User login
Germline testing in advanced cancer can lead to targeted treatment
The study involved 11,974 patients with various tumor types. All the patients underwent germline genetic testing from 2015 to 2019 at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, using the next-generation sequencing panel MSK-IMPACT.
This testing showed that 17.1% of patients had variants in cancer predisposition genes, and 7.1%-8.6% had variants that could potentially be targeted.
“Of course, these numbers are not static,” commented lead author Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, a medical oncologist at MSKCC. “And with the emergence of novel targeted treatments with new FDA indications, the therapeutic actionability of germline variants is likely to increase over time.
“Our study demonstrates the first comprehensive assessment of the clinical utility of germline alterations for therapeutic actionability in a population of patients with advanced cancer,” she added.
Dr. Stadler presented the study results during a virtual scientific program of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020.
Testing for somatic mutations is evolving as the standard of care in many cancer types, and somatic genomic testing is rapidly becoming an integral part of the regimen for patients with advanced disease. Some studies suggest that 9%-11% of patients harbor actionable genetic alterations, as determined on the basis of tumor profiling.
“The take-home message from this is that now, more than ever before, germline testing is indicated for the selection of cancer treatment,” said Erin Wysong Hofstatter, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a Highlights of the Day session.
An emerging indication for germline testing is the selection of treatment in the advanced setting, she noted. “And it is important to know your test. Remember that tumor sequencing is not a substitute for comprehensive germline testing.”
Implications in cancer treatment
For their study, Dr. Stadler and colleagues reviewed the medical records of patients with likely pathogenic/pathogenic germline (LP/P) alterations in genes that had known therapeutic targets so as to identify germline-targeted treatment either in a clinical or research setting.
“Since 2015, patients undergoing MSK-IMPACT may also choose to provide additional consent for secondary germline genetic analysis, wherein up to 88 genes known to be associated with cancer predisposition are analyzed,” she said. “Likely pathogenic and pathogenic germline alterations identified are disclosed to the patient and treating physician via the Clinical Genetic Service.”
A total of 2043 (17.1%) patients who harbored LP/P variants in a cancer predisposition gene were identified. Of these, 11% of patients harbored pathogenic alterations in high or moderate penetrance cancer predisposition genes. When the analysis was limited to genes with targeted therapeutic actionability, or what the authors defined as tier 1 and tier 2 genes, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) harbored a targetable pathogenic germline alteration.
BRCA alterations accounted for half (52%) of the findings, and 20% were associated with Lynch syndrome.
The tier 2 genes, which included PALB2, ATM, RAD51C, and RAD51D, accounted for about a quarter of the findings. Dr. Hofstatter noted that, using strict criteria, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) were found to harbor a pathogenic alteration and a targetable gene. Using less stringent criteria, additional tier 3 genes and additional genes associated with DNA homologous recombination repair brought the number up to 8.6% (n = 1,003).
Therapeutic action
For determining therapeutic actionability, the strict criteria were used; 593 patients (4.95%) with recurrent or metastatic disease were identified. For these patients, consideration of a targeted therapy, either as part of standard care or as part of an investigation or research protocol, was important.
Of this group, 44% received therapy targeting the germline alteration. Regarding specific genes, 50% of BRCA1/2 carriers and 58% of Lynch syndrome patients received targeted treatment. With respect to tier 2 genes, 40% of patients with PALB2, 19% with ATM, and 37% with RAD51C or 51D received a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Among patients with a BRCA1/2 mutation who received a PARP inhibitor, 55.1% had breast or ovarian cancer, and 44.8% had other tumor types, including pancreas, prostate, bile duct, gastric cancers. These patients received the drug in a research setting.
For patients with PALB2 alterations who received PARP inhibitors, 53.3% had breast or pancreas cancer, and 46.7% had cancer of the prostate, ovary, or an unknown primary.
Looking ahead
The discussant for the paper, Funda Meric-Bernstam, MD, chair of the Department of Investigational Cancer Therapeutics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, pointed out that most of the BRCA-positive patients had cancers traditionally associated with the mutation. “There were no patients with PTEN mutations treated, and interestingly, no patients with NF1 were treated,” she said. “But actionability is evolving, as the MEK inhibitor selumitinib was recently approved for NF1.”
Some questions remain unanswered, she noted, such as: “What percentage of patients undergoing tumor-normal testing signed a germline protocol?” and “Does the population introduce a bias – such as younger patients, family history, and so on?”
It is also unknown what percentage of germline alterations were known in comparison with those identified through tumor/normal testing. Also of importance is the fact that in this study, the results of germline testing were delivered in an academic setting, she emphasized. “What if they were delivered elsewhere? What would be the impact of identifying these alterations in an environment with less access to trials?
“But to be fair, it is not easy to seek the germline mutations,” Dr. Meric-Bernstam continued. “These studies were done under institutional review board protocols, and it is important to note that most profiling is done as standard of care without consenting and soliciting patient preference on the return of germline results.”
An infrastructure is needed to return/counsel/offer cascade testing, and “analyses need to be facilitated to ensure that findings can be acted upon in a timely fashion,” she added.
The study was supported by MSKCC internal funding. Dr. Stadler reported relationships (institutional) with Adverum, Alimera Sciences, Allergan, Biomarin, Fortress Biotech, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Optos, Regeneron, Regenxbio, and Spark Therapeutics. Dr. Meric-Bernstram reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study involved 11,974 patients with various tumor types. All the patients underwent germline genetic testing from 2015 to 2019 at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, using the next-generation sequencing panel MSK-IMPACT.
This testing showed that 17.1% of patients had variants in cancer predisposition genes, and 7.1%-8.6% had variants that could potentially be targeted.
“Of course, these numbers are not static,” commented lead author Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, a medical oncologist at MSKCC. “And with the emergence of novel targeted treatments with new FDA indications, the therapeutic actionability of germline variants is likely to increase over time.
“Our study demonstrates the first comprehensive assessment of the clinical utility of germline alterations for therapeutic actionability in a population of patients with advanced cancer,” she added.
Dr. Stadler presented the study results during a virtual scientific program of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020.
Testing for somatic mutations is evolving as the standard of care in many cancer types, and somatic genomic testing is rapidly becoming an integral part of the regimen for patients with advanced disease. Some studies suggest that 9%-11% of patients harbor actionable genetic alterations, as determined on the basis of tumor profiling.
“The take-home message from this is that now, more than ever before, germline testing is indicated for the selection of cancer treatment,” said Erin Wysong Hofstatter, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a Highlights of the Day session.
An emerging indication for germline testing is the selection of treatment in the advanced setting, she noted. “And it is important to know your test. Remember that tumor sequencing is not a substitute for comprehensive germline testing.”
Implications in cancer treatment
For their study, Dr. Stadler and colleagues reviewed the medical records of patients with likely pathogenic/pathogenic germline (LP/P) alterations in genes that had known therapeutic targets so as to identify germline-targeted treatment either in a clinical or research setting.
“Since 2015, patients undergoing MSK-IMPACT may also choose to provide additional consent for secondary germline genetic analysis, wherein up to 88 genes known to be associated with cancer predisposition are analyzed,” she said. “Likely pathogenic and pathogenic germline alterations identified are disclosed to the patient and treating physician via the Clinical Genetic Service.”
A total of 2043 (17.1%) patients who harbored LP/P variants in a cancer predisposition gene were identified. Of these, 11% of patients harbored pathogenic alterations in high or moderate penetrance cancer predisposition genes. When the analysis was limited to genes with targeted therapeutic actionability, or what the authors defined as tier 1 and tier 2 genes, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) harbored a targetable pathogenic germline alteration.
BRCA alterations accounted for half (52%) of the findings, and 20% were associated with Lynch syndrome.
The tier 2 genes, which included PALB2, ATM, RAD51C, and RAD51D, accounted for about a quarter of the findings. Dr. Hofstatter noted that, using strict criteria, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) were found to harbor a pathogenic alteration and a targetable gene. Using less stringent criteria, additional tier 3 genes and additional genes associated with DNA homologous recombination repair brought the number up to 8.6% (n = 1,003).
Therapeutic action
For determining therapeutic actionability, the strict criteria were used; 593 patients (4.95%) with recurrent or metastatic disease were identified. For these patients, consideration of a targeted therapy, either as part of standard care or as part of an investigation or research protocol, was important.
Of this group, 44% received therapy targeting the germline alteration. Regarding specific genes, 50% of BRCA1/2 carriers and 58% of Lynch syndrome patients received targeted treatment. With respect to tier 2 genes, 40% of patients with PALB2, 19% with ATM, and 37% with RAD51C or 51D received a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Among patients with a BRCA1/2 mutation who received a PARP inhibitor, 55.1% had breast or ovarian cancer, and 44.8% had other tumor types, including pancreas, prostate, bile duct, gastric cancers. These patients received the drug in a research setting.
For patients with PALB2 alterations who received PARP inhibitors, 53.3% had breast or pancreas cancer, and 46.7% had cancer of the prostate, ovary, or an unknown primary.
Looking ahead
The discussant for the paper, Funda Meric-Bernstam, MD, chair of the Department of Investigational Cancer Therapeutics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, pointed out that most of the BRCA-positive patients had cancers traditionally associated with the mutation. “There were no patients with PTEN mutations treated, and interestingly, no patients with NF1 were treated,” she said. “But actionability is evolving, as the MEK inhibitor selumitinib was recently approved for NF1.”
Some questions remain unanswered, she noted, such as: “What percentage of patients undergoing tumor-normal testing signed a germline protocol?” and “Does the population introduce a bias – such as younger patients, family history, and so on?”
It is also unknown what percentage of germline alterations were known in comparison with those identified through tumor/normal testing. Also of importance is the fact that in this study, the results of germline testing were delivered in an academic setting, she emphasized. “What if they were delivered elsewhere? What would be the impact of identifying these alterations in an environment with less access to trials?
“But to be fair, it is not easy to seek the germline mutations,” Dr. Meric-Bernstam continued. “These studies were done under institutional review board protocols, and it is important to note that most profiling is done as standard of care without consenting and soliciting patient preference on the return of germline results.”
An infrastructure is needed to return/counsel/offer cascade testing, and “analyses need to be facilitated to ensure that findings can be acted upon in a timely fashion,” she added.
The study was supported by MSKCC internal funding. Dr. Stadler reported relationships (institutional) with Adverum, Alimera Sciences, Allergan, Biomarin, Fortress Biotech, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Optos, Regeneron, Regenxbio, and Spark Therapeutics. Dr. Meric-Bernstram reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study involved 11,974 patients with various tumor types. All the patients underwent germline genetic testing from 2015 to 2019 at the Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSKCC) in New York, using the next-generation sequencing panel MSK-IMPACT.
This testing showed that 17.1% of patients had variants in cancer predisposition genes, and 7.1%-8.6% had variants that could potentially be targeted.
“Of course, these numbers are not static,” commented lead author Zsofia K. Stadler, MD, a medical oncologist at MSKCC. “And with the emergence of novel targeted treatments with new FDA indications, the therapeutic actionability of germline variants is likely to increase over time.
“Our study demonstrates the first comprehensive assessment of the clinical utility of germline alterations for therapeutic actionability in a population of patients with advanced cancer,” she added.
Dr. Stadler presented the study results during a virtual scientific program of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2020.
Testing for somatic mutations is evolving as the standard of care in many cancer types, and somatic genomic testing is rapidly becoming an integral part of the regimen for patients with advanced disease. Some studies suggest that 9%-11% of patients harbor actionable genetic alterations, as determined on the basis of tumor profiling.
“The take-home message from this is that now, more than ever before, germline testing is indicated for the selection of cancer treatment,” said Erin Wysong Hofstatter, MD, from Yale University, New Haven, Conn., in a Highlights of the Day session.
An emerging indication for germline testing is the selection of treatment in the advanced setting, she noted. “And it is important to know your test. Remember that tumor sequencing is not a substitute for comprehensive germline testing.”
Implications in cancer treatment
For their study, Dr. Stadler and colleagues reviewed the medical records of patients with likely pathogenic/pathogenic germline (LP/P) alterations in genes that had known therapeutic targets so as to identify germline-targeted treatment either in a clinical or research setting.
“Since 2015, patients undergoing MSK-IMPACT may also choose to provide additional consent for secondary germline genetic analysis, wherein up to 88 genes known to be associated with cancer predisposition are analyzed,” she said. “Likely pathogenic and pathogenic germline alterations identified are disclosed to the patient and treating physician via the Clinical Genetic Service.”
A total of 2043 (17.1%) patients who harbored LP/P variants in a cancer predisposition gene were identified. Of these, 11% of patients harbored pathogenic alterations in high or moderate penetrance cancer predisposition genes. When the analysis was limited to genes with targeted therapeutic actionability, or what the authors defined as tier 1 and tier 2 genes, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) harbored a targetable pathogenic germline alteration.
BRCA alterations accounted for half (52%) of the findings, and 20% were associated with Lynch syndrome.
The tier 2 genes, which included PALB2, ATM, RAD51C, and RAD51D, accounted for about a quarter of the findings. Dr. Hofstatter noted that, using strict criteria, 7.1% of patients (n = 849) were found to harbor a pathogenic alteration and a targetable gene. Using less stringent criteria, additional tier 3 genes and additional genes associated with DNA homologous recombination repair brought the number up to 8.6% (n = 1,003).
Therapeutic action
For determining therapeutic actionability, the strict criteria were used; 593 patients (4.95%) with recurrent or metastatic disease were identified. For these patients, consideration of a targeted therapy, either as part of standard care or as part of an investigation or research protocol, was important.
Of this group, 44% received therapy targeting the germline alteration. Regarding specific genes, 50% of BRCA1/2 carriers and 58% of Lynch syndrome patients received targeted treatment. With respect to tier 2 genes, 40% of patients with PALB2, 19% with ATM, and 37% with RAD51C or 51D received a poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor.
Among patients with a BRCA1/2 mutation who received a PARP inhibitor, 55.1% had breast or ovarian cancer, and 44.8% had other tumor types, including pancreas, prostate, bile duct, gastric cancers. These patients received the drug in a research setting.
For patients with PALB2 alterations who received PARP inhibitors, 53.3% had breast or pancreas cancer, and 46.7% had cancer of the prostate, ovary, or an unknown primary.
Looking ahead
The discussant for the paper, Funda Meric-Bernstam, MD, chair of the Department of Investigational Cancer Therapeutics at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, pointed out that most of the BRCA-positive patients had cancers traditionally associated with the mutation. “There were no patients with PTEN mutations treated, and interestingly, no patients with NF1 were treated,” she said. “But actionability is evolving, as the MEK inhibitor selumitinib was recently approved for NF1.”
Some questions remain unanswered, she noted, such as: “What percentage of patients undergoing tumor-normal testing signed a germline protocol?” and “Does the population introduce a bias – such as younger patients, family history, and so on?”
It is also unknown what percentage of germline alterations were known in comparison with those identified through tumor/normal testing. Also of importance is the fact that in this study, the results of germline testing were delivered in an academic setting, she emphasized. “What if they were delivered elsewhere? What would be the impact of identifying these alterations in an environment with less access to trials?
“But to be fair, it is not easy to seek the germline mutations,” Dr. Meric-Bernstam continued. “These studies were done under institutional review board protocols, and it is important to note that most profiling is done as standard of care without consenting and soliciting patient preference on the return of germline results.”
An infrastructure is needed to return/counsel/offer cascade testing, and “analyses need to be facilitated to ensure that findings can be acted upon in a timely fashion,” she added.
The study was supported by MSKCC internal funding. Dr. Stadler reported relationships (institutional) with Adverum, Alimera Sciences, Allergan, Biomarin, Fortress Biotech, Genentech/Roche, Novartis, Optos, Regeneron, Regenxbio, and Spark Therapeutics. Dr. Meric-Bernstram reported relationships with numerous pharmaceutical companies.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ASCO 2020
Patient-focused precautions, testing help blunt pandemic effects on heme-onc unit
Keeping hematologic oncology patients on their treatment regimens and caring for inpatients with hematologic malignancies remained “manageable” during the first 2 months of the COVID-19 pandemic at Levine Cancer Institute in Charlotte, N.C.
That level of manageability has partly been because a surge in cases so far hasn’t arrived at Levine or in most of the surrounding North Carolina and South Carolina communities it serves. As of May 15, 2020, the total number of confirmed and reported COVID-19 cases had reached about 19,000 in North Carolina, and just under 9,000 in South Carolina, out of a total population in the two states of close to 16 million. What’s happened instead at Levine Cancer Institute (LCI) has been a steady but low drumbeat of cases that, by mid-May 2020, totaled fewer than 10 patients with hematologic malignancies diagnosed with COVID-19.
“For a large system with multiple sites throughout North and South Carolina that saw 17,200 new patients in 2019 – including solid tumor, benign hematology, and malignant hematology patients – with 198,000 total patient visits, it is safe to say that we are off to a good start. However, we remain in the early throes of the pandemic and we will need to remain vigilant going forward,” said Peter Voorhees, MD, professor of medicine and director of Medical Operations and Outreach Services in LCI’s Department of Hematologic Oncology and Blood Disorders.
The limited effects to date of COVID-19 at LCI has been thanks to a regimen of great caution for preventing infections that’s been consistently conveyed to LCI patients from before the pandemic’s onset, liberal testing that started early, a proactive plan to defer and temporarily replace infusion care when medically appropriate, a novel staffing approach designed to minimize and contain potential staff outbreaks, and an early pivot to virtual patient contact when feasible.
COVID-19 has had limited penetration into the LCI case load because patients have, in general, “been very careful,” said Dr. Voorhees.
“My impression is that the incidence has been low partly because our patients, especially those with hematologic malignancies including those on active chemotherapy, were already getting warned to be cautious even before the coronavirus using distancing, masking, and meticulous hand hygiene,” he said in an interview that reviewed the steps LCI took starting in March to confront and manage the effects of the then-nascent pandemic. “Since we started screening asymptomatic patients in the inpatient and outpatient settings we have identified only one patient with COVID-19 infection, which supports the low rate of infection in our patient population thus far.”
Another key step was the launch of “robust” testing for the COVID-19 virus starting on March 9, using an in-house assay from LCI’s parent health system, Atrium Health, that delivered results within 24 hours. Testing became available at LCI “earlier than at many other health systems.” At first, testing was limited to patients or staff presenting with symptoms, but in the following weeks, it expanded to more patients, including those without symptoms who were scheduled for treatment at the apheresis center, cell donors and cell recipients, patients arriving for inpatient chemotherapy or cellular therapy, patients arriving from a skilled nursing facility or similar environments, and more recently, outpatient chemotherapy patients. “We’re now doing a lot of screening,” Dr. Voorhees said. “In general, screening has been well received because patients recognize that it’s for their own safety.”
Another piece of COVID-19 preparedness was a move toward technology as an alternative to face-to-face encounters between patients and staff. “We adopted virtual technology early.” When medically appropriate, they provided either video consultations with more tech-savvy patients or telephone-based virtual visits for patients who preferred a more familiar interface. As LCI starts the process of reentry for patients whose face-to-face encounters were deferred, virtual visits will remain an important facet of maintaining care while limiting exposure for appropriate patients and facilitating adequate space for social distancing in the clinics and infusion centers.
Atrium Health also launched a “virtual hospital” geared to intensified remote management of COVID-19 patients who aren’t sick enough for hospitalization. “People who test positive automatically enter the virtual hospital and have regular interactions with their team of providers,” with LCI providing additional support for their patients who get infected. Patients receive an equipment kit that lets them monitor and transmit their vital signs. The virtual hospital program also helps expedite personal needs like delivery of prescriptions and food. “It helps patients manage at home, and has been incredibly useful,” said Dr. Voorhees.
Perhaps the most challenging step LCI clinicians took to preclude a potential COVID-19 case surge was to review all patients receiving infusional therapy or planned cellular therapy and triage those who could potentially tolerate a temporary change to either an oral, at-home regimen or to a brief hold on their treatment. Some patients on maintenance, outpatient infusion-therapy regimens “expressed concern about coming to the clinic. We looked at the patients scheduled to come for infusions and decided which visits were essential and which were deferrable without disrupting care by briefly using a noninfusional approach,” said Dr. Voorhees. The number of patients who had their regimens modified or held was “relatively small,” and with the recent recognition that a surge of infections has not occurred, “we’re now rolling out cautious reentry of those patients back to their originally prescribed chemotherapy.”
In addition to concerns of exposure at infusion clinics, there are concerns about the heightened susceptibility of immunosuppressed hematologic oncology patients to COVID-19 and their risk for more severe infection. “Our view is that, if patients tested positive, continuing immunosuppressive treatment would likely be detrimental,” so when possible treatment is temporarily suspended and then resumed when the infection has cleared. “When patients test positive for a prolonged period, a decision to resume treatment must be in the best interests of the patient and weigh the benefits of resuming therapy against the risks of incurring a more severe infection by restarting potentially immunosuppressive therapy,” Dr. Voorhees said.
The enhanced risk that cancer patients face if they develop COVID-19 was documented in a recent review of 218 cancer patients hospitalized for COVID-19 during parts of March and April in a large New York health system. The results showed an overall mortality rate of 28%, including a 37% rate among 54 patients with hematologic malignancies and a 25% rate among 164 patients with solid tumors. The mortality rate “may not be quite as high as they reported because that depends on how many patients you test, but there is no question that patients with more comorbidities are at higher risk. Patients with active cancer on chemotherapy are a particularly vulnerable population, and many have expressed concerns about their vulnerability,” he observed.
For the few LCI patients who developed COVID-19 infection, the medical staff has had several therapeutic options they could match to each patient’s needs, with help from the Atrium Health infectious disease team. LCI and Atrium Health are participating in several COVID-19 clinical treatment trials, including an investigational convalescent plasma protocol spearheaded by the Mayo Clinic. They have also opened a randomized, phase 2 trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of selinexor (Xpovio), an oral drug that’s Food and Drug Administration approved for patients with multiple myeloma, for treatment of moderate or severe COVID-19 infection. Additional studies evaluating blockade of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, as well as inhaled antiviral therapy, have recently launched, and several additional studies are poised to open in the coming weeks.
The LCI and Atrium Health team also has a supply of the antiviral agent remdesivir as part of the FDA’s expanded access protocol and emergency use authorization. They also have a supply of and experience administering the interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab (Actemra), which showed some suggestion of efficacy in limited experience treating patients with severe or critical COVID-19 infections. Clinicians at LCI have not used the investigational and unproven agents hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and azithromycin to either prevent or treat COVID-19.
LCI also instituted measures to try to minimize the risk that staff members could become infected and transmit the virus while asymptomatic. Following conversations held early on with COVID-19–experienced health authorities in China and Italy, the patient-facing LCI staff split into two teams starting on March 23 that alternated responsibility for direct patient interactions every 2 weeks. When one of these teams was off from direct patient contact they continued to care for patients remotely through virtual technologies. The concept was that, if a staffer became infected while remaining asymptomatic during their contact with patients, their status would either become diagnosable or resolve during their 2 weeks away from seeing any patients. Perhaps in part because of this approach infections among staff members “have not been a big issue. We’ve had an incredibly low infection rate among the LCI staff,” Dr. Voorhees noted.
By mid-May, with the imminent threat of a sudden CODIV-19 surge moderated, heme-onc operations at LCI began to cautiously revert to more normal operations. “We’re continuing patient screening for signs and symptoms of COVID-19 infection, testing for asymptomatic infections, and requiring masking and social distancing in the clinics and hospitals, but we’re starting to slowly restore the number of patients at our clinics [virtual and face to face[ and infusion centers,” and the staff’s division into two teams ended. “The idea was to get past a surge and make sure our system was not overwhelmed. We anticipated a local surge in late April, but then it kept getting pushed back. Current projections are for the infection rate among LCI patients to remain low provided that community spread remains stable or, ideally, decreases.” The LCI infectious disease staff is closely monitoring infection rates for early recognition of an outbreak, with plans to follow any new cases with contact tracing. So far, the COVID-19 pandemic at LCI “has been very manageable,” Dr. Voorhees concluded.
“We’re now better positioned to deal with a case surge if it were to happen. We could resume the two-team approach, hospital-wide plans are now in place for a future surge, and we are now up and running with robust testing and inpatient and outpatient virtual technology. The first time, we were all learning on the fly.”
The LCI biostatistics team has been prospectively collecting the Institutes’s COVID-19 patient data, with plans to report their findings.
Dr. Voorhees has had financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Oncopeptides, none of which are relevant to this article.
Keeping hematologic oncology patients on their treatment regimens and caring for inpatients with hematologic malignancies remained “manageable” during the first 2 months of the COVID-19 pandemic at Levine Cancer Institute in Charlotte, N.C.
That level of manageability has partly been because a surge in cases so far hasn’t arrived at Levine or in most of the surrounding North Carolina and South Carolina communities it serves. As of May 15, 2020, the total number of confirmed and reported COVID-19 cases had reached about 19,000 in North Carolina, and just under 9,000 in South Carolina, out of a total population in the two states of close to 16 million. What’s happened instead at Levine Cancer Institute (LCI) has been a steady but low drumbeat of cases that, by mid-May 2020, totaled fewer than 10 patients with hematologic malignancies diagnosed with COVID-19.
“For a large system with multiple sites throughout North and South Carolina that saw 17,200 new patients in 2019 – including solid tumor, benign hematology, and malignant hematology patients – with 198,000 total patient visits, it is safe to say that we are off to a good start. However, we remain in the early throes of the pandemic and we will need to remain vigilant going forward,” said Peter Voorhees, MD, professor of medicine and director of Medical Operations and Outreach Services in LCI’s Department of Hematologic Oncology and Blood Disorders.
The limited effects to date of COVID-19 at LCI has been thanks to a regimen of great caution for preventing infections that’s been consistently conveyed to LCI patients from before the pandemic’s onset, liberal testing that started early, a proactive plan to defer and temporarily replace infusion care when medically appropriate, a novel staffing approach designed to minimize and contain potential staff outbreaks, and an early pivot to virtual patient contact when feasible.
COVID-19 has had limited penetration into the LCI case load because patients have, in general, “been very careful,” said Dr. Voorhees.
“My impression is that the incidence has been low partly because our patients, especially those with hematologic malignancies including those on active chemotherapy, were already getting warned to be cautious even before the coronavirus using distancing, masking, and meticulous hand hygiene,” he said in an interview that reviewed the steps LCI took starting in March to confront and manage the effects of the then-nascent pandemic. “Since we started screening asymptomatic patients in the inpatient and outpatient settings we have identified only one patient with COVID-19 infection, which supports the low rate of infection in our patient population thus far.”
Another key step was the launch of “robust” testing for the COVID-19 virus starting on March 9, using an in-house assay from LCI’s parent health system, Atrium Health, that delivered results within 24 hours. Testing became available at LCI “earlier than at many other health systems.” At first, testing was limited to patients or staff presenting with symptoms, but in the following weeks, it expanded to more patients, including those without symptoms who were scheduled for treatment at the apheresis center, cell donors and cell recipients, patients arriving for inpatient chemotherapy or cellular therapy, patients arriving from a skilled nursing facility or similar environments, and more recently, outpatient chemotherapy patients. “We’re now doing a lot of screening,” Dr. Voorhees said. “In general, screening has been well received because patients recognize that it’s for their own safety.”
Another piece of COVID-19 preparedness was a move toward technology as an alternative to face-to-face encounters between patients and staff. “We adopted virtual technology early.” When medically appropriate, they provided either video consultations with more tech-savvy patients or telephone-based virtual visits for patients who preferred a more familiar interface. As LCI starts the process of reentry for patients whose face-to-face encounters were deferred, virtual visits will remain an important facet of maintaining care while limiting exposure for appropriate patients and facilitating adequate space for social distancing in the clinics and infusion centers.
Atrium Health also launched a “virtual hospital” geared to intensified remote management of COVID-19 patients who aren’t sick enough for hospitalization. “People who test positive automatically enter the virtual hospital and have regular interactions with their team of providers,” with LCI providing additional support for their patients who get infected. Patients receive an equipment kit that lets them monitor and transmit their vital signs. The virtual hospital program also helps expedite personal needs like delivery of prescriptions and food. “It helps patients manage at home, and has been incredibly useful,” said Dr. Voorhees.
Perhaps the most challenging step LCI clinicians took to preclude a potential COVID-19 case surge was to review all patients receiving infusional therapy or planned cellular therapy and triage those who could potentially tolerate a temporary change to either an oral, at-home regimen or to a brief hold on their treatment. Some patients on maintenance, outpatient infusion-therapy regimens “expressed concern about coming to the clinic. We looked at the patients scheduled to come for infusions and decided which visits were essential and which were deferrable without disrupting care by briefly using a noninfusional approach,” said Dr. Voorhees. The number of patients who had their regimens modified or held was “relatively small,” and with the recent recognition that a surge of infections has not occurred, “we’re now rolling out cautious reentry of those patients back to their originally prescribed chemotherapy.”
In addition to concerns of exposure at infusion clinics, there are concerns about the heightened susceptibility of immunosuppressed hematologic oncology patients to COVID-19 and their risk for more severe infection. “Our view is that, if patients tested positive, continuing immunosuppressive treatment would likely be detrimental,” so when possible treatment is temporarily suspended and then resumed when the infection has cleared. “When patients test positive for a prolonged period, a decision to resume treatment must be in the best interests of the patient and weigh the benefits of resuming therapy against the risks of incurring a more severe infection by restarting potentially immunosuppressive therapy,” Dr. Voorhees said.
The enhanced risk that cancer patients face if they develop COVID-19 was documented in a recent review of 218 cancer patients hospitalized for COVID-19 during parts of March and April in a large New York health system. The results showed an overall mortality rate of 28%, including a 37% rate among 54 patients with hematologic malignancies and a 25% rate among 164 patients with solid tumors. The mortality rate “may not be quite as high as they reported because that depends on how many patients you test, but there is no question that patients with more comorbidities are at higher risk. Patients with active cancer on chemotherapy are a particularly vulnerable population, and many have expressed concerns about their vulnerability,” he observed.
For the few LCI patients who developed COVID-19 infection, the medical staff has had several therapeutic options they could match to each patient’s needs, with help from the Atrium Health infectious disease team. LCI and Atrium Health are participating in several COVID-19 clinical treatment trials, including an investigational convalescent plasma protocol spearheaded by the Mayo Clinic. They have also opened a randomized, phase 2 trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of selinexor (Xpovio), an oral drug that’s Food and Drug Administration approved for patients with multiple myeloma, for treatment of moderate or severe COVID-19 infection. Additional studies evaluating blockade of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, as well as inhaled antiviral therapy, have recently launched, and several additional studies are poised to open in the coming weeks.
The LCI and Atrium Health team also has a supply of the antiviral agent remdesivir as part of the FDA’s expanded access protocol and emergency use authorization. They also have a supply of and experience administering the interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab (Actemra), which showed some suggestion of efficacy in limited experience treating patients with severe or critical COVID-19 infections. Clinicians at LCI have not used the investigational and unproven agents hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and azithromycin to either prevent or treat COVID-19.
LCI also instituted measures to try to minimize the risk that staff members could become infected and transmit the virus while asymptomatic. Following conversations held early on with COVID-19–experienced health authorities in China and Italy, the patient-facing LCI staff split into two teams starting on March 23 that alternated responsibility for direct patient interactions every 2 weeks. When one of these teams was off from direct patient contact they continued to care for patients remotely through virtual technologies. The concept was that, if a staffer became infected while remaining asymptomatic during their contact with patients, their status would either become diagnosable or resolve during their 2 weeks away from seeing any patients. Perhaps in part because of this approach infections among staff members “have not been a big issue. We’ve had an incredibly low infection rate among the LCI staff,” Dr. Voorhees noted.
By mid-May, with the imminent threat of a sudden CODIV-19 surge moderated, heme-onc operations at LCI began to cautiously revert to more normal operations. “We’re continuing patient screening for signs and symptoms of COVID-19 infection, testing for asymptomatic infections, and requiring masking and social distancing in the clinics and hospitals, but we’re starting to slowly restore the number of patients at our clinics [virtual and face to face[ and infusion centers,” and the staff’s division into two teams ended. “The idea was to get past a surge and make sure our system was not overwhelmed. We anticipated a local surge in late April, but then it kept getting pushed back. Current projections are for the infection rate among LCI patients to remain low provided that community spread remains stable or, ideally, decreases.” The LCI infectious disease staff is closely monitoring infection rates for early recognition of an outbreak, with plans to follow any new cases with contact tracing. So far, the COVID-19 pandemic at LCI “has been very manageable,” Dr. Voorhees concluded.
“We’re now better positioned to deal with a case surge if it were to happen. We could resume the two-team approach, hospital-wide plans are now in place for a future surge, and we are now up and running with robust testing and inpatient and outpatient virtual technology. The first time, we were all learning on the fly.”
The LCI biostatistics team has been prospectively collecting the Institutes’s COVID-19 patient data, with plans to report their findings.
Dr. Voorhees has had financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Oncopeptides, none of which are relevant to this article.
Keeping hematologic oncology patients on their treatment regimens and caring for inpatients with hematologic malignancies remained “manageable” during the first 2 months of the COVID-19 pandemic at Levine Cancer Institute in Charlotte, N.C.
That level of manageability has partly been because a surge in cases so far hasn’t arrived at Levine or in most of the surrounding North Carolina and South Carolina communities it serves. As of May 15, 2020, the total number of confirmed and reported COVID-19 cases had reached about 19,000 in North Carolina, and just under 9,000 in South Carolina, out of a total population in the two states of close to 16 million. What’s happened instead at Levine Cancer Institute (LCI) has been a steady but low drumbeat of cases that, by mid-May 2020, totaled fewer than 10 patients with hematologic malignancies diagnosed with COVID-19.
“For a large system with multiple sites throughout North and South Carolina that saw 17,200 new patients in 2019 – including solid tumor, benign hematology, and malignant hematology patients – with 198,000 total patient visits, it is safe to say that we are off to a good start. However, we remain in the early throes of the pandemic and we will need to remain vigilant going forward,” said Peter Voorhees, MD, professor of medicine and director of Medical Operations and Outreach Services in LCI’s Department of Hematologic Oncology and Blood Disorders.
The limited effects to date of COVID-19 at LCI has been thanks to a regimen of great caution for preventing infections that’s been consistently conveyed to LCI patients from before the pandemic’s onset, liberal testing that started early, a proactive plan to defer and temporarily replace infusion care when medically appropriate, a novel staffing approach designed to minimize and contain potential staff outbreaks, and an early pivot to virtual patient contact when feasible.
COVID-19 has had limited penetration into the LCI case load because patients have, in general, “been very careful,” said Dr. Voorhees.
“My impression is that the incidence has been low partly because our patients, especially those with hematologic malignancies including those on active chemotherapy, were already getting warned to be cautious even before the coronavirus using distancing, masking, and meticulous hand hygiene,” he said in an interview that reviewed the steps LCI took starting in March to confront and manage the effects of the then-nascent pandemic. “Since we started screening asymptomatic patients in the inpatient and outpatient settings we have identified only one patient with COVID-19 infection, which supports the low rate of infection in our patient population thus far.”
Another key step was the launch of “robust” testing for the COVID-19 virus starting on March 9, using an in-house assay from LCI’s parent health system, Atrium Health, that delivered results within 24 hours. Testing became available at LCI “earlier than at many other health systems.” At first, testing was limited to patients or staff presenting with symptoms, but in the following weeks, it expanded to more patients, including those without symptoms who were scheduled for treatment at the apheresis center, cell donors and cell recipients, patients arriving for inpatient chemotherapy or cellular therapy, patients arriving from a skilled nursing facility or similar environments, and more recently, outpatient chemotherapy patients. “We’re now doing a lot of screening,” Dr. Voorhees said. “In general, screening has been well received because patients recognize that it’s for their own safety.”
Another piece of COVID-19 preparedness was a move toward technology as an alternative to face-to-face encounters between patients and staff. “We adopted virtual technology early.” When medically appropriate, they provided either video consultations with more tech-savvy patients or telephone-based virtual visits for patients who preferred a more familiar interface. As LCI starts the process of reentry for patients whose face-to-face encounters were deferred, virtual visits will remain an important facet of maintaining care while limiting exposure for appropriate patients and facilitating adequate space for social distancing in the clinics and infusion centers.
Atrium Health also launched a “virtual hospital” geared to intensified remote management of COVID-19 patients who aren’t sick enough for hospitalization. “People who test positive automatically enter the virtual hospital and have regular interactions with their team of providers,” with LCI providing additional support for their patients who get infected. Patients receive an equipment kit that lets them monitor and transmit their vital signs. The virtual hospital program also helps expedite personal needs like delivery of prescriptions and food. “It helps patients manage at home, and has been incredibly useful,” said Dr. Voorhees.
Perhaps the most challenging step LCI clinicians took to preclude a potential COVID-19 case surge was to review all patients receiving infusional therapy or planned cellular therapy and triage those who could potentially tolerate a temporary change to either an oral, at-home regimen or to a brief hold on their treatment. Some patients on maintenance, outpatient infusion-therapy regimens “expressed concern about coming to the clinic. We looked at the patients scheduled to come for infusions and decided which visits were essential and which were deferrable without disrupting care by briefly using a noninfusional approach,” said Dr. Voorhees. The number of patients who had their regimens modified or held was “relatively small,” and with the recent recognition that a surge of infections has not occurred, “we’re now rolling out cautious reentry of those patients back to their originally prescribed chemotherapy.”
In addition to concerns of exposure at infusion clinics, there are concerns about the heightened susceptibility of immunosuppressed hematologic oncology patients to COVID-19 and their risk for more severe infection. “Our view is that, if patients tested positive, continuing immunosuppressive treatment would likely be detrimental,” so when possible treatment is temporarily suspended and then resumed when the infection has cleared. “When patients test positive for a prolonged period, a decision to resume treatment must be in the best interests of the patient and weigh the benefits of resuming therapy against the risks of incurring a more severe infection by restarting potentially immunosuppressive therapy,” Dr. Voorhees said.
The enhanced risk that cancer patients face if they develop COVID-19 was documented in a recent review of 218 cancer patients hospitalized for COVID-19 during parts of March and April in a large New York health system. The results showed an overall mortality rate of 28%, including a 37% rate among 54 patients with hematologic malignancies and a 25% rate among 164 patients with solid tumors. The mortality rate “may not be quite as high as they reported because that depends on how many patients you test, but there is no question that patients with more comorbidities are at higher risk. Patients with active cancer on chemotherapy are a particularly vulnerable population, and many have expressed concerns about their vulnerability,” he observed.
For the few LCI patients who developed COVID-19 infection, the medical staff has had several therapeutic options they could match to each patient’s needs, with help from the Atrium Health infectious disease team. LCI and Atrium Health are participating in several COVID-19 clinical treatment trials, including an investigational convalescent plasma protocol spearheaded by the Mayo Clinic. They have also opened a randomized, phase 2 trial evaluating the safety and efficacy of selinexor (Xpovio), an oral drug that’s Food and Drug Administration approved for patients with multiple myeloma, for treatment of moderate or severe COVID-19 infection. Additional studies evaluating blockade of granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, as well as inhaled antiviral therapy, have recently launched, and several additional studies are poised to open in the coming weeks.
The LCI and Atrium Health team also has a supply of the antiviral agent remdesivir as part of the FDA’s expanded access protocol and emergency use authorization. They also have a supply of and experience administering the interleukin-6 receptor inhibitor tocilizumab (Actemra), which showed some suggestion of efficacy in limited experience treating patients with severe or critical COVID-19 infections. Clinicians at LCI have not used the investigational and unproven agents hydroxychloroquine, chloroquine, and azithromycin to either prevent or treat COVID-19.
LCI also instituted measures to try to minimize the risk that staff members could become infected and transmit the virus while asymptomatic. Following conversations held early on with COVID-19–experienced health authorities in China and Italy, the patient-facing LCI staff split into two teams starting on March 23 that alternated responsibility for direct patient interactions every 2 weeks. When one of these teams was off from direct patient contact they continued to care for patients remotely through virtual technologies. The concept was that, if a staffer became infected while remaining asymptomatic during their contact with patients, their status would either become diagnosable or resolve during their 2 weeks away from seeing any patients. Perhaps in part because of this approach infections among staff members “have not been a big issue. We’ve had an incredibly low infection rate among the LCI staff,” Dr. Voorhees noted.
By mid-May, with the imminent threat of a sudden CODIV-19 surge moderated, heme-onc operations at LCI began to cautiously revert to more normal operations. “We’re continuing patient screening for signs and symptoms of COVID-19 infection, testing for asymptomatic infections, and requiring masking and social distancing in the clinics and hospitals, but we’re starting to slowly restore the number of patients at our clinics [virtual and face to face[ and infusion centers,” and the staff’s division into two teams ended. “The idea was to get past a surge and make sure our system was not overwhelmed. We anticipated a local surge in late April, but then it kept getting pushed back. Current projections are for the infection rate among LCI patients to remain low provided that community spread remains stable or, ideally, decreases.” The LCI infectious disease staff is closely monitoring infection rates for early recognition of an outbreak, with plans to follow any new cases with contact tracing. So far, the COVID-19 pandemic at LCI “has been very manageable,” Dr. Voorhees concluded.
“We’re now better positioned to deal with a case surge if it were to happen. We could resume the two-team approach, hospital-wide plans are now in place for a future surge, and we are now up and running with robust testing and inpatient and outpatient virtual technology. The first time, we were all learning on the fly.”
The LCI biostatistics team has been prospectively collecting the Institutes’s COVID-19 patient data, with plans to report their findings.
Dr. Voorhees has had financial relationships with Bristol-Myers Squibb/Celgene, Janssen, Novartis, and Oncopeptides, none of which are relevant to this article.
Oncologists’ income and satisfaction are up
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.
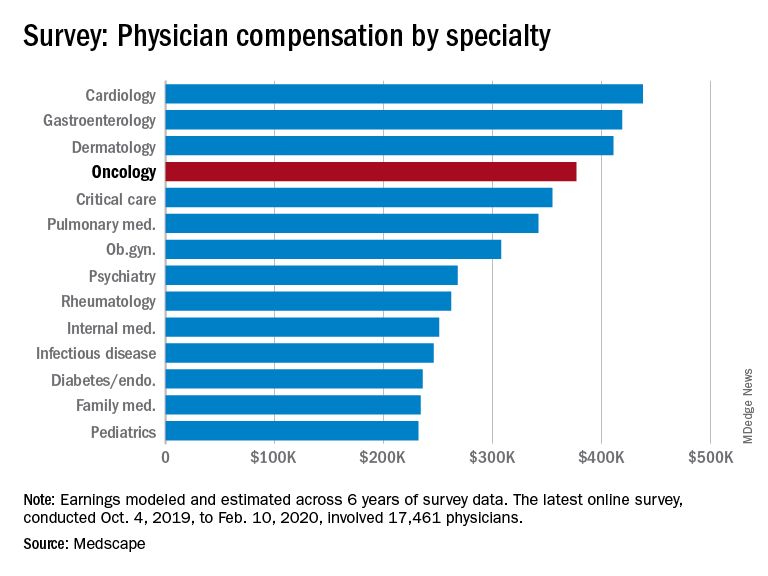
At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.

At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Oncologists continue to rank above the middle range for all specialties in annual compensation for physicians, according to findings from the newly released Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020.
The average earnings for oncologists who participated in the survey was $377,000, which was a 5% increase from the $359,000 reported for 2018.
Just over two-thirds (67%) of oncologists reported that they felt that they were fairly compensated, which is quite a jump from 53% last year.
In addition, oncologists appear to be very satisfied with their profession. Similar to last year’s findings, 84% said they would choose medicine again, and 96% said they would choose the specialty of oncology again.
Earning in top third of all specialties
The average annual earnings reported by oncologists put this specialty in eleventh place among 29 specialties. Orthopedic specialists remain at the head of the list, with estimated earnings of $511,000, followed by plastic surgeons ($479,000), otolaryngologists ($455,000), and cardiologists ($438,000), according to Medscape’s compensation report, which included responses from 17,461 physicians in over 30 specialties.

At the bottom of the estimated earnings list were public health and preventive medicine doctors and pediatricians. For both specialties, the reported annual earnings was $232,000. Family medicine specialists were only marginally higher at $234,000.
Radiologists ($427,000), gastroenterologists ($419,000), and urologists ($417,000) all reported higher earnings than oncologists, whereas neurologists, at $280,000, rheumatologists, at $262,000, and internal medicine physicians, at $251,000, earned less.
The report also found that gender disparities in income persist, with male oncologists earning 17% more than their female colleagues. The gender gap in oncology is somewhat less than that seen for all specialties combined, in which men earned 31% more than women, similar to last year’s figure of 33%.
Male oncologists reported spending 38.8 hours per week seeing patients, compared with 34.9 hours reported by female oncologists. This could be a factor contributing to the gender pay disparity. Overall, the average amount of time seeing patients was 37.9 hours per week.
Frustrations with paperwork and denied claims
Surveyed oncologists cited some of the frustrations they are facing, such as spending nearly 17 hours a week on paperwork and administrative tasks. They reported that 16% of claims are denied or have to be resubmitted. As for the most challenging part of the job, oncologists (22%), similar to physicians overall (26%), found that having so many rules and regulations takes first place, followed by working with electronic health record systems (20%), difficulties getting fair reimbursement (19%), having to work long hours (12%), and dealing with difficult patients (8%). Few oncologists were concerned about lawsuits (4%), and 4% reported that there were no challenges.
Oncologists reported that the most rewarding part of their job was gratitude/relationships with patients (31%), followed by knowing that they are making the world a better place (27%). After that, oncologists agreed with statements about being very good at what they do/finding answers/diagnoses (22%), having pride in being a doctor (9%), and making good money at a job they like (8%).
Other key findings
Other key findings from the Medscape Oncologist Compensation Report 2020 included the following:
- Regarding payment models, 80% take insurance, 41% are in fee-for-service arrangements, and 18% are in accountable care organizations (21%). Only 3% are in direct primary care, and 1% are cash-only practices or have a concierge practice.
- 65% of oncologists state that they will continue taking new and current Medicare/Medicaid patients. None said that they would not take on new Medicare/Medicaid patients, and 35% remain undecided. These numbers differed from physicians overall; 73% of all physicians surveyed said they would continue taking new/current Medicare/Medicaid patients, 6% said that will not take on new Medicare patients, and 4% said they will not take new Medicaid patients. In addition, 3% and 2% said that they would stop treating some or all of their Medicare and Medicaid patients, respectively.
- About half (51%) of oncologists use nurse practitioners, about a third (34%) use physician assistants, and 37% use neither. This was about the same as physicians overall.
- A larger percentage of oncologists (38%) expect to participate in MIPS (merit-based incentive payment system), and only 8% expect to participate in APMs (alternative payment models). This was similar to the findings for physicians overall, with more than one-third (37%) expecting to participate in MIPS and 9% planning to take part in APMs.
Impact of COVID-19 pandemic
The Medscape compensation reports also gives a glimpse of the impact the COVID-19 pandemic is having on physician compensation.
Since the beginning of the pandemic, practices have reported a 55% decrease in revenue and a 60% drop in patient volume. Physician practices and hospitals have laid off or furloughed personnel and have cut pay, and 9% of practices have closed their doors, at least for the time being.
A total of 43,000 health care workers were laid off in March, the report notes.
The findings tie in with those reported elsewhere. For example, a survey conducted by the Medical Group Management Association, which was reported by Medscape Medical News, found that 97% of physician practices have experienced negative financial effects directly or indirectly related to COVID-19.
Specialties were hard hit, especially those that rely on elective procedures, such as dermatology and cardiology. Oncology care has also been disrupted. For example, a survey conducted by the American Cancer Society Cancer Action Network found that half of the cancer patients and survivors who responded reported changes, delays, or disruptions to the care they were receiving.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
World first: Saliva test detects occult HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer
A saliva test for detecting oropharyngeal cancer caused by human papillomavirus–16 (HPV-16) has scored a world first: It detected such a cancer in an asymptomatic adult.
If the finding can be replicated in a larger cohort of healthy asymptomatic individuals, widespread screening for HPV-16 – the main driver behind skyrocketing rates of oropharyngeal cancer – could be one step closer, the researchers suggested.
“Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas often presents at a late stage with patients suffering huge morbidity as a result of treatment, [so] we must find strategies to detect these cancers earlier,” senior author Chamindie Punyadeera, PhD, Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
“This study, for the first time, provides a solid scientific foundation to initiate a screening trial in high-risk individuals to detect HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer, she added. “Saliva testing could be broadly implemented and [used] in a screening trial in the future,” she said.
The case report was published online March 31 in Frontiers in Oncology.
The saliva test was developed by Dr. Punyadeera and first author Kai Dun Tang, PhD, also from Queensland University of Technology. It is administered as an oral rinse: the individual swishes a saline solution around in his or her mouth for a minute or 2, and then spits the sample into a tube.
Prevalence Study
The saliva test was being scrutinized in an ongoing HPV-16 DNA prevalence study, which involved 650 healthy participants being tested for oral HPV-16 DNA.
“Of these, 3 have been identified to have persistent oral HPV-16 DNA infection,” the investigators reported.
After having approached these three participants, one middle-aged male who had been consistently HPV-16 DNA positive for a period of 36 months – and whose HPV-16 viral load had been steadily rising over time – was invited to attend an ear, nose, and throat clinic for assessment.
“Initial clinical examination of the oropharynx including palpation and white light revealed no significant abnormalities,” the researchers emphasized.
As Dr. Punyadeera explained, standard clinical assessment for oropharyngeal malignancy includes white light examination for masses, detection of irregularities or asymmetry of the underlying structures and palpation of the tonsil and tongue base.
Cross-sectional imaging with CT or MRI can be helpful as well, she said, but these imaging studies are unable to detect lesions smaller than a few millimeters in size.
In the case of this individual, salivary oral rinse samples had been collected at baseline, and again at 6, 12, and 36 months after study enrollment as well as 2 weeks after the patient decided to undergo a bilateral tonsillectomy.
DNA was extracted from the salivary oral rinse samples, as well as from the tonsillar tissue obtained after resection. HPV-16 DNA genotyping and viral loads were analyzed with a PCR assay.
Results from the salivary samples indicated that the patient’s HPV-16 DNA viral load had increased exponentially across the 36 months of follow-up, from 3.43 copies/50 ng at baseline to 1281.69 copies/50 ng at 36 months.
On surgery, the patient was found to have a 2 mm squamous cell carcinoma in the left tonsil, but all other oropharyngeal tissues were normal and HPV-16 DNA negative.
Two weeks after undergoing the tonsillectomy, the patient’s HPV-16 DNA viral load in the saliva samples became undetectable.
This case report demonstrates that salivary HPV can both detect smaller lesions than either clinical examination or even radiological investigation, and that the same salivary test can likely also be used to monitor treatment response, Dr. Punyadeera commented.
Long-term persistence
As researchers explained in their paper, long-term persistence of HPV-16 infection is most likely a prerequisite for the development of subsequent malignancy.
Unlike cervical cancer caused by HPV-16 infection, the natural history of HPV infection in the oropharyngeal cavity is not known.
However, clinical assessment of patients with either persistent HPV infection or microscopic carcinoma has failed to detect any identifiable abnormalities.
Thus, this is the first report of a histologically confirmed diagnosis of an asymptomatic occult oropharyngeal cancer detected by a screening test through serial measurements of HPV-16 DNA, the investigators emphasized.
The report also demonstrated that very early lesions can be eradicated with minimal morbidity. Unfortunately, most oropharyngeal cancer is currently diagnosed at much later stages, and surgical removal of these is often associated with significant disabilities including difficulties with swallowing and even communicating.
“It’s amazing to think that this man was cured of his disease with a 15-minute procedure which left him with no lasting issues at all,” Dr. Punyadeera commented. “We need to try and make this the norm, not the exception.
“So we must have a well-designed screening study using all the insights we have gained from this case. We owe it to patients to explore these findings to their fullest,” Dr. Punyadeera emphasized.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A saliva test for detecting oropharyngeal cancer caused by human papillomavirus–16 (HPV-16) has scored a world first: It detected such a cancer in an asymptomatic adult.
If the finding can be replicated in a larger cohort of healthy asymptomatic individuals, widespread screening for HPV-16 – the main driver behind skyrocketing rates of oropharyngeal cancer – could be one step closer, the researchers suggested.
“Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas often presents at a late stage with patients suffering huge morbidity as a result of treatment, [so] we must find strategies to detect these cancers earlier,” senior author Chamindie Punyadeera, PhD, Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
“This study, for the first time, provides a solid scientific foundation to initiate a screening trial in high-risk individuals to detect HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer, she added. “Saliva testing could be broadly implemented and [used] in a screening trial in the future,” she said.
The case report was published online March 31 in Frontiers in Oncology.
The saliva test was developed by Dr. Punyadeera and first author Kai Dun Tang, PhD, also from Queensland University of Technology. It is administered as an oral rinse: the individual swishes a saline solution around in his or her mouth for a minute or 2, and then spits the sample into a tube.
Prevalence Study
The saliva test was being scrutinized in an ongoing HPV-16 DNA prevalence study, which involved 650 healthy participants being tested for oral HPV-16 DNA.
“Of these, 3 have been identified to have persistent oral HPV-16 DNA infection,” the investigators reported.
After having approached these three participants, one middle-aged male who had been consistently HPV-16 DNA positive for a period of 36 months – and whose HPV-16 viral load had been steadily rising over time – was invited to attend an ear, nose, and throat clinic for assessment.
“Initial clinical examination of the oropharynx including palpation and white light revealed no significant abnormalities,” the researchers emphasized.
As Dr. Punyadeera explained, standard clinical assessment for oropharyngeal malignancy includes white light examination for masses, detection of irregularities or asymmetry of the underlying structures and palpation of the tonsil and tongue base.
Cross-sectional imaging with CT or MRI can be helpful as well, she said, but these imaging studies are unable to detect lesions smaller than a few millimeters in size.
In the case of this individual, salivary oral rinse samples had been collected at baseline, and again at 6, 12, and 36 months after study enrollment as well as 2 weeks after the patient decided to undergo a bilateral tonsillectomy.
DNA was extracted from the salivary oral rinse samples, as well as from the tonsillar tissue obtained after resection. HPV-16 DNA genotyping and viral loads were analyzed with a PCR assay.
Results from the salivary samples indicated that the patient’s HPV-16 DNA viral load had increased exponentially across the 36 months of follow-up, from 3.43 copies/50 ng at baseline to 1281.69 copies/50 ng at 36 months.
On surgery, the patient was found to have a 2 mm squamous cell carcinoma in the left tonsil, but all other oropharyngeal tissues were normal and HPV-16 DNA negative.
Two weeks after undergoing the tonsillectomy, the patient’s HPV-16 DNA viral load in the saliva samples became undetectable.
This case report demonstrates that salivary HPV can both detect smaller lesions than either clinical examination or even radiological investigation, and that the same salivary test can likely also be used to monitor treatment response, Dr. Punyadeera commented.
Long-term persistence
As researchers explained in their paper, long-term persistence of HPV-16 infection is most likely a prerequisite for the development of subsequent malignancy.
Unlike cervical cancer caused by HPV-16 infection, the natural history of HPV infection in the oropharyngeal cavity is not known.
However, clinical assessment of patients with either persistent HPV infection or microscopic carcinoma has failed to detect any identifiable abnormalities.
Thus, this is the first report of a histologically confirmed diagnosis of an asymptomatic occult oropharyngeal cancer detected by a screening test through serial measurements of HPV-16 DNA, the investigators emphasized.
The report also demonstrated that very early lesions can be eradicated with minimal morbidity. Unfortunately, most oropharyngeal cancer is currently diagnosed at much later stages, and surgical removal of these is often associated with significant disabilities including difficulties with swallowing and even communicating.
“It’s amazing to think that this man was cured of his disease with a 15-minute procedure which left him with no lasting issues at all,” Dr. Punyadeera commented. “We need to try and make this the norm, not the exception.
“So we must have a well-designed screening study using all the insights we have gained from this case. We owe it to patients to explore these findings to their fullest,” Dr. Punyadeera emphasized.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A saliva test for detecting oropharyngeal cancer caused by human papillomavirus–16 (HPV-16) has scored a world first: It detected such a cancer in an asymptomatic adult.
If the finding can be replicated in a larger cohort of healthy asymptomatic individuals, widespread screening for HPV-16 – the main driver behind skyrocketing rates of oropharyngeal cancer – could be one step closer, the researchers suggested.
“Oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinomas often presents at a late stage with patients suffering huge morbidity as a result of treatment, [so] we must find strategies to detect these cancers earlier,” senior author Chamindie Punyadeera, PhD, Queensland University of Technology in Brisbane, Australia, told Medscape Medical News in an email.
“This study, for the first time, provides a solid scientific foundation to initiate a screening trial in high-risk individuals to detect HPV-driven oropharyngeal cancer, she added. “Saliva testing could be broadly implemented and [used] in a screening trial in the future,” she said.
The case report was published online March 31 in Frontiers in Oncology.
The saliva test was developed by Dr. Punyadeera and first author Kai Dun Tang, PhD, also from Queensland University of Technology. It is administered as an oral rinse: the individual swishes a saline solution around in his or her mouth for a minute or 2, and then spits the sample into a tube.
Prevalence Study
The saliva test was being scrutinized in an ongoing HPV-16 DNA prevalence study, which involved 650 healthy participants being tested for oral HPV-16 DNA.
“Of these, 3 have been identified to have persistent oral HPV-16 DNA infection,” the investigators reported.
After having approached these three participants, one middle-aged male who had been consistently HPV-16 DNA positive for a period of 36 months – and whose HPV-16 viral load had been steadily rising over time – was invited to attend an ear, nose, and throat clinic for assessment.
“Initial clinical examination of the oropharynx including palpation and white light revealed no significant abnormalities,” the researchers emphasized.
As Dr. Punyadeera explained, standard clinical assessment for oropharyngeal malignancy includes white light examination for masses, detection of irregularities or asymmetry of the underlying structures and palpation of the tonsil and tongue base.
Cross-sectional imaging with CT or MRI can be helpful as well, she said, but these imaging studies are unable to detect lesions smaller than a few millimeters in size.
In the case of this individual, salivary oral rinse samples had been collected at baseline, and again at 6, 12, and 36 months after study enrollment as well as 2 weeks after the patient decided to undergo a bilateral tonsillectomy.
DNA was extracted from the salivary oral rinse samples, as well as from the tonsillar tissue obtained after resection. HPV-16 DNA genotyping and viral loads were analyzed with a PCR assay.
Results from the salivary samples indicated that the patient’s HPV-16 DNA viral load had increased exponentially across the 36 months of follow-up, from 3.43 copies/50 ng at baseline to 1281.69 copies/50 ng at 36 months.
On surgery, the patient was found to have a 2 mm squamous cell carcinoma in the left tonsil, but all other oropharyngeal tissues were normal and HPV-16 DNA negative.
Two weeks after undergoing the tonsillectomy, the patient’s HPV-16 DNA viral load in the saliva samples became undetectable.
This case report demonstrates that salivary HPV can both detect smaller lesions than either clinical examination or even radiological investigation, and that the same salivary test can likely also be used to monitor treatment response, Dr. Punyadeera commented.
Long-term persistence
As researchers explained in their paper, long-term persistence of HPV-16 infection is most likely a prerequisite for the development of subsequent malignancy.
Unlike cervical cancer caused by HPV-16 infection, the natural history of HPV infection in the oropharyngeal cavity is not known.
However, clinical assessment of patients with either persistent HPV infection or microscopic carcinoma has failed to detect any identifiable abnormalities.
Thus, this is the first report of a histologically confirmed diagnosis of an asymptomatic occult oropharyngeal cancer detected by a screening test through serial measurements of HPV-16 DNA, the investigators emphasized.
The report also demonstrated that very early lesions can be eradicated with minimal morbidity. Unfortunately, most oropharyngeal cancer is currently diagnosed at much later stages, and surgical removal of these is often associated with significant disabilities including difficulties with swallowing and even communicating.
“It’s amazing to think that this man was cured of his disease with a 15-minute procedure which left him with no lasting issues at all,” Dr. Punyadeera commented. “We need to try and make this the norm, not the exception.
“So we must have a well-designed screening study using all the insights we have gained from this case. We owe it to patients to explore these findings to their fullest,” Dr. Punyadeera emphasized.
The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Video coaching may relieve anxiety and distress for long-distance cancer caregivers
Anxiety and distress related to caring for a cancer patient who lives far away may be alleviated through an intervention that includes video-based coaching sessions with a nurse practitioner or social worker, a randomized study suggests.
About 20% of long-distance caregivers had a significant reduction in anxiety and 25% had a significant reduction in distress when they received video coaching sessions, attended oncologist visits via video, and had access to a website specifically designed for their needs.
Adding the caregiver to oncologist office visits made the patients feel better supported and didn’t add a significant amount of time to the encounter, said Sara L. Douglas, PhD, RN, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Taken together, these results suggest that fairly simple technologies can be leveraged to help caregivers cope with psychological strains related to supporting a patient who doesn’t live nearby, Dr. Douglas said.
Distance caregivers, defined as those who live an hour or more away from the patient, can experience high rates of distress and anxiety because they lack first-hand information or may have uncertainty about the patient’s current condition, according to Dr. Douglas and colleagues.
“Caregivers’ high rates of anxiety and distress have been found to have a negative impact not only upon their own health but upon their ability to provide high quality care to the patient,” Dr. Douglas said.
With this in mind, she and her colleagues conducted a 4-month study of distance caregivers. Dr. Douglas presented results from the study at the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program during a press briefing in advance of the meeting. This year, ASCO’s annual meeting is split into two parts. The virtual scientific program will be presented online on May 29-31, and the virtual education program will be available Aug. 8-10.
Study details
The study enrolled 441 distance caregivers of cancer patients, and Dr. Douglas presented results in 311 of those caregivers. (Data in the presentation differ from the abstract.) The caregivers were, on average, 47 years of age. Most were female (72%), white (67%), the child of the patient (63%), currently employed (81%), and new to the distance caregiver role (89%).
The caregivers were randomized to one of three study arms.
One arm received the full intervention, which consisted of four video-coaching sessions with an advanced practice nurse or social worker, videoconference office visits with the physician and patient, and access to a website with information for cancer distance caregivers. A second arm received no video coaching but had access to the website and participated in video visits with the physician and patient. The third arm, which only received access to the website, served as the study’s control group.
Results
Dr. Douglas said that the full intervention had the biggest impact on caregivers’ distress and anxiety.
Among distance caregivers who received the full intervention, 19.2% had a significant reduction in anxiety (P = .03), as measured in online surveys before and after the intervention using the PROMIS Anxiety instrument. Furthermore, 24.8% of these caregivers had a significant reduction in distress (P = .02) from preintervention to post intervention, as measured by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Distress Thermometer. Overall, distress and anxiety scores decreased in this arm.
Distance caregivers who only had physician-patient video visits and website access had a “moderate” reduction in distress and anxiety, Dr. Douglas said. Among these caregivers, 17.3% had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 19.8% had an improvement in distress. Overall, distress scores decreased, but anxiety scores increased slightly in this arm.
In the control arm, 13.1% of caregivers had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 18% had an improvement in distress. Overall, both anxiety and distress scores increased in this arm.
“While the full intervention yielded the best results for distance caregivers, we recognize that not all health care systems have the resources to provide individualized coaching sessions to distance caregivers,” Dr. Douglas said. “Therefore, it is worth noting that videoconference office visits alone are found to be of some benefit in improving distress and anxiety in this group of cancer caregivers.”
The study results suggest videoconferencing interventions can improve the emotional well-being of remote caregivers who provide “critical support” for cancer patients, said ASCO President Howard A. “Skip” Burris III, MD.
“As COVID-19 forces separation from loved ones and increases anxiety for people with cancer and their caregivers, providing emotional support virtually is more important than ever,” Dr. Burris said in a news release highlighting the study.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Dr. Douglas reported having no disclosures. Other researchers involved in the study disclosed relationships with BridgeBio Pharma, Cardinal Health, Apexigen, Roche/Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Tesaro, Array BioPharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Celgene. A full list of Dr. Burris’s financial disclosures is available on the ASCO website.
SOURCE: Douglas SL et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 12123.
Anxiety and distress related to caring for a cancer patient who lives far away may be alleviated through an intervention that includes video-based coaching sessions with a nurse practitioner or social worker, a randomized study suggests.
About 20% of long-distance caregivers had a significant reduction in anxiety and 25% had a significant reduction in distress when they received video coaching sessions, attended oncologist visits via video, and had access to a website specifically designed for their needs.
Adding the caregiver to oncologist office visits made the patients feel better supported and didn’t add a significant amount of time to the encounter, said Sara L. Douglas, PhD, RN, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Taken together, these results suggest that fairly simple technologies can be leveraged to help caregivers cope with psychological strains related to supporting a patient who doesn’t live nearby, Dr. Douglas said.
Distance caregivers, defined as those who live an hour or more away from the patient, can experience high rates of distress and anxiety because they lack first-hand information or may have uncertainty about the patient’s current condition, according to Dr. Douglas and colleagues.
“Caregivers’ high rates of anxiety and distress have been found to have a negative impact not only upon their own health but upon their ability to provide high quality care to the patient,” Dr. Douglas said.
With this in mind, she and her colleagues conducted a 4-month study of distance caregivers. Dr. Douglas presented results from the study at the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program during a press briefing in advance of the meeting. This year, ASCO’s annual meeting is split into two parts. The virtual scientific program will be presented online on May 29-31, and the virtual education program will be available Aug. 8-10.
Study details
The study enrolled 441 distance caregivers of cancer patients, and Dr. Douglas presented results in 311 of those caregivers. (Data in the presentation differ from the abstract.) The caregivers were, on average, 47 years of age. Most were female (72%), white (67%), the child of the patient (63%), currently employed (81%), and new to the distance caregiver role (89%).
The caregivers were randomized to one of three study arms.
One arm received the full intervention, which consisted of four video-coaching sessions with an advanced practice nurse or social worker, videoconference office visits with the physician and patient, and access to a website with information for cancer distance caregivers. A second arm received no video coaching but had access to the website and participated in video visits with the physician and patient. The third arm, which only received access to the website, served as the study’s control group.
Results
Dr. Douglas said that the full intervention had the biggest impact on caregivers’ distress and anxiety.
Among distance caregivers who received the full intervention, 19.2% had a significant reduction in anxiety (P = .03), as measured in online surveys before and after the intervention using the PROMIS Anxiety instrument. Furthermore, 24.8% of these caregivers had a significant reduction in distress (P = .02) from preintervention to post intervention, as measured by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Distress Thermometer. Overall, distress and anxiety scores decreased in this arm.
Distance caregivers who only had physician-patient video visits and website access had a “moderate” reduction in distress and anxiety, Dr. Douglas said. Among these caregivers, 17.3% had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 19.8% had an improvement in distress. Overall, distress scores decreased, but anxiety scores increased slightly in this arm.
In the control arm, 13.1% of caregivers had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 18% had an improvement in distress. Overall, both anxiety and distress scores increased in this arm.
“While the full intervention yielded the best results for distance caregivers, we recognize that not all health care systems have the resources to provide individualized coaching sessions to distance caregivers,” Dr. Douglas said. “Therefore, it is worth noting that videoconference office visits alone are found to be of some benefit in improving distress and anxiety in this group of cancer caregivers.”
The study results suggest videoconferencing interventions can improve the emotional well-being of remote caregivers who provide “critical support” for cancer patients, said ASCO President Howard A. “Skip” Burris III, MD.
“As COVID-19 forces separation from loved ones and increases anxiety for people with cancer and their caregivers, providing emotional support virtually is more important than ever,” Dr. Burris said in a news release highlighting the study.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Dr. Douglas reported having no disclosures. Other researchers involved in the study disclosed relationships with BridgeBio Pharma, Cardinal Health, Apexigen, Roche/Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Tesaro, Array BioPharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Celgene. A full list of Dr. Burris’s financial disclosures is available on the ASCO website.
SOURCE: Douglas SL et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 12123.
Anxiety and distress related to caring for a cancer patient who lives far away may be alleviated through an intervention that includes video-based coaching sessions with a nurse practitioner or social worker, a randomized study suggests.
About 20% of long-distance caregivers had a significant reduction in anxiety and 25% had a significant reduction in distress when they received video coaching sessions, attended oncologist visits via video, and had access to a website specifically designed for their needs.
Adding the caregiver to oncologist office visits made the patients feel better supported and didn’t add a significant amount of time to the encounter, said Sara L. Douglas, PhD, RN, of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Taken together, these results suggest that fairly simple technologies can be leveraged to help caregivers cope with psychological strains related to supporting a patient who doesn’t live nearby, Dr. Douglas said.
Distance caregivers, defined as those who live an hour or more away from the patient, can experience high rates of distress and anxiety because they lack first-hand information or may have uncertainty about the patient’s current condition, according to Dr. Douglas and colleagues.
“Caregivers’ high rates of anxiety and distress have been found to have a negative impact not only upon their own health but upon their ability to provide high quality care to the patient,” Dr. Douglas said.
With this in mind, she and her colleagues conducted a 4-month study of distance caregivers. Dr. Douglas presented results from the study at the American Society of Clinical Oncology virtual scientific program during a press briefing in advance of the meeting. This year, ASCO’s annual meeting is split into two parts. The virtual scientific program will be presented online on May 29-31, and the virtual education program will be available Aug. 8-10.
Study details
The study enrolled 441 distance caregivers of cancer patients, and Dr. Douglas presented results in 311 of those caregivers. (Data in the presentation differ from the abstract.) The caregivers were, on average, 47 years of age. Most were female (72%), white (67%), the child of the patient (63%), currently employed (81%), and new to the distance caregiver role (89%).
The caregivers were randomized to one of three study arms.
One arm received the full intervention, which consisted of four video-coaching sessions with an advanced practice nurse or social worker, videoconference office visits with the physician and patient, and access to a website with information for cancer distance caregivers. A second arm received no video coaching but had access to the website and participated in video visits with the physician and patient. The third arm, which only received access to the website, served as the study’s control group.
Results
Dr. Douglas said that the full intervention had the biggest impact on caregivers’ distress and anxiety.
Among distance caregivers who received the full intervention, 19.2% had a significant reduction in anxiety (P = .03), as measured in online surveys before and after the intervention using the PROMIS Anxiety instrument. Furthermore, 24.8% of these caregivers had a significant reduction in distress (P = .02) from preintervention to post intervention, as measured by the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Distress Thermometer. Overall, distress and anxiety scores decreased in this arm.
Distance caregivers who only had physician-patient video visits and website access had a “moderate” reduction in distress and anxiety, Dr. Douglas said. Among these caregivers, 17.3% had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 19.8% had an improvement in distress. Overall, distress scores decreased, but anxiety scores increased slightly in this arm.
In the control arm, 13.1% of caregivers had an improvement in anxiety from baseline, and 18% had an improvement in distress. Overall, both anxiety and distress scores increased in this arm.
“While the full intervention yielded the best results for distance caregivers, we recognize that not all health care systems have the resources to provide individualized coaching sessions to distance caregivers,” Dr. Douglas said. “Therefore, it is worth noting that videoconference office visits alone are found to be of some benefit in improving distress and anxiety in this group of cancer caregivers.”
The study results suggest videoconferencing interventions can improve the emotional well-being of remote caregivers who provide “critical support” for cancer patients, said ASCO President Howard A. “Skip” Burris III, MD.
“As COVID-19 forces separation from loved ones and increases anxiety for people with cancer and their caregivers, providing emotional support virtually is more important than ever,” Dr. Burris said in a news release highlighting the study.
This study was funded by the National Institutes of Health and Case Comprehensive Cancer Center. Dr. Douglas reported having no disclosures. Other researchers involved in the study disclosed relationships with BridgeBio Pharma, Cardinal Health, Apexigen, Roche/Genentech, Seattle Genetics, Tesaro, Array BioPharma, Abbvie, Bristol-Myers Squibb, and Celgene. A full list of Dr. Burris’s financial disclosures is available on the ASCO website.
SOURCE: Douglas SL et al. ASCO 2020, Abstract 12123.
FROM ASCO 2020
ASCO goes ahead online, as conference center is used as hospital
Traditionally at this time of year, everyone working in cancer turns their attention toward Chicago, and 40,000 or so travel to the city for the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Not this year.
The McCormick Place convention center has been converted to a field hospital to cope with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The cavernous meeting halls have been filled with makeshift wards with 750 acute care beds, as shown in a tweet from Toni Choueiri, MD, chief of genitourinary oncology at the Dana Farber Cancer Center in Boston.
But the annual meeting is still going ahead, having been transferred online.
“We have to remember that even though there’s a pandemic going on and people are dying every day from coronavirus, people are still dying every day from cancer,” Richard Schilsky, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at ASCO, told Medscape Medical News.
“This pandemic will end, but cancer will continue, and we need to be able to continue to get the most cutting edge scientific results out there to our members and our constituents so they can act on those results on behalf of their patients,” he said.
The ASCO Virtual Scientific Program will take place over the weekend of May 30-31.
“We’re certainly hoping that we’re going to deliver a program that features all of the most important science that would have been presented in person in Chicago,” Schilsky commented in an interview.
Most of the presentations will be prerecorded and then streamed, which “we hope will mitigate any of the technical glitches that could come from trying to do a live broadcast of the meeting,” he said.
There will be 250 oral and 2500 poster presentations in 24 disease-based and specialty tracks.
The majority of the abstracts will be released online on May 13. The majority of the on-demand content will be released on May 29. Some of the abstracts will be highlighted at ASCO press briefings and released on those two dates.
But some of the material will be made available only on the weekend of the meeting. The opening session, plenaries featuring late-breaking abstracts, special highlights sessions, and other clinical science symposia will be broadcast on Saturday, May 30, and Sunday, May 31 (the schedule for the weekend program is available on the ASCO meeting website).
Among the plenary presentations are some clinical results that are likely to change practice immediately, Schilsky predicted. These include data to be presented in the following abstracts:
- Abstract LBA4 on the KEYNOTE-177 study comparing immunotherapy using pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck & Co) with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors show microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency;
- Abstract LBA5 on the ADAURA study exploring osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca) as adjuvant therapy after complete tumor reseaction in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer whose tumors are EGFR mutation positive;
- Abstract LBA1 on the JAVELIN Bladder 100 study exploring maintenance avelumab (Bavencio, Merck and Pfizer) with best supportive care after platinum-based first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma.
However, some of the material that would have been part of the annual meeting, which includes mostly educational sessions and invited talks, has been moved to another event, the ASCO Educational Program, to be held in August 2020.
“So I suppose, in the grand scheme of things, the meeting is going to be compressed a little bit,” Schilsky commented. “Obviously, we can’t deliver all the interactions that happen in the hallways and everywhere else at the meeting that really gives so much energy to the meeting, but, at this moment in our history, probably getting the science out there is what’s most important.”
Virtual exhibition hall
There will also be a virtual exhibition hall, which will open on May 29.
“Just as there is a typical exhibit hall in the convention center,” Schilsky commented, most of the companies that were planning to be in Chicago have “now transitioned to creating a virtual booth that people who are participating in the virtual meeting can visit.
“I don’t know exactly how each company is going to use their time and their virtual space, and that’s part of the whole learning process here to see how this whole experiment is going to work out,” he added.
Unlike some of the other conferences that have gone virtual, in which access has been made available to everyone for free, registration is still required for the ASCO meeting. But the society notes that the registration fee has been discounted for nonmembers and has been waived for ASCO members. Also, the fee covers both the Virtual Scientific Program in May and the ASCO Educational Program in August.
Registrants will have access to video and slide presentations, as well as discussant commentaries, for 180 days.
The article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Traditionally at this time of year, everyone working in cancer turns their attention toward Chicago, and 40,000 or so travel to the city for the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Not this year.
The McCormick Place convention center has been converted to a field hospital to cope with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The cavernous meeting halls have been filled with makeshift wards with 750 acute care beds, as shown in a tweet from Toni Choueiri, MD, chief of genitourinary oncology at the Dana Farber Cancer Center in Boston.
But the annual meeting is still going ahead, having been transferred online.
“We have to remember that even though there’s a pandemic going on and people are dying every day from coronavirus, people are still dying every day from cancer,” Richard Schilsky, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at ASCO, told Medscape Medical News.
“This pandemic will end, but cancer will continue, and we need to be able to continue to get the most cutting edge scientific results out there to our members and our constituents so they can act on those results on behalf of their patients,” he said.
The ASCO Virtual Scientific Program will take place over the weekend of May 30-31.
“We’re certainly hoping that we’re going to deliver a program that features all of the most important science that would have been presented in person in Chicago,” Schilsky commented in an interview.
Most of the presentations will be prerecorded and then streamed, which “we hope will mitigate any of the technical glitches that could come from trying to do a live broadcast of the meeting,” he said.
There will be 250 oral and 2500 poster presentations in 24 disease-based and specialty tracks.
The majority of the abstracts will be released online on May 13. The majority of the on-demand content will be released on May 29. Some of the abstracts will be highlighted at ASCO press briefings and released on those two dates.
But some of the material will be made available only on the weekend of the meeting. The opening session, plenaries featuring late-breaking abstracts, special highlights sessions, and other clinical science symposia will be broadcast on Saturday, May 30, and Sunday, May 31 (the schedule for the weekend program is available on the ASCO meeting website).
Among the plenary presentations are some clinical results that are likely to change practice immediately, Schilsky predicted. These include data to be presented in the following abstracts:
- Abstract LBA4 on the KEYNOTE-177 study comparing immunotherapy using pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck & Co) with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors show microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency;
- Abstract LBA5 on the ADAURA study exploring osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca) as adjuvant therapy after complete tumor reseaction in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer whose tumors are EGFR mutation positive;
- Abstract LBA1 on the JAVELIN Bladder 100 study exploring maintenance avelumab (Bavencio, Merck and Pfizer) with best supportive care after platinum-based first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma.
However, some of the material that would have been part of the annual meeting, which includes mostly educational sessions and invited talks, has been moved to another event, the ASCO Educational Program, to be held in August 2020.
“So I suppose, in the grand scheme of things, the meeting is going to be compressed a little bit,” Schilsky commented. “Obviously, we can’t deliver all the interactions that happen in the hallways and everywhere else at the meeting that really gives so much energy to the meeting, but, at this moment in our history, probably getting the science out there is what’s most important.”
Virtual exhibition hall
There will also be a virtual exhibition hall, which will open on May 29.
“Just as there is a typical exhibit hall in the convention center,” Schilsky commented, most of the companies that were planning to be in Chicago have “now transitioned to creating a virtual booth that people who are participating in the virtual meeting can visit.
“I don’t know exactly how each company is going to use their time and their virtual space, and that’s part of the whole learning process here to see how this whole experiment is going to work out,” he added.
Unlike some of the other conferences that have gone virtual, in which access has been made available to everyone for free, registration is still required for the ASCO meeting. But the society notes that the registration fee has been discounted for nonmembers and has been waived for ASCO members. Also, the fee covers both the Virtual Scientific Program in May and the ASCO Educational Program in August.
Registrants will have access to video and slide presentations, as well as discussant commentaries, for 180 days.
The article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Traditionally at this time of year, everyone working in cancer turns their attention toward Chicago, and 40,000 or so travel to the city for the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO).
Not this year.
The McCormick Place convention center has been converted to a field hospital to cope with the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic. The cavernous meeting halls have been filled with makeshift wards with 750 acute care beds, as shown in a tweet from Toni Choueiri, MD, chief of genitourinary oncology at the Dana Farber Cancer Center in Boston.
But the annual meeting is still going ahead, having been transferred online.
“We have to remember that even though there’s a pandemic going on and people are dying every day from coronavirus, people are still dying every day from cancer,” Richard Schilsky, MD, PhD, chief medical officer at ASCO, told Medscape Medical News.
“This pandemic will end, but cancer will continue, and we need to be able to continue to get the most cutting edge scientific results out there to our members and our constituents so they can act on those results on behalf of their patients,” he said.
The ASCO Virtual Scientific Program will take place over the weekend of May 30-31.
“We’re certainly hoping that we’re going to deliver a program that features all of the most important science that would have been presented in person in Chicago,” Schilsky commented in an interview.
Most of the presentations will be prerecorded and then streamed, which “we hope will mitigate any of the technical glitches that could come from trying to do a live broadcast of the meeting,” he said.
There will be 250 oral and 2500 poster presentations in 24 disease-based and specialty tracks.
The majority of the abstracts will be released online on May 13. The majority of the on-demand content will be released on May 29. Some of the abstracts will be highlighted at ASCO press briefings and released on those two dates.
But some of the material will be made available only on the weekend of the meeting. The opening session, plenaries featuring late-breaking abstracts, special highlights sessions, and other clinical science symposia will be broadcast on Saturday, May 30, and Sunday, May 31 (the schedule for the weekend program is available on the ASCO meeting website).
Among the plenary presentations are some clinical results that are likely to change practice immediately, Schilsky predicted. These include data to be presented in the following abstracts:
- Abstract LBA4 on the KEYNOTE-177 study comparing immunotherapy using pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck & Co) with chemotherapy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer whose tumors show microsatellite instability or mismatch repair deficiency;
- Abstract LBA5 on the ADAURA study exploring osimertinib (Tagrisso, AstraZeneca) as adjuvant therapy after complete tumor reseaction in patients with early-stage non–small cell lung cancer whose tumors are EGFR mutation positive;
- Abstract LBA1 on the JAVELIN Bladder 100 study exploring maintenance avelumab (Bavencio, Merck and Pfizer) with best supportive care after platinum-based first-line chemotherapy in patients with advanced urothelial carcinoma.
However, some of the material that would have been part of the annual meeting, which includes mostly educational sessions and invited talks, has been moved to another event, the ASCO Educational Program, to be held in August 2020.
“So I suppose, in the grand scheme of things, the meeting is going to be compressed a little bit,” Schilsky commented. “Obviously, we can’t deliver all the interactions that happen in the hallways and everywhere else at the meeting that really gives so much energy to the meeting, but, at this moment in our history, probably getting the science out there is what’s most important.”
Virtual exhibition hall
There will also be a virtual exhibition hall, which will open on May 29.
“Just as there is a typical exhibit hall in the convention center,” Schilsky commented, most of the companies that were planning to be in Chicago have “now transitioned to creating a virtual booth that people who are participating in the virtual meeting can visit.
“I don’t know exactly how each company is going to use their time and their virtual space, and that’s part of the whole learning process here to see how this whole experiment is going to work out,” he added.
Unlike some of the other conferences that have gone virtual, in which access has been made available to everyone for free, registration is still required for the ASCO meeting. But the society notes that the registration fee has been discounted for nonmembers and has been waived for ASCO members. Also, the fee covers both the Virtual Scientific Program in May and the ASCO Educational Program in August.
Registrants will have access to video and slide presentations, as well as discussant commentaries, for 180 days.
The article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves selpercatinib for lung and thyroid RET tumors
Selpercatinib (Retevmo) becomes the first targeted therapy to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with cancer who have certain tumors that have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in the RET gene.
The drug is indicated for use in RET-positive tumors found in the following:
- Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread in adult patients
- Advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) who require systemic therapy
- Thyroid cancer that requires systemic therapy and that has stopped responding to or is not appropriate for radioactive iodine therapy in adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients.
Before initiating treatment, a RET gene alteration must be determined via laboratory testing, the FDA emphasized. However, no FDA-approved test is currently available for detecting RET fusions/mutations.
Approval based on responses in open-label trial
This was an accelerated approval based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) seen in an open-label clinical trial (the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 study), which involved patients with each of the three types of tumors.
All patients received selpercatinib 160 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
For this trial, identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in plasma or tumor tissue by local laboratories using next-generation sequencing, polymerase chain reaction testing, or fluorescence in situ hybridization, according to Eli Lilly, the company marketing selpercatinib. Immunohistochemistry was not used in the clinical trial.
Efficacy for NSCLC was evaluated in 105 adult patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy. The ORR was 64%.
Efficacy was also evaluated in 39 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had not received any previous treatment. The ORR for these patients was 84%.
For both groups, among patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted more than 6 months.
“In the clinical trial, we observed that the majority of metastatic lung cancer patients experienced clinically meaningful responses when treated with selpercatinib, including responses in difficult-to-treat brain metastases,” LIBRETTO-001 lead investigator Alexander Drilon, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, N.Y., said in an Eli Lilly press release.
“The approval of selpercatinib marks an important milestone in the treatment of NSCLC, making RET-driven cancers now specifically targetable in the same manner as cancers with activating EGFR and ALK alterations, across all lines of therapy,” Dr. Drilon added.
About 1% to 2% of NSCLC tumors are thought to have a RET alteration.
The same trial also included patients with thyroid cancer.
Efficacy for MTC was evaluated in 55 adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had previously been treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib, or both. The ORR in these patients was 69%.
In addition, selpercatinib was evaluated in 88 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib. The ORR for these patients was 73%.
The trial also enrolled 19 patients with RET-positive thyroid cancer whose condition was refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment and who had received another prior systemic treatment. The ORR was 79%. Eight patients had received only RAI. The ORR for these patients was 100%.
In all the cases of thyroid cancer and lung cancer, among the patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted longer than 6 months.
“RET alterations account for the majority of medullary thyroid cancers and a meaningful percentage of other thyroid cancers,” Lori J. Wirth, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, noted in the company release.
A fact sheet from Eli Lilly notes that RET mutations are found in about 60% of sporadic MTC cases and in over 90% of familial MTC cases, and that RET fusions are found in approximately 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid cancers.
“For patients living with these cancers, the approval of selpercatinib means they now have a treatment option that selectively and potently inhibits RET,” Dr. Wirth commented. “Based on the published data for this new medicine, as well as my personal experience treating patients, this may be a good treatment option.”
In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, the rate of discontinuations because of adverse reactions (ARs) was 5%, the company reported. The most common ARs, including laboratory abnormalities (≥25%), were increased aspartate aminotransferase level, increased alanine aminotransferase level, increased glucose level, decreased leukocyte count, decreased albumin level, decreased calcium level, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine level, increased alkaline phosphatase level, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelet count, increased total cholesterol level, rash, decreased sodium levels, and constipation. The most frequent serious AR (≥2%) was pneumonia.
The FDA warned that selpercatinib can cause hepatotoxicity, elevation in blood pressure, QT prolongation, bleeding, and allergic reactions. It may also be toxic to a fetus or newborn baby so should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Selpercatinib is currently being assessed in two phase 3 confirmatory trials. LIBRETTO-431 will test the drug in previously untreated patients with RET-positive NSCLC. LIBRETTO-531 involves treatment-naive patients with RET-positive MTC.
The company that developed selpercaptinib, Loxo Oncology, was acquired by Eli Lilly last year in an $8 billion takeover. This drug was billed as the most promising asset in that deal, alongside oral BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, according to a report in Pharmaphorum.
Loxo developed Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), the first TRK inhibitor to reach the market, as well as the follow-up drug LOXO-195. Both were acquired by Bayer ahead of the Lilly takeover, that report notes.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Selpercatinib (Retevmo) becomes the first targeted therapy to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with cancer who have certain tumors that have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in the RET gene.
The drug is indicated for use in RET-positive tumors found in the following:
- Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread in adult patients
- Advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) who require systemic therapy
- Thyroid cancer that requires systemic therapy and that has stopped responding to or is not appropriate for radioactive iodine therapy in adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients.
Before initiating treatment, a RET gene alteration must be determined via laboratory testing, the FDA emphasized. However, no FDA-approved test is currently available for detecting RET fusions/mutations.
Approval based on responses in open-label trial
This was an accelerated approval based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) seen in an open-label clinical trial (the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 study), which involved patients with each of the three types of tumors.
All patients received selpercatinib 160 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
For this trial, identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in plasma or tumor tissue by local laboratories using next-generation sequencing, polymerase chain reaction testing, or fluorescence in situ hybridization, according to Eli Lilly, the company marketing selpercatinib. Immunohistochemistry was not used in the clinical trial.
Efficacy for NSCLC was evaluated in 105 adult patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy. The ORR was 64%.
Efficacy was also evaluated in 39 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had not received any previous treatment. The ORR for these patients was 84%.
For both groups, among patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted more than 6 months.
“In the clinical trial, we observed that the majority of metastatic lung cancer patients experienced clinically meaningful responses when treated with selpercatinib, including responses in difficult-to-treat brain metastases,” LIBRETTO-001 lead investigator Alexander Drilon, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, N.Y., said in an Eli Lilly press release.
“The approval of selpercatinib marks an important milestone in the treatment of NSCLC, making RET-driven cancers now specifically targetable in the same manner as cancers with activating EGFR and ALK alterations, across all lines of therapy,” Dr. Drilon added.
About 1% to 2% of NSCLC tumors are thought to have a RET alteration.
The same trial also included patients with thyroid cancer.
Efficacy for MTC was evaluated in 55 adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had previously been treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib, or both. The ORR in these patients was 69%.
In addition, selpercatinib was evaluated in 88 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib. The ORR for these patients was 73%.
The trial also enrolled 19 patients with RET-positive thyroid cancer whose condition was refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment and who had received another prior systemic treatment. The ORR was 79%. Eight patients had received only RAI. The ORR for these patients was 100%.
In all the cases of thyroid cancer and lung cancer, among the patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted longer than 6 months.
“RET alterations account for the majority of medullary thyroid cancers and a meaningful percentage of other thyroid cancers,” Lori J. Wirth, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, noted in the company release.
A fact sheet from Eli Lilly notes that RET mutations are found in about 60% of sporadic MTC cases and in over 90% of familial MTC cases, and that RET fusions are found in approximately 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid cancers.
“For patients living with these cancers, the approval of selpercatinib means they now have a treatment option that selectively and potently inhibits RET,” Dr. Wirth commented. “Based on the published data for this new medicine, as well as my personal experience treating patients, this may be a good treatment option.”
In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, the rate of discontinuations because of adverse reactions (ARs) was 5%, the company reported. The most common ARs, including laboratory abnormalities (≥25%), were increased aspartate aminotransferase level, increased alanine aminotransferase level, increased glucose level, decreased leukocyte count, decreased albumin level, decreased calcium level, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine level, increased alkaline phosphatase level, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelet count, increased total cholesterol level, rash, decreased sodium levels, and constipation. The most frequent serious AR (≥2%) was pneumonia.
The FDA warned that selpercatinib can cause hepatotoxicity, elevation in blood pressure, QT prolongation, bleeding, and allergic reactions. It may also be toxic to a fetus or newborn baby so should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Selpercatinib is currently being assessed in two phase 3 confirmatory trials. LIBRETTO-431 will test the drug in previously untreated patients with RET-positive NSCLC. LIBRETTO-531 involves treatment-naive patients with RET-positive MTC.
The company that developed selpercaptinib, Loxo Oncology, was acquired by Eli Lilly last year in an $8 billion takeover. This drug was billed as the most promising asset in that deal, alongside oral BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, according to a report in Pharmaphorum.
Loxo developed Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), the first TRK inhibitor to reach the market, as well as the follow-up drug LOXO-195. Both were acquired by Bayer ahead of the Lilly takeover, that report notes.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Selpercatinib (Retevmo) becomes the first targeted therapy to be approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for use in patients with cancer who have certain tumors that have an alteration (mutation or fusion) in the RET gene.
The drug is indicated for use in RET-positive tumors found in the following:
- Non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread in adult patients
- Advanced medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) or MTC that has spread in adult and pediatric patients (older than 12 years) who require systemic therapy
- Thyroid cancer that requires systemic therapy and that has stopped responding to or is not appropriate for radioactive iodine therapy in adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients.
Before initiating treatment, a RET gene alteration must be determined via laboratory testing, the FDA emphasized. However, no FDA-approved test is currently available for detecting RET fusions/mutations.
Approval based on responses in open-label trial
This was an accelerated approval based on the overall response rate (ORR) and duration of response (DOR) seen in an open-label clinical trial (the phase 1/2 LIBRETTO-001 study), which involved patients with each of the three types of tumors.
All patients received selpercatinib 160 mg orally twice daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity occurred.
For this trial, identification of a RET gene alteration was prospectively determined in plasma or tumor tissue by local laboratories using next-generation sequencing, polymerase chain reaction testing, or fluorescence in situ hybridization, according to Eli Lilly, the company marketing selpercatinib. Immunohistochemistry was not used in the clinical trial.
Efficacy for NSCLC was evaluated in 105 adult patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who were previously treated with platinum chemotherapy. The ORR was 64%.
Efficacy was also evaluated in 39 patients with RET fusion-positive NSCLC who had not received any previous treatment. The ORR for these patients was 84%.
For both groups, among patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted more than 6 months.
“In the clinical trial, we observed that the majority of metastatic lung cancer patients experienced clinically meaningful responses when treated with selpercatinib, including responses in difficult-to-treat brain metastases,” LIBRETTO-001 lead investigator Alexander Drilon, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center in New York, N.Y., said in an Eli Lilly press release.
“The approval of selpercatinib marks an important milestone in the treatment of NSCLC, making RET-driven cancers now specifically targetable in the same manner as cancers with activating EGFR and ALK alterations, across all lines of therapy,” Dr. Drilon added.
About 1% to 2% of NSCLC tumors are thought to have a RET alteration.
The same trial also included patients with thyroid cancer.
Efficacy for MTC was evaluated in 55 adult and pediatric (older than 12 years) patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had previously been treated with cabozantinib, vandetanib, or both. The ORR in these patients was 69%.
In addition, selpercatinib was evaluated in 88 patients with advanced or metastatic RET-mutant MTC who had not received prior treatment with cabozantinib or vandetanib. The ORR for these patients was 73%.
The trial also enrolled 19 patients with RET-positive thyroid cancer whose condition was refractory to radioactive iodine (RAI) treatment and who had received another prior systemic treatment. The ORR was 79%. Eight patients had received only RAI. The ORR for these patients was 100%.
In all the cases of thyroid cancer and lung cancer, among the patients who responded to treatment, the response lasted longer than 6 months.
“RET alterations account for the majority of medullary thyroid cancers and a meaningful percentage of other thyroid cancers,” Lori J. Wirth, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital Cancer Center in Boston, noted in the company release.
A fact sheet from Eli Lilly notes that RET mutations are found in about 60% of sporadic MTC cases and in over 90% of familial MTC cases, and that RET fusions are found in approximately 10% to 20% of papillary thyroid cancers.
“For patients living with these cancers, the approval of selpercatinib means they now have a treatment option that selectively and potently inhibits RET,” Dr. Wirth commented. “Based on the published data for this new medicine, as well as my personal experience treating patients, this may be a good treatment option.”
In the LIBRETTO-001 trial, the rate of discontinuations because of adverse reactions (ARs) was 5%, the company reported. The most common ARs, including laboratory abnormalities (≥25%), were increased aspartate aminotransferase level, increased alanine aminotransferase level, increased glucose level, decreased leukocyte count, decreased albumin level, decreased calcium level, dry mouth, diarrhea, increased creatinine level, increased alkaline phosphatase level, hypertension, fatigue, edema, decreased platelet count, increased total cholesterol level, rash, decreased sodium levels, and constipation. The most frequent serious AR (≥2%) was pneumonia.
The FDA warned that selpercatinib can cause hepatotoxicity, elevation in blood pressure, QT prolongation, bleeding, and allergic reactions. It may also be toxic to a fetus or newborn baby so should not be taken by pregnant or breastfeeding women.
Selpercatinib is currently being assessed in two phase 3 confirmatory trials. LIBRETTO-431 will test the drug in previously untreated patients with RET-positive NSCLC. LIBRETTO-531 involves treatment-naive patients with RET-positive MTC.
The company that developed selpercaptinib, Loxo Oncology, was acquired by Eli Lilly last year in an $8 billion takeover. This drug was billed as the most promising asset in that deal, alongside oral BTK inhibitor LOXO-305, according to a report in Pharmaphorum.
Loxo developed Vitrakvi (larotrectinib), the first TRK inhibitor to reach the market, as well as the follow-up drug LOXO-195. Both were acquired by Bayer ahead of the Lilly takeover, that report notes.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 death rate was twice as high in cancer patients in NYC study
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
COVID-19 patients with cancer had double the fatality rate of COVID-19 patients without cancer treated in an urban New York hospital system, according to data from a retrospective study.
with COVID-19 treated during the same time period in the same hospital system.
Vikas Mehta, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center, New York, and colleagues reported these results in Cancer Discovery.
“As New York has emerged as the current epicenter of the pandemic, we sought to investigate the risk posed by COVID-19 to our cancer population,” the authors wrote.
They identified 218 cancer patients treated for COVID-19 in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020. Three-quarters of patients had solid tumors, and 25% had hematologic malignancies. Most patients were adults (98.6%), their median age was 69 years (range, 10-92 years), and 58% were men.
In all, 28% of the cancer patients (61/218) died from COVID-19, including 25% (41/164) of those with solid tumors and 37% (20/54) of those with hematologic malignancies.
Deaths by cancer type
Among the 164 patients with solid tumors, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Pancreatic – 67% (2/3)
- Lung – 55% (6/11)
- Colorectal – 38% (8/21)
- Upper gastrointestinal – 38% (3/8)
- Gynecologic – 38% (5/13)
- Skin – 33% (1/3)
- Hepatobiliary – 29% (2/7)
- Bone/soft tissue – 20% (1/5)
- Genitourinary – 15% (7/46)
- Breast – 14% (4/28)
- Neurologic – 13% (1/8)
- Head and neck – 13% (1/8).
None of the three patients with neuroendocrine tumors died.
Among the 54 patients with hematologic malignancies, case fatality rates were as follows:
- Chronic myeloid leukemia – 100% (1/1)
- Hodgkin lymphoma – 60% (3/5)
- Myelodysplastic syndromes – 60% (3/5)
- Multiple myeloma – 38% (5/13)
- Non-Hodgkin lymphoma – 33% (5/15)
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia – 33% (1/3)
- Myeloproliferative neoplasms – 29% (2/7).
None of the four patients with acute lymphoblastic leukemia died, and there was one patient with acute myeloid leukemia who did not die.
Factors associated with increased mortality
The researchers compared the 218 cancer patients with COVID-19 with 1,090 age- and sex-matched noncancer patients with COVID-19 treated in the Montefiore Health System between March 18 and April 8, 2020.
Case fatality rates in cancer patients with COVID-19 were significantly increased in all age groups, but older age was associated with higher mortality.
“We observed case fatality rates were elevated in all age cohorts in cancer patients and achieved statistical significance in the age groups 45-64 and in patients older than 75 years of age,” the authors reported.
Other factors significantly associated with higher mortality in a multivariable analysis included the presence of multiple comorbidities; the need for ICU support; and increased levels of d-dimer, lactate, and lactate dehydrogenase.
Additional factors, such as socioeconomic and health disparities, may also be significant predictors of mortality, according to the authors. They noted that this cohort largely consisted of patients from a socioeconomically underprivileged community where mortality because of COVID-19 is reportedly higher.
Proactive strategies moving forward
“We have been addressing the significant burden of the COVID-19 pandemic on our vulnerable cancer patients through a variety of ways,” said study author Balazs Halmos, MD, of Montefiore Medical Center.
The center set up a separate infusion unit exclusively for COVID-positive patients and established separate inpatient areas. Dr. Halmos and colleagues are also providing telemedicine, virtual supportive care services, telephonic counseling, and bilingual peer-support programs.
“Many questions remain as we continue to establish new practices for our cancer patients,” Dr. Halmos said. “We will find answers to these questions as we continue to focus on adaptation and not acceptance in response to the COVID crisis. Our patients deserve nothing less.”
The Albert Einstein Cancer Center supported this study. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Mehta V et al. Cancer Discov. 2020 May 1. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-20-0516.
FROM CANCER DISCOVERY
Excess cancer deaths predicted as care is disrupted by COVID-19
The majority of patients who have cancer or are suspected of having cancer are not accessing healthcare services in the United Kingdom or the United States because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the first report of its kind estimates.
As a result, there will be an excess of deaths among patients who have cancer and multiple comorbidities in both countries during the current coronavirus emergency, the report warns.
The authors calculate that there will be 6,270 excess deaths among cancer patients 1 year from now in England and 33,890 excess deaths among cancer patients in the United States. (In the United States, the estimated excess number of deaths applies only to patients older than 40 years, they note.)
“The recorded underlying cause of these excess deaths may be cancer, COVID-19, or comorbidity (such as myocardial infarction),” Alvina Lai, PhD, University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues observe.
“Our data have highlighted how cancer patients with multimorbidity are a particularly at-risk group during the current pandemic,” they emphasize.
The study was published on ResearchGate as a preprint and has not undergone peer review.
Commenting on the study on the UK Science Media Center, several experts emphasized the lack of peer review, noting that interpretation of these data needs to be further refined on the basis of that input. One expert suggested that there are “substantial uncertainties that this paper does not adequately communicate.” But others argued that this topic was important enough to warrant early release of the data.
Chris Bunce, PhD, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, said this study represents “a highly valuable contribution.”
“It is universally accepted that early diagnosis and treatment and adherence to treatment regimens saves lives,” he pointed out.
“Therefore, these COVID-19-related impacts will cost lives,” Bunce said.
“And if this information is to influence cancer care and guide policy during the COVID-19 crisis, then it is important that the findings are disseminated and discussed immediately, warranting their release ahead of peer view,” he added.
In a Medscape UK commentary, oncologist Karol Sikora, MD, PhD, argues that “restarting cancer services can’t come soon enough.”
“Resonably Argued Numerical Estimate”
“It’s well known that there have been considerable changes in the provision of health care for many conditions, including cancers, as a result of all the measures to deal with the COVID-19 crisis,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, professor emeritus of applied statistics, the Open University, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom.
“It seems inevitable that there will be increased deaths in cancer patients if they are infected with the virus or because of changes in the health services available to them, and quite possibly also from socio-economic effects of the responses to the crisis,” he continued.
“This study is the first that I have seen that produces a reasonably argued numerical estimate of the number of excess deaths of people with cancer arising from these factors in the UK and the USA,” he added.
Declines in Urgent Referrals and Chemo Attendance
For the study, the team used DATA-CAN, the UK National Health Data Research Hub for Cancer, to assess weekly returns for urgent cancer referrals for early diagnosis and also chemotherapy attendances for hospitals in Leeds, London, and Northern Ireland going back to 2018.
The data revealed that there have been major declines in chemotherapy attendances. There has been, on average, a 60% decrease from prepandemic levels in eight hospitals in the three regions that were assessed.
Urgent cancer referrals have dropped by an average of 76% compared to prepandemic levels in the three regions.
On the conservative assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic will only affect patients with newly diagnosed cancer (incident cases), the researchers estimate that the proportion of the population affected by the emergency (PAE) is 40% and that the relative impact of the emergency (RIE) is 1.5.
PAE is a summary measure of exposure to the adverse health consequences of the emergency; RIE is a summary measure of the combined impact on mortality of infection, health service change, physical distancing, and economic downturn, the authors explain.
Comorbidities Common
“Comorbidities were common in people with cancer,” the study authors note. For example, more than one quarter of the study population had at least one comorbidity; more than 14% had two.
For incident cancers, the number of excess deaths steadily increased in conjunction with an increase in the number of comorbidities, such that more than 80% of deaths occurred in patients with one or more comorbidities.
“When considering both prevalent and incident cancers together with a COVID-19 PAE of 40%, we estimated 17,991 excess deaths at a RIE of 1.5; 78.1% of these deaths occur in patients with ≥1 comorbidities,” the authors report.
“The excess risk of death in people living with cancer during the COVID-19 emergency may be due not only to COVID-19 infection, but also to the unintended health consequences of changes in health service provision, the physical or psychological effects of social distancing, and economic upheaval,” they state.
“This is the first study demonstrating profound recent changes in cancer care delivery in multiple centers,” the authors observe.
Lai has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have various relationships with industry, as listed in their article. The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The majority of patients who have cancer or are suspected of having cancer are not accessing healthcare services in the United Kingdom or the United States because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the first report of its kind estimates.
As a result, there will be an excess of deaths among patients who have cancer and multiple comorbidities in both countries during the current coronavirus emergency, the report warns.
The authors calculate that there will be 6,270 excess deaths among cancer patients 1 year from now in England and 33,890 excess deaths among cancer patients in the United States. (In the United States, the estimated excess number of deaths applies only to patients older than 40 years, they note.)
“The recorded underlying cause of these excess deaths may be cancer, COVID-19, or comorbidity (such as myocardial infarction),” Alvina Lai, PhD, University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues observe.
“Our data have highlighted how cancer patients with multimorbidity are a particularly at-risk group during the current pandemic,” they emphasize.
The study was published on ResearchGate as a preprint and has not undergone peer review.
Commenting on the study on the UK Science Media Center, several experts emphasized the lack of peer review, noting that interpretation of these data needs to be further refined on the basis of that input. One expert suggested that there are “substantial uncertainties that this paper does not adequately communicate.” But others argued that this topic was important enough to warrant early release of the data.
Chris Bunce, PhD, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, said this study represents “a highly valuable contribution.”
“It is universally accepted that early diagnosis and treatment and adherence to treatment regimens saves lives,” he pointed out.
“Therefore, these COVID-19-related impacts will cost lives,” Bunce said.
“And if this information is to influence cancer care and guide policy during the COVID-19 crisis, then it is important that the findings are disseminated and discussed immediately, warranting their release ahead of peer view,” he added.
In a Medscape UK commentary, oncologist Karol Sikora, MD, PhD, argues that “restarting cancer services can’t come soon enough.”
“Resonably Argued Numerical Estimate”
“It’s well known that there have been considerable changes in the provision of health care for many conditions, including cancers, as a result of all the measures to deal with the COVID-19 crisis,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, professor emeritus of applied statistics, the Open University, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom.
“It seems inevitable that there will be increased deaths in cancer patients if they are infected with the virus or because of changes in the health services available to them, and quite possibly also from socio-economic effects of the responses to the crisis,” he continued.
“This study is the first that I have seen that produces a reasonably argued numerical estimate of the number of excess deaths of people with cancer arising from these factors in the UK and the USA,” he added.
Declines in Urgent Referrals and Chemo Attendance
For the study, the team used DATA-CAN, the UK National Health Data Research Hub for Cancer, to assess weekly returns for urgent cancer referrals for early diagnosis and also chemotherapy attendances for hospitals in Leeds, London, and Northern Ireland going back to 2018.
The data revealed that there have been major declines in chemotherapy attendances. There has been, on average, a 60% decrease from prepandemic levels in eight hospitals in the three regions that were assessed.
Urgent cancer referrals have dropped by an average of 76% compared to prepandemic levels in the three regions.
On the conservative assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic will only affect patients with newly diagnosed cancer (incident cases), the researchers estimate that the proportion of the population affected by the emergency (PAE) is 40% and that the relative impact of the emergency (RIE) is 1.5.
PAE is a summary measure of exposure to the adverse health consequences of the emergency; RIE is a summary measure of the combined impact on mortality of infection, health service change, physical distancing, and economic downturn, the authors explain.
Comorbidities Common
“Comorbidities were common in people with cancer,” the study authors note. For example, more than one quarter of the study population had at least one comorbidity; more than 14% had two.
For incident cancers, the number of excess deaths steadily increased in conjunction with an increase in the number of comorbidities, such that more than 80% of deaths occurred in patients with one or more comorbidities.
“When considering both prevalent and incident cancers together with a COVID-19 PAE of 40%, we estimated 17,991 excess deaths at a RIE of 1.5; 78.1% of these deaths occur in patients with ≥1 comorbidities,” the authors report.
“The excess risk of death in people living with cancer during the COVID-19 emergency may be due not only to COVID-19 infection, but also to the unintended health consequences of changes in health service provision, the physical or psychological effects of social distancing, and economic upheaval,” they state.
“This is the first study demonstrating profound recent changes in cancer care delivery in multiple centers,” the authors observe.
Lai has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have various relationships with industry, as listed in their article. The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The majority of patients who have cancer or are suspected of having cancer are not accessing healthcare services in the United Kingdom or the United States because of the COVID-19 pandemic, the first report of its kind estimates.
As a result, there will be an excess of deaths among patients who have cancer and multiple comorbidities in both countries during the current coronavirus emergency, the report warns.
The authors calculate that there will be 6,270 excess deaths among cancer patients 1 year from now in England and 33,890 excess deaths among cancer patients in the United States. (In the United States, the estimated excess number of deaths applies only to patients older than 40 years, they note.)
“The recorded underlying cause of these excess deaths may be cancer, COVID-19, or comorbidity (such as myocardial infarction),” Alvina Lai, PhD, University College London, United Kingdom, and colleagues observe.
“Our data have highlighted how cancer patients with multimorbidity are a particularly at-risk group during the current pandemic,” they emphasize.
The study was published on ResearchGate as a preprint and has not undergone peer review.
Commenting on the study on the UK Science Media Center, several experts emphasized the lack of peer review, noting that interpretation of these data needs to be further refined on the basis of that input. One expert suggested that there are “substantial uncertainties that this paper does not adequately communicate.” But others argued that this topic was important enough to warrant early release of the data.
Chris Bunce, PhD, University of Birmingham, United Kingdom, said this study represents “a highly valuable contribution.”
“It is universally accepted that early diagnosis and treatment and adherence to treatment regimens saves lives,” he pointed out.
“Therefore, these COVID-19-related impacts will cost lives,” Bunce said.
“And if this information is to influence cancer care and guide policy during the COVID-19 crisis, then it is important that the findings are disseminated and discussed immediately, warranting their release ahead of peer view,” he added.
In a Medscape UK commentary, oncologist Karol Sikora, MD, PhD, argues that “restarting cancer services can’t come soon enough.”
“Resonably Argued Numerical Estimate”
“It’s well known that there have been considerable changes in the provision of health care for many conditions, including cancers, as a result of all the measures to deal with the COVID-19 crisis,” said Kevin McConway, PhD, professor emeritus of applied statistics, the Open University, Milton Keynes, United Kingdom.
“It seems inevitable that there will be increased deaths in cancer patients if they are infected with the virus or because of changes in the health services available to them, and quite possibly also from socio-economic effects of the responses to the crisis,” he continued.
“This study is the first that I have seen that produces a reasonably argued numerical estimate of the number of excess deaths of people with cancer arising from these factors in the UK and the USA,” he added.
Declines in Urgent Referrals and Chemo Attendance
For the study, the team used DATA-CAN, the UK National Health Data Research Hub for Cancer, to assess weekly returns for urgent cancer referrals for early diagnosis and also chemotherapy attendances for hospitals in Leeds, London, and Northern Ireland going back to 2018.
The data revealed that there have been major declines in chemotherapy attendances. There has been, on average, a 60% decrease from prepandemic levels in eight hospitals in the three regions that were assessed.
Urgent cancer referrals have dropped by an average of 76% compared to prepandemic levels in the three regions.
On the conservative assumption that the COVID-19 pandemic will only affect patients with newly diagnosed cancer (incident cases), the researchers estimate that the proportion of the population affected by the emergency (PAE) is 40% and that the relative impact of the emergency (RIE) is 1.5.
PAE is a summary measure of exposure to the adverse health consequences of the emergency; RIE is a summary measure of the combined impact on mortality of infection, health service change, physical distancing, and economic downturn, the authors explain.
Comorbidities Common
“Comorbidities were common in people with cancer,” the study authors note. For example, more than one quarter of the study population had at least one comorbidity; more than 14% had two.
For incident cancers, the number of excess deaths steadily increased in conjunction with an increase in the number of comorbidities, such that more than 80% of deaths occurred in patients with one or more comorbidities.
“When considering both prevalent and incident cancers together with a COVID-19 PAE of 40%, we estimated 17,991 excess deaths at a RIE of 1.5; 78.1% of these deaths occur in patients with ≥1 comorbidities,” the authors report.
“The excess risk of death in people living with cancer during the COVID-19 emergency may be due not only to COVID-19 infection, but also to the unintended health consequences of changes in health service provision, the physical or psychological effects of social distancing, and economic upheaval,” they state.
“This is the first study demonstrating profound recent changes in cancer care delivery in multiple centers,” the authors observe.
Lai has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Several coauthors have various relationships with industry, as listed in their article. The commentators have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Antitumor treatment may increase risk of severe events in COVID-19 patients
Cancer patients who received antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of severe events, according to data from three hospitals in Wuhan.
Patients with patchy consolidation at hospital admission also had an increased risk of severe events, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, these findings are limited by the small number of patients studied and the retrospective nature of the analysis, according to researchers.
Li Zhang, MD, PhD, of Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China, presented this research at the AACR virtual meeting I. Some of the data were previously published in Annals of Oncology.
The researchers studied 28 patients with cancer among 1,276 patients with COVID-19 treated at three hospitals in Wuhan. The most common cancer types were lung (n = 7), esophageal (n = 4), and breast (n = 3). Patients had other gastrointestinal, gynecologic, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers as well.
The patients’ median age was 65 years (range, 56-70 years), 60.9% were men, 35.7% had stage IV cancer, and 28.6% had hospital-acquired COVID-19. Antitumor treatments included chemotherapy (n = 22), surgery (n = 21), radiotherapy (n = 21), targeted therapy (n = 5), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n = 2).
COVID-19 treatment
Most patients (n = 22) received oxygen as their only respiratory intervention, although 10 received mechanical ventilation.
For systemic therapy, patients received antibiotic treatment (n = 23), corticosteroids (n = 15), intravenous immunoglobulin (n = 10), and tocilizumab (n = 1).
Antiviral treatments included umifenovir (n = 14), lopinavir/ritonavir (n = 10), ganciclovir (n = 9), ribavirin (n = 1), or a combination of antiviral drugs (n = 9).
“No cancer patients were enrolled in clinical trials, so no one received hydroxychloroquine or remdesivir,” Dr. Zhang noted.
Outcomes
In all, 15 patients (53.6%) had severe events. The median time from COVID-19 diagnosis to severe events was 7 days (range, 5-15 days).
A total of eight patients (28.6%) died – three with lung cancer, two with prostate cancer, one with liver cancer, one with rectal cancer, and one with testicular cancer.
Causes of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 5), septic shock (n = 1), suspected pulmonary embolism (n = 1), and acute myocardial infarction (n = 1).
By April 4, 14 patients had been discharged from the hospital, and 6 were still hospitalized. The median duration of hospitalization was 18.4 days for discharged patients and 29.4 days for patients still in hospital.
Follow-up CT scans showed improvement in 13 patients, no changes in 5 patients, and deterioration in 6 patients.
Factors associated with severe events
In a multivariable analysis, receiving antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis was associated with severe events (hazard ratio, 4.079; P = .037).
However, only seven patients received antitumor treatments within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis – three chemotherapy, two targeted therapy, one radiotherapy, and one immune checkpoint inhibitor. Five of these seven patients had severe events.
Another factor associated with severe events in multivariable analysis was patchy consolidation on CT scan at admission (HR, 5.438; P = .01). Age and gender were not significantly associated with severe events.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Dr. Zhang and colleagues also analyzed a second group of cancer patients and their family members to determine if patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors have an increased risk of COVID-19.
This group included 124 cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for at least 2 months. The patients had a median age of 59 years (range, 54-65 years), and 61.8% were men. Most patients (95.2%) had stage IV cancer, and the most common cancers were lung (54.0%), esophageal (18.6%), and head and neck (10.7%).
In this group, only one cancer patient developed COVID-19 (via nosocomial infection). In another case, a patient’s spouse developed COVID-19, but the patient did not.
Dr. Zhang said this “limited information did not suggest cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors were more vulnerable to COVID infection.”
Dr. Zhang and colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology COVID-19 Rapid Response Call China.
SOURCE: Zhang L et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.296.
Cancer patients who received antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of severe events, according to data from three hospitals in Wuhan.
Patients with patchy consolidation at hospital admission also had an increased risk of severe events, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, these findings are limited by the small number of patients studied and the retrospective nature of the analysis, according to researchers.
Li Zhang, MD, PhD, of Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China, presented this research at the AACR virtual meeting I. Some of the data were previously published in Annals of Oncology.
The researchers studied 28 patients with cancer among 1,276 patients with COVID-19 treated at three hospitals in Wuhan. The most common cancer types were lung (n = 7), esophageal (n = 4), and breast (n = 3). Patients had other gastrointestinal, gynecologic, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers as well.
The patients’ median age was 65 years (range, 56-70 years), 60.9% were men, 35.7% had stage IV cancer, and 28.6% had hospital-acquired COVID-19. Antitumor treatments included chemotherapy (n = 22), surgery (n = 21), radiotherapy (n = 21), targeted therapy (n = 5), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n = 2).
COVID-19 treatment
Most patients (n = 22) received oxygen as their only respiratory intervention, although 10 received mechanical ventilation.
For systemic therapy, patients received antibiotic treatment (n = 23), corticosteroids (n = 15), intravenous immunoglobulin (n = 10), and tocilizumab (n = 1).
Antiviral treatments included umifenovir (n = 14), lopinavir/ritonavir (n = 10), ganciclovir (n = 9), ribavirin (n = 1), or a combination of antiviral drugs (n = 9).
“No cancer patients were enrolled in clinical trials, so no one received hydroxychloroquine or remdesivir,” Dr. Zhang noted.
Outcomes
In all, 15 patients (53.6%) had severe events. The median time from COVID-19 diagnosis to severe events was 7 days (range, 5-15 days).
A total of eight patients (28.6%) died – three with lung cancer, two with prostate cancer, one with liver cancer, one with rectal cancer, and one with testicular cancer.
Causes of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 5), septic shock (n = 1), suspected pulmonary embolism (n = 1), and acute myocardial infarction (n = 1).
By April 4, 14 patients had been discharged from the hospital, and 6 were still hospitalized. The median duration of hospitalization was 18.4 days for discharged patients and 29.4 days for patients still in hospital.
Follow-up CT scans showed improvement in 13 patients, no changes in 5 patients, and deterioration in 6 patients.
Factors associated with severe events
In a multivariable analysis, receiving antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis was associated with severe events (hazard ratio, 4.079; P = .037).
However, only seven patients received antitumor treatments within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis – three chemotherapy, two targeted therapy, one radiotherapy, and one immune checkpoint inhibitor. Five of these seven patients had severe events.
Another factor associated with severe events in multivariable analysis was patchy consolidation on CT scan at admission (HR, 5.438; P = .01). Age and gender were not significantly associated with severe events.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Dr. Zhang and colleagues also analyzed a second group of cancer patients and their family members to determine if patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors have an increased risk of COVID-19.
This group included 124 cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for at least 2 months. The patients had a median age of 59 years (range, 54-65 years), and 61.8% were men. Most patients (95.2%) had stage IV cancer, and the most common cancers were lung (54.0%), esophageal (18.6%), and head and neck (10.7%).
In this group, only one cancer patient developed COVID-19 (via nosocomial infection). In another case, a patient’s spouse developed COVID-19, but the patient did not.
Dr. Zhang said this “limited information did not suggest cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors were more vulnerable to COVID infection.”
Dr. Zhang and colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology COVID-19 Rapid Response Call China.
SOURCE: Zhang L et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.296.
Cancer patients who received antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis had an increased risk of severe events, according to data from three hospitals in Wuhan.
Patients with patchy consolidation at hospital admission also had an increased risk of severe events, defined as ICU admission, mechanical ventilation, or death.
However, these findings are limited by the small number of patients studied and the retrospective nature of the analysis, according to researchers.
Li Zhang, MD, PhD, of Tongji Hospital in Wuhan, China, presented this research at the AACR virtual meeting I. Some of the data were previously published in Annals of Oncology.
The researchers studied 28 patients with cancer among 1,276 patients with COVID-19 treated at three hospitals in Wuhan. The most common cancer types were lung (n = 7), esophageal (n = 4), and breast (n = 3). Patients had other gastrointestinal, gynecologic, genitourinary, and head and neck cancers as well.
The patients’ median age was 65 years (range, 56-70 years), 60.9% were men, 35.7% had stage IV cancer, and 28.6% had hospital-acquired COVID-19. Antitumor treatments included chemotherapy (n = 22), surgery (n = 21), radiotherapy (n = 21), targeted therapy (n = 5), and immune checkpoint inhibitors (n = 2).
COVID-19 treatment
Most patients (n = 22) received oxygen as their only respiratory intervention, although 10 received mechanical ventilation.
For systemic therapy, patients received antibiotic treatment (n = 23), corticosteroids (n = 15), intravenous immunoglobulin (n = 10), and tocilizumab (n = 1).
Antiviral treatments included umifenovir (n = 14), lopinavir/ritonavir (n = 10), ganciclovir (n = 9), ribavirin (n = 1), or a combination of antiviral drugs (n = 9).
“No cancer patients were enrolled in clinical trials, so no one received hydroxychloroquine or remdesivir,” Dr. Zhang noted.
Outcomes
In all, 15 patients (53.6%) had severe events. The median time from COVID-19 diagnosis to severe events was 7 days (range, 5-15 days).
A total of eight patients (28.6%) died – three with lung cancer, two with prostate cancer, one with liver cancer, one with rectal cancer, and one with testicular cancer.
Causes of death were acute respiratory distress syndrome (n = 5), septic shock (n = 1), suspected pulmonary embolism (n = 1), and acute myocardial infarction (n = 1).
By April 4, 14 patients had been discharged from the hospital, and 6 were still hospitalized. The median duration of hospitalization was 18.4 days for discharged patients and 29.4 days for patients still in hospital.
Follow-up CT scans showed improvement in 13 patients, no changes in 5 patients, and deterioration in 6 patients.
Factors associated with severe events
In a multivariable analysis, receiving antitumor treatment within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis was associated with severe events (hazard ratio, 4.079; P = .037).
However, only seven patients received antitumor treatments within 14 days of COVID-19 diagnosis – three chemotherapy, two targeted therapy, one radiotherapy, and one immune checkpoint inhibitor. Five of these seven patients had severe events.
Another factor associated with severe events in multivariable analysis was patchy consolidation on CT scan at admission (HR, 5.438; P = .01). Age and gender were not significantly associated with severe events.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors
Dr. Zhang and colleagues also analyzed a second group of cancer patients and their family members to determine if patients on immune checkpoint inhibitors have an increased risk of COVID-19.
This group included 124 cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors for at least 2 months. The patients had a median age of 59 years (range, 54-65 years), and 61.8% were men. Most patients (95.2%) had stage IV cancer, and the most common cancers were lung (54.0%), esophageal (18.6%), and head and neck (10.7%).
In this group, only one cancer patient developed COVID-19 (via nosocomial infection). In another case, a patient’s spouse developed COVID-19, but the patient did not.
Dr. Zhang said this “limited information did not suggest cancer patients treated with immune checkpoint inhibitors were more vulnerable to COVID infection.”
Dr. Zhang and colleagues reported no conflicts of interest. This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Huazhong University of Science and Technology COVID-19 Rapid Response Call China.
SOURCE: Zhang L et al. Ann Oncol. 2020 Mar 26. doi: 10.1016/j.annonc.2020.03.296.
FROM AACR 2020



