User login
NAMS affirms value of hormone therapy for menopausal women
Hormone therapy remains a topic for debate, but a constant in the 2 decades since the Women’s Health Initiative has been the demonstrated effectiveness for relief of vasomotor symptoms and reduction of fracture risk in menopausal women, according to the latest hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society.
“Healthcare professionals caring for menopausal women should understand the basic concepts of relative risk and absolute risk,” wrote Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health and medical director of NAMS, and members of the NAMS 2022 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel in Menopause.
The authors noted that the risks of hormone therapy vary considerably based on type, dose, duration, route of administration, timing of the start of therapy, and whether or not a progestogen is included.
The 2022 statement was commissioned to review new literature and identify the strength of recommendations and quality of evidence since the previous statement in 2017.
The current statement represents not so much a practice-changing update, “but rather that the literature has filled out in some areas,” Dr. Faubion said in an interview. “The recommendations overall haven’t changed,” she said. “The position statement reiterates that hormone therapy, which is significantly underutilized, remains a safe and effective treatment for menopause symptoms, which remain undertreated, with the benefits outweighing the risks for most healthy women who are within 10 years of menopause onset and under the age of 60 years,” she emphasized. “Individualizing therapy is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing risks,” she added.
Overall, the authors confirmed that hormone therapy remains the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture. The risks of hormone therapy differ depending on type, dose, duration of use, route of administration, timing of initiation, and whether a progestogen is used.
Risks and benefits should be stratified by age and time since the start of menopause, according to the statement.
For women younger than 60 years or within 10 years of the onset of menopause who have no contraindications, the potential benefits outweigh the risks in most cases for use of hormone therapy to manage vasomotor symptoms and to help prevent bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
For women who begin hormone therapy more than 10 or 20 years from the start of menopause, or who are aged 60 years and older, the risk-benefit ratio may be less favorable because of the increased absolute risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and dementia. However, strategies such as lower doses and transdermal administration may reduce this risk, according to the statement.
The authors continue to recommend that longer durations of hormone therapy be for documented indications, such as VMS relief, and that patients on longer duration of therapy be reassessed periodically as part of a shared decision-making process. Women with persistent VMS or quality of life issues, or those at risk for osteoporosis, may continue hormone therapy beyond age 60 or 65 years after appropriate evaluation and risk-benefit counseling.
Women with ongoing GSM without indications for systemic therapy whose GSM persists after over-the-counter therapies may try low-dose vaginal estrogen or other nonestrogen therapies regardless of age and for an extended duration if needed, according to the statement.
Challenges, research gaps, and goals
“Barriers to the use of hormone therapy include lack of access to high quality care,” Dr. Faubion said in an interview. The NAMS website, menopause.org, features an option to search for a NAMS-certified provider by ZIP code, she noted.
“Coverage of hormone therapy is highly variable and depends on the insurance company, but most women have access to one form or another with insurance coverage,” she said. “We need to continue to advocate for adequate coverage of menopause symptom treatments, including hormone therapy, so that women’s symptoms – which can significantly affect quality of life – are adequately managed.
“Additional research is needed on the thrombotic risk (venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, and stroke) of oral versus transdermal therapies (including different formulations, doses, and durations of therapy),” Dr. Faubion told this news organization. “More clinical trial data are needed to confirm or refute the potential beneficial effects of hormone therapy on coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality when initiated in perimenopause or early postmenopause,” she said.
Other areas for research include “the breast effects of different estrogen preparations, including the role for selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and tissue selective estrogen complex therapies, optimal progestogen or SERM regimens to prevent endometrial hyperplasia, the relationship between vasomotor symptoms and the risk for heart disease and cognitive changes, and the risks of premature ovarian insufficiency,” Dr. Faubion emphasized.
Looking ahead, “Studies are needed on the effects of longer use of low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy after breast or endometrial cancer, extended use of hormone therapy in women who are early initiators, improved tools to personalize or individualize benefits and risks of hormone therapy, and the role of aging and genetics,” said Dr. Faubion. Other areas for further research include “the long-term benefits and risks on women’s health of lifestyle modification or complementary or nonhormone therapies, if chosen in addition to or over hormone therapy for vasomotor symptoms, bone health, and cardiovascular disease risk reduction,” she added.
The complete statement was published in Menopause: The Journal of the North American Menopause Society.
The position statement received no outside funding. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Hormone therapy remains a topic for debate, but a constant in the 2 decades since the Women’s Health Initiative has been the demonstrated effectiveness for relief of vasomotor symptoms and reduction of fracture risk in menopausal women, according to the latest hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society.
“Healthcare professionals caring for menopausal women should understand the basic concepts of relative risk and absolute risk,” wrote Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health and medical director of NAMS, and members of the NAMS 2022 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel in Menopause.
The authors noted that the risks of hormone therapy vary considerably based on type, dose, duration, route of administration, timing of the start of therapy, and whether or not a progestogen is included.
The 2022 statement was commissioned to review new literature and identify the strength of recommendations and quality of evidence since the previous statement in 2017.
The current statement represents not so much a practice-changing update, “but rather that the literature has filled out in some areas,” Dr. Faubion said in an interview. “The recommendations overall haven’t changed,” she said. “The position statement reiterates that hormone therapy, which is significantly underutilized, remains a safe and effective treatment for menopause symptoms, which remain undertreated, with the benefits outweighing the risks for most healthy women who are within 10 years of menopause onset and under the age of 60 years,” she emphasized. “Individualizing therapy is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing risks,” she added.
Overall, the authors confirmed that hormone therapy remains the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture. The risks of hormone therapy differ depending on type, dose, duration of use, route of administration, timing of initiation, and whether a progestogen is used.
Risks and benefits should be stratified by age and time since the start of menopause, according to the statement.
For women younger than 60 years or within 10 years of the onset of menopause who have no contraindications, the potential benefits outweigh the risks in most cases for use of hormone therapy to manage vasomotor symptoms and to help prevent bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
For women who begin hormone therapy more than 10 or 20 years from the start of menopause, or who are aged 60 years and older, the risk-benefit ratio may be less favorable because of the increased absolute risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and dementia. However, strategies such as lower doses and transdermal administration may reduce this risk, according to the statement.
The authors continue to recommend that longer durations of hormone therapy be for documented indications, such as VMS relief, and that patients on longer duration of therapy be reassessed periodically as part of a shared decision-making process. Women with persistent VMS or quality of life issues, or those at risk for osteoporosis, may continue hormone therapy beyond age 60 or 65 years after appropriate evaluation and risk-benefit counseling.
Women with ongoing GSM without indications for systemic therapy whose GSM persists after over-the-counter therapies may try low-dose vaginal estrogen or other nonestrogen therapies regardless of age and for an extended duration if needed, according to the statement.
Challenges, research gaps, and goals
“Barriers to the use of hormone therapy include lack of access to high quality care,” Dr. Faubion said in an interview. The NAMS website, menopause.org, features an option to search for a NAMS-certified provider by ZIP code, she noted.
“Coverage of hormone therapy is highly variable and depends on the insurance company, but most women have access to one form or another with insurance coverage,” she said. “We need to continue to advocate for adequate coverage of menopause symptom treatments, including hormone therapy, so that women’s symptoms – which can significantly affect quality of life – are adequately managed.
“Additional research is needed on the thrombotic risk (venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, and stroke) of oral versus transdermal therapies (including different formulations, doses, and durations of therapy),” Dr. Faubion told this news organization. “More clinical trial data are needed to confirm or refute the potential beneficial effects of hormone therapy on coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality when initiated in perimenopause or early postmenopause,” she said.
Other areas for research include “the breast effects of different estrogen preparations, including the role for selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and tissue selective estrogen complex therapies, optimal progestogen or SERM regimens to prevent endometrial hyperplasia, the relationship between vasomotor symptoms and the risk for heart disease and cognitive changes, and the risks of premature ovarian insufficiency,” Dr. Faubion emphasized.
Looking ahead, “Studies are needed on the effects of longer use of low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy after breast or endometrial cancer, extended use of hormone therapy in women who are early initiators, improved tools to personalize or individualize benefits and risks of hormone therapy, and the role of aging and genetics,” said Dr. Faubion. Other areas for further research include “the long-term benefits and risks on women’s health of lifestyle modification or complementary or nonhormone therapies, if chosen in addition to or over hormone therapy for vasomotor symptoms, bone health, and cardiovascular disease risk reduction,” she added.
The complete statement was published in Menopause: The Journal of the North American Menopause Society.
The position statement received no outside funding. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
Hormone therapy remains a topic for debate, but a constant in the 2 decades since the Women’s Health Initiative has been the demonstrated effectiveness for relief of vasomotor symptoms and reduction of fracture risk in menopausal women, according to the latest hormone therapy position statement of the North American Menopause Society.
“Healthcare professionals caring for menopausal women should understand the basic concepts of relative risk and absolute risk,” wrote Stephanie S. Faubion, MD, director of the Mayo Clinic Center for Women’s Health and medical director of NAMS, and members of the NAMS 2022 Hormone Therapy Position Statement Advisory Panel in Menopause.
The authors noted that the risks of hormone therapy vary considerably based on type, dose, duration, route of administration, timing of the start of therapy, and whether or not a progestogen is included.
The 2022 statement was commissioned to review new literature and identify the strength of recommendations and quality of evidence since the previous statement in 2017.
The current statement represents not so much a practice-changing update, “but rather that the literature has filled out in some areas,” Dr. Faubion said in an interview. “The recommendations overall haven’t changed,” she said. “The position statement reiterates that hormone therapy, which is significantly underutilized, remains a safe and effective treatment for menopause symptoms, which remain undertreated, with the benefits outweighing the risks for most healthy women who are within 10 years of menopause onset and under the age of 60 years,” she emphasized. “Individualizing therapy is key to maximizing benefits and minimizing risks,” she added.
Overall, the authors confirmed that hormone therapy remains the most effective treatment for vasomotor symptoms (VMS) and the genitourinary syndrome of menopause (GSM), and has been shown to prevent bone loss and fracture. The risks of hormone therapy differ depending on type, dose, duration of use, route of administration, timing of initiation, and whether a progestogen is used.
Risks and benefits should be stratified by age and time since the start of menopause, according to the statement.
For women younger than 60 years or within 10 years of the onset of menopause who have no contraindications, the potential benefits outweigh the risks in most cases for use of hormone therapy to manage vasomotor symptoms and to help prevent bone loss and reduce fracture risk.
For women who begin hormone therapy more than 10 or 20 years from the start of menopause, or who are aged 60 years and older, the risk-benefit ratio may be less favorable because of the increased absolute risk of coronary heart disease, stroke, venous thromboembolism, and dementia. However, strategies such as lower doses and transdermal administration may reduce this risk, according to the statement.
The authors continue to recommend that longer durations of hormone therapy be for documented indications, such as VMS relief, and that patients on longer duration of therapy be reassessed periodically as part of a shared decision-making process. Women with persistent VMS or quality of life issues, or those at risk for osteoporosis, may continue hormone therapy beyond age 60 or 65 years after appropriate evaluation and risk-benefit counseling.
Women with ongoing GSM without indications for systemic therapy whose GSM persists after over-the-counter therapies may try low-dose vaginal estrogen or other nonestrogen therapies regardless of age and for an extended duration if needed, according to the statement.
Challenges, research gaps, and goals
“Barriers to the use of hormone therapy include lack of access to high quality care,” Dr. Faubion said in an interview. The NAMS website, menopause.org, features an option to search for a NAMS-certified provider by ZIP code, she noted.
“Coverage of hormone therapy is highly variable and depends on the insurance company, but most women have access to one form or another with insurance coverage,” she said. “We need to continue to advocate for adequate coverage of menopause symptom treatments, including hormone therapy, so that women’s symptoms – which can significantly affect quality of life – are adequately managed.
“Additional research is needed on the thrombotic risk (venous thromboembolism, pulmonary embolism, and stroke) of oral versus transdermal therapies (including different formulations, doses, and durations of therapy),” Dr. Faubion told this news organization. “More clinical trial data are needed to confirm or refute the potential beneficial effects of hormone therapy on coronary heart disease and all-cause mortality when initiated in perimenopause or early postmenopause,” she said.
Other areas for research include “the breast effects of different estrogen preparations, including the role for selective estrogen receptor modulator (SERM) and tissue selective estrogen complex therapies, optimal progestogen or SERM regimens to prevent endometrial hyperplasia, the relationship between vasomotor symptoms and the risk for heart disease and cognitive changes, and the risks of premature ovarian insufficiency,” Dr. Faubion emphasized.
Looking ahead, “Studies are needed on the effects of longer use of low-dose vaginal estrogen therapy after breast or endometrial cancer, extended use of hormone therapy in women who are early initiators, improved tools to personalize or individualize benefits and risks of hormone therapy, and the role of aging and genetics,” said Dr. Faubion. Other areas for further research include “the long-term benefits and risks on women’s health of lifestyle modification or complementary or nonhormone therapies, if chosen in addition to or over hormone therapy for vasomotor symptoms, bone health, and cardiovascular disease risk reduction,” she added.
The complete statement was published in Menopause: The Journal of the North American Menopause Society.
The position statement received no outside funding. The authors had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM MENOPAUSE
Comments open for U.K.’s transgender care guideline
Gynecologic and obstetric health care needs of transgender and gender-diverse adults, including fertility preservation, ending masculinizing hormones in pregnancy, and support for “chest-feeding” are proposed in a novel draft guideline issued by the U.K.’s Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists.
The draft Green-top Guideline on Care of Trans and Gender Diverse Adults in Obstetrics and Gynaecology is open for consultation and comment until Sept. 6. It aims to address the specific needs of transgender and gender-diverse individuals that, according to the guideline, are currently not consistently included in specialist training programs or in continuing professional development.
With a rise in the number of people seeking to transition, obstetricians and gynecologists are seeing more transgender and gender-diverse patients. Phil Rolland, MD, consultant gynecological oncologist from Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Cheltenham, and member of the guideline committee, said that, “It is highly likely that if an obstetrician or gynaecologist hasn’t already consulted or treated a trans or gender-diverse patient then it is only a matter of time before they do.”
He stressed the importance of ensuring inclusivity in obstetric and gynecologic care. “We know that trans people are more likely to have poor experiences when accessing health care, and we can do better.”
The U.K.-based guideline follows a similar document from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, put in place in March 2021, as reported by this news organization. It called for greater “awareness, knowledge, and sensitivity” in caring for these patients and noted that “bias from health care professionals leads to inadequate access to, underuse of, and inequities within the health care system for transgender patients.”
Guideline addresses fertility preservation, obstetric care, and more
Regarding fertility preservation, discussions around protecting future options should be held before endocrine interventions and/or gender-affirming genital or pelvic surgery procedures, says the guideline. In addition, gynecologic problems that can be experienced need to be explained.
The guideline also addresses obstetric care, advising that trans men on long-acting masculinizing hormone therapy should stop therapy 3 months prior to conception. People who conceive while taking masculinizing hormone therapy should discontinue the therapy as soon as possible.
Birth mode should be discussed with all trans men who plan to conceive, ideally at a prepregnancy counseling appointment, but at minimum, before the third trimester. Choice of feeding manner should also be addressed in the antenatal period, with trans men who wish to chest feed offered chest-feeding support, similar to that given to cis women.
The RCOG guideline comes in the wake of the U.K. government’s new Women’s Health Strategy for England, released in July, which notes that trans men (with female reproductive organs) should be able to access screening services for cervical and breast cancer, a position upheld by the RCOG guideline.
Other key recommendations include that obstetricians and gynecologists, when approached by transgender and gender-diverse people to help with identity-related issues, should liaise with gender-identity specialist services to provide appropriate care.
Removing bias, providing affirming care
Asha Kasliwal, MD, consultant in Community Gynaecology and Reproductive Health Care, Manchester, England, and president of the Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare, also reflected on how transgender and gender-diverse people often feel uncomfortable accessing care, which could lead to, “many people failing to seek or continue health care because of concerns over how they will be treated,” adding that there were associated reports of poor clinical outcomes.
She highlighted that the draft guideline pointed out the importance of language during consultation with transgender and gender-diverse people, noting that “misuse of language, and particularly deliberate misuse of language associated with the sex assigned at birth (misgendering), may cause profound offence.”
Dr. Kasliwal cited the example of “using the correct pronouns when addressing someone and receiving any information about a person’s gender diversity neutrally and nonjudgementally.”
Edward Morris, MD, president of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, acknowledged that trans and gender-diverse individuals say they often feel judged and misunderstood by the health service. “This can act as a barrier for them when it comes to accessing vital care, and we as health care professionals have a role to play in making them feel listened to and recognized.”
“This draft guideline is our first attempt to ensure we are providing personalised care for all our patients,” said Dr. Morris. “We welcome feedback on this draft to ensure the guideline is the best as it can be for clinicians and the trans and gender-diverse individuals who use our services.”
The draft guideline as peer-review draft, Care of Trans and Gender Diverse Adults in Obstetrics and Gynaecology is available on the RCOG website. Consultation is open until Sept. 6, 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gynecologic and obstetric health care needs of transgender and gender-diverse adults, including fertility preservation, ending masculinizing hormones in pregnancy, and support for “chest-feeding” are proposed in a novel draft guideline issued by the U.K.’s Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists.
The draft Green-top Guideline on Care of Trans and Gender Diverse Adults in Obstetrics and Gynaecology is open for consultation and comment until Sept. 6. It aims to address the specific needs of transgender and gender-diverse individuals that, according to the guideline, are currently not consistently included in specialist training programs or in continuing professional development.
With a rise in the number of people seeking to transition, obstetricians and gynecologists are seeing more transgender and gender-diverse patients. Phil Rolland, MD, consultant gynecological oncologist from Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Cheltenham, and member of the guideline committee, said that, “It is highly likely that if an obstetrician or gynaecologist hasn’t already consulted or treated a trans or gender-diverse patient then it is only a matter of time before they do.”
He stressed the importance of ensuring inclusivity in obstetric and gynecologic care. “We know that trans people are more likely to have poor experiences when accessing health care, and we can do better.”
The U.K.-based guideline follows a similar document from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, put in place in March 2021, as reported by this news organization. It called for greater “awareness, knowledge, and sensitivity” in caring for these patients and noted that “bias from health care professionals leads to inadequate access to, underuse of, and inequities within the health care system for transgender patients.”
Guideline addresses fertility preservation, obstetric care, and more
Regarding fertility preservation, discussions around protecting future options should be held before endocrine interventions and/or gender-affirming genital or pelvic surgery procedures, says the guideline. In addition, gynecologic problems that can be experienced need to be explained.
The guideline also addresses obstetric care, advising that trans men on long-acting masculinizing hormone therapy should stop therapy 3 months prior to conception. People who conceive while taking masculinizing hormone therapy should discontinue the therapy as soon as possible.
Birth mode should be discussed with all trans men who plan to conceive, ideally at a prepregnancy counseling appointment, but at minimum, before the third trimester. Choice of feeding manner should also be addressed in the antenatal period, with trans men who wish to chest feed offered chest-feeding support, similar to that given to cis women.
The RCOG guideline comes in the wake of the U.K. government’s new Women’s Health Strategy for England, released in July, which notes that trans men (with female reproductive organs) should be able to access screening services for cervical and breast cancer, a position upheld by the RCOG guideline.
Other key recommendations include that obstetricians and gynecologists, when approached by transgender and gender-diverse people to help with identity-related issues, should liaise with gender-identity specialist services to provide appropriate care.
Removing bias, providing affirming care
Asha Kasliwal, MD, consultant in Community Gynaecology and Reproductive Health Care, Manchester, England, and president of the Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare, also reflected on how transgender and gender-diverse people often feel uncomfortable accessing care, which could lead to, “many people failing to seek or continue health care because of concerns over how they will be treated,” adding that there were associated reports of poor clinical outcomes.
She highlighted that the draft guideline pointed out the importance of language during consultation with transgender and gender-diverse people, noting that “misuse of language, and particularly deliberate misuse of language associated with the sex assigned at birth (misgendering), may cause profound offence.”
Dr. Kasliwal cited the example of “using the correct pronouns when addressing someone and receiving any information about a person’s gender diversity neutrally and nonjudgementally.”
Edward Morris, MD, president of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, acknowledged that trans and gender-diverse individuals say they often feel judged and misunderstood by the health service. “This can act as a barrier for them when it comes to accessing vital care, and we as health care professionals have a role to play in making them feel listened to and recognized.”
“This draft guideline is our first attempt to ensure we are providing personalised care for all our patients,” said Dr. Morris. “We welcome feedback on this draft to ensure the guideline is the best as it can be for clinicians and the trans and gender-diverse individuals who use our services.”
The draft guideline as peer-review draft, Care of Trans and Gender Diverse Adults in Obstetrics and Gynaecology is available on the RCOG website. Consultation is open until Sept. 6, 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Gynecologic and obstetric health care needs of transgender and gender-diverse adults, including fertility preservation, ending masculinizing hormones in pregnancy, and support for “chest-feeding” are proposed in a novel draft guideline issued by the U.K.’s Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists.
The draft Green-top Guideline on Care of Trans and Gender Diverse Adults in Obstetrics and Gynaecology is open for consultation and comment until Sept. 6. It aims to address the specific needs of transgender and gender-diverse individuals that, according to the guideline, are currently not consistently included in specialist training programs or in continuing professional development.
With a rise in the number of people seeking to transition, obstetricians and gynecologists are seeing more transgender and gender-diverse patients. Phil Rolland, MD, consultant gynecological oncologist from Gloucestershire Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, Cheltenham, and member of the guideline committee, said that, “It is highly likely that if an obstetrician or gynaecologist hasn’t already consulted or treated a trans or gender-diverse patient then it is only a matter of time before they do.”
He stressed the importance of ensuring inclusivity in obstetric and gynecologic care. “We know that trans people are more likely to have poor experiences when accessing health care, and we can do better.”
The U.K.-based guideline follows a similar document from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, put in place in March 2021, as reported by this news organization. It called for greater “awareness, knowledge, and sensitivity” in caring for these patients and noted that “bias from health care professionals leads to inadequate access to, underuse of, and inequities within the health care system for transgender patients.”
Guideline addresses fertility preservation, obstetric care, and more
Regarding fertility preservation, discussions around protecting future options should be held before endocrine interventions and/or gender-affirming genital or pelvic surgery procedures, says the guideline. In addition, gynecologic problems that can be experienced need to be explained.
The guideline also addresses obstetric care, advising that trans men on long-acting masculinizing hormone therapy should stop therapy 3 months prior to conception. People who conceive while taking masculinizing hormone therapy should discontinue the therapy as soon as possible.
Birth mode should be discussed with all trans men who plan to conceive, ideally at a prepregnancy counseling appointment, but at minimum, before the third trimester. Choice of feeding manner should also be addressed in the antenatal period, with trans men who wish to chest feed offered chest-feeding support, similar to that given to cis women.
The RCOG guideline comes in the wake of the U.K. government’s new Women’s Health Strategy for England, released in July, which notes that trans men (with female reproductive organs) should be able to access screening services for cervical and breast cancer, a position upheld by the RCOG guideline.
Other key recommendations include that obstetricians and gynecologists, when approached by transgender and gender-diverse people to help with identity-related issues, should liaise with gender-identity specialist services to provide appropriate care.
Removing bias, providing affirming care
Asha Kasliwal, MD, consultant in Community Gynaecology and Reproductive Health Care, Manchester, England, and president of the Faculty of Sexual and Reproductive Healthcare, also reflected on how transgender and gender-diverse people often feel uncomfortable accessing care, which could lead to, “many people failing to seek or continue health care because of concerns over how they will be treated,” adding that there were associated reports of poor clinical outcomes.
She highlighted that the draft guideline pointed out the importance of language during consultation with transgender and gender-diverse people, noting that “misuse of language, and particularly deliberate misuse of language associated with the sex assigned at birth (misgendering), may cause profound offence.”
Dr. Kasliwal cited the example of “using the correct pronouns when addressing someone and receiving any information about a person’s gender diversity neutrally and nonjudgementally.”
Edward Morris, MD, president of the Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists, acknowledged that trans and gender-diverse individuals say they often feel judged and misunderstood by the health service. “This can act as a barrier for them when it comes to accessing vital care, and we as health care professionals have a role to play in making them feel listened to and recognized.”
“This draft guideline is our first attempt to ensure we are providing personalised care for all our patients,” said Dr. Morris. “We welcome feedback on this draft to ensure the guideline is the best as it can be for clinicians and the trans and gender-diverse individuals who use our services.”
The draft guideline as peer-review draft, Care of Trans and Gender Diverse Adults in Obstetrics and Gynaecology is available on the RCOG website. Consultation is open until Sept. 6, 2022.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Detransitioners lament inadequate clinical support
Transgender people who medically detransition – those who stop or switch gender-affirming hormone therapy or who undergo a reversal of a surgical reconstruction – report feeling stigmatized by clinicians and receiving inadequate professional support, researchers have found. As a result, such patients often avoid health care at the time they stop undergoing medical interventions, and many consider their overall care to be “suboptimal.”
“Clinicians providing gender-affirming care must be careful to avoid shaming patients who are pursuing hormonal cessation or switching or surgical reversals and instead strive to address current mental and physical health needs,” wrote the authors of the new study, which was published in JAMA Network Open.
In a commentary accompanying the journal article, Jack L. Turban, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of California, San Francisco, argues that discontinuation of gender-affirming care is rare and is “woefully politicized”.
Dr. Turban wrote, “clinical protocols should be in place to support patients who have dynamic needs surrounding these interventions.” He added that “gender-affirming care should encompass the entirety of an individual’s embodiment goals, even when those goals may have pivoted over time.”
For the study, Kinnon R. MacKinnon, PhD, of York University, Toronto, and colleagues conducted video interviews with 28 Canadian individuals older than 18 years. All identified as “detransitioning, retransitioning, detrans, retrans, reidentifying, [experiencing] a shift in gender identity after initiating transition, or having stopped transition.”
Eighteen (64%) were assigned female sex at birth, and 10 (36%) were assigned male sex at birth. Twenty (71%) were aged 20-29; six were aged 30-39, and two were older than 40. Twenty-one were White. One participant who only socially transitioned was removed from the analysis of medical transitions. About half who medically transitioned did so between the ages of 18 and 24.
Reasons for stopping a medical transition included concerns about physical or mental health, surgical complications, postoperative pain, unsupportive parents or romantic partners, discrimination in the workplace, and difficulty accessing clinical care or gender-affirming surgery.
One participant, who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as female, said the transition did not help. The process was “a hot mess,” she said. Because she’d known people who had experienced improvements in mental and physical health as a result of transitioning, especially after initiating hormone therapy, she kept going. But, she said, “the farther I got into transition, the worse my [borderline personality disorder] symptoms and my presentation was.”
Lack of clinician support – going ‘cold turkey’
Many individuals reported that they stopped taking hormones “cold turkey,” without the support of a therapist or a clinician, because they did not trust health care providers or had had bad interactions with the medical system.
Most of those who had undergone gender-affirming surgical removal of testes or ovaries in their initial transition said the care they received when they decided to detransition was “bad.” Clinicians were judgmental or had inadequate knowledge about the process, the researchers reported. Some detransitioners said such encounters with clinicians added to their feelings of shame.
One participant who was born female and transitioned to male said she had good relationships with her clinicians and therapist, but she still felt “guilt and shame” about detransitioning back to female. She also worried that those clinicians would view her initial decision as a “mistake” or “through a lens of ‘regret,’ which was inauthentic to her feelings,” the researchers reported.
Another individual who had been assigned female sex at birth said that when she wanted to detransition, she consulted a physician about switching back to estrogen. “She wasn’t very tactful,” the person, who now identifies as female, recalled. “She made comments about how I should have thought about [my initial transition] harder.”
Participants said clinicians lacked sufficient information on detransitioning.
Dr. Turban noted that data are limited on the physiologic and psychological effects of discontinuing exogenous hormone therapy, “because it is such a rare occurrence.” He acknowledged that “more research is needed on the effects of discontinuation so that clinicians can better educate patients.”
The researchers found that most who sought to detransition consulted online forums and networks. The r/detrans discussion group on Reddit, for instance, now has 36,400 members.
Some reported regret that they had transitioned, while others – especially those who identify now as nonbinary or gender-fluid – said they were happy with their initial choice.
Eighteen of the 27 had no regrets and/or had positive feelings about the gender-affirming medications or procedures they had received in the past. Six (22%) had regret, and three were ambivalent. The rate of regret in the relatively small sample is higher than that observed in several other studies. Trans advocates also point out that detransitioning does not necessarily equate with regret.
When asked whether she regretted having undergone a double mastectomy, an individual who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as female said, “Some days I do, some days I don’t.” She also said she is not considering breast augmentation. “I’m just going to leave myself alone,” she said, adding that “it’s part of my journey.”
A participant who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as a cisgender woman said that she is mostly regarded by others as a trans person now, although she does not identify that way. But she said taking testosterone in the past was the right decision. “At the time, that was absolutely what I knew I had to do,” she said. “I’m actually not upset about any of the permanent changes it had on my body.”
The researchers noted that some participants said that “their parents or family circumstances explicitly forced, or implicitly encouraged detransition.”
Dr. Turban encouraged clinicians to consider how such external factors might “exacerbate internal factors,” such as internalized transphobia, which could lead to a discontinuation of gender-affirming care.
The study received funding from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) Insight Development Program and a York University SSHRC Explore grant. Travis Salway, MD, a coauthor, has received grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Michael Smith Health Research BC, BC SUPPORT Unit Fraser Centre, Simon Fraser University’s Community-Engaged Research Initiative, and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council outside the submitted work. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was been updated on 8/5/22 to include additional information about detransitioning.
Transgender people who medically detransition – those who stop or switch gender-affirming hormone therapy or who undergo a reversal of a surgical reconstruction – report feeling stigmatized by clinicians and receiving inadequate professional support, researchers have found. As a result, such patients often avoid health care at the time they stop undergoing medical interventions, and many consider their overall care to be “suboptimal.”
“Clinicians providing gender-affirming care must be careful to avoid shaming patients who are pursuing hormonal cessation or switching or surgical reversals and instead strive to address current mental and physical health needs,” wrote the authors of the new study, which was published in JAMA Network Open.
In a commentary accompanying the journal article, Jack L. Turban, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of California, San Francisco, argues that discontinuation of gender-affirming care is rare and is “woefully politicized”.
Dr. Turban wrote, “clinical protocols should be in place to support patients who have dynamic needs surrounding these interventions.” He added that “gender-affirming care should encompass the entirety of an individual’s embodiment goals, even when those goals may have pivoted over time.”
For the study, Kinnon R. MacKinnon, PhD, of York University, Toronto, and colleagues conducted video interviews with 28 Canadian individuals older than 18 years. All identified as “detransitioning, retransitioning, detrans, retrans, reidentifying, [experiencing] a shift in gender identity after initiating transition, or having stopped transition.”
Eighteen (64%) were assigned female sex at birth, and 10 (36%) were assigned male sex at birth. Twenty (71%) were aged 20-29; six were aged 30-39, and two were older than 40. Twenty-one were White. One participant who only socially transitioned was removed from the analysis of medical transitions. About half who medically transitioned did so between the ages of 18 and 24.
Reasons for stopping a medical transition included concerns about physical or mental health, surgical complications, postoperative pain, unsupportive parents or romantic partners, discrimination in the workplace, and difficulty accessing clinical care or gender-affirming surgery.
One participant, who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as female, said the transition did not help. The process was “a hot mess,” she said. Because she’d known people who had experienced improvements in mental and physical health as a result of transitioning, especially after initiating hormone therapy, she kept going. But, she said, “the farther I got into transition, the worse my [borderline personality disorder] symptoms and my presentation was.”
Lack of clinician support – going ‘cold turkey’
Many individuals reported that they stopped taking hormones “cold turkey,” without the support of a therapist or a clinician, because they did not trust health care providers or had had bad interactions with the medical system.
Most of those who had undergone gender-affirming surgical removal of testes or ovaries in their initial transition said the care they received when they decided to detransition was “bad.” Clinicians were judgmental or had inadequate knowledge about the process, the researchers reported. Some detransitioners said such encounters with clinicians added to their feelings of shame.
One participant who was born female and transitioned to male said she had good relationships with her clinicians and therapist, but she still felt “guilt and shame” about detransitioning back to female. She also worried that those clinicians would view her initial decision as a “mistake” or “through a lens of ‘regret,’ which was inauthentic to her feelings,” the researchers reported.
Another individual who had been assigned female sex at birth said that when she wanted to detransition, she consulted a physician about switching back to estrogen. “She wasn’t very tactful,” the person, who now identifies as female, recalled. “She made comments about how I should have thought about [my initial transition] harder.”
Participants said clinicians lacked sufficient information on detransitioning.
Dr. Turban noted that data are limited on the physiologic and psychological effects of discontinuing exogenous hormone therapy, “because it is such a rare occurrence.” He acknowledged that “more research is needed on the effects of discontinuation so that clinicians can better educate patients.”
The researchers found that most who sought to detransition consulted online forums and networks. The r/detrans discussion group on Reddit, for instance, now has 36,400 members.
Some reported regret that they had transitioned, while others – especially those who identify now as nonbinary or gender-fluid – said they were happy with their initial choice.
Eighteen of the 27 had no regrets and/or had positive feelings about the gender-affirming medications or procedures they had received in the past. Six (22%) had regret, and three were ambivalent. The rate of regret in the relatively small sample is higher than that observed in several other studies. Trans advocates also point out that detransitioning does not necessarily equate with regret.
When asked whether she regretted having undergone a double mastectomy, an individual who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as female said, “Some days I do, some days I don’t.” She also said she is not considering breast augmentation. “I’m just going to leave myself alone,” she said, adding that “it’s part of my journey.”
A participant who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as a cisgender woman said that she is mostly regarded by others as a trans person now, although she does not identify that way. But she said taking testosterone in the past was the right decision. “At the time, that was absolutely what I knew I had to do,” she said. “I’m actually not upset about any of the permanent changes it had on my body.”
The researchers noted that some participants said that “their parents or family circumstances explicitly forced, or implicitly encouraged detransition.”
Dr. Turban encouraged clinicians to consider how such external factors might “exacerbate internal factors,” such as internalized transphobia, which could lead to a discontinuation of gender-affirming care.
The study received funding from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) Insight Development Program and a York University SSHRC Explore grant. Travis Salway, MD, a coauthor, has received grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Michael Smith Health Research BC, BC SUPPORT Unit Fraser Centre, Simon Fraser University’s Community-Engaged Research Initiative, and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council outside the submitted work. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was been updated on 8/5/22 to include additional information about detransitioning.
Transgender people who medically detransition – those who stop or switch gender-affirming hormone therapy or who undergo a reversal of a surgical reconstruction – report feeling stigmatized by clinicians and receiving inadequate professional support, researchers have found. As a result, such patients often avoid health care at the time they stop undergoing medical interventions, and many consider their overall care to be “suboptimal.”
“Clinicians providing gender-affirming care must be careful to avoid shaming patients who are pursuing hormonal cessation or switching or surgical reversals and instead strive to address current mental and physical health needs,” wrote the authors of the new study, which was published in JAMA Network Open.
In a commentary accompanying the journal article, Jack L. Turban, MD, a psychiatrist at the University of California, San Francisco, argues that discontinuation of gender-affirming care is rare and is “woefully politicized”.
Dr. Turban wrote, “clinical protocols should be in place to support patients who have dynamic needs surrounding these interventions.” He added that “gender-affirming care should encompass the entirety of an individual’s embodiment goals, even when those goals may have pivoted over time.”
For the study, Kinnon R. MacKinnon, PhD, of York University, Toronto, and colleagues conducted video interviews with 28 Canadian individuals older than 18 years. All identified as “detransitioning, retransitioning, detrans, retrans, reidentifying, [experiencing] a shift in gender identity after initiating transition, or having stopped transition.”
Eighteen (64%) were assigned female sex at birth, and 10 (36%) were assigned male sex at birth. Twenty (71%) were aged 20-29; six were aged 30-39, and two were older than 40. Twenty-one were White. One participant who only socially transitioned was removed from the analysis of medical transitions. About half who medically transitioned did so between the ages of 18 and 24.
Reasons for stopping a medical transition included concerns about physical or mental health, surgical complications, postoperative pain, unsupportive parents or romantic partners, discrimination in the workplace, and difficulty accessing clinical care or gender-affirming surgery.
One participant, who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as female, said the transition did not help. The process was “a hot mess,” she said. Because she’d known people who had experienced improvements in mental and physical health as a result of transitioning, especially after initiating hormone therapy, she kept going. But, she said, “the farther I got into transition, the worse my [borderline personality disorder] symptoms and my presentation was.”
Lack of clinician support – going ‘cold turkey’
Many individuals reported that they stopped taking hormones “cold turkey,” without the support of a therapist or a clinician, because they did not trust health care providers or had had bad interactions with the medical system.
Most of those who had undergone gender-affirming surgical removal of testes or ovaries in their initial transition said the care they received when they decided to detransition was “bad.” Clinicians were judgmental or had inadequate knowledge about the process, the researchers reported. Some detransitioners said such encounters with clinicians added to their feelings of shame.
One participant who was born female and transitioned to male said she had good relationships with her clinicians and therapist, but she still felt “guilt and shame” about detransitioning back to female. She also worried that those clinicians would view her initial decision as a “mistake” or “through a lens of ‘regret,’ which was inauthentic to her feelings,” the researchers reported.
Another individual who had been assigned female sex at birth said that when she wanted to detransition, she consulted a physician about switching back to estrogen. “She wasn’t very tactful,” the person, who now identifies as female, recalled. “She made comments about how I should have thought about [my initial transition] harder.”
Participants said clinicians lacked sufficient information on detransitioning.
Dr. Turban noted that data are limited on the physiologic and psychological effects of discontinuing exogenous hormone therapy, “because it is such a rare occurrence.” He acknowledged that “more research is needed on the effects of discontinuation so that clinicians can better educate patients.”
The researchers found that most who sought to detransition consulted online forums and networks. The r/detrans discussion group on Reddit, for instance, now has 36,400 members.
Some reported regret that they had transitioned, while others – especially those who identify now as nonbinary or gender-fluid – said they were happy with their initial choice.
Eighteen of the 27 had no regrets and/or had positive feelings about the gender-affirming medications or procedures they had received in the past. Six (22%) had regret, and three were ambivalent. The rate of regret in the relatively small sample is higher than that observed in several other studies. Trans advocates also point out that detransitioning does not necessarily equate with regret.
When asked whether she regretted having undergone a double mastectomy, an individual who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as female said, “Some days I do, some days I don’t.” She also said she is not considering breast augmentation. “I’m just going to leave myself alone,” she said, adding that “it’s part of my journey.”
A participant who had been assigned female sex at birth and who now identifies as a cisgender woman said that she is mostly regarded by others as a trans person now, although she does not identify that way. But she said taking testosterone in the past was the right decision. “At the time, that was absolutely what I knew I had to do,” she said. “I’m actually not upset about any of the permanent changes it had on my body.”
The researchers noted that some participants said that “their parents or family circumstances explicitly forced, or implicitly encouraged detransition.”
Dr. Turban encouraged clinicians to consider how such external factors might “exacerbate internal factors,” such as internalized transphobia, which could lead to a discontinuation of gender-affirming care.
The study received funding from the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council (SSHRC) Insight Development Program and a York University SSHRC Explore grant. Travis Salway, MD, a coauthor, has received grants from Canadian Institutes of Health Research, Michael Smith Health Research BC, BC SUPPORT Unit Fraser Centre, Simon Fraser University’s Community-Engaged Research Initiative, and the Social Sciences and Humanities Research Council outside the submitted work. The other authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This article was been updated on 8/5/22 to include additional information about detransitioning.
Moms using frozen embryos carry higher hypertensive risk
Women who become pregnant during in vitro fertilization (IVF) from previously frozen embryos have a significantly higher chance of developing hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia than do women who become pregnant through natural conception, researchers have found.
The new findings come from a study presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. In the study, which will soon be published in Hypertension, researchers analyzed more than 4.5 million pregnancies from Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
“Our findings are significant because frozen embryo transfers are increasingly common all over the world, partly due to the elective freezing of all embryos,” said Sindre Hoff Petersen, PhD, a fellow in the department of public health and nursing at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, who led the study.
More than 320,000 IVF procedures were performed in the United States in 2020, according to preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Of those, more than 123,000 eggs or embryos were frozen for future use.
The use of assisted reproductive technology, which includes IVF, has more than doubled during the past decade, the CDC reports. Roughly 2% of all babies born in the United States each year are conceived through assisted reproductive technology.
Dr. Petersen and his colleagues compared maternal complications in sibling pregnancies. Women who became pregnant following the transfer of a frozen embryo were 74% more likely to develop a hypertensive disorder than women who became pregnant following natural conception (7.4% vs. 4.3%; adjusted odds ratio, 1.74; 95% confidence interval, P < .001). The difference was even higher with respect to sibling births: Women who became pregnant using frozen embryos were 102% more likely than women who became pregnant using natural conception to develop a hypertensive disorder (adjusted odds ratio 2.02; 95% CI, 1.72-2.39, P < .001).
The researchers found no difference in the risk of hypertensive disorders between women who used fresh embryos during IVF and women who used natural conception (5.9% vs. 4.3%, 95% CI, P = .382).
“When we find that the association between frozen embryo transfer and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy persists in sibling comparisons, we believe we have strong indications that treatment factors might in fact contribute to the higher risk,” Dr. Petersen told this news organization.
Women in the study who became pregnant after natural conception had a 4.3% chance of developing hypertensive disorders. That effect persisted after controlling for maternal body mass index, smoking, and time between deliveries, he said.
The findings can add to discussions between patients and doctors on the potential benefits and harms of freezing embryos on an elective basis if there is no clinical indication, Dr. Petersen said. The frozen method is most often used to transfer a single embryo in order to reduce the incidence of multiple pregnancies, such as twins and triplets, which in turn reduces pregnancy complications.
“The vast majority of IVF pregnancies, including frozen embryo transfer, are healthy and uncomplicated, and both short- and long-term outcomes for both the mother and the children are very reassuring,” Dr. Petersen said.
Women who become pregnant through use of frozen embryos should be more closely monitored for potential hypertensive disorders, although more work is needed to determine the reasons for the association, said Elizabeth S. Ginsburg, MD, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
“This is something general ob.gyns. need to be aware of, but it’s not clear which subpopulations of patients are going to be affected,” Dr. Ginsburg said. “More investigation is needed to determine if this is caused by the way the uterus is readied for the embryo transfer or if it’s patient population etiology.”
Some studies have suggested that the absence of a hormone-producing cyst, which forms on the ovary during each menstrual cycle, could explain the link between frozen embryo transfer and heightened preeclampsia risk.
Dr. Petersen and Dr. Ginsburg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women who become pregnant during in vitro fertilization (IVF) from previously frozen embryos have a significantly higher chance of developing hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia than do women who become pregnant through natural conception, researchers have found.
The new findings come from a study presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. In the study, which will soon be published in Hypertension, researchers analyzed more than 4.5 million pregnancies from Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
“Our findings are significant because frozen embryo transfers are increasingly common all over the world, partly due to the elective freezing of all embryos,” said Sindre Hoff Petersen, PhD, a fellow in the department of public health and nursing at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, who led the study.
More than 320,000 IVF procedures were performed in the United States in 2020, according to preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Of those, more than 123,000 eggs or embryos were frozen for future use.
The use of assisted reproductive technology, which includes IVF, has more than doubled during the past decade, the CDC reports. Roughly 2% of all babies born in the United States each year are conceived through assisted reproductive technology.
Dr. Petersen and his colleagues compared maternal complications in sibling pregnancies. Women who became pregnant following the transfer of a frozen embryo were 74% more likely to develop a hypertensive disorder than women who became pregnant following natural conception (7.4% vs. 4.3%; adjusted odds ratio, 1.74; 95% confidence interval, P < .001). The difference was even higher with respect to sibling births: Women who became pregnant using frozen embryos were 102% more likely than women who became pregnant using natural conception to develop a hypertensive disorder (adjusted odds ratio 2.02; 95% CI, 1.72-2.39, P < .001).
The researchers found no difference in the risk of hypertensive disorders between women who used fresh embryos during IVF and women who used natural conception (5.9% vs. 4.3%, 95% CI, P = .382).
“When we find that the association between frozen embryo transfer and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy persists in sibling comparisons, we believe we have strong indications that treatment factors might in fact contribute to the higher risk,” Dr. Petersen told this news organization.
Women in the study who became pregnant after natural conception had a 4.3% chance of developing hypertensive disorders. That effect persisted after controlling for maternal body mass index, smoking, and time between deliveries, he said.
The findings can add to discussions between patients and doctors on the potential benefits and harms of freezing embryos on an elective basis if there is no clinical indication, Dr. Petersen said. The frozen method is most often used to transfer a single embryo in order to reduce the incidence of multiple pregnancies, such as twins and triplets, which in turn reduces pregnancy complications.
“The vast majority of IVF pregnancies, including frozen embryo transfer, are healthy and uncomplicated, and both short- and long-term outcomes for both the mother and the children are very reassuring,” Dr. Petersen said.
Women who become pregnant through use of frozen embryos should be more closely monitored for potential hypertensive disorders, although more work is needed to determine the reasons for the association, said Elizabeth S. Ginsburg, MD, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
“This is something general ob.gyns. need to be aware of, but it’s not clear which subpopulations of patients are going to be affected,” Dr. Ginsburg said. “More investigation is needed to determine if this is caused by the way the uterus is readied for the embryo transfer or if it’s patient population etiology.”
Some studies have suggested that the absence of a hormone-producing cyst, which forms on the ovary during each menstrual cycle, could explain the link between frozen embryo transfer and heightened preeclampsia risk.
Dr. Petersen and Dr. Ginsburg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women who become pregnant during in vitro fertilization (IVF) from previously frozen embryos have a significantly higher chance of developing hypertensive disorders such as preeclampsia than do women who become pregnant through natural conception, researchers have found.
The new findings come from a study presented at the 2022 annual meeting of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology. In the study, which will soon be published in Hypertension, researchers analyzed more than 4.5 million pregnancies from Denmark, Norway, and Sweden.
“Our findings are significant because frozen embryo transfers are increasingly common all over the world, partly due to the elective freezing of all embryos,” said Sindre Hoff Petersen, PhD, a fellow in the department of public health and nursing at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology, Trondheim, who led the study.
More than 320,000 IVF procedures were performed in the United States in 2020, according to preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Of those, more than 123,000 eggs or embryos were frozen for future use.
The use of assisted reproductive technology, which includes IVF, has more than doubled during the past decade, the CDC reports. Roughly 2% of all babies born in the United States each year are conceived through assisted reproductive technology.
Dr. Petersen and his colleagues compared maternal complications in sibling pregnancies. Women who became pregnant following the transfer of a frozen embryo were 74% more likely to develop a hypertensive disorder than women who became pregnant following natural conception (7.4% vs. 4.3%; adjusted odds ratio, 1.74; 95% confidence interval, P < .001). The difference was even higher with respect to sibling births: Women who became pregnant using frozen embryos were 102% more likely than women who became pregnant using natural conception to develop a hypertensive disorder (adjusted odds ratio 2.02; 95% CI, 1.72-2.39, P < .001).
The researchers found no difference in the risk of hypertensive disorders between women who used fresh embryos during IVF and women who used natural conception (5.9% vs. 4.3%, 95% CI, P = .382).
“When we find that the association between frozen embryo transfer and hypertensive disorders in pregnancy persists in sibling comparisons, we believe we have strong indications that treatment factors might in fact contribute to the higher risk,” Dr. Petersen told this news organization.
Women in the study who became pregnant after natural conception had a 4.3% chance of developing hypertensive disorders. That effect persisted after controlling for maternal body mass index, smoking, and time between deliveries, he said.
The findings can add to discussions between patients and doctors on the potential benefits and harms of freezing embryos on an elective basis if there is no clinical indication, Dr. Petersen said. The frozen method is most often used to transfer a single embryo in order to reduce the incidence of multiple pregnancies, such as twins and triplets, which in turn reduces pregnancy complications.
“The vast majority of IVF pregnancies, including frozen embryo transfer, are healthy and uncomplicated, and both short- and long-term outcomes for both the mother and the children are very reassuring,” Dr. Petersen said.
Women who become pregnant through use of frozen embryos should be more closely monitored for potential hypertensive disorders, although more work is needed to determine the reasons for the association, said Elizabeth S. Ginsburg, MD, at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive biology at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston.
“This is something general ob.gyns. need to be aware of, but it’s not clear which subpopulations of patients are going to be affected,” Dr. Ginsburg said. “More investigation is needed to determine if this is caused by the way the uterus is readied for the embryo transfer or if it’s patient population etiology.”
Some studies have suggested that the absence of a hormone-producing cyst, which forms on the ovary during each menstrual cycle, could explain the link between frozen embryo transfer and heightened preeclampsia risk.
Dr. Petersen and Dr. Ginsburg reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Nurses’ cohort study: Endometriosis elevates stroke risk
Women who’ve had endometriosis carry an elevated risk of stroke with them for the rest of their lives, with the greatest risk found in women who’ve had a hysterectomy with an oophorectomy, according to a cohort study of the Nurses’ Health Study.
“This is yet additional evidence that those girls and women with endometriosis are having effects across their lives and in multiple aspects of their health and well-being,” senior study author Stacey A. Missmer, ScD, of the Michigan State University, East Lansing, said in an interview. “This is not, in quotes ‘just a gynecologic condition,’ ” Dr. Missmer added. “It is not strictly about the pelvic pain or infertility, but it really is about the whole health across the life course.”
The study included 112,056 women in the NHSII cohort study who were followed from 1989 to June 2017, documenting 893 incident cases of stroke among them – an incidence of less than 1%. Endometriosis was reported in 5,244 women, and 93% of the cohort were White.
Multivariate adjusted models showed that women who had laparoscopically confirmed endometriosis had a 34% greater risk of stroke than women without a history of endometriosis. Leslie V. Farland, ScD, of the University of Arizona, Tucson, was lead author of the study.
While previous studies have demonstrated an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attack, angina, and atherosclerosis in women who’ve had endometriosis, this is the first study that has confirmed an additional increased risk of stroke, Dr. Missmer said.
Another novel finding, Dr. Missmer said, is that while the CVD risks for these women “seem to peak at an earlier age,” the study found no age differences for stroke risk. “That also reinforces that these stroke events are often happening in an age range typical for stroke, which is further removed from when women are thinking about their gynecologic health specifically.”
These findings don’t translate into a significantly greater risk for stroke overall in women who’ve had endometriosis, Dr. Missmer said. She characterized the risk as “not negligible, but it’s not a huge increased risk.” The absolute risk is still fairly low, she said.
“We don’t want to give the impression that all women with endometriosis need to be panicked or fearful about stroke, she said. “Rather, the messaging is that this yet another bit of evidence that whole health care for those with endometriosis is important.”
Women who’ve had endometriosis and their primary care providers need to be attuned to stroke risk, she said. “This is a critical condition that primary care physicians need to engage around, and perhaps if symptoms related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease emerge in their patients, they need to be engaging cardiology and similar types of support. This is not just about the gynecologists.”
The study also explored other factors that may contribute to stroke risk, with the most significant being hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy, Dr. Missmer said.
This study was unique because it used laparoscopically confirmed rather than self-reported endometriosis, said Louise D. McCullough, MD, neurology chair at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. Another strength of the study she noted was its longitudinal design, although the cohort study design yielded a low number of stroke patients.
“Regardless, I do think it was a very important study because we have a growing recognition about how women’s health and factors such as pregnancy, infertility, parity, complications, and gonadal hormones such as estrogen can influence a woman’s stroke risk much later in life,” Dr. McCullough said in an interview.
Future studies into the relationship between endometriosis and CVD and stroke risk should focus on the mechanism behind the inflammation that occurs in endometriosis, Dr. McCullough said. “Part of it is probably the loss of hormones if a patient has to have an oophorectomy, but part of it is just what do these diseases do for a woman’s later risk – and for primary care physicians, ob.gyns., and stroke neurologists to recognize that these are questions we should ask: Have you ever had eclampsia or preeclampsia? Did you have endometriosis? Have you had miscarriages?”
The study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Missmer disclosed relationships with Shanghai Huilun Biotechnology, Roche, and AbbVie. Dr. McCullough has no relevant disclosures.
Women who’ve had endometriosis carry an elevated risk of stroke with them for the rest of their lives, with the greatest risk found in women who’ve had a hysterectomy with an oophorectomy, according to a cohort study of the Nurses’ Health Study.
“This is yet additional evidence that those girls and women with endometriosis are having effects across their lives and in multiple aspects of their health and well-being,” senior study author Stacey A. Missmer, ScD, of the Michigan State University, East Lansing, said in an interview. “This is not, in quotes ‘just a gynecologic condition,’ ” Dr. Missmer added. “It is not strictly about the pelvic pain or infertility, but it really is about the whole health across the life course.”
The study included 112,056 women in the NHSII cohort study who were followed from 1989 to June 2017, documenting 893 incident cases of stroke among them – an incidence of less than 1%. Endometriosis was reported in 5,244 women, and 93% of the cohort were White.
Multivariate adjusted models showed that women who had laparoscopically confirmed endometriosis had a 34% greater risk of stroke than women without a history of endometriosis. Leslie V. Farland, ScD, of the University of Arizona, Tucson, was lead author of the study.
While previous studies have demonstrated an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attack, angina, and atherosclerosis in women who’ve had endometriosis, this is the first study that has confirmed an additional increased risk of stroke, Dr. Missmer said.
Another novel finding, Dr. Missmer said, is that while the CVD risks for these women “seem to peak at an earlier age,” the study found no age differences for stroke risk. “That also reinforces that these stroke events are often happening in an age range typical for stroke, which is further removed from when women are thinking about their gynecologic health specifically.”
These findings don’t translate into a significantly greater risk for stroke overall in women who’ve had endometriosis, Dr. Missmer said. She characterized the risk as “not negligible, but it’s not a huge increased risk.” The absolute risk is still fairly low, she said.
“We don’t want to give the impression that all women with endometriosis need to be panicked or fearful about stroke, she said. “Rather, the messaging is that this yet another bit of evidence that whole health care for those with endometriosis is important.”
Women who’ve had endometriosis and their primary care providers need to be attuned to stroke risk, she said. “This is a critical condition that primary care physicians need to engage around, and perhaps if symptoms related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease emerge in their patients, they need to be engaging cardiology and similar types of support. This is not just about the gynecologists.”
The study also explored other factors that may contribute to stroke risk, with the most significant being hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy, Dr. Missmer said.
This study was unique because it used laparoscopically confirmed rather than self-reported endometriosis, said Louise D. McCullough, MD, neurology chair at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. Another strength of the study she noted was its longitudinal design, although the cohort study design yielded a low number of stroke patients.
“Regardless, I do think it was a very important study because we have a growing recognition about how women’s health and factors such as pregnancy, infertility, parity, complications, and gonadal hormones such as estrogen can influence a woman’s stroke risk much later in life,” Dr. McCullough said in an interview.
Future studies into the relationship between endometriosis and CVD and stroke risk should focus on the mechanism behind the inflammation that occurs in endometriosis, Dr. McCullough said. “Part of it is probably the loss of hormones if a patient has to have an oophorectomy, but part of it is just what do these diseases do for a woman’s later risk – and for primary care physicians, ob.gyns., and stroke neurologists to recognize that these are questions we should ask: Have you ever had eclampsia or preeclampsia? Did you have endometriosis? Have you had miscarriages?”
The study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Missmer disclosed relationships with Shanghai Huilun Biotechnology, Roche, and AbbVie. Dr. McCullough has no relevant disclosures.
Women who’ve had endometriosis carry an elevated risk of stroke with them for the rest of their lives, with the greatest risk found in women who’ve had a hysterectomy with an oophorectomy, according to a cohort study of the Nurses’ Health Study.
“This is yet additional evidence that those girls and women with endometriosis are having effects across their lives and in multiple aspects of their health and well-being,” senior study author Stacey A. Missmer, ScD, of the Michigan State University, East Lansing, said in an interview. “This is not, in quotes ‘just a gynecologic condition,’ ” Dr. Missmer added. “It is not strictly about the pelvic pain or infertility, but it really is about the whole health across the life course.”
The study included 112,056 women in the NHSII cohort study who were followed from 1989 to June 2017, documenting 893 incident cases of stroke among them – an incidence of less than 1%. Endometriosis was reported in 5,244 women, and 93% of the cohort were White.
Multivariate adjusted models showed that women who had laparoscopically confirmed endometriosis had a 34% greater risk of stroke than women without a history of endometriosis. Leslie V. Farland, ScD, of the University of Arizona, Tucson, was lead author of the study.
While previous studies have demonstrated an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, heart attack, angina, and atherosclerosis in women who’ve had endometriosis, this is the first study that has confirmed an additional increased risk of stroke, Dr. Missmer said.
Another novel finding, Dr. Missmer said, is that while the CVD risks for these women “seem to peak at an earlier age,” the study found no age differences for stroke risk. “That also reinforces that these stroke events are often happening in an age range typical for stroke, which is further removed from when women are thinking about their gynecologic health specifically.”
These findings don’t translate into a significantly greater risk for stroke overall in women who’ve had endometriosis, Dr. Missmer said. She characterized the risk as “not negligible, but it’s not a huge increased risk.” The absolute risk is still fairly low, she said.
“We don’t want to give the impression that all women with endometriosis need to be panicked or fearful about stroke, she said. “Rather, the messaging is that this yet another bit of evidence that whole health care for those with endometriosis is important.”
Women who’ve had endometriosis and their primary care providers need to be attuned to stroke risk, she said. “This is a critical condition that primary care physicians need to engage around, and perhaps if symptoms related to cardiovascular and cerebrovascular disease emerge in their patients, they need to be engaging cardiology and similar types of support. This is not just about the gynecologists.”
The study also explored other factors that may contribute to stroke risk, with the most significant being hysterectomy with bilateral oophorectomy, Dr. Missmer said.
This study was unique because it used laparoscopically confirmed rather than self-reported endometriosis, said Louise D. McCullough, MD, neurology chair at the University of Texas Health Science Center, Houston. Another strength of the study she noted was its longitudinal design, although the cohort study design yielded a low number of stroke patients.
“Regardless, I do think it was a very important study because we have a growing recognition about how women’s health and factors such as pregnancy, infertility, parity, complications, and gonadal hormones such as estrogen can influence a woman’s stroke risk much later in life,” Dr. McCullough said in an interview.
Future studies into the relationship between endometriosis and CVD and stroke risk should focus on the mechanism behind the inflammation that occurs in endometriosis, Dr. McCullough said. “Part of it is probably the loss of hormones if a patient has to have an oophorectomy, but part of it is just what do these diseases do for a woman’s later risk – and for primary care physicians, ob.gyns., and stroke neurologists to recognize that these are questions we should ask: Have you ever had eclampsia or preeclampsia? Did you have endometriosis? Have you had miscarriages?”
The study received funding from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institute for Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Missmer disclosed relationships with Shanghai Huilun Biotechnology, Roche, and AbbVie. Dr. McCullough has no relevant disclosures.
FROM STROKE
PCOS in mothers tied to health problems in children
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Children whose mothers have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) have increased rates of hospitalization for various conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and ear infection, a study of more than 1 million children shows.
The associations were not particularly strong, according to the researchers. But they raise questions about the reasons for the increased risk and whether interventions such as diet, exercise, or medications could lead to healthier outcomes for children whose mothers have PCOS.
“The findings suggest that maternal PCOS may have a negative impact on offspring development, enough to lead to a measurable increase in the risk of childhood hospitalization,” study coauthor Nathalie Auger, MD, associate professor of epidemiology at University of Montreal, and colleagues reported in Human Reproduction.
“They are minor differences, just enough that we can statistically identify them. They’re not something where everyone should be worrying at this point,” Dr. Auger told this news organization.
Still, some of the hospitalizations, such as those related to infection or allergy, could be prevented with earlier ambulatory care, so some degree of greater awareness among parents and clinicians may be warranted, she said.
Thirteen years of follow-up
PCOS – a reproductive disorder characterized by irregular periods, increased male hormones, and metabolic complications – affects some 10% of women. People with the condition are at increased risk for obesity, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular disease.
Although prior research has shown that maternal PCOS may be associated with higher body mass index and attention deficit disorder in children, data on long-term childhood health outcomes have been limited, Dr. Auger’s group noted.
To examine illness in children exposed to maternal PCOS, the investigators analyzed hospitalization rates for nearly 1.04 million children in Quebec between 2006 and 2020; 7,160 of the children had mothers with PCOS.
In all, 275,354 children were hospitalized during 13 years of follow-up, including 2,314 whose mothers had PCOS.
Children exposed to PCOS were hospitalized at a rate of 68.9 per 1,000 person-years – roughly 50% more often than the rate of 45.3 per 1,000 person-years for children not exposed to maternal PCOS.
In an analysis that adjusted for maternal characteristics, childhood hospitalization for any reason was 1.32 times more likely for children exposed to maternal PCOS.
Hospitalizations linked to infectious diseases – such as for bronchitis, bronchiolitis, pneumonia, nephritis, otitis media, or meningitis – were 1.31 times more likely among children exposed to PCOS. Allergy-related hospitalizations, such as for allergic asthma and anaphylaxis, were 1.47 times more likely, according to the researchers.
Metabolic hospitalizations were 1.59 times more likely. For gastrointestinal hospitalizations, the hazard ratio was 1.72. For central nervous system hospitalizations, it was 1.74.
The associations were stronger in earlier childhood, and results were similar for boys and girls, the investigators reported.
Hospitalizations for cardiovascular disease, musculoskeletal conditions, or malignancy were not increased.
‘Surprising’ links
“The findings are surprising in that some of the conditions that they showed increased risk for, like asthma and some infections, are not conditions that we think of as being typically associated with PCOS,” said Andrea E. Dunaif, MD, chief of the Hilda and J. Lester Gabrilove Division of Endocrinology, Diabetes, and Bone Disease at Mount Sinai Health System, New York, who was not part of the study team.
Earlier studies of offspring of women with PCOS have suggested that children may be at increased risk for insulin resistance and obesity.
Differences in genetics, intrauterine environments, patterns of health care use by women with PCOS, and behavioral factors, such as diet and how children are raised, are variables that could have contributed to the different hospitalization rates among children exposed to maternal PCOS, Dr. Auger said.
“Everything is interconnected,” she said.
The study was supported by a grant from the Canadian Institutes of Health Research. Dr. Auger has received a career award from Fonds de Recherche du Québec-Santé. Dr. Dunaif has consulted for Novo Nordisk and Fractyl Laboratories (now Fractyl Health).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HUMAN REPRODUCTION
PCOS ups risk of heart complications during delivery period
Pregnant women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) appear to be at significantly increased risk of experiencing cardiac complications while hospitalized during and after delivery.
An estimated 5 million women of childbearing age in the United States have PCOS, a hormone disorder linked to infertility. PCOS is also known to contribute to the development of cardiometabolic abnormalities like high cholesterol and high blood pressure, which are associated with acute cardiovascular complications during delivery.
But a study, published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association, found that even after accounting for pre-eclampsia, age, comorbidities, and race, PCOS was linked to a 76% increased risk for heart failure, a 79% higher risk of a weakened heart, and an 82% increased risk of having blood clots in the hours and days around giving birth in hospital settings, compared with women without PCOS.
“Perhaps women need a closer follow-up during their pregnancy,” said Erin Michos, MD, MHS, associate director of preventive cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, and a co-author of the study. “They’re counseled about the difficulties of getting pregnant, but what about when they get pregnant?”
Hospitalizations of women with PCOS were also associated with longer stays (3 vs. 2 days) and higher costs ($4,901 vs. $3616; P < .01), compared with women without PCOS.
Over the 17-year analysis period, the number of women with PCOS rose from 569 per 100,000 deliveries to 15,349 per 100,000 deliveries. The researchers attributed the increase in part to greater awareness and diagnosis of the disorder. Dr. Michos and her colleagues used the National Inpatient Sample, managed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, to pull claims data for women who gave birth in hospitals between 2002 and 2019.
Solutions?
Dr. Michos said there may be more prevention work from og.gyns. to both educate patients about their heart risks during the delivery process and also to refer them to relevant cardiac specialists.
“These women may seek out a gynecologist because of the symptoms, perhaps irregular menses, but along with that should come counseling of the long-term cardiovascular complication,” Dr. Michos said. “And after a pregnancy there should be a good handoff to a primary care provider, so they get a cardiovascular assessment.”
Lifestyle management before, during, and after pregnancy can help prevent the onset of the long-term consequences of cardiac complications during delivery, according to Valerie Baker, MD, director of the division of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Hopkins Medicine, and her colleagues in a viewpoint published in the journal Fertility and Sterility.
“Once women with PCOS are identified by screening to be at higher risk for [cardiovascular disease], the foundational approach should be lifestyle management followed by statin therapy,” Dr. Baker’s group wrote. “These interventions should include dietary management and physical activity, especially for those who are prediabetic.”
The current study came on the heels of a June 14 meta-analysis by Dr. Michos’ group that found that women with PCOS may be twice as likely as those without PCOS to have coronary artery calcification, a precursor to atherosclerosis and a sign of the early onset of cardiovascular disease.
“We shouldn’t assume that all women of reproductive age are low risk,” Dr. Michos said. “This is the window of time that we can reshape the trajectory early in life.”
The study was supported by the Amato Fund for Women’s Cardiovascular Health research at Johns Hopkins University and through grant support from the American Heart Association (940166). Dr. Michos reported advisory board participation for AstraZeneca, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, and Pfizer. Study coauthor Michael Honigberg, MD, reported consulting fees from CRISPR Therapeutics, unrelated to the present work. The remaining authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) appear to be at significantly increased risk of experiencing cardiac complications while hospitalized during and after delivery.
An estimated 5 million women of childbearing age in the United States have PCOS, a hormone disorder linked to infertility. PCOS is also known to contribute to the development of cardiometabolic abnormalities like high cholesterol and high blood pressure, which are associated with acute cardiovascular complications during delivery.
But a study, published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association, found that even after accounting for pre-eclampsia, age, comorbidities, and race, PCOS was linked to a 76% increased risk for heart failure, a 79% higher risk of a weakened heart, and an 82% increased risk of having blood clots in the hours and days around giving birth in hospital settings, compared with women without PCOS.
“Perhaps women need a closer follow-up during their pregnancy,” said Erin Michos, MD, MHS, associate director of preventive cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, and a co-author of the study. “They’re counseled about the difficulties of getting pregnant, but what about when they get pregnant?”
Hospitalizations of women with PCOS were also associated with longer stays (3 vs. 2 days) and higher costs ($4,901 vs. $3616; P < .01), compared with women without PCOS.
Over the 17-year analysis period, the number of women with PCOS rose from 569 per 100,000 deliveries to 15,349 per 100,000 deliveries. The researchers attributed the increase in part to greater awareness and diagnosis of the disorder. Dr. Michos and her colleagues used the National Inpatient Sample, managed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, to pull claims data for women who gave birth in hospitals between 2002 and 2019.
Solutions?
Dr. Michos said there may be more prevention work from og.gyns. to both educate patients about their heart risks during the delivery process and also to refer them to relevant cardiac specialists.
“These women may seek out a gynecologist because of the symptoms, perhaps irregular menses, but along with that should come counseling of the long-term cardiovascular complication,” Dr. Michos said. “And after a pregnancy there should be a good handoff to a primary care provider, so they get a cardiovascular assessment.”
Lifestyle management before, during, and after pregnancy can help prevent the onset of the long-term consequences of cardiac complications during delivery, according to Valerie Baker, MD, director of the division of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Hopkins Medicine, and her colleagues in a viewpoint published in the journal Fertility and Sterility.
“Once women with PCOS are identified by screening to be at higher risk for [cardiovascular disease], the foundational approach should be lifestyle management followed by statin therapy,” Dr. Baker’s group wrote. “These interventions should include dietary management and physical activity, especially for those who are prediabetic.”
The current study came on the heels of a June 14 meta-analysis by Dr. Michos’ group that found that women with PCOS may be twice as likely as those without PCOS to have coronary artery calcification, a precursor to atherosclerosis and a sign of the early onset of cardiovascular disease.
“We shouldn’t assume that all women of reproductive age are low risk,” Dr. Michos said. “This is the window of time that we can reshape the trajectory early in life.”
The study was supported by the Amato Fund for Women’s Cardiovascular Health research at Johns Hopkins University and through grant support from the American Heart Association (940166). Dr. Michos reported advisory board participation for AstraZeneca, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, and Pfizer. Study coauthor Michael Honigberg, MD, reported consulting fees from CRISPR Therapeutics, unrelated to the present work. The remaining authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pregnant women with polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) appear to be at significantly increased risk of experiencing cardiac complications while hospitalized during and after delivery.
An estimated 5 million women of childbearing age in the United States have PCOS, a hormone disorder linked to infertility. PCOS is also known to contribute to the development of cardiometabolic abnormalities like high cholesterol and high blood pressure, which are associated with acute cardiovascular complications during delivery.
But a study, published online in the Journal of the American Heart Association, found that even after accounting for pre-eclampsia, age, comorbidities, and race, PCOS was linked to a 76% increased risk for heart failure, a 79% higher risk of a weakened heart, and an 82% increased risk of having blood clots in the hours and days around giving birth in hospital settings, compared with women without PCOS.
“Perhaps women need a closer follow-up during their pregnancy,” said Erin Michos, MD, MHS, associate director of preventive cardiology at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, and a co-author of the study. “They’re counseled about the difficulties of getting pregnant, but what about when they get pregnant?”
Hospitalizations of women with PCOS were also associated with longer stays (3 vs. 2 days) and higher costs ($4,901 vs. $3616; P < .01), compared with women without PCOS.
Over the 17-year analysis period, the number of women with PCOS rose from 569 per 100,000 deliveries to 15,349 per 100,000 deliveries. The researchers attributed the increase in part to greater awareness and diagnosis of the disorder. Dr. Michos and her colleagues used the National Inpatient Sample, managed by the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, to pull claims data for women who gave birth in hospitals between 2002 and 2019.
Solutions?
Dr. Michos said there may be more prevention work from og.gyns. to both educate patients about their heart risks during the delivery process and also to refer them to relevant cardiac specialists.
“These women may seek out a gynecologist because of the symptoms, perhaps irregular menses, but along with that should come counseling of the long-term cardiovascular complication,” Dr. Michos said. “And after a pregnancy there should be a good handoff to a primary care provider, so they get a cardiovascular assessment.”
Lifestyle management before, during, and after pregnancy can help prevent the onset of the long-term consequences of cardiac complications during delivery, according to Valerie Baker, MD, director of the division of reproductive endocrinology and infertility at Hopkins Medicine, and her colleagues in a viewpoint published in the journal Fertility and Sterility.
“Once women with PCOS are identified by screening to be at higher risk for [cardiovascular disease], the foundational approach should be lifestyle management followed by statin therapy,” Dr. Baker’s group wrote. “These interventions should include dietary management and physical activity, especially for those who are prediabetic.”
The current study came on the heels of a June 14 meta-analysis by Dr. Michos’ group that found that women with PCOS may be twice as likely as those without PCOS to have coronary artery calcification, a precursor to atherosclerosis and a sign of the early onset of cardiovascular disease.
“We shouldn’t assume that all women of reproductive age are low risk,” Dr. Michos said. “This is the window of time that we can reshape the trajectory early in life.”
The study was supported by the Amato Fund for Women’s Cardiovascular Health research at Johns Hopkins University and through grant support from the American Heart Association (940166). Dr. Michos reported advisory board participation for AstraZeneca, Amarin, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Esperion, and Pfizer. Study coauthor Michael Honigberg, MD, reported consulting fees from CRISPR Therapeutics, unrelated to the present work. The remaining authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Precocious puberty – how early is too soon?
A 6-year-old girl presents with breast development. Her medical history is unremarkable. The parents are of average height, and the mother reports her thelarche was age 11 years. The girl is at the 97th percentile for her height and 90th percentile for her weight. She has Tanner stage 3 breast development and Tanner stage 2 pubic hair development. She has grown slightly more than 3 inches over the past year. How should she be evaluated and managed (N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2366-77)?
The premature onset of puberty, i.e., precocious puberty (PP), can be an emotionally traumatic event for the child and parents. Over the past century, improvements in public health and nutrition, and, more recently, increased obesity, have been associated with earlier puberty and the dominant factor has been attributed to genetics (Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25[1]:49-54). This month’s article will focus on understanding what is considered “early” puberty, evaluating for causes, and managing precocious puberty.
More commonly seen in girls than boys, PP is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 7.5 years in Black and Hispanic girls, and prior to 8 years in White girls, which is 2-2.5 standard deviations below the average age of pubertal onset in healthy children (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:455-9). As a comparison, PP is diagnosed with onset before age 9 years in boys. For White compared with Black girls, the average timing of thelarche is age 10 vs. 9.5 years, peak growth velocity is age 11.5, menarche is age 12.5 vs. 12, while completion of puberty is near age 14.5 vs. 13.5, respectively (J Pediatr. 1985;107:317). Fortunately, most girls with PP have common variants rather than serious pathology.
Classification: Central (CPP) vs. peripheral (PPP)
CPP is gonadotropin dependent, meaning the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO) is prematurely activated resulting in the normal progression of puberty.
PPP is gonadotropin independent, caused by sex steroid secretion from any source – ovaries, adrenal gland, exogenous or ectopic production, e.g., germ-cell tumor. This results in a disordered progression of pubertal milestones.
Whereas CPP is typically isosexual development, i.e., consistent with the child’s gender, PPP can be isosexual or contrasexual, e.g., virilization of girls. A third classification is “benign or nonprogressive pubertal variants” manifesting as isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche.
Causes (see table)
CPP. Idiopathic causes account for 80%-90% of presentations in girls and 25%-80% in boys. Remarkably, international and domestic adoption, as well as a family history of PP increases the likelihood of CPP in girls. Other etiologies include CNS lesions, e.g., hamartomas, which are the most common cause of PP in young children. MRI with contrast has been the traditional mode of diagnosis for CNS tumors, yet the yield is dubious in girls above age 6. Genetic causes are found in only a small percentage of PP cases. Rarely, CPP can result from gonadotropin-secreting tumors because of elevated luteinizing hormone levels.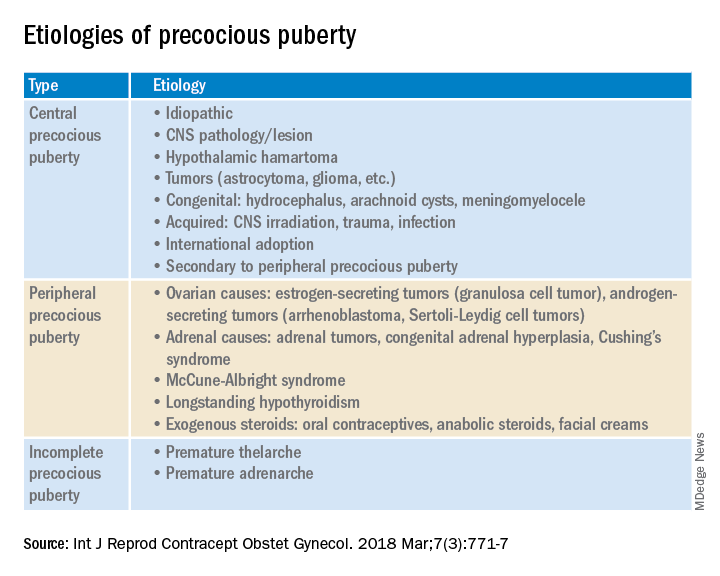
PPP. As a result of sex steroid secretion, peripheral causes of PPP include ovarian cysts and ovarian tumors that increase circulating estradiol, such as granulosa cell tumors, which would cause isosexual PPP and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors that secrete testosterone, which can result in contrasexual PPP. Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia can result in PPP with virilization (contrasexual) and markedly advanced bone age.
McCune-Albright syndrome is rare and presents with the classic triad of PPP, skin pigmentation called café-au-lait, and fibrous dysplasia of bone. The pathophysiology of McCune-Albright syndrome is autoactivation of the G-protein leading to activation of ovarian tissue that results in formation of large ovarian cysts and extreme elevations in serum estradiol as well as the potential production of other hormones, e.g., thyrotoxicosis, excess growth hormone (acromegaly), and Cushing syndrome.
Premature thelarche. Premature thelarche typically occurs in girls between the ages of 1 and 3 years and is limited to breast enlargement. While no cause has been determined, the plausible explanations include partial activation of the HPO axis, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or a genetic origin. A small percentage of these girls progress to CPP.
EDCs have been considered as potential influencers of early puberty, but no consensus has been established. (Examples of EDCs in the environment include air, soil, or water supply along with food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that can affect the endocrine system.)
Premature adenarche. Premature adrenarche presents with adult body odor and/or body hair (pubic and/or axillary) in girls who have an elevated body mass index, most commonly at the ages of 6-7 years. The presumed mechanism is normal maturation of the adrenal gland with resultant elevation of circulating androgens. Bone age may be mildly accelerated and DHEAS is prematurely elevated for age. These girls appear to be at increased risk for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Evaluation
The initial step in the evaluation of PP is to determine whether the cause is CPP or PPP; the latter includes distinguishing isosexual from contrasexual development. A thorough history (growth, headaches, behavior or visual change, seizures, abdominal pain), physical exam, including Tanner staging, and bone age is required. However, with isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche, a bone age may not be necessary, as initial close clinical observation for pubertal progression is likely sufficient.
For CPP, the diagnosis is based on serum LH, whether random levels or elevations follow GnRH stimulation. Puberty milestones progress normally although adrenarche is not consistently apparent. For girls younger than age 6, a brain MRI is recommended but not in asymptomatic older girls with CPP. LH and FSH along with estradiol or testosterone, the latter especially in boys, are the first line of serum testing. Serum TSH is recommended for suspicion of primary hypothyroidism. In girls with premature adrenarche, a bone age, testosterone, DHEAS, and 17-OHP to rule out adrenal hyperplasia should be obtained. Pelvic ultrasound may be a useful adjunct to assess uterine volume and/or ovarian cysts/tumors.
Rapidity of onset can also lead the evaluation since a normal growth chart and skeletal maturation suggests a benign pubertal variant whereas a more rapid rate can signal CPP or PPP. Of note, health care providers should ensure prescription, over-the-counter oral or topical sources of hormones, and EDCs are ruled out.
Consequences
An association between childhood sexual abuse and earlier pubertal onset has been cited. These girls may be at increased risk for psychosocial difficulties, menstrual and fertility problems, and even reproductive cancers because of prolonged exposure to sex hormones (J Adolesc Health. 2016;60[1]:65-71).
Treatment
The mainstay of CPP treatment is maximizing adult height, typically through the use of a GnRH agonist for HPO suppression from pituitary downregulation. For girls above age 8 years, attempts at improving adult height have not shown a benefit.
In girls with PPP, treatment is directed at the prevailing pathology. Interestingly, early PPP can activate the HPO axis thereby converting to “secondary” CPP. In PPP, McCune-Albright syndrome treatment targets reducing circulating estrogens through letrozole or tamoxifen as well as addressing other autoactivated hormone production. Ovarian and adrenal tumors, albeit rare, can cause PP; therefore, surgical excision is the goal of treatment.
PP should be approached with equal concerns about the physical and emotional effects while including the family to help them understand the pathophysiology and psychosocial risks.
Dr. Mark P. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
A 6-year-old girl presents with breast development. Her medical history is unremarkable. The parents are of average height, and the mother reports her thelarche was age 11 years. The girl is at the 97th percentile for her height and 90th percentile for her weight. She has Tanner stage 3 breast development and Tanner stage 2 pubic hair development. She has grown slightly more than 3 inches over the past year. How should she be evaluated and managed (N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2366-77)?
The premature onset of puberty, i.e., precocious puberty (PP), can be an emotionally traumatic event for the child and parents. Over the past century, improvements in public health and nutrition, and, more recently, increased obesity, have been associated with earlier puberty and the dominant factor has been attributed to genetics (Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25[1]:49-54). This month’s article will focus on understanding what is considered “early” puberty, evaluating for causes, and managing precocious puberty.
More commonly seen in girls than boys, PP is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 7.5 years in Black and Hispanic girls, and prior to 8 years in White girls, which is 2-2.5 standard deviations below the average age of pubertal onset in healthy children (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:455-9). As a comparison, PP is diagnosed with onset before age 9 years in boys. For White compared with Black girls, the average timing of thelarche is age 10 vs. 9.5 years, peak growth velocity is age 11.5, menarche is age 12.5 vs. 12, while completion of puberty is near age 14.5 vs. 13.5, respectively (J Pediatr. 1985;107:317). Fortunately, most girls with PP have common variants rather than serious pathology.
Classification: Central (CPP) vs. peripheral (PPP)
CPP is gonadotropin dependent, meaning the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO) is prematurely activated resulting in the normal progression of puberty.
PPP is gonadotropin independent, caused by sex steroid secretion from any source – ovaries, adrenal gland, exogenous or ectopic production, e.g., germ-cell tumor. This results in a disordered progression of pubertal milestones.
Whereas CPP is typically isosexual development, i.e., consistent with the child’s gender, PPP can be isosexual or contrasexual, e.g., virilization of girls. A third classification is “benign or nonprogressive pubertal variants” manifesting as isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche.
Causes (see table)
CPP. Idiopathic causes account for 80%-90% of presentations in girls and 25%-80% in boys. Remarkably, international and domestic adoption, as well as a family history of PP increases the likelihood of CPP in girls. Other etiologies include CNS lesions, e.g., hamartomas, which are the most common cause of PP in young children. MRI with contrast has been the traditional mode of diagnosis for CNS tumors, yet the yield is dubious in girls above age 6. Genetic causes are found in only a small percentage of PP cases. Rarely, CPP can result from gonadotropin-secreting tumors because of elevated luteinizing hormone levels.
PPP. As a result of sex steroid secretion, peripheral causes of PPP include ovarian cysts and ovarian tumors that increase circulating estradiol, such as granulosa cell tumors, which would cause isosexual PPP and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors that secrete testosterone, which can result in contrasexual PPP. Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia can result in PPP with virilization (contrasexual) and markedly advanced bone age.
McCune-Albright syndrome is rare and presents with the classic triad of PPP, skin pigmentation called café-au-lait, and fibrous dysplasia of bone. The pathophysiology of McCune-Albright syndrome is autoactivation of the G-protein leading to activation of ovarian tissue that results in formation of large ovarian cysts and extreme elevations in serum estradiol as well as the potential production of other hormones, e.g., thyrotoxicosis, excess growth hormone (acromegaly), and Cushing syndrome.
Premature thelarche. Premature thelarche typically occurs in girls between the ages of 1 and 3 years and is limited to breast enlargement. While no cause has been determined, the plausible explanations include partial activation of the HPO axis, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or a genetic origin. A small percentage of these girls progress to CPP.
EDCs have been considered as potential influencers of early puberty, but no consensus has been established. (Examples of EDCs in the environment include air, soil, or water supply along with food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that can affect the endocrine system.)
Premature adenarche. Premature adrenarche presents with adult body odor and/or body hair (pubic and/or axillary) in girls who have an elevated body mass index, most commonly at the ages of 6-7 years. The presumed mechanism is normal maturation of the adrenal gland with resultant elevation of circulating androgens. Bone age may be mildly accelerated and DHEAS is prematurely elevated for age. These girls appear to be at increased risk for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Evaluation
The initial step in the evaluation of PP is to determine whether the cause is CPP or PPP; the latter includes distinguishing isosexual from contrasexual development. A thorough history (growth, headaches, behavior or visual change, seizures, abdominal pain), physical exam, including Tanner staging, and bone age is required. However, with isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche, a bone age may not be necessary, as initial close clinical observation for pubertal progression is likely sufficient.
For CPP, the diagnosis is based on serum LH, whether random levels or elevations follow GnRH stimulation. Puberty milestones progress normally although adrenarche is not consistently apparent. For girls younger than age 6, a brain MRI is recommended but not in asymptomatic older girls with CPP. LH and FSH along with estradiol or testosterone, the latter especially in boys, are the first line of serum testing. Serum TSH is recommended for suspicion of primary hypothyroidism. In girls with premature adrenarche, a bone age, testosterone, DHEAS, and 17-OHP to rule out adrenal hyperplasia should be obtained. Pelvic ultrasound may be a useful adjunct to assess uterine volume and/or ovarian cysts/tumors.
Rapidity of onset can also lead the evaluation since a normal growth chart and skeletal maturation suggests a benign pubertal variant whereas a more rapid rate can signal CPP or PPP. Of note, health care providers should ensure prescription, over-the-counter oral or topical sources of hormones, and EDCs are ruled out.
Consequences
An association between childhood sexual abuse and earlier pubertal onset has been cited. These girls may be at increased risk for psychosocial difficulties, menstrual and fertility problems, and even reproductive cancers because of prolonged exposure to sex hormones (J Adolesc Health. 2016;60[1]:65-71).
Treatment
The mainstay of CPP treatment is maximizing adult height, typically through the use of a GnRH agonist for HPO suppression from pituitary downregulation. For girls above age 8 years, attempts at improving adult height have not shown a benefit.
In girls with PPP, treatment is directed at the prevailing pathology. Interestingly, early PPP can activate the HPO axis thereby converting to “secondary” CPP. In PPP, McCune-Albright syndrome treatment targets reducing circulating estrogens through letrozole or tamoxifen as well as addressing other autoactivated hormone production. Ovarian and adrenal tumors, albeit rare, can cause PP; therefore, surgical excision is the goal of treatment.
PP should be approached with equal concerns about the physical and emotional effects while including the family to help them understand the pathophysiology and psychosocial risks.
Dr. Mark P. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
A 6-year-old girl presents with breast development. Her medical history is unremarkable. The parents are of average height, and the mother reports her thelarche was age 11 years. The girl is at the 97th percentile for her height and 90th percentile for her weight. She has Tanner stage 3 breast development and Tanner stage 2 pubic hair development. She has grown slightly more than 3 inches over the past year. How should she be evaluated and managed (N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2366-77)?
The premature onset of puberty, i.e., precocious puberty (PP), can be an emotionally traumatic event for the child and parents. Over the past century, improvements in public health and nutrition, and, more recently, increased obesity, have been associated with earlier puberty and the dominant factor has been attributed to genetics (Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25[1]:49-54). This month’s article will focus on understanding what is considered “early” puberty, evaluating for causes, and managing precocious puberty.
More commonly seen in girls than boys, PP is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 7.5 years in Black and Hispanic girls, and prior to 8 years in White girls, which is 2-2.5 standard deviations below the average age of pubertal onset in healthy children (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:455-9). As a comparison, PP is diagnosed with onset before age 9 years in boys. For White compared with Black girls, the average timing of thelarche is age 10 vs. 9.5 years, peak growth velocity is age 11.5, menarche is age 12.5 vs. 12, while completion of puberty is near age 14.5 vs. 13.5, respectively (J Pediatr. 1985;107:317). Fortunately, most girls with PP have common variants rather than serious pathology.
Classification: Central (CPP) vs. peripheral (PPP)
CPP is gonadotropin dependent, meaning the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO) is prematurely activated resulting in the normal progression of puberty.
PPP is gonadotropin independent, caused by sex steroid secretion from any source – ovaries, adrenal gland, exogenous or ectopic production, e.g., germ-cell tumor. This results in a disordered progression of pubertal milestones.
Whereas CPP is typically isosexual development, i.e., consistent with the child’s gender, PPP can be isosexual or contrasexual, e.g., virilization of girls. A third classification is “benign or nonprogressive pubertal variants” manifesting as isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche.
Causes (see table)
CPP. Idiopathic causes account for 80%-90% of presentations in girls and 25%-80% in boys. Remarkably, international and domestic adoption, as well as a family history of PP increases the likelihood of CPP in girls. Other etiologies include CNS lesions, e.g., hamartomas, which are the most common cause of PP in young children. MRI with contrast has been the traditional mode of diagnosis for CNS tumors, yet the yield is dubious in girls above age 6. Genetic causes are found in only a small percentage of PP cases. Rarely, CPP can result from gonadotropin-secreting tumors because of elevated luteinizing hormone levels.
PPP. As a result of sex steroid secretion, peripheral causes of PPP include ovarian cysts and ovarian tumors that increase circulating estradiol, such as granulosa cell tumors, which would cause isosexual PPP and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors that secrete testosterone, which can result in contrasexual PPP. Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia can result in PPP with virilization (contrasexual) and markedly advanced bone age.
McCune-Albright syndrome is rare and presents with the classic triad of PPP, skin pigmentation called café-au-lait, and fibrous dysplasia of bone. The pathophysiology of McCune-Albright syndrome is autoactivation of the G-protein leading to activation of ovarian tissue that results in formation of large ovarian cysts and extreme elevations in serum estradiol as well as the potential production of other hormones, e.g., thyrotoxicosis, excess growth hormone (acromegaly), and Cushing syndrome.
Premature thelarche. Premature thelarche typically occurs in girls between the ages of 1 and 3 years and is limited to breast enlargement. While no cause has been determined, the plausible explanations include partial activation of the HPO axis, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or a genetic origin. A small percentage of these girls progress to CPP.
EDCs have been considered as potential influencers of early puberty, but no consensus has been established. (Examples of EDCs in the environment include air, soil, or water supply along with food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that can affect the endocrine system.)
Premature adenarche. Premature adrenarche presents with adult body odor and/or body hair (pubic and/or axillary) in girls who have an elevated body mass index, most commonly at the ages of 6-7 years. The presumed mechanism is normal maturation of the adrenal gland with resultant elevation of circulating androgens. Bone age may be mildly accelerated and DHEAS is prematurely elevated for age. These girls appear to be at increased risk for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Evaluation
The initial step in the evaluation of PP is to determine whether the cause is CPP or PPP; the latter includes distinguishing isosexual from contrasexual development. A thorough history (growth, headaches, behavior or visual change, seizures, abdominal pain), physical exam, including Tanner staging, and bone age is required. However, with isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche, a bone age may not be necessary, as initial close clinical observation for pubertal progression is likely sufficient.
For CPP, the diagnosis is based on serum LH, whether random levels or elevations follow GnRH stimulation. Puberty milestones progress normally although adrenarche is not consistently apparent. For girls younger than age 6, a brain MRI is recommended but not in asymptomatic older girls with CPP. LH and FSH along with estradiol or testosterone, the latter especially in boys, are the first line of serum testing. Serum TSH is recommended for suspicion of primary hypothyroidism. In girls with premature adrenarche, a bone age, testosterone, DHEAS, and 17-OHP to rule out adrenal hyperplasia should be obtained. Pelvic ultrasound may be a useful adjunct to assess uterine volume and/or ovarian cysts/tumors.
Rapidity of onset can also lead the evaluation since a normal growth chart and skeletal maturation suggests a benign pubertal variant whereas a more rapid rate can signal CPP or PPP. Of note, health care providers should ensure prescription, over-the-counter oral or topical sources of hormones, and EDCs are ruled out.
Consequences
An association between childhood sexual abuse and earlier pubertal onset has been cited. These girls may be at increased risk for psychosocial difficulties, menstrual and fertility problems, and even reproductive cancers because of prolonged exposure to sex hormones (J Adolesc Health. 2016;60[1]:65-71).
Treatment
The mainstay of CPP treatment is maximizing adult height, typically through the use of a GnRH agonist for HPO suppression from pituitary downregulation. For girls above age 8 years, attempts at improving adult height have not shown a benefit.
In girls with PPP, treatment is directed at the prevailing pathology. Interestingly, early PPP can activate the HPO axis thereby converting to “secondary” CPP. In PPP, McCune-Albright syndrome treatment targets reducing circulating estrogens through letrozole or tamoxifen as well as addressing other autoactivated hormone production. Ovarian and adrenal tumors, albeit rare, can cause PP; therefore, surgical excision is the goal of treatment.
PP should be approached with equal concerns about the physical and emotional effects while including the family to help them understand the pathophysiology and psychosocial risks.
Dr. Mark P. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
Hormone therapy and breast cancer: An overview
It is projected that by 2050, 1.6 billion women in the world will have reached menopause or the postmenopausal period, a significant increase, compared with a billion women in 2020. Of all menopausal women, around 75% are affected by troublesome menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Around 84% of postmenopausal women experience genitourinary symptoms, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and incontinence.
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is the most effective treatment for managing these symptoms; however, its effects on numerous aspects of female health remain uncertain, in particular with regard to breast cancer. The influence of MHT on breast cancer remains unsettled, with discordant findings from observational studies and randomized clinical trials, a factor that affects the decisions made by doctors concerning hormone therapy in menopausal women.
Background
Conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs) were introduced into clinical practice in the 1940s. For decades, MHT was the main treatment in conventional medicine for the symptoms of menopause. MHT was used in Western countries for about 600 million women starting from 1970, and it progressively increased during the 1990s. Professional organizations recommended MHT for the prevention of osteoporosis and chronic heart disease (CHD), and a third of prescriptions were for women older than 60 years.
Against this background, the National Institutes of Health launched randomized trials of MHT through the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) to test whether the association with reduced risk for CHD found in observational studies was real and to obtain reliable information on the overall risks and benefits regarding the prevention of chronic disease for postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years.
The WHI trials tested standard-dose oral CEEs with and without standard-dose continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (EPT). In 2002, the results of the WHI studies raised a series of concerns about the long-term safety of MHT, in particular the finding of an increased risk of breast cancer for women undergoing therapy. That risk exceeded the benefits from reductions in hip fractures and colorectal cancer.
The WHI findings received wide attention. Prescriptions for MHT dropped precipitously after 2002 and continued to decline in subsequent years. Declines were most marked for standard-dose EPT and in older women. The results of the CEE study were less negative, compared with those for EPT, as they showed no effect on CHD, a nonsignificant reduction in the risk of breast cancer, and a more favorable risk-benefit ratio for younger women, compared with older women. A decade later, it had become widely accepted that MHT should not be used for the prevention of chronic disease in older women; however, short-term use for treatment of vasomotor symptoms remains an accepted indication.
Risks and outcomes
Emerging from a series of WHI reports are complex models on the effect of hormonal therapy on the risk and outcome of breast cancer. In one study, women with an intact uterus received CEEs plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). An increase in the risk of breast cancer was observed over a median of 5.6 years of treatment, followed by a moderate reduction, with the risk increasing after 13 years of cumulative follow-up. For women treated with CEE alone, the reduction in risk observed over an average of 7.2 years of treatment was maintained for 13 years of follow-up.
Results from observational studies contrast with those from randomized controlled trials, particularly those concerning the use of estrogens only. A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer showed that both EPT and CEE were associated with a higher risk of breast neoplasia. Results of the Million Women Study showed a higher death rate.
Treatment methods and duration
Information from prospective studies on the effects of commencing MHT at various ages between 40 and 59 years show that for women who commenced treatment at any time within this age range, the relative risk was similar and was highly significant for all ages. Few women had started MHT treatment well after menopause at ages 60-69 years, and their excess risks during years 5-14 of current use were significant for estrogen-progestogen but not for estrogen-only MHT.
If these associations are largely causal, then for women of average weight in developed countries, 5 years of MHT, starting at age 50 years, would increase breast cancer incidence at ages 50-69 years by about 1 in every 50 users of estrogen plus daily progestogen preparations; 1 in every 70 users of estrogen plus intermittent progestogen preparations; and 1 in every 200 users of estrogen-only preparations. The corresponding excesses from 10 years of MHT would be about twice as great.
During 5-14 years of MHT use, the RRs were similarly increased if MHT use had started at ages 40-44 years, 45-49 years, 50-54 years, and 55-59 years; RRs appeared to be attenuated if MHT use had started after age 60 years. They were also attenuated by adiposity, particularly for estrogen-only MHT (which had little effect in obese women). After MHT use ceased, some excess risk of breast cancer persisted for more than a decade; this is directly correlated with the duration of treatment.
Therefore, it can be expected that the effects of MHT may vary between participants on the basis of age or time since menopause, as well as treatments (MHT type, dose, formulation, duration of use, and route of administration). Regarding formulation effects on the risk of breast cancer, new evidence shows an increased risk of 28%. Progestogens appeared to be differentially associated with breast cancer (micronized progesterone: odds ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval 0.55-1.79; synthetic progestin: OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.22-1.35). When prescribing MHT, micronized progesterone may be the safer progestogen to use.
In conclusion, MHT has a complex balance of benefits and risk on various health outcomes. Some effects differ qualitatively between ET and EPT. Regarding use of MHT, consideration should be given to the full range of effects, along with patients’ values and preferences. The overall quality of existing systematic reviews is moderate to poor. Clinicians should evaluate their scientific strength before considering applying their results in clinical practice. Regarding use of any hormone therapy regimen, consideration should be given to the full range of risk and benefits and should involve shared decisionmaking with the patient. It should be recognized that risk-benefit balance is altered by factors such as age, time from menopause, oophorectomy status, and prior hysterectomy and that some outcomes persist and there is some attenuation after stopping use.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
A version of the article appeared on Medscape.com.
It is projected that by 2050, 1.6 billion women in the world will have reached menopause or the postmenopausal period, a significant increase, compared with a billion women in 2020. Of all menopausal women, around 75% are affected by troublesome menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Around 84% of postmenopausal women experience genitourinary symptoms, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and incontinence.
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is the most effective treatment for managing these symptoms; however, its effects on numerous aspects of female health remain uncertain, in particular with regard to breast cancer. The influence of MHT on breast cancer remains unsettled, with discordant findings from observational studies and randomized clinical trials, a factor that affects the decisions made by doctors concerning hormone therapy in menopausal women.
Background
Conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs) were introduced into clinical practice in the 1940s. For decades, MHT was the main treatment in conventional medicine for the symptoms of menopause. MHT was used in Western countries for about 600 million women starting from 1970, and it progressively increased during the 1990s. Professional organizations recommended MHT for the prevention of osteoporosis and chronic heart disease (CHD), and a third of prescriptions were for women older than 60 years.
Against this background, the National Institutes of Health launched randomized trials of MHT through the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) to test whether the association with reduced risk for CHD found in observational studies was real and to obtain reliable information on the overall risks and benefits regarding the prevention of chronic disease for postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years.
The WHI trials tested standard-dose oral CEEs with and without standard-dose continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (EPT). In 2002, the results of the WHI studies raised a series of concerns about the long-term safety of MHT, in particular the finding of an increased risk of breast cancer for women undergoing therapy. That risk exceeded the benefits from reductions in hip fractures and colorectal cancer.
The WHI findings received wide attention. Prescriptions for MHT dropped precipitously after 2002 and continued to decline in subsequent years. Declines were most marked for standard-dose EPT and in older women. The results of the CEE study were less negative, compared with those for EPT, as they showed no effect on CHD, a nonsignificant reduction in the risk of breast cancer, and a more favorable risk-benefit ratio for younger women, compared with older women. A decade later, it had become widely accepted that MHT should not be used for the prevention of chronic disease in older women; however, short-term use for treatment of vasomotor symptoms remains an accepted indication.
Risks and outcomes
Emerging from a series of WHI reports are complex models on the effect of hormonal therapy on the risk and outcome of breast cancer. In one study, women with an intact uterus received CEEs plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). An increase in the risk of breast cancer was observed over a median of 5.6 years of treatment, followed by a moderate reduction, with the risk increasing after 13 years of cumulative follow-up. For women treated with CEE alone, the reduction in risk observed over an average of 7.2 years of treatment was maintained for 13 years of follow-up.
Results from observational studies contrast with those from randomized controlled trials, particularly those concerning the use of estrogens only. A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer showed that both EPT and CEE were associated with a higher risk of breast neoplasia. Results of the Million Women Study showed a higher death rate.
Treatment methods and duration
Information from prospective studies on the effects of commencing MHT at various ages between 40 and 59 years show that for women who commenced treatment at any time within this age range, the relative risk was similar and was highly significant for all ages. Few women had started MHT treatment well after menopause at ages 60-69 years, and their excess risks during years 5-14 of current use were significant for estrogen-progestogen but not for estrogen-only MHT.
If these associations are largely causal, then for women of average weight in developed countries, 5 years of MHT, starting at age 50 years, would increase breast cancer incidence at ages 50-69 years by about 1 in every 50 users of estrogen plus daily progestogen preparations; 1 in every 70 users of estrogen plus intermittent progestogen preparations; and 1 in every 200 users of estrogen-only preparations. The corresponding excesses from 10 years of MHT would be about twice as great.
During 5-14 years of MHT use, the RRs were similarly increased if MHT use had started at ages 40-44 years, 45-49 years, 50-54 years, and 55-59 years; RRs appeared to be attenuated if MHT use had started after age 60 years. They were also attenuated by adiposity, particularly for estrogen-only MHT (which had little effect in obese women). After MHT use ceased, some excess risk of breast cancer persisted for more than a decade; this is directly correlated with the duration of treatment.
Therefore, it can be expected that the effects of MHT may vary between participants on the basis of age or time since menopause, as well as treatments (MHT type, dose, formulation, duration of use, and route of administration). Regarding formulation effects on the risk of breast cancer, new evidence shows an increased risk of 28%. Progestogens appeared to be differentially associated with breast cancer (micronized progesterone: odds ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval 0.55-1.79; synthetic progestin: OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.22-1.35). When prescribing MHT, micronized progesterone may be the safer progestogen to use.
In conclusion, MHT has a complex balance of benefits and risk on various health outcomes. Some effects differ qualitatively between ET and EPT. Regarding use of MHT, consideration should be given to the full range of effects, along with patients’ values and preferences. The overall quality of existing systematic reviews is moderate to poor. Clinicians should evaluate their scientific strength before considering applying their results in clinical practice. Regarding use of any hormone therapy regimen, consideration should be given to the full range of risk and benefits and should involve shared decisionmaking with the patient. It should be recognized that risk-benefit balance is altered by factors such as age, time from menopause, oophorectomy status, and prior hysterectomy and that some outcomes persist and there is some attenuation after stopping use.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
A version of the article appeared on Medscape.com.
It is projected that by 2050, 1.6 billion women in the world will have reached menopause or the postmenopausal period, a significant increase, compared with a billion women in 2020. Of all menopausal women, around 75% are affected by troublesome menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Around 84% of postmenopausal women experience genitourinary symptoms, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and incontinence.
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is the most effective treatment for managing these symptoms; however, its effects on numerous aspects of female health remain uncertain, in particular with regard to breast cancer. The influence of MHT on breast cancer remains unsettled, with discordant findings from observational studies and randomized clinical trials, a factor that affects the decisions made by doctors concerning hormone therapy in menopausal women.
Background
Conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs) were introduced into clinical practice in the 1940s. For decades, MHT was the main treatment in conventional medicine for the symptoms of menopause. MHT was used in Western countries for about 600 million women starting from 1970, and it progressively increased during the 1990s. Professional organizations recommended MHT for the prevention of osteoporosis and chronic heart disease (CHD), and a third of prescriptions were for women older than 60 years.
Against this background, the National Institutes of Health launched randomized trials of MHT through the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) to test whether the association with reduced risk for CHD found in observational studies was real and to obtain reliable information on the overall risks and benefits regarding the prevention of chronic disease for postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years.
The WHI trials tested standard-dose oral CEEs with and without standard-dose continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (EPT). In 2002, the results of the WHI studies raised a series of concerns about the long-term safety of MHT, in particular the finding of an increased risk of breast cancer for women undergoing therapy. That risk exceeded the benefits from reductions in hip fractures and colorectal cancer.
The WHI findings received wide attention. Prescriptions for MHT dropped precipitously after 2002 and continued to decline in subsequent years. Declines were most marked for standard-dose EPT and in older women. The results of the CEE study were less negative, compared with those for EPT, as they showed no effect on CHD, a nonsignificant reduction in the risk of breast cancer, and a more favorable risk-benefit ratio for younger women, compared with older women. A decade later, it had become widely accepted that MHT should not be used for the prevention of chronic disease in older women; however, short-term use for treatment of vasomotor symptoms remains an accepted indication.
Risks and outcomes
Emerging from a series of WHI reports are complex models on the effect of hormonal therapy on the risk and outcome of breast cancer. In one study, women with an intact uterus received CEEs plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). An increase in the risk of breast cancer was observed over a median of 5.6 years of treatment, followed by a moderate reduction, with the risk increasing after 13 years of cumulative follow-up. For women treated with CEE alone, the reduction in risk observed over an average of 7.2 years of treatment was maintained for 13 years of follow-up.
Results from observational studies contrast with those from randomized controlled trials, particularly those concerning the use of estrogens only. A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer showed that both EPT and CEE were associated with a higher risk of breast neoplasia. Results of the Million Women Study showed a higher death rate.
Treatment methods and duration
Information from prospective studies on the effects of commencing MHT at various ages between 40 and 59 years show that for women who commenced treatment at any time within this age range, the relative risk was similar and was highly significant for all ages. Few women had started MHT treatment well after menopause at ages 60-69 years, and their excess risks during years 5-14 of current use were significant for estrogen-progestogen but not for estrogen-only MHT.
If these associations are largely causal, then for women of average weight in developed countries, 5 years of MHT, starting at age 50 years, would increase breast cancer incidence at ages 50-69 years by about 1 in every 50 users of estrogen plus daily progestogen preparations; 1 in every 70 users of estrogen plus intermittent progestogen preparations; and 1 in every 200 users of estrogen-only preparations. The corresponding excesses from 10 years of MHT would be about twice as great.
During 5-14 years of MHT use, the RRs were similarly increased if MHT use had started at ages 40-44 years, 45-49 years, 50-54 years, and 55-59 years; RRs appeared to be attenuated if MHT use had started after age 60 years. They were also attenuated by adiposity, particularly for estrogen-only MHT (which had little effect in obese women). After MHT use ceased, some excess risk of breast cancer persisted for more than a decade; this is directly correlated with the duration of treatment.
Therefore, it can be expected that the effects of MHT may vary between participants on the basis of age or time since menopause, as well as treatments (MHT type, dose, formulation, duration of use, and route of administration). Regarding formulation effects on the risk of breast cancer, new evidence shows an increased risk of 28%. Progestogens appeared to be differentially associated with breast cancer (micronized progesterone: odds ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval 0.55-1.79; synthetic progestin: OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.22-1.35). When prescribing MHT, micronized progesterone may be the safer progestogen to use.
In conclusion, MHT has a complex balance of benefits and risk on various health outcomes. Some effects differ qualitatively between ET and EPT. Regarding use of MHT, consideration should be given to the full range of effects, along with patients’ values and preferences. The overall quality of existing systematic reviews is moderate to poor. Clinicians should evaluate their scientific strength before considering applying their results in clinical practice. Regarding use of any hormone therapy regimen, consideration should be given to the full range of risk and benefits and should involve shared decisionmaking with the patient. It should be recognized that risk-benefit balance is altered by factors such as age, time from menopause, oophorectomy status, and prior hysterectomy and that some outcomes persist and there is some attenuation after stopping use.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
A version of the article appeared on Medscape.com.
Menstrual phase impacts exercise effects in type 1 diabetes
Women with type 1 diabetes may need additional glucose after exercise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared with other times, according to a study in nine women.
“We know that exercise is very beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes; we also know that fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to exercise in this population,” said Jane E. Yardley, PhD, in a presentation at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, New Orleans. Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) perceive more barriers, compared with men, she added.
The menstrual cycle could be an additional barrier to exercise for women with T1D because it increases glucose fluctuations that have not been well documented in the literature to date, said Dr. Yardley, of the University of Alberta, Augustana.
The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle lasts from menses to the midcycle, about 14 days later. This is followed by the luteal phase, which lasts until approximately day 28, Dr. Yardley explained. Data on insulin sensitivity have shown that the late luteal phase is associated with “a little less insulin sensitivity” in women with T1D, she noted.
To assess the relationship between menstrual cycle, glucose control, and exercise, Dr. Yardley and colleagues compared the effects of a moderate aerobic exercise on glycemic responses between the early follicular and late luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in nine female participants with T1D.
The exercise involved 45 minutes of aerobic cycling at 50% of predetermined peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) for 45 min. The mean age of the participants was 30.2 years, the mean hemoglobin A1C was 7.4%, and the mean VO2peak was 32.5 mL/kg per min. The women reported regular menstrual cycles, and none were using oral contraceptives.
Blood samples were collected before and immediately after exercise and after an hour of recovery. Participants wore continuous glucose monitors for at least 1 hour before and after exercise.
Menstrual cycle was confirmed via estrogen, estradiol, and progesterone.
Insulin levels varied greatly among the study participants, but the differences were not significant, Dr. Yardley said. Glucose levels consistently decreased during exercise and increased after exercise, she noted.
No significant difference in glucose was observed between the follicular and luteal phases.
However, “this needs to be interpreted in the context of the safety profiles that are in place in our lab,” which include carbohydrate supplements for individuals whose blood glucose levels drop below 4.5 mmol/L, she said.
In the current study, 6 of 9 participants required additional carbohydrates during the luteal phase, but only 1 participant needed additional carbohydrates during the follicular phase, she noted. For this reason, no differences were noted. “We actually prevented changes,” she said.
No significant differences were noted in mean glucose levels or number of hypoglycemic episodes at any of the time points between the two phases.
“One place where we did see a difference was in hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise,” Dr. Yardley said. Level 1 hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise was significantly more frequent in the follicular phase, compared with the luteal phase (P = .028).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and homogenous population, and more research is needed to interpret the data, said Dr. Yardley.
However, the need for more glucose supplementation to prevent hypoglycemia during the luteal phase suggests a higher hypoglycemic risk associated with aerobic exercise during this time, she said.
In addition, the results suggest that the menstrual cycle should be taken into consideration when female participants are involved in exercise studies, she noted.
Study supports personalized exercise plans
“It is important to evaluate effects of exercise in people with type 1 diabetes and evaluate whether there is a difference those effects in men and women,” said Helena W. Rodbard, MD, an endocrinologist in private practice in Rockville, Md., in an interview. “There is also a need to evaluate to what extent the changes in blood glucose patterns in women in response to exercise differ depending on the phase of the ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard, who was not involved in the study.
In the current study, “the researchers observed a decline in glucose during a 45-minute period of moderate aerobic exercise, cycling at 50% VO2peak followed by an increase during a 60-minute recovery period. There was a suggestive finding, in the nine subjects, that more carbohydrate supplementation was needed during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle than during the follicular phase,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “In contrast, the authors reported a significantly increased degree of hyperglycemia during the recovery phase for subjects during the follicular phase. These findings are consistent with and extend several recent studies from Dr. Yardley and coworkers, who have been focused on this area of research,” she said.
“This study provides provocative evidence that glucose responses to aerobic exercise in women may depend on the timing in relationship to their ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard. “These findings are based on a small group of subjects and were present in some but not all subjects. Clinicians should encourage women to evaluate and record their experiences during and after exercise in terms of need for carbohydrate supplementation for documented or symptomatic hypoglycemia and in terms of glucose changes as recorded using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), both in relation to type of exercise and in relation to time in the menstrual cycle,” she said.
The findings also highlight the importance of individualized therapy that is “based on subjective inputs combined with analysis of CGM data during and following exercise,” said Dr. Rodbard. “It is likely that use of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) will be helpful in achieving this level of individualization in view of the wide range of types, intensity, and duration of physical activity and exercise in which people with T1D engage and the myriad factors that can influence the glycemic response,” she said.
Looking ahead, “the authors and others should expand the present series of subjects using aerobic exercise and examine other types of exercise as well,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “It will be important to evaluate the consistency of these changes in glucose patterns within individuals on multiple occasions, and it would be helpful to repeat the studies in women using oral contraceptives.”
Dr. Yardley disclosed research support from Abbott, Dexcom, and LifeScan and disclosed serving on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott Diabetes. Dr. Rodbard had no financial conflicts to disclose. She serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Endocrinology News.
Women with type 1 diabetes may need additional glucose after exercise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared with other times, according to a study in nine women.
“We know that exercise is very beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes; we also know that fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to exercise in this population,” said Jane E. Yardley, PhD, in a presentation at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, New Orleans. Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) perceive more barriers, compared with men, she added.
The menstrual cycle could be an additional barrier to exercise for women with T1D because it increases glucose fluctuations that have not been well documented in the literature to date, said Dr. Yardley, of the University of Alberta, Augustana.
The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle lasts from menses to the midcycle, about 14 days later. This is followed by the luteal phase, which lasts until approximately day 28, Dr. Yardley explained. Data on insulin sensitivity have shown that the late luteal phase is associated with “a little less insulin sensitivity” in women with T1D, she noted.
To assess the relationship between menstrual cycle, glucose control, and exercise, Dr. Yardley and colleagues compared the effects of a moderate aerobic exercise on glycemic responses between the early follicular and late luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in nine female participants with T1D.
The exercise involved 45 minutes of aerobic cycling at 50% of predetermined peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) for 45 min. The mean age of the participants was 30.2 years, the mean hemoglobin A1C was 7.4%, and the mean VO2peak was 32.5 mL/kg per min. The women reported regular menstrual cycles, and none were using oral contraceptives.
Blood samples were collected before and immediately after exercise and after an hour of recovery. Participants wore continuous glucose monitors for at least 1 hour before and after exercise.
Menstrual cycle was confirmed via estrogen, estradiol, and progesterone.
Insulin levels varied greatly among the study participants, but the differences were not significant, Dr. Yardley said. Glucose levels consistently decreased during exercise and increased after exercise, she noted.
No significant difference in glucose was observed between the follicular and luteal phases.
However, “this needs to be interpreted in the context of the safety profiles that are in place in our lab,” which include carbohydrate supplements for individuals whose blood glucose levels drop below 4.5 mmol/L, she said.
In the current study, 6 of 9 participants required additional carbohydrates during the luteal phase, but only 1 participant needed additional carbohydrates during the follicular phase, she noted. For this reason, no differences were noted. “We actually prevented changes,” she said.
No significant differences were noted in mean glucose levels or number of hypoglycemic episodes at any of the time points between the two phases.
“One place where we did see a difference was in hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise,” Dr. Yardley said. Level 1 hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise was significantly more frequent in the follicular phase, compared with the luteal phase (P = .028).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and homogenous population, and more research is needed to interpret the data, said Dr. Yardley.
However, the need for more glucose supplementation to prevent hypoglycemia during the luteal phase suggests a higher hypoglycemic risk associated with aerobic exercise during this time, she said.
In addition, the results suggest that the menstrual cycle should be taken into consideration when female participants are involved in exercise studies, she noted.
Study supports personalized exercise plans
“It is important to evaluate effects of exercise in people with type 1 diabetes and evaluate whether there is a difference those effects in men and women,” said Helena W. Rodbard, MD, an endocrinologist in private practice in Rockville, Md., in an interview. “There is also a need to evaluate to what extent the changes in blood glucose patterns in women in response to exercise differ depending on the phase of the ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard, who was not involved in the study.
In the current study, “the researchers observed a decline in glucose during a 45-minute period of moderate aerobic exercise, cycling at 50% VO2peak followed by an increase during a 60-minute recovery period. There was a suggestive finding, in the nine subjects, that more carbohydrate supplementation was needed during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle than during the follicular phase,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “In contrast, the authors reported a significantly increased degree of hyperglycemia during the recovery phase for subjects during the follicular phase. These findings are consistent with and extend several recent studies from Dr. Yardley and coworkers, who have been focused on this area of research,” she said.
“This study provides provocative evidence that glucose responses to aerobic exercise in women may depend on the timing in relationship to their ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard. “These findings are based on a small group of subjects and were present in some but not all subjects. Clinicians should encourage women to evaluate and record their experiences during and after exercise in terms of need for carbohydrate supplementation for documented or symptomatic hypoglycemia and in terms of glucose changes as recorded using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), both in relation to type of exercise and in relation to time in the menstrual cycle,” she said.
The findings also highlight the importance of individualized therapy that is “based on subjective inputs combined with analysis of CGM data during and following exercise,” said Dr. Rodbard. “It is likely that use of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) will be helpful in achieving this level of individualization in view of the wide range of types, intensity, and duration of physical activity and exercise in which people with T1D engage and the myriad factors that can influence the glycemic response,” she said.
Looking ahead, “the authors and others should expand the present series of subjects using aerobic exercise and examine other types of exercise as well,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “It will be important to evaluate the consistency of these changes in glucose patterns within individuals on multiple occasions, and it would be helpful to repeat the studies in women using oral contraceptives.”
Dr. Yardley disclosed research support from Abbott, Dexcom, and LifeScan and disclosed serving on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott Diabetes. Dr. Rodbard had no financial conflicts to disclose. She serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Endocrinology News.
Women with type 1 diabetes may need additional glucose after exercise during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle, compared with other times, according to a study in nine women.
“We know that exercise is very beneficial for people with type 1 diabetes; we also know that fear of hypoglycemia is a major barrier to exercise in this population,” said Jane E. Yardley, PhD, in a presentation at the annual scientific sessions of the American Diabetes Association, New Orleans. Women with type 1 diabetes (T1D) perceive more barriers, compared with men, she added.
The menstrual cycle could be an additional barrier to exercise for women with T1D because it increases glucose fluctuations that have not been well documented in the literature to date, said Dr. Yardley, of the University of Alberta, Augustana.
The follicular phase of the menstrual cycle lasts from menses to the midcycle, about 14 days later. This is followed by the luteal phase, which lasts until approximately day 28, Dr. Yardley explained. Data on insulin sensitivity have shown that the late luteal phase is associated with “a little less insulin sensitivity” in women with T1D, she noted.
To assess the relationship between menstrual cycle, glucose control, and exercise, Dr. Yardley and colleagues compared the effects of a moderate aerobic exercise on glycemic responses between the early follicular and late luteal phases of the menstrual cycle in nine female participants with T1D.
The exercise involved 45 minutes of aerobic cycling at 50% of predetermined peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak) for 45 min. The mean age of the participants was 30.2 years, the mean hemoglobin A1C was 7.4%, and the mean VO2peak was 32.5 mL/kg per min. The women reported regular menstrual cycles, and none were using oral contraceptives.
Blood samples were collected before and immediately after exercise and after an hour of recovery. Participants wore continuous glucose monitors for at least 1 hour before and after exercise.
Menstrual cycle was confirmed via estrogen, estradiol, and progesterone.
Insulin levels varied greatly among the study participants, but the differences were not significant, Dr. Yardley said. Glucose levels consistently decreased during exercise and increased after exercise, she noted.
No significant difference in glucose was observed between the follicular and luteal phases.
However, “this needs to be interpreted in the context of the safety profiles that are in place in our lab,” which include carbohydrate supplements for individuals whose blood glucose levels drop below 4.5 mmol/L, she said.
In the current study, 6 of 9 participants required additional carbohydrates during the luteal phase, but only 1 participant needed additional carbohydrates during the follicular phase, she noted. For this reason, no differences were noted. “We actually prevented changes,” she said.
No significant differences were noted in mean glucose levels or number of hypoglycemic episodes at any of the time points between the two phases.
“One place where we did see a difference was in hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise,” Dr. Yardley said. Level 1 hyperglycemia 24 hours after exercise was significantly more frequent in the follicular phase, compared with the luteal phase (P = .028).
The study findings were limited by the small sample size and homogenous population, and more research is needed to interpret the data, said Dr. Yardley.
However, the need for more glucose supplementation to prevent hypoglycemia during the luteal phase suggests a higher hypoglycemic risk associated with aerobic exercise during this time, she said.
In addition, the results suggest that the menstrual cycle should be taken into consideration when female participants are involved in exercise studies, she noted.
Study supports personalized exercise plans
“It is important to evaluate effects of exercise in people with type 1 diabetes and evaluate whether there is a difference those effects in men and women,” said Helena W. Rodbard, MD, an endocrinologist in private practice in Rockville, Md., in an interview. “There is also a need to evaluate to what extent the changes in blood glucose patterns in women in response to exercise differ depending on the phase of the ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard, who was not involved in the study.
In the current study, “the researchers observed a decline in glucose during a 45-minute period of moderate aerobic exercise, cycling at 50% VO2peak followed by an increase during a 60-minute recovery period. There was a suggestive finding, in the nine subjects, that more carbohydrate supplementation was needed during the late luteal phase of the menstrual cycle than during the follicular phase,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “In contrast, the authors reported a significantly increased degree of hyperglycemia during the recovery phase for subjects during the follicular phase. These findings are consistent with and extend several recent studies from Dr. Yardley and coworkers, who have been focused on this area of research,” she said.
“This study provides provocative evidence that glucose responses to aerobic exercise in women may depend on the timing in relationship to their ovarian cycle,” said Dr. Rodbard. “These findings are based on a small group of subjects and were present in some but not all subjects. Clinicians should encourage women to evaluate and record their experiences during and after exercise in terms of need for carbohydrate supplementation for documented or symptomatic hypoglycemia and in terms of glucose changes as recorded using continuous glucose monitoring (CGM), both in relation to type of exercise and in relation to time in the menstrual cycle,” she said.
The findings also highlight the importance of individualized therapy that is “based on subjective inputs combined with analysis of CGM data during and following exercise,” said Dr. Rodbard. “It is likely that use of Automated Insulin Delivery (AID) will be helpful in achieving this level of individualization in view of the wide range of types, intensity, and duration of physical activity and exercise in which people with T1D engage and the myriad factors that can influence the glycemic response,” she said.
Looking ahead, “the authors and others should expand the present series of subjects using aerobic exercise and examine other types of exercise as well,” Dr. Rodbard noted. “It will be important to evaluate the consistency of these changes in glucose patterns within individuals on multiple occasions, and it would be helpful to repeat the studies in women using oral contraceptives.”
Dr. Yardley disclosed research support from Abbott, Dexcom, and LifeScan and disclosed serving on the speaker’s bureau for Abbott Diabetes. Dr. Rodbard had no financial conflicts to disclose. She serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Clinical Endocrinology News.
FROM ADA 2022










