User login
Obesity interactions complex in acute pancreatitis
Obesity, in combination with other risk factors, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in acute pancreatitis (AP); however, body mass index (BMI) alone is not a successful predictor of disease severity, new research shows.
“As there was no agreement or consistency between BMI and AP severity, it can be concluded that AP severity cannot be predicted successfully by examining BMI only,” reported the authors in research published recently in Pancreatology.
The course of acute pancreatitis is typically mild in the majority (80%-85%) of cases; however, in severe cases, permanent organ failure can occur, with much worse outcomes and mortality rates of up to 35%.
Research has previously shown not only a link between obesity and acute pancreatitis but also an increased risk for complications and in-hospital mortality in obese patients with severe cases of acute pancreatitis – though a wide range of factors and comorbidities may complicate the association.
To more closely evaluate the course and outcomes of acute pancreatitis based on BMI classification, study authors led by Ali Tuzun Ince, MD, of the department of internal medicine, Gastroenterology Clinic of Bezmialem Vakif University, Istanbul, analyzed retrospective data from 2010 to 2020 on 1,334 adult patients (720 female, 614 male) who were diagnosed with acute pancreatitis per the Revised Atlanta Classification (RAC) criteria.
The patients were stratified based on their BMI as normal weight, overweight, or obese and whether they had mild, moderate, or severe (with permanent organ failure) acute pancreatitis.
In terms of acute pancreatitis severity, based on RAC criteria, 57.1% of patients had mild disease, 20.4% had moderate disease, and 22.5% had severe disease.
The overall mortality rate was 9.9% (n = 132); half of these patients were obese, and 87% had severe acute pancreatitis.
The overall rate of complications was 42.9%, including 20.8% in the normal weight group, 40.6% in the overweight group, and 38.6% in the obese group.
Patients in the overweight and obese groups also had higher mortality rates (3.7% and 4.9%, respectively), interventional procedures (36% and 39%, respectively), and length of hospital stay (11.6% and 9.8%, respectively), compared with the normal-weight group.
Other factors that were significantly associated with an increased mortality risk, in addition to obesity (P = .046), included old age (P = .000), male sex (P = .05), alcohol use (P = .014), low hematocrit (P = .044), high C-reactive protein (P = .024), moderate to severe and severe acute pancreatitis (P = .02 and P < .001, respectively), and any complications (P < .001).
Risk factors associated with increased admission to the ICU differed from those for mortality, and included female gender (P = .024), smoking (P = .021), hypertriglyceridemia (P = .047), idiopathic etiology (P = .023), and moderate to severe and severe acute pancreatitis (P < .001).
Of note, there were no significant associations between BMI and either the RAC score or Balthazar CT severity index (Balthazar CTSI) groups.
Specifically, among patients considered to have severe acute pancreatitis per Balthazar CTSI, 6.3% were of normal weight, 5% were overweight, and 7.1% were obese.
“In addition, since agreement and consistency between BMI and Balthazar score cannot be determined, the Balthazar score cannot be estimated from BMI,” the authors reported.
While the prediction of prognosis in acute pancreatitis is gaining interest, the findings underscore the role of combined factors, they added.
“Although many scoring systems are currently in use attempt to estimate the severity [in acute pancreatitis], none is 100% accurate yet,” the authors noted. “Each risk factor exacerbates the course of disease. Therefore, it would be better to consider the combined effects of risk factors.”
That being said, the findings show “mortality is increased significantly by the combined presence of risk factors such as male sex, OB [obesity], alcohol, MSAP [moderate to severe acute pancreatitis] and SAP [severe acute pancreatitis], all kinds of complications, old age, low Hct, and high CRP,” they wrote.
Obesity’s complex interactions
Commenting on the study, Vijay P. Singh, MD, a professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz., agreed that the complexities risk factors, particularly with obesity, can be tricky to detangle.
“Broadly, the study confirms several previous reports from different parts of the world that obesity was associated with increased mortality in acute pancreatitis,” he said in an interview.
“However, obesity had two complex interactions, the first that obesity is also associated with increased diabetes, and hypertriglyceridemia, which may themselves be risk factors for severity,” he explained.
“The second one is that intermediary severity markers [e.g., Balthazar score on imaging] did not correlate with the BMI categories.”
Dr. Singh noted that is “likely because therapies like IV fluids that may get more intense in predicted severe disease alter the natural course of pancreatitis.”
The findings are a reminder that “BMI is only a number that attempts to quantify fat,” Dr. Singh said, noting that BMI doesn’t address either the location of fat, such as being in close proximity to the pancreas, or fat composition, such as the proportion of unsaturated fat.
“When the unsaturated fat proportion is higher, the pancreatitis is worse, even at smaller total fat amounts [for example, at a lower BMI],” he said. “Taking these aspects into account may help in risk assessment.”
The authors and Dr. Singh had no disclosures to report.
Obesity, in combination with other risk factors, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in acute pancreatitis (AP); however, body mass index (BMI) alone is not a successful predictor of disease severity, new research shows.
“As there was no agreement or consistency between BMI and AP severity, it can be concluded that AP severity cannot be predicted successfully by examining BMI only,” reported the authors in research published recently in Pancreatology.
The course of acute pancreatitis is typically mild in the majority (80%-85%) of cases; however, in severe cases, permanent organ failure can occur, with much worse outcomes and mortality rates of up to 35%.
Research has previously shown not only a link between obesity and acute pancreatitis but also an increased risk for complications and in-hospital mortality in obese patients with severe cases of acute pancreatitis – though a wide range of factors and comorbidities may complicate the association.
To more closely evaluate the course and outcomes of acute pancreatitis based on BMI classification, study authors led by Ali Tuzun Ince, MD, of the department of internal medicine, Gastroenterology Clinic of Bezmialem Vakif University, Istanbul, analyzed retrospective data from 2010 to 2020 on 1,334 adult patients (720 female, 614 male) who were diagnosed with acute pancreatitis per the Revised Atlanta Classification (RAC) criteria.
The patients were stratified based on their BMI as normal weight, overweight, or obese and whether they had mild, moderate, or severe (with permanent organ failure) acute pancreatitis.
In terms of acute pancreatitis severity, based on RAC criteria, 57.1% of patients had mild disease, 20.4% had moderate disease, and 22.5% had severe disease.
The overall mortality rate was 9.9% (n = 132); half of these patients were obese, and 87% had severe acute pancreatitis.
The overall rate of complications was 42.9%, including 20.8% in the normal weight group, 40.6% in the overweight group, and 38.6% in the obese group.
Patients in the overweight and obese groups also had higher mortality rates (3.7% and 4.9%, respectively), interventional procedures (36% and 39%, respectively), and length of hospital stay (11.6% and 9.8%, respectively), compared with the normal-weight group.
Other factors that were significantly associated with an increased mortality risk, in addition to obesity (P = .046), included old age (P = .000), male sex (P = .05), alcohol use (P = .014), low hematocrit (P = .044), high C-reactive protein (P = .024), moderate to severe and severe acute pancreatitis (P = .02 and P < .001, respectively), and any complications (P < .001).
Risk factors associated with increased admission to the ICU differed from those for mortality, and included female gender (P = .024), smoking (P = .021), hypertriglyceridemia (P = .047), idiopathic etiology (P = .023), and moderate to severe and severe acute pancreatitis (P < .001).
Of note, there were no significant associations between BMI and either the RAC score or Balthazar CT severity index (Balthazar CTSI) groups.
Specifically, among patients considered to have severe acute pancreatitis per Balthazar CTSI, 6.3% were of normal weight, 5% were overweight, and 7.1% were obese.
“In addition, since agreement and consistency between BMI and Balthazar score cannot be determined, the Balthazar score cannot be estimated from BMI,” the authors reported.
While the prediction of prognosis in acute pancreatitis is gaining interest, the findings underscore the role of combined factors, they added.
“Although many scoring systems are currently in use attempt to estimate the severity [in acute pancreatitis], none is 100% accurate yet,” the authors noted. “Each risk factor exacerbates the course of disease. Therefore, it would be better to consider the combined effects of risk factors.”
That being said, the findings show “mortality is increased significantly by the combined presence of risk factors such as male sex, OB [obesity], alcohol, MSAP [moderate to severe acute pancreatitis] and SAP [severe acute pancreatitis], all kinds of complications, old age, low Hct, and high CRP,” they wrote.
Obesity’s complex interactions
Commenting on the study, Vijay P. Singh, MD, a professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz., agreed that the complexities risk factors, particularly with obesity, can be tricky to detangle.
“Broadly, the study confirms several previous reports from different parts of the world that obesity was associated with increased mortality in acute pancreatitis,” he said in an interview.
“However, obesity had two complex interactions, the first that obesity is also associated with increased diabetes, and hypertriglyceridemia, which may themselves be risk factors for severity,” he explained.
“The second one is that intermediary severity markers [e.g., Balthazar score on imaging] did not correlate with the BMI categories.”
Dr. Singh noted that is “likely because therapies like IV fluids that may get more intense in predicted severe disease alter the natural course of pancreatitis.”
The findings are a reminder that “BMI is only a number that attempts to quantify fat,” Dr. Singh said, noting that BMI doesn’t address either the location of fat, such as being in close proximity to the pancreas, or fat composition, such as the proportion of unsaturated fat.
“When the unsaturated fat proportion is higher, the pancreatitis is worse, even at smaller total fat amounts [for example, at a lower BMI],” he said. “Taking these aspects into account may help in risk assessment.”
The authors and Dr. Singh had no disclosures to report.
Obesity, in combination with other risk factors, is associated with increased morbidity and mortality in acute pancreatitis (AP); however, body mass index (BMI) alone is not a successful predictor of disease severity, new research shows.
“As there was no agreement or consistency between BMI and AP severity, it can be concluded that AP severity cannot be predicted successfully by examining BMI only,” reported the authors in research published recently in Pancreatology.
The course of acute pancreatitis is typically mild in the majority (80%-85%) of cases; however, in severe cases, permanent organ failure can occur, with much worse outcomes and mortality rates of up to 35%.
Research has previously shown not only a link between obesity and acute pancreatitis but also an increased risk for complications and in-hospital mortality in obese patients with severe cases of acute pancreatitis – though a wide range of factors and comorbidities may complicate the association.
To more closely evaluate the course and outcomes of acute pancreatitis based on BMI classification, study authors led by Ali Tuzun Ince, MD, of the department of internal medicine, Gastroenterology Clinic of Bezmialem Vakif University, Istanbul, analyzed retrospective data from 2010 to 2020 on 1,334 adult patients (720 female, 614 male) who were diagnosed with acute pancreatitis per the Revised Atlanta Classification (RAC) criteria.
The patients were stratified based on their BMI as normal weight, overweight, or obese and whether they had mild, moderate, or severe (with permanent organ failure) acute pancreatitis.
In terms of acute pancreatitis severity, based on RAC criteria, 57.1% of patients had mild disease, 20.4% had moderate disease, and 22.5% had severe disease.
The overall mortality rate was 9.9% (n = 132); half of these patients were obese, and 87% had severe acute pancreatitis.
The overall rate of complications was 42.9%, including 20.8% in the normal weight group, 40.6% in the overweight group, and 38.6% in the obese group.
Patients in the overweight and obese groups also had higher mortality rates (3.7% and 4.9%, respectively), interventional procedures (36% and 39%, respectively), and length of hospital stay (11.6% and 9.8%, respectively), compared with the normal-weight group.
Other factors that were significantly associated with an increased mortality risk, in addition to obesity (P = .046), included old age (P = .000), male sex (P = .05), alcohol use (P = .014), low hematocrit (P = .044), high C-reactive protein (P = .024), moderate to severe and severe acute pancreatitis (P = .02 and P < .001, respectively), and any complications (P < .001).
Risk factors associated with increased admission to the ICU differed from those for mortality, and included female gender (P = .024), smoking (P = .021), hypertriglyceridemia (P = .047), idiopathic etiology (P = .023), and moderate to severe and severe acute pancreatitis (P < .001).
Of note, there were no significant associations between BMI and either the RAC score or Balthazar CT severity index (Balthazar CTSI) groups.
Specifically, among patients considered to have severe acute pancreatitis per Balthazar CTSI, 6.3% were of normal weight, 5% were overweight, and 7.1% were obese.
“In addition, since agreement and consistency between BMI and Balthazar score cannot be determined, the Balthazar score cannot be estimated from BMI,” the authors reported.
While the prediction of prognosis in acute pancreatitis is gaining interest, the findings underscore the role of combined factors, they added.
“Although many scoring systems are currently in use attempt to estimate the severity [in acute pancreatitis], none is 100% accurate yet,” the authors noted. “Each risk factor exacerbates the course of disease. Therefore, it would be better to consider the combined effects of risk factors.”
That being said, the findings show “mortality is increased significantly by the combined presence of risk factors such as male sex, OB [obesity], alcohol, MSAP [moderate to severe acute pancreatitis] and SAP [severe acute pancreatitis], all kinds of complications, old age, low Hct, and high CRP,” they wrote.
Obesity’s complex interactions
Commenting on the study, Vijay P. Singh, MD, a professor of medicine in the division of gastroenterology and hepatology at the Mayo Clinic in Scottsdale, Ariz., agreed that the complexities risk factors, particularly with obesity, can be tricky to detangle.
“Broadly, the study confirms several previous reports from different parts of the world that obesity was associated with increased mortality in acute pancreatitis,” he said in an interview.
“However, obesity had two complex interactions, the first that obesity is also associated with increased diabetes, and hypertriglyceridemia, which may themselves be risk factors for severity,” he explained.
“The second one is that intermediary severity markers [e.g., Balthazar score on imaging] did not correlate with the BMI categories.”
Dr. Singh noted that is “likely because therapies like IV fluids that may get more intense in predicted severe disease alter the natural course of pancreatitis.”
The findings are a reminder that “BMI is only a number that attempts to quantify fat,” Dr. Singh said, noting that BMI doesn’t address either the location of fat, such as being in close proximity to the pancreas, or fat composition, such as the proportion of unsaturated fat.
“When the unsaturated fat proportion is higher, the pancreatitis is worse, even at smaller total fat amounts [for example, at a lower BMI],” he said. “Taking these aspects into account may help in risk assessment.”
The authors and Dr. Singh had no disclosures to report.
FROM PANCREATOLOGY
In diabetes, fast-growing pancreatic cysts may be a red flag
LAS VEGAS – New results from a single center, retrospective analysis suggest that individuals with diabetes and pancreatic cysts have larger cyst sizes at diagnosis, and a faster subsequent cyst growth rate. Smoking was independently associated with faster growth rate.
Most pancreatic cancer patients were previously diagnosed with hyperglycemia and diabetes, and pancreatic cancer can cause diabetes. “This sort of dual causality raises questions as to whether or not hyperglycemia, or the new diagnosis of diabetes itself, could be a harbinger of cancer or precancer. And should these patients be more closely monitored?” David Robbins, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Robbins, associate professor of medicine and program director in gastroenterology in the Northwell Health System, New York, presented the study at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Faster growth rates of pancreatic cysts in the presence of diabetes are important because they represent a potential mark for cyst aggressiveness. “So the question really is, in the setting of diabetes, are there factors perhaps circulating in the bloodstream, or other intrinsic factors, that make these cysts more dangerous and require a different surveillance approach than someone who doesn’t have diabetes? We have (surveillance) guidelines that address the average population, but they don’t really hone in on what do you do with (individuals with diabetes),” Dr. Robbins said during the presentation.
The study could have implications for screening, said session moderator Dayna Early, MD, professor of medicine at Washington University and director of endoscopy at Barnes Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis. “I think this is important information to guide us to look more closely at patients with diabetes who do have pancreatic cysts,” she said in an interview.
The study included 177 adults with pancreatic cysts or abnormal imaging results between 2013 and 2020. Sixty-five percent were female, and the mean age was 65.4 years; 64% were White, 10% were Black, and 8.5% were Asian. Among the participants, 24.8% were smokers and 32.2% had type 2 diabetes.
Patients with diabetes had larger cyst sizes (2.23 cm versus 2.76 cm), as well as a higher annual cyst growth rate (1.90 cm versus 1.30 cm). Cyst size and growth rate were similar between patients with controlled and uncontrolled diabetes. Smoking was associated with a larger cyst size overall (2.2 cm versus 1.81 cm), and were larger still among patients with diabetes who smoked (2.35 cm).
Seventy-one patients went on to have pathologic confirmation by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. “In the diabetic group, two developed adenocarcinoma, six of the nondiabetics developed adenocarcinoma, and there was no difference in CEA or serum CA 19-9,” Dr. Robbins said during his presentation.
Of 28 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, 13 had type 2 diabetes.
Defining danger
There remains uncertainty about what cyst growth rate is most dangerous. Some guidelines recommend that individuals with new-onset or worsening diabetes and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm or mucinous cystic neoplasm cysts, or cysts alone that are growing faster than 3 mm per year, may be at significantly increased risk of pancreatic cancer. These guidelines recommend that they be screened with short-interval magnetic resonance imaging or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) fine needle aspiration. However, this recommendation is conditional and is backed by a very low level of evidence.
Other reports have shown varying risks at different growth rates. “It’s not really clear at this point. And that’s why I think, while our study is small and exploratory, this is a particular area that is relatively easy to evaluate. We have huge databases of pancreatic cyst evolution, and we know that 30 million Americans have diabetes. So, the next obvious study is to do a more systematic look at that, and work towards refining and making sense of these divergent guidelines, all of which are saying the same thing but using different threshold numbers,” said Dr. Robbins.
The next step is do larger, multicenter studies in the context of other risk factors such as family history and smoking, but the current finding represents an opportunity to catch at least some pancreatic cancers earlier, according to Dr. Robbins. He suggested that individuals with diabetes who are diagnosed with a pancreatic cyst should be referred to a gastroenterologist or another specialist to track cyst growth. “That is going to miss a lot of folks who didn’t get imaging for whatever reason (and so don’t have a cyst identified), but it is an early opportunity, and it’s better than what we’re doing now.”
During the talk, Dr. Robbins said, “Given the ease, availability and low cost of diabetes screening in the general clinic population, we encourage the inclusion of HbA1c and fasting glucose in algorithms for pancreatic cyst surveillance.”
Dr. Early found the suggestion intriguing, but wasn’t ready to lend full support. “I think looking at the suggestion of possibly monitoring hemoglobin A1c levels was novel. I don’t know that we’ll necessarily adopt that as standard practice, but that’s something I think that could be looked at in the future as a way to help risk stratify whether patients need to be surveyed more frequently,” she said.
Dr. Robbins and Dr. Early have no relevant financial disclosures.
LAS VEGAS – New results from a single center, retrospective analysis suggest that individuals with diabetes and pancreatic cysts have larger cyst sizes at diagnosis, and a faster subsequent cyst growth rate. Smoking was independently associated with faster growth rate.
Most pancreatic cancer patients were previously diagnosed with hyperglycemia and diabetes, and pancreatic cancer can cause diabetes. “This sort of dual causality raises questions as to whether or not hyperglycemia, or the new diagnosis of diabetes itself, could be a harbinger of cancer or precancer. And should these patients be more closely monitored?” David Robbins, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Robbins, associate professor of medicine and program director in gastroenterology in the Northwell Health System, New York, presented the study at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Faster growth rates of pancreatic cysts in the presence of diabetes are important because they represent a potential mark for cyst aggressiveness. “So the question really is, in the setting of diabetes, are there factors perhaps circulating in the bloodstream, or other intrinsic factors, that make these cysts more dangerous and require a different surveillance approach than someone who doesn’t have diabetes? We have (surveillance) guidelines that address the average population, but they don’t really hone in on what do you do with (individuals with diabetes),” Dr. Robbins said during the presentation.
The study could have implications for screening, said session moderator Dayna Early, MD, professor of medicine at Washington University and director of endoscopy at Barnes Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis. “I think this is important information to guide us to look more closely at patients with diabetes who do have pancreatic cysts,” she said in an interview.
The study included 177 adults with pancreatic cysts or abnormal imaging results between 2013 and 2020. Sixty-five percent were female, and the mean age was 65.4 years; 64% were White, 10% were Black, and 8.5% were Asian. Among the participants, 24.8% were smokers and 32.2% had type 2 diabetes.
Patients with diabetes had larger cyst sizes (2.23 cm versus 2.76 cm), as well as a higher annual cyst growth rate (1.90 cm versus 1.30 cm). Cyst size and growth rate were similar between patients with controlled and uncontrolled diabetes. Smoking was associated with a larger cyst size overall (2.2 cm versus 1.81 cm), and were larger still among patients with diabetes who smoked (2.35 cm).
Seventy-one patients went on to have pathologic confirmation by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. “In the diabetic group, two developed adenocarcinoma, six of the nondiabetics developed adenocarcinoma, and there was no difference in CEA or serum CA 19-9,” Dr. Robbins said during his presentation.
Of 28 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, 13 had type 2 diabetes.
Defining danger
There remains uncertainty about what cyst growth rate is most dangerous. Some guidelines recommend that individuals with new-onset or worsening diabetes and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm or mucinous cystic neoplasm cysts, or cysts alone that are growing faster than 3 mm per year, may be at significantly increased risk of pancreatic cancer. These guidelines recommend that they be screened with short-interval magnetic resonance imaging or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) fine needle aspiration. However, this recommendation is conditional and is backed by a very low level of evidence.
Other reports have shown varying risks at different growth rates. “It’s not really clear at this point. And that’s why I think, while our study is small and exploratory, this is a particular area that is relatively easy to evaluate. We have huge databases of pancreatic cyst evolution, and we know that 30 million Americans have diabetes. So, the next obvious study is to do a more systematic look at that, and work towards refining and making sense of these divergent guidelines, all of which are saying the same thing but using different threshold numbers,” said Dr. Robbins.
The next step is do larger, multicenter studies in the context of other risk factors such as family history and smoking, but the current finding represents an opportunity to catch at least some pancreatic cancers earlier, according to Dr. Robbins. He suggested that individuals with diabetes who are diagnosed with a pancreatic cyst should be referred to a gastroenterologist or another specialist to track cyst growth. “That is going to miss a lot of folks who didn’t get imaging for whatever reason (and so don’t have a cyst identified), but it is an early opportunity, and it’s better than what we’re doing now.”
During the talk, Dr. Robbins said, “Given the ease, availability and low cost of diabetes screening in the general clinic population, we encourage the inclusion of HbA1c and fasting glucose in algorithms for pancreatic cyst surveillance.”
Dr. Early found the suggestion intriguing, but wasn’t ready to lend full support. “I think looking at the suggestion of possibly monitoring hemoglobin A1c levels was novel. I don’t know that we’ll necessarily adopt that as standard practice, but that’s something I think that could be looked at in the future as a way to help risk stratify whether patients need to be surveyed more frequently,” she said.
Dr. Robbins and Dr. Early have no relevant financial disclosures.
LAS VEGAS – New results from a single center, retrospective analysis suggest that individuals with diabetes and pancreatic cysts have larger cyst sizes at diagnosis, and a faster subsequent cyst growth rate. Smoking was independently associated with faster growth rate.
Most pancreatic cancer patients were previously diagnosed with hyperglycemia and diabetes, and pancreatic cancer can cause diabetes. “This sort of dual causality raises questions as to whether or not hyperglycemia, or the new diagnosis of diabetes itself, could be a harbinger of cancer or precancer. And should these patients be more closely monitored?” David Robbins, MD, said in an interview.
Dr. Robbins, associate professor of medicine and program director in gastroenterology in the Northwell Health System, New York, presented the study at the annual meeting of the American College of Gastroenterology.
Faster growth rates of pancreatic cysts in the presence of diabetes are important because they represent a potential mark for cyst aggressiveness. “So the question really is, in the setting of diabetes, are there factors perhaps circulating in the bloodstream, or other intrinsic factors, that make these cysts more dangerous and require a different surveillance approach than someone who doesn’t have diabetes? We have (surveillance) guidelines that address the average population, but they don’t really hone in on what do you do with (individuals with diabetes),” Dr. Robbins said during the presentation.
The study could have implications for screening, said session moderator Dayna Early, MD, professor of medicine at Washington University and director of endoscopy at Barnes Jewish Hospital, both in St. Louis. “I think this is important information to guide us to look more closely at patients with diabetes who do have pancreatic cysts,” she said in an interview.
The study included 177 adults with pancreatic cysts or abnormal imaging results between 2013 and 2020. Sixty-five percent were female, and the mean age was 65.4 years; 64% were White, 10% were Black, and 8.5% were Asian. Among the participants, 24.8% were smokers and 32.2% had type 2 diabetes.
Patients with diabetes had larger cyst sizes (2.23 cm versus 2.76 cm), as well as a higher annual cyst growth rate (1.90 cm versus 1.30 cm). Cyst size and growth rate were similar between patients with controlled and uncontrolled diabetes. Smoking was associated with a larger cyst size overall (2.2 cm versus 1.81 cm), and were larger still among patients with diabetes who smoked (2.35 cm).
Seventy-one patients went on to have pathologic confirmation by endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration. “In the diabetic group, two developed adenocarcinoma, six of the nondiabetics developed adenocarcinoma, and there was no difference in CEA or serum CA 19-9,” Dr. Robbins said during his presentation.
Of 28 patients diagnosed with pancreatic cancer, 13 had type 2 diabetes.
Defining danger
There remains uncertainty about what cyst growth rate is most dangerous. Some guidelines recommend that individuals with new-onset or worsening diabetes and intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm or mucinous cystic neoplasm cysts, or cysts alone that are growing faster than 3 mm per year, may be at significantly increased risk of pancreatic cancer. These guidelines recommend that they be screened with short-interval magnetic resonance imaging or endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) fine needle aspiration. However, this recommendation is conditional and is backed by a very low level of evidence.
Other reports have shown varying risks at different growth rates. “It’s not really clear at this point. And that’s why I think, while our study is small and exploratory, this is a particular area that is relatively easy to evaluate. We have huge databases of pancreatic cyst evolution, and we know that 30 million Americans have diabetes. So, the next obvious study is to do a more systematic look at that, and work towards refining and making sense of these divergent guidelines, all of which are saying the same thing but using different threshold numbers,” said Dr. Robbins.
The next step is do larger, multicenter studies in the context of other risk factors such as family history and smoking, but the current finding represents an opportunity to catch at least some pancreatic cancers earlier, according to Dr. Robbins. He suggested that individuals with diabetes who are diagnosed with a pancreatic cyst should be referred to a gastroenterologist or another specialist to track cyst growth. “That is going to miss a lot of folks who didn’t get imaging for whatever reason (and so don’t have a cyst identified), but it is an early opportunity, and it’s better than what we’re doing now.”
During the talk, Dr. Robbins said, “Given the ease, availability and low cost of diabetes screening in the general clinic population, we encourage the inclusion of HbA1c and fasting glucose in algorithms for pancreatic cyst surveillance.”
Dr. Early found the suggestion intriguing, but wasn’t ready to lend full support. “I think looking at the suggestion of possibly monitoring hemoglobin A1c levels was novel. I don’t know that we’ll necessarily adopt that as standard practice, but that’s something I think that could be looked at in the future as a way to help risk stratify whether patients need to be surveyed more frequently,” she said.
Dr. Robbins and Dr. Early have no relevant financial disclosures.
AT ACG 2021
Developing a career in medical pancreatology: An emerging postfellowship career path
Although described by the Greek physician Herophilos around 300 B.C., it was not until the 19th century that enzymes began to be isolated from pancreatic secretions and their digestive action described, and not until early in the 20th century that Banting, Macleod, and Best received the Nobel prize for purifying insulin from the pancreata of dogs. For centuries in between, the pancreas was considered to be just a ‘beautiful piece of flesh’ (kallikreas), the main role of which was to protect the blood vessels in the abdomen and to serve as a cushion to the stomach.1 Certainly, the pancreas has come a long way since then but, like most other organs in the body, is oft ignored until it develops issues.
Like many other disorders in gastroenterology, pancreatic disorders were historically approached as mechanical or “plumbing” issues. As modern technology and innovation percolated through the world of endoscopy, a wide array of state-of-the-art tools were devised. Availability of newer “toys” and development of newer techniques also means that an ever-increasing curriculum has been squeezed into a generally single year of therapeutic endoscopy training, such that trainees can no longer limit themselves to learning only endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or intervening on pancreatic disease alone. Modern, subspecialized approaches to disease and economic considerations often dictate that the therapeutic endoscopist of today must perform a wide range of procedures besides ERCP and EUS, such as advanced resection using endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), endoscopic bariatric procedures, and newer techniques and acronyms that continue to evolve on a regular basis. This leaves the therapeutic endoscopist with little time for outpatient management of many patients that don’t need interventional procedures but are often very complex and need ongoing, long-term follow-up. In addition, any clinic slots available for interventional endoscopists may be utilized by patients coming in to discuss complex procedures or for postprocedure follow-up. Endoscopic management is not the definitive treatment for most pancreatic disorders. In fact, as our knowledge of pancreatic disease has continued to evolve, endoscopic intervention is now required in a minority of cases.
Role of the medical pancreatologist
Patient Care
As part of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary team that also includes an interventional gastroenterologist, pancreatic surgeon, transplant surgeon (in centers offering islet autotransplantation with total pancreatectomy), radiology, endocrinology, and GI pathologist, the medical pancreatologist helps lead the care of patients with pancreatic disorders, such as pancreatic cysts, acute and chronic pancreatitis (especially in cases where there is no role for active endoscopic intervention), autoimmune pancreatitis, indeterminate pancreatic masses, as well as screens high-risk patients for pancreatic cancer in conjunction with a genetic counselor. The medical pancreatologist often also serves as a bridge between various members of a large multidisciplinary team that, formally in the form of conferences or informally, discusses the management of complex patients, with each member available to help the other based on the patient’s most immediate clinical need at that time. A schematic showing how the medical pancreatologist collaborates with the therapeutic endoscopist is provided in Figure 1.
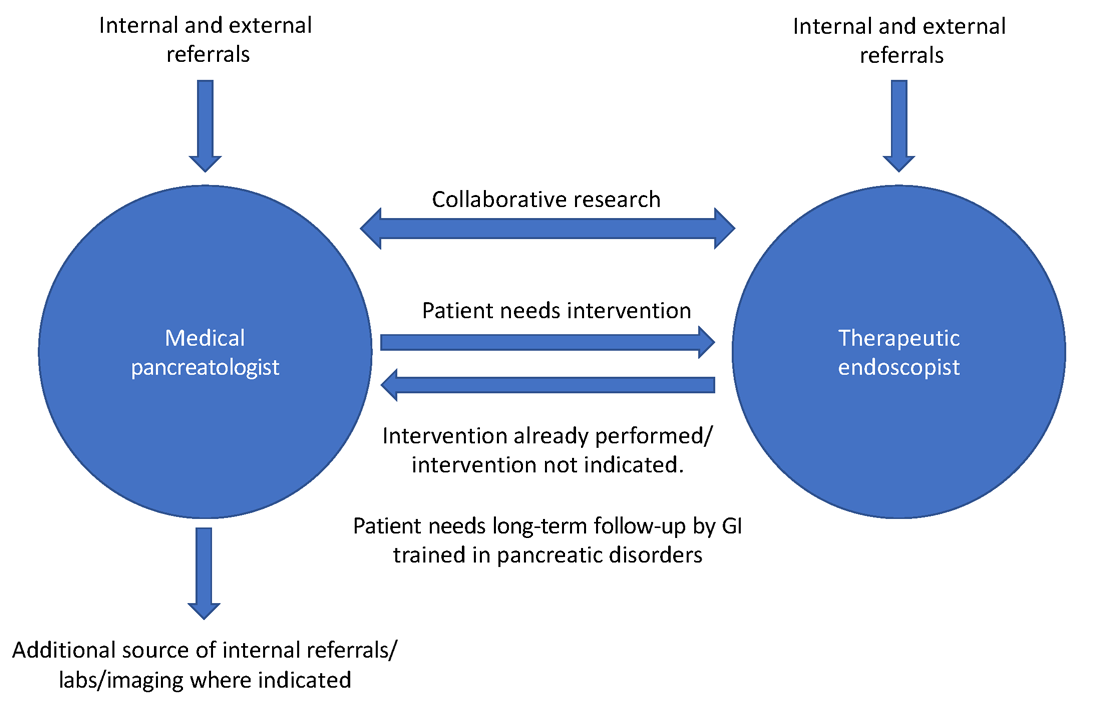
Uzma Siddiqui, MD, director for the Center for Endoscopic Research and Technology (CERT) at the University of Chicago said, “The management of pancreatic diseases is often challenging. Surgeons and endoscopists can offer some treatments that focus on one aspect or symptom, but the medical pancreatologist brings focus to the patient as a whole and helps organize care. It is only with everyone’s combined efforts and the added perspective of the medical pancreatologist that we can provide the best care for our shared patients.”
David Xin, MD, MPH, a medical pancreatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, added, “I am often asked what it means to be a medical pancreatologist. What do I do if not EUS and ERCP? I provide longitudinal care, coordinate multidisciplinary management, assess nutritional status, optimize quality of life, and manage pain. But perhaps most importantly, I make myself available for patients who seek understanding and sympathy regarding their complex disease. I became a medical pancreatologist because my mentors during training helped me recognize how rewarding this career would be.”
Insights from other medical pancreatologists and therapeutic endoscopists are provided in Figure 2.

Education
Having a dedicated medical pancreatology clinic has the potential to add a unique element to the training of gastroenterology fellows. In my own experience, besides fellows interested in medical pancreatology, even those interested in therapeutic endoscopy find it useful to rotate through the pancreas clinic and follow patients after or leading to their procedures, becoming comfortable with noninterventional pain management of patients with pancreatic disorders and risk stratification of pancreatic cystic lesions, and learning about the management of rare disorders such as autoimmune pancreatitis. Most importantly, this allows trainees to identify cases where endoscopic intervention may not offer definitive treatment for complex conditions such as pancreatic pain. Trainee-centered organizations such as the Collaborative Alliance for Pancreatic Education and Research (CAPER) enable trainees and young investigators to network with other physicians who are passionate about the pancreas and establish early research collaborations for current and future research endeavors that will help advance this field.
Research
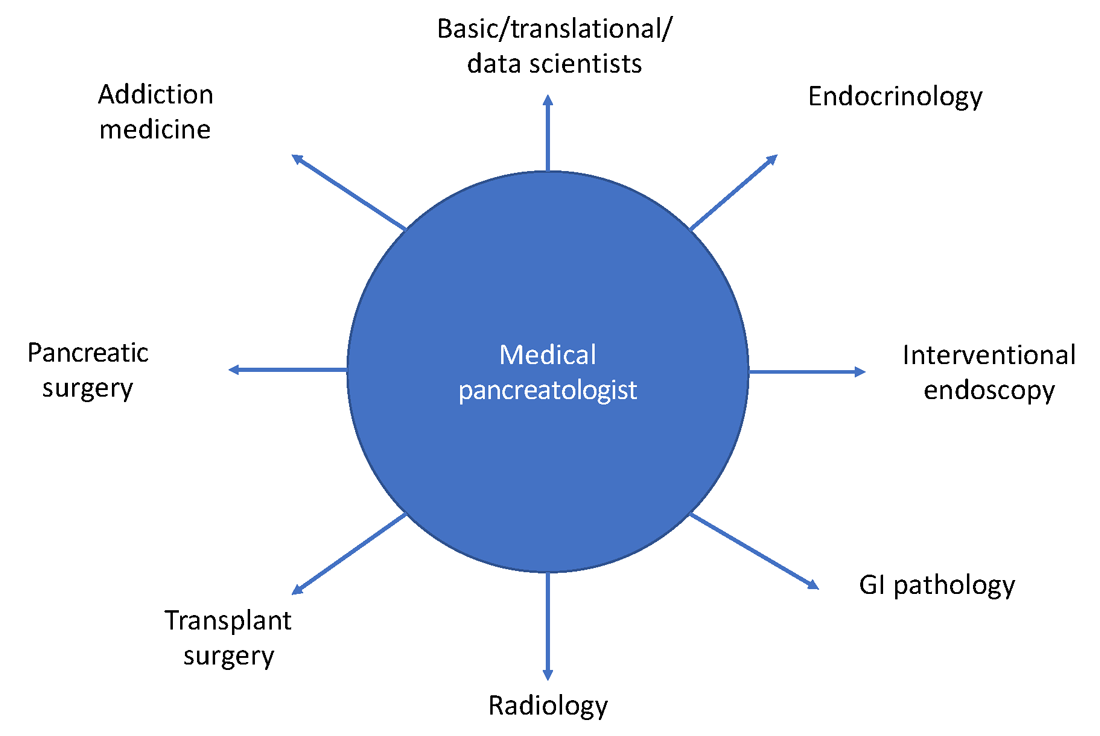
Having a trained medical pancreatologist adds the possibility of adding a unique angle to ongoing research within a gastroenterology division, especially in collaboration with others. For example, during my fellowship training I was able to focus on histological changes in pancreatic islets of patients with pancreatic cancer that develop diabetes, compared with those that do not, in collaboration with a pathologist who focused on studying islet pathology and under the guidance of my mentor, Dr. Suresh Chari, a medical pancreatologist.2 I was also part of other studies within the GI division with other medical pancreatologists, such as Dr. Santhi Vege and Dr. Shounak Majumder, who have continued to serve as career and research mentors.3 Collaborative, multicenter studies on pancreatic disease are also conducted by CAPER, the organization mentioned above. A list of potential collaborations for the fellow interested
in medical pancreatology is provided in Figure 3.
Marketing considerations for the gastroenterology division
Having a medical pancreatologist in the team is not only attractive for referring physicians within an institution but is often a great asset from a marketing standpoint, especially for tertiary care academic centers and large community practices with a broad referral base. Given that there are a limited number of medical pancreatologists in the country, having one as part of the faculty can certainly provide a competitive edge to that center within the area, especially with an ever-increasing preference of patients for hyperspecialized care.
How to develop a career in medical pancreatology
Gastroenterology fellows often start their fellowships “undifferentiated” and try to get exposed to a wide variety of GI pathology, either through general GI clinics or as part of subspecialized clinics, as they attempt to decide how they want their careers to look down the line. Similar to other subspecialities, if a trainee has already decided to pursue medical pancreatology (as happened in my case), they should strongly consider ranking programs with available opportunities for research/clinic in medical pancreatology and ideally undergo an additional year of training. Fellows who decide during the course of their fellowship that they want to pursue a career in medical pancreatology should consider applying for a 4th year in the subject to not only obtain further training in the field but to also conduct research in the area and become more “marketable” as a person that could start a medical pancreatology program at their future academic or community position. Trainees interested in medical pancreatology should try to focus their time on long-term, clinical management of patients with pancreatic disorders, engaging a multidisciplinary team composed of interventional endoscopists, pancreatic surgeons, transplant surgeons (if total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation is available), radiology, addiction medicine (if available), endocrinology, and pathology. The list of places that offer a 4th year in medical pancreatology is increasing every year, and as of the writing of this article there are six programs that have this opportunity, which include:
- Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore
- University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Penn.
The CAPER website is also a great resource for education as well as for identifying potential medical pancreatology programs.
In summary, medical pancreatology is an evolving and rapidly growing career path for gastroenterology fellows interested in providing care to patients with pancreatic disease in close collaboration with multiple other subspecialties, especially therapeutic endoscopy and pancreatic surgery. The field is also ripe for fellows interested in clinical, translational, and basic science research related to pancreatic disorders.
Dr. Nagpal is assistant professor of medicine, director, pancreas clinic, University of Chicago. He had no conflicts to disclose.
References
1. Feldman M et al. “Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease,” 11th ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2021).
2. Nagpal SJS et al. Pancreatology. 2020 Jul;20(5):929-35.
3. Nagpal SJS et al. Pancreatology. 2019 Mar;19(2):290-5.
Although described by the Greek physician Herophilos around 300 B.C., it was not until the 19th century that enzymes began to be isolated from pancreatic secretions and their digestive action described, and not until early in the 20th century that Banting, Macleod, and Best received the Nobel prize for purifying insulin from the pancreata of dogs. For centuries in between, the pancreas was considered to be just a ‘beautiful piece of flesh’ (kallikreas), the main role of which was to protect the blood vessels in the abdomen and to serve as a cushion to the stomach.1 Certainly, the pancreas has come a long way since then but, like most other organs in the body, is oft ignored until it develops issues.
Like many other disorders in gastroenterology, pancreatic disorders were historically approached as mechanical or “plumbing” issues. As modern technology and innovation percolated through the world of endoscopy, a wide array of state-of-the-art tools were devised. Availability of newer “toys” and development of newer techniques also means that an ever-increasing curriculum has been squeezed into a generally single year of therapeutic endoscopy training, such that trainees can no longer limit themselves to learning only endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or intervening on pancreatic disease alone. Modern, subspecialized approaches to disease and economic considerations often dictate that the therapeutic endoscopist of today must perform a wide range of procedures besides ERCP and EUS, such as advanced resection using endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), endoscopic bariatric procedures, and newer techniques and acronyms that continue to evolve on a regular basis. This leaves the therapeutic endoscopist with little time for outpatient management of many patients that don’t need interventional procedures but are often very complex and need ongoing, long-term follow-up. In addition, any clinic slots available for interventional endoscopists may be utilized by patients coming in to discuss complex procedures or for postprocedure follow-up. Endoscopic management is not the definitive treatment for most pancreatic disorders. In fact, as our knowledge of pancreatic disease has continued to evolve, endoscopic intervention is now required in a minority of cases.
Role of the medical pancreatologist
Patient Care
As part of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary team that also includes an interventional gastroenterologist, pancreatic surgeon, transplant surgeon (in centers offering islet autotransplantation with total pancreatectomy), radiology, endocrinology, and GI pathologist, the medical pancreatologist helps lead the care of patients with pancreatic disorders, such as pancreatic cysts, acute and chronic pancreatitis (especially in cases where there is no role for active endoscopic intervention), autoimmune pancreatitis, indeterminate pancreatic masses, as well as screens high-risk patients for pancreatic cancer in conjunction with a genetic counselor. The medical pancreatologist often also serves as a bridge between various members of a large multidisciplinary team that, formally in the form of conferences or informally, discusses the management of complex patients, with each member available to help the other based on the patient’s most immediate clinical need at that time. A schematic showing how the medical pancreatologist collaborates with the therapeutic endoscopist is provided in Figure 1.

Uzma Siddiqui, MD, director for the Center for Endoscopic Research and Technology (CERT) at the University of Chicago said, “The management of pancreatic diseases is often challenging. Surgeons and endoscopists can offer some treatments that focus on one aspect or symptom, but the medical pancreatologist brings focus to the patient as a whole and helps organize care. It is only with everyone’s combined efforts and the added perspective of the medical pancreatologist that we can provide the best care for our shared patients.”
David Xin, MD, MPH, a medical pancreatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, added, “I am often asked what it means to be a medical pancreatologist. What do I do if not EUS and ERCP? I provide longitudinal care, coordinate multidisciplinary management, assess nutritional status, optimize quality of life, and manage pain. But perhaps most importantly, I make myself available for patients who seek understanding and sympathy regarding their complex disease. I became a medical pancreatologist because my mentors during training helped me recognize how rewarding this career would be.”
Insights from other medical pancreatologists and therapeutic endoscopists are provided in Figure 2.

Education
Having a dedicated medical pancreatology clinic has the potential to add a unique element to the training of gastroenterology fellows. In my own experience, besides fellows interested in medical pancreatology, even those interested in therapeutic endoscopy find it useful to rotate through the pancreas clinic and follow patients after or leading to their procedures, becoming comfortable with noninterventional pain management of patients with pancreatic disorders and risk stratification of pancreatic cystic lesions, and learning about the management of rare disorders such as autoimmune pancreatitis. Most importantly, this allows trainees to identify cases where endoscopic intervention may not offer definitive treatment for complex conditions such as pancreatic pain. Trainee-centered organizations such as the Collaborative Alliance for Pancreatic Education and Research (CAPER) enable trainees and young investigators to network with other physicians who are passionate about the pancreas and establish early research collaborations for current and future research endeavors that will help advance this field.
Research
Having a trained medical pancreatologist adds the possibility of adding a unique angle to ongoing research within a gastroenterology division, especially in collaboration with others. For example, during my fellowship training I was able to focus on histological changes in pancreatic islets of patients with pancreatic cancer that develop diabetes, compared with those that do not, in collaboration with a pathologist who focused on studying islet pathology and under the guidance of my mentor, Dr. Suresh Chari, a medical pancreatologist.2 I was also part of other studies within the GI division with other medical pancreatologists, such as Dr. Santhi Vege and Dr. Shounak Majumder, who have continued to serve as career and research mentors.3 Collaborative, multicenter studies on pancreatic disease are also conducted by CAPER, the organization mentioned above. A list of potential collaborations for the fellow interested
in medical pancreatology is provided in Figure 3.

Marketing considerations for the gastroenterology division
Having a medical pancreatologist in the team is not only attractive for referring physicians within an institution but is often a great asset from a marketing standpoint, especially for tertiary care academic centers and large community practices with a broad referral base. Given that there are a limited number of medical pancreatologists in the country, having one as part of the faculty can certainly provide a competitive edge to that center within the area, especially with an ever-increasing preference of patients for hyperspecialized care.
How to develop a career in medical pancreatology
Gastroenterology fellows often start their fellowships “undifferentiated” and try to get exposed to a wide variety of GI pathology, either through general GI clinics or as part of subspecialized clinics, as they attempt to decide how they want their careers to look down the line. Similar to other subspecialities, if a trainee has already decided to pursue medical pancreatology (as happened in my case), they should strongly consider ranking programs with available opportunities for research/clinic in medical pancreatology and ideally undergo an additional year of training. Fellows who decide during the course of their fellowship that they want to pursue a career in medical pancreatology should consider applying for a 4th year in the subject to not only obtain further training in the field but to also conduct research in the area and become more “marketable” as a person that could start a medical pancreatology program at their future academic or community position. Trainees interested in medical pancreatology should try to focus their time on long-term, clinical management of patients with pancreatic disorders, engaging a multidisciplinary team composed of interventional endoscopists, pancreatic surgeons, transplant surgeons (if total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation is available), radiology, addiction medicine (if available), endocrinology, and pathology. The list of places that offer a 4th year in medical pancreatology is increasing every year, and as of the writing of this article there are six programs that have this opportunity, which include:
- Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore
- University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Penn.
The CAPER website is also a great resource for education as well as for identifying potential medical pancreatology programs.
In summary, medical pancreatology is an evolving and rapidly growing career path for gastroenterology fellows interested in providing care to patients with pancreatic disease in close collaboration with multiple other subspecialties, especially therapeutic endoscopy and pancreatic surgery. The field is also ripe for fellows interested in clinical, translational, and basic science research related to pancreatic disorders.
Dr. Nagpal is assistant professor of medicine, director, pancreas clinic, University of Chicago. He had no conflicts to disclose.
References
1. Feldman M et al. “Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease,” 11th ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2021).
2. Nagpal SJS et al. Pancreatology. 2020 Jul;20(5):929-35.
3. Nagpal SJS et al. Pancreatology. 2019 Mar;19(2):290-5.
Although described by the Greek physician Herophilos around 300 B.C., it was not until the 19th century that enzymes began to be isolated from pancreatic secretions and their digestive action described, and not until early in the 20th century that Banting, Macleod, and Best received the Nobel prize for purifying insulin from the pancreata of dogs. For centuries in between, the pancreas was considered to be just a ‘beautiful piece of flesh’ (kallikreas), the main role of which was to protect the blood vessels in the abdomen and to serve as a cushion to the stomach.1 Certainly, the pancreas has come a long way since then but, like most other organs in the body, is oft ignored until it develops issues.
Like many other disorders in gastroenterology, pancreatic disorders were historically approached as mechanical or “plumbing” issues. As modern technology and innovation percolated through the world of endoscopy, a wide array of state-of-the-art tools were devised. Availability of newer “toys” and development of newer techniques also means that an ever-increasing curriculum has been squeezed into a generally single year of therapeutic endoscopy training, such that trainees can no longer limit themselves to learning only endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) and endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) or intervening on pancreatic disease alone. Modern, subspecialized approaches to disease and economic considerations often dictate that the therapeutic endoscopist of today must perform a wide range of procedures besides ERCP and EUS, such as advanced resection using endoscopic mucosal resection (EMR), endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD), per-oral endoscopic myotomy (POEM), endoscopic bariatric procedures, and newer techniques and acronyms that continue to evolve on a regular basis. This leaves the therapeutic endoscopist with little time for outpatient management of many patients that don’t need interventional procedures but are often very complex and need ongoing, long-term follow-up. In addition, any clinic slots available for interventional endoscopists may be utilized by patients coming in to discuss complex procedures or for postprocedure follow-up. Endoscopic management is not the definitive treatment for most pancreatic disorders. In fact, as our knowledge of pancreatic disease has continued to evolve, endoscopic intervention is now required in a minority of cases.
Role of the medical pancreatologist
Patient Care
As part of a comprehensive, multidisciplinary team that also includes an interventional gastroenterologist, pancreatic surgeon, transplant surgeon (in centers offering islet autotransplantation with total pancreatectomy), radiology, endocrinology, and GI pathologist, the medical pancreatologist helps lead the care of patients with pancreatic disorders, such as pancreatic cysts, acute and chronic pancreatitis (especially in cases where there is no role for active endoscopic intervention), autoimmune pancreatitis, indeterminate pancreatic masses, as well as screens high-risk patients for pancreatic cancer in conjunction with a genetic counselor. The medical pancreatologist often also serves as a bridge between various members of a large multidisciplinary team that, formally in the form of conferences or informally, discusses the management of complex patients, with each member available to help the other based on the patient’s most immediate clinical need at that time. A schematic showing how the medical pancreatologist collaborates with the therapeutic endoscopist is provided in Figure 1.

Uzma Siddiqui, MD, director for the Center for Endoscopic Research and Technology (CERT) at the University of Chicago said, “The management of pancreatic diseases is often challenging. Surgeons and endoscopists can offer some treatments that focus on one aspect or symptom, but the medical pancreatologist brings focus to the patient as a whole and helps organize care. It is only with everyone’s combined efforts and the added perspective of the medical pancreatologist that we can provide the best care for our shared patients.”
David Xin, MD, MPH, a medical pancreatologist at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston, added, “I am often asked what it means to be a medical pancreatologist. What do I do if not EUS and ERCP? I provide longitudinal care, coordinate multidisciplinary management, assess nutritional status, optimize quality of life, and manage pain. But perhaps most importantly, I make myself available for patients who seek understanding and sympathy regarding their complex disease. I became a medical pancreatologist because my mentors during training helped me recognize how rewarding this career would be.”
Insights from other medical pancreatologists and therapeutic endoscopists are provided in Figure 2.

Education
Having a dedicated medical pancreatology clinic has the potential to add a unique element to the training of gastroenterology fellows. In my own experience, besides fellows interested in medical pancreatology, even those interested in therapeutic endoscopy find it useful to rotate through the pancreas clinic and follow patients after or leading to their procedures, becoming comfortable with noninterventional pain management of patients with pancreatic disorders and risk stratification of pancreatic cystic lesions, and learning about the management of rare disorders such as autoimmune pancreatitis. Most importantly, this allows trainees to identify cases where endoscopic intervention may not offer definitive treatment for complex conditions such as pancreatic pain. Trainee-centered organizations such as the Collaborative Alliance for Pancreatic Education and Research (CAPER) enable trainees and young investigators to network with other physicians who are passionate about the pancreas and establish early research collaborations for current and future research endeavors that will help advance this field.
Research
Having a trained medical pancreatologist adds the possibility of adding a unique angle to ongoing research within a gastroenterology division, especially in collaboration with others. For example, during my fellowship training I was able to focus on histological changes in pancreatic islets of patients with pancreatic cancer that develop diabetes, compared with those that do not, in collaboration with a pathologist who focused on studying islet pathology and under the guidance of my mentor, Dr. Suresh Chari, a medical pancreatologist.2 I was also part of other studies within the GI division with other medical pancreatologists, such as Dr. Santhi Vege and Dr. Shounak Majumder, who have continued to serve as career and research mentors.3 Collaborative, multicenter studies on pancreatic disease are also conducted by CAPER, the organization mentioned above. A list of potential collaborations for the fellow interested
in medical pancreatology is provided in Figure 3.

Marketing considerations for the gastroenterology division
Having a medical pancreatologist in the team is not only attractive for referring physicians within an institution but is often a great asset from a marketing standpoint, especially for tertiary care academic centers and large community practices with a broad referral base. Given that there are a limited number of medical pancreatologists in the country, having one as part of the faculty can certainly provide a competitive edge to that center within the area, especially with an ever-increasing preference of patients for hyperspecialized care.
How to develop a career in medical pancreatology
Gastroenterology fellows often start their fellowships “undifferentiated” and try to get exposed to a wide variety of GI pathology, either through general GI clinics or as part of subspecialized clinics, as they attempt to decide how they want their careers to look down the line. Similar to other subspecialities, if a trainee has already decided to pursue medical pancreatology (as happened in my case), they should strongly consider ranking programs with available opportunities for research/clinic in medical pancreatology and ideally undergo an additional year of training. Fellows who decide during the course of their fellowship that they want to pursue a career in medical pancreatology should consider applying for a 4th year in the subject to not only obtain further training in the field but to also conduct research in the area and become more “marketable” as a person that could start a medical pancreatology program at their future academic or community position. Trainees interested in medical pancreatology should try to focus their time on long-term, clinical management of patients with pancreatic disorders, engaging a multidisciplinary team composed of interventional endoscopists, pancreatic surgeons, transplant surgeons (if total pancreatectomy and islet autotransplantation is available), radiology, addiction medicine (if available), endocrinology, and pathology. The list of places that offer a 4th year in medical pancreatology is increasing every year, and as of the writing of this article there are six programs that have this opportunity, which include:
- Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
- Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Boston
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore
- University of Pittsburgh Medical Center, Pittsburgh, Penn.
The CAPER website is also a great resource for education as well as for identifying potential medical pancreatology programs.
In summary, medical pancreatology is an evolving and rapidly growing career path for gastroenterology fellows interested in providing care to patients with pancreatic disease in close collaboration with multiple other subspecialties, especially therapeutic endoscopy and pancreatic surgery. The field is also ripe for fellows interested in clinical, translational, and basic science research related to pancreatic disorders.
Dr. Nagpal is assistant professor of medicine, director, pancreas clinic, University of Chicago. He had no conflicts to disclose.
References
1. Feldman M et al. “Sleisenger and Fordtran’s Gastrointestinal and Liver Disease,” 11th ed. (Philadelphia: Elsevier, 2021).
2. Nagpal SJS et al. Pancreatology. 2020 Jul;20(5):929-35.
3. Nagpal SJS et al. Pancreatology. 2019 Mar;19(2):290-5.
The risk factors behind infected pancreatic necrosis’ deadly toll
Patients with infected pancreatic necrosis (IPN) are more likely to experience organ failure and mortality, which makes identifying them as quickly as possible especially crucial. A new study aimed to make this task a bit easier by categorizing the main risk factors for IPN in a cohort of patients with severe acute pancreatitis, which included extensive spread of necrotic collections, preceding bacteremia, and preceding open abdomen treatment, as well as postinterventional pancreatitis.
In their study, published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Henrik L. Husu, MD, of the University of Helsinki, and colleagues noted the inherent challenges of rendering a preoperative diagnosis of IPN.
“Fever and increasing inflammation markers may indicate suspicion of IPN, but these are very common in patients with severe acute pancreatitis treated in the ICU,” and more knowledge of specific IPN risk factors is needed to improve clinical decision-making, they said.
Dr. Husu and colleagues identified 163 adults with acute pancreatitis admitted to the ICU at a single center between 2010 and 2018, approximately 68% of whom had alcoholic necrotizing pancreatitis. Pneumonia, bacteremia, and IPN occurred at an average of 4, 16, and 23 days, respectively, after ICU admission.
Forty-seven patients (28.8%) developed IPN within 90 days of ICU admission, all patients had a least one persistent organ failure, and 60% had multiple organ failure within 24 hours of ICU admission.
In a multivariate regression analysis, independent risk factors for IPN included postoperative or postendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) pancreatitis (odds ratio,13.5) and widespread necrotic collections (OR, 5.7 for unilateral paracolic or retromesenteric; OR, 21.8 for bilateral paracolic or unilateral paracolic and retromesenteric). Other risk factors were preceding bacteremia (OR, 4.8) and preceding open abdomen treatment for abdominal compartment syndrome (OR, 3.6).
After 90 days, 29 patients had died, including 7 with IPN and 22 without IPN. In addition, patients with IPN had longer overall hospital stays and ICU stays, higher rates of ICU readmission, and greater use of open necrosectomy, the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design, lack of controls, potential differences in treatment protocols, and the survival bias that prevented direct comparison of mortality in patients with and without IPN, the researchers noted. “This study cannot provide a reliable estimate of the difference in mortality attributable to IPN itself.”
However, the researchers noted that “the strength of the present study was to include only patients with persistent organ failure and admission to ICU in the early disease course,” and results indicate a significant morbid outcome associated with IPN. “In attempting to decrease the rate of IPN, efforts to identify and treat incipient organ failure with subsequent low threshold for admission to ICU becomes essential,” they emphasized.
More data may prompt greater intervention
“IPN portends a poor prognosis, and can be challenging to both diagnose and treat,” Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview. “Identifying risk factors for development of IPN may facilitate earlier therapy that could modify the natural history of this disease.”
Dr. Ketwaroo said he was not surprised by the study findings. “This was a small single-center, retrospective study, where infection could only be ascertained among those who received interventions, and the findings should thus be interpreted within these limitations. Overall, however, I was not surprised. More extensive necrosis and opportunities for infectious seeding of necrosis such as interventions (ERCP) and bacteremia would be expected risk factors. I was surprised by the use of prophylactic antibiotics, as well as the high rate of open necrosectomy, though this should not affect the main findings of risk factors for infection.
“The studies highlight that a significant portion of patients with severe acute pancreatitis with necrosis will develop infection,” said Dr. Ketwaroo. “Being aware of the risk factors for infection, as identified in this study, can add to our clinical judgment in suspecting infection and opting for debridement. Especially with advancements in endoscopic necrosectomy, gastroenterologists may be more inclined to intervene when suspecting IPN. The next steps for research are to validate risk factors in larger, prospective studies.”
The study was supported by governmental competitive funds for medical research, a research grant from the Medical Society of Finland, and a research grant from Perkléns Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Ketwaroo had no financial conflicts to disclose but is a member of the GI & Hepatology News editorial advisory board.
Patients with infected pancreatic necrosis (IPN) are more likely to experience organ failure and mortality, which makes identifying them as quickly as possible especially crucial. A new study aimed to make this task a bit easier by categorizing the main risk factors for IPN in a cohort of patients with severe acute pancreatitis, which included extensive spread of necrotic collections, preceding bacteremia, and preceding open abdomen treatment, as well as postinterventional pancreatitis.
In their study, published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Henrik L. Husu, MD, of the University of Helsinki, and colleagues noted the inherent challenges of rendering a preoperative diagnosis of IPN.
“Fever and increasing inflammation markers may indicate suspicion of IPN, but these are very common in patients with severe acute pancreatitis treated in the ICU,” and more knowledge of specific IPN risk factors is needed to improve clinical decision-making, they said.
Dr. Husu and colleagues identified 163 adults with acute pancreatitis admitted to the ICU at a single center between 2010 and 2018, approximately 68% of whom had alcoholic necrotizing pancreatitis. Pneumonia, bacteremia, and IPN occurred at an average of 4, 16, and 23 days, respectively, after ICU admission.
Forty-seven patients (28.8%) developed IPN within 90 days of ICU admission, all patients had a least one persistent organ failure, and 60% had multiple organ failure within 24 hours of ICU admission.
In a multivariate regression analysis, independent risk factors for IPN included postoperative or postendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) pancreatitis (odds ratio,13.5) and widespread necrotic collections (OR, 5.7 for unilateral paracolic or retromesenteric; OR, 21.8 for bilateral paracolic or unilateral paracolic and retromesenteric). Other risk factors were preceding bacteremia (OR, 4.8) and preceding open abdomen treatment for abdominal compartment syndrome (OR, 3.6).
After 90 days, 29 patients had died, including 7 with IPN and 22 without IPN. In addition, patients with IPN had longer overall hospital stays and ICU stays, higher rates of ICU readmission, and greater use of open necrosectomy, the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design, lack of controls, potential differences in treatment protocols, and the survival bias that prevented direct comparison of mortality in patients with and without IPN, the researchers noted. “This study cannot provide a reliable estimate of the difference in mortality attributable to IPN itself.”
However, the researchers noted that “the strength of the present study was to include only patients with persistent organ failure and admission to ICU in the early disease course,” and results indicate a significant morbid outcome associated with IPN. “In attempting to decrease the rate of IPN, efforts to identify and treat incipient organ failure with subsequent low threshold for admission to ICU becomes essential,” they emphasized.
More data may prompt greater intervention
“IPN portends a poor prognosis, and can be challenging to both diagnose and treat,” Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview. “Identifying risk factors for development of IPN may facilitate earlier therapy that could modify the natural history of this disease.”
Dr. Ketwaroo said he was not surprised by the study findings. “This was a small single-center, retrospective study, where infection could only be ascertained among those who received interventions, and the findings should thus be interpreted within these limitations. Overall, however, I was not surprised. More extensive necrosis and opportunities for infectious seeding of necrosis such as interventions (ERCP) and bacteremia would be expected risk factors. I was surprised by the use of prophylactic antibiotics, as well as the high rate of open necrosectomy, though this should not affect the main findings of risk factors for infection.
“The studies highlight that a significant portion of patients with severe acute pancreatitis with necrosis will develop infection,” said Dr. Ketwaroo. “Being aware of the risk factors for infection, as identified in this study, can add to our clinical judgment in suspecting infection and opting for debridement. Especially with advancements in endoscopic necrosectomy, gastroenterologists may be more inclined to intervene when suspecting IPN. The next steps for research are to validate risk factors in larger, prospective studies.”
The study was supported by governmental competitive funds for medical research, a research grant from the Medical Society of Finland, and a research grant from Perkléns Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Ketwaroo had no financial conflicts to disclose but is a member of the GI & Hepatology News editorial advisory board.
Patients with infected pancreatic necrosis (IPN) are more likely to experience organ failure and mortality, which makes identifying them as quickly as possible especially crucial. A new study aimed to make this task a bit easier by categorizing the main risk factors for IPN in a cohort of patients with severe acute pancreatitis, which included extensive spread of necrotic collections, preceding bacteremia, and preceding open abdomen treatment, as well as postinterventional pancreatitis.
In their study, published in the Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery, Henrik L. Husu, MD, of the University of Helsinki, and colleagues noted the inherent challenges of rendering a preoperative diagnosis of IPN.
“Fever and increasing inflammation markers may indicate suspicion of IPN, but these are very common in patients with severe acute pancreatitis treated in the ICU,” and more knowledge of specific IPN risk factors is needed to improve clinical decision-making, they said.
Dr. Husu and colleagues identified 163 adults with acute pancreatitis admitted to the ICU at a single center between 2010 and 2018, approximately 68% of whom had alcoholic necrotizing pancreatitis. Pneumonia, bacteremia, and IPN occurred at an average of 4, 16, and 23 days, respectively, after ICU admission.
Forty-seven patients (28.8%) developed IPN within 90 days of ICU admission, all patients had a least one persistent organ failure, and 60% had multiple organ failure within 24 hours of ICU admission.
In a multivariate regression analysis, independent risk factors for IPN included postoperative or postendoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) pancreatitis (odds ratio,13.5) and widespread necrotic collections (OR, 5.7 for unilateral paracolic or retromesenteric; OR, 21.8 for bilateral paracolic or unilateral paracolic and retromesenteric). Other risk factors were preceding bacteremia (OR, 4.8) and preceding open abdomen treatment for abdominal compartment syndrome (OR, 3.6).
After 90 days, 29 patients had died, including 7 with IPN and 22 without IPN. In addition, patients with IPN had longer overall hospital stays and ICU stays, higher rates of ICU readmission, and greater use of open necrosectomy, the researchers noted.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the retrospective design, lack of controls, potential differences in treatment protocols, and the survival bias that prevented direct comparison of mortality in patients with and without IPN, the researchers noted. “This study cannot provide a reliable estimate of the difference in mortality attributable to IPN itself.”
However, the researchers noted that “the strength of the present study was to include only patients with persistent organ failure and admission to ICU in the early disease course,” and results indicate a significant morbid outcome associated with IPN. “In attempting to decrease the rate of IPN, efforts to identify and treat incipient organ failure with subsequent low threshold for admission to ICU becomes essential,” they emphasized.
More data may prompt greater intervention
“IPN portends a poor prognosis, and can be challenging to both diagnose and treat,” Gyanprakash A. Ketwaroo, MD, of Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, said in an interview. “Identifying risk factors for development of IPN may facilitate earlier therapy that could modify the natural history of this disease.”
Dr. Ketwaroo said he was not surprised by the study findings. “This was a small single-center, retrospective study, where infection could only be ascertained among those who received interventions, and the findings should thus be interpreted within these limitations. Overall, however, I was not surprised. More extensive necrosis and opportunities for infectious seeding of necrosis such as interventions (ERCP) and bacteremia would be expected risk factors. I was surprised by the use of prophylactic antibiotics, as well as the high rate of open necrosectomy, though this should not affect the main findings of risk factors for infection.
“The studies highlight that a significant portion of patients with severe acute pancreatitis with necrosis will develop infection,” said Dr. Ketwaroo. “Being aware of the risk factors for infection, as identified in this study, can add to our clinical judgment in suspecting infection and opting for debridement. Especially with advancements in endoscopic necrosectomy, gastroenterologists may be more inclined to intervene when suspecting IPN. The next steps for research are to validate risk factors in larger, prospective studies.”
The study was supported by governmental competitive funds for medical research, a research grant from the Medical Society of Finland, and a research grant from Perkléns Foundation. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Ketwaroo had no financial conflicts to disclose but is a member of the GI & Hepatology News editorial advisory board.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF GASTROINTESTINAL SURGERY
AGA Shark Tank 2021: A simple design survives
William of Ockham would have been proud because, at this year’s American Gastroenterological Association’s Shark Tank pitch competition, one product clearly demonstrated Ockham’s razor – that sometimes the simplest solution is best – and came away as the winner at the 2021 AGA Tech Summit sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
Out of five innovative products, ranging from an educational app to a high-tech anorectal sensor, all aimed at improving outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal disorders, the winner was ... drumroll please ...
A needle.
That’s it. A needle. But not like any other needle.
Winner: Toufic Kachaamy, MD, FASGE, AGAF – An EUS-guided access needle
This EUS-guided access needle, invented by Dr. Kachaamy, enterprise clinical leader at Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Phoenix, is a simple device that overcomes a longstanding challenge presented by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): biliary access.
Many “ERCPs are considered difficult, and sometimes fail, depending on the center and the endoscopist,” Dr. Kachaamy said during a virtual presentation. “Most failures are due to failed initial access to the bile duct.”
Indeed, one study cited a failure rate in ductal cannulation of 5%-15% even among experienced hands.
Failure can have several consequences, Dr. Kachaamy noted, including increased complications, higher cost, delayed care, longer hospitalization, and greater likelihood of patient transfer.
He went on to explain why biliary access can be so challenging and how this EUS-guided access needle helps address these issues.
“[The] two main limitations [during endoscopic ultrasound–guided biliary access] are directing the wire into the narrowed areas and the wire shearing as we are manipulating the wire to get it to where we want it,” Dr. Kachaamy said. “[This EUS-guided access needle] is a 19-22 gauge, rotatable needle with a smooth, side exit for the wire to allow wire manipulation and direction without shearing.”
Dr. Kachaamy highlighted the simple design, which will keep the production cost below $300 per unit, and suggested that failed ERCPs are just the first potential indication of many. Future uses may include gallbladder access, peri-GI collection, gastrojejunostomy, and others.
In an interview, Dr. Kachaamy reacted to the win, which follows 2 years of collaborative development with Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
“For people who are innovators, there’s nothing that feels more rewarding than their ideas being recognized as adding something to the field and potentially helping people and patients,” Dr. Kachaamy said. “So [this is] very, very, very exciting. Very rewarding. Pride would probably be the best way I’d describe it.”
Dr. Kachaamy anticipates that this EUS-guided access needle will be commercially available within 1-2 years, pending regulatory approval. In the meantime, he and his colleagues are seeking a strategic partner.
A shark speaks
V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, AGAF, immediate past chair of the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology and director of endoscopy at UCLA Health System, moderated the Shark Tank session, calling it “the highlight” of the AGA Tech Summit.
Dr. Muthusamy and four other “sharks,” including a gastroenterologist, venture capitalist, regulatory device reviewer, and entrepreneur, scored the pitches using three equally weighted categories: the quality of the pitch, the level of innovation and impact on the field, and the quality of the business plan and overall feasibility.
“We saw a full spectrum [of innovations],” Dr. Muthusamy said. “I think it was an enjoyable session.”
Behind closed doors, the sharks narrowed the field to two top contenders. Ultimately, however, there could be only one winner: Dr. Kachaamy. Their decision aligned with a “Fan Favorite” audience poll.
“A lot of [Dr. Kachaamy’s win] had to do with the potential applications and commonality of the problem,” Dr. Muthusamy said in an interview. He highlighted how the EUS-guided access needle allows for an immediate response to ERCP failure without the need for a second procedure.
Dr. Muthusamy also noted that several product designs previously failed to achieve what the EUS-guided access needle has the potential to do.
“I think the feeling was that this seemed to be a way that may address some of the limitations and challenges that we’ve had with earlier [attempts at solving this problem],” Dr. Muthusamy said.
For innovators who didn’t make the cut this year, or those with products still in development, Dr. Muthusamy suggested applying next year.
“We encourage our colleagues and members of the AGA to continue to apply to this program,” Dr. Muthusamy said.
Other fish in the sea
Four other innovators entered the AGA Shark Tank this year. Here are snippets of their pitches:
Hans Gregersen, MD, PhD, MPH – Fecobionics
“Fecobionics is a simulated electronic stool with the consistency and shape of normal stool,” Dr. Gregersen said.
The balloon device, which contains multiple sensors, provides “real-time, quantitative, and mechanistic insights by simulating defecation.”
“It ... is inserted into the rectum,” Dr. Gregersen said. “It measures multiple pressures; it has gyroscopes that measure orientation; we can compute the bending of the device; and we can calculate the shape of the device.”
According to Dr. Gregersen, Fecobionics has “diagnostic potential for patients with fecal incontinence and for subtyping patients with constipation.” He highlighted fewer false-positives than current technology, alongside greater efficiency and lower cost.
Dr. Gregersen is a research professor at California Medical Innovations Institute, San Diego.
Mary J. Pattison, RN – Trans-Abdominal Gastric Surgical System (TAGSS)
TAGSS is a trans-abdominal gastric access device that “represents a novel and exciting means to address multiple gastrointestinal conditions that are without a standardized approach,” Ms. Pattison said. “Placed as simply as a [percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube], TAGSS offers disruptive technology to address [gastroesophageal reflux disease], fundoplication, achalasia, gastroparesis, gastric tumors, and even obesity in a safe, efficient, and cost effective manner. TAGSS offers the first true hybrid approach for endoscopic/laparoscopic collaboration.”
Ms. Pattison is a nurse clinician and endoscopy assistant at WestGlen GI Consultants, Weston, Mo.
Pankaj Rajvanshi, MD, FAASLD – Healthswim App
“At this time, most patient education is provided by Dr. Google,” Dr. Rajvanshi said, “and we want to change that. We have built a platform which allows you, the physician, to create custom, curated, credible content that can be delivered seamlessly to your patients on an ongoing basis.”
Through the Healthswim app, patients subscribe to their providers, allowing access physician-approved content. Subscribers also receive provider updates through their social media feeds.
Dr. Rajvanshi is a gastroenterologist at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle.
Ali S. Karakurum, MD, FACP, FACG – A Device for Removal of Esophageal Food Impactions
“I would like to propose a device which consists of a clear overtube, a collapsible plastic cylindrical basket secured to the distal end of the overtube ... and a snare wire attached to the distal end of the basket which is controlled by the snare handle externally,” Dr. Karakurum said. “The device is ... gradually advanced over the scope for the basket to encompass the food bolus under direct visualization. Once the food bolus is within the basket, the wire loop at the end of the basket is closed via the external handle, securing the food bolus in the basket for safe removal.”
Dr. Karakurum is a gastroenterologist at Advanced Gastroenterology & Endoscopy, Port Jefferson, N.Y.
This article was updated 5/14/21.
William of Ockham would have been proud because, at this year’s American Gastroenterological Association’s Shark Tank pitch competition, one product clearly demonstrated Ockham’s razor – that sometimes the simplest solution is best – and came away as the winner at the 2021 AGA Tech Summit sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
Out of five innovative products, ranging from an educational app to a high-tech anorectal sensor, all aimed at improving outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal disorders, the winner was ... drumroll please ...
A needle.
That’s it. A needle. But not like any other needle.
Winner: Toufic Kachaamy, MD, FASGE, AGAF – An EUS-guided access needle
This EUS-guided access needle, invented by Dr. Kachaamy, enterprise clinical leader at Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Phoenix, is a simple device that overcomes a longstanding challenge presented by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): biliary access.
Many “ERCPs are considered difficult, and sometimes fail, depending on the center and the endoscopist,” Dr. Kachaamy said during a virtual presentation. “Most failures are due to failed initial access to the bile duct.”
Indeed, one study cited a failure rate in ductal cannulation of 5%-15% even among experienced hands.
Failure can have several consequences, Dr. Kachaamy noted, including increased complications, higher cost, delayed care, longer hospitalization, and greater likelihood of patient transfer.
He went on to explain why biliary access can be so challenging and how this EUS-guided access needle helps address these issues.
“[The] two main limitations [during endoscopic ultrasound–guided biliary access] are directing the wire into the narrowed areas and the wire shearing as we are manipulating the wire to get it to where we want it,” Dr. Kachaamy said. “[This EUS-guided access needle] is a 19-22 gauge, rotatable needle with a smooth, side exit for the wire to allow wire manipulation and direction without shearing.”
Dr. Kachaamy highlighted the simple design, which will keep the production cost below $300 per unit, and suggested that failed ERCPs are just the first potential indication of many. Future uses may include gallbladder access, peri-GI collection, gastrojejunostomy, and others.
In an interview, Dr. Kachaamy reacted to the win, which follows 2 years of collaborative development with Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
“For people who are innovators, there’s nothing that feels more rewarding than their ideas being recognized as adding something to the field and potentially helping people and patients,” Dr. Kachaamy said. “So [this is] very, very, very exciting. Very rewarding. Pride would probably be the best way I’d describe it.”
Dr. Kachaamy anticipates that this EUS-guided access needle will be commercially available within 1-2 years, pending regulatory approval. In the meantime, he and his colleagues are seeking a strategic partner.
A shark speaks
V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, AGAF, immediate past chair of the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology and director of endoscopy at UCLA Health System, moderated the Shark Tank session, calling it “the highlight” of the AGA Tech Summit.
Dr. Muthusamy and four other “sharks,” including a gastroenterologist, venture capitalist, regulatory device reviewer, and entrepreneur, scored the pitches using three equally weighted categories: the quality of the pitch, the level of innovation and impact on the field, and the quality of the business plan and overall feasibility.
“We saw a full spectrum [of innovations],” Dr. Muthusamy said. “I think it was an enjoyable session.”
Behind closed doors, the sharks narrowed the field to two top contenders. Ultimately, however, there could be only one winner: Dr. Kachaamy. Their decision aligned with a “Fan Favorite” audience poll.
“A lot of [Dr. Kachaamy’s win] had to do with the potential applications and commonality of the problem,” Dr. Muthusamy said in an interview. He highlighted how the EUS-guided access needle allows for an immediate response to ERCP failure without the need for a second procedure.
Dr. Muthusamy also noted that several product designs previously failed to achieve what the EUS-guided access needle has the potential to do.
“I think the feeling was that this seemed to be a way that may address some of the limitations and challenges that we’ve had with earlier [attempts at solving this problem],” Dr. Muthusamy said.
For innovators who didn’t make the cut this year, or those with products still in development, Dr. Muthusamy suggested applying next year.
“We encourage our colleagues and members of the AGA to continue to apply to this program,” Dr. Muthusamy said.
Other fish in the sea
Four other innovators entered the AGA Shark Tank this year. Here are snippets of their pitches:
Hans Gregersen, MD, PhD, MPH – Fecobionics
“Fecobionics is a simulated electronic stool with the consistency and shape of normal stool,” Dr. Gregersen said.
The balloon device, which contains multiple sensors, provides “real-time, quantitative, and mechanistic insights by simulating defecation.”
“It ... is inserted into the rectum,” Dr. Gregersen said. “It measures multiple pressures; it has gyroscopes that measure orientation; we can compute the bending of the device; and we can calculate the shape of the device.”
According to Dr. Gregersen, Fecobionics has “diagnostic potential for patients with fecal incontinence and for subtyping patients with constipation.” He highlighted fewer false-positives than current technology, alongside greater efficiency and lower cost.
Dr. Gregersen is a research professor at California Medical Innovations Institute, San Diego.
Mary J. Pattison, RN – Trans-Abdominal Gastric Surgical System (TAGSS)
TAGSS is a trans-abdominal gastric access device that “represents a novel and exciting means to address multiple gastrointestinal conditions that are without a standardized approach,” Ms. Pattison said. “Placed as simply as a [percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube], TAGSS offers disruptive technology to address [gastroesophageal reflux disease], fundoplication, achalasia, gastroparesis, gastric tumors, and even obesity in a safe, efficient, and cost effective manner. TAGSS offers the first true hybrid approach for endoscopic/laparoscopic collaboration.”
Ms. Pattison is a nurse clinician and endoscopy assistant at WestGlen GI Consultants, Weston, Mo.
Pankaj Rajvanshi, MD, FAASLD – Healthswim App
“At this time, most patient education is provided by Dr. Google,” Dr. Rajvanshi said, “and we want to change that. We have built a platform which allows you, the physician, to create custom, curated, credible content that can be delivered seamlessly to your patients on an ongoing basis.”
Through the Healthswim app, patients subscribe to their providers, allowing access physician-approved content. Subscribers also receive provider updates through their social media feeds.
Dr. Rajvanshi is a gastroenterologist at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle.
Ali S. Karakurum, MD, FACP, FACG – A Device for Removal of Esophageal Food Impactions
“I would like to propose a device which consists of a clear overtube, a collapsible plastic cylindrical basket secured to the distal end of the overtube ... and a snare wire attached to the distal end of the basket which is controlled by the snare handle externally,” Dr. Karakurum said. “The device is ... gradually advanced over the scope for the basket to encompass the food bolus under direct visualization. Once the food bolus is within the basket, the wire loop at the end of the basket is closed via the external handle, securing the food bolus in the basket for safe removal.”
Dr. Karakurum is a gastroenterologist at Advanced Gastroenterology & Endoscopy, Port Jefferson, N.Y.
This article was updated 5/14/21.
William of Ockham would have been proud because, at this year’s American Gastroenterological Association’s Shark Tank pitch competition, one product clearly demonstrated Ockham’s razor – that sometimes the simplest solution is best – and came away as the winner at the 2021 AGA Tech Summit sponsored by the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology.
Out of five innovative products, ranging from an educational app to a high-tech anorectal sensor, all aimed at improving outcomes in patients with gastrointestinal disorders, the winner was ... drumroll please ...
A needle.
That’s it. A needle. But not like any other needle.
Winner: Toufic Kachaamy, MD, FASGE, AGAF – An EUS-guided access needle
This EUS-guided access needle, invented by Dr. Kachaamy, enterprise clinical leader at Cancer Treatment Centers of America, Phoenix, is a simple device that overcomes a longstanding challenge presented by endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP): biliary access.
Many “ERCPs are considered difficult, and sometimes fail, depending on the center and the endoscopist,” Dr. Kachaamy said during a virtual presentation. “Most failures are due to failed initial access to the bile duct.”
Indeed, one study cited a failure rate in ductal cannulation of 5%-15% even among experienced hands.
Failure can have several consequences, Dr. Kachaamy noted, including increased complications, higher cost, delayed care, longer hospitalization, and greater likelihood of patient transfer.
He went on to explain why biliary access can be so challenging and how this EUS-guided access needle helps address these issues.
“[The] two main limitations [during endoscopic ultrasound–guided biliary access] are directing the wire into the narrowed areas and the wire shearing as we are manipulating the wire to get it to where we want it,” Dr. Kachaamy said. “[This EUS-guided access needle] is a 19-22 gauge, rotatable needle with a smooth, side exit for the wire to allow wire manipulation and direction without shearing.”
Dr. Kachaamy highlighted the simple design, which will keep the production cost below $300 per unit, and suggested that failed ERCPs are just the first potential indication of many. Future uses may include gallbladder access, peri-GI collection, gastrojejunostomy, and others.
In an interview, Dr. Kachaamy reacted to the win, which follows 2 years of collaborative development with Cancer Treatment Centers of America.
“For people who are innovators, there’s nothing that feels more rewarding than their ideas being recognized as adding something to the field and potentially helping people and patients,” Dr. Kachaamy said. “So [this is] very, very, very exciting. Very rewarding. Pride would probably be the best way I’d describe it.”
Dr. Kachaamy anticipates that this EUS-guided access needle will be commercially available within 1-2 years, pending regulatory approval. In the meantime, he and his colleagues are seeking a strategic partner.
A shark speaks
V. Raman Muthusamy, MD, AGAF, immediate past chair of the AGA Center for GI Innovation and Technology and director of endoscopy at UCLA Health System, moderated the Shark Tank session, calling it “the highlight” of the AGA Tech Summit.
Dr. Muthusamy and four other “sharks,” including a gastroenterologist, venture capitalist, regulatory device reviewer, and entrepreneur, scored the pitches using three equally weighted categories: the quality of the pitch, the level of innovation and impact on the field, and the quality of the business plan and overall feasibility.
“We saw a full spectrum [of innovations],” Dr. Muthusamy said. “I think it was an enjoyable session.”
Behind closed doors, the sharks narrowed the field to two top contenders. Ultimately, however, there could be only one winner: Dr. Kachaamy. Their decision aligned with a “Fan Favorite” audience poll.
“A lot of [Dr. Kachaamy’s win] had to do with the potential applications and commonality of the problem,” Dr. Muthusamy said in an interview. He highlighted how the EUS-guided access needle allows for an immediate response to ERCP failure without the need for a second procedure.
Dr. Muthusamy also noted that several product designs previously failed to achieve what the EUS-guided access needle has the potential to do.
“I think the feeling was that this seemed to be a way that may address some of the limitations and challenges that we’ve had with earlier [attempts at solving this problem],” Dr. Muthusamy said.
For innovators who didn’t make the cut this year, or those with products still in development, Dr. Muthusamy suggested applying next year.
“We encourage our colleagues and members of the AGA to continue to apply to this program,” Dr. Muthusamy said.
Other fish in the sea
Four other innovators entered the AGA Shark Tank this year. Here are snippets of their pitches:
Hans Gregersen, MD, PhD, MPH – Fecobionics
“Fecobionics is a simulated electronic stool with the consistency and shape of normal stool,” Dr. Gregersen said.
The balloon device, which contains multiple sensors, provides “real-time, quantitative, and mechanistic insights by simulating defecation.”
“It ... is inserted into the rectum,” Dr. Gregersen said. “It measures multiple pressures; it has gyroscopes that measure orientation; we can compute the bending of the device; and we can calculate the shape of the device.”
According to Dr. Gregersen, Fecobionics has “diagnostic potential for patients with fecal incontinence and for subtyping patients with constipation.” He highlighted fewer false-positives than current technology, alongside greater efficiency and lower cost.
Dr. Gregersen is a research professor at California Medical Innovations Institute, San Diego.
Mary J. Pattison, RN – Trans-Abdominal Gastric Surgical System (TAGSS)
TAGSS is a trans-abdominal gastric access device that “represents a novel and exciting means to address multiple gastrointestinal conditions that are without a standardized approach,” Ms. Pattison said. “Placed as simply as a [percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy tube], TAGSS offers disruptive technology to address [gastroesophageal reflux disease], fundoplication, achalasia, gastroparesis, gastric tumors, and even obesity in a safe, efficient, and cost effective manner. TAGSS offers the first true hybrid approach for endoscopic/laparoscopic collaboration.”
Ms. Pattison is a nurse clinician and endoscopy assistant at WestGlen GI Consultants, Weston, Mo.
Pankaj Rajvanshi, MD, FAASLD – Healthswim App
“At this time, most patient education is provided by Dr. Google,” Dr. Rajvanshi said, “and we want to change that. We have built a platform which allows you, the physician, to create custom, curated, credible content that can be delivered seamlessly to your patients on an ongoing basis.”
Through the Healthswim app, patients subscribe to their providers, allowing access physician-approved content. Subscribers also receive provider updates through their social media feeds.
Dr. Rajvanshi is a gastroenterologist at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle.
Ali S. Karakurum, MD, FACP, FACG – A Device for Removal of Esophageal Food Impactions
“I would like to propose a device which consists of a clear overtube, a collapsible plastic cylindrical basket secured to the distal end of the overtube ... and a snare wire attached to the distal end of the basket which is controlled by the snare handle externally,” Dr. Karakurum said. “The device is ... gradually advanced over the scope for the basket to encompass the food bolus under direct visualization. Once the food bolus is within the basket, the wire loop at the end of the basket is closed via the external handle, securing the food bolus in the basket for safe removal.”
Dr. Karakurum is a gastroenterologist at Advanced Gastroenterology & Endoscopy, Port Jefferson, N.Y.
This article was updated 5/14/21.
FROM THE 2021 AGA TECH SUMMIT MEETING
Mitochondrial DNA variant increases gallstone risk
A mitochondrial DNA variant may increase the risk of gallstone disease more than fourfold, according to investigators.
Mitochondrial DNA 827A>G disrupts mitochondrial function and leads to abnormal cholesterol transport, which increases gallstone development, reported Dayan Sun, of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
The investigators noted that the findings add support to a genetic role in gallstone development, which could allow for identification of at-risk individuals and implementation of preventive measures.
“The etiology of gallstone disease is multifactorial; age, sex, pregnancy, diet (macronutrients, alcohol, and coffee), and other factors are involved,” the investigators wrote in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Moreover, the significant familial predisposition and ethnic differences in prevalence of this disease indicate the potential influences of genetic factors.”
In 2002, Nakeeb and colleagues reported that at least 30% of gallstone disease cases stemmed from genetic factors. And genetics may play an even greater role in certain populations, such as Native Americans, among whom more than 70% of women have gallstone disease, based on a study by Everhart and colleagues.
According to Ms. Sun and colleagues, a variety of genetic drivers of gallstone disease have been identified, such as ABCG8, identified as the most common genetic risk factor by at least one study, along with a list of other rare mutations, such as one affecting CFTR that leads to altered bile composition.
Based on previous research that linked mitochondrial DNA variants with metabolic defects and, more specifically, aberrations in lipid metabolism, as well as an observed “maternal bias in the maternal transmission of gallstone disease” that suggest mitochondrial influence, the investigators looked for patterns specifically in mitochondrial DNA variants among patients with gallstones.
The study enrolled 104 probands with confirmed gallstone disease and 300 unrelated controls. After collecting DNA samples from all participants, the investigators sequenced mitochondrial DNA HVS1 regions. A comparison of haplogroups showed that B4b’d’e’j was more common among patients with gallstone disease than among controls (odds ratio, 4.428; P = .00012), and further analysis pinpointed 827A>G, a variant in 12S ribosomal RNA.
“During the evolutionary history of modern humans, haplogroup B4 might have originated in East Asia approximately 40,000 years ago,” the investigators wrote, noting that B2, a subhaplogroup of B4, “was a founder haplogroup and expanded in the Americas after the Last Glacial Maximum (approximately 20,000 years ago).”
According to the investigators, this may explain why Native Americans have a higher prevalence of gallstones than East Asians (14%-35% vs. 3%-12%) because they are more often carriers of B4 (14%-44% vs. 2%-8%).
The investigators sought to characterize the impact that the 827A>G variant has on mitochondrial function and found effects ranging from lower respiratory chain complex activity, diminished mitochondrial function, activated mitochondrial protein quality control and retrograde signaling pathways, abnormal lipid metabolism, and abnormal cholesterol transport processes.
For example, the investigators investigated respiratory chain complex activity by creating two sister branch haplogroup cell models, including six cybrids for 827A and six more for 827G, which is how they detected the lower activity. Another step the investigators took was corroborating this finding by detecting OXPHOS function in the 827A and 827G cybrids to determine mitochondrial function.
“In summary, our study demonstrates a potential link between mitochondrial DNA 827A>G and gallstone disease,” the investigators wrote. “Our findings provide a significant biological basis for the clinical diagnosis and prevention of gallstone disease in the future.”
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the 111 Project, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, the Scientific and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, and the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
Cholesterol gallstone disease results from imbalances in cholesterol metabolism. Other than the well-known lifestyle risk factors, there is also a strong genetic predisposition to gallstone formation. This study by Sun and colleagues examined the possible association between mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variants and cholesterol gallstone development because of the importance of the mitochondria in cellular metabolism and the increased maternal transmission of gallstone disease.
This study highlighted gallstone disease as a multifactorial condition that results from complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Interestingly, the allele frequency of the 827A>G mtDNA variant was noted to be higher in Native Americans, which may partially explain the high prevalence of gallstones in this population. Further studies are needed to identify additional genetic risk factors in ethnic groups that also have a significant burden of cholelithiasis.
Xiao Zhao, MD, is an assistant professor of medicine of division of digestive diseases in the department of medicine at Columbia University, New York. She reported having no conflicts of interest.
Cholesterol gallstone disease results from imbalances in cholesterol metabolism. Other than the well-known lifestyle risk factors, there is also a strong genetic predisposition to gallstone formation. This study by Sun and colleagues examined the possible association between mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variants and cholesterol gallstone development because of the importance of the mitochondria in cellular metabolism and the increased maternal transmission of gallstone disease.
This study highlighted gallstone disease as a multifactorial condition that results from complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Interestingly, the allele frequency of the 827A>G mtDNA variant was noted to be higher in Native Americans, which may partially explain the high prevalence of gallstones in this population. Further studies are needed to identify additional genetic risk factors in ethnic groups that also have a significant burden of cholelithiasis.
Xiao Zhao, MD, is an assistant professor of medicine of division of digestive diseases in the department of medicine at Columbia University, New York. She reported having no conflicts of interest.
Cholesterol gallstone disease results from imbalances in cholesterol metabolism. Other than the well-known lifestyle risk factors, there is also a strong genetic predisposition to gallstone formation. This study by Sun and colleagues examined the possible association between mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) variants and cholesterol gallstone development because of the importance of the mitochondria in cellular metabolism and the increased maternal transmission of gallstone disease.
This study highlighted gallstone disease as a multifactorial condition that results from complex interaction between genetic and environmental factors. Interestingly, the allele frequency of the 827A>G mtDNA variant was noted to be higher in Native Americans, which may partially explain the high prevalence of gallstones in this population. Further studies are needed to identify additional genetic risk factors in ethnic groups that also have a significant burden of cholelithiasis.
Xiao Zhao, MD, is an assistant professor of medicine of division of digestive diseases in the department of medicine at Columbia University, New York. She reported having no conflicts of interest.
A mitochondrial DNA variant may increase the risk of gallstone disease more than fourfold, according to investigators.
Mitochondrial DNA 827A>G disrupts mitochondrial function and leads to abnormal cholesterol transport, which increases gallstone development, reported Dayan Sun, of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
The investigators noted that the findings add support to a genetic role in gallstone development, which could allow for identification of at-risk individuals and implementation of preventive measures.
“The etiology of gallstone disease is multifactorial; age, sex, pregnancy, diet (macronutrients, alcohol, and coffee), and other factors are involved,” the investigators wrote in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Moreover, the significant familial predisposition and ethnic differences in prevalence of this disease indicate the potential influences of genetic factors.”
In 2002, Nakeeb and colleagues reported that at least 30% of gallstone disease cases stemmed from genetic factors. And genetics may play an even greater role in certain populations, such as Native Americans, among whom more than 70% of women have gallstone disease, based on a study by Everhart and colleagues.
According to Ms. Sun and colleagues, a variety of genetic drivers of gallstone disease have been identified, such as ABCG8, identified as the most common genetic risk factor by at least one study, along with a list of other rare mutations, such as one affecting CFTR that leads to altered bile composition.
Based on previous research that linked mitochondrial DNA variants with metabolic defects and, more specifically, aberrations in lipid metabolism, as well as an observed “maternal bias in the maternal transmission of gallstone disease” that suggest mitochondrial influence, the investigators looked for patterns specifically in mitochondrial DNA variants among patients with gallstones.
The study enrolled 104 probands with confirmed gallstone disease and 300 unrelated controls. After collecting DNA samples from all participants, the investigators sequenced mitochondrial DNA HVS1 regions. A comparison of haplogroups showed that B4b’d’e’j was more common among patients with gallstone disease than among controls (odds ratio, 4.428; P = .00012), and further analysis pinpointed 827A>G, a variant in 12S ribosomal RNA.
“During the evolutionary history of modern humans, haplogroup B4 might have originated in East Asia approximately 40,000 years ago,” the investigators wrote, noting that B2, a subhaplogroup of B4, “was a founder haplogroup and expanded in the Americas after the Last Glacial Maximum (approximately 20,000 years ago).”
According to the investigators, this may explain why Native Americans have a higher prevalence of gallstones than East Asians (14%-35% vs. 3%-12%) because they are more often carriers of B4 (14%-44% vs. 2%-8%).
The investigators sought to characterize the impact that the 827A>G variant has on mitochondrial function and found effects ranging from lower respiratory chain complex activity, diminished mitochondrial function, activated mitochondrial protein quality control and retrograde signaling pathways, abnormal lipid metabolism, and abnormal cholesterol transport processes.
For example, the investigators investigated respiratory chain complex activity by creating two sister branch haplogroup cell models, including six cybrids for 827A and six more for 827G, which is how they detected the lower activity. Another step the investigators took was corroborating this finding by detecting OXPHOS function in the 827A and 827G cybrids to determine mitochondrial function.
“In summary, our study demonstrates a potential link between mitochondrial DNA 827A>G and gallstone disease,” the investigators wrote. “Our findings provide a significant biological basis for the clinical diagnosis and prevention of gallstone disease in the future.”
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the 111 Project, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, the Scientific and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, and the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
A mitochondrial DNA variant may increase the risk of gallstone disease more than fourfold, according to investigators.
Mitochondrial DNA 827A>G disrupts mitochondrial function and leads to abnormal cholesterol transport, which increases gallstone development, reported Dayan Sun, of Fudan University, Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
The investigators noted that the findings add support to a genetic role in gallstone development, which could allow for identification of at-risk individuals and implementation of preventive measures.
“The etiology of gallstone disease is multifactorial; age, sex, pregnancy, diet (macronutrients, alcohol, and coffee), and other factors are involved,” the investigators wrote in Cellular and Molecular Gastroenterology and Hepatology. “Moreover, the significant familial predisposition and ethnic differences in prevalence of this disease indicate the potential influences of genetic factors.”
In 2002, Nakeeb and colleagues reported that at least 30% of gallstone disease cases stemmed from genetic factors. And genetics may play an even greater role in certain populations, such as Native Americans, among whom more than 70% of women have gallstone disease, based on a study by Everhart and colleagues.
According to Ms. Sun and colleagues, a variety of genetic drivers of gallstone disease have been identified, such as ABCG8, identified as the most common genetic risk factor by at least one study, along with a list of other rare mutations, such as one affecting CFTR that leads to altered bile composition.
Based on previous research that linked mitochondrial DNA variants with metabolic defects and, more specifically, aberrations in lipid metabolism, as well as an observed “maternal bias in the maternal transmission of gallstone disease” that suggest mitochondrial influence, the investigators looked for patterns specifically in mitochondrial DNA variants among patients with gallstones.
The study enrolled 104 probands with confirmed gallstone disease and 300 unrelated controls. After collecting DNA samples from all participants, the investigators sequenced mitochondrial DNA HVS1 regions. A comparison of haplogroups showed that B4b’d’e’j was more common among patients with gallstone disease than among controls (odds ratio, 4.428; P = .00012), and further analysis pinpointed 827A>G, a variant in 12S ribosomal RNA.
“During the evolutionary history of modern humans, haplogroup B4 might have originated in East Asia approximately 40,000 years ago,” the investigators wrote, noting that B2, a subhaplogroup of B4, “was a founder haplogroup and expanded in the Americas after the Last Glacial Maximum (approximately 20,000 years ago).”
According to the investigators, this may explain why Native Americans have a higher prevalence of gallstones than East Asians (14%-35% vs. 3%-12%) because they are more often carriers of B4 (14%-44% vs. 2%-8%).
The investigators sought to characterize the impact that the 827A>G variant has on mitochondrial function and found effects ranging from lower respiratory chain complex activity, diminished mitochondrial function, activated mitochondrial protein quality control and retrograde signaling pathways, abnormal lipid metabolism, and abnormal cholesterol transport processes.
For example, the investigators investigated respiratory chain complex activity by creating two sister branch haplogroup cell models, including six cybrids for 827A and six more for 827G, which is how they detected the lower activity. Another step the investigators took was corroborating this finding by detecting OXPHOS function in the 827A and 827G cybrids to determine mitochondrial function.
“In summary, our study demonstrates a potential link between mitochondrial DNA 827A>G and gallstone disease,” the investigators wrote. “Our findings provide a significant biological basis for the clinical diagnosis and prevention of gallstone disease in the future.”
The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the 111 Project, the Shanghai Municipal Science and Technology Major Project, the Scientific and Technology Committee of Shanghai Municipality, and the CAMS Innovation Fund for Medical Sciences. The investigators reported no conflicts of interest.
FROM CELLULAR AND MOLECULAR GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Automated software accurately generates ERCP quality reports
Modified endoscopy documentation software can automatically generate endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) quality metrics, based on a trial at two referral centers.
Providers were prompted during procedures, and inputting any missed data took providers less than 30 additional seconds per patient. The approach led to highly accurate quality reports, lead author Gregory A. Coté, MD, MS, of the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The investigators suggested that these findings may lead to the kind of quality reports already used for colonoscopy, which are easier to produce. Such reports are important, they wrote, as the U.S. health care system shifts to value-based reimbursement models, which in turn puts greater scrutiny on the quality of endoscopic procedures. However, doing so with ERCP isn’t entirely straightforward.
“Measuring adherence to ERCP quality indicators is especially challenging given: variance in indications, intraprocedural maneuvers, potential outcomes of a complex procedure, and variability in physician report documentation,” Dr. Coté and colleagues wrote. “In order to operationalize robust tracking of clinically relevant adherence to ERCP quality indicators in clinical practice – that is, to provide real-time feedback to providers, health systems, payors, and patients – an automated system of measurement must be developed.”
The quality indicators used in the study were largely drawn from an American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy/American College of Gastroenterology task force document, with exclusion of those that were subjective or required systematic follow-up. The investigators modified existing endoscopy documentation software at two referral centers to include mandatory, structured data fields, principally with inclusion of quality improvements deemed high priority by the society consensus document, study authors, or both. For instance, providers were obligated to select a specific indication instead of various, synonymous terms (for example, “biliary stricture” vs. “common bile duct stricture”). Examples of quality indicators included successful cannulation of the desired duct, successful retrieval of stone less than 10 mm, or successful placement of a bile duct stent when indicated. Endoscopists were also required to note the presence of postoperative foregut anatomy or presence of existing sphincterotomy, variables which serve to stratefy the quality indicator outcome for degree of difficulty and allow appropriate comparisons of data. In addition, the study authors included inquiries about use of rectal indomethacin, use of prophylactic pancreatic duct stent, and documentation of need for repeat ERCP, follow-up x-ray, or both.
After 9 months, the system recorded 1,376 ERCP procedures conducted by eight providers, with a median annualized volume of 237 procedures (range, 37-336). Almost one-third (29%) of the patients had not had prior sphincterotomy.
Automated reporting of ERCP was compared with manual record review, which confirmed high (98%-100%) accuracy. This high level of accuracy “obviates the need for manual adjudication of medical records,” the investigators wrote.
They used data from one provider to create a template report card, and while exact comparisons across providers and institutions were not published, an example report card that was published with the study showed how such comparisons could be generated in the real world.
“The tool presented in this study allows for an objective assessment of ERCP performance which can provide explicit feedback to providers and allow transparent assessment of quality outcomes; it has the potential to improve the quality of ERCP akin to what has been demonstrated using colonoscopy report cards,” the investigators wrote. “Importantly, this can be achieved with minimal alteration to providers’ routine procedure documentation.”
Dr. Coté and colleagues also noted that the software modifications “can be implemented in other endoscopy units using the same or similar software.”
Taking the project to the next level would require widespread collaboration, according to the investigators.
“A key next step is to operationalize the transfer of data across multiple institutions, allowing for the creation of interim, standard-quality indicator reports that could be disseminated to providers, health systems, and payors,” they wrote. “If applied to a national cohort, this tool could accurately assess the current landscape of ERCP quality and provide tremendous opportunities for systematic improvement.”
One author disclosed a relationship with Provation Medical, but the remaining authors declared no relevant conflicts.
Quality indicators have been proposed to improve the outcome of patients undergoing endoscopic procedures. The path toward quality improvement begins with selection of parameters, which matters a great deal and have wide performance variation. Endoscopists then track their own performance, compare it with targets based on community standards, and improve their patients’ outcomes using this feedback. Great progress has been made in the area of tracking and improving adenoma detection rate, an indicator closely tied to reduction in colorectal cancer mortality.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a high-stakes procedure with great potential therapeutic benefit and with a small but significant risk of life-threatening complications such as pancreatitis. This study by Coté and colleagues illuminates an effective and straightforward step to making ERCP quality improvement feasible. The report card concept is not new, but the novel innovation is to leverage the use of required fields in the electronic report generator. Seamlessly, this produces nuanced reports that link provider performance to patient characteristics and indication. The authors have shown extremely high accuracy of automatic electronic ERCP quality indicator recording, compared with manual data collection. Such data have clear and immediate utility in the credentialing process and quality improvement arena. With this means of recording outcomes, deidentified ERCP quality data might soon join colonoscopy data in national data repositories such as the GI Quality Improvement Consortium, and government quality reporting on ERCP outcomes would become much more feasible. Fellow self-assessment and logging of progress could also be facilitated if report generators were further amended to require recording of fellow participation.
Jonathan Cohen, MD, FASGE, is a clinical professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health. He reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
Quality indicators have been proposed to improve the outcome of patients undergoing endoscopic procedures. The path toward quality improvement begins with selection of parameters, which matters a great deal and have wide performance variation. Endoscopists then track their own performance, compare it with targets based on community standards, and improve their patients’ outcomes using this feedback. Great progress has been made in the area of tracking and improving adenoma detection rate, an indicator closely tied to reduction in colorectal cancer mortality.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a high-stakes procedure with great potential therapeutic benefit and with a small but significant risk of life-threatening complications such as pancreatitis. This study by Coté and colleagues illuminates an effective and straightforward step to making ERCP quality improvement feasible. The report card concept is not new, but the novel innovation is to leverage the use of required fields in the electronic report generator. Seamlessly, this produces nuanced reports that link provider performance to patient characteristics and indication. The authors have shown extremely high accuracy of automatic electronic ERCP quality indicator recording, compared with manual data collection. Such data have clear and immediate utility in the credentialing process and quality improvement arena. With this means of recording outcomes, deidentified ERCP quality data might soon join colonoscopy data in national data repositories such as the GI Quality Improvement Consortium, and government quality reporting on ERCP outcomes would become much more feasible. Fellow self-assessment and logging of progress could also be facilitated if report generators were further amended to require recording of fellow participation.
Jonathan Cohen, MD, FASGE, is a clinical professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health. He reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
Quality indicators have been proposed to improve the outcome of patients undergoing endoscopic procedures. The path toward quality improvement begins with selection of parameters, which matters a great deal and have wide performance variation. Endoscopists then track their own performance, compare it with targets based on community standards, and improve their patients’ outcomes using this feedback. Great progress has been made in the area of tracking and improving adenoma detection rate, an indicator closely tied to reduction in colorectal cancer mortality.
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) is a high-stakes procedure with great potential therapeutic benefit and with a small but significant risk of life-threatening complications such as pancreatitis. This study by Coté and colleagues illuminates an effective and straightforward step to making ERCP quality improvement feasible. The report card concept is not new, but the novel innovation is to leverage the use of required fields in the electronic report generator. Seamlessly, this produces nuanced reports that link provider performance to patient characteristics and indication. The authors have shown extremely high accuracy of automatic electronic ERCP quality indicator recording, compared with manual data collection. Such data have clear and immediate utility in the credentialing process and quality improvement arena. With this means of recording outcomes, deidentified ERCP quality data might soon join colonoscopy data in national data repositories such as the GI Quality Improvement Consortium, and government quality reporting on ERCP outcomes would become much more feasible. Fellow self-assessment and logging of progress could also be facilitated if report generators were further amended to require recording of fellow participation.
Jonathan Cohen, MD, FASGE, is a clinical professor of medicine at New York University Langone Health. He reported having no relevant conflicts of interest.
Modified endoscopy documentation software can automatically generate endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) quality metrics, based on a trial at two referral centers.
Providers were prompted during procedures, and inputting any missed data took providers less than 30 additional seconds per patient. The approach led to highly accurate quality reports, lead author Gregory A. Coté, MD, MS, of the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The investigators suggested that these findings may lead to the kind of quality reports already used for colonoscopy, which are easier to produce. Such reports are important, they wrote, as the U.S. health care system shifts to value-based reimbursement models, which in turn puts greater scrutiny on the quality of endoscopic procedures. However, doing so with ERCP isn’t entirely straightforward.
“Measuring adherence to ERCP quality indicators is especially challenging given: variance in indications, intraprocedural maneuvers, potential outcomes of a complex procedure, and variability in physician report documentation,” Dr. Coté and colleagues wrote. “In order to operationalize robust tracking of clinically relevant adherence to ERCP quality indicators in clinical practice – that is, to provide real-time feedback to providers, health systems, payors, and patients – an automated system of measurement must be developed.”
The quality indicators used in the study were largely drawn from an American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy/American College of Gastroenterology task force document, with exclusion of those that were subjective or required systematic follow-up. The investigators modified existing endoscopy documentation software at two referral centers to include mandatory, structured data fields, principally with inclusion of quality improvements deemed high priority by the society consensus document, study authors, or both. For instance, providers were obligated to select a specific indication instead of various, synonymous terms (for example, “biliary stricture” vs. “common bile duct stricture”). Examples of quality indicators included successful cannulation of the desired duct, successful retrieval of stone less than 10 mm, or successful placement of a bile duct stent when indicated. Endoscopists were also required to note the presence of postoperative foregut anatomy or presence of existing sphincterotomy, variables which serve to stratefy the quality indicator outcome for degree of difficulty and allow appropriate comparisons of data. In addition, the study authors included inquiries about use of rectal indomethacin, use of prophylactic pancreatic duct stent, and documentation of need for repeat ERCP, follow-up x-ray, or both.
After 9 months, the system recorded 1,376 ERCP procedures conducted by eight providers, with a median annualized volume of 237 procedures (range, 37-336). Almost one-third (29%) of the patients had not had prior sphincterotomy.
Automated reporting of ERCP was compared with manual record review, which confirmed high (98%-100%) accuracy. This high level of accuracy “obviates the need for manual adjudication of medical records,” the investigators wrote.
They used data from one provider to create a template report card, and while exact comparisons across providers and institutions were not published, an example report card that was published with the study showed how such comparisons could be generated in the real world.
“The tool presented in this study allows for an objective assessment of ERCP performance which can provide explicit feedback to providers and allow transparent assessment of quality outcomes; it has the potential to improve the quality of ERCP akin to what has been demonstrated using colonoscopy report cards,” the investigators wrote. “Importantly, this can be achieved with minimal alteration to providers’ routine procedure documentation.”
Dr. Coté and colleagues also noted that the software modifications “can be implemented in other endoscopy units using the same or similar software.”
Taking the project to the next level would require widespread collaboration, according to the investigators.
“A key next step is to operationalize the transfer of data across multiple institutions, allowing for the creation of interim, standard-quality indicator reports that could be disseminated to providers, health systems, and payors,” they wrote. “If applied to a national cohort, this tool could accurately assess the current landscape of ERCP quality and provide tremendous opportunities for systematic improvement.”
One author disclosed a relationship with Provation Medical, but the remaining authors declared no relevant conflicts.
Modified endoscopy documentation software can automatically generate endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP) quality metrics, based on a trial at two referral centers.
Providers were prompted during procedures, and inputting any missed data took providers less than 30 additional seconds per patient. The approach led to highly accurate quality reports, lead author Gregory A. Coté, MD, MS, of the Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, and colleagues wrote in Techniques and Innovations in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy.
The investigators suggested that these findings may lead to the kind of quality reports already used for colonoscopy, which are easier to produce. Such reports are important, they wrote, as the U.S. health care system shifts to value-based reimbursement models, which in turn puts greater scrutiny on the quality of endoscopic procedures. However, doing so with ERCP isn’t entirely straightforward.
“Measuring adherence to ERCP quality indicators is especially challenging given: variance in indications, intraprocedural maneuvers, potential outcomes of a complex procedure, and variability in physician report documentation,” Dr. Coté and colleagues wrote. “In order to operationalize robust tracking of clinically relevant adherence to ERCP quality indicators in clinical practice – that is, to provide real-time feedback to providers, health systems, payors, and patients – an automated system of measurement must be developed.”
The quality indicators used in the study were largely drawn from an American Society for Gastrointestinal Endoscopy/American College of Gastroenterology task force document, with exclusion of those that were subjective or required systematic follow-up. The investigators modified existing endoscopy documentation software at two referral centers to include mandatory, structured data fields, principally with inclusion of quality improvements deemed high priority by the society consensus document, study authors, or both. For instance, providers were obligated to select a specific indication instead of various, synonymous terms (for example, “biliary stricture” vs. “common bile duct stricture”). Examples of quality indicators included successful cannulation of the desired duct, successful retrieval of stone less than 10 mm, or successful placement of a bile duct stent when indicated. Endoscopists were also required to note the presence of postoperative foregut anatomy or presence of existing sphincterotomy, variables which serve to stratefy the quality indicator outcome for degree of difficulty and allow appropriate comparisons of data. In addition, the study authors included inquiries about use of rectal indomethacin, use of prophylactic pancreatic duct stent, and documentation of need for repeat ERCP, follow-up x-ray, or both.
After 9 months, the system recorded 1,376 ERCP procedures conducted by eight providers, with a median annualized volume of 237 procedures (range, 37-336). Almost one-third (29%) of the patients had not had prior sphincterotomy.
Automated reporting of ERCP was compared with manual record review, which confirmed high (98%-100%) accuracy. This high level of accuracy “obviates the need for manual adjudication of medical records,” the investigators wrote.
They used data from one provider to create a template report card, and while exact comparisons across providers and institutions were not published, an example report card that was published with the study showed how such comparisons could be generated in the real world.
“The tool presented in this study allows for an objective assessment of ERCP performance which can provide explicit feedback to providers and allow transparent assessment of quality outcomes; it has the potential to improve the quality of ERCP akin to what has been demonstrated using colonoscopy report cards,” the investigators wrote. “Importantly, this can be achieved with minimal alteration to providers’ routine procedure documentation.”
Dr. Coté and colleagues also noted that the software modifications “can be implemented in other endoscopy units using the same or similar software.”
Taking the project to the next level would require widespread collaboration, according to the investigators.
“A key next step is to operationalize the transfer of data across multiple institutions, allowing for the creation of interim, standard-quality indicator reports that could be disseminated to providers, health systems, and payors,” they wrote. “If applied to a national cohort, this tool could accurately assess the current landscape of ERCP quality and provide tremendous opportunities for systematic improvement.”
One author disclosed a relationship with Provation Medical, but the remaining authors declared no relevant conflicts.
FROM TECHNIQUES AND INNOVATIONS IN GASTROINTESTINAL ENDOSCOPY
Test could help patients with pancreatic cysts avoid unneeded surgery
A test that uses machine learning may improve the management of patients with pancreatic cysts, sparing some of them unnecessary surgery, a cohort study suggests.
The test, called CompCyst, integrates clinical, imaging, and biomarker data. It proved more accurate than the current standard of care for correctly determining whether patients should be discharged from follow-up, immediately operated on, or monitored.
Rachel Karchin, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins Whiting School of Engineering in Baltimore, reported these results at the AACR Virtual Special Conference: Artificial Intelligence, Diagnosis, and Imaging (Abstract IA-13).
“Preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic cysts and managing patients who present with a cyst are a clinical conundrum because pancreatic cancer is so deadly, while the decision to surgically resect a cyst is complicated by the danger of the surgery, which has high morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Karchin explained. “The challenge of the diagnostic test is to place patients into one of three groups: those who should be discharged, who should be operated on, and who should be monitored.”
High sensitivity is important for the operate and monitor groups to ensure identification of all patients needing these approaches, whereas higher specificity is important for the discharge group to avoid falsely classifying premalignant cysts, Dr. Karchin said.
She and her colleagues applied machine learning to this classification challenge, using data from 862 patients who had undergone resection of pancreatic cysts at 16 centers in the United States, Europe, and Asia. All patients had a known cyst histopathology, which served as the gold standard, and a known clinical management strategy (discharge, operate, or monitor).
The investigators used a multivariate organization of combinatorial alterations algorithm that integrates clinical features, imaging characteristics, cyst fluid genetics, and serum biomarkers to create classifiers. This algorithm can be trained to maximize sensitivity, maximize specificity, or balance these metrics, Dr. Karchin noted.
The resulting test, CompCyst, was trained using data from 436 of the patients and then validated in the remaining 426 patients.
In the validation cohort, for classifying patients who should be discharged from care, the test had a sensitivity of 46% and a specificity of 100%, according to results reported at the conference and published previously (Sci Transl Med. 2019 Jul 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav4772).
For immediately operating, CompCyst had a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 54%. And for monitoring the patient, the test had a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 30%.
When CompCyst was compared against the standard of care based on conventional clinical and imaging criteria alone, the former was more accurate. CompCyst correctly identified larger shares of patients who should have been discharged (60% vs. 19%) and who should have been monitored (49% vs. 34%), and the test identified a similar share of patients who should have immediately had an operation (91% vs. 89%).
“The takeaway from this is that standard of care is sending too many patients unnecessarily to surgery,” Dr. Karchin commented. “The CompCyst test, with application of the three classifiers sequentially – discharge, operate, or monitor – could reduce unnecessary surgery by 60% or more based on our calculations.”
“While our study was retrospective, it shows promising results in reducing unnecessary surgeries, compared to current standard of care,” she said, adding that a prospective study is planned next.
“In 10-12 weeks, this CompCyst diagnostic test is going to be available at Johns Hopkins for patients. I’m very excited about that,” Dr. Karchin concluded. “We hope that our study shows the potential of combining clinical, imaging, and genetic features with machine learning to improve clinical judgment about many diseases.”
Dr. Karchin disclosed no conflicts of interest. The study was supported by the Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, the Sol Goldman Pancreatic Cancer Research Center, the Michael Rolfe Pancreatic Cancer Research Foundation, the Benjamin Baker Scholarship, and the National Institutes of Health.
Help your patients understand pancreatitis testing and treatment options, symptoms and complications by sharing AGA’s patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/pancreatitis.
A test that uses machine learning may improve the management of patients with pancreatic cysts, sparing some of them unnecessary surgery, a cohort study suggests.
The test, called CompCyst, integrates clinical, imaging, and biomarker data. It proved more accurate than the current standard of care for correctly determining whether patients should be discharged from follow-up, immediately operated on, or monitored.
Rachel Karchin, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins Whiting School of Engineering in Baltimore, reported these results at the AACR Virtual Special Conference: Artificial Intelligence, Diagnosis, and Imaging (Abstract IA-13).
“Preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic cysts and managing patients who present with a cyst are a clinical conundrum because pancreatic cancer is so deadly, while the decision to surgically resect a cyst is complicated by the danger of the surgery, which has high morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Karchin explained. “The challenge of the diagnostic test is to place patients into one of three groups: those who should be discharged, who should be operated on, and who should be monitored.”
High sensitivity is important for the operate and monitor groups to ensure identification of all patients needing these approaches, whereas higher specificity is important for the discharge group to avoid falsely classifying premalignant cysts, Dr. Karchin said.
She and her colleagues applied machine learning to this classification challenge, using data from 862 patients who had undergone resection of pancreatic cysts at 16 centers in the United States, Europe, and Asia. All patients had a known cyst histopathology, which served as the gold standard, and a known clinical management strategy (discharge, operate, or monitor).
The investigators used a multivariate organization of combinatorial alterations algorithm that integrates clinical features, imaging characteristics, cyst fluid genetics, and serum biomarkers to create classifiers. This algorithm can be trained to maximize sensitivity, maximize specificity, or balance these metrics, Dr. Karchin noted.
The resulting test, CompCyst, was trained using data from 436 of the patients and then validated in the remaining 426 patients.
In the validation cohort, for classifying patients who should be discharged from care, the test had a sensitivity of 46% and a specificity of 100%, according to results reported at the conference and published previously (Sci Transl Med. 2019 Jul 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav4772).
For immediately operating, CompCyst had a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 54%. And for monitoring the patient, the test had a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 30%.
When CompCyst was compared against the standard of care based on conventional clinical and imaging criteria alone, the former was more accurate. CompCyst correctly identified larger shares of patients who should have been discharged (60% vs. 19%) and who should have been monitored (49% vs. 34%), and the test identified a similar share of patients who should have immediately had an operation (91% vs. 89%).
“The takeaway from this is that standard of care is sending too many patients unnecessarily to surgery,” Dr. Karchin commented. “The CompCyst test, with application of the three classifiers sequentially – discharge, operate, or monitor – could reduce unnecessary surgery by 60% or more based on our calculations.”
“While our study was retrospective, it shows promising results in reducing unnecessary surgeries, compared to current standard of care,” she said, adding that a prospective study is planned next.
“In 10-12 weeks, this CompCyst diagnostic test is going to be available at Johns Hopkins for patients. I’m very excited about that,” Dr. Karchin concluded. “We hope that our study shows the potential of combining clinical, imaging, and genetic features with machine learning to improve clinical judgment about many diseases.”
Dr. Karchin disclosed no conflicts of interest. The study was supported by the Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, the Sol Goldman Pancreatic Cancer Research Center, the Michael Rolfe Pancreatic Cancer Research Foundation, the Benjamin Baker Scholarship, and the National Institutes of Health.
Help your patients understand pancreatitis testing and treatment options, symptoms and complications by sharing AGA’s patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/pancreatitis.
A test that uses machine learning may improve the management of patients with pancreatic cysts, sparing some of them unnecessary surgery, a cohort study suggests.
The test, called CompCyst, integrates clinical, imaging, and biomarker data. It proved more accurate than the current standard of care for correctly determining whether patients should be discharged from follow-up, immediately operated on, or monitored.
Rachel Karchin, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins Whiting School of Engineering in Baltimore, reported these results at the AACR Virtual Special Conference: Artificial Intelligence, Diagnosis, and Imaging (Abstract IA-13).
“Preoperative diagnosis of pancreatic cysts and managing patients who present with a cyst are a clinical conundrum because pancreatic cancer is so deadly, while the decision to surgically resect a cyst is complicated by the danger of the surgery, which has high morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Karchin explained. “The challenge of the diagnostic test is to place patients into one of three groups: those who should be discharged, who should be operated on, and who should be monitored.”
High sensitivity is important for the operate and monitor groups to ensure identification of all patients needing these approaches, whereas higher specificity is important for the discharge group to avoid falsely classifying premalignant cysts, Dr. Karchin said.
She and her colleagues applied machine learning to this classification challenge, using data from 862 patients who had undergone resection of pancreatic cysts at 16 centers in the United States, Europe, and Asia. All patients had a known cyst histopathology, which served as the gold standard, and a known clinical management strategy (discharge, operate, or monitor).
The investigators used a multivariate organization of combinatorial alterations algorithm that integrates clinical features, imaging characteristics, cyst fluid genetics, and serum biomarkers to create classifiers. This algorithm can be trained to maximize sensitivity, maximize specificity, or balance these metrics, Dr. Karchin noted.
The resulting test, CompCyst, was trained using data from 436 of the patients and then validated in the remaining 426 patients.
In the validation cohort, for classifying patients who should be discharged from care, the test had a sensitivity of 46% and a specificity of 100%, according to results reported at the conference and published previously (Sci Transl Med. 2019 Jul 19. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.aav4772).
For immediately operating, CompCyst had a sensitivity of 91% and a specificity of 54%. And for monitoring the patient, the test had a sensitivity of 99% and a specificity of 30%.
When CompCyst was compared against the standard of care based on conventional clinical and imaging criteria alone, the former was more accurate. CompCyst correctly identified larger shares of patients who should have been discharged (60% vs. 19%) and who should have been monitored (49% vs. 34%), and the test identified a similar share of patients who should have immediately had an operation (91% vs. 89%).
“The takeaway from this is that standard of care is sending too many patients unnecessarily to surgery,” Dr. Karchin commented. “The CompCyst test, with application of the three classifiers sequentially – discharge, operate, or monitor – could reduce unnecessary surgery by 60% or more based on our calculations.”
“While our study was retrospective, it shows promising results in reducing unnecessary surgeries, compared to current standard of care,” she said, adding that a prospective study is planned next.
“In 10-12 weeks, this CompCyst diagnostic test is going to be available at Johns Hopkins for patients. I’m very excited about that,” Dr. Karchin concluded. “We hope that our study shows the potential of combining clinical, imaging, and genetic features with machine learning to improve clinical judgment about many diseases.”
Dr. Karchin disclosed no conflicts of interest. The study was supported by the Lustgarten Foundation for Pancreatic Cancer Research, the Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Fund for Cancer Research, the Sol Goldman Pancreatic Cancer Research Center, the Michael Rolfe Pancreatic Cancer Research Foundation, the Benjamin Baker Scholarship, and the National Institutes of Health.
Help your patients understand pancreatitis testing and treatment options, symptoms and complications by sharing AGA’s patient education from the GI Patient Center: www.gastro.org/pancreatitis.
FROM AACR: AI, DIAGNOSIS, AND IMAGING 2021
High cost of pancreatic enzymes a barrier for patients with cancer
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) is often an essential component of the treatment regimen for patients with pancreatic cancer, but it can be very pricey.
“Out-of-pocket costs for a 30-day supply of enzymes for Medicare beneficiaries can be as high as $1,000,” commented Arjun Gupta, MD, an oncology fellow at Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore.
This can contribute to financial toxicity for patients who already have a high symptom burden and distress. The high cost of this supportive care has been underappreciated, he said.
In addition to its use for patients with pancreatic cancer, PERT is also prescribed to patients with chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis. These enzymes can reduce symptoms of indigestion and improve nutrition for patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, he explained.
“Out-of-pocket costs for two large pancreas enzyme capsules, which are often required for a meal, may be $15. And these need to be taken at every meal and may be more expensive than the meal itself,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta led a new study which showed that, among Medicare beneficiaries, the expected out-of-pocket costs for a 30-day supply of optimally dosed PERT averaged $999 across formulations. Patients’ costs, including deductibles and coinsurance, ranged from $853 to $1,536.
The out-of-pocket costs were lower after patients met the deductible ($673; range, $527-$1,210) and continued to decrease after reaching catastrophic coverage ($135; range, $105-$242).
The findings were presented at the 2021 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
Dr. Gupta noted that there has been a lot of publicity about very expensive anticancer drugs, but little has been said about the costs of products used in supportive care. “While it’s true that many patients cannot afford the drugs, there are patient-assistance programs where they can often get them free of charge,” he said. “But supportive care agents, such as those for constipation or the enzymes – all of those can nickel and dime you and end up being very costly.”
These agents add substantially to the drug cost burden. “Some patients also need insulin, which is also insanely expensive,” he said.
One of the reasons for the high cost of PERT is that there are very few options, and all the available products are brand-name agents. Dr. Gupta noted that clinicians often underprescribe pancreatic enzymes in clinical practice. “Because of this, we wanted to look at what are the estimated out-of-pocket costs for patients directly when they’re prescribed an optimal regimen of pancreatic enzymes,” he said.
Study details
For their study, Dr. Gupta and colleagues assessed PERT costs using the Medicare Part D formulary and pricing files for the first quarter of 2020. Point-of-sale and out-of-pocket costs for each PERT formulation were calculated among Part D standalone and Medicare Advantage prescription drug plans.
Costs were then assessed using three scenarios: the standard-benefit design, with a $435 deductible and 25% coinsurance after the deductible is met; 25% coinsurance to fill a prescription after the deductible while in the coverage gap until the patient spends $6,350 out of pocket; and 5% coinsurance once catastrophic coverage is reached.
Across 3,974 plans nationwide, four formulations in 17 different doses were covered by Medicare plans during the study period. Doses ranged from 3,000 to 40,000 lipase units, and the per-unit list price ranged from $1.44 to $13.89.
The point-of-sale price for a 30-day supply of optimally dosed PERT ranged from $2,109 to $4,840.
Dr. Gupta noted that a “good-sized meal often requires 80,000 units of lipase, or two of the very largest pills. Of note, these pills need to be taken meal after meal every meal throughout a patient’s life.”
Prescribers and dietitians try to find the least expensive options, including patient-assistance programs, but in the end, they are sometimes forced to underprescribe. “Some patients will go and buy over-the-counter pancreatic enzyme supplements, and it seems like a good way to cut costs,” said Dr. Gupta, “but it is not recommended for people with pancreatic cancer.”
The problem with these formulations is that they are not regulated. “The enzyme content in them is also minuscule, in the range of hundreds of units instead of the 50,000 units needed per meal,” he said. “Patients end up spending much more for ineffective therapies.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) is often an essential component of the treatment regimen for patients with pancreatic cancer, but it can be very pricey.
“Out-of-pocket costs for a 30-day supply of enzymes for Medicare beneficiaries can be as high as $1,000,” commented Arjun Gupta, MD, an oncology fellow at Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore.
This can contribute to financial toxicity for patients who already have a high symptom burden and distress. The high cost of this supportive care has been underappreciated, he said.
In addition to its use for patients with pancreatic cancer, PERT is also prescribed to patients with chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis. These enzymes can reduce symptoms of indigestion and improve nutrition for patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, he explained.
“Out-of-pocket costs for two large pancreas enzyme capsules, which are often required for a meal, may be $15. And these need to be taken at every meal and may be more expensive than the meal itself,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta led a new study which showed that, among Medicare beneficiaries, the expected out-of-pocket costs for a 30-day supply of optimally dosed PERT averaged $999 across formulations. Patients’ costs, including deductibles and coinsurance, ranged from $853 to $1,536.
The out-of-pocket costs were lower after patients met the deductible ($673; range, $527-$1,210) and continued to decrease after reaching catastrophic coverage ($135; range, $105-$242).
The findings were presented at the 2021 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
Dr. Gupta noted that there has been a lot of publicity about very expensive anticancer drugs, but little has been said about the costs of products used in supportive care. “While it’s true that many patients cannot afford the drugs, there are patient-assistance programs where they can often get them free of charge,” he said. “But supportive care agents, such as those for constipation or the enzymes – all of those can nickel and dime you and end up being very costly.”
These agents add substantially to the drug cost burden. “Some patients also need insulin, which is also insanely expensive,” he said.
One of the reasons for the high cost of PERT is that there are very few options, and all the available products are brand-name agents. Dr. Gupta noted that clinicians often underprescribe pancreatic enzymes in clinical practice. “Because of this, we wanted to look at what are the estimated out-of-pocket costs for patients directly when they’re prescribed an optimal regimen of pancreatic enzymes,” he said.
Study details
For their study, Dr. Gupta and colleagues assessed PERT costs using the Medicare Part D formulary and pricing files for the first quarter of 2020. Point-of-sale and out-of-pocket costs for each PERT formulation were calculated among Part D standalone and Medicare Advantage prescription drug plans.
Costs were then assessed using three scenarios: the standard-benefit design, with a $435 deductible and 25% coinsurance after the deductible is met; 25% coinsurance to fill a prescription after the deductible while in the coverage gap until the patient spends $6,350 out of pocket; and 5% coinsurance once catastrophic coverage is reached.
Across 3,974 plans nationwide, four formulations in 17 different doses were covered by Medicare plans during the study period. Doses ranged from 3,000 to 40,000 lipase units, and the per-unit list price ranged from $1.44 to $13.89.
The point-of-sale price for a 30-day supply of optimally dosed PERT ranged from $2,109 to $4,840.
Dr. Gupta noted that a “good-sized meal often requires 80,000 units of lipase, or two of the very largest pills. Of note, these pills need to be taken meal after meal every meal throughout a patient’s life.”
Prescribers and dietitians try to find the least expensive options, including patient-assistance programs, but in the end, they are sometimes forced to underprescribe. “Some patients will go and buy over-the-counter pancreatic enzyme supplements, and it seems like a good way to cut costs,” said Dr. Gupta, “but it is not recommended for people with pancreatic cancer.”
The problem with these formulations is that they are not regulated. “The enzyme content in them is also minuscule, in the range of hundreds of units instead of the 50,000 units needed per meal,” he said. “Patients end up spending much more for ineffective therapies.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pancreatic enzyme replacement therapy (PERT) is often an essential component of the treatment regimen for patients with pancreatic cancer, but it can be very pricey.
“Out-of-pocket costs for a 30-day supply of enzymes for Medicare beneficiaries can be as high as $1,000,” commented Arjun Gupta, MD, an oncology fellow at Johns Hopkins Sidney Kimmel Comprehensive Cancer Center, Baltimore.
This can contribute to financial toxicity for patients who already have a high symptom burden and distress. The high cost of this supportive care has been underappreciated, he said.
In addition to its use for patients with pancreatic cancer, PERT is also prescribed to patients with chronic pancreatitis and cystic fibrosis. These enzymes can reduce symptoms of indigestion and improve nutrition for patients with exocrine pancreatic insufficiency, he explained.
“Out-of-pocket costs for two large pancreas enzyme capsules, which are often required for a meal, may be $15. And these need to be taken at every meal and may be more expensive than the meal itself,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Gupta led a new study which showed that, among Medicare beneficiaries, the expected out-of-pocket costs for a 30-day supply of optimally dosed PERT averaged $999 across formulations. Patients’ costs, including deductibles and coinsurance, ranged from $853 to $1,536.
The out-of-pocket costs were lower after patients met the deductible ($673; range, $527-$1,210) and continued to decrease after reaching catastrophic coverage ($135; range, $105-$242).
The findings were presented at the 2021 Gastrointestinal Cancers Symposium.
Dr. Gupta noted that there has been a lot of publicity about very expensive anticancer drugs, but little has been said about the costs of products used in supportive care. “While it’s true that many patients cannot afford the drugs, there are patient-assistance programs where they can often get them free of charge,” he said. “But supportive care agents, such as those for constipation or the enzymes – all of those can nickel and dime you and end up being very costly.”
These agents add substantially to the drug cost burden. “Some patients also need insulin, which is also insanely expensive,” he said.
One of the reasons for the high cost of PERT is that there are very few options, and all the available products are brand-name agents. Dr. Gupta noted that clinicians often underprescribe pancreatic enzymes in clinical practice. “Because of this, we wanted to look at what are the estimated out-of-pocket costs for patients directly when they’re prescribed an optimal regimen of pancreatic enzymes,” he said.
Study details
For their study, Dr. Gupta and colleagues assessed PERT costs using the Medicare Part D formulary and pricing files for the first quarter of 2020. Point-of-sale and out-of-pocket costs for each PERT formulation were calculated among Part D standalone and Medicare Advantage prescription drug plans.
Costs were then assessed using three scenarios: the standard-benefit design, with a $435 deductible and 25% coinsurance after the deductible is met; 25% coinsurance to fill a prescription after the deductible while in the coverage gap until the patient spends $6,350 out of pocket; and 5% coinsurance once catastrophic coverage is reached.
Across 3,974 plans nationwide, four formulations in 17 different doses were covered by Medicare plans during the study period. Doses ranged from 3,000 to 40,000 lipase units, and the per-unit list price ranged from $1.44 to $13.89.
The point-of-sale price for a 30-day supply of optimally dosed PERT ranged from $2,109 to $4,840.
Dr. Gupta noted that a “good-sized meal often requires 80,000 units of lipase, or two of the very largest pills. Of note, these pills need to be taken meal after meal every meal throughout a patient’s life.”
Prescribers and dietitians try to find the least expensive options, including patient-assistance programs, but in the end, they are sometimes forced to underprescribe. “Some patients will go and buy over-the-counter pancreatic enzyme supplements, and it seems like a good way to cut costs,” said Dr. Gupta, “but it is not recommended for people with pancreatic cancer.”
The problem with these formulations is that they are not regulated. “The enzyme content in them is also minuscule, in the range of hundreds of units instead of the 50,000 units needed per meal,” he said. “Patients end up spending much more for ineffective therapies.”
The study received no outside funding. Dr. Gupta disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Bezafibrate eased pruritus in patients with fibrosing cholangiopathies
Once-daily treatment with the lipid-lowering agent bezafibrate significantly reduced moderate to severe pruritis among patients with cholestasis, according to the findings of a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (Fibrates for Itch, or FITCH).
Two weeks after completing treatment, 45% of bezafibrate recipients met the primary endpoint, reporting at least a 50% decrease in itch on a 10-point visual analog scale (VAS), compared with 11% of patients in the placebo group (P = .003). There was also a statistically significant decrease in serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels from baseline (35% vs. 6%, respectively; P = .03) that corresponded with improved pruritus, and bezafibrate significantly improved both morning and evening pruritus. Bezafibrate was not associated with myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, or serum alanine transaminase elevations but did lead to a 3% increase in serum creatinine that “was not different from the placebo group,” wrote Elsemieke de Vries, MD, PhD, of the department of gastroenterology & hepatology at Tytgat Institute for Liver and Intestinal Research, Amsterdam, and of department of gastroenterology & metabolism at Amsterdam University Medical Centers, and associates. Their report is in Gastroenterology.
Up to 70% of patients with cholangitis experience pruritus. Current guidelines recommend management with cholestyramine, rifampin, naltrexone, or sertraline, but efficacy and tolerability are subpar, the investigators wrote. In a recent study, a selective inhibitor of an ileal bile acid transporter (GSK2330672) reduced pruritus in primary biliary cholangitis but frequently was associated with diarrhea. In another recent study of patients with primary biliary cholangitis who had responded inadequately to ursodeoxycholic acid (BEZURSO), bezafibrate induced biochemical responses that correlated with improvements in pruritis (a secondary endpoint).
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) has been implicated in cholangiopathy-associated pruritus but is not found in bile. However, biliary drainage rapidly improves severe itch in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Therefore, Dr. de Vries and associates hypothesized that an as-yet unknown factor in bile contributes to pruritus in fibrosing cholangiopathies and that bezafibrate reduces itch by “alleviating hepatobiliary cholestasis and injury and, thereby, reducing formation and biliary secretion of this biliary factor X.”
The FITCH study, which was conducted at seven academic hospitals in the Netherlands and one in Spain, enrolled 74 patients 18 years and older with primary biliary cholangitis or primary or secondary sclerosing cholangitis who reported having pruritus with an intensity of at least 5 on the 10-point VAS at baseline (with 10 indicating “worst itch possible”; median, 7; interquartile range, 7-8). Patients with hepatocellular cholestasis caused by medications or pregnancy were excluded. Ages among most participants ranged from 30s to 50s, and approximately two-thirds were female. None had received another pruritus treatment within 10 days of enrollment, and prior treatment with bezafibrate was not allowed. Patients received once-daily bezafibrate (400 mg) or placebo tablets for 21 days, with visits to the outpatient clinic on days 0, 21, and 35.
There were no serious adverse events or new safety signals. One event of oral pain was considered possibly related to bezafibrate, and itch and jaundice worsened in two patients after completing treatment. As in the 24-month BEZURSO study, increases in serum creatinine were modest and similar between groups (3% with bezafibrate and 5% with placebo). Myalgia and increases in serum alanine transaminase were observed in BEZURSO but not in FITCH. However, the short treatment duration provides “no judgment on long-term safety [of bezafibrate] in complex diseases such as primary sclerosing cholangitis or primary biliary cholangitis,” the investigators wrote.
Four patients discontinued treatment – three stopped placebo because of “unbearable pruritus,” and one stopped bezafibrate after developing acute bacterial cholangitis that required emergency treatment. Although FITCH excluded patients whose estimated glomerular filtration rate was less than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, one such patient was accidentally enrolled. Her serum creatinine, measured in mmol/L, rose from 121 at baseline to 148 on day 21, and then dropped to 134 after 2 weeks off treatment.
The trial was supported by patient donations, the Netherlands Society of Gastroenterology, and Instituto de Salud Carlos III. The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: de Vries E et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct 5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.001.
Itch really matters to patients with cholestatic liver diseases, and effective treatment can make a significant difference to life quality. Although therapies exist for cholestatic itch (such as cholestyramine, rifampin, and naltrexone) recent data from the United Kingdom and United States suggest that therapy in practice is poor. It is likely that this results, at least in part, from the limitations of the existing treatments which can be unpleasant to take (cholestyramine) or difficult to use because of monitoring needs and side-effects (rifampin and naltrexone). Itch has therefore been identified as an area of real unmet need in cholestatic disease and there are a number of trials in progress or in set-up. This is extremely positive for patients.
The FITCH trial is one of the first of these “new generation” cholestatic itch trials to report and explore the efficacy of the PPAR-agonist bezafibrate in a mixed cholestatic population. Clear benefit was seen with around 50% of all disease groups meeting the primary endpoint and good drug tolerance. Is bezafibrate therefore the answer to cholestatic itch? The cautious answer is ... possibly, but more experience is needed. The trial duration was only 21 days, which means that long-term safety and efficacy remain to be explored. Bezafibrate is now being used in practice to treat cholestatic itch with effects similar to those reported in the trial. It is therefore clearly an important new option. Where it ultimately ends up in the treatment pathway only time and experience will tell.
David Jones, BM, BCh, PhD, is a professor of liver immunology at Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne, England. He reported having no disclosures relevant to this commentary.
Itch really matters to patients with cholestatic liver diseases, and effective treatment can make a significant difference to life quality. Although therapies exist for cholestatic itch (such as cholestyramine, rifampin, and naltrexone) recent data from the United Kingdom and United States suggest that therapy in practice is poor. It is likely that this results, at least in part, from the limitations of the existing treatments which can be unpleasant to take (cholestyramine) or difficult to use because of monitoring needs and side-effects (rifampin and naltrexone). Itch has therefore been identified as an area of real unmet need in cholestatic disease and there are a number of trials in progress or in set-up. This is extremely positive for patients.
The FITCH trial is one of the first of these “new generation” cholestatic itch trials to report and explore the efficacy of the PPAR-agonist bezafibrate in a mixed cholestatic population. Clear benefit was seen with around 50% of all disease groups meeting the primary endpoint and good drug tolerance. Is bezafibrate therefore the answer to cholestatic itch? The cautious answer is ... possibly, but more experience is needed. The trial duration was only 21 days, which means that long-term safety and efficacy remain to be explored. Bezafibrate is now being used in practice to treat cholestatic itch with effects similar to those reported in the trial. It is therefore clearly an important new option. Where it ultimately ends up in the treatment pathway only time and experience will tell.
David Jones, BM, BCh, PhD, is a professor of liver immunology at Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne, England. He reported having no disclosures relevant to this commentary.
Itch really matters to patients with cholestatic liver diseases, and effective treatment can make a significant difference to life quality. Although therapies exist for cholestatic itch (such as cholestyramine, rifampin, and naltrexone) recent data from the United Kingdom and United States suggest that therapy in practice is poor. It is likely that this results, at least in part, from the limitations of the existing treatments which can be unpleasant to take (cholestyramine) or difficult to use because of monitoring needs and side-effects (rifampin and naltrexone). Itch has therefore been identified as an area of real unmet need in cholestatic disease and there are a number of trials in progress or in set-up. This is extremely positive for patients.
The FITCH trial is one of the first of these “new generation” cholestatic itch trials to report and explore the efficacy of the PPAR-agonist bezafibrate in a mixed cholestatic population. Clear benefit was seen with around 50% of all disease groups meeting the primary endpoint and good drug tolerance. Is bezafibrate therefore the answer to cholestatic itch? The cautious answer is ... possibly, but more experience is needed. The trial duration was only 21 days, which means that long-term safety and efficacy remain to be explored. Bezafibrate is now being used in practice to treat cholestatic itch with effects similar to those reported in the trial. It is therefore clearly an important new option. Where it ultimately ends up in the treatment pathway only time and experience will tell.
David Jones, BM, BCh, PhD, is a professor of liver immunology at Newcastle University, Newcastle Upon Tyne, England. He reported having no disclosures relevant to this commentary.
Once-daily treatment with the lipid-lowering agent bezafibrate significantly reduced moderate to severe pruritis among patients with cholestasis, according to the findings of a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (Fibrates for Itch, or FITCH).
Two weeks after completing treatment, 45% of bezafibrate recipients met the primary endpoint, reporting at least a 50% decrease in itch on a 10-point visual analog scale (VAS), compared with 11% of patients in the placebo group (P = .003). There was also a statistically significant decrease in serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels from baseline (35% vs. 6%, respectively; P = .03) that corresponded with improved pruritus, and bezafibrate significantly improved both morning and evening pruritus. Bezafibrate was not associated with myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, or serum alanine transaminase elevations but did lead to a 3% increase in serum creatinine that “was not different from the placebo group,” wrote Elsemieke de Vries, MD, PhD, of the department of gastroenterology & hepatology at Tytgat Institute for Liver and Intestinal Research, Amsterdam, and of department of gastroenterology & metabolism at Amsterdam University Medical Centers, and associates. Their report is in Gastroenterology.
Up to 70% of patients with cholangitis experience pruritus. Current guidelines recommend management with cholestyramine, rifampin, naltrexone, or sertraline, but efficacy and tolerability are subpar, the investigators wrote. In a recent study, a selective inhibitor of an ileal bile acid transporter (GSK2330672) reduced pruritus in primary biliary cholangitis but frequently was associated with diarrhea. In another recent study of patients with primary biliary cholangitis who had responded inadequately to ursodeoxycholic acid (BEZURSO), bezafibrate induced biochemical responses that correlated with improvements in pruritis (a secondary endpoint).
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) has been implicated in cholangiopathy-associated pruritus but is not found in bile. However, biliary drainage rapidly improves severe itch in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Therefore, Dr. de Vries and associates hypothesized that an as-yet unknown factor in bile contributes to pruritus in fibrosing cholangiopathies and that bezafibrate reduces itch by “alleviating hepatobiliary cholestasis and injury and, thereby, reducing formation and biliary secretion of this biliary factor X.”
The FITCH study, which was conducted at seven academic hospitals in the Netherlands and one in Spain, enrolled 74 patients 18 years and older with primary biliary cholangitis or primary or secondary sclerosing cholangitis who reported having pruritus with an intensity of at least 5 on the 10-point VAS at baseline (with 10 indicating “worst itch possible”; median, 7; interquartile range, 7-8). Patients with hepatocellular cholestasis caused by medications or pregnancy were excluded. Ages among most participants ranged from 30s to 50s, and approximately two-thirds were female. None had received another pruritus treatment within 10 days of enrollment, and prior treatment with bezafibrate was not allowed. Patients received once-daily bezafibrate (400 mg) or placebo tablets for 21 days, with visits to the outpatient clinic on days 0, 21, and 35.
There were no serious adverse events or new safety signals. One event of oral pain was considered possibly related to bezafibrate, and itch and jaundice worsened in two patients after completing treatment. As in the 24-month BEZURSO study, increases in serum creatinine were modest and similar between groups (3% with bezafibrate and 5% with placebo). Myalgia and increases in serum alanine transaminase were observed in BEZURSO but not in FITCH. However, the short treatment duration provides “no judgment on long-term safety [of bezafibrate] in complex diseases such as primary sclerosing cholangitis or primary biliary cholangitis,” the investigators wrote.
Four patients discontinued treatment – three stopped placebo because of “unbearable pruritus,” and one stopped bezafibrate after developing acute bacterial cholangitis that required emergency treatment. Although FITCH excluded patients whose estimated glomerular filtration rate was less than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, one such patient was accidentally enrolled. Her serum creatinine, measured in mmol/L, rose from 121 at baseline to 148 on day 21, and then dropped to 134 after 2 weeks off treatment.
The trial was supported by patient donations, the Netherlands Society of Gastroenterology, and Instituto de Salud Carlos III. The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: de Vries E et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct 5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.001.
Once-daily treatment with the lipid-lowering agent bezafibrate significantly reduced moderate to severe pruritis among patients with cholestasis, according to the findings of a multicenter, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study (Fibrates for Itch, or FITCH).
Two weeks after completing treatment, 45% of bezafibrate recipients met the primary endpoint, reporting at least a 50% decrease in itch on a 10-point visual analog scale (VAS), compared with 11% of patients in the placebo group (P = .003). There was also a statistically significant decrease in serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP) levels from baseline (35% vs. 6%, respectively; P = .03) that corresponded with improved pruritus, and bezafibrate significantly improved both morning and evening pruritus. Bezafibrate was not associated with myalgia, rhabdomyolysis, or serum alanine transaminase elevations but did lead to a 3% increase in serum creatinine that “was not different from the placebo group,” wrote Elsemieke de Vries, MD, PhD, of the department of gastroenterology & hepatology at Tytgat Institute for Liver and Intestinal Research, Amsterdam, and of department of gastroenterology & metabolism at Amsterdam University Medical Centers, and associates. Their report is in Gastroenterology.
Up to 70% of patients with cholangitis experience pruritus. Current guidelines recommend management with cholestyramine, rifampin, naltrexone, or sertraline, but efficacy and tolerability are subpar, the investigators wrote. In a recent study, a selective inhibitor of an ileal bile acid transporter (GSK2330672) reduced pruritus in primary biliary cholangitis but frequently was associated with diarrhea. In another recent study of patients with primary biliary cholangitis who had responded inadequately to ursodeoxycholic acid (BEZURSO), bezafibrate induced biochemical responses that correlated with improvements in pruritis (a secondary endpoint).
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) has been implicated in cholangiopathy-associated pruritus but is not found in bile. However, biliary drainage rapidly improves severe itch in patients with primary biliary cholangitis. Therefore, Dr. de Vries and associates hypothesized that an as-yet unknown factor in bile contributes to pruritus in fibrosing cholangiopathies and that bezafibrate reduces itch by “alleviating hepatobiliary cholestasis and injury and, thereby, reducing formation and biliary secretion of this biliary factor X.”
The FITCH study, which was conducted at seven academic hospitals in the Netherlands and one in Spain, enrolled 74 patients 18 years and older with primary biliary cholangitis or primary or secondary sclerosing cholangitis who reported having pruritus with an intensity of at least 5 on the 10-point VAS at baseline (with 10 indicating “worst itch possible”; median, 7; interquartile range, 7-8). Patients with hepatocellular cholestasis caused by medications or pregnancy were excluded. Ages among most participants ranged from 30s to 50s, and approximately two-thirds were female. None had received another pruritus treatment within 10 days of enrollment, and prior treatment with bezafibrate was not allowed. Patients received once-daily bezafibrate (400 mg) or placebo tablets for 21 days, with visits to the outpatient clinic on days 0, 21, and 35.
There were no serious adverse events or new safety signals. One event of oral pain was considered possibly related to bezafibrate, and itch and jaundice worsened in two patients after completing treatment. As in the 24-month BEZURSO study, increases in serum creatinine were modest and similar between groups (3% with bezafibrate and 5% with placebo). Myalgia and increases in serum alanine transaminase were observed in BEZURSO but not in FITCH. However, the short treatment duration provides “no judgment on long-term safety [of bezafibrate] in complex diseases such as primary sclerosing cholangitis or primary biliary cholangitis,” the investigators wrote.
Four patients discontinued treatment – three stopped placebo because of “unbearable pruritus,” and one stopped bezafibrate after developing acute bacterial cholangitis that required emergency treatment. Although FITCH excluded patients whose estimated glomerular filtration rate was less than 60 mL/min per 1.73 m2, one such patient was accidentally enrolled. Her serum creatinine, measured in mmol/L, rose from 121 at baseline to 148 on day 21, and then dropped to 134 after 2 weeks off treatment.
The trial was supported by patient donations, the Netherlands Society of Gastroenterology, and Instituto de Salud Carlos III. The investigators reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: de Vries E et al. Gastroenterology. 2020 Oct 5. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2020.10.001.
FROM GASTROENTEROLOGY