User login
New secondary fracture–prevention recommendations carry simple messages
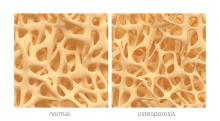
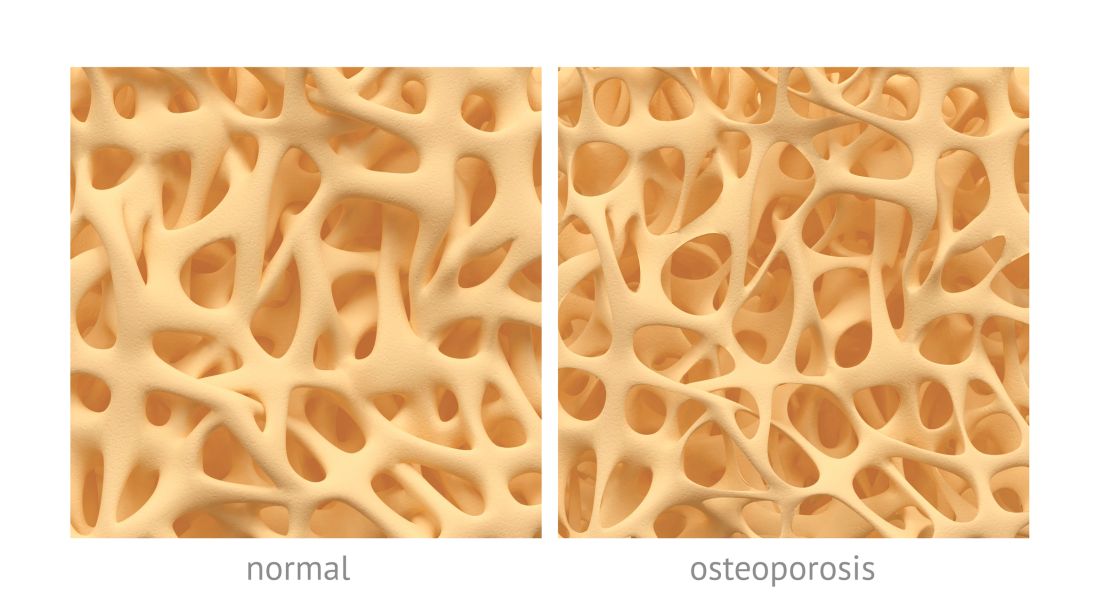
Ensuring that older adults who have experienced a hip or vertebral fracture understand they likely have osteoporosis, and offering prompt drug treatment for the condition, are among five fundamental
The recommendations were announced at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) in Montreal. The 40-member group that developed the recommendations, called the ASBMR Secondary Fracture Prevention Initiative Coalition, includes the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, the Endocrine Society, the American College of Rheumatology, the American College of Physicians, the American Geriatrics Society, the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Additional fundamental recommendations from the Coalition advised ensuring that patients’ primary health care providers are aware of the fracture, regularly assessing the risk of falls, and routinely reevaluating patients who are being treated for osteoporosis. These suggestions were developed in response to growing evidence of a rising trend in osteoporosis patients not being prescribed appropriate medications or not taking them, the ASBMR said.
“The very simple message is if you’ve got somebody who has had a hip fracture or a vertebral fracture, that needs secondary prevention just like somebody who’s had an MI needs to be on a statin and a beta blocker,” said coalition cochair Sundeep Khosla, MD, a past president of the ASBMR and director of the Center for Clinical and Translational Science at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “You can’t ignore the fracture because it’s not immediately life-threatening. Down the road they’re going to have another hip fracture if nothing is done.”
Only 23% of elderly patients who have a hip fracture receive osteoporosis medication to reduce future fracture risk, according to the ASBMR. A 30-year downward trend in the number of hip fractures in the United States has recently plateaued, raising concerns this may have been caused by doctors and patients not following diagnostic and treatment guidelines, the organization noted.
The reasons for the plateau are uncertain, Dr. Khosla said, but could include a reluctance by patients to take bisphosphonates following some reports of relatively rare side effects, such as atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw. In addition, he said, reimbursement for dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans to measure bone mineral density has gone down, which has led to fewer osteoporosis diagnoses. But fracture prevention is important, he said. Of the 300,000 hip fractures in the United States each year, one of every two patients never regains their previous functioning. In addition, one of every four hip fracture patients ends up in a nursing home or dies within a year, according to the ASBMR.
The recommendations and more data about osteoporosis treatment are available on the coalition’s website, www.secondaryfractures.org. An action plan for clinicians should be added to the site sometime this fall, Dr. Khosla said.
There are five fundamental recommendations:
First, communicate three simple messages to patients and their family/caregivers throughout the fracture care and healing process. These include: Their broken bone likely means they have osteoporosis and are at high risk for breaking more bones; breaking bones means they may have to use a walker, cane, or wheelchair or move from their home to a residential facility and will be at higher risk for premature death; and there are actions they can take to reduce their risk.
This is key, said coalition cochair Douglas P. Kiel, MD, a past president of ASBMR, the director of the Musculoskeletal Research Center at the Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife in Boston, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“If you talk to people who have had a broken bone, they view this as an accident and not that they have anything wrong with them,” he said. “The communication should be that if you broke something, it is not a random, chance event. You have osteoporosis, and if you don’t do anything about it, you’re going to be at great risk of a life-threatening, independence-threatening fracture in the future.”
Second, ensure the patient’s primary health care provider is made aware of the occurrence of the fracture. Take action to be sure the communication is made.
Third, regularly assess the risk of falling in women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture. At minimum, take a history of falls within the last year, minimize the use of medications associated with increased risk for falls, evaluate patients for conditions associated with an increased risk for falls, and strongly consider referring patients to physical and/or occupational therapy or a physiatrist for evaluation and interventions to improve impairments in mobility, gait, and balance to reduce the risk for falls.
Fourth, reduce the risk of additional fractures by offering pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis to women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture. This can begin in the hospital and be included in discharge orders. Do not delay initiation of therapy for bone mineral density (BMD) testing. Consider patients’ oral health before starting therapy with bisphosphonates or denosumab (Prolia).
Most hip fracture patients leave the hospital without osteoporosis medications, Dr. Kiel said. It could be that hospital-based physicians are concerned patients are still unsteady such that they may not want to start patients on a new medication when they’re discharging them. Physicians in rehabilitation units may not prescribe these medications because they feel they have the patients for a short time, so by the time the patient returns to their primary care provider, the patient may have the same mistaken impression the fracture was an accident.
“We’re advocating not to delay treatment for any of these care transitions or because you think they need a BMD test,” Dr. Kiel said. “Just get them treated like they do with heart attacks.”
Finally, follow and reevaluate women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture and are being treated for osteoporosis because it is a life-long chronic condition. This can help reinforce key messages about osteoporosis and associated fractures, identify any barriers to treatment adherence, assess the risk of falls, evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment plan, monitor for adverse effects, and determine whether any changes in treatment should be made, including whether any osteoporosis pharmacotherapy should be changed or discontinued.
Ideally, patients should be managed in the context of a multidisciplinary clinical system that includes case management, such as a fracture liaison service, according to the recommendations.
Besides the fundamental five recommendations, the documents lists another seven that deal with referring patients, prescribing vitamin D, counseling on lifestyle and diet, discussing pharmacotherapy benefits and risks, weighing first-line therapy options, and determining the duration of pharmacotherapy.
Ensuring that older adults who have experienced a hip or vertebral fracture understand they likely have osteoporosis, and offering prompt drug treatment for the condition, are among five fundamental
The recommendations were announced at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) in Montreal. The 40-member group that developed the recommendations, called the ASBMR Secondary Fracture Prevention Initiative Coalition, includes the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, the Endocrine Society, the American College of Rheumatology, the American College of Physicians, the American Geriatrics Society, the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Additional fundamental recommendations from the Coalition advised ensuring that patients’ primary health care providers are aware of the fracture, regularly assessing the risk of falls, and routinely reevaluating patients who are being treated for osteoporosis. These suggestions were developed in response to growing evidence of a rising trend in osteoporosis patients not being prescribed appropriate medications or not taking them, the ASBMR said.
“The very simple message is if you’ve got somebody who has had a hip fracture or a vertebral fracture, that needs secondary prevention just like somebody who’s had an MI needs to be on a statin and a beta blocker,” said coalition cochair Sundeep Khosla, MD, a past president of the ASBMR and director of the Center for Clinical and Translational Science at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “You can’t ignore the fracture because it’s not immediately life-threatening. Down the road they’re going to have another hip fracture if nothing is done.”
Only 23% of elderly patients who have a hip fracture receive osteoporosis medication to reduce future fracture risk, according to the ASBMR. A 30-year downward trend in the number of hip fractures in the United States has recently plateaued, raising concerns this may have been caused by doctors and patients not following diagnostic and treatment guidelines, the organization noted.
The reasons for the plateau are uncertain, Dr. Khosla said, but could include a reluctance by patients to take bisphosphonates following some reports of relatively rare side effects, such as atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw. In addition, he said, reimbursement for dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans to measure bone mineral density has gone down, which has led to fewer osteoporosis diagnoses. But fracture prevention is important, he said. Of the 300,000 hip fractures in the United States each year, one of every two patients never regains their previous functioning. In addition, one of every four hip fracture patients ends up in a nursing home or dies within a year, according to the ASBMR.
The recommendations and more data about osteoporosis treatment are available on the coalition’s website, www.secondaryfractures.org. An action plan for clinicians should be added to the site sometime this fall, Dr. Khosla said.
There are five fundamental recommendations:
First, communicate three simple messages to patients and their family/caregivers throughout the fracture care and healing process. These include: Their broken bone likely means they have osteoporosis and are at high risk for breaking more bones; breaking bones means they may have to use a walker, cane, or wheelchair or move from their home to a residential facility and will be at higher risk for premature death; and there are actions they can take to reduce their risk.
This is key, said coalition cochair Douglas P. Kiel, MD, a past president of ASBMR, the director of the Musculoskeletal Research Center at the Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife in Boston, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“If you talk to people who have had a broken bone, they view this as an accident and not that they have anything wrong with them,” he said. “The communication should be that if you broke something, it is not a random, chance event. You have osteoporosis, and if you don’t do anything about it, you’re going to be at great risk of a life-threatening, independence-threatening fracture in the future.”
Second, ensure the patient’s primary health care provider is made aware of the occurrence of the fracture. Take action to be sure the communication is made.
Third, regularly assess the risk of falling in women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture. At minimum, take a history of falls within the last year, minimize the use of medications associated with increased risk for falls, evaluate patients for conditions associated with an increased risk for falls, and strongly consider referring patients to physical and/or occupational therapy or a physiatrist for evaluation and interventions to improve impairments in mobility, gait, and balance to reduce the risk for falls.
Fourth, reduce the risk of additional fractures by offering pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis to women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture. This can begin in the hospital and be included in discharge orders. Do not delay initiation of therapy for bone mineral density (BMD) testing. Consider patients’ oral health before starting therapy with bisphosphonates or denosumab (Prolia).
Most hip fracture patients leave the hospital without osteoporosis medications, Dr. Kiel said. It could be that hospital-based physicians are concerned patients are still unsteady such that they may not want to start patients on a new medication when they’re discharging them. Physicians in rehabilitation units may not prescribe these medications because they feel they have the patients for a short time, so by the time the patient returns to their primary care provider, the patient may have the same mistaken impression the fracture was an accident.
“We’re advocating not to delay treatment for any of these care transitions or because you think they need a BMD test,” Dr. Kiel said. “Just get them treated like they do with heart attacks.”
Finally, follow and reevaluate women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture and are being treated for osteoporosis because it is a life-long chronic condition. This can help reinforce key messages about osteoporosis and associated fractures, identify any barriers to treatment adherence, assess the risk of falls, evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment plan, monitor for adverse effects, and determine whether any changes in treatment should be made, including whether any osteoporosis pharmacotherapy should be changed or discontinued.
Ideally, patients should be managed in the context of a multidisciplinary clinical system that includes case management, such as a fracture liaison service, according to the recommendations.
Besides the fundamental five recommendations, the documents lists another seven that deal with referring patients, prescribing vitamin D, counseling on lifestyle and diet, discussing pharmacotherapy benefits and risks, weighing first-line therapy options, and determining the duration of pharmacotherapy.
Ensuring that older adults who have experienced a hip or vertebral fracture understand they likely have osteoporosis, and offering prompt drug treatment for the condition, are among five fundamental
The recommendations were announced at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research (ASBMR) in Montreal. The 40-member group that developed the recommendations, called the ASBMR Secondary Fracture Prevention Initiative Coalition, includes the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists/American College of Endocrinology, the Endocrine Society, the American College of Rheumatology, the American College of Physicians, the American Geriatrics Society, the American Academy of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, and the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons.
Additional fundamental recommendations from the Coalition advised ensuring that patients’ primary health care providers are aware of the fracture, regularly assessing the risk of falls, and routinely reevaluating patients who are being treated for osteoporosis. These suggestions were developed in response to growing evidence of a rising trend in osteoporosis patients not being prescribed appropriate medications or not taking them, the ASBMR said.
“The very simple message is if you’ve got somebody who has had a hip fracture or a vertebral fracture, that needs secondary prevention just like somebody who’s had an MI needs to be on a statin and a beta blocker,” said coalition cochair Sundeep Khosla, MD, a past president of the ASBMR and director of the Center for Clinical and Translational Science at the Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn. “You can’t ignore the fracture because it’s not immediately life-threatening. Down the road they’re going to have another hip fracture if nothing is done.”
Only 23% of elderly patients who have a hip fracture receive osteoporosis medication to reduce future fracture risk, according to the ASBMR. A 30-year downward trend in the number of hip fractures in the United States has recently plateaued, raising concerns this may have been caused by doctors and patients not following diagnostic and treatment guidelines, the organization noted.
The reasons for the plateau are uncertain, Dr. Khosla said, but could include a reluctance by patients to take bisphosphonates following some reports of relatively rare side effects, such as atypical femoral fractures and osteonecrosis of the jaw. In addition, he said, reimbursement for dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA) scans to measure bone mineral density has gone down, which has led to fewer osteoporosis diagnoses. But fracture prevention is important, he said. Of the 300,000 hip fractures in the United States each year, one of every two patients never regains their previous functioning. In addition, one of every four hip fracture patients ends up in a nursing home or dies within a year, according to the ASBMR.
The recommendations and more data about osteoporosis treatment are available on the coalition’s website, www.secondaryfractures.org. An action plan for clinicians should be added to the site sometime this fall, Dr. Khosla said.
There are five fundamental recommendations:
First, communicate three simple messages to patients and their family/caregivers throughout the fracture care and healing process. These include: Their broken bone likely means they have osteoporosis and are at high risk for breaking more bones; breaking bones means they may have to use a walker, cane, or wheelchair or move from their home to a residential facility and will be at higher risk for premature death; and there are actions they can take to reduce their risk.
This is key, said coalition cochair Douglas P. Kiel, MD, a past president of ASBMR, the director of the Musculoskeletal Research Center at the Institute for Aging Research at Hebrew SeniorLife in Boston, and a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
“If you talk to people who have had a broken bone, they view this as an accident and not that they have anything wrong with them,” he said. “The communication should be that if you broke something, it is not a random, chance event. You have osteoporosis, and if you don’t do anything about it, you’re going to be at great risk of a life-threatening, independence-threatening fracture in the future.”
Second, ensure the patient’s primary health care provider is made aware of the occurrence of the fracture. Take action to be sure the communication is made.
Third, regularly assess the risk of falling in women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture. At minimum, take a history of falls within the last year, minimize the use of medications associated with increased risk for falls, evaluate patients for conditions associated with an increased risk for falls, and strongly consider referring patients to physical and/or occupational therapy or a physiatrist for evaluation and interventions to improve impairments in mobility, gait, and balance to reduce the risk for falls.
Fourth, reduce the risk of additional fractures by offering pharmacologic therapy for osteoporosis to women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture. This can begin in the hospital and be included in discharge orders. Do not delay initiation of therapy for bone mineral density (BMD) testing. Consider patients’ oral health before starting therapy with bisphosphonates or denosumab (Prolia).
Most hip fracture patients leave the hospital without osteoporosis medications, Dr. Kiel said. It could be that hospital-based physicians are concerned patients are still unsteady such that they may not want to start patients on a new medication when they’re discharging them. Physicians in rehabilitation units may not prescribe these medications because they feel they have the patients for a short time, so by the time the patient returns to their primary care provider, the patient may have the same mistaken impression the fracture was an accident.
“We’re advocating not to delay treatment for any of these care transitions or because you think they need a BMD test,” Dr. Kiel said. “Just get them treated like they do with heart attacks.”
Finally, follow and reevaluate women and men age 65 years or older who have had a hip or vertebral fracture and are being treated for osteoporosis because it is a life-long chronic condition. This can help reinforce key messages about osteoporosis and associated fractures, identify any barriers to treatment adherence, assess the risk of falls, evaluate the effectiveness of a treatment plan, monitor for adverse effects, and determine whether any changes in treatment should be made, including whether any osteoporosis pharmacotherapy should be changed or discontinued.
Ideally, patients should be managed in the context of a multidisciplinary clinical system that includes case management, such as a fracture liaison service, according to the recommendations.
Besides the fundamental five recommendations, the documents lists another seven that deal with referring patients, prescribing vitamin D, counseling on lifestyle and diet, discussing pharmacotherapy benefits and risks, weighing first-line therapy options, and determining the duration of pharmacotherapy.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM ASBMR 2018
No falls, fractures, or bone density benefits from vitamin D supplements
There is little justification for the use of vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of fractures or falls or for increasing bone density, according to the authors of a meta-analysis that found no benefits from supplementation.
A systematic review and meta-analysis, published in the Oct. 4 edition of Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, examined 81 randomized controlled trials – involving 53,537 participants – of the effects of vitamin D supplementation on fractures, falls, or bone mineral density.
In the pooled analyses, researchers found that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce total fracture, hip fracture, or falls, even in trials in which participants took doses greater than 800 IU/day. Their results were similar when researchers compared high doses and low doses in their trials.
Similarly, vitamin D supplementation was not associated with any clinically relevant improvements in bone mineral density at any site; lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, forearm, or total body.
Even a post hoc analysis of randomized, controlled trials that compared daily high doses with daily low doses, as well as trials that compared intermittent high doses with intermittent low doses found no significant interactions for any outcome.
The paper also explored whether baseline vitamin D levels might influence outcomes. Eighteen trials in the analysis reported the results of subgroup analyses using baseline serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D); three found no effects of vitamin D supplements in different subgroups of baseline, five studies found no effects of subgroups or interaction with baseline serum 25[OH]D, and one found mixed effects with respect to falls.
The outcomes for bone mineral density, as related to baseline serum 25[OH]D, were slightly more mixed. One trial found a positive effect of vitamin D supplements a bone mineral density for different subgroups of baseline serum, five trials reported mixed effects, and eight trials found no effects.
“The strengths of the current analyses are that they are comprehensive, include all available data from a large number of new trials, and concomitantly assess the major clinical and surrogate endpoints for musculoskeletal health,” wrote Mark J. Bolland, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Auckland (New Zealand), and his coauthors. “Therefore, there is little justification for the use of vitamin D supplements to maintain or improve musculoskeletal health, and clinical guidelines should reflect these findings.”
They also conducted trial sequential analyses, which is a type of cumulative meta-analysis. For each outcome, they set a relative risk reduction threshold, then progressively reduced that threshold until the optimum sample size for that threshold exceeded the actual sample size.
“The trial sequential analyses are important because they provide estimates about the reliability of current evidence and the likelihood of future trials to change current conclusions,” the authors wrote.
Using this approach, they once again found clear evidence that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce fractures or falls for any measure of relative risk reduction. For hip fracture, the trial sequential analysis even found some uncertainty as to whether vitamin D supplementation might increase the risk of hip fractures.
Given the results of the trial sequential analyses, the authors argued that further similar trials were unlikely to alter their conclusion.
“If a large future trial has markedly different results to the current trials, adding its results will substantially increase the heterogeneity of the trial results, which in turn will reduce the weighting the new large trial receives in the pooled analyses,” they wrote. “Thus, adding a positive result from a large randomized, controlled trial will have only a small effect on the pooled result and is unlikely to alter the conclusions of these meta-analyses.”
They also noted that some of the studies had methodological limitations, and smaller studies of shorter duration tended to have “inflated” effect sizes, such that “the results of small, short-duration studies should be interpreted very cautiously, since they might not be replicated in larger, longer studies.”
The study was funded by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. Two authors declared grants from the Health Research Council during the study, one author is a shareholder in a company that provides bone mineral density measurements, and one reported grants from the Scottish Government Health and Social Care Directorates during the study.
SOURCE: Bolland M et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30265-1.
While there have been more than a dozen meta-analyses exploring the effect of vitamin D supplements on fractures, falls, and bone mineral density, this latest one incorporates a large amount of new research information. It also comes at a time when vitamin D often is touted as a cure-all, both in research and on social media.
One of the unanswered questions is that the majority of the daily treatment groups in the studies involved doses less than 1,000 IU per day, so serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) concentrations may not have reached the range of interest.
There are still likely to be questions about the extraskeletal benefits of vitamin D supplementation, which may be answered by large randomized, controlled trials currently underway that are expected to report in the next few years.
J. Chris Gallagher, MD, is a professor at the Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587[18]30269-9). No conflicts of interest were declared.
While there have been more than a dozen meta-analyses exploring the effect of vitamin D supplements on fractures, falls, and bone mineral density, this latest one incorporates a large amount of new research information. It also comes at a time when vitamin D often is touted as a cure-all, both in research and on social media.
One of the unanswered questions is that the majority of the daily treatment groups in the studies involved doses less than 1,000 IU per day, so serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) concentrations may not have reached the range of interest.
There are still likely to be questions about the extraskeletal benefits of vitamin D supplementation, which may be answered by large randomized, controlled trials currently underway that are expected to report in the next few years.
J. Chris Gallagher, MD, is a professor at the Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587[18]30269-9). No conflicts of interest were declared.
While there have been more than a dozen meta-analyses exploring the effect of vitamin D supplements on fractures, falls, and bone mineral density, this latest one incorporates a large amount of new research information. It also comes at a time when vitamin D often is touted as a cure-all, both in research and on social media.
One of the unanswered questions is that the majority of the daily treatment groups in the studies involved doses less than 1,000 IU per day, so serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D) concentrations may not have reached the range of interest.
There are still likely to be questions about the extraskeletal benefits of vitamin D supplementation, which may be answered by large randomized, controlled trials currently underway that are expected to report in the next few years.
J. Chris Gallagher, MD, is a professor at the Creighton University Medical Center, Omaha. These comments are taken from an accompanying editorial (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587[18]30269-9). No conflicts of interest were declared.
There is little justification for the use of vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of fractures or falls or for increasing bone density, according to the authors of a meta-analysis that found no benefits from supplementation.
A systematic review and meta-analysis, published in the Oct. 4 edition of Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, examined 81 randomized controlled trials – involving 53,537 participants – of the effects of vitamin D supplementation on fractures, falls, or bone mineral density.
In the pooled analyses, researchers found that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce total fracture, hip fracture, or falls, even in trials in which participants took doses greater than 800 IU/day. Their results were similar when researchers compared high doses and low doses in their trials.
Similarly, vitamin D supplementation was not associated with any clinically relevant improvements in bone mineral density at any site; lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, forearm, or total body.
Even a post hoc analysis of randomized, controlled trials that compared daily high doses with daily low doses, as well as trials that compared intermittent high doses with intermittent low doses found no significant interactions for any outcome.
The paper also explored whether baseline vitamin D levels might influence outcomes. Eighteen trials in the analysis reported the results of subgroup analyses using baseline serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D); three found no effects of vitamin D supplements in different subgroups of baseline, five studies found no effects of subgroups or interaction with baseline serum 25[OH]D, and one found mixed effects with respect to falls.
The outcomes for bone mineral density, as related to baseline serum 25[OH]D, were slightly more mixed. One trial found a positive effect of vitamin D supplements a bone mineral density for different subgroups of baseline serum, five trials reported mixed effects, and eight trials found no effects.
“The strengths of the current analyses are that they are comprehensive, include all available data from a large number of new trials, and concomitantly assess the major clinical and surrogate endpoints for musculoskeletal health,” wrote Mark J. Bolland, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Auckland (New Zealand), and his coauthors. “Therefore, there is little justification for the use of vitamin D supplements to maintain or improve musculoskeletal health, and clinical guidelines should reflect these findings.”
They also conducted trial sequential analyses, which is a type of cumulative meta-analysis. For each outcome, they set a relative risk reduction threshold, then progressively reduced that threshold until the optimum sample size for that threshold exceeded the actual sample size.
“The trial sequential analyses are important because they provide estimates about the reliability of current evidence and the likelihood of future trials to change current conclusions,” the authors wrote.
Using this approach, they once again found clear evidence that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce fractures or falls for any measure of relative risk reduction. For hip fracture, the trial sequential analysis even found some uncertainty as to whether vitamin D supplementation might increase the risk of hip fractures.
Given the results of the trial sequential analyses, the authors argued that further similar trials were unlikely to alter their conclusion.
“If a large future trial has markedly different results to the current trials, adding its results will substantially increase the heterogeneity of the trial results, which in turn will reduce the weighting the new large trial receives in the pooled analyses,” they wrote. “Thus, adding a positive result from a large randomized, controlled trial will have only a small effect on the pooled result and is unlikely to alter the conclusions of these meta-analyses.”
They also noted that some of the studies had methodological limitations, and smaller studies of shorter duration tended to have “inflated” effect sizes, such that “the results of small, short-duration studies should be interpreted very cautiously, since they might not be replicated in larger, longer studies.”
The study was funded by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. Two authors declared grants from the Health Research Council during the study, one author is a shareholder in a company that provides bone mineral density measurements, and one reported grants from the Scottish Government Health and Social Care Directorates during the study.
SOURCE: Bolland M et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30265-1.
There is little justification for the use of vitamin D supplementation for the prevention of fractures or falls or for increasing bone density, according to the authors of a meta-analysis that found no benefits from supplementation.
A systematic review and meta-analysis, published in the Oct. 4 edition of Lancet Diabetes & Endocrinology, examined 81 randomized controlled trials – involving 53,537 participants – of the effects of vitamin D supplementation on fractures, falls, or bone mineral density.
In the pooled analyses, researchers found that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce total fracture, hip fracture, or falls, even in trials in which participants took doses greater than 800 IU/day. Their results were similar when researchers compared high doses and low doses in their trials.
Similarly, vitamin D supplementation was not associated with any clinically relevant improvements in bone mineral density at any site; lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, forearm, or total body.
Even a post hoc analysis of randomized, controlled trials that compared daily high doses with daily low doses, as well as trials that compared intermittent high doses with intermittent low doses found no significant interactions for any outcome.
The paper also explored whether baseline vitamin D levels might influence outcomes. Eighteen trials in the analysis reported the results of subgroup analyses using baseline serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D (25[OH]D); three found no effects of vitamin D supplements in different subgroups of baseline, five studies found no effects of subgroups or interaction with baseline serum 25[OH]D, and one found mixed effects with respect to falls.
The outcomes for bone mineral density, as related to baseline serum 25[OH]D, were slightly more mixed. One trial found a positive effect of vitamin D supplements a bone mineral density for different subgroups of baseline serum, five trials reported mixed effects, and eight trials found no effects.
“The strengths of the current analyses are that they are comprehensive, include all available data from a large number of new trials, and concomitantly assess the major clinical and surrogate endpoints for musculoskeletal health,” wrote Mark J. Bolland, MD, of the department of medicine at the University of Auckland (New Zealand), and his coauthors. “Therefore, there is little justification for the use of vitamin D supplements to maintain or improve musculoskeletal health, and clinical guidelines should reflect these findings.”
They also conducted trial sequential analyses, which is a type of cumulative meta-analysis. For each outcome, they set a relative risk reduction threshold, then progressively reduced that threshold until the optimum sample size for that threshold exceeded the actual sample size.
“The trial sequential analyses are important because they provide estimates about the reliability of current evidence and the likelihood of future trials to change current conclusions,” the authors wrote.
Using this approach, they once again found clear evidence that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce fractures or falls for any measure of relative risk reduction. For hip fracture, the trial sequential analysis even found some uncertainty as to whether vitamin D supplementation might increase the risk of hip fractures.
Given the results of the trial sequential analyses, the authors argued that further similar trials were unlikely to alter their conclusion.
“If a large future trial has markedly different results to the current trials, adding its results will substantially increase the heterogeneity of the trial results, which in turn will reduce the weighting the new large trial receives in the pooled analyses,” they wrote. “Thus, adding a positive result from a large randomized, controlled trial will have only a small effect on the pooled result and is unlikely to alter the conclusions of these meta-analyses.”
They also noted that some of the studies had methodological limitations, and smaller studies of shorter duration tended to have “inflated” effect sizes, such that “the results of small, short-duration studies should be interpreted very cautiously, since they might not be replicated in larger, longer studies.”
The study was funded by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. Two authors declared grants from the Health Research Council during the study, one author is a shareholder in a company that provides bone mineral density measurements, and one reported grants from the Scottish Government Health and Social Care Directorates during the study.
SOURCE: Bolland M et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30265-1.
FROM LANCET DIABETES & ENDOCRINOLOGY
Key clinical point: Vitamin D does not reduce the risk of falls or fractures or to improve bone mineral density.
Major finding: Researchers found that vitamin D supplementation did not reduce total fracture, hip fracture, or falls, even in trials in which participants took doses greater than 800 IU/day.
Study details: Systematic review, meta-analysis, and trial sequential analysis of 81 randomized controlled trials of vitamin D supplementation.
Disclosures: The study was funded by the Health Research Council of New Zealand. Two authors declared grants from the Health Research Council during the study, one author is a shareholder in a company that provides bone mineral density measurements, and one reported grants from the Scottish Government Health and Social Care Directorates during the study.
Source: Bolland M et al. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018 Oct 4. doi. org/10.1016/S2213-8587(18)30265-1.
Secondary fractures in older men spike soon after first, but exercise may help
Older men have a higher risk than women of sustaining secondary fractures within a few years of their first fracture, but moderate physical activity may improve bone strength, potentially reducing their risk of fractures, according to two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research in Montreal.
The first study, a matched historical cohort of 57,783 people aged 50 or older (40,062 women and 17,721 men) in Manitoba, Canada, found that men had a threefold higher risk of sustaining a secondary major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) within 1 year of a first fracture, compared with healthy controls. The risk for women, by comparison, was 1.8 times higher than in age-matched controls who did not experience a fracture. These risks declined over time but remained elevated even as much as 15-25 years after the index fracture, according to primary investigator Suzanne N. Morin, MD, of the department of medicine at McGill University in Montreal.
“Often, men and clinicians don’t think men have skeletal fragility – everybody thinks it’s a women’s disease,” Dr. Morin said. “It’s true that it’s more frequent in women, but men do have osteoporosis, and often when they have it, they tend to have more serious complications following the fractures.” This includes higher risk of subsequent fractures and higher mortality, she said. “If you see an older gentleman with a fracture, it really should be some kind of an alarm signal.”
Using administrative health care databases, Dr. Morin and her colleagues reviewed records of patients who had an index MOF between 1989 and 2006. They compared rates of subsequent MOFs until 2016 with those of age- and sex-matched controls (n = 165,965), allowing for between 10 and 25 years of follow-up.
Researchers identified 29,694 index MOF cases (11,028 to the wrist, 9,313 to the hip, 5,799 to the humerus, and 3,554 to the spine). The annual crude rate of subsequent MOFs per 1,000 person-years was 18.5 in men (95% confidence interval, 17.3-19.8) and 29.6 in women (95% CI, 28.8-30.4). The cumulative incidence of subsequent MOFs up to 25 years later was higher in cases versus controls for both sexes and across all ages except those over 80.
Hazard ratios for subsequent MOFs were higher in men than women, particularly in the first year following the index fracture and remained very high for men during the first 3 years of follow-up. Across all follow-up years, men who had fractures were 2.5 times more likely to experience a secondary MOF (95% CI, 2.3-2.7) and women who had fractures were 1.6 times more likely to experience a secondary MOF (95% CI, 1.6-1.7), compared with controls.
To prevent fractures, clinicians should consider gait or balance training for older men and women, especially those who already have experienced a fracture, Dr. Morin said. Physicians also should note any medications such as sedatives that put patients at higher risk for falls and consider medications like bisphosphonates to reduce fracture risk. Additionally, they should ensure there are no underlying causes for skeletal fragility, such as severe vitamin D deficiency or a hormonal imbalance, she said.
Physical activity could reduce risk
In a second, unrelated study, researchers found that moderate physical activity may have a modest effect on bone strength in older men, accounting for up to a 20% lower fracture risk, according to Lisa Langsetmo, PhD, primary investigator and a senior research associate at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. She and her colleagues studied physical activity and bone strength in 994 older men (mean age 83.9) participating in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study, a longitudinal, observational study of musculoskeletal health in older American men that initially enrolled about 6,000 participants.
Participants wore armband activity monitors for 5 days during their year-7 and year-14 assessments; investigators averaged their physical activity over the two time points and used armband data along with factors like height, weight, and smoking status to estimate total energy expenditure (TEE), total steps per day, and level of activity, from sedentary to at least moderate. The men also underwent bone microarchitecture assessments of the distal radius and tibia using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT), a technique that produces detailed pictures of the bones. Investigators used mathematical models to predict failure load, or the force required to break a bone – a predictor of osteoporotic fractures in men. They also computed total, cortical, and trabecular volumetric bone mineral density (BMD).
Overall, researchers found that time spent doing at least moderate activity versus time spent in sedentary activity was related to better bone strength at both sites, whereas time spent in light activity was not. The results suggest that at least moderate physical activity such as vigorous walking averaged over a period of time may have a modest effect on bone strength among older men, Dr. Langsetmo said.
“This is important for older men,” she said. “They may not be able to jog any more but they may be able to do more moderate activity.” Physicians should ask older male patients about their activity levels and any barriers to activity, or consider a referral to a physical therapist to keep them active, she said.
Higher TEE, step count, and peak 30-minute cadence (P30MC), a measure of vigorous activity, were each associated with higher failure load of the distal radius (effect size 0.08-0.13) but not higher volumetric or compartment-specific BMD. These measures also were associated with higher failure load of the distal tibia (effect size 0.19-0.21), higher volumetric BMD (effect size 0.08-0.15), higher trabecular BMD (effect size 0.07-0.11), and higher cortical BMD (0.09-0.13).
The first study was funded internally; Manitoba Health provided the data. The second study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Morin and Dr. Langsetmo reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Older men have a higher risk than women of sustaining secondary fractures within a few years of their first fracture, but moderate physical activity may improve bone strength, potentially reducing their risk of fractures, according to two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research in Montreal.
The first study, a matched historical cohort of 57,783 people aged 50 or older (40,062 women and 17,721 men) in Manitoba, Canada, found that men had a threefold higher risk of sustaining a secondary major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) within 1 year of a first fracture, compared with healthy controls. The risk for women, by comparison, was 1.8 times higher than in age-matched controls who did not experience a fracture. These risks declined over time but remained elevated even as much as 15-25 years after the index fracture, according to primary investigator Suzanne N. Morin, MD, of the department of medicine at McGill University in Montreal.
“Often, men and clinicians don’t think men have skeletal fragility – everybody thinks it’s a women’s disease,” Dr. Morin said. “It’s true that it’s more frequent in women, but men do have osteoporosis, and often when they have it, they tend to have more serious complications following the fractures.” This includes higher risk of subsequent fractures and higher mortality, she said. “If you see an older gentleman with a fracture, it really should be some kind of an alarm signal.”
Using administrative health care databases, Dr. Morin and her colleagues reviewed records of patients who had an index MOF between 1989 and 2006. They compared rates of subsequent MOFs until 2016 with those of age- and sex-matched controls (n = 165,965), allowing for between 10 and 25 years of follow-up.
Researchers identified 29,694 index MOF cases (11,028 to the wrist, 9,313 to the hip, 5,799 to the humerus, and 3,554 to the spine). The annual crude rate of subsequent MOFs per 1,000 person-years was 18.5 in men (95% confidence interval, 17.3-19.8) and 29.6 in women (95% CI, 28.8-30.4). The cumulative incidence of subsequent MOFs up to 25 years later was higher in cases versus controls for both sexes and across all ages except those over 80.
Hazard ratios for subsequent MOFs were higher in men than women, particularly in the first year following the index fracture and remained very high for men during the first 3 years of follow-up. Across all follow-up years, men who had fractures were 2.5 times more likely to experience a secondary MOF (95% CI, 2.3-2.7) and women who had fractures were 1.6 times more likely to experience a secondary MOF (95% CI, 1.6-1.7), compared with controls.
To prevent fractures, clinicians should consider gait or balance training for older men and women, especially those who already have experienced a fracture, Dr. Morin said. Physicians also should note any medications such as sedatives that put patients at higher risk for falls and consider medications like bisphosphonates to reduce fracture risk. Additionally, they should ensure there are no underlying causes for skeletal fragility, such as severe vitamin D deficiency or a hormonal imbalance, she said.
Physical activity could reduce risk
In a second, unrelated study, researchers found that moderate physical activity may have a modest effect on bone strength in older men, accounting for up to a 20% lower fracture risk, according to Lisa Langsetmo, PhD, primary investigator and a senior research associate at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. She and her colleagues studied physical activity and bone strength in 994 older men (mean age 83.9) participating in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study, a longitudinal, observational study of musculoskeletal health in older American men that initially enrolled about 6,000 participants.
Participants wore armband activity monitors for 5 days during their year-7 and year-14 assessments; investigators averaged their physical activity over the two time points and used armband data along with factors like height, weight, and smoking status to estimate total energy expenditure (TEE), total steps per day, and level of activity, from sedentary to at least moderate. The men also underwent bone microarchitecture assessments of the distal radius and tibia using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT), a technique that produces detailed pictures of the bones. Investigators used mathematical models to predict failure load, or the force required to break a bone – a predictor of osteoporotic fractures in men. They also computed total, cortical, and trabecular volumetric bone mineral density (BMD).
Overall, researchers found that time spent doing at least moderate activity versus time spent in sedentary activity was related to better bone strength at both sites, whereas time spent in light activity was not. The results suggest that at least moderate physical activity such as vigorous walking averaged over a period of time may have a modest effect on bone strength among older men, Dr. Langsetmo said.
“This is important for older men,” she said. “They may not be able to jog any more but they may be able to do more moderate activity.” Physicians should ask older male patients about their activity levels and any barriers to activity, or consider a referral to a physical therapist to keep them active, she said.
Higher TEE, step count, and peak 30-minute cadence (P30MC), a measure of vigorous activity, were each associated with higher failure load of the distal radius (effect size 0.08-0.13) but not higher volumetric or compartment-specific BMD. These measures also were associated with higher failure load of the distal tibia (effect size 0.19-0.21), higher volumetric BMD (effect size 0.08-0.15), higher trabecular BMD (effect size 0.07-0.11), and higher cortical BMD (0.09-0.13).
The first study was funded internally; Manitoba Health provided the data. The second study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Morin and Dr. Langsetmo reported no relevant financial disclosures.
Older men have a higher risk than women of sustaining secondary fractures within a few years of their first fracture, but moderate physical activity may improve bone strength, potentially reducing their risk of fractures, according to two studies presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research in Montreal.
The first study, a matched historical cohort of 57,783 people aged 50 or older (40,062 women and 17,721 men) in Manitoba, Canada, found that men had a threefold higher risk of sustaining a secondary major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) within 1 year of a first fracture, compared with healthy controls. The risk for women, by comparison, was 1.8 times higher than in age-matched controls who did not experience a fracture. These risks declined over time but remained elevated even as much as 15-25 years after the index fracture, according to primary investigator Suzanne N. Morin, MD, of the department of medicine at McGill University in Montreal.
“Often, men and clinicians don’t think men have skeletal fragility – everybody thinks it’s a women’s disease,” Dr. Morin said. “It’s true that it’s more frequent in women, but men do have osteoporosis, and often when they have it, they tend to have more serious complications following the fractures.” This includes higher risk of subsequent fractures and higher mortality, she said. “If you see an older gentleman with a fracture, it really should be some kind of an alarm signal.”
Using administrative health care databases, Dr. Morin and her colleagues reviewed records of patients who had an index MOF between 1989 and 2006. They compared rates of subsequent MOFs until 2016 with those of age- and sex-matched controls (n = 165,965), allowing for between 10 and 25 years of follow-up.
Researchers identified 29,694 index MOF cases (11,028 to the wrist, 9,313 to the hip, 5,799 to the humerus, and 3,554 to the spine). The annual crude rate of subsequent MOFs per 1,000 person-years was 18.5 in men (95% confidence interval, 17.3-19.8) and 29.6 in women (95% CI, 28.8-30.4). The cumulative incidence of subsequent MOFs up to 25 years later was higher in cases versus controls for both sexes and across all ages except those over 80.
Hazard ratios for subsequent MOFs were higher in men than women, particularly in the first year following the index fracture and remained very high for men during the first 3 years of follow-up. Across all follow-up years, men who had fractures were 2.5 times more likely to experience a secondary MOF (95% CI, 2.3-2.7) and women who had fractures were 1.6 times more likely to experience a secondary MOF (95% CI, 1.6-1.7), compared with controls.
To prevent fractures, clinicians should consider gait or balance training for older men and women, especially those who already have experienced a fracture, Dr. Morin said. Physicians also should note any medications such as sedatives that put patients at higher risk for falls and consider medications like bisphosphonates to reduce fracture risk. Additionally, they should ensure there are no underlying causes for skeletal fragility, such as severe vitamin D deficiency or a hormonal imbalance, she said.
Physical activity could reduce risk
In a second, unrelated study, researchers found that moderate physical activity may have a modest effect on bone strength in older men, accounting for up to a 20% lower fracture risk, according to Lisa Langsetmo, PhD, primary investigator and a senior research associate at the University of Minnesota, Minneapolis. She and her colleagues studied physical activity and bone strength in 994 older men (mean age 83.9) participating in the Osteoporotic Fractures in Men (MrOS) Study, a longitudinal, observational study of musculoskeletal health in older American men that initially enrolled about 6,000 participants.
Participants wore armband activity monitors for 5 days during their year-7 and year-14 assessments; investigators averaged their physical activity over the two time points and used armband data along with factors like height, weight, and smoking status to estimate total energy expenditure (TEE), total steps per day, and level of activity, from sedentary to at least moderate. The men also underwent bone microarchitecture assessments of the distal radius and tibia using high-resolution peripheral quantitative computed tomography (HR-pQCT), a technique that produces detailed pictures of the bones. Investigators used mathematical models to predict failure load, or the force required to break a bone – a predictor of osteoporotic fractures in men. They also computed total, cortical, and trabecular volumetric bone mineral density (BMD).
Overall, researchers found that time spent doing at least moderate activity versus time spent in sedentary activity was related to better bone strength at both sites, whereas time spent in light activity was not. The results suggest that at least moderate physical activity such as vigorous walking averaged over a period of time may have a modest effect on bone strength among older men, Dr. Langsetmo said.
“This is important for older men,” she said. “They may not be able to jog any more but they may be able to do more moderate activity.” Physicians should ask older male patients about their activity levels and any barriers to activity, or consider a referral to a physical therapist to keep them active, she said.
Higher TEE, step count, and peak 30-minute cadence (P30MC), a measure of vigorous activity, were each associated with higher failure load of the distal radius (effect size 0.08-0.13) but not higher volumetric or compartment-specific BMD. These measures also were associated with higher failure load of the distal tibia (effect size 0.19-0.21), higher volumetric BMD (effect size 0.08-0.15), higher trabecular BMD (effect size 0.07-0.11), and higher cortical BMD (0.09-0.13).
The first study was funded internally; Manitoba Health provided the data. The second study was funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Morin and Dr. Langsetmo reported no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM ASBMR 2018
Zoledronate reduces fracture risk in elderly women with osteopenia
Intravenous zoledronate therapy given once every 18 months, with minimal use of calcium supplements, was associated with an increase in bone mass and significantly reduced the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women, compared with a placebo, based on data from a 6-year trial of 2,000 ambulatory women aged 65 and older with osteopenia.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bisphosphonates have been shown to prevent fractures in osteoporosis patients, but their effectiveness has not been well studied in patients with osteopenia alone, noted Ian R. Reid, MD, of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and his colleagues. “Many patients at high risk for fracture do not have T scores of less than –2.5 but rather have osteopenia in combination with other risk factors such as age.”
The researchers randomized 2,000 women aged 65 years and older with osteopenia to receive four infusions of zoledronate or a saline placebo every 18 months. A dietary intake of 1 g of calcium per day was advised, but calcium supplements were not provided; 2% of the women took supplements. Those not taking vitamin D before the trial were given a single 2.5-mg dose of cholecalciferol and a monthly 1.25-mg dose during the trial. Trial participants were followed for 6 years.
Demographic characteristics were similar between the groups, and their T scores ranged from –1.0 to –2.5 at the total hip or femoral neck. The primary endpoint was the time to a first fragility fracture, defined as nonvertebral fractures and vertebral fractures confirmed by radiography.
Overall, 122 women in the zoledronate group experienced 131 fractures, and 190 women in the placebo group experienced 227 fractures (hazard ratio 0.63, P less than .001). Differences in bone mineral density between the two groups were observed by 3 years.
The number needed to treat to prevent a single fragility fracture was 10; the number needed to treat to prevent a symptomatic fracture was 20.
The findings were consistent with data on reduced fracture risk in osteoporosis patients treated with zoledronate. The study differed from other similar trials in its use of 18-month dosing intervals and low use of calcium supplements (2%), they noted.
The data were limited by the older age of the study individuals, so the results should not be extrapolated to younger women or individuals with normal bone mineral density, the researchers said. The results suggest that annual zoledronate dosing may be unnecessary, but further research is needed to explore longer dose intervals.
Dr. Reid disclosed grants from Health Research Council of New Zealand, nonfinancial support from Novartis during the study, and financial relationships with Amgen, Merck, Novartis, and Eli Lilly unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Reid I et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.
This trial reminds us that risk assessment and treatment decisions go well beyond bone mineral density and should focus particularly on age and a history of fractures.
Osteoporosis is defined as a T score below –2.5, but several longitudinal studies have shown that most fractures among postmenopausal women occur in those with osteopenia. Further, alendronate therapy did not reduce the risk of fractures among women with osteopenia which contributed to a treatment gap for women with osteopenic T scores but strong risk factors for an osteoporotic fracture.
In the current study, zoledronate was associated with a greater increase in bone mass and a lower fracture risk compared with placebo. Plus, zoledronate prevented fractures among women with an average T score of –1.27 at the total hip and –1.64 at the femoral neck. The positive data, coupled with the low number of adverse events over the 6-year study period, support the addition of zoledronate to the treatment options for osteoporosis. However, the average age of the patients in the current study was 3.5 years older than that of patients in previous alendronate studies. As a result, the findings should not be extrapolated to postmenopausal women under the age of 65 years with osteopenia.
Clifford J. Rosen, MD, is affiliated with the Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, and serves as an associate editor at the New England Journal of Medicine. He made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1812434). Dr. Rosen had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
This trial reminds us that risk assessment and treatment decisions go well beyond bone mineral density and should focus particularly on age and a history of fractures.
Osteoporosis is defined as a T score below –2.5, but several longitudinal studies have shown that most fractures among postmenopausal women occur in those with osteopenia. Further, alendronate therapy did not reduce the risk of fractures among women with osteopenia which contributed to a treatment gap for women with osteopenic T scores but strong risk factors for an osteoporotic fracture.
In the current study, zoledronate was associated with a greater increase in bone mass and a lower fracture risk compared with placebo. Plus, zoledronate prevented fractures among women with an average T score of –1.27 at the total hip and –1.64 at the femoral neck. The positive data, coupled with the low number of adverse events over the 6-year study period, support the addition of zoledronate to the treatment options for osteoporosis. However, the average age of the patients in the current study was 3.5 years older than that of patients in previous alendronate studies. As a result, the findings should not be extrapolated to postmenopausal women under the age of 65 years with osteopenia.
Clifford J. Rosen, MD, is affiliated with the Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, and serves as an associate editor at the New England Journal of Medicine. He made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1812434). Dr. Rosen had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
This trial reminds us that risk assessment and treatment decisions go well beyond bone mineral density and should focus particularly on age and a history of fractures.
Osteoporosis is defined as a T score below –2.5, but several longitudinal studies have shown that most fractures among postmenopausal women occur in those with osteopenia. Further, alendronate therapy did not reduce the risk of fractures among women with osteopenia which contributed to a treatment gap for women with osteopenic T scores but strong risk factors for an osteoporotic fracture.
In the current study, zoledronate was associated with a greater increase in bone mass and a lower fracture risk compared with placebo. Plus, zoledronate prevented fractures among women with an average T score of –1.27 at the total hip and –1.64 at the femoral neck. The positive data, coupled with the low number of adverse events over the 6-year study period, support the addition of zoledronate to the treatment options for osteoporosis. However, the average age of the patients in the current study was 3.5 years older than that of patients in previous alendronate studies. As a result, the findings should not be extrapolated to postmenopausal women under the age of 65 years with osteopenia.
Clifford J. Rosen, MD, is affiliated with the Maine Medical Center Research Institute, Scarborough, and serves as an associate editor at the New England Journal of Medicine. He made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1812434). Dr. Rosen had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Intravenous zoledronate therapy given once every 18 months, with minimal use of calcium supplements, was associated with an increase in bone mass and significantly reduced the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women, compared with a placebo, based on data from a 6-year trial of 2,000 ambulatory women aged 65 and older with osteopenia.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bisphosphonates have been shown to prevent fractures in osteoporosis patients, but their effectiveness has not been well studied in patients with osteopenia alone, noted Ian R. Reid, MD, of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and his colleagues. “Many patients at high risk for fracture do not have T scores of less than –2.5 but rather have osteopenia in combination with other risk factors such as age.”
The researchers randomized 2,000 women aged 65 years and older with osteopenia to receive four infusions of zoledronate or a saline placebo every 18 months. A dietary intake of 1 g of calcium per day was advised, but calcium supplements were not provided; 2% of the women took supplements. Those not taking vitamin D before the trial were given a single 2.5-mg dose of cholecalciferol and a monthly 1.25-mg dose during the trial. Trial participants were followed for 6 years.
Demographic characteristics were similar between the groups, and their T scores ranged from –1.0 to –2.5 at the total hip or femoral neck. The primary endpoint was the time to a first fragility fracture, defined as nonvertebral fractures and vertebral fractures confirmed by radiography.
Overall, 122 women in the zoledronate group experienced 131 fractures, and 190 women in the placebo group experienced 227 fractures (hazard ratio 0.63, P less than .001). Differences in bone mineral density between the two groups were observed by 3 years.
The number needed to treat to prevent a single fragility fracture was 10; the number needed to treat to prevent a symptomatic fracture was 20.
The findings were consistent with data on reduced fracture risk in osteoporosis patients treated with zoledronate. The study differed from other similar trials in its use of 18-month dosing intervals and low use of calcium supplements (2%), they noted.
The data were limited by the older age of the study individuals, so the results should not be extrapolated to younger women or individuals with normal bone mineral density, the researchers said. The results suggest that annual zoledronate dosing may be unnecessary, but further research is needed to explore longer dose intervals.
Dr. Reid disclosed grants from Health Research Council of New Zealand, nonfinancial support from Novartis during the study, and financial relationships with Amgen, Merck, Novartis, and Eli Lilly unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Reid I et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.
Intravenous zoledronate therapy given once every 18 months, with minimal use of calcium supplements, was associated with an increase in bone mass and significantly reduced the risk of vertebral and nonvertebral fractures in postmenopausal women, compared with a placebo, based on data from a 6-year trial of 2,000 ambulatory women aged 65 and older with osteopenia.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society for Bone and Mineral Research and published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Bisphosphonates have been shown to prevent fractures in osteoporosis patients, but their effectiveness has not been well studied in patients with osteopenia alone, noted Ian R. Reid, MD, of the University of Auckland, New Zealand, and his colleagues. “Many patients at high risk for fracture do not have T scores of less than –2.5 but rather have osteopenia in combination with other risk factors such as age.”
The researchers randomized 2,000 women aged 65 years and older with osteopenia to receive four infusions of zoledronate or a saline placebo every 18 months. A dietary intake of 1 g of calcium per day was advised, but calcium supplements were not provided; 2% of the women took supplements. Those not taking vitamin D before the trial were given a single 2.5-mg dose of cholecalciferol and a monthly 1.25-mg dose during the trial. Trial participants were followed for 6 years.
Demographic characteristics were similar between the groups, and their T scores ranged from –1.0 to –2.5 at the total hip or femoral neck. The primary endpoint was the time to a first fragility fracture, defined as nonvertebral fractures and vertebral fractures confirmed by radiography.
Overall, 122 women in the zoledronate group experienced 131 fractures, and 190 women in the placebo group experienced 227 fractures (hazard ratio 0.63, P less than .001). Differences in bone mineral density between the two groups were observed by 3 years.
The number needed to treat to prevent a single fragility fracture was 10; the number needed to treat to prevent a symptomatic fracture was 20.
The findings were consistent with data on reduced fracture risk in osteoporosis patients treated with zoledronate. The study differed from other similar trials in its use of 18-month dosing intervals and low use of calcium supplements (2%), they noted.
The data were limited by the older age of the study individuals, so the results should not be extrapolated to younger women or individuals with normal bone mineral density, the researchers said. The results suggest that annual zoledronate dosing may be unnecessary, but further research is needed to explore longer dose intervals.
Dr. Reid disclosed grants from Health Research Council of New Zealand, nonfinancial support from Novartis during the study, and financial relationships with Amgen, Merck, Novartis, and Eli Lilly unrelated to the study.
SOURCE: Reid I et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.
REPORTING FROM ASBMR
Key clinical point: Vertebral and nonvertebral fracture risk was significantly lower in osteopenic women who received zoledronate, compared with those who received a placebo.
Major finding: Fragility fractures occurred in 122 women in a zoledronate group and 190 women in a placebo group. The number needed to treat to prevent a single fragility fracture was 10; the number needed to treat to prevent a symptomatic fracture was 20.
Study details: A 6-year randomized, double-blind trial of 2,000 women aged 65 years and older with osteopenia.
Disclosures: The study was supported in part by grants from the Health Research Council of New Zealand; Novartis provided the medication. Dr. Reid disclosed grants from Health Research Council of New Zealand, nonfinancial support from Novartis during the study, and financial relationships with Amgen, Merck, Novartis, and Eli Lilly unrelated to the study.
Source: Reid I et al. N Engl J Med. 2018 Oct 1. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1808082.
Pregnancy registries are a valuable resource
Pregnancy registries are valuable sources of information. For many drugs, they are the primary source of the human pregnancy experience. However, although most of the registries use the word “pregnancy,” it is important to note that many also enroll women who took the target drug shortly before conception.
The strengths of these registries are their prospective nature (enrolled before the outcome is known) and enrollment over a wide geographical area. Typically, two types of pregnancy outcomes are obtained: those with birth defects and those without known birth defects (classified as live births, fetal deaths, and spontaneous abortions). Registries can identify early signals of teratogenicity, but they have several limitations: selection bias that results from voluntary reporting; target populations that are not representative; lost-to-follow-up pregnancies that may have had different outcomes than those with documented outcomes; elective terminations and fetal deaths without birth defects and spontaneous abortions, all of which may lack details; the lack of control groups (with some exceptions); and the publication of results that may be delayed or not be in a peer-reviewed journal. Because the total number of exposed pregnancies is unknown, the data cannot be used to calculate prevalences, but they can be used to estimate the proportion of birth defects. Some registries also collect data on retrospective reports (reported after outcome is known). Such reports are less representative of the target population because they can be biased toward the reporting of more unusual and severe outcomes. But they may be helpful in detecting unusual patterns of birth defects.
For the following drugs, web addresses can be obtained from the Food and Drug Administration website, List of Pregnancy Exposure Registries.
MotherToBaby
A large registry, the MotherToBaby Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS) (877-311-8972), involves patients in several different categories and the effects of the drugs on the embryo-fetus: autoimmune diseases (ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and multiple sclerosis); asthma at less than 20 weeks’ gestation; vaccines; and heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
For the autoimmune diseases, the drugs and trade names are abatacept (Orencia), adalimumab (Humira), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia), etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), leflunomide (Arava), otezla (Apremilast), teriflunomide (Aubagio), tocilizumab (Actemra), tofacitinib (Xeljanz), and ustekinumab (Stelara).
For the asthma group, the drug being investigated is mepolizumab (Nucala).
Two vaccines – for tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap) and meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (Menveo) – are being studied.
The last category is heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. The two agents in this category are alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha).
Other registries
Breast cancer
The Mother Pregnancy Registry, INC Research (800-690-6720), is enrolling breast cancer patients who have been treated during pregnancy with ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), pertuzumab (Perjeta), or trastuzumab (Herceptin).
Epilepsy
The Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy registry (888-233-2334) is studying eslicarbazepine (Aptiom) and pregabalin (Lyrica).
Fabry disease
The Fabry Registry, Genzyme Corp (617-591-5500) is studying the use in pregnancy of agalsidase beta (Fabrazyme) for Fabry disease.
Fibromyalgia
The Savella Pregnancy Registry (877-643-3010) is looking for patients with fibromyalgia who are being treated with milnacipran (Savella).
Hepatitis B
The Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry, INC Research (800-593-2214) is looking for subjects with hepatitis C who have been treated with ribavirin (Copegus).
Hypercholesterolemia
Lomitapide (Juxtapid) is being studied by the Global Lomitapide Pregnancy Exposure Registry managed by Aegerion (877-902-4099). The drug is used for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
Mucopolysaccharidosis
The Mucopolysaccharidosis I (MPS I) registry, Genzyme (617-591-5500) is studying the use of laronidase (Aldurazyme) for Hurler syndrome, Scheie syndrome, and Hurler-Scheie syndrome.
The use of galsulfase (Naglazyme) for Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome during pregnancy is under study by the Mucopolysaccharidosis VI (MPS VI), clinical surveillance program (BioMarin Pharmaceutical) (415-506-6849 or 415-506-6703).
Multiple sclerosis
Novartis is conducting the Gilenya Pregnancy Registry (877-598-7237) for patients with multiple sclerosis who are taking fingolimod (Gilenya).
Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), also indicated for multiple sclerosis, is the target agent for the LEMTRADA Pregnancy Exposure Registry (866-758-2990).
Narcolepsy and other sleep disorders
Armodafinil (Nuvigil), used for excessive sleepiness associated with narcolepsy and other sleep disorders, is being studied in the Nuvigil Pregnancy Registry (866-404-4106). A second drug with the same indication and telephone number, modafinil (Provigil), is in the Provigil Pregnancy Registry.
Osteoporosis
Amgen’s Pregnancy Surveillance Program (800-772-6436) is enrolling pregnant subjects with osteoporosis who are being treated with denosumab (Prolia).
Others
Two Merck pregnancy registries (800-986-8999) cover the following conditions: type 2 diabetes sitagliptin+metformin (Janumet) or sitagliptin (Januvia); and migraine headaches rizatriptan (Maxalt).
GlaxoSmithKline is conducting two registries: the Belimumab Pregnancy Registry for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with belimumab (Benlysta) (877-681-6296); and Promacta Pregnancy Registry for women treated for thrombocytopenia with eltrombopag (Promacta) (888-825-5249).
Psychiatric Drugs
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (866-961-2388) is studying 10 drugs: aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), clozapine (Clozaril), iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), olanzapine (Zyprexa), paliperidone (Invega), quetiapine (Seroquel), risperidone (Risperdal), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
The National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants (844-405-6185) is studying amitriptyline (Elavil), amoxapine (Asendin), bupropion (Forfivo XL and Wellbutrin), citalopram (Celexa), clomipramine (Anafranil), desipramine (Norpramin), desvenlafaxine (Prisiq), doxepin (Sinequan), escitalopram (Lexapro), fluvoxamine (Luvox), fluoxetine (Prozac), imipramine (Tofranil), isocarboxazid (Marplan), levomilnacipran (Fetzima), maprotiline (Ludiomil), mirtazapine (Remeron), nefazodone (Serzone), nortriptyline (Pamelor), paroxetine (Paxil), phenelzine (Nardill), protriptyline (Vivactil), selegiline (Emsam), sertraline (Zoloft), tranylcypromine (Pamate), trazodone (Desyrel), trimipramine (Surmontil), venlafaxine (Effexor), and vilazodone (Viibryd).
The National Pregnancy Registry of Psychostimulants (866-961-2388) is studying amphetamine (Adderall), dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine and Focalin), lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Concerta, Daytrana, Desoxyn, Ritalin), and modafinil (Provigil).
The antidepressant duloxetine (Cymbalta) is being studied by the Cymbalta Pregnancy Registry (866-814-6975).
Transplant patients
Renal transplant patients exposed to mycophenolate (CellCept) can be enrolled in the Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International (877-955-6877) or the Mycophenolate Pregnancy Registry (800-617-8191). The Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International also is enrolling renal transplant patients exposed to belatacept (Nulojix).
Vaccines
A quadrivalent influenza vaccine (Afluria) is being studied by the Seqirus Influenza Vaccine Pregnancy Registry (855-358-8972). A second vaccine for meningococcal disease meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (Menactra) is under study by the Menactra Vaccine Pregnancy Registry (800-822-2463). The Bexsero Pregnancy Registry (877-413-4759) is open to patients who have received the meningococcal group B vaccine (Bexsero). The Hepatitis B Vaccine [Recombinant] Adjuvanted Pregnancy Registry, also listed as HEPLISAV-B, is enrolling patients who have received that vaccine (844-443-7734); it is supported by the Dynavax Technologies Corporation.
Because the strength of a registry is based on numbers, health care professionals are encouraged to enroll potential subjects or have their patients call to enroll themselves.
Mr. Briggs is clinical professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco, and adjunct professor of pharmacy at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, as well as at Washington State University, Spokane. Mr. Briggs said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Pregnancy registries are valuable sources of information. For many drugs, they are the primary source of the human pregnancy experience. However, although most of the registries use the word “pregnancy,” it is important to note that many also enroll women who took the target drug shortly before conception.
The strengths of these registries are their prospective nature (enrolled before the outcome is known) and enrollment over a wide geographical area. Typically, two types of pregnancy outcomes are obtained: those with birth defects and those without known birth defects (classified as live births, fetal deaths, and spontaneous abortions). Registries can identify early signals of teratogenicity, but they have several limitations: selection bias that results from voluntary reporting; target populations that are not representative; lost-to-follow-up pregnancies that may have had different outcomes than those with documented outcomes; elective terminations and fetal deaths without birth defects and spontaneous abortions, all of which may lack details; the lack of control groups (with some exceptions); and the publication of results that may be delayed or not be in a peer-reviewed journal. Because the total number of exposed pregnancies is unknown, the data cannot be used to calculate prevalences, but they can be used to estimate the proportion of birth defects. Some registries also collect data on retrospective reports (reported after outcome is known). Such reports are less representative of the target population because they can be biased toward the reporting of more unusual and severe outcomes. But they may be helpful in detecting unusual patterns of birth defects.
For the following drugs, web addresses can be obtained from the Food and Drug Administration website, List of Pregnancy Exposure Registries.
MotherToBaby
A large registry, the MotherToBaby Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS) (877-311-8972), involves patients in several different categories and the effects of the drugs on the embryo-fetus: autoimmune diseases (ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and multiple sclerosis); asthma at less than 20 weeks’ gestation; vaccines; and heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
For the autoimmune diseases, the drugs and trade names are abatacept (Orencia), adalimumab (Humira), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia), etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), leflunomide (Arava), otezla (Apremilast), teriflunomide (Aubagio), tocilizumab (Actemra), tofacitinib (Xeljanz), and ustekinumab (Stelara).
For the asthma group, the drug being investigated is mepolizumab (Nucala).
Two vaccines – for tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap) and meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (Menveo) – are being studied.
The last category is heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. The two agents in this category are alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha).
Other registries
Breast cancer
The Mother Pregnancy Registry, INC Research (800-690-6720), is enrolling breast cancer patients who have been treated during pregnancy with ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), pertuzumab (Perjeta), or trastuzumab (Herceptin).
Epilepsy
The Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy registry (888-233-2334) is studying eslicarbazepine (Aptiom) and pregabalin (Lyrica).
Fabry disease
The Fabry Registry, Genzyme Corp (617-591-5500) is studying the use in pregnancy of agalsidase beta (Fabrazyme) for Fabry disease.
Fibromyalgia
The Savella Pregnancy Registry (877-643-3010) is looking for patients with fibromyalgia who are being treated with milnacipran (Savella).
Hepatitis B
The Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry, INC Research (800-593-2214) is looking for subjects with hepatitis C who have been treated with ribavirin (Copegus).
Hypercholesterolemia
Lomitapide (Juxtapid) is being studied by the Global Lomitapide Pregnancy Exposure Registry managed by Aegerion (877-902-4099). The drug is used for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
Mucopolysaccharidosis
The Mucopolysaccharidosis I (MPS I) registry, Genzyme (617-591-5500) is studying the use of laronidase (Aldurazyme) for Hurler syndrome, Scheie syndrome, and Hurler-Scheie syndrome.
The use of galsulfase (Naglazyme) for Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome during pregnancy is under study by the Mucopolysaccharidosis VI (MPS VI), clinical surveillance program (BioMarin Pharmaceutical) (415-506-6849 or 415-506-6703).
Multiple sclerosis
Novartis is conducting the Gilenya Pregnancy Registry (877-598-7237) for patients with multiple sclerosis who are taking fingolimod (Gilenya).
Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), also indicated for multiple sclerosis, is the target agent for the LEMTRADA Pregnancy Exposure Registry (866-758-2990).
Narcolepsy and other sleep disorders
Armodafinil (Nuvigil), used for excessive sleepiness associated with narcolepsy and other sleep disorders, is being studied in the Nuvigil Pregnancy Registry (866-404-4106). A second drug with the same indication and telephone number, modafinil (Provigil), is in the Provigil Pregnancy Registry.
Osteoporosis
Amgen’s Pregnancy Surveillance Program (800-772-6436) is enrolling pregnant subjects with osteoporosis who are being treated with denosumab (Prolia).
Others
Two Merck pregnancy registries (800-986-8999) cover the following conditions: type 2 diabetes sitagliptin+metformin (Janumet) or sitagliptin (Januvia); and migraine headaches rizatriptan (Maxalt).
GlaxoSmithKline is conducting two registries: the Belimumab Pregnancy Registry for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with belimumab (Benlysta) (877-681-6296); and Promacta Pregnancy Registry for women treated for thrombocytopenia with eltrombopag (Promacta) (888-825-5249).
Psychiatric Drugs
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (866-961-2388) is studying 10 drugs: aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), clozapine (Clozaril), iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), olanzapine (Zyprexa), paliperidone (Invega), quetiapine (Seroquel), risperidone (Risperdal), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
The National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants (844-405-6185) is studying amitriptyline (Elavil), amoxapine (Asendin), bupropion (Forfivo XL and Wellbutrin), citalopram (Celexa), clomipramine (Anafranil), desipramine (Norpramin), desvenlafaxine (Prisiq), doxepin (Sinequan), escitalopram (Lexapro), fluvoxamine (Luvox), fluoxetine (Prozac), imipramine (Tofranil), isocarboxazid (Marplan), levomilnacipran (Fetzima), maprotiline (Ludiomil), mirtazapine (Remeron), nefazodone (Serzone), nortriptyline (Pamelor), paroxetine (Paxil), phenelzine (Nardill), protriptyline (Vivactil), selegiline (Emsam), sertraline (Zoloft), tranylcypromine (Pamate), trazodone (Desyrel), trimipramine (Surmontil), venlafaxine (Effexor), and vilazodone (Viibryd).
The National Pregnancy Registry of Psychostimulants (866-961-2388) is studying amphetamine (Adderall), dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine and Focalin), lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Concerta, Daytrana, Desoxyn, Ritalin), and modafinil (Provigil).
The antidepressant duloxetine (Cymbalta) is being studied by the Cymbalta Pregnancy Registry (866-814-6975).
Transplant patients
Renal transplant patients exposed to mycophenolate (CellCept) can be enrolled in the Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International (877-955-6877) or the Mycophenolate Pregnancy Registry (800-617-8191). The Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International also is enrolling renal transplant patients exposed to belatacept (Nulojix).
Vaccines
A quadrivalent influenza vaccine (Afluria) is being studied by the Seqirus Influenza Vaccine Pregnancy Registry (855-358-8972). A second vaccine for meningococcal disease meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (Menactra) is under study by the Menactra Vaccine Pregnancy Registry (800-822-2463). The Bexsero Pregnancy Registry (877-413-4759) is open to patients who have received the meningococcal group B vaccine (Bexsero). The Hepatitis B Vaccine [Recombinant] Adjuvanted Pregnancy Registry, also listed as HEPLISAV-B, is enrolling patients who have received that vaccine (844-443-7734); it is supported by the Dynavax Technologies Corporation.
Because the strength of a registry is based on numbers, health care professionals are encouraged to enroll potential subjects or have their patients call to enroll themselves.
Mr. Briggs is clinical professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco, and adjunct professor of pharmacy at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, as well as at Washington State University, Spokane. Mr. Briggs said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Pregnancy registries are valuable sources of information. For many drugs, they are the primary source of the human pregnancy experience. However, although most of the registries use the word “pregnancy,” it is important to note that many also enroll women who took the target drug shortly before conception.
The strengths of these registries are their prospective nature (enrolled before the outcome is known) and enrollment over a wide geographical area. Typically, two types of pregnancy outcomes are obtained: those with birth defects and those without known birth defects (classified as live births, fetal deaths, and spontaneous abortions). Registries can identify early signals of teratogenicity, but they have several limitations: selection bias that results from voluntary reporting; target populations that are not representative; lost-to-follow-up pregnancies that may have had different outcomes than those with documented outcomes; elective terminations and fetal deaths without birth defects and spontaneous abortions, all of which may lack details; the lack of control groups (with some exceptions); and the publication of results that may be delayed or not be in a peer-reviewed journal. Because the total number of exposed pregnancies is unknown, the data cannot be used to calculate prevalences, but they can be used to estimate the proportion of birth defects. Some registries also collect data on retrospective reports (reported after outcome is known). Such reports are less representative of the target population because they can be biased toward the reporting of more unusual and severe outcomes. But they may be helpful in detecting unusual patterns of birth defects.
For the following drugs, web addresses can be obtained from the Food and Drug Administration website, List of Pregnancy Exposure Registries.
MotherToBaby
A large registry, the MotherToBaby Organization of Teratology Information Specialists (OTIS) (877-311-8972), involves patients in several different categories and the effects of the drugs on the embryo-fetus: autoimmune diseases (ankylosing spondylitis, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, ulcerative colitis, psoriasis, Crohn’s disease, and multiple sclerosis); asthma at less than 20 weeks’ gestation; vaccines; and heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
For the autoimmune diseases, the drugs and trade names are abatacept (Orencia), adalimumab (Humira), certolizumab pegol (Cimzia), etanercept (Enbrel), infliximab (Remicade), leflunomide (Arava), otezla (Apremilast), teriflunomide (Aubagio), tocilizumab (Actemra), tofacitinib (Xeljanz), and ustekinumab (Stelara).
For the asthma group, the drug being investigated is mepolizumab (Nucala).
Two vaccines – for tetanus, diphtheria, and pertussis (Tdap) and meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (Menveo) – are being studied.
The last category is heterozygous or homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. The two agents in this category are alirocumab (Praluent) and evolocumab (Repatha).
Other registries
Breast cancer
The Mother Pregnancy Registry, INC Research (800-690-6720), is enrolling breast cancer patients who have been treated during pregnancy with ado-trastuzumab emtansine (Kadcyla), pertuzumab (Perjeta), or trastuzumab (Herceptin).
Epilepsy
The Antiepileptic Drug Pregnancy registry (888-233-2334) is studying eslicarbazepine (Aptiom) and pregabalin (Lyrica).
Fabry disease
The Fabry Registry, Genzyme Corp (617-591-5500) is studying the use in pregnancy of agalsidase beta (Fabrazyme) for Fabry disease.
Fibromyalgia
The Savella Pregnancy Registry (877-643-3010) is looking for patients with fibromyalgia who are being treated with milnacipran (Savella).
Hepatitis B
The Ribavirin Pregnancy Registry, INC Research (800-593-2214) is looking for subjects with hepatitis C who have been treated with ribavirin (Copegus).
Hypercholesterolemia
Lomitapide (Juxtapid) is being studied by the Global Lomitapide Pregnancy Exposure Registry managed by Aegerion (877-902-4099). The drug is used for homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia.
Mucopolysaccharidosis
The Mucopolysaccharidosis I (MPS I) registry, Genzyme (617-591-5500) is studying the use of laronidase (Aldurazyme) for Hurler syndrome, Scheie syndrome, and Hurler-Scheie syndrome.
The use of galsulfase (Naglazyme) for Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome during pregnancy is under study by the Mucopolysaccharidosis VI (MPS VI), clinical surveillance program (BioMarin Pharmaceutical) (415-506-6849 or 415-506-6703).
Multiple sclerosis
Novartis is conducting the Gilenya Pregnancy Registry (877-598-7237) for patients with multiple sclerosis who are taking fingolimod (Gilenya).
Alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), also indicated for multiple sclerosis, is the target agent for the LEMTRADA Pregnancy Exposure Registry (866-758-2990).
Narcolepsy and other sleep disorders
Armodafinil (Nuvigil), used for excessive sleepiness associated with narcolepsy and other sleep disorders, is being studied in the Nuvigil Pregnancy Registry (866-404-4106). A second drug with the same indication and telephone number, modafinil (Provigil), is in the Provigil Pregnancy Registry.
Osteoporosis
Amgen’s Pregnancy Surveillance Program (800-772-6436) is enrolling pregnant subjects with osteoporosis who are being treated with denosumab (Prolia).
Others
Two Merck pregnancy registries (800-986-8999) cover the following conditions: type 2 diabetes sitagliptin+metformin (Janumet) or sitagliptin (Januvia); and migraine headaches rizatriptan (Maxalt).
GlaxoSmithKline is conducting two registries: the Belimumab Pregnancy Registry for patients with systemic lupus erythematosus treated with belimumab (Benlysta) (877-681-6296); and Promacta Pregnancy Registry for women treated for thrombocytopenia with eltrombopag (Promacta) (888-825-5249).
Psychiatric Drugs
The National Pregnancy Registry for Atypical Antipsychotics (866-961-2388) is studying 10 drugs: aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), clozapine (Clozaril), iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), olanzapine (Zyprexa), paliperidone (Invega), quetiapine (Seroquel), risperidone (Risperdal), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
The National Pregnancy Registry for Antidepressants (844-405-6185) is studying amitriptyline (Elavil), amoxapine (Asendin), bupropion (Forfivo XL and Wellbutrin), citalopram (Celexa), clomipramine (Anafranil), desipramine (Norpramin), desvenlafaxine (Prisiq), doxepin (Sinequan), escitalopram (Lexapro), fluvoxamine (Luvox), fluoxetine (Prozac), imipramine (Tofranil), isocarboxazid (Marplan), levomilnacipran (Fetzima), maprotiline (Ludiomil), mirtazapine (Remeron), nefazodone (Serzone), nortriptyline (Pamelor), paroxetine (Paxil), phenelzine (Nardill), protriptyline (Vivactil), selegiline (Emsam), sertraline (Zoloft), tranylcypromine (Pamate), trazodone (Desyrel), trimipramine (Surmontil), venlafaxine (Effexor), and vilazodone (Viibryd).
The National Pregnancy Registry of Psychostimulants (866-961-2388) is studying amphetamine (Adderall), dextroamphetamine (Dexedrine and Focalin), lisdexamfetamine (Vyvanse), methylphenidate (Concerta, Daytrana, Desoxyn, Ritalin), and modafinil (Provigil).
The antidepressant duloxetine (Cymbalta) is being studied by the Cymbalta Pregnancy Registry (866-814-6975).
Transplant patients
Renal transplant patients exposed to mycophenolate (CellCept) can be enrolled in the Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International (877-955-6877) or the Mycophenolate Pregnancy Registry (800-617-8191). The Transplantation Pregnancy Registry International also is enrolling renal transplant patients exposed to belatacept (Nulojix).
Vaccines
A quadrivalent influenza vaccine (Afluria) is being studied by the Seqirus Influenza Vaccine Pregnancy Registry (855-358-8972). A second vaccine for meningococcal disease meningococcal disease caused by Neisseria meningitidis serogroups A, C, Y and W-135 (Menactra) is under study by the Menactra Vaccine Pregnancy Registry (800-822-2463). The Bexsero Pregnancy Registry (877-413-4759) is open to patients who have received the meningococcal group B vaccine (Bexsero). The Hepatitis B Vaccine [Recombinant] Adjuvanted Pregnancy Registry, also listed as HEPLISAV-B, is enrolling patients who have received that vaccine (844-443-7734); it is supported by the Dynavax Technologies Corporation.
Because the strength of a registry is based on numbers, health care professionals are encouraged to enroll potential subjects or have their patients call to enroll themselves.
Mr. Briggs is clinical professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco, and adjunct professor of pharmacy at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, as well as at Washington State University, Spokane. Mr. Briggs said he had no relevant financial disclosures. Email him at [email protected].
Fracture risk linked to mortality in women with myeloma
Preexisting osteoporosis is an important risk factor for mortality risk in cancer-free postmenopausal women who go on to develop multiple myeloma, results of a recent analysis suggest.
High fracture risk was associated with an increased risk of death, independent of other clinical risk factors, in this analysis of postmenopausal women in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) data set.
The findings help define osteoporosis as an important prognostic factor associated with mortality in postmenopausal women who develop myeloma, according to study author Ashley E. Rosko, MD, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and her colleagues.
“Osteoporosis is highly prevalent in aging adults, and very little is known on how this comorbid condition contributes to outcomes in individuals who develop myeloma,” wrote Dr. Rosko and her coauthors. Their report is in the journal Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The analysis involved 362 women in the WHI data set who developed myeloma and had no history of any cancer at baseline. Women in the WHI were between 50 and 79 years of age and postmenopausal at baseline when originally recruited at 40 U.S. centers between 1993 and 1998.
Dr. Rosko and her colleagues calculated bone health for women in the data set using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), a web-based tool that calculates 10-year probability of hip and other major osteoporotic fractures.
Of the 362 women who developed myeloma, 98 were classified as having high FRAX scores, defined as a 10-year probability of 3% or greater for hip fracture, or 20% or greater for other major osteoporosis-related fractures.
With a median follow-up of 10.5 years, the adjusted risk of death was elevated in women with high FRAX scores, according to investigators, with a covariate-adjusted hazard ratio of 1.51 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P = .044) versus women with low FRAX scores.
Of the 362 patients who developed myeloma, 226 died during the follow-up period. That included 71 women with high FRAX scores, or 72% of that subset; and 155 women with low FRAX scores, or 59% of that subset, investigators reported.
These findings suggest osteoporosis is an “important comorbidity” in women who develop multiple myeloma, Dr. Rosko and her coauthors said in a discussion of the study results.
“Recognizing osteoporosis as a risk factor associated with multiple myeloma mortality is an important prognostic factor in postmenopausal women,” they said.
This investigation was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Rosko AE et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Sep;18(9):597-602.e1.
Preexisting osteoporosis is an important risk factor for mortality risk in cancer-free postmenopausal women who go on to develop multiple myeloma, results of a recent analysis suggest.
High fracture risk was associated with an increased risk of death, independent of other clinical risk factors, in this analysis of postmenopausal women in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) data set.
The findings help define osteoporosis as an important prognostic factor associated with mortality in postmenopausal women who develop myeloma, according to study author Ashley E. Rosko, MD, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and her colleagues.
“Osteoporosis is highly prevalent in aging adults, and very little is known on how this comorbid condition contributes to outcomes in individuals who develop myeloma,” wrote Dr. Rosko and her coauthors. Their report is in the journal Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The analysis involved 362 women in the WHI data set who developed myeloma and had no history of any cancer at baseline. Women in the WHI were between 50 and 79 years of age and postmenopausal at baseline when originally recruited at 40 U.S. centers between 1993 and 1998.
Dr. Rosko and her colleagues calculated bone health for women in the data set using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), a web-based tool that calculates 10-year probability of hip and other major osteoporotic fractures.
Of the 362 women who developed myeloma, 98 were classified as having high FRAX scores, defined as a 10-year probability of 3% or greater for hip fracture, or 20% or greater for other major osteoporosis-related fractures.
With a median follow-up of 10.5 years, the adjusted risk of death was elevated in women with high FRAX scores, according to investigators, with a covariate-adjusted hazard ratio of 1.51 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P = .044) versus women with low FRAX scores.
Of the 362 patients who developed myeloma, 226 died during the follow-up period. That included 71 women with high FRAX scores, or 72% of that subset; and 155 women with low FRAX scores, or 59% of that subset, investigators reported.
These findings suggest osteoporosis is an “important comorbidity” in women who develop multiple myeloma, Dr. Rosko and her coauthors said in a discussion of the study results.
“Recognizing osteoporosis as a risk factor associated with multiple myeloma mortality is an important prognostic factor in postmenopausal women,” they said.
This investigation was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Rosko AE et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Sep;18(9):597-602.e1.
Preexisting osteoporosis is an important risk factor for mortality risk in cancer-free postmenopausal women who go on to develop multiple myeloma, results of a recent analysis suggest.
High fracture risk was associated with an increased risk of death, independent of other clinical risk factors, in this analysis of postmenopausal women in the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) data set.
The findings help define osteoporosis as an important prognostic factor associated with mortality in postmenopausal women who develop myeloma, according to study author Ashley E. Rosko, MD, of Ohio State University, Columbus, and her colleagues.
“Osteoporosis is highly prevalent in aging adults, and very little is known on how this comorbid condition contributes to outcomes in individuals who develop myeloma,” wrote Dr. Rosko and her coauthors. Their report is in the journal Clinical Lymphoma, Myeloma and Leukemia.
The analysis involved 362 women in the WHI data set who developed myeloma and had no history of any cancer at baseline. Women in the WHI were between 50 and 79 years of age and postmenopausal at baseline when originally recruited at 40 U.S. centers between 1993 and 1998.
Dr. Rosko and her colleagues calculated bone health for women in the data set using the Fracture Risk Assessment Tool (FRAX), a web-based tool that calculates 10-year probability of hip and other major osteoporotic fractures.
Of the 362 women who developed myeloma, 98 were classified as having high FRAX scores, defined as a 10-year probability of 3% or greater for hip fracture, or 20% or greater for other major osteoporosis-related fractures.
With a median follow-up of 10.5 years, the adjusted risk of death was elevated in women with high FRAX scores, according to investigators, with a covariate-adjusted hazard ratio of 1.51 (95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P = .044) versus women with low FRAX scores.
Of the 362 patients who developed myeloma, 226 died during the follow-up period. That included 71 women with high FRAX scores, or 72% of that subset; and 155 women with low FRAX scores, or 59% of that subset, investigators reported.
These findings suggest osteoporosis is an “important comorbidity” in women who develop multiple myeloma, Dr. Rosko and her coauthors said in a discussion of the study results.
“Recognizing osteoporosis as a risk factor associated with multiple myeloma mortality is an important prognostic factor in postmenopausal women,” they said.
This investigation was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Rosko AE et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Sep;18(9):597-602.e1.
FROM CLINICAL LYMPHOMA, MYELOMA AND LEUKEMIA
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Risk of death was elevated in women at high risk of fracture (covariate-adjusted hazard ratio, 1.51; 95% confidence interval, 1.01-2.25; P = .044) versus women with low fracture risk.
Study details: Retrospective analysis of the Women’s Health Initiative data set including 362 postmenopausal women who were cancer free at baseline and developed myeloma over the course of study follow-up.
Disclosures: The analysis was supported in part by the National Cancer Institute. The researchers reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Rosko AE et al. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk. 2018 Sep;18(9):597-602.e1.
Breast arterial calcification, low bone mass predict CAD in women
Breast arterial calcification and low bone mass (LBM) were strongly linked to risk of coronary artery disease in asymptomatic women, according to a cross-sectional registry study.
The results suggest that breast arterial calcification – easily visible on every mammogram – “provides an independent and incremental predictive value over conventional risk factors,” wrote Yeonyee E. Yoon, MD, and colleagues from Seoul National University Bundang Hospital in Seongnam, South Korea.
In addition, they show that “atherosclerosis imaging allows a more direct visualization of the cumulative effects of all risk determinants in an individual patient,” they noted. The report is in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
The researchers evaluated 2,100 asymptomatic women aged at least 40 years in the Women Health Registry Study for Bone, Breast, and Coronary Artery Disease (BBC study). All underwent a self-referred health evaluation that included simultaneous dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), and digital mammography. They predicted the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) with the Korean Risk Prediction Model (KRPM) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE).
Overall, Dr. Yoon and colleagues found that 199 patients (9.5%) had BAC and 716 patients (34.1%) had LBM, with 235 patients (11.2%) having coronary artery calcification (CAC) and 328 with coronary artery plaque (CAP, 15.6%). BAC presence was associated with CAC (unadjusted odds ratio, 3.54), with mild (OR, 2.84) and severe BAC scores (OR, 5.50) having a greater association with CAC. All associations were statistically significant at P less than .001.
LBM also had a positive link with CAC that grew with its severity. Specifically, the odds ratio of CAC with osteopenia, defined as a T-score between –1.0 and –2.5, was 2.06, and that for osteoporosis, defined as a T-score at or below –2.5, was 3.21. All links were significant at P less than .001.
Similarly, BAC and LBM were also significantly tied to coronary artery plaque, with mild (OR, 2.61) and moderate (OR, 4.15) BAC severity as well as osteopenia (OR, 1.76) and osteoporosis (OR 2.82) being significantly associated with CAP (all P less than .001).
In a multivariable analysis, BAC presence and BAC score were significantly associated with CAC and CAP after adjustment for 10-year ASCVD risk. Predictions for CAC and CAP under the KRPM and PCE curve analyses showed a significant increase of areas under the curve (0.71 vs. 0.64), while adding BAC presence significantly increased the AUCs for the KRPM curve analysis (0.61 vs 0.64).
“Being able to predict CAC or CAP presence in an individual patient based on the presence and severity of BAC in addition to the use of conventional risk stratification algorithms may help clinicians decide when to recommend further cardiac tests and how aggressive interventions to prescribe in order to prevent the onset of clinical CAD,” the researchers noted.
They added that patients were all self-referred women, and results may not be generalizable to a larger population. The study’s retrospective nature also is a limitation, the researchers wrote. However, they said they are planning a future trial that will attempt to determine whether there is a long-term clinical benefit to identifying BAC and LBM in women without symptoms of CAD.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea; the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning; and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund. The authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Yoon YE et al. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Aug 15. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.004.
Breast arterial calcification and low bone mass (LBM) were strongly linked to risk of coronary artery disease in asymptomatic women, according to a cross-sectional registry study.
The results suggest that breast arterial calcification – easily visible on every mammogram – “provides an independent and incremental predictive value over conventional risk factors,” wrote Yeonyee E. Yoon, MD, and colleagues from Seoul National University Bundang Hospital in Seongnam, South Korea.
In addition, they show that “atherosclerosis imaging allows a more direct visualization of the cumulative effects of all risk determinants in an individual patient,” they noted. The report is in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
The researchers evaluated 2,100 asymptomatic women aged at least 40 years in the Women Health Registry Study for Bone, Breast, and Coronary Artery Disease (BBC study). All underwent a self-referred health evaluation that included simultaneous dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), and digital mammography. They predicted the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) with the Korean Risk Prediction Model (KRPM) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE).
Overall, Dr. Yoon and colleagues found that 199 patients (9.5%) had BAC and 716 patients (34.1%) had LBM, with 235 patients (11.2%) having coronary artery calcification (CAC) and 328 with coronary artery plaque (CAP, 15.6%). BAC presence was associated with CAC (unadjusted odds ratio, 3.54), with mild (OR, 2.84) and severe BAC scores (OR, 5.50) having a greater association with CAC. All associations were statistically significant at P less than .001.
LBM also had a positive link with CAC that grew with its severity. Specifically, the odds ratio of CAC with osteopenia, defined as a T-score between –1.0 and –2.5, was 2.06, and that for osteoporosis, defined as a T-score at or below –2.5, was 3.21. All links were significant at P less than .001.
Similarly, BAC and LBM were also significantly tied to coronary artery plaque, with mild (OR, 2.61) and moderate (OR, 4.15) BAC severity as well as osteopenia (OR, 1.76) and osteoporosis (OR 2.82) being significantly associated with CAP (all P less than .001).
In a multivariable analysis, BAC presence and BAC score were significantly associated with CAC and CAP after adjustment for 10-year ASCVD risk. Predictions for CAC and CAP under the KRPM and PCE curve analyses showed a significant increase of areas under the curve (0.71 vs. 0.64), while adding BAC presence significantly increased the AUCs for the KRPM curve analysis (0.61 vs 0.64).
“Being able to predict CAC or CAP presence in an individual patient based on the presence and severity of BAC in addition to the use of conventional risk stratification algorithms may help clinicians decide when to recommend further cardiac tests and how aggressive interventions to prescribe in order to prevent the onset of clinical CAD,” the researchers noted.
They added that patients were all self-referred women, and results may not be generalizable to a larger population. The study’s retrospective nature also is a limitation, the researchers wrote. However, they said they are planning a future trial that will attempt to determine whether there is a long-term clinical benefit to identifying BAC and LBM in women without symptoms of CAD.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea; the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning; and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund. The authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Yoon YE et al. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Aug 15. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.004.
Breast arterial calcification and low bone mass (LBM) were strongly linked to risk of coronary artery disease in asymptomatic women, according to a cross-sectional registry study.
The results suggest that breast arterial calcification – easily visible on every mammogram – “provides an independent and incremental predictive value over conventional risk factors,” wrote Yeonyee E. Yoon, MD, and colleagues from Seoul National University Bundang Hospital in Seongnam, South Korea.
In addition, they show that “atherosclerosis imaging allows a more direct visualization of the cumulative effects of all risk determinants in an individual patient,” they noted. The report is in JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging.
The researchers evaluated 2,100 asymptomatic women aged at least 40 years in the Women Health Registry Study for Bone, Breast, and Coronary Artery Disease (BBC study). All underwent a self-referred health evaluation that included simultaneous dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), coronary computed tomography angiography (CCTA), and digital mammography. They predicted the 10-year risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) with the Korean Risk Prediction Model (KRPM) and Pooled Cohort Equation (PCE).
Overall, Dr. Yoon and colleagues found that 199 patients (9.5%) had BAC and 716 patients (34.1%) had LBM, with 235 patients (11.2%) having coronary artery calcification (CAC) and 328 with coronary artery plaque (CAP, 15.6%). BAC presence was associated with CAC (unadjusted odds ratio, 3.54), with mild (OR, 2.84) and severe BAC scores (OR, 5.50) having a greater association with CAC. All associations were statistically significant at P less than .001.
LBM also had a positive link with CAC that grew with its severity. Specifically, the odds ratio of CAC with osteopenia, defined as a T-score between –1.0 and –2.5, was 2.06, and that for osteoporosis, defined as a T-score at or below –2.5, was 3.21. All links were significant at P less than .001.
Similarly, BAC and LBM were also significantly tied to coronary artery plaque, with mild (OR, 2.61) and moderate (OR, 4.15) BAC severity as well as osteopenia (OR, 1.76) and osteoporosis (OR 2.82) being significantly associated with CAP (all P less than .001).
In a multivariable analysis, BAC presence and BAC score were significantly associated with CAC and CAP after adjustment for 10-year ASCVD risk. Predictions for CAC and CAP under the KRPM and PCE curve analyses showed a significant increase of areas under the curve (0.71 vs. 0.64), while adding BAC presence significantly increased the AUCs for the KRPM curve analysis (0.61 vs 0.64).
“Being able to predict CAC or CAP presence in an individual patient based on the presence and severity of BAC in addition to the use of conventional risk stratification algorithms may help clinicians decide when to recommend further cardiac tests and how aggressive interventions to prescribe in order to prevent the onset of clinical CAD,” the researchers noted.
They added that patients were all self-referred women, and results may not be generalizable to a larger population. The study’s retrospective nature also is a limitation, the researchers wrote. However, they said they are planning a future trial that will attempt to determine whether there is a long-term clinical benefit to identifying BAC and LBM in women without symptoms of CAD.
This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea; the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning; and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund. The authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Yoon YE et al. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Aug 15. doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.004.
FROM JACC: CARDIOVASCULAR IMAGING
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Breast arterial calcification (BAC) carried an odds ratio of 3.54 and low bone mass (LBM) carried an OR of 2.22 for the associated presence of coronary artery calcification, while BAC had an OR of 3.02 and LBM had an OR of 1.92 for associated presence of coronary atherosclerotic plaque.
Study details: A cross-sectional study of 2,100 women analyzed for subclinical coronary artery disease in the Bone, Breast, and CAD health registry study.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea; the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning; and the Seoul National University Bundang Hospital Research Fund. The authors report no relevant financial disclosures.
Source: Yoon YE et al. JACC: Cardiovasc Imaging. 2018 Aug 15; doi: 10.1016/j.jcmg.2018.07.004.
Screening for osteoporosis to prevent fractures: USPSTF recommendation statement
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force commissioned a systematic evidence review of 168 fair-good quality articles to examine newer evidence on screening for and treatment of osteoporotic fracture in women and men and update its 2011 guideline. For postmenopausal women older than 65 years and those younger than 65 years with increased risk of osteoporosis, USPSTF found convincing evidence that screening can detect osteoporosis and that treatment can provide at least a moderate benefit in preventing fractures (grade B). For men, they report inadequate evidence on the benefits and harms of screening for osteoporosis to reduce the risk of fractures (I statement).
Importance
Osteoporosis leads to increased bone fragility and risk of fractures, specifically hip fractures, that are associated with limitations in ambulation, chronic pain, disability and loss of independence, and decreased quality of life: 21%-30% of those who suffer hip fractures die within 1 year. Osteoporosis is usually asymptomatic until a fracture occurs, thus preventing fractures is the main goal of an osteoporosis screening strategy. With the increasing life expectancy of the U.S. population, the potential preventable burden is likely to increase in future years.
Screening tests
The most commonly used test is central dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), which provides measurement of bone mineral density (BMD) of the hip and lumbar spine. Most treatment guidelines already use central DXA BMD to define osteoporosis and the threshold at which to start drug therapies for prevention. Other lower-cost and more accessible alternatives include peripheral DXA, which measures BMD at lower forearm and heel, and quantitative ultrasound (QUS), which also evaluates peripheral sites like the calcaneus. QUS does not measure BMD. USPSTF found that the harms associated with screening were small (mainly radiation exposure from DXA and opportunity costs).
Population and risk assessment
The review included adults older than 40 years of age, mostly postmenopausal women, without a history of previous low-trauma fractures, without conditions or medications that may cause secondary osteoporosis, and without increased risk of falls.
Patients at increased risk of osteoporotic fractures include those with parental history of hip fractures, low body weight, excessive alcohol consumption, and smokers. For postmenopausal women younger than 65 years of age with at least one risk factor, a reasonable approach to determine who should be screened with BMD is to use one of the various clinical risk assessment tools available. The most frequently studied tools in women are the Osteoporosis Risk Assessment Instrument (ORAI), Osteoporosis Index of Risk (OSIRIS), Osteoporosis Self-Assessment Tool (OST), and Simple Calculated Osteoporosis Risk Estimation (SCORE). The Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool calculates the 10-year risk of a major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) using clinical risk factors. For example, one approach is to perform BMD in women younger than 65 years with a FRAX risk greater than 8.4% (the FRAX risk of a 65-year-old woman of mean height and weight without major risk factors).
In men, the prevalence of osteoporosis (4.3%) is generally lower than in women (15.4%). In the absence of other risk factors, it is not till age 80 that the prevalence of osteoporosis in white men starts to reach that of a 65-year-old white woman. While men have similar risk factors as women described above, men with hypogonadism, history of cerebrovascular accident, and history of diabetes are also at increased risk of fracture.
Preventative measures to reduce osteoporotic fractures
Approved drug therapies. The majority of studies were conducted in postmenopausal women. Bisphosphonates, most commonly used and studied, significantly reduced vertebral and nonvertebral fractures but not hip fractures (possibly because of underpowered studies). Raloxifene and parathyroid hormone reduced vertebral fractures but not nonvertebral fractures. Denosumab significantly reduced all three types of fractures. A 2011 review identified that estrogen reduced vertebral fractures, but no new studies were identified for the current review. Data from the Women’s Health Initiative show that women receiving estrogen with or without progesterone had an elevated risk of stroke, venous thromboembolism, and gallbladder disease; their risk for urinary incontinence was increased during the first year of follow-up. In addition, women receiving estrogen plus progestin had a higher risk of invasive breast cancer, coronary heart disease, and probable dementia. The risk of serious adverse events, upper-gastrointestinal events, or cardiovascular events associated with the most common class of medications used, bisphosphonates, is small. Evidence on the effectiveness of medications to treat osteoporosis in men is lacking (only two studies conducted).
Exercise. Engagement in 120-300 minutes of weekly moderate-intensity aerobic activity can reduce the risk of hip fractures, and performance of weekly balance and muscle-strengthening activities can help prevent falls in older adults.
Supplements. In a separate recommendation, USPSTF recommends against daily supplementation with less than 400 IU of vitamin D and less than 1,000 mg of calcium for the primary prevention of fractures in community-dwelling, postmenopausal women. They found insufficient evidence on supplementation with higher doses of vitamin D and calcium in postmenopausal women, or at any dose in men and premenopausal women.
Recommendations from others
The National Osteoporosis Foundation and the International Society for Clinical Densitometry recommend BMD testing in all women older than 65 years, all men over 70 years, postmenopausal women younger than 65 years, and men aged 50-69 years with increased risk factors. The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends against DXA screening in women younger than 65 years and men younger than 70 years with no risk factors.
The bottom line
For all women older than 65 years and postmenopausal women younger than 65 years who are at increased risk, screen for and treat osteoporosis to prevent fractures. For men, there is insufficient evidence to screen.
Dr. Shrestha is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) - Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is a professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington - Jefferson Health.
References
1. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018 Jun 26;319(24):2521-31.
2. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018 Jun 26;319(24):2532-51.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force commissioned a systematic evidence review of 168 fair-good quality articles to examine newer evidence on screening for and treatment of osteoporotic fracture in women and men and update its 2011 guideline. For postmenopausal women older than 65 years and those younger than 65 years with increased risk of osteoporosis, USPSTF found convincing evidence that screening can detect osteoporosis and that treatment can provide at least a moderate benefit in preventing fractures (grade B). For men, they report inadequate evidence on the benefits and harms of screening for osteoporosis to reduce the risk of fractures (I statement).
Importance
Osteoporosis leads to increased bone fragility and risk of fractures, specifically hip fractures, that are associated with limitations in ambulation, chronic pain, disability and loss of independence, and decreased quality of life: 21%-30% of those who suffer hip fractures die within 1 year. Osteoporosis is usually asymptomatic until a fracture occurs, thus preventing fractures is the main goal of an osteoporosis screening strategy. With the increasing life expectancy of the U.S. population, the potential preventable burden is likely to increase in future years.
Screening tests
The most commonly used test is central dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), which provides measurement of bone mineral density (BMD) of the hip and lumbar spine. Most treatment guidelines already use central DXA BMD to define osteoporosis and the threshold at which to start drug therapies for prevention. Other lower-cost and more accessible alternatives include peripheral DXA, which measures BMD at lower forearm and heel, and quantitative ultrasound (QUS), which also evaluates peripheral sites like the calcaneus. QUS does not measure BMD. USPSTF found that the harms associated with screening were small (mainly radiation exposure from DXA and opportunity costs).
Population and risk assessment
The review included adults older than 40 years of age, mostly postmenopausal women, without a history of previous low-trauma fractures, without conditions or medications that may cause secondary osteoporosis, and without increased risk of falls.
Patients at increased risk of osteoporotic fractures include those with parental history of hip fractures, low body weight, excessive alcohol consumption, and smokers. For postmenopausal women younger than 65 years of age with at least one risk factor, a reasonable approach to determine who should be screened with BMD is to use one of the various clinical risk assessment tools available. The most frequently studied tools in women are the Osteoporosis Risk Assessment Instrument (ORAI), Osteoporosis Index of Risk (OSIRIS), Osteoporosis Self-Assessment Tool (OST), and Simple Calculated Osteoporosis Risk Estimation (SCORE). The Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool calculates the 10-year risk of a major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) using clinical risk factors. For example, one approach is to perform BMD in women younger than 65 years with a FRAX risk greater than 8.4% (the FRAX risk of a 65-year-old woman of mean height and weight without major risk factors).
In men, the prevalence of osteoporosis (4.3%) is generally lower than in women (15.4%). In the absence of other risk factors, it is not till age 80 that the prevalence of osteoporosis in white men starts to reach that of a 65-year-old white woman. While men have similar risk factors as women described above, men with hypogonadism, history of cerebrovascular accident, and history of diabetes are also at increased risk of fracture.
Preventative measures to reduce osteoporotic fractures
Approved drug therapies. The majority of studies were conducted in postmenopausal women. Bisphosphonates, most commonly used and studied, significantly reduced vertebral and nonvertebral fractures but not hip fractures (possibly because of underpowered studies). Raloxifene and parathyroid hormone reduced vertebral fractures but not nonvertebral fractures. Denosumab significantly reduced all three types of fractures. A 2011 review identified that estrogen reduced vertebral fractures, but no new studies were identified for the current review. Data from the Women’s Health Initiative show that women receiving estrogen with or without progesterone had an elevated risk of stroke, venous thromboembolism, and gallbladder disease; their risk for urinary incontinence was increased during the first year of follow-up. In addition, women receiving estrogen plus progestin had a higher risk of invasive breast cancer, coronary heart disease, and probable dementia. The risk of serious adverse events, upper-gastrointestinal events, or cardiovascular events associated with the most common class of medications used, bisphosphonates, is small. Evidence on the effectiveness of medications to treat osteoporosis in men is lacking (only two studies conducted).
Exercise. Engagement in 120-300 minutes of weekly moderate-intensity aerobic activity can reduce the risk of hip fractures, and performance of weekly balance and muscle-strengthening activities can help prevent falls in older adults.
Supplements. In a separate recommendation, USPSTF recommends against daily supplementation with less than 400 IU of vitamin D and less than 1,000 mg of calcium for the primary prevention of fractures in community-dwelling, postmenopausal women. They found insufficient evidence on supplementation with higher doses of vitamin D and calcium in postmenopausal women, or at any dose in men and premenopausal women.
Recommendations from others
The National Osteoporosis Foundation and the International Society for Clinical Densitometry recommend BMD testing in all women older than 65 years, all men over 70 years, postmenopausal women younger than 65 years, and men aged 50-69 years with increased risk factors. The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends against DXA screening in women younger than 65 years and men younger than 70 years with no risk factors.
The bottom line
For all women older than 65 years and postmenopausal women younger than 65 years who are at increased risk, screen for and treat osteoporosis to prevent fractures. For men, there is insufficient evidence to screen.
Dr. Shrestha is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) - Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is a professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington - Jefferson Health.
References
1. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018 Jun 26;319(24):2521-31.
2. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018 Jun 26;319(24):2532-51.
The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force commissioned a systematic evidence review of 168 fair-good quality articles to examine newer evidence on screening for and treatment of osteoporotic fracture in women and men and update its 2011 guideline. For postmenopausal women older than 65 years and those younger than 65 years with increased risk of osteoporosis, USPSTF found convincing evidence that screening can detect osteoporosis and that treatment can provide at least a moderate benefit in preventing fractures (grade B). For men, they report inadequate evidence on the benefits and harms of screening for osteoporosis to reduce the risk of fractures (I statement).
Importance
Osteoporosis leads to increased bone fragility and risk of fractures, specifically hip fractures, that are associated with limitations in ambulation, chronic pain, disability and loss of independence, and decreased quality of life: 21%-30% of those who suffer hip fractures die within 1 year. Osteoporosis is usually asymptomatic until a fracture occurs, thus preventing fractures is the main goal of an osteoporosis screening strategy. With the increasing life expectancy of the U.S. population, the potential preventable burden is likely to increase in future years.
Screening tests
The most commonly used test is central dual energy x-ray absorptiometry (DXA), which provides measurement of bone mineral density (BMD) of the hip and lumbar spine. Most treatment guidelines already use central DXA BMD to define osteoporosis and the threshold at which to start drug therapies for prevention. Other lower-cost and more accessible alternatives include peripheral DXA, which measures BMD at lower forearm and heel, and quantitative ultrasound (QUS), which also evaluates peripheral sites like the calcaneus. QUS does not measure BMD. USPSTF found that the harms associated with screening were small (mainly radiation exposure from DXA and opportunity costs).
Population and risk assessment
The review included adults older than 40 years of age, mostly postmenopausal women, without a history of previous low-trauma fractures, without conditions or medications that may cause secondary osteoporosis, and without increased risk of falls.
Patients at increased risk of osteoporotic fractures include those with parental history of hip fractures, low body weight, excessive alcohol consumption, and smokers. For postmenopausal women younger than 65 years of age with at least one risk factor, a reasonable approach to determine who should be screened with BMD is to use one of the various clinical risk assessment tools available. The most frequently studied tools in women are the Osteoporosis Risk Assessment Instrument (ORAI), Osteoporosis Index of Risk (OSIRIS), Osteoporosis Self-Assessment Tool (OST), and Simple Calculated Osteoporosis Risk Estimation (SCORE). The Fracture Risk Assessment (FRAX) tool calculates the 10-year risk of a major osteoporotic fracture (MOF) using clinical risk factors. For example, one approach is to perform BMD in women younger than 65 years with a FRAX risk greater than 8.4% (the FRAX risk of a 65-year-old woman of mean height and weight without major risk factors).
In men, the prevalence of osteoporosis (4.3%) is generally lower than in women (15.4%). In the absence of other risk factors, it is not till age 80 that the prevalence of osteoporosis in white men starts to reach that of a 65-year-old white woman. While men have similar risk factors as women described above, men with hypogonadism, history of cerebrovascular accident, and history of diabetes are also at increased risk of fracture.
Preventative measures to reduce osteoporotic fractures
Approved drug therapies. The majority of studies were conducted in postmenopausal women. Bisphosphonates, most commonly used and studied, significantly reduced vertebral and nonvertebral fractures but not hip fractures (possibly because of underpowered studies). Raloxifene and parathyroid hormone reduced vertebral fractures but not nonvertebral fractures. Denosumab significantly reduced all three types of fractures. A 2011 review identified that estrogen reduced vertebral fractures, but no new studies were identified for the current review. Data from the Women’s Health Initiative show that women receiving estrogen with or without progesterone had an elevated risk of stroke, venous thromboembolism, and gallbladder disease; their risk for urinary incontinence was increased during the first year of follow-up. In addition, women receiving estrogen plus progestin had a higher risk of invasive breast cancer, coronary heart disease, and probable dementia. The risk of serious adverse events, upper-gastrointestinal events, or cardiovascular events associated with the most common class of medications used, bisphosphonates, is small. Evidence on the effectiveness of medications to treat osteoporosis in men is lacking (only two studies conducted).
Exercise. Engagement in 120-300 minutes of weekly moderate-intensity aerobic activity can reduce the risk of hip fractures, and performance of weekly balance and muscle-strengthening activities can help prevent falls in older adults.
Supplements. In a separate recommendation, USPSTF recommends against daily supplementation with less than 400 IU of vitamin D and less than 1,000 mg of calcium for the primary prevention of fractures in community-dwelling, postmenopausal women. They found insufficient evidence on supplementation with higher doses of vitamin D and calcium in postmenopausal women, or at any dose in men and premenopausal women.
Recommendations from others
The National Osteoporosis Foundation and the International Society for Clinical Densitometry recommend BMD testing in all women older than 65 years, all men over 70 years, postmenopausal women younger than 65 years, and men aged 50-69 years with increased risk factors. The American Academy of Family Physicians recommends against DXA screening in women younger than 65 years and men younger than 70 years with no risk factors.
The bottom line
For all women older than 65 years and postmenopausal women younger than 65 years who are at increased risk, screen for and treat osteoporosis to prevent fractures. For men, there is insufficient evidence to screen.
Dr. Shrestha is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) - Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is a professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington - Jefferson Health.
References
1. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018 Jun 26;319(24):2521-31.
2. U.S. Preventative Services Task Force. JAMA. 2018 Jun 26;319(24):2532-51.
Prolia tops risedronate at 2 years in steroid-induced osteoporosis
AMSTERDAM – Greater increases in bone strength were achieved with denosumab (Prolia) than with risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoid treatment in a phase 3 trial, suggesting it may prove to be an effective means of preventing osteoporosis in this at-risk population of patients.
At 2 years, the percentage change in bone mineral density (BMD) from baseline with denosumab compared to risedronate in patients initiating steroid treatment was significantly higher (all P values less than .001) at the lumbar spine (6% vs. 2%), total hip (3% vs. 0%), and the femoral neck (1.5% vs. –1%). Similar results were seen in patients who were continuing steroid treatment when they entered the randomized, multicenter, double blind trial.
These data build on the 1-year data that have just been published (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6[6]:445-54), Willem F. Lems, MD, the presenting study investigator, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Denosumab continued to increased BMD significantly more then risedronate through 24 months,” said Dr. Lems of VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam. He added that “the treatment differences at all skeletal sites were larger at 24 months than as 12 months.”
The Food and Drug Administration approved an additional indication in May of 2018 for denosumab to treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in adults at high risk of fracture. The biologic, a monoclonal antibody that targets the RANK ligand, was already approved to treat postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high fracture risk, to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis at high fracture risk, and to increase bone mass in women receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer and in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer.
Secondary osteoporosis is a well known downside of glucocorticoid treatment, and despite there being approved therapies, many patients do not receive such treatment, Dr. Lems noted.
“This 24-month study assessed the safety and efficacy of denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-treated individuals, in whom guidelines advocate treatment,” Dr. Lems said.
In all, 795 adults who were taking glucocorticoids (7.5 mg prednisone or more daily, or equivalent) were enrolled at 79 sites in Europe, North America, Latin America, and Asia. Patients were subdivided into two populations based on their duration of glucocorticoid use, with 290 designated “glucocorticoid initiating” as they had been treated for less than 3 months, and 505 as “glucocorticoid continuing” as they had been treated for 3 or more months. Within these groups, approximately half were randomized to receive denosumab at a 60-mg subcutaneous dose every 6 months and half to receive risedronate 5 mg orally every day. All participants received calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
Bone turnover markers also declined “significantly more” with denosumab than with risedronate, with the exception of procollagen type 1 N-terminal telopeptide on day 10 and at 2 years and serum C-telopeptide of type 1 collagen at 2 years.
As for safety, a similar percentage of adverse events, including serious adverse events, was seen, Dr. Lems said. So far, he added, “data seem to be reassuring” regarding the risk for serious infections in high-risk subgroups of patients, such as those also taking biologic or immunosuppressant medications. There were no infections reported in patients taking biologics (vs. 12.1% for risedronate) and fewer infections in those taking immunosuppressant or biologic medication (3.6% vs. 6.8%).
Although the study was not powered to look at the rate of fractures between the two treatments, Dr. Lems noted that there was no significant difference in the rates of either new vertebral (4.1% for denosumab; 5.8% risedronate) or clinical (5.8% vs. 6.3%) fractures at 2 years.
“Additional studies are needed to confirm if denosumab is superior to other bisphosphonates for BMD improvement and fracture reduction,” Dr. Lems said. “Denosumab may offer a useful osteoporosis treatment option for patients receiving glucocorticoids,” he concluded.
Amgen sponsored the study. Dr. Lems acknowledged ties to Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Merck: being on the speakers bureau, receiving honoraria for advisory board meetings, and acting as a consultant. All but one other author disclosed ties to Amgen.
SOURCE: Saag KG et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(Suppl 2):218. Abstract OP0345.
AMSTERDAM – Greater increases in bone strength were achieved with denosumab (Prolia) than with risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoid treatment in a phase 3 trial, suggesting it may prove to be an effective means of preventing osteoporosis in this at-risk population of patients.
At 2 years, the percentage change in bone mineral density (BMD) from baseline with denosumab compared to risedronate in patients initiating steroid treatment was significantly higher (all P values less than .001) at the lumbar spine (6% vs. 2%), total hip (3% vs. 0%), and the femoral neck (1.5% vs. –1%). Similar results were seen in patients who were continuing steroid treatment when they entered the randomized, multicenter, double blind trial.
These data build on the 1-year data that have just been published (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6[6]:445-54), Willem F. Lems, MD, the presenting study investigator, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Denosumab continued to increased BMD significantly more then risedronate through 24 months,” said Dr. Lems of VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam. He added that “the treatment differences at all skeletal sites were larger at 24 months than as 12 months.”
The Food and Drug Administration approved an additional indication in May of 2018 for denosumab to treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in adults at high risk of fracture. The biologic, a monoclonal antibody that targets the RANK ligand, was already approved to treat postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high fracture risk, to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis at high fracture risk, and to increase bone mass in women receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer and in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer.
Secondary osteoporosis is a well known downside of glucocorticoid treatment, and despite there being approved therapies, many patients do not receive such treatment, Dr. Lems noted.
“This 24-month study assessed the safety and efficacy of denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-treated individuals, in whom guidelines advocate treatment,” Dr. Lems said.
In all, 795 adults who were taking glucocorticoids (7.5 mg prednisone or more daily, or equivalent) were enrolled at 79 sites in Europe, North America, Latin America, and Asia. Patients were subdivided into two populations based on their duration of glucocorticoid use, with 290 designated “glucocorticoid initiating” as they had been treated for less than 3 months, and 505 as “glucocorticoid continuing” as they had been treated for 3 or more months. Within these groups, approximately half were randomized to receive denosumab at a 60-mg subcutaneous dose every 6 months and half to receive risedronate 5 mg orally every day. All participants received calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
Bone turnover markers also declined “significantly more” with denosumab than with risedronate, with the exception of procollagen type 1 N-terminal telopeptide on day 10 and at 2 years and serum C-telopeptide of type 1 collagen at 2 years.
As for safety, a similar percentage of adverse events, including serious adverse events, was seen, Dr. Lems said. So far, he added, “data seem to be reassuring” regarding the risk for serious infections in high-risk subgroups of patients, such as those also taking biologic or immunosuppressant medications. There were no infections reported in patients taking biologics (vs. 12.1% for risedronate) and fewer infections in those taking immunosuppressant or biologic medication (3.6% vs. 6.8%).
Although the study was not powered to look at the rate of fractures between the two treatments, Dr. Lems noted that there was no significant difference in the rates of either new vertebral (4.1% for denosumab; 5.8% risedronate) or clinical (5.8% vs. 6.3%) fractures at 2 years.
“Additional studies are needed to confirm if denosumab is superior to other bisphosphonates for BMD improvement and fracture reduction,” Dr. Lems said. “Denosumab may offer a useful osteoporosis treatment option for patients receiving glucocorticoids,” he concluded.
Amgen sponsored the study. Dr. Lems acknowledged ties to Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Merck: being on the speakers bureau, receiving honoraria for advisory board meetings, and acting as a consultant. All but one other author disclosed ties to Amgen.
SOURCE: Saag KG et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(Suppl 2):218. Abstract OP0345.
AMSTERDAM – Greater increases in bone strength were achieved with denosumab (Prolia) than with risedronate in patients receiving glucocorticoid treatment in a phase 3 trial, suggesting it may prove to be an effective means of preventing osteoporosis in this at-risk population of patients.
At 2 years, the percentage change in bone mineral density (BMD) from baseline with denosumab compared to risedronate in patients initiating steroid treatment was significantly higher (all P values less than .001) at the lumbar spine (6% vs. 2%), total hip (3% vs. 0%), and the femoral neck (1.5% vs. –1%). Similar results were seen in patients who were continuing steroid treatment when they entered the randomized, multicenter, double blind trial.
These data build on the 1-year data that have just been published (Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2018;6[6]:445-54), Willem F. Lems, MD, the presenting study investigator, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
“Denosumab continued to increased BMD significantly more then risedronate through 24 months,” said Dr. Lems of VU University Medical Center, Amsterdam. He added that “the treatment differences at all skeletal sites were larger at 24 months than as 12 months.”
The Food and Drug Administration approved an additional indication in May of 2018 for denosumab to treat glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis in adults at high risk of fracture. The biologic, a monoclonal antibody that targets the RANK ligand, was already approved to treat postmenopausal women with osteoporosis at high fracture risk, to increase bone mass in men with osteoporosis at high fracture risk, and to increase bone mass in women receiving adjuvant aromatase inhibitor therapy for breast cancer and in men receiving androgen deprivation therapy for nonmetastatic prostate cancer.
Secondary osteoporosis is a well known downside of glucocorticoid treatment, and despite there being approved therapies, many patients do not receive such treatment, Dr. Lems noted.
“This 24-month study assessed the safety and efficacy of denosumab versus risedronate in glucocorticoid-treated individuals, in whom guidelines advocate treatment,” Dr. Lems said.
In all, 795 adults who were taking glucocorticoids (7.5 mg prednisone or more daily, or equivalent) were enrolled at 79 sites in Europe, North America, Latin America, and Asia. Patients were subdivided into two populations based on their duration of glucocorticoid use, with 290 designated “glucocorticoid initiating” as they had been treated for less than 3 months, and 505 as “glucocorticoid continuing” as they had been treated for 3 or more months. Within these groups, approximately half were randomized to receive denosumab at a 60-mg subcutaneous dose every 6 months and half to receive risedronate 5 mg orally every day. All participants received calcium and vitamin D supplementation.
Bone turnover markers also declined “significantly more” with denosumab than with risedronate, with the exception of procollagen type 1 N-terminal telopeptide on day 10 and at 2 years and serum C-telopeptide of type 1 collagen at 2 years.
As for safety, a similar percentage of adverse events, including serious adverse events, was seen, Dr. Lems said. So far, he added, “data seem to be reassuring” regarding the risk for serious infections in high-risk subgroups of patients, such as those also taking biologic or immunosuppressant medications. There were no infections reported in patients taking biologics (vs. 12.1% for risedronate) and fewer infections in those taking immunosuppressant or biologic medication (3.6% vs. 6.8%).
Although the study was not powered to look at the rate of fractures between the two treatments, Dr. Lems noted that there was no significant difference in the rates of either new vertebral (4.1% for denosumab; 5.8% risedronate) or clinical (5.8% vs. 6.3%) fractures at 2 years.
“Additional studies are needed to confirm if denosumab is superior to other bisphosphonates for BMD improvement and fracture reduction,” Dr. Lems said. “Denosumab may offer a useful osteoporosis treatment option for patients receiving glucocorticoids,” he concluded.
Amgen sponsored the study. Dr. Lems acknowledged ties to Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Merck: being on the speakers bureau, receiving honoraria for advisory board meetings, and acting as a consultant. All but one other author disclosed ties to Amgen.
SOURCE: Saag KG et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(Suppl 2):218. Abstract OP0345.
REPORTING FROM THE EULAR 2018 CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Denosumab may offer a useful alternative to risedronate in patients at risk for steroid-induced osteoporosis.
Major finding: Treatment differences were greater at 2 years than at 1 year at all skeletal sites assessed.
Study details: A phase 3, randomized, double-blind, active-controlled study to evaluate the efficacy and safety of denosumab versus risedronate in 795 glucocorticoid-treated individuals.
Disclosures: Amgen sponsored the study. Dr. Lems acknowledged ties to Amgen, Eli Lilly, and Merck: being on the speakers bureau, receiving honoraria for advisory board meetings, and acting as a consultant. All but one other author disclosed ties to Amgen.
Source: Saag KG et al. Ann Rheum Dis. 2018;77(Suppl 2):218. Abstract OP0345.
Bisphosphonate ‘holidays’ exceeding 2 years linked to increased fractures
AMSTERDAM – Older women on bisphosphonate treatment for at least 3 years who then stopped taking the drug showed a 40% increased risk for hip fracture after they were off the bisphosphonate for more than 2 years, compared with women who never stopped using the drug, according to an analysis of more than 150,000 women in a Medicare database.
The implication of this observational-data finding is that drug holidays from a bisphosphonate regimen “may not be appropriate for all patients,” Kenneth G. Saag, MD, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
The finding seems to dispute a recent recommendation from the American College of Physicians (Ann Intern Med. 2017 June 6;166[11]:818-39) that drug treatment to prevent bone fractures in osteoporotic women should stop after 5 years, noted Dr. Saag, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at the University of Alabama, Birmingham. The median duration of bisphosphonate treatment in the studied cohort before the drug use stopped was 5.5 years.
“Drug holidays [from a bisphosphonate] have become increasingly common” because of concerns about potential adverse effects from prolonged, continuous bisphosphonate treatment, especially the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fractures, he said. These bisphosphonate stoppages are sometimes permanent and sometimes temporary, Dr. Saag noted. Ideally, assessment of the risks and benefits from a bisphosphonate drug holiday should occur in a randomized study, but in current U.S. practice such a trial would be “impossible because there is not equipoise around the decision of whether or not to stop,” he said.
To try to gain insight into the impact of halting bisphosphonate treatment with observational data, Dr. Saag and his associates used records collected by Medicare on 153,236 women who started a new course of bisphosphonate treatment and remained on it for at least 3 years during 2006 to 2014. When selecting these women, the researchers also focused on those with at least 80% adherence to their bisphosphonate regimen, based on prescription coverage data. The analysis censored women who also received other treatments that can affect bone density, such as estrogen or denosumab (Prolia, Xgeva). The average age of the women was 79 years; two-thirds were aged 75 years or older. The median duration of follow-up information after bisphosphonate stoppage was 2.1 years. Forty percent of the women stopped their bisphosphonate treatment for at least 6 months, and 13% of the women who stopped treatment subsequently restarted a bisphosphonate drug. The most commonly used bisphosphonate was alendronate (Fosamax, Binosto), used by 72%, followed by zoledronic acid (Reclast, Zometa), used by 16%.
The analysis divided women who stopped their bisphosphonate treatment into subgroups based on the duration of stoppage, and showed that the rate of hip fracture was 40% higher among women who stopped treatment for more than 2 years but not more than 3 years, compared with the women who never interrupted their bisphosphonate treatment, a statistically significant difference, Dr. Saag said. In contrast, among women who halted bisphosphonate treatment for more than 1 year but not more than 2 years, the hip fracture risk was 20% higher than that of nonstoppers, also a statistically significant difference. These and all the other analyses the researchers ran adjusted for the possible impact from baseline differences in several demographic and clinical variables.
Dr. Saag cautioned that while the relatively increased risk for hip fracture from a prolonged halt to bisphosphonate treatment was 40%, the absolute increase in risk was “relatively modest,” representing an increased fracture rate of 0.5-1 additional fractures during every 100 patient years of follow-up.
For the endpoint of major osteoporotic fracture at any location, the risk was 10% higher among women who stopped treatment for more than 2 years but not for longer than 3 years, compared with nonstoppers.
The researchers also focused on two key subgroups. Among women who only took alendronate, a drug holiday of more than 2 years was linked with a statistically significant 20% rise in hip fractures, compared with women who never stopped the drug. And among the 4% of studied women who had a history of a bone fracture because of bone fragility, stoppage of their bisphosphonate treatment for more than 2 years doubled their hip fracture rate, compared with similar women who did not stop their treatment.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Saag has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Lilly, and Radius.
SOURCE: Curtis J et al. EULAR 2018 Congress, abstract OP0017.
AMSTERDAM – Older women on bisphosphonate treatment for at least 3 years who then stopped taking the drug showed a 40% increased risk for hip fracture after they were off the bisphosphonate for more than 2 years, compared with women who never stopped using the drug, according to an analysis of more than 150,000 women in a Medicare database.
The implication of this observational-data finding is that drug holidays from a bisphosphonate regimen “may not be appropriate for all patients,” Kenneth G. Saag, MD, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
The finding seems to dispute a recent recommendation from the American College of Physicians (Ann Intern Med. 2017 June 6;166[11]:818-39) that drug treatment to prevent bone fractures in osteoporotic women should stop after 5 years, noted Dr. Saag, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at the University of Alabama, Birmingham. The median duration of bisphosphonate treatment in the studied cohort before the drug use stopped was 5.5 years.
“Drug holidays [from a bisphosphonate] have become increasingly common” because of concerns about potential adverse effects from prolonged, continuous bisphosphonate treatment, especially the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fractures, he said. These bisphosphonate stoppages are sometimes permanent and sometimes temporary, Dr. Saag noted. Ideally, assessment of the risks and benefits from a bisphosphonate drug holiday should occur in a randomized study, but in current U.S. practice such a trial would be “impossible because there is not equipoise around the decision of whether or not to stop,” he said.
To try to gain insight into the impact of halting bisphosphonate treatment with observational data, Dr. Saag and his associates used records collected by Medicare on 153,236 women who started a new course of bisphosphonate treatment and remained on it for at least 3 years during 2006 to 2014. When selecting these women, the researchers also focused on those with at least 80% adherence to their bisphosphonate regimen, based on prescription coverage data. The analysis censored women who also received other treatments that can affect bone density, such as estrogen or denosumab (Prolia, Xgeva). The average age of the women was 79 years; two-thirds were aged 75 years or older. The median duration of follow-up information after bisphosphonate stoppage was 2.1 years. Forty percent of the women stopped their bisphosphonate treatment for at least 6 months, and 13% of the women who stopped treatment subsequently restarted a bisphosphonate drug. The most commonly used bisphosphonate was alendronate (Fosamax, Binosto), used by 72%, followed by zoledronic acid (Reclast, Zometa), used by 16%.
The analysis divided women who stopped their bisphosphonate treatment into subgroups based on the duration of stoppage, and showed that the rate of hip fracture was 40% higher among women who stopped treatment for more than 2 years but not more than 3 years, compared with the women who never interrupted their bisphosphonate treatment, a statistically significant difference, Dr. Saag said. In contrast, among women who halted bisphosphonate treatment for more than 1 year but not more than 2 years, the hip fracture risk was 20% higher than that of nonstoppers, also a statistically significant difference. These and all the other analyses the researchers ran adjusted for the possible impact from baseline differences in several demographic and clinical variables.
Dr. Saag cautioned that while the relatively increased risk for hip fracture from a prolonged halt to bisphosphonate treatment was 40%, the absolute increase in risk was “relatively modest,” representing an increased fracture rate of 0.5-1 additional fractures during every 100 patient years of follow-up.
For the endpoint of major osteoporotic fracture at any location, the risk was 10% higher among women who stopped treatment for more than 2 years but not for longer than 3 years, compared with nonstoppers.
The researchers also focused on two key subgroups. Among women who only took alendronate, a drug holiday of more than 2 years was linked with a statistically significant 20% rise in hip fractures, compared with women who never stopped the drug. And among the 4% of studied women who had a history of a bone fracture because of bone fragility, stoppage of their bisphosphonate treatment for more than 2 years doubled their hip fracture rate, compared with similar women who did not stop their treatment.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Saag has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Lilly, and Radius.
SOURCE: Curtis J et al. EULAR 2018 Congress, abstract OP0017.
AMSTERDAM – Older women on bisphosphonate treatment for at least 3 years who then stopped taking the drug showed a 40% increased risk for hip fracture after they were off the bisphosphonate for more than 2 years, compared with women who never stopped using the drug, according to an analysis of more than 150,000 women in a Medicare database.
The implication of this observational-data finding is that drug holidays from a bisphosphonate regimen “may not be appropriate for all patients,” Kenneth G. Saag, MD, said at the European Congress of Rheumatology.
The finding seems to dispute a recent recommendation from the American College of Physicians (Ann Intern Med. 2017 June 6;166[11]:818-39) that drug treatment to prevent bone fractures in osteoporotic women should stop after 5 years, noted Dr. Saag, a rheumatologist and professor of medicine at the University of Alabama, Birmingham. The median duration of bisphosphonate treatment in the studied cohort before the drug use stopped was 5.5 years.
“Drug holidays [from a bisphosphonate] have become increasingly common” because of concerns about potential adverse effects from prolonged, continuous bisphosphonate treatment, especially the risk for osteonecrosis of the jaw and atypical femoral fractures, he said. These bisphosphonate stoppages are sometimes permanent and sometimes temporary, Dr. Saag noted. Ideally, assessment of the risks and benefits from a bisphosphonate drug holiday should occur in a randomized study, but in current U.S. practice such a trial would be “impossible because there is not equipoise around the decision of whether or not to stop,” he said.
To try to gain insight into the impact of halting bisphosphonate treatment with observational data, Dr. Saag and his associates used records collected by Medicare on 153,236 women who started a new course of bisphosphonate treatment and remained on it for at least 3 years during 2006 to 2014. When selecting these women, the researchers also focused on those with at least 80% adherence to their bisphosphonate regimen, based on prescription coverage data. The analysis censored women who also received other treatments that can affect bone density, such as estrogen or denosumab (Prolia, Xgeva). The average age of the women was 79 years; two-thirds were aged 75 years or older. The median duration of follow-up information after bisphosphonate stoppage was 2.1 years. Forty percent of the women stopped their bisphosphonate treatment for at least 6 months, and 13% of the women who stopped treatment subsequently restarted a bisphosphonate drug. The most commonly used bisphosphonate was alendronate (Fosamax, Binosto), used by 72%, followed by zoledronic acid (Reclast, Zometa), used by 16%.
The analysis divided women who stopped their bisphosphonate treatment into subgroups based on the duration of stoppage, and showed that the rate of hip fracture was 40% higher among women who stopped treatment for more than 2 years but not more than 3 years, compared with the women who never interrupted their bisphosphonate treatment, a statistically significant difference, Dr. Saag said. In contrast, among women who halted bisphosphonate treatment for more than 1 year but not more than 2 years, the hip fracture risk was 20% higher than that of nonstoppers, also a statistically significant difference. These and all the other analyses the researchers ran adjusted for the possible impact from baseline differences in several demographic and clinical variables.
Dr. Saag cautioned that while the relatively increased risk for hip fracture from a prolonged halt to bisphosphonate treatment was 40%, the absolute increase in risk was “relatively modest,” representing an increased fracture rate of 0.5-1 additional fractures during every 100 patient years of follow-up.
For the endpoint of major osteoporotic fracture at any location, the risk was 10% higher among women who stopped treatment for more than 2 years but not for longer than 3 years, compared with nonstoppers.
The researchers also focused on two key subgroups. Among women who only took alendronate, a drug holiday of more than 2 years was linked with a statistically significant 20% rise in hip fractures, compared with women who never stopped the drug. And among the 4% of studied women who had a history of a bone fracture because of bone fragility, stoppage of their bisphosphonate treatment for more than 2 years doubled their hip fracture rate, compared with similar women who did not stop their treatment.
The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Saag has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Lilly, and Radius.
SOURCE: Curtis J et al. EULAR 2018 Congress, abstract OP0017.
REPORTING FROM THE EULAR 2018 CONGRESS
Key clinical point: Stopping a bisphosphonate for more than 2 years boosts hip fracture risk.
Major finding: Women stopping bisphosphonate use for more than 2 years had a 40% higher rate of hip fractures compared with women who didn’t stop the drug.
Study details: Review of data collected by Medicare for 153,236 women treated with a bisphosphonate drug.
Disclosures: The study received no commercial funding. Dr. Saag has been a consultant to and has received research funding from Amgen, Lilly, and Radius.
Source: Curtis J et al. EULAR 2018 Congress, abstract OP0017.