User login
Navigating your childcare options in a post-COVID world
When we found out we were expecting our first child, we were ecstatic. Our excitement soon gave way to panic, however, as we realized that we needed a plan for childcare. As full-time physicians early in our careers, neither of us was prepared to drop to part-time or become a stay-at-home caregiver. Not knowing where to start, we turned to our friends and colleagues, and of course, the Internet, for advice on our options.
In our research, we discovered three things. First, with COVID-19, the cost of childcare has skyrocketed, and availability has decreased. Second, there are several options for childcare, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Third, there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Family
Using family members to provide childcare is often cost-effective and provides a familiar, supportive environment for children. Proximity does not guarantee a willingness or ability to provide long-term care, however, and it can cause strain on family relationships, lead to intrusions and boundary issues, and create feelings of obligation and guilt. It is important to have very honest, up-front discussions with family members about hopes and expectations if this is your childcare plan.
Daycare, facility-based
Daycare centers are commercial facilities that offer care to multiple children of varying ages, starting from as young as 6 weeks. They have trained professionals and provide structured activities and educational programs for children. Many daycares also provide snacks and lunch, which is included in their tuition. They are a popular choice for families seeking full-time childcare and the social and educational benefits that come with a structured setting.
Daycares also have some downsides. They usually operate during normal workday hours, from 7:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m., which may not be convenient for physicians who work outside of these hours. Even with feasible hours, getting children dressed, ready, and dropped off each morning could add significant time and stress to your morning routine. Additionally, most daycares have policies that prohibit attendance if a child is sick or febrile, which is a common occurrence, particularly for daycare kids. In case of an illness outbreak, the daycare may even close for several days. Both scenarios require at least one parent to take a day off or have an alternative childcare plan available on short notice.
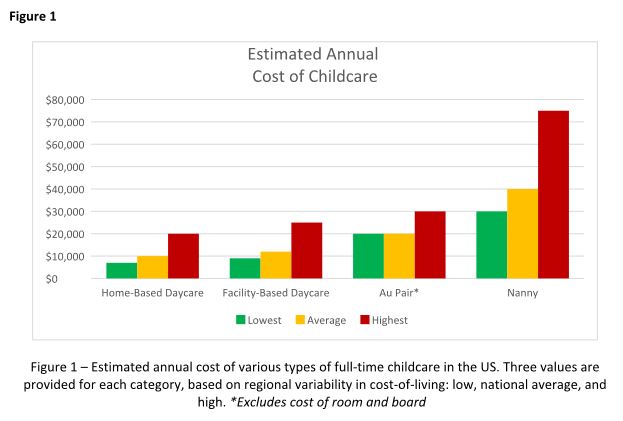
Availability of daycare can be limited, particularly since the COVID pandemic, creating waitlists that can be several months long. Early registration, even during pregnancy, is recommended to secure a spot. It can be helpful to find out if your employer has an agreement with a specific daycare that has “physician-friendly” hours and gives waitlist priority to trainees or even attending physicians. The cost of daycare for one child is typically affordable, around $12,000 per year on average, but can be as high as $25,000 in cities with high cost of living. A sibling discount may be offered, but the cost of daycare for multiple children could still exceed in-home childcare options.1
Daycare, home-based (also known as family care centers)
Family care centers offer a home-like alternative to daycares, with smaller staff-to-child ratios and often more personalized care. They are favored by families seeking a more intimate setting. They might offer more flexible scheduling and are typically less expensive than facility-based daycares, at up to 25% lower cost.1 They may lack the same structure and educational opportunities as facility-based daycares, however, and are not subject to the same health and safety regulations.
Nannies
Nannies are professional caregivers who provide in-home childcare services. Their responsibilities may include feeding, changing, dressing, bathing, and playing with children. In some cases, they may also be expected to do light housekeeping tasks like meal preparation, laundry, and cleaning. It is common for nannies in high-demand markets to refuse to perform these additional tasks, however. Nannies are preferred by families with hectic schedules due to their flexibility. They can work early, late, or even overnight shifts, and provide care in the comfort of your home, avoiding the hassle of drop-off and pick-up times. Nannies also can provide personalized care to meet each child’s specific needs, and they can care for children who are sick or febrile.
When hiring a nanny, it is important to have a written contract outlining their expected hours, wages, benefits, and duties to prevent misunderstandings in the future. Finding a trustworthy and reliable nanny can be a challenge, and families have several options for finding one. They can post jobs on free websites and browse nanny CVs or use a fee-based nanny agency. The cost of using an agency can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, so it is important to ask friends and colleagues for recommendations before paying for an agency’s services.
The cost of hiring a nanny is one of its main drawbacks. Nannies typically earn $15 to $30 per hour, and if they work in the family’s home, they are typically considered “household employees” by the IRS. Household employees are entitled to overtime pay for work beyond 40 hours per week, and the employer (you!) is responsible for payroll taxes, withholding, and providing an annual W-2 tax statement.2 There are affordable online nanny payroll services that handle payroll and tax-filing to simplify the process, however. The average annual cost of a full-time nanny is around $40,000 and can be as high as $75,000 in some markets.1 A nanny-share with other families can lower costs, but it may also result in less control over the caregiver and schedule.
It is important to consult a tax professional or the IRS for guidance on nanny wages, taxes, and payroll, as a nanny might rarely be considered an “independent contractor” if they meet certain criteria.
Au pair
An au pair is a live-in childcare provider who travels to a host family’s home from a foreign country on a special J-1 visa. The goal is to provide care for children and participate in cultural exchange activities. Au pairs bring many benefits, such as cost savings compared to traditional childcare options and greater flexibility and customization. They can work up to 10 hours per day and 45 hours a week, performing tasks such as light housekeeping, meal preparation, and transportation for the children. Host families must provide a safe and comfortable living environment, including a private room, meals, and some travel and education expenses.1
The process of hiring an au pair involves working with a designated agency that matches families with applicants and sponsors the J-1 visa. The entire process can take several months, and average program fees cost around $10,000 per placement. Au pairs are hired on a 12-month J-1 visa, which can be extended for up to an additional 12 months, allowing families up to 2 years with the same au pair before needing to find a new placement.
Au pairs earn a minimum weekly stipend of $195.75, set forth by the U.S. State Department.3 Currently, au pairs are not subject to local and state wage requirements, but legal proceedings in various states have recently questioned whether au pairs should be protected under local regulations. Massachusetts has been the most progressive, explicitly protecting au pairs as domestic workers under state labor laws, raising their weekly stipend to roughly $600 to comply with state minimum wage requirements.4 The federal government is expected to provide clarity on this issue, but for the time being, au pairs remain an affordable alternative to a nanny in most states.
Conclusion
Choosing childcare is a complicated process with multiple factors to consider. Figure 1 breaks down the estimated annual cost of each of the options outlined above for a single child in low, average, and high cost-of-living areas. But your decision likely hinges on much more than just cost, and may include family dynamics, scheduling needs, and personal preferences. Gather as much advice and information as possible, but remember to trust your instincts and make the decision that works best for your family. At the end of the day, what matters most is the happiness and well-being of your child.
Dr. Hathorn and Dr. Creighton are married, and both work full-time with a 1-year-old child. Dr. Hathorn is a bariatric and advanced therapeutic endoscopist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Creighton is an anesthesiologist at UNC Chapel Hill. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
References
1. Care.com. This is how much childcare costs in 2022. 2022 Jun 15.
2. Internal Revenue Service. Publication 926 - Household Employer’s Tax Guide 2023.
3. U.S. Department of State. Au Pair.
4. Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Domestic workers.
Disclaimer
The financial and tax information presented in this article are believed to be true and accurate at the time of writing. However, it’s important to note that tax laws and regulations are subject to change. The authors are not certified financial advisers or tax specialists. It is recommended to seek verification from a local tax expert or the Internal Revenue Service to discuss your specific situation.
When we found out we were expecting our first child, we were ecstatic. Our excitement soon gave way to panic, however, as we realized that we needed a plan for childcare. As full-time physicians early in our careers, neither of us was prepared to drop to part-time or become a stay-at-home caregiver. Not knowing where to start, we turned to our friends and colleagues, and of course, the Internet, for advice on our options.
In our research, we discovered three things. First, with COVID-19, the cost of childcare has skyrocketed, and availability has decreased. Second, there are several options for childcare, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Third, there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Family
Using family members to provide childcare is often cost-effective and provides a familiar, supportive environment for children. Proximity does not guarantee a willingness or ability to provide long-term care, however, and it can cause strain on family relationships, lead to intrusions and boundary issues, and create feelings of obligation and guilt. It is important to have very honest, up-front discussions with family members about hopes and expectations if this is your childcare plan.
Daycare, facility-based
Daycare centers are commercial facilities that offer care to multiple children of varying ages, starting from as young as 6 weeks. They have trained professionals and provide structured activities and educational programs for children. Many daycares also provide snacks and lunch, which is included in their tuition. They are a popular choice for families seeking full-time childcare and the social and educational benefits that come with a structured setting.
Daycares also have some downsides. They usually operate during normal workday hours, from 7:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m., which may not be convenient for physicians who work outside of these hours. Even with feasible hours, getting children dressed, ready, and dropped off each morning could add significant time and stress to your morning routine. Additionally, most daycares have policies that prohibit attendance if a child is sick or febrile, which is a common occurrence, particularly for daycare kids. In case of an illness outbreak, the daycare may even close for several days. Both scenarios require at least one parent to take a day off or have an alternative childcare plan available on short notice.
Availability of daycare can be limited, particularly since the COVID pandemic, creating waitlists that can be several months long. Early registration, even during pregnancy, is recommended to secure a spot. It can be helpful to find out if your employer has an agreement with a specific daycare that has “physician-friendly” hours and gives waitlist priority to trainees or even attending physicians. The cost of daycare for one child is typically affordable, around $12,000 per year on average, but can be as high as $25,000 in cities with high cost of living. A sibling discount may be offered, but the cost of daycare for multiple children could still exceed in-home childcare options.1
Daycare, home-based (also known as family care centers)
Family care centers offer a home-like alternative to daycares, with smaller staff-to-child ratios and often more personalized care. They are favored by families seeking a more intimate setting. They might offer more flexible scheduling and are typically less expensive than facility-based daycares, at up to 25% lower cost.1 They may lack the same structure and educational opportunities as facility-based daycares, however, and are not subject to the same health and safety regulations.
Nannies
Nannies are professional caregivers who provide in-home childcare services. Their responsibilities may include feeding, changing, dressing, bathing, and playing with children. In some cases, they may also be expected to do light housekeeping tasks like meal preparation, laundry, and cleaning. It is common for nannies in high-demand markets to refuse to perform these additional tasks, however. Nannies are preferred by families with hectic schedules due to their flexibility. They can work early, late, or even overnight shifts, and provide care in the comfort of your home, avoiding the hassle of drop-off and pick-up times. Nannies also can provide personalized care to meet each child’s specific needs, and they can care for children who are sick or febrile.
When hiring a nanny, it is important to have a written contract outlining their expected hours, wages, benefits, and duties to prevent misunderstandings in the future. Finding a trustworthy and reliable nanny can be a challenge, and families have several options for finding one. They can post jobs on free websites and browse nanny CVs or use a fee-based nanny agency. The cost of using an agency can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, so it is important to ask friends and colleagues for recommendations before paying for an agency’s services.
The cost of hiring a nanny is one of its main drawbacks. Nannies typically earn $15 to $30 per hour, and if they work in the family’s home, they are typically considered “household employees” by the IRS. Household employees are entitled to overtime pay for work beyond 40 hours per week, and the employer (you!) is responsible for payroll taxes, withholding, and providing an annual W-2 tax statement.2 There are affordable online nanny payroll services that handle payroll and tax-filing to simplify the process, however. The average annual cost of a full-time nanny is around $40,000 and can be as high as $75,000 in some markets.1 A nanny-share with other families can lower costs, but it may also result in less control over the caregiver and schedule.
It is important to consult a tax professional or the IRS for guidance on nanny wages, taxes, and payroll, as a nanny might rarely be considered an “independent contractor” if they meet certain criteria.
Au pair
An au pair is a live-in childcare provider who travels to a host family’s home from a foreign country on a special J-1 visa. The goal is to provide care for children and participate in cultural exchange activities. Au pairs bring many benefits, such as cost savings compared to traditional childcare options and greater flexibility and customization. They can work up to 10 hours per day and 45 hours a week, performing tasks such as light housekeeping, meal preparation, and transportation for the children. Host families must provide a safe and comfortable living environment, including a private room, meals, and some travel and education expenses.1
The process of hiring an au pair involves working with a designated agency that matches families with applicants and sponsors the J-1 visa. The entire process can take several months, and average program fees cost around $10,000 per placement. Au pairs are hired on a 12-month J-1 visa, which can be extended for up to an additional 12 months, allowing families up to 2 years with the same au pair before needing to find a new placement.
Au pairs earn a minimum weekly stipend of $195.75, set forth by the U.S. State Department.3 Currently, au pairs are not subject to local and state wage requirements, but legal proceedings in various states have recently questioned whether au pairs should be protected under local regulations. Massachusetts has been the most progressive, explicitly protecting au pairs as domestic workers under state labor laws, raising their weekly stipend to roughly $600 to comply with state minimum wage requirements.4 The federal government is expected to provide clarity on this issue, but for the time being, au pairs remain an affordable alternative to a nanny in most states.
Conclusion
Choosing childcare is a complicated process with multiple factors to consider. Figure 1 breaks down the estimated annual cost of each of the options outlined above for a single child in low, average, and high cost-of-living areas. But your decision likely hinges on much more than just cost, and may include family dynamics, scheduling needs, and personal preferences. Gather as much advice and information as possible, but remember to trust your instincts and make the decision that works best for your family. At the end of the day, what matters most is the happiness and well-being of your child.
Dr. Hathorn and Dr. Creighton are married, and both work full-time with a 1-year-old child. Dr. Hathorn is a bariatric and advanced therapeutic endoscopist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Creighton is an anesthesiologist at UNC Chapel Hill. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
References
1. Care.com. This is how much childcare costs in 2022. 2022 Jun 15.
2. Internal Revenue Service. Publication 926 - Household Employer’s Tax Guide 2023.
3. U.S. Department of State. Au Pair.
4. Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Domestic workers.
Disclaimer
The financial and tax information presented in this article are believed to be true and accurate at the time of writing. However, it’s important to note that tax laws and regulations are subject to change. The authors are not certified financial advisers or tax specialists. It is recommended to seek verification from a local tax expert or the Internal Revenue Service to discuss your specific situation.
When we found out we were expecting our first child, we were ecstatic. Our excitement soon gave way to panic, however, as we realized that we needed a plan for childcare. As full-time physicians early in our careers, neither of us was prepared to drop to part-time or become a stay-at-home caregiver. Not knowing where to start, we turned to our friends and colleagues, and of course, the Internet, for advice on our options.
In our research, we discovered three things. First, with COVID-19, the cost of childcare has skyrocketed, and availability has decreased. Second, there are several options for childcare, each with its own benefits and drawbacks. Third, there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Family
Using family members to provide childcare is often cost-effective and provides a familiar, supportive environment for children. Proximity does not guarantee a willingness or ability to provide long-term care, however, and it can cause strain on family relationships, lead to intrusions and boundary issues, and create feelings of obligation and guilt. It is important to have very honest, up-front discussions with family members about hopes and expectations if this is your childcare plan.
Daycare, facility-based
Daycare centers are commercial facilities that offer care to multiple children of varying ages, starting from as young as 6 weeks. They have trained professionals and provide structured activities and educational programs for children. Many daycares also provide snacks and lunch, which is included in their tuition. They are a popular choice for families seeking full-time childcare and the social and educational benefits that come with a structured setting.
Daycares also have some downsides. They usually operate during normal workday hours, from 7:00 a.m. to 6:00 p.m., which may not be convenient for physicians who work outside of these hours. Even with feasible hours, getting children dressed, ready, and dropped off each morning could add significant time and stress to your morning routine. Additionally, most daycares have policies that prohibit attendance if a child is sick or febrile, which is a common occurrence, particularly for daycare kids. In case of an illness outbreak, the daycare may even close for several days. Both scenarios require at least one parent to take a day off or have an alternative childcare plan available on short notice.
Availability of daycare can be limited, particularly since the COVID pandemic, creating waitlists that can be several months long. Early registration, even during pregnancy, is recommended to secure a spot. It can be helpful to find out if your employer has an agreement with a specific daycare that has “physician-friendly” hours and gives waitlist priority to trainees or even attending physicians. The cost of daycare for one child is typically affordable, around $12,000 per year on average, but can be as high as $25,000 in cities with high cost of living. A sibling discount may be offered, but the cost of daycare for multiple children could still exceed in-home childcare options.1
Daycare, home-based (also known as family care centers)
Family care centers offer a home-like alternative to daycares, with smaller staff-to-child ratios and often more personalized care. They are favored by families seeking a more intimate setting. They might offer more flexible scheduling and are typically less expensive than facility-based daycares, at up to 25% lower cost.1 They may lack the same structure and educational opportunities as facility-based daycares, however, and are not subject to the same health and safety regulations.
Nannies
Nannies are professional caregivers who provide in-home childcare services. Their responsibilities may include feeding, changing, dressing, bathing, and playing with children. In some cases, they may also be expected to do light housekeeping tasks like meal preparation, laundry, and cleaning. It is common for nannies in high-demand markets to refuse to perform these additional tasks, however. Nannies are preferred by families with hectic schedules due to their flexibility. They can work early, late, or even overnight shifts, and provide care in the comfort of your home, avoiding the hassle of drop-off and pick-up times. Nannies also can provide personalized care to meet each child’s specific needs, and they can care for children who are sick or febrile.
When hiring a nanny, it is important to have a written contract outlining their expected hours, wages, benefits, and duties to prevent misunderstandings in the future. Finding a trustworthy and reliable nanny can be a challenge, and families have several options for finding one. They can post jobs on free websites and browse nanny CVs or use a fee-based nanny agency. The cost of using an agency can range from a few hundred to several thousand dollars, so it is important to ask friends and colleagues for recommendations before paying for an agency’s services.
The cost of hiring a nanny is one of its main drawbacks. Nannies typically earn $15 to $30 per hour, and if they work in the family’s home, they are typically considered “household employees” by the IRS. Household employees are entitled to overtime pay for work beyond 40 hours per week, and the employer (you!) is responsible for payroll taxes, withholding, and providing an annual W-2 tax statement.2 There are affordable online nanny payroll services that handle payroll and tax-filing to simplify the process, however. The average annual cost of a full-time nanny is around $40,000 and can be as high as $75,000 in some markets.1 A nanny-share with other families can lower costs, but it may also result in less control over the caregiver and schedule.
It is important to consult a tax professional or the IRS for guidance on nanny wages, taxes, and payroll, as a nanny might rarely be considered an “independent contractor” if they meet certain criteria.
Au pair
An au pair is a live-in childcare provider who travels to a host family’s home from a foreign country on a special J-1 visa. The goal is to provide care for children and participate in cultural exchange activities. Au pairs bring many benefits, such as cost savings compared to traditional childcare options and greater flexibility and customization. They can work up to 10 hours per day and 45 hours a week, performing tasks such as light housekeeping, meal preparation, and transportation for the children. Host families must provide a safe and comfortable living environment, including a private room, meals, and some travel and education expenses.1
The process of hiring an au pair involves working with a designated agency that matches families with applicants and sponsors the J-1 visa. The entire process can take several months, and average program fees cost around $10,000 per placement. Au pairs are hired on a 12-month J-1 visa, which can be extended for up to an additional 12 months, allowing families up to 2 years with the same au pair before needing to find a new placement.
Au pairs earn a minimum weekly stipend of $195.75, set forth by the U.S. State Department.3 Currently, au pairs are not subject to local and state wage requirements, but legal proceedings in various states have recently questioned whether au pairs should be protected under local regulations. Massachusetts has been the most progressive, explicitly protecting au pairs as domestic workers under state labor laws, raising their weekly stipend to roughly $600 to comply with state minimum wage requirements.4 The federal government is expected to provide clarity on this issue, but for the time being, au pairs remain an affordable alternative to a nanny in most states.
Conclusion
Choosing childcare is a complicated process with multiple factors to consider. Figure 1 breaks down the estimated annual cost of each of the options outlined above for a single child in low, average, and high cost-of-living areas. But your decision likely hinges on much more than just cost, and may include family dynamics, scheduling needs, and personal preferences. Gather as much advice and information as possible, but remember to trust your instincts and make the decision that works best for your family. At the end of the day, what matters most is the happiness and well-being of your child.
Dr. Hathorn and Dr. Creighton are married, and both work full-time with a 1-year-old child. Dr. Hathorn is a bariatric and advanced therapeutic endoscopist at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Creighton is an anesthesiologist at UNC Chapel Hill. Neither reported any conflicts of interest.
References
1. Care.com. This is how much childcare costs in 2022. 2022 Jun 15.
2. Internal Revenue Service. Publication 926 - Household Employer’s Tax Guide 2023.
3. U.S. Department of State. Au Pair.
4. Commonwealth of Massachusetts. Domestic workers.
Disclaimer
The financial and tax information presented in this article are believed to be true and accurate at the time of writing. However, it’s important to note that tax laws and regulations are subject to change. The authors are not certified financial advisers or tax specialists. It is recommended to seek verification from a local tax expert or the Internal Revenue Service to discuss your specific situation.
From private practice to academic medicine: My journey and lessons learned
Loyalty.
This is a quality that I value in relationships. Loyalty was a significant factor contributing to my postfellowship commitment to private practice. In 2001, I graduated from physician assistant school and accepted a job with a private practice GI group in Omaha. I was fortunate to work with supportive gastroenterologists who encouraged me to pursue further training after I expressed an interest in medical school. My goal was to become a gastroenterologist but like every medical student, I would keep an open mind. My decision did not waver, and the support from my first mentors continued. As I graduated from fellowship in 2014, I gravitated toward the same private practice largely based on loyalty and my experience as a PA.

COURTESY AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
My experience in private practice was positive. My focus at that time and currently is clinical medicine with a focus on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. My colleagues were supportive, and I worked with a great team of nurses and APPs. I cared for many patients in both the inpatient and outpatient setting and had an opportunity to complete a high volume and variety of procedures. Overall, the various aspects of my job were rewarding. However, something was missing, and I made personal and professional adjustments. My schedule pulled me from valued family time with my kids (mostly) in the early mornings, therefore, I altered my work schedule. My clinical interest in IBD was diluted by the emphasis to see mostly general GI patients, as is the case for many in private practice. I missed the academic environment, especially working with medical students, residents, and fellows, so I occasionally had residents shadow me. Unfortunately, adjustments did not “fix” that missing component – to me, this was a job that did not feel like a career. I was not professionally fulfilled and on several occasions during the 6 years in private practice, I connected with mentors from my medical training to explore career options while trying to define what was missing.
During the latter part of years 5 and 6, it became apparent to me that loyalty pulled me toward working with a great group of supportive gastroenterologists, but it became increasingly more apparent that this job was not in line with my career goals. I had identified that I wanted to actively participate in medical education while practicing as a gastroenterologist in an academic setting. Additionally, time with my family was a critical part to the work-life integration.
My approach to the next step in my journey was different than my initial job. My goal was to define what was important, as in what were my absolute requirements for career satisfaction and where was I willing to be flexible. Each of us has different absolute and relative requirements based on our values, and I neglected to clearly identify these components with my first job. Admittedly, I have (at times) struggled to acknowledge my values, because I might somehow appear less committed to a career. Owning these values has provided clarity in my path from private practice to academic medicine. During the 3 years I have been in my current position, I have stepped into a leadership role in the University of Nebraska Medicine GI fellowship program while providing clinical medicine at the Fred Paustian IBD Center at Nebraska Medicine. In addition, I continue to have an active endoscopy schedule and derive great satisfaction teaching the fellows how to be effective endoscopists. Personally, the difference in compensation between academic medicine and private practice was not an important factor, although this is a factor for some people (and that’s okay).
When I graduated from fellowship, my path seemed clear, and I did not anticipate the road ahead. However, with each hurdle, I was gifted with lessons that would prove to be valuable as I moved ahead. Thank you for giving me the space to share my story.
Lessons that have helped in my journey from private practice to academics
- Mentorship: Find mentors, not just one mentor. Over the years, I have had several mentors, but what I recognize is that, early in my career, I did not have a mentor. Although a mentor cannot make decisions for you, he/she can provide guidance from a place of experience (both career and life experience).
- Define a mission statement: My mentor pushed me to first define my values and then my mission statement. This serves as the foundation that I reference when making decisions that will impact my family and my career. For example, if I am invited to participate on a committee, I look at how this will impact my family and whether it aligns with my mission. This helps to clarify what I am willing to say yes to and what to pass along to another colleague. Remember that last part ... if you are saying no to something, suggest another colleague for the opportunity.
- Advocate for yourself: Only you know what is best for you. Sometimes the path to discovering what that is can be tortuous and require guidance. Throughout my journey, I worked with colleagues who were supportive of my journey back to medical school and supportive of my job in private practice, but only I could define what a career meant to me.
- Assume positive intent: In medicine, we frequently work in a high-stakes, stressful environment. Assume positive intent in your interactions with others, especially colleagues. This will serve you well.
- Life happens: Each of us will experience an unexpected event in our personal life or career path or both. This will be okay. The path forward may look different and require a pivot. This unexpected event might be that you find your job leaves you wanting something more or something different. Your journey will be right for you.
Dr. Hutchins is an assistant professor in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha. She reported no conflicts of interest.
Loyalty.
This is a quality that I value in relationships. Loyalty was a significant factor contributing to my postfellowship commitment to private practice. In 2001, I graduated from physician assistant school and accepted a job with a private practice GI group in Omaha. I was fortunate to work with supportive gastroenterologists who encouraged me to pursue further training after I expressed an interest in medical school. My goal was to become a gastroenterologist but like every medical student, I would keep an open mind. My decision did not waver, and the support from my first mentors continued. As I graduated from fellowship in 2014, I gravitated toward the same private practice largely based on loyalty and my experience as a PA.

COURTESY AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
My experience in private practice was positive. My focus at that time and currently is clinical medicine with a focus on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. My colleagues were supportive, and I worked with a great team of nurses and APPs. I cared for many patients in both the inpatient and outpatient setting and had an opportunity to complete a high volume and variety of procedures. Overall, the various aspects of my job were rewarding. However, something was missing, and I made personal and professional adjustments. My schedule pulled me from valued family time with my kids (mostly) in the early mornings, therefore, I altered my work schedule. My clinical interest in IBD was diluted by the emphasis to see mostly general GI patients, as is the case for many in private practice. I missed the academic environment, especially working with medical students, residents, and fellows, so I occasionally had residents shadow me. Unfortunately, adjustments did not “fix” that missing component – to me, this was a job that did not feel like a career. I was not professionally fulfilled and on several occasions during the 6 years in private practice, I connected with mentors from my medical training to explore career options while trying to define what was missing.
During the latter part of years 5 and 6, it became apparent to me that loyalty pulled me toward working with a great group of supportive gastroenterologists, but it became increasingly more apparent that this job was not in line with my career goals. I had identified that I wanted to actively participate in medical education while practicing as a gastroenterologist in an academic setting. Additionally, time with my family was a critical part to the work-life integration.
My approach to the next step in my journey was different than my initial job. My goal was to define what was important, as in what were my absolute requirements for career satisfaction and where was I willing to be flexible. Each of us has different absolute and relative requirements based on our values, and I neglected to clearly identify these components with my first job. Admittedly, I have (at times) struggled to acknowledge my values, because I might somehow appear less committed to a career. Owning these values has provided clarity in my path from private practice to academic medicine. During the 3 years I have been in my current position, I have stepped into a leadership role in the University of Nebraska Medicine GI fellowship program while providing clinical medicine at the Fred Paustian IBD Center at Nebraska Medicine. In addition, I continue to have an active endoscopy schedule and derive great satisfaction teaching the fellows how to be effective endoscopists. Personally, the difference in compensation between academic medicine and private practice was not an important factor, although this is a factor for some people (and that’s okay).
When I graduated from fellowship, my path seemed clear, and I did not anticipate the road ahead. However, with each hurdle, I was gifted with lessons that would prove to be valuable as I moved ahead. Thank you for giving me the space to share my story.
Lessons that have helped in my journey from private practice to academics
- Mentorship: Find mentors, not just one mentor. Over the years, I have had several mentors, but what I recognize is that, early in my career, I did not have a mentor. Although a mentor cannot make decisions for you, he/she can provide guidance from a place of experience (both career and life experience).
- Define a mission statement: My mentor pushed me to first define my values and then my mission statement. This serves as the foundation that I reference when making decisions that will impact my family and my career. For example, if I am invited to participate on a committee, I look at how this will impact my family and whether it aligns with my mission. This helps to clarify what I am willing to say yes to and what to pass along to another colleague. Remember that last part ... if you are saying no to something, suggest another colleague for the opportunity.
- Advocate for yourself: Only you know what is best for you. Sometimes the path to discovering what that is can be tortuous and require guidance. Throughout my journey, I worked with colleagues who were supportive of my journey back to medical school and supportive of my job in private practice, but only I could define what a career meant to me.
- Assume positive intent: In medicine, we frequently work in a high-stakes, stressful environment. Assume positive intent in your interactions with others, especially colleagues. This will serve you well.
- Life happens: Each of us will experience an unexpected event in our personal life or career path or both. This will be okay. The path forward may look different and require a pivot. This unexpected event might be that you find your job leaves you wanting something more or something different. Your journey will be right for you.
Dr. Hutchins is an assistant professor in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha. She reported no conflicts of interest.
Loyalty.
This is a quality that I value in relationships. Loyalty was a significant factor contributing to my postfellowship commitment to private practice. In 2001, I graduated from physician assistant school and accepted a job with a private practice GI group in Omaha. I was fortunate to work with supportive gastroenterologists who encouraged me to pursue further training after I expressed an interest in medical school. My goal was to become a gastroenterologist but like every medical student, I would keep an open mind. My decision did not waver, and the support from my first mentors continued. As I graduated from fellowship in 2014, I gravitated toward the same private practice largely based on loyalty and my experience as a PA.

COURTESY AMERICAN GASTROENTEROLOGICAL ASSOCIATION
My experience in private practice was positive. My focus at that time and currently is clinical medicine with a focus on inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) patients. My colleagues were supportive, and I worked with a great team of nurses and APPs. I cared for many patients in both the inpatient and outpatient setting and had an opportunity to complete a high volume and variety of procedures. Overall, the various aspects of my job were rewarding. However, something was missing, and I made personal and professional adjustments. My schedule pulled me from valued family time with my kids (mostly) in the early mornings, therefore, I altered my work schedule. My clinical interest in IBD was diluted by the emphasis to see mostly general GI patients, as is the case for many in private practice. I missed the academic environment, especially working with medical students, residents, and fellows, so I occasionally had residents shadow me. Unfortunately, adjustments did not “fix” that missing component – to me, this was a job that did not feel like a career. I was not professionally fulfilled and on several occasions during the 6 years in private practice, I connected with mentors from my medical training to explore career options while trying to define what was missing.
During the latter part of years 5 and 6, it became apparent to me that loyalty pulled me toward working with a great group of supportive gastroenterologists, but it became increasingly more apparent that this job was not in line with my career goals. I had identified that I wanted to actively participate in medical education while practicing as a gastroenterologist in an academic setting. Additionally, time with my family was a critical part to the work-life integration.
My approach to the next step in my journey was different than my initial job. My goal was to define what was important, as in what were my absolute requirements for career satisfaction and where was I willing to be flexible. Each of us has different absolute and relative requirements based on our values, and I neglected to clearly identify these components with my first job. Admittedly, I have (at times) struggled to acknowledge my values, because I might somehow appear less committed to a career. Owning these values has provided clarity in my path from private practice to academic medicine. During the 3 years I have been in my current position, I have stepped into a leadership role in the University of Nebraska Medicine GI fellowship program while providing clinical medicine at the Fred Paustian IBD Center at Nebraska Medicine. In addition, I continue to have an active endoscopy schedule and derive great satisfaction teaching the fellows how to be effective endoscopists. Personally, the difference in compensation between academic medicine and private practice was not an important factor, although this is a factor for some people (and that’s okay).
When I graduated from fellowship, my path seemed clear, and I did not anticipate the road ahead. However, with each hurdle, I was gifted with lessons that would prove to be valuable as I moved ahead. Thank you for giving me the space to share my story.
Lessons that have helped in my journey from private practice to academics
- Mentorship: Find mentors, not just one mentor. Over the years, I have had several mentors, but what I recognize is that, early in my career, I did not have a mentor. Although a mentor cannot make decisions for you, he/she can provide guidance from a place of experience (both career and life experience).
- Define a mission statement: My mentor pushed me to first define my values and then my mission statement. This serves as the foundation that I reference when making decisions that will impact my family and my career. For example, if I am invited to participate on a committee, I look at how this will impact my family and whether it aligns with my mission. This helps to clarify what I am willing to say yes to and what to pass along to another colleague. Remember that last part ... if you are saying no to something, suggest another colleague for the opportunity.
- Advocate for yourself: Only you know what is best for you. Sometimes the path to discovering what that is can be tortuous and require guidance. Throughout my journey, I worked with colleagues who were supportive of my journey back to medical school and supportive of my job in private practice, but only I could define what a career meant to me.
- Assume positive intent: In medicine, we frequently work in a high-stakes, stressful environment. Assume positive intent in your interactions with others, especially colleagues. This will serve you well.
- Life happens: Each of us will experience an unexpected event in our personal life or career path or both. This will be okay. The path forward may look different and require a pivot. This unexpected event might be that you find your job leaves you wanting something more or something different. Your journey will be right for you.
Dr. Hutchins is an assistant professor in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha. She reported no conflicts of interest.
Digital rectal exam fails as screening tool for prostate cancer
, say investigators reporting the PROBASE study.
The study compared risk-adapted screening measures in men who had prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measured at age 45 with those who had PSA measurements plus DRE at age 50.
The results show that as a solitary screening tool, 99% of DREs did not raise suspicion for prostate cancer, and among the 57 cases where DRE did raise suspicion, only three men were found to have cancer, all of which were low-grade, reported Agne Krilaviciute, PhD, from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, and colleagues.
“We also see that the cancer detection rate by PSA is four times higher compared to the DRE detection. Around 18% of the tumors are located in the part of the prostate where DRE cannot detect them,” she said in an oral presentation at the European Association of Urology Congress.
The investigators found that the majority of prostate cancers that occurred in this relatively young population were International Society of Urological Pathology grade 1 (Gleason score 3 + 3 = 6) or grade 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7). DRE yields positive results in only about 12% of cases of ISUP grade 1 or 2, they noted.
“We conclude that DRE as a solitary screening test does not lead to a significant PCa [prostate cancer] detection rate in young men,” Dr. Krilaviciute said.
Falling by the wayside
The study adds to the growing body of evidence that DRE may not be especially helpful as either a screening tool or when used in active surveillance of men with prostate cancer.
An international consensus panel found that DRE could be safely skipped for active surveillance when MRI and other more accurate and objective measures, such as biomarkers, are available.
A prostate cancer expert who was not involved in the PROBASE study told this news organization that when he was in medical school, it would have been considered a serious lapse of practice not to perform a DRE, but that things have changed considerably over the past several years.
“We have PSA now, we have technology with MRI, and the yield of digital rectal examination is very low,” commented Julio Pow-Sang, MD, chief of the genitourinary oncology program at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.
“Empirically, it’s very rare to find positive cancer through rectal exam in this day and age of PSA,” he said, adding that the examination itself is highly subjective, with varying results depending on the skills of the particular examiner.
“I think that in time, with good studies like this, digital rectal exam specifically for prostate cancer is going to slowly fade away,” Dr. Pow-Sang said.
PROBASE results
PROBASE was a randomized screening study enrolling men at age 45 to test a risk-adapted screening strategy using a baseline PSA value with the additional offer of DRE in a large subcohort of participants.
The study was conducted in Germany, and the authors note that the “German statutory early detection program recommends DRE as a stand-alone screening test starting annually at age 45.”
The PROBASE investigators enrolled 46,495 men from February 2014 through December 2019.
Among the first 23,194 men enrolled, 6,537 underwent DRE at enrollment without a study PSA test.
In this group, 6,480 DREs (99%) were not suspicious for cancer, and 57 (1%) were. Of those with suspected prostate cancer, 37 underwent biopsy and 20 did not. Of those biopsied, only two were found to have prostate cancer. This translated into a cancer detection rate of 0.03% for DRE.
After a median of 6.6 years of follow-up, only one additional case of ISUP grade 2 prostate cancer was detected among the 6,357 men who had DREs at enrollment, translating into a prostate cancer detection rate of .05%.
The investigators also looked at men who suspicious DRE findings at baseline. They assumed that a DRE-detectable tumor at age 45 would still be manifest 5 years later and should be detectable with PSA at age 50. Of the 57 men with initially suspicious findings, 11 returned for PSA screening but refused biopsy, and of this group only one had an elevated PSA level. He then underwent biopsy, but the findings were negative.
Of those who underwent biopsy on the basis of DRE, 16 had prostatitis, 14 had benign prostatic hyperplasia, 1 had high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, 1 had atypical small acinar proliferation, and 3 had equivocal findings.
In total, the investigators found 24 tumors among men screened with DRE. Of these, 3 occurred in men with results deemed suspicious and 21 were in men with unsuspicious digital exams. All of the tumors were ISUP grade 1, 2, or 3 tumors.
Among 245 men who had biopsies for a PSA level equal to or higher than 3 ng/mL, primarily Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 3-5 tumors, DRE findings at the time of biopsy were unsuspicious in about 82% of cases, Dr. Krilaviciute said.
“We also used MRI data to determine what proportion of tumors would be potentially detectable by DRE. We estimated that around 18% of tumors are located in the upper part of the prostate, which is not detectable by DRE,” she said. “Even excluding those tumors, still the DRE detection rate is low in palpable tumors.”
Although DRE performed better in higher-grade tumors, 80% of the tumors in the PROBASE participants were ISUP grade 1 or 2 and were likely to be undetected by DRE, she added.
“In Germany, the recommendations for the screening still include 45-year-olds to go with annual DRE. The PROBASE trial allowed us to evaluate for the first time what was the diagnostic performance for DRE at such a young age, and we see that 99% of men undergoing DRE have no suspicious findings, and among the 1% of suspicious findings having cancers extremely unlikely,” she said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). Dr. Krilaviciute and Dr. Pow-Sang reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say investigators reporting the PROBASE study.
The study compared risk-adapted screening measures in men who had prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measured at age 45 with those who had PSA measurements plus DRE at age 50.
The results show that as a solitary screening tool, 99% of DREs did not raise suspicion for prostate cancer, and among the 57 cases where DRE did raise suspicion, only three men were found to have cancer, all of which were low-grade, reported Agne Krilaviciute, PhD, from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, and colleagues.
“We also see that the cancer detection rate by PSA is four times higher compared to the DRE detection. Around 18% of the tumors are located in the part of the prostate where DRE cannot detect them,” she said in an oral presentation at the European Association of Urology Congress.
The investigators found that the majority of prostate cancers that occurred in this relatively young population were International Society of Urological Pathology grade 1 (Gleason score 3 + 3 = 6) or grade 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7). DRE yields positive results in only about 12% of cases of ISUP grade 1 or 2, they noted.
“We conclude that DRE as a solitary screening test does not lead to a significant PCa [prostate cancer] detection rate in young men,” Dr. Krilaviciute said.
Falling by the wayside
The study adds to the growing body of evidence that DRE may not be especially helpful as either a screening tool or when used in active surveillance of men with prostate cancer.
An international consensus panel found that DRE could be safely skipped for active surveillance when MRI and other more accurate and objective measures, such as biomarkers, are available.
A prostate cancer expert who was not involved in the PROBASE study told this news organization that when he was in medical school, it would have been considered a serious lapse of practice not to perform a DRE, but that things have changed considerably over the past several years.
“We have PSA now, we have technology with MRI, and the yield of digital rectal examination is very low,” commented Julio Pow-Sang, MD, chief of the genitourinary oncology program at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.
“Empirically, it’s very rare to find positive cancer through rectal exam in this day and age of PSA,” he said, adding that the examination itself is highly subjective, with varying results depending on the skills of the particular examiner.
“I think that in time, with good studies like this, digital rectal exam specifically for prostate cancer is going to slowly fade away,” Dr. Pow-Sang said.
PROBASE results
PROBASE was a randomized screening study enrolling men at age 45 to test a risk-adapted screening strategy using a baseline PSA value with the additional offer of DRE in a large subcohort of participants.
The study was conducted in Germany, and the authors note that the “German statutory early detection program recommends DRE as a stand-alone screening test starting annually at age 45.”
The PROBASE investigators enrolled 46,495 men from February 2014 through December 2019.
Among the first 23,194 men enrolled, 6,537 underwent DRE at enrollment without a study PSA test.
In this group, 6,480 DREs (99%) were not suspicious for cancer, and 57 (1%) were. Of those with suspected prostate cancer, 37 underwent biopsy and 20 did not. Of those biopsied, only two were found to have prostate cancer. This translated into a cancer detection rate of 0.03% for DRE.
After a median of 6.6 years of follow-up, only one additional case of ISUP grade 2 prostate cancer was detected among the 6,357 men who had DREs at enrollment, translating into a prostate cancer detection rate of .05%.
The investigators also looked at men who suspicious DRE findings at baseline. They assumed that a DRE-detectable tumor at age 45 would still be manifest 5 years later and should be detectable with PSA at age 50. Of the 57 men with initially suspicious findings, 11 returned for PSA screening but refused biopsy, and of this group only one had an elevated PSA level. He then underwent biopsy, but the findings were negative.
Of those who underwent biopsy on the basis of DRE, 16 had prostatitis, 14 had benign prostatic hyperplasia, 1 had high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, 1 had atypical small acinar proliferation, and 3 had equivocal findings.
In total, the investigators found 24 tumors among men screened with DRE. Of these, 3 occurred in men with results deemed suspicious and 21 were in men with unsuspicious digital exams. All of the tumors were ISUP grade 1, 2, or 3 tumors.
Among 245 men who had biopsies for a PSA level equal to or higher than 3 ng/mL, primarily Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 3-5 tumors, DRE findings at the time of biopsy were unsuspicious in about 82% of cases, Dr. Krilaviciute said.
“We also used MRI data to determine what proportion of tumors would be potentially detectable by DRE. We estimated that around 18% of tumors are located in the upper part of the prostate, which is not detectable by DRE,” she said. “Even excluding those tumors, still the DRE detection rate is low in palpable tumors.”
Although DRE performed better in higher-grade tumors, 80% of the tumors in the PROBASE participants were ISUP grade 1 or 2 and were likely to be undetected by DRE, she added.
“In Germany, the recommendations for the screening still include 45-year-olds to go with annual DRE. The PROBASE trial allowed us to evaluate for the first time what was the diagnostic performance for DRE at such a young age, and we see that 99% of men undergoing DRE have no suspicious findings, and among the 1% of suspicious findings having cancers extremely unlikely,” she said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). Dr. Krilaviciute and Dr. Pow-Sang reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, say investigators reporting the PROBASE study.
The study compared risk-adapted screening measures in men who had prostate-specific antigen (PSA) measured at age 45 with those who had PSA measurements plus DRE at age 50.
The results show that as a solitary screening tool, 99% of DREs did not raise suspicion for prostate cancer, and among the 57 cases where DRE did raise suspicion, only three men were found to have cancer, all of which were low-grade, reported Agne Krilaviciute, PhD, from the German Cancer Research Center in Heidelberg, and colleagues.
“We also see that the cancer detection rate by PSA is four times higher compared to the DRE detection. Around 18% of the tumors are located in the part of the prostate where DRE cannot detect them,” she said in an oral presentation at the European Association of Urology Congress.
The investigators found that the majority of prostate cancers that occurred in this relatively young population were International Society of Urological Pathology grade 1 (Gleason score 3 + 3 = 6) or grade 2 (Gleason 3 + 4 = 7). DRE yields positive results in only about 12% of cases of ISUP grade 1 or 2, they noted.
“We conclude that DRE as a solitary screening test does not lead to a significant PCa [prostate cancer] detection rate in young men,” Dr. Krilaviciute said.
Falling by the wayside
The study adds to the growing body of evidence that DRE may not be especially helpful as either a screening tool or when used in active surveillance of men with prostate cancer.
An international consensus panel found that DRE could be safely skipped for active surveillance when MRI and other more accurate and objective measures, such as biomarkers, are available.
A prostate cancer expert who was not involved in the PROBASE study told this news organization that when he was in medical school, it would have been considered a serious lapse of practice not to perform a DRE, but that things have changed considerably over the past several years.
“We have PSA now, we have technology with MRI, and the yield of digital rectal examination is very low,” commented Julio Pow-Sang, MD, chief of the genitourinary oncology program at Moffitt Cancer Center in Tampa, Fla.
“Empirically, it’s very rare to find positive cancer through rectal exam in this day and age of PSA,” he said, adding that the examination itself is highly subjective, with varying results depending on the skills of the particular examiner.
“I think that in time, with good studies like this, digital rectal exam specifically for prostate cancer is going to slowly fade away,” Dr. Pow-Sang said.
PROBASE results
PROBASE was a randomized screening study enrolling men at age 45 to test a risk-adapted screening strategy using a baseline PSA value with the additional offer of DRE in a large subcohort of participants.
The study was conducted in Germany, and the authors note that the “German statutory early detection program recommends DRE as a stand-alone screening test starting annually at age 45.”
The PROBASE investigators enrolled 46,495 men from February 2014 through December 2019.
Among the first 23,194 men enrolled, 6,537 underwent DRE at enrollment without a study PSA test.
In this group, 6,480 DREs (99%) were not suspicious for cancer, and 57 (1%) were. Of those with suspected prostate cancer, 37 underwent biopsy and 20 did not. Of those biopsied, only two were found to have prostate cancer. This translated into a cancer detection rate of 0.03% for DRE.
After a median of 6.6 years of follow-up, only one additional case of ISUP grade 2 prostate cancer was detected among the 6,357 men who had DREs at enrollment, translating into a prostate cancer detection rate of .05%.
The investigators also looked at men who suspicious DRE findings at baseline. They assumed that a DRE-detectable tumor at age 45 would still be manifest 5 years later and should be detectable with PSA at age 50. Of the 57 men with initially suspicious findings, 11 returned for PSA screening but refused biopsy, and of this group only one had an elevated PSA level. He then underwent biopsy, but the findings were negative.
Of those who underwent biopsy on the basis of DRE, 16 had prostatitis, 14 had benign prostatic hyperplasia, 1 had high-grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia, 1 had atypical small acinar proliferation, and 3 had equivocal findings.
In total, the investigators found 24 tumors among men screened with DRE. Of these, 3 occurred in men with results deemed suspicious and 21 were in men with unsuspicious digital exams. All of the tumors were ISUP grade 1, 2, or 3 tumors.
Among 245 men who had biopsies for a PSA level equal to or higher than 3 ng/mL, primarily Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) 3-5 tumors, DRE findings at the time of biopsy were unsuspicious in about 82% of cases, Dr. Krilaviciute said.
“We also used MRI data to determine what proportion of tumors would be potentially detectable by DRE. We estimated that around 18% of tumors are located in the upper part of the prostate, which is not detectable by DRE,” she said. “Even excluding those tumors, still the DRE detection rate is low in palpable tumors.”
Although DRE performed better in higher-grade tumors, 80% of the tumors in the PROBASE participants were ISUP grade 1 or 2 and were likely to be undetected by DRE, she added.
“In Germany, the recommendations for the screening still include 45-year-olds to go with annual DRE. The PROBASE trial allowed us to evaluate for the first time what was the diagnostic performance for DRE at such a young age, and we see that 99% of men undergoing DRE have no suspicious findings, and among the 1% of suspicious findings having cancers extremely unlikely,” she said.
The study was supported by Deutsche Krebshilfe (German Cancer Aid). Dr. Krilaviciute and Dr. Pow-Sang reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EAU 2023
The 2023 ‘Meddy’ awards
Without further ado (or comedy skits or musical numbers or extended tributes or commercials), the Meddys go to ...
Best depiction of emergency medicine’s rollercoaster
M*A*S*H (1970)
The original film, not the TV show, jumps from Frank Burns being hauled away in a straitjacket to a soldier’s spurting neck wound. Hawkeye Pierce calmly steps in and we see the entire sequence of him applying pressure, then stepping back to gown-and-glove (“it’s going to spurt a bit”), then jumping back in with arterial sutures, quipping, “Baby, we’re gonna see some stitchin’ like you never saw before.” After that, cocktail hour. Yes, medicine in Hollywood can be overdramatized and even inaccurate, but Robert Altman’s take on the novel by former U.S. Army surgeon Richard Hooker still stands tall for just how crazy emergency medicine can be.
Best ‘is there a doctor in the house?’ moment
Field of Dreams (1989)
When Ray Kinsella’s daughter gets knocked off the back of the bleachers, everything stops. No one knows what to do … except Doc “Moonlight” Graham, who gives up his life’s (and afterlife’s) dream to step off the field and save the girl from choking to death. Burt Lancaster, in his final movie role, embodies everything people wish a doctor to be: Calm, kind, and able to offer a quick, effective solution to a crisis. “Hey rookie! You were good.” Yes, he sure was.
Most unethical doctor
Elvis (2022)
No doctor wants to be remembered as the guy who killed Elvis. But that legacy clings to Dr. George Nichopoulos, Elvis’s personal physician in the 1970s. In Elvis, Dr. Nichopoulos, played by Tony Nixon, hovers in the background, enabling the King’s worsening addictions. Taking late-night calls for narcotics and injecting the unconscious star with stimulants, “unethical” is an understatement for the fictional “Dr. Nick.” The real Dr. Nichopoulos was acquitted of wrongdoing in Elvis’ death, although there is little doubt that the thousands of medication doses he prescribed played a role. When his license was finally revoked for overprescribing in the 1990s, the obliging doc reportedly claimed, “I cared too much.”
Best self-use of a defibrillator
Casino Royale (2006)
We expect backlash in the post-award press conference since James Bond technically only attempted to self-defibrillate in the passenger seat of his car. He never attached the device to the leads. Vesper Lynd had to pick up his slack and save the day. Also, supporters of fellow self-defibrillating nominee Jason Statham in Crank will no doubt raise a stink on Twitter. But we stand by our choice because it was such an, ahem, heart-stopper of a scene.
Best worst patient lying about an injury
Tár (2022)
Love it or hate it, few recent movies have been as polarizing as Tár. Cate Blanchett’s portrayal of a musical genius might be toweringly brilliant or outrageously offensive (or both) depending on whom you ask. But clearly the character has a loose relationship with facts. More than a few doctors might have raised an eyebrow had Lydia Tár appeared with injuries to her face, claiming to have been attacked in a mugging. In reality, Lydia tripped and fell while pursuing an attractive young cellist into a hazardous basement. Did she lie to protect her image, preserve her marriage, or – like many patients – avoid a lecture on unhealthy behavior? We pick D, all of the above.
Best therapy for a speech disorder
The King’s Speech (2010)
Public speaking might cause anxiety for many of us, but how about doing it in front of a global radio audience while wrestling with a speech disorder? Based on a true story, The King’s Speech revealed that terrifying experience for England’s King George VI. Enter Lionel Logue, played by Geoffrey Rush. Irreverent, unconventional, and untrained, the Australian pioneer in speech and language therapy uses a range of strategies – some of which are still used today – to help the royal find his voice. But when singing, shouting swear words, and provoking rage don’t do the trick, Mr. Logue turns to psychotherapy to unearth the childhood traumas at the root of the king’s disability. Experience, as Mr. Logue tells his patient, matters just as much as “letters after your name.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Without further ado (or comedy skits or musical numbers or extended tributes or commercials), the Meddys go to ...
Best depiction of emergency medicine’s rollercoaster
M*A*S*H (1970)
The original film, not the TV show, jumps from Frank Burns being hauled away in a straitjacket to a soldier’s spurting neck wound. Hawkeye Pierce calmly steps in and we see the entire sequence of him applying pressure, then stepping back to gown-and-glove (“it’s going to spurt a bit”), then jumping back in with arterial sutures, quipping, “Baby, we’re gonna see some stitchin’ like you never saw before.” After that, cocktail hour. Yes, medicine in Hollywood can be overdramatized and even inaccurate, but Robert Altman’s take on the novel by former U.S. Army surgeon Richard Hooker still stands tall for just how crazy emergency medicine can be.
Best ‘is there a doctor in the house?’ moment
Field of Dreams (1989)
When Ray Kinsella’s daughter gets knocked off the back of the bleachers, everything stops. No one knows what to do … except Doc “Moonlight” Graham, who gives up his life’s (and afterlife’s) dream to step off the field and save the girl from choking to death. Burt Lancaster, in his final movie role, embodies everything people wish a doctor to be: Calm, kind, and able to offer a quick, effective solution to a crisis. “Hey rookie! You were good.” Yes, he sure was.
Most unethical doctor
Elvis (2022)
No doctor wants to be remembered as the guy who killed Elvis. But that legacy clings to Dr. George Nichopoulos, Elvis’s personal physician in the 1970s. In Elvis, Dr. Nichopoulos, played by Tony Nixon, hovers in the background, enabling the King’s worsening addictions. Taking late-night calls for narcotics and injecting the unconscious star with stimulants, “unethical” is an understatement for the fictional “Dr. Nick.” The real Dr. Nichopoulos was acquitted of wrongdoing in Elvis’ death, although there is little doubt that the thousands of medication doses he prescribed played a role. When his license was finally revoked for overprescribing in the 1990s, the obliging doc reportedly claimed, “I cared too much.”
Best self-use of a defibrillator
Casino Royale (2006)
We expect backlash in the post-award press conference since James Bond technically only attempted to self-defibrillate in the passenger seat of his car. He never attached the device to the leads. Vesper Lynd had to pick up his slack and save the day. Also, supporters of fellow self-defibrillating nominee Jason Statham in Crank will no doubt raise a stink on Twitter. But we stand by our choice because it was such an, ahem, heart-stopper of a scene.
Best worst patient lying about an injury
Tár (2022)
Love it or hate it, few recent movies have been as polarizing as Tár. Cate Blanchett’s portrayal of a musical genius might be toweringly brilliant or outrageously offensive (or both) depending on whom you ask. But clearly the character has a loose relationship with facts. More than a few doctors might have raised an eyebrow had Lydia Tár appeared with injuries to her face, claiming to have been attacked in a mugging. In reality, Lydia tripped and fell while pursuing an attractive young cellist into a hazardous basement. Did she lie to protect her image, preserve her marriage, or – like many patients – avoid a lecture on unhealthy behavior? We pick D, all of the above.
Best therapy for a speech disorder
The King’s Speech (2010)
Public speaking might cause anxiety for many of us, but how about doing it in front of a global radio audience while wrestling with a speech disorder? Based on a true story, The King’s Speech revealed that terrifying experience for England’s King George VI. Enter Lionel Logue, played by Geoffrey Rush. Irreverent, unconventional, and untrained, the Australian pioneer in speech and language therapy uses a range of strategies – some of which are still used today – to help the royal find his voice. But when singing, shouting swear words, and provoking rage don’t do the trick, Mr. Logue turns to psychotherapy to unearth the childhood traumas at the root of the king’s disability. Experience, as Mr. Logue tells his patient, matters just as much as “letters after your name.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Without further ado (or comedy skits or musical numbers or extended tributes or commercials), the Meddys go to ...
Best depiction of emergency medicine’s rollercoaster
M*A*S*H (1970)
The original film, not the TV show, jumps from Frank Burns being hauled away in a straitjacket to a soldier’s spurting neck wound. Hawkeye Pierce calmly steps in and we see the entire sequence of him applying pressure, then stepping back to gown-and-glove (“it’s going to spurt a bit”), then jumping back in with arterial sutures, quipping, “Baby, we’re gonna see some stitchin’ like you never saw before.” After that, cocktail hour. Yes, medicine in Hollywood can be overdramatized and even inaccurate, but Robert Altman’s take on the novel by former U.S. Army surgeon Richard Hooker still stands tall for just how crazy emergency medicine can be.
Best ‘is there a doctor in the house?’ moment
Field of Dreams (1989)
When Ray Kinsella’s daughter gets knocked off the back of the bleachers, everything stops. No one knows what to do … except Doc “Moonlight” Graham, who gives up his life’s (and afterlife’s) dream to step off the field and save the girl from choking to death. Burt Lancaster, in his final movie role, embodies everything people wish a doctor to be: Calm, kind, and able to offer a quick, effective solution to a crisis. “Hey rookie! You were good.” Yes, he sure was.
Most unethical doctor
Elvis (2022)
No doctor wants to be remembered as the guy who killed Elvis. But that legacy clings to Dr. George Nichopoulos, Elvis’s personal physician in the 1970s. In Elvis, Dr. Nichopoulos, played by Tony Nixon, hovers in the background, enabling the King’s worsening addictions. Taking late-night calls for narcotics and injecting the unconscious star with stimulants, “unethical” is an understatement for the fictional “Dr. Nick.” The real Dr. Nichopoulos was acquitted of wrongdoing in Elvis’ death, although there is little doubt that the thousands of medication doses he prescribed played a role. When his license was finally revoked for overprescribing in the 1990s, the obliging doc reportedly claimed, “I cared too much.”
Best self-use of a defibrillator
Casino Royale (2006)
We expect backlash in the post-award press conference since James Bond technically only attempted to self-defibrillate in the passenger seat of his car. He never attached the device to the leads. Vesper Lynd had to pick up his slack and save the day. Also, supporters of fellow self-defibrillating nominee Jason Statham in Crank will no doubt raise a stink on Twitter. But we stand by our choice because it was such an, ahem, heart-stopper of a scene.
Best worst patient lying about an injury
Tár (2022)
Love it or hate it, few recent movies have been as polarizing as Tár. Cate Blanchett’s portrayal of a musical genius might be toweringly brilliant or outrageously offensive (or both) depending on whom you ask. But clearly the character has a loose relationship with facts. More than a few doctors might have raised an eyebrow had Lydia Tár appeared with injuries to her face, claiming to have been attacked in a mugging. In reality, Lydia tripped and fell while pursuing an attractive young cellist into a hazardous basement. Did she lie to protect her image, preserve her marriage, or – like many patients – avoid a lecture on unhealthy behavior? We pick D, all of the above.
Best therapy for a speech disorder
The King’s Speech (2010)
Public speaking might cause anxiety for many of us, but how about doing it in front of a global radio audience while wrestling with a speech disorder? Based on a true story, The King’s Speech revealed that terrifying experience for England’s King George VI. Enter Lionel Logue, played by Geoffrey Rush. Irreverent, unconventional, and untrained, the Australian pioneer in speech and language therapy uses a range of strategies – some of which are still used today – to help the royal find his voice. But when singing, shouting swear words, and provoking rage don’t do the trick, Mr. Logue turns to psychotherapy to unearth the childhood traumas at the root of the king’s disability. Experience, as Mr. Logue tells his patient, matters just as much as “letters after your name.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Clinician violence: Virtual reality to the rescue?
This discussion was recorded on Feb. 21, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Welcome, Dr. Salazar. It’s a pleasure to have you join us today.
Gilberto A. Salazar, MD: The pleasure is all mine, Dr. Glatter. Thank you so much for having me.
Dr. Glatter: This is such an important topic, as you can imagine. Workplace violence is affecting so many providers in hospital emergency departments but also throughout other parts of the hospital.
First, can you describe how the virtual reality (VR) program was designed that you developed and what type of situations it simulates?
Dr. Salazar: We worked in conjunction with the University of Texas at Dallas. They help people like me, subject matter experts in health care, to bring ideas to reality. I worked very closely with a group of engineers from their department in designing a module specifically designed to tackle, as you mentioned, one of our biggest threats in workplace violence.
We decided to bring in a series of competencies and proficiencies that we wanted to bring into the virtual reality space. In leveraging the technology and the expertise from UT Dallas, we were able to make that happen.
Dr. Glatter: I think it’s important to understand, in terms of virtual reality, what type of environment the program creates. Can you describe what a provider who puts the goggles on is experiencing? Do they feel anything? Is there technology that enables this?
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. We were able to bring to reality a series of scenarios very common from what you and I see in the emergency department on a daily basis. We wanted to immerse a learner into that specific environment. We didn’t feel that a module or something on a computer or a slide set could really bring the reality of what it’s like to interact with a patient who may be escalating or may be aggressive.
We are immersing learners into an actual hospital room to our specifications, very similar to exactly where we practice each and every day, and taking the learners through different situations that we designed with various levels of escalation and aggression, and asking the learner to manage that situation as best as they possibly can using the competencies and proficiencies that we taught them.
Dr. Glatter: Haptic feedback is an important part of the program and also the approach and technique that you’re using. Can you describe what haptic feedback means and what people actually feel?
Dr. Salazar: Absolutely. One of the most unfortunate things in my professional career is physical abuse suffered by people like me and you and our colleagues, nursing personnel, technicians, and others, resulting in injury.
We wanted to provide the most realistic experience that we could design. Haptics engage digital senses other than your auditory and your visuals. They really engage your tactile senses. These haptic vests and gloves and technology allow us to provide a third set of sensory stimuli for the learner.
At one of the modules, we have an actual physical assault that takes place, and the learner is actually able to feel in their body the strikes – of course, not painful – but just bringing in those senses and that stimulus, really leaving the learner with an experience that’s going to be long-lasting.
Dr. Glatter: Feeling that stimulus certainly affects your vital signs. Do you monitor a provider’s vital signs, such as their blood pressure and heart rate, as the situation and the threat escalate? That could potentially trigger some issues in people with prior PTSD or people with other mental health issues. Has that ever been considered in the design of your program?
Dr. Salazar: Yes, 100%. The beautiful thing about haptics is that they can be tailored to our specific parameters. The sensory stimulus that’s provided is actually very mild. It feels more like a tap than an actual strike. It just reminds us that when we’re having or experiencing an actual physical attack, we’re really engaging the senses.
We have an emergency physician or an EMT-paramedic on site at all times during the training so that we can monitor our subjects and make sure that they’re comfortable and healthy.
Dr. Glatter: Do they have actual sensors attached to their bodies that are part of your program or distinct in terms of monitoring their vital signs?
Dr. Salazar: It’s completely different. We have two different systems that we are planning on utilizing. Frankly, in the final version of this virtual reality module, we may not even involve the haptics. We’re going to study it and see how our learners behave and how much information they’re able to acquire and retain.
It may be very possible that just the visuals – the auditory and the immersion taking place within the hospital room – may be enough. It’s very possible that, in the next final version of this, we may find that haptics bring in quite a bit of value, and we may incorporate that. If that is the case, then we will, of course, acquire different technology to monitor the patient’s vital signs.
Dr. Glatter: Clearly, when situations escalate in the department, everyone gets more concerned about the patient, but providers are part of this equation, as you allude to.
In 2022, there was a poll by the American College of Emergency Physicians that stated that 85% of emergency physicians reported an increase in violent activity in their ERs in the past 5 years. Nearly two-thirds of nearly 3,000 emergency physicians surveyed reported being assaulted in the past year. This is an important module that we integrate into training providers in terms of these types of tense situations that can result not only in mental anguish but also in physical injury.
Dr. Salazar: One hundred percent. I frankly got tired of seeing my friends and my colleagues suffer both the physical and mental effects of verbal and physical abuse, and I wanted to design a project that was very patient centric while allowing our personnel to really manage these situations a little bit better.
Frankly, we don’t receive great training in this space, and I wanted to rewrite that narrative and make things better for our clinicians out there while remaining patient centric. I wanted to do something about it, and hopefully this dream will become a reality.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. There are other data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics stating that health care workers are five times more likely than employees in any other area of work to experience workplace violence. This could, again, range from verbal to physical violence. This is a very important module that you’re developing.
Are there any thoughts to extend this to active-shooter scenarios or any other high-stakes scenarios that you can imagine in the department?
Dr. Salazar: We’re actually working with the same developer that’s helping us with this VR module in developing a mass-casualty incident module so that we can get better training in responding to these very unfortunate high-stakes situations.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of using the module remotely, certainly not requiring resources or having to be in a physical place, can providers in your plan be able to take such a headset home and practice on their own in the sense of being able to deal with a situation? Would this be more reserved for in-department use?
Dr. Salazar: That’s a phenomenal question. I wanted to create the most flexible module that I possibly could. Ideally, a dream scenario is leveraging a simulation center at an academic center and not just do the VR module but also have a brief didactics incorporating a small slide set, some feedback, and some standardized patients. I wanted it to be flexible enough so that folks here in my state, a different state, or even internationally could take advantage of this technology and do it from the comfort of their home.
As you mentioned, this is going to strike some people. It’s going to hit them heavier than others in terms of prior experience as PTSD. For some people, it may be more comfortable to do it in the comfort of their homes. I wanted to create something very flexible and dynamic.
Dr. Glatter: I think that’s ideal. Just one other point. Can you discuss the different levels of competencies involved in this module and how that would be attained?
Dr. Salazar: It’s all evidence based, so we borrowed from literature and the specialties of emergency medicine. We collaborated with psychiatrists within our medical center. We looked at all available literature and methods, proficiencies, competencies, and best practices, and we took all of them together to form something that we think is organized and concise.
We were able to create our own algorithm, but it’s not brand new. We’re just borrowing what we think is the best to create something that the majority of health care personnel are going to be able to relate to and be able to really be proficient at.
This includes things like active listening, bargaining, how to respond, where to put yourself in a situation, and the best possible situation to respond to a scenario, how to prevent things – how to get out of a chokehold, for example. We’re borrowing from several different disciplines and creating something that can be very concise and organized.
Dr. Glatter: Does this program that you’ve developed allow the provider to get feedback in the sense that when they’re in such a danger, their life could be at risk? For example, if they don’t remove themselves in a certain amount of time, this could be lethal.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, 100%. Probably the one thing that differentiates our project from any others is the ability to customize the experience so that a learner who is doing the things that we ask them to do in terms of safety and response is able to get out of a situation successfully within the environment. If they don’t, they get some kind of feedback.
Not to spoil the surprise here, but we’re going to be doing things like looking at decibel meters to see what the volume in the room is doing and how you’re managing the volume and the stimulation within the room. If you are able to maintain the decibel readings at a specific level, you’re going to succeed through the module. If you don’t, we keep the patient escalation going.
Dr. Glatter: There is a debrief built into this type of approach where, in other words, learning points are emphasized – where you could have done better and such.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. We are going to be able to get individualized data for each learner so that we can tailor the debrief to their own performance and be able to give them actionable items to work on. It’s a debrief that’s productive and individualized, and folks can walk away with something useful in the end.
Dr. Glatter: Are the data shared or confidential at present?
Dr. Salazar: At this very moment, the data are confidential. We are going to look at how to best use this. We’re hoping to eventually write this up and see how this information can be best used to train personnel.
Eventually, we may see that some of the advice that we’re giving is very common to most folks. Others may require some individualized type of feedback. That said, it remains to be seen, but right now, it’s confidential.
Dr. Glatter: Is this currently being implemented as part of your curriculum for emergency medicine residents?
Dr. Salazar: We’re going to study it first. We’re very excited to include our emergency medicine residents as one of our cohorts that’s going to be undergoing the module, and we’re going to be studying other forms of workplace violence mitigation strategies. We’re really excited about the possibility of this eventually becoming the standard of education for not only our emergency medicine residents, but also health care personnel all over the world.
Dr. Glatter: I’m glad you mentioned that, because obviously nurses, clerks in the department, and anyone who’s working in the department, for that matter, and who interfaces with patients really should undergo such training.
Dr. Salazar: Absolutely. The folks at intake, at check-in, and at kiosks. Do they go through a separate area for screening? You’re absolutely right. There are many folks who interface with patients and all of us are potential victims of workplace violence. We want to give our health care family the best opportunity to succeed in these situations.
Dr. Glatter:: Absolutely. Even EMS providers, being on the front lines and encountering patients in such situations, would benefit, in my opinion.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. Behavioral health emergencies and organically induced altered mental status results in injury, both physical and mental, to EMS professionals as well, and there’s good evidence of that. I’ll be very glad to see this type of education make it out to our initial and continuing education efforts for EMS as well.
Dr. Glatter: I want to thank you. This has been very helpful. It’s such an important task that you’ve started to explore, and I look forward to follow-up on this. Again, thank you for your time.
Dr. Salazar: It was my pleasure. Thank you so much for having me.
Dr. Glatter is an attending physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, N.Y. He is an editorial adviser and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series on Medscape. He is also a medical contributor for Forbes. Dr. Salazar is a board-certified emergency physician and associate professor at UT Southwestern Medicine Center in Dallas. He is involved with the UTSW Emergency Medicine Education Program and serves as the medical director to teach both initial and continuing the emergency medicine education for emergency medical technicians and paramedics, which trains most of the Dallas Fire Rescue personnel and the vast majority for EMS providers in the Dallas County. In addition, he serves as an associate chief of service at Parkland’s emergency department, and liaison to surgical services. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This discussion was recorded on Feb. 21, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Welcome, Dr. Salazar. It’s a pleasure to have you join us today.
Gilberto A. Salazar, MD: The pleasure is all mine, Dr. Glatter. Thank you so much for having me.
Dr. Glatter: This is such an important topic, as you can imagine. Workplace violence is affecting so many providers in hospital emergency departments but also throughout other parts of the hospital.
First, can you describe how the virtual reality (VR) program was designed that you developed and what type of situations it simulates?
Dr. Salazar: We worked in conjunction with the University of Texas at Dallas. They help people like me, subject matter experts in health care, to bring ideas to reality. I worked very closely with a group of engineers from their department in designing a module specifically designed to tackle, as you mentioned, one of our biggest threats in workplace violence.
We decided to bring in a series of competencies and proficiencies that we wanted to bring into the virtual reality space. In leveraging the technology and the expertise from UT Dallas, we were able to make that happen.
Dr. Glatter: I think it’s important to understand, in terms of virtual reality, what type of environment the program creates. Can you describe what a provider who puts the goggles on is experiencing? Do they feel anything? Is there technology that enables this?
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. We were able to bring to reality a series of scenarios very common from what you and I see in the emergency department on a daily basis. We wanted to immerse a learner into that specific environment. We didn’t feel that a module or something on a computer or a slide set could really bring the reality of what it’s like to interact with a patient who may be escalating or may be aggressive.
We are immersing learners into an actual hospital room to our specifications, very similar to exactly where we practice each and every day, and taking the learners through different situations that we designed with various levels of escalation and aggression, and asking the learner to manage that situation as best as they possibly can using the competencies and proficiencies that we taught them.
Dr. Glatter: Haptic feedback is an important part of the program and also the approach and technique that you’re using. Can you describe what haptic feedback means and what people actually feel?
Dr. Salazar: Absolutely. One of the most unfortunate things in my professional career is physical abuse suffered by people like me and you and our colleagues, nursing personnel, technicians, and others, resulting in injury.
We wanted to provide the most realistic experience that we could design. Haptics engage digital senses other than your auditory and your visuals. They really engage your tactile senses. These haptic vests and gloves and technology allow us to provide a third set of sensory stimuli for the learner.
At one of the modules, we have an actual physical assault that takes place, and the learner is actually able to feel in their body the strikes – of course, not painful – but just bringing in those senses and that stimulus, really leaving the learner with an experience that’s going to be long-lasting.
Dr. Glatter: Feeling that stimulus certainly affects your vital signs. Do you monitor a provider’s vital signs, such as their blood pressure and heart rate, as the situation and the threat escalate? That could potentially trigger some issues in people with prior PTSD or people with other mental health issues. Has that ever been considered in the design of your program?
Dr. Salazar: Yes, 100%. The beautiful thing about haptics is that they can be tailored to our specific parameters. The sensory stimulus that’s provided is actually very mild. It feels more like a tap than an actual strike. It just reminds us that when we’re having or experiencing an actual physical attack, we’re really engaging the senses.
We have an emergency physician or an EMT-paramedic on site at all times during the training so that we can monitor our subjects and make sure that they’re comfortable and healthy.
Dr. Glatter: Do they have actual sensors attached to their bodies that are part of your program or distinct in terms of monitoring their vital signs?
Dr. Salazar: It’s completely different. We have two different systems that we are planning on utilizing. Frankly, in the final version of this virtual reality module, we may not even involve the haptics. We’re going to study it and see how our learners behave and how much information they’re able to acquire and retain.
It may be very possible that just the visuals – the auditory and the immersion taking place within the hospital room – may be enough. It’s very possible that, in the next final version of this, we may find that haptics bring in quite a bit of value, and we may incorporate that. If that is the case, then we will, of course, acquire different technology to monitor the patient’s vital signs.
Dr. Glatter: Clearly, when situations escalate in the department, everyone gets more concerned about the patient, but providers are part of this equation, as you allude to.
In 2022, there was a poll by the American College of Emergency Physicians that stated that 85% of emergency physicians reported an increase in violent activity in their ERs in the past 5 years. Nearly two-thirds of nearly 3,000 emergency physicians surveyed reported being assaulted in the past year. This is an important module that we integrate into training providers in terms of these types of tense situations that can result not only in mental anguish but also in physical injury.
Dr. Salazar: One hundred percent. I frankly got tired of seeing my friends and my colleagues suffer both the physical and mental effects of verbal and physical abuse, and I wanted to design a project that was very patient centric while allowing our personnel to really manage these situations a little bit better.
Frankly, we don’t receive great training in this space, and I wanted to rewrite that narrative and make things better for our clinicians out there while remaining patient centric. I wanted to do something about it, and hopefully this dream will become a reality.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. There are other data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics stating that health care workers are five times more likely than employees in any other area of work to experience workplace violence. This could, again, range from verbal to physical violence. This is a very important module that you’re developing.
Are there any thoughts to extend this to active-shooter scenarios or any other high-stakes scenarios that you can imagine in the department?
Dr. Salazar: We’re actually working with the same developer that’s helping us with this VR module in developing a mass-casualty incident module so that we can get better training in responding to these very unfortunate high-stakes situations.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of using the module remotely, certainly not requiring resources or having to be in a physical place, can providers in your plan be able to take such a headset home and practice on their own in the sense of being able to deal with a situation? Would this be more reserved for in-department use?
Dr. Salazar: That’s a phenomenal question. I wanted to create the most flexible module that I possibly could. Ideally, a dream scenario is leveraging a simulation center at an academic center and not just do the VR module but also have a brief didactics incorporating a small slide set, some feedback, and some standardized patients. I wanted it to be flexible enough so that folks here in my state, a different state, or even internationally could take advantage of this technology and do it from the comfort of their home.
As you mentioned, this is going to strike some people. It’s going to hit them heavier than others in terms of prior experience as PTSD. For some people, it may be more comfortable to do it in the comfort of their homes. I wanted to create something very flexible and dynamic.
Dr. Glatter: I think that’s ideal. Just one other point. Can you discuss the different levels of competencies involved in this module and how that would be attained?
Dr. Salazar: It’s all evidence based, so we borrowed from literature and the specialties of emergency medicine. We collaborated with psychiatrists within our medical center. We looked at all available literature and methods, proficiencies, competencies, and best practices, and we took all of them together to form something that we think is organized and concise.
We were able to create our own algorithm, but it’s not brand new. We’re just borrowing what we think is the best to create something that the majority of health care personnel are going to be able to relate to and be able to really be proficient at.
This includes things like active listening, bargaining, how to respond, where to put yourself in a situation, and the best possible situation to respond to a scenario, how to prevent things – how to get out of a chokehold, for example. We’re borrowing from several different disciplines and creating something that can be very concise and organized.
Dr. Glatter: Does this program that you’ve developed allow the provider to get feedback in the sense that when they’re in such a danger, their life could be at risk? For example, if they don’t remove themselves in a certain amount of time, this could be lethal.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, 100%. Probably the one thing that differentiates our project from any others is the ability to customize the experience so that a learner who is doing the things that we ask them to do in terms of safety and response is able to get out of a situation successfully within the environment. If they don’t, they get some kind of feedback.
Not to spoil the surprise here, but we’re going to be doing things like looking at decibel meters to see what the volume in the room is doing and how you’re managing the volume and the stimulation within the room. If you are able to maintain the decibel readings at a specific level, you’re going to succeed through the module. If you don’t, we keep the patient escalation going.
Dr. Glatter: There is a debrief built into this type of approach where, in other words, learning points are emphasized – where you could have done better and such.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. We are going to be able to get individualized data for each learner so that we can tailor the debrief to their own performance and be able to give them actionable items to work on. It’s a debrief that’s productive and individualized, and folks can walk away with something useful in the end.
Dr. Glatter: Are the data shared or confidential at present?
Dr. Salazar: At this very moment, the data are confidential. We are going to look at how to best use this. We’re hoping to eventually write this up and see how this information can be best used to train personnel.
Eventually, we may see that some of the advice that we’re giving is very common to most folks. Others may require some individualized type of feedback. That said, it remains to be seen, but right now, it’s confidential.
Dr. Glatter: Is this currently being implemented as part of your curriculum for emergency medicine residents?
Dr. Salazar: We’re going to study it first. We’re very excited to include our emergency medicine residents as one of our cohorts that’s going to be undergoing the module, and we’re going to be studying other forms of workplace violence mitigation strategies. We’re really excited about the possibility of this eventually becoming the standard of education for not only our emergency medicine residents, but also health care personnel all over the world.
Dr. Glatter: I’m glad you mentioned that, because obviously nurses, clerks in the department, and anyone who’s working in the department, for that matter, and who interfaces with patients really should undergo such training.
Dr. Salazar: Absolutely. The folks at intake, at check-in, and at kiosks. Do they go through a separate area for screening? You’re absolutely right. There are many folks who interface with patients and all of us are potential victims of workplace violence. We want to give our health care family the best opportunity to succeed in these situations.
Dr. Glatter:: Absolutely. Even EMS providers, being on the front lines and encountering patients in such situations, would benefit, in my opinion.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. Behavioral health emergencies and organically induced altered mental status results in injury, both physical and mental, to EMS professionals as well, and there’s good evidence of that. I’ll be very glad to see this type of education make it out to our initial and continuing education efforts for EMS as well.
Dr. Glatter: I want to thank you. This has been very helpful. It’s such an important task that you’ve started to explore, and I look forward to follow-up on this. Again, thank you for your time.
Dr. Salazar: It was my pleasure. Thank you so much for having me.
Dr. Glatter is an attending physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, N.Y. He is an editorial adviser and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series on Medscape. He is also a medical contributor for Forbes. Dr. Salazar is a board-certified emergency physician and associate professor at UT Southwestern Medicine Center in Dallas. He is involved with the UTSW Emergency Medicine Education Program and serves as the medical director to teach both initial and continuing the emergency medicine education for emergency medical technicians and paramedics, which trains most of the Dallas Fire Rescue personnel and the vast majority for EMS providers in the Dallas County. In addition, he serves as an associate chief of service at Parkland’s emergency department, and liaison to surgical services. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
This discussion was recorded on Feb. 21, 2023. This transcript has been edited for clarity.
Robert D. Glatter, MD: Welcome. I’m Dr. Robert Glatter, medical adviser for Medscape Emergency Medicine. Welcome, Dr. Salazar. It’s a pleasure to have you join us today.
Gilberto A. Salazar, MD: The pleasure is all mine, Dr. Glatter. Thank you so much for having me.
Dr. Glatter: This is such an important topic, as you can imagine. Workplace violence is affecting so many providers in hospital emergency departments but also throughout other parts of the hospital.
First, can you describe how the virtual reality (VR) program was designed that you developed and what type of situations it simulates?
Dr. Salazar: We worked in conjunction with the University of Texas at Dallas. They help people like me, subject matter experts in health care, to bring ideas to reality. I worked very closely with a group of engineers from their department in designing a module specifically designed to tackle, as you mentioned, one of our biggest threats in workplace violence.
We decided to bring in a series of competencies and proficiencies that we wanted to bring into the virtual reality space. In leveraging the technology and the expertise from UT Dallas, we were able to make that happen.
Dr. Glatter: I think it’s important to understand, in terms of virtual reality, what type of environment the program creates. Can you describe what a provider who puts the goggles on is experiencing? Do they feel anything? Is there technology that enables this?
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. We were able to bring to reality a series of scenarios very common from what you and I see in the emergency department on a daily basis. We wanted to immerse a learner into that specific environment. We didn’t feel that a module or something on a computer or a slide set could really bring the reality of what it’s like to interact with a patient who may be escalating or may be aggressive.
We are immersing learners into an actual hospital room to our specifications, very similar to exactly where we practice each and every day, and taking the learners through different situations that we designed with various levels of escalation and aggression, and asking the learner to manage that situation as best as they possibly can using the competencies and proficiencies that we taught them.
Dr. Glatter: Haptic feedback is an important part of the program and also the approach and technique that you’re using. Can you describe what haptic feedback means and what people actually feel?
Dr. Salazar: Absolutely. One of the most unfortunate things in my professional career is physical abuse suffered by people like me and you and our colleagues, nursing personnel, technicians, and others, resulting in injury.
We wanted to provide the most realistic experience that we could design. Haptics engage digital senses other than your auditory and your visuals. They really engage your tactile senses. These haptic vests and gloves and technology allow us to provide a third set of sensory stimuli for the learner.
At one of the modules, we have an actual physical assault that takes place, and the learner is actually able to feel in their body the strikes – of course, not painful – but just bringing in those senses and that stimulus, really leaving the learner with an experience that’s going to be long-lasting.
Dr. Glatter: Feeling that stimulus certainly affects your vital signs. Do you monitor a provider’s vital signs, such as their blood pressure and heart rate, as the situation and the threat escalate? That could potentially trigger some issues in people with prior PTSD or people with other mental health issues. Has that ever been considered in the design of your program?
Dr. Salazar: Yes, 100%. The beautiful thing about haptics is that they can be tailored to our specific parameters. The sensory stimulus that’s provided is actually very mild. It feels more like a tap than an actual strike. It just reminds us that when we’re having or experiencing an actual physical attack, we’re really engaging the senses.
We have an emergency physician or an EMT-paramedic on site at all times during the training so that we can monitor our subjects and make sure that they’re comfortable and healthy.
Dr. Glatter: Do they have actual sensors attached to their bodies that are part of your program or distinct in terms of monitoring their vital signs?
Dr. Salazar: It’s completely different. We have two different systems that we are planning on utilizing. Frankly, in the final version of this virtual reality module, we may not even involve the haptics. We’re going to study it and see how our learners behave and how much information they’re able to acquire and retain.
It may be very possible that just the visuals – the auditory and the immersion taking place within the hospital room – may be enough. It’s very possible that, in the next final version of this, we may find that haptics bring in quite a bit of value, and we may incorporate that. If that is the case, then we will, of course, acquire different technology to monitor the patient’s vital signs.
Dr. Glatter: Clearly, when situations escalate in the department, everyone gets more concerned about the patient, but providers are part of this equation, as you allude to.
In 2022, there was a poll by the American College of Emergency Physicians that stated that 85% of emergency physicians reported an increase in violent activity in their ERs in the past 5 years. Nearly two-thirds of nearly 3,000 emergency physicians surveyed reported being assaulted in the past year. This is an important module that we integrate into training providers in terms of these types of tense situations that can result not only in mental anguish but also in physical injury.
Dr. Salazar: One hundred percent. I frankly got tired of seeing my friends and my colleagues suffer both the physical and mental effects of verbal and physical abuse, and I wanted to design a project that was very patient centric while allowing our personnel to really manage these situations a little bit better.
Frankly, we don’t receive great training in this space, and I wanted to rewrite that narrative and make things better for our clinicians out there while remaining patient centric. I wanted to do something about it, and hopefully this dream will become a reality.
Dr. Glatter: Absolutely. There are other data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics stating that health care workers are five times more likely than employees in any other area of work to experience workplace violence. This could, again, range from verbal to physical violence. This is a very important module that you’re developing.
Are there any thoughts to extend this to active-shooter scenarios or any other high-stakes scenarios that you can imagine in the department?
Dr. Salazar: We’re actually working with the same developer that’s helping us with this VR module in developing a mass-casualty incident module so that we can get better training in responding to these very unfortunate high-stakes situations.
Dr. Glatter: In terms of using the module remotely, certainly not requiring resources or having to be in a physical place, can providers in your plan be able to take such a headset home and practice on their own in the sense of being able to deal with a situation? Would this be more reserved for in-department use?
Dr. Salazar: That’s a phenomenal question. I wanted to create the most flexible module that I possibly could. Ideally, a dream scenario is leveraging a simulation center at an academic center and not just do the VR module but also have a brief didactics incorporating a small slide set, some feedback, and some standardized patients. I wanted it to be flexible enough so that folks here in my state, a different state, or even internationally could take advantage of this technology and do it from the comfort of their home.
As you mentioned, this is going to strike some people. It’s going to hit them heavier than others in terms of prior experience as PTSD. For some people, it may be more comfortable to do it in the comfort of their homes. I wanted to create something very flexible and dynamic.
Dr. Glatter: I think that’s ideal. Just one other point. Can you discuss the different levels of competencies involved in this module and how that would be attained?
Dr. Salazar: It’s all evidence based, so we borrowed from literature and the specialties of emergency medicine. We collaborated with psychiatrists within our medical center. We looked at all available literature and methods, proficiencies, competencies, and best practices, and we took all of them together to form something that we think is organized and concise.
We were able to create our own algorithm, but it’s not brand new. We’re just borrowing what we think is the best to create something that the majority of health care personnel are going to be able to relate to and be able to really be proficient at.
This includes things like active listening, bargaining, how to respond, where to put yourself in a situation, and the best possible situation to respond to a scenario, how to prevent things – how to get out of a chokehold, for example. We’re borrowing from several different disciplines and creating something that can be very concise and organized.
Dr. Glatter: Does this program that you’ve developed allow the provider to get feedback in the sense that when they’re in such a danger, their life could be at risk? For example, if they don’t remove themselves in a certain amount of time, this could be lethal.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, 100%. Probably the one thing that differentiates our project from any others is the ability to customize the experience so that a learner who is doing the things that we ask them to do in terms of safety and response is able to get out of a situation successfully within the environment. If they don’t, they get some kind of feedback.
Not to spoil the surprise here, but we’re going to be doing things like looking at decibel meters to see what the volume in the room is doing and how you’re managing the volume and the stimulation within the room. If you are able to maintain the decibel readings at a specific level, you’re going to succeed through the module. If you don’t, we keep the patient escalation going.
Dr. Glatter: There is a debrief built into this type of approach where, in other words, learning points are emphasized – where you could have done better and such.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. We are going to be able to get individualized data for each learner so that we can tailor the debrief to their own performance and be able to give them actionable items to work on. It’s a debrief that’s productive and individualized, and folks can walk away with something useful in the end.
Dr. Glatter: Are the data shared or confidential at present?
Dr. Salazar: At this very moment, the data are confidential. We are going to look at how to best use this. We’re hoping to eventually write this up and see how this information can be best used to train personnel.
Eventually, we may see that some of the advice that we’re giving is very common to most folks. Others may require some individualized type of feedback. That said, it remains to be seen, but right now, it’s confidential.
Dr. Glatter: Is this currently being implemented as part of your curriculum for emergency medicine residents?
Dr. Salazar: We’re going to study it first. We’re very excited to include our emergency medicine residents as one of our cohorts that’s going to be undergoing the module, and we’re going to be studying other forms of workplace violence mitigation strategies. We’re really excited about the possibility of this eventually becoming the standard of education for not only our emergency medicine residents, but also health care personnel all over the world.
Dr. Glatter: I’m glad you mentioned that, because obviously nurses, clerks in the department, and anyone who’s working in the department, for that matter, and who interfaces with patients really should undergo such training.
Dr. Salazar: Absolutely. The folks at intake, at check-in, and at kiosks. Do they go through a separate area for screening? You’re absolutely right. There are many folks who interface with patients and all of us are potential victims of workplace violence. We want to give our health care family the best opportunity to succeed in these situations.
Dr. Glatter:: Absolutely. Even EMS providers, being on the front lines and encountering patients in such situations, would benefit, in my opinion.
Dr. Salazar: Yes, absolutely. Behavioral health emergencies and organically induced altered mental status results in injury, both physical and mental, to EMS professionals as well, and there’s good evidence of that. I’ll be very glad to see this type of education make it out to our initial and continuing education efforts for EMS as well.
Dr. Glatter: I want to thank you. This has been very helpful. It’s such an important task that you’ve started to explore, and I look forward to follow-up on this. Again, thank you for your time.
Dr. Salazar: It was my pleasure. Thank you so much for having me.
Dr. Glatter is an attending physician at Lenox Hill Hospital in New York City and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell in Hempstead, N.Y. He is an editorial adviser and hosts the Hot Topics in EM series on Medscape. He is also a medical contributor for Forbes. Dr. Salazar is a board-certified emergency physician and associate professor at UT Southwestern Medicine Center in Dallas. He is involved with the UTSW Emergency Medicine Education Program and serves as the medical director to teach both initial and continuing the emergency medicine education for emergency medical technicians and paramedics, which trains most of the Dallas Fire Rescue personnel and the vast majority for EMS providers in the Dallas County. In addition, he serves as an associate chief of service at Parkland’s emergency department, and liaison to surgical services. A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Who can sue docs for wrongful death? Some states are trying to expand that group
In addition, the types of emotional damage that physicians can be sued for is expanding in pockets across the nation. The latest effort to expand the capacity to sue, a bill in New York state, failed when it was not signed by the governor – but a toned-down bill is in the works.
The impact of New York’s proposed expansion of wrongful death lawsuits would have been widespread. The New York legislation would have expanded the definition of “close family members” to include spouses, domestic partners, children, parents, stepparents, siblings, grandparents, and perhaps more. Additionally, lawsuits could have allowed juries to determine “close family members” of the deceased patient on the basis of specific circumstances of the person’s relationship with the decedent.
Currently, every state allows a wrongful death claim to be filed by immediate family members. If the patient who died was married, a surviving spouse could bring the lawsuit. If the patient had been unmarried, an adult child could bring the lawsuit in some states. A parent typically brings a lawsuit if their minor child has died from alleged wrongful death. In some states, one member of a civil union or domestic partnership may bring a wrongful death lawsuit. And if a single adult has no children or spouse/partner, more distant family members, including aunts, uncles, siblings, or grandparents, may file the suit.
The New York bill would also have expanded compensable damages to include loss of affection and companionship, and it would have expanded emotional damages, which are not currently included in New York. It would also have extended the statute of limitations of a wrongful death claim from 2 years to 3.5 years.
In general, in states that allow emotional distress to be included in wrongful death lawsuits, attorneys must demonstrate that survivors have suffered mental harm, such as depression, loss of sleep, fear, and anger, says Russ Haven, JD, general counsel for the New York Public Interest Research Group. While mental harm is not particularly easy to prove, attorneys must show that survivors have ongoing distress that is the direct result of the loss of the loved one and that the distress is significant enough to severely affect their quality of life.
Mr. Haven gives an example of emotional distress: “We worked with a woman who lost her fiancé in a motor vehicle accident,” he says. “The funeral ended up on the day she had scheduled her wedding dress fitting. A situation like that causes a good deal of lasting emotional distress.”
Expanding family members who can bring the lawsuit
The fact that a fiancé could be included in a wrongful death settlement is another aspect of the New York bill that was central to arguments both for and against the expansion of family members who can make claims. “We think a modern society includes unmarried partners, grandparents, siblings, and others,” says Mr. Haven.
“The language of who is a close family member might seem clear, but to a defense attorney, it isn’t,” says Tom Stebbins, executive director of the Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York. “This could end up being a situation where someone has 40 grandchildren, and all could be considered close family members.”
Many states currently allow damages for claims of grief and mental anguish resulting from a wrongful death.
In her recent veto of the Grieving Families Act, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul took fire for her choices. The bill represented years of effort by the state legislature to expand the qualifiers for wrongful death lawsuits. Those supporting what ultimately became Senate Bill S74A believed they finally had the law over the finish line. Those opposed breathed a sigh of relief when the bill was vetoed.
Had Gov. Hochul signed Bill 274A, the effect on costs would have been enormous for physicians. New York already has the highest cumulative medical liability payouts in the nation, according to the Medical Society of the State of New York.
The MSSNY was among many parties that fought against the law. The Greater New York Hospital Association, insurance companies, the Defense Association of New York, and the New York Conference of Mayors all joined in lobbying against the bill.
“Gov. Hochul, in her veto message, correctly noted that the proposed New York legislation represented an extraordinary departure from New York’s wrongful death jurisprudence,” says Remi Stone, director of government relations at The Doctors Company, part of the TDC Group. “I would add that while there are some other states that allow grief damages, none are as wide-ranging as the proposed legislation.”
The NYPIRG, the AARP, and the New York Immigration Coalition supported the bill. In a statement following the veto, the New York State Trial Lawyers Association said: “By vetoing the Grieving Families Act, Gov. Hochul has sided with insurance companies, the health care industry, big corporations, and anyone else who doesn’t want to be held accountable for the negligent killing of a person. This bill passed with overwhelming bipartisan support and would rectify over a century of injustice.”
Following Gov. Hochul’s veto, the bill’s proponents and the state legislature vowed to return to the drawing board and construct a bill that the governor would eventually approve. For now, however, the controversial legislation has been put to rest.
Mr. Haven and the NYPIRG argue that New York lags behind many other states in allowing survivors to claim loss for their emotional distress. “When there is relationship loss, it has a great impact on your life,” Mr. Haven says, “and this goes beyond simply the financial impact.”
“The bill was well intended but completely vague on who could bring lawsuits and would have increased medical malpractice insurance by far too much,” says MSSNY President Parag Mehta, MD. “For safety net hospitals, one lawsuit would halt their ability to provide many programs aimed at underserved populations.”
Peter Kolbert, JD, senior vice president of claim and litigation services at Healthcare Risk Advisors (part of the TDC Group), had this to say: “The current ‘recoverable’ damages in New York in a wrongful death case include loss of guidance and support for minor children of a decedent. Those damages have been sustained at $2 million per child. It is rationally very challenging, if not impossible, to distinguish between those damages and the proposed damages that the very same people would have been entitled to under the proposed statute.”
What will happen in the future?
While the veto has stalled New York’s wrongful death expansion for now, supporters in and out of the legislature remain determined to continue their fight. “Advocates argue that the bill would have brought the state in line with wrongful death law in others,” says Brian Whitelaw, JD, a partner at Michigan’s Foley, Baron, Metzger & Juip. “But if the bill had become law as written, the economic impact would have been substantial.”
Mr. Whitelaw says that such wide-ranging lawsuits can have consequences that extend far beyond physicians’ insurance premiums. “This could impact the average person on the street’s ability to obtain the medical care they need, because doctors will go elsewhere to practice,” he says. “Beyond impacting the health care system, it can hurt small businesses as well.”
Mr. Haven says supporters of the expansion are far from finished with their efforts. “New York’s current law dates back to 1847, and it was cutting edge then,” he says. “It was designed for an agrarian society where if the husband died, his widow and children wouldn’t become destitute. Now, 175 years later, we realize that the law has biases, and tort law has evolved. The state needs to evolve as well.”
For his part, Dr. Mehta is open to a dialogue with lawmakers to revise the law in a manner agreeable to all parties. “We want to work together to make the system right,” he says. “The liability system in New York needs an overall holistic change, and we are available at any time to have discussions. The vetoed bill was a Band-Aid and didn’t address the main, underlying issues in the state.”
Mr. Stebbins, too, says he would like to continue the debate over how an expansion should look. “We hope to go through a discussion on caps to these suits,” he explains. “We have already seen the cap of $10 million broken four times in the past few years through nuclear verdicts. That’s something we need to address.”
Given the legislature’s overwhelming support for the bill, some version of it will likely make another appearance in the coming session. Whether or not it can strike the middle ground that will make all parties happy – including the governor – is yet to be seen. “Is it wrong to seek compensation for pain and suffering from a wrongful death?” asks Mr. Whitelaw. “No. But there must be limits to such laws, or where does it end?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In addition, the types of emotional damage that physicians can be sued for is expanding in pockets across the nation. The latest effort to expand the capacity to sue, a bill in New York state, failed when it was not signed by the governor – but a toned-down bill is in the works.
The impact of New York’s proposed expansion of wrongful death lawsuits would have been widespread. The New York legislation would have expanded the definition of “close family members” to include spouses, domestic partners, children, parents, stepparents, siblings, grandparents, and perhaps more. Additionally, lawsuits could have allowed juries to determine “close family members” of the deceased patient on the basis of specific circumstances of the person’s relationship with the decedent.
Currently, every state allows a wrongful death claim to be filed by immediate family members. If the patient who died was married, a surviving spouse could bring the lawsuit. If the patient had been unmarried, an adult child could bring the lawsuit in some states. A parent typically brings a lawsuit if their minor child has died from alleged wrongful death. In some states, one member of a civil union or domestic partnership may bring a wrongful death lawsuit. And if a single adult has no children or spouse/partner, more distant family members, including aunts, uncles, siblings, or grandparents, may file the suit.
The New York bill would also have expanded compensable damages to include loss of affection and companionship, and it would have expanded emotional damages, which are not currently included in New York. It would also have extended the statute of limitations of a wrongful death claim from 2 years to 3.5 years.
In general, in states that allow emotional distress to be included in wrongful death lawsuits, attorneys must demonstrate that survivors have suffered mental harm, such as depression, loss of sleep, fear, and anger, says Russ Haven, JD, general counsel for the New York Public Interest Research Group. While mental harm is not particularly easy to prove, attorneys must show that survivors have ongoing distress that is the direct result of the loss of the loved one and that the distress is significant enough to severely affect their quality of life.
Mr. Haven gives an example of emotional distress: “We worked with a woman who lost her fiancé in a motor vehicle accident,” he says. “The funeral ended up on the day she had scheduled her wedding dress fitting. A situation like that causes a good deal of lasting emotional distress.”
Expanding family members who can bring the lawsuit
The fact that a fiancé could be included in a wrongful death settlement is another aspect of the New York bill that was central to arguments both for and against the expansion of family members who can make claims. “We think a modern society includes unmarried partners, grandparents, siblings, and others,” says Mr. Haven.
“The language of who is a close family member might seem clear, but to a defense attorney, it isn’t,” says Tom Stebbins, executive director of the Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York. “This could end up being a situation where someone has 40 grandchildren, and all could be considered close family members.”
Many states currently allow damages for claims of grief and mental anguish resulting from a wrongful death.
In her recent veto of the Grieving Families Act, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul took fire for her choices. The bill represented years of effort by the state legislature to expand the qualifiers for wrongful death lawsuits. Those supporting what ultimately became Senate Bill S74A believed they finally had the law over the finish line. Those opposed breathed a sigh of relief when the bill was vetoed.
Had Gov. Hochul signed Bill 274A, the effect on costs would have been enormous for physicians. New York already has the highest cumulative medical liability payouts in the nation, according to the Medical Society of the State of New York.
The MSSNY was among many parties that fought against the law. The Greater New York Hospital Association, insurance companies, the Defense Association of New York, and the New York Conference of Mayors all joined in lobbying against the bill.
“Gov. Hochul, in her veto message, correctly noted that the proposed New York legislation represented an extraordinary departure from New York’s wrongful death jurisprudence,” says Remi Stone, director of government relations at The Doctors Company, part of the TDC Group. “I would add that while there are some other states that allow grief damages, none are as wide-ranging as the proposed legislation.”
The NYPIRG, the AARP, and the New York Immigration Coalition supported the bill. In a statement following the veto, the New York State Trial Lawyers Association said: “By vetoing the Grieving Families Act, Gov. Hochul has sided with insurance companies, the health care industry, big corporations, and anyone else who doesn’t want to be held accountable for the negligent killing of a person. This bill passed with overwhelming bipartisan support and would rectify over a century of injustice.”
Following Gov. Hochul’s veto, the bill’s proponents and the state legislature vowed to return to the drawing board and construct a bill that the governor would eventually approve. For now, however, the controversial legislation has been put to rest.
Mr. Haven and the NYPIRG argue that New York lags behind many other states in allowing survivors to claim loss for their emotional distress. “When there is relationship loss, it has a great impact on your life,” Mr. Haven says, “and this goes beyond simply the financial impact.”
“The bill was well intended but completely vague on who could bring lawsuits and would have increased medical malpractice insurance by far too much,” says MSSNY President Parag Mehta, MD. “For safety net hospitals, one lawsuit would halt their ability to provide many programs aimed at underserved populations.”
Peter Kolbert, JD, senior vice president of claim and litigation services at Healthcare Risk Advisors (part of the TDC Group), had this to say: “The current ‘recoverable’ damages in New York in a wrongful death case include loss of guidance and support for minor children of a decedent. Those damages have been sustained at $2 million per child. It is rationally very challenging, if not impossible, to distinguish between those damages and the proposed damages that the very same people would have been entitled to under the proposed statute.”
What will happen in the future?
While the veto has stalled New York’s wrongful death expansion for now, supporters in and out of the legislature remain determined to continue their fight. “Advocates argue that the bill would have brought the state in line with wrongful death law in others,” says Brian Whitelaw, JD, a partner at Michigan’s Foley, Baron, Metzger & Juip. “But if the bill had become law as written, the economic impact would have been substantial.”
Mr. Whitelaw says that such wide-ranging lawsuits can have consequences that extend far beyond physicians’ insurance premiums. “This could impact the average person on the street’s ability to obtain the medical care they need, because doctors will go elsewhere to practice,” he says. “Beyond impacting the health care system, it can hurt small businesses as well.”
Mr. Haven says supporters of the expansion are far from finished with their efforts. “New York’s current law dates back to 1847, and it was cutting edge then,” he says. “It was designed for an agrarian society where if the husband died, his widow and children wouldn’t become destitute. Now, 175 years later, we realize that the law has biases, and tort law has evolved. The state needs to evolve as well.”
For his part, Dr. Mehta is open to a dialogue with lawmakers to revise the law in a manner agreeable to all parties. “We want to work together to make the system right,” he says. “The liability system in New York needs an overall holistic change, and we are available at any time to have discussions. The vetoed bill was a Band-Aid and didn’t address the main, underlying issues in the state.”
Mr. Stebbins, too, says he would like to continue the debate over how an expansion should look. “We hope to go through a discussion on caps to these suits,” he explains. “We have already seen the cap of $10 million broken four times in the past few years through nuclear verdicts. That’s something we need to address.”
Given the legislature’s overwhelming support for the bill, some version of it will likely make another appearance in the coming session. Whether or not it can strike the middle ground that will make all parties happy – including the governor – is yet to be seen. “Is it wrong to seek compensation for pain and suffering from a wrongful death?” asks Mr. Whitelaw. “No. But there must be limits to such laws, or where does it end?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In addition, the types of emotional damage that physicians can be sued for is expanding in pockets across the nation. The latest effort to expand the capacity to sue, a bill in New York state, failed when it was not signed by the governor – but a toned-down bill is in the works.
The impact of New York’s proposed expansion of wrongful death lawsuits would have been widespread. The New York legislation would have expanded the definition of “close family members” to include spouses, domestic partners, children, parents, stepparents, siblings, grandparents, and perhaps more. Additionally, lawsuits could have allowed juries to determine “close family members” of the deceased patient on the basis of specific circumstances of the person’s relationship with the decedent.
Currently, every state allows a wrongful death claim to be filed by immediate family members. If the patient who died was married, a surviving spouse could bring the lawsuit. If the patient had been unmarried, an adult child could bring the lawsuit in some states. A parent typically brings a lawsuit if their minor child has died from alleged wrongful death. In some states, one member of a civil union or domestic partnership may bring a wrongful death lawsuit. And if a single adult has no children or spouse/partner, more distant family members, including aunts, uncles, siblings, or grandparents, may file the suit.
The New York bill would also have expanded compensable damages to include loss of affection and companionship, and it would have expanded emotional damages, which are not currently included in New York. It would also have extended the statute of limitations of a wrongful death claim from 2 years to 3.5 years.
In general, in states that allow emotional distress to be included in wrongful death lawsuits, attorneys must demonstrate that survivors have suffered mental harm, such as depression, loss of sleep, fear, and anger, says Russ Haven, JD, general counsel for the New York Public Interest Research Group. While mental harm is not particularly easy to prove, attorneys must show that survivors have ongoing distress that is the direct result of the loss of the loved one and that the distress is significant enough to severely affect their quality of life.
Mr. Haven gives an example of emotional distress: “We worked with a woman who lost her fiancé in a motor vehicle accident,” he says. “The funeral ended up on the day she had scheduled her wedding dress fitting. A situation like that causes a good deal of lasting emotional distress.”
Expanding family members who can bring the lawsuit
The fact that a fiancé could be included in a wrongful death settlement is another aspect of the New York bill that was central to arguments both for and against the expansion of family members who can make claims. “We think a modern society includes unmarried partners, grandparents, siblings, and others,” says Mr. Haven.
“The language of who is a close family member might seem clear, but to a defense attorney, it isn’t,” says Tom Stebbins, executive director of the Lawsuit Reform Alliance of New York. “This could end up being a situation where someone has 40 grandchildren, and all could be considered close family members.”
Many states currently allow damages for claims of grief and mental anguish resulting from a wrongful death.
In her recent veto of the Grieving Families Act, New York Gov. Kathy Hochul took fire for her choices. The bill represented years of effort by the state legislature to expand the qualifiers for wrongful death lawsuits. Those supporting what ultimately became Senate Bill S74A believed they finally had the law over the finish line. Those opposed breathed a sigh of relief when the bill was vetoed.
Had Gov. Hochul signed Bill 274A, the effect on costs would have been enormous for physicians. New York already has the highest cumulative medical liability payouts in the nation, according to the Medical Society of the State of New York.
The MSSNY was among many parties that fought against the law. The Greater New York Hospital Association, insurance companies, the Defense Association of New York, and the New York Conference of Mayors all joined in lobbying against the bill.
“Gov. Hochul, in her veto message, correctly noted that the proposed New York legislation represented an extraordinary departure from New York’s wrongful death jurisprudence,” says Remi Stone, director of government relations at The Doctors Company, part of the TDC Group. “I would add that while there are some other states that allow grief damages, none are as wide-ranging as the proposed legislation.”
The NYPIRG, the AARP, and the New York Immigration Coalition supported the bill. In a statement following the veto, the New York State Trial Lawyers Association said: “By vetoing the Grieving Families Act, Gov. Hochul has sided with insurance companies, the health care industry, big corporations, and anyone else who doesn’t want to be held accountable for the negligent killing of a person. This bill passed with overwhelming bipartisan support and would rectify over a century of injustice.”
Following Gov. Hochul’s veto, the bill’s proponents and the state legislature vowed to return to the drawing board and construct a bill that the governor would eventually approve. For now, however, the controversial legislation has been put to rest.
Mr. Haven and the NYPIRG argue that New York lags behind many other states in allowing survivors to claim loss for their emotional distress. “When there is relationship loss, it has a great impact on your life,” Mr. Haven says, “and this goes beyond simply the financial impact.”
“The bill was well intended but completely vague on who could bring lawsuits and would have increased medical malpractice insurance by far too much,” says MSSNY President Parag Mehta, MD. “For safety net hospitals, one lawsuit would halt their ability to provide many programs aimed at underserved populations.”
Peter Kolbert, JD, senior vice president of claim and litigation services at Healthcare Risk Advisors (part of the TDC Group), had this to say: “The current ‘recoverable’ damages in New York in a wrongful death case include loss of guidance and support for minor children of a decedent. Those damages have been sustained at $2 million per child. It is rationally very challenging, if not impossible, to distinguish between those damages and the proposed damages that the very same people would have been entitled to under the proposed statute.”
What will happen in the future?
While the veto has stalled New York’s wrongful death expansion for now, supporters in and out of the legislature remain determined to continue their fight. “Advocates argue that the bill would have brought the state in line with wrongful death law in others,” says Brian Whitelaw, JD, a partner at Michigan’s Foley, Baron, Metzger & Juip. “But if the bill had become law as written, the economic impact would have been substantial.”
Mr. Whitelaw says that such wide-ranging lawsuits can have consequences that extend far beyond physicians’ insurance premiums. “This could impact the average person on the street’s ability to obtain the medical care they need, because doctors will go elsewhere to practice,” he says. “Beyond impacting the health care system, it can hurt small businesses as well.”
Mr. Haven says supporters of the expansion are far from finished with their efforts. “New York’s current law dates back to 1847, and it was cutting edge then,” he says. “It was designed for an agrarian society where if the husband died, his widow and children wouldn’t become destitute. Now, 175 years later, we realize that the law has biases, and tort law has evolved. The state needs to evolve as well.”
For his part, Dr. Mehta is open to a dialogue with lawmakers to revise the law in a manner agreeable to all parties. “We want to work together to make the system right,” he says. “The liability system in New York needs an overall holistic change, and we are available at any time to have discussions. The vetoed bill was a Band-Aid and didn’t address the main, underlying issues in the state.”
Mr. Stebbins, too, says he would like to continue the debate over how an expansion should look. “We hope to go through a discussion on caps to these suits,” he explains. “We have already seen the cap of $10 million broken four times in the past few years through nuclear verdicts. That’s something we need to address.”
Given the legislature’s overwhelming support for the bill, some version of it will likely make another appearance in the coming session. Whether or not it can strike the middle ground that will make all parties happy – including the governor – is yet to be seen. “Is it wrong to seek compensation for pain and suffering from a wrongful death?” asks Mr. Whitelaw. “No. But there must be limits to such laws, or where does it end?”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA strengthens mammography regulations: Final rule
A final rule, updating the regulations issued under the Mammography Quality Standards Act of 1992, requires that mammography facilities notify patients about the density of their breasts, strengthens the FDA’s oversight of facilities, and provides guidance to help physicians better categorize and assess mammograms, according to a March 9 press release.
The rule requires implementation of the changes within 18 months.
According to the final rule document, the updates are “intended to improve the delivery of mammography services” in ways that reflect changes in mammography technology, quality standards, and the way results are categorized, reported, and communicated to patients and providers.
For instance, mammography reports must include an assessment of breast density to provide greater detail on the potential limitations of the mammogram results and allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, such as the possibility of additional imaging for women with dense breast tissue.
“Today’s action represents the agency’s broader commitment to support innovation to prevent, detect and treat cancer,” said Hilary Marston, MD, MPH, FDA’s chief medical officer, in the agency’s press release. The FDA remains “committed to advancing efforts to improve the health of women and strengthen the fight against breast cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A final rule, updating the regulations issued under the Mammography Quality Standards Act of 1992, requires that mammography facilities notify patients about the density of their breasts, strengthens the FDA’s oversight of facilities, and provides guidance to help physicians better categorize and assess mammograms, according to a March 9 press release.
The rule requires implementation of the changes within 18 months.
According to the final rule document, the updates are “intended to improve the delivery of mammography services” in ways that reflect changes in mammography technology, quality standards, and the way results are categorized, reported, and communicated to patients and providers.
For instance, mammography reports must include an assessment of breast density to provide greater detail on the potential limitations of the mammogram results and allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, such as the possibility of additional imaging for women with dense breast tissue.
“Today’s action represents the agency’s broader commitment to support innovation to prevent, detect and treat cancer,” said Hilary Marston, MD, MPH, FDA’s chief medical officer, in the agency’s press release. The FDA remains “committed to advancing efforts to improve the health of women and strengthen the fight against breast cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A final rule, updating the regulations issued under the Mammography Quality Standards Act of 1992, requires that mammography facilities notify patients about the density of their breasts, strengthens the FDA’s oversight of facilities, and provides guidance to help physicians better categorize and assess mammograms, according to a March 9 press release.
The rule requires implementation of the changes within 18 months.
According to the final rule document, the updates are “intended to improve the delivery of mammography services” in ways that reflect changes in mammography technology, quality standards, and the way results are categorized, reported, and communicated to patients and providers.
For instance, mammography reports must include an assessment of breast density to provide greater detail on the potential limitations of the mammogram results and allow patients and physicians to make more informed decisions, such as the possibility of additional imaging for women with dense breast tissue.
“Today’s action represents the agency’s broader commitment to support innovation to prevent, detect and treat cancer,” said Hilary Marston, MD, MPH, FDA’s chief medical officer, in the agency’s press release. The FDA remains “committed to advancing efforts to improve the health of women and strengthen the fight against breast cancer.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Telehealth doctor indicted on health care fraud, opioid distribution charges
Sangita Patel, MD, 50, practiced at Advance Medical Home Physicians in Troy.
According to court documents, between July 2020 and June 2022 Patel was responsible for submitting Medicare claims for improper telehealth visits she didn’t conduct herself.
Dr. Patel, who accepted patients who paid in cash as well as those with Medicare and Medicaid coverage, billed approximately $3.4 million to Medicare between 2018 and 2022, according to court documents. An unusual number of these visits were billed using complex codes, an indication of health care fraud. The investigation also found that on many days, Dr. Patel billed for more than 24 hours of services. During this period, according to the document, 76% of Dr. Patel’s Medicare reimbursements were for telehealth.
Prosecutors say that Dr. Patel prescribed Schedule II controlled substances to more than 90% of the patients in these telehealth visits. She delegated her prescription authority to an unlicensed medical assistant. Through undercover visits and cell site search warrant data, the investigation found that Dr. Patel directed patients to contact, via cell phone, this assistant, who then entered electronic prescriptions into the electronic medical records system. Dr. Patel then signed the prescriptions and sent them to the pharmacies without ever interacting with the patients. Prosecutors also used text messages, obtained by search warrant, between Dr. Patel and her assistant and between the assistant and undercover informers to build their case.
Dr. Patel is also accused of referring patients to other providers, who in turn billed Medicare for claims associated with those patients. Advance Medical received $143,000 from these providers, potentially in violation of anti-kickback laws, according to bank records obtained by subpoena.
If convicted, Dr. Patel could be sentenced to up to 10 years in federal prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sangita Patel, MD, 50, practiced at Advance Medical Home Physicians in Troy.
According to court documents, between July 2020 and June 2022 Patel was responsible for submitting Medicare claims for improper telehealth visits she didn’t conduct herself.
Dr. Patel, who accepted patients who paid in cash as well as those with Medicare and Medicaid coverage, billed approximately $3.4 million to Medicare between 2018 and 2022, according to court documents. An unusual number of these visits were billed using complex codes, an indication of health care fraud. The investigation also found that on many days, Dr. Patel billed for more than 24 hours of services. During this period, according to the document, 76% of Dr. Patel’s Medicare reimbursements were for telehealth.
Prosecutors say that Dr. Patel prescribed Schedule II controlled substances to more than 90% of the patients in these telehealth visits. She delegated her prescription authority to an unlicensed medical assistant. Through undercover visits and cell site search warrant data, the investigation found that Dr. Patel directed patients to contact, via cell phone, this assistant, who then entered electronic prescriptions into the electronic medical records system. Dr. Patel then signed the prescriptions and sent them to the pharmacies without ever interacting with the patients. Prosecutors also used text messages, obtained by search warrant, between Dr. Patel and her assistant and between the assistant and undercover informers to build their case.
Dr. Patel is also accused of referring patients to other providers, who in turn billed Medicare for claims associated with those patients. Advance Medical received $143,000 from these providers, potentially in violation of anti-kickback laws, according to bank records obtained by subpoena.
If convicted, Dr. Patel could be sentenced to up to 10 years in federal prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sangita Patel, MD, 50, practiced at Advance Medical Home Physicians in Troy.
According to court documents, between July 2020 and June 2022 Patel was responsible for submitting Medicare claims for improper telehealth visits she didn’t conduct herself.
Dr. Patel, who accepted patients who paid in cash as well as those with Medicare and Medicaid coverage, billed approximately $3.4 million to Medicare between 2018 and 2022, according to court documents. An unusual number of these visits were billed using complex codes, an indication of health care fraud. The investigation also found that on many days, Dr. Patel billed for more than 24 hours of services. During this period, according to the document, 76% of Dr. Patel’s Medicare reimbursements were for telehealth.
Prosecutors say that Dr. Patel prescribed Schedule II controlled substances to more than 90% of the patients in these telehealth visits. She delegated her prescription authority to an unlicensed medical assistant. Through undercover visits and cell site search warrant data, the investigation found that Dr. Patel directed patients to contact, via cell phone, this assistant, who then entered electronic prescriptions into the electronic medical records system. Dr. Patel then signed the prescriptions and sent them to the pharmacies without ever interacting with the patients. Prosecutors also used text messages, obtained by search warrant, between Dr. Patel and her assistant and between the assistant and undercover informers to build their case.
Dr. Patel is also accused of referring patients to other providers, who in turn billed Medicare for claims associated with those patients. Advance Medical received $143,000 from these providers, potentially in violation of anti-kickback laws, according to bank records obtained by subpoena.
If convicted, Dr. Patel could be sentenced to up to 10 years in federal prison.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Specialty and age may contribute to suicidal thoughts among physicians
A physician’s specialty can make a difference when it comes to having suicidal thoughts. Doctors who specialize in family medicine, obstetrics-gynecology, and psychiatry reported double the rates of suicidal thoughts than doctors in oncology, rheumatology, and pulmonary medicine, according to Doctors’ Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023.
“The specialties with the highest reporting of physician suicidal thoughts are also those with the greatest physician shortages, based on the number of job openings posted by recruiting sites,” said Peter Yellowlees, MD, professor of psychiatry and chief wellness officer at UC Davis Health.
Doctors in those specialties are overworked, which can lead to burnout, he said.
There’s also a generational divide among physicians who reported suicidal thoughts. Millennials (age 27-41) and Gen-X physicians (age 42-56) were more likely to report these thoughts than were Baby Boomers (age 57-75) and the Silent Generation (age 76-95).
“Younger physicians are more burned out – they may have less control over their lives and less meaning than some older doctors who can do what they want,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
One millennial respondent commented that being on call and being required to chart detailed notes in the EHR has contributed to her burnout. “I’m more impatient and make less time and effort to see my friends and family.”
One Silent Generation respondent commented, “I am semi-retired, I take no call, I work no weekends, I provide anesthesia care in my area of special expertise, I work clinically about 46 days a year. Life is good, particularly compared to my younger colleagues who are working 60-plus hours a week with evening work, weekend work, and call. I feel really sorry for them.”
When young people enter medical school, they’re quite healthy, with low rates of depression and burnout, said Dr. Yellowlees. Yet, studies have shown that rates of burnout and suicidal thoughts increased within 2 years. “That reflects what happens when a group of idealistic young people hit a horrible system,” he said.
Who’s responsible?
Millennials were three times as likely as baby boomers to say that a medical school or health care organization should be responsible when a student or physician commits suicide.
“Young physicians may expect more of their employers than my generation did, which we see in residency programs that have unionized,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a Baby Boomer.
“As more young doctors are employed by health care organizations, they also may expect more resources to be available to them, such as wellness programs,” he added.
Younger doctors also focus more on work-life balance than older doctors, including time off and having hobbies, he said. “They are much more rational in terms of their overall beliefs and expectations than the older generation.”
Whom doctors confide in
Nearly 60% of physician-respondents with suicidal thoughts said they confided in a professional or someone they knew. Men were just as likely as women to reach out to a therapist (38%), whereas men were slightly more likely to confide in a family member and women were slightly more likely to confide in a colleague.
“It’s interesting that women are more active in seeking support at work – they often have developed a network of colleagues to support each other’s careers and whom they can confide in,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
He emphasized that 40% of physicians said they didn’t confide in anyone when they had suicidal thoughts. Of those, just over half said they could cope without professional help.
One respondent commented, “It’s just a thought; nothing I would actually do.” Another commented, “Mental health professionals can’t fix the underlying reason for the problem.”
Many doctors were concerned about risking disclosure to their medical boards (42%); that it would show up on their insurance records (33%); and that their colleagues would find out (25%), according to the report.
One respondent commented, “I don’t trust doctors to keep it to themselves.”
Another barrier doctors mentioned was a lack of time to seek help. One commented, “Time. I have none, when am I supposed to find an hour for counseling?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A physician’s specialty can make a difference when it comes to having suicidal thoughts. Doctors who specialize in family medicine, obstetrics-gynecology, and psychiatry reported double the rates of suicidal thoughts than doctors in oncology, rheumatology, and pulmonary medicine, according to Doctors’ Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023.
“The specialties with the highest reporting of physician suicidal thoughts are also those with the greatest physician shortages, based on the number of job openings posted by recruiting sites,” said Peter Yellowlees, MD, professor of psychiatry and chief wellness officer at UC Davis Health.
Doctors in those specialties are overworked, which can lead to burnout, he said.
There’s also a generational divide among physicians who reported suicidal thoughts. Millennials (age 27-41) and Gen-X physicians (age 42-56) were more likely to report these thoughts than were Baby Boomers (age 57-75) and the Silent Generation (age 76-95).
“Younger physicians are more burned out – they may have less control over their lives and less meaning than some older doctors who can do what they want,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
One millennial respondent commented that being on call and being required to chart detailed notes in the EHR has contributed to her burnout. “I’m more impatient and make less time and effort to see my friends and family.”
One Silent Generation respondent commented, “I am semi-retired, I take no call, I work no weekends, I provide anesthesia care in my area of special expertise, I work clinically about 46 days a year. Life is good, particularly compared to my younger colleagues who are working 60-plus hours a week with evening work, weekend work, and call. I feel really sorry for them.”
When young people enter medical school, they’re quite healthy, with low rates of depression and burnout, said Dr. Yellowlees. Yet, studies have shown that rates of burnout and suicidal thoughts increased within 2 years. “That reflects what happens when a group of idealistic young people hit a horrible system,” he said.
Who’s responsible?
Millennials were three times as likely as baby boomers to say that a medical school or health care organization should be responsible when a student or physician commits suicide.
“Young physicians may expect more of their employers than my generation did, which we see in residency programs that have unionized,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a Baby Boomer.
“As more young doctors are employed by health care organizations, they also may expect more resources to be available to them, such as wellness programs,” he added.
Younger doctors also focus more on work-life balance than older doctors, including time off and having hobbies, he said. “They are much more rational in terms of their overall beliefs and expectations than the older generation.”
Whom doctors confide in
Nearly 60% of physician-respondents with suicidal thoughts said they confided in a professional or someone they knew. Men were just as likely as women to reach out to a therapist (38%), whereas men were slightly more likely to confide in a family member and women were slightly more likely to confide in a colleague.
“It’s interesting that women are more active in seeking support at work – they often have developed a network of colleagues to support each other’s careers and whom they can confide in,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
He emphasized that 40% of physicians said they didn’t confide in anyone when they had suicidal thoughts. Of those, just over half said they could cope without professional help.
One respondent commented, “It’s just a thought; nothing I would actually do.” Another commented, “Mental health professionals can’t fix the underlying reason for the problem.”
Many doctors were concerned about risking disclosure to their medical boards (42%); that it would show up on their insurance records (33%); and that their colleagues would find out (25%), according to the report.
One respondent commented, “I don’t trust doctors to keep it to themselves.”
Another barrier doctors mentioned was a lack of time to seek help. One commented, “Time. I have none, when am I supposed to find an hour for counseling?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A physician’s specialty can make a difference when it comes to having suicidal thoughts. Doctors who specialize in family medicine, obstetrics-gynecology, and psychiatry reported double the rates of suicidal thoughts than doctors in oncology, rheumatology, and pulmonary medicine, according to Doctors’ Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023.
“The specialties with the highest reporting of physician suicidal thoughts are also those with the greatest physician shortages, based on the number of job openings posted by recruiting sites,” said Peter Yellowlees, MD, professor of psychiatry and chief wellness officer at UC Davis Health.
Doctors in those specialties are overworked, which can lead to burnout, he said.
There’s also a generational divide among physicians who reported suicidal thoughts. Millennials (age 27-41) and Gen-X physicians (age 42-56) were more likely to report these thoughts than were Baby Boomers (age 57-75) and the Silent Generation (age 76-95).
“Younger physicians are more burned out – they may have less control over their lives and less meaning than some older doctors who can do what they want,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
One millennial respondent commented that being on call and being required to chart detailed notes in the EHR has contributed to her burnout. “I’m more impatient and make less time and effort to see my friends and family.”
One Silent Generation respondent commented, “I am semi-retired, I take no call, I work no weekends, I provide anesthesia care in my area of special expertise, I work clinically about 46 days a year. Life is good, particularly compared to my younger colleagues who are working 60-plus hours a week with evening work, weekend work, and call. I feel really sorry for them.”
When young people enter medical school, they’re quite healthy, with low rates of depression and burnout, said Dr. Yellowlees. Yet, studies have shown that rates of burnout and suicidal thoughts increased within 2 years. “That reflects what happens when a group of idealistic young people hit a horrible system,” he said.
Who’s responsible?
Millennials were three times as likely as baby boomers to say that a medical school or health care organization should be responsible when a student or physician commits suicide.
“Young physicians may expect more of their employers than my generation did, which we see in residency programs that have unionized,” said Dr. Yellowlees, a Baby Boomer.
“As more young doctors are employed by health care organizations, they also may expect more resources to be available to them, such as wellness programs,” he added.
Younger doctors also focus more on work-life balance than older doctors, including time off and having hobbies, he said. “They are much more rational in terms of their overall beliefs and expectations than the older generation.”
Whom doctors confide in
Nearly 60% of physician-respondents with suicidal thoughts said they confided in a professional or someone they knew. Men were just as likely as women to reach out to a therapist (38%), whereas men were slightly more likely to confide in a family member and women were slightly more likely to confide in a colleague.
“It’s interesting that women are more active in seeking support at work – they often have developed a network of colleagues to support each other’s careers and whom they can confide in,” said Dr. Yellowlees.
He emphasized that 40% of physicians said they didn’t confide in anyone when they had suicidal thoughts. Of those, just over half said they could cope without professional help.
One respondent commented, “It’s just a thought; nothing I would actually do.” Another commented, “Mental health professionals can’t fix the underlying reason for the problem.”
Many doctors were concerned about risking disclosure to their medical boards (42%); that it would show up on their insurance records (33%); and that their colleagues would find out (25%), according to the report.
One respondent commented, “I don’t trust doctors to keep it to themselves.”
Another barrier doctors mentioned was a lack of time to seek help. One commented, “Time. I have none, when am I supposed to find an hour for counseling?”
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Popular book by USC oncologist pulled because of plagiarism
The Los Angeles Times reported earlier this week that it identified at least 95 instances of plagiarism by author David B. Agus, MD, in “The Book of Animal Secrets: Nature’s Lessons for a Long and Happy Life.”
According to the LA Times, Dr. Agus copied passages from numerous sources, including The New York Times, National Geographic, Wikipedia, and smaller niche sites. Some instances involved a sentence or two; others involved multiparagraph, word-for-word copying without attribution.
The book by Dr. Agus – who interviews celebrities for a health-related miniseries on Paramount Plus – had reached the top spot on Amazon’s list of best-selling books about animals a week before its planned March 7 release.
Publisher Simon & Schuster released a statement announcing a recall of the book at Dr. Agus’ expense “until a fully revised and corrected edition can be released.”
Dr. Agus included his own statement apologizing “to the scientists and writers whose work or words were used or not fully attributed,” and said he will “rewrite the passages in question with new language, will provide proper and full attribution, and when ready will announce a new publication date.”
“Writers should always be credited for their work, and I deeply regret these mistakes and the lack of rigor in finalizing the book,” he stated, adding that “[t]his book contains important lessons, messages, and guidance about health that I wanted to convey to the readers. I do not want these mistakes to interfere with that effort.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Los Angeles Times reported earlier this week that it identified at least 95 instances of plagiarism by author David B. Agus, MD, in “The Book of Animal Secrets: Nature’s Lessons for a Long and Happy Life.”
According to the LA Times, Dr. Agus copied passages from numerous sources, including The New York Times, National Geographic, Wikipedia, and smaller niche sites. Some instances involved a sentence or two; others involved multiparagraph, word-for-word copying without attribution.
The book by Dr. Agus – who interviews celebrities for a health-related miniseries on Paramount Plus – had reached the top spot on Amazon’s list of best-selling books about animals a week before its planned March 7 release.
Publisher Simon & Schuster released a statement announcing a recall of the book at Dr. Agus’ expense “until a fully revised and corrected edition can be released.”
Dr. Agus included his own statement apologizing “to the scientists and writers whose work or words were used or not fully attributed,” and said he will “rewrite the passages in question with new language, will provide proper and full attribution, and when ready will announce a new publication date.”
“Writers should always be credited for their work, and I deeply regret these mistakes and the lack of rigor in finalizing the book,” he stated, adding that “[t]his book contains important lessons, messages, and guidance about health that I wanted to convey to the readers. I do not want these mistakes to interfere with that effort.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Los Angeles Times reported earlier this week that it identified at least 95 instances of plagiarism by author David B. Agus, MD, in “The Book of Animal Secrets: Nature’s Lessons for a Long and Happy Life.”
According to the LA Times, Dr. Agus copied passages from numerous sources, including The New York Times, National Geographic, Wikipedia, and smaller niche sites. Some instances involved a sentence or two; others involved multiparagraph, word-for-word copying without attribution.
The book by Dr. Agus – who interviews celebrities for a health-related miniseries on Paramount Plus – had reached the top spot on Amazon’s list of best-selling books about animals a week before its planned March 7 release.
Publisher Simon & Schuster released a statement announcing a recall of the book at Dr. Agus’ expense “until a fully revised and corrected edition can be released.”
Dr. Agus included his own statement apologizing “to the scientists and writers whose work or words were used or not fully attributed,” and said he will “rewrite the passages in question with new language, will provide proper and full attribution, and when ready will announce a new publication date.”
“Writers should always be credited for their work, and I deeply regret these mistakes and the lack of rigor in finalizing the book,” he stated, adding that “[t]his book contains important lessons, messages, and guidance about health that I wanted to convey to the readers. I do not want these mistakes to interfere with that effort.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.