of preoperative epirubicin and ifosfamide was found to be noninferior to 5 cycles with regards to overall survival.38
• What is this patient’s risk for recurrence?
The patient is at intermediate risk for recurrence. Numerous studies have demonstrated that tumor size, grade, and location are the most important factors to determine risk of recurrence, with larger size, higher grades, and deeper locations being associated with higher risk of recurrence. In an analysis of 1041 patients with STS of the extremities, high grade was the most important risk factor for distant metastases.39 The highest risk of recurrence is within the first 2 years. Given that the patient’s initial tumor was located in the extremity, he is more likely to have a distant metastasis as his site of recurrence; individuals with retroperitoneal tumors and visceral tumors are more likely to recur locally.40 For STSs of the extremity, distant metastases determine overall survival, whereas patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas can die from complications of local metastases.41 Once a patient develops distant metastases, the most important prognostic factor is the size of the tumor, with tumors larger than 10 cm having a relative risk of 1.5 (95% CI 1.0 to 2.0).39
• What are the recommendations for surveillance?
Surveillance recommendations are based on the stage of the sarcoma. Stage I tumors are the least likely to recur either locally or distally. As a result, it is recommended that stage I tumors be followed with history and physical exam every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 to 3 years, and then annually after the first 2 to 3 years. Chest x-rays should be considered every 6 to 12 months.2 For stage II–IV tumors, history and physical exam is recommended every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 to 3 years. Chest and distant metastases imaging should also be performed every 3 to 6 months during this time frame. For the next 2 years, history and physical exam and imaging are recommended every 6 months. After the first 4 to 5 years, annual follow-up is recommended.2
A study that followed 141 patients with primary extremity STSs for a median interval of 49 months found that high-grade tumors were most likely to recur during the first 2 years, with 20% of their patients recurring locally and 40% recurring distally. Chest x-rays performed during surveillance follow-up found distant lung metastases in 36 asymptomatic patients and had a positive predictive value of 92%, a negative predictive value of 97%, and a quality-adjusted life-year of $30,000.40,41 No laboratory testing was found to aid in detection of recurrence.
CASE CONTINUED
The patient does well for 1 year. With physical therapy, he regains most of the strength and coordination of the lower extremity. He is followed every 3 months with chest x-rays and a MRI of the thigh for the first year. On his fourth follow-up clinic visit, he describes increased dyspnea on exertion over the previous few weeks and is found to have multiple lung metastases in both lungs on chest x-ray. He undergoes further evaluation for metastases and is not found to have any other metastatic lesions. Bronchoscopy and biopsy of 1 of the lung nodules confirms recurrent dedifferentiated liposarcoma.
• Should this patient undergo metastectomy?
An analysis of 3149 patients with STS treated at Memorial Sloan-Kettering who developed lung metastases found that patients with pulmonary metastases have survival rates of 25%. The most important prognostic factor for survival was complete resection of all metastases.42 For stage IV disease, surgery is used only in certain instances. In instances where tumor is more localized or limited, removal of metastases or metastectomy can play a role in management.2
CASE CONTINUED
Because the patient’s metastases are limited to the lungs, he is referred for metastectomy. He undergoes wedge resection for definitive diagnosis but it is not possible to completely resect all of the metastases. He is thus referred to a medical oncologist to discuss his treatment options.
• What are treatment options for unresectable or metastatic disease?
Metastatic Disease
Unlike local and locally advanced disease, chemotherapy forms the backbone of treatment in stage IV disease. Doxorubicin and olaratumab or doxorubicin and ifosfamide in combination are considered first line in metastatic disease. Response rates for single-agent doxorubicin range from 16% to 27%, while phase 2 and phase 3 studies of doxorubicin and ifosfamide have found response rates ranging from 18% to 36%.43 In addition, the effectiveness of doxorubicin and ifosfamide phase 2 and 3 trials varied. Edmonson et al found a tumor regression rate of 34% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide as compared to 20% for doxorubicin alone.44 In comparison, Santoro et al found a response rate of 21.3% for doxorubicin alone and 25.2% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide.45 Neither study found increased survival benefit for doxorubicin and ifosfamide when compared to doxorubicin alone. In a Cochrane review evaluating randomized trials that compared doxorubicin and combination chemotherapy regimens, response rates varied from 14% for doxorubicin in combination with streptomycin to 34% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide. Most trials did not show a significant benefit for combination therapies when compared to doxorubicin alone.43 Mean survival with doxorubicin or doxorubicin and ifosfamide is 12 months. High rates of recurrence highlight the need for additional chemotherapy regimens.
The newest approved agent is olaratumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and prevents receptor activation. A phase 1-b and phase 2 trial evaluated patients with locally advanced and metastatic STS and randomly assigned them to either olaratumab and doxorubicin or doxorubicin alone.46 Progression-free survival for olaratumab/doxorubicin was 6.6 months (95% CI 4.1 to 8.3) compared to 4.1 months (95% CI 2.8 to 5.4) for doxorubicin alone. The objective response rate was 18.2% (95% CI 9.8 to 29.6) for olaratumab/doxorubicin compared to 7.5% (95% CI 2.5 to 6.6) for doxorubicin alone. Furthermore, the median overall survival for olaratumab plus doxorubicin was 26.5 months (95% CI 20.9 to 31.7) compared to 14.7 months for doxorubicin alone (95% CI 5.5 to 26.0). Impressively, this improved response was notable across histological types. Furthermore, patients who had previously been treated with more than 1 regimen and those who were treatment naïve had similar response rates.46
• What are second-line treatment options?
Doxorubicin has been used in combination with several other agents including dacarbazine (DTIC) as well as DTIC and ifosfamide (MAID). Borden et al evaluated patients with metastatic STS and randomly assigned the patients to either doxorubicin or doxorubicin and DTIC. Combination therapy demonstrated better tumor response than doxorubicin alone: 30% complete or partial response for combination therapy and 18% for doxorubicin alone.47 However, Omura et al
found similar rates of efficacy between doxorubicin and combination doxorubicin and DTIC in women with recurrent or nonresectable uterine sarcomas.48 MAID has never been directly compared in a randomized trial to doxorubicin alone. In a study that compared MAID to doxorubicin and DTIC (AD) in patients with unresectable or metastatic sarcomas, MAID had superior response rates (32% versus 17%), but there was no difference with regards to overall survival (mean survival of 12.5 months).49
Several additional regimens have undergone evaluation in metastatic and recurrent STSs. Gemcitabine has been used both as a single agent and as part of combination therapy in many studies. Studies with gemcitabine in combination with either docetaxel or DTIC have been the most efficacious. In a phase 2 trial, patients with metastatic STS were randomly assigned to either gemcitabine alone or gemcitabine and docetaxel. Combination therapy had a higher response rate (16% versus 8%) and longer overall survival (17.9 months versus 11.5 months) than gemcitabine alone.50 Furthermore, a phase 2 trial of gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with unresectable leiomyosarcoma showed an overall response rate of 56%, with 3 complete and 15 partial responses among the 34 patients enrolled in the study.51
A phase 2 trial randomly assigned patients with unresectable or metastatic STS to either DTIC or combination gemcitabine and DTIC.52 Gemcitabine-DTIC had a superior progression-free survival at 3 months (56% [95% CI 43% to 69%]) as compared to DTIC alone (37% [95% CI 23.5% to 50%]). Furthermore, mean progression-free survival and overall survival were improved in the gemcitabine-DTIC group (4.2 months and 16.8 months) as compared to the DTIC group (2.0 months and 8.2 months).52 DTIC has a single-agent response rate of 16%, but has been shown to be particularly effective in the setting of leiomyosarcomas.49
• Does response to treatment regimens differ by histologic subtype?
The majority of STS trials include many different histologic subtypes. Given the rarity of sarcomas as a whole, many trials have had difficulty recruiting adequate numbers of patients to have sufficient power to definitely determine if the treatment under investigation has clinical benefit. Furthermore, the patients recruited have been heterogeneous with regard to subtype. Many older studies hypothesized that the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents vary based on histologic subtype; however, for most subtypes the number of individuals included in those trials was too low to evaluate efficacy based on subtype.
Some exceptions exist, however. For example, both gemcitabine-DTIC and gemcitabine-docetaxel have been found to be particularly effective in the treatment of leiomyosarcomas.50,52 Additionally, a retrospective study found a 51% overall response rate for patients with myxoid liposarcomas treated with trabectedin.53 Studies of patients with angiosarcoma treated with paclitaxel have demonstrated response rates of 43% and 53%.54,55
• What are the newest approved and investigational agents?
A recently approved agent is trabectedin, a tris tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from ascidians that binds to the minor groove of DNA and causes disruptions in the cell cycle. Samuels et al reported data from a single-arm, open-label expanded access trial that evaluated patients with advanced metastatic sarcomas.56 In this study, patients with liposarcomas and leiomyosarcomas had an objective response rate of 6.9% (95% CI 4.8 to 9.6) as compared to a rate of 5.9% (95% CI 4.4 to 7.8) for all assessable patients. Median survival was 11.9 months for all patients, with improved median survivals for liposarcoma and leiomyosarcomas of 16.2 months (95% CI 14.1 to 19.5) compared to 8.4 months (95% CI 7.1 to 10.7 months) for other subtypes.56
Schöffski et al evaluated eribulin, a chemotherapeutic agent that affects microtubule dynamics, in a phase 2 trial of patients with progressive or high-grade STS with progression on previous chemotherapy. They found a median progression-free survival of 2.6 months (95% CI 1.7 to 6.2) for adipocytic sarcoma, 2.9 months (95% CI 2.4 to 4.6) for leiomyosarcoma, 2.6 months (95% CI 2.3 to 4.3) for synovial sarcoma, and 2.1 months (95% CI 1.4 to 2.9) for other sarcomas.57
Van der Graaf and colleagues randomly assigned patients with metastatic nonadipocytic STS to pazopanib or placebo in a phase 3 trial. Pazopanib is a small-molecule endothelial growth factor inhibitor with activity against vascular endothelial growth factors 1, 2, and 3 as well as platelet-derived growth factors. Median progression-free survival was 4.6 months (95% CI 3.7 to 4.8) with pazopanib compared to 1.6 months (95% CI 0.9 to 1.8) with placebo.58 Adipocytic sarcomas (liposarcomas) were excluded from the trial because phase 2 trials had found a lower rate of progression-free survival (26%) for them compared to other subtypes.
• What are the most common toxicities associated with the approved and investigational chemotherapeutic agents?
Toxicities were seen with each of the regimens studied and were common in the randomized trials, with higher rates of toxicities in the combination chemotherapy regimens. The most common toxicities are myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting. In the doxorubicin trials, the most common toxicities were myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting.44
Ifosfamide both as an individual agent and in combination with doxorubicin has higher rates and higher grades of toxicity than doxorubicin alone. Myelosuppression is the most common toxicity associated with ifosfamide, and the most commonly affected cell line is leukocytes.44 Combination doxorubicin and ifosfamide also had high rates of nausea and vomiting (95%) and alopecia (100%).35
Neutropenia is the most common toxicity associated with gemcitabine and dacarbazine, while their most common nonhematologic toxicities are fatigue and nausea.52,59 Trabectedin’s most common toxicities are nausea (29%), neutropenia (24%), and fatigue (23%). It has also been shown to cause increased alkaline phosphatase (20%) and alanine aminotransferase (19%) levels.56 In a phase 2 study of eribulin, 50% of patients had neutropenia, and other toxicities included fatigue, alopecia, nausea, sensory neuropathy, and thrombocytopenia.57 Pazopanib is generally well tolerated; the most common toxicities are fatigue (65%), diarrhea (58%), nausea (54%), and hypertension (41%).58 Higher rates of neutropenia, mucositis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and transfusion reactions were seen with olaratumab and doxorubicin compared to doxorubicin alone in phase 1b and 2 studies.46
CASE CONCLUSION
Given his poor prognosis with unresectable metastatic undifferentiated liposarcoma, the patient considers a clinical trial prior to undergoing combined therapy with doxorubicin and ifosfamide. He tolerates therapy well with stable disease at 6 months.
CONCLUSION
STSs are a heterogeneous collection of rare tumors. Low-grade, localized tumors have the best prognosis, and patients who undergo complete resection have the best long-term survival. Due to the rarity of STSs, trials often have limited enrollment, and little progress has been made with regards to treatment and survival rates for metastatic and unresectable disease. All patients should be evaluated and treated at specialized sarcoma centers. This case highlights the need for continued research and clinical trials to improve overall survival of patients with sarcoma.
INTRODUCTION
Soft tissue sarcomas (STSs) are rare adult tumors, with 3.4 new cases per 100,000 persons or 12,310 expected new cases in 2016.1 Sarcomas are a heterogeneous collection of tumors that affect fat, muscle, nerve, nerve sheath, vascular, and connective tissues. There are more than 50 histological subtypes that comprise this diverse category of tumors. Treatment varies by stage, with limb-sparing surgery representing the mainstay of curative-intent treatment. Radiation and chemotherapy may also be considered depending on the size, grade, and location of the tumor. Survival rates have been stagnant until recently, with a disease-specific survival hovering around 65%.1 Given the complexity of these cases, all patients ideally should be evaluated and treated by a multidisciplinary team at an institution with extensive experience treating STS.2
EPIDEMIOLOGY AND CLASSIFICATION
The most common STS subtypes are gastrointestinal stromal tumor (GIST), undifferentiate pleomorphic sarcoma (previously referred to as malignant fibrous histiocytoma), liposarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, synovial sarcoma, malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor, rhabdomyosarcoma, and unclassified sarcoma.3 Liposarcoma is one of the most common subtypes, comprising 20% of all STSs; it is subdivided into well-differentiated/dedifferentiated liposarcomas, myxoid/round cell liposarcomas, and pleomorphic liposarcomas. Well-differentiated liposarcomas tend to occur in the retroperitoneum and limbs, while both myxoid and round cell as well as pleomorphic liposarcomas more commonly originate on the limbs. Histology varies based on subtype and ranges from mature-appearing adipocytes and fibroblasts to undifferentiated cells with minimal lipogenic differentiation.4
Leiomyosarcomas are smooth muscle tumors and are usually located in the retroperitoneum, but have also been associated with peripheral soft tissue and vasculature. Typical histology ranges from well-defined areas of spindle-shaped cells to poorly differentiated anaplastic spindle cells.5,6 Synovial sarcomas are a distinct type of STS that can show epithelial differentiation and account for 5% of adult STSs. The extremities are the most common presenting location (90%).7
Rhabdomyosarcomas are skeletal muscle tumors and are further subdivided into embryonal, alveolar, and pleomorphic subtypes. Embryonal histology ranges from primitive mesenchymal-appearing cells to highly differentiated muscle cells. Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma has the worst prognosis of the subtypes and consists of round cells with high nuclear-to-chromatin ratios that form “glandular-like” or “alveolar” spaces.8 Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcomas are composed of rhabdomyoblasts that can affect many different locations, but most commonly present on the lower extremities.9
Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumor (MPNST) comprises 5% to 10% of all STSs. These tumors are associated with neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF-1), with 25% to 50% of tumors occurring in NF-1 patients. Additionally, most patients have a truncating lesion in the NF1 gene on chromosome 17.10 Anghileri et al in their single institution analysis of 205 patients with MPNSTs found the 2 most common presenting sites were the trunk and extremities. Histologically, these tumors have dense fascicles of spindle cells.10
GISTs are the most common STS of the gastrointestinal (GI) tract. Previously, GISTs were classified as smooth muscle tumors and were not accounted for in the literature as a separate entity distinct from leiomyomas, leiomyoblastomas, and leiomyosarcomas.11 GISTs are found throughout the GI tract: the most common sites are the stomach (60%) and small intestine (30%). Less common sites include duodenum (4%–5%), esophagus (1%), rectum (1%–2%), and appendix (< 0.2%).12 GISTs can be spindle cell, epithelioid, or mesenchymal tumors. Immunohistochemically, GISTs are KIT (CD117) positive. Other cell markers that are also commonly positive include CD34 (60%–70%) and smooth muscle actin (SMA) (25%).11 The majority of GISTs (80%) have an activating c-KIT gene mutation. The most common mutation site is exon 11, with less common c-KIT gene mutations also occurring at exon 9 or 13. Not all GISTs have KIT mutations. The second most common mutation is the PDGFRA mutation (5%–10% of GISTs).2 A minority of GISTs are negative for both KIT and PDGFRA mutations. These tumors were previously called wild-type, but as the majority have either a succinate dehydrogenase (SDH) loss of function or loss of SDHB protein expression, they are now referred to as SDH-deficient GISTs.2 GISTs vary in aggressiveness from incidental to aggressive. Typically, small intestine and rectal GISTs are more aggressive than gastric GISTs. Both size and mitotic rate help to predict the metastatic potential of the tumor. Tumors less than 2 cm in size and having a mitotic rate of less than 5 per 50 high-power fields (hpf) have the lowest risk of metastases, while tumors greater than 5 cm and with more than 5 mitoses per 50 hpf have the highest rates of metastases.12
Angiosarcomas are rare tumors comprising 4% of all STSs. Although they can occur in any site, the majority are cutaneous and occur most frequently in the head and neck regions. These tumors are either of vascular or lymphatic origin and are comprised of abnormal, pleomorphic, malignant endothelial cells. The most useful immunohistochemical markers include von Willebrand factor, CD31, and Ulex europaeus agglutinin 1. The majority of these tumors occur sporadically; however, radiation exposure, chronic lymphedema, and certain toxins including vinyl chloride and thorium dioxide are known risk factors.13
Undifferentiated sarcomas have no specific features and typically consist of primitive mesenchymal cells.
CLINICAL EVALUATION
CASE PRESENTATION
Initial Presentation and History
A 55-year-old man presents to his primary care physician with a painless mass in his anterior thigh. The mass has been present for the past 3 months and he believes that it is enlarging. The patient has a history of well-controlled hypertension and hyperlipidemia. His medications include atorvastatin and hydrochlorothiazide. He has no known drug allergies. Family history is notable for diabetes and hypertension. He drinks 4 to 5 alcoholic drinks a week and he is a former smoker. He quit smoking in his 30s and only smoked intermittently prior to quitting. He denies any illicit drug use. He works as a high school principal. Currently, he feels well. His review of systems is otherwise noncontributory.
Physical Examination
On physical exam, he is afebrile with a blood pressure of 132/75 mm Hg, respiratory rate of 10 breaths/min, and oxygen saturation of 99% on room air. He is a well appearing, overweight male. His head and neck exam is unremarkable. Lung exam reveals clear breath sounds, and cardiac exam reveals a regular rate and rhythm. His abdomen is obese, soft, and without hepatosplenomegaly. There is a large, fixed mass on the anterior lateral aspect of his right thigh. He has no appreciable lymphadenopathy. His neurological exam is unremarkable.
• What are risk factors for sarcoma?
There are few known risk factors for sarcoma. Established risks factors include prior radiation therapy, chronic lymphedema, viruses, and genetic cancer syndromes including Li-Fraumeni syndrome, hereditary retinoblastoma, and NF-1. Other environmental exposures include phenoxyacetic acids and chlorophenols.14 The majority of cases are sporadic, with only a minority of patients having one of these known risk factors.15 Up to one third of sarcomas have a specific translocation and are driven by fusion oncogenes (Table 1).

A painless mass is the most typical presenting symptom. Size at presentation varies based on location, with extremity and head and neck locations typically presenting at smaller sizes than retroperitoneal tumors.14 Patients may experience pain and numbness as the mass enlarges and impinges on surrounding structures including nerves and vasculature. The vast majority of patients are without systemic symptoms.
• How is sarcoma staged?
The American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC) staging system is the most widely used staging system in the United States. The latest AJCC manual was updated in 2010 to include a 3-tiered grading system where the tumor is classified according to tumor size, lymph node involvement, metastases, and grade at time of diagnosis (Table 2 and Table 3). Additionally, tumor depth in relation to deep fascia is also taken into account, with superficial tumors being assigned a designation of “a” and deep tumors a designation of “b.”


Previously, 2 of the most widely used grading systems were the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group (FNCLCC) systems, both 3-tier grading systems. The main components that determine the NCI grade are the tumor’s histologic type and location and the amount of tumor necrosis. The FNCLCC system evaluation focuses on tumor differentiation, mitotic rate, and amount of tumor necrosis. A study that compared the NCI and FNCLCC grading systems found that FNCLCC was a better predictor of mortality and distant metastasis.16 Previously, the AJCC was a 4-tier grading system, but the 2010 version was updated to the 3-tier FNCLCC grading system. Additionally, the AJCC system has reclassified single lymph node disease as stage III as it confers better survival than metastatic disease.17 It is important that pathology be evaluated by a sarcoma specialist as disagreements with regard to histologic subtype and grade are common.18,19
• What are the most important prognostic factors?
Prognostic factors include grade, size, and presence of metastases at presentation. Best survival is associated with low-grade, small tumors with no metastases at time of diagnosis.14
• What imaging should be considered?
Imaging should be undertaken to help differentiate between benign and malignant lesions. Ideally, it should be undertaken before a biopsy is planned as the imaging can be used to plan biopsy as well as provide invaluable prognostic information. There are several imaging modalities that should be considered during the preliminary work-up and staging of STSs. Conventional imaging includes magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the original tumor site; computed tomography (CT) to evaluate for pulmonary metastases and, depending on location, liver metastases; and in the case of small, low-grade tumors, chest radiography. MRI is considered the test of choice for soft tissue masses and can help delineate benign masses such as hematomas, lipomas, and hemangiomas from sarcomas.20 It is difficult to compare the accuracy of positron emission tomography (PET)/CT to CT and MRI because most studies have evaluated PET/CT in parallel with CT and MRI.21 Tateishi et al compared the accuracy of conventional imaging, PET/CT, and PET/CT combined with conventional imaging at determining the TNM staging for 117 patients. They found that conventional imaging correctly classified 77% of patients, PET alone correctly classified 70%, PET/CT correctly classified 83%, and PET/CT combined with conventional imaging correctly staged 87%.22
• Which subtypes are most likely to metastasize?
Although the vast majority of sarcomas spread hematogenously, 3 have a propensity to spread lymphogenously: epithelioid sarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, and clear-cell sarcoma. Additionally, certain subtypes are more likely to metastasize: leiomyosarcomas, synovial sarcomas, neurogenic sarcomas, rhabdomyosarcomas, and epithelioid sarcomas.23 Sarcomas metastasize to the lungs more frequently than to the liver. The metastatic pattern is defined primarily by sarcoma subtype and site of primary tumor. Sarcomas rarely metastasize to the brain (~1%).
MANAGEMENT
CASE CONTINUED
The patient undergoes an ultrasound to better visualize the mass. Given the heterogeneous character of the mass, he is referred for an MRI to evaluate the mass and a CT scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis to evaluate for distant metastases. MRI reveals a 5.1 cm × 4.6 cm heterogeneous mass invading the superficial fascia of the rectus femoris muscle. No suspicious lymph nodes or other masses are identified on imaging. The patient next undergoes an image-guided core needle biopsy. Pathology from that procedure is consistent with a stage III, T2bNxMx, grade 3, dedifferentiated liposarcoma.
• What is the best management approach for this patient?
SURGERY
Surgery is the mainstay of treatment for STS. Patients with the best prognosis are those who undergo complete resection with negative surgical margins.24,25 Goal tumor-free margin is 1 to 3 cm.26 Complete resection confers the best long-term survival. Both local and metastatic recurrence is higher in patients with incomplete resection and positive margins.24,25 In a study that analyzed 2084 localized primary STSs, patients with negative margins had a local recurrence rate of 15% versus a rate of 28% in patients with positive margins. This translated into higher 5-year local recurrence-free survival for patients with negative surgical margins (82%) compared to patients with positive margins (65%).27 Another study similarly found that patients with negative margins at referral to their institution who underwent postoperative radiation had high local control rates of 93% (95% confidence interval [CI] 87% to 97%) at 5, 10, and 15 years.26 Although radiation improves local control, neither preoperative or postoperative radiation has been shown to improve progression-free or overall survival.28 Other factors that are associated with risk of recurrence are tumor location, history of previous recurrence, age of patient, histopathology, tumor grade, and tumor size. Approximately 40% to 50% of patients with high-grade tumors (defined as size > 5 cm, deep location, and high grade) will develop distant metastases.29
Zagars et al found that positive or uncertain resection margin had a relative risk of local recurrence of 2.0 (95% CI 1.3 to 3.1; P = 0.002), and presentation with locally recurrent disease (vs new tumor) had a relative risk of local recurrence of 2.0 (95% CI 1.2 to 3.4; P = 0.013).26 Patients with STS of head and neck and deep trunk have higher recurrence rates than those with superficial trunk and extremity STS. A single-institution retrospective review demonstrated that patients with completely resectable retroperitoneal sarcomas have longer median survival (103 months) compared to patients with incompletely resected abdominal sarcomas (18 months).25
Rosenberg and colleagues compared amputation to limb-sparing surgery and radiation.24 Their prospective analysis of 65 patients found no difference in disease-free and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups. The limb-sparing treatment group had higher rates of local recurrence, which was highly correlated with positive surgical margins on pathology.24 Evidence from this and similar studies has resulted in radical amputations being replaced by conservative limb-sparing procedures and radiation therapy. In those found to have positive margins, re-resection is an option for some. Patients who undergo re-resection have higher local control rates than patients with positive margins who do not undergo re-resection. The 5-year control rate for patients who undergo re-resection is 85% (95% CI 80% to 89%) compared to 78% (95% CI 71% to 83%) for those who do not undergo re-resection. Similarly, patients who undergo re-resection have lower rates of metastases at 5, 10, and 15 years as well as higher 5-, 10-, and 15-year disease-free survival rates.26
CASE CONTINUED
The patient is referred for limb-sparing surgery after presentation at a multidisciplinary tumor board. Prior to undergoing resection of the tumor, he is also referred to radiation-oncology to discuss the risks and benefits of combination radiotherapy and surgery as opposed to surgical resection alone.
• What is the evidence for radiation therapy?
RADIATION THERAPY
Radiation therapy is used in the preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative settings to reduce the risk of local recurrence. There are several options for radiation, including external beam radiation therapy (EBRT), intraoperative radiation, and brachytherapy. A newer strategy, intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT), utilizes 3-dimensional modeling to reduce radiation dosages. Overall there are no differences in overall survival or local recurrence rates between preoperative and postoperative radiation in STS.28
The rationale behind preoperative radiation is that it reduces seeding of tumor cells, especially at the time of surgery.30 Additionally, for EBRT, preoperative radiation has smaller field sizes and lower radiation doses. It can also help to reduce the size of the tumor prior to resection. Intraoperative radiation is often paired with preoperative radiation as a boost dose given only to the area of residual tumor.
Suit et al reviewed patients treated at a single institution with limb-sparing surgery and different radiation strategies. Local control rates between preoperative and postoperative radiation groups were not statistically significant. Local recurrence was linked to grade and size of the tumor in both groups. The authors did note, however, that the preoperative radiation group tended to have larger tumor sizes at baseline compared to the patients who received postoperative radiation.30 A study that compared 190 patients who received preoperative and postoperative EBRT or brachytherapy (primary end point was wound complications, and local control was a secondary end point) showed a trend towards greater local control with preoperative radiation; however, the preoperative radiation group had significantly more wound complications compared to the postoperative radiation group.31
Yang et al found that postoperative EBRT decreases rates of local recurrence compared to surgery alone in high-grade extremity sarcomas.32 However, there were no differences in rates of distant metastases and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups. Similarly, in patients with low-grade sarcoma, there were fewer local recurrences in those who received EBRT and surgery as compared to surgery alone.32 Another study that evaluated 164 patients who received either adjuvant brachytherapy or no further therapy after complete resection found that brachytherapy reduced local recurrence in high-grade sarcomas. No difference in local recurrence rates was found in patients with low-grade sarcomas, nor was a significant difference found in the rates of distant metastases and overall survival between the 2 treatment groups.33 With regards to IMRT, a single institution cohort experience with 41 patients who received IMRT following limb-sparing surgery had similar local control rates when compared to historical controls.34
CASE CONTINUED
After discussion of the risks and benefits of radiation therapy, the patient opts for preoperative radiation prior to resection of his liposarcoma. He receives 50 Gy of EBRT prior to undergoing resection. Resection results in R1 margin consistent with microscopic disease. He receives 16 Gy of EBRT as a boost after recovery from his resection.2
• What is the evidence for neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy for stage I tumors?
CHEMOTHERAPY
Localized Sarcoma
For localized sarcoma, limb-sparing resection with or without radiation forms the backbone of treatment. Studies have evaluated chemotherapy in both the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings, with the vast majority of studies evaluating doxorubicin-based chemotherapy regimens in the adjuvant settings. Due to the rare nature of sarcomas, most studies are not sufficiently powered to detect significant benefit from chemotherapy. Several trials evaluating chemotherapy regimens in the neoadjuvant and adjuvant settings needed to be terminated prematurely due to inadequate enrollment into the study. 35,36
For stage IA (T1a-Tb, N0, M0, low grade) tumors, no additional therapy is recommended after limb-sparing surgery with appropriate surgical margins. For stage IB (T2a-2b, N0, M0, low grade) tumors with insufficient margins, re-resection and radiation therapy should be considered, while for stage IIA (T1a-1b, N0, M0, G2-3) tumors preoperative or postoperative radiation therapy is recommended.2 Studies have not found benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy in these low-grade, stage I tumors in terms of progression-free survival and overall survival.37
• At what stage should chemotherapy be considered?
For stage IIb and stage III tumors, surgery and radiation therapy again form the backbone of therapy; however, neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy are also recommended as considerations. Anthracycline-based chemotherapy with either single-agent doxorubicin or doxorubicin and ifosfamide in combination are considered first-line chemotherapy agents in locally advanced STS.2,29,37
Evidence regarding the efficacy of both neoadjuvant and adjuvant chemotherapy regimens in the setting of locally advanced high-grade STS has been mixed. The Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration evaluated 14 trials of doxorubicin-based adjuvant chemotherapy and found a trend towards overall survival in the treatment groups that received chemotherapy.37 All trials included in the meta-analysis compared patients with localized resectable soft-tissue sarcomas who were randomized to either adjuvant chemotherapy or no adjuvant chemotherapy after limb-sparing surgery with or without radiation therapy. None of the individual trials showed a significant benefit, and all trials had large confidence intervals; however, the meta-analysis showed significant benefit in the chemotherapy treatment groups with regard to local recurrence, distant recurrence, and progression-free survival. No significant difference in overall survival was found.37 Pervais et al updated the Sarcoma Meta-analysis Collaboration’s 1997 meta-analysis with the inclusion of 4 new trials that evaluated doxorubicin combined with ifosfamide and found that both patients who received doxorubicin-based regimens or doxorubicin with ifosfamide had significant decreases in distant and overall recurrences. Only the trials that utilized doxorubicin and ifosfamide had an improved overall survival that was statistically significant (hazard ratio 0.56 [95% CI 0.36 to 0.85]; P = 0.01).29 Although no significant heterogeneity was found among the trials included in either meta-analysis, a variety of sarcomas were included in each clinical trial evaluated. Given the extremely small number of each sarcoma subtype present in each trial, subgroup analysis is difficult and prone to inaccuracies. As a result, it is not known if certain histological subtypes are more or less responsive to chemotherapy.37–39
One randomized controlled trial evaluated neoadjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk sarcomas defined as tumors greater than 8 cm or grade II/III tumors. This study evaluated doxorubicin and ifosfamide and found no significant difference in disease-free and overall survival in the neoadjuvant therapy group compared to the control group.35 There remains controversy in the literature with regards to adjuvant chemotherapy. Many oncologists offer adjuvant chemotherapy to patients with certain stage III subtypes. Examples of subtypes that may be offered adjuvant therapy include myxoid liposarcomas, synovial sarcomas, and leiomyosarcomas.2 With regards to how many cycles of chemotherapy should be considered, a noninferiority study compared 3 cycles of epirubicin and ifosfamide to 5 cycles of epirubicin and ifosfamide in patients with high-risk locally advanced adult STSs. Three cycles of preoperative epirubicin and ifosfamide was found to be noninferior to 5 cycles with regards to overall survival.38
• What is this patient’s risk for recurrence?
The patient is at intermediate risk for recurrence. Numerous studies have demonstrated that tumor size, grade, and location are the most important factors to determine risk of recurrence, with larger size, higher grades, and deeper locations being associated with higher risk of recurrence. In an analysis of 1041 patients with STS of the extremities, high grade was the most important risk factor for distant metastases.39 The highest risk of recurrence is within the first 2 years. Given that the patient’s initial tumor was located in the extremity, he is more likely to have a distant metastasis as his site of recurrence; individuals with retroperitoneal tumors and visceral tumors are more likely to recur locally.40 For STSs of the extremity, distant metastases determine overall survival, whereas patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas can die from complications of local metastases.41 Once a patient develops distant metastases, the most important prognostic factor is the size of the tumor, with tumors larger than 10 cm having a relative risk of 1.5 (95% CI 1.0 to 2.0).39
• What are the recommendations for surveillance?
Surveillance recommendations are based on the stage of the sarcoma. Stage I tumors are the least likely to recur either locally or distally. As a result, it is recommended that stage I tumors be followed with history and physical exam every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 to 3 years, and then annually after the first 2 to 3 years. Chest x-rays should be considered every 6 to 12 months.2 For stage II–IV tumors, history and physical exam is recommended every 3 to 6 months for the first 2 to 3 years. Chest and distant metastases imaging should also be performed every 3 to 6 months during this time frame. For the next 2 years, history and physical exam and imaging are recommended every 6 months. After the first 4 to 5 years, annual follow-up is recommended.2
A study that followed 141 patients with primary extremity STSs for a median interval of 49 months found that high-grade tumors were most likely to recur during the first 2 years, with 20% of their patients recurring locally and 40% recurring distally. Chest x-rays performed during surveillance follow-up found distant lung metastases in 36 asymptomatic patients and had a positive predictive value of 92%, a negative predictive value of 97%, and a quality-adjusted life-year of $30,000.40,41 No laboratory testing was found to aid in detection of recurrence.
CASE CONTINUED
The patient does well for 1 year. With physical therapy, he regains most of the strength and coordination of the lower extremity. He is followed every 3 months with chest x-rays and a MRI of the thigh for the first year. On his fourth follow-up clinic visit, he describes increased dyspnea on exertion over the previous few weeks and is found to have multiple lung metastases in both lungs on chest x-ray. He undergoes further evaluation for metastases and is not found to have any other metastatic lesions. Bronchoscopy and biopsy of 1 of the lung nodules confirms recurrent dedifferentiated liposarcoma.
• Should this patient undergo metastectomy?
An analysis of 3149 patients with STS treated at Memorial Sloan-Kettering who developed lung metastases found that patients with pulmonary metastases have survival rates of 25%. The most important prognostic factor for survival was complete resection of all metastases.42 For stage IV disease, surgery is used only in certain instances. In instances where tumor is more localized or limited, removal of metastases or metastectomy can play a role in management.2
CASE CONTINUED
Because the patient’s metastases are limited to the lungs, he is referred for metastectomy. He undergoes wedge resection for definitive diagnosis but it is not possible to completely resect all of the metastases. He is thus referred to a medical oncologist to discuss his treatment options.
• What are treatment options for unresectable or metastatic disease?
Metastatic Disease
Unlike local and locally advanced disease, chemotherapy forms the backbone of treatment in stage IV disease. Doxorubicin and olaratumab or doxorubicin and ifosfamide in combination are considered first line in metastatic disease. Response rates for single-agent doxorubicin range from 16% to 27%, while phase 2 and phase 3 studies of doxorubicin and ifosfamide have found response rates ranging from 18% to 36%.43 In addition, the effectiveness of doxorubicin and ifosfamide phase 2 and 3 trials varied. Edmonson et al found a tumor regression rate of 34% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide as compared to 20% for doxorubicin alone.44 In comparison, Santoro et al found a response rate of 21.3% for doxorubicin alone and 25.2% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide.45 Neither study found increased survival benefit for doxorubicin and ifosfamide when compared to doxorubicin alone. In a Cochrane review evaluating randomized trials that compared doxorubicin and combination chemotherapy regimens, response rates varied from 14% for doxorubicin in combination with streptomycin to 34% for doxorubicin and ifosfamide. Most trials did not show a significant benefit for combination therapies when compared to doxorubicin alone.43 Mean survival with doxorubicin or doxorubicin and ifosfamide is 12 months. High rates of recurrence highlight the need for additional chemotherapy regimens.
The newest approved agent is olaratumab, a monoclonal antibody that binds platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha and prevents receptor activation. A phase 1-b and phase 2 trial evaluated patients with locally advanced and metastatic STS and randomly assigned them to either olaratumab and doxorubicin or doxorubicin alone.46 Progression-free survival for olaratumab/doxorubicin was 6.6 months (95% CI 4.1 to 8.3) compared to 4.1 months (95% CI 2.8 to 5.4) for doxorubicin alone. The objective response rate was 18.2% (95% CI 9.8 to 29.6) for olaratumab/doxorubicin compared to 7.5% (95% CI 2.5 to 6.6) for doxorubicin alone. Furthermore, the median overall survival for olaratumab plus doxorubicin was 26.5 months (95% CI 20.9 to 31.7) compared to 14.7 months for doxorubicin alone (95% CI 5.5 to 26.0). Impressively, this improved response was notable across histological types. Furthermore, patients who had previously been treated with more than 1 regimen and those who were treatment naïve had similar response rates.46
• What are second-line treatment options?
Doxorubicin has been used in combination with several other agents including dacarbazine (DTIC) as well as DTIC and ifosfamide (MAID). Borden et al evaluated patients with metastatic STS and randomly assigned the patients to either doxorubicin or doxorubicin and DTIC. Combination therapy demonstrated better tumor response than doxorubicin alone: 30% complete or partial response for combination therapy and 18% for doxorubicin alone.47 However, Omura et al
found similar rates of efficacy between doxorubicin and combination doxorubicin and DTIC in women with recurrent or nonresectable uterine sarcomas.48 MAID has never been directly compared in a randomized trial to doxorubicin alone. In a study that compared MAID to doxorubicin and DTIC (AD) in patients with unresectable or metastatic sarcomas, MAID had superior response rates (32% versus 17%), but there was no difference with regards to overall survival (mean survival of 12.5 months).49
Several additional regimens have undergone evaluation in metastatic and recurrent STSs. Gemcitabine has been used both as a single agent and as part of combination therapy in many studies. Studies with gemcitabine in combination with either docetaxel or DTIC have been the most efficacious. In a phase 2 trial, patients with metastatic STS were randomly assigned to either gemcitabine alone or gemcitabine and docetaxel. Combination therapy had a higher response rate (16% versus 8%) and longer overall survival (17.9 months versus 11.5 months) than gemcitabine alone.50 Furthermore, a phase 2 trial of gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with unresectable leiomyosarcoma showed an overall response rate of 56%, with 3 complete and 15 partial responses among the 34 patients enrolled in the study.51
A phase 2 trial randomly assigned patients with unresectable or metastatic STS to either DTIC or combination gemcitabine and DTIC.52 Gemcitabine-DTIC had a superior progression-free survival at 3 months (56% [95% CI 43% to 69%]) as compared to DTIC alone (37% [95% CI 23.5% to 50%]). Furthermore, mean progression-free survival and overall survival were improved in the gemcitabine-DTIC group (4.2 months and 16.8 months) as compared to the DTIC group (2.0 months and 8.2 months).52 DTIC has a single-agent response rate of 16%, but has been shown to be particularly effective in the setting of leiomyosarcomas.49
• Does response to treatment regimens differ by histologic subtype?
The majority of STS trials include many different histologic subtypes. Given the rarity of sarcomas as a whole, many trials have had difficulty recruiting adequate numbers of patients to have sufficient power to definitely determine if the treatment under investigation has clinical benefit. Furthermore, the patients recruited have been heterogeneous with regard to subtype. Many older studies hypothesized that the efficacy of chemotherapeutic agents vary based on histologic subtype; however, for most subtypes the number of individuals included in those trials was too low to evaluate efficacy based on subtype.
Some exceptions exist, however. For example, both gemcitabine-DTIC and gemcitabine-docetaxel have been found to be particularly effective in the treatment of leiomyosarcomas.50,52 Additionally, a retrospective study found a 51% overall response rate for patients with myxoid liposarcomas treated with trabectedin.53 Studies of patients with angiosarcoma treated with paclitaxel have demonstrated response rates of 43% and 53%.54,55
• What are the newest approved and investigational agents?
A recently approved agent is trabectedin, a tris tetrahydroisoquinoline alkaloid isolated from ascidians that binds to the minor groove of DNA and causes disruptions in the cell cycle. Samuels et al reported data from a single-arm, open-label expanded access trial that evaluated patients with advanced metastatic sarcomas.56 In this study, patients with liposarcomas and leiomyosarcomas had an objective response rate of 6.9% (95% CI 4.8 to 9.6) as compared to a rate of 5.9% (95% CI 4.4 to 7.8) for all assessable patients. Median survival was 11.9 months for all patients, with improved median survivals for liposarcoma and leiomyosarcomas of 16.2 months (95% CI 14.1 to 19.5) compared to 8.4 months (95% CI 7.1 to 10.7 months) for other subtypes.56
Schöffski et al evaluated eribulin, a chemotherapeutic agent that affects microtubule dynamics, in a phase 2 trial of patients with progressive or high-grade STS with progression on previous chemotherapy. They found a median progression-free survival of 2.6 months (95% CI 1.7 to 6.2) for adipocytic sarcoma, 2.9 months (95% CI 2.4 to 4.6) for leiomyosarcoma, 2.6 months (95% CI 2.3 to 4.3) for synovial sarcoma, and 2.1 months (95% CI 1.4 to 2.9) for other sarcomas.57
Van der Graaf and colleagues randomly assigned patients with metastatic nonadipocytic STS to pazopanib or placebo in a phase 3 trial. Pazopanib is a small-molecule endothelial growth factor inhibitor with activity against vascular endothelial growth factors 1, 2, and 3 as well as platelet-derived growth factors. Median progression-free survival was 4.6 months (95% CI 3.7 to 4.8) with pazopanib compared to 1.6 months (95% CI 0.9 to 1.8) with placebo.58 Adipocytic sarcomas (liposarcomas) were excluded from the trial because phase 2 trials had found a lower rate of progression-free survival (26%) for them compared to other subtypes.
• What are the most common toxicities associated with the approved and investigational chemotherapeutic agents?
Toxicities were seen with each of the regimens studied and were common in the randomized trials, with higher rates of toxicities in the combination chemotherapy regimens. The most common toxicities are myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting. In the doxorubicin trials, the most common toxicities were myelosuppression, nausea, and vomiting.44
Ifosfamide both as an individual agent and in combination with doxorubicin has higher rates and higher grades of toxicity than doxorubicin alone. Myelosuppression is the most common toxicity associated with ifosfamide, and the most commonly affected cell line is leukocytes.44 Combination doxorubicin and ifosfamide also had high rates of nausea and vomiting (95%) and alopecia (100%).35
Neutropenia is the most common toxicity associated with gemcitabine and dacarbazine, while their most common nonhematologic toxicities are fatigue and nausea.52,59 Trabectedin’s most common toxicities are nausea (29%), neutropenia (24%), and fatigue (23%). It has also been shown to cause increased alkaline phosphatase (20%) and alanine aminotransferase (19%) levels.56 In a phase 2 study of eribulin, 50% of patients had neutropenia, and other toxicities included fatigue, alopecia, nausea, sensory neuropathy, and thrombocytopenia.57 Pazopanib is generally well tolerated; the most common toxicities are fatigue (65%), diarrhea (58%), nausea (54%), and hypertension (41%).58 Higher rates of neutropenia, mucositis, nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and transfusion reactions were seen with olaratumab and doxorubicin compared to doxorubicin alone in phase 1b and 2 studies.46
CASE CONCLUSION
Given his poor prognosis with unresectable metastatic undifferentiated liposarcoma, the patient considers a clinical trial prior to undergoing combined therapy with doxorubicin and ifosfamide. He tolerates therapy well with stable disease at 6 months.
CONCLUSION
STSs are a heterogeneous collection of rare tumors. Low-grade, localized tumors have the best prognosis, and patients who undergo complete resection have the best long-term survival. Due to the rarity of STSs, trials often have limited enrollment, and little progress has been made with regards to treatment and survival rates for metastatic and unresectable disease. All patients should be evaluated and treated at specialized sarcoma centers. This case highlights the need for continued research and clinical trials to improve overall survival of patients with sarcoma.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2016. American Cancer Society Web site. www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@research/documents/document/acspc-047079.pdf. Accessed December 20, 2016.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical guidelines in oncology: soft tissue sarcoma. 2016
- Coindre J, Terrier P, Guillou L, et al. Predictive value of grade for metastasis development in the main histologic types of adult soft tissue sarcomas: a study of 1240 patients from the French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group. Cancer 2001;91:1914–26.
- Dei Tos A. Liposarcoma: new entities and evolving concepts. Ann Diagn Pathol 2000;4:252–66.
- Wile AG, Evans HL, Romsdahl MM. Leiomyosarcoma of soft tissue: a clinicopathologic study. Cancer 1981;48:1022–32.
- Hashimoto H, Daimaru Y, Tsuneyoshi M, Enjoji M. Leiomyosarcoma of the external soft tissues. A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopic study. Cancer 1986;57:2077–88
- Fisher C. Synovial sarcoma. Ann Diagn Pathol 1998;2:401–21.
- Newton WA Jr, Gehan EA, Webber BL, et al. Classification of rhabdomyosarcomas and related sarcomas. Pathologic aspects and proposal for a new classification--an Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Cancer 1995;76:1073–85.
- Furlong MA. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: a clinicopathologic study of 38 cases with emphasis on morphologic variants and recent skeletal muscle-specific markers. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:595–603.
- Anghileri M, Miceli R, Fiore M. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: prognostic factors and survival in a series of patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2006;107:1065–74.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors–definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Archive 2001;438:1–12.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol 2006;23:70–83.
- Young RJ, Brown NJ, Reed MW, et al. Angiosarcoma. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:983–91.
- Cormier JN, Pollock RE. Soft tissue sarcomas. CA Cancer J Clin 2004;54:94–109.
- Penel N, Grosjean J, Robin YM, et al. Frequency of certain established risk factors in soft tissue sarcomas in adults: a prospective descriptive study of 658 cases. Sarcoma 2008;2008:459386.
- Guillou L, Coindre JM, Bonichon F, et al. Comparative study of the National Cancer Institute and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group grading systems in a population of 410 adult patients with soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1997;15:350–62.
- Maki RG, Moraco N, Antonescu CR, et al. Toward better soft tissue sarcoma staging: building on American joint committee on cancer staging systems versions 6 and 7. Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:3377–83.
- Shiraki M, Enterline HT, Brooks JJ, et al. Pathologic analysis of advanced adult soft tissue sarcomas, bone sarcomas, and mesotheliomas. The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) experience. Cancer 1989;64:484–90.
- Presant CA, Russell WO, Alexander RW, Fu YS. Soft-tissue and bone sarcoma histopathology peer review: The frequency of disagreement in diagnosis and the need for second pathology opinions. The Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol 1986; 4:1658–61.
- Sundaram M, McLeod RA. MR imaging of tumor and tumorlike lesions of bone and soft tissue. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1990;155:817–24.
- Ioannidis JP, Lau J. 18F-FDG PET for the diagnosis and grading of soft-tissue sarcoma: a meta-analysis. J Nucl Med 2003;44:717–24.
- Tateishi U, Yamaguchi U, Seki K, et al. Bone and soft-tissue sarcoma: preoperative staging with fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT and conventional imaging. Radiology 2007;245:839–47.
- Zagars GK, Ballo MT, Pisters PW, et al. Prognostic factors for patients with localized soft-tissue sarcoma treated with conservation surgery and radiation therapy: an analysis of 1225 patients. Cancer 2003;97:2530–43
- Rosenberg S, Tepper J, Glatstein E, et al. The treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities: prospective randomized evaluations of (1) limb-sparing surgery plus radiation therapy compared with amputation and (2) the role of adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg 1982;196:305–14.
- Lewis J, Leung D, Woodruff J, et al. Retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma: analysis of 500 patients treated and followed at a single institution. Ann Surg 1998;288:355–65.
- Zagars GK, Ballo MT, Pisters PW, et al. Surgical margins and reresection in the management of patients with soft tissue sarcoma using conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Cancer 2003;97:2544–53.
- Stojadinovic A, Leung DH, Hoos A. Analysis of the prognostic significance of microscopic margins in 2,084 localized primary adult soft tisusse sarcomas. Ann Surg 2002;235:424–34.
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomized trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235–41.
- Pervaiz N, Colterjohn N, Farrokhyar F, et al. A systematic meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2008;113:573–81.
- Suit HD, Mankin HJ, Wood WC, Proppe KH. Preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative radiation in the treatment of primary soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer 1985;55:2659–67
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomized trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235–41.
- Yang J, Chang A, Baker A, et al. Randomized prospective study of the benefit of adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 1998;16:197–203.
- Pisters PW, Harrison LB, Leung DH, et al. Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:859–68.
- Alektiar KM, Brennan MF, Healey JH, Singer S. Impact of intensity-modulated radiation therapy on local control in primary soft-tissue sarcoma of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:3440–5.
- Gortzak E, Azzarelli A, Buesa J, et al. A randomized phase II study on neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for ‘high-risk’ adult soft-tissue sarcoma. Eur J Cancer 2001;37:1096–1103.
- Fakhari N, Ebm C, Kostler WJ, et al. Intensified adjuvant IFADIC chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for soft tissue sarcoma: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized feasibility trial. Wein Klin Wochenschr 2010;122:614–9.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy for localised resectable soft-tissue sarcoma of adults: meta-analysis of individual data. Lancet 1997;350:1647–54.
- Gronchi A, Frustaci S, Mercuri M, et al. Short, full-dose adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk adult soft tissue sarcomas: a randomized clinical trial from the Italian Sarcoma Group and the Spanish Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:850–56.
- Pisters PW, Leung DH, Woodruff J. Analysis of prognostic factors in 1,041 patients with localized soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:1679–89.
- Whooley B, Gibbs J, Mooney M. Primary Extremity Sarcoma: What is the Appropriate Follow-up? Annals of Surg Oncol 2000; 7: 9-14.
- Whooley BP, Mooney MN, Gibbs JF, Graybill WG. Effective follow-up strategies in soft tissue sarcoma. Sem Surg Oncol 1999;17:83–87.
- Billingsley KG, Burt ME, Jara E, et al. Pulmonary metastases from soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of patterns of diseases and postmetastasis survival. Ann Surg 1999;229:602–10.
- Bramwell VH, Anderson D, Charette ML; Sarcoma Disease Site Group. Doxorubicin-based chemotherapy for the palliative treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(3):CD003293.
- Edmonson J, Ryan L, Blum R. Randomized comparison of doxorubicin alone versus ifosfamide plus doxorubicin or mitomycin, doxorubicin, and cisplatin against advanced soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1269–75.
- Santoro A, Tursz T, Mouridsen H. Doxorubicin versus CYVADIC versus doxorubicin plus ifosfamide in first-line treatment of advanced soft tissue sarcomas: a randomized study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol 1995;13:1537–45.
- Tap WD, Jones RL, Van Tine B, et al. Olaratumab and doxorubicin versus doxorubicin alone for treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: an open-label phase 1b and randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016;388:488–97.
- Borden EC, Amato DA, Rosenbaum C, et al. Randomized comparison of three adriamycin regimens for metastatic soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1987;5:840–50.
- Omura GA, Major FJ, Blessing JA, et al. A randomized study of adriamycin with and without dimethyl triazenoimidazole carboxamide in advanced uterine sarcomas. Cancer 1983;52:626–32.
- Antman K, Crowley J, Balcerzak SP, et al. An intergroup phase III randomized study of doxorubicin and dacarbazine with or without ifosfamide and mesna in advanced soft tissue and bone sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1276–85.
- Maki R, Wathen K, Patel SR, et al. Randomized phase II study of gemcitabine and docetaxel compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcomas: results of sarcoma alliance for research through collaboration study 002 [corrected]. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2755–63.
- Hensley ML, Maki R, Venkatraman E, et al. Gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with unresectable leiomyosarcoma: results of a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 2002;12:2824–31.
- Garcia-del-Muro X, Lopez-Pousa A, Maurel J, et al. Randomized phase II study comparing gemcitabine plus dacarbazine versus dacarbazine alone in patients with previously treated soft tissue sarcoma: a Spanish Group for Research on Sarcomas study. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:2528–33.
- Grosso F, Jones RL, Demetri GD, et al. Efficacy of trabectedin (ecteinascidin-743) in advanced pretreated myxoid liposarcomas: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol 2007;7:595–602.
- Italiano A, Cioffi A, Penel N, et al. Comparison of doxorubicin and weekly paclitaxel efficacy in metastatic angiosarcomas. Cancer 2012;118:3330–6.
- Penel N, Italiano A, Ray-Coquard I, et al. Metastatic angiosarcomas: doxorubicin-based regimens, weekly paclitaxel and metastasectomy significantly improve outcome. Ann Oncol 2012;23:517–23.
- Samuels BL, Chawla S, Patel S, et al. Clinical outcomes and safety with trabectedin therapy in patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas following failure of prior chemotherapy: results of a worldwide expanded access program study. Ann Oncol 2013;24:1703–9.
- Schöffski P, Ray-Coquard IL, Cioffi A, et al. Activity of eribulin mesylate in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma: a phase 2 study in four independent histolical subtypes. Lancet 2011;11:1045–52.
- Van der Graaf W, Blay JY, Chawla S, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012;379:1879–86.
- Dileo P, Morgan JA, Zahrieh D, et al. Gemcitabine and vinorelbine combination chemotherapy for patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas: results of a phase II trial. Cancer 2007;109:1863–9.
- American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures 2016. American Cancer Society Web site. www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@research/documents/document/acspc-047079.pdf. Accessed December 20, 2016.
- National Comprehensive Cancer Network. NCCN clinical guidelines in oncology: soft tissue sarcoma. 2016
- Coindre J, Terrier P, Guillou L, et al. Predictive value of grade for metastasis development in the main histologic types of adult soft tissue sarcomas: a study of 1240 patients from the French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group. Cancer 2001;91:1914–26.
- Dei Tos A. Liposarcoma: new entities and evolving concepts. Ann Diagn Pathol 2000;4:252–66.
- Wile AG, Evans HL, Romsdahl MM. Leiomyosarcoma of soft tissue: a clinicopathologic study. Cancer 1981;48:1022–32.
- Hashimoto H, Daimaru Y, Tsuneyoshi M, Enjoji M. Leiomyosarcoma of the external soft tissues. A clinicopathologic, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopic study. Cancer 1986;57:2077–88
- Fisher C. Synovial sarcoma. Ann Diagn Pathol 1998;2:401–21.
- Newton WA Jr, Gehan EA, Webber BL, et al. Classification of rhabdomyosarcomas and related sarcomas. Pathologic aspects and proposal for a new classification--an Intergroup Rhabdomyosarcoma Study. Cancer 1995;76:1073–85.
- Furlong MA. Pleomorphic rhabdomyosarcoma in adults: a clinicopathologic study of 38 cases with emphasis on morphologic variants and recent skeletal muscle-specific markers. Mod Pathol. 2001;14:595–603.
- Anghileri M, Miceli R, Fiore M. Malignant peripheral nerve sheath tumors: prognostic factors and survival in a series of patients treated at a single institution. Cancer 2006;107:1065–74.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors–definition, clinical, histological, immunohistochemical, and molecular genetic features and differential diagnosis. Virchows Archive 2001;438:1–12.
- Miettinen M, Lasota J. Gastrointestinal stromal tumors: pathology and prognosis at different sites. Semin Diagn Pathol 2006;23:70–83.
- Young RJ, Brown NJ, Reed MW, et al. Angiosarcoma. Lancet Oncol 2010;11:983–91.
- Cormier JN, Pollock RE. Soft tissue sarcomas. CA Cancer J Clin 2004;54:94–109.
- Penel N, Grosjean J, Robin YM, et al. Frequency of certain established risk factors in soft tissue sarcomas in adults: a prospective descriptive study of 658 cases. Sarcoma 2008;2008:459386.
- Guillou L, Coindre JM, Bonichon F, et al. Comparative study of the National Cancer Institute and French Federation of Cancer Centers Sarcoma Group grading systems in a population of 410 adult patients with soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1997;15:350–62.
- Maki RG, Moraco N, Antonescu CR, et al. Toward better soft tissue sarcoma staging: building on American joint committee on cancer staging systems versions 6 and 7. Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:3377–83.
- Shiraki M, Enterline HT, Brooks JJ, et al. Pathologic analysis of advanced adult soft tissue sarcomas, bone sarcomas, and mesotheliomas. The Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) experience. Cancer 1989;64:484–90.
- Presant CA, Russell WO, Alexander RW, Fu YS. Soft-tissue and bone sarcoma histopathology peer review: The frequency of disagreement in diagnosis and the need for second pathology opinions. The Southeastern Cancer Study Group experience. J Clin Oncol 1986; 4:1658–61.
- Sundaram M, McLeod RA. MR imaging of tumor and tumorlike lesions of bone and soft tissue. AJR Am J Roentgenol 1990;155:817–24.
- Ioannidis JP, Lau J. 18F-FDG PET for the diagnosis and grading of soft-tissue sarcoma: a meta-analysis. J Nucl Med 2003;44:717–24.
- Tateishi U, Yamaguchi U, Seki K, et al. Bone and soft-tissue sarcoma: preoperative staging with fluorine 18 fluorodeoxyglucose PET/CT and conventional imaging. Radiology 2007;245:839–47.
- Zagars GK, Ballo MT, Pisters PW, et al. Prognostic factors for patients with localized soft-tissue sarcoma treated with conservation surgery and radiation therapy: an analysis of 1225 patients. Cancer 2003;97:2530–43
- Rosenberg S, Tepper J, Glatstein E, et al. The treatment of soft-tissue sarcomas of the extremities: prospective randomized evaluations of (1) limb-sparing surgery plus radiation therapy compared with amputation and (2) the role of adjuvant chemotherapy. Ann Surg 1982;196:305–14.
- Lewis J, Leung D, Woodruff J, et al. Retroperitoneal soft-tissue sarcoma: analysis of 500 patients treated and followed at a single institution. Ann Surg 1998;288:355–65.
- Zagars GK, Ballo MT, Pisters PW, et al. Surgical margins and reresection in the management of patients with soft tissue sarcoma using conservative surgery and radiation therapy. Cancer 2003;97:2544–53.
- Stojadinovic A, Leung DH, Hoos A. Analysis of the prognostic significance of microscopic margins in 2,084 localized primary adult soft tisusse sarcomas. Ann Surg 2002;235:424–34.
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomized trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235–41.
- Pervaiz N, Colterjohn N, Farrokhyar F, et al. A systematic meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials of adjuvant chemotherapy for localized resectable soft-tissue sarcoma. Cancer 2008;113:573–81.
- Suit HD, Mankin HJ, Wood WC, Proppe KH. Preoperative, intraoperative, and postoperative radiation in the treatment of primary soft tissue sarcoma. Cancer 1985;55:2659–67
- O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomized trial. Lancet 2002;359:2235–41.
- Yang J, Chang A, Baker A, et al. Randomized prospective study of the benefit of adjuvant radiation therapy in the treatment of soft tissue sarcomas of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 1998;16:197–203.
- Pisters PW, Harrison LB, Leung DH, et al. Long-term results of a prospective randomized trial of adjuvant brachytherapy in soft tissue sarcoma. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:859–68.
- Alektiar KM, Brennan MF, Healey JH, Singer S. Impact of intensity-modulated radiation therapy on local control in primary soft-tissue sarcoma of the extremity. J Clin Oncol 2008;26:3440–5.
- Gortzak E, Azzarelli A, Buesa J, et al. A randomized phase II study on neo-adjuvant chemotherapy for ‘high-risk’ adult soft-tissue sarcoma. Eur J Cancer 2001;37:1096–1103.
- Fakhari N, Ebm C, Kostler WJ, et al. Intensified adjuvant IFADIC chemotherapy in combination with radiotherapy versus radiotherapy alone for soft tissue sarcoma: long-term follow-up of a prospective randomized feasibility trial. Wein Klin Wochenschr 2010;122:614–9.
- Adjuvant chemotherapy for localised resectable soft-tissue sarcoma of adults: meta-analysis of individual data. Lancet 1997;350:1647–54.
- Gronchi A, Frustaci S, Mercuri M, et al. Short, full-dose adjuvant chemotherapy in high-risk adult soft tissue sarcomas: a randomized clinical trial from the Italian Sarcoma Group and the Spanish Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol 2012;30:850–56.
- Pisters PW, Leung DH, Woodruff J. Analysis of prognostic factors in 1,041 patients with localized soft tissue sarcomas of the extremities. J Clin Oncol 1996;14:1679–89.
- Whooley B, Gibbs J, Mooney M. Primary Extremity Sarcoma: What is the Appropriate Follow-up? Annals of Surg Oncol 2000; 7: 9-14.
- Whooley BP, Mooney MN, Gibbs JF, Graybill WG. Effective follow-up strategies in soft tissue sarcoma. Sem Surg Oncol 1999;17:83–87.
- Billingsley KG, Burt ME, Jara E, et al. Pulmonary metastases from soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of patterns of diseases and postmetastasis survival. Ann Surg 1999;229:602–10.
- Bramwell VH, Anderson D, Charette ML; Sarcoma Disease Site Group. Doxorubicin-based chemotherapy for the palliative treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic soft tissue sarcoma. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2003;(3):CD003293.
- Edmonson J, Ryan L, Blum R. Randomized comparison of doxorubicin alone versus ifosfamide plus doxorubicin or mitomycin, doxorubicin, and cisplatin against advanced soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1269–75.
- Santoro A, Tursz T, Mouridsen H. Doxorubicin versus CYVADIC versus doxorubicin plus ifosfamide in first-line treatment of advanced soft tissue sarcomas: a randomized study of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Soft Tissue and Bone Sarcoma Group. J Clin Oncol 1995;13:1537–45.
- Tap WD, Jones RL, Van Tine B, et al. Olaratumab and doxorubicin versus doxorubicin alone for treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma: an open-label phase 1b and randomised phase 2 trial. Lancet 2016;388:488–97.
- Borden EC, Amato DA, Rosenbaum C, et al. Randomized comparison of three adriamycin regimens for metastatic soft tissue sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1987;5:840–50.
- Omura GA, Major FJ, Blessing JA, et al. A randomized study of adriamycin with and without dimethyl triazenoimidazole carboxamide in advanced uterine sarcomas. Cancer 1983;52:626–32.
- Antman K, Crowley J, Balcerzak SP, et al. An intergroup phase III randomized study of doxorubicin and dacarbazine with or without ifosfamide and mesna in advanced soft tissue and bone sarcomas. J Clin Oncol 1993;11:1276–85.
- Maki R, Wathen K, Patel SR, et al. Randomized phase II study of gemcitabine and docetaxel compared with gemcitabine alone in patients with metastatic soft tissue sarcomas: results of sarcoma alliance for research through collaboration study 002 [corrected]. J Clin Oncol 2007; 25: 2755–63.
- Hensley ML, Maki R, Venkatraman E, et al. Gemcitabine and docetaxel in patients with unresectable leiomyosarcoma: results of a phase II trial. J Clin Oncol 2002;12:2824–31.
- Garcia-del-Muro X, Lopez-Pousa A, Maurel J, et al. Randomized phase II study comparing gemcitabine plus dacarbazine versus dacarbazine alone in patients with previously treated soft tissue sarcoma: a Spanish Group for Research on Sarcomas study. J Clin Oncol 2011;29:2528–33.
- Grosso F, Jones RL, Demetri GD, et al. Efficacy of trabectedin (ecteinascidin-743) in advanced pretreated myxoid liposarcomas: a retrospective study. Lancet Oncol 2007;7:595–602.
- Italiano A, Cioffi A, Penel N, et al. Comparison of doxorubicin and weekly paclitaxel efficacy in metastatic angiosarcomas. Cancer 2012;118:3330–6.
- Penel N, Italiano A, Ray-Coquard I, et al. Metastatic angiosarcomas: doxorubicin-based regimens, weekly paclitaxel and metastasectomy significantly improve outcome. Ann Oncol 2012;23:517–23.
- Samuels BL, Chawla S, Patel S, et al. Clinical outcomes and safety with trabectedin therapy in patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas following failure of prior chemotherapy: results of a worldwide expanded access program study. Ann Oncol 2013;24:1703–9.
- Schöffski P, Ray-Coquard IL, Cioffi A, et al. Activity of eribulin mesylate in patients with soft-tissue sarcoma: a phase 2 study in four independent histolical subtypes. Lancet 2011;11:1045–52.
- Van der Graaf W, Blay JY, Chawla S, et al. Pazopanib for metastatic soft-tissue sarcoma (PALETTE): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trial. Lancet 2012;379:1879–86.
- Dileo P, Morgan JA, Zahrieh D, et al. Gemcitabine and vinorelbine combination chemotherapy for patients with advanced soft tissue sarcomas: results of a phase II trial. Cancer 2007;109:1863–9.
Oral pomalidomide effective against Kaposi’s sarcoma
Oral pomalidomide, a derivative of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antiproliferative properties, proved to be well tolerated and effective against Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) in a small phase I/II study, investigators reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
There is a substantial need for oral therapies for KS, which often recurs and requires treatment, at least intermittently, for years. Existing treatments are cytotoxic agents, such as anthracyclines that are poorly tolerated and unsuitable for long-term use, said Mark N. Polizzotto, MD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., and his associates.
They examined the tolerability and efficacy of pomalidomide against KS in a single-center, open-label trial involving 21 men and 1 transgender woman who had at least five evaluable cutaneous lesions. Fifteen of these participants had HIV infection. All of the patients were heavily pretreated with antiretrovirals and other agents, including thalidomide or lenalidomide, and most (17) had advanced KS with tumor-associated edema. The study participants received 5-mg oral pomalidomide once daily for 21 days in 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles.
Sixteen patients showed an objective tumor response (overall response rate, 73%), including four who achieved a complete response (ORR, 18%). All 7 of the participants who didn’t have HIV showed an objective tumor response (ORR, 100%), as did 9 of the 15 HIV-infected participants (ORR, 60%). Three more participants, including one who was nonadeherent and lost to follow-up, achieved a partial tumor response.
Tumor responses included a decrease in the number of lesions and a decrease in the number of nodular lesions, as well as complete flattening of lesions, resolution of edema, and improvement in appearance. “The latter is particularly important because visible KS is a major source of stigma,” Dr. Polizzotto and his associates said (J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct 3;34[34]:4125-32).
Two patients reported substantial subjective improvement in foot pain and appearance; one said he was pleased to be able to resume wearing closed shoes, the investigators noted. Treatment response generally was rapid, often commencing before the first follow-up at 4 weeks.
Pomalidomide was generally well tolerated. Adverse effects were frequent but mild and self-limiting, and they included neutropenia, constipation, anemia, fatigue, and rash. No patients required hospitalization, and there were no thromboembolic events. Three study participants developed malignancies after treatment: an Epstein-Barr-virus–associated Hodgkin lymphoma 1 year after the trial, a primary effusion lymphoma 15 months after, and a squamous-cell skin carcinoma. These probably reflect the patients’ underlying immunodeficiency, but the possibility that pomalidomide could contribute to malignancies in this high-risk population should be carefully explored in future studies, the investigators said.
“In resource-rich regions, pomalidomide may be of particular use in HIV-uninfected patients, in patients who have received substantial cumulative doses of anthracyclines, and in patients with less extensive but symptomatic disease for whom avoidance of cytotoxic chemotherapy would be beneficial. In resource-limited regions, there is an urgent need for effective and tolerable oral agents; with appropriate safeguards and monitoring, pomalidomide could address this,” Dr. Polizzotto and his associates wrote.
“Confirmatory studies of pomalidomide, alone and in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy, are planned, including in sub-Saharan Africa,” they added.
Oral pomalidomide, a derivative of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antiproliferative properties, proved to be well tolerated and effective against Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) in a small phase I/II study, investigators reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
There is a substantial need for oral therapies for KS, which often recurs and requires treatment, at least intermittently, for years. Existing treatments are cytotoxic agents, such as anthracyclines that are poorly tolerated and unsuitable for long-term use, said Mark N. Polizzotto, MD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., and his associates.
They examined the tolerability and efficacy of pomalidomide against KS in a single-center, open-label trial involving 21 men and 1 transgender woman who had at least five evaluable cutaneous lesions. Fifteen of these participants had HIV infection. All of the patients were heavily pretreated with antiretrovirals and other agents, including thalidomide or lenalidomide, and most (17) had advanced KS with tumor-associated edema. The study participants received 5-mg oral pomalidomide once daily for 21 days in 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles.
Sixteen patients showed an objective tumor response (overall response rate, 73%), including four who achieved a complete response (ORR, 18%). All 7 of the participants who didn’t have HIV showed an objective tumor response (ORR, 100%), as did 9 of the 15 HIV-infected participants (ORR, 60%). Three more participants, including one who was nonadeherent and lost to follow-up, achieved a partial tumor response.
Tumor responses included a decrease in the number of lesions and a decrease in the number of nodular lesions, as well as complete flattening of lesions, resolution of edema, and improvement in appearance. “The latter is particularly important because visible KS is a major source of stigma,” Dr. Polizzotto and his associates said (J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct 3;34[34]:4125-32).
Two patients reported substantial subjective improvement in foot pain and appearance; one said he was pleased to be able to resume wearing closed shoes, the investigators noted. Treatment response generally was rapid, often commencing before the first follow-up at 4 weeks.
Pomalidomide was generally well tolerated. Adverse effects were frequent but mild and self-limiting, and they included neutropenia, constipation, anemia, fatigue, and rash. No patients required hospitalization, and there were no thromboembolic events. Three study participants developed malignancies after treatment: an Epstein-Barr-virus–associated Hodgkin lymphoma 1 year after the trial, a primary effusion lymphoma 15 months after, and a squamous-cell skin carcinoma. These probably reflect the patients’ underlying immunodeficiency, but the possibility that pomalidomide could contribute to malignancies in this high-risk population should be carefully explored in future studies, the investigators said.
“In resource-rich regions, pomalidomide may be of particular use in HIV-uninfected patients, in patients who have received substantial cumulative doses of anthracyclines, and in patients with less extensive but symptomatic disease for whom avoidance of cytotoxic chemotherapy would be beneficial. In resource-limited regions, there is an urgent need for effective and tolerable oral agents; with appropriate safeguards and monitoring, pomalidomide could address this,” Dr. Polizzotto and his associates wrote.
“Confirmatory studies of pomalidomide, alone and in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy, are planned, including in sub-Saharan Africa,” they added.
Oral pomalidomide, a derivative of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antiproliferative properties, proved to be well tolerated and effective against Kaposi’s sarcoma (KS) in a small phase I/II study, investigators reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
There is a substantial need for oral therapies for KS, which often recurs and requires treatment, at least intermittently, for years. Existing treatments are cytotoxic agents, such as anthracyclines that are poorly tolerated and unsuitable for long-term use, said Mark N. Polizzotto, MD, of the National Cancer Institute, Bethesda, Md., and his associates.
They examined the tolerability and efficacy of pomalidomide against KS in a single-center, open-label trial involving 21 men and 1 transgender woman who had at least five evaluable cutaneous lesions. Fifteen of these participants had HIV infection. All of the patients were heavily pretreated with antiretrovirals and other agents, including thalidomide or lenalidomide, and most (17) had advanced KS with tumor-associated edema. The study participants received 5-mg oral pomalidomide once daily for 21 days in 28-day cycles for up to 12 cycles.
Sixteen patients showed an objective tumor response (overall response rate, 73%), including four who achieved a complete response (ORR, 18%). All 7 of the participants who didn’t have HIV showed an objective tumor response (ORR, 100%), as did 9 of the 15 HIV-infected participants (ORR, 60%). Three more participants, including one who was nonadeherent and lost to follow-up, achieved a partial tumor response.
Tumor responses included a decrease in the number of lesions and a decrease in the number of nodular lesions, as well as complete flattening of lesions, resolution of edema, and improvement in appearance. “The latter is particularly important because visible KS is a major source of stigma,” Dr. Polizzotto and his associates said (J Clin Oncol. 2016 Oct 3;34[34]:4125-32).
Two patients reported substantial subjective improvement in foot pain and appearance; one said he was pleased to be able to resume wearing closed shoes, the investigators noted. Treatment response generally was rapid, often commencing before the first follow-up at 4 weeks.
Pomalidomide was generally well tolerated. Adverse effects were frequent but mild and self-limiting, and they included neutropenia, constipation, anemia, fatigue, and rash. No patients required hospitalization, and there were no thromboembolic events. Three study participants developed malignancies after treatment: an Epstein-Barr-virus–associated Hodgkin lymphoma 1 year after the trial, a primary effusion lymphoma 15 months after, and a squamous-cell skin carcinoma. These probably reflect the patients’ underlying immunodeficiency, but the possibility that pomalidomide could contribute to malignancies in this high-risk population should be carefully explored in future studies, the investigators said.
“In resource-rich regions, pomalidomide may be of particular use in HIV-uninfected patients, in patients who have received substantial cumulative doses of anthracyclines, and in patients with less extensive but symptomatic disease for whom avoidance of cytotoxic chemotherapy would be beneficial. In resource-limited regions, there is an urgent need for effective and tolerable oral agents; with appropriate safeguards and monitoring, pomalidomide could address this,” Dr. Polizzotto and his associates wrote.
“Confirmatory studies of pomalidomide, alone and in combination with cytotoxic chemotherapy, are planned, including in sub-Saharan Africa,” they added.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: Oral pomalidomide, a derivative of thalidomide with immunomodulatory, antiangiogenic, and antiproliferative properties, proved to be well tolerated and effective against Kaposi’s sarcoma in a small phase I/II study.
Major finding: All 7 of the participants who didn’t have HIV showed an objective tumor response with pomalidomide (ORR, 100%), as did 9 of the 15 HIV-infected participants (ORR, 60%).
Data source: A single-center open-label phase I/II study involving 22 adults with KS, including 15 who had HIV infection.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Cancer Institute, Celgene, and the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases. Dr. Polizzotto and some of his associates reported that their institutions received research funding from Celgene; one of his associates also reported ties to Ovid, Trek, PTC, Avila, Semorex, and Sorrento.
Adding metronomic chemo provides no benefit to MAP for osteosarcoma
Adding low-dose metronomic chemotherapy (oral cyclophosphamide and methotrexate) to standard methotrexate, adriamycin, and platinum (MAP) maintenance treatment did not extend event-free survival in adolescents and young adults with high-grade, resectable osteosarcoma of the extremities, according to investigators.
“In pediatric tumors such as localized osteosarcomas, in situ tumor angiogenesis and levels of circulating angiogenic factors correlate with metastatic disease and a poor prognosis,” noted Andreza A. Senerchia, MD, of the Institute of Pediatric Oncology/Support Group for Adolescents and Children With Cancer, Federal University of Sao Paulo (Brazil), and her associates.
Since metronomic chemotherapy can prevent tumor angiogenesis and is a readily available, low-cost treatment with low toxicity, it could serve as a useful add-on to established MAP maintenance therapy in this patient population, they speculated.
The investigators assessed this approach in a prospective clinical trial involving 296 patients aged younger than 30 (mean age, 14 years; range, 0-29 years) who were treated at 27 medical centers in Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay. All the study participants had high-grade but nonmetastatic operable osteosarcomas of the extremities, and all underwent preoperative chemotherapy followed by surgical resection, with limb salvage whenever possible.
A total of 139 patients were then randomly assigned to receive MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy (intervention group) and 157 to receive MAP alone (control group). However, 35% of the intervention group never started metronomic chemotherapy for a variety of reasons, and another 10% stopped the treatment very early.
At 5 years, cumulative event-free survival was 61% with MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy and 64% with MAP alone, a nonsignificant difference. When the analysis was restricted to only the patients in the intervention group who actually received metronomic chemotherapy, there still was no evidence that the add-on treatment made any difference in event-free survival. Similarly, mean overall survival was not significantly different between the two study groups, at 76% and 73%, respectively, Dr. Senerchia and her associates wrote (Cancer 2016 Nov 7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30411).
There were 27 deaths (19%) in the intervention group, 81% of which were due to disease progression and 11% of which were due to treatment-related toxicity. Similarly, there were 24 deaths (15%) in the control group, of which 83% were due to disease progression and 17% to treatment-related toxicity.
These findings “do not support the routine use of cyclophosphamide and methotrexate as metronomic agents after standard chemotherapy for nonmetastatic osteosarcoma. However, our results should not preclude further investigation into the potential of maintenance for patients with osteosarcoma ... The combination tested here may not be optimal. In addition, adding a targeted-like effect through drug repositioning could allow more potent treatment with the addition of, for instance, valproic acid or beta-blockers,” the investigators said.
Adding low-dose metronomic chemotherapy (oral cyclophosphamide and methotrexate) to standard methotrexate, adriamycin, and platinum (MAP) maintenance treatment did not extend event-free survival in adolescents and young adults with high-grade, resectable osteosarcoma of the extremities, according to investigators.
“In pediatric tumors such as localized osteosarcomas, in situ tumor angiogenesis and levels of circulating angiogenic factors correlate with metastatic disease and a poor prognosis,” noted Andreza A. Senerchia, MD, of the Institute of Pediatric Oncology/Support Group for Adolescents and Children With Cancer, Federal University of Sao Paulo (Brazil), and her associates.
Since metronomic chemotherapy can prevent tumor angiogenesis and is a readily available, low-cost treatment with low toxicity, it could serve as a useful add-on to established MAP maintenance therapy in this patient population, they speculated.
The investigators assessed this approach in a prospective clinical trial involving 296 patients aged younger than 30 (mean age, 14 years; range, 0-29 years) who were treated at 27 medical centers in Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay. All the study participants had high-grade but nonmetastatic operable osteosarcomas of the extremities, and all underwent preoperative chemotherapy followed by surgical resection, with limb salvage whenever possible.
A total of 139 patients were then randomly assigned to receive MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy (intervention group) and 157 to receive MAP alone (control group). However, 35% of the intervention group never started metronomic chemotherapy for a variety of reasons, and another 10% stopped the treatment very early.
At 5 years, cumulative event-free survival was 61% with MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy and 64% with MAP alone, a nonsignificant difference. When the analysis was restricted to only the patients in the intervention group who actually received metronomic chemotherapy, there still was no evidence that the add-on treatment made any difference in event-free survival. Similarly, mean overall survival was not significantly different between the two study groups, at 76% and 73%, respectively, Dr. Senerchia and her associates wrote (Cancer 2016 Nov 7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30411).
There were 27 deaths (19%) in the intervention group, 81% of which were due to disease progression and 11% of which were due to treatment-related toxicity. Similarly, there were 24 deaths (15%) in the control group, of which 83% were due to disease progression and 17% to treatment-related toxicity.
These findings “do not support the routine use of cyclophosphamide and methotrexate as metronomic agents after standard chemotherapy for nonmetastatic osteosarcoma. However, our results should not preclude further investigation into the potential of maintenance for patients with osteosarcoma ... The combination tested here may not be optimal. In addition, adding a targeted-like effect through drug repositioning could allow more potent treatment with the addition of, for instance, valproic acid or beta-blockers,” the investigators said.
Adding low-dose metronomic chemotherapy (oral cyclophosphamide and methotrexate) to standard methotrexate, adriamycin, and platinum (MAP) maintenance treatment did not extend event-free survival in adolescents and young adults with high-grade, resectable osteosarcoma of the extremities, according to investigators.
“In pediatric tumors such as localized osteosarcomas, in situ tumor angiogenesis and levels of circulating angiogenic factors correlate with metastatic disease and a poor prognosis,” noted Andreza A. Senerchia, MD, of the Institute of Pediatric Oncology/Support Group for Adolescents and Children With Cancer, Federal University of Sao Paulo (Brazil), and her associates.
Since metronomic chemotherapy can prevent tumor angiogenesis and is a readily available, low-cost treatment with low toxicity, it could serve as a useful add-on to established MAP maintenance therapy in this patient population, they speculated.
The investigators assessed this approach in a prospective clinical trial involving 296 patients aged younger than 30 (mean age, 14 years; range, 0-29 years) who were treated at 27 medical centers in Brazil, Argentina, and Uruguay. All the study participants had high-grade but nonmetastatic operable osteosarcomas of the extremities, and all underwent preoperative chemotherapy followed by surgical resection, with limb salvage whenever possible.
A total of 139 patients were then randomly assigned to receive MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy (intervention group) and 157 to receive MAP alone (control group). However, 35% of the intervention group never started metronomic chemotherapy for a variety of reasons, and another 10% stopped the treatment very early.
At 5 years, cumulative event-free survival was 61% with MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy and 64% with MAP alone, a nonsignificant difference. When the analysis was restricted to only the patients in the intervention group who actually received metronomic chemotherapy, there still was no evidence that the add-on treatment made any difference in event-free survival. Similarly, mean overall survival was not significantly different between the two study groups, at 76% and 73%, respectively, Dr. Senerchia and her associates wrote (Cancer 2016 Nov 7. doi: 10.1002/cncr.30411).
There were 27 deaths (19%) in the intervention group, 81% of which were due to disease progression and 11% of which were due to treatment-related toxicity. Similarly, there were 24 deaths (15%) in the control group, of which 83% were due to disease progression and 17% to treatment-related toxicity.
These findings “do not support the routine use of cyclophosphamide and methotrexate as metronomic agents after standard chemotherapy for nonmetastatic osteosarcoma. However, our results should not preclude further investigation into the potential of maintenance for patients with osteosarcoma ... The combination tested here may not be optimal. In addition, adding a targeted-like effect through drug repositioning could allow more potent treatment with the addition of, for instance, valproic acid or beta-blockers,” the investigators said.
FROM CANCER
Key clinical point: Adding low-dose metronomic chemotherapy to MAP as maintenance treatment did not extend event-free survival in adolescents and young adults with high-grade, resectable osteosarcoma of the extremities.
Major finding: At 5 years, cumulative event-free survival was 61% with MAP plus metronomic chemotherapy and 64% with MAP alone, a nonsignificant difference.
Data source: A prospective randomized clinical trial involving 296 patients in South America followed for 5 years.
Disclosures: The authors did not provide information on the funding of this study and did not report any conflict-of-interest disclosures.