User login
Few meet eligibility for newer Alzheimer’s drugs
, a cross sectional study has found.
Reporting in the journal Neurology, researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and the University of Chicago found that only a small percentage of patients in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging (MCSA) with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease would meet the clinical trial eligibility requirements of either agent.
“Our study results show only a small percentage of people with early Alzheimer’s disease may be eligible to receive treatment, mostly due to chronic health conditions and brain scan abnormalities common in older adults,” said lead researcher Maria Vassilaki, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Applying clinical trial exclusion criteria to a broader population
The study included 237 people aged 50-90, 222 who had MCI and 15 with mild dementia, and whose brain scans showed increased amounts of amyloid-beta plaques. Average age of the participants was 80.9 years and 97.5% were White (99.6% not Hispanic or Latino).
The researchers then looked at the eligibility criteria for the pivotal clinical trials for lecanemab, which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved in January this year, and aducanumab, which the FDA cleared in 2021. Both drugs received FDA accelerated approval.
For lecanemab, clinical trial inclusion required specific scores for the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) (other than 0.5 or 1.0), Wechsler Memory Scale (WMS-R) Logical Memory II (which varied with age group), or Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) (22 to 30). A body mass index between 17 and 35 kg/m2 was also an inclusion criteria. Only 112 people, or 47%, met the inclusion criteria. Exclusion criteria included a history of cardiovascular disease or cancer, Parkinson’s disease, or brain injury, or a positive brain scan. When the exclusion criteria were applied, only 19 people, or 8%, qualified for the lecanemab trial.
When the researchers modified the exclusion criteria to include all study participants with MCI but not applying results from additional cognitive tests, 17.4% of MCSA patients would have been eligible for the lecanemab trial.
Aducanumab clinical trial inclusion criteria were a CDR global score other than 0.5 and an MMSE below 24, with an age cutoff of 85 years. Only 104 of the MCSA population, or 44%, met the clinical trial criteria. When the researchers applied the exclusion criteria for cardiovascular disease, central nervous system-related exclusions (such as brain cancer or epilepsy), a history of cancer, or brain scan abnormalities, they found that only 12 people, or 5%, would have been eligible for an aducanumab trial.
“Clinical trials often have strict eligibility criteria and could exclude those with other conditions that could be common in older adults,” Dr. Vassilaki said in emailed comments. “Thus, we wanted to examine if we apply these criteria to a study that recruits participants from the community, how many of the individuals in the early symptomatic stages, mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease, would be eligible for the treatment.”
Dr. Vassilaki said these drugs need to be studied in larger, more diverse populations, as well as in less healthy populations, before they’re more widely available to people with Alzheimer’s disease. “In addition,” she said, “we can learn more from the postmarketing surveillance of side effects and also from registries of patients receiving these treatments.”
One limitation of the study Dr. Vassilaki pointed out is the overwhelmingly White population. Evaluating the clinical trial eligibility criteria in more diverse populations is crucial, she said.
Estimating the number of patients who would qualify for treatment
In an accompanying commentary, Matthew Howes, MD, of Butler Hospital and Brown University in Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote that the study findings provide health systems planning to offer amyloid-lowering antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease an estimate of how many patients would be eligible for the treatments. “Providers must exercise clinical judgment in selecting patients for treatment with shared decision-making with patients and families,” the commentators wrote.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Alexander Family Alzheimer’s Disease Research Professorship of the Mayo Clinic, the Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, the Liston Award, the GHR Foundation, and the Schuler Foundation. Dr. Vassilaki disclosed relationships with F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Abbott Laboratories, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, Merck, and Amgen. Dr. Howe has no relevant disclosures.
, a cross sectional study has found.
Reporting in the journal Neurology, researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and the University of Chicago found that only a small percentage of patients in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging (MCSA) with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease would meet the clinical trial eligibility requirements of either agent.
“Our study results show only a small percentage of people with early Alzheimer’s disease may be eligible to receive treatment, mostly due to chronic health conditions and brain scan abnormalities common in older adults,” said lead researcher Maria Vassilaki, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Applying clinical trial exclusion criteria to a broader population
The study included 237 people aged 50-90, 222 who had MCI and 15 with mild dementia, and whose brain scans showed increased amounts of amyloid-beta plaques. Average age of the participants was 80.9 years and 97.5% were White (99.6% not Hispanic or Latino).
The researchers then looked at the eligibility criteria for the pivotal clinical trials for lecanemab, which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved in January this year, and aducanumab, which the FDA cleared in 2021. Both drugs received FDA accelerated approval.
For lecanemab, clinical trial inclusion required specific scores for the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) (other than 0.5 or 1.0), Wechsler Memory Scale (WMS-R) Logical Memory II (which varied with age group), or Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) (22 to 30). A body mass index between 17 and 35 kg/m2 was also an inclusion criteria. Only 112 people, or 47%, met the inclusion criteria. Exclusion criteria included a history of cardiovascular disease or cancer, Parkinson’s disease, or brain injury, or a positive brain scan. When the exclusion criteria were applied, only 19 people, or 8%, qualified for the lecanemab trial.
When the researchers modified the exclusion criteria to include all study participants with MCI but not applying results from additional cognitive tests, 17.4% of MCSA patients would have been eligible for the lecanemab trial.
Aducanumab clinical trial inclusion criteria were a CDR global score other than 0.5 and an MMSE below 24, with an age cutoff of 85 years. Only 104 of the MCSA population, or 44%, met the clinical trial criteria. When the researchers applied the exclusion criteria for cardiovascular disease, central nervous system-related exclusions (such as brain cancer or epilepsy), a history of cancer, or brain scan abnormalities, they found that only 12 people, or 5%, would have been eligible for an aducanumab trial.
“Clinical trials often have strict eligibility criteria and could exclude those with other conditions that could be common in older adults,” Dr. Vassilaki said in emailed comments. “Thus, we wanted to examine if we apply these criteria to a study that recruits participants from the community, how many of the individuals in the early symptomatic stages, mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease, would be eligible for the treatment.”
Dr. Vassilaki said these drugs need to be studied in larger, more diverse populations, as well as in less healthy populations, before they’re more widely available to people with Alzheimer’s disease. “In addition,” she said, “we can learn more from the postmarketing surveillance of side effects and also from registries of patients receiving these treatments.”
One limitation of the study Dr. Vassilaki pointed out is the overwhelmingly White population. Evaluating the clinical trial eligibility criteria in more diverse populations is crucial, she said.
Estimating the number of patients who would qualify for treatment
In an accompanying commentary, Matthew Howes, MD, of Butler Hospital and Brown University in Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote that the study findings provide health systems planning to offer amyloid-lowering antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease an estimate of how many patients would be eligible for the treatments. “Providers must exercise clinical judgment in selecting patients for treatment with shared decision-making with patients and families,” the commentators wrote.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Alexander Family Alzheimer’s Disease Research Professorship of the Mayo Clinic, the Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, the Liston Award, the GHR Foundation, and the Schuler Foundation. Dr. Vassilaki disclosed relationships with F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Abbott Laboratories, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, Merck, and Amgen. Dr. Howe has no relevant disclosures.
, a cross sectional study has found.
Reporting in the journal Neurology, researchers from the Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and the University of Chicago found that only a small percentage of patients in the Mayo Clinic Study of Aging (MCSA) with mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease would meet the clinical trial eligibility requirements of either agent.
“Our study results show only a small percentage of people with early Alzheimer’s disease may be eligible to receive treatment, mostly due to chronic health conditions and brain scan abnormalities common in older adults,” said lead researcher Maria Vassilaki, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn.
Applying clinical trial exclusion criteria to a broader population
The study included 237 people aged 50-90, 222 who had MCI and 15 with mild dementia, and whose brain scans showed increased amounts of amyloid-beta plaques. Average age of the participants was 80.9 years and 97.5% were White (99.6% not Hispanic or Latino).
The researchers then looked at the eligibility criteria for the pivotal clinical trials for lecanemab, which the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved in January this year, and aducanumab, which the FDA cleared in 2021. Both drugs received FDA accelerated approval.
For lecanemab, clinical trial inclusion required specific scores for the Clinical Dementia Rating (CDR) (other than 0.5 or 1.0), Wechsler Memory Scale (WMS-R) Logical Memory II (which varied with age group), or Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE) (22 to 30). A body mass index between 17 and 35 kg/m2 was also an inclusion criteria. Only 112 people, or 47%, met the inclusion criteria. Exclusion criteria included a history of cardiovascular disease or cancer, Parkinson’s disease, or brain injury, or a positive brain scan. When the exclusion criteria were applied, only 19 people, or 8%, qualified for the lecanemab trial.
When the researchers modified the exclusion criteria to include all study participants with MCI but not applying results from additional cognitive tests, 17.4% of MCSA patients would have been eligible for the lecanemab trial.
Aducanumab clinical trial inclusion criteria were a CDR global score other than 0.5 and an MMSE below 24, with an age cutoff of 85 years. Only 104 of the MCSA population, or 44%, met the clinical trial criteria. When the researchers applied the exclusion criteria for cardiovascular disease, central nervous system-related exclusions (such as brain cancer or epilepsy), a history of cancer, or brain scan abnormalities, they found that only 12 people, or 5%, would have been eligible for an aducanumab trial.
“Clinical trials often have strict eligibility criteria and could exclude those with other conditions that could be common in older adults,” Dr. Vassilaki said in emailed comments. “Thus, we wanted to examine if we apply these criteria to a study that recruits participants from the community, how many of the individuals in the early symptomatic stages, mild cognitive impairment or mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease, would be eligible for the treatment.”
Dr. Vassilaki said these drugs need to be studied in larger, more diverse populations, as well as in less healthy populations, before they’re more widely available to people with Alzheimer’s disease. “In addition,” she said, “we can learn more from the postmarketing surveillance of side effects and also from registries of patients receiving these treatments.”
One limitation of the study Dr. Vassilaki pointed out is the overwhelmingly White population. Evaluating the clinical trial eligibility criteria in more diverse populations is crucial, she said.
Estimating the number of patients who would qualify for treatment
In an accompanying commentary, Matthew Howes, MD, of Butler Hospital and Brown University in Providence, R.I., and colleagues wrote that the study findings provide health systems planning to offer amyloid-lowering antibodies for Alzheimer’s disease an estimate of how many patients would be eligible for the treatments. “Providers must exercise clinical judgment in selecting patients for treatment with shared decision-making with patients and families,” the commentators wrote.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, the National Institute on Aging, the Alexander Family Alzheimer’s Disease Research Professorship of the Mayo Clinic, the Mayo Foundation for Medical Education and Research, the Liston Award, the GHR Foundation, and the Schuler Foundation. Dr. Vassilaki disclosed relationships with F. Hoffmann-La Roche, Abbott Laboratories, Johnson & Johnson, Medtronic, Merck, and Amgen. Dr. Howe has no relevant disclosures.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Playing football linked to higher Parkinson’s risk
In a cross-sectional study of older men, former tackle football players had a 61% higher likelihood of reporting a diagnosis of parkinsonism or PD, compared with men who played non-football sports.
Longer duration of football participation and higher level of play (college and professional) were associated with higher risk.
Lead researcher Michael L. Alosco, PhD, director of the Boston University Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, said it’s important to note that the findings are from a cohort of men “enriched” for having PD.
“These are people who are likely already concerned for or at risk for having this disease. We don’t yet know how our findings translate to the general population,” Dr. Alosco said in an interview.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Repetitive head impacts
Dating back to the 1920s, PD and parkinsonism an umbrella term that refers to motor symptoms associated with PD and other conditions have long been described in boxers who suffer repetitive head impacts.
Multiple studies have linked tackle football with progressive brain diseases such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Few studies, however, have investigated the association between participation in football and PD.
For their study, Dr. Alosco and colleagues leveraged data from Fox Insight, a longitudinal online study of some people with and some without PD that is sponsored by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
They focused their analyses on 1,875 men (mean age, 67 years) who reported playing any organized sport. As noted, the cohort was enriched for parkinsonism or PD. A total of 1,602 (85%) had received a diagnosis of parkinsonism/PD, and 273 had not.
Altogether, 729 men had a history of playing tackle football, and 1,146 men played non-football sports (control group). Among the football players, 82% played at youth sports or at the high school level; 17% played at the college level; and fewer than 1% played at the pro or semi-pro level.
Among the football players, 648 (89%) reported a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis.
A history of playing football was associated with higher odds of reporting a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis (odds ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.19-2.17) after accounting for age, education level, history of diabetes and heart disease, body mass index (BMI), traumatic brain injury with loss of consciousness, and family history of PD.
Football players who had longer careers and who played at higher levels of competition were at increased risk of having parkinsonism or PD.
Playing one to four seasons yielded an OR of 1.39 (95% CI, 0.98-1.98). The OR was 2.18 (95% CI, 1.36-3.49) for playing five or more seasons.
Football players who competed at the college or professional level had nearly triple the odds of reporting a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis (OR, 2.93; 95% CI, 1.28-6.73), compared with athletes who played at the youth or high school level.
Age at first exposure to football was not associated with a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis.
The researchers cautioned that this was a convenience sample of mostly White people, and the sample was enriched for having PD – factors that limit the generalizability of the findings.
Also, diagnosis of PD was self-reported by participants through online assessments, and objective in-person evaluations were not conducted.
Unequivocal link?
“This is among the first and largest to look at the relationship between football and having a diagnosis of PD in a large cohort of people from the Fox Insight online study,” Dr. Alosco said.
He cautioned that “not all people who play football will develop later-life neurological problems. That being said, the study adds to the accumulating evidence that suggests playing football is one risk factor for the development of later-life brain diseases.
“This represents an opportunity to educate the communities on the potential risks of playing football (short and long term), including what we know and what we don’t know, so that people can make informed decisions on participating in tackle football and develop additional ways to mitigate risk,” Dr. Alosco said.
In a comment, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher from Boston, said: “The emerging body of research leaves little doubt that engaging in football raises the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism.
“This progressive line of investigation serves to enhance our understanding, unequivocally demonstrating that even participation in amateur football, including at the youth and high school levels, constitutes a significant risk factor for the onset of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved in the study.
However, he said it’s “crucial to underscore that the statistics reveal a notable distinction: individuals who have a history of college or professional football play face odds nearly three times higher of receiving a diagnosis of parkinsonism or Parkinson’s disease when compared to their counterparts who engaged in football during their youth or high-school years.
“Ultimately, determinations regarding involvement in sports should be a collaborative endeavor involving parents, young athletes, and health care providers. It is incumbent upon physicians to equip parents and youth with a comprehensive comprehension of the potential risks and rewards inherent in football participation,” Dr. Lakhan said.
He added, though, that there are multifaceted advantages to playing football. “This pursuit nurtures cardiovascular well-being, fosters invaluable social interactions, cultivates teamwork, instills discipline through regimented routines, and hones a spectrum of physical proficiencies,” Dr. Lakhan said.
“It’s worth noting that a constellation of alternative sports, including track and field, swimming, soccer, baseball, and tennis, can be cogently discussed as substitutes, all while preserving the manifold benefits of athletic engagement,” Dr. Lakhan added.
The Fox Insight Study is funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. The study was conducted in collaboration with the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, the sponsor of the Fox Insight study, which collected and aggregated data used in the study. It was also supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Alosco received grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study, an honorarium from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for work unrelated to the study, and royalties from Oxford University Press outside the submitted work. Dr. Lakhan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cross-sectional study of older men, former tackle football players had a 61% higher likelihood of reporting a diagnosis of parkinsonism or PD, compared with men who played non-football sports.
Longer duration of football participation and higher level of play (college and professional) were associated with higher risk.
Lead researcher Michael L. Alosco, PhD, director of the Boston University Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, said it’s important to note that the findings are from a cohort of men “enriched” for having PD.
“These are people who are likely already concerned for or at risk for having this disease. We don’t yet know how our findings translate to the general population,” Dr. Alosco said in an interview.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Repetitive head impacts
Dating back to the 1920s, PD and parkinsonism an umbrella term that refers to motor symptoms associated with PD and other conditions have long been described in boxers who suffer repetitive head impacts.
Multiple studies have linked tackle football with progressive brain diseases such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Few studies, however, have investigated the association between participation in football and PD.
For their study, Dr. Alosco and colleagues leveraged data from Fox Insight, a longitudinal online study of some people with and some without PD that is sponsored by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
They focused their analyses on 1,875 men (mean age, 67 years) who reported playing any organized sport. As noted, the cohort was enriched for parkinsonism or PD. A total of 1,602 (85%) had received a diagnosis of parkinsonism/PD, and 273 had not.
Altogether, 729 men had a history of playing tackle football, and 1,146 men played non-football sports (control group). Among the football players, 82% played at youth sports or at the high school level; 17% played at the college level; and fewer than 1% played at the pro or semi-pro level.
Among the football players, 648 (89%) reported a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis.
A history of playing football was associated with higher odds of reporting a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis (odds ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.19-2.17) after accounting for age, education level, history of diabetes and heart disease, body mass index (BMI), traumatic brain injury with loss of consciousness, and family history of PD.
Football players who had longer careers and who played at higher levels of competition were at increased risk of having parkinsonism or PD.
Playing one to four seasons yielded an OR of 1.39 (95% CI, 0.98-1.98). The OR was 2.18 (95% CI, 1.36-3.49) for playing five or more seasons.
Football players who competed at the college or professional level had nearly triple the odds of reporting a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis (OR, 2.93; 95% CI, 1.28-6.73), compared with athletes who played at the youth or high school level.
Age at first exposure to football was not associated with a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis.
The researchers cautioned that this was a convenience sample of mostly White people, and the sample was enriched for having PD – factors that limit the generalizability of the findings.
Also, diagnosis of PD was self-reported by participants through online assessments, and objective in-person evaluations were not conducted.
Unequivocal link?
“This is among the first and largest to look at the relationship between football and having a diagnosis of PD in a large cohort of people from the Fox Insight online study,” Dr. Alosco said.
He cautioned that “not all people who play football will develop later-life neurological problems. That being said, the study adds to the accumulating evidence that suggests playing football is one risk factor for the development of later-life brain diseases.
“This represents an opportunity to educate the communities on the potential risks of playing football (short and long term), including what we know and what we don’t know, so that people can make informed decisions on participating in tackle football and develop additional ways to mitigate risk,” Dr. Alosco said.
In a comment, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher from Boston, said: “The emerging body of research leaves little doubt that engaging in football raises the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism.
“This progressive line of investigation serves to enhance our understanding, unequivocally demonstrating that even participation in amateur football, including at the youth and high school levels, constitutes a significant risk factor for the onset of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved in the study.
However, he said it’s “crucial to underscore that the statistics reveal a notable distinction: individuals who have a history of college or professional football play face odds nearly three times higher of receiving a diagnosis of parkinsonism or Parkinson’s disease when compared to their counterparts who engaged in football during their youth or high-school years.
“Ultimately, determinations regarding involvement in sports should be a collaborative endeavor involving parents, young athletes, and health care providers. It is incumbent upon physicians to equip parents and youth with a comprehensive comprehension of the potential risks and rewards inherent in football participation,” Dr. Lakhan said.
He added, though, that there are multifaceted advantages to playing football. “This pursuit nurtures cardiovascular well-being, fosters invaluable social interactions, cultivates teamwork, instills discipline through regimented routines, and hones a spectrum of physical proficiencies,” Dr. Lakhan said.
“It’s worth noting that a constellation of alternative sports, including track and field, swimming, soccer, baseball, and tennis, can be cogently discussed as substitutes, all while preserving the manifold benefits of athletic engagement,” Dr. Lakhan added.
The Fox Insight Study is funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. The study was conducted in collaboration with the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, the sponsor of the Fox Insight study, which collected and aggregated data used in the study. It was also supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Alosco received grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study, an honorarium from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for work unrelated to the study, and royalties from Oxford University Press outside the submitted work. Dr. Lakhan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a cross-sectional study of older men, former tackle football players had a 61% higher likelihood of reporting a diagnosis of parkinsonism or PD, compared with men who played non-football sports.
Longer duration of football participation and higher level of play (college and professional) were associated with higher risk.
Lead researcher Michael L. Alosco, PhD, director of the Boston University Alzheimer’s Disease Research Center, said it’s important to note that the findings are from a cohort of men “enriched” for having PD.
“These are people who are likely already concerned for or at risk for having this disease. We don’t yet know how our findings translate to the general population,” Dr. Alosco said in an interview.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Repetitive head impacts
Dating back to the 1920s, PD and parkinsonism an umbrella term that refers to motor symptoms associated with PD and other conditions have long been described in boxers who suffer repetitive head impacts.
Multiple studies have linked tackle football with progressive brain diseases such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy. Few studies, however, have investigated the association between participation in football and PD.
For their study, Dr. Alosco and colleagues leveraged data from Fox Insight, a longitudinal online study of some people with and some without PD that is sponsored by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research.
They focused their analyses on 1,875 men (mean age, 67 years) who reported playing any organized sport. As noted, the cohort was enriched for parkinsonism or PD. A total of 1,602 (85%) had received a diagnosis of parkinsonism/PD, and 273 had not.
Altogether, 729 men had a history of playing tackle football, and 1,146 men played non-football sports (control group). Among the football players, 82% played at youth sports or at the high school level; 17% played at the college level; and fewer than 1% played at the pro or semi-pro level.
Among the football players, 648 (89%) reported a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis.
A history of playing football was associated with higher odds of reporting a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis (odds ratio, 1.61; 95% confidence interval, 1.19-2.17) after accounting for age, education level, history of diabetes and heart disease, body mass index (BMI), traumatic brain injury with loss of consciousness, and family history of PD.
Football players who had longer careers and who played at higher levels of competition were at increased risk of having parkinsonism or PD.
Playing one to four seasons yielded an OR of 1.39 (95% CI, 0.98-1.98). The OR was 2.18 (95% CI, 1.36-3.49) for playing five or more seasons.
Football players who competed at the college or professional level had nearly triple the odds of reporting a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis (OR, 2.93; 95% CI, 1.28-6.73), compared with athletes who played at the youth or high school level.
Age at first exposure to football was not associated with a parkinsonism/PD diagnosis.
The researchers cautioned that this was a convenience sample of mostly White people, and the sample was enriched for having PD – factors that limit the generalizability of the findings.
Also, diagnosis of PD was self-reported by participants through online assessments, and objective in-person evaluations were not conducted.
Unequivocal link?
“This is among the first and largest to look at the relationship between football and having a diagnosis of PD in a large cohort of people from the Fox Insight online study,” Dr. Alosco said.
He cautioned that “not all people who play football will develop later-life neurological problems. That being said, the study adds to the accumulating evidence that suggests playing football is one risk factor for the development of later-life brain diseases.
“This represents an opportunity to educate the communities on the potential risks of playing football (short and long term), including what we know and what we don’t know, so that people can make informed decisions on participating in tackle football and develop additional ways to mitigate risk,” Dr. Alosco said.
In a comment, Shaheen Lakhan, MD, PhD, a neurologist and researcher from Boston, said: “The emerging body of research leaves little doubt that engaging in football raises the risk of developing Parkinson’s disease and parkinsonism.
“This progressive line of investigation serves to enhance our understanding, unequivocally demonstrating that even participation in amateur football, including at the youth and high school levels, constitutes a significant risk factor for the onset of Parkinson’s disease,” said Dr. Lakhan, who was not involved in the study.
However, he said it’s “crucial to underscore that the statistics reveal a notable distinction: individuals who have a history of college or professional football play face odds nearly three times higher of receiving a diagnosis of parkinsonism or Parkinson’s disease when compared to their counterparts who engaged in football during their youth or high-school years.
“Ultimately, determinations regarding involvement in sports should be a collaborative endeavor involving parents, young athletes, and health care providers. It is incumbent upon physicians to equip parents and youth with a comprehensive comprehension of the potential risks and rewards inherent in football participation,” Dr. Lakhan said.
He added, though, that there are multifaceted advantages to playing football. “This pursuit nurtures cardiovascular well-being, fosters invaluable social interactions, cultivates teamwork, instills discipline through regimented routines, and hones a spectrum of physical proficiencies,” Dr. Lakhan said.
“It’s worth noting that a constellation of alternative sports, including track and field, swimming, soccer, baseball, and tennis, can be cogently discussed as substitutes, all while preserving the manifold benefits of athletic engagement,” Dr. Lakhan added.
The Fox Insight Study is funded by the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research. The study was conducted in collaboration with the Michael J. Fox Foundation for Parkinson’s Research, the sponsor of the Fox Insight study, which collected and aggregated data used in the study. It was also supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Alosco received grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study, an honorarium from the Michael J. Fox Foundation for work unrelated to the study, and royalties from Oxford University Press outside the submitted work. Dr. Lakhan disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Which factors distinguish superagers from the rest of us?
Even at an advanced age, superagers have the memory of someone 20 or 30 years their junior. But why is that? A new study shows that, in superagers, However, the study also emphasizes the importance of physical and mental fitness for a healthy aging process.
“One of the most important unanswered questions with regard to superagers is: ‘Are they resistant to age-related memory loss, or do they have coping mechanisms that allow them to better offset this memory loss?’ ” wrote Marta Garo-Pascual, a PhD candidate at the Autonomous University of Madrid, Spain, and colleagues in the Lancet Healthy Longevity. “Our results indicate that superagers are resistant to these processes.”
Six years’ monitoring
From a cohort of older adults who had participated in a study aiming to identify early indicators of Alzheimer’s disease, the research group chose 64 superagers and 55 normal senior citizens. The latter served as the control group. While the superagers performed just as well in a memory test as people 30 years their junior, the control group’s performance was in line with their age and level of education.
All study participants were over age 79 years. Both the group of superagers and the control group included more females than males. On average, they were monitored for 6 years. During this period, a checkup was scheduled annually with an MRI examination, clinical tests, blood tests, and documentation of lifestyle factors.
For Alessandro Cellerino, PhD, of the Leibniz Institute on Aging–Fritz Lipmann Institute in Jena, Germany, this is the most crucial aspect of the study. “Even before this study, we knew that superagers demonstrated less atrophy in certain areas of the brain, but this was always only ever based on a single measurement.”
Memory centers protected
The MRI examinations confirmed that in superagers, gray matter atrophy in the regions responsible for memory (such as the medial temporal lobe and cholinergic forebrain), as well in regions important for movement (such as the motor thalamus), was less pronounced. In addition, the volume of gray matter in these regions, especially in the medial temporal lobe, decreased much more slowly in the superagers than in the control subjects over the study period.
Ms. Garo-Pascual and associates used a machine-learning algorithm to differentiate between superagers and normal older adults. From the 89 demographic, lifestyle, and clinical factors entered into the algorithm, two were the most important for the classification: the ability to move and mental health.
Mobility and mental health
Clinical tests such as the Timed Up-and-Go Test and the Finger Tapping Test revealed that superagers can be distinguished from the normally aging control subjects with regard to their mobility and fine motor skills. Their physical condition was better, although they, by their own admission, did not move any more than the control subjects in day-to-day life. According to Dr. Cellerino, this finding confirms that physical activity is paramount for cognitive function. “These people were over 80 years old – the fact that there was not much difference between their levels of activity is not surprising. Much more relevant is the question of how you get there – i.e., how active you are at the ages of 40, 50 or even 60 years old.”
Remaining active is important
As a matter of fact, the superagers indicated that generally they had been more active than the control subjects during their middle years. “Attempting to stay physically fit is essential; even if it just means going for a walk or taking the stairs,” said Dr. Cellerino.
On average, the superagers also fared much better in tests on physical health than the control subjects. They suffered significantly less from depression or anxiety disorders. “Earlier studies suggest that depression and anxiety disorders may influence performance in memory tests across all ages and that they are risk factors for developing dementia,” said Dr. Cellerino.
To avoid mental health issues in later life, gerontologist Dr. Cellerino recommended remaining socially engaged and involved. “Depression and anxiety are commonly also a consequence of social isolation,” he said.
Potential genetic differences
Blood sample analyses demonstrated that the superagers exhibited lower concentrations of biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases than the control group did. In contrast, there was no difference between the two groups in the prevalence of the apo e4 allele, one of the most important genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Nevertheless, Ms. Garo-Pascual and associates assume that genetics also play a role. They found that, despite 89 variables employed, the algorithm used could only distinguish superagers from normal older adults 66% of the time. This suggests that additional factors must be in play, such as genetic differences.
Body and mind
Since this is an observational study, whether the determined factors have a direct effect on superaging cannot be ascertained, the authors wrote. However, the results are consistent with earlier findings.
“Regarding the management of old age, we actually haven’t learned anything more than what we already knew. But it does confirm that physical and mental function are closely entwined and that we must maintain both to age healthily,” Dr. Cellerino concluded.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Even at an advanced age, superagers have the memory of someone 20 or 30 years their junior. But why is that? A new study shows that, in superagers, However, the study also emphasizes the importance of physical and mental fitness for a healthy aging process.
“One of the most important unanswered questions with regard to superagers is: ‘Are they resistant to age-related memory loss, or do they have coping mechanisms that allow them to better offset this memory loss?’ ” wrote Marta Garo-Pascual, a PhD candidate at the Autonomous University of Madrid, Spain, and colleagues in the Lancet Healthy Longevity. “Our results indicate that superagers are resistant to these processes.”
Six years’ monitoring
From a cohort of older adults who had participated in a study aiming to identify early indicators of Alzheimer’s disease, the research group chose 64 superagers and 55 normal senior citizens. The latter served as the control group. While the superagers performed just as well in a memory test as people 30 years their junior, the control group’s performance was in line with their age and level of education.
All study participants were over age 79 years. Both the group of superagers and the control group included more females than males. On average, they were monitored for 6 years. During this period, a checkup was scheduled annually with an MRI examination, clinical tests, blood tests, and documentation of lifestyle factors.
For Alessandro Cellerino, PhD, of the Leibniz Institute on Aging–Fritz Lipmann Institute in Jena, Germany, this is the most crucial aspect of the study. “Even before this study, we knew that superagers demonstrated less atrophy in certain areas of the brain, but this was always only ever based on a single measurement.”
Memory centers protected
The MRI examinations confirmed that in superagers, gray matter atrophy in the regions responsible for memory (such as the medial temporal lobe and cholinergic forebrain), as well in regions important for movement (such as the motor thalamus), was less pronounced. In addition, the volume of gray matter in these regions, especially in the medial temporal lobe, decreased much more slowly in the superagers than in the control subjects over the study period.
Ms. Garo-Pascual and associates used a machine-learning algorithm to differentiate between superagers and normal older adults. From the 89 demographic, lifestyle, and clinical factors entered into the algorithm, two were the most important for the classification: the ability to move and mental health.
Mobility and mental health
Clinical tests such as the Timed Up-and-Go Test and the Finger Tapping Test revealed that superagers can be distinguished from the normally aging control subjects with regard to their mobility and fine motor skills. Their physical condition was better, although they, by their own admission, did not move any more than the control subjects in day-to-day life. According to Dr. Cellerino, this finding confirms that physical activity is paramount for cognitive function. “These people were over 80 years old – the fact that there was not much difference between their levels of activity is not surprising. Much more relevant is the question of how you get there – i.e., how active you are at the ages of 40, 50 or even 60 years old.”
Remaining active is important
As a matter of fact, the superagers indicated that generally they had been more active than the control subjects during their middle years. “Attempting to stay physically fit is essential; even if it just means going for a walk or taking the stairs,” said Dr. Cellerino.
On average, the superagers also fared much better in tests on physical health than the control subjects. They suffered significantly less from depression or anxiety disorders. “Earlier studies suggest that depression and anxiety disorders may influence performance in memory tests across all ages and that they are risk factors for developing dementia,” said Dr. Cellerino.
To avoid mental health issues in later life, gerontologist Dr. Cellerino recommended remaining socially engaged and involved. “Depression and anxiety are commonly also a consequence of social isolation,” he said.
Potential genetic differences
Blood sample analyses demonstrated that the superagers exhibited lower concentrations of biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases than the control group did. In contrast, there was no difference between the two groups in the prevalence of the apo e4 allele, one of the most important genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Nevertheless, Ms. Garo-Pascual and associates assume that genetics also play a role. They found that, despite 89 variables employed, the algorithm used could only distinguish superagers from normal older adults 66% of the time. This suggests that additional factors must be in play, such as genetic differences.
Body and mind
Since this is an observational study, whether the determined factors have a direct effect on superaging cannot be ascertained, the authors wrote. However, the results are consistent with earlier findings.
“Regarding the management of old age, we actually haven’t learned anything more than what we already knew. But it does confirm that physical and mental function are closely entwined and that we must maintain both to age healthily,” Dr. Cellerino concluded.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
Even at an advanced age, superagers have the memory of someone 20 or 30 years their junior. But why is that? A new study shows that, in superagers, However, the study also emphasizes the importance of physical and mental fitness for a healthy aging process.
“One of the most important unanswered questions with regard to superagers is: ‘Are they resistant to age-related memory loss, or do they have coping mechanisms that allow them to better offset this memory loss?’ ” wrote Marta Garo-Pascual, a PhD candidate at the Autonomous University of Madrid, Spain, and colleagues in the Lancet Healthy Longevity. “Our results indicate that superagers are resistant to these processes.”
Six years’ monitoring
From a cohort of older adults who had participated in a study aiming to identify early indicators of Alzheimer’s disease, the research group chose 64 superagers and 55 normal senior citizens. The latter served as the control group. While the superagers performed just as well in a memory test as people 30 years their junior, the control group’s performance was in line with their age and level of education.
All study participants were over age 79 years. Both the group of superagers and the control group included more females than males. On average, they were monitored for 6 years. During this period, a checkup was scheduled annually with an MRI examination, clinical tests, blood tests, and documentation of lifestyle factors.
For Alessandro Cellerino, PhD, of the Leibniz Institute on Aging–Fritz Lipmann Institute in Jena, Germany, this is the most crucial aspect of the study. “Even before this study, we knew that superagers demonstrated less atrophy in certain areas of the brain, but this was always only ever based on a single measurement.”
Memory centers protected
The MRI examinations confirmed that in superagers, gray matter atrophy in the regions responsible for memory (such as the medial temporal lobe and cholinergic forebrain), as well in regions important for movement (such as the motor thalamus), was less pronounced. In addition, the volume of gray matter in these regions, especially in the medial temporal lobe, decreased much more slowly in the superagers than in the control subjects over the study period.
Ms. Garo-Pascual and associates used a machine-learning algorithm to differentiate between superagers and normal older adults. From the 89 demographic, lifestyle, and clinical factors entered into the algorithm, two were the most important for the classification: the ability to move and mental health.
Mobility and mental health
Clinical tests such as the Timed Up-and-Go Test and the Finger Tapping Test revealed that superagers can be distinguished from the normally aging control subjects with regard to their mobility and fine motor skills. Their physical condition was better, although they, by their own admission, did not move any more than the control subjects in day-to-day life. According to Dr. Cellerino, this finding confirms that physical activity is paramount for cognitive function. “These people were over 80 years old – the fact that there was not much difference between their levels of activity is not surprising. Much more relevant is the question of how you get there – i.e., how active you are at the ages of 40, 50 or even 60 years old.”
Remaining active is important
As a matter of fact, the superagers indicated that generally they had been more active than the control subjects during their middle years. “Attempting to stay physically fit is essential; even if it just means going for a walk or taking the stairs,” said Dr. Cellerino.
On average, the superagers also fared much better in tests on physical health than the control subjects. They suffered significantly less from depression or anxiety disorders. “Earlier studies suggest that depression and anxiety disorders may influence performance in memory tests across all ages and that they are risk factors for developing dementia,” said Dr. Cellerino.
To avoid mental health issues in later life, gerontologist Dr. Cellerino recommended remaining socially engaged and involved. “Depression and anxiety are commonly also a consequence of social isolation,” he said.
Potential genetic differences
Blood sample analyses demonstrated that the superagers exhibited lower concentrations of biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases than the control group did. In contrast, there was no difference between the two groups in the prevalence of the apo e4 allele, one of the most important genetic risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Nevertheless, Ms. Garo-Pascual and associates assume that genetics also play a role. They found that, despite 89 variables employed, the algorithm used could only distinguish superagers from normal older adults 66% of the time. This suggests that additional factors must be in play, such as genetic differences.
Body and mind
Since this is an observational study, whether the determined factors have a direct effect on superaging cannot be ascertained, the authors wrote. However, the results are consistent with earlier findings.
“Regarding the management of old age, we actually haven’t learned anything more than what we already knew. But it does confirm that physical and mental function are closely entwined and that we must maintain both to age healthily,” Dr. Cellerino concluded.
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition. A version appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET HEALTHY LONGEVITY
West Nile infections rising in the U.S.
Several signs are pointing to an impending surge in the number of human cases of West Nile virus in several regions of the United States.
West Nile virus is spread by infected mosquitoes and currently there is no cure or virus-specific treatment. In rare cases, it can be deadly. It can infect humans, birds, horses, and other mammals.
West Nile Virus is the leading cause of mosquito-borne disease in the continental United States. As of Aug. 8, 126 human cases had been identified across 22 states, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Particularly here in California, it’s peak risk right now,” said Vicki Kramer, PhD, chief of vector-borne diseases in the California Department of Public Health. She said scientists there are seeing higher mosquito and infected mosquito numbers.
“Peak risk right now”
Dead birds are tested for the virus and by Aug. 4, 181 of the 913 birds tested in California have been positive, three times the total testing positive by this time in 2022.
“Last year at this time, we had 60 positive dead birds out of 817 tested,” Dr. Kramer said.
Severe flooding and high heat can contribute to the rise in mosquito populations and many parts of the country have seen plenty of both.
One of the ways scientists track infected mosquito patterns in California is by using flocks of strategically placed sentinel chickens.
“Chickens are a mosquito magnet,” Dr. Kramer said.
Chickens don’t get sick with the virus, but they do build antibodies to it. Surveillance teams check their blood every other week to track the virus.
Daniel Pastula, MD, MHS, chief of neuroinfectious diseases and global neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and the Colorado School of Public Health, said the state is watching troubling signs as well.
“The concern this year,” Dr. Pastula said, “particularly along the Front Range in Colorado, is we’ve found many more mosquitoes [that are] positive for West Nile earlier in the season compared with other years.
“We’re bracing for higher-than-baseline human cases,” he said.
Asked about this year’s first human case, reported in Toronto, a region with a long winter and low incidence of the virus, he said that provides a further example that people need to be prepared even in climates not known to be mosquito-dense.
He added, however, that climate is only one factor in the severity of the season. Others include birds’ immunity and migratory patterns.
Dr. Pastula said that fluctuations in temperature and rainfall are rising with climate change and are disrupting normal baseline levels of West Nile.
“That shows we need to be prepared for West Nile virus and other mosquito-borne diseases in any place in North America or really the world. We recently saw malaria cases in the southern United States. It just shows you how dangerous mosquitoes can be.”
Avoid mosquito bites
Dr. Pastula and Dr. Kramer list the precautions people can take to protect themselves from West Nile virus:
- Limit outdoor exposure particularly at dusk and dawn.
- Wear protective clothing.
- Use .
- Repair window screens so mosquitoes cannot fly through.
- Dump and drain standing water on your property and maintain swimming pools.
Dr. Pastula noted that summer is the time human cases start to mount – typically from July and August to the first hard freeze.
“We have been warning people here up and down the Front Range of Colorado to take prevention very seriously,” Dr. Pastula said.
He pointed out that 80% who are infected with West Nile will have no symptoms.
About 20% will have flu-like illness – high fever, body and joint aches, rash, diarrhea, or headaches. Symptoms may last for weeks. About 1% of the time, he said, people can get neuroinvasive West Nile.
Dr. Pastula explained that the virus can infect the covering of the brain and spinal cord causing meningitis with very high fever, severe headaches, stiff neck, and sensitivity to light.
So far this year, there have been 89 neuroinvasive cases reported nationally, according to the CDC.
With West Nile encephalitis, the virus “can infect the brain itself causing altered mental status, movement disorders, or weakness,” Dr. Pastula said.
Sometimes it can infect the gray matter of the spinal cord causing a West Nile virus poliomyelitis, which brings polio-like symptoms.
“The West Nile encephalitis and poliomyelitis can cause permanent deficits or even death,” he said. “It’s uncommon but it’s not trivial.”
Several vaccine candidates are in development, Dr. Pastula said, but none has reached clinical trials. Part of the reason for that, he said, is that scientists must be able to predict the timing of an outbreak.
“We’re not really great at predicting outbreaks,” he said.
Although the risk for neuroinvasive disease is small, it can be higher in certain groups, he said – those who are over age 60 years or are immunocompromised; those who have diabetes, cancer, or kidney disease; or those who have undergone organ transplants.
Those infected should see a health care professional and may be able to get relief with the usual medications for flu-like illness.
Some with severe infection may need to go to the hospital, Dr. Pastula said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Several signs are pointing to an impending surge in the number of human cases of West Nile virus in several regions of the United States.
West Nile virus is spread by infected mosquitoes and currently there is no cure or virus-specific treatment. In rare cases, it can be deadly. It can infect humans, birds, horses, and other mammals.
West Nile Virus is the leading cause of mosquito-borne disease in the continental United States. As of Aug. 8, 126 human cases had been identified across 22 states, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Particularly here in California, it’s peak risk right now,” said Vicki Kramer, PhD, chief of vector-borne diseases in the California Department of Public Health. She said scientists there are seeing higher mosquito and infected mosquito numbers.
“Peak risk right now”
Dead birds are tested for the virus and by Aug. 4, 181 of the 913 birds tested in California have been positive, three times the total testing positive by this time in 2022.
“Last year at this time, we had 60 positive dead birds out of 817 tested,” Dr. Kramer said.
Severe flooding and high heat can contribute to the rise in mosquito populations and many parts of the country have seen plenty of both.
One of the ways scientists track infected mosquito patterns in California is by using flocks of strategically placed sentinel chickens.
“Chickens are a mosquito magnet,” Dr. Kramer said.
Chickens don’t get sick with the virus, but they do build antibodies to it. Surveillance teams check their blood every other week to track the virus.
Daniel Pastula, MD, MHS, chief of neuroinfectious diseases and global neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and the Colorado School of Public Health, said the state is watching troubling signs as well.
“The concern this year,” Dr. Pastula said, “particularly along the Front Range in Colorado, is we’ve found many more mosquitoes [that are] positive for West Nile earlier in the season compared with other years.
“We’re bracing for higher-than-baseline human cases,” he said.
Asked about this year’s first human case, reported in Toronto, a region with a long winter and low incidence of the virus, he said that provides a further example that people need to be prepared even in climates not known to be mosquito-dense.
He added, however, that climate is only one factor in the severity of the season. Others include birds’ immunity and migratory patterns.
Dr. Pastula said that fluctuations in temperature and rainfall are rising with climate change and are disrupting normal baseline levels of West Nile.
“That shows we need to be prepared for West Nile virus and other mosquito-borne diseases in any place in North America or really the world. We recently saw malaria cases in the southern United States. It just shows you how dangerous mosquitoes can be.”
Avoid mosquito bites
Dr. Pastula and Dr. Kramer list the precautions people can take to protect themselves from West Nile virus:
- Limit outdoor exposure particularly at dusk and dawn.
- Wear protective clothing.
- Use .
- Repair window screens so mosquitoes cannot fly through.
- Dump and drain standing water on your property and maintain swimming pools.
Dr. Pastula noted that summer is the time human cases start to mount – typically from July and August to the first hard freeze.
“We have been warning people here up and down the Front Range of Colorado to take prevention very seriously,” Dr. Pastula said.
He pointed out that 80% who are infected with West Nile will have no symptoms.
About 20% will have flu-like illness – high fever, body and joint aches, rash, diarrhea, or headaches. Symptoms may last for weeks. About 1% of the time, he said, people can get neuroinvasive West Nile.
Dr. Pastula explained that the virus can infect the covering of the brain and spinal cord causing meningitis with very high fever, severe headaches, stiff neck, and sensitivity to light.
So far this year, there have been 89 neuroinvasive cases reported nationally, according to the CDC.
With West Nile encephalitis, the virus “can infect the brain itself causing altered mental status, movement disorders, or weakness,” Dr. Pastula said.
Sometimes it can infect the gray matter of the spinal cord causing a West Nile virus poliomyelitis, which brings polio-like symptoms.
“The West Nile encephalitis and poliomyelitis can cause permanent deficits or even death,” he said. “It’s uncommon but it’s not trivial.”
Several vaccine candidates are in development, Dr. Pastula said, but none has reached clinical trials. Part of the reason for that, he said, is that scientists must be able to predict the timing of an outbreak.
“We’re not really great at predicting outbreaks,” he said.
Although the risk for neuroinvasive disease is small, it can be higher in certain groups, he said – those who are over age 60 years or are immunocompromised; those who have diabetes, cancer, or kidney disease; or those who have undergone organ transplants.
Those infected should see a health care professional and may be able to get relief with the usual medications for flu-like illness.
Some with severe infection may need to go to the hospital, Dr. Pastula said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Several signs are pointing to an impending surge in the number of human cases of West Nile virus in several regions of the United States.
West Nile virus is spread by infected mosquitoes and currently there is no cure or virus-specific treatment. In rare cases, it can be deadly. It can infect humans, birds, horses, and other mammals.
West Nile Virus is the leading cause of mosquito-borne disease in the continental United States. As of Aug. 8, 126 human cases had been identified across 22 states, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
“Particularly here in California, it’s peak risk right now,” said Vicki Kramer, PhD, chief of vector-borne diseases in the California Department of Public Health. She said scientists there are seeing higher mosquito and infected mosquito numbers.
“Peak risk right now”
Dead birds are tested for the virus and by Aug. 4, 181 of the 913 birds tested in California have been positive, three times the total testing positive by this time in 2022.
“Last year at this time, we had 60 positive dead birds out of 817 tested,” Dr. Kramer said.
Severe flooding and high heat can contribute to the rise in mosquito populations and many parts of the country have seen plenty of both.
One of the ways scientists track infected mosquito patterns in California is by using flocks of strategically placed sentinel chickens.
“Chickens are a mosquito magnet,” Dr. Kramer said.
Chickens don’t get sick with the virus, but they do build antibodies to it. Surveillance teams check their blood every other week to track the virus.
Daniel Pastula, MD, MHS, chief of neuroinfectious diseases and global neurology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and the Colorado School of Public Health, said the state is watching troubling signs as well.
“The concern this year,” Dr. Pastula said, “particularly along the Front Range in Colorado, is we’ve found many more mosquitoes [that are] positive for West Nile earlier in the season compared with other years.
“We’re bracing for higher-than-baseline human cases,” he said.
Asked about this year’s first human case, reported in Toronto, a region with a long winter and low incidence of the virus, he said that provides a further example that people need to be prepared even in climates not known to be mosquito-dense.
He added, however, that climate is only one factor in the severity of the season. Others include birds’ immunity and migratory patterns.
Dr. Pastula said that fluctuations in temperature and rainfall are rising with climate change and are disrupting normal baseline levels of West Nile.
“That shows we need to be prepared for West Nile virus and other mosquito-borne diseases in any place in North America or really the world. We recently saw malaria cases in the southern United States. It just shows you how dangerous mosquitoes can be.”
Avoid mosquito bites
Dr. Pastula and Dr. Kramer list the precautions people can take to protect themselves from West Nile virus:
- Limit outdoor exposure particularly at dusk and dawn.
- Wear protective clothing.
- Use .
- Repair window screens so mosquitoes cannot fly through.
- Dump and drain standing water on your property and maintain swimming pools.
Dr. Pastula noted that summer is the time human cases start to mount – typically from July and August to the first hard freeze.
“We have been warning people here up and down the Front Range of Colorado to take prevention very seriously,” Dr. Pastula said.
He pointed out that 80% who are infected with West Nile will have no symptoms.
About 20% will have flu-like illness – high fever, body and joint aches, rash, diarrhea, or headaches. Symptoms may last for weeks. About 1% of the time, he said, people can get neuroinvasive West Nile.
Dr. Pastula explained that the virus can infect the covering of the brain and spinal cord causing meningitis with very high fever, severe headaches, stiff neck, and sensitivity to light.
So far this year, there have been 89 neuroinvasive cases reported nationally, according to the CDC.
With West Nile encephalitis, the virus “can infect the brain itself causing altered mental status, movement disorders, or weakness,” Dr. Pastula said.
Sometimes it can infect the gray matter of the spinal cord causing a West Nile virus poliomyelitis, which brings polio-like symptoms.
“The West Nile encephalitis and poliomyelitis can cause permanent deficits or even death,” he said. “It’s uncommon but it’s not trivial.”
Several vaccine candidates are in development, Dr. Pastula said, but none has reached clinical trials. Part of the reason for that, he said, is that scientists must be able to predict the timing of an outbreak.
“We’re not really great at predicting outbreaks,” he said.
Although the risk for neuroinvasive disease is small, it can be higher in certain groups, he said – those who are over age 60 years or are immunocompromised; those who have diabetes, cancer, or kidney disease; or those who have undergone organ transplants.
Those infected should see a health care professional and may be able to get relief with the usual medications for flu-like illness.
Some with severe infection may need to go to the hospital, Dr. Pastula said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TBI tied to increased mental health diagnoses, time to suicide
Investigators also found that increases in new mental health diagnoses are significantly higher in soldiers with a history of TBI – in some cases, strikingly higher. For example, cases of substance use disorder rose by 100% among veterans with TBI compared to just 14.5% in those with no brain injury.
“We had had pieces of these findings for a long time but to be able to lay out this longitudinal story over time is the part that’s new and important to really switch the focus to people’s whole lives and things that happen over time, both psychological and physical,” lead author Lisa Brenner, PhD, director of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Rocky Mountain Mental Illness Research Education and Clinical Center, Aurora, Colo., said in an interview.
“If we take that life-course view, it’s a very different way about thinking about conceptualizing exposures and conceptualizing risk and it’s a different way of thinking about treatment and prevention,” added Dr. Brenner, professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation, psychiatry, and neurology at the University of Colorado, Aurora. “I think that definitely applies to civilian populations.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Largest, longest study to date
Researchers have long suspected that TBI and a higher rate of new mental illness and a shorter time to suicide are all somehow linked. But this study examined all three components longitudinally, in what is thought to be the largest and longest study on the topic to date, including more than 860,000 people who were followed for up to a decade.
Investigators studied health data from the Substance Use and Psychological Injury Combat Study database on 860,892 U.S. Army soldiers who returned from deployment in Iraq or Afghanistan between 2008 and 2014 and were 18-24 years old at the end of that deployment. They then examined new mental health diagnoses and suicide trends over time.
Nearly 109,000 (12.6%) experienced a TBI during deployment, and 2,695 had died by suicide through the end of 2018.
New-onset diagnoses of anxiety, mood disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, alcohol use, and substance use disorder (SUD) after deployment were all more common in soldiers who experienced PTSD while serving compared with those with no history of TBI.
There was a 67.7% increase in mood disorders in participants with TBI compared with a 37.5% increase in those without TBI. The increase in new cases of alcohol use disorder was also greater in the TBI group (a 31.9% increase vs. a 10.3% increase).
But the sharpest difference was the increase in substance use disorder among those with TBI, which rose 100% compared with a 14.5% increase in solders with no history of TBI.
Sharp differences in time to suicide
Death by suicide was only slightly more common in those with TBI compared with those without (0.4% vs. 0.3%, respectively). But those with a brain injury committed suicide 21.3% sooner than did those without a head injury, after the researchers controlled for sex, age, race, ethnicity, and fiscal year of return from deployment.
Time to suicide was faster in those with a TBI and two or more new mental health diagnoses and fastest among those with TBI and a new SUD diagnosis, who took their own lives 62.8% faster than did those without a TBI.
The findings offer an important message to medical professionals in many different specialties, Dr. Brenner said.
“Folks in mental health probably have a lot of patients who have brain injury in their practice, and they don’t know it and that’s an important thing to know,” she said, adding that “neurologists should screen for depression and other mental health conditions and make sure those people have evidence-based treatments for those mental health conditions while they’re addressing the TBI-related symptoms.”
Applicable to civilians?
“The complex interplay between TBI, its potential effects on mental health, and risk of suicide remains a vexing focus of ongoing investigations and academic inquiry,” Ross Zafonte, DO, president of Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Network and professor and chair of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The study builds on earlier work, they added, and praised the study’s longitudinal design and large cohort as key to the findings. The data on increased rates of new-onset substance use disorder, which was also associated with a faster time to suicide in the TBI group, were of particular interest.
“In this work, Brenner and colleagues identified substance use disorder as a key factor in faster time to suicide for active-duty service members with a history of TBI compared with those without TBI and theorized that a multiple stress or exposure burden may enhance risk,” they wrote. “This theory is reasonable and has been postulated among individuals with medical sequelae linked to TBI.”
However, the authors caution against applying these findings in military veterans to civilians.
“While this work is critical in the military population, caution should be given to avoid direct generalization to other populations, such as athletes, for whom the linkage to suicidal ideation is less understood,” they wrote.
The study was funded by National Institute of Mental Health and Office of the Director at National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brenner has received personal fees from Wolters Kluwer, Rand, American Psychological Association, and Oxford University Press and serves as a consultant to sports leagues via her university affiliation. Dr. Zafonte reported receiving royalties from Springer/Demos; serving as a member of the editorial boards of Journal of Neurotrauma and Frontiers in Neurology and scientific advisory boards of Myomo, Nanodiagnostics, Onecare.ai, and Kisbee; and evaluating patients in the MGH Brain and Body-TRUST Program, which is funded by the National Football League Players Association.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators also found that increases in new mental health diagnoses are significantly higher in soldiers with a history of TBI – in some cases, strikingly higher. For example, cases of substance use disorder rose by 100% among veterans with TBI compared to just 14.5% in those with no brain injury.
“We had had pieces of these findings for a long time but to be able to lay out this longitudinal story over time is the part that’s new and important to really switch the focus to people’s whole lives and things that happen over time, both psychological and physical,” lead author Lisa Brenner, PhD, director of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Rocky Mountain Mental Illness Research Education and Clinical Center, Aurora, Colo., said in an interview.
“If we take that life-course view, it’s a very different way about thinking about conceptualizing exposures and conceptualizing risk and it’s a different way of thinking about treatment and prevention,” added Dr. Brenner, professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation, psychiatry, and neurology at the University of Colorado, Aurora. “I think that definitely applies to civilian populations.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Largest, longest study to date
Researchers have long suspected that TBI and a higher rate of new mental illness and a shorter time to suicide are all somehow linked. But this study examined all three components longitudinally, in what is thought to be the largest and longest study on the topic to date, including more than 860,000 people who were followed for up to a decade.
Investigators studied health data from the Substance Use and Psychological Injury Combat Study database on 860,892 U.S. Army soldiers who returned from deployment in Iraq or Afghanistan between 2008 and 2014 and were 18-24 years old at the end of that deployment. They then examined new mental health diagnoses and suicide trends over time.
Nearly 109,000 (12.6%) experienced a TBI during deployment, and 2,695 had died by suicide through the end of 2018.
New-onset diagnoses of anxiety, mood disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, alcohol use, and substance use disorder (SUD) after deployment were all more common in soldiers who experienced PTSD while serving compared with those with no history of TBI.
There was a 67.7% increase in mood disorders in participants with TBI compared with a 37.5% increase in those without TBI. The increase in new cases of alcohol use disorder was also greater in the TBI group (a 31.9% increase vs. a 10.3% increase).
But the sharpest difference was the increase in substance use disorder among those with TBI, which rose 100% compared with a 14.5% increase in solders with no history of TBI.
Sharp differences in time to suicide
Death by suicide was only slightly more common in those with TBI compared with those without (0.4% vs. 0.3%, respectively). But those with a brain injury committed suicide 21.3% sooner than did those without a head injury, after the researchers controlled for sex, age, race, ethnicity, and fiscal year of return from deployment.
Time to suicide was faster in those with a TBI and two or more new mental health diagnoses and fastest among those with TBI and a new SUD diagnosis, who took their own lives 62.8% faster than did those without a TBI.
The findings offer an important message to medical professionals in many different specialties, Dr. Brenner said.
“Folks in mental health probably have a lot of patients who have brain injury in their practice, and they don’t know it and that’s an important thing to know,” she said, adding that “neurologists should screen for depression and other mental health conditions and make sure those people have evidence-based treatments for those mental health conditions while they’re addressing the TBI-related symptoms.”
Applicable to civilians?
“The complex interplay between TBI, its potential effects on mental health, and risk of suicide remains a vexing focus of ongoing investigations and academic inquiry,” Ross Zafonte, DO, president of Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Network and professor and chair of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The study builds on earlier work, they added, and praised the study’s longitudinal design and large cohort as key to the findings. The data on increased rates of new-onset substance use disorder, which was also associated with a faster time to suicide in the TBI group, were of particular interest.
“In this work, Brenner and colleagues identified substance use disorder as a key factor in faster time to suicide for active-duty service members with a history of TBI compared with those without TBI and theorized that a multiple stress or exposure burden may enhance risk,” they wrote. “This theory is reasonable and has been postulated among individuals with medical sequelae linked to TBI.”
However, the authors caution against applying these findings in military veterans to civilians.
“While this work is critical in the military population, caution should be given to avoid direct generalization to other populations, such as athletes, for whom the linkage to suicidal ideation is less understood,” they wrote.
The study was funded by National Institute of Mental Health and Office of the Director at National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brenner has received personal fees from Wolters Kluwer, Rand, American Psychological Association, and Oxford University Press and serves as a consultant to sports leagues via her university affiliation. Dr. Zafonte reported receiving royalties from Springer/Demos; serving as a member of the editorial boards of Journal of Neurotrauma and Frontiers in Neurology and scientific advisory boards of Myomo, Nanodiagnostics, Onecare.ai, and Kisbee; and evaluating patients in the MGH Brain and Body-TRUST Program, which is funded by the National Football League Players Association.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Investigators also found that increases in new mental health diagnoses are significantly higher in soldiers with a history of TBI – in some cases, strikingly higher. For example, cases of substance use disorder rose by 100% among veterans with TBI compared to just 14.5% in those with no brain injury.
“We had had pieces of these findings for a long time but to be able to lay out this longitudinal story over time is the part that’s new and important to really switch the focus to people’s whole lives and things that happen over time, both psychological and physical,” lead author Lisa Brenner, PhD, director of the Veterans Health Administration (VHA) Rocky Mountain Mental Illness Research Education and Clinical Center, Aurora, Colo., said in an interview.
“If we take that life-course view, it’s a very different way about thinking about conceptualizing exposures and conceptualizing risk and it’s a different way of thinking about treatment and prevention,” added Dr. Brenner, professor of physical medicine and rehabilitation, psychiatry, and neurology at the University of Colorado, Aurora. “I think that definitely applies to civilian populations.”
The findings were published online in JAMA Network Open.
Largest, longest study to date
Researchers have long suspected that TBI and a higher rate of new mental illness and a shorter time to suicide are all somehow linked. But this study examined all three components longitudinally, in what is thought to be the largest and longest study on the topic to date, including more than 860,000 people who were followed for up to a decade.
Investigators studied health data from the Substance Use and Psychological Injury Combat Study database on 860,892 U.S. Army soldiers who returned from deployment in Iraq or Afghanistan between 2008 and 2014 and were 18-24 years old at the end of that deployment. They then examined new mental health diagnoses and suicide trends over time.
Nearly 109,000 (12.6%) experienced a TBI during deployment, and 2,695 had died by suicide through the end of 2018.
New-onset diagnoses of anxiety, mood disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, alcohol use, and substance use disorder (SUD) after deployment were all more common in soldiers who experienced PTSD while serving compared with those with no history of TBI.
There was a 67.7% increase in mood disorders in participants with TBI compared with a 37.5% increase in those without TBI. The increase in new cases of alcohol use disorder was also greater in the TBI group (a 31.9% increase vs. a 10.3% increase).
But the sharpest difference was the increase in substance use disorder among those with TBI, which rose 100% compared with a 14.5% increase in solders with no history of TBI.
Sharp differences in time to suicide
Death by suicide was only slightly more common in those with TBI compared with those without (0.4% vs. 0.3%, respectively). But those with a brain injury committed suicide 21.3% sooner than did those without a head injury, after the researchers controlled for sex, age, race, ethnicity, and fiscal year of return from deployment.
Time to suicide was faster in those with a TBI and two or more new mental health diagnoses and fastest among those with TBI and a new SUD diagnosis, who took their own lives 62.8% faster than did those without a TBI.
The findings offer an important message to medical professionals in many different specialties, Dr. Brenner said.
“Folks in mental health probably have a lot of patients who have brain injury in their practice, and they don’t know it and that’s an important thing to know,” she said, adding that “neurologists should screen for depression and other mental health conditions and make sure those people have evidence-based treatments for those mental health conditions while they’re addressing the TBI-related symptoms.”
Applicable to civilians?
“The complex interplay between TBI, its potential effects on mental health, and risk of suicide remains a vexing focus of ongoing investigations and academic inquiry,” Ross Zafonte, DO, president of Spaulding Rehabilitation Hospital Network and professor and chair of physical medicine and rehabilitation at Harvard Medical School, Boston, and colleagues, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The study builds on earlier work, they added, and praised the study’s longitudinal design and large cohort as key to the findings. The data on increased rates of new-onset substance use disorder, which was also associated with a faster time to suicide in the TBI group, were of particular interest.
“In this work, Brenner and colleagues identified substance use disorder as a key factor in faster time to suicide for active-duty service members with a history of TBI compared with those without TBI and theorized that a multiple stress or exposure burden may enhance risk,” they wrote. “This theory is reasonable and has been postulated among individuals with medical sequelae linked to TBI.”
However, the authors caution against applying these findings in military veterans to civilians.
“While this work is critical in the military population, caution should be given to avoid direct generalization to other populations, such as athletes, for whom the linkage to suicidal ideation is less understood,” they wrote.
The study was funded by National Institute of Mental Health and Office of the Director at National Institutes of Health. Dr. Brenner has received personal fees from Wolters Kluwer, Rand, American Psychological Association, and Oxford University Press and serves as a consultant to sports leagues via her university affiliation. Dr. Zafonte reported receiving royalties from Springer/Demos; serving as a member of the editorial boards of Journal of Neurotrauma and Frontiers in Neurology and scientific advisory boards of Myomo, Nanodiagnostics, Onecare.ai, and Kisbee; and evaluating patients in the MGH Brain and Body-TRUST Program, which is funded by the National Football League Players Association.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
‘Emerging’ biomarker may predict mild cognitive impairment years before symptoms
, new research indicates.
“Our study shows that low NPTX2 levels are predictive of MCI symptom onset more than 7 years in advance, including among individuals who are in late middle age,” said study investigator Anja Soldan, PhD, associate professor of neurology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
NPTX2 is still considered an “emerging biomarker” because knowledge about this protein is limited, Dr. Soldan noted.
Prior studies have shown that levels of NPTX2 are lower in people with MCI and dementia than in those with normal cognition and that low levels of this protein in people with MCI are associated with an increased risk of developing dementia.
“Our study extends these prior findings by showing that low protein levels are also associated with the onset of MCI symptoms,” Dr. Soldan said.
The study was published online in Annals of Neurology.
New therapeutic target?
The researchers measured NPTX2, as well as amyloid beta 42/40, phosphorylated (p)-tau181, and total (t)-tau in CSF collected longitudinally from 269 cognitively normal adults from the BIOCARD study.
The average age at baseline was 57.7 years. Nearly all were White, 59% were women, most were college educated, and three-quarters had a close relative with Alzheimer’s disease.
During a mean follow-up average of 16 years, 77 participants progressed to MCI or dementia within or after 7 years of baseline measurements.
In Cox regression models, lower baseline NPTX2 levels were associated with an earlier time to MCI symptom onset (hazard ratio, 0.76; P = .023). This association was significant for progression within 7 years (P = .036) and after 7 years from baseline (P = .001), the investigators reported.
Adults who progressed to MCI had, on average, about 15% lower levels of NPTX2 at baseline, compared with adults who remained cognitively normal.
Baseline NPTX2 levels improved prediction of time to MCI symptom onset after accounting for baseline Alzheimer’s disease biomarker levels (P < .01), and NPTX2 did not interact with the CSF Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers or APOE-ε4 genetic status.
Higher baseline levels of p-tau181 and t-tau were associated with higher baseline NPTX2 levels (both P < .001) and with greater declines in NPTX2 over time, suggesting that NPTX2 may decline in response to tau pathology, the investigators suggested.
Dr. Soldan said NPTX2 may be “a novel target” for developing new therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementing and neurodegenerative disorders, as it is not an Alzheimer’s disease–specific protein.
“Efforts are underway for developing a sensitive way to measure NPTX2 brain levels in blood, which could then help clinicians identify individuals at greatest risk for cognitive decline,” she explained.
“Other next steps are to examine how changes in NPTX2 over time relate to changes in brain structure and function and to identify factors that alter levels of NPTX2, including genetic factors and potentially modifiable lifestyle factors,” Dr. Soldan said.
“If having higher levels of NPTX2 in the brain provides some resilience against developing symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, it would be great if we could somehow increase levels of the protein,” she noted.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Commenting on this research, Christopher Weber, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of global science initiatives, said, “Research has shown that when NPTX2 levels are low, it may lead to weaker connections between neurons and could potentially affect cognitive functions, including memory and learning.”
“This new study found an association between lower levels of NPTX2 in CSF and earlier time to MCI symptom onset, and when combined with other established Alzheimer’s biomarkers, they found that NPTX2 improved the prediction of Alzheimer’s symptom onset,” Dr. Weber said.
“This is in line with previous research that suggests NPTX2 levels are associated with an increased risk of progression from MCI to Alzheimer’s dementia,” Dr. Weber said.
However, he noted some limitations of the study. “Participants were primarily White [and] highly educated, and therefore findings may not be generalizable to a real-world population,” he cautioned.
Dr. Weber said it’s also important to note that NPTX2 is not considered an Alzheimer’s-specific biomarker but rather a marker of synaptic activity and neurodegeneration. “The exact role of NPTX2 in predicting dementia is unknown,” Dr. Weber said.
He said that more studies with larger, more diverse cohorts are needed to fully understand its significance as a biomarker or therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases, as well as to develop a blood test for NPTX2.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Soldan and Dr. Weber report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research indicates.
“Our study shows that low NPTX2 levels are predictive of MCI symptom onset more than 7 years in advance, including among individuals who are in late middle age,” said study investigator Anja Soldan, PhD, associate professor of neurology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
NPTX2 is still considered an “emerging biomarker” because knowledge about this protein is limited, Dr. Soldan noted.
Prior studies have shown that levels of NPTX2 are lower in people with MCI and dementia than in those with normal cognition and that low levels of this protein in people with MCI are associated with an increased risk of developing dementia.
“Our study extends these prior findings by showing that low protein levels are also associated with the onset of MCI symptoms,” Dr. Soldan said.
The study was published online in Annals of Neurology.
New therapeutic target?
The researchers measured NPTX2, as well as amyloid beta 42/40, phosphorylated (p)-tau181, and total (t)-tau in CSF collected longitudinally from 269 cognitively normal adults from the BIOCARD study.
The average age at baseline was 57.7 years. Nearly all were White, 59% were women, most were college educated, and three-quarters had a close relative with Alzheimer’s disease.
During a mean follow-up average of 16 years, 77 participants progressed to MCI or dementia within or after 7 years of baseline measurements.
In Cox regression models, lower baseline NPTX2 levels were associated with an earlier time to MCI symptom onset (hazard ratio, 0.76; P = .023). This association was significant for progression within 7 years (P = .036) and after 7 years from baseline (P = .001), the investigators reported.
Adults who progressed to MCI had, on average, about 15% lower levels of NPTX2 at baseline, compared with adults who remained cognitively normal.
Baseline NPTX2 levels improved prediction of time to MCI symptom onset after accounting for baseline Alzheimer’s disease biomarker levels (P < .01), and NPTX2 did not interact with the CSF Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers or APOE-ε4 genetic status.
Higher baseline levels of p-tau181 and t-tau were associated with higher baseline NPTX2 levels (both P < .001) and with greater declines in NPTX2 over time, suggesting that NPTX2 may decline in response to tau pathology, the investigators suggested.
Dr. Soldan said NPTX2 may be “a novel target” for developing new therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementing and neurodegenerative disorders, as it is not an Alzheimer’s disease–specific protein.
“Efforts are underway for developing a sensitive way to measure NPTX2 brain levels in blood, which could then help clinicians identify individuals at greatest risk for cognitive decline,” she explained.
“Other next steps are to examine how changes in NPTX2 over time relate to changes in brain structure and function and to identify factors that alter levels of NPTX2, including genetic factors and potentially modifiable lifestyle factors,” Dr. Soldan said.
“If having higher levels of NPTX2 in the brain provides some resilience against developing symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, it would be great if we could somehow increase levels of the protein,” she noted.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Commenting on this research, Christopher Weber, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of global science initiatives, said, “Research has shown that when NPTX2 levels are low, it may lead to weaker connections between neurons and could potentially affect cognitive functions, including memory and learning.”
“This new study found an association between lower levels of NPTX2 in CSF and earlier time to MCI symptom onset, and when combined with other established Alzheimer’s biomarkers, they found that NPTX2 improved the prediction of Alzheimer’s symptom onset,” Dr. Weber said.
“This is in line with previous research that suggests NPTX2 levels are associated with an increased risk of progression from MCI to Alzheimer’s dementia,” Dr. Weber said.
However, he noted some limitations of the study. “Participants were primarily White [and] highly educated, and therefore findings may not be generalizable to a real-world population,” he cautioned.
Dr. Weber said it’s also important to note that NPTX2 is not considered an Alzheimer’s-specific biomarker but rather a marker of synaptic activity and neurodegeneration. “The exact role of NPTX2 in predicting dementia is unknown,” Dr. Weber said.
He said that more studies with larger, more diverse cohorts are needed to fully understand its significance as a biomarker or therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases, as well as to develop a blood test for NPTX2.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Soldan and Dr. Weber report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research indicates.
“Our study shows that low NPTX2 levels are predictive of MCI symptom onset more than 7 years in advance, including among individuals who are in late middle age,” said study investigator Anja Soldan, PhD, associate professor of neurology, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore.
NPTX2 is still considered an “emerging biomarker” because knowledge about this protein is limited, Dr. Soldan noted.
Prior studies have shown that levels of NPTX2 are lower in people with MCI and dementia than in those with normal cognition and that low levels of this protein in people with MCI are associated with an increased risk of developing dementia.
“Our study extends these prior findings by showing that low protein levels are also associated with the onset of MCI symptoms,” Dr. Soldan said.
The study was published online in Annals of Neurology.
New therapeutic target?
The researchers measured NPTX2, as well as amyloid beta 42/40, phosphorylated (p)-tau181, and total (t)-tau in CSF collected longitudinally from 269 cognitively normal adults from the BIOCARD study.
The average age at baseline was 57.7 years. Nearly all were White, 59% were women, most were college educated, and three-quarters had a close relative with Alzheimer’s disease.
During a mean follow-up average of 16 years, 77 participants progressed to MCI or dementia within or after 7 years of baseline measurements.
In Cox regression models, lower baseline NPTX2 levels were associated with an earlier time to MCI symptom onset (hazard ratio, 0.76; P = .023). This association was significant for progression within 7 years (P = .036) and after 7 years from baseline (P = .001), the investigators reported.
Adults who progressed to MCI had, on average, about 15% lower levels of NPTX2 at baseline, compared with adults who remained cognitively normal.
Baseline NPTX2 levels improved prediction of time to MCI symptom onset after accounting for baseline Alzheimer’s disease biomarker levels (P < .01), and NPTX2 did not interact with the CSF Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers or APOE-ε4 genetic status.
Higher baseline levels of p-tau181 and t-tau were associated with higher baseline NPTX2 levels (both P < .001) and with greater declines in NPTX2 over time, suggesting that NPTX2 may decline in response to tau pathology, the investigators suggested.
Dr. Soldan said NPTX2 may be “a novel target” for developing new therapeutics for Alzheimer’s disease and other dementing and neurodegenerative disorders, as it is not an Alzheimer’s disease–specific protein.
“Efforts are underway for developing a sensitive way to measure NPTX2 brain levels in blood, which could then help clinicians identify individuals at greatest risk for cognitive decline,” she explained.
“Other next steps are to examine how changes in NPTX2 over time relate to changes in brain structure and function and to identify factors that alter levels of NPTX2, including genetic factors and potentially modifiable lifestyle factors,” Dr. Soldan said.
“If having higher levels of NPTX2 in the brain provides some resilience against developing symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease, it would be great if we could somehow increase levels of the protein,” she noted.
Caveats, cautionary notes
Commenting on this research, Christopher Weber, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association director of global science initiatives, said, “Research has shown that when NPTX2 levels are low, it may lead to weaker connections between neurons and could potentially affect cognitive functions, including memory and learning.”
“This new study found an association between lower levels of NPTX2 in CSF and earlier time to MCI symptom onset, and when combined with other established Alzheimer’s biomarkers, they found that NPTX2 improved the prediction of Alzheimer’s symptom onset,” Dr. Weber said.
“This is in line with previous research that suggests NPTX2 levels are associated with an increased risk of progression from MCI to Alzheimer’s dementia,” Dr. Weber said.
However, he noted some limitations of the study. “Participants were primarily White [and] highly educated, and therefore findings may not be generalizable to a real-world population,” he cautioned.
Dr. Weber said it’s also important to note that NPTX2 is not considered an Alzheimer’s-specific biomarker but rather a marker of synaptic activity and neurodegeneration. “The exact role of NPTX2 in predicting dementia is unknown,” Dr. Weber said.
He said that more studies with larger, more diverse cohorts are needed to fully understand its significance as a biomarker or therapeutic target for neurodegenerative diseases, as well as to develop a blood test for NPTX2.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Soldan and Dr. Weber report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF NEUROLOGY
Inhaling pleasant scents during sleep tied to a dramatic boost in cognition
In a small, randomized controlled trial researchers found that when cognitively normal individuals were exposed to the scent of an essential oil for 2 hours every night over 6 months, they experienced a 226% improvement in memory compared with a control group who received only a trace amount of the diffused scent.
In addition, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed that those in the enriched group had improved functioning of the left uncinate fasciculus, an area of the brain linked to memory and cognition, which typically declines with age.
“To my knowledge, that level of [memory] improvement is far greater than anything that has been reported for healthy older adults and we also found a critical memory pathway in their brains improved to a similar extent relative to unenriched older adults,” senior investigator Michael Leon, PhD, professor emeritus, University of California, Irvine, said in an interview.
The study was published online in Frontiers of Neuroscience.
The brain’s “superhighway”
Olfactory enrichment “involves the daily exposure of individuals to multiple odorants” and has been shown in mouse models to improve memory and neurogenesis, the investigators noted.
A previous study showed that exposure to individual essential oils for 30 minutes a day over 3 months induced neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb and the hippocampus.
“The olfactory system is the only sense that has a direct ‘superhighway’ input to the memory centers areas of the brain; all the other senses have to reach those brain areas through what you might call the ‘side streets’ of the brain, and so consequently, they have much less impact on maintaining the health of those memory centers.”
When olfaction is compromised, “the memory centers of the brain start to deteriorate and, conversely, when people are given olfactory enrichment, their memory areas become larger and more functional,” he added.
Olfactory dysfunction is the first symptom of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and is also found in virtually all neurological and psychiatric disorders.
“I’ve counted 68 of them – including anorexia, anxiety, [attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder], depression, epilepsy, and stroke. In fact, by mid-life, your all-cause mortality can be predicted by your ability to smell things,” Dr. Leon said.
Dr. Leon and colleagues previously developed an effective treatment for autism using environmental enrichment that focused on odor stimulation, along with stimulating other senses. “We then considered the possibility that olfactory enrichment alone might improve brain function.”
Rose, orange, eucalyptus …
For the study, the researchers randomly assigned 43 older adults, aged 60-85 years, to receive either nightly exposure to essential oil scents delivered via a diffuser (n = 20; mean [SD] age, 70.1 [6.6] years) or to a sham control with only trace amounts of odorants (n = 23; mean age, 69.2 [7.1] years) for a period of 6 months.
The intervention group was exposed to a single odorant, delivered through a diffuser, for 2 hours nightly, rotating through seven pleasant aromas each week. They included rose, orange, eucalyptus, lemon, peppermint, rosemary, and lavender scents.
All participants completed a battery of tests at baseline, including the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), which confirmed normal cognitive functioning. At baseline and after a 6-month follow-up, participants completed the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) as well as three subsets of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale–Third Edition (WAIS-III).
Olfactory system function was assessed using “Sniffin Sticks,” allowing the researchers to determine if olfactory enrichment enhanced olfactory performance.
Participants underwent fMRI at baseline and again at 6 months.
Brain imaging results showed a “clear, statistically significant 226% difference between enriched and control older adults in performance on the RAVLT, which evaluates learning and memory (timepoint × group interaction; F = 6.63; P = .02; Cohen’s d = 1.08; a “large effect size”).
They also found a significant change in the mean diffusivity of the left uncinate fasciculus in the enriched group compared with the controls (timepoint × group interaction; F = 4.39; P = .043; h 2 p = .101; a “medium-size effect”).
The uncinate fasciculus is a “major pathway” connecting the basolateral amygdala and the entorhinal cortex to the prefrontal cortex. This pathway deteriorates in aging and in AD and “has been suggested to play a role in mediating episodic memory, language, socio-emotional processing, and selecting among competing memories during retrieval.”
No significant differences were found between the groups in olfactory ability.
Limitations of the study include its small sample size. The investigators hope the findings will “stimulate larger scale clinical trials systematically testing the therapeutic efficacy of olfactory enrichment in treating memory loss in older adults.”
Exciting but preliminary
Commenting for this article, Donald Wilson, PhD, professor of child and adolescent psychiatry and of neuroscience and physiology, the Child Study Center, NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, said that multiple studies have “demonstrated that problems with sense of smell are associated with and sometimes can precede other symptoms for many disorders, including AD, Parkinson’s disease, and depression.”
Recent work has suggested that this relationship can be “bidirectional” – for example, losing one’s sense of smell might promote depression, while depressive disorder might lead to impaired smell, according to Dr. Wilson, also director and senior research scientist, the Emotional Brain Institute, Nathan Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research. He was not involved with the study.
This “two-way interaction” may raise the possibility that “improving olfaction could impact nonolfactory disorders.”
This paper “brings together” previous research findings to show that odors during bedtime can improve some aspects of cognitive function and circuits that are known to be important for memory and cognition – which Dr. Wilson called “a very exciting, though relatively preliminary, finding.”
A caveat is that several measures of cognitive function were assessed and only one (verbal memory) showed clear improvement.
Nevertheless, there’s “very strong interest now in the olfactory and nonolfactory aspects of odor training and this training expands the training possibilities to sleep. This could be a powerful tool for cognitive improvement and/or rescue if follow-up studies support these findings,” Dr. Wilson said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a small, randomized controlled trial researchers found that when cognitively normal individuals were exposed to the scent of an essential oil for 2 hours every night over 6 months, they experienced a 226% improvement in memory compared with a control group who received only a trace amount of the diffused scent.
In addition, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed that those in the enriched group had improved functioning of the left uncinate fasciculus, an area of the brain linked to memory and cognition, which typically declines with age.
“To my knowledge, that level of [memory] improvement is far greater than anything that has been reported for healthy older adults and we also found a critical memory pathway in their brains improved to a similar extent relative to unenriched older adults,” senior investigator Michael Leon, PhD, professor emeritus, University of California, Irvine, said in an interview.
The study was published online in Frontiers of Neuroscience.
The brain’s “superhighway”
Olfactory enrichment “involves the daily exposure of individuals to multiple odorants” and has been shown in mouse models to improve memory and neurogenesis, the investigators noted.
A previous study showed that exposure to individual essential oils for 30 minutes a day over 3 months induced neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb and the hippocampus.
“The olfactory system is the only sense that has a direct ‘superhighway’ input to the memory centers areas of the brain; all the other senses have to reach those brain areas through what you might call the ‘side streets’ of the brain, and so consequently, they have much less impact on maintaining the health of those memory centers.”
When olfaction is compromised, “the memory centers of the brain start to deteriorate and, conversely, when people are given olfactory enrichment, their memory areas become larger and more functional,” he added.
Olfactory dysfunction is the first symptom of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and is also found in virtually all neurological and psychiatric disorders.
“I’ve counted 68 of them – including anorexia, anxiety, [attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder], depression, epilepsy, and stroke. In fact, by mid-life, your all-cause mortality can be predicted by your ability to smell things,” Dr. Leon said.
Dr. Leon and colleagues previously developed an effective treatment for autism using environmental enrichment that focused on odor stimulation, along with stimulating other senses. “We then considered the possibility that olfactory enrichment alone might improve brain function.”
Rose, orange, eucalyptus …
For the study, the researchers randomly assigned 43 older adults, aged 60-85 years, to receive either nightly exposure to essential oil scents delivered via a diffuser (n = 20; mean [SD] age, 70.1 [6.6] years) or to a sham control with only trace amounts of odorants (n = 23; mean age, 69.2 [7.1] years) for a period of 6 months.
The intervention group was exposed to a single odorant, delivered through a diffuser, for 2 hours nightly, rotating through seven pleasant aromas each week. They included rose, orange, eucalyptus, lemon, peppermint, rosemary, and lavender scents.
All participants completed a battery of tests at baseline, including the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), which confirmed normal cognitive functioning. At baseline and after a 6-month follow-up, participants completed the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) as well as three subsets of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale–Third Edition (WAIS-III).
Olfactory system function was assessed using “Sniffin Sticks,” allowing the researchers to determine if olfactory enrichment enhanced olfactory performance.
Participants underwent fMRI at baseline and again at 6 months.
Brain imaging results showed a “clear, statistically significant 226% difference between enriched and control older adults in performance on the RAVLT, which evaluates learning and memory (timepoint × group interaction; F = 6.63; P = .02; Cohen’s d = 1.08; a “large effect size”).
They also found a significant change in the mean diffusivity of the left uncinate fasciculus in the enriched group compared with the controls (timepoint × group interaction; F = 4.39; P = .043; h 2 p = .101; a “medium-size effect”).
The uncinate fasciculus is a “major pathway” connecting the basolateral amygdala and the entorhinal cortex to the prefrontal cortex. This pathway deteriorates in aging and in AD and “has been suggested to play a role in mediating episodic memory, language, socio-emotional processing, and selecting among competing memories during retrieval.”
No significant differences were found between the groups in olfactory ability.
Limitations of the study include its small sample size. The investigators hope the findings will “stimulate larger scale clinical trials systematically testing the therapeutic efficacy of olfactory enrichment in treating memory loss in older adults.”
Exciting but preliminary
Commenting for this article, Donald Wilson, PhD, professor of child and adolescent psychiatry and of neuroscience and physiology, the Child Study Center, NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, said that multiple studies have “demonstrated that problems with sense of smell are associated with and sometimes can precede other symptoms for many disorders, including AD, Parkinson’s disease, and depression.”
Recent work has suggested that this relationship can be “bidirectional” – for example, losing one’s sense of smell might promote depression, while depressive disorder might lead to impaired smell, according to Dr. Wilson, also director and senior research scientist, the Emotional Brain Institute, Nathan Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research. He was not involved with the study.
This “two-way interaction” may raise the possibility that “improving olfaction could impact nonolfactory disorders.”
This paper “brings together” previous research findings to show that odors during bedtime can improve some aspects of cognitive function and circuits that are known to be important for memory and cognition – which Dr. Wilson called “a very exciting, though relatively preliminary, finding.”
A caveat is that several measures of cognitive function were assessed and only one (verbal memory) showed clear improvement.
Nevertheless, there’s “very strong interest now in the olfactory and nonolfactory aspects of odor training and this training expands the training possibilities to sleep. This could be a powerful tool for cognitive improvement and/or rescue if follow-up studies support these findings,” Dr. Wilson said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
In a small, randomized controlled trial researchers found that when cognitively normal individuals were exposed to the scent of an essential oil for 2 hours every night over 6 months, they experienced a 226% improvement in memory compared with a control group who received only a trace amount of the diffused scent.
In addition, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed that those in the enriched group had improved functioning of the left uncinate fasciculus, an area of the brain linked to memory and cognition, which typically declines with age.
“To my knowledge, that level of [memory] improvement is far greater than anything that has been reported for healthy older adults and we also found a critical memory pathway in their brains improved to a similar extent relative to unenriched older adults,” senior investigator Michael Leon, PhD, professor emeritus, University of California, Irvine, said in an interview.
The study was published online in Frontiers of Neuroscience.
The brain’s “superhighway”
Olfactory enrichment “involves the daily exposure of individuals to multiple odorants” and has been shown in mouse models to improve memory and neurogenesis, the investigators noted.
A previous study showed that exposure to individual essential oils for 30 minutes a day over 3 months induced neurogenesis in the olfactory bulb and the hippocampus.
“The olfactory system is the only sense that has a direct ‘superhighway’ input to the memory centers areas of the brain; all the other senses have to reach those brain areas through what you might call the ‘side streets’ of the brain, and so consequently, they have much less impact on maintaining the health of those memory centers.”
When olfaction is compromised, “the memory centers of the brain start to deteriorate and, conversely, when people are given olfactory enrichment, their memory areas become larger and more functional,” he added.
Olfactory dysfunction is the first symptom of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and is also found in virtually all neurological and psychiatric disorders.
“I’ve counted 68 of them – including anorexia, anxiety, [attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder], depression, epilepsy, and stroke. In fact, by mid-life, your all-cause mortality can be predicted by your ability to smell things,” Dr. Leon said.
Dr. Leon and colleagues previously developed an effective treatment for autism using environmental enrichment that focused on odor stimulation, along with stimulating other senses. “We then considered the possibility that olfactory enrichment alone might improve brain function.”
Rose, orange, eucalyptus …
For the study, the researchers randomly assigned 43 older adults, aged 60-85 years, to receive either nightly exposure to essential oil scents delivered via a diffuser (n = 20; mean [SD] age, 70.1 [6.6] years) or to a sham control with only trace amounts of odorants (n = 23; mean age, 69.2 [7.1] years) for a period of 6 months.
The intervention group was exposed to a single odorant, delivered through a diffuser, for 2 hours nightly, rotating through seven pleasant aromas each week. They included rose, orange, eucalyptus, lemon, peppermint, rosemary, and lavender scents.
All participants completed a battery of tests at baseline, including the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), which confirmed normal cognitive functioning. At baseline and after a 6-month follow-up, participants completed the Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (RAVLT) as well as three subsets of the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale–Third Edition (WAIS-III).
Olfactory system function was assessed using “Sniffin Sticks,” allowing the researchers to determine if olfactory enrichment enhanced olfactory performance.
Participants underwent fMRI at baseline and again at 6 months.
Brain imaging results showed a “clear, statistically significant 226% difference between enriched and control older adults in performance on the RAVLT, which evaluates learning and memory (timepoint × group interaction; F = 6.63; P = .02; Cohen’s d = 1.08; a “large effect size”).
They also found a significant change in the mean diffusivity of the left uncinate fasciculus in the enriched group compared with the controls (timepoint × group interaction; F = 4.39; P = .043; h 2 p = .101; a “medium-size effect”).
The uncinate fasciculus is a “major pathway” connecting the basolateral amygdala and the entorhinal cortex to the prefrontal cortex. This pathway deteriorates in aging and in AD and “has been suggested to play a role in mediating episodic memory, language, socio-emotional processing, and selecting among competing memories during retrieval.”
No significant differences were found between the groups in olfactory ability.
Limitations of the study include its small sample size. The investigators hope the findings will “stimulate larger scale clinical trials systematically testing the therapeutic efficacy of olfactory enrichment in treating memory loss in older adults.”
Exciting but preliminary
Commenting for this article, Donald Wilson, PhD, professor of child and adolescent psychiatry and of neuroscience and physiology, the Child Study Center, NYU Langone Medical Center, New York, said that multiple studies have “demonstrated that problems with sense of smell are associated with and sometimes can precede other symptoms for many disorders, including AD, Parkinson’s disease, and depression.”
Recent work has suggested that this relationship can be “bidirectional” – for example, losing one’s sense of smell might promote depression, while depressive disorder might lead to impaired smell, according to Dr. Wilson, also director and senior research scientist, the Emotional Brain Institute, Nathan Kline Institute for Psychiatric Research. He was not involved with the study.
This “two-way interaction” may raise the possibility that “improving olfaction could impact nonolfactory disorders.”
This paper “brings together” previous research findings to show that odors during bedtime can improve some aspects of cognitive function and circuits that are known to be important for memory and cognition – which Dr. Wilson called “a very exciting, though relatively preliminary, finding.”
A caveat is that several measures of cognitive function were assessed and only one (verbal memory) showed clear improvement.
Nevertheless, there’s “very strong interest now in the olfactory and nonolfactory aspects of odor training and this training expands the training possibilities to sleep. This could be a powerful tool for cognitive improvement and/or rescue if follow-up studies support these findings,” Dr. Wilson said.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM FRONTIERS IN NEUROSCIENCE
Thrombectomy improves outcomes in pediatric stroke
A matched case-control study followed 52 patients in Canada and Australia with acute stroke and assessed functional outcomes at 3 months for those who received thrombectomy, compared with those who did not. Patients receiving the procedure had significantly improved clinical outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 3.76). The procedure is the standard of care for adults with large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke, but limited data exist for children.
“In the absence of a randomized trial, this case-control study demonstrates better clinical outcomes with thrombectomy than medical management for pediatric patients aged 2 to 18 years with anterior circulation LVO stroke,” the authors concluded. The study was published in JAMA Neurology.
Improved results
Untreated LVO stroke is associated with poor outcomes, indicated in this study with scoring based on the modified Rankin Scale. Based on this scoring, 53.8% of patients who were managed conservatively had poor outcomes (moderate disability or greater) at 3 months, confirming previous findings. The data were drawn from five hospitals in Australia and Canada between January 2011 and April 2022.
Removing blood clots with mechanical thrombectomy resulted in improved outcomes 3 months after stroke for the patients included in the study, compared with the neuroprotective measures of medical therapy alone. The improved outcomes persisted in the final available follow-up (OR, 3.65).
In adults, thrombectomy has previously been demonstrated to be a safe and effective treatment for LVO stroke and is currently the standard of care. This study sought to expand the data for pediatric patients, for whom stroke is rarer and difficult to diagnose.
The authors cautioned, however, that the outcomes are from hospitals with pediatric neurology expertise and should not be generalized to settings without specialists.
Case-control study
While previous population-based studies of children with LVO stroke found that conservative treatment was associated with poor outcomes, these studies may include significant selection bias. The investigators chose to conduct the case-control study as an alternative to a randomized control trial, which would require withholding treatment from some patients and would not be considered ethical.
The study included 26 patients in each cohort, either receiving mechanical thrombectomy or medical treatment alone. The investigators matched patients by site and side of occlusion, age, and sex. Cases that could not be matched by site of occlusion, the primary criterion, were excluded.
With this methodology, the investigators reduced the impact of selection bias with the aim of providing “the next highest level of comparative evidence,” they stated in the study. However, they also noted that, without randomization, there is likely still some selection bias present.
The two cohorts were not significantly different based on factors such as sex or age. All patients in the study presented within 24 hours of symptom onset, with most eligible for thrombectomy by adult standards. There was a difference between the two cohorts in the timing of arrival to a dedicated hospital and imaging. “Our triage, imaging, and decision-making pathways require streamlining,” the authors concluded, regarding the difference.
‘A heterogeneous condition’
In a comment, Ratika Srivastava, MD, a pediatric neurologist at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, said she was glad to see a well-designed study dedicated to pediatric stroke. Neurologists have traditionally extrapolated from research on adult stroke due to the rarity of pediatric stroke and difficulty of diagnosis.
While physicians have previously relied on findings in adults, stroke presents differently in children. “The challenge is that it’s such a heterogeneous condition,” said Dr. Srivastava, who was not involved in the study. In children, stroke may have several different etiologies, such as a lesion in the heart or arterial disease. “Sometimes it’s amenable to taking the clot out and sometimes it’s not. So you have to figure out: Are they a good candidate for thrombectomy?” This study helps demonstrate that thrombectomy is a good option for some children with LVO stroke, she said.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Srivastava reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A matched case-control study followed 52 patients in Canada and Australia with acute stroke and assessed functional outcomes at 3 months for those who received thrombectomy, compared with those who did not. Patients receiving the procedure had significantly improved clinical outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 3.76). The procedure is the standard of care for adults with large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke, but limited data exist for children.
“In the absence of a randomized trial, this case-control study demonstrates better clinical outcomes with thrombectomy than medical management for pediatric patients aged 2 to 18 years with anterior circulation LVO stroke,” the authors concluded. The study was published in JAMA Neurology.
Improved results
Untreated LVO stroke is associated with poor outcomes, indicated in this study with scoring based on the modified Rankin Scale. Based on this scoring, 53.8% of patients who were managed conservatively had poor outcomes (moderate disability or greater) at 3 months, confirming previous findings. The data were drawn from five hospitals in Australia and Canada between January 2011 and April 2022.
Removing blood clots with mechanical thrombectomy resulted in improved outcomes 3 months after stroke for the patients included in the study, compared with the neuroprotective measures of medical therapy alone. The improved outcomes persisted in the final available follow-up (OR, 3.65).
In adults, thrombectomy has previously been demonstrated to be a safe and effective treatment for LVO stroke and is currently the standard of care. This study sought to expand the data for pediatric patients, for whom stroke is rarer and difficult to diagnose.
The authors cautioned, however, that the outcomes are from hospitals with pediatric neurology expertise and should not be generalized to settings without specialists.
Case-control study
While previous population-based studies of children with LVO stroke found that conservative treatment was associated with poor outcomes, these studies may include significant selection bias. The investigators chose to conduct the case-control study as an alternative to a randomized control trial, which would require withholding treatment from some patients and would not be considered ethical.
The study included 26 patients in each cohort, either receiving mechanical thrombectomy or medical treatment alone. The investigators matched patients by site and side of occlusion, age, and sex. Cases that could not be matched by site of occlusion, the primary criterion, were excluded.
With this methodology, the investigators reduced the impact of selection bias with the aim of providing “the next highest level of comparative evidence,” they stated in the study. However, they also noted that, without randomization, there is likely still some selection bias present.
The two cohorts were not significantly different based on factors such as sex or age. All patients in the study presented within 24 hours of symptom onset, with most eligible for thrombectomy by adult standards. There was a difference between the two cohorts in the timing of arrival to a dedicated hospital and imaging. “Our triage, imaging, and decision-making pathways require streamlining,” the authors concluded, regarding the difference.
‘A heterogeneous condition’
In a comment, Ratika Srivastava, MD, a pediatric neurologist at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, said she was glad to see a well-designed study dedicated to pediatric stroke. Neurologists have traditionally extrapolated from research on adult stroke due to the rarity of pediatric stroke and difficulty of diagnosis.
While physicians have previously relied on findings in adults, stroke presents differently in children. “The challenge is that it’s such a heterogeneous condition,” said Dr. Srivastava, who was not involved in the study. In children, stroke may have several different etiologies, such as a lesion in the heart or arterial disease. “Sometimes it’s amenable to taking the clot out and sometimes it’s not. So you have to figure out: Are they a good candidate for thrombectomy?” This study helps demonstrate that thrombectomy is a good option for some children with LVO stroke, she said.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Srivastava reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A matched case-control study followed 52 patients in Canada and Australia with acute stroke and assessed functional outcomes at 3 months for those who received thrombectomy, compared with those who did not. Patients receiving the procedure had significantly improved clinical outcomes (odds ratio [OR], 3.76). The procedure is the standard of care for adults with large vessel occlusion (LVO) stroke, but limited data exist for children.
“In the absence of a randomized trial, this case-control study demonstrates better clinical outcomes with thrombectomy than medical management for pediatric patients aged 2 to 18 years with anterior circulation LVO stroke,” the authors concluded. The study was published in JAMA Neurology.
Improved results
Untreated LVO stroke is associated with poor outcomes, indicated in this study with scoring based on the modified Rankin Scale. Based on this scoring, 53.8% of patients who were managed conservatively had poor outcomes (moderate disability or greater) at 3 months, confirming previous findings. The data were drawn from five hospitals in Australia and Canada between January 2011 and April 2022.
Removing blood clots with mechanical thrombectomy resulted in improved outcomes 3 months after stroke for the patients included in the study, compared with the neuroprotective measures of medical therapy alone. The improved outcomes persisted in the final available follow-up (OR, 3.65).
In adults, thrombectomy has previously been demonstrated to be a safe and effective treatment for LVO stroke and is currently the standard of care. This study sought to expand the data for pediatric patients, for whom stroke is rarer and difficult to diagnose.
The authors cautioned, however, that the outcomes are from hospitals with pediatric neurology expertise and should not be generalized to settings without specialists.
Case-control study
While previous population-based studies of children with LVO stroke found that conservative treatment was associated with poor outcomes, these studies may include significant selection bias. The investigators chose to conduct the case-control study as an alternative to a randomized control trial, which would require withholding treatment from some patients and would not be considered ethical.
The study included 26 patients in each cohort, either receiving mechanical thrombectomy or medical treatment alone. The investigators matched patients by site and side of occlusion, age, and sex. Cases that could not be matched by site of occlusion, the primary criterion, were excluded.
With this methodology, the investigators reduced the impact of selection bias with the aim of providing “the next highest level of comparative evidence,” they stated in the study. However, they also noted that, without randomization, there is likely still some selection bias present.
The two cohorts were not significantly different based on factors such as sex or age. All patients in the study presented within 24 hours of symptom onset, with most eligible for thrombectomy by adult standards. There was a difference between the two cohorts in the timing of arrival to a dedicated hospital and imaging. “Our triage, imaging, and decision-making pathways require streamlining,” the authors concluded, regarding the difference.
‘A heterogeneous condition’
In a comment, Ratika Srivastava, MD, a pediatric neurologist at the University of Alberta, Edmonton, said she was glad to see a well-designed study dedicated to pediatric stroke. Neurologists have traditionally extrapolated from research on adult stroke due to the rarity of pediatric stroke and difficulty of diagnosis.
While physicians have previously relied on findings in adults, stroke presents differently in children. “The challenge is that it’s such a heterogeneous condition,” said Dr. Srivastava, who was not involved in the study. In children, stroke may have several different etiologies, such as a lesion in the heart or arterial disease. “Sometimes it’s amenable to taking the clot out and sometimes it’s not. So you have to figure out: Are they a good candidate for thrombectomy?” This study helps demonstrate that thrombectomy is a good option for some children with LVO stroke, she said.
The study was independently supported. Dr. Srivastava reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NEUROLOGY
Top U.S. neurology, neurosurgery hospitals ranked
of best hospitals for neurology and neurosurgery.
NYU Langone also claimed the top spot in last year’s ranking.
In the latest rankings, UCSF Health–UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco, holds the No. 2 spot and New York–Presbyterian Hospital–Columbia and Cornell in New York City holds the No. 3 spot for neurology care, with no change from last year.
This year, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., is ranked No. 4 in neurology and neurosurgery care, up from No. 6 last year, while Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, ranks fifth this year, rising two spots from No. 7 last year.
Rounding out the top 10 hospitals for neurology and neurosurgery (in order) are UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles; Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore; Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; Mount Sinai Hospital, New York; and Northwestern Medicine–Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago.
U.S. News evaluated 1,245 hospitals and ranked the top 50 that treat patients with challenging neurological issues including stroke, conditions affecting the central nervous system, spinal disorders and injuries, seizures, and degenerative nervous system diagnoses such as multiple sclerosis.
“Consumers want useful resources to help them assess which hospital can best meet their specific care needs,” Ben Harder, chief of health analysis and managing editor at U.S. News, said in a statement.
“The 2023-2024 Best Hospitals rankings offer patients and the physicians with whom they consult a data-driven source for comparing performance in outcomes, patient satisfaction, and other metrics that matter to them,” Mr. Harder said.
Honor roll
This year, as in prior years, U.S. News recognized “honor roll” hospitals that have excelled across multiple areas of care. However, this year, for the first time, there is no ordinal ranking of hospitals making the honor roll. Instead, they are listed in alphabetical order.
In a letter to hospital leaders, U.S. News explained that the major change in format came after months of deliberation, feedback from health care organizations and professionals, and an analysis of how consumers navigate the organization’s website.
Ordinal ranking of hospitals that make the honor roll “obscures the fact that all of the honor roll hospitals have attained the highest standard of care in the nation,” the letter reads.
This year there are 22 honor roll hospitals:
- Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
- Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles
- Cleveland Clinic
- Hospitals of the University of Pennsylvania-Penn Medicine, Philadelphia
- Houston Methodist Hospital
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore
- Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
- Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
- Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City
- New York–Presbyterian Hospital–Columbia and Cornell, New York City
- North Shore University Hospital at Northwell Health, Manhasset, N.Y.
- Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago
- NYU Langone Hospitals, New York City
- Rush University Medical Center, Chicago
- Stanford (Calif.) Health Care–Stanford Hospital
- UC San Diego Health–La Jolla and Hillcrest Hospitals
- UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles
- UCSF Health–UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco
- University of Michigan Health–Ann Arbor
- UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas
- Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
U.S. News noted that to keep pace with consumers’ needs and the ever-evolving landscape of health care, “several refinements” are reflected in the latest best hospitals rankings.
These include the introduction of outpatient outcomes in key specialty rankings and surgical ratings, the expanded inclusion of other outpatient data, an increased weight on objective quality measures, and a reduced weight on expert opinion.
In addition, hospital profiles at usnews.com feature refined health equity measures, including a new measure of racial disparities in outcomes.
The full report for best hospitals, best specialty hospitals, and methodology is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
of best hospitals for neurology and neurosurgery.
NYU Langone also claimed the top spot in last year’s ranking.
In the latest rankings, UCSF Health–UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco, holds the No. 2 spot and New York–Presbyterian Hospital–Columbia and Cornell in New York City holds the No. 3 spot for neurology care, with no change from last year.
This year, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., is ranked No. 4 in neurology and neurosurgery care, up from No. 6 last year, while Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, ranks fifth this year, rising two spots from No. 7 last year.
Rounding out the top 10 hospitals for neurology and neurosurgery (in order) are UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles; Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore; Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; Mount Sinai Hospital, New York; and Northwestern Medicine–Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago.
U.S. News evaluated 1,245 hospitals and ranked the top 50 that treat patients with challenging neurological issues including stroke, conditions affecting the central nervous system, spinal disorders and injuries, seizures, and degenerative nervous system diagnoses such as multiple sclerosis.
“Consumers want useful resources to help them assess which hospital can best meet their specific care needs,” Ben Harder, chief of health analysis and managing editor at U.S. News, said in a statement.
“The 2023-2024 Best Hospitals rankings offer patients and the physicians with whom they consult a data-driven source for comparing performance in outcomes, patient satisfaction, and other metrics that matter to them,” Mr. Harder said.
Honor roll
This year, as in prior years, U.S. News recognized “honor roll” hospitals that have excelled across multiple areas of care. However, this year, for the first time, there is no ordinal ranking of hospitals making the honor roll. Instead, they are listed in alphabetical order.
In a letter to hospital leaders, U.S. News explained that the major change in format came after months of deliberation, feedback from health care organizations and professionals, and an analysis of how consumers navigate the organization’s website.
Ordinal ranking of hospitals that make the honor roll “obscures the fact that all of the honor roll hospitals have attained the highest standard of care in the nation,” the letter reads.
This year there are 22 honor roll hospitals:
- Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
- Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles
- Cleveland Clinic
- Hospitals of the University of Pennsylvania-Penn Medicine, Philadelphia
- Houston Methodist Hospital
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore
- Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
- Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
- Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City
- New York–Presbyterian Hospital–Columbia and Cornell, New York City
- North Shore University Hospital at Northwell Health, Manhasset, N.Y.
- Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago
- NYU Langone Hospitals, New York City
- Rush University Medical Center, Chicago
- Stanford (Calif.) Health Care–Stanford Hospital
- UC San Diego Health–La Jolla and Hillcrest Hospitals
- UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles
- UCSF Health–UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco
- University of Michigan Health–Ann Arbor
- UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas
- Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
U.S. News noted that to keep pace with consumers’ needs and the ever-evolving landscape of health care, “several refinements” are reflected in the latest best hospitals rankings.
These include the introduction of outpatient outcomes in key specialty rankings and surgical ratings, the expanded inclusion of other outpatient data, an increased weight on objective quality measures, and a reduced weight on expert opinion.
In addition, hospital profiles at usnews.com feature refined health equity measures, including a new measure of racial disparities in outcomes.
The full report for best hospitals, best specialty hospitals, and methodology is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
of best hospitals for neurology and neurosurgery.
NYU Langone also claimed the top spot in last year’s ranking.
In the latest rankings, UCSF Health–UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco, holds the No. 2 spot and New York–Presbyterian Hospital–Columbia and Cornell in New York City holds the No. 3 spot for neurology care, with no change from last year.
This year, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., is ranked No. 4 in neurology and neurosurgery care, up from No. 6 last year, while Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, ranks fifth this year, rising two spots from No. 7 last year.
Rounding out the top 10 hospitals for neurology and neurosurgery (in order) are UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles; Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore; Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston; Mount Sinai Hospital, New York; and Northwestern Medicine–Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago.
U.S. News evaluated 1,245 hospitals and ranked the top 50 that treat patients with challenging neurological issues including stroke, conditions affecting the central nervous system, spinal disorders and injuries, seizures, and degenerative nervous system diagnoses such as multiple sclerosis.
“Consumers want useful resources to help them assess which hospital can best meet their specific care needs,” Ben Harder, chief of health analysis and managing editor at U.S. News, said in a statement.
“The 2023-2024 Best Hospitals rankings offer patients and the physicians with whom they consult a data-driven source for comparing performance in outcomes, patient satisfaction, and other metrics that matter to them,” Mr. Harder said.
Honor roll
This year, as in prior years, U.S. News recognized “honor roll” hospitals that have excelled across multiple areas of care. However, this year, for the first time, there is no ordinal ranking of hospitals making the honor roll. Instead, they are listed in alphabetical order.
In a letter to hospital leaders, U.S. News explained that the major change in format came after months of deliberation, feedback from health care organizations and professionals, and an analysis of how consumers navigate the organization’s website.
Ordinal ranking of hospitals that make the honor roll “obscures the fact that all of the honor roll hospitals have attained the highest standard of care in the nation,” the letter reads.
This year there are 22 honor roll hospitals:
- Barnes-Jewish Hospital, St. Louis
- Brigham and Women’s Hospital, Boston
- Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles
- Cleveland Clinic
- Hospitals of the University of Pennsylvania-Penn Medicine, Philadelphia
- Houston Methodist Hospital
- Johns Hopkins Hospital, Baltimore
- Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston
- Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn.
- Mount Sinai Hospital, New York City
- New York–Presbyterian Hospital–Columbia and Cornell, New York City
- North Shore University Hospital at Northwell Health, Manhasset, N.Y.
- Northwestern Memorial Hospital, Chicago
- NYU Langone Hospitals, New York City
- Rush University Medical Center, Chicago
- Stanford (Calif.) Health Care–Stanford Hospital
- UC San Diego Health–La Jolla and Hillcrest Hospitals
- UCLA Medical Center, Los Angeles
- UCSF Health–UCSF Medical Center, San Francisco
- University of Michigan Health–Ann Arbor
- UT Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas
- Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn.
U.S. News noted that to keep pace with consumers’ needs and the ever-evolving landscape of health care, “several refinements” are reflected in the latest best hospitals rankings.
These include the introduction of outpatient outcomes in key specialty rankings and surgical ratings, the expanded inclusion of other outpatient data, an increased weight on objective quality measures, and a reduced weight on expert opinion.
In addition, hospital profiles at usnews.com feature refined health equity measures, including a new measure of racial disparities in outcomes.
The full report for best hospitals, best specialty hospitals, and methodology is available online.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new and completely different pain medicine
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When you stub your toe or get a paper cut on your finger, you feel the pain in that part of your body. It feels like the pain is coming from that place. But, of course, that’s not really what is happening. Pain doesn’t really happen in your toe or your finger. It happens in your brain.
It’s a game of telephone, really. The afferent nerve fiber detects the noxious stimulus, passing that signal to the second-order neuron in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, which runs it up to the thalamus to be passed to the third-order neuron which brings it to the cortex for localization and conscious perception. It’s not even a very good game of telephone. It takes about 100 ms for a pain signal to get from the hand to the brain – longer from the feet, given the greater distance. You see your foot hit the corner of the coffee table and have just enough time to think: “Oh no!” before the pain hits.
Given the Rube Goldberg nature of the process, it would seem like there are any number of places we could stop pain sensation. And sure, local anesthetics at the site of injury, or even spinal anesthetics, are powerful – if temporary and hard to administer – solutions to acute pain.
But in our everyday armamentarium, let’s be honest – we essentially have three options: opiates and opioids, which activate the mu-receptors in the brain to dull pain (and cause a host of other nasty side effects); NSAIDs, which block prostaglandin synthesis and thus limit the ability for pain-conducting neurons to get excited; and acetaminophen, which, despite being used for a century, is poorly understood.
But
If you were to zoom in on the connection between that first afferent pain fiber and the secondary nerve in the spinal cord dorsal root ganglion, you would see a receptor called Nav1.8, a voltage-gated sodium channel.
This receptor is a key part of the apparatus that passes information from nerve 1 to nerve 2, but only for fibers that transmit pain signals. In fact, humans with mutations in this receptor that leave it always in the “open” state have a severe pain syndrome. Blocking the receptor, therefore, might reduce pain.
In preclinical work, researchers identified VX-548, which doesn’t have a brand name yet, as a potent blocker of that channel even in nanomolar concentrations. Importantly, the compound was highly selective for that particular channel – about 30,000 times more selective than it was for the other sodium channels in that family.
Of course, a highly selective and specific drug does not a blockbuster analgesic make. To determine how this drug would work on humans in pain, they turned to two populations: 303 individuals undergoing abdominoplasty and 274 undergoing bunionectomy, as reported in a new paper in the New England Journal of Medicine.
I know this seems a bit random, but abdominoplasty is quite painful and a good model for soft-tissue pain. Bunionectomy is also quite a painful procedure and a useful model of bone pain. After the surgeries, patients were randomized to several different doses of VX-548, hydrocodone plus acetaminophen, or placebo for 48 hours.
At 19 time points over that 48-hour period, participants were asked to rate their pain on a scale from 0 to 10. The primary outcome was the cumulative pain experienced over the 48 hours. So, higher pain would be worse here, but longer duration of pain would also be worse.
The story of the study is really told in this chart.
Yes, those assigned to the highest dose of VX-548 had a statistically significant lower cumulative amount of pain in the 48 hours after surgery. But the picture is really worth more than the stats here. You can see that the onset of pain relief was fairly quick, and that pain relief was sustained over time. You can also see that this is not a miracle drug. Pain scores were a bit better 48 hours out, but only by about a point and a half.
Placebo isn’t really the fair comparison here; few of us treat our postabdominoplasty patients with placebo, after all. The authors do not formally compare the effect of VX-548 with that of the opioid hydrocodone, for instance. But that doesn’t stop us.
This graph, which I put together from data in the paper, shows pain control across the four randomization categories, with higher numbers indicating more (cumulative) control. While all the active agents do a bit better than placebo, VX-548 at the higher dose appears to do the best. But I should note that 5 mg of hydrocodone may not be an adequate dose for most people.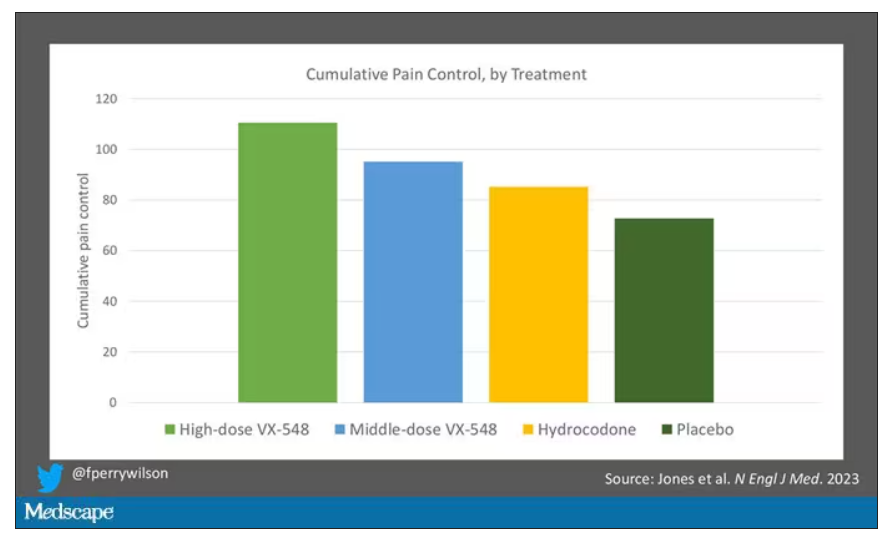
Yes, I would really have killed for an NSAID arm in this trial. Its absence, given that NSAIDs are a staple of postoperative care, is ... well, let’s just say, notable.
Although not a pain-destroying machine, VX-548 has some other things to recommend it. The receptor is really not found in the brain at all, which suggests that the drug should not carry much risk for dependency, though that has not been formally studied.
The side effects were generally mild – headache was the most common – and less prevalent than what you see even in the placebo arm.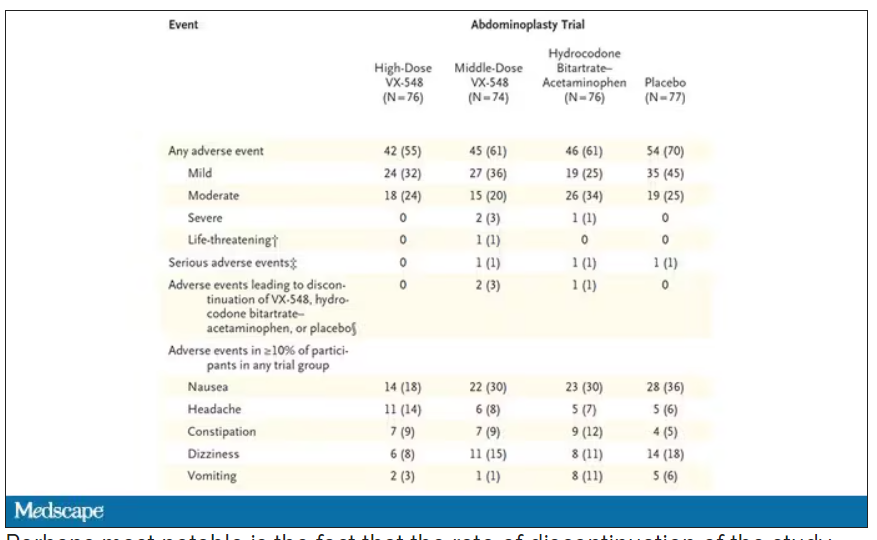
Perhaps most notable is the fact that the rate of discontinuation of the study drug was lowest in the VX-548 arm. Patients could stop taking the pill they were assigned for any reason, ranging from perceived lack of efficacy to side effects. A low discontinuation rate indicates to me a sort of “voting with your feet” that suggests this might be a well-tolerated and reasonably effective drug.
VX-548 isn’t on the market yet; phase 3 trials are ongoing. But whether it is this particular drug or another in this class, I’m happy to see researchers trying to find new ways to target that most primeval form of suffering: pain.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When you stub your toe or get a paper cut on your finger, you feel the pain in that part of your body. It feels like the pain is coming from that place. But, of course, that’s not really what is happening. Pain doesn’t really happen in your toe or your finger. It happens in your brain.
It’s a game of telephone, really. The afferent nerve fiber detects the noxious stimulus, passing that signal to the second-order neuron in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, which runs it up to the thalamus to be passed to the third-order neuron which brings it to the cortex for localization and conscious perception. It’s not even a very good game of telephone. It takes about 100 ms for a pain signal to get from the hand to the brain – longer from the feet, given the greater distance. You see your foot hit the corner of the coffee table and have just enough time to think: “Oh no!” before the pain hits.
Given the Rube Goldberg nature of the process, it would seem like there are any number of places we could stop pain sensation. And sure, local anesthetics at the site of injury, or even spinal anesthetics, are powerful – if temporary and hard to administer – solutions to acute pain.
But in our everyday armamentarium, let’s be honest – we essentially have three options: opiates and opioids, which activate the mu-receptors in the brain to dull pain (and cause a host of other nasty side effects); NSAIDs, which block prostaglandin synthesis and thus limit the ability for pain-conducting neurons to get excited; and acetaminophen, which, despite being used for a century, is poorly understood.
But
If you were to zoom in on the connection between that first afferent pain fiber and the secondary nerve in the spinal cord dorsal root ganglion, you would see a receptor called Nav1.8, a voltage-gated sodium channel.
This receptor is a key part of the apparatus that passes information from nerve 1 to nerve 2, but only for fibers that transmit pain signals. In fact, humans with mutations in this receptor that leave it always in the “open” state have a severe pain syndrome. Blocking the receptor, therefore, might reduce pain.
In preclinical work, researchers identified VX-548, which doesn’t have a brand name yet, as a potent blocker of that channel even in nanomolar concentrations. Importantly, the compound was highly selective for that particular channel – about 30,000 times more selective than it was for the other sodium channels in that family.
Of course, a highly selective and specific drug does not a blockbuster analgesic make. To determine how this drug would work on humans in pain, they turned to two populations: 303 individuals undergoing abdominoplasty and 274 undergoing bunionectomy, as reported in a new paper in the New England Journal of Medicine.
I know this seems a bit random, but abdominoplasty is quite painful and a good model for soft-tissue pain. Bunionectomy is also quite a painful procedure and a useful model of bone pain. After the surgeries, patients were randomized to several different doses of VX-548, hydrocodone plus acetaminophen, or placebo for 48 hours.
At 19 time points over that 48-hour period, participants were asked to rate their pain on a scale from 0 to 10. The primary outcome was the cumulative pain experienced over the 48 hours. So, higher pain would be worse here, but longer duration of pain would also be worse.
The story of the study is really told in this chart.
Yes, those assigned to the highest dose of VX-548 had a statistically significant lower cumulative amount of pain in the 48 hours after surgery. But the picture is really worth more than the stats here. You can see that the onset of pain relief was fairly quick, and that pain relief was sustained over time. You can also see that this is not a miracle drug. Pain scores were a bit better 48 hours out, but only by about a point and a half.
Placebo isn’t really the fair comparison here; few of us treat our postabdominoplasty patients with placebo, after all. The authors do not formally compare the effect of VX-548 with that of the opioid hydrocodone, for instance. But that doesn’t stop us.
This graph, which I put together from data in the paper, shows pain control across the four randomization categories, with higher numbers indicating more (cumulative) control. While all the active agents do a bit better than placebo, VX-548 at the higher dose appears to do the best. But I should note that 5 mg of hydrocodone may not be an adequate dose for most people.
Yes, I would really have killed for an NSAID arm in this trial. Its absence, given that NSAIDs are a staple of postoperative care, is ... well, let’s just say, notable.
Although not a pain-destroying machine, VX-548 has some other things to recommend it. The receptor is really not found in the brain at all, which suggests that the drug should not carry much risk for dependency, though that has not been formally studied.
The side effects were generally mild – headache was the most common – and less prevalent than what you see even in the placebo arm.
Perhaps most notable is the fact that the rate of discontinuation of the study drug was lowest in the VX-548 arm. Patients could stop taking the pill they were assigned for any reason, ranging from perceived lack of efficacy to side effects. A low discontinuation rate indicates to me a sort of “voting with your feet” that suggests this might be a well-tolerated and reasonably effective drug.
VX-548 isn’t on the market yet; phase 3 trials are ongoing. But whether it is this particular drug or another in this class, I’m happy to see researchers trying to find new ways to target that most primeval form of suffering: pain.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
When you stub your toe or get a paper cut on your finger, you feel the pain in that part of your body. It feels like the pain is coming from that place. But, of course, that’s not really what is happening. Pain doesn’t really happen in your toe or your finger. It happens in your brain.
It’s a game of telephone, really. The afferent nerve fiber detects the noxious stimulus, passing that signal to the second-order neuron in the dorsal root ganglia of the spinal cord, which runs it up to the thalamus to be passed to the third-order neuron which brings it to the cortex for localization and conscious perception. It’s not even a very good game of telephone. It takes about 100 ms for a pain signal to get from the hand to the brain – longer from the feet, given the greater distance. You see your foot hit the corner of the coffee table and have just enough time to think: “Oh no!” before the pain hits.
Given the Rube Goldberg nature of the process, it would seem like there are any number of places we could stop pain sensation. And sure, local anesthetics at the site of injury, or even spinal anesthetics, are powerful – if temporary and hard to administer – solutions to acute pain.
But in our everyday armamentarium, let’s be honest – we essentially have three options: opiates and opioids, which activate the mu-receptors in the brain to dull pain (and cause a host of other nasty side effects); NSAIDs, which block prostaglandin synthesis and thus limit the ability for pain-conducting neurons to get excited; and acetaminophen, which, despite being used for a century, is poorly understood.
But
If you were to zoom in on the connection between that first afferent pain fiber and the secondary nerve in the spinal cord dorsal root ganglion, you would see a receptor called Nav1.8, a voltage-gated sodium channel.
This receptor is a key part of the apparatus that passes information from nerve 1 to nerve 2, but only for fibers that transmit pain signals. In fact, humans with mutations in this receptor that leave it always in the “open” state have a severe pain syndrome. Blocking the receptor, therefore, might reduce pain.
In preclinical work, researchers identified VX-548, which doesn’t have a brand name yet, as a potent blocker of that channel even in nanomolar concentrations. Importantly, the compound was highly selective for that particular channel – about 30,000 times more selective than it was for the other sodium channels in that family.
Of course, a highly selective and specific drug does not a blockbuster analgesic make. To determine how this drug would work on humans in pain, they turned to two populations: 303 individuals undergoing abdominoplasty and 274 undergoing bunionectomy, as reported in a new paper in the New England Journal of Medicine.
I know this seems a bit random, but abdominoplasty is quite painful and a good model for soft-tissue pain. Bunionectomy is also quite a painful procedure and a useful model of bone pain. After the surgeries, patients were randomized to several different doses of VX-548, hydrocodone plus acetaminophen, or placebo for 48 hours.
At 19 time points over that 48-hour period, participants were asked to rate their pain on a scale from 0 to 10. The primary outcome was the cumulative pain experienced over the 48 hours. So, higher pain would be worse here, but longer duration of pain would also be worse.
The story of the study is really told in this chart.
Yes, those assigned to the highest dose of VX-548 had a statistically significant lower cumulative amount of pain in the 48 hours after surgery. But the picture is really worth more than the stats here. You can see that the onset of pain relief was fairly quick, and that pain relief was sustained over time. You can also see that this is not a miracle drug. Pain scores were a bit better 48 hours out, but only by about a point and a half.
Placebo isn’t really the fair comparison here; few of us treat our postabdominoplasty patients with placebo, after all. The authors do not formally compare the effect of VX-548 with that of the opioid hydrocodone, for instance. But that doesn’t stop us.
This graph, which I put together from data in the paper, shows pain control across the four randomization categories, with higher numbers indicating more (cumulative) control. While all the active agents do a bit better than placebo, VX-548 at the higher dose appears to do the best. But I should note that 5 mg of hydrocodone may not be an adequate dose for most people.
Yes, I would really have killed for an NSAID arm in this trial. Its absence, given that NSAIDs are a staple of postoperative care, is ... well, let’s just say, notable.
Although not a pain-destroying machine, VX-548 has some other things to recommend it. The receptor is really not found in the brain at all, which suggests that the drug should not carry much risk for dependency, though that has not been formally studied.
The side effects were generally mild – headache was the most common – and less prevalent than what you see even in the placebo arm.
Perhaps most notable is the fact that the rate of discontinuation of the study drug was lowest in the VX-548 arm. Patients could stop taking the pill they were assigned for any reason, ranging from perceived lack of efficacy to side effects. A low discontinuation rate indicates to me a sort of “voting with your feet” that suggests this might be a well-tolerated and reasonably effective drug.
VX-548 isn’t on the market yet; phase 3 trials are ongoing. But whether it is this particular drug or another in this class, I’m happy to see researchers trying to find new ways to target that most primeval form of suffering: pain.
Dr. Wilson is an associate professor of medicine and public health and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator, New Haven, Conn. He disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.