User login
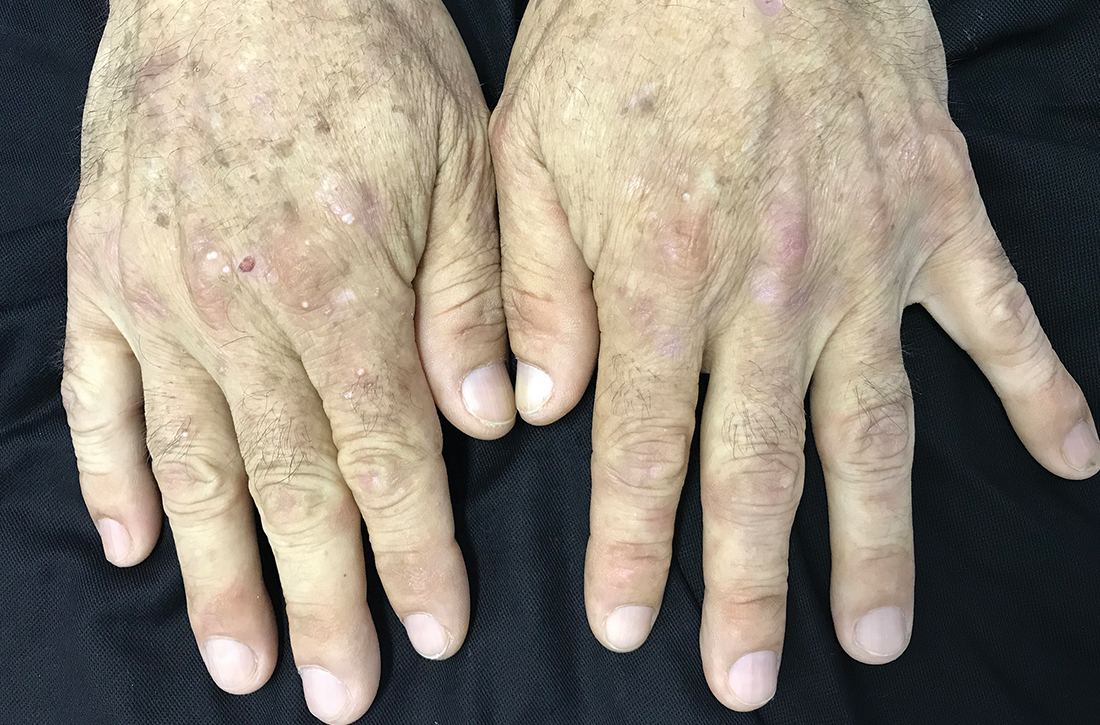
Milium cysts on hands; hypertrichosis on face
A 55-YEAR-OLD MAN with hypertension and untreated hepatitis C virus (HCV) was referred to the Dermatology Clinic after reporting a 2-year history of photosensitivity and intermittent episodes of blistering and scars on the dorsal side of his hands and feet. No alcohol consumption or drug use was reported.
Physical examination revealed small and shallow erosions on the dorsal aspect of the hands and feet (but no visible blisters) and milium cysts (FIGURE 1A). Additionally, hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation were observed in the zygomatic areas (FIGURE 1B). Complete blood count and kidney function test results were within normal ranges. Liver function tests showed slightly elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (79 U/L; normal range, 0-41 U/L), aspartate aminotransferase (62 U/L; normal range, 0-40 U/L), and ferritin (121 ng/mL; normal range, 30-100 ng/mL). Serologies for syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis B virus were negative.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Porphyria cutanea tarda

The porphyrias are a group of metabolic diseases that affect the heme biosynthesis. They can be classified into 1 of 3 groups, according to clinical features:
- acute hepatic porphyrias, with neurovisceral symptoms (eg, acute intermittent porphyria),
- nonblistering cutaneous porphyrias, with severe photosensitivity but without bullae formation (eg, erythropoietic protoporphyria), or
- blistering cutaneous porphyrias (eg, PCT, hepatoerythropoietic porphyria, and variegate porphyria).
PCT is the most common type of porphyria, with a global prevalence of 1 per 10,000 people.1,2 It affects adults after the third or fourth decade of life.
PCT involves dysfunction of the uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase enzyme (UROD), the fifth enzyme in heme biosynthesis, which catalyzes the conversion of uroporphyrinogen to coproporphyrinogen. This dysfunction causes the accumulation of porphyrinogens that are auto-oxidized to photosensitizing porphyrins.1-4 PCT can be classified as “sporadic” or “familial” based on the absence or presence of UROD mutation. Approximately 80% of cases of PCT are sporadic.2
In sporadic PCT, triggers for UROD dysfunction include alcohol use, use of estrogens, hemochromatosis or iron overload, chronic HCV infection, and HIV infection.1-4 HCV (which this patient had) is the most common infection associated with sporadic PCT, with a prevalence of about 50% among these patients.5
Continue to: Dermatologic manifestations of PCT
Dermatologic manifestations of PCT include photosensitivity, skin fragility, vesicles, bullae, erosions, and crusts observed in sun-exposed areas. A nonvirilizing type of hypertrichosis may appear prominently on the temples and the cheeks.2-4 After blisters rupture, atrophy and scarring occur. Milia cysts can form on the dorsal side of the hands and fingers. Less common manifestations include pruritus, scarring alopecia, sclerodermatous changes, and periorbital purple-red suffusion.
Hepatic involvement is demonstrated with elevated serum transaminases and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Hepatomegaly is common, and cirrhosis manifests in 30% to 40% of patients.2-5 On liver biopsy, some degree of siderosis is found in 80% of patients with PCT, and most of them have increased levels of serum iron. The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with PCT is greater than in patients with other liver diseases.2
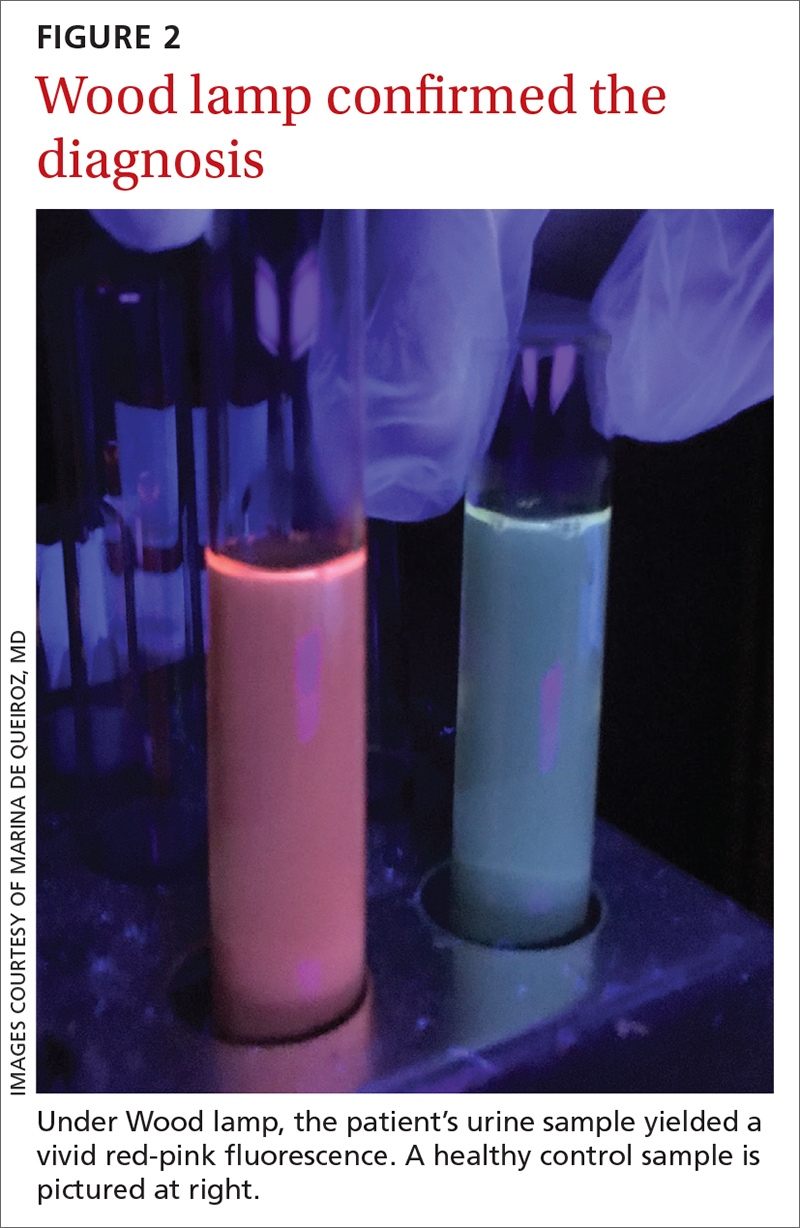
A Wood lamp can be a useful diagnostic first step
Plasma or urine porphyrin lab tests are the gold standard for PCT diagnosis. These tests can be followed by more specific tests (eg, porphyrin fractionation) to exclude other forms of porphyria. However, if plasma or urine porphyrin testing is not readily available, a good first step is a Wood lamp exam, which can be performed on urine or stool. (Plasma or urine porphyrin testing may ultimately be necessary if there is doubt about the diagnosis following the Wood lamp screening.) Histopathologic examination does not confirm the diagnosis of PCT4; however, it can be helpful in differential diagnosis.
Wood lamp is a source of long-wave UV light (320 to 400 nm), visualized as a purple or violet light. When porphyrins are present in a urine sample, a red-pink fluorescence may be seen.3,4,6 The Wood lamp examination should be performed in a completely dark room after the lamp has been warmed up for about 1 minute; time should be allowed for the clinician’s vision to adapt to the dark.6 There are no data regarding the sensitivity or specificity of the Wood lamp test in the diagnosis of PCT.
These conditions also cause skin fragility and photosensitivity
The differential diagnosis for PCT includes diseases that also cause skin fragility, blistering, or photosensitivity, such as pseudoporphyria, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA).3
Continue to: In pseudoporphyria
In pseudoporphyria, the clinical findings may be indistinguishable from PCT. Thus, the patient’s history will be especially important; suspect pseudoporphyria if the patient has a history of chronic renal failure or use of a photosensitizing drug.1,3
Bullous SLE usually manifests with systemic involvement and widespread, tense bullae. Serologic investigation will demonstrate the presence of antinuclear antibodies in high titers (> 1:80), as well as other circulating autoantibodies.
Skin lesions of EBA usually manifest with skin fragility and noninflammatory tense bullae in traumatized skin, such as the extensor surfaces of the hands, feet, and fingers.
None of the above-mentioned diagnoses manifest with hypertrichosis or red-pink fluorescent urine on Wood lamp, and results of porphyrin studies would be normal.3
Address triggers, provide treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, steps must be taken to avoid triggering factors, such as any alcohol consumption, use of estrogen, sun exposure (until plasma porphyrin levels are normal), and potential sources of excessive iron intake.
Two therapeutic options are available for treating PCT—whether it’s sporadic or familial. Phlebotomy sessions reduce iron overload and iron depletion and may prevent the formation of a porphomethene inhibitor of UROD. The other treatment option is antimalarial agents—usually hydroxychloroquine— and is indicated for patients with lower serum ferritin levels.1-4 In patients with HCV-associated PCT, effective treatment of the infection has resulted in resolution of the PCT, in some cases.3
Treatment involving phlebotomy or an antimalarial agent can be stopped when plasma porphyrins reach normal levels.
Our patient was initially managed with 2 sessions of phlebotomy. He subsequently received treatment for the HCV infection at another hospital.
1. Handler NS, Handler MZ, Stephany MP, et. Porphyria cutanea tarda: an intriguing genetic disease and marker. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:e106-e117.doi: 10.1111/ijd.13580
2. Lambrecht RW, Thapar M, Bonkovsky HL. Genetic aspects of porphyria cutanea tarda. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:99-108.doi: 10.1055/s-2006-960173
3. Callen JP. Hepatitis C viral infection and porphyria cutanea tarda. Am J Med Sci. 2017;354:5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.06.009
4. Frank J, Poblete-Gutiérrez P. Porphyria cutanea tarda—when skin meets liver. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24:735-745. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2010.07.002
5. Gisbert JP, García-Buey L, Pajares JM, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in porphyria cutanea tarda: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2003;39:620-627.doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00346-5
6. Asawanonda P, Taylor CR. Wood’s light in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 1999;38:801-807. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.1999.00794.x
A 55-YEAR-OLD MAN with hypertension and untreated hepatitis C virus (HCV) was referred to the Dermatology Clinic after reporting a 2-year history of photosensitivity and intermittent episodes of blistering and scars on the dorsal side of his hands and feet. No alcohol consumption or drug use was reported.
Physical examination revealed small and shallow erosions on the dorsal aspect of the hands and feet (but no visible blisters) and milium cysts (FIGURE 1A). Additionally, hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation were observed in the zygomatic areas (FIGURE 1B). Complete blood count and kidney function test results were within normal ranges. Liver function tests showed slightly elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (79 U/L; normal range, 0-41 U/L), aspartate aminotransferase (62 U/L; normal range, 0-40 U/L), and ferritin (121 ng/mL; normal range, 30-100 ng/mL). Serologies for syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis B virus were negative.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Porphyria cutanea tarda

The porphyrias are a group of metabolic diseases that affect the heme biosynthesis. They can be classified into 1 of 3 groups, according to clinical features:
- acute hepatic porphyrias, with neurovisceral symptoms (eg, acute intermittent porphyria),
- nonblistering cutaneous porphyrias, with severe photosensitivity but without bullae formation (eg, erythropoietic protoporphyria), or
- blistering cutaneous porphyrias (eg, PCT, hepatoerythropoietic porphyria, and variegate porphyria).
PCT is the most common type of porphyria, with a global prevalence of 1 per 10,000 people.1,2 It affects adults after the third or fourth decade of life.
PCT involves dysfunction of the uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase enzyme (UROD), the fifth enzyme in heme biosynthesis, which catalyzes the conversion of uroporphyrinogen to coproporphyrinogen. This dysfunction causes the accumulation of porphyrinogens that are auto-oxidized to photosensitizing porphyrins.1-4 PCT can be classified as “sporadic” or “familial” based on the absence or presence of UROD mutation. Approximately 80% of cases of PCT are sporadic.2
In sporadic PCT, triggers for UROD dysfunction include alcohol use, use of estrogens, hemochromatosis or iron overload, chronic HCV infection, and HIV infection.1-4 HCV (which this patient had) is the most common infection associated with sporadic PCT, with a prevalence of about 50% among these patients.5
Continue to: Dermatologic manifestations of PCT
Dermatologic manifestations of PCT include photosensitivity, skin fragility, vesicles, bullae, erosions, and crusts observed in sun-exposed areas. A nonvirilizing type of hypertrichosis may appear prominently on the temples and the cheeks.2-4 After blisters rupture, atrophy and scarring occur. Milia cysts can form on the dorsal side of the hands and fingers. Less common manifestations include pruritus, scarring alopecia, sclerodermatous changes, and periorbital purple-red suffusion.
Hepatic involvement is demonstrated with elevated serum transaminases and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Hepatomegaly is common, and cirrhosis manifests in 30% to 40% of patients.2-5 On liver biopsy, some degree of siderosis is found in 80% of patients with PCT, and most of them have increased levels of serum iron. The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with PCT is greater than in patients with other liver diseases.2
A Wood lamp can be a useful diagnostic first step
Plasma or urine porphyrin lab tests are the gold standard for PCT diagnosis. These tests can be followed by more specific tests (eg, porphyrin fractionation) to exclude other forms of porphyria. However, if plasma or urine porphyrin testing is not readily available, a good first step is a Wood lamp exam, which can be performed on urine or stool. (Plasma or urine porphyrin testing may ultimately be necessary if there is doubt about the diagnosis following the Wood lamp screening.) Histopathologic examination does not confirm the diagnosis of PCT4; however, it can be helpful in differential diagnosis.
Wood lamp is a source of long-wave UV light (320 to 400 nm), visualized as a purple or violet light. When porphyrins are present in a urine sample, a red-pink fluorescence may be seen.3,4,6 The Wood lamp examination should be performed in a completely dark room after the lamp has been warmed up for about 1 minute; time should be allowed for the clinician’s vision to adapt to the dark.6 There are no data regarding the sensitivity or specificity of the Wood lamp test in the diagnosis of PCT.
These conditions also cause skin fragility and photosensitivity
The differential diagnosis for PCT includes diseases that also cause skin fragility, blistering, or photosensitivity, such as pseudoporphyria, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA).3
Continue to: In pseudoporphyria
In pseudoporphyria, the clinical findings may be indistinguishable from PCT. Thus, the patient’s history will be especially important; suspect pseudoporphyria if the patient has a history of chronic renal failure or use of a photosensitizing drug.1,3
Bullous SLE usually manifests with systemic involvement and widespread, tense bullae. Serologic investigation will demonstrate the presence of antinuclear antibodies in high titers (> 1:80), as well as other circulating autoantibodies.
Skin lesions of EBA usually manifest with skin fragility and noninflammatory tense bullae in traumatized skin, such as the extensor surfaces of the hands, feet, and fingers.
None of the above-mentioned diagnoses manifest with hypertrichosis or red-pink fluorescent urine on Wood lamp, and results of porphyrin studies would be normal.3
Address triggers, provide treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, steps must be taken to avoid triggering factors, such as any alcohol consumption, use of estrogen, sun exposure (until plasma porphyrin levels are normal), and potential sources of excessive iron intake.
Two therapeutic options are available for treating PCT—whether it’s sporadic or familial. Phlebotomy sessions reduce iron overload and iron depletion and may prevent the formation of a porphomethene inhibitor of UROD. The other treatment option is antimalarial agents—usually hydroxychloroquine— and is indicated for patients with lower serum ferritin levels.1-4 In patients with HCV-associated PCT, effective treatment of the infection has resulted in resolution of the PCT, in some cases.3
Treatment involving phlebotomy or an antimalarial agent can be stopped when plasma porphyrins reach normal levels.
Our patient was initially managed with 2 sessions of phlebotomy. He subsequently received treatment for the HCV infection at another hospital.
A 55-YEAR-OLD MAN with hypertension and untreated hepatitis C virus (HCV) was referred to the Dermatology Clinic after reporting a 2-year history of photosensitivity and intermittent episodes of blistering and scars on the dorsal side of his hands and feet. No alcohol consumption or drug use was reported.
Physical examination revealed small and shallow erosions on the dorsal aspect of the hands and feet (but no visible blisters) and milium cysts (FIGURE 1A). Additionally, hypertrichosis and hyperpigmentation were observed in the zygomatic areas (FIGURE 1B). Complete blood count and kidney function test results were within normal ranges. Liver function tests showed slightly elevated levels of alanine aminotransferase (79 U/L; normal range, 0-41 U/L), aspartate aminotransferase (62 U/L; normal range, 0-40 U/L), and ferritin (121 ng/mL; normal range, 30-100 ng/mL). Serologies for syphilis, HIV, and hepatitis B virus were negative.

WHAT IS YOUR DIAGNOSIS?
HOW WOULD YOU TREAT THIS PATIENT?
Diagnosis: Porphyria cutanea tarda

The porphyrias are a group of metabolic diseases that affect the heme biosynthesis. They can be classified into 1 of 3 groups, according to clinical features:
- acute hepatic porphyrias, with neurovisceral symptoms (eg, acute intermittent porphyria),
- nonblistering cutaneous porphyrias, with severe photosensitivity but without bullae formation (eg, erythropoietic protoporphyria), or
- blistering cutaneous porphyrias (eg, PCT, hepatoerythropoietic porphyria, and variegate porphyria).
PCT is the most common type of porphyria, with a global prevalence of 1 per 10,000 people.1,2 It affects adults after the third or fourth decade of life.
PCT involves dysfunction of the uroporphyrinogen decarboxylase enzyme (UROD), the fifth enzyme in heme biosynthesis, which catalyzes the conversion of uroporphyrinogen to coproporphyrinogen. This dysfunction causes the accumulation of porphyrinogens that are auto-oxidized to photosensitizing porphyrins.1-4 PCT can be classified as “sporadic” or “familial” based on the absence or presence of UROD mutation. Approximately 80% of cases of PCT are sporadic.2
In sporadic PCT, triggers for UROD dysfunction include alcohol use, use of estrogens, hemochromatosis or iron overload, chronic HCV infection, and HIV infection.1-4 HCV (which this patient had) is the most common infection associated with sporadic PCT, with a prevalence of about 50% among these patients.5
Continue to: Dermatologic manifestations of PCT
Dermatologic manifestations of PCT include photosensitivity, skin fragility, vesicles, bullae, erosions, and crusts observed in sun-exposed areas. A nonvirilizing type of hypertrichosis may appear prominently on the temples and the cheeks.2-4 After blisters rupture, atrophy and scarring occur. Milia cysts can form on the dorsal side of the hands and fingers. Less common manifestations include pruritus, scarring alopecia, sclerodermatous changes, and periorbital purple-red suffusion.
Hepatic involvement is demonstrated with elevated serum transaminases and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase. Hepatomegaly is common, and cirrhosis manifests in 30% to 40% of patients.2-5 On liver biopsy, some degree of siderosis is found in 80% of patients with PCT, and most of them have increased levels of serum iron. The incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with PCT is greater than in patients with other liver diseases.2
A Wood lamp can be a useful diagnostic first step
Plasma or urine porphyrin lab tests are the gold standard for PCT diagnosis. These tests can be followed by more specific tests (eg, porphyrin fractionation) to exclude other forms of porphyria. However, if plasma or urine porphyrin testing is not readily available, a good first step is a Wood lamp exam, which can be performed on urine or stool. (Plasma or urine porphyrin testing may ultimately be necessary if there is doubt about the diagnosis following the Wood lamp screening.) Histopathologic examination does not confirm the diagnosis of PCT4; however, it can be helpful in differential diagnosis.
Wood lamp is a source of long-wave UV light (320 to 400 nm), visualized as a purple or violet light. When porphyrins are present in a urine sample, a red-pink fluorescence may be seen.3,4,6 The Wood lamp examination should be performed in a completely dark room after the lamp has been warmed up for about 1 minute; time should be allowed for the clinician’s vision to adapt to the dark.6 There are no data regarding the sensitivity or specificity of the Wood lamp test in the diagnosis of PCT.
These conditions also cause skin fragility and photosensitivity
The differential diagnosis for PCT includes diseases that also cause skin fragility, blistering, or photosensitivity, such as pseudoporphyria, bullous systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), and epidermolysis bullosa acquisita (EBA).3
Continue to: In pseudoporphyria
In pseudoporphyria, the clinical findings may be indistinguishable from PCT. Thus, the patient’s history will be especially important; suspect pseudoporphyria if the patient has a history of chronic renal failure or use of a photosensitizing drug.1,3
Bullous SLE usually manifests with systemic involvement and widespread, tense bullae. Serologic investigation will demonstrate the presence of antinuclear antibodies in high titers (> 1:80), as well as other circulating autoantibodies.
Skin lesions of EBA usually manifest with skin fragility and noninflammatory tense bullae in traumatized skin, such as the extensor surfaces of the hands, feet, and fingers.
None of the above-mentioned diagnoses manifest with hypertrichosis or red-pink fluorescent urine on Wood lamp, and results of porphyrin studies would be normal.3
Address triggers, provide treatment
Once the diagnosis is confirmed, steps must be taken to avoid triggering factors, such as any alcohol consumption, use of estrogen, sun exposure (until plasma porphyrin levels are normal), and potential sources of excessive iron intake.
Two therapeutic options are available for treating PCT—whether it’s sporadic or familial. Phlebotomy sessions reduce iron overload and iron depletion and may prevent the formation of a porphomethene inhibitor of UROD. The other treatment option is antimalarial agents—usually hydroxychloroquine— and is indicated for patients with lower serum ferritin levels.1-4 In patients with HCV-associated PCT, effective treatment of the infection has resulted in resolution of the PCT, in some cases.3
Treatment involving phlebotomy or an antimalarial agent can be stopped when plasma porphyrins reach normal levels.
Our patient was initially managed with 2 sessions of phlebotomy. He subsequently received treatment for the HCV infection at another hospital.
1. Handler NS, Handler MZ, Stephany MP, et. Porphyria cutanea tarda: an intriguing genetic disease and marker. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:e106-e117.doi: 10.1111/ijd.13580
2. Lambrecht RW, Thapar M, Bonkovsky HL. Genetic aspects of porphyria cutanea tarda. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:99-108.doi: 10.1055/s-2006-960173
3. Callen JP. Hepatitis C viral infection and porphyria cutanea tarda. Am J Med Sci. 2017;354:5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.06.009
4. Frank J, Poblete-Gutiérrez P. Porphyria cutanea tarda—when skin meets liver. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24:735-745. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2010.07.002
5. Gisbert JP, García-Buey L, Pajares JM, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in porphyria cutanea tarda: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2003;39:620-627.doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00346-5
6. Asawanonda P, Taylor CR. Wood’s light in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 1999;38:801-807. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.1999.00794.x
1. Handler NS, Handler MZ, Stephany MP, et. Porphyria cutanea tarda: an intriguing genetic disease and marker. Int J Dermatol. 2017;56:e106-e117.doi: 10.1111/ijd.13580
2. Lambrecht RW, Thapar M, Bonkovsky HL. Genetic aspects of porphyria cutanea tarda. Semin Liver Dis. 2007;27:99-108.doi: 10.1055/s-2006-960173
3. Callen JP. Hepatitis C viral infection and porphyria cutanea tarda. Am J Med Sci. 2017;354:5-6. doi: 10.1016/j.amjms.2017.06.009
4. Frank J, Poblete-Gutiérrez P. Porphyria cutanea tarda—when skin meets liver. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2010;24:735-745. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2010.07.002
5. Gisbert JP, García-Buey L, Pajares JM, et al. Prevalence of hepatitis C virus infection in porphyria cutanea tarda: systematic review and meta-analysis. J Hepatol. 2003;39:620-627.doi: 10.1016/s0168-8278(03)00346-5
6. Asawanonda P, Taylor CR. Wood’s light in dermatology. Int J Dermatol. 1999;38:801-807. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-4362.1999.00794.x
Statins linked to lower diabetes risk after acute pancreatitis
Use of cholesterol-lowering statins was linked to a lower risk of developing a subtype of diabetes that occurs after acute pancreatitis, according to a new report.
The benefits of statins depended on the consistency of usage, with regular users having a lower risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes than irregular users. The results were similar with low, moderate, and high statin doses, as well as in cases of both mild and severe acute pancreatitis.
“About 15% of patients with acute pancreatitis will develop diabetes mellitus in the next 5 years, and although we can monitor for it, we can’t do anything to prevent it,” Nikhil Thiruvengadam, MD, the lead study author and a gastroenterologist at Loma Linda (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“This could push you as a clinician to prescribe [a statin if you have a reason to] because it could provide two benefits instead of just one,” he said.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Steady use mattered, not dose
Patients with acute pancreatitis face at least a twofold increased risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes, the study authors write. Although previous studies have shown that statins can lower the incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis, they haven’t been studied for the prevention of postpancreatitis diabetes.
In a collaborative study with several other universities, Dr. Thiruvengadam and colleagues examined commercial insurance claims from the Optum Clinformatics database to assess the impact of statins on 118,479 patients without preexisting diabetes admitted for a first episode of acute pancreatitis between 2008 and 2020.
They compared patients who consistently used statins with irregular users and nonusers. Regular statin usage was defined as patients who had statin prescriptions filled for at least 80% of the year prior to their acute pancreatitis diagnosis. The analysis included 9,048 patients (7.6%) who used statins regularly, 27,272 (23%) who used statins irregularly, and 82,159 (69.3%) nonusers.
With a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the 5-year cumulative incidence of postpancreatitis diabetes was 7.5% among regular statin users and 12.7% among nonusers. Regular statin users had a 42% lower risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes, compared with nonusers. Irregular statin users had a 15% lower risk of postpancreatitis diabetes.
In addition, the 5-year cumulative incidence of insulin-dependent postpancreatitis diabetes was 2.4% among regular statin users and 6.6% among nonusers. Regular statin users had a 52% lower risk of developing insulin-dependent diabetes as compared with nonusers.
Daily dosage didn’t demonstrate a linear dose-response relationship. That means high-dose statins may not be more effective in preventing diabetes as compared with lower doses, the study authors write.
Statin usage was effective across additional analyses, including sex, etiologies of pancreatitis, and in both mild and severe acute pancreatitis. According to the study authors, this suggests that a broad population of these patients may benefit from statins.
“We were pleasantly surprised by the variety of findings,” Dr. Thiruvengadam said. “We’re seeing strong signals, especially with consistency of usage.”
Ongoing studies
The results may seem paradoxical, the study authors write, given an epidemiologic association with a slight increase in new-onset diabetes with statin initiation. But, as other researchers have reported, postpancreatitis diabetes and type 2 diabetes have different clinical features and underlying pathophysiology. For example, patients with postpancreatitis diabetes have much higher rates of requiring insulin, hospitalization, and all-cause mortality, the study authors write.
In fact, postpancreatitis diabetes is thought to be driven by chronic low-grade inflammation attributable to interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Statins have been shown to reduce tumor necrosis factor–alpha secretion and the production of C-reactive protein in response to circulating interleukin-6 in hepatocytes, they write.
The results should inform long-term prospective studies of acute pancreatitis, the study authors write, as well as randomized controlled trials of statins.
In the meantime, gastroenterologists and primary care physicians who see outpatients after hospitalization for acute pancreatitis may consider using statins, particularly in those who may have another possible indication for statin therapy, such as mild hyperlipidemia.
“There appears to be a low-dose benefit, which is another reason why providers may consider using statins, though it’s not for everyone with pancreatitis,” Dr. Thiruvengadam said. “This could be an exploratory pathway and suggested for use in the right setting.”
The Type 1 Diabetes in Acute Pancreatitis Consortium, sponsored by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, is conducting an observational cohort study at more than a dozen locations across the country to investigate the incidence, etiology, and pathophysiology of diabetes after acute pancreatitis.
“Diabetes is surprisingly common after even a single attack of acute pancreatitis,” Chris Forsmark, MD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at the University of Florida, Gainesville, told this news organization.
Dr. Forsmark, who wasn’t involved with this study, is a member of T1DAPC and one of the principal investigators in Florida.
“The reduction of risk by 42% is quite substantial,” he said. “Like all such studies, there is risk of bias and confounding in determining the actual risk. Nonetheless, the results provide a strong reason for confirmation in other datasets and for further study.”
The study didn’t report funding support. Dr. Thiruvengadam and Dr. Forsmark report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of cholesterol-lowering statins was linked to a lower risk of developing a subtype of diabetes that occurs after acute pancreatitis, according to a new report.
The benefits of statins depended on the consistency of usage, with regular users having a lower risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes than irregular users. The results were similar with low, moderate, and high statin doses, as well as in cases of both mild and severe acute pancreatitis.
“About 15% of patients with acute pancreatitis will develop diabetes mellitus in the next 5 years, and although we can monitor for it, we can’t do anything to prevent it,” Nikhil Thiruvengadam, MD, the lead study author and a gastroenterologist at Loma Linda (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“This could push you as a clinician to prescribe [a statin if you have a reason to] because it could provide two benefits instead of just one,” he said.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Steady use mattered, not dose
Patients with acute pancreatitis face at least a twofold increased risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes, the study authors write. Although previous studies have shown that statins can lower the incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis, they haven’t been studied for the prevention of postpancreatitis diabetes.
In a collaborative study with several other universities, Dr. Thiruvengadam and colleagues examined commercial insurance claims from the Optum Clinformatics database to assess the impact of statins on 118,479 patients without preexisting diabetes admitted for a first episode of acute pancreatitis between 2008 and 2020.
They compared patients who consistently used statins with irregular users and nonusers. Regular statin usage was defined as patients who had statin prescriptions filled for at least 80% of the year prior to their acute pancreatitis diagnosis. The analysis included 9,048 patients (7.6%) who used statins regularly, 27,272 (23%) who used statins irregularly, and 82,159 (69.3%) nonusers.
With a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the 5-year cumulative incidence of postpancreatitis diabetes was 7.5% among regular statin users and 12.7% among nonusers. Regular statin users had a 42% lower risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes, compared with nonusers. Irregular statin users had a 15% lower risk of postpancreatitis diabetes.
In addition, the 5-year cumulative incidence of insulin-dependent postpancreatitis diabetes was 2.4% among regular statin users and 6.6% among nonusers. Regular statin users had a 52% lower risk of developing insulin-dependent diabetes as compared with nonusers.
Daily dosage didn’t demonstrate a linear dose-response relationship. That means high-dose statins may not be more effective in preventing diabetes as compared with lower doses, the study authors write.
Statin usage was effective across additional analyses, including sex, etiologies of pancreatitis, and in both mild and severe acute pancreatitis. According to the study authors, this suggests that a broad population of these patients may benefit from statins.
“We were pleasantly surprised by the variety of findings,” Dr. Thiruvengadam said. “We’re seeing strong signals, especially with consistency of usage.”
Ongoing studies
The results may seem paradoxical, the study authors write, given an epidemiologic association with a slight increase in new-onset diabetes with statin initiation. But, as other researchers have reported, postpancreatitis diabetes and type 2 diabetes have different clinical features and underlying pathophysiology. For example, patients with postpancreatitis diabetes have much higher rates of requiring insulin, hospitalization, and all-cause mortality, the study authors write.
In fact, postpancreatitis diabetes is thought to be driven by chronic low-grade inflammation attributable to interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Statins have been shown to reduce tumor necrosis factor–alpha secretion and the production of C-reactive protein in response to circulating interleukin-6 in hepatocytes, they write.
The results should inform long-term prospective studies of acute pancreatitis, the study authors write, as well as randomized controlled trials of statins.
In the meantime, gastroenterologists and primary care physicians who see outpatients after hospitalization for acute pancreatitis may consider using statins, particularly in those who may have another possible indication for statin therapy, such as mild hyperlipidemia.
“There appears to be a low-dose benefit, which is another reason why providers may consider using statins, though it’s not for everyone with pancreatitis,” Dr. Thiruvengadam said. “This could be an exploratory pathway and suggested for use in the right setting.”
The Type 1 Diabetes in Acute Pancreatitis Consortium, sponsored by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, is conducting an observational cohort study at more than a dozen locations across the country to investigate the incidence, etiology, and pathophysiology of diabetes after acute pancreatitis.
“Diabetes is surprisingly common after even a single attack of acute pancreatitis,” Chris Forsmark, MD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at the University of Florida, Gainesville, told this news organization.
Dr. Forsmark, who wasn’t involved with this study, is a member of T1DAPC and one of the principal investigators in Florida.
“The reduction of risk by 42% is quite substantial,” he said. “Like all such studies, there is risk of bias and confounding in determining the actual risk. Nonetheless, the results provide a strong reason for confirmation in other datasets and for further study.”
The study didn’t report funding support. Dr. Thiruvengadam and Dr. Forsmark report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Use of cholesterol-lowering statins was linked to a lower risk of developing a subtype of diabetes that occurs after acute pancreatitis, according to a new report.
The benefits of statins depended on the consistency of usage, with regular users having a lower risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes than irregular users. The results were similar with low, moderate, and high statin doses, as well as in cases of both mild and severe acute pancreatitis.
“About 15% of patients with acute pancreatitis will develop diabetes mellitus in the next 5 years, and although we can monitor for it, we can’t do anything to prevent it,” Nikhil Thiruvengadam, MD, the lead study author and a gastroenterologist at Loma Linda (Calif.) University, told this news organization.
“This could push you as a clinician to prescribe [a statin if you have a reason to] because it could provide two benefits instead of just one,” he said.
The study was published online in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
Steady use mattered, not dose
Patients with acute pancreatitis face at least a twofold increased risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes, the study authors write. Although previous studies have shown that statins can lower the incidence and severity of acute pancreatitis, they haven’t been studied for the prevention of postpancreatitis diabetes.
In a collaborative study with several other universities, Dr. Thiruvengadam and colleagues examined commercial insurance claims from the Optum Clinformatics database to assess the impact of statins on 118,479 patients without preexisting diabetes admitted for a first episode of acute pancreatitis between 2008 and 2020.
They compared patients who consistently used statins with irregular users and nonusers. Regular statin usage was defined as patients who had statin prescriptions filled for at least 80% of the year prior to their acute pancreatitis diagnosis. The analysis included 9,048 patients (7.6%) who used statins regularly, 27,272 (23%) who used statins irregularly, and 82,159 (69.3%) nonusers.
With a median follow-up of 3.5 years, the 5-year cumulative incidence of postpancreatitis diabetes was 7.5% among regular statin users and 12.7% among nonusers. Regular statin users had a 42% lower risk of developing postpancreatitis diabetes, compared with nonusers. Irregular statin users had a 15% lower risk of postpancreatitis diabetes.
In addition, the 5-year cumulative incidence of insulin-dependent postpancreatitis diabetes was 2.4% among regular statin users and 6.6% among nonusers. Regular statin users had a 52% lower risk of developing insulin-dependent diabetes as compared with nonusers.
Daily dosage didn’t demonstrate a linear dose-response relationship. That means high-dose statins may not be more effective in preventing diabetes as compared with lower doses, the study authors write.
Statin usage was effective across additional analyses, including sex, etiologies of pancreatitis, and in both mild and severe acute pancreatitis. According to the study authors, this suggests that a broad population of these patients may benefit from statins.
“We were pleasantly surprised by the variety of findings,” Dr. Thiruvengadam said. “We’re seeing strong signals, especially with consistency of usage.”
Ongoing studies
The results may seem paradoxical, the study authors write, given an epidemiologic association with a slight increase in new-onset diabetes with statin initiation. But, as other researchers have reported, postpancreatitis diabetes and type 2 diabetes have different clinical features and underlying pathophysiology. For example, patients with postpancreatitis diabetes have much higher rates of requiring insulin, hospitalization, and all-cause mortality, the study authors write.
In fact, postpancreatitis diabetes is thought to be driven by chronic low-grade inflammation attributable to interleukin-6 and tumor necrosis factor–alpha. Statins have been shown to reduce tumor necrosis factor–alpha secretion and the production of C-reactive protein in response to circulating interleukin-6 in hepatocytes, they write.
The results should inform long-term prospective studies of acute pancreatitis, the study authors write, as well as randomized controlled trials of statins.
In the meantime, gastroenterologists and primary care physicians who see outpatients after hospitalization for acute pancreatitis may consider using statins, particularly in those who may have another possible indication for statin therapy, such as mild hyperlipidemia.
“There appears to be a low-dose benefit, which is another reason why providers may consider using statins, though it’s not for everyone with pancreatitis,” Dr. Thiruvengadam said. “This could be an exploratory pathway and suggested for use in the right setting.”
The Type 1 Diabetes in Acute Pancreatitis Consortium, sponsored by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, is conducting an observational cohort study at more than a dozen locations across the country to investigate the incidence, etiology, and pathophysiology of diabetes after acute pancreatitis.
“Diabetes is surprisingly common after even a single attack of acute pancreatitis,” Chris Forsmark, MD, professor of medicine and chief of the division of gastroenterology, hepatology, and nutrition at the University of Florida, Gainesville, told this news organization.
Dr. Forsmark, who wasn’t involved with this study, is a member of T1DAPC and one of the principal investigators in Florida.
“The reduction of risk by 42% is quite substantial,” he said. “Like all such studies, there is risk of bias and confounding in determining the actual risk. Nonetheless, the results provide a strong reason for confirmation in other datasets and for further study.”
The study didn’t report funding support. Dr. Thiruvengadam and Dr. Forsmark report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
An avocado a day doesn’t shrink belly fat, but helps with cholesterol
according to the findings of a new study.
But it did improve diet quality and led to modest lowering of total cholesterol.
More than 1,000 adults with overweight or obesity and a large waist – at least 35 inches in women and 40 inches in men – took part in this U.S. study, called the Habitual Diet and Avocado Trial (HAT).
The people in the study were divided into two groups: usual diet plus one large avocado every day and usual diet with two avocados at most per month (control group).
Those in the avocado-a-day group were given a regular supply of fresh avocados along with written instructions for how to ripen and prepare them.
They had MRI scans to measure belly fat and fat around other organs at the beginning of the study and after 6 months.
After 6 months, the people who ate an avocado a day did not have less fat around their middles – the main trial outcome – compared with people in the control group.
But at 6 months, those in the avocado-a-day group had:
- No weight gain. People’s weight remained stable in both groups.
- Improved diet quality by 8 points on a 100-point scale
- A 2.9-mg/dL decrease in total cholesterol
- A 2.5-mg/dL decrease in LDL cholesterol
The study was done by researchers at Penn State University; Tufts University; Loma Linda University; and the University of California, Los Angeles, with coordinating support from Wake Forest University.
It was published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“While the avocados did not affect belly fat or weight gain, the study still provides evidence that avocados can be a beneficial addition to a well-balanced diet,” Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, one of the researchers and a professor of nutritional sciences at Penn State University, University Park, said in a news release.
“Incorporating an avocado per day in this study did not cause weight gain and also caused a slight decrease in LDL cholesterol, which are all important findings for better health,” she said.
Similarly, study researcher Joan Sabaté, MD, a professor at Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said: “While one avocado a day did not lead to clinically significant improvements in abdominal fat and other cardiometabolic risk factors, consuming one avocado a day did not result in body weight gain.”
“This is positive,” he said, “because eating extra calories from avocados doesn’t impact body weight or abdominal fat, and it slightly decreases total and LDL cholesterol.”
Kristina S. Petersen, PhD, another of the researchers and an assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, Lubbock, pointed out that people are generally poor at adhering to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
This study suggests that an avocado a day can improve diet quality, she noted, which “ is important because we know a higher diet quality is associated with lower risk of several diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers.”
But the researchers also stressed that it is important to consider the diet as a whole.
“Consistent with prior observations, a change in dietary patterns rather than a single food or nutrient may be necessary to achieve clinically significant improvements” in belly fat and other risk factors for heart attack, stroke, and diabetes, they wrote.
HAT was funded by the Hass Avocado Board, which also supplied the avocados.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the findings of a new study.
But it did improve diet quality and led to modest lowering of total cholesterol.
More than 1,000 adults with overweight or obesity and a large waist – at least 35 inches in women and 40 inches in men – took part in this U.S. study, called the Habitual Diet and Avocado Trial (HAT).
The people in the study were divided into two groups: usual diet plus one large avocado every day and usual diet with two avocados at most per month (control group).
Those in the avocado-a-day group were given a regular supply of fresh avocados along with written instructions for how to ripen and prepare them.
They had MRI scans to measure belly fat and fat around other organs at the beginning of the study and after 6 months.
After 6 months, the people who ate an avocado a day did not have less fat around their middles – the main trial outcome – compared with people in the control group.
But at 6 months, those in the avocado-a-day group had:
- No weight gain. People’s weight remained stable in both groups.
- Improved diet quality by 8 points on a 100-point scale
- A 2.9-mg/dL decrease in total cholesterol
- A 2.5-mg/dL decrease in LDL cholesterol
The study was done by researchers at Penn State University; Tufts University; Loma Linda University; and the University of California, Los Angeles, with coordinating support from Wake Forest University.
It was published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“While the avocados did not affect belly fat or weight gain, the study still provides evidence that avocados can be a beneficial addition to a well-balanced diet,” Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, one of the researchers and a professor of nutritional sciences at Penn State University, University Park, said in a news release.
“Incorporating an avocado per day in this study did not cause weight gain and also caused a slight decrease in LDL cholesterol, which are all important findings for better health,” she said.
Similarly, study researcher Joan Sabaté, MD, a professor at Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said: “While one avocado a day did not lead to clinically significant improvements in abdominal fat and other cardiometabolic risk factors, consuming one avocado a day did not result in body weight gain.”
“This is positive,” he said, “because eating extra calories from avocados doesn’t impact body weight or abdominal fat, and it slightly decreases total and LDL cholesterol.”
Kristina S. Petersen, PhD, another of the researchers and an assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, Lubbock, pointed out that people are generally poor at adhering to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
This study suggests that an avocado a day can improve diet quality, she noted, which “ is important because we know a higher diet quality is associated with lower risk of several diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers.”
But the researchers also stressed that it is important to consider the diet as a whole.
“Consistent with prior observations, a change in dietary patterns rather than a single food or nutrient may be necessary to achieve clinically significant improvements” in belly fat and other risk factors for heart attack, stroke, and diabetes, they wrote.
HAT was funded by the Hass Avocado Board, which also supplied the avocados.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
according to the findings of a new study.
But it did improve diet quality and led to modest lowering of total cholesterol.
More than 1,000 adults with overweight or obesity and a large waist – at least 35 inches in women and 40 inches in men – took part in this U.S. study, called the Habitual Diet and Avocado Trial (HAT).
The people in the study were divided into two groups: usual diet plus one large avocado every day and usual diet with two avocados at most per month (control group).
Those in the avocado-a-day group were given a regular supply of fresh avocados along with written instructions for how to ripen and prepare them.
They had MRI scans to measure belly fat and fat around other organs at the beginning of the study and after 6 months.
After 6 months, the people who ate an avocado a day did not have less fat around their middles – the main trial outcome – compared with people in the control group.
But at 6 months, those in the avocado-a-day group had:
- No weight gain. People’s weight remained stable in both groups.
- Improved diet quality by 8 points on a 100-point scale
- A 2.9-mg/dL decrease in total cholesterol
- A 2.5-mg/dL decrease in LDL cholesterol
The study was done by researchers at Penn State University; Tufts University; Loma Linda University; and the University of California, Los Angeles, with coordinating support from Wake Forest University.
It was published in the Journal of the American Heart Association.
“While the avocados did not affect belly fat or weight gain, the study still provides evidence that avocados can be a beneficial addition to a well-balanced diet,” Penny M. Kris-Etherton, PhD, one of the researchers and a professor of nutritional sciences at Penn State University, University Park, said in a news release.
“Incorporating an avocado per day in this study did not cause weight gain and also caused a slight decrease in LDL cholesterol, which are all important findings for better health,” she said.
Similarly, study researcher Joan Sabaté, MD, a professor at Loma Linda (Calif.) University, said: “While one avocado a day did not lead to clinically significant improvements in abdominal fat and other cardiometabolic risk factors, consuming one avocado a day did not result in body weight gain.”
“This is positive,” he said, “because eating extra calories from avocados doesn’t impact body weight or abdominal fat, and it slightly decreases total and LDL cholesterol.”
Kristina S. Petersen, PhD, another of the researchers and an assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, Lubbock, pointed out that people are generally poor at adhering to the Dietary Guidelines for Americans.
This study suggests that an avocado a day can improve diet quality, she noted, which “ is important because we know a higher diet quality is associated with lower risk of several diseases, including heart disease, type 2 diabetes, and some cancers.”
But the researchers also stressed that it is important to consider the diet as a whole.
“Consistent with prior observations, a change in dietary patterns rather than a single food or nutrient may be necessary to achieve clinically significant improvements” in belly fat and other risk factors for heart attack, stroke, and diabetes, they wrote.
HAT was funded by the Hass Avocado Board, which also supplied the avocados.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
27-year-old man • muscle weakness • fatigue • electrolyte abnormalities • Dx?
THE CASE
A 27-year-old man with no past medical history presented to his primary care physician (PCP) for a routine physical. He reported experiencing muscle weakness and fatigue for the previous 1 to 2 months. Two blood pressure measurements were recorded: 138/80 mm Hg and 142/95 mm Hg. The patient was given a diagnosis of hypertension and started on triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide. Labwork was ordered, including a complete metabolic panel, lipid panel, urinalysis, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) plus thyroxine (T4), HIV antibodies, and a complete blood count.
The samples were drawn 1 week later, and the results were notable for low-normal TSH with a T4 of 0.8 ng/dL (normal range, 0.9-2.3 ng/dL); sodium, 151 mmol/L (normal range, 136-145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (normal range, 3.6-5.2 mmol/L); and white blood cell count, 13.8 x 103/mcL. The electrolyte abnormalities were attributed to the triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide, which was stopped. One week later, repeat labs showed a persistent potassium level of 3.0 mmol/L; sodium, 141 mmol/L; and glucose, 310 mg/dL. Follow-up A1C was measured at 7.4%.
At the next appointment (2 weeks after initial evaluation), the patient received a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in addition to new-onset essential hypertension. He expressed surprise at his diagnoses, as he said he primarily ate a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables and lots of healthy home-cooked meals. His body mass index (BMI) was in normal range, and he said he exercised regularly.
The patient was started on metformin 500 mg/d and referred to Endocrinology. After seeing the endocrinologist, who agreed with metformin for initial management, the patient contacted his PCP with concerns about worsening “muscle wasting.” Based on these ongoing symptoms, the patient was advised to go to the emergency department (ED).
In the ED, the patient reported muscle aches and weakness, weight gain, dyspnea on exertion, and polyuria. He also said that his face had widened with his weight gain, and his weakness was greatest in his thighs compared to his distal lower extremities. Labs drawn in the ED indicated hyperglycemia (glucose, 334 mg/dL) and severe hypokalemia (potassium, 2.2 mmol/L).
THE DIAGNOSIS
The patient was admitted in the afternoon for further evaluation, and a random serum cortisol measurement was ordered. The results showed an elevated cortisol level (55.2 mcg/dL; normal range, 3-20 mcg/dL). This was followed by a profoundly positive low-dose dexamethasone suppression test with a morning cortisol level of 75.9 mcg/dL (normal range, < 1.8 mcg/dL). With these findings, the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome was made and the focus of the evaluation shifted to localization.
An adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) measurement was ordered, as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary gland and of the abdomen to assess the adrenal glands. Both MRIs were negative, prompting a high-dose 8-mg dexamethasone suppression test to be performed. The patient’s morning cortisol level remained elevated (69.9 mcg/dL), confirming the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome.
Continue to: Based on the results...
Based on the results of the dexamethasone suppression test, a pituitary adenoma was unlikely (as they are often suppressed to < 5 mcg/dL with this test). The patient’s morning ACTH results came back as elevated (356.6 pg/mL; normal range, 10-60 pg/mL), suggesting inappropriate ACTH secretion, which most often has an ectopic source. However, a nuclear medicine octreotide scan and multiple computed tomography scans failed to locate such a source.
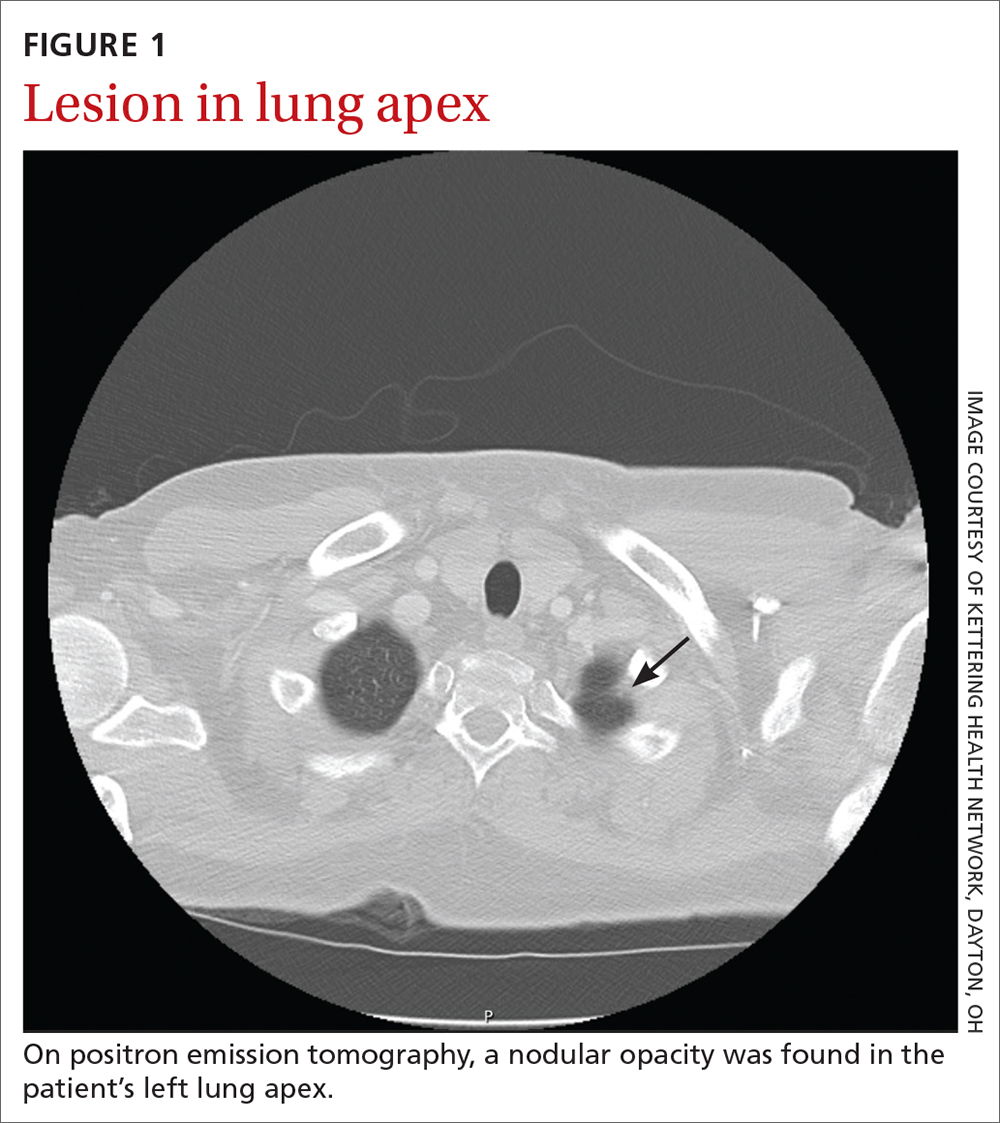
The patient eventually underwent bilateral petrosal venous sinus sampling to definitively rule out a pituitary source. Lastly, he underwent nuclear medicine positron emission tomography, which identified a nodular opacity in the anterior left lung apex, demonstrating moderate radiotracer activity (FIGURE 1).
THE DISCUSSION
Cushing syndrome is rarely encountered—it is estimated to affect 2% of patients with uncontrolled diabetes1 and 1% of those with uncontrolled hypertension2—and requires a high level of clinical suspicion. This case highlights the importance of considering secondary causes of diabetes in patients who present atypically. This patient presented with symptoms consistent with Cushing syndrome that went unrecognized initially; these included high blood pressure, rounded face, weak muscles, hypokalemia, and intermittent hypernatremia in addition to new-onset hyperglycemia.2-5 Despite the atypical findings, evaluation for diabetes and potential secondary causes was neglected until an ED evaluation 1 month after initial presentation. The work-up for possible Cushing syndrome was completed in the hospital but could easily have been conducted in the outpatient setting.
Making the diagnosis. When Cushing syndrome is suspected, consider consultation with Endocrinology. It is important to exclude exogenous glucocorticoid exposure through a thorough review of the patient’s medications.2 The Endocrine Society2 recommends that one of the following tests be performed:
- 24-hour urine free cortisol (≥ 2 tests)
- Overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test
- Late-night salivary cortisol test.
Results within normal range make Cushing syndrome an unlikely diagnosis; however, for patients with suggestive clinical features, further work-up may be warranted.
Continue to: Any abnormal result...
Any abnormal result is an indication to exclude a physiologic cause of hypercortisolism by repeating at least 1 of the previous studies. As with the initial testing, normal results may rule out Cushing syndrome, while abnormal results would be confirmatory. (Conflicting results require additional evaluation.)
Morbidity and mortality. Finding the etiology of Cushing syndrome can present a challenge but is also rewarding due to the reversible nature of most of the abnormalities. That said, Cushing syndrome can have a significant impact on morbidity and mortality.
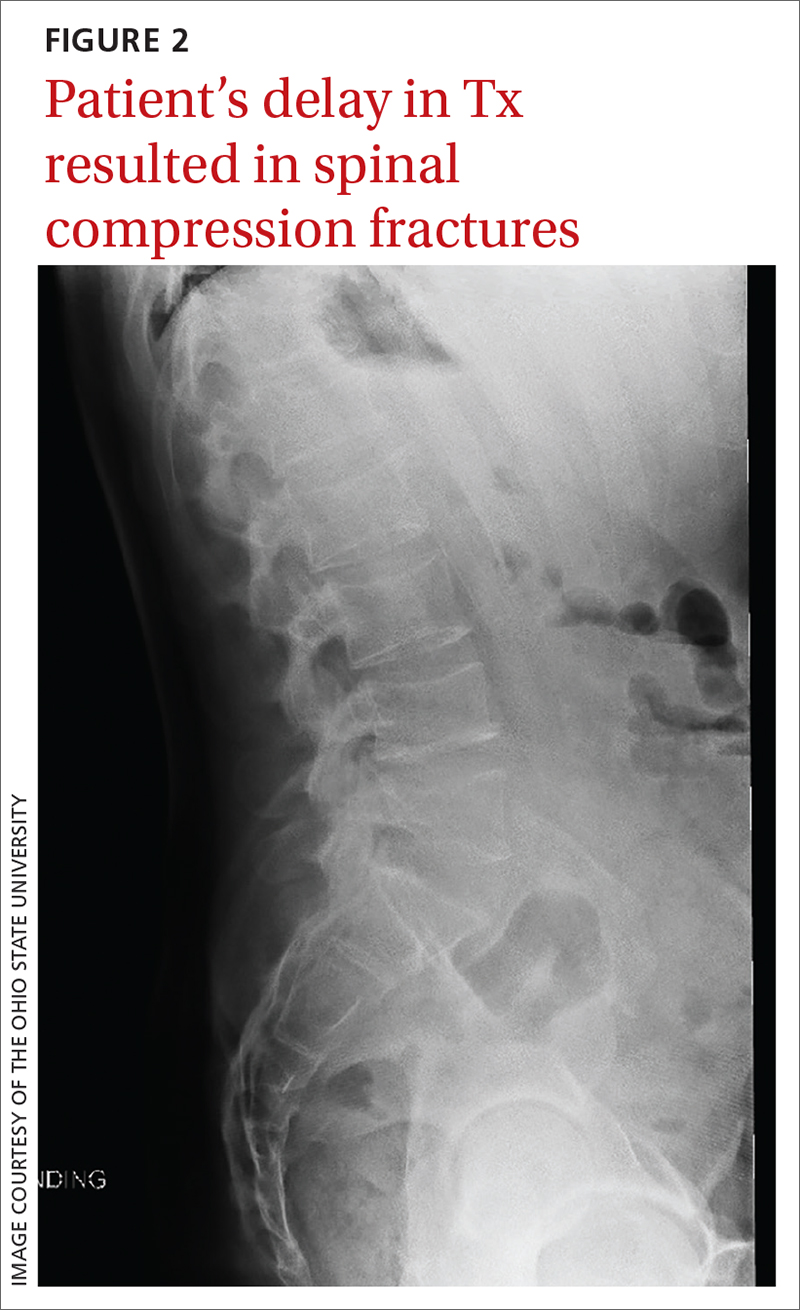
Morbidity. The case patient developed compression fractures throughout his thoracic and lumbar spine, with a loss of 4 inches in height, attributed to the delay in curative treatment (FIGURE 2); these were identified about 2 months after his initial presentation to a health care facility. In addition to bone mineral density, cognitive function and quality of life can be impacted by untreated hypercortisolism and Cushing syndrome.2
Mortality. In the earliest studies6,7 (from the 1930s-1950s), the average survival rate was about 4.6 years and the 5-year survival was just 50%—and yet, outcomes data from modern treatment modalities are scant. While there is limited data on outcomes in untreated disease, the Endocrine Society states that treatment of moderate-to-severe cases “clearly reduces mortality and morbidity” while early identification and treatment of mild cases “would reduce the risk of residual morbidity.”2
Our patient underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery, during which a nodule in the anterior lingula was removed. In addition, lymph node dissection was performed. Two lymph nodes were positive for atypical well-differentiated carcinoid tumor. After surgical removal, the patient’s cortisol levels normalized and his diabetes resolved.
THE TAKEAWAY
In primary care, the frequency at which we evaluate and diagnose type 2 diabetes without secondary cause can lead to cognitive biases, such as anchoring bias, that impact patient care. In this case, the atypical secondary nature of the diabetes was missed at 3 outpatient appointments prior to presentation at the hospital ED. In an active patient who has a normal BMI and a healthy diet—but systemic symptoms—it is critical to consider secondary causes of diabetes, such as Cushing syndrome.
CORRESPONDENCE
Anna Murley Squibb, MD, 2145 North Fairfield Road, Suite 100, Beavercreek, OH 45385; [email protected]
1. Bulow B, Jansson S, Juhlin C, et al. Adrenal incidentaloma—follow-up results from a Swedish prospective study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;154:419-423. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.02110
2. Nieman LK, Biller BMK, Findling JW, et al. The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1526-1540. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-0125
3. Juszczak A, Morris DG, Grossman AB, et al. Chapter 13: Cushing’s syndrome. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. 7th ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2016:227-255.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-18907-1.00013-5
4. Lacroix A, Feelders RA, Stratakis CA, et al. Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet. 2015;386:913-927. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61375-1
5. Arnaldi G, Angeli A, Atkinson AB, et al. Diagnosis and complications of Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:5593-5602. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030871
6. Cushing H. The basophil adenomas of the pituitary body and their clinical manifestations. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1932;50:137-195. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1994.tb00097.x
7. Plotz CM, Knowlton AI, Ragan C. The natural history of Cushing’s syndrome. Am J Med. 1952;13:597-614. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(52)90027-2
THE CASE
A 27-year-old man with no past medical history presented to his primary care physician (PCP) for a routine physical. He reported experiencing muscle weakness and fatigue for the previous 1 to 2 months. Two blood pressure measurements were recorded: 138/80 mm Hg and 142/95 mm Hg. The patient was given a diagnosis of hypertension and started on triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide. Labwork was ordered, including a complete metabolic panel, lipid panel, urinalysis, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) plus thyroxine (T4), HIV antibodies, and a complete blood count.
The samples were drawn 1 week later, and the results were notable for low-normal TSH with a T4 of 0.8 ng/dL (normal range, 0.9-2.3 ng/dL); sodium, 151 mmol/L (normal range, 136-145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (normal range, 3.6-5.2 mmol/L); and white blood cell count, 13.8 x 103/mcL. The electrolyte abnormalities were attributed to the triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide, which was stopped. One week later, repeat labs showed a persistent potassium level of 3.0 mmol/L; sodium, 141 mmol/L; and glucose, 310 mg/dL. Follow-up A1C was measured at 7.4%.
At the next appointment (2 weeks after initial evaluation), the patient received a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in addition to new-onset essential hypertension. He expressed surprise at his diagnoses, as he said he primarily ate a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables and lots of healthy home-cooked meals. His body mass index (BMI) was in normal range, and he said he exercised regularly.
The patient was started on metformin 500 mg/d and referred to Endocrinology. After seeing the endocrinologist, who agreed with metformin for initial management, the patient contacted his PCP with concerns about worsening “muscle wasting.” Based on these ongoing symptoms, the patient was advised to go to the emergency department (ED).
In the ED, the patient reported muscle aches and weakness, weight gain, dyspnea on exertion, and polyuria. He also said that his face had widened with his weight gain, and his weakness was greatest in his thighs compared to his distal lower extremities. Labs drawn in the ED indicated hyperglycemia (glucose, 334 mg/dL) and severe hypokalemia (potassium, 2.2 mmol/L).
THE DIAGNOSIS
The patient was admitted in the afternoon for further evaluation, and a random serum cortisol measurement was ordered. The results showed an elevated cortisol level (55.2 mcg/dL; normal range, 3-20 mcg/dL). This was followed by a profoundly positive low-dose dexamethasone suppression test with a morning cortisol level of 75.9 mcg/dL (normal range, < 1.8 mcg/dL). With these findings, the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome was made and the focus of the evaluation shifted to localization.
An adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) measurement was ordered, as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary gland and of the abdomen to assess the adrenal glands. Both MRIs were negative, prompting a high-dose 8-mg dexamethasone suppression test to be performed. The patient’s morning cortisol level remained elevated (69.9 mcg/dL), confirming the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome.
Continue to: Based on the results...
Based on the results of the dexamethasone suppression test, a pituitary adenoma was unlikely (as they are often suppressed to < 5 mcg/dL with this test). The patient’s morning ACTH results came back as elevated (356.6 pg/mL; normal range, 10-60 pg/mL), suggesting inappropriate ACTH secretion, which most often has an ectopic source. However, a nuclear medicine octreotide scan and multiple computed tomography scans failed to locate such a source.
The patient eventually underwent bilateral petrosal venous sinus sampling to definitively rule out a pituitary source. Lastly, he underwent nuclear medicine positron emission tomography, which identified a nodular opacity in the anterior left lung apex, demonstrating moderate radiotracer activity (FIGURE 1).

THE DISCUSSION
Cushing syndrome is rarely encountered—it is estimated to affect 2% of patients with uncontrolled diabetes1 and 1% of those with uncontrolled hypertension2—and requires a high level of clinical suspicion. This case highlights the importance of considering secondary causes of diabetes in patients who present atypically. This patient presented with symptoms consistent with Cushing syndrome that went unrecognized initially; these included high blood pressure, rounded face, weak muscles, hypokalemia, and intermittent hypernatremia in addition to new-onset hyperglycemia.2-5 Despite the atypical findings, evaluation for diabetes and potential secondary causes was neglected until an ED evaluation 1 month after initial presentation. The work-up for possible Cushing syndrome was completed in the hospital but could easily have been conducted in the outpatient setting.
Making the diagnosis. When Cushing syndrome is suspected, consider consultation with Endocrinology. It is important to exclude exogenous glucocorticoid exposure through a thorough review of the patient’s medications.2 The Endocrine Society2 recommends that one of the following tests be performed:
- 24-hour urine free cortisol (≥ 2 tests)
- Overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test
- Late-night salivary cortisol test.
Results within normal range make Cushing syndrome an unlikely diagnosis; however, for patients with suggestive clinical features, further work-up may be warranted.
Continue to: Any abnormal result...
Any abnormal result is an indication to exclude a physiologic cause of hypercortisolism by repeating at least 1 of the previous studies. As with the initial testing, normal results may rule out Cushing syndrome, while abnormal results would be confirmatory. (Conflicting results require additional evaluation.)
Morbidity and mortality. Finding the etiology of Cushing syndrome can present a challenge but is also rewarding due to the reversible nature of most of the abnormalities. That said, Cushing syndrome can have a significant impact on morbidity and mortality.
Morbidity. The case patient developed compression fractures throughout his thoracic and lumbar spine, with a loss of 4 inches in height, attributed to the delay in curative treatment (FIGURE 2); these were identified about 2 months after his initial presentation to a health care facility. In addition to bone mineral density, cognitive function and quality of life can be impacted by untreated hypercortisolism and Cushing syndrome.2

Mortality. In the earliest studies6,7 (from the 1930s-1950s), the average survival rate was about 4.6 years and the 5-year survival was just 50%—and yet, outcomes data from modern treatment modalities are scant. While there is limited data on outcomes in untreated disease, the Endocrine Society states that treatment of moderate-to-severe cases “clearly reduces mortality and morbidity” while early identification and treatment of mild cases “would reduce the risk of residual morbidity.”2
Our patient underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery, during which a nodule in the anterior lingula was removed. In addition, lymph node dissection was performed. Two lymph nodes were positive for atypical well-differentiated carcinoid tumor. After surgical removal, the patient’s cortisol levels normalized and his diabetes resolved.
THE TAKEAWAY
In primary care, the frequency at which we evaluate and diagnose type 2 diabetes without secondary cause can lead to cognitive biases, such as anchoring bias, that impact patient care. In this case, the atypical secondary nature of the diabetes was missed at 3 outpatient appointments prior to presentation at the hospital ED. In an active patient who has a normal BMI and a healthy diet—but systemic symptoms—it is critical to consider secondary causes of diabetes, such as Cushing syndrome.
CORRESPONDENCE
Anna Murley Squibb, MD, 2145 North Fairfield Road, Suite 100, Beavercreek, OH 45385; [email protected]
THE CASE
A 27-year-old man with no past medical history presented to his primary care physician (PCP) for a routine physical. He reported experiencing muscle weakness and fatigue for the previous 1 to 2 months. Two blood pressure measurements were recorded: 138/80 mm Hg and 142/95 mm Hg. The patient was given a diagnosis of hypertension and started on triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide. Labwork was ordered, including a complete metabolic panel, lipid panel, urinalysis, thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) plus thyroxine (T4), HIV antibodies, and a complete blood count.
The samples were drawn 1 week later, and the results were notable for low-normal TSH with a T4 of 0.8 ng/dL (normal range, 0.9-2.3 ng/dL); sodium, 151 mmol/L (normal range, 136-145 mmol/L); potassium, 3.4 mmol/L (normal range, 3.6-5.2 mmol/L); and white blood cell count, 13.8 x 103/mcL. The electrolyte abnormalities were attributed to the triamterene/hydrochlorothiazide, which was stopped. One week later, repeat labs showed a persistent potassium level of 3.0 mmol/L; sodium, 141 mmol/L; and glucose, 310 mg/dL. Follow-up A1C was measured at 7.4%.
At the next appointment (2 weeks after initial evaluation), the patient received a diagnosis of type 2 diabetes in addition to new-onset essential hypertension. He expressed surprise at his diagnoses, as he said he primarily ate a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables and lots of healthy home-cooked meals. His body mass index (BMI) was in normal range, and he said he exercised regularly.
The patient was started on metformin 500 mg/d and referred to Endocrinology. After seeing the endocrinologist, who agreed with metformin for initial management, the patient contacted his PCP with concerns about worsening “muscle wasting.” Based on these ongoing symptoms, the patient was advised to go to the emergency department (ED).
In the ED, the patient reported muscle aches and weakness, weight gain, dyspnea on exertion, and polyuria. He also said that his face had widened with his weight gain, and his weakness was greatest in his thighs compared to his distal lower extremities. Labs drawn in the ED indicated hyperglycemia (glucose, 334 mg/dL) and severe hypokalemia (potassium, 2.2 mmol/L).
THE DIAGNOSIS
The patient was admitted in the afternoon for further evaluation, and a random serum cortisol measurement was ordered. The results showed an elevated cortisol level (55.2 mcg/dL; normal range, 3-20 mcg/dL). This was followed by a profoundly positive low-dose dexamethasone suppression test with a morning cortisol level of 75.9 mcg/dL (normal range, < 1.8 mcg/dL). With these findings, the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome was made and the focus of the evaluation shifted to localization.
An adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) measurement was ordered, as well as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the pituitary gland and of the abdomen to assess the adrenal glands. Both MRIs were negative, prompting a high-dose 8-mg dexamethasone suppression test to be performed. The patient’s morning cortisol level remained elevated (69.9 mcg/dL), confirming the diagnosis of Cushing syndrome.
Continue to: Based on the results...
Based on the results of the dexamethasone suppression test, a pituitary adenoma was unlikely (as they are often suppressed to < 5 mcg/dL with this test). The patient’s morning ACTH results came back as elevated (356.6 pg/mL; normal range, 10-60 pg/mL), suggesting inappropriate ACTH secretion, which most often has an ectopic source. However, a nuclear medicine octreotide scan and multiple computed tomography scans failed to locate such a source.
The patient eventually underwent bilateral petrosal venous sinus sampling to definitively rule out a pituitary source. Lastly, he underwent nuclear medicine positron emission tomography, which identified a nodular opacity in the anterior left lung apex, demonstrating moderate radiotracer activity (FIGURE 1).

THE DISCUSSION
Cushing syndrome is rarely encountered—it is estimated to affect 2% of patients with uncontrolled diabetes1 and 1% of those with uncontrolled hypertension2—and requires a high level of clinical suspicion. This case highlights the importance of considering secondary causes of diabetes in patients who present atypically. This patient presented with symptoms consistent with Cushing syndrome that went unrecognized initially; these included high blood pressure, rounded face, weak muscles, hypokalemia, and intermittent hypernatremia in addition to new-onset hyperglycemia.2-5 Despite the atypical findings, evaluation for diabetes and potential secondary causes was neglected until an ED evaluation 1 month after initial presentation. The work-up for possible Cushing syndrome was completed in the hospital but could easily have been conducted in the outpatient setting.
Making the diagnosis. When Cushing syndrome is suspected, consider consultation with Endocrinology. It is important to exclude exogenous glucocorticoid exposure through a thorough review of the patient’s medications.2 The Endocrine Society2 recommends that one of the following tests be performed:
- 24-hour urine free cortisol (≥ 2 tests)
- Overnight 1-mg dexamethasone suppression test
- Late-night salivary cortisol test.
Results within normal range make Cushing syndrome an unlikely diagnosis; however, for patients with suggestive clinical features, further work-up may be warranted.
Continue to: Any abnormal result...
Any abnormal result is an indication to exclude a physiologic cause of hypercortisolism by repeating at least 1 of the previous studies. As with the initial testing, normal results may rule out Cushing syndrome, while abnormal results would be confirmatory. (Conflicting results require additional evaluation.)
Morbidity and mortality. Finding the etiology of Cushing syndrome can present a challenge but is also rewarding due to the reversible nature of most of the abnormalities. That said, Cushing syndrome can have a significant impact on morbidity and mortality.
Morbidity. The case patient developed compression fractures throughout his thoracic and lumbar spine, with a loss of 4 inches in height, attributed to the delay in curative treatment (FIGURE 2); these were identified about 2 months after his initial presentation to a health care facility. In addition to bone mineral density, cognitive function and quality of life can be impacted by untreated hypercortisolism and Cushing syndrome.2

Mortality. In the earliest studies6,7 (from the 1930s-1950s), the average survival rate was about 4.6 years and the 5-year survival was just 50%—and yet, outcomes data from modern treatment modalities are scant. While there is limited data on outcomes in untreated disease, the Endocrine Society states that treatment of moderate-to-severe cases “clearly reduces mortality and morbidity” while early identification and treatment of mild cases “would reduce the risk of residual morbidity.”2
Our patient underwent video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery, during which a nodule in the anterior lingula was removed. In addition, lymph node dissection was performed. Two lymph nodes were positive for atypical well-differentiated carcinoid tumor. After surgical removal, the patient’s cortisol levels normalized and his diabetes resolved.
THE TAKEAWAY
In primary care, the frequency at which we evaluate and diagnose type 2 diabetes without secondary cause can lead to cognitive biases, such as anchoring bias, that impact patient care. In this case, the atypical secondary nature of the diabetes was missed at 3 outpatient appointments prior to presentation at the hospital ED. In an active patient who has a normal BMI and a healthy diet—but systemic symptoms—it is critical to consider secondary causes of diabetes, such as Cushing syndrome.
CORRESPONDENCE
Anna Murley Squibb, MD, 2145 North Fairfield Road, Suite 100, Beavercreek, OH 45385; [email protected]
1. Bulow B, Jansson S, Juhlin C, et al. Adrenal incidentaloma—follow-up results from a Swedish prospective study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;154:419-423. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.02110
2. Nieman LK, Biller BMK, Findling JW, et al. The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1526-1540. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-0125
3. Juszczak A, Morris DG, Grossman AB, et al. Chapter 13: Cushing’s syndrome. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. 7th ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2016:227-255.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-18907-1.00013-5
4. Lacroix A, Feelders RA, Stratakis CA, et al. Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet. 2015;386:913-927. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61375-1
5. Arnaldi G, Angeli A, Atkinson AB, et al. Diagnosis and complications of Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:5593-5602. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030871
6. Cushing H. The basophil adenomas of the pituitary body and their clinical manifestations. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1932;50:137-195. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1994.tb00097.x
7. Plotz CM, Knowlton AI, Ragan C. The natural history of Cushing’s syndrome. Am J Med. 1952;13:597-614. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(52)90027-2
1. Bulow B, Jansson S, Juhlin C, et al. Adrenal incidentaloma—follow-up results from a Swedish prospective study. Eur J Endocrinol. 2006;154:419-423. doi: 10.1530/eje.1.02110
2. Nieman LK, Biller BMK, Findling JW, et al. The diagnosis of Cushing’s syndrome: an Endocrine Society Clinical Practice Guideline. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93:1526-1540. doi: 10.1210/jc.2008-0125
3. Juszczak A, Morris DG, Grossman AB, et al. Chapter 13: Cushing’s syndrome. In: Jameson JL, De Groot LJ. Endocrinology: Adult and Pediatric. 7th ed. Elsevier Saunders; 2016:227-255.e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-18907-1.00013-5
4. Lacroix A, Feelders RA, Stratakis CA, et al. Cushing’s syndrome. Lancet. 2015;386:913-927. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61375-1
5. Arnaldi G, Angeli A, Atkinson AB, et al. Diagnosis and complications of Cushing’s syndrome: a consensus statement. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2003;88:5593-5602. doi: 10.1210/jc.2003-030871
6. Cushing H. The basophil adenomas of the pituitary body and their clinical manifestations. Bull Johns Hopkins Hosp. 1932;50:137-195. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1994.tb00097.x
7. Plotz CM, Knowlton AI, Ragan C. The natural history of Cushing’s syndrome. Am J Med. 1952;13:597-614. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(52)90027-2
Moderate drinking shows more benefit for older vs. younger adults
The health risks and benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are complex and remain a hot topic of debate. The data suggest that small amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of certain health outcomes over time, but increase the risk of others, wrote Dana Bryazka, MS, a researcher at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues, in a paper published in the Lancet.
“The amount of alcohol that minimizes health loss is likely to depend on the distribution of underlying causes of disease burden in a given population. Since this distribution varies widely by geography, age, sex, and time, the level of alcohol consumption associated with the lowest risk to health would depend on the age structure and disease composition of that population,” the researchers wrote.
“We estimate that 1.78 million people worldwide died due to alcohol use in 2020,” Ms. Bryazka said in an interview. “It is important that alcohol consumption guidelines and policies are updated to minimize this harm, particularly in the populations at greatest risk,” she said.
“Existing alcohol consumption guidelines frequently vary by sex, with higher consumption thresholds set for males compared to females. Interestingly, with the currently available data we do not see evidence that risk of alcohol use varies by sex,” she noted.
Methods and results
In the study, the researchers conducted a systematic analysis of burden-weighted dose-response relative risk curves across 22 health outcomes. They used disease rates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2020 for the years 1990-2020 for 21 regions, including 204 countries and territories. The data were analyzed by 5-year age group, sex, and year for individuals aged 15-95 years and older. The researchers estimated the theoretical minimum risk exposure level (TMREL) and nondrinker equivalent (NDE), meaning the amount of alcohol at which the health risk equals that of a nondrinker.
One standard drink was defined as 10 g of pure alcohol, equivalent to a small glass of red wine (100 mL or 3.4 fluid ounces) at 13% alcohol by volume, a can or bottle of beer (375 mL or 12 fluid ounces) at 3.5% alcohol by volume, or a shot of whiskey or other spirits (30 mL or 1.0 fluid ounces) at 40% alcohol by volume.
Overall, the TMREL was low regardless of age, sex, time, or geography, and varied from 0 to 1.87 standard drinks per day. However, it was lowest for males aged 15-39 years (0.136 drinks per day) and only slightly higher for females aged 15-39 (0.273), representing 1-2 tenths of a standard drink.
For adults aged 40 and older without any underlying health conditions, drinking a small amount of alcohol may provide some benefits, such as reducing the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, the researchers noted. In general, for individuals aged 40-64 years, TMRELs ranged from about half a standard drink per day (0.527 drinks for males and 0.562 standard drinks per day for females) to almost two standard drinks (1.69 standard drinks per day for males and 1.82 for females). For those older than 65 years, the TMRELs represented just over 3 standard drinks per day (3.19 for males and 3.51 for females). For individuals aged 40 years and older, the distribution of disease burden varied by region, but was J-shaped across all regions, the researchers noted.
The researchers also found that those individuals consuming harmful amounts of alcohol were most likely to be aged 15-39 (59.1%) and male (76.9%).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and lack of data on drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the lack of data reflecting patterns of alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, and exclusion of outcomes often associated with alcohol use, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia, that might reduce estimates of TMREL and NDE.
However, the results add to the ongoing discussion of the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and health, the researchers said.
“The findings of this study support the development of tailored guidelines and recommendations on alcohol consumption by age and across regions and highlight that existing low consumption thresholds are too high for younger populations in all regions,” they concluded.
Consider individual factors when counseling patients
The takeaway message for primary care is that alcohol consumed in moderation can reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, Ms. Bryazka noted. “However, it also increases the risk of many cancers, intentional and unintentional injuries, and infectious diseases like tuberculosis,” she said. “Of these health outcomes, young people are most likely to experience injuries, and as a result, we find that there are significant health risks associated with consuming alcohol for young people. Among older individuals, the relative proportions of these outcomes vary by geography, and so do the risks associated with consuming alcohol,” she explained.
“Importantly, our analysis was conducted at the population level; when evaluating risk at the individual level, it is also important to consider other factors such as the presence of comorbidities and interactions between alcohol and medications,” she emphasized.
Health and alcohol interaction is complicated
“These findings seemingly contradict a previous [Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study] estimate published in The Lancet, which emphasized that any alcohol use, regardless of amount, leads to health loss across populations,” wrote Robyn Burton, PhD, and Nick Sheron, MD, both of King’s College, London, in an accompanying comment.
However, the novel methods of weighting relative risk curves according to levels of underlying disease drive the difference in results, along with disaggregated estimates by age, sex, and region, they said.
“Across most geographical regions in this latest analysis, injuries accounted for most alcohol-related harm in younger age groups. This led to a minimum risk level of zero, or very close to zero, among individuals aged 15-39 years across all geographical regions,” which is lower than the level for older adults because of the shift in alcohol-related disease burden towards cardiovascular disease and cancers, they said. “This highlights the need to consider existing rates of disease in a population when trying to determine the total harm posed by alcohol,” the commentators wrote.
In an additional commentary, Tony Rao, MD, a visiting clinical research fellow in psychiatry at King’s College, London, noted that “the elephant in the room with this study is the interpretation of risk based on outcomes for cardiovascular disease – particularly in older people. We know that any purported health benefits from alcohol on the heart and circulation are balanced out by the increased risk from other conditions such as cancer, liver disease, and mental disorders such as depression and dementia,” Dr. Rao said. “If we are to simply draw the conclusion that older people should continue or start drinking small amounts because it protects against diseases affecting heart and circulation – which still remains controversial – other lifestyle changes or the use of drugs targeted at individual cardiovascular disorders seem like a less harmful way of improving health and wellbeing.”
Data can guide clinical practice
No previous study has examined the effect of the theoretical minimum risk of alcohol consumption by geography, age, sex, and time in the context of background disease rates, said Noel Deep, MD, in an interview.
“This study enabled the researchers to quantify the proportion of the population that consumed alcohol in amounts that exceeded the thresholds by location, age, sex, and year, and this can serve as a guide in our efforts to target the control of alcohol intake by individuals,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc. He also serves as chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
The first take-home message for clinicians is that even low levels of alcohol consumption can have deleterious effects on the health of patients, and patients should be advised accordingly based on the prevalence of diseases in that community and geographic area, Dr. Deep said. “Secondly, clinicians should also consider the risk of alcohol consumption on all forms of health impacts in a given population rather than just focusing on alcohol-related health conditions,” he added.
“This study provides us with the data to tailor our efforts in educating the clinicians and the public about the relationship between alcohol consumption and disease outcomes based on the observed disease rates in each population,” Dr. Deep explained. “The data should provide another reason for physicians to advise their younger patients, especially the younger males, to avoid or minimize alcohol use,” he said. The data also can help clinicians formulate public health messaging and community education to reduce harmful alcohol use, he added.
As for additional research, Dr. Deep said he would like to see data on the difference in the health-related effects of alcohol in binge-drinkers vs. those who regularly consume alcohol on a daily basis. “It would probably also be helpful to figure out what type of alcohol is being studied and the quality of the alcohol,” he said.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Ms. Bryazka and colleagues had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Burton disclosed serving as a consultant to the World Health Organization European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Dr. Sheron had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Internal Medicine News.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
The health risks and benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are complex and remain a hot topic of debate. The data suggest that small amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of certain health outcomes over time, but increase the risk of others, wrote Dana Bryazka, MS, a researcher at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues, in a paper published in the Lancet.
“The amount of alcohol that minimizes health loss is likely to depend on the distribution of underlying causes of disease burden in a given population. Since this distribution varies widely by geography, age, sex, and time, the level of alcohol consumption associated with the lowest risk to health would depend on the age structure and disease composition of that population,” the researchers wrote.
“We estimate that 1.78 million people worldwide died due to alcohol use in 2020,” Ms. Bryazka said in an interview. “It is important that alcohol consumption guidelines and policies are updated to minimize this harm, particularly in the populations at greatest risk,” she said.
“Existing alcohol consumption guidelines frequently vary by sex, with higher consumption thresholds set for males compared to females. Interestingly, with the currently available data we do not see evidence that risk of alcohol use varies by sex,” she noted.
Methods and results
In the study, the researchers conducted a systematic analysis of burden-weighted dose-response relative risk curves across 22 health outcomes. They used disease rates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2020 for the years 1990-2020 for 21 regions, including 204 countries and territories. The data were analyzed by 5-year age group, sex, and year for individuals aged 15-95 years and older. The researchers estimated the theoretical minimum risk exposure level (TMREL) and nondrinker equivalent (NDE), meaning the amount of alcohol at which the health risk equals that of a nondrinker.
One standard drink was defined as 10 g of pure alcohol, equivalent to a small glass of red wine (100 mL or 3.4 fluid ounces) at 13% alcohol by volume, a can or bottle of beer (375 mL or 12 fluid ounces) at 3.5% alcohol by volume, or a shot of whiskey or other spirits (30 mL or 1.0 fluid ounces) at 40% alcohol by volume.
Overall, the TMREL was low regardless of age, sex, time, or geography, and varied from 0 to 1.87 standard drinks per day. However, it was lowest for males aged 15-39 years (0.136 drinks per day) and only slightly higher for females aged 15-39 (0.273), representing 1-2 tenths of a standard drink.
For adults aged 40 and older without any underlying health conditions, drinking a small amount of alcohol may provide some benefits, such as reducing the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, the researchers noted. In general, for individuals aged 40-64 years, TMRELs ranged from about half a standard drink per day (0.527 drinks for males and 0.562 standard drinks per day for females) to almost two standard drinks (1.69 standard drinks per day for males and 1.82 for females). For those older than 65 years, the TMRELs represented just over 3 standard drinks per day (3.19 for males and 3.51 for females). For individuals aged 40 years and older, the distribution of disease burden varied by region, but was J-shaped across all regions, the researchers noted.
The researchers also found that those individuals consuming harmful amounts of alcohol were most likely to be aged 15-39 (59.1%) and male (76.9%).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and lack of data on drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the lack of data reflecting patterns of alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, and exclusion of outcomes often associated with alcohol use, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia, that might reduce estimates of TMREL and NDE.
However, the results add to the ongoing discussion of the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and health, the researchers said.
“The findings of this study support the development of tailored guidelines and recommendations on alcohol consumption by age and across regions and highlight that existing low consumption thresholds are too high for younger populations in all regions,” they concluded.
Consider individual factors when counseling patients
The takeaway message for primary care is that alcohol consumed in moderation can reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, Ms. Bryazka noted. “However, it also increases the risk of many cancers, intentional and unintentional injuries, and infectious diseases like tuberculosis,” she said. “Of these health outcomes, young people are most likely to experience injuries, and as a result, we find that there are significant health risks associated with consuming alcohol for young people. Among older individuals, the relative proportions of these outcomes vary by geography, and so do the risks associated with consuming alcohol,” she explained.
“Importantly, our analysis was conducted at the population level; when evaluating risk at the individual level, it is also important to consider other factors such as the presence of comorbidities and interactions between alcohol and medications,” she emphasized.
Health and alcohol interaction is complicated
“These findings seemingly contradict a previous [Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study] estimate published in The Lancet, which emphasized that any alcohol use, regardless of amount, leads to health loss across populations,” wrote Robyn Burton, PhD, and Nick Sheron, MD, both of King’s College, London, in an accompanying comment.
However, the novel methods of weighting relative risk curves according to levels of underlying disease drive the difference in results, along with disaggregated estimates by age, sex, and region, they said.
“Across most geographical regions in this latest analysis, injuries accounted for most alcohol-related harm in younger age groups. This led to a minimum risk level of zero, or very close to zero, among individuals aged 15-39 years across all geographical regions,” which is lower than the level for older adults because of the shift in alcohol-related disease burden towards cardiovascular disease and cancers, they said. “This highlights the need to consider existing rates of disease in a population when trying to determine the total harm posed by alcohol,” the commentators wrote.
In an additional commentary, Tony Rao, MD, a visiting clinical research fellow in psychiatry at King’s College, London, noted that “the elephant in the room with this study is the interpretation of risk based on outcomes for cardiovascular disease – particularly in older people. We know that any purported health benefits from alcohol on the heart and circulation are balanced out by the increased risk from other conditions such as cancer, liver disease, and mental disorders such as depression and dementia,” Dr. Rao said. “If we are to simply draw the conclusion that older people should continue or start drinking small amounts because it protects against diseases affecting heart and circulation – which still remains controversial – other lifestyle changes or the use of drugs targeted at individual cardiovascular disorders seem like a less harmful way of improving health and wellbeing.”
Data can guide clinical practice
No previous study has examined the effect of the theoretical minimum risk of alcohol consumption by geography, age, sex, and time in the context of background disease rates, said Noel Deep, MD, in an interview.
“This study enabled the researchers to quantify the proportion of the population that consumed alcohol in amounts that exceeded the thresholds by location, age, sex, and year, and this can serve as a guide in our efforts to target the control of alcohol intake by individuals,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc. He also serves as chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
The first take-home message for clinicians is that even low levels of alcohol consumption can have deleterious effects on the health of patients, and patients should be advised accordingly based on the prevalence of diseases in that community and geographic area, Dr. Deep said. “Secondly, clinicians should also consider the risk of alcohol consumption on all forms of health impacts in a given population rather than just focusing on alcohol-related health conditions,” he added.
“This study provides us with the data to tailor our efforts in educating the clinicians and the public about the relationship between alcohol consumption and disease outcomes based on the observed disease rates in each population,” Dr. Deep explained. “The data should provide another reason for physicians to advise their younger patients, especially the younger males, to avoid or minimize alcohol use,” he said. The data also can help clinicians formulate public health messaging and community education to reduce harmful alcohol use, he added.
As for additional research, Dr. Deep said he would like to see data on the difference in the health-related effects of alcohol in binge-drinkers vs. those who regularly consume alcohol on a daily basis. “It would probably also be helpful to figure out what type of alcohol is being studied and the quality of the alcohol,” he said.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Ms. Bryazka and colleagues had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Burton disclosed serving as a consultant to the World Health Organization European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Dr. Sheron had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Internal Medicine News.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
The health risks and benefits of moderate alcohol consumption are complex and remain a hot topic of debate. The data suggest that small amounts of alcohol may reduce the risk of certain health outcomes over time, but increase the risk of others, wrote Dana Bryazka, MS, a researcher at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) at the University of Washington, Seattle, and colleagues, in a paper published in the Lancet.
“The amount of alcohol that minimizes health loss is likely to depend on the distribution of underlying causes of disease burden in a given population. Since this distribution varies widely by geography, age, sex, and time, the level of alcohol consumption associated with the lowest risk to health would depend on the age structure and disease composition of that population,” the researchers wrote.
“We estimate that 1.78 million people worldwide died due to alcohol use in 2020,” Ms. Bryazka said in an interview. “It is important that alcohol consumption guidelines and policies are updated to minimize this harm, particularly in the populations at greatest risk,” she said.
“Existing alcohol consumption guidelines frequently vary by sex, with higher consumption thresholds set for males compared to females. Interestingly, with the currently available data we do not see evidence that risk of alcohol use varies by sex,” she noted.
Methods and results
In the study, the researchers conducted a systematic analysis of burden-weighted dose-response relative risk curves across 22 health outcomes. They used disease rates from the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2020 for the years 1990-2020 for 21 regions, including 204 countries and territories. The data were analyzed by 5-year age group, sex, and year for individuals aged 15-95 years and older. The researchers estimated the theoretical minimum risk exposure level (TMREL) and nondrinker equivalent (NDE), meaning the amount of alcohol at which the health risk equals that of a nondrinker.
One standard drink was defined as 10 g of pure alcohol, equivalent to a small glass of red wine (100 mL or 3.4 fluid ounces) at 13% alcohol by volume, a can or bottle of beer (375 mL or 12 fluid ounces) at 3.5% alcohol by volume, or a shot of whiskey or other spirits (30 mL or 1.0 fluid ounces) at 40% alcohol by volume.
Overall, the TMREL was low regardless of age, sex, time, or geography, and varied from 0 to 1.87 standard drinks per day. However, it was lowest for males aged 15-39 years (0.136 drinks per day) and only slightly higher for females aged 15-39 (0.273), representing 1-2 tenths of a standard drink.
For adults aged 40 and older without any underlying health conditions, drinking a small amount of alcohol may provide some benefits, such as reducing the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, the researchers noted. In general, for individuals aged 40-64 years, TMRELs ranged from about half a standard drink per day (0.527 drinks for males and 0.562 standard drinks per day for females) to almost two standard drinks (1.69 standard drinks per day for males and 1.82 for females). For those older than 65 years, the TMRELs represented just over 3 standard drinks per day (3.19 for males and 3.51 for females). For individuals aged 40 years and older, the distribution of disease burden varied by region, but was J-shaped across all regions, the researchers noted.
The researchers also found that those individuals consuming harmful amounts of alcohol were most likely to be aged 15-39 (59.1%) and male (76.9%).
The study findings were limited by several factors including the observational design and lack of data on drinking patterns, such as binge drinking, the researchers noted. Other limitations include the lack of data reflecting patterns of alcohol consumption during the COVID-19 pandemic, and exclusion of outcomes often associated with alcohol use, such as depression, anxiety, and dementia, that might reduce estimates of TMREL and NDE.
However, the results add to the ongoing discussion of the relationship between moderate alcohol consumption and health, the researchers said.
“The findings of this study support the development of tailored guidelines and recommendations on alcohol consumption by age and across regions and highlight that existing low consumption thresholds are too high for younger populations in all regions,” they concluded.
Consider individual factors when counseling patients
The takeaway message for primary care is that alcohol consumed in moderation can reduce the risk of ischemic heart disease, stroke, and diabetes, Ms. Bryazka noted. “However, it also increases the risk of many cancers, intentional and unintentional injuries, and infectious diseases like tuberculosis,” she said. “Of these health outcomes, young people are most likely to experience injuries, and as a result, we find that there are significant health risks associated with consuming alcohol for young people. Among older individuals, the relative proportions of these outcomes vary by geography, and so do the risks associated with consuming alcohol,” she explained.
“Importantly, our analysis was conducted at the population level; when evaluating risk at the individual level, it is also important to consider other factors such as the presence of comorbidities and interactions between alcohol and medications,” she emphasized.
Health and alcohol interaction is complicated
“These findings seemingly contradict a previous [Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study] estimate published in The Lancet, which emphasized that any alcohol use, regardless of amount, leads to health loss across populations,” wrote Robyn Burton, PhD, and Nick Sheron, MD, both of King’s College, London, in an accompanying comment.
However, the novel methods of weighting relative risk curves according to levels of underlying disease drive the difference in results, along with disaggregated estimates by age, sex, and region, they said.
“Across most geographical regions in this latest analysis, injuries accounted for most alcohol-related harm in younger age groups. This led to a minimum risk level of zero, or very close to zero, among individuals aged 15-39 years across all geographical regions,” which is lower than the level for older adults because of the shift in alcohol-related disease burden towards cardiovascular disease and cancers, they said. “This highlights the need to consider existing rates of disease in a population when trying to determine the total harm posed by alcohol,” the commentators wrote.
In an additional commentary, Tony Rao, MD, a visiting clinical research fellow in psychiatry at King’s College, London, noted that “the elephant in the room with this study is the interpretation of risk based on outcomes for cardiovascular disease – particularly in older people. We know that any purported health benefits from alcohol on the heart and circulation are balanced out by the increased risk from other conditions such as cancer, liver disease, and mental disorders such as depression and dementia,” Dr. Rao said. “If we are to simply draw the conclusion that older people should continue or start drinking small amounts because it protects against diseases affecting heart and circulation – which still remains controversial – other lifestyle changes or the use of drugs targeted at individual cardiovascular disorders seem like a less harmful way of improving health and wellbeing.”
Data can guide clinical practice
No previous study has examined the effect of the theoretical minimum risk of alcohol consumption by geography, age, sex, and time in the context of background disease rates, said Noel Deep, MD, in an interview.
“This study enabled the researchers to quantify the proportion of the population that consumed alcohol in amounts that exceeded the thresholds by location, age, sex, and year, and this can serve as a guide in our efforts to target the control of alcohol intake by individuals,” said Dr. Deep, a general internist in private practice in Antigo, Wisc. He also serves as chief medical officer and a staff physician at Aspirus Langlade Hospital in Antigo.
The first take-home message for clinicians is that even low levels of alcohol consumption can have deleterious effects on the health of patients, and patients should be advised accordingly based on the prevalence of diseases in that community and geographic area, Dr. Deep said. “Secondly, clinicians should also consider the risk of alcohol consumption on all forms of health impacts in a given population rather than just focusing on alcohol-related health conditions,” he added.
“This study provides us with the data to tailor our efforts in educating the clinicians and the public about the relationship between alcohol consumption and disease outcomes based on the observed disease rates in each population,” Dr. Deep explained. “The data should provide another reason for physicians to advise their younger patients, especially the younger males, to avoid or minimize alcohol use,” he said. The data also can help clinicians formulate public health messaging and community education to reduce harmful alcohol use, he added.
As for additional research, Dr. Deep said he would like to see data on the difference in the health-related effects of alcohol in binge-drinkers vs. those who regularly consume alcohol on a daily basis. “It would probably also be helpful to figure out what type of alcohol is being studied and the quality of the alcohol,” he said.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Ms. Bryazka and colleagues had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Burton disclosed serving as a consultant to the World Health Organization European Office for the Prevention and Control of Noncommunicable Diseases. Dr. Sheron had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Deep had no financial conflicts to disclose, but serves on the Editorial Advisory Board of Internal Medicine News.
The study was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation.
FROM THE LANCET
Transgender youth on hormone therapy risk substantial bone loss
, and this is true regardless of gender assignment at birth.
The problem worsens as the time during which these patients receive sex steroid hormones increases. So far, the “bone mineral density effects of these therapies are understudied,” warned Natalie Nokoff, MD, who presented a cross-sectional study at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The study of bone density is part of a larger body of research being conducted by Dr. Nokoff and her co-investigators on the long-term health effects of gender-affirming therapy in children and adolescents. In one of several recent studies, transgender youths taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which effectively block puberty, were shown to be at greater risk of adverse changes in body composition and markers of cardiometabolic health than youths who were not taking them.
“We need more information on the optimal length of treatment with puberty-delaying medications before either discontinuation or introduction of gender-affirming hormones,” said Dr. Nokoff, an assistant professor of pediatrics and endocrinology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
In this study, 56 transgender youth underwent total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The patients ranged in age from 10 years to almost 20 years. Just over half (53%) were assigned female sex at birth.
The mean Z scores, signifying deviation from age-matched norms, were lower regardless of current use or past use of GnRH agonists in both transgender males or transgender females, relative to age-matched norms.
Asked to comment, Michele A. O’Connell, MBBCh, department of endocrinology and diabetes, Royal Children’s Hospital, Victoria, Australia, said the risk of bone loss is real.
“Monitoring of bone health is recommended for all transgender-diverse adolescents treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists,” said Dr. O’Connell. He referred to multiple guidelines, including those issued by the World Professional Association of Transgender Health in 2012 and those from the Endocrine Society that were issued in 2017.
Inverse correlation between duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores
In Dr. Nokoff’s study, for transgender males, the BMD Z score was reduced 0.2 relative to male norms and by 0.4 relative to female norms. For transgender females, the scores were reduced by 0.4 relative to male norms and by 0.2 relative to female norms.
Among transgender males who were taking testosterone and who had previously been exposed to GnRH agonists, the Z score was significantly lower than those taking testosterone alone (P = .004). There were no differences in Z score for transgender females taking estradiol alone relative to estradiol with current or past use of GnRH agonists.
There was a significant inverse correlation for duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores for transgender females relative to male norms (P = .005) or female norms (P = .029). However, Z scores were unrelated to length of time receiving testosterone or estradiol therapy or to sex steroid concentrations.
The number of children and adolescents taking puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies is increasing. Although reliable data are limited, the exploration of gender identify appears to have become more common with the growing social acceptance of gender dysphoria. That term refers to a sense of unease among individuals who feel that their biological sex does not match their gender identity, according to Dr. Nokoff.
“It is now estimated that 2% of youths identify as transgender,” she said.
Findings from studies investigating the relationship between gender-affirming therapy and bone loss among adults have not been consistent. In a single-center study that followed 543 transgender men and 711 transgender women who had undergone DEXA scanning at baseline prior to starting hormone therapy, there did not appear to be any substantial negative effects on lumbar bone density over time (J Bone Min Res. 2018 Dec;34:447-54).
For adolescents, there is growing evidence of the risk of bone loss in relation to gender-affirming therapy, but there is limited agreement on clinical risks and how they can be avoided. Relevant variables include genetics and diet, as well as the types, doses, and length of time receiving gender-affirming therapy.
Monitor bone in transgender youth; Use vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise
Dr. O’Connell is the first author of a recent summary of the pharmacologic management of trans and gender-diverse adolescents. That summary covered multiple topics in addition to risk of bone loss, including the impact on growth, cognition, and mental health (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;107:241-257).
Overall, she believes that bone health should be monitored for children receiving puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies but agrees with Dr. Nokoff that the clinical impact remains poorly defined.
“Long-term follow-up studies will be required to assess the impact, if any, on functional outcomes such as fracture risk,” she reported. Still, she encouraged use of standard ways of improving bone health, including adequate vitamin D intake and weight-bearing exercise.
Dr. Nokoff and Dr. O’Connell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, and this is true regardless of gender assignment at birth.
The problem worsens as the time during which these patients receive sex steroid hormones increases. So far, the “bone mineral density effects of these therapies are understudied,” warned Natalie Nokoff, MD, who presented a cross-sectional study at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The study of bone density is part of a larger body of research being conducted by Dr. Nokoff and her co-investigators on the long-term health effects of gender-affirming therapy in children and adolescents. In one of several recent studies, transgender youths taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which effectively block puberty, were shown to be at greater risk of adverse changes in body composition and markers of cardiometabolic health than youths who were not taking them.
“We need more information on the optimal length of treatment with puberty-delaying medications before either discontinuation or introduction of gender-affirming hormones,” said Dr. Nokoff, an assistant professor of pediatrics and endocrinology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
In this study, 56 transgender youth underwent total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The patients ranged in age from 10 years to almost 20 years. Just over half (53%) were assigned female sex at birth.
The mean Z scores, signifying deviation from age-matched norms, were lower regardless of current use or past use of GnRH agonists in both transgender males or transgender females, relative to age-matched norms.
Asked to comment, Michele A. O’Connell, MBBCh, department of endocrinology and diabetes, Royal Children’s Hospital, Victoria, Australia, said the risk of bone loss is real.
“Monitoring of bone health is recommended for all transgender-diverse adolescents treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists,” said Dr. O’Connell. He referred to multiple guidelines, including those issued by the World Professional Association of Transgender Health in 2012 and those from the Endocrine Society that were issued in 2017.
Inverse correlation between duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores
In Dr. Nokoff’s study, for transgender males, the BMD Z score was reduced 0.2 relative to male norms and by 0.4 relative to female norms. For transgender females, the scores were reduced by 0.4 relative to male norms and by 0.2 relative to female norms.
Among transgender males who were taking testosterone and who had previously been exposed to GnRH agonists, the Z score was significantly lower than those taking testosterone alone (P = .004). There were no differences in Z score for transgender females taking estradiol alone relative to estradiol with current or past use of GnRH agonists.
There was a significant inverse correlation for duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores for transgender females relative to male norms (P = .005) or female norms (P = .029). However, Z scores were unrelated to length of time receiving testosterone or estradiol therapy or to sex steroid concentrations.
The number of children and adolescents taking puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies is increasing. Although reliable data are limited, the exploration of gender identify appears to have become more common with the growing social acceptance of gender dysphoria. That term refers to a sense of unease among individuals who feel that their biological sex does not match their gender identity, according to Dr. Nokoff.
“It is now estimated that 2% of youths identify as transgender,” she said.
Findings from studies investigating the relationship between gender-affirming therapy and bone loss among adults have not been consistent. In a single-center study that followed 543 transgender men and 711 transgender women who had undergone DEXA scanning at baseline prior to starting hormone therapy, there did not appear to be any substantial negative effects on lumbar bone density over time (J Bone Min Res. 2018 Dec;34:447-54).
For adolescents, there is growing evidence of the risk of bone loss in relation to gender-affirming therapy, but there is limited agreement on clinical risks and how they can be avoided. Relevant variables include genetics and diet, as well as the types, doses, and length of time receiving gender-affirming therapy.
Monitor bone in transgender youth; Use vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise
Dr. O’Connell is the first author of a recent summary of the pharmacologic management of trans and gender-diverse adolescents. That summary covered multiple topics in addition to risk of bone loss, including the impact on growth, cognition, and mental health (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;107:241-257).
Overall, she believes that bone health should be monitored for children receiving puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies but agrees with Dr. Nokoff that the clinical impact remains poorly defined.
“Long-term follow-up studies will be required to assess the impact, if any, on functional outcomes such as fracture risk,” she reported. Still, she encouraged use of standard ways of improving bone health, including adequate vitamin D intake and weight-bearing exercise.
Dr. Nokoff and Dr. O’Connell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, and this is true regardless of gender assignment at birth.
The problem worsens as the time during which these patients receive sex steroid hormones increases. So far, the “bone mineral density effects of these therapies are understudied,” warned Natalie Nokoff, MD, who presented a cross-sectional study at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The study of bone density is part of a larger body of research being conducted by Dr. Nokoff and her co-investigators on the long-term health effects of gender-affirming therapy in children and adolescents. In one of several recent studies, transgender youths taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which effectively block puberty, were shown to be at greater risk of adverse changes in body composition and markers of cardiometabolic health than youths who were not taking them.
“We need more information on the optimal length of treatment with puberty-delaying medications before either discontinuation or introduction of gender-affirming hormones,” said Dr. Nokoff, an assistant professor of pediatrics and endocrinology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
In this study, 56 transgender youth underwent total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The patients ranged in age from 10 years to almost 20 years. Just over half (53%) were assigned female sex at birth.
The mean Z scores, signifying deviation from age-matched norms, were lower regardless of current use or past use of GnRH agonists in both transgender males or transgender females, relative to age-matched norms.
Asked to comment, Michele A. O’Connell, MBBCh, department of endocrinology and diabetes, Royal Children’s Hospital, Victoria, Australia, said the risk of bone loss is real.
“Monitoring of bone health is recommended for all transgender-diverse adolescents treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists,” said Dr. O’Connell. He referred to multiple guidelines, including those issued by the World Professional Association of Transgender Health in 2012 and those from the Endocrine Society that were issued in 2017.
Inverse correlation between duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores
In Dr. Nokoff’s study, for transgender males, the BMD Z score was reduced 0.2 relative to male norms and by 0.4 relative to female norms. For transgender females, the scores were reduced by 0.4 relative to male norms and by 0.2 relative to female norms.
Among transgender males who were taking testosterone and who had previously been exposed to GnRH agonists, the Z score was significantly lower than those taking testosterone alone (P = .004). There were no differences in Z score for transgender females taking estradiol alone relative to estradiol with current or past use of GnRH agonists.
There was a significant inverse correlation for duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores for transgender females relative to male norms (P = .005) or female norms (P = .029). However, Z scores were unrelated to length of time receiving testosterone or estradiol therapy or to sex steroid concentrations.
The number of children and adolescents taking puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies is increasing. Although reliable data are limited, the exploration of gender identify appears to have become more common with the growing social acceptance of gender dysphoria. That term refers to a sense of unease among individuals who feel that their biological sex does not match their gender identity, according to Dr. Nokoff.
“It is now estimated that 2% of youths identify as transgender,” she said.
Findings from studies investigating the relationship between gender-affirming therapy and bone loss among adults have not been consistent. In a single-center study that followed 543 transgender men and 711 transgender women who had undergone DEXA scanning at baseline prior to starting hormone therapy, there did not appear to be any substantial negative effects on lumbar bone density over time (J Bone Min Res. 2018 Dec;34:447-54).
For adolescents, there is growing evidence of the risk of bone loss in relation to gender-affirming therapy, but there is limited agreement on clinical risks and how they can be avoided. Relevant variables include genetics and diet, as well as the types, doses, and length of time receiving gender-affirming therapy.
Monitor bone in transgender youth; Use vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise
Dr. O’Connell is the first author of a recent summary of the pharmacologic management of trans and gender-diverse adolescents. That summary covered multiple topics in addition to risk of bone loss, including the impact on growth, cognition, and mental health (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;107:241-257).
Overall, she believes that bone health should be monitored for children receiving puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies but agrees with Dr. Nokoff that the clinical impact remains poorly defined.
“Long-term follow-up studies will be required to assess the impact, if any, on functional outcomes such as fracture risk,” she reported. Still, she encouraged use of standard ways of improving bone health, including adequate vitamin D intake and weight-bearing exercise.
Dr. Nokoff and Dr. O’Connell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ENDO 2022
Precocious puberty – how early is too soon?
A 6-year-old girl presents with breast development. Her medical history is unremarkable. The parents are of average height, and the mother reports her thelarche was age 11 years. The girl is at the 97th percentile for her height and 90th percentile for her weight. She has Tanner stage 3 breast development and Tanner stage 2 pubic hair development. She has grown slightly more than 3 inches over the past year. How should she be evaluated and managed (N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2366-77)?
The premature onset of puberty, i.e., precocious puberty (PP), can be an emotionally traumatic event for the child and parents. Over the past century, improvements in public health and nutrition, and, more recently, increased obesity, have been associated with earlier puberty and the dominant factor has been attributed to genetics (Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25[1]:49-54). This month’s article will focus on understanding what is considered “early” puberty, evaluating for causes, and managing precocious puberty.
More commonly seen in girls than boys, PP is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 7.5 years in Black and Hispanic girls, and prior to 8 years in White girls, which is 2-2.5 standard deviations below the average age of pubertal onset in healthy children (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:455-9). As a comparison, PP is diagnosed with onset before age 9 years in boys. For White compared with Black girls, the average timing of thelarche is age 10 vs. 9.5 years, peak growth velocity is age 11.5, menarche is age 12.5 vs. 12, while completion of puberty is near age 14.5 vs. 13.5, respectively (J Pediatr. 1985;107:317). Fortunately, most girls with PP have common variants rather than serious pathology.
Classification: Central (CPP) vs. peripheral (PPP)
CPP is gonadotropin dependent, meaning the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO) is prematurely activated resulting in the normal progression of puberty.
PPP is gonadotropin independent, caused by sex steroid secretion from any source – ovaries, adrenal gland, exogenous or ectopic production, e.g., germ-cell tumor. This results in a disordered progression of pubertal milestones.
Whereas CPP is typically isosexual development, i.e., consistent with the child’s gender, PPP can be isosexual or contrasexual, e.g., virilization of girls. A third classification is “benign or nonprogressive pubertal variants” manifesting as isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche.
Causes (see table)
CPP. Idiopathic causes account for 80%-90% of presentations in girls and 25%-80% in boys. Remarkably, international and domestic adoption, as well as a family history of PP increases the likelihood of CPP in girls. Other etiologies include CNS lesions, e.g., hamartomas, which are the most common cause of PP in young children. MRI with contrast has been the traditional mode of diagnosis for CNS tumors, yet the yield is dubious in girls above age 6. Genetic causes are found in only a small percentage of PP cases. Rarely, CPP can result from gonadotropin-secreting tumors because of elevated luteinizing hormone levels.
PPP. As a result of sex steroid secretion, peripheral causes of PPP include ovarian cysts and ovarian tumors that increase circulating estradiol, such as granulosa cell tumors, which would cause isosexual PPP and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors that secrete testosterone, which can result in contrasexual PPP. Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia can result in PPP with virilization (contrasexual) and markedly advanced bone age.
McCune-Albright syndrome is rare and presents with the classic triad of PPP, skin pigmentation called café-au-lait, and fibrous dysplasia of bone. The pathophysiology of McCune-Albright syndrome is autoactivation of the G-protein leading to activation of ovarian tissue that results in formation of large ovarian cysts and extreme elevations in serum estradiol as well as the potential production of other hormones, e.g., thyrotoxicosis, excess growth hormone (acromegaly), and Cushing syndrome.
Premature thelarche. Premature thelarche typically occurs in girls between the ages of 1 and 3 years and is limited to breast enlargement. While no cause has been determined, the plausible explanations include partial activation of the HPO axis, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or a genetic origin. A small percentage of these girls progress to CPP.
EDCs have been considered as potential influencers of early puberty, but no consensus has been established. (Examples of EDCs in the environment include air, soil, or water supply along with food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that can affect the endocrine system.)
Premature adenarche. Premature adrenarche presents with adult body odor and/or body hair (pubic and/or axillary) in girls who have an elevated body mass index, most commonly at the ages of 6-7 years. The presumed mechanism is normal maturation of the adrenal gland with resultant elevation of circulating androgens. Bone age may be mildly accelerated and DHEAS is prematurely elevated for age. These girls appear to be at increased risk for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Evaluation
The initial step in the evaluation of PP is to determine whether the cause is CPP or PPP; the latter includes distinguishing isosexual from contrasexual development. A thorough history (growth, headaches, behavior or visual change, seizures, abdominal pain), physical exam, including Tanner staging, and bone age is required. However, with isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche, a bone age may not be necessary, as initial close clinical observation for pubertal progression is likely sufficient.
For CPP, the diagnosis is based on serum LH, whether random levels or elevations follow GnRH stimulation. Puberty milestones progress normally although adrenarche is not consistently apparent. For girls younger than age 6, a brain MRI is recommended but not in asymptomatic older girls with CPP. LH and FSH along with estradiol or testosterone, the latter especially in boys, are the first line of serum testing. Serum TSH is recommended for suspicion of primary hypothyroidism. In girls with premature adrenarche, a bone age, testosterone, DHEAS, and 17-OHP to rule out adrenal hyperplasia should be obtained. Pelvic ultrasound may be a useful adjunct to assess uterine volume and/or ovarian cysts/tumors.
Rapidity of onset can also lead the evaluation since a normal growth chart and skeletal maturation suggests a benign pubertal variant whereas a more rapid rate can signal CPP or PPP. Of note, health care providers should ensure prescription, over-the-counter oral or topical sources of hormones, and EDCs are ruled out.
Consequences
An association between childhood sexual abuse and earlier pubertal onset has been cited. These girls may be at increased risk for psychosocial difficulties, menstrual and fertility problems, and even reproductive cancers because of prolonged exposure to sex hormones (J Adolesc Health. 2016;60[1]:65-71).
Treatment
The mainstay of CPP treatment is maximizing adult height, typically through the use of a GnRH agonist for HPO suppression from pituitary downregulation. For girls above age 8 years, attempts at improving adult height have not shown a benefit.
In girls with PPP, treatment is directed at the prevailing pathology. Interestingly, early PPP can activate the HPO axis thereby converting to “secondary” CPP. In PPP, McCune-Albright syndrome treatment targets reducing circulating estrogens through letrozole or tamoxifen as well as addressing other autoactivated hormone production. Ovarian and adrenal tumors, albeit rare, can cause PP; therefore, surgical excision is the goal of treatment.
PP should be approached with equal concerns about the physical and emotional effects while including the family to help them understand the pathophysiology and psychosocial risks.
Dr. Mark P. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
A 6-year-old girl presents with breast development. Her medical history is unremarkable. The parents are of average height, and the mother reports her thelarche was age 11 years. The girl is at the 97th percentile for her height and 90th percentile for her weight. She has Tanner stage 3 breast development and Tanner stage 2 pubic hair development. She has grown slightly more than 3 inches over the past year. How should she be evaluated and managed (N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2366-77)?
The premature onset of puberty, i.e., precocious puberty (PP), can be an emotionally traumatic event for the child and parents. Over the past century, improvements in public health and nutrition, and, more recently, increased obesity, have been associated with earlier puberty and the dominant factor has been attributed to genetics (Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25[1]:49-54). This month’s article will focus on understanding what is considered “early” puberty, evaluating for causes, and managing precocious puberty.
More commonly seen in girls than boys, PP is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 7.5 years in Black and Hispanic girls, and prior to 8 years in White girls, which is 2-2.5 standard deviations below the average age of pubertal onset in healthy children (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:455-9). As a comparison, PP is diagnosed with onset before age 9 years in boys. For White compared with Black girls, the average timing of thelarche is age 10 vs. 9.5 years, peak growth velocity is age 11.5, menarche is age 12.5 vs. 12, while completion of puberty is near age 14.5 vs. 13.5, respectively (J Pediatr. 1985;107:317). Fortunately, most girls with PP have common variants rather than serious pathology.
Classification: Central (CPP) vs. peripheral (PPP)
CPP is gonadotropin dependent, meaning the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO) is prematurely activated resulting in the normal progression of puberty.
PPP is gonadotropin independent, caused by sex steroid secretion from any source – ovaries, adrenal gland, exogenous or ectopic production, e.g., germ-cell tumor. This results in a disordered progression of pubertal milestones.
Whereas CPP is typically isosexual development, i.e., consistent with the child’s gender, PPP can be isosexual or contrasexual, e.g., virilization of girls. A third classification is “benign or nonprogressive pubertal variants” manifesting as isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche.
Causes (see table)
CPP. Idiopathic causes account for 80%-90% of presentations in girls and 25%-80% in boys. Remarkably, international and domestic adoption, as well as a family history of PP increases the likelihood of CPP in girls. Other etiologies include CNS lesions, e.g., hamartomas, which are the most common cause of PP in young children. MRI with contrast has been the traditional mode of diagnosis for CNS tumors, yet the yield is dubious in girls above age 6. Genetic causes are found in only a small percentage of PP cases. Rarely, CPP can result from gonadotropin-secreting tumors because of elevated luteinizing hormone levels.
PPP. As a result of sex steroid secretion, peripheral causes of PPP include ovarian cysts and ovarian tumors that increase circulating estradiol, such as granulosa cell tumors, which would cause isosexual PPP and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors that secrete testosterone, which can result in contrasexual PPP. Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia can result in PPP with virilization (contrasexual) and markedly advanced bone age.
McCune-Albright syndrome is rare and presents with the classic triad of PPP, skin pigmentation called café-au-lait, and fibrous dysplasia of bone. The pathophysiology of McCune-Albright syndrome is autoactivation of the G-protein leading to activation of ovarian tissue that results in formation of large ovarian cysts and extreme elevations in serum estradiol as well as the potential production of other hormones, e.g., thyrotoxicosis, excess growth hormone (acromegaly), and Cushing syndrome.
Premature thelarche. Premature thelarche typically occurs in girls between the ages of 1 and 3 years and is limited to breast enlargement. While no cause has been determined, the plausible explanations include partial activation of the HPO axis, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or a genetic origin. A small percentage of these girls progress to CPP.
EDCs have been considered as potential influencers of early puberty, but no consensus has been established. (Examples of EDCs in the environment include air, soil, or water supply along with food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that can affect the endocrine system.)
Premature adenarche. Premature adrenarche presents with adult body odor and/or body hair (pubic and/or axillary) in girls who have an elevated body mass index, most commonly at the ages of 6-7 years. The presumed mechanism is normal maturation of the adrenal gland with resultant elevation of circulating androgens. Bone age may be mildly accelerated and DHEAS is prematurely elevated for age. These girls appear to be at increased risk for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Evaluation
The initial step in the evaluation of PP is to determine whether the cause is CPP or PPP; the latter includes distinguishing isosexual from contrasexual development. A thorough history (growth, headaches, behavior or visual change, seizures, abdominal pain), physical exam, including Tanner staging, and bone age is required. However, with isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche, a bone age may not be necessary, as initial close clinical observation for pubertal progression is likely sufficient.
For CPP, the diagnosis is based on serum LH, whether random levels or elevations follow GnRH stimulation. Puberty milestones progress normally although adrenarche is not consistently apparent. For girls younger than age 6, a brain MRI is recommended but not in asymptomatic older girls with CPP. LH and FSH along with estradiol or testosterone, the latter especially in boys, are the first line of serum testing. Serum TSH is recommended for suspicion of primary hypothyroidism. In girls with premature adrenarche, a bone age, testosterone, DHEAS, and 17-OHP to rule out adrenal hyperplasia should be obtained. Pelvic ultrasound may be a useful adjunct to assess uterine volume and/or ovarian cysts/tumors.
Rapidity of onset can also lead the evaluation since a normal growth chart and skeletal maturation suggests a benign pubertal variant whereas a more rapid rate can signal CPP or PPP. Of note, health care providers should ensure prescription, over-the-counter oral or topical sources of hormones, and EDCs are ruled out.
Consequences
An association between childhood sexual abuse and earlier pubertal onset has been cited. These girls may be at increased risk for psychosocial difficulties, menstrual and fertility problems, and even reproductive cancers because of prolonged exposure to sex hormones (J Adolesc Health. 2016;60[1]:65-71).
Treatment
The mainstay of CPP treatment is maximizing adult height, typically through the use of a GnRH agonist for HPO suppression from pituitary downregulation. For girls above age 8 years, attempts at improving adult height have not shown a benefit.
In girls with PPP, treatment is directed at the prevailing pathology. Interestingly, early PPP can activate the HPO axis thereby converting to “secondary” CPP. In PPP, McCune-Albright syndrome treatment targets reducing circulating estrogens through letrozole or tamoxifen as well as addressing other autoactivated hormone production. Ovarian and adrenal tumors, albeit rare, can cause PP; therefore, surgical excision is the goal of treatment.
PP should be approached with equal concerns about the physical and emotional effects while including the family to help them understand the pathophysiology and psychosocial risks.
Dr. Mark P. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
A 6-year-old girl presents with breast development. Her medical history is unremarkable. The parents are of average height, and the mother reports her thelarche was age 11 years. The girl is at the 97th percentile for her height and 90th percentile for her weight. She has Tanner stage 3 breast development and Tanner stage 2 pubic hair development. She has grown slightly more than 3 inches over the past year. How should she be evaluated and managed (N Engl J Med. 2008;358:2366-77)?
The premature onset of puberty, i.e., precocious puberty (PP), can be an emotionally traumatic event for the child and parents. Over the past century, improvements in public health and nutrition, and, more recently, increased obesity, have been associated with earlier puberty and the dominant factor has been attributed to genetics (Curr Opin Endocrinol Diabetes Obes. 2018;25[1]:49-54). This month’s article will focus on understanding what is considered “early” puberty, evaluating for causes, and managing precocious puberty.
More commonly seen in girls than boys, PP is defined as the onset of secondary sexual characteristics before age 7.5 years in Black and Hispanic girls, and prior to 8 years in White girls, which is 2-2.5 standard deviations below the average age of pubertal onset in healthy children (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol. 2019;32:455-9). As a comparison, PP is diagnosed with onset before age 9 years in boys. For White compared with Black girls, the average timing of thelarche is age 10 vs. 9.5 years, peak growth velocity is age 11.5, menarche is age 12.5 vs. 12, while completion of puberty is near age 14.5 vs. 13.5, respectively (J Pediatr. 1985;107:317). Fortunately, most girls with PP have common variants rather than serious pathology.
Classification: Central (CPP) vs. peripheral (PPP)
CPP is gonadotropin dependent, meaning the hypothalamic-pituitary-ovarian axis (HPO) is prematurely activated resulting in the normal progression of puberty.
PPP is gonadotropin independent, caused by sex steroid secretion from any source – ovaries, adrenal gland, exogenous or ectopic production, e.g., germ-cell tumor. This results in a disordered progression of pubertal milestones.
Whereas CPP is typically isosexual development, i.e., consistent with the child’s gender, PPP can be isosexual or contrasexual, e.g., virilization of girls. A third classification is “benign or nonprogressive pubertal variants” manifesting as isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche.
Causes (see table)
CPP. Idiopathic causes account for 80%-90% of presentations in girls and 25%-80% in boys. Remarkably, international and domestic adoption, as well as a family history of PP increases the likelihood of CPP in girls. Other etiologies include CNS lesions, e.g., hamartomas, which are the most common cause of PP in young children. MRI with contrast has been the traditional mode of diagnosis for CNS tumors, yet the yield is dubious in girls above age 6. Genetic causes are found in only a small percentage of PP cases. Rarely, CPP can result from gonadotropin-secreting tumors because of elevated luteinizing hormone levels.
PPP. As a result of sex steroid secretion, peripheral causes of PPP include ovarian cysts and ovarian tumors that increase circulating estradiol, such as granulosa cell tumors, which would cause isosexual PPP and Sertoli-Leydig cell tumors that secrete testosterone, which can result in contrasexual PPP. Mild congenital adrenal hyperplasia can result in PPP with virilization (contrasexual) and markedly advanced bone age.
McCune-Albright syndrome is rare and presents with the classic triad of PPP, skin pigmentation called café-au-lait, and fibrous dysplasia of bone. The pathophysiology of McCune-Albright syndrome is autoactivation of the G-protein leading to activation of ovarian tissue that results in formation of large ovarian cysts and extreme elevations in serum estradiol as well as the potential production of other hormones, e.g., thyrotoxicosis, excess growth hormone (acromegaly), and Cushing syndrome.
Premature thelarche. Premature thelarche typically occurs in girls between the ages of 1 and 3 years and is limited to breast enlargement. While no cause has been determined, the plausible explanations include partial activation of the HPO axis, endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs), or a genetic origin. A small percentage of these girls progress to CPP.
EDCs have been considered as potential influencers of early puberty, but no consensus has been established. (Examples of EDCs in the environment include air, soil, or water supply along with food sources, personal care products, and manufactured products that can affect the endocrine system.)
Premature adenarche. Premature adrenarche presents with adult body odor and/or body hair (pubic and/or axillary) in girls who have an elevated body mass index, most commonly at the ages of 6-7 years. The presumed mechanism is normal maturation of the adrenal gland with resultant elevation of circulating androgens. Bone age may be mildly accelerated and DHEAS is prematurely elevated for age. These girls appear to be at increased risk for polycystic ovary syndrome.
Evaluation
The initial step in the evaluation of PP is to determine whether the cause is CPP or PPP; the latter includes distinguishing isosexual from contrasexual development. A thorough history (growth, headaches, behavior or visual change, seizures, abdominal pain), physical exam, including Tanner staging, and bone age is required. However, with isolated premature thelarche or adrenarche, a bone age may not be necessary, as initial close clinical observation for pubertal progression is likely sufficient.
For CPP, the diagnosis is based on serum LH, whether random levels or elevations follow GnRH stimulation. Puberty milestones progress normally although adrenarche is not consistently apparent. For girls younger than age 6, a brain MRI is recommended but not in asymptomatic older girls with CPP. LH and FSH along with estradiol or testosterone, the latter especially in boys, are the first line of serum testing. Serum TSH is recommended for suspicion of primary hypothyroidism. In girls with premature adrenarche, a bone age, testosterone, DHEAS, and 17-OHP to rule out adrenal hyperplasia should be obtained. Pelvic ultrasound may be a useful adjunct to assess uterine volume and/or ovarian cysts/tumors.
Rapidity of onset can also lead the evaluation since a normal growth chart and skeletal maturation suggests a benign pubertal variant whereas a more rapid rate can signal CPP or PPP. Of note, health care providers should ensure prescription, over-the-counter oral or topical sources of hormones, and EDCs are ruled out.
Consequences
An association between childhood sexual abuse and earlier pubertal onset has been cited. These girls may be at increased risk for psychosocial difficulties, menstrual and fertility problems, and even reproductive cancers because of prolonged exposure to sex hormones (J Adolesc Health. 2016;60[1]:65-71).
Treatment
The mainstay of CPP treatment is maximizing adult height, typically through the use of a GnRH agonist for HPO suppression from pituitary downregulation. For girls above age 8 years, attempts at improving adult height have not shown a benefit.
In girls with PPP, treatment is directed at the prevailing pathology. Interestingly, early PPP can activate the HPO axis thereby converting to “secondary” CPP. In PPP, McCune-Albright syndrome treatment targets reducing circulating estrogens through letrozole or tamoxifen as well as addressing other autoactivated hormone production. Ovarian and adrenal tumors, albeit rare, can cause PP; therefore, surgical excision is the goal of treatment.
PP should be approached with equal concerns about the physical and emotional effects while including the family to help them understand the pathophysiology and psychosocial risks.
Dr. Mark P. Trolice is director of The IVF Center in Winter Park, Fla., and professor of obstetrics and gynecology at the University of Central Florida, Orlando.
Hormone therapy and breast cancer: An overview
It is projected that by 2050, 1.6 billion women in the world will have reached menopause or the postmenopausal period, a significant increase, compared with a billion women in 2020. Of all menopausal women, around 75% are affected by troublesome menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Around 84% of postmenopausal women experience genitourinary symptoms, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and incontinence.
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is the most effective treatment for managing these symptoms; however, its effects on numerous aspects of female health remain uncertain, in particular with regard to breast cancer. The influence of MHT on breast cancer remains unsettled, with discordant findings from observational studies and randomized clinical trials, a factor that affects the decisions made by doctors concerning hormone therapy in menopausal women.
Background
Conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs) were introduced into clinical practice in the 1940s. For decades, MHT was the main treatment in conventional medicine for the symptoms of menopause. MHT was used in Western countries for about 600 million women starting from 1970, and it progressively increased during the 1990s. Professional organizations recommended MHT for the prevention of osteoporosis and chronic heart disease (CHD), and a third of prescriptions were for women older than 60 years.
Against this background, the National Institutes of Health launched randomized trials of MHT through the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) to test whether the association with reduced risk for CHD found in observational studies was real and to obtain reliable information on the overall risks and benefits regarding the prevention of chronic disease for postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years.
The WHI trials tested standard-dose oral CEEs with and without standard-dose continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (EPT). In 2002, the results of the WHI studies raised a series of concerns about the long-term safety of MHT, in particular the finding of an increased risk of breast cancer for women undergoing therapy. That risk exceeded the benefits from reductions in hip fractures and colorectal cancer.
The WHI findings received wide attention. Prescriptions for MHT dropped precipitously after 2002 and continued to decline in subsequent years. Declines were most marked for standard-dose EPT and in older women. The results of the CEE study were less negative, compared with those for EPT, as they showed no effect on CHD, a nonsignificant reduction in the risk of breast cancer, and a more favorable risk-benefit ratio for younger women, compared with older women. A decade later, it had become widely accepted that MHT should not be used for the prevention of chronic disease in older women; however, short-term use for treatment of vasomotor symptoms remains an accepted indication.
Risks and outcomes
Emerging from a series of WHI reports are complex models on the effect of hormonal therapy on the risk and outcome of breast cancer. In one study, women with an intact uterus received CEEs plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). An increase in the risk of breast cancer was observed over a median of 5.6 years of treatment, followed by a moderate reduction, with the risk increasing after 13 years of cumulative follow-up. For women treated with CEE alone, the reduction in risk observed over an average of 7.2 years of treatment was maintained for 13 years of follow-up.
Results from observational studies contrast with those from randomized controlled trials, particularly those concerning the use of estrogens only. A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer showed that both EPT and CEE were associated with a higher risk of breast neoplasia. Results of the Million Women Study showed a higher death rate.
Treatment methods and duration
Information from prospective studies on the effects of commencing MHT at various ages between 40 and 59 years show that for women who commenced treatment at any time within this age range, the relative risk was similar and was highly significant for all ages. Few women had started MHT treatment well after menopause at ages 60-69 years, and their excess risks during years 5-14 of current use were significant for estrogen-progestogen but not for estrogen-only MHT.
If these associations are largely causal, then for women of average weight in developed countries, 5 years of MHT, starting at age 50 years, would increase breast cancer incidence at ages 50-69 years by about 1 in every 50 users of estrogen plus daily progestogen preparations; 1 in every 70 users of estrogen plus intermittent progestogen preparations; and 1 in every 200 users of estrogen-only preparations. The corresponding excesses from 10 years of MHT would be about twice as great.
During 5-14 years of MHT use, the RRs were similarly increased if MHT use had started at ages 40-44 years, 45-49 years, 50-54 years, and 55-59 years; RRs appeared to be attenuated if MHT use had started after age 60 years. They were also attenuated by adiposity, particularly for estrogen-only MHT (which had little effect in obese women). After MHT use ceased, some excess risk of breast cancer persisted for more than a decade; this is directly correlated with the duration of treatment.
Therefore, it can be expected that the effects of MHT may vary between participants on the basis of age or time since menopause, as well as treatments (MHT type, dose, formulation, duration of use, and route of administration). Regarding formulation effects on the risk of breast cancer, new evidence shows an increased risk of 28%. Progestogens appeared to be differentially associated with breast cancer (micronized progesterone: odds ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval 0.55-1.79; synthetic progestin: OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.22-1.35). When prescribing MHT, micronized progesterone may be the safer progestogen to use.
In conclusion, MHT has a complex balance of benefits and risk on various health outcomes. Some effects differ qualitatively between ET and EPT. Regarding use of MHT, consideration should be given to the full range of effects, along with patients’ values and preferences. The overall quality of existing systematic reviews is moderate to poor. Clinicians should evaluate their scientific strength before considering applying their results in clinical practice. Regarding use of any hormone therapy regimen, consideration should be given to the full range of risk and benefits and should involve shared decisionmaking with the patient. It should be recognized that risk-benefit balance is altered by factors such as age, time from menopause, oophorectomy status, and prior hysterectomy and that some outcomes persist and there is some attenuation after stopping use.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
A version of the article appeared on Medscape.com.
It is projected that by 2050, 1.6 billion women in the world will have reached menopause or the postmenopausal period, a significant increase, compared with a billion women in 2020. Of all menopausal women, around 75% are affected by troublesome menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Around 84% of postmenopausal women experience genitourinary symptoms, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and incontinence.
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is the most effective treatment for managing these symptoms; however, its effects on numerous aspects of female health remain uncertain, in particular with regard to breast cancer. The influence of MHT on breast cancer remains unsettled, with discordant findings from observational studies and randomized clinical trials, a factor that affects the decisions made by doctors concerning hormone therapy in menopausal women.
Background
Conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs) were introduced into clinical practice in the 1940s. For decades, MHT was the main treatment in conventional medicine for the symptoms of menopause. MHT was used in Western countries for about 600 million women starting from 1970, and it progressively increased during the 1990s. Professional organizations recommended MHT for the prevention of osteoporosis and chronic heart disease (CHD), and a third of prescriptions were for women older than 60 years.
Against this background, the National Institutes of Health launched randomized trials of MHT through the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) to test whether the association with reduced risk for CHD found in observational studies was real and to obtain reliable information on the overall risks and benefits regarding the prevention of chronic disease for postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years.
The WHI trials tested standard-dose oral CEEs with and without standard-dose continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (EPT). In 2002, the results of the WHI studies raised a series of concerns about the long-term safety of MHT, in particular the finding of an increased risk of breast cancer for women undergoing therapy. That risk exceeded the benefits from reductions in hip fractures and colorectal cancer.
The WHI findings received wide attention. Prescriptions for MHT dropped precipitously after 2002 and continued to decline in subsequent years. Declines were most marked for standard-dose EPT and in older women. The results of the CEE study were less negative, compared with those for EPT, as they showed no effect on CHD, a nonsignificant reduction in the risk of breast cancer, and a more favorable risk-benefit ratio for younger women, compared with older women. A decade later, it had become widely accepted that MHT should not be used for the prevention of chronic disease in older women; however, short-term use for treatment of vasomotor symptoms remains an accepted indication.
Risks and outcomes
Emerging from a series of WHI reports are complex models on the effect of hormonal therapy on the risk and outcome of breast cancer. In one study, women with an intact uterus received CEEs plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). An increase in the risk of breast cancer was observed over a median of 5.6 years of treatment, followed by a moderate reduction, with the risk increasing after 13 years of cumulative follow-up. For women treated with CEE alone, the reduction in risk observed over an average of 7.2 years of treatment was maintained for 13 years of follow-up.
Results from observational studies contrast with those from randomized controlled trials, particularly those concerning the use of estrogens only. A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer showed that both EPT and CEE were associated with a higher risk of breast neoplasia. Results of the Million Women Study showed a higher death rate.
Treatment methods and duration
Information from prospective studies on the effects of commencing MHT at various ages between 40 and 59 years show that for women who commenced treatment at any time within this age range, the relative risk was similar and was highly significant for all ages. Few women had started MHT treatment well after menopause at ages 60-69 years, and their excess risks during years 5-14 of current use were significant for estrogen-progestogen but not for estrogen-only MHT.
If these associations are largely causal, then for women of average weight in developed countries, 5 years of MHT, starting at age 50 years, would increase breast cancer incidence at ages 50-69 years by about 1 in every 50 users of estrogen plus daily progestogen preparations; 1 in every 70 users of estrogen plus intermittent progestogen preparations; and 1 in every 200 users of estrogen-only preparations. The corresponding excesses from 10 years of MHT would be about twice as great.
During 5-14 years of MHT use, the RRs were similarly increased if MHT use had started at ages 40-44 years, 45-49 years, 50-54 years, and 55-59 years; RRs appeared to be attenuated if MHT use had started after age 60 years. They were also attenuated by adiposity, particularly for estrogen-only MHT (which had little effect in obese women). After MHT use ceased, some excess risk of breast cancer persisted for more than a decade; this is directly correlated with the duration of treatment.
Therefore, it can be expected that the effects of MHT may vary between participants on the basis of age or time since menopause, as well as treatments (MHT type, dose, formulation, duration of use, and route of administration). Regarding formulation effects on the risk of breast cancer, new evidence shows an increased risk of 28%. Progestogens appeared to be differentially associated with breast cancer (micronized progesterone: odds ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval 0.55-1.79; synthetic progestin: OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.22-1.35). When prescribing MHT, micronized progesterone may be the safer progestogen to use.
In conclusion, MHT has a complex balance of benefits and risk on various health outcomes. Some effects differ qualitatively between ET and EPT. Regarding use of MHT, consideration should be given to the full range of effects, along with patients’ values and preferences. The overall quality of existing systematic reviews is moderate to poor. Clinicians should evaluate their scientific strength before considering applying their results in clinical practice. Regarding use of any hormone therapy regimen, consideration should be given to the full range of risk and benefits and should involve shared decisionmaking with the patient. It should be recognized that risk-benefit balance is altered by factors such as age, time from menopause, oophorectomy status, and prior hysterectomy and that some outcomes persist and there is some attenuation after stopping use.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
A version of the article appeared on Medscape.com.
It is projected that by 2050, 1.6 billion women in the world will have reached menopause or the postmenopausal period, a significant increase, compared with a billion women in 2020. Of all menopausal women, around 75% are affected by troublesome menopause symptoms, such as hot flashes and night sweats.
Around 84% of postmenopausal women experience genitourinary symptoms, such as vulvovaginal atrophy and incontinence.
Menopausal hormone therapy (MHT) is the most effective treatment for managing these symptoms; however, its effects on numerous aspects of female health remain uncertain, in particular with regard to breast cancer. The influence of MHT on breast cancer remains unsettled, with discordant findings from observational studies and randomized clinical trials, a factor that affects the decisions made by doctors concerning hormone therapy in menopausal women.
Background
Conjugated equine estrogens (CEEs) were introduced into clinical practice in the 1940s. For decades, MHT was the main treatment in conventional medicine for the symptoms of menopause. MHT was used in Western countries for about 600 million women starting from 1970, and it progressively increased during the 1990s. Professional organizations recommended MHT for the prevention of osteoporosis and chronic heart disease (CHD), and a third of prescriptions were for women older than 60 years.
Against this background, the National Institutes of Health launched randomized trials of MHT through the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) to test whether the association with reduced risk for CHD found in observational studies was real and to obtain reliable information on the overall risks and benefits regarding the prevention of chronic disease for postmenopausal women aged 50-79 years.
The WHI trials tested standard-dose oral CEEs with and without standard-dose continuous medroxyprogesterone acetate (EPT). In 2002, the results of the WHI studies raised a series of concerns about the long-term safety of MHT, in particular the finding of an increased risk of breast cancer for women undergoing therapy. That risk exceeded the benefits from reductions in hip fractures and colorectal cancer.
The WHI findings received wide attention. Prescriptions for MHT dropped precipitously after 2002 and continued to decline in subsequent years. Declines were most marked for standard-dose EPT and in older women. The results of the CEE study were less negative, compared with those for EPT, as they showed no effect on CHD, a nonsignificant reduction in the risk of breast cancer, and a more favorable risk-benefit ratio for younger women, compared with older women. A decade later, it had become widely accepted that MHT should not be used for the prevention of chronic disease in older women; however, short-term use for treatment of vasomotor symptoms remains an accepted indication.
Risks and outcomes
Emerging from a series of WHI reports are complex models on the effect of hormonal therapy on the risk and outcome of breast cancer. In one study, women with an intact uterus received CEEs plus medroxyprogesterone acetate (MPA). An increase in the risk of breast cancer was observed over a median of 5.6 years of treatment, followed by a moderate reduction, with the risk increasing after 13 years of cumulative follow-up. For women treated with CEE alone, the reduction in risk observed over an average of 7.2 years of treatment was maintained for 13 years of follow-up.
Results from observational studies contrast with those from randomized controlled trials, particularly those concerning the use of estrogens only. A meta-analysis by the Collaborative Group on Hormonal Factors in Breast Cancer showed that both EPT and CEE were associated with a higher risk of breast neoplasia. Results of the Million Women Study showed a higher death rate.
Treatment methods and duration
Information from prospective studies on the effects of commencing MHT at various ages between 40 and 59 years show that for women who commenced treatment at any time within this age range, the relative risk was similar and was highly significant for all ages. Few women had started MHT treatment well after menopause at ages 60-69 years, and their excess risks during years 5-14 of current use were significant for estrogen-progestogen but not for estrogen-only MHT.
If these associations are largely causal, then for women of average weight in developed countries, 5 years of MHT, starting at age 50 years, would increase breast cancer incidence at ages 50-69 years by about 1 in every 50 users of estrogen plus daily progestogen preparations; 1 in every 70 users of estrogen plus intermittent progestogen preparations; and 1 in every 200 users of estrogen-only preparations. The corresponding excesses from 10 years of MHT would be about twice as great.
During 5-14 years of MHT use, the RRs were similarly increased if MHT use had started at ages 40-44 years, 45-49 years, 50-54 years, and 55-59 years; RRs appeared to be attenuated if MHT use had started after age 60 years. They were also attenuated by adiposity, particularly for estrogen-only MHT (which had little effect in obese women). After MHT use ceased, some excess risk of breast cancer persisted for more than a decade; this is directly correlated with the duration of treatment.
Therefore, it can be expected that the effects of MHT may vary between participants on the basis of age or time since menopause, as well as treatments (MHT type, dose, formulation, duration of use, and route of administration). Regarding formulation effects on the risk of breast cancer, new evidence shows an increased risk of 28%. Progestogens appeared to be differentially associated with breast cancer (micronized progesterone: odds ratio, 0.99; 95% confidence interval 0.55-1.79; synthetic progestin: OR, 1.28; 95% CI, 1.22-1.35). When prescribing MHT, micronized progesterone may be the safer progestogen to use.
In conclusion, MHT has a complex balance of benefits and risk on various health outcomes. Some effects differ qualitatively between ET and EPT. Regarding use of MHT, consideration should be given to the full range of effects, along with patients’ values and preferences. The overall quality of existing systematic reviews is moderate to poor. Clinicians should evaluate their scientific strength before considering applying their results in clinical practice. Regarding use of any hormone therapy regimen, consideration should be given to the full range of risk and benefits and should involve shared decisionmaking with the patient. It should be recognized that risk-benefit balance is altered by factors such as age, time from menopause, oophorectomy status, and prior hysterectomy and that some outcomes persist and there is some attenuation after stopping use.
This article was translated from Univadis Italy.
A version of the article appeared on Medscape.com.
New biomarker data add to concerns over REDUCE-IT trial
A new analysis of the REDUCE-IT study has reignited concerns that the benefit shown by the high-dose fish oil product in the study, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), may have been related to harms caused by the placebo mineral oil.
Results show that allocation to icosapent ethyl had minimal effects on a series of biomarkers associated with atherosclerotic disease, whereas levels of these biomarkers increased among those allocated to mineral oil.
At 12 months, the median percent increases from baseline in the mineral oil group were 1.5% for homocysteine, 2.2% for lipoprotein(a), 10.9% for oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, 16.2% for interleukin (IL)-6, 18.5% for lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, 21.9% for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and 28.9% for IL-1β. The changes were similar at 24 months. However, in the icosapent ethyl group, there were minimal changes in these biomarkers at 12 and 24 months.
The study was published online in Circulation.
The authors, led by Paul Ridker, MD, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, do not voice much opinion on what the results mean, concluding that “the effect of these findings on the interpretation of the REDUCE-IT trial results remains unclear and will require further investigation.”
They also say that a second icosapent ethyl trial using a nonmineral oil comparator “would help resolve ongoing controversy.”
However, the authors are a mixed group; Dr. Ridker and some of his coauthors were not part of the original REDUCE-IT trial, whereas other coauthors were members of the REDUCE-IT steering committee, and one was an employee of Amarin.
Lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, Deepak Bhatt, MD, also from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, who is the senior author of the current study, played down the new findings, saying they did not offer much new incremental information on mechanistic insight.
“These are small degrees of biomarker increases on an absolute level we are seeing with the placebo that would not be expected to produce harm,” Dr. Bhatt told this news organization. He also said the Circulation peer-review process had removed some of the discussion, which could lead to some “misinterpretation” of the authors’ views.
Dr. Ridker was unavailable for further comment.
The publication of this study has inevitably poured fuel on the fire regarding the controversy that has long dogged the REDUCE-IT trial, with questions about the large reduction in event rates seen with icosapent ethyl without an obvious mechanistic explanation.
‘Smoking gun’
One of the loudest critics of the study, Steve Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, described the new findings as “the closest thing I’ve seen to a smoking gun in medicine for a long, long time.”
“The result of this new analysis shows that mineral oil increases virtually every inflammatory and lipid marker that they measured,” he commented.
“There are a lot of theories, but the bottom line is that something really bad happened in the mineral-oil group, which makes icosapent ethyl look efficacious. In my view, this needs to be reviewed by the FDA for consideration of removing the label claim for cardiovascular benefit.”
Other experts in the field not directly involved in the study voiced concern about these new findings, adding to calls for another trial.
In a Twitter thread on the issue, Harlan Krumholz, MD, describes the Circulation publication as “an exceptionally important article,” adding that it is “time to rethink this drug.”
“My point is ... once you know you have non-neutral comparator and the effect on risk biomarkers is far from trivial ... then you have introduced substantial uncertainty about the trial result, as conveyed by the authors ... and no one can say what would happen with a neutral comparator,” Dr. Krumholz writes.
In an accompanying editorial in Circulation, Robert Harrington, MD, professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, concludes that “the hard reality is that we are left with uncertainties and the questions raised by use of the mineral oil as placebo can only be answered by another randomized controlled trial.”
“My main points are that the chosen placebo was not inert (an essential characteristic for an active control–placebo comparison), that the biomarker data show elevations in multiple markers involved with inflammatory pathways associated with atherosclerosis, and that these data create enough uncertainty in the trial interpretation that the best recourse to answer the criticisms is to do another trial with a truly inert placebo,” Dr. Harrington said in an interview.
He added that Dr. Bhatt’s point that the changes in biomarkers are too small to really matter clinically may be right. “But for me, the uncertainties mean that I have less confidence in the true magnitude of the treatment effect than I would have if there were no changes in the inflammatory markers.”
In Circulation, the authors say it is unclear why multiple biomarkers increased over time among REDUCE-IT participants allocated to mineral oil. They note that no substantive changes in these biomarkers were observed in the placebo groups over periods of 3-5 years in other trials, including JUPITER, CIRT, CANTOS, SPIRE, and the STRENGTH trials, which evaluated a different high-dose omega-3 oil product but used corn oil as the placebo.
“The core design of REDUCE-IT does not make it possible to resolve convincingly whether any adverse effects associated with mineral oil use as a comparator may have affected clinical outcomes,” they write.
They point out that regulatory agencies evaluating REDUCE-IT estimated that approximately 3% of the net clinical benefit observed with icosapent ethyl might have been a consequence of adverse biomarker effects on LDL cholesterol and hsCRP attributable to mineral oil. But in the context of an overall 25% relative risk reduction in first events and a 30% reduction in total ischemic events observed, a potential bias of this magnitude, even if doubled in size, would be unlikely to fully attenuate the overall benefit of icosapent ethyl observed.
They add that they are not aware of a method to assess what the potential magnitude might be of a combination of the multiple effects.
New data do not change the debate
“We did a large, well-powered randomized trial, and this paper shouldn’t change anything in how that trial should be interpreted,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
He claims the new biomarkers evaluated in the study are correlated with LDL and CRP, data which have already been reported and analyzed so have limited relevance.
“It’s not really independent biomarker information; this is what we would expect to see when we see small increases in LDL and CRP. So, I don’t think this new information fundamentally changes the debate,” he said.
Dr. Bhatt also pointed out that the study highlights relative increases rather than absolute increases in the biomarkers, making it seem more alarming than is actually the case.
“The paper makes it seem like that there are large increases in these other biomarkers, but the values reported are relative increases and the absolute increases were actually rather small. In many cases, the changes reported are less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay used,” he noted.
He added: “Even if one is unable to get around the placebo issue in the REDUCE-IT trial, there will always be the JELIS trial – a randomized trial with no placebo showing a 19% relative risk reduction. While the biomarker data may be interesting, what really matters in the end is clinical events. And significant reductions in two independent trials should be enough.”
Dr. Bhatt says the REDUCE-IT steering committee does not believe another trial is needed. “Maybe a different population would be good – such as primary prevention, patients without elevated triglycerides – but just repeating REDUCE- IT with a different placebo would be a waste of resources,” he commented.
But Dr. Nissen refuted Dr. Bhatt’s claims.
“These biomarkers are not in the same pathways as LDL and CRP, and these are not small increases. In the CANTOS trial, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-1β beta showed a significant benefit. The increase in interleukin-1β now reported in REDUCE-IT is exactly the opposite of CANTOS,” he pointed out.
“The FDA did not know about these additional biomarkers when it reviewed the data on LDL and CRP. Now we have new information. It needs to be looked at again,” Dr. Nissen added.
Funding for the study was provided by Amarin Pharma. Dr. Bhatt was the lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial. Dr. Nissen was the lead investigator the STRENGTH trial. Further disclosures of the authors can be found in Circulation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis of the REDUCE-IT study has reignited concerns that the benefit shown by the high-dose fish oil product in the study, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), may have been related to harms caused by the placebo mineral oil.
Results show that allocation to icosapent ethyl had minimal effects on a series of biomarkers associated with atherosclerotic disease, whereas levels of these biomarkers increased among those allocated to mineral oil.
At 12 months, the median percent increases from baseline in the mineral oil group were 1.5% for homocysteine, 2.2% for lipoprotein(a), 10.9% for oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, 16.2% for interleukin (IL)-6, 18.5% for lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, 21.9% for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and 28.9% for IL-1β. The changes were similar at 24 months. However, in the icosapent ethyl group, there were minimal changes in these biomarkers at 12 and 24 months.
The study was published online in Circulation.
The authors, led by Paul Ridker, MD, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, do not voice much opinion on what the results mean, concluding that “the effect of these findings on the interpretation of the REDUCE-IT trial results remains unclear and will require further investigation.”
They also say that a second icosapent ethyl trial using a nonmineral oil comparator “would help resolve ongoing controversy.”
However, the authors are a mixed group; Dr. Ridker and some of his coauthors were not part of the original REDUCE-IT trial, whereas other coauthors were members of the REDUCE-IT steering committee, and one was an employee of Amarin.
Lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, Deepak Bhatt, MD, also from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, who is the senior author of the current study, played down the new findings, saying they did not offer much new incremental information on mechanistic insight.
“These are small degrees of biomarker increases on an absolute level we are seeing with the placebo that would not be expected to produce harm,” Dr. Bhatt told this news organization. He also said the Circulation peer-review process had removed some of the discussion, which could lead to some “misinterpretation” of the authors’ views.
Dr. Ridker was unavailable for further comment.
The publication of this study has inevitably poured fuel on the fire regarding the controversy that has long dogged the REDUCE-IT trial, with questions about the large reduction in event rates seen with icosapent ethyl without an obvious mechanistic explanation.
‘Smoking gun’
One of the loudest critics of the study, Steve Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, described the new findings as “the closest thing I’ve seen to a smoking gun in medicine for a long, long time.”
“The result of this new analysis shows that mineral oil increases virtually every inflammatory and lipid marker that they measured,” he commented.
“There are a lot of theories, but the bottom line is that something really bad happened in the mineral-oil group, which makes icosapent ethyl look efficacious. In my view, this needs to be reviewed by the FDA for consideration of removing the label claim for cardiovascular benefit.”
Other experts in the field not directly involved in the study voiced concern about these new findings, adding to calls for another trial.
In a Twitter thread on the issue, Harlan Krumholz, MD, describes the Circulation publication as “an exceptionally important article,” adding that it is “time to rethink this drug.”
“My point is ... once you know you have non-neutral comparator and the effect on risk biomarkers is far from trivial ... then you have introduced substantial uncertainty about the trial result, as conveyed by the authors ... and no one can say what would happen with a neutral comparator,” Dr. Krumholz writes.
In an accompanying editorial in Circulation, Robert Harrington, MD, professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, concludes that “the hard reality is that we are left with uncertainties and the questions raised by use of the mineral oil as placebo can only be answered by another randomized controlled trial.”
“My main points are that the chosen placebo was not inert (an essential characteristic for an active control–placebo comparison), that the biomarker data show elevations in multiple markers involved with inflammatory pathways associated with atherosclerosis, and that these data create enough uncertainty in the trial interpretation that the best recourse to answer the criticisms is to do another trial with a truly inert placebo,” Dr. Harrington said in an interview.
He added that Dr. Bhatt’s point that the changes in biomarkers are too small to really matter clinically may be right. “But for me, the uncertainties mean that I have less confidence in the true magnitude of the treatment effect than I would have if there were no changes in the inflammatory markers.”
In Circulation, the authors say it is unclear why multiple biomarkers increased over time among REDUCE-IT participants allocated to mineral oil. They note that no substantive changes in these biomarkers were observed in the placebo groups over periods of 3-5 years in other trials, including JUPITER, CIRT, CANTOS, SPIRE, and the STRENGTH trials, which evaluated a different high-dose omega-3 oil product but used corn oil as the placebo.
“The core design of REDUCE-IT does not make it possible to resolve convincingly whether any adverse effects associated with mineral oil use as a comparator may have affected clinical outcomes,” they write.
They point out that regulatory agencies evaluating REDUCE-IT estimated that approximately 3% of the net clinical benefit observed with icosapent ethyl might have been a consequence of adverse biomarker effects on LDL cholesterol and hsCRP attributable to mineral oil. But in the context of an overall 25% relative risk reduction in first events and a 30% reduction in total ischemic events observed, a potential bias of this magnitude, even if doubled in size, would be unlikely to fully attenuate the overall benefit of icosapent ethyl observed.
They add that they are not aware of a method to assess what the potential magnitude might be of a combination of the multiple effects.
New data do not change the debate
“We did a large, well-powered randomized trial, and this paper shouldn’t change anything in how that trial should be interpreted,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
He claims the new biomarkers evaluated in the study are correlated with LDL and CRP, data which have already been reported and analyzed so have limited relevance.
“It’s not really independent biomarker information; this is what we would expect to see when we see small increases in LDL and CRP. So, I don’t think this new information fundamentally changes the debate,” he said.
Dr. Bhatt also pointed out that the study highlights relative increases rather than absolute increases in the biomarkers, making it seem more alarming than is actually the case.
“The paper makes it seem like that there are large increases in these other biomarkers, but the values reported are relative increases and the absolute increases were actually rather small. In many cases, the changes reported are less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay used,” he noted.
He added: “Even if one is unable to get around the placebo issue in the REDUCE-IT trial, there will always be the JELIS trial – a randomized trial with no placebo showing a 19% relative risk reduction. While the biomarker data may be interesting, what really matters in the end is clinical events. And significant reductions in two independent trials should be enough.”
Dr. Bhatt says the REDUCE-IT steering committee does not believe another trial is needed. “Maybe a different population would be good – such as primary prevention, patients without elevated triglycerides – but just repeating REDUCE- IT with a different placebo would be a waste of resources,” he commented.
But Dr. Nissen refuted Dr. Bhatt’s claims.
“These biomarkers are not in the same pathways as LDL and CRP, and these are not small increases. In the CANTOS trial, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-1β beta showed a significant benefit. The increase in interleukin-1β now reported in REDUCE-IT is exactly the opposite of CANTOS,” he pointed out.
“The FDA did not know about these additional biomarkers when it reviewed the data on LDL and CRP. Now we have new information. It needs to be looked at again,” Dr. Nissen added.
Funding for the study was provided by Amarin Pharma. Dr. Bhatt was the lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial. Dr. Nissen was the lead investigator the STRENGTH trial. Further disclosures of the authors can be found in Circulation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis of the REDUCE-IT study has reignited concerns that the benefit shown by the high-dose fish oil product in the study, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), may have been related to harms caused by the placebo mineral oil.
Results show that allocation to icosapent ethyl had minimal effects on a series of biomarkers associated with atherosclerotic disease, whereas levels of these biomarkers increased among those allocated to mineral oil.
At 12 months, the median percent increases from baseline in the mineral oil group were 1.5% for homocysteine, 2.2% for lipoprotein(a), 10.9% for oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, 16.2% for interleukin (IL)-6, 18.5% for lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, 21.9% for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and 28.9% for IL-1β. The changes were similar at 24 months. However, in the icosapent ethyl group, there were minimal changes in these biomarkers at 12 and 24 months.
The study was published online in Circulation.
The authors, led by Paul Ridker, MD, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, do not voice much opinion on what the results mean, concluding that “the effect of these findings on the interpretation of the REDUCE-IT trial results remains unclear and will require further investigation.”
They also say that a second icosapent ethyl trial using a nonmineral oil comparator “would help resolve ongoing controversy.”
However, the authors are a mixed group; Dr. Ridker and some of his coauthors were not part of the original REDUCE-IT trial, whereas other coauthors were members of the REDUCE-IT steering committee, and one was an employee of Amarin.
Lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, Deepak Bhatt, MD, also from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, who is the senior author of the current study, played down the new findings, saying they did not offer much new incremental information on mechanistic insight.
“These are small degrees of biomarker increases on an absolute level we are seeing with the placebo that would not be expected to produce harm,” Dr. Bhatt told this news organization. He also said the Circulation peer-review process had removed some of the discussion, which could lead to some “misinterpretation” of the authors’ views.
Dr. Ridker was unavailable for further comment.
The publication of this study has inevitably poured fuel on the fire regarding the controversy that has long dogged the REDUCE-IT trial, with questions about the large reduction in event rates seen with icosapent ethyl without an obvious mechanistic explanation.
‘Smoking gun’
One of the loudest critics of the study, Steve Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, described the new findings as “the closest thing I’ve seen to a smoking gun in medicine for a long, long time.”
“The result of this new analysis shows that mineral oil increases virtually every inflammatory and lipid marker that they measured,” he commented.
“There are a lot of theories, but the bottom line is that something really bad happened in the mineral-oil group, which makes icosapent ethyl look efficacious. In my view, this needs to be reviewed by the FDA for consideration of removing the label claim for cardiovascular benefit.”
Other experts in the field not directly involved in the study voiced concern about these new findings, adding to calls for another trial.
In a Twitter thread on the issue, Harlan Krumholz, MD, describes the Circulation publication as “an exceptionally important article,” adding that it is “time to rethink this drug.”
“My point is ... once you know you have non-neutral comparator and the effect on risk biomarkers is far from trivial ... then you have introduced substantial uncertainty about the trial result, as conveyed by the authors ... and no one can say what would happen with a neutral comparator,” Dr. Krumholz writes.
In an accompanying editorial in Circulation, Robert Harrington, MD, professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, concludes that “the hard reality is that we are left with uncertainties and the questions raised by use of the mineral oil as placebo can only be answered by another randomized controlled trial.”
“My main points are that the chosen placebo was not inert (an essential characteristic for an active control–placebo comparison), that the biomarker data show elevations in multiple markers involved with inflammatory pathways associated with atherosclerosis, and that these data create enough uncertainty in the trial interpretation that the best recourse to answer the criticisms is to do another trial with a truly inert placebo,” Dr. Harrington said in an interview.
He added that Dr. Bhatt’s point that the changes in biomarkers are too small to really matter clinically may be right. “But for me, the uncertainties mean that I have less confidence in the true magnitude of the treatment effect than I would have if there were no changes in the inflammatory markers.”
In Circulation, the authors say it is unclear why multiple biomarkers increased over time among REDUCE-IT participants allocated to mineral oil. They note that no substantive changes in these biomarkers were observed in the placebo groups over periods of 3-5 years in other trials, including JUPITER, CIRT, CANTOS, SPIRE, and the STRENGTH trials, which evaluated a different high-dose omega-3 oil product but used corn oil as the placebo.
“The core design of REDUCE-IT does not make it possible to resolve convincingly whether any adverse effects associated with mineral oil use as a comparator may have affected clinical outcomes,” they write.
They point out that regulatory agencies evaluating REDUCE-IT estimated that approximately 3% of the net clinical benefit observed with icosapent ethyl might have been a consequence of adverse biomarker effects on LDL cholesterol and hsCRP attributable to mineral oil. But in the context of an overall 25% relative risk reduction in first events and a 30% reduction in total ischemic events observed, a potential bias of this magnitude, even if doubled in size, would be unlikely to fully attenuate the overall benefit of icosapent ethyl observed.
They add that they are not aware of a method to assess what the potential magnitude might be of a combination of the multiple effects.
New data do not change the debate
“We did a large, well-powered randomized trial, and this paper shouldn’t change anything in how that trial should be interpreted,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
He claims the new biomarkers evaluated in the study are correlated with LDL and CRP, data which have already been reported and analyzed so have limited relevance.
“It’s not really independent biomarker information; this is what we would expect to see when we see small increases in LDL and CRP. So, I don’t think this new information fundamentally changes the debate,” he said.
Dr. Bhatt also pointed out that the study highlights relative increases rather than absolute increases in the biomarkers, making it seem more alarming than is actually the case.
“The paper makes it seem like that there are large increases in these other biomarkers, but the values reported are relative increases and the absolute increases were actually rather small. In many cases, the changes reported are less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay used,” he noted.
He added: “Even if one is unable to get around the placebo issue in the REDUCE-IT trial, there will always be the JELIS trial – a randomized trial with no placebo showing a 19% relative risk reduction. While the biomarker data may be interesting, what really matters in the end is clinical events. And significant reductions in two independent trials should be enough.”
Dr. Bhatt says the REDUCE-IT steering committee does not believe another trial is needed. “Maybe a different population would be good – such as primary prevention, patients without elevated triglycerides – but just repeating REDUCE- IT with a different placebo would be a waste of resources,” he commented.
But Dr. Nissen refuted Dr. Bhatt’s claims.
“These biomarkers are not in the same pathways as LDL and CRP, and these are not small increases. In the CANTOS trial, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-1β beta showed a significant benefit. The increase in interleukin-1β now reported in REDUCE-IT is exactly the opposite of CANTOS,” he pointed out.
“The FDA did not know about these additional biomarkers when it reviewed the data on LDL and CRP. Now we have new information. It needs to be looked at again,” Dr. Nissen added.
Funding for the study was provided by Amarin Pharma. Dr. Bhatt was the lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial. Dr. Nissen was the lead investigator the STRENGTH trial. Further disclosures of the authors can be found in Circulation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Fertility rates lower in disadvantaged neighborhoods
A new study ties the odds of conception to the advantages of the neighborhood a woman lives in.
In a cohort of more than 6,000 women who were trying to get pregnant without fertility treatments, the probability of conception was reduced 21%-23% per menstrual cycle when comparing the most disadvantaged neighborhoods with the least disadvantaged.
“When disadvantaged neighborhood status was categorized within each state (as opposed to nationally), the results were slightly larger in magnitude,” wrote authors of the study published online in JAMA Network Open.
Among 6,356 participants, 3,725 pregnancies were observed for 27,427 menstrual cycles of follow-up. Average age was 30, and most participants were non-Hispanic White (5,297 [83.3%]) and had not previously given birth (4,179 [65.7%]).
When the researchers compared the top and bottom deciles of disadvantaged neighborhood status, adjusted fecundability ratios (the per-cycle probability of conception) were 0.79 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66-0.96) for national-level area deprivation index (ADI) rankings and 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92) for within-state ADI rankings. ADI score includes population indicators related to educational attainment, housing, employment, and poverty.
“These findings suggest that investments in disadvantaged neighborhoods may yield positive cobenefits for fertility,” the authors wrote.
The researchers used the Pregnancy Study Online, for which baseline data were collected from women in the United States from June 19, 2013, through April 12, 2019.
In the United States, 10%-15% of reproductive-aged couples experience infertility, defined as the inability to conceive after a year of unprotected intercourse.
Reason behind the numbers unclear
Mark Hornstein, MD, director in the reproductive endocrinology division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview that this study gives the “what” but the “why” is harder to pinpoint.
What is not known, he said, is what kind of access the women had to fertility counseling or treatment.
The association between fertility and neighborhood advantage status is very plausible given the well-established links between disadvantaged regions and poorer health outcomes, he said, adding that the authors make a good case for their conclusions in the paper.
The authors ruled out many potential confounders, such as age of the women, reproductive history, multivitamin use, education level, household income, and frequency of intercourse, and still there was a difference between disadvantaged and advantaged neighborhoods, he noted.
Dr. Hornstein said his own research team has found that lack of knowledge about insurance coverage regarding infertility services may keep women from seeking the services.
“One of the things I worry about it access,” he said. “[The study authors] didn’t really look at that. They just looked at what the chances were that they got pregnant. But they didn’t say how many of those women had a workup, an evaluation, for why they were having difficulty, if they were, or had treatment. So I don’t know if some or all or none of that difference that they saw from the highest neighborhood health score to the most disadvantaged – if that was from inherent problems in the area, access to the best health care, or some combination.”
Discussions have focused on changing personal behaviors
Discussions on improving fertility often center on changing personal behaviors, the authors noted. “However, structural, political, and environmental factors may also play a substantial role,” they wrote.
The findings are in line with previous research on the effect of stress on in vitro outcomes, they pointed out. “Perceived stress has been associated with poorer in vitro fertilization outcomes and reduced fecundability among couples attempting spontaneous conception,” the authors noted.
Studies also have shown that living in a disadvantaged neighborhood is linked with comorbidities during pregnancy, such as increased risks of gestational hypertension (risk ratio for lowest vs. highest quartile: 1.24 [95% CI, 1.14-1.35]) and poor gestational weight gain (relative risk for lowest vs. highest quartile: 1.1 [95% CI, 1.1-1.2]).
In addition, policies such as those that support civil rights, protect the environment, and invest in underresourced communities have been shown to improve health markers such as life expectancy.
Policy decisions can also perpetuate a cycle of stress, they wrote. Disadvantaged communities may have more air pollution, which has been shown to have negative effects on fertility. Unemployment has been linked with decreased population-level fertility rates. Lack of green space may result in fewer areas to reduce stress.
A study coauthor reported grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study; nonfinancial support from Swiss Precision Diagnostics GmbH, Labcorp, Kindara.com, and FertilityFriend.com; and consulting for AbbVie outside the submitted work. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Hornstein reported no relevant financial relationships.
A new study ties the odds of conception to the advantages of the neighborhood a woman lives in.
In a cohort of more than 6,000 women who were trying to get pregnant without fertility treatments, the probability of conception was reduced 21%-23% per menstrual cycle when comparing the most disadvantaged neighborhoods with the least disadvantaged.
“When disadvantaged neighborhood status was categorized within each state (as opposed to nationally), the results were slightly larger in magnitude,” wrote authors of the study published online in JAMA Network Open.
Among 6,356 participants, 3,725 pregnancies were observed for 27,427 menstrual cycles of follow-up. Average age was 30, and most participants were non-Hispanic White (5,297 [83.3%]) and had not previously given birth (4,179 [65.7%]).
When the researchers compared the top and bottom deciles of disadvantaged neighborhood status, adjusted fecundability ratios (the per-cycle probability of conception) were 0.79 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66-0.96) for national-level area deprivation index (ADI) rankings and 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92) for within-state ADI rankings. ADI score includes population indicators related to educational attainment, housing, employment, and poverty.
“These findings suggest that investments in disadvantaged neighborhoods may yield positive cobenefits for fertility,” the authors wrote.
The researchers used the Pregnancy Study Online, for which baseline data were collected from women in the United States from June 19, 2013, through April 12, 2019.
In the United States, 10%-15% of reproductive-aged couples experience infertility, defined as the inability to conceive after a year of unprotected intercourse.
Reason behind the numbers unclear
Mark Hornstein, MD, director in the reproductive endocrinology division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview that this study gives the “what” but the “why” is harder to pinpoint.
What is not known, he said, is what kind of access the women had to fertility counseling or treatment.
The association between fertility and neighborhood advantage status is very plausible given the well-established links between disadvantaged regions and poorer health outcomes, he said, adding that the authors make a good case for their conclusions in the paper.
The authors ruled out many potential confounders, such as age of the women, reproductive history, multivitamin use, education level, household income, and frequency of intercourse, and still there was a difference between disadvantaged and advantaged neighborhoods, he noted.
Dr. Hornstein said his own research team has found that lack of knowledge about insurance coverage regarding infertility services may keep women from seeking the services.
“One of the things I worry about it access,” he said. “[The study authors] didn’t really look at that. They just looked at what the chances were that they got pregnant. But they didn’t say how many of those women had a workup, an evaluation, for why they were having difficulty, if they were, or had treatment. So I don’t know if some or all or none of that difference that they saw from the highest neighborhood health score to the most disadvantaged – if that was from inherent problems in the area, access to the best health care, or some combination.”
Discussions have focused on changing personal behaviors
Discussions on improving fertility often center on changing personal behaviors, the authors noted. “However, structural, political, and environmental factors may also play a substantial role,” they wrote.
The findings are in line with previous research on the effect of stress on in vitro outcomes, they pointed out. “Perceived stress has been associated with poorer in vitro fertilization outcomes and reduced fecundability among couples attempting spontaneous conception,” the authors noted.
Studies also have shown that living in a disadvantaged neighborhood is linked with comorbidities during pregnancy, such as increased risks of gestational hypertension (risk ratio for lowest vs. highest quartile: 1.24 [95% CI, 1.14-1.35]) and poor gestational weight gain (relative risk for lowest vs. highest quartile: 1.1 [95% CI, 1.1-1.2]).
In addition, policies such as those that support civil rights, protect the environment, and invest in underresourced communities have been shown to improve health markers such as life expectancy.
Policy decisions can also perpetuate a cycle of stress, they wrote. Disadvantaged communities may have more air pollution, which has been shown to have negative effects on fertility. Unemployment has been linked with decreased population-level fertility rates. Lack of green space may result in fewer areas to reduce stress.
A study coauthor reported grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study; nonfinancial support from Swiss Precision Diagnostics GmbH, Labcorp, Kindara.com, and FertilityFriend.com; and consulting for AbbVie outside the submitted work. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Hornstein reported no relevant financial relationships.
A new study ties the odds of conception to the advantages of the neighborhood a woman lives in.
In a cohort of more than 6,000 women who were trying to get pregnant without fertility treatments, the probability of conception was reduced 21%-23% per menstrual cycle when comparing the most disadvantaged neighborhoods with the least disadvantaged.
“When disadvantaged neighborhood status was categorized within each state (as opposed to nationally), the results were slightly larger in magnitude,” wrote authors of the study published online in JAMA Network Open.
Among 6,356 participants, 3,725 pregnancies were observed for 27,427 menstrual cycles of follow-up. Average age was 30, and most participants were non-Hispanic White (5,297 [83.3%]) and had not previously given birth (4,179 [65.7%]).
When the researchers compared the top and bottom deciles of disadvantaged neighborhood status, adjusted fecundability ratios (the per-cycle probability of conception) were 0.79 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.66-0.96) for national-level area deprivation index (ADI) rankings and 0.77 (95% CI, 0.65-0.92) for within-state ADI rankings. ADI score includes population indicators related to educational attainment, housing, employment, and poverty.
“These findings suggest that investments in disadvantaged neighborhoods may yield positive cobenefits for fertility,” the authors wrote.
The researchers used the Pregnancy Study Online, for which baseline data were collected from women in the United States from June 19, 2013, through April 12, 2019.
In the United States, 10%-15% of reproductive-aged couples experience infertility, defined as the inability to conceive after a year of unprotected intercourse.
Reason behind the numbers unclear
Mark Hornstein, MD, director in the reproductive endocrinology division of Brigham and Women’s Hospital and professor at Harvard Medical School, both in Boston, said in an interview that this study gives the “what” but the “why” is harder to pinpoint.
What is not known, he said, is what kind of access the women had to fertility counseling or treatment.
The association between fertility and neighborhood advantage status is very plausible given the well-established links between disadvantaged regions and poorer health outcomes, he said, adding that the authors make a good case for their conclusions in the paper.
The authors ruled out many potential confounders, such as age of the women, reproductive history, multivitamin use, education level, household income, and frequency of intercourse, and still there was a difference between disadvantaged and advantaged neighborhoods, he noted.
Dr. Hornstein said his own research team has found that lack of knowledge about insurance coverage regarding infertility services may keep women from seeking the services.
“One of the things I worry about it access,” he said. “[The study authors] didn’t really look at that. They just looked at what the chances were that they got pregnant. But they didn’t say how many of those women had a workup, an evaluation, for why they were having difficulty, if they were, or had treatment. So I don’t know if some or all or none of that difference that they saw from the highest neighborhood health score to the most disadvantaged – if that was from inherent problems in the area, access to the best health care, or some combination.”
Discussions have focused on changing personal behaviors
Discussions on improving fertility often center on changing personal behaviors, the authors noted. “However, structural, political, and environmental factors may also play a substantial role,” they wrote.
The findings are in line with previous research on the effect of stress on in vitro outcomes, they pointed out. “Perceived stress has been associated with poorer in vitro fertilization outcomes and reduced fecundability among couples attempting spontaneous conception,” the authors noted.
Studies also have shown that living in a disadvantaged neighborhood is linked with comorbidities during pregnancy, such as increased risks of gestational hypertension (risk ratio for lowest vs. highest quartile: 1.24 [95% CI, 1.14-1.35]) and poor gestational weight gain (relative risk for lowest vs. highest quartile: 1.1 [95% CI, 1.1-1.2]).
In addition, policies such as those that support civil rights, protect the environment, and invest in underresourced communities have been shown to improve health markers such as life expectancy.
Policy decisions can also perpetuate a cycle of stress, they wrote. Disadvantaged communities may have more air pollution, which has been shown to have negative effects on fertility. Unemployment has been linked with decreased population-level fertility rates. Lack of green space may result in fewer areas to reduce stress.
A study coauthor reported grants from the National Institutes of Health during the conduct of the study; nonfinancial support from Swiss Precision Diagnostics GmbH, Labcorp, Kindara.com, and FertilityFriend.com; and consulting for AbbVie outside the submitted work. No other author disclosures were reported. Dr. Hornstein reported no relevant financial relationships.