User login
Dasatinib activity prominent in subset of GIST patients
Dasatinib might have activity in some subsets of patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), investigators have reported.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor had a 29% rate of 6-month progression-free survival (PFS) in a nonrandomized, 50-patient study.
That PFS rate was well above the 10% threshold that would have constituted evidence of inactive treatment, but it “fell just short of our goal” of 30% that would have been considered evidence of drug activity, wrote Scott M. Schuetze, MD, PhD, of the department of internal medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and his coauthors. The report was published in JAMA Oncology.
It was also higher than the 16% 6-month PFS rate reported in a randomized trial of sunitinib, which was approved for imatinib-resistant GIST treatment in 2006. However, it was lower than the 38% 6-month PFS rate reported for regorafenib, which was approved in 2013 for that indication, the researchers noted.
Exploratory analyses did identify a few biomarker-driven subsets that might particularly benefit from dasatinib therapy. Notably, the 6-month PFS rate was 50% for patients with tumors expressing phosphorylated SRC.
While intriguing, the results of the exploratory analyses are hampered by the small number of patients enrolled in the trial; only 14 patients in the study had phosphorylated SRC.
“Further studies should explore whether activated SRC is a prognostic biomarker of more indolent disease, or is a predictive biomarker of response to tyrosine kinase therapy,” the researchers wrote.
Patients in the study had imatinib refractory GIST. They received dasatinib 70 mg twice daily. They were enrolled in 2008-2009 and followed for at least 5 years.
In addition to previously receiving imatinib, most enrollees (80%) had already been treated with sunitinib as well. The study started before the approval of sunitinib in GIST, but after the approval of regorafenib, the investigators noted.
“Preclinical research suggested that dasatinib had higher potency against mutations in the activation domain of KIT and PDGFRA than imatinib and sunitinib,” the authors recounted.
This trial did provide some evidence in support of that preclinical data: One patient with a specific mutation in PDGFRA exhibited prolonged tumor control.
Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the trial and dasatinib. Dr. Schuetze reported disclosures related to Novartis, Amgen, Janssen, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and AB Science.
SOURCE: Schuetze SM et al. 2018 Apr 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0601.
Dasatinib might have activity in some subsets of patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), investigators have reported.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor had a 29% rate of 6-month progression-free survival (PFS) in a nonrandomized, 50-patient study.
That PFS rate was well above the 10% threshold that would have constituted evidence of inactive treatment, but it “fell just short of our goal” of 30% that would have been considered evidence of drug activity, wrote Scott M. Schuetze, MD, PhD, of the department of internal medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and his coauthors. The report was published in JAMA Oncology.
It was also higher than the 16% 6-month PFS rate reported in a randomized trial of sunitinib, which was approved for imatinib-resistant GIST treatment in 2006. However, it was lower than the 38% 6-month PFS rate reported for regorafenib, which was approved in 2013 for that indication, the researchers noted.
Exploratory analyses did identify a few biomarker-driven subsets that might particularly benefit from dasatinib therapy. Notably, the 6-month PFS rate was 50% for patients with tumors expressing phosphorylated SRC.
While intriguing, the results of the exploratory analyses are hampered by the small number of patients enrolled in the trial; only 14 patients in the study had phosphorylated SRC.
“Further studies should explore whether activated SRC is a prognostic biomarker of more indolent disease, or is a predictive biomarker of response to tyrosine kinase therapy,” the researchers wrote.
Patients in the study had imatinib refractory GIST. They received dasatinib 70 mg twice daily. They were enrolled in 2008-2009 and followed for at least 5 years.
In addition to previously receiving imatinib, most enrollees (80%) had already been treated with sunitinib as well. The study started before the approval of sunitinib in GIST, but after the approval of regorafenib, the investigators noted.
“Preclinical research suggested that dasatinib had higher potency against mutations in the activation domain of KIT and PDGFRA than imatinib and sunitinib,” the authors recounted.
This trial did provide some evidence in support of that preclinical data: One patient with a specific mutation in PDGFRA exhibited prolonged tumor control.
Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the trial and dasatinib. Dr. Schuetze reported disclosures related to Novartis, Amgen, Janssen, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and AB Science.
SOURCE: Schuetze SM et al. 2018 Apr 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0601.
Dasatinib might have activity in some subsets of patients with imatinib-resistant gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), investigators have reported.
The tyrosine kinase inhibitor had a 29% rate of 6-month progression-free survival (PFS) in a nonrandomized, 50-patient study.
That PFS rate was well above the 10% threshold that would have constituted evidence of inactive treatment, but it “fell just short of our goal” of 30% that would have been considered evidence of drug activity, wrote Scott M. Schuetze, MD, PhD, of the department of internal medicine, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and his coauthors. The report was published in JAMA Oncology.
It was also higher than the 16% 6-month PFS rate reported in a randomized trial of sunitinib, which was approved for imatinib-resistant GIST treatment in 2006. However, it was lower than the 38% 6-month PFS rate reported for regorafenib, which was approved in 2013 for that indication, the researchers noted.
Exploratory analyses did identify a few biomarker-driven subsets that might particularly benefit from dasatinib therapy. Notably, the 6-month PFS rate was 50% for patients with tumors expressing phosphorylated SRC.
While intriguing, the results of the exploratory analyses are hampered by the small number of patients enrolled in the trial; only 14 patients in the study had phosphorylated SRC.
“Further studies should explore whether activated SRC is a prognostic biomarker of more indolent disease, or is a predictive biomarker of response to tyrosine kinase therapy,” the researchers wrote.
Patients in the study had imatinib refractory GIST. They received dasatinib 70 mg twice daily. They were enrolled in 2008-2009 and followed for at least 5 years.
In addition to previously receiving imatinib, most enrollees (80%) had already been treated with sunitinib as well. The study started before the approval of sunitinib in GIST, but after the approval of regorafenib, the investigators noted.
“Preclinical research suggested that dasatinib had higher potency against mutations in the activation domain of KIT and PDGFRA than imatinib and sunitinib,” the authors recounted.
This trial did provide some evidence in support of that preclinical data: One patient with a specific mutation in PDGFRA exhibited prolonged tumor control.
Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the trial and dasatinib. Dr. Schuetze reported disclosures related to Novartis, Amgen, Janssen, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and AB Science.
SOURCE: Schuetze SM et al. 2018 Apr 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0601.
FROM JAMA ONCOLOGY
Key clinical point: The efficacy of dasatinib in imatinib-resistant GIST was just short of what investigators considered evidence of an active drug.
Major finding: The estimated rate of 6-month progression-free survival was 29% overall, though it was 50% in one biomarker-defined patient subset.
Study details: A nonrandomized single-arm study of 50 patients with GIST treated with dasatinib 70 mg twice daily.
Disclosures: Bristol-Myers Squibb provided funding for the trial and dasatinib. Dr. Schuetze reported disclosures related to Novartis, Amgen, Janssen, Daiichi-Sankyo, Eli Lilly, and AB Science.
Source: Schuetze SM et al. JAMA Oncol. 2018 Apr 26. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.0601.
Updates of ongoing clinical trials
Randomized Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Addition of the IGF-1R Monoclonal Antibody Ganitumab (AMG 479, NSC# 750008) to Multiagent Chemotherapy for Patients With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Ewing Sarcoma
NCT02306161
Sponsor: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Principal Investigator: Steven DuBois, Children’s Oncology Group and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Study locations: Over 300 U.S. cancer centers
Study summary: This randomized phase 3 trial examines whether the monoclonal antibody ganitumab plus combination chemotherapy (vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and etoposide) improves event-free survival for patients with newly-diagnosed, metastatic Ewing sarcoma. Secondary outcomes include overall survival rate and comparative evaluations of toxicity.
Patients are randomized to induction and consolidation therapy with vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride and cyclophosphamide [VDC] and ifosfamide and etoposide [IE]) or to the same regimen plus ganitumab. Between weeks 13-18 of the trial, patients undergo surgery and/or radiation therapy for local control. Patients with lung metastases undergo definitive stereotactic body radiation therapy or external beam radiation therapy over 5 days.
Study inclusion summary: Patients up to 50 years old are eligible to participate in this trial if they have newly-diagnosed Ewing sarcoma or peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) arising from bone or soft tissue and with metastatic disease involving lung, bone, bone marrow, or other metastatic site. Submission of pre-treatment serum, tumor tissue and whole blood is required. Patients should only have had a biopsy of the primary tumor without an attempt at complete or partial resection; patients will still be eligible if excision was attempted or accomplished as long as adequate anatomic imaging (MRI for most primary tumor sites) was obtained prior to surgery. Creatinine clearance or radioisotope glomerular filtration rate (GFR) must be at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater. Total bilirubin must be less than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal, alanine aminotransferase must be less than 3 times the upper limit of normal, blood sugar must be normal, and heart ejection fraction must exceed 50%.
Induction therapy: Patients receive vincristine sulfate intravenously (IV) over 1 minute on day 1; doxorubicin hydrochloride IV over 1-15 minutes on days 1 and 2; and cyclophosphamide IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 5, and 9; and ifosfamide IV over 1 hour on days 1 to 5 and etoposide IV over 1-2 hours on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 7, and 11. Patients in the control group receive induction therapy and placebo and patients in the treatment group receive induction therapy and ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11.
Consolidation therapy: Patients receive vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 9, and 13; doxorubicin hydrochloride IV over 1-15 minutes on days 1 and 2 of weeks 1 and 7; cyclophosphamide IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 9, and 13; ifosfamide IV over 1 hour on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 5, 11, and 15; and etoposide IV over 1-2 hours on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 5, 11, and 15. In addition to this standard consolidation therapy, pPatients in the active treatment group receive ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 of weeks 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15.
Maintenance therapy: Patients receive ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 in weeks 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, and 22.
Follow up: After completion of study treatment, patients are followed for 10 years.
Combination Chemotherapy With or Without Temsirolimus in Treating Patients With Intermediate Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma
NCT02567435
Sponsor: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Principal Investigator: Abha Gupta, Children’s Oncology Group, The Hospital for Sick Children and Princess Margaret Cancer Centre.
Study locations: 293 cancer centers in the U.S. and Canada
Study summary: This randomized phase 3 trial compares standard combination chemotherapy with and without temsirolimus for patients with rhabdomyosarcoma that has an intermediate chance of recurrence after treatment. It is not yet known whether combination chemotherapy or combination chemotherapy plus temsirolimus is more effective in treating patients with intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma.
Study inclusion summary: Patients up to age 40 with newly diagnosed RMS of any subtype, except adult-type pleomorphic, based upon institutional histopathologic classification, are eligible to enroll on the study. Lansky performance status score must be at least 50 for patients age 16 years and under; Karnofsky performance status score must be 50 or greater for patients over age 16. Peripheral absolute neutrophil count must be at least 750/uL and platelet count at least 75,000/uL. Creatinine clearance or radioisotope glomerular filtration rate must be at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2. Total bilirubin must be no more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal for patient age.
Treatment regimen: Patients are randomized to one of three study arms. One group receives vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1-13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 22-26, 28, 31-34, 37, 38, and 40, dactinomycin IV over 1-5 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 13, 22, 28, 34, and 40, cyclophosphamide IV over 60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 13, 22, 28, 34, and 40, irinotecan hydrochloride IV over 90 minutes on days 1-5 of weeks 4, 10, 16, 19, 25, 31, and 37. The second group receives the same regimen plus temsirolimus IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1-12 and 21-42. The third group receives vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1-10 and 13-22, dactinomycin IV over 1-5 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, and 22, cyclophosphamide IV over 60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 4, 7, and 10. Patients in all three groups also undergo radiation therapy beginning at week 13 for 6 weeks. Treatment continues in all three groups in the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Outcome Measures: The primary outcome measure is event-free survival (EFS) measured from study enrollment to the first occurrence of progression, relapse, second malignant neoplasm, or death as a first event. The secondary outcome measure is overall survival measured from study enrollment to death from any cause, assessed up to 10 years. TSJ
Randomized Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Addition of the IGF-1R Monoclonal Antibody Ganitumab (AMG 479, NSC# 750008) to Multiagent Chemotherapy for Patients With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Ewing Sarcoma
NCT02306161
Sponsor: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Principal Investigator: Steven DuBois, Children’s Oncology Group and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Study locations: Over 300 U.S. cancer centers
Study summary: This randomized phase 3 trial examines whether the monoclonal antibody ganitumab plus combination chemotherapy (vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and etoposide) improves event-free survival for patients with newly-diagnosed, metastatic Ewing sarcoma. Secondary outcomes include overall survival rate and comparative evaluations of toxicity.
Patients are randomized to induction and consolidation therapy with vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride and cyclophosphamide [VDC] and ifosfamide and etoposide [IE]) or to the same regimen plus ganitumab. Between weeks 13-18 of the trial, patients undergo surgery and/or radiation therapy for local control. Patients with lung metastases undergo definitive stereotactic body radiation therapy or external beam radiation therapy over 5 days.
Study inclusion summary: Patients up to 50 years old are eligible to participate in this trial if they have newly-diagnosed Ewing sarcoma or peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) arising from bone or soft tissue and with metastatic disease involving lung, bone, bone marrow, or other metastatic site. Submission of pre-treatment serum, tumor tissue and whole blood is required. Patients should only have had a biopsy of the primary tumor without an attempt at complete or partial resection; patients will still be eligible if excision was attempted or accomplished as long as adequate anatomic imaging (MRI for most primary tumor sites) was obtained prior to surgery. Creatinine clearance or radioisotope glomerular filtration rate (GFR) must be at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater. Total bilirubin must be less than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal, alanine aminotransferase must be less than 3 times the upper limit of normal, blood sugar must be normal, and heart ejection fraction must exceed 50%.
Induction therapy: Patients receive vincristine sulfate intravenously (IV) over 1 minute on day 1; doxorubicin hydrochloride IV over 1-15 minutes on days 1 and 2; and cyclophosphamide IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 5, and 9; and ifosfamide IV over 1 hour on days 1 to 5 and etoposide IV over 1-2 hours on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 7, and 11. Patients in the control group receive induction therapy and placebo and patients in the treatment group receive induction therapy and ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11.
Consolidation therapy: Patients receive vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 9, and 13; doxorubicin hydrochloride IV over 1-15 minutes on days 1 and 2 of weeks 1 and 7; cyclophosphamide IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 9, and 13; ifosfamide IV over 1 hour on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 5, 11, and 15; and etoposide IV over 1-2 hours on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 5, 11, and 15. In addition to this standard consolidation therapy, pPatients in the active treatment group receive ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 of weeks 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15.
Maintenance therapy: Patients receive ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 in weeks 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, and 22.
Follow up: After completion of study treatment, patients are followed for 10 years.
Combination Chemotherapy With or Without Temsirolimus in Treating Patients With Intermediate Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma
NCT02567435
Sponsor: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Principal Investigator: Abha Gupta, Children’s Oncology Group, The Hospital for Sick Children and Princess Margaret Cancer Centre.
Study locations: 293 cancer centers in the U.S. and Canada
Study summary: This randomized phase 3 trial compares standard combination chemotherapy with and without temsirolimus for patients with rhabdomyosarcoma that has an intermediate chance of recurrence after treatment. It is not yet known whether combination chemotherapy or combination chemotherapy plus temsirolimus is more effective in treating patients with intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma.
Study inclusion summary: Patients up to age 40 with newly diagnosed RMS of any subtype, except adult-type pleomorphic, based upon institutional histopathologic classification, are eligible to enroll on the study. Lansky performance status score must be at least 50 for patients age 16 years and under; Karnofsky performance status score must be 50 or greater for patients over age 16. Peripheral absolute neutrophil count must be at least 750/uL and platelet count at least 75,000/uL. Creatinine clearance or radioisotope glomerular filtration rate must be at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2. Total bilirubin must be no more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal for patient age.
Treatment regimen: Patients are randomized to one of three study arms. One group receives vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1-13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 22-26, 28, 31-34, 37, 38, and 40, dactinomycin IV over 1-5 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 13, 22, 28, 34, and 40, cyclophosphamide IV over 60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 13, 22, 28, 34, and 40, irinotecan hydrochloride IV over 90 minutes on days 1-5 of weeks 4, 10, 16, 19, 25, 31, and 37. The second group receives the same regimen plus temsirolimus IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1-12 and 21-42. The third group receives vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1-10 and 13-22, dactinomycin IV over 1-5 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, and 22, cyclophosphamide IV over 60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 4, 7, and 10. Patients in all three groups also undergo radiation therapy beginning at week 13 for 6 weeks. Treatment continues in all three groups in the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Outcome Measures: The primary outcome measure is event-free survival (EFS) measured from study enrollment to the first occurrence of progression, relapse, second malignant neoplasm, or death as a first event. The secondary outcome measure is overall survival measured from study enrollment to death from any cause, assessed up to 10 years. TSJ
Randomized Phase 3 Trial Evaluating the Addition of the IGF-1R Monoclonal Antibody Ganitumab (AMG 479, NSC# 750008) to Multiagent Chemotherapy for Patients With Newly Diagnosed Metastatic Ewing Sarcoma
NCT02306161
Sponsor: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Principal Investigator: Steven DuBois, Children’s Oncology Group and Dana-Farber Cancer Institute, Boston.
Study locations: Over 300 U.S. cancer centers
Study summary: This randomized phase 3 trial examines whether the monoclonal antibody ganitumab plus combination chemotherapy (vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride, cyclophosphamide, ifosfamide, and etoposide) improves event-free survival for patients with newly-diagnosed, metastatic Ewing sarcoma. Secondary outcomes include overall survival rate and comparative evaluations of toxicity.
Patients are randomized to induction and consolidation therapy with vincristine sulfate, doxorubicin hydrochloride and cyclophosphamide [VDC] and ifosfamide and etoposide [IE]) or to the same regimen plus ganitumab. Between weeks 13-18 of the trial, patients undergo surgery and/or radiation therapy for local control. Patients with lung metastases undergo definitive stereotactic body radiation therapy or external beam radiation therapy over 5 days.
Study inclusion summary: Patients up to 50 years old are eligible to participate in this trial if they have newly-diagnosed Ewing sarcoma or peripheral primitive neuroectodermal tumor (PNET) arising from bone or soft tissue and with metastatic disease involving lung, bone, bone marrow, or other metastatic site. Submission of pre-treatment serum, tumor tissue and whole blood is required. Patients should only have had a biopsy of the primary tumor without an attempt at complete or partial resection; patients will still be eligible if excision was attempted or accomplished as long as adequate anatomic imaging (MRI for most primary tumor sites) was obtained prior to surgery. Creatinine clearance or radioisotope glomerular filtration rate (GFR) must be at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2 or greater. Total bilirubin must be less than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal, alanine aminotransferase must be less than 3 times the upper limit of normal, blood sugar must be normal, and heart ejection fraction must exceed 50%.
Induction therapy: Patients receive vincristine sulfate intravenously (IV) over 1 minute on day 1; doxorubicin hydrochloride IV over 1-15 minutes on days 1 and 2; and cyclophosphamide IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 5, and 9; and ifosfamide IV over 1 hour on days 1 to 5 and etoposide IV over 1-2 hours on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 7, and 11. Patients in the control group receive induction therapy and placebo and patients in the treatment group receive induction therapy and ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, and 11.
Consolidation therapy: Patients receive vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 9, and 13; doxorubicin hydrochloride IV over 1-15 minutes on days 1 and 2 of weeks 1 and 7; cyclophosphamide IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 9, and 13; ifosfamide IV over 1 hour on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 5, 11, and 15; and etoposide IV over 1-2 hours on days 1 to 5 of weeks 3, 5, 11, and 15. In addition to this standard consolidation therapy, pPatients in the active treatment group receive ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 of weeks 7, 9, 11, 13, and 15.
Maintenance therapy: Patients receive ganitumab IV over 30-60 minutes or 60-120 minutes on day 1 in weeks 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, and 22.
Follow up: After completion of study treatment, patients are followed for 10 years.
Combination Chemotherapy With or Without Temsirolimus in Treating Patients With Intermediate Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma
NCT02567435
Sponsor: National Cancer Institute (NCI)
Principal Investigator: Abha Gupta, Children’s Oncology Group, The Hospital for Sick Children and Princess Margaret Cancer Centre.
Study locations: 293 cancer centers in the U.S. and Canada
Study summary: This randomized phase 3 trial compares standard combination chemotherapy with and without temsirolimus for patients with rhabdomyosarcoma that has an intermediate chance of recurrence after treatment. It is not yet known whether combination chemotherapy or combination chemotherapy plus temsirolimus is more effective in treating patients with intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma.
Study inclusion summary: Patients up to age 40 with newly diagnosed RMS of any subtype, except adult-type pleomorphic, based upon institutional histopathologic classification, are eligible to enroll on the study. Lansky performance status score must be at least 50 for patients age 16 years and under; Karnofsky performance status score must be 50 or greater for patients over age 16. Peripheral absolute neutrophil count must be at least 750/uL and platelet count at least 75,000/uL. Creatinine clearance or radioisotope glomerular filtration rate must be at least 70 mL/min/1.73 m2. Total bilirubin must be no more than 1.5 times the upper limit of normal for patient age.
Treatment regimen: Patients are randomized to one of three study arms. One group receives vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1-13, 16, 17, 19, 20, 22-26, 28, 31-34, 37, 38, and 40, dactinomycin IV over 1-5 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 13, 22, 28, 34, and 40, cyclophosphamide IV over 60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 7, 13, 22, 28, 34, and 40, irinotecan hydrochloride IV over 90 minutes on days 1-5 of weeks 4, 10, 16, 19, 25, 31, and 37. The second group receives the same regimen plus temsirolimus IV over 30-60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1-12 and 21-42. The third group receives vincristine sulfate IV over 1 minute on day 1 of weeks 1-10 and 13-22, dactinomycin IV over 1-5 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 4, 7, 10, 13, 16, 19, and 22, cyclophosphamide IV over 60 minutes on day 1 of weeks 1, 4, 7, and 10. Patients in all three groups also undergo radiation therapy beginning at week 13 for 6 weeks. Treatment continues in all three groups in the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Outcome Measures: The primary outcome measure is event-free survival (EFS) measured from study enrollment to the first occurrence of progression, relapse, second malignant neoplasm, or death as a first event. The secondary outcome measure is overall survival measured from study enrollment to death from any cause, assessed up to 10 years. TSJ
Chemotherapy, metabolic pathway may affect CAR T-cell potential
Two critical factors – prior exposure to chemotherapy and a glycolytic metabolism – appear to degrade the potential of T cells to become chimeric antigen receptor–T cells.
Chemotherapy, especially with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, seems particularly toxic to T cells, damaging the mitochondria and decreasing the cells’ spare respiratory capacity – a measure of mitochondrial health, David Barrett, MD, said during a press briefing held in advance of the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
These new findings may help explain why children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) tend to respond so vigorously to CAR T treatment, and why T cells from patients with solid tumors simply don’t grow, or die soon after patient infusion, he said in an interview. They also suggest a benefit of harvesting T cells before any chemotherapy, a procedure Dr. Barrett and his colleagues have advocated.
“Based on these data we have altered our practice for T-cell therapy in high-risk leukemia patients. If we have a patient who may have a poor prognosis, we try to collect the cells early and store them before proceeding, because we know chemotherapy will progressively degrade them.”
There still is no successful CAR T-cell protocol for solid tumors, but Dr. Barrett said these findings eventually may help such patients, particularly if more advanced experiments in manipulating the cells’ metabolism prove successful.
He and his colleagues investigated why T cells from some patients result in a poor clinical product that either fails manufacture or does not proliferate in the patient. They examined T cells from 157 pediatric patients with a variety of cancers, including ALL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, neuroblastoma, osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Wilms tumor, Hodgkin disease, chronic myelogenous leukemia, and Ewing sarcoma. The team obtained cells at diagnosis and after each cycle of chemotherapy.
They examined how well the cells grew in the transformation and expansion process. A “pass” was considered a fivefold expansion in response to CD3/CD28 exposure for 7 days. Normal donor cells typically expand 20- to 30-fold in this time.
Only T cells taken from ALL and Wilms tumor patients before chemotherapy achieved a pass, Dr. Barrett said. Most of the ALL expansions (80%) and half of the Wilms tumor expansions passed. “We noted very poor CAR T-cell potential in all the other tumor types – less than a 30% pass. We noted a decline in potential with cumulative chemotherapy in all cases, though this was particularly significant in children less than 3 years old.”
The team also used RNA profiling to look at the cells’ metabolic pathways. Dr. Barrett noted that T cells are highly metabolically adaptable, capable of using several different fuel types and switching from one to another. Glucose and fatty acids are frequent fuels. Most of the cells from patients with solid tumors exhibited a glycolytic metabolism, while cells from patients with ALL and Wilms tumor appeared to rely more on fatty acids.
“One is not inherently worse than the other,” he said. “But glycolysis appears to be a bad thing when we’re trying to turn them into CAR T cells. Those T cells were too exhausted to do anything.”
However, Dr. Barrett encouraged the cells to switch fuels by treating them in vitro with palmitic acid, the most common fatty acid in plants and animals.
“We were growing the cells in a media containing sugar, fatty acids, and amino acids,” he explained. “We just started overloading them with palmitic acid, which has a natural transporter on the T-cell surface, so it already had a good pathway to get into the cell. It helped restore some of the performance of these T cells in some assays, although it wasn’t a complete reversal. But it was encouraging that something as simple as providing an alternate fuel was enough to get some positive effect. Whether or not we would also have to block glucose use to get it to really work is something we continue to study.”
T cells that had been exposed to chemotherapy also did poorly. Cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin seemed particularly toxic. Cells with exposure to these two agents had severely depleted CAR T cell potential with very poor spare respiratory capacity. This is a marker of mitochondrial injury, Dr. Barrett said. “That wasn’t a huge surprise. We already knew that cyclophosphamide is very toxic to T cells.”
But the finding did suggest the simple intervention of harvesting T cells before chemotherapy, which is what Dr. Barrett and his colleagues now do in their high-risk ALL patients. Whether or not this would improve response in patients with solid tumors is still unknown.
He had no financial disclosures. This study was supported by the AACR, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Science Development Award, the Jeffrey Pride Foundation Research Award, and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation Scholar Award.
SOURCE: Barrett DM et al. AACR 2018, Abstract 1631.
Two critical factors – prior exposure to chemotherapy and a glycolytic metabolism – appear to degrade the potential of T cells to become chimeric antigen receptor–T cells.
Chemotherapy, especially with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, seems particularly toxic to T cells, damaging the mitochondria and decreasing the cells’ spare respiratory capacity – a measure of mitochondrial health, David Barrett, MD, said during a press briefing held in advance of the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
These new findings may help explain why children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) tend to respond so vigorously to CAR T treatment, and why T cells from patients with solid tumors simply don’t grow, or die soon after patient infusion, he said in an interview. They also suggest a benefit of harvesting T cells before any chemotherapy, a procedure Dr. Barrett and his colleagues have advocated.
“Based on these data we have altered our practice for T-cell therapy in high-risk leukemia patients. If we have a patient who may have a poor prognosis, we try to collect the cells early and store them before proceeding, because we know chemotherapy will progressively degrade them.”
There still is no successful CAR T-cell protocol for solid tumors, but Dr. Barrett said these findings eventually may help such patients, particularly if more advanced experiments in manipulating the cells’ metabolism prove successful.
He and his colleagues investigated why T cells from some patients result in a poor clinical product that either fails manufacture or does not proliferate in the patient. They examined T cells from 157 pediatric patients with a variety of cancers, including ALL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, neuroblastoma, osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Wilms tumor, Hodgkin disease, chronic myelogenous leukemia, and Ewing sarcoma. The team obtained cells at diagnosis and after each cycle of chemotherapy.
They examined how well the cells grew in the transformation and expansion process. A “pass” was considered a fivefold expansion in response to CD3/CD28 exposure for 7 days. Normal donor cells typically expand 20- to 30-fold in this time.
Only T cells taken from ALL and Wilms tumor patients before chemotherapy achieved a pass, Dr. Barrett said. Most of the ALL expansions (80%) and half of the Wilms tumor expansions passed. “We noted very poor CAR T-cell potential in all the other tumor types – less than a 30% pass. We noted a decline in potential with cumulative chemotherapy in all cases, though this was particularly significant in children less than 3 years old.”
The team also used RNA profiling to look at the cells’ metabolic pathways. Dr. Barrett noted that T cells are highly metabolically adaptable, capable of using several different fuel types and switching from one to another. Glucose and fatty acids are frequent fuels. Most of the cells from patients with solid tumors exhibited a glycolytic metabolism, while cells from patients with ALL and Wilms tumor appeared to rely more on fatty acids.
“One is not inherently worse than the other,” he said. “But glycolysis appears to be a bad thing when we’re trying to turn them into CAR T cells. Those T cells were too exhausted to do anything.”
However, Dr. Barrett encouraged the cells to switch fuels by treating them in vitro with palmitic acid, the most common fatty acid in plants and animals.
“We were growing the cells in a media containing sugar, fatty acids, and amino acids,” he explained. “We just started overloading them with palmitic acid, which has a natural transporter on the T-cell surface, so it already had a good pathway to get into the cell. It helped restore some of the performance of these T cells in some assays, although it wasn’t a complete reversal. But it was encouraging that something as simple as providing an alternate fuel was enough to get some positive effect. Whether or not we would also have to block glucose use to get it to really work is something we continue to study.”
T cells that had been exposed to chemotherapy also did poorly. Cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin seemed particularly toxic. Cells with exposure to these two agents had severely depleted CAR T cell potential with very poor spare respiratory capacity. This is a marker of mitochondrial injury, Dr. Barrett said. “That wasn’t a huge surprise. We already knew that cyclophosphamide is very toxic to T cells.”
But the finding did suggest the simple intervention of harvesting T cells before chemotherapy, which is what Dr. Barrett and his colleagues now do in their high-risk ALL patients. Whether or not this would improve response in patients with solid tumors is still unknown.
He had no financial disclosures. This study was supported by the AACR, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Science Development Award, the Jeffrey Pride Foundation Research Award, and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation Scholar Award.
SOURCE: Barrett DM et al. AACR 2018, Abstract 1631.
Two critical factors – prior exposure to chemotherapy and a glycolytic metabolism – appear to degrade the potential of T cells to become chimeric antigen receptor–T cells.
Chemotherapy, especially with cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin, seems particularly toxic to T cells, damaging the mitochondria and decreasing the cells’ spare respiratory capacity – a measure of mitochondrial health, David Barrett, MD, said during a press briefing held in advance of the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
These new findings may help explain why children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) tend to respond so vigorously to CAR T treatment, and why T cells from patients with solid tumors simply don’t grow, or die soon after patient infusion, he said in an interview. They also suggest a benefit of harvesting T cells before any chemotherapy, a procedure Dr. Barrett and his colleagues have advocated.
“Based on these data we have altered our practice for T-cell therapy in high-risk leukemia patients. If we have a patient who may have a poor prognosis, we try to collect the cells early and store them before proceeding, because we know chemotherapy will progressively degrade them.”
There still is no successful CAR T-cell protocol for solid tumors, but Dr. Barrett said these findings eventually may help such patients, particularly if more advanced experiments in manipulating the cells’ metabolism prove successful.
He and his colleagues investigated why T cells from some patients result in a poor clinical product that either fails manufacture or does not proliferate in the patient. They examined T cells from 157 pediatric patients with a variety of cancers, including ALL, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, neuroblastoma, osteosarcoma, rhabdomyosarcoma, Wilms tumor, Hodgkin disease, chronic myelogenous leukemia, and Ewing sarcoma. The team obtained cells at diagnosis and after each cycle of chemotherapy.
They examined how well the cells grew in the transformation and expansion process. A “pass” was considered a fivefold expansion in response to CD3/CD28 exposure for 7 days. Normal donor cells typically expand 20- to 30-fold in this time.
Only T cells taken from ALL and Wilms tumor patients before chemotherapy achieved a pass, Dr. Barrett said. Most of the ALL expansions (80%) and half of the Wilms tumor expansions passed. “We noted very poor CAR T-cell potential in all the other tumor types – less than a 30% pass. We noted a decline in potential with cumulative chemotherapy in all cases, though this was particularly significant in children less than 3 years old.”
The team also used RNA profiling to look at the cells’ metabolic pathways. Dr. Barrett noted that T cells are highly metabolically adaptable, capable of using several different fuel types and switching from one to another. Glucose and fatty acids are frequent fuels. Most of the cells from patients with solid tumors exhibited a glycolytic metabolism, while cells from patients with ALL and Wilms tumor appeared to rely more on fatty acids.
“One is not inherently worse than the other,” he said. “But glycolysis appears to be a bad thing when we’re trying to turn them into CAR T cells. Those T cells were too exhausted to do anything.”
However, Dr. Barrett encouraged the cells to switch fuels by treating them in vitro with palmitic acid, the most common fatty acid in plants and animals.
“We were growing the cells in a media containing sugar, fatty acids, and amino acids,” he explained. “We just started overloading them with palmitic acid, which has a natural transporter on the T-cell surface, so it already had a good pathway to get into the cell. It helped restore some of the performance of these T cells in some assays, although it wasn’t a complete reversal. But it was encouraging that something as simple as providing an alternate fuel was enough to get some positive effect. Whether or not we would also have to block glucose use to get it to really work is something we continue to study.”
T cells that had been exposed to chemotherapy also did poorly. Cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin seemed particularly toxic. Cells with exposure to these two agents had severely depleted CAR T cell potential with very poor spare respiratory capacity. This is a marker of mitochondrial injury, Dr. Barrett said. “That wasn’t a huge surprise. We already knew that cyclophosphamide is very toxic to T cells.”
But the finding did suggest the simple intervention of harvesting T cells before chemotherapy, which is what Dr. Barrett and his colleagues now do in their high-risk ALL patients. Whether or not this would improve response in patients with solid tumors is still unknown.
He had no financial disclosures. This study was supported by the AACR, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Science Development Award, the Jeffrey Pride Foundation Research Award, and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation Scholar Award.
SOURCE: Barrett DM et al. AACR 2018, Abstract 1631.
FROM AACR 2018
Key clinical point: Prior exposure to chemotherapy may degrade the potential of T cells to become CAR T cells, suggesting a benefit of harvesting T cells before any chemotherapy.
Major finding: Only T cells taken from ALL and Wilm’s tumor patients before chemotherapy achieved a fivefold expansion in response to CD3/CD28 exposure for 7 days.
Study details: An examination of T cells from 157 pediatric patients with a variety of cancers at diagnosis and after each cycle of chemotherapy.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the American Association of Cancer Research, the Doris Duke Charitable Foundation Clinical Science Development Award, the Jeffrey Pride Foundation Research Award, and the St. Baldrick’s Foundation Scholar Award. Dr. Barrett and his coauthors had no financial disclosures.
Source: Barrett DM et al. AACR 2018, Abstract 1631.
Anti-PD-1 therapy with nivolumab in the treatment of metastatic malignant PEComa
Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms (PEComas) are an uncommon class of tumors consisting on histology of perivascular epithelioid cells occurring in both localized and metastatic forms at various body sites. The approach to treatment of these tumors generally involves a combination of surgical resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy.1
Case presentation and summary
A 46-year-old man presented to our institution with a non-tender, slowly enlarging, 8.3 cm mass in his right popliteal fossa. Upon biopsy, the pathologic findings were consistent with an epithelioid malignancy with melanocytic differentiation most consistent with a PEComa. Discussion of the pathologic diagnosis of our patient has been reported by the pathology group at our institution in a separate case report.2
Our patient was initially offered and refused amputation. He was started on therapy with the mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor everolimus, but was unable to tolerate the side effects after the first week of treatment. He then elected to monitor his symptoms clinically.
Approximately one year after his initial diagnosis, he presented to our facility with sepsis and bleeding from a now fungating tumor on his right knee. At this time, emergent above-knee amputation was performed. Re-staging images now showed the presence of multiple pulmonary nodules in his right lung as well as a lytic rib lesion, a concerning finding for metastatic disease. Video-Assisted Thorascopic Surgery (VATS) and right lower lobe wedge resection were performed and findings confirmed metastatic PEComa.
Given the patient’s intolerance to everolimus, he was started on the growth factor inhibitor, pazopanib. His disease did not progress on pazopanib, and improvement was noted in the dominant pulmonary nodule. Subsequently, however, he developed significant skin irritation and discontinued pazopanib. Repeat imaging approximately 2 months after stopping pazopanib showed significant disease progression.
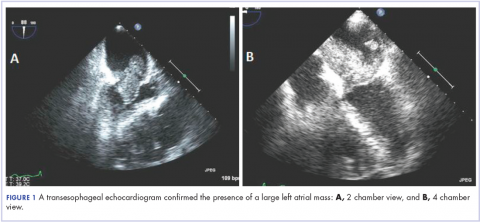
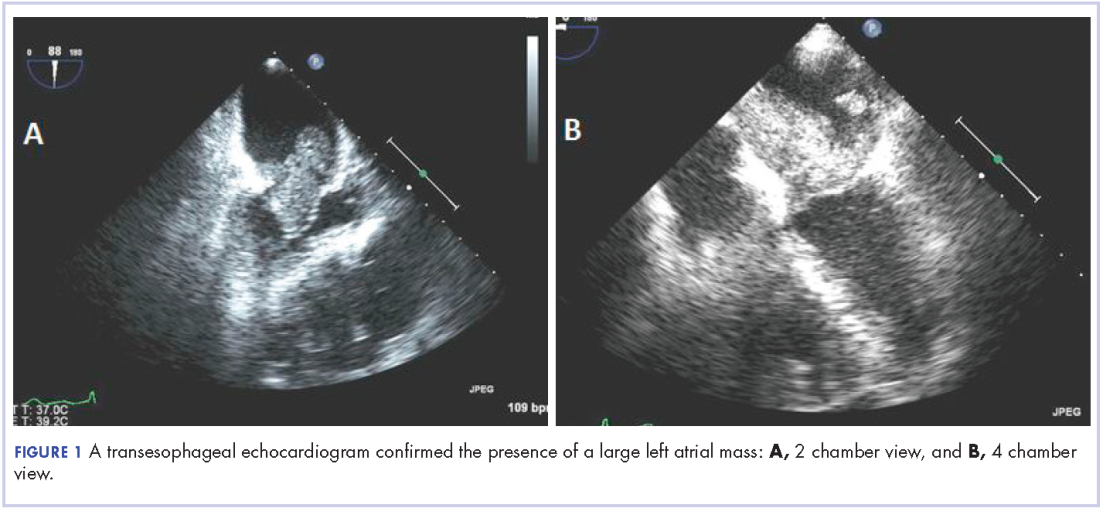
We elected to start the patient on a non-standard approach to therapy with nivolumab infusions once every 2 weeks and concurrent radiation therapy to the rib lesion. At 2 and 5 months after initiating this treatment approach, CT imaging showed improvement in disease. At 12 months, significant disease response was noted (Figure 1).
The patient is now at 12 months of nivolumab therapy with progression free survival and no new identifiable metastatic lesions. He has been tolerating the medication with minimal side effects and has had an overall improvement in his pain and functional status. He continues to work full time.
Discussion
Our patient’s response presents a unique opportunity to talk about the role of immunotherapy as a treatment modality in patients with PEComa. The efficacy of check-point blockade in soft tissue sarcoma is still unclear predominantly because it is difficult to assess the degree of expression of immunogenic cell surface markers such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1).1,3 Nivolumab has been tried in small cohorts for treatment of soft tissue sarcomas that express PD-1 and results showed some clinical benefit in about half of patients.4 Further, the expression of PD-1 has been assessed in soft tissue sarcomas and has been reported to suggest a negative prognostic role.5
To our knowledge, there has not yet been another reported case of PEComa that has been treated with immunotherapy and achieved a sustained response. Further clinical studies need to be done to assess response to agents such as nivolumab in the treatment of PEComa to bolster our observation that nivolumab is a viable treatment option that may lead to lasting remission. Our patient’s case also brings to light the need for further inquiry into assessing the immune tumor microenvironments, particularly looking at the expression of cell surface proteins such as PD-1, as it ultimately affects treatment options. TSJ
Correspondence
REFERENCES
1. Burgess, Melissa, et al. “Immunotherapy in Sarcoma: Future Horizons.” Current Oncology Reports, vol. 17, no. 11, 2015, doi:10.1007/s11912-015-0476-7.
2. Alnajar, Hussein, et al. “Metastatic Malignant PEComa of the Leg with Identification of ATRX Mutation by next-Generation Sequencing.” Virchows Archiv (2017). https://doi:10.1007/s004280172208-x.
3. Ghosn, Marwan, et al. “Immunotherapies in Sarcoma: Updates and Future Perspectives.” World Journal of Clinical Oncology, vol. 8, no. 2, 2017, p. 145., doi:10.5306/wjco.v8.i2.145.
4. Paoluzzi, L., et al. “Response to Anti-PD1 Therapy with Nivolumab in Metastatic Sarcomas.” Clinical Sarcoma Research, vol. 6, no. 1, 2016, doi:10.1186/s13569-016 0064-0.
5. Kim, Chan, et al. “Prognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma.” BMC Cancer, BioMed Central 8 July 2016.
Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms (PEComas) are an uncommon class of tumors consisting on histology of perivascular epithelioid cells occurring in both localized and metastatic forms at various body sites. The approach to treatment of these tumors generally involves a combination of surgical resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy.1
Case presentation and summary
A 46-year-old man presented to our institution with a non-tender, slowly enlarging, 8.3 cm mass in his right popliteal fossa. Upon biopsy, the pathologic findings were consistent with an epithelioid malignancy with melanocytic differentiation most consistent with a PEComa. Discussion of the pathologic diagnosis of our patient has been reported by the pathology group at our institution in a separate case report.2
Our patient was initially offered and refused amputation. He was started on therapy with the mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor everolimus, but was unable to tolerate the side effects after the first week of treatment. He then elected to monitor his symptoms clinically.
Approximately one year after his initial diagnosis, he presented to our facility with sepsis and bleeding from a now fungating tumor on his right knee. At this time, emergent above-knee amputation was performed. Re-staging images now showed the presence of multiple pulmonary nodules in his right lung as well as a lytic rib lesion, a concerning finding for metastatic disease. Video-Assisted Thorascopic Surgery (VATS) and right lower lobe wedge resection were performed and findings confirmed metastatic PEComa.
Given the patient’s intolerance to everolimus, he was started on the growth factor inhibitor, pazopanib. His disease did not progress on pazopanib, and improvement was noted in the dominant pulmonary nodule. Subsequently, however, he developed significant skin irritation and discontinued pazopanib. Repeat imaging approximately 2 months after stopping pazopanib showed significant disease progression.
We elected to start the patient on a non-standard approach to therapy with nivolumab infusions once every 2 weeks and concurrent radiation therapy to the rib lesion. At 2 and 5 months after initiating this treatment approach, CT imaging showed improvement in disease. At 12 months, significant disease response was noted (Figure 1).
The patient is now at 12 months of nivolumab therapy with progression free survival and no new identifiable metastatic lesions. He has been tolerating the medication with minimal side effects and has had an overall improvement in his pain and functional status. He continues to work full time.
Discussion
Our patient’s response presents a unique opportunity to talk about the role of immunotherapy as a treatment modality in patients with PEComa. The efficacy of check-point blockade in soft tissue sarcoma is still unclear predominantly because it is difficult to assess the degree of expression of immunogenic cell surface markers such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1).1,3 Nivolumab has been tried in small cohorts for treatment of soft tissue sarcomas that express PD-1 and results showed some clinical benefit in about half of patients.4 Further, the expression of PD-1 has been assessed in soft tissue sarcomas and has been reported to suggest a negative prognostic role.5
To our knowledge, there has not yet been another reported case of PEComa that has been treated with immunotherapy and achieved a sustained response. Further clinical studies need to be done to assess response to agents such as nivolumab in the treatment of PEComa to bolster our observation that nivolumab is a viable treatment option that may lead to lasting remission. Our patient’s case also brings to light the need for further inquiry into assessing the immune tumor microenvironments, particularly looking at the expression of cell surface proteins such as PD-1, as it ultimately affects treatment options. TSJ
Correspondence
REFERENCES
1. Burgess, Melissa, et al. “Immunotherapy in Sarcoma: Future Horizons.” Current Oncology Reports, vol. 17, no. 11, 2015, doi:10.1007/s11912-015-0476-7.
2. Alnajar, Hussein, et al. “Metastatic Malignant PEComa of the Leg with Identification of ATRX Mutation by next-Generation Sequencing.” Virchows Archiv (2017). https://doi:10.1007/s004280172208-x.
3. Ghosn, Marwan, et al. “Immunotherapies in Sarcoma: Updates and Future Perspectives.” World Journal of Clinical Oncology, vol. 8, no. 2, 2017, p. 145., doi:10.5306/wjco.v8.i2.145.
4. Paoluzzi, L., et al. “Response to Anti-PD1 Therapy with Nivolumab in Metastatic Sarcomas.” Clinical Sarcoma Research, vol. 6, no. 1, 2016, doi:10.1186/s13569-016 0064-0.
5. Kim, Chan, et al. “Prognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma.” BMC Cancer, BioMed Central 8 July 2016.
Perivascular epithelioid cell neoplasms (PEComas) are an uncommon class of tumors consisting on histology of perivascular epithelioid cells occurring in both localized and metastatic forms at various body sites. The approach to treatment of these tumors generally involves a combination of surgical resection, chemotherapy, and/or radiation therapy.1
Case presentation and summary
A 46-year-old man presented to our institution with a non-tender, slowly enlarging, 8.3 cm mass in his right popliteal fossa. Upon biopsy, the pathologic findings were consistent with an epithelioid malignancy with melanocytic differentiation most consistent with a PEComa. Discussion of the pathologic diagnosis of our patient has been reported by the pathology group at our institution in a separate case report.2
Our patient was initially offered and refused amputation. He was started on therapy with the mechanistic Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitor everolimus, but was unable to tolerate the side effects after the first week of treatment. He then elected to monitor his symptoms clinically.
Approximately one year after his initial diagnosis, he presented to our facility with sepsis and bleeding from a now fungating tumor on his right knee. At this time, emergent above-knee amputation was performed. Re-staging images now showed the presence of multiple pulmonary nodules in his right lung as well as a lytic rib lesion, a concerning finding for metastatic disease. Video-Assisted Thorascopic Surgery (VATS) and right lower lobe wedge resection were performed and findings confirmed metastatic PEComa.
Given the patient’s intolerance to everolimus, he was started on the growth factor inhibitor, pazopanib. His disease did not progress on pazopanib, and improvement was noted in the dominant pulmonary nodule. Subsequently, however, he developed significant skin irritation and discontinued pazopanib. Repeat imaging approximately 2 months after stopping pazopanib showed significant disease progression.
We elected to start the patient on a non-standard approach to therapy with nivolumab infusions once every 2 weeks and concurrent radiation therapy to the rib lesion. At 2 and 5 months after initiating this treatment approach, CT imaging showed improvement in disease. At 12 months, significant disease response was noted (Figure 1).
The patient is now at 12 months of nivolumab therapy with progression free survival and no new identifiable metastatic lesions. He has been tolerating the medication with minimal side effects and has had an overall improvement in his pain and functional status. He continues to work full time.
Discussion
Our patient’s response presents a unique opportunity to talk about the role of immunotherapy as a treatment modality in patients with PEComa. The efficacy of check-point blockade in soft tissue sarcoma is still unclear predominantly because it is difficult to assess the degree of expression of immunogenic cell surface markers such as programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1).1,3 Nivolumab has been tried in small cohorts for treatment of soft tissue sarcomas that express PD-1 and results showed some clinical benefit in about half of patients.4 Further, the expression of PD-1 has been assessed in soft tissue sarcomas and has been reported to suggest a negative prognostic role.5
To our knowledge, there has not yet been another reported case of PEComa that has been treated with immunotherapy and achieved a sustained response. Further clinical studies need to be done to assess response to agents such as nivolumab in the treatment of PEComa to bolster our observation that nivolumab is a viable treatment option that may lead to lasting remission. Our patient’s case also brings to light the need for further inquiry into assessing the immune tumor microenvironments, particularly looking at the expression of cell surface proteins such as PD-1, as it ultimately affects treatment options. TSJ
Correspondence
REFERENCES
1. Burgess, Melissa, et al. “Immunotherapy in Sarcoma: Future Horizons.” Current Oncology Reports, vol. 17, no. 11, 2015, doi:10.1007/s11912-015-0476-7.
2. Alnajar, Hussein, et al. “Metastatic Malignant PEComa of the Leg with Identification of ATRX Mutation by next-Generation Sequencing.” Virchows Archiv (2017). https://doi:10.1007/s004280172208-x.
3. Ghosn, Marwan, et al. “Immunotherapies in Sarcoma: Updates and Future Perspectives.” World Journal of Clinical Oncology, vol. 8, no. 2, 2017, p. 145., doi:10.5306/wjco.v8.i2.145.
4. Paoluzzi, L., et al. “Response to Anti-PD1 Therapy with Nivolumab in Metastatic Sarcomas.” Clinical Sarcoma Research, vol. 6, no. 1, 2016, doi:10.1186/s13569-016 0064-0.
5. Kim, Chan, et al. “Prognostic Implications of PD-L1 Expression in Patients with Soft Tissue Sarcoma.” BMC Cancer, BioMed Central 8 July 2016.
Tumor lysis syndrome in an adolescent with recurrence of abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma: A case report and literature review
Introduction
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a life-threatening oncologic emergency that results when massive cell breakdown occurs either spontaneously or in response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. TLS is characterized by metabolic derangements, including hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia, secondary to the release of intracellular components into the systemic circulatory system. In addition, purine degradation can lead to hyperuricemia, and precipitation of calcium phosphate can result in hypocalcemia. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels are often elevated, especially in higher risk patients; however, this finding is not a specific marker for TLS.
TLS more commonly occurs in patients with rapidly proliferating hematological malignancies, such as acute leukemias with a high white blood cell count and Burkitt’s lymphoma, and is a relatively rare event in patients with solid malignancies.1-3 It is even more rare in patients with tumor recurrence.
There are few reported cases of TLS in children with solid malignancies. To our knowledge, only one case of TLS has previously been reported in a pediatric patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. We report the second such case, and what we believe to be the only reported case of TLS occurring in a pediatric patient with recurrence of a solid tumor.
Case Description
A 15-year-old male from Saudi Arabia presented to our hospital with confirmed stage IV abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma and lung metastases diagnosed in 2012. His initial treatment consisted of complete surgical resection, lung irradiation, and chemotherapy with intercalating cycles of ifosfamide/etoposide and vincristine/doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide, as per the COG-ARST0431 high-risk sarcoma protocol (NCT00354744). He completed treatment without any reported TLS in Saudi Arabia in June 2014. He had no residual tumor at the end of therapy, but six months later he was found to have an abdominal recurrence and started treatment with single-agent topotecan chemotherapy. He experienced worsening abdominal distention, pain, and difficulty voiding, prompting his family to seek further treatment options abroad.
The patient was admitted to our hospital in March 2015. Despite being severely malnourished, he was in stable condition. He was noted to have a markedly enlarged, firm, distended abdomen with dilated veins, abdominal and lower back pain, lower extremity pitting edema, and difficulty urinating.
Initial laboratory findings were unremarkable except for elevated levels of BUN (29 mg/dL), creatinine (1.69 mg/dL), and phosphorus (5.6 mg/dL). MRI revealed a large pelvic mass measuring 15.3 x 15.2 x 21.3 centimeters in transverse, anterior-posterior, and craniocaudal dimensions, respectively; with concomitant severe bilateral hydroureternephrosis (FIGURE 1).
FIGURE 1. Sagittal (A) and Axial (B) T2-weighted MR images of the pelvis (prior to initiating therapy) demonstrating a large heterogeneous mass occupying the entire pelvis. There is evidence of edema involving the soft tissues of the perineum (long arrow) and a large associated hydrocele (short arrow).
Three days following admission, the patient’s urine output decreased and his creatinine level rose rapidly. His worsening abdominal distention was attributed to growing tumor bulk and obstructive nephropathy. He required emergency placement of bilateral nephrostomy tubes. Urine output subsequently improved; although, serum creatinine remained persistently elevated.
Given his worsening condition, chemotherapy was begun three days after nephrostomy tube placement with vinorelbine, cyclophosphamide, and temsirolimus, as per COG-ARST0921 (NCT01222715), at renal-adjusted doses. Laboratory studies approximately 24 hours after chemotherapy initiation demonstrated the presence of TLS (TABLE 1). Potassium level was at the upper end of normal at 4.9 mmol/L, calcium level was decreased to 7.1 mg/dL, phosphorus level elevated to 12 mg/dL, uric acid level was markedly elevated to 19.5 mg/dL, and LDH elevated to 662 unit/L. A dose of 0.15 mg/kg of rasburicase was immediately given with a second dose repeated 14 hours later, after which the uric acid level decreased to less than 0.5 mg/dL. Sevelamer, sodium polystyrene, calcium carbonate, and magnesium gluconate were also administered to treat other electrolyte imbalances. The patient remained at clinical baseline throughout, and the TLS laboratory derangements normalized by three days after the TLS diagnosis; LDH level normalized after one week. The patient continued with chemotherapy, per protocol, with no further TLS-related complications. Over subsequent weeks, his tumor continued to shrink dramatically. Pain related to intra-abdominal compression, lower extremity edema, and difficulty voiding resolved.
Discussion
A literature search was performed using Pubmed/Medline and Scopus from 1950 to July 2016 using key words “TLS,” “tumor lysis syndrome,” “pediatric tumor lysis syndrome,” “tumor lysis syndrome in solid malignancies,” “recurrence,” “solid tumor,” “sarcoma,” “rhabdomyosarcoma,” and their combinations. The references of relevant articles were reviewed. Baeksgaard and Sorensen,3 and Vodopivec, et al4 provide an organized review of reported cases of TLS in solid tumors until 2002 and 2011 respectively; their articles are supported by the 2014 literature review by Mirrakhimov, et al.1 Excluding our case, 13 cases of TLS have been described in pediatric patients with solid tumors, with only one occurring in patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma5. Patients’ ages ranged from 2 days to 23 years; the cases are summarized in the following table (TABLE 2). To our knowledge, ours is the first case of TLS reported in association with a pediatric solid tumor recurrence.
It is important to note that the three reported cases of disseminated rhabdomyosarcoma6,7 were initially believed to be hematologic malignancies because of their presentation with lymphadenopathy, metastases to the bone marrow, and spontaneous onset of TLS. Rhabdomyosarcoma with bone marrow involvement without an obvious primary tumor is easily confused with acute leukemia, particularly of the lymphoblastic type.12 However, this disseminated-hematologic presentation of rhabdomyosarcoma differs from the solid abdominal-pelvic tumor, which we describe.
Cairo and Bishop13 categorize patients as either laboratory TLS, depicted by metabolic abnormalities alone, or clinical TLS, occurring when laboratory imbalances lead to significant, life-threatening clinical manifestations. Hyperkalemia may lead to cardiac arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes and cardiac arrest. Obstructive nephropathy can occur from the precipitation of calcium phosphate or uric acid crystals in the renal tubules. Hypocalcemia may cause neuromuscular irritability including tetany, convulsions, and altered mental status.13, 14The 2015 “Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology”4 state there are well-recognized risk factors for the development of TLS including, but not limited to, high tumor burden, tumors with rapid cell turnover, and pre-existing renal impairment. Cairo and Bishop, on behalf of the TLS expert panel consensus of 20102, classify patients as having low-risk disease (LRD), intermediate-risk disease (IRD), or high-risk disease (HRD) based on the risk factors and type of malignancy. All patients with solid tumors are classified into LRD, unless the tumors are bulky or sensitive to chemotherapy, mentioning specifically that neuroblastomas, germ-cell tumors and small cell lung cancers are classified as IRD. Cairo and Bishop take into account the risk factor of renal dysfunction/ involvement, which if present, increases the risk by one level. For example, if the patient has IRD and has renal dysfunction, risk increases to HRD2. However, these guidelines do not mention or address the significance of recurrence in any kind of malignancy with regards to assessing risk for TLS.
The British Committee’s 2015 Guidelines for management of TLS in hematologic malignancies14 provide recommendations for treatment based on the patient’s risk classification (TABLE 3). Children with HRD are recommended to be treated prophylactically with a single dose of 0.2 mg/kg of rasburicase. Patients with IRD are recommended to be offered up to 7 days of allopurinol prophylaxis with increased hydration post initiation of treatment or until risk of TLS has resolved. Patients with LRD are recommended to be managed essentially with close observation. Patients with established TLS should receive rasburicase 0.2 mg/kg/day - duration to depend on clinical response. If the patient is receiving rasburicase, the addition of allopurinol is not recommended, as it has the potential to reduce the effectiveness of rasburicase. Further, rasburicase is to be avoided in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency14.
Our patient likely developed TLS because of a fast growing tumor that caused significant tumor burden and renal involvement, indicated by an elevated phosphorus level. Despite these risk factors, TLS was not anticipated in the case presented; therefore, a uric acid level was not collected at the time of admission. Review of the literature indicates that the incidence of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence is either unheard of, or is likely under-reported and truly unknown. Further, the TLS expert panel consensus of 20102, which provides guidelines on risk assessment for TLS, does not address the risk of TLS in a malignancy recurrence. The British Committee’s 2015 guidelines14 also do not address hyperuricemia prophylaxis in a solid tumor recurrence.
Our case presents a question regarding the degree of risk for the development of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence. If the guidelines had existed at the time of the case presentation and had been applied, our patient would likely be classified as having IRD because of his renal involvement. This classification would have lead to a different course of management when initiating chemotherapy, likely prevented laboratory TLS, and provided more cost effective treatment, as rasburicase is known to be expensive.
On the other hand, it can also be argued that our patient classifies as LRD, considering the rarity of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence, that the patient had no TLS complication with his initial course of therapy, and also had a normal LDH on admission. LDH is sometimes used to assess risk in hematological malignancies, although it is not used to make the diagnosis of TLS2. However, with such an argument, it is assumed that the risk of TLS in a solid tumor malignancy recurrence, with no previous TLS complication, is less than the risk associated with a new-onset solid tumor malignancy when, truly, the actual risk is not known. Again, the question is raised of the degree of risk for the development of TLS in a case of a malignancy recurrence, and also in a pediatric patient with risk factors.
In our patient’s case, close observation allowed for prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment of laboratory TLS, and prevented clinical symptoms from developing. However, a screening or baseline uric acid level may have lead to a more conservative approach towards hyperuricemia prophylaxis, similar to treating the patient as IRD. Therefore, we recommend that a screening or baseline uric acid level and LDH level be obtained when initiating chemotherapy, even in patients with LRD.
Our patient was never hyperkalemic, likely because of concomitant administration of furosemide in an attempt to improve his decreased urine output. Hyperuricemia dropped from 19.5 mg/dL to less than 0.5 mg/dL within 24 hours, following two doses of 0.15 mg/kg of rasburicase, confirming the efficacy of this therapy in cases of established TLS, as is recommended by the British Committee’s 2015 guidelines.14
Conclusion
TLS is a relatively rare event in patients with solid malignancies and even more rare in a tumor recurrence. While there is only one previously reported case of TLS occurring in a pediatric patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma, there are not any reported cases to date of TLS occurring in pediatric solid tumor recurrence. This may be because the incidence is truly rare or because cases may be under-reported. Thus, a question is raised regarding the risk for TLS in a solid tumor recurrence, and moreover in a pediatric patient with pre-existing risk factors, such as renal involvement.
TLS remains a life-threatening emergency that can be prevented and reversed if a high index of suspicion is maintained. We recommend all patients with malignancies receiving chemotherapy, especially those with risk factors, have a baseline or screening uric acid and LDH level drawn, as part of the assessment and risk-stratification for TLS which should always be performed. TSJ
Correspondence
References
1. Mirrakhimov AE, Ali AM, Khan M, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors: an up to date review of the literature. Rare Tumors. 2014;6:68-74.
2. Cairo MS, Bertrand C, Reiter A, et al. Recommendation for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149:578-586.
3. Baeksgaard L, Sorensen JB. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors – a case report and review of the literature. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:187-192.
4. Vodopivec D, Rubio J, Fornoni A, et al. An unusual presentation of tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:1-12.
5. Khan J, Broadbent VA. Tumor lysis syndrome complicating treatment of widespread metastatic abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;10:151-155.
6. Bien E, Maciejka-Kapuscinka L, Niedzwiecki M, et al. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma metastatic to bone marrow presenting with disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute tumour lysis syndrome: review of the literature apropos of two cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:399-407.
7. Patiroglu T, Isik B, Unal E, et al. Cranial metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mimicking hematological malignancy in an adolescent boy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:1737-1741.
8. Hain RD, Rayner L, Weitzman S, et al. Acute tumour lysis syndrome complicating treatment of stage IVS neuroblastoma in infants under six months old. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23:136-139.
9. Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Modak S, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome, neuroblastoma, and correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and MYCN-amplification. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;41:80-82.
10. Bercovitz RS, Greffe BS, Hunger SP. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in a 7-month-old with hepatoblastoma. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:113-116.
11. Lobe TE, Karkera MS, Custer MD, et al. Fatal refractory hyperkalemia due to tumor lysis during primary resection for hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:249-250.
12. Sandberg A, Stone J, Czarnecki L, et al. Hematologic Masquerade of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol. 2001;68:51-57
13. Cairo M, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:3-11.
14. Jones G, Will A, Jackson GH, et al. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:661-671.
References
1. Mirrakhimov AE, Ali AM, Khan M, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors: an up to date review of the literature. Rare Tumors. 2014;6:68-74.
2. Cairo MS, Bertrand C, Reiter A, et al. Recommendation for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149:578-586.
3. Baeksgaard L, Sorensen JB. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors – a case report and review of the literature. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:187-192.
4. Vodopivec D, Rubio J, Fornoni A, et al. An unusual presentation of tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:1-12.
5. Khan J, Broadbent VA. Tumor lysis syndrome complicating treatment of widespread metastatic abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;10:151-155.
6. Bien E, Maciejka-Kapuscinka L, Niedzwiecki M, et al. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma metastatic to bone marrow presenting with disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute tumour lysis syndrome: review of the literature apropos of two cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:399-407.
7. Patiroglu T, Isik B, Unal E, et al. Cranial metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mimicking hematological malignancy in an adolescent boy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:1737-1741.
8. Hain RD, Rayner L, Weitzman S, et al. Acute tumour lysis syndrome complicating treatment of stage IVS neuroblastoma in infants under six months old. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23:136-139.
9. Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Modak S, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome, neuroblastoma, and correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and MYCN-amplification. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;41:80-82.
10. Bercovitz RS, Greffe BS, Hunger SP. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in a 7-month-old with hepatoblastoma. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:113-116.
11. Lobe TE, Karkera MS, Custer MD, et al. Fatal refractory hyperkalemia due to tumor lysis during primary resection for hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:249-250.
12. Sandberg A, Stone J, Czarnecki L, et al. Hematologic Masquerade of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol. 2001;68:51-57
13. Cairo M, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:3-11.
14. Jones G, Will A, Jackson GH, et al. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:661-671.
Introduction
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a life-threatening oncologic emergency that results when massive cell breakdown occurs either spontaneously or in response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. TLS is characterized by metabolic derangements, including hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia, secondary to the release of intracellular components into the systemic circulatory system. In addition, purine degradation can lead to hyperuricemia, and precipitation of calcium phosphate can result in hypocalcemia. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels are often elevated, especially in higher risk patients; however, this finding is not a specific marker for TLS.
TLS more commonly occurs in patients with rapidly proliferating hematological malignancies, such as acute leukemias with a high white blood cell count and Burkitt’s lymphoma, and is a relatively rare event in patients with solid malignancies.1-3 It is even more rare in patients with tumor recurrence.
There are few reported cases of TLS in children with solid malignancies. To our knowledge, only one case of TLS has previously been reported in a pediatric patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. We report the second such case, and what we believe to be the only reported case of TLS occurring in a pediatric patient with recurrence of a solid tumor.
Case Description
A 15-year-old male from Saudi Arabia presented to our hospital with confirmed stage IV abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma and lung metastases diagnosed in 2012. His initial treatment consisted of complete surgical resection, lung irradiation, and chemotherapy with intercalating cycles of ifosfamide/etoposide and vincristine/doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide, as per the COG-ARST0431 high-risk sarcoma protocol (NCT00354744). He completed treatment without any reported TLS in Saudi Arabia in June 2014. He had no residual tumor at the end of therapy, but six months later he was found to have an abdominal recurrence and started treatment with single-agent topotecan chemotherapy. He experienced worsening abdominal distention, pain, and difficulty voiding, prompting his family to seek further treatment options abroad.
The patient was admitted to our hospital in March 2015. Despite being severely malnourished, he was in stable condition. He was noted to have a markedly enlarged, firm, distended abdomen with dilated veins, abdominal and lower back pain, lower extremity pitting edema, and difficulty urinating.
Initial laboratory findings were unremarkable except for elevated levels of BUN (29 mg/dL), creatinine (1.69 mg/dL), and phosphorus (5.6 mg/dL). MRI revealed a large pelvic mass measuring 15.3 x 15.2 x 21.3 centimeters in transverse, anterior-posterior, and craniocaudal dimensions, respectively; with concomitant severe bilateral hydroureternephrosis (FIGURE 1).
FIGURE 1. Sagittal (A) and Axial (B) T2-weighted MR images of the pelvis (prior to initiating therapy) demonstrating a large heterogeneous mass occupying the entire pelvis. There is evidence of edema involving the soft tissues of the perineum (long arrow) and a large associated hydrocele (short arrow).
Three days following admission, the patient’s urine output decreased and his creatinine level rose rapidly. His worsening abdominal distention was attributed to growing tumor bulk and obstructive nephropathy. He required emergency placement of bilateral nephrostomy tubes. Urine output subsequently improved; although, serum creatinine remained persistently elevated.
Given his worsening condition, chemotherapy was begun three days after nephrostomy tube placement with vinorelbine, cyclophosphamide, and temsirolimus, as per COG-ARST0921 (NCT01222715), at renal-adjusted doses. Laboratory studies approximately 24 hours after chemotherapy initiation demonstrated the presence of TLS (TABLE 1). Potassium level was at the upper end of normal at 4.9 mmol/L, calcium level was decreased to 7.1 mg/dL, phosphorus level elevated to 12 mg/dL, uric acid level was markedly elevated to 19.5 mg/dL, and LDH elevated to 662 unit/L. A dose of 0.15 mg/kg of rasburicase was immediately given with a second dose repeated 14 hours later, after which the uric acid level decreased to less than 0.5 mg/dL. Sevelamer, sodium polystyrene, calcium carbonate, and magnesium gluconate were also administered to treat other electrolyte imbalances. The patient remained at clinical baseline throughout, and the TLS laboratory derangements normalized by three days after the TLS diagnosis; LDH level normalized after one week. The patient continued with chemotherapy, per protocol, with no further TLS-related complications. Over subsequent weeks, his tumor continued to shrink dramatically. Pain related to intra-abdominal compression, lower extremity edema, and difficulty voiding resolved.
Discussion
A literature search was performed using Pubmed/Medline and Scopus from 1950 to July 2016 using key words “TLS,” “tumor lysis syndrome,” “pediatric tumor lysis syndrome,” “tumor lysis syndrome in solid malignancies,” “recurrence,” “solid tumor,” “sarcoma,” “rhabdomyosarcoma,” and their combinations. The references of relevant articles were reviewed. Baeksgaard and Sorensen,3 and Vodopivec, et al4 provide an organized review of reported cases of TLS in solid tumors until 2002 and 2011 respectively; their articles are supported by the 2014 literature review by Mirrakhimov, et al.1 Excluding our case, 13 cases of TLS have been described in pediatric patients with solid tumors, with only one occurring in patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma5. Patients’ ages ranged from 2 days to 23 years; the cases are summarized in the following table (TABLE 2). To our knowledge, ours is the first case of TLS reported in association with a pediatric solid tumor recurrence.
It is important to note that the three reported cases of disseminated rhabdomyosarcoma6,7 were initially believed to be hematologic malignancies because of their presentation with lymphadenopathy, metastases to the bone marrow, and spontaneous onset of TLS. Rhabdomyosarcoma with bone marrow involvement without an obvious primary tumor is easily confused with acute leukemia, particularly of the lymphoblastic type.12 However, this disseminated-hematologic presentation of rhabdomyosarcoma differs from the solid abdominal-pelvic tumor, which we describe.
Cairo and Bishop13 categorize patients as either laboratory TLS, depicted by metabolic abnormalities alone, or clinical TLS, occurring when laboratory imbalances lead to significant, life-threatening clinical manifestations. Hyperkalemia may lead to cardiac arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes and cardiac arrest. Obstructive nephropathy can occur from the precipitation of calcium phosphate or uric acid crystals in the renal tubules. Hypocalcemia may cause neuromuscular irritability including tetany, convulsions, and altered mental status.13, 14The 2015 “Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology”4 state there are well-recognized risk factors for the development of TLS including, but not limited to, high tumor burden, tumors with rapid cell turnover, and pre-existing renal impairment. Cairo and Bishop, on behalf of the TLS expert panel consensus of 20102, classify patients as having low-risk disease (LRD), intermediate-risk disease (IRD), or high-risk disease (HRD) based on the risk factors and type of malignancy. All patients with solid tumors are classified into LRD, unless the tumors are bulky or sensitive to chemotherapy, mentioning specifically that neuroblastomas, germ-cell tumors and small cell lung cancers are classified as IRD. Cairo and Bishop take into account the risk factor of renal dysfunction/ involvement, which if present, increases the risk by one level. For example, if the patient has IRD and has renal dysfunction, risk increases to HRD2. However, these guidelines do not mention or address the significance of recurrence in any kind of malignancy with regards to assessing risk for TLS.
The British Committee’s 2015 Guidelines for management of TLS in hematologic malignancies14 provide recommendations for treatment based on the patient’s risk classification (TABLE 3). Children with HRD are recommended to be treated prophylactically with a single dose of 0.2 mg/kg of rasburicase. Patients with IRD are recommended to be offered up to 7 days of allopurinol prophylaxis with increased hydration post initiation of treatment or until risk of TLS has resolved. Patients with LRD are recommended to be managed essentially with close observation. Patients with established TLS should receive rasburicase 0.2 mg/kg/day - duration to depend on clinical response. If the patient is receiving rasburicase, the addition of allopurinol is not recommended, as it has the potential to reduce the effectiveness of rasburicase. Further, rasburicase is to be avoided in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency14.
Our patient likely developed TLS because of a fast growing tumor that caused significant tumor burden and renal involvement, indicated by an elevated phosphorus level. Despite these risk factors, TLS was not anticipated in the case presented; therefore, a uric acid level was not collected at the time of admission. Review of the literature indicates that the incidence of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence is either unheard of, or is likely under-reported and truly unknown. Further, the TLS expert panel consensus of 20102, which provides guidelines on risk assessment for TLS, does not address the risk of TLS in a malignancy recurrence. The British Committee’s 2015 guidelines14 also do not address hyperuricemia prophylaxis in a solid tumor recurrence.
Our case presents a question regarding the degree of risk for the development of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence. If the guidelines had existed at the time of the case presentation and had been applied, our patient would likely be classified as having IRD because of his renal involvement. This classification would have lead to a different course of management when initiating chemotherapy, likely prevented laboratory TLS, and provided more cost effective treatment, as rasburicase is known to be expensive.
On the other hand, it can also be argued that our patient classifies as LRD, considering the rarity of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence, that the patient had no TLS complication with his initial course of therapy, and also had a normal LDH on admission. LDH is sometimes used to assess risk in hematological malignancies, although it is not used to make the diagnosis of TLS2. However, with such an argument, it is assumed that the risk of TLS in a solid tumor malignancy recurrence, with no previous TLS complication, is less than the risk associated with a new-onset solid tumor malignancy when, truly, the actual risk is not known. Again, the question is raised of the degree of risk for the development of TLS in a case of a malignancy recurrence, and also in a pediatric patient with risk factors.
In our patient’s case, close observation allowed for prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment of laboratory TLS, and prevented clinical symptoms from developing. However, a screening or baseline uric acid level may have lead to a more conservative approach towards hyperuricemia prophylaxis, similar to treating the patient as IRD. Therefore, we recommend that a screening or baseline uric acid level and LDH level be obtained when initiating chemotherapy, even in patients with LRD.
Our patient was never hyperkalemic, likely because of concomitant administration of furosemide in an attempt to improve his decreased urine output. Hyperuricemia dropped from 19.5 mg/dL to less than 0.5 mg/dL within 24 hours, following two doses of 0.15 mg/kg of rasburicase, confirming the efficacy of this therapy in cases of established TLS, as is recommended by the British Committee’s 2015 guidelines.14
Conclusion
TLS is a relatively rare event in patients with solid malignancies and even more rare in a tumor recurrence. While there is only one previously reported case of TLS occurring in a pediatric patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma, there are not any reported cases to date of TLS occurring in pediatric solid tumor recurrence. This may be because the incidence is truly rare or because cases may be under-reported. Thus, a question is raised regarding the risk for TLS in a solid tumor recurrence, and moreover in a pediatric patient with pre-existing risk factors, such as renal involvement.
TLS remains a life-threatening emergency that can be prevented and reversed if a high index of suspicion is maintained. We recommend all patients with malignancies receiving chemotherapy, especially those with risk factors, have a baseline or screening uric acid and LDH level drawn, as part of the assessment and risk-stratification for TLS which should always be performed. TSJ
Correspondence
References
1. Mirrakhimov AE, Ali AM, Khan M, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors: an up to date review of the literature. Rare Tumors. 2014;6:68-74.
2. Cairo MS, Bertrand C, Reiter A, et al. Recommendation for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149:578-586.
3. Baeksgaard L, Sorensen JB. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors – a case report and review of the literature. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:187-192.
4. Vodopivec D, Rubio J, Fornoni A, et al. An unusual presentation of tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:1-12.
5. Khan J, Broadbent VA. Tumor lysis syndrome complicating treatment of widespread metastatic abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;10:151-155.
6. Bien E, Maciejka-Kapuscinka L, Niedzwiecki M, et al. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma metastatic to bone marrow presenting with disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute tumour lysis syndrome: review of the literature apropos of two cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:399-407.
7. Patiroglu T, Isik B, Unal E, et al. Cranial metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mimicking hematological malignancy in an adolescent boy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:1737-1741.
8. Hain RD, Rayner L, Weitzman S, et al. Acute tumour lysis syndrome complicating treatment of stage IVS neuroblastoma in infants under six months old. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23:136-139.
9. Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Modak S, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome, neuroblastoma, and correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and MYCN-amplification. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;41:80-82.
10. Bercovitz RS, Greffe BS, Hunger SP. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in a 7-month-old with hepatoblastoma. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:113-116.
11. Lobe TE, Karkera MS, Custer MD, et al. Fatal refractory hyperkalemia due to tumor lysis during primary resection for hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:249-250.
12. Sandberg A, Stone J, Czarnecki L, et al. Hematologic Masquerade of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol. 2001;68:51-57
13. Cairo M, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:3-11.
14. Jones G, Will A, Jackson GH, et al. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:661-671.
Introduction
Tumor lysis syndrome (TLS) is a life-threatening oncologic emergency that results when massive cell breakdown occurs either spontaneously or in response to cytotoxic chemotherapy. TLS is characterized by metabolic derangements, including hyperkalemia and hyperphosphatemia, secondary to the release of intracellular components into the systemic circulatory system. In addition, purine degradation can lead to hyperuricemia, and precipitation of calcium phosphate can result in hypocalcemia. Lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) levels are often elevated, especially in higher risk patients; however, this finding is not a specific marker for TLS.
TLS more commonly occurs in patients with rapidly proliferating hematological malignancies, such as acute leukemias with a high white blood cell count and Burkitt’s lymphoma, and is a relatively rare event in patients with solid malignancies.1-3 It is even more rare in patients with tumor recurrence.
There are few reported cases of TLS in children with solid malignancies. To our knowledge, only one case of TLS has previously been reported in a pediatric patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. We report the second such case, and what we believe to be the only reported case of TLS occurring in a pediatric patient with recurrence of a solid tumor.
Case Description
A 15-year-old male from Saudi Arabia presented to our hospital with confirmed stage IV abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma and lung metastases diagnosed in 2012. His initial treatment consisted of complete surgical resection, lung irradiation, and chemotherapy with intercalating cycles of ifosfamide/etoposide and vincristine/doxorubicin/cyclophosphamide, as per the COG-ARST0431 high-risk sarcoma protocol (NCT00354744). He completed treatment without any reported TLS in Saudi Arabia in June 2014. He had no residual tumor at the end of therapy, but six months later he was found to have an abdominal recurrence and started treatment with single-agent topotecan chemotherapy. He experienced worsening abdominal distention, pain, and difficulty voiding, prompting his family to seek further treatment options abroad.
The patient was admitted to our hospital in March 2015. Despite being severely malnourished, he was in stable condition. He was noted to have a markedly enlarged, firm, distended abdomen with dilated veins, abdominal and lower back pain, lower extremity pitting edema, and difficulty urinating.
Initial laboratory findings were unremarkable except for elevated levels of BUN (29 mg/dL), creatinine (1.69 mg/dL), and phosphorus (5.6 mg/dL). MRI revealed a large pelvic mass measuring 15.3 x 15.2 x 21.3 centimeters in transverse, anterior-posterior, and craniocaudal dimensions, respectively; with concomitant severe bilateral hydroureternephrosis (FIGURE 1).
FIGURE 1. Sagittal (A) and Axial (B) T2-weighted MR images of the pelvis (prior to initiating therapy) demonstrating a large heterogeneous mass occupying the entire pelvis. There is evidence of edema involving the soft tissues of the perineum (long arrow) and a large associated hydrocele (short arrow).
Three days following admission, the patient’s urine output decreased and his creatinine level rose rapidly. His worsening abdominal distention was attributed to growing tumor bulk and obstructive nephropathy. He required emergency placement of bilateral nephrostomy tubes. Urine output subsequently improved; although, serum creatinine remained persistently elevated.
Given his worsening condition, chemotherapy was begun three days after nephrostomy tube placement with vinorelbine, cyclophosphamide, and temsirolimus, as per COG-ARST0921 (NCT01222715), at renal-adjusted doses. Laboratory studies approximately 24 hours after chemotherapy initiation demonstrated the presence of TLS (TABLE 1). Potassium level was at the upper end of normal at 4.9 mmol/L, calcium level was decreased to 7.1 mg/dL, phosphorus level elevated to 12 mg/dL, uric acid level was markedly elevated to 19.5 mg/dL, and LDH elevated to 662 unit/L. A dose of 0.15 mg/kg of rasburicase was immediately given with a second dose repeated 14 hours later, after which the uric acid level decreased to less than 0.5 mg/dL. Sevelamer, sodium polystyrene, calcium carbonate, and magnesium gluconate were also administered to treat other electrolyte imbalances. The patient remained at clinical baseline throughout, and the TLS laboratory derangements normalized by three days after the TLS diagnosis; LDH level normalized after one week. The patient continued with chemotherapy, per protocol, with no further TLS-related complications. Over subsequent weeks, his tumor continued to shrink dramatically. Pain related to intra-abdominal compression, lower extremity edema, and difficulty voiding resolved.
Discussion
A literature search was performed using Pubmed/Medline and Scopus from 1950 to July 2016 using key words “TLS,” “tumor lysis syndrome,” “pediatric tumor lysis syndrome,” “tumor lysis syndrome in solid malignancies,” “recurrence,” “solid tumor,” “sarcoma,” “rhabdomyosarcoma,” and their combinations. The references of relevant articles were reviewed. Baeksgaard and Sorensen,3 and Vodopivec, et al4 provide an organized review of reported cases of TLS in solid tumors until 2002 and 2011 respectively; their articles are supported by the 2014 literature review by Mirrakhimov, et al.1 Excluding our case, 13 cases of TLS have been described in pediatric patients with solid tumors, with only one occurring in patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma5. Patients’ ages ranged from 2 days to 23 years; the cases are summarized in the following table (TABLE 2). To our knowledge, ours is the first case of TLS reported in association with a pediatric solid tumor recurrence.
It is important to note that the three reported cases of disseminated rhabdomyosarcoma6,7 were initially believed to be hematologic malignancies because of their presentation with lymphadenopathy, metastases to the bone marrow, and spontaneous onset of TLS. Rhabdomyosarcoma with bone marrow involvement without an obvious primary tumor is easily confused with acute leukemia, particularly of the lymphoblastic type.12 However, this disseminated-hematologic presentation of rhabdomyosarcoma differs from the solid abdominal-pelvic tumor, which we describe.
Cairo and Bishop13 categorize patients as either laboratory TLS, depicted by metabolic abnormalities alone, or clinical TLS, occurring when laboratory imbalances lead to significant, life-threatening clinical manifestations. Hyperkalemia may lead to cardiac arrhythmias such as torsades de pointes and cardiac arrest. Obstructive nephropathy can occur from the precipitation of calcium phosphate or uric acid crystals in the renal tubules. Hypocalcemia may cause neuromuscular irritability including tetany, convulsions, and altered mental status.13, 14The 2015 “Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology”4 state there are well-recognized risk factors for the development of TLS including, but not limited to, high tumor burden, tumors with rapid cell turnover, and pre-existing renal impairment. Cairo and Bishop, on behalf of the TLS expert panel consensus of 20102, classify patients as having low-risk disease (LRD), intermediate-risk disease (IRD), or high-risk disease (HRD) based on the risk factors and type of malignancy. All patients with solid tumors are classified into LRD, unless the tumors are bulky or sensitive to chemotherapy, mentioning specifically that neuroblastomas, germ-cell tumors and small cell lung cancers are classified as IRD. Cairo and Bishop take into account the risk factor of renal dysfunction/ involvement, which if present, increases the risk by one level. For example, if the patient has IRD and has renal dysfunction, risk increases to HRD2. However, these guidelines do not mention or address the significance of recurrence in any kind of malignancy with regards to assessing risk for TLS.
The British Committee’s 2015 Guidelines for management of TLS in hematologic malignancies14 provide recommendations for treatment based on the patient’s risk classification (TABLE 3). Children with HRD are recommended to be treated prophylactically with a single dose of 0.2 mg/kg of rasburicase. Patients with IRD are recommended to be offered up to 7 days of allopurinol prophylaxis with increased hydration post initiation of treatment or until risk of TLS has resolved. Patients with LRD are recommended to be managed essentially with close observation. Patients with established TLS should receive rasburicase 0.2 mg/kg/day - duration to depend on clinical response. If the patient is receiving rasburicase, the addition of allopurinol is not recommended, as it has the potential to reduce the effectiveness of rasburicase. Further, rasburicase is to be avoided in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency14.
Our patient likely developed TLS because of a fast growing tumor that caused significant tumor burden and renal involvement, indicated by an elevated phosphorus level. Despite these risk factors, TLS was not anticipated in the case presented; therefore, a uric acid level was not collected at the time of admission. Review of the literature indicates that the incidence of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence is either unheard of, or is likely under-reported and truly unknown. Further, the TLS expert panel consensus of 20102, which provides guidelines on risk assessment for TLS, does not address the risk of TLS in a malignancy recurrence. The British Committee’s 2015 guidelines14 also do not address hyperuricemia prophylaxis in a solid tumor recurrence.
Our case presents a question regarding the degree of risk for the development of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence. If the guidelines had existed at the time of the case presentation and had been applied, our patient would likely be classified as having IRD because of his renal involvement. This classification would have lead to a different course of management when initiating chemotherapy, likely prevented laboratory TLS, and provided more cost effective treatment, as rasburicase is known to be expensive.
On the other hand, it can also be argued that our patient classifies as LRD, considering the rarity of TLS in a solid tumor recurrence, that the patient had no TLS complication with his initial course of therapy, and also had a normal LDH on admission. LDH is sometimes used to assess risk in hematological malignancies, although it is not used to make the diagnosis of TLS2. However, with such an argument, it is assumed that the risk of TLS in a solid tumor malignancy recurrence, with no previous TLS complication, is less than the risk associated with a new-onset solid tumor malignancy when, truly, the actual risk is not known. Again, the question is raised of the degree of risk for the development of TLS in a case of a malignancy recurrence, and also in a pediatric patient with risk factors.
In our patient’s case, close observation allowed for prompt diagnosis, appropriate treatment of laboratory TLS, and prevented clinical symptoms from developing. However, a screening or baseline uric acid level may have lead to a more conservative approach towards hyperuricemia prophylaxis, similar to treating the patient as IRD. Therefore, we recommend that a screening or baseline uric acid level and LDH level be obtained when initiating chemotherapy, even in patients with LRD.
Our patient was never hyperkalemic, likely because of concomitant administration of furosemide in an attempt to improve his decreased urine output. Hyperuricemia dropped from 19.5 mg/dL to less than 0.5 mg/dL within 24 hours, following two doses of 0.15 mg/kg of rasburicase, confirming the efficacy of this therapy in cases of established TLS, as is recommended by the British Committee’s 2015 guidelines.14
Conclusion
TLS is a relatively rare event in patients with solid malignancies and even more rare in a tumor recurrence. While there is only one previously reported case of TLS occurring in a pediatric patient with abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma, there are not any reported cases to date of TLS occurring in pediatric solid tumor recurrence. This may be because the incidence is truly rare or because cases may be under-reported. Thus, a question is raised regarding the risk for TLS in a solid tumor recurrence, and moreover in a pediatric patient with pre-existing risk factors, such as renal involvement.
TLS remains a life-threatening emergency that can be prevented and reversed if a high index of suspicion is maintained. We recommend all patients with malignancies receiving chemotherapy, especially those with risk factors, have a baseline or screening uric acid and LDH level drawn, as part of the assessment and risk-stratification for TLS which should always be performed. TSJ
Correspondence
References
1. Mirrakhimov AE, Ali AM, Khan M, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors: an up to date review of the literature. Rare Tumors. 2014;6:68-74.
2. Cairo MS, Bertrand C, Reiter A, et al. Recommendation for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149:578-586.
3. Baeksgaard L, Sorensen JB. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors – a case report and review of the literature. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:187-192.
4. Vodopivec D, Rubio J, Fornoni A, et al. An unusual presentation of tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:1-12.
5. Khan J, Broadbent VA. Tumor lysis syndrome complicating treatment of widespread metastatic abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;10:151-155.
6. Bien E, Maciejka-Kapuscinka L, Niedzwiecki M, et al. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma metastatic to bone marrow presenting with disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute tumour lysis syndrome: review of the literature apropos of two cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:399-407.
7. Patiroglu T, Isik B, Unal E, et al. Cranial metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mimicking hematological malignancy in an adolescent boy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:1737-1741.
8. Hain RD, Rayner L, Weitzman S, et al. Acute tumour lysis syndrome complicating treatment of stage IVS neuroblastoma in infants under six months old. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23:136-139.
9. Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Modak S, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome, neuroblastoma, and correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and MYCN-amplification. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;41:80-82.
10. Bercovitz RS, Greffe BS, Hunger SP. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in a 7-month-old with hepatoblastoma. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:113-116.
11. Lobe TE, Karkera MS, Custer MD, et al. Fatal refractory hyperkalemia due to tumor lysis during primary resection for hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:249-250.
12. Sandberg A, Stone J, Czarnecki L, et al. Hematologic Masquerade of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol. 2001;68:51-57
13. Cairo M, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:3-11.
14. Jones G, Will A, Jackson GH, et al. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:661-671.
References
1. Mirrakhimov AE, Ali AM, Khan M, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors: an up to date review of the literature. Rare Tumors. 2014;6:68-74.
2. Cairo MS, Bertrand C, Reiter A, et al. Recommendation for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149:578-586.
3. Baeksgaard L, Sorensen JB. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors – a case report and review of the literature. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:187-192.
4. Vodopivec D, Rubio J, Fornoni A, et al. An unusual presentation of tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:1-12.
5. Khan J, Broadbent VA. Tumor lysis syndrome complicating treatment of widespread metastatic abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;10:151-155.
6. Bien E, Maciejka-Kapuscinka L, Niedzwiecki M, et al. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma metastatic to bone marrow presenting with disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute tumour lysis syndrome: review of the literature apropos of two cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:399-407.
7. Patiroglu T, Isik B, Unal E, et al. Cranial metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mimicking hematological malignancy in an adolescent boy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:1737-1741.
8. Hain RD, Rayner L, Weitzman S, et al. Acute tumour lysis syndrome complicating treatment of stage IVS neuroblastoma in infants under six months old. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23:136-139.
9. Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Modak S, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome, neuroblastoma, and correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and MYCN-amplification. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;41:80-82.
10. Bercovitz RS, Greffe BS, Hunger SP. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in a 7-month-old with hepatoblastoma. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:113-116.
11. Lobe TE, Karkera MS, Custer MD, et al. Fatal refractory hyperkalemia due to tumor lysis during primary resection for hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:249-250.
12. Sandberg A, Stone J, Czarnecki L, et al. Hematologic Masquerade of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol. 2001;68:51-57
13. Cairo M, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:3-11.
14. Jones G, Will A, Jackson GH, et al. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:661-671.
References
1. Mirrakhimov AE, Ali AM, Khan M, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors: an up to date review of the literature. Rare Tumors. 2014;6:68-74.
2. Cairo MS, Bertrand C, Reiter A, et al. Recommendation for the evaluation of risk and prophylaxis of tumour lysis syndrome (TLS) in adults and children with malignant diseases: an expert TLS panel consensus. Br J Haematol. 2010;149:578-586.
3. Baeksgaard L, Sorensen JB. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in solid tumors – a case report and review of the literature. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2003;51:187-192.
4. Vodopivec D, Rubio J, Fornoni A, et al. An unusual presentation of tumor lysis syndrome in a patient with advanced gastric adenocarcinoma: case report and literature review. Case Rep Med. 2012;2012:1-12.
5. Khan J, Broadbent VA. Tumor lysis syndrome complicating treatment of widespread metastatic abdominal rhabdomyosarcoma. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 1993;10:151-155.
6. Bien E, Maciejka-Kapuscinka L, Niedzwiecki M, et al. Childhood rhabdomyosarcoma metastatic to bone marrow presenting with disseminated intravascular coagulation and acute tumour lysis syndrome: review of the literature apropos of two cases. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2010;27:399-407.
7. Patiroglu T, Isik B, Unal E, et al. Cranial metastatic alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma mimicking hematological malignancy in an adolescent boy. Childs Nerv Syst. 2014;30:1737-1741.
8. Hain RD, Rayner L, Weitzman S, et al. Acute tumour lysis syndrome complicating treatment of stage IVS neuroblastoma in infants under six months old. Med Pediatr Oncol. 1994;23:136-139.
9. Kushner BH, LaQuaglia MP, Modak S, et al. Tumor lysis syndrome, neuroblastoma, and correlation between serum lactate dehydrogenase levels and MYCN-amplification. Med Pediatr Oncol. 2003;41:80-82.
10. Bercovitz RS, Greffe BS, Hunger SP. Acute tumor lysis syndrome in a 7-month-old with hepatoblastoma. Curr Opin Pediatr. 2010;22:113-116.
11. Lobe TE, Karkera MS, Custer MD, et al. Fatal refractory hyperkalemia due to tumor lysis during primary resection for hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Surg. 1990;25:249-250.
12. Sandberg A, Stone J, Czarnecki L, et al. Hematologic Masquerade of Rhabdomyosarcoma. Am J Hematol. 2001;68:51-57
13. Cairo M, Bishop M. Tumour lysis syndrome: new therapeutic strategies and classification. Br J Haematol. 2004;127:3-11.
14. Jones G, Will A, Jackson GH, et al. Guidelines for the management of tumour lysis syndrome in adults and children with haematological malignancies on behalf of the British Committee for Standards in Haematology. Br J Haematol. 2015;169:661-671.
Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index in soft tissue sarcoma patients as a predictor of wound complications
Background The ability to predict a wound complication after radiation therapy and surgery for soft tissue sarcomas remains difficult. Preoperative nutritional status, as determined by Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index (OPNI), has been a predictor of complications in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. However, the role OPNI has in predicting wound complications for soft tissue sarcoma remains unknown.
Objective To evaluate the role OPNI has in predicting wound complication in patients treated with radiation and surgery for soft tissue sarcomas.
Methods OPNI was calculated based on the published formula OPNI = (10*albumin level [g/dL]) + (0.005*total lymphocyte count). The albumin level and total lymphocyte counts closest to the index operation were chosen. Major and minor wound complications were identified. A receiver operating curve was calculated to identify a cut-off point value for OPNI and for age based on the best combination of sensitivity and specificity.
Results 44 patients were included in the study. Patients with an OPNI of <45.4 had a 7.5-times increased risk of a wound complication (P = .005; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.8-31.0). An OPNI of <45.4 had a sensitivity of 62% and specificity of 82% of predicting a wound complication. Being older than 73 years was associated with a 6.8-times increased risk of wound complications (P = .01; 95% CI, 1.6-28.7).
Limitations Small sample size for patients with a rare condition
Conclusion An OPNI of <45.4 and being older than 73 years are strong predictors of which patients will have a wound complication after radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. Preoperative nutritional status could be an important modifiable factor to help decrease wound complications.
Wound complications after pre- or post-operative radiation for soft tissue sarcomas are well established.1 The ability to predict who will have a wound complication remains difficult. Some studies have looked at risk factors such as smoking, and the preoperative nutritional status of patients has been identified as a risk factor for wound complication in patients with elective orthopedic surgical procedures.2 One validated method of measuring preoperative nutritional status in patients with gastrointestinal malignant tumors has been with Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index (OPNI). It uses the patient’s preoperative albumin (g/dL) and absolute lymphocyte values (per mm3). The prognostic value of the OPNI has been demonstrated in patients with colorectal, esophageal, and gastric cancers, and has been shown to be prognostic for postoperative wound healing and overall prognosis.3-5 In this study, we investigate the significance of preoperative nutritional status, measured by OPNI, as a predictor of wound complications in patients treated with pre- or postoperative radiation for soft tissue sarcoma.
Methods
After receiving Institutional Review Board approval for the study, we conducted a retrospective review of consecutive patients treated during July 2012-April 2016 for a soft tissue sarcoma by the orthopedic oncology division at Cooper University Hospital in Camden, New Jersey. Inclusion criteria were patients with biopsy-proven soft tissue sarcoma, who were older than 18 years, had received pre- or postoperative radiation, and who had a recorded preoperative albumin and total lymphocyte count. A minimum follow-up of 3 months was required to assess for postoperative wound complications. Exclusion criteria included patients who had a bone sarcoma, had not received radiation therapy, or had a missing preoperative albumin or total lymphocyte count.
All of the surgeries were performed by 2 fellowshiptrained orthopedic oncologists. Patients received either pre- or postoperative radiation therapy by multiple radiation oncologists.
The OPNI was calculated based on the published formula OPNI = (10*albumin level [g/dL]) + (0.005*total lymphocyte count [per mm3]). The albumin level and total lymphocyte counts closest to the index operation were chosen.
Demographic information including gender, age at diagnosis, height, and weight were recorded. Data related to the patients’ pathologic diagnosis, stage at presentation, radiation therapy, and surgical resection were collected. A minor wound complication was defined as a wound problem that did not require operative intervention. Major wound complication was defined as a complication requiring operative intervention with or without flap reconstruction. Wound complications occurring within the 3-month postoperative period were considered.
Univariate and multiple variable analysis was performed. A P value <.05 was considered significant. A receiver operating curve as well as recursive partitioning was performed for OPNI and age to determine the best cut-off point to use in the analysis. The Sobel test was used to evaluate mediation. All statistical analysis was performed using SAS v9.4 and JMP10. (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Results
In all, 44 patients (28 men, 16 women) were included in the study. Their mean age was 61.2 years (range, 19-94). The average size of the tumors was 8.5 cm in greatest dimension (range, 1.2-27.4 cm), and all of the patients had nonmetastatic disease at the time of surgical resection; 37 patients had R0 resections, and 7 patients had a positive margin from an outside hospital, but obtained R0 resections on a subsequent resection (Table 1 and Table 2). In all, 30 patients received preoperative radiation, 14 patients received postoperative radiation, 32 patients received external beam radiation, 8 received Cyberknife treatment, and information for 4 patients was not unavailable. Mean preoperative external beam radiation and Cyberknife dose was 4,931 Gy and 3,750 Gy, respectively. Mean postoperative external beam and Cyberknife radiation dose was 6,077 Gy and 4,000 Gy, respectively. When evaluating radiation dose delivered between those who had wound complications and those who did not, there was no significant difference (Table 3).
Of the total, 13 patients had a wound complication (30%). Ten patients had preoperative radiation, and 3 had postoperative radiation. Ten patients had major wound complications requiring a combined 27 surgeries. Three patients had minor wound complications, which resolved with conservative management. One patient had a major wound complication in the group that had an initial R1 resection.
The OPNI was calculated based on the aforementioned formula. When the univariate analysis was performed, only age and OPNI were statistically significant. Patients older than 72.6 years had a 6.8 times higher risk of a wound complication (P = .01; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-28.7). When the OPNI value of 45.4 was used as the threshold, a patient with a preoperative OPNI value of <45.4 had a 7.5 times increased risk of developing a wound complication (P = .005; 95% CI, 1.8-31.0).
When the receiver operating curve and recursive partitioning was performed, an OPNI value of 45.4 showed a sensitivity of 62% and specificity of 82% in predicting wound complications (Figure 1).
When a multiple variable analysis was performed, OPNI and age were not statistically significant (P = .06 and P = .11, respectively). A test for mediation was performed, and the OPNI seemed to mediate the effect age has on wound complications, accounting for 36% of the total effect (Sobel test statistic, 1.79; P = .07).
Discussion
Wound complications after pre- and postoperative radiation for soft tissue sarcomas are well known. The best study to date to demonstrate that relationship was a randomized controlled trial performed in Canada, which showed that preoperative radiation resulted in 37% wound complications, compared with 17% for postoperative radiation.6 In that study, of the wound complications in both radiation types, more than 50%-60% required a secondary surgical procedure, designating it as a major wound complication. Other variables that have been shown to contribute to wound complications include being older than 40 years and/or having large tumors, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and begin a smoker.7-10
In our study, we applied OPNI to orthopedic oncology and showed that the patient’s age and preoperative nutritional status were significant predictors of developing a wound complication. An OPNI of <45.4 increased the chance of a wound complication by 7.5 times. Being older than 73 years increased the risk of a wound complication by 6.8 times. Most of these wound complications were major and required surgical intervention.
In general surgical oncology, the evaluation of nutritional status has had a significant impact on the care of patients, especially for those patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. The OPNI was initially designed to assess the nutritional and immunological statuses of patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery.11 Preoperative OPNI has been shown to be a good predictor of postoperative complications and survival in patients with colorectal cancer, malignant mesothelioma, hepatocellular carcinoma and in patients who undergo total gastrectomy.12-15 Chen and colleagues evaluated the significance of OPNI in patients with colorectal cancer. They found an optimal cut-off value of 45. An OPNI value <45 has a sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 69%, respectively, in predicting 5-year overall survival.16 Hong and colleagues noted that an OPNI cut-off value of 52.6 as a predictor of overall survival.17
Poor preoperative nutritional status has been shown to have a negative impact on wound healing. In patients who underwent emergency laparotomy, a low OPNI had significantly higher rates of wound dehiscence and infection.18 This happens because protein deficiency leads to decreased wound tensile strength, decreased T-cell function, decreased phagocytic activity, which ultimately diminish the patient’s ability to heal and defend against wound infections.19-21
In soft tissue sarcoma patients, poor preoperative nutritional status is further compromised by radiation therapy to the wound. Gu and colleagues showed that radiation to wounds in mice showed early inhibition of the inflammatory phase, injury and inhibition of fibroblasts, and collagen formation, and then prolonged re-epithelialization.22 This “double hit” with radiation onto host tissue that is already nutritionally compromised could be an important cause of why wound complications occur at such high rates in our soft tissue sarcoma patients.
There are several limitations to this study. First, the study has a small sample size, which was a direct result of the number of patients who were excluded because an OPNI value could not be calculated for them. Second, we could not determine if the OPNI was more valuable in patients who underwent pre- or postoperative radiation. This study did not look at other nutritional indices such as prealbumin and vitamin levels. Third, the radiation was provided by different providers, so technique was variable, but the patients received nearly equivalent doses and variability in technique is likely limited. Fourth, we were not able to meaningfully analyze the role of chemotherapy in this patient population because there was a significant heterogeneity of patients receiving pre- and postoperative chemotherapy.
Our findings strongly suggest that a preoperative OPNI of <45.4 and being older than 73 years are strong predictors of patients who will experience a wound complication after radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. This study has led us to start measuring preoperative albumin levels and assess complete metabolic panels. Our goal is to identify patients who are at high risk of wound complication and perform interventions to improve nutrition, then to study whether the interventions help lower the rates of wound complications. TSJ
Correspondence
References
1. Ormsby MV, Hilaris BS, Nori D, Brennan MF. Wound complications of adjuvant radiation therapy in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg. 1989;210(1):93-99.
2. Greene KA, Wilde AH, Stulberg BN. Preoperative nutritional status of total joint patients: relationship to postoperative wound complications. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6(4):321-325.
3. Nozoe T, Kimura Y, Ishida M, Saeki H, Korenaga D, Sugimachi K. Correlation of pre-operative nutritional condition with post-operative complications in surgical treatment for oesophageal carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(4):396-400.
4. Nozoe T, Kohno M, Iguchi T, et al. The prognostic nutritional index can be a prognostic indicator in colorectal carcinoma. Surg Today. 2012;42(6):532-535.
5. Nozoe T, Ninomiya M, Maeda T, Matsukuma A, Nakashima H, Ezaki T. Prognostic nutritional index: a tool to predict the biological aggressiveness of gastric carcinoma. Surg Today. 2010;40(5):440-443.
6. O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, Bell R, Catton C, Chabot P, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9325):2235-2241.
7. Peat BG, Bell RS, Davis A, et al. Wound-healing complications after soft-tissue sarcoma surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(5):980-987.
8. Kunisada T, Ngan SY, Powell G, Choong PF. Wound complications following pre-operative radiotherapy for soft tissue sarcoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(1):75-79.
9. Saddegh MK, Bauer HC. Wound complication in surgery of soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of 103 consecutive patients managed without adjuvant therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;289:247-253.
10. Tseng JF, Ballo MT, Langstein HN, et al. The effect of preoperative radiotherapy and reconstructive surgery on wound complications after resection of extremity soft-tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(9):1209-1215.
11. Smale BF, Mullen JL, Buzby GP, Rosato EF. The efficacy of nutritional assessment and support in cancer surgery. Cancer. 1981;47(10):2375-2381.
12. Mohri Y, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Hiro J, Uchida K, Kusunoki M. Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative outcome in colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2013;37(11):2688-2692.
13. Jiang N, Deng JY, Ding XW, et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative complications and long-term outcomes of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(30):10537-10544.
14. Pinato DJ, North BV, Sharma R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: the prognostic nutritional index (PNI). Brit J Cancer. 2012;106(8):1439-1445.
15. Yao ZH, Tian GY, Wan YY, et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(12):2117-2123.
16. Jian-Hui C, Iskandar EA, Cai Sh I, et al. Significance of Onodera’s prognostic nutritional index in patients with colorectal cancer: a large cohort study in a single Chinese institution. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):3277-3283.
17. Hong S, Zhou T, Fang W, et al. The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts overall survival of small-cell lung cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3389-9337.
18. Mohil RS, Agarwal A, Singh N, Arora J, Bhatnagar D. Does nutritional status play a role in patients undergoing emergency laparotomy? E Spen Eur E J Clin Nutr Metab. 2008;3(5):e226-e231.
19. Kay SP, Moreland JR, Schmitter E. Nutritional status and wound healing in lower extremity amputations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(217):253-256.
20. Dickhaut SC, DeLee JC, Page CP. Nutritional status: importance in predicting wound-healing after amputation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(1):71-75.
21. Casey J, Flinn WR, Yao JS, Fahey V, Pawlowski J, Bergan JJ. Correlation of immune and nutritional status with wound complications in patients undergoing vascular operations. Surgery. 1983;93(6):822-827.
22. Gu Q, Wang D, Cui C, Gao Y, Xia G, Cui X. Effects of radiation on wound healing. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1998;17(2):117-123.
Background The ability to predict a wound complication after radiation therapy and surgery for soft tissue sarcomas remains difficult. Preoperative nutritional status, as determined by Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index (OPNI), has been a predictor of complications in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. However, the role OPNI has in predicting wound complications for soft tissue sarcoma remains unknown.
Objective To evaluate the role OPNI has in predicting wound complication in patients treated with radiation and surgery for soft tissue sarcomas.
Methods OPNI was calculated based on the published formula OPNI = (10*albumin level [g/dL]) + (0.005*total lymphocyte count). The albumin level and total lymphocyte counts closest to the index operation were chosen. Major and minor wound complications were identified. A receiver operating curve was calculated to identify a cut-off point value for OPNI and for age based on the best combination of sensitivity and specificity.
Results 44 patients were included in the study. Patients with an OPNI of <45.4 had a 7.5-times increased risk of a wound complication (P = .005; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.8-31.0). An OPNI of <45.4 had a sensitivity of 62% and specificity of 82% of predicting a wound complication. Being older than 73 years was associated with a 6.8-times increased risk of wound complications (P = .01; 95% CI, 1.6-28.7).
Limitations Small sample size for patients with a rare condition
Conclusion An OPNI of <45.4 and being older than 73 years are strong predictors of which patients will have a wound complication after radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. Preoperative nutritional status could be an important modifiable factor to help decrease wound complications.
Wound complications after pre- or post-operative radiation for soft tissue sarcomas are well established.1 The ability to predict who will have a wound complication remains difficult. Some studies have looked at risk factors such as smoking, and the preoperative nutritional status of patients has been identified as a risk factor for wound complication in patients with elective orthopedic surgical procedures.2 One validated method of measuring preoperative nutritional status in patients with gastrointestinal malignant tumors has been with Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index (OPNI). It uses the patient’s preoperative albumin (g/dL) and absolute lymphocyte values (per mm3). The prognostic value of the OPNI has been demonstrated in patients with colorectal, esophageal, and gastric cancers, and has been shown to be prognostic for postoperative wound healing and overall prognosis.3-5 In this study, we investigate the significance of preoperative nutritional status, measured by OPNI, as a predictor of wound complications in patients treated with pre- or postoperative radiation for soft tissue sarcoma.
Methods
After receiving Institutional Review Board approval for the study, we conducted a retrospective review of consecutive patients treated during July 2012-April 2016 for a soft tissue sarcoma by the orthopedic oncology division at Cooper University Hospital in Camden, New Jersey. Inclusion criteria were patients with biopsy-proven soft tissue sarcoma, who were older than 18 years, had received pre- or postoperative radiation, and who had a recorded preoperative albumin and total lymphocyte count. A minimum follow-up of 3 months was required to assess for postoperative wound complications. Exclusion criteria included patients who had a bone sarcoma, had not received radiation therapy, or had a missing preoperative albumin or total lymphocyte count.
All of the surgeries were performed by 2 fellowshiptrained orthopedic oncologists. Patients received either pre- or postoperative radiation therapy by multiple radiation oncologists.
The OPNI was calculated based on the published formula OPNI = (10*albumin level [g/dL]) + (0.005*total lymphocyte count [per mm3]). The albumin level and total lymphocyte counts closest to the index operation were chosen.
Demographic information including gender, age at diagnosis, height, and weight were recorded. Data related to the patients’ pathologic diagnosis, stage at presentation, radiation therapy, and surgical resection were collected. A minor wound complication was defined as a wound problem that did not require operative intervention. Major wound complication was defined as a complication requiring operative intervention with or without flap reconstruction. Wound complications occurring within the 3-month postoperative period were considered.
Univariate and multiple variable analysis was performed. A P value <.05 was considered significant. A receiver operating curve as well as recursive partitioning was performed for OPNI and age to determine the best cut-off point to use in the analysis. The Sobel test was used to evaluate mediation. All statistical analysis was performed using SAS v9.4 and JMP10. (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Results
In all, 44 patients (28 men, 16 women) were included in the study. Their mean age was 61.2 years (range, 19-94). The average size of the tumors was 8.5 cm in greatest dimension (range, 1.2-27.4 cm), and all of the patients had nonmetastatic disease at the time of surgical resection; 37 patients had R0 resections, and 7 patients had a positive margin from an outside hospital, but obtained R0 resections on a subsequent resection (Table 1 and Table 2). In all, 30 patients received preoperative radiation, 14 patients received postoperative radiation, 32 patients received external beam radiation, 8 received Cyberknife treatment, and information for 4 patients was not unavailable. Mean preoperative external beam radiation and Cyberknife dose was 4,931 Gy and 3,750 Gy, respectively. Mean postoperative external beam and Cyberknife radiation dose was 6,077 Gy and 4,000 Gy, respectively. When evaluating radiation dose delivered between those who had wound complications and those who did not, there was no significant difference (Table 3).
Of the total, 13 patients had a wound complication (30%). Ten patients had preoperative radiation, and 3 had postoperative radiation. Ten patients had major wound complications requiring a combined 27 surgeries. Three patients had minor wound complications, which resolved with conservative management. One patient had a major wound complication in the group that had an initial R1 resection.
The OPNI was calculated based on the aforementioned formula. When the univariate analysis was performed, only age and OPNI were statistically significant. Patients older than 72.6 years had a 6.8 times higher risk of a wound complication (P = .01; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-28.7). When the OPNI value of 45.4 was used as the threshold, a patient with a preoperative OPNI value of <45.4 had a 7.5 times increased risk of developing a wound complication (P = .005; 95% CI, 1.8-31.0).
When the receiver operating curve and recursive partitioning was performed, an OPNI value of 45.4 showed a sensitivity of 62% and specificity of 82% in predicting wound complications (Figure 1).
When a multiple variable analysis was performed, OPNI and age were not statistically significant (P = .06 and P = .11, respectively). A test for mediation was performed, and the OPNI seemed to mediate the effect age has on wound complications, accounting for 36% of the total effect (Sobel test statistic, 1.79; P = .07).
Discussion
Wound complications after pre- and postoperative radiation for soft tissue sarcomas are well known. The best study to date to demonstrate that relationship was a randomized controlled trial performed in Canada, which showed that preoperative radiation resulted in 37% wound complications, compared with 17% for postoperative radiation.6 In that study, of the wound complications in both radiation types, more than 50%-60% required a secondary surgical procedure, designating it as a major wound complication. Other variables that have been shown to contribute to wound complications include being older than 40 years and/or having large tumors, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and begin a smoker.7-10
In our study, we applied OPNI to orthopedic oncology and showed that the patient’s age and preoperative nutritional status were significant predictors of developing a wound complication. An OPNI of <45.4 increased the chance of a wound complication by 7.5 times. Being older than 73 years increased the risk of a wound complication by 6.8 times. Most of these wound complications were major and required surgical intervention.
In general surgical oncology, the evaluation of nutritional status has had a significant impact on the care of patients, especially for those patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. The OPNI was initially designed to assess the nutritional and immunological statuses of patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery.11 Preoperative OPNI has been shown to be a good predictor of postoperative complications and survival in patients with colorectal cancer, malignant mesothelioma, hepatocellular carcinoma and in patients who undergo total gastrectomy.12-15 Chen and colleagues evaluated the significance of OPNI in patients with colorectal cancer. They found an optimal cut-off value of 45. An OPNI value <45 has a sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 69%, respectively, in predicting 5-year overall survival.16 Hong and colleagues noted that an OPNI cut-off value of 52.6 as a predictor of overall survival.17
Poor preoperative nutritional status has been shown to have a negative impact on wound healing. In patients who underwent emergency laparotomy, a low OPNI had significantly higher rates of wound dehiscence and infection.18 This happens because protein deficiency leads to decreased wound tensile strength, decreased T-cell function, decreased phagocytic activity, which ultimately diminish the patient’s ability to heal and defend against wound infections.19-21
In soft tissue sarcoma patients, poor preoperative nutritional status is further compromised by radiation therapy to the wound. Gu and colleagues showed that radiation to wounds in mice showed early inhibition of the inflammatory phase, injury and inhibition of fibroblasts, and collagen formation, and then prolonged re-epithelialization.22 This “double hit” with radiation onto host tissue that is already nutritionally compromised could be an important cause of why wound complications occur at such high rates in our soft tissue sarcoma patients.
There are several limitations to this study. First, the study has a small sample size, which was a direct result of the number of patients who were excluded because an OPNI value could not be calculated for them. Second, we could not determine if the OPNI was more valuable in patients who underwent pre- or postoperative radiation. This study did not look at other nutritional indices such as prealbumin and vitamin levels. Third, the radiation was provided by different providers, so technique was variable, but the patients received nearly equivalent doses and variability in technique is likely limited. Fourth, we were not able to meaningfully analyze the role of chemotherapy in this patient population because there was a significant heterogeneity of patients receiving pre- and postoperative chemotherapy.
Our findings strongly suggest that a preoperative OPNI of <45.4 and being older than 73 years are strong predictors of patients who will experience a wound complication after radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. This study has led us to start measuring preoperative albumin levels and assess complete metabolic panels. Our goal is to identify patients who are at high risk of wound complication and perform interventions to improve nutrition, then to study whether the interventions help lower the rates of wound complications. TSJ
Correspondence
References
1. Ormsby MV, Hilaris BS, Nori D, Brennan MF. Wound complications of adjuvant radiation therapy in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg. 1989;210(1):93-99.
2. Greene KA, Wilde AH, Stulberg BN. Preoperative nutritional status of total joint patients: relationship to postoperative wound complications. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6(4):321-325.
3. Nozoe T, Kimura Y, Ishida M, Saeki H, Korenaga D, Sugimachi K. Correlation of pre-operative nutritional condition with post-operative complications in surgical treatment for oesophageal carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(4):396-400.
4. Nozoe T, Kohno M, Iguchi T, et al. The prognostic nutritional index can be a prognostic indicator in colorectal carcinoma. Surg Today. 2012;42(6):532-535.
5. Nozoe T, Ninomiya M, Maeda T, Matsukuma A, Nakashima H, Ezaki T. Prognostic nutritional index: a tool to predict the biological aggressiveness of gastric carcinoma. Surg Today. 2010;40(5):440-443.
6. O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, Bell R, Catton C, Chabot P, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9325):2235-2241.
7. Peat BG, Bell RS, Davis A, et al. Wound-healing complications after soft-tissue sarcoma surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(5):980-987.
8. Kunisada T, Ngan SY, Powell G, Choong PF. Wound complications following pre-operative radiotherapy for soft tissue sarcoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(1):75-79.
9. Saddegh MK, Bauer HC. Wound complication in surgery of soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of 103 consecutive patients managed without adjuvant therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;289:247-253.
10. Tseng JF, Ballo MT, Langstein HN, et al. The effect of preoperative radiotherapy and reconstructive surgery on wound complications after resection of extremity soft-tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(9):1209-1215.
11. Smale BF, Mullen JL, Buzby GP, Rosato EF. The efficacy of nutritional assessment and support in cancer surgery. Cancer. 1981;47(10):2375-2381.
12. Mohri Y, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Hiro J, Uchida K, Kusunoki M. Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative outcome in colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2013;37(11):2688-2692.
13. Jiang N, Deng JY, Ding XW, et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative complications and long-term outcomes of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(30):10537-10544.
14. Pinato DJ, North BV, Sharma R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: the prognostic nutritional index (PNI). Brit J Cancer. 2012;106(8):1439-1445.
15. Yao ZH, Tian GY, Wan YY, et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(12):2117-2123.
16. Jian-Hui C, Iskandar EA, Cai Sh I, et al. Significance of Onodera’s prognostic nutritional index in patients with colorectal cancer: a large cohort study in a single Chinese institution. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):3277-3283.
17. Hong S, Zhou T, Fang W, et al. The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts overall survival of small-cell lung cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3389-9337.
18. Mohil RS, Agarwal A, Singh N, Arora J, Bhatnagar D. Does nutritional status play a role in patients undergoing emergency laparotomy? E Spen Eur E J Clin Nutr Metab. 2008;3(5):e226-e231.
19. Kay SP, Moreland JR, Schmitter E. Nutritional status and wound healing in lower extremity amputations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(217):253-256.
20. Dickhaut SC, DeLee JC, Page CP. Nutritional status: importance in predicting wound-healing after amputation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(1):71-75.
21. Casey J, Flinn WR, Yao JS, Fahey V, Pawlowski J, Bergan JJ. Correlation of immune and nutritional status with wound complications in patients undergoing vascular operations. Surgery. 1983;93(6):822-827.
22. Gu Q, Wang D, Cui C, Gao Y, Xia G, Cui X. Effects of radiation on wound healing. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1998;17(2):117-123.
Background The ability to predict a wound complication after radiation therapy and surgery for soft tissue sarcomas remains difficult. Preoperative nutritional status, as determined by Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index (OPNI), has been a predictor of complications in patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. However, the role OPNI has in predicting wound complications for soft tissue sarcoma remains unknown.
Objective To evaluate the role OPNI has in predicting wound complication in patients treated with radiation and surgery for soft tissue sarcomas.
Methods OPNI was calculated based on the published formula OPNI = (10*albumin level [g/dL]) + (0.005*total lymphocyte count). The albumin level and total lymphocyte counts closest to the index operation were chosen. Major and minor wound complications were identified. A receiver operating curve was calculated to identify a cut-off point value for OPNI and for age based on the best combination of sensitivity and specificity.
Results 44 patients were included in the study. Patients with an OPNI of <45.4 had a 7.5-times increased risk of a wound complication (P = .005; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.8-31.0). An OPNI of <45.4 had a sensitivity of 62% and specificity of 82% of predicting a wound complication. Being older than 73 years was associated with a 6.8-times increased risk of wound complications (P = .01; 95% CI, 1.6-28.7).
Limitations Small sample size for patients with a rare condition
Conclusion An OPNI of <45.4 and being older than 73 years are strong predictors of which patients will have a wound complication after radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. Preoperative nutritional status could be an important modifiable factor to help decrease wound complications.
Wound complications after pre- or post-operative radiation for soft tissue sarcomas are well established.1 The ability to predict who will have a wound complication remains difficult. Some studies have looked at risk factors such as smoking, and the preoperative nutritional status of patients has been identified as a risk factor for wound complication in patients with elective orthopedic surgical procedures.2 One validated method of measuring preoperative nutritional status in patients with gastrointestinal malignant tumors has been with Onodera’s Prognostic Nutritional Index (OPNI). It uses the patient’s preoperative albumin (g/dL) and absolute lymphocyte values (per mm3). The prognostic value of the OPNI has been demonstrated in patients with colorectal, esophageal, and gastric cancers, and has been shown to be prognostic for postoperative wound healing and overall prognosis.3-5 In this study, we investigate the significance of preoperative nutritional status, measured by OPNI, as a predictor of wound complications in patients treated with pre- or postoperative radiation for soft tissue sarcoma.
Methods
After receiving Institutional Review Board approval for the study, we conducted a retrospective review of consecutive patients treated during July 2012-April 2016 for a soft tissue sarcoma by the orthopedic oncology division at Cooper University Hospital in Camden, New Jersey. Inclusion criteria were patients with biopsy-proven soft tissue sarcoma, who were older than 18 years, had received pre- or postoperative radiation, and who had a recorded preoperative albumin and total lymphocyte count. A minimum follow-up of 3 months was required to assess for postoperative wound complications. Exclusion criteria included patients who had a bone sarcoma, had not received radiation therapy, or had a missing preoperative albumin or total lymphocyte count.
All of the surgeries were performed by 2 fellowshiptrained orthopedic oncologists. Patients received either pre- or postoperative radiation therapy by multiple radiation oncologists.
The OPNI was calculated based on the published formula OPNI = (10*albumin level [g/dL]) + (0.005*total lymphocyte count [per mm3]). The albumin level and total lymphocyte counts closest to the index operation were chosen.
Demographic information including gender, age at diagnosis, height, and weight were recorded. Data related to the patients’ pathologic diagnosis, stage at presentation, radiation therapy, and surgical resection were collected. A minor wound complication was defined as a wound problem that did not require operative intervention. Major wound complication was defined as a complication requiring operative intervention with or without flap reconstruction. Wound complications occurring within the 3-month postoperative period were considered.
Univariate and multiple variable analysis was performed. A P value <.05 was considered significant. A receiver operating curve as well as recursive partitioning was performed for OPNI and age to determine the best cut-off point to use in the analysis. The Sobel test was used to evaluate mediation. All statistical analysis was performed using SAS v9.4 and JMP10. (SAS Institute, Cary, NC).
Results
In all, 44 patients (28 men, 16 women) were included in the study. Their mean age was 61.2 years (range, 19-94). The average size of the tumors was 8.5 cm in greatest dimension (range, 1.2-27.4 cm), and all of the patients had nonmetastatic disease at the time of surgical resection; 37 patients had R0 resections, and 7 patients had a positive margin from an outside hospital, but obtained R0 resections on a subsequent resection (Table 1 and Table 2). In all, 30 patients received preoperative radiation, 14 patients received postoperative radiation, 32 patients received external beam radiation, 8 received Cyberknife treatment, and information for 4 patients was not unavailable. Mean preoperative external beam radiation and Cyberknife dose was 4,931 Gy and 3,750 Gy, respectively. Mean postoperative external beam and Cyberknife radiation dose was 6,077 Gy and 4,000 Gy, respectively. When evaluating radiation dose delivered between those who had wound complications and those who did not, there was no significant difference (Table 3).
Of the total, 13 patients had a wound complication (30%). Ten patients had preoperative radiation, and 3 had postoperative radiation. Ten patients had major wound complications requiring a combined 27 surgeries. Three patients had minor wound complications, which resolved with conservative management. One patient had a major wound complication in the group that had an initial R1 resection.
The OPNI was calculated based on the aforementioned formula. When the univariate analysis was performed, only age and OPNI were statistically significant. Patients older than 72.6 years had a 6.8 times higher risk of a wound complication (P = .01; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.6-28.7). When the OPNI value of 45.4 was used as the threshold, a patient with a preoperative OPNI value of <45.4 had a 7.5 times increased risk of developing a wound complication (P = .005; 95% CI, 1.8-31.0).
When the receiver operating curve and recursive partitioning was performed, an OPNI value of 45.4 showed a sensitivity of 62% and specificity of 82% in predicting wound complications (Figure 1).
When a multiple variable analysis was performed, OPNI and age were not statistically significant (P = .06 and P = .11, respectively). A test for mediation was performed, and the OPNI seemed to mediate the effect age has on wound complications, accounting for 36% of the total effect (Sobel test statistic, 1.79; P = .07).
Discussion
Wound complications after pre- and postoperative radiation for soft tissue sarcomas are well known. The best study to date to demonstrate that relationship was a randomized controlled trial performed in Canada, which showed that preoperative radiation resulted in 37% wound complications, compared with 17% for postoperative radiation.6 In that study, of the wound complications in both radiation types, more than 50%-60% required a secondary surgical procedure, designating it as a major wound complication. Other variables that have been shown to contribute to wound complications include being older than 40 years and/or having large tumors, diabetes, peripheral vascular disease, and begin a smoker.7-10
In our study, we applied OPNI to orthopedic oncology and showed that the patient’s age and preoperative nutritional status were significant predictors of developing a wound complication. An OPNI of <45.4 increased the chance of a wound complication by 7.5 times. Being older than 73 years increased the risk of a wound complication by 6.8 times. Most of these wound complications were major and required surgical intervention.
In general surgical oncology, the evaluation of nutritional status has had a significant impact on the care of patients, especially for those patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery. The OPNI was initially designed to assess the nutritional and immunological statuses of patients undergoing gastrointestinal surgery.11 Preoperative OPNI has been shown to be a good predictor of postoperative complications and survival in patients with colorectal cancer, malignant mesothelioma, hepatocellular carcinoma and in patients who undergo total gastrectomy.12-15 Chen and colleagues evaluated the significance of OPNI in patients with colorectal cancer. They found an optimal cut-off value of 45. An OPNI value <45 has a sensitivity and specificity of 85% and 69%, respectively, in predicting 5-year overall survival.16 Hong and colleagues noted that an OPNI cut-off value of 52.6 as a predictor of overall survival.17
Poor preoperative nutritional status has been shown to have a negative impact on wound healing. In patients who underwent emergency laparotomy, a low OPNI had significantly higher rates of wound dehiscence and infection.18 This happens because protein deficiency leads to decreased wound tensile strength, decreased T-cell function, decreased phagocytic activity, which ultimately diminish the patient’s ability to heal and defend against wound infections.19-21
In soft tissue sarcoma patients, poor preoperative nutritional status is further compromised by radiation therapy to the wound. Gu and colleagues showed that radiation to wounds in mice showed early inhibition of the inflammatory phase, injury and inhibition of fibroblasts, and collagen formation, and then prolonged re-epithelialization.22 This “double hit” with radiation onto host tissue that is already nutritionally compromised could be an important cause of why wound complications occur at such high rates in our soft tissue sarcoma patients.
There are several limitations to this study. First, the study has a small sample size, which was a direct result of the number of patients who were excluded because an OPNI value could not be calculated for them. Second, we could not determine if the OPNI was more valuable in patients who underwent pre- or postoperative radiation. This study did not look at other nutritional indices such as prealbumin and vitamin levels. Third, the radiation was provided by different providers, so technique was variable, but the patients received nearly equivalent doses and variability in technique is likely limited. Fourth, we were not able to meaningfully analyze the role of chemotherapy in this patient population because there was a significant heterogeneity of patients receiving pre- and postoperative chemotherapy.
Our findings strongly suggest that a preoperative OPNI of <45.4 and being older than 73 years are strong predictors of patients who will experience a wound complication after radiation therapy for soft tissue sarcomas. This study has led us to start measuring preoperative albumin levels and assess complete metabolic panels. Our goal is to identify patients who are at high risk of wound complication and perform interventions to improve nutrition, then to study whether the interventions help lower the rates of wound complications. TSJ
Correspondence
References
1. Ormsby MV, Hilaris BS, Nori D, Brennan MF. Wound complications of adjuvant radiation therapy in patients with soft-tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg. 1989;210(1):93-99.
2. Greene KA, Wilde AH, Stulberg BN. Preoperative nutritional status of total joint patients: relationship to postoperative wound complications. J Arthroplasty. 1991;6(4):321-325.
3. Nozoe T, Kimura Y, Ishida M, Saeki H, Korenaga D, Sugimachi K. Correlation of pre-operative nutritional condition with post-operative complications in surgical treatment for oesophageal carcinoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(4):396-400.
4. Nozoe T, Kohno M, Iguchi T, et al. The prognostic nutritional index can be a prognostic indicator in colorectal carcinoma. Surg Today. 2012;42(6):532-535.
5. Nozoe T, Ninomiya M, Maeda T, Matsukuma A, Nakashima H, Ezaki T. Prognostic nutritional index: a tool to predict the biological aggressiveness of gastric carcinoma. Surg Today. 2010;40(5):440-443.
6. O’Sullivan B, Davis AM, Turcotte R, Bell R, Catton C, Chabot P, et al. Preoperative versus postoperative radiotherapy in soft-tissue sarcoma of the limbs: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2002;359(9325):2235-2241.
7. Peat BG, Bell RS, Davis A, et al. Wound-healing complications after soft-tissue sarcoma surgery. Plast Reconstr Surg. 1994;93(5):980-987.
8. Kunisada T, Ngan SY, Powell G, Choong PF. Wound complications following pre-operative radiotherapy for soft tissue sarcoma. Eur J Surg Oncol. 2002;28(1):75-79.
9. Saddegh MK, Bauer HC. Wound complication in surgery of soft tissue sarcoma: analysis of 103 consecutive patients managed without adjuvant therapy. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1993;289:247-253.
10. Tseng JF, Ballo MT, Langstein HN, et al. The effect of preoperative radiotherapy and reconstructive surgery on wound complications after resection of extremity soft-tissue sarcomas. Ann Surg Oncol. 2006;13(9):1209-1215.
11. Smale BF, Mullen JL, Buzby GP, Rosato EF. The efficacy of nutritional assessment and support in cancer surgery. Cancer. 1981;47(10):2375-2381.
12. Mohri Y, Inoue Y, Tanaka K, Hiro J, Uchida K, Kusunoki M. Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative outcome in colorectal cancer. World J Surg. 2013;37(11):2688-2692.
13. Jiang N, Deng JY, Ding XW, et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts postoperative complications and long-term outcomes of gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 2014;20(30):10537-10544.
14. Pinato DJ, North BV, Sharma R. A novel, externally validated inflammation-based prognostic algorithm in hepatocellular carcinoma: the prognostic nutritional index (PNI). Brit J Cancer. 2012;106(8):1439-1445.
15. Yao ZH, Tian GY, Wan YY, et al. Prognostic nutritional index predicts outcomes of malignant pleural mesothelioma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2013;139(12):2117-2123.
16. Jian-Hui C, Iskandar EA, Cai Sh I, et al. Significance of Onodera’s prognostic nutritional index in patients with colorectal cancer: a large cohort study in a single Chinese institution. Tumour Biol. 2016;37(3):3277-3283.
17. Hong S, Zhou T, Fang W, et al. The prognostic nutritional index (PNI) predicts overall survival of small-cell lung cancer patients. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(5):3389-9337.
18. Mohil RS, Agarwal A, Singh N, Arora J, Bhatnagar D. Does nutritional status play a role in patients undergoing emergency laparotomy? E Spen Eur E J Clin Nutr Metab. 2008;3(5):e226-e231.
19. Kay SP, Moreland JR, Schmitter E. Nutritional status and wound healing in lower extremity amputations. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1987;(217):253-256.
20. Dickhaut SC, DeLee JC, Page CP. Nutritional status: importance in predicting wound-healing after amputation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1984;66(1):71-75.
21. Casey J, Flinn WR, Yao JS, Fahey V, Pawlowski J, Bergan JJ. Correlation of immune and nutritional status with wound complications in patients undergoing vascular operations. Surgery. 1983;93(6):822-827.
22. Gu Q, Wang D, Cui C, Gao Y, Xia G, Cui X. Effects of radiation on wound healing. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol. 1998;17(2):117-123.
Cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma after placement of a Dacron graft
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-month mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis. TSJ
Correspondence
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-month mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis. TSJ
Correspondence
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-month mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis. TSJ
Correspondence
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
Cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma after placement of Dacron graft
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-months mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis.
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-months mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis.
Primary cardiac tumors, either benign or malignant, are very rare. The combined incidence is 0.002% on pooled autopsy series.1 The benign tumors account for 63% of primary cardiac tumors and include myxoma, the most common, and followed by papillary fibroelastoma, fibroma, and hemangioma. The remaining 37% are malignant tumors, essentially predominated by sarcomas.1
Although myxoma is the most common tumor arising in the left atrium, we present a case that shows that sarcoma can also arise from the same chamber. In fact, sarcomas could mimic cardiac myxoma.2 The cardiac sarcomas can have similar clinical presentation and more importantly can share similar histopathological features. Sarcomas may have myxoid features.2 Cases diagnosed as cardiac myxomas should be diligently worked up to rule out the presence of sarcomas with myxoid features. In addition, foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals.3,4 In particular, 2 case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses in humans.5,6 We present here the case of a patient who was diagnosed with cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma 8 years after the placement of a Dacron graft.
Case presentation and summary
A 56-year-old woman with history of left atrial myxoma status after resection in 2005 and placement of a Dacron graft, morbid obesity, hypertension, and asthma presented to the emergency department with progressively worsening shortness of breath and blurry vision over period of 2 months. Acute coronary syndrome was ruled out by electrocardiogram and serial biomarkers. A computed-tomography angiogram was pursued because of her history of left atrial myxoma, and the results suggested the presence of a left atrial tumor. She underwent a transesophageal echocardiogram, which confirmed the presence of a large left atrial mass that likely was attached to the interatrial septum prolapsing across the mitral valve and was suggestive for recurrent left atrial myxoma (Figure 1). The results of a cardiac catheterization showed normal coronaries.
The patient subsequently underwent an excision of the left atrial tumor with profound internal and external myocardial cooling using antegrade blood cardioplegia under mildly hypothermic cardiopulmonary bypass. Frozen sections showed high-grade malignancy in favor of sarcoma. The hematoxylin and eosin stained permanent sections showed sheets of malignant pleomorphic spindle cells focally arranged in a storiform pattern. There were areas of necrosis and abundant mitotic activity. By immunohistochemical (IHC) stains, the tumor cells were diffusely positive for vimentin, and negative for pan-cytokeratin antibody (AE1/AE3), S-100 protein, Melan-A antibody, HMB45, CD34, CD31, myogenin, and MYOD1. IHC stains for CK-OSCAR, desmin, and smooth muscle actin were focally positive, and a ki-67 stain showed a proliferation index of about 80%. The histologic and IHC findings were consistent with a final diagnosis of high-grade undifferentiated pleomorphic sarcoma (Figure 2).
A positron emission tomography scan performed November 2013 did not show any other activity. The patient was scheduled for chemotherapy with adriamycin and ifosfamide with a plan for total of 6 cycles. Before her admission for the chemotherapy, the patient was admitted to the hospital for atrial fibrillation with rapid ventricular response and had multiple complications requiring prolonged hospitalization and rehabilitation. Repeat imaging 2 months later showed diffuse metastatic disease. However, her performance status had declined and she was not eligible for chemotherapy. She was placed under hospice care.
Discussion
This case demonstrates development of a cardiac pleomorphic sarcoma, a rare tumor, after placement of a Dacron graft. Given that foreign bodies have been found to induce sarcomas in experimental animals,3,4 and a few case reports have described sarcomas arising in association with Dacron vascular prostheses, 5-10 it seems that an exuberant host response around the foreign body might represent an important intermediate step in the development of the sarcoma.
There is no clearly defined pathogenesis that explains the link between a Dacron graft and sarcomas. In 1950s, Oppenheimer and colleagues described the formation of malignant tumors by various types of plastics, including Dacron, that were embedded in rats. 3,4 Most of the tumors were some form of sarcomas. It was inferred that physical properties of the plastics may have some role in tumor development. Plastics in sheet form or film that remained in situ for more than 6 months induced significant number of tumors compared with other forms such as sponges, films with holes, or powders.3,4 The 3-dimensional polymeric structure of the Dacron graft seems to play a role in induction of sarcoma as well. A pore diameter of less than 0.4 mm may increase tumorigenicity.11 The removal of the material before the 6-months mark does not lead to malignant tumors, which further supports the link between Dacron graft and formation of tumor. A pocket is formed around the foreign material after a certain period, as has been shown in histologic studies as the site of tumor origin.9,10
At the molecular level, the MDM-2/p53 pathway has been cited as possible mechanism for pathogenesis of intimal sarcoma.12,13 It has been suggested that endothelial dysplasia occurs as a precursor lesion in these sarcomas.14 The Dacron graft may cause a dysplastic effect on the endothelium leading to this precursor lesion and in certain cases transforming into sarcoma. Further definitive studies are required.
The primary treatment for cardiac sarcoma is surgical removal, although it is not always feasible. Findings in a Mayo clinic study showed that the median survival was 17 months for patients who underwent complete surgical excision, compared with 6 months for those who complete resection was not possible.15 In addition, a 10% survival rate at 1 year has been reported in primary cardiac sarcomas that are treated without any type of surgery.16
There is no clear-cut evidence supporting or refuting adjuvant chemotherapy for cardiac sarcoma. Some have inferred a potential benefit of adjuvant chemotherapy although definitive conclusions cannot be drawn. The median survival was 16.5 months in a case series of patients who received adjuvant chemotherapy, compared with 9 months and 11 months in 2 other case series.17,18,19 Multiple chemotherapy regimens have been used in the past for treatment. A retrospective s
Radiation showed some benefit in progression-free survival in a French retrospective study.21 Radiation therapies have been tried in other cases, as well in addition to chemotherapy. However, there is not enough data to support or refute it at this time.15,17,20 Several sporadic cases reported show benefit of cardiac transplantation.21,22
Conclusion
In consideration of the placement of the Dacron graft 8 years before the tumor occurrence, the anatomic proximity of the tumor to the Dacron graft, and the association between sarcoma with Dacron in medical literature, it seems logical to infer that this unusual malignancy in our patient is associated with the Dacron prosthesis.
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
1. Patil HR, Singh D, Hajdu M. Cardiac sarcoma presenting as heart failure and diagnosed as recurrent myxoma by echocardiogram. Eur J Echocardiogr. 2010;11(4):E12.
2. Awamleh P, Alberca MT, Gamallo C, Enrech S, Sarraj A. Left atrium myxosarcoma: an exceptional cardiac malignant primary tumor. Clin Cardiol. 2007;30(6):306-308.
3. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Danishefsky I. Malignant tumors resulting from embedding plastics in rodents. Science. 1953;118:305-306.
4. Oppenheimer BS, Oppenheimer ET, Stout AP, Willhite M, Danishefski, I. The latent period in carcinogenesis by plastics in rats and its relation to the presarcomatous stage. Cancer. 1958;11(1):204-213.
5. Almeida NJ, Hoang P, Biddle P, Arouni A, Esterbrooks D. Primary cardiac angiosarcoma: in a patient with a Dacron aortic prosthesis. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(1):61-65; discussion 65.
6. Stewart B, Manglik N, Zhao B, et al. Aortic intimal sarcoma: report of two cases with immunohistochemical analysis for pathogenesis. Cardiovasc Pathol. 2013;22(5):351-356.
7. Umscheid TW, Rouhani G, Morlang T, et al. Hemangiosarcoma after endovascular aortic aneurysm repair. J Endovasc Ther. 2007;14(1):101-105.
8. Ben-Izhak O, Vlodavsky E, Ofer A, Engel A, Nitecky S, Hoffman A. Epithelioid angiosarcoma associated with a Dacron vascular graft. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999;23(11):1418-1422.
9. Fyfe BS, Quintana CS, Kaneko M, Griepp RB. Aortic sarcoma four years after Dacron graft insertion. Ann Thorac Surg. 1994;58(6):1752-1754.
10. O’Connell TX, Fee HJ, Golding A. Sarcoma associated with Dacron prosthetic material: case report and review of the literature. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 1976;72(1):94-96.
11. Karp RD, Johnson KH, Buoen LC, et al. Tumorogenesis by millipore filters in mice: histology and ultastructure of tissue reactions, as related to pore size. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973;51:1275-1285.
12. Bode-Lesniewska B, Zhao J, Speel EJ, et al. Gains of 12q13-14 and overexpression of mdm2 are frequent findings in intimal sarcomas of the pulmonary artery. Virchows Arch. 2001;438:57-65.
13. Zeitz C, Rossle M, Haas C, et al. MDM-2 oncoprotein overexpression, p53 gene mutation, and VEGF up-regulation in angiosarcomas. Am J Surg Pathol. 1998;153:1425-1433.
14. Haber LM, Truong L. Immunohistochemical demonstration of the endothelialnature of aortic intimal sarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 1988 Oct;12(10):798-802. PubMed PMID: 3138923.
15. Simpson L, Kumar SK, Okuno SH, et al. Malignant primary cardiac tumors: review of a single institution experience. Cancer. 2008;112(11):2440-2446.
16. Leja MJ, Shah DJ, Reardon MJ. Primary cardiac tumors. Tex Heart Inst J. 2011;38(3):261-262.
17. Donsbeck AV, Ranchere D, Coindre JM, Le Gall F, Cordier JF, Loire R. Primary cardiac sarcomas: an immunohistochemical and grading study with long-term follow-up of 24 cases. Histopathology. 1999;34(4):295-304.
18. Putnam JB, Sweeney MS, Colon R, Lanza LA, Frazier OH, Cooley DC. Primary cardiac sarcomas. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990; 51; 906-910.
19. Murphy WR, Sweeney MS, Putnam JB et al. Surgical treatment of cardiac tumors: a 25-year experience. Ann Thorac Surg. 1990;49;612-618.
20. Llombart-Cussac A, Pivot X, Contesso G, et al. Adjuvant chemotherapy for primary cardiac sarcomas: the IGR experience. Br J Cancer. 1998;78(12):1624-1628.
21. Isambert N, Ray-Coquard I, Italiano A, et al. Primary cardiac sarcomas: a retrospective study of the French Sarcoma Group. Eur J Cancer. 2014;50(1):128-136.
22. Agaimy A, Rösch J, Weyand M, Strecker T. Primary and metastatic cardiac sarcomas: a 12-year experience at a German heart center. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2012;5(9):928-938.
Introducing The Sarcoma Journal—The Official Journal of the Sarcoma Foundation of America ™ : An Exciting Initiative in Peer-Reviewed Professional Education and Patient Advocacy
The Sarcoma Journal — Official Journal of the Sarcoma Foundation of America™ represents a new and exciting initiative in professional education. We invite you to share in the excitement surrounding the launch of a medical journal designed to be your most authoritative and comprehensive source of scientific information on the diagnosis and treatment of sarcomas and sarcoma sub-types.
On behalf of myself, our editorial board, and editorial staff, I welcome you to this journal as we explore new treatment paradigms for this disease, translational research that bridges the bench and the clinic, and a broad range of science to encompass the many facets of sarcoma. In my opinion, the startup of this publication could not come at a better time.
As cancer specialists and allied health care professionals who attend regular meetings of your peers, including ASCO and CTOS, we have seen a dramatic shift in management within the last few years. In many ways we are at a threshold of a new era in sarcoma management, and the spectrum of treatment is expanding across subspecialties, promising more effective strategies for our patients that are based on an improved understanding of disease biology. We need a resource to maintain and clarify our focus on this disease as research opens new avenues for us to consider in the management of patients with sarcoma.
When I was approached to serve as Editor-in-Chief of The Sarcoma Journal by the Sarcoma Foundation of America, I began to recruit an esteemed group of colleagues whose knowledge, worldwide reputation as thought leaders, and dedicated work as researchers would reflect our commitment toward finding a cure for sarcoma. Many of the colleagues who will join me on the Editorial Advisory Board have long-standing affiliations with the Sarcoma Foundation of America and its comprehensive program of sarcoma research, patient support and education and advocacy. As you explore the first issue of the journal, you will discover how our editorial content is an extension of this three-tiered approach. The SFA program is characterized by a multi-dimensional and uniquely coordinated outreach program of videos and webinars, websites (a new journal website is launching as well) a sarcoma-specific clinical trials database, newsletters and related materials— all aimed ultimately at finding a cure for this disease. This professional journal complements and extends the SFA’s mission.
Although The Sarcoma Journal has a position within the SFA umbrella, my focus is foremost on ensuring that The Sarcoma Journal contains the most accurate, relevant and up to date information available. I urge you to explore our highly informative and relevant sarcoma-specific content—including original reports, review articles, a Journal Club, expert opinion, meeting reports, and patient advocacy that encapsulates the latest findings from the bench with implications for the bedside.
Whether it is discussing the latest findings in advanced sarcoma sub-types or implications of genetics as a prognostic factor, you will find the information in this journal, reliably analyzed by our team of experts who are leading sarcoma clinicians and investigators. All of the content we provide is presented in a thought-provoking, lively and peer-reviewed format; we welcome your comments and suggestions to keep us on the forefront of patient care as we cover a rapidly evolving landscape of new information in the treatment of sarcomas and frame it within a context directly applicable to enhancing the quality of patient care.
The Sarcoma Journal — Official Journal of the Sarcoma Foundation of America™ represents a new and exciting initiative in professional education. We invite you to share in the excitement surrounding the launch of a medical journal designed to be your most authoritative and comprehensive source of scientific information on the diagnosis and treatment of sarcomas and sarcoma sub-types.
On behalf of myself, our editorial board, and editorial staff, I welcome you to this journal as we explore new treatment paradigms for this disease, translational research that bridges the bench and the clinic, and a broad range of science to encompass the many facets of sarcoma. In my opinion, the startup of this publication could not come at a better time.
As cancer specialists and allied health care professionals who attend regular meetings of your peers, including ASCO and CTOS, we have seen a dramatic shift in management within the last few years. In many ways we are at a threshold of a new era in sarcoma management, and the spectrum of treatment is expanding across subspecialties, promising more effective strategies for our patients that are based on an improved understanding of disease biology. We need a resource to maintain and clarify our focus on this disease as research opens new avenues for us to consider in the management of patients with sarcoma.
When I was approached to serve as Editor-in-Chief of The Sarcoma Journal by the Sarcoma Foundation of America, I began to recruit an esteemed group of colleagues whose knowledge, worldwide reputation as thought leaders, and dedicated work as researchers would reflect our commitment toward finding a cure for sarcoma. Many of the colleagues who will join me on the Editorial Advisory Board have long-standing affiliations with the Sarcoma Foundation of America and its comprehensive program of sarcoma research, patient support and education and advocacy. As you explore the first issue of the journal, you will discover how our editorial content is an extension of this three-tiered approach. The SFA program is characterized by a multi-dimensional and uniquely coordinated outreach program of videos and webinars, websites (a new journal website is launching as well) a sarcoma-specific clinical trials database, newsletters and related materials— all aimed ultimately at finding a cure for this disease. This professional journal complements and extends the SFA’s mission.
Although The Sarcoma Journal has a position within the SFA umbrella, my focus is foremost on ensuring that The Sarcoma Journal contains the most accurate, relevant and up to date information available. I urge you to explore our highly informative and relevant sarcoma-specific content—including original reports, review articles, a Journal Club, expert opinion, meeting reports, and patient advocacy that encapsulates the latest findings from the bench with implications for the bedside.
Whether it is discussing the latest findings in advanced sarcoma sub-types or implications of genetics as a prognostic factor, you will find the information in this journal, reliably analyzed by our team of experts who are leading sarcoma clinicians and investigators. All of the content we provide is presented in a thought-provoking, lively and peer-reviewed format; we welcome your comments and suggestions to keep us on the forefront of patient care as we cover a rapidly evolving landscape of new information in the treatment of sarcomas and frame it within a context directly applicable to enhancing the quality of patient care.
The Sarcoma Journal — Official Journal of the Sarcoma Foundation of America™ represents a new and exciting initiative in professional education. We invite you to share in the excitement surrounding the launch of a medical journal designed to be your most authoritative and comprehensive source of scientific information on the diagnosis and treatment of sarcomas and sarcoma sub-types.
On behalf of myself, our editorial board, and editorial staff, I welcome you to this journal as we explore new treatment paradigms for this disease, translational research that bridges the bench and the clinic, and a broad range of science to encompass the many facets of sarcoma. In my opinion, the startup of this publication could not come at a better time.
As cancer specialists and allied health care professionals who attend regular meetings of your peers, including ASCO and CTOS, we have seen a dramatic shift in management within the last few years. In many ways we are at a threshold of a new era in sarcoma management, and the spectrum of treatment is expanding across subspecialties, promising more effective strategies for our patients that are based on an improved understanding of disease biology. We need a resource to maintain and clarify our focus on this disease as research opens new avenues for us to consider in the management of patients with sarcoma.
When I was approached to serve as Editor-in-Chief of The Sarcoma Journal by the Sarcoma Foundation of America, I began to recruit an esteemed group of colleagues whose knowledge, worldwide reputation as thought leaders, and dedicated work as researchers would reflect our commitment toward finding a cure for sarcoma. Many of the colleagues who will join me on the Editorial Advisory Board have long-standing affiliations with the Sarcoma Foundation of America and its comprehensive program of sarcoma research, patient support and education and advocacy. As you explore the first issue of the journal, you will discover how our editorial content is an extension of this three-tiered approach. The SFA program is characterized by a multi-dimensional and uniquely coordinated outreach program of videos and webinars, websites (a new journal website is launching as well) a sarcoma-specific clinical trials database, newsletters and related materials— all aimed ultimately at finding a cure for this disease. This professional journal complements and extends the SFA’s mission.
Although The Sarcoma Journal has a position within the SFA umbrella, my focus is foremost on ensuring that The Sarcoma Journal contains the most accurate, relevant and up to date information available. I urge you to explore our highly informative and relevant sarcoma-specific content—including original reports, review articles, a Journal Club, expert opinion, meeting reports, and patient advocacy that encapsulates the latest findings from the bench with implications for the bedside.
Whether it is discussing the latest findings in advanced sarcoma sub-types or implications of genetics as a prognostic factor, you will find the information in this journal, reliably analyzed by our team of experts who are leading sarcoma clinicians and investigators. All of the content we provide is presented in a thought-provoking, lively and peer-reviewed format; we welcome your comments and suggestions to keep us on the forefront of patient care as we cover a rapidly evolving landscape of new information in the treatment of sarcomas and frame it within a context directly applicable to enhancing the quality of patient care.
Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma presenting as a necrotizing cavitary lung lesion: diagnostic dilemma
Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma (PSC) is a rare histological subtype that has an aggressive course with average survival of 11-13 months.1 In clinical practice, the possible presentations of this rare cancer are not widely known, resulting in a misdiagnosis. That is what happened with our patient, who presented with necrotizing cavitary lung lesion and soft tissue necrotizing lymphadenitis. The clinical picture was reminiscent of tuberculosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis and was further confounded by negative computed-tomography (CT)-guided biopsy and bronchoscopy findings, which added to the delay in diagnosis. With the currently available knowledge, the diagnosis of PSC depends largely on evaluation of the surgically resected specimen, which in most cases is avoided until there is a high suspicion of PSC. Biopsy is not useful due to extensive necrosis, as will be seen in our case. Consequently, most of the data in the literature is based on case series of autopsy specimen, and the clinical characteristics of PSC remain unclear. The rarity of PSC has prevented its characterization in literature. We report here a rare presentation of PSC with necrotizing lung lesion, to add to the paucity of the current data.
Case presentation and summary
A 58-year-old homeless man presented to the Upstate University Hospital, Syracuse, New York, with a 25-pound weight loss during the previous month and associated productive cough and hemoptysis for a week and a painful mass in the nape of his neck. He denied any fever, chest pain, sick contacts, or joint pain. He had a history of about 40 pack-years of smoking, and his brother had recently been diagnosed with lung cancer. A tender fluctuant mass was detected in the nape of his neck on examination (Figure 1).
The patient had presented 9 months earlier with persistent cough and hemoptysis, and at that visit was found to have a cavitary lesion in the right lung measuring 2 cm (0.8 in). He had undergone a computed-tomograpghy (CT)-guided biopsy of the lesion, which had shown acute and chronic inflammation with fibrosis, and he had negative bronchoscopy findings. The patient tested negative for tuberculosis during the first visit but he left the hospital against the medical advice of the physicians and he was lost to follow-up until his re-presentation.
On physical examination at his re-presentation, the patient seemed cachectic, with a blood pressure of 94/62 mm of Hg. The mass in the nape of his neck was about 3 cm (1.2 in) long, with erythema of the surrounding skin (Figure 1). Bronchial breath sounds were heard in the right upper lobe of the lung, likely due to the underlying cavitary lesion (Figure 2B). Relevant lab findings included a negative HIV test and repeat AFB (acid-fast bacilli) sputum cultures. A CT-guided biopsy with contrast of the thorax showed an interval increase in the size of the cavitary lesion in the patient’s right upper lobe, now measuring about 10 cm (4 in). Also seen were multiple nodules elsewhere in both lungs, with the largest measuring 8 mm (0.3 in). A CT scan of the neck showed 3 cm cystic mass within the posterior subcutaneous soft tissue of the C3 level, confirming the examination finding of the neck mass (Figure 2A) with peripheral enhancement and surrounding infiltrative changes, likely abscess or malignant lymph node versus necrotic infection. He underwent bronchoscopy, which again failed to reveal any endobronchial lesions. Bronchoalveolar lavage was sent for microbiological analysis, including AFB and fungus, but came back negative. Transbronchial biopsy cytology revealed fragments of tumor composed of large pleomorphic cells without glandular or squamous differentiation, within large areas of necrosis (Figure 3). Immunohistochemical studies showed strong reactivity with cytokeratin CAM5.2 (Figure 4), weak and focal reactivity with cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (Figure 5), and lack of reactivity with CD20, CD3, CD30, S-100, MART-1, TTF-1 and p63, all findings consistent with sarcomatoid carcinoma.
The patient underwent fine-needle aspiration and drainage of the neck lesion and the culture grew mixed organisms The results of a bone scan, which was done within a week, showed multiple foci of uptake in the ribs and cervical spine. Given the patient’s advanced disease, he was started on palliative radiotherapy with radiosensitizing chemotherapy with carboplatin (target AUC 6) and paclitaxel (135 mg/m2 over 24 hours). His symptoms of hemoptysis improved transiently after the first cycle, but he became hypotensive and drowsy during the second cycle of therapy, and the family decided to make the patient comfort care and withdraw all further treatment. He was discharged to hospice.
Discussion
PSC is a rare variant of non-small-cell carcinoma lung cancer, accounting for up to 0.4% of lung malignancy.1 It was
recently subtyped by the World Health Organization as a non-small cell lung carcinoma with certain amount of differentiation resembling sarcoma or containing elements of sarcoma.2-4 It is not known why both elements co-exist in the tumor, but Franks and colleagues some theories have been postulated in the literature, including possible origin from a single, aberrant stem cell with progenies differentiating in two separate pathways.3
Sarcomatoid carcinoma consists of spectrum of tumors including pleomorphic carcinoma, spindle cell carcinoma, giant cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, and blastoma.3,4 It usually shows male preponderance, and association with smoking.3 The diagnosis commonly occurs in the sixth decade of life, except for pulmonary blastoma, which is more common in the fourth decade andnwith equal gender distribution.4
The presenting symptoms can be variable and nonspecific, but predominantly include chest pain, cough, hemoptysis, and/or weight loss.5 Radiologically, pulmonary sarcomatoid cancer presenting as a necrotizing cavitary lesion in the lung is a rare finding, seldom reported in the past.6,7 The presentation in our case, with necrotizing lymphadenitis, was reminiscent of an infectious or autoimmune etiology such as tuberculosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis. The presence of extensive necrosis in the lesion and the characteristic heterogeneity of the tumor had resulted in inconclusive biopsy findings during the previous presentation. In clinical practice, there is over-reliance on biopsy findings to make the distinction between cancer and other mimicking conditions. This is especially true for rare tumors such as PSC, which often results in misdiagnosis and a delay in administering the proper treatment. Transbronchial biopsy in cases such as the present case, carries little benefit because the diagnosis depends on the site from which the biopsy is taken and whether the biopsied tissue is representative of the entire mass. The diagnosis can be suspected based on the clinical and radiological findings but confirmation requires a surgical resection to delineate the accurate cytology and architecture.5,6,8 Huang and colleagues showed a misdiagnosis rate of PSC of >70% preoperatively.4 Resective surgery is feasible only in patients with high index of suspicion for a malignancy, which in most cases requires previous confirmation with a biopsy. The rarity of this cancer, its unusual presentations, and the lack of specific testing preclude early diagnosis and timely treatment of this fatal condition.
Initial treatment options for localized or with limited spread disease is resective surgery. The role of chemo- or radiation therapy is not known, but they have not previously shown promising results,6,8 except in some cases when they are used as postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy4 or in bulky, locally invasive tumors.1 The recurrence rate after surgery is very high, resulting in a poor 5-year survival rate.1,8 Experimental therapies, such as antibodies that target epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, have not shown much success either.8 In conclusion, the outlook for patients with PSC with the current available knowledge and treatment protocols, is dismal.
Most of the current knowledge and data in the literature is based on cases from autopsy or early-stage surgical resections rather than on patients with advanced cancer.5 Moreover, the role of surgical resection in PSC is questionable, given the high recurrence rate. Subsequently, the clinical and pathological manifestations have yet to be well characterized.4 There has been advance with the publication of more studies recently. Cytokeratin markers such as CAM 5.2 and AE1/AE3 are commonly useful to support the diagnosis when suspected.3 Other markers, including the carcinoembryonic antigen, CD15, and thyroid transcription factor-1 may be variably positive, based on the differentiation of the cancer. Other exciting prospects in the study of PSC include the suggestion of a modified vimentin histologic score for better characterization of the cancer and the discovery of high plateletderived growth factor receptor beta immunohistochemistry expression in PSC as a potential target for future therapy.
Conclusion
Pulmonary sarcomatoid lung cancer can present with a predominant necrotizing picture that mimics diseases such as tuberculosis. In such case, transbronchial biopsy carries little benefit because the diagnosis depends on whether the biopsied tissue is representative of the entire mass, often confounded by the extensive necrosis. More data is needed to determine prognostic factors and appropriate therapeutic strategies. TSJ
Correspondence
Gaurang Nandkishor Vaidya, MD
References
1. Martin LW, Correa AM, Ordonez NG, et al. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: a predictor of poor prognosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(3):973-980.
2. Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y. The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 2001;18(6):1059-1068.
3. Franks TJ, Galvin JR. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: histologic criteria and common lesions in the differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(1):49-54.
4. Huang SY, Shen SJ, Li XY. Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study and prognostic analysis of 51 cases. http://wjso. biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7819-11-252. Published 2013. Accessed March 12, 2017.
5. Travis WD. Sarcomatoid neoplasms of the lung and pleura. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(11):1645-1658.
6. Pelosi G, Sonzogni A, De Pas T, et al. Review article: pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas: a practical overview. Int J Surg Pathol. 2010;18(2):103-120.
7. Chang YL, Lee YC, Shih JY, Wu CT. Pulmonary pleomorphic (spindle) cell carcinoma: peculiar clinicopathologic manifestations different from ordinary non-small cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2001;34(1):91-97.
8. Park JS, Lee Y, Han J, et al. Clinicopathologic outcomes of curative resection for sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung. Oncology. 2011;81(3-4):206-213.
Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma (PSC) is a rare histological subtype that has an aggressive course with average survival of 11-13 months.1 In clinical practice, the possible presentations of this rare cancer are not widely known, resulting in a misdiagnosis. That is what happened with our patient, who presented with necrotizing cavitary lung lesion and soft tissue necrotizing lymphadenitis. The clinical picture was reminiscent of tuberculosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis and was further confounded by negative computed-tomography (CT)-guided biopsy and bronchoscopy findings, which added to the delay in diagnosis. With the currently available knowledge, the diagnosis of PSC depends largely on evaluation of the surgically resected specimen, which in most cases is avoided until there is a high suspicion of PSC. Biopsy is not useful due to extensive necrosis, as will be seen in our case. Consequently, most of the data in the literature is based on case series of autopsy specimen, and the clinical characteristics of PSC remain unclear. The rarity of PSC has prevented its characterization in literature. We report here a rare presentation of PSC with necrotizing lung lesion, to add to the paucity of the current data.
Case presentation and summary
A 58-year-old homeless man presented to the Upstate University Hospital, Syracuse, New York, with a 25-pound weight loss during the previous month and associated productive cough and hemoptysis for a week and a painful mass in the nape of his neck. He denied any fever, chest pain, sick contacts, or joint pain. He had a history of about 40 pack-years of smoking, and his brother had recently been diagnosed with lung cancer. A tender fluctuant mass was detected in the nape of his neck on examination (Figure 1).
The patient had presented 9 months earlier with persistent cough and hemoptysis, and at that visit was found to have a cavitary lesion in the right lung measuring 2 cm (0.8 in). He had undergone a computed-tomograpghy (CT)-guided biopsy of the lesion, which had shown acute and chronic inflammation with fibrosis, and he had negative bronchoscopy findings. The patient tested negative for tuberculosis during the first visit but he left the hospital against the medical advice of the physicians and he was lost to follow-up until his re-presentation.
On physical examination at his re-presentation, the patient seemed cachectic, with a blood pressure of 94/62 mm of Hg. The mass in the nape of his neck was about 3 cm (1.2 in) long, with erythema of the surrounding skin (Figure 1). Bronchial breath sounds were heard in the right upper lobe of the lung, likely due to the underlying cavitary lesion (Figure 2B). Relevant lab findings included a negative HIV test and repeat AFB (acid-fast bacilli) sputum cultures. A CT-guided biopsy with contrast of the thorax showed an interval increase in the size of the cavitary lesion in the patient’s right upper lobe, now measuring about 10 cm (4 in). Also seen were multiple nodules elsewhere in both lungs, with the largest measuring 8 mm (0.3 in). A CT scan of the neck showed 3 cm cystic mass within the posterior subcutaneous soft tissue of the C3 level, confirming the examination finding of the neck mass (Figure 2A) with peripheral enhancement and surrounding infiltrative changes, likely abscess or malignant lymph node versus necrotic infection. He underwent bronchoscopy, which again failed to reveal any endobronchial lesions. Bronchoalveolar lavage was sent for microbiological analysis, including AFB and fungus, but came back negative. Transbronchial biopsy cytology revealed fragments of tumor composed of large pleomorphic cells without glandular or squamous differentiation, within large areas of necrosis (Figure 3). Immunohistochemical studies showed strong reactivity with cytokeratin CAM5.2 (Figure 4), weak and focal reactivity with cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (Figure 5), and lack of reactivity with CD20, CD3, CD30, S-100, MART-1, TTF-1 and p63, all findings consistent with sarcomatoid carcinoma.
The patient underwent fine-needle aspiration and drainage of the neck lesion and the culture grew mixed organisms The results of a bone scan, which was done within a week, showed multiple foci of uptake in the ribs and cervical spine. Given the patient’s advanced disease, he was started on palliative radiotherapy with radiosensitizing chemotherapy with carboplatin (target AUC 6) and paclitaxel (135 mg/m2 over 24 hours). His symptoms of hemoptysis improved transiently after the first cycle, but he became hypotensive and drowsy during the second cycle of therapy, and the family decided to make the patient comfort care and withdraw all further treatment. He was discharged to hospice.
Discussion
PSC is a rare variant of non-small-cell carcinoma lung cancer, accounting for up to 0.4% of lung malignancy.1 It was
recently subtyped by the World Health Organization as a non-small cell lung carcinoma with certain amount of differentiation resembling sarcoma or containing elements of sarcoma.2-4 It is not known why both elements co-exist in the tumor, but Franks and colleagues some theories have been postulated in the literature, including possible origin from a single, aberrant stem cell with progenies differentiating in two separate pathways.3
Sarcomatoid carcinoma consists of spectrum of tumors including pleomorphic carcinoma, spindle cell carcinoma, giant cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, and blastoma.3,4 It usually shows male preponderance, and association with smoking.3 The diagnosis commonly occurs in the sixth decade of life, except for pulmonary blastoma, which is more common in the fourth decade andnwith equal gender distribution.4
The presenting symptoms can be variable and nonspecific, but predominantly include chest pain, cough, hemoptysis, and/or weight loss.5 Radiologically, pulmonary sarcomatoid cancer presenting as a necrotizing cavitary lesion in the lung is a rare finding, seldom reported in the past.6,7 The presentation in our case, with necrotizing lymphadenitis, was reminiscent of an infectious or autoimmune etiology such as tuberculosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis. The presence of extensive necrosis in the lesion and the characteristic heterogeneity of the tumor had resulted in inconclusive biopsy findings during the previous presentation. In clinical practice, there is over-reliance on biopsy findings to make the distinction between cancer and other mimicking conditions. This is especially true for rare tumors such as PSC, which often results in misdiagnosis and a delay in administering the proper treatment. Transbronchial biopsy in cases such as the present case, carries little benefit because the diagnosis depends on the site from which the biopsy is taken and whether the biopsied tissue is representative of the entire mass. The diagnosis can be suspected based on the clinical and radiological findings but confirmation requires a surgical resection to delineate the accurate cytology and architecture.5,6,8 Huang and colleagues showed a misdiagnosis rate of PSC of >70% preoperatively.4 Resective surgery is feasible only in patients with high index of suspicion for a malignancy, which in most cases requires previous confirmation with a biopsy. The rarity of this cancer, its unusual presentations, and the lack of specific testing preclude early diagnosis and timely treatment of this fatal condition.
Initial treatment options for localized or with limited spread disease is resective surgery. The role of chemo- or radiation therapy is not known, but they have not previously shown promising results,6,8 except in some cases when they are used as postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy4 or in bulky, locally invasive tumors.1 The recurrence rate after surgery is very high, resulting in a poor 5-year survival rate.1,8 Experimental therapies, such as antibodies that target epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, have not shown much success either.8 In conclusion, the outlook for patients with PSC with the current available knowledge and treatment protocols, is dismal.
Most of the current knowledge and data in the literature is based on cases from autopsy or early-stage surgical resections rather than on patients with advanced cancer.5 Moreover, the role of surgical resection in PSC is questionable, given the high recurrence rate. Subsequently, the clinical and pathological manifestations have yet to be well characterized.4 There has been advance with the publication of more studies recently. Cytokeratin markers such as CAM 5.2 and AE1/AE3 are commonly useful to support the diagnosis when suspected.3 Other markers, including the carcinoembryonic antigen, CD15, and thyroid transcription factor-1 may be variably positive, based on the differentiation of the cancer. Other exciting prospects in the study of PSC include the suggestion of a modified vimentin histologic score for better characterization of the cancer and the discovery of high plateletderived growth factor receptor beta immunohistochemistry expression in PSC as a potential target for future therapy.
Conclusion
Pulmonary sarcomatoid lung cancer can present with a predominant necrotizing picture that mimics diseases such as tuberculosis. In such case, transbronchial biopsy carries little benefit because the diagnosis depends on whether the biopsied tissue is representative of the entire mass, often confounded by the extensive necrosis. More data is needed to determine prognostic factors and appropriate therapeutic strategies. TSJ
Correspondence
Gaurang Nandkishor Vaidya, MD
References
1. Martin LW, Correa AM, Ordonez NG, et al. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: a predictor of poor prognosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(3):973-980.
2. Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y. The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 2001;18(6):1059-1068.
3. Franks TJ, Galvin JR. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: histologic criteria and common lesions in the differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(1):49-54.
4. Huang SY, Shen SJ, Li XY. Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study and prognostic analysis of 51 cases. http://wjso. biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7819-11-252. Published 2013. Accessed March 12, 2017.
5. Travis WD. Sarcomatoid neoplasms of the lung and pleura. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(11):1645-1658.
6. Pelosi G, Sonzogni A, De Pas T, et al. Review article: pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas: a practical overview. Int J Surg Pathol. 2010;18(2):103-120.
7. Chang YL, Lee YC, Shih JY, Wu CT. Pulmonary pleomorphic (spindle) cell carcinoma: peculiar clinicopathologic manifestations different from ordinary non-small cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2001;34(1):91-97.
8. Park JS, Lee Y, Han J, et al. Clinicopathologic outcomes of curative resection for sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung. Oncology. 2011;81(3-4):206-213.
Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma (PSC) is a rare histological subtype that has an aggressive course with average survival of 11-13 months.1 In clinical practice, the possible presentations of this rare cancer are not widely known, resulting in a misdiagnosis. That is what happened with our patient, who presented with necrotizing cavitary lung lesion and soft tissue necrotizing lymphadenitis. The clinical picture was reminiscent of tuberculosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis and was further confounded by negative computed-tomography (CT)-guided biopsy and bronchoscopy findings, which added to the delay in diagnosis. With the currently available knowledge, the diagnosis of PSC depends largely on evaluation of the surgically resected specimen, which in most cases is avoided until there is a high suspicion of PSC. Biopsy is not useful due to extensive necrosis, as will be seen in our case. Consequently, most of the data in the literature is based on case series of autopsy specimen, and the clinical characteristics of PSC remain unclear. The rarity of PSC has prevented its characterization in literature. We report here a rare presentation of PSC with necrotizing lung lesion, to add to the paucity of the current data.
Case presentation and summary
A 58-year-old homeless man presented to the Upstate University Hospital, Syracuse, New York, with a 25-pound weight loss during the previous month and associated productive cough and hemoptysis for a week and a painful mass in the nape of his neck. He denied any fever, chest pain, sick contacts, or joint pain. He had a history of about 40 pack-years of smoking, and his brother had recently been diagnosed with lung cancer. A tender fluctuant mass was detected in the nape of his neck on examination (Figure 1).
The patient had presented 9 months earlier with persistent cough and hemoptysis, and at that visit was found to have a cavitary lesion in the right lung measuring 2 cm (0.8 in). He had undergone a computed-tomograpghy (CT)-guided biopsy of the lesion, which had shown acute and chronic inflammation with fibrosis, and he had negative bronchoscopy findings. The patient tested negative for tuberculosis during the first visit but he left the hospital against the medical advice of the physicians and he was lost to follow-up until his re-presentation.
On physical examination at his re-presentation, the patient seemed cachectic, with a blood pressure of 94/62 mm of Hg. The mass in the nape of his neck was about 3 cm (1.2 in) long, with erythema of the surrounding skin (Figure 1). Bronchial breath sounds were heard in the right upper lobe of the lung, likely due to the underlying cavitary lesion (Figure 2B). Relevant lab findings included a negative HIV test and repeat AFB (acid-fast bacilli) sputum cultures. A CT-guided biopsy with contrast of the thorax showed an interval increase in the size of the cavitary lesion in the patient’s right upper lobe, now measuring about 10 cm (4 in). Also seen were multiple nodules elsewhere in both lungs, with the largest measuring 8 mm (0.3 in). A CT scan of the neck showed 3 cm cystic mass within the posterior subcutaneous soft tissue of the C3 level, confirming the examination finding of the neck mass (Figure 2A) with peripheral enhancement and surrounding infiltrative changes, likely abscess or malignant lymph node versus necrotic infection. He underwent bronchoscopy, which again failed to reveal any endobronchial lesions. Bronchoalveolar lavage was sent for microbiological analysis, including AFB and fungus, but came back negative. Transbronchial biopsy cytology revealed fragments of tumor composed of large pleomorphic cells without glandular or squamous differentiation, within large areas of necrosis (Figure 3). Immunohistochemical studies showed strong reactivity with cytokeratin CAM5.2 (Figure 4), weak and focal reactivity with cytokeratin AE1/AE3 (Figure 5), and lack of reactivity with CD20, CD3, CD30, S-100, MART-1, TTF-1 and p63, all findings consistent with sarcomatoid carcinoma.
The patient underwent fine-needle aspiration and drainage of the neck lesion and the culture grew mixed organisms The results of a bone scan, which was done within a week, showed multiple foci of uptake in the ribs and cervical spine. Given the patient’s advanced disease, he was started on palliative radiotherapy with radiosensitizing chemotherapy with carboplatin (target AUC 6) and paclitaxel (135 mg/m2 over 24 hours). His symptoms of hemoptysis improved transiently after the first cycle, but he became hypotensive and drowsy during the second cycle of therapy, and the family decided to make the patient comfort care and withdraw all further treatment. He was discharged to hospice.
Discussion
PSC is a rare variant of non-small-cell carcinoma lung cancer, accounting for up to 0.4% of lung malignancy.1 It was
recently subtyped by the World Health Organization as a non-small cell lung carcinoma with certain amount of differentiation resembling sarcoma or containing elements of sarcoma.2-4 It is not known why both elements co-exist in the tumor, but Franks and colleagues some theories have been postulated in the literature, including possible origin from a single, aberrant stem cell with progenies differentiating in two separate pathways.3
Sarcomatoid carcinoma consists of spectrum of tumors including pleomorphic carcinoma, spindle cell carcinoma, giant cell carcinoma, carcinosarcoma, and blastoma.3,4 It usually shows male preponderance, and association with smoking.3 The diagnosis commonly occurs in the sixth decade of life, except for pulmonary blastoma, which is more common in the fourth decade andnwith equal gender distribution.4
The presenting symptoms can be variable and nonspecific, but predominantly include chest pain, cough, hemoptysis, and/or weight loss.5 Radiologically, pulmonary sarcomatoid cancer presenting as a necrotizing cavitary lesion in the lung is a rare finding, seldom reported in the past.6,7 The presentation in our case, with necrotizing lymphadenitis, was reminiscent of an infectious or autoimmune etiology such as tuberculosis or granulomatosis with polyangiitis. The presence of extensive necrosis in the lesion and the characteristic heterogeneity of the tumor had resulted in inconclusive biopsy findings during the previous presentation. In clinical practice, there is over-reliance on biopsy findings to make the distinction between cancer and other mimicking conditions. This is especially true for rare tumors such as PSC, which often results in misdiagnosis and a delay in administering the proper treatment. Transbronchial biopsy in cases such as the present case, carries little benefit because the diagnosis depends on the site from which the biopsy is taken and whether the biopsied tissue is representative of the entire mass. The diagnosis can be suspected based on the clinical and radiological findings but confirmation requires a surgical resection to delineate the accurate cytology and architecture.5,6,8 Huang and colleagues showed a misdiagnosis rate of PSC of >70% preoperatively.4 Resective surgery is feasible only in patients with high index of suspicion for a malignancy, which in most cases requires previous confirmation with a biopsy. The rarity of this cancer, its unusual presentations, and the lack of specific testing preclude early diagnosis and timely treatment of this fatal condition.
Initial treatment options for localized or with limited spread disease is resective surgery. The role of chemo- or radiation therapy is not known, but they have not previously shown promising results,6,8 except in some cases when they are used as postoperative adjuvant chemotherapy4 or in bulky, locally invasive tumors.1 The recurrence rate after surgery is very high, resulting in a poor 5-year survival rate.1,8 Experimental therapies, such as antibodies that target epidermal growth factor receptor mutations, have not shown much success either.8 In conclusion, the outlook for patients with PSC with the current available knowledge and treatment protocols, is dismal.
Most of the current knowledge and data in the literature is based on cases from autopsy or early-stage surgical resections rather than on patients with advanced cancer.5 Moreover, the role of surgical resection in PSC is questionable, given the high recurrence rate. Subsequently, the clinical and pathological manifestations have yet to be well characterized.4 There has been advance with the publication of more studies recently. Cytokeratin markers such as CAM 5.2 and AE1/AE3 are commonly useful to support the diagnosis when suspected.3 Other markers, including the carcinoembryonic antigen, CD15, and thyroid transcription factor-1 may be variably positive, based on the differentiation of the cancer. Other exciting prospects in the study of PSC include the suggestion of a modified vimentin histologic score for better characterization of the cancer and the discovery of high plateletderived growth factor receptor beta immunohistochemistry expression in PSC as a potential target for future therapy.
Conclusion
Pulmonary sarcomatoid lung cancer can present with a predominant necrotizing picture that mimics diseases such as tuberculosis. In such case, transbronchial biopsy carries little benefit because the diagnosis depends on whether the biopsied tissue is representative of the entire mass, often confounded by the extensive necrosis. More data is needed to determine prognostic factors and appropriate therapeutic strategies. TSJ
Correspondence
Gaurang Nandkishor Vaidya, MD
References
1. Martin LW, Correa AM, Ordonez NG, et al. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: a predictor of poor prognosis. Ann Thorac Surg. 2007;84(3):973-980.
2. Brambilla E, Travis WD, Colby TV, Corrin B, Shimosato Y. The new World Health Organization classification of lung tumours. Eur Respir J. 2001;18(6):1059-1068.
3. Franks TJ, Galvin JR. Sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung: histologic criteria and common lesions in the differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(1):49-54.
4. Huang SY, Shen SJ, Li XY. Pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinoma: a clinicopathologic study and prognostic analysis of 51 cases. http://wjso. biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1477-7819-11-252. Published 2013. Accessed March 12, 2017.
5. Travis WD. Sarcomatoid neoplasms of the lung and pleura. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134(11):1645-1658.
6. Pelosi G, Sonzogni A, De Pas T, et al. Review article: pulmonary sarcomatoid carcinomas: a practical overview. Int J Surg Pathol. 2010;18(2):103-120.
7. Chang YL, Lee YC, Shih JY, Wu CT. Pulmonary pleomorphic (spindle) cell carcinoma: peculiar clinicopathologic manifestations different from ordinary non-small cell carcinoma. Lung Cancer. 2001;34(1):91-97.
8. Park JS, Lee Y, Han J, et al. Clinicopathologic outcomes of curative resection for sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung. Oncology. 2011;81(3-4):206-213.
This article was originally published in the Journal of Community and Supportive Oncology (JCSO 2017;15(2):103-105). doi: https://doi.org/10.12788/jcso.0259. It is reproduced here with permission of the copyright owner. Further reproduction is prohibited without permission.