User login
FDA Approves Deuruxolitinib for Severe Alopecia Areata in Adults
The
The development, which was announced in a July 25, 2024, news release from the drug’s manufacturer Sun Pharma, is based on data from two pivotal randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 clinical trials: THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE-AA2, which included 1220 adults with severe alopecia areata enrolled at sites in the United States, Canada, and Europe. Study participants had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Data were also collected from two open-label, long-term extension trials in which patients were eligible to enroll upon completion of the 24-week trials.
Deuruxolitinib, which comes in 8-mg tablets, is an oral selective inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 and is administered twice a day. According to the company press release, the average patient enrolled in the clinical trials had only 13% of their scalp hair coverage at baseline. At week 24, more than 30% of patients taking deuruxolitinib experiencing 80% or more scalp hair coverage (SALT score ≤ 20). Also, up to 25% of patients had almost all of their scalp hair back at 24 weeks (≥ 90% coverage).
In terms of safety, the data showed that 3.1% of patients who received deuruxolitinib 8 mg twice daily in the phase 2 dose-ranging study and phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trials discontinued treatment owing to adverse reactions. The three most common adverse events in placebo-controlled trials were headache (12.4% vs 9.4% with placebo), acne (10% vs 4.3% with placebo), and nasopharyngitis (8.1% vs 6.7% with placebo). More than 100 people continued taking deuruxolitinib for more than 3 years.
Deuruxolitinib is the third treatment and third JAK inhibitor approved by the FDA for severe alopecia areata. Baricitinib (Olumiant) was approved in June 2022 for adults with alopecia areata, followed by ritlecitinib (Litfulo) approved in June 2023 for patients aged 12 years and older.
In a statement from the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (NAAF), Nicole Friedland, NAAF’s president and CEO, said that “it is with tremendous excitement that we welcome the FDA’s approval of a third treatment for severe alopecia areata in as many years.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The
The development, which was announced in a July 25, 2024, news release from the drug’s manufacturer Sun Pharma, is based on data from two pivotal randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 clinical trials: THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE-AA2, which included 1220 adults with severe alopecia areata enrolled at sites in the United States, Canada, and Europe. Study participants had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Data were also collected from two open-label, long-term extension trials in which patients were eligible to enroll upon completion of the 24-week trials.
Deuruxolitinib, which comes in 8-mg tablets, is an oral selective inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 and is administered twice a day. According to the company press release, the average patient enrolled in the clinical trials had only 13% of their scalp hair coverage at baseline. At week 24, more than 30% of patients taking deuruxolitinib experiencing 80% or more scalp hair coverage (SALT score ≤ 20). Also, up to 25% of patients had almost all of their scalp hair back at 24 weeks (≥ 90% coverage).
In terms of safety, the data showed that 3.1% of patients who received deuruxolitinib 8 mg twice daily in the phase 2 dose-ranging study and phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trials discontinued treatment owing to adverse reactions. The three most common adverse events in placebo-controlled trials were headache (12.4% vs 9.4% with placebo), acne (10% vs 4.3% with placebo), and nasopharyngitis (8.1% vs 6.7% with placebo). More than 100 people continued taking deuruxolitinib for more than 3 years.
Deuruxolitinib is the third treatment and third JAK inhibitor approved by the FDA for severe alopecia areata. Baricitinib (Olumiant) was approved in June 2022 for adults with alopecia areata, followed by ritlecitinib (Litfulo) approved in June 2023 for patients aged 12 years and older.
In a statement from the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (NAAF), Nicole Friedland, NAAF’s president and CEO, said that “it is with tremendous excitement that we welcome the FDA’s approval of a third treatment for severe alopecia areata in as many years.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The
The development, which was announced in a July 25, 2024, news release from the drug’s manufacturer Sun Pharma, is based on data from two pivotal randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 clinical trials: THRIVE-AA1 and THRIVE-AA2, which included 1220 adults with severe alopecia areata enrolled at sites in the United States, Canada, and Europe. Study participants had at least 50% scalp hair loss as measured by Severity of Alopecia Tool (SALT) for more than 6 months. Data were also collected from two open-label, long-term extension trials in which patients were eligible to enroll upon completion of the 24-week trials.
Deuruxolitinib, which comes in 8-mg tablets, is an oral selective inhibitor of JAK1 and JAK2 and is administered twice a day. According to the company press release, the average patient enrolled in the clinical trials had only 13% of their scalp hair coverage at baseline. At week 24, more than 30% of patients taking deuruxolitinib experiencing 80% or more scalp hair coverage (SALT score ≤ 20). Also, up to 25% of patients had almost all of their scalp hair back at 24 weeks (≥ 90% coverage).
In terms of safety, the data showed that 3.1% of patients who received deuruxolitinib 8 mg twice daily in the phase 2 dose-ranging study and phase 3 randomized placebo-controlled trials discontinued treatment owing to adverse reactions. The three most common adverse events in placebo-controlled trials were headache (12.4% vs 9.4% with placebo), acne (10% vs 4.3% with placebo), and nasopharyngitis (8.1% vs 6.7% with placebo). More than 100 people continued taking deuruxolitinib for more than 3 years.
Deuruxolitinib is the third treatment and third JAK inhibitor approved by the FDA for severe alopecia areata. Baricitinib (Olumiant) was approved in June 2022 for adults with alopecia areata, followed by ritlecitinib (Litfulo) approved in June 2023 for patients aged 12 years and older.
In a statement from the National Alopecia Areata Foundation (NAAF), Nicole Friedland, NAAF’s president and CEO, said that “it is with tremendous excitement that we welcome the FDA’s approval of a third treatment for severe alopecia areata in as many years.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pilot Study Finds Experimental CBD Cream Decreases UVA Skin Damage
, results from a small prospective pilot study showed.
“This study hopefully reinvigorates interest in the utilization of whether it be plant-based, human-derived, or synthetic cannabinoids in the management of dermatologic disease,” one of the study investigators, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization. The study was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
For the prospective, single-center, pilot trial, which is believed to be the first of its kind, 19 volunteers aged 22-65 with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III applied either a nano-encapsulated CBD cream or a vehicle cream to blind spots on the skin of the buttocks twice daily for 14 days. Next, researchers applied a minimal erythema dose of UV radiation to the treated skin areas for 30 minutes. After 24 hours, they visually inspected the treated areas to clinically compare the erythema. They also performed five 4-mm punch biopsies from UVA- and non-UVA–exposed treatment sites on each buttock, as well as from an untreated control site that was at least 5 cm away from the treated left buttock.
At 24 hours, 21% of study participants showed less redness on CBD-treated skin compared with control-treated skin, while histology showed that CBD-treated skin demonstrated reduced UVA-induced epidermal hyperplasia compared with control-treated skin (a mean 11.3% change from baseline vs 28.7%, respectively; P = .01). In other findings, application of CBD cream reduced DNA damage and DNA mutations associated with UVA-induced skin aging/damage and ultimately skin cancer.
In addition, the CBD-treated skin samples had a reduction in the UVA-associated increase in the premutagenic marker 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and a reduction of two major UVA-induced mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with skin photoaging.
The research, Dr. Friedman noted, “took a village of collaborators and almost 3 years to pull together,” including collaborating with his long-standing mentor, Brian Berman, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, and a study coauthor. The study “demonstrated that purposeful delivery of CBD using an established nanoparticle platform ... can have a quantifiable impact on preventing the expected DNA damage and cellular injury one should see from UVA exposure,” said Dr. Friedman, who codeveloped the nanoparticle platform with his father, Joel M. Friedman, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City.
“Never before has a dermatologic study on topical cannabinoids dove so deeply into the biological impact of this natural ingredient to highlight its potential, here, as a mitigation strategy for unprotected exposure to prevent the downstream sequelae of UV radiation,” Dr. Friedman said.
In the paper, he and his coauthors acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its small sample size and the single-center design.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he coinvented the nanoparticle technology used in the trial. Dr. Berman is a consultant at MINO Labs, which funded the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures. The study was done in collaboration with the Center for Clinical and Cosmetic Research in Aventura, Florida.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results from a small prospective pilot study showed.
“This study hopefully reinvigorates interest in the utilization of whether it be plant-based, human-derived, or synthetic cannabinoids in the management of dermatologic disease,” one of the study investigators, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization. The study was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
For the prospective, single-center, pilot trial, which is believed to be the first of its kind, 19 volunteers aged 22-65 with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III applied either a nano-encapsulated CBD cream or a vehicle cream to blind spots on the skin of the buttocks twice daily for 14 days. Next, researchers applied a minimal erythema dose of UV radiation to the treated skin areas for 30 minutes. After 24 hours, they visually inspected the treated areas to clinically compare the erythema. They also performed five 4-mm punch biopsies from UVA- and non-UVA–exposed treatment sites on each buttock, as well as from an untreated control site that was at least 5 cm away from the treated left buttock.
At 24 hours, 21% of study participants showed less redness on CBD-treated skin compared with control-treated skin, while histology showed that CBD-treated skin demonstrated reduced UVA-induced epidermal hyperplasia compared with control-treated skin (a mean 11.3% change from baseline vs 28.7%, respectively; P = .01). In other findings, application of CBD cream reduced DNA damage and DNA mutations associated with UVA-induced skin aging/damage and ultimately skin cancer.
In addition, the CBD-treated skin samples had a reduction in the UVA-associated increase in the premutagenic marker 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and a reduction of two major UVA-induced mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with skin photoaging.
The research, Dr. Friedman noted, “took a village of collaborators and almost 3 years to pull together,” including collaborating with his long-standing mentor, Brian Berman, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, and a study coauthor. The study “demonstrated that purposeful delivery of CBD using an established nanoparticle platform ... can have a quantifiable impact on preventing the expected DNA damage and cellular injury one should see from UVA exposure,” said Dr. Friedman, who codeveloped the nanoparticle platform with his father, Joel M. Friedman, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City.
“Never before has a dermatologic study on topical cannabinoids dove so deeply into the biological impact of this natural ingredient to highlight its potential, here, as a mitigation strategy for unprotected exposure to prevent the downstream sequelae of UV radiation,” Dr. Friedman said.
In the paper, he and his coauthors acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its small sample size and the single-center design.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he coinvented the nanoparticle technology used in the trial. Dr. Berman is a consultant at MINO Labs, which funded the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures. The study was done in collaboration with the Center for Clinical and Cosmetic Research in Aventura, Florida.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, results from a small prospective pilot study showed.
“This study hopefully reinvigorates interest in the utilization of whether it be plant-based, human-derived, or synthetic cannabinoids in the management of dermatologic disease,” one of the study investigators, Adam Friedman, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University, Washington, DC, told this news organization. The study was published in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
For the prospective, single-center, pilot trial, which is believed to be the first of its kind, 19 volunteers aged 22-65 with Fitzpatrick skin types I-III applied either a nano-encapsulated CBD cream or a vehicle cream to blind spots on the skin of the buttocks twice daily for 14 days. Next, researchers applied a minimal erythema dose of UV radiation to the treated skin areas for 30 minutes. After 24 hours, they visually inspected the treated areas to clinically compare the erythema. They also performed five 4-mm punch biopsies from UVA- and non-UVA–exposed treatment sites on each buttock, as well as from an untreated control site that was at least 5 cm away from the treated left buttock.
At 24 hours, 21% of study participants showed less redness on CBD-treated skin compared with control-treated skin, while histology showed that CBD-treated skin demonstrated reduced UVA-induced epidermal hyperplasia compared with control-treated skin (a mean 11.3% change from baseline vs 28.7%, respectively; P = .01). In other findings, application of CBD cream reduced DNA damage and DNA mutations associated with UVA-induced skin aging/damage and ultimately skin cancer.
In addition, the CBD-treated skin samples had a reduction in the UVA-associated increase in the premutagenic marker 8-oxoguanine DNA glycosylase 1 and a reduction of two major UVA-induced mitochondrial DNA deletions associated with skin photoaging.
The research, Dr. Friedman noted, “took a village of collaborators and almost 3 years to pull together,” including collaborating with his long-standing mentor, Brian Berman, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of dermatology and dermatologic surgery at the University of Miami, Coral Gables, Florida, and a study coauthor. The study “demonstrated that purposeful delivery of CBD using an established nanoparticle platform ... can have a quantifiable impact on preventing the expected DNA damage and cellular injury one should see from UVA exposure,” said Dr. Friedman, who codeveloped the nanoparticle platform with his father, Joel M. Friedman, MD, PhD, professor of microbiology and immunology at Albert Einstein College of Medicine, New York City.
“Never before has a dermatologic study on topical cannabinoids dove so deeply into the biological impact of this natural ingredient to highlight its potential, here, as a mitigation strategy for unprotected exposure to prevent the downstream sequelae of UV radiation,” Dr. Friedman said.
In the paper, he and his coauthors acknowledged certain limitations of their study, including its small sample size and the single-center design.
Dr. Friedman disclosed that he coinvented the nanoparticle technology used in the trial. Dr. Berman is a consultant at MINO Labs, which funded the study. The remaining authors had no disclosures. The study was done in collaboration with the Center for Clinical and Cosmetic Research in Aventura, Florida.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
Study Finds Differences in Side Effect Profiles With Two Oral Psoriasis Therapies
TOPLINE:
, according to a retrospective comparison using US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) data.
METHODOLOGY:
- To evaluate the adverse events associated with apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, and deucravacitinib, an oral tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, data were drawn from the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System database.
- The Medex_UIMA_1.8.3 system was used to standardize drug names, and MedDRA terminology was used to encode, categorize, and localize signals.
- AE event signals were grouped by skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, infections and infestations, and nervous system disorders.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 95,734 AE reports for apremilast and 760 AE reports for deucravacitinib, and AEs were found to be significant over time.
- The more common cutaneous AEs were psoriasis recurrence and acne (associated with apremilast) and skin burning and erythema (associated with deucravacitinib).
- The more common gastrointestinal AEs were diarrhea and nausea (apremilast) and mouth ulceration (deucravacitinib).
- Deucravacitinib-related pruritus and rash, as well as apremilast-related tension headache, were more common in women than men; deucravacitinib-related skin burning was more common in men.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “can help the doctors to choose the right treatment options based on the baseline characteristics of different patients,” said Yuanyuan Xu, a graduate student in the Department of Dermatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
SOURCE:
Mr. Xu presented the study as a poster at the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis 2024 annual meeting.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and cannot prove causality, and there were far fewer AE reports related to deucravacitinib, likely because the drug was introduced more recently.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no funding, and the authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to a retrospective comparison using US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) data.
METHODOLOGY:
- To evaluate the adverse events associated with apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, and deucravacitinib, an oral tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, data were drawn from the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System database.
- The Medex_UIMA_1.8.3 system was used to standardize drug names, and MedDRA terminology was used to encode, categorize, and localize signals.
- AE event signals were grouped by skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, infections and infestations, and nervous system disorders.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 95,734 AE reports for apremilast and 760 AE reports for deucravacitinib, and AEs were found to be significant over time.
- The more common cutaneous AEs were psoriasis recurrence and acne (associated with apremilast) and skin burning and erythema (associated with deucravacitinib).
- The more common gastrointestinal AEs were diarrhea and nausea (apremilast) and mouth ulceration (deucravacitinib).
- Deucravacitinib-related pruritus and rash, as well as apremilast-related tension headache, were more common in women than men; deucravacitinib-related skin burning was more common in men.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “can help the doctors to choose the right treatment options based on the baseline characteristics of different patients,” said Yuanyuan Xu, a graduate student in the Department of Dermatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
SOURCE:
Mr. Xu presented the study as a poster at the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis 2024 annual meeting.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and cannot prove causality, and there were far fewer AE reports related to deucravacitinib, likely because the drug was introduced more recently.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no funding, and the authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
, according to a retrospective comparison using US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) data.
METHODOLOGY:
- To evaluate the adverse events associated with apremilast, an oral phosphodiesterase-4 (PDE4) inhibitor, and deucravacitinib, an oral tyrosine kinase 2 (TYK2) inhibitor, data were drawn from the FDA’s Adverse Event Reporting System database.
- The Medex_UIMA_1.8.3 system was used to standardize drug names, and MedDRA terminology was used to encode, categorize, and localize signals.
- AE event signals were grouped by skin and subcutaneous tissue disorders, gastrointestinal disorders, infections and infestations, and nervous system disorders.
TAKEAWAY:
- There were 95,734 AE reports for apremilast and 760 AE reports for deucravacitinib, and AEs were found to be significant over time.
- The more common cutaneous AEs were psoriasis recurrence and acne (associated with apremilast) and skin burning and erythema (associated with deucravacitinib).
- The more common gastrointestinal AEs were diarrhea and nausea (apremilast) and mouth ulceration (deucravacitinib).
- Deucravacitinib-related pruritus and rash, as well as apremilast-related tension headache, were more common in women than men; deucravacitinib-related skin burning was more common in men.
IN PRACTICE:
The results “can help the doctors to choose the right treatment options based on the baseline characteristics of different patients,” said Yuanyuan Xu, a graduate student in the Department of Dermatology, Sichuan University, Chengdu, China.
SOURCE:
Mr. Xu presented the study as a poster at the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis 2024 annual meeting.
LIMITATIONS:
The study was retrospective and cannot prove causality, and there were far fewer AE reports related to deucravacitinib, likely because the drug was introduced more recently.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no funding, and the authors had no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Risk of MACE Comparable Among Biologic Classes for Psoriasis, PsA
TOPLINE:
a database analysis finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data from the TriNetX health records database included 32,758 patients treated with TNF inhibitors (TNFi, 62.9%), interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i, 15.4%), IL-23i (10.7%), and IL-12i/IL-23i (10.7%).
- The researchers calculated time-dependent risk for MACE using multinomial Cox proportional hazard ratios. The reference was TNFi exposure.
- Subset analyses compared MACE in patients with and without existing cardiovascular disease.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with TNFi use, there was no difference in the incidence of MACE events in the IL-17i, IL-23i, or IL-12i/IL-23i group.
- There were also no significant differences between biologic groups in the incidence of congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, or cerebral vascular accident/stroke.
IN PRACTICE:
Despite some concern about increased risk for MACE with TNFi use, this study suggests no special risk for patients with psoriasis or PsA associated with TNFi vs other biologics. “Given our results, as it pertains to MACE, prescribers shouldn’t favor any one biologic class over another,” said lead investigator Shikha Singla, MD, medical director of the Psoriatic Arthritis Program at Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
SOURCE:
Bonit Gill, MD, a second-year fellow at Medical College of Wisconsin, presented the study as a poster at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s retrospective nature makes it impossible to prove causation and the patients included in the study were from Wisconsin, which may limit generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Gill had no relevant financial disclosures. Other study authors participated in trials or consulted for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Janssen, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
a database analysis finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data from the TriNetX health records database included 32,758 patients treated with TNF inhibitors (TNFi, 62.9%), interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i, 15.4%), IL-23i (10.7%), and IL-12i/IL-23i (10.7%).
- The researchers calculated time-dependent risk for MACE using multinomial Cox proportional hazard ratios. The reference was TNFi exposure.
- Subset analyses compared MACE in patients with and without existing cardiovascular disease.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with TNFi use, there was no difference in the incidence of MACE events in the IL-17i, IL-23i, or IL-12i/IL-23i group.
- There were also no significant differences between biologic groups in the incidence of congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, or cerebral vascular accident/stroke.
IN PRACTICE:
Despite some concern about increased risk for MACE with TNFi use, this study suggests no special risk for patients with psoriasis or PsA associated with TNFi vs other biologics. “Given our results, as it pertains to MACE, prescribers shouldn’t favor any one biologic class over another,” said lead investigator Shikha Singla, MD, medical director of the Psoriatic Arthritis Program at Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
SOURCE:
Bonit Gill, MD, a second-year fellow at Medical College of Wisconsin, presented the study as a poster at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s retrospective nature makes it impossible to prove causation and the patients included in the study were from Wisconsin, which may limit generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Gill had no relevant financial disclosures. Other study authors participated in trials or consulted for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Janssen, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
a database analysis finds.
METHODOLOGY:
- Data from the TriNetX health records database included 32,758 patients treated with TNF inhibitors (TNFi, 62.9%), interleukin-17 inhibitors (IL-17i, 15.4%), IL-23i (10.7%), and IL-12i/IL-23i (10.7%).
- The researchers calculated time-dependent risk for MACE using multinomial Cox proportional hazard ratios. The reference was TNFi exposure.
- Subset analyses compared MACE in patients with and without existing cardiovascular disease.
TAKEAWAY:
- Compared with TNFi use, there was no difference in the incidence of MACE events in the IL-17i, IL-23i, or IL-12i/IL-23i group.
- There were also no significant differences between biologic groups in the incidence of congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, or cerebral vascular accident/stroke.
IN PRACTICE:
Despite some concern about increased risk for MACE with TNFi use, this study suggests no special risk for patients with psoriasis or PsA associated with TNFi vs other biologics. “Given our results, as it pertains to MACE, prescribers shouldn’t favor any one biologic class over another,” said lead investigator Shikha Singla, MD, medical director of the Psoriatic Arthritis Program at Medical College of Wisconsin in Milwaukee, Wisconsin.
SOURCE:
Bonit Gill, MD, a second-year fellow at Medical College of Wisconsin, presented the study as a poster at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
LIMITATIONS:
The study’s retrospective nature makes it impossible to prove causation and the patients included in the study were from Wisconsin, which may limit generalizability.
DISCLOSURES:
Dr. Gill had no relevant financial disclosures. Other study authors participated in trials or consulted for AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Novartis, Eli Lilly, Janssen, and UCB.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Study Links Newer Shingles Vaccine to Delayed Dementia Diagnosis
The study builds on previous observations of a reduction in dementia risk with the older live shingles vaccine and reports a delay in dementia diagnosis of 164 days with the newer recombinant version, compared with the live vaccine.
“Given the prevalence of dementia, a delay of 164 days in diagnosis would not be a trivial effect at the public health level. It’s a big enough effect that if there is a causality it feels meaningful,” said senior author Paul Harrison, DM, FRCPsych, professor of psychiatry at the University of Oxford, Oxford, England.
But Dr. Harrison stressed that the study had not proven that the shingles vaccine reduced dementia risk.
“The design of the study allows us to do away with many of the confounding effects we usually see in observational studies, but this is still an observational study, and as such it cannot prove a definite causal effect,” he said.
The study was published online on July 25 in Nature Medicine.
‘Natural Experiment’
Given the risk for deleterious consequences of shingles, vaccination is now recommended for older adults in many countries. The previously used live shingles vaccine (Zostavax) is being replaced in most countries with the new recombinant shingles vaccine (Shingrix), which is more effective at preventing shingles infection.
The current study made use of a “natural experiment” in the United States, which switched over from use of the live vaccine to the recombinant vaccine in October 2017.
Researchers used electronic heath records to compare the incidence of a dementia diagnosis in individuals who received the live shingles vaccine prior to October 2017 with those who received the recombinant version after the United States made the switch.
They also used propensity score matching to further control for confounding factors, comparing 103,837 individuals who received a first dose of the live shingles vaccine between October 2014 and September 2017 with the same number of matched people who received the recombinant vaccine between November 2017 and October 2020.
Results showed that within the 6 years after vaccination, the recombinant vaccine was associated with a delay in the diagnosis of dementia, compared with the live vaccine. Specifically, receiving the recombinant vaccine was associated with a 17% increase in diagnosis-free time, translating to 164 additional days lived without a diagnosis of dementia in those subsequently affected.
As an additional control, the researchers also found significantly lower risks for dementia in individuals receiving the new recombinant shingles vaccine vs two other vaccines commonly used in older people: influenza and tetanus/diphtheria/pertussis vaccines, with increases in diagnosis-free time of 14%-27%.
Reduced Risk or Delayed Diagnosis?
Speaking at a Science Media Centre press conference on the study, lead author Maxime Taquet, PhD, FRCPsych, clinical lecturer in psychiatry at the University of Oxford, noted that the total number of dementia cases were similar in the two shingles vaccine groups by the end of the 6-year follow-up period but there was a difference in the time at which they received a diagnosis of dementia.
“The study suggests that rather than actually reducing dementia risk, the recombinant vaccine delays the onset of dementia compared to the live vaccine in patients who go on to develop the condition,” he explained.
But when comparing the recombinant vaccine with the influenza and tetanus/diphtheria/pertussis vaccines there was a clear reduction in dementia risk itself, Dr. Taquet reported.
“It might well be that the live vaccine has a potential effect on the risk of dementia itself and therefore the recombinant vaccine only shows a delay in dementia compared to the live vaccine, but both of them might decrease the overall risk of dementia,” he suggested.
But the researchers cautioned that this study could not prove causality.
“While the two groups were very carefully matched in terms of factors that might influence the development of dementia, we still have to be cautious before assuming that the vaccine is indeed causally reducing the risk of onset of dementia,” Dr. Harrison warned.
The researchers say the results would need to be confirmed in a randomized trial, which may have to be conducted in a slightly younger age group, as currently shingles vaccine is recommended for all older individuals in the United Kingdom.
Vaccine recommendations vary from country to country, Dr. Harrison added. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the recombinant shingles vaccine for all adults aged 50 years or older.
In the meantime, it would be interesting to see whether further observational studies in other countries find similar results as this US study, Dr. Harrison said.
Mechanism Uncertain
Speculating on a possible mechanism behind the findings, Dr. Harrison suggested two plausible explanations.
“First, it is thought that the herpes virus could be one of many factors that could promote dementia, so a vaccine that stops reactivation of this virus might therefore be delaying that process,” he noted.
The other possibility is that adjuvants included in the recombinant vaccine to stimulate the immune system might have played a role.
“We don’t have any data on the mechanism, and thus study did not address that, so further studies are needed to look into this,” Dr. Harrison said.
Stronger Effect in Women
Another intriguing finding is that the association with the recombinant vaccine and delayed dementia diagnosis seemed to be stronger in women vs men.
In the original study of the live shingles vaccine, a protective effect against dementia was shown only in women.
In the current study, the delay in dementia diagnosis was seen in both sexes but was stronger in women, showing a 22% increased time without dementia in women versus a 13% increased time in men with the recombinant versus the live vaccine.
As expected, the recombinant vaccine was associated with a lower risk for shingles disease vs the live vaccine (2.5% versus 3.5%), but women did not have a better response than men did in this respect.
“The better protection against shingles with the recombinant vaccine was similar in men and women, an observation that might be one reason to question the possible mechanism behind the dementia effect being better suppression of the herpes zoster virus by the recombinant vaccine,” Dr. Harrison commented.
Though these findings are not likely to lead to any immediate changes in policy regarding the shingles vaccine, Dr. Harrison said it would be interesting to see whether uptake of the vaccine increased after this study.
He estimated that, currently in the United Kingdom, about 60% of older adults choose to have the shingles vaccine. A 2020 study in the United States found that only about one-third of US adults over 60 had received the vaccine.
“It will be interesting to see if that figure increases after these data are publicized, but I am not recommending that people have the vaccine specifically to lower their risk of dementia because of the caveats about the study that we have discussed,” he commented.
Outside Experts Positive
Outside experts, providing comment to the Science Media Centre, welcomed the new research.
“ The study is very well-conducted and adds to previous data indicating that vaccination against shingles is associated with lower dementia risk. More research is needed in future to determine why this vaccine is associated with lower dementia risk,” said Tara Spires-Jones, FMedSci, president of the British Neuroscience Association.
The high number of patients in the study and the adjustments for potential confounders are also strong points, noted Andrew Doig, PhD, professor of biochemistry, University of Manchester, Manchester, England.
“This is a significant result, comparable in effectiveness to the recent antibody drugs for Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Doig said. “Administering the recombinant shingles vaccine could well be a simple and cheap way to lower the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.”
Dr. Doig noted that a link between herpes zoster infection and the onset of dementia has been suspected for some time, and a trial of the antiviral drug valacyclovir against Alzheimer’s disease is currently underway.
In regard to the shingles vaccine, he said a placebo-controlled trial would be needed to prove causality.
“We also need to see how many years the effect might last and whether we should vaccinate people at a younger age. We know that the path to Alzheimer’s can start decades before any symptoms are apparent, so the vaccine might be even more effective if given to people in their 40s or 50s,” he said.
Dr. Harrison and Dr. Taquet reported no disclosures. Dr. Doig is a founder, director, and consultant for PharmaKure, which works on Alzheimer’s drugs and diagnostics. Other commentators declared no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study builds on previous observations of a reduction in dementia risk with the older live shingles vaccine and reports a delay in dementia diagnosis of 164 days with the newer recombinant version, compared with the live vaccine.
“Given the prevalence of dementia, a delay of 164 days in diagnosis would not be a trivial effect at the public health level. It’s a big enough effect that if there is a causality it feels meaningful,” said senior author Paul Harrison, DM, FRCPsych, professor of psychiatry at the University of Oxford, Oxford, England.
But Dr. Harrison stressed that the study had not proven that the shingles vaccine reduced dementia risk.
“The design of the study allows us to do away with many of the confounding effects we usually see in observational studies, but this is still an observational study, and as such it cannot prove a definite causal effect,” he said.
The study was published online on July 25 in Nature Medicine.
‘Natural Experiment’
Given the risk for deleterious consequences of shingles, vaccination is now recommended for older adults in many countries. The previously used live shingles vaccine (Zostavax) is being replaced in most countries with the new recombinant shingles vaccine (Shingrix), which is more effective at preventing shingles infection.
The current study made use of a “natural experiment” in the United States, which switched over from use of the live vaccine to the recombinant vaccine in October 2017.
Researchers used electronic heath records to compare the incidence of a dementia diagnosis in individuals who received the live shingles vaccine prior to October 2017 with those who received the recombinant version after the United States made the switch.
They also used propensity score matching to further control for confounding factors, comparing 103,837 individuals who received a first dose of the live shingles vaccine between October 2014 and September 2017 with the same number of matched people who received the recombinant vaccine between November 2017 and October 2020.
Results showed that within the 6 years after vaccination, the recombinant vaccine was associated with a delay in the diagnosis of dementia, compared with the live vaccine. Specifically, receiving the recombinant vaccine was associated with a 17% increase in diagnosis-free time, translating to 164 additional days lived without a diagnosis of dementia in those subsequently affected.
As an additional control, the researchers also found significantly lower risks for dementia in individuals receiving the new recombinant shingles vaccine vs two other vaccines commonly used in older people: influenza and tetanus/diphtheria/pertussis vaccines, with increases in diagnosis-free time of 14%-27%.
Reduced Risk or Delayed Diagnosis?
Speaking at a Science Media Centre press conference on the study, lead author Maxime Taquet, PhD, FRCPsych, clinical lecturer in psychiatry at the University of Oxford, noted that the total number of dementia cases were similar in the two shingles vaccine groups by the end of the 6-year follow-up period but there was a difference in the time at which they received a diagnosis of dementia.
“The study suggests that rather than actually reducing dementia risk, the recombinant vaccine delays the onset of dementia compared to the live vaccine in patients who go on to develop the condition,” he explained.
But when comparing the recombinant vaccine with the influenza and tetanus/diphtheria/pertussis vaccines there was a clear reduction in dementia risk itself, Dr. Taquet reported.
“It might well be that the live vaccine has a potential effect on the risk of dementia itself and therefore the recombinant vaccine only shows a delay in dementia compared to the live vaccine, but both of them might decrease the overall risk of dementia,” he suggested.
But the researchers cautioned that this study could not prove causality.
“While the two groups were very carefully matched in terms of factors that might influence the development of dementia, we still have to be cautious before assuming that the vaccine is indeed causally reducing the risk of onset of dementia,” Dr. Harrison warned.
The researchers say the results would need to be confirmed in a randomized trial, which may have to be conducted in a slightly younger age group, as currently shingles vaccine is recommended for all older individuals in the United Kingdom.
Vaccine recommendations vary from country to country, Dr. Harrison added. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the recombinant shingles vaccine for all adults aged 50 years or older.
In the meantime, it would be interesting to see whether further observational studies in other countries find similar results as this US study, Dr. Harrison said.
Mechanism Uncertain
Speculating on a possible mechanism behind the findings, Dr. Harrison suggested two plausible explanations.
“First, it is thought that the herpes virus could be one of many factors that could promote dementia, so a vaccine that stops reactivation of this virus might therefore be delaying that process,” he noted.
The other possibility is that adjuvants included in the recombinant vaccine to stimulate the immune system might have played a role.
“We don’t have any data on the mechanism, and thus study did not address that, so further studies are needed to look into this,” Dr. Harrison said.
Stronger Effect in Women
Another intriguing finding is that the association with the recombinant vaccine and delayed dementia diagnosis seemed to be stronger in women vs men.
In the original study of the live shingles vaccine, a protective effect against dementia was shown only in women.
In the current study, the delay in dementia diagnosis was seen in both sexes but was stronger in women, showing a 22% increased time without dementia in women versus a 13% increased time in men with the recombinant versus the live vaccine.
As expected, the recombinant vaccine was associated with a lower risk for shingles disease vs the live vaccine (2.5% versus 3.5%), but women did not have a better response than men did in this respect.
“The better protection against shingles with the recombinant vaccine was similar in men and women, an observation that might be one reason to question the possible mechanism behind the dementia effect being better suppression of the herpes zoster virus by the recombinant vaccine,” Dr. Harrison commented.
Though these findings are not likely to lead to any immediate changes in policy regarding the shingles vaccine, Dr. Harrison said it would be interesting to see whether uptake of the vaccine increased after this study.
He estimated that, currently in the United Kingdom, about 60% of older adults choose to have the shingles vaccine. A 2020 study in the United States found that only about one-third of US adults over 60 had received the vaccine.
“It will be interesting to see if that figure increases after these data are publicized, but I am not recommending that people have the vaccine specifically to lower their risk of dementia because of the caveats about the study that we have discussed,” he commented.
Outside Experts Positive
Outside experts, providing comment to the Science Media Centre, welcomed the new research.
“ The study is very well-conducted and adds to previous data indicating that vaccination against shingles is associated with lower dementia risk. More research is needed in future to determine why this vaccine is associated with lower dementia risk,” said Tara Spires-Jones, FMedSci, president of the British Neuroscience Association.
The high number of patients in the study and the adjustments for potential confounders are also strong points, noted Andrew Doig, PhD, professor of biochemistry, University of Manchester, Manchester, England.
“This is a significant result, comparable in effectiveness to the recent antibody drugs for Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Doig said. “Administering the recombinant shingles vaccine could well be a simple and cheap way to lower the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.”
Dr. Doig noted that a link between herpes zoster infection and the onset of dementia has been suspected for some time, and a trial of the antiviral drug valacyclovir against Alzheimer’s disease is currently underway.
In regard to the shingles vaccine, he said a placebo-controlled trial would be needed to prove causality.
“We also need to see how many years the effect might last and whether we should vaccinate people at a younger age. We know that the path to Alzheimer’s can start decades before any symptoms are apparent, so the vaccine might be even more effective if given to people in their 40s or 50s,” he said.
Dr. Harrison and Dr. Taquet reported no disclosures. Dr. Doig is a founder, director, and consultant for PharmaKure, which works on Alzheimer’s drugs and diagnostics. Other commentators declared no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study builds on previous observations of a reduction in dementia risk with the older live shingles vaccine and reports a delay in dementia diagnosis of 164 days with the newer recombinant version, compared with the live vaccine.
“Given the prevalence of dementia, a delay of 164 days in diagnosis would not be a trivial effect at the public health level. It’s a big enough effect that if there is a causality it feels meaningful,” said senior author Paul Harrison, DM, FRCPsych, professor of psychiatry at the University of Oxford, Oxford, England.
But Dr. Harrison stressed that the study had not proven that the shingles vaccine reduced dementia risk.
“The design of the study allows us to do away with many of the confounding effects we usually see in observational studies, but this is still an observational study, and as such it cannot prove a definite causal effect,” he said.
The study was published online on July 25 in Nature Medicine.
‘Natural Experiment’
Given the risk for deleterious consequences of shingles, vaccination is now recommended for older adults in many countries. The previously used live shingles vaccine (Zostavax) is being replaced in most countries with the new recombinant shingles vaccine (Shingrix), which is more effective at preventing shingles infection.
The current study made use of a “natural experiment” in the United States, which switched over from use of the live vaccine to the recombinant vaccine in October 2017.
Researchers used electronic heath records to compare the incidence of a dementia diagnosis in individuals who received the live shingles vaccine prior to October 2017 with those who received the recombinant version after the United States made the switch.
They also used propensity score matching to further control for confounding factors, comparing 103,837 individuals who received a first dose of the live shingles vaccine between October 2014 and September 2017 with the same number of matched people who received the recombinant vaccine between November 2017 and October 2020.
Results showed that within the 6 years after vaccination, the recombinant vaccine was associated with a delay in the diagnosis of dementia, compared with the live vaccine. Specifically, receiving the recombinant vaccine was associated with a 17% increase in diagnosis-free time, translating to 164 additional days lived without a diagnosis of dementia in those subsequently affected.
As an additional control, the researchers also found significantly lower risks for dementia in individuals receiving the new recombinant shingles vaccine vs two other vaccines commonly used in older people: influenza and tetanus/diphtheria/pertussis vaccines, with increases in diagnosis-free time of 14%-27%.
Reduced Risk or Delayed Diagnosis?
Speaking at a Science Media Centre press conference on the study, lead author Maxime Taquet, PhD, FRCPsych, clinical lecturer in psychiatry at the University of Oxford, noted that the total number of dementia cases were similar in the two shingles vaccine groups by the end of the 6-year follow-up period but there was a difference in the time at which they received a diagnosis of dementia.
“The study suggests that rather than actually reducing dementia risk, the recombinant vaccine delays the onset of dementia compared to the live vaccine in patients who go on to develop the condition,” he explained.
But when comparing the recombinant vaccine with the influenza and tetanus/diphtheria/pertussis vaccines there was a clear reduction in dementia risk itself, Dr. Taquet reported.
“It might well be that the live vaccine has a potential effect on the risk of dementia itself and therefore the recombinant vaccine only shows a delay in dementia compared to the live vaccine, but both of them might decrease the overall risk of dementia,” he suggested.
But the researchers cautioned that this study could not prove causality.
“While the two groups were very carefully matched in terms of factors that might influence the development of dementia, we still have to be cautious before assuming that the vaccine is indeed causally reducing the risk of onset of dementia,” Dr. Harrison warned.
The researchers say the results would need to be confirmed in a randomized trial, which may have to be conducted in a slightly younger age group, as currently shingles vaccine is recommended for all older individuals in the United Kingdom.
Vaccine recommendations vary from country to country, Dr. Harrison added. In the United States, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommends the recombinant shingles vaccine for all adults aged 50 years or older.
In the meantime, it would be interesting to see whether further observational studies in other countries find similar results as this US study, Dr. Harrison said.
Mechanism Uncertain
Speculating on a possible mechanism behind the findings, Dr. Harrison suggested two plausible explanations.
“First, it is thought that the herpes virus could be one of many factors that could promote dementia, so a vaccine that stops reactivation of this virus might therefore be delaying that process,” he noted.
The other possibility is that adjuvants included in the recombinant vaccine to stimulate the immune system might have played a role.
“We don’t have any data on the mechanism, and thus study did not address that, so further studies are needed to look into this,” Dr. Harrison said.
Stronger Effect in Women
Another intriguing finding is that the association with the recombinant vaccine and delayed dementia diagnosis seemed to be stronger in women vs men.
In the original study of the live shingles vaccine, a protective effect against dementia was shown only in women.
In the current study, the delay in dementia diagnosis was seen in both sexes but was stronger in women, showing a 22% increased time without dementia in women versus a 13% increased time in men with the recombinant versus the live vaccine.
As expected, the recombinant vaccine was associated with a lower risk for shingles disease vs the live vaccine (2.5% versus 3.5%), but women did not have a better response than men did in this respect.
“The better protection against shingles with the recombinant vaccine was similar in men and women, an observation that might be one reason to question the possible mechanism behind the dementia effect being better suppression of the herpes zoster virus by the recombinant vaccine,” Dr. Harrison commented.
Though these findings are not likely to lead to any immediate changes in policy regarding the shingles vaccine, Dr. Harrison said it would be interesting to see whether uptake of the vaccine increased after this study.
He estimated that, currently in the United Kingdom, about 60% of older adults choose to have the shingles vaccine. A 2020 study in the United States found that only about one-third of US adults over 60 had received the vaccine.
“It will be interesting to see if that figure increases after these data are publicized, but I am not recommending that people have the vaccine specifically to lower their risk of dementia because of the caveats about the study that we have discussed,” he commented.
Outside Experts Positive
Outside experts, providing comment to the Science Media Centre, welcomed the new research.
“ The study is very well-conducted and adds to previous data indicating that vaccination against shingles is associated with lower dementia risk. More research is needed in future to determine why this vaccine is associated with lower dementia risk,” said Tara Spires-Jones, FMedSci, president of the British Neuroscience Association.
The high number of patients in the study and the adjustments for potential confounders are also strong points, noted Andrew Doig, PhD, professor of biochemistry, University of Manchester, Manchester, England.
“This is a significant result, comparable in effectiveness to the recent antibody drugs for Alzheimer’s disease,” Dr. Doig said. “Administering the recombinant shingles vaccine could well be a simple and cheap way to lower the risk of Alzheimer’s disease.”
Dr. Doig noted that a link between herpes zoster infection and the onset of dementia has been suspected for some time, and a trial of the antiviral drug valacyclovir against Alzheimer’s disease is currently underway.
In regard to the shingles vaccine, he said a placebo-controlled trial would be needed to prove causality.
“We also need to see how many years the effect might last and whether we should vaccinate people at a younger age. We know that the path to Alzheimer’s can start decades before any symptoms are apparent, so the vaccine might be even more effective if given to people in their 40s or 50s,” he said.
Dr. Harrison and Dr. Taquet reported no disclosures. Dr. Doig is a founder, director, and consultant for PharmaKure, which works on Alzheimer’s drugs and diagnostics. Other commentators declared no disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
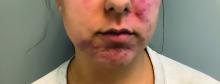
A young adult with a 1-year history of erythema, papules, and pustules on her cheeks and skin
. It typically presents with a sudden onset of papules, pustules, cysts, painful inflammatory nodules, and erythema on the centrofacial areas. The etiology is unknown but has been speculated to be hormone-related as it is more common in women and can be triggered by acute changes such as stress or medications.
Because of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, an accurate clinical assessment is crucial. Typically, there are no comedones and about half of the patients have a history of acne. Some cases have shown a possible link between pyoderma faciale with inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease and liver disease, highlighting the importance of considering these associations in treatment decisions.
Treatment options for pyoderma faciale include isotretinoin, corticosteroids, dapsone, and antibiotics such as doxycycline. Isotretinoin is usually the first-line treatment, with dapsone reserved for cases where other methods have failed. Despite concerns about isotretinoin exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there has been at least one reported case where a patient with ulcerative colitis who had pyoderma faciale that was successfully treated with isotretinoin with no adverse effects.
Isotretinoin has been shown to be effective in treating pyoderma faciale by significantly reducing inflammation and scarring. This is imperative because the scarring from pyoderma faciale can be disfiguring and psychologically harmful for patients. Therefore, an early diagnosis and effective treatment method are essential in preventing these scars and improving patients’ confidence and overall dermatological care.
This patient’s initial bacterial culture was negative. She was treated with a course of low dose isotretinoin. Prednisone was initiated two weeks before starting isotretinoin and then was tapered off during the first month of isotretinoin treatment. The patient was also started on spironolactone. The course of isotretinoin was 9 months. She has remained clear and still takes oral contraceptive pills and low dose spironolactone.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD, of Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Angileri L et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 Feb;32(1):110-3. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1628175.
Coutinho JC et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;91(5 suppl 1):151-3. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164943.
Rosen T and Unkefer RP. Cutis. 1999 Aug;64(2):107-9.
. It typically presents with a sudden onset of papules, pustules, cysts, painful inflammatory nodules, and erythema on the centrofacial areas. The etiology is unknown but has been speculated to be hormone-related as it is more common in women and can be triggered by acute changes such as stress or medications.
Because of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, an accurate clinical assessment is crucial. Typically, there are no comedones and about half of the patients have a history of acne. Some cases have shown a possible link between pyoderma faciale with inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease and liver disease, highlighting the importance of considering these associations in treatment decisions.
Treatment options for pyoderma faciale include isotretinoin, corticosteroids, dapsone, and antibiotics such as doxycycline. Isotretinoin is usually the first-line treatment, with dapsone reserved for cases where other methods have failed. Despite concerns about isotretinoin exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there has been at least one reported case where a patient with ulcerative colitis who had pyoderma faciale that was successfully treated with isotretinoin with no adverse effects.
Isotretinoin has been shown to be effective in treating pyoderma faciale by significantly reducing inflammation and scarring. This is imperative because the scarring from pyoderma faciale can be disfiguring and psychologically harmful for patients. Therefore, an early diagnosis and effective treatment method are essential in preventing these scars and improving patients’ confidence and overall dermatological care.
This patient’s initial bacterial culture was negative. She was treated with a course of low dose isotretinoin. Prednisone was initiated two weeks before starting isotretinoin and then was tapered off during the first month of isotretinoin treatment. The patient was also started on spironolactone. The course of isotretinoin was 9 months. She has remained clear and still takes oral contraceptive pills and low dose spironolactone.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD, of Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Angileri L et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 Feb;32(1):110-3. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1628175.
Coutinho JC et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;91(5 suppl 1):151-3. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164943.
Rosen T and Unkefer RP. Cutis. 1999 Aug;64(2):107-9.
. It typically presents with a sudden onset of papules, pustules, cysts, painful inflammatory nodules, and erythema on the centrofacial areas. The etiology is unknown but has been speculated to be hormone-related as it is more common in women and can be triggered by acute changes such as stress or medications.
Because of overlapping symptoms with other conditions, an accurate clinical assessment is crucial. Typically, there are no comedones and about half of the patients have a history of acne. Some cases have shown a possible link between pyoderma faciale with inflammatory bowel disease, thyroid disease and liver disease, highlighting the importance of considering these associations in treatment decisions.
Treatment options for pyoderma faciale include isotretinoin, corticosteroids, dapsone, and antibiotics such as doxycycline. Isotretinoin is usually the first-line treatment, with dapsone reserved for cases where other methods have failed. Despite concerns about isotretinoin exacerbating inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), there has been at least one reported case where a patient with ulcerative colitis who had pyoderma faciale that was successfully treated with isotretinoin with no adverse effects.
Isotretinoin has been shown to be effective in treating pyoderma faciale by significantly reducing inflammation and scarring. This is imperative because the scarring from pyoderma faciale can be disfiguring and psychologically harmful for patients. Therefore, an early diagnosis and effective treatment method are essential in preventing these scars and improving patients’ confidence and overall dermatological care.
This patient’s initial bacterial culture was negative. She was treated with a course of low dose isotretinoin. Prednisone was initiated two weeks before starting isotretinoin and then was tapered off during the first month of isotretinoin treatment. The patient was also started on spironolactone. The course of isotretinoin was 9 months. She has remained clear and still takes oral contraceptive pills and low dose spironolactone.
This case and the photos were submitted by Ms. Towe, Nova Southeastern University College of Osteopathic Medicine, Fort Lauderdale, Florida, and Donna Bilu Martin, MD, of Premier Dermatology, MD, Aventura, Florida. The column was edited by Dr. Bilu Martin.
Dr. Bilu Martin is a board-certified dermatologist in private practice at Premier Dermatology, MD, in Aventura, Fla. More diagnostic cases are available at mdedge.com/dermatology. To submit a case for possible publication, send an email to [email protected].
References
Angileri L et al. J Dermatolog Treat. 2021 Feb;32(1):110-3. doi: 10.1080/09546634.2019.1628175.
Coutinho JC et al. An Bras Dermatol. 2016 Sep-Oct;91(5 suppl 1):151-3. doi: 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20164943.
Rosen T and Unkefer RP. Cutis. 1999 Aug;64(2):107-9.
Emergency Contraception Recommended for Teens on Isotretinoin
TORONTO —
That was one of the main messages from Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, who discussed hormonal therapies for pediatric acne at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Many doctors are reluctant to prescribe EC, which refers to contraceptive methods used to prevent unintended pregnancy after unprotected sexual intercourse or contraceptive failure, whether that’s from discomfort with EC or lack of training, Dr. Zaenglein said in an interview.
Isotretinoin, a retinoid marketed as Accutane and other brand names, is an effective treatment for acne but carries serious teratogenicity risks; the iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy is designed to manage this risk and minimize fetal exposure. Yet from 2011 to 2017, 210-310 pregnancies per year were reported to the Food and Drug Administration, according to a 2019 study.
There is a knowledge gap regarding EC among dermatologists who prescribe isotretinoin, which “is perpetuated by the iPLEDGE program because it is inadequate in guiding clinicians or educating patients about the use of EC,” Dr. Zaenglein and colleagues wrote in a recently published viewpoint on EC prescribing in patients on isotretinoin.
Types of EC include oral levonorgestrel (plan B), available over the counter; oral ulipristal acetate (ella), which requires a prescription; and the copper/hormonal intrauterine device.
Not all teens taking isotretinoin can be trusted to be sexually abstinent. Dr. Zaenglein cited research showing 39% of female high school students have had sexual relations. “In my opinion, these patients should have emergency contraception prescribed to them as a backup,” she said.
Dr. Zaenglein believes there’s a fair amount of “misunderstanding” about EC, with many people thinking it’s an abortion pill. “It’s a totally different medicine. This is contraception; if you’re pregnant, it’s not going to affect your fetus.”
Outgoing SPD President Sheilagh Maguiness, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, agreed that Dr. Zaenglein raised an important issue. “She has identified a practice gap and a knowledge gap that we need to address,” she said in an interview.
When discussing contraception with female patients taking isotretinoin, assume they’re sexually active or could be, Dr. Zaenglein told meeting attendees. Be explicit about the risks to the fetus and consider their past compliance.
Complex Disorder
During her presentation, Dr. Zaenglein described acne as a “very complex, multifactorial inflammatory disorder” of the skin. It involves four steps: Increased sebum production, hyperkeratinization, Cutibacterium acnes, and inflammation. External factors such as diet, genes, and the environment play a role.
“But at the heart of all of it is androgens; if you didn’t have androgens, you wouldn’t have acne.” That’s why some acne treatments block androgen receptors.
Clinicians are increasingly using one such therapy, spironolactone, to treat acne in female adolescents. Dr. Zaenglein referred to a Mayo Clinic study of 80 patients (mean age, 19 years), who had moderate to severe acne treated with a mean dose of 100 mg/day, that found 80% had improvement with a favorable side effect profile. This included nearly 23% who had a complete response (90% or more) and 36% who had a partial response (more than 50%); 20% had no response.
However, response rates are higher in adults, said Dr. Zaenglein, noting that spironolactone works “much better” in adult women.
Side effects of spironolactone can include menstrual disturbances, breast enlargement and tenderness, and premenstrual syndrome–like symptoms.
Dermatologists should also consider combined oral contraceptives (COCs) in their adolescent patients with acne. These have an estrogen component as well as a progestin component.
They have proven effectiveness for acne in adolescents, yet a US survey of 170 dermatology residents found only 60% felt comfortable prescribing them to healthy adolescents. The survey also found only 62% of respondents felt adequately trained on the efficacy of COCs, and 42% felt adequately trained on their safety.
Contraindications for COCs include thrombosis, migraine with aura, lupus, seizures, and hypertension. Complex valvular heart disease and liver tumors also need to be ruled out, said Dr. Zaenglein. One of the “newer concerns” with COCs is depression. “There’s biological plausibility because, obviously, hormones impact the brain.”
Preventing Drug Interactions
Before prescribing hormonal therapy, clinicians should carry out an acne assessment, aimed in part at preventing drug interactions. “The one we mostly have to watch out for is rifampin,” an antibiotic that could interact with COCs, said Dr. Zaenglein.
The herbal supplement St John’s Wort can reduce the efficacy of COCs. “You also want to make sure that they’re not on any medicines that will increase potassium, such as ACE inhibitors,” said Dr. Zaenglein. But tetracyclines, ampicillin, or metronidazole are usually “all okay” when combined with COCs.
It’s important to get baseline blood pressure levels and to check these along with weight on a regular basis, she added.
Always Consider PCOS
Before starting hormonal therapy, she advises dermatologists to “always consider” polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition that’s “probably much underdiagnosed.” Acne is common in adolescents with PCOS. She suggests using a PCOS checklist, a reminder to ask about irregular periods, hirsutism, signs of insulin resistance such as increased body mass index, a history of premature adrenarche, and a family history of PCOS, said Dr. Zaenglein, noting that a person with a sibling who has PCOS has about a 40% chance of developing the condition.
“We play an important role in getting kids diagnosed at an early age so that we can make interventions because the impact of the metabolic syndrome can have lifelong effects on their cardiovascular system, as well as infertility.”
Dr. Zaenglein is a member of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Acne Guidelines work group, the immediate past president of the American Acne and Rosacea Society, a member of the AAD iPLEDGE work group, co–editor in chief of Pediatric Dermatology, an advisory board member of Ortho Dermatologics, and a consultant for Church & Dwight. Dr. Maguiness had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TORONTO —
That was one of the main messages from Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, who discussed hormonal therapies for pediatric acne at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Many doctors are reluctant to prescribe EC, which refers to contraceptive methods used to prevent unintended pregnancy after unprotected sexual intercourse or contraceptive failure, whether that’s from discomfort with EC or lack of training, Dr. Zaenglein said in an interview.
Isotretinoin, a retinoid marketed as Accutane and other brand names, is an effective treatment for acne but carries serious teratogenicity risks; the iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy is designed to manage this risk and minimize fetal exposure. Yet from 2011 to 2017, 210-310 pregnancies per year were reported to the Food and Drug Administration, according to a 2019 study.
There is a knowledge gap regarding EC among dermatologists who prescribe isotretinoin, which “is perpetuated by the iPLEDGE program because it is inadequate in guiding clinicians or educating patients about the use of EC,” Dr. Zaenglein and colleagues wrote in a recently published viewpoint on EC prescribing in patients on isotretinoin.
Types of EC include oral levonorgestrel (plan B), available over the counter; oral ulipristal acetate (ella), which requires a prescription; and the copper/hormonal intrauterine device.
Not all teens taking isotretinoin can be trusted to be sexually abstinent. Dr. Zaenglein cited research showing 39% of female high school students have had sexual relations. “In my opinion, these patients should have emergency contraception prescribed to them as a backup,” she said.
Dr. Zaenglein believes there’s a fair amount of “misunderstanding” about EC, with many people thinking it’s an abortion pill. “It’s a totally different medicine. This is contraception; if you’re pregnant, it’s not going to affect your fetus.”
Outgoing SPD President Sheilagh Maguiness, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, agreed that Dr. Zaenglein raised an important issue. “She has identified a practice gap and a knowledge gap that we need to address,” she said in an interview.
When discussing contraception with female patients taking isotretinoin, assume they’re sexually active or could be, Dr. Zaenglein told meeting attendees. Be explicit about the risks to the fetus and consider their past compliance.
Complex Disorder
During her presentation, Dr. Zaenglein described acne as a “very complex, multifactorial inflammatory disorder” of the skin. It involves four steps: Increased sebum production, hyperkeratinization, Cutibacterium acnes, and inflammation. External factors such as diet, genes, and the environment play a role.
“But at the heart of all of it is androgens; if you didn’t have androgens, you wouldn’t have acne.” That’s why some acne treatments block androgen receptors.
Clinicians are increasingly using one such therapy, spironolactone, to treat acne in female adolescents. Dr. Zaenglein referred to a Mayo Clinic study of 80 patients (mean age, 19 years), who had moderate to severe acne treated with a mean dose of 100 mg/day, that found 80% had improvement with a favorable side effect profile. This included nearly 23% who had a complete response (90% or more) and 36% who had a partial response (more than 50%); 20% had no response.
However, response rates are higher in adults, said Dr. Zaenglein, noting that spironolactone works “much better” in adult women.
Side effects of spironolactone can include menstrual disturbances, breast enlargement and tenderness, and premenstrual syndrome–like symptoms.
Dermatologists should also consider combined oral contraceptives (COCs) in their adolescent patients with acne. These have an estrogen component as well as a progestin component.
They have proven effectiveness for acne in adolescents, yet a US survey of 170 dermatology residents found only 60% felt comfortable prescribing them to healthy adolescents. The survey also found only 62% of respondents felt adequately trained on the efficacy of COCs, and 42% felt adequately trained on their safety.
Contraindications for COCs include thrombosis, migraine with aura, lupus, seizures, and hypertension. Complex valvular heart disease and liver tumors also need to be ruled out, said Dr. Zaenglein. One of the “newer concerns” with COCs is depression. “There’s biological plausibility because, obviously, hormones impact the brain.”
Preventing Drug Interactions
Before prescribing hormonal therapy, clinicians should carry out an acne assessment, aimed in part at preventing drug interactions. “The one we mostly have to watch out for is rifampin,” an antibiotic that could interact with COCs, said Dr. Zaenglein.
The herbal supplement St John’s Wort can reduce the efficacy of COCs. “You also want to make sure that they’re not on any medicines that will increase potassium, such as ACE inhibitors,” said Dr. Zaenglein. But tetracyclines, ampicillin, or metronidazole are usually “all okay” when combined with COCs.
It’s important to get baseline blood pressure levels and to check these along with weight on a regular basis, she added.
Always Consider PCOS
Before starting hormonal therapy, she advises dermatologists to “always consider” polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition that’s “probably much underdiagnosed.” Acne is common in adolescents with PCOS. She suggests using a PCOS checklist, a reminder to ask about irregular periods, hirsutism, signs of insulin resistance such as increased body mass index, a history of premature adrenarche, and a family history of PCOS, said Dr. Zaenglein, noting that a person with a sibling who has PCOS has about a 40% chance of developing the condition.
“We play an important role in getting kids diagnosed at an early age so that we can make interventions because the impact of the metabolic syndrome can have lifelong effects on their cardiovascular system, as well as infertility.”
Dr. Zaenglein is a member of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Acne Guidelines work group, the immediate past president of the American Acne and Rosacea Society, a member of the AAD iPLEDGE work group, co–editor in chief of Pediatric Dermatology, an advisory board member of Ortho Dermatologics, and a consultant for Church & Dwight. Dr. Maguiness had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TORONTO —
That was one of the main messages from Andrea L. Zaenglein, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, Penn State University, Hershey, who discussed hormonal therapies for pediatric acne at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Many doctors are reluctant to prescribe EC, which refers to contraceptive methods used to prevent unintended pregnancy after unprotected sexual intercourse or contraceptive failure, whether that’s from discomfort with EC or lack of training, Dr. Zaenglein said in an interview.
Isotretinoin, a retinoid marketed as Accutane and other brand names, is an effective treatment for acne but carries serious teratogenicity risks; the iPLEDGE Risk Evaluation and Mitigation Strategy is designed to manage this risk and minimize fetal exposure. Yet from 2011 to 2017, 210-310 pregnancies per year were reported to the Food and Drug Administration, according to a 2019 study.
There is a knowledge gap regarding EC among dermatologists who prescribe isotretinoin, which “is perpetuated by the iPLEDGE program because it is inadequate in guiding clinicians or educating patients about the use of EC,” Dr. Zaenglein and colleagues wrote in a recently published viewpoint on EC prescribing in patients on isotretinoin.
Types of EC include oral levonorgestrel (plan B), available over the counter; oral ulipristal acetate (ella), which requires a prescription; and the copper/hormonal intrauterine device.
Not all teens taking isotretinoin can be trusted to be sexually abstinent. Dr. Zaenglein cited research showing 39% of female high school students have had sexual relations. “In my opinion, these patients should have emergency contraception prescribed to them as a backup,” she said.
Dr. Zaenglein believes there’s a fair amount of “misunderstanding” about EC, with many people thinking it’s an abortion pill. “It’s a totally different medicine. This is contraception; if you’re pregnant, it’s not going to affect your fetus.”
Outgoing SPD President Sheilagh Maguiness, MD, professor of dermatology and pediatrics, University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, agreed that Dr. Zaenglein raised an important issue. “She has identified a practice gap and a knowledge gap that we need to address,” she said in an interview.
When discussing contraception with female patients taking isotretinoin, assume they’re sexually active or could be, Dr. Zaenglein told meeting attendees. Be explicit about the risks to the fetus and consider their past compliance.
Complex Disorder
During her presentation, Dr. Zaenglein described acne as a “very complex, multifactorial inflammatory disorder” of the skin. It involves four steps: Increased sebum production, hyperkeratinization, Cutibacterium acnes, and inflammation. External factors such as diet, genes, and the environment play a role.
“But at the heart of all of it is androgens; if you didn’t have androgens, you wouldn’t have acne.” That’s why some acne treatments block androgen receptors.
Clinicians are increasingly using one such therapy, spironolactone, to treat acne in female adolescents. Dr. Zaenglein referred to a Mayo Clinic study of 80 patients (mean age, 19 years), who had moderate to severe acne treated with a mean dose of 100 mg/day, that found 80% had improvement with a favorable side effect profile. This included nearly 23% who had a complete response (90% or more) and 36% who had a partial response (more than 50%); 20% had no response.
However, response rates are higher in adults, said Dr. Zaenglein, noting that spironolactone works “much better” in adult women.
Side effects of spironolactone can include menstrual disturbances, breast enlargement and tenderness, and premenstrual syndrome–like symptoms.
Dermatologists should also consider combined oral contraceptives (COCs) in their adolescent patients with acne. These have an estrogen component as well as a progestin component.
They have proven effectiveness for acne in adolescents, yet a US survey of 170 dermatology residents found only 60% felt comfortable prescribing them to healthy adolescents. The survey also found only 62% of respondents felt adequately trained on the efficacy of COCs, and 42% felt adequately trained on their safety.
Contraindications for COCs include thrombosis, migraine with aura, lupus, seizures, and hypertension. Complex valvular heart disease and liver tumors also need to be ruled out, said Dr. Zaenglein. One of the “newer concerns” with COCs is depression. “There’s biological plausibility because, obviously, hormones impact the brain.”
Preventing Drug Interactions
Before prescribing hormonal therapy, clinicians should carry out an acne assessment, aimed in part at preventing drug interactions. “The one we mostly have to watch out for is rifampin,” an antibiotic that could interact with COCs, said Dr. Zaenglein.
The herbal supplement St John’s Wort can reduce the efficacy of COCs. “You also want to make sure that they’re not on any medicines that will increase potassium, such as ACE inhibitors,” said Dr. Zaenglein. But tetracyclines, ampicillin, or metronidazole are usually “all okay” when combined with COCs.
It’s important to get baseline blood pressure levels and to check these along with weight on a regular basis, she added.
Always Consider PCOS
Before starting hormonal therapy, she advises dermatologists to “always consider” polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a condition that’s “probably much underdiagnosed.” Acne is common in adolescents with PCOS. She suggests using a PCOS checklist, a reminder to ask about irregular periods, hirsutism, signs of insulin resistance such as increased body mass index, a history of premature adrenarche, and a family history of PCOS, said Dr. Zaenglein, noting that a person with a sibling who has PCOS has about a 40% chance of developing the condition.
“We play an important role in getting kids diagnosed at an early age so that we can make interventions because the impact of the metabolic syndrome can have lifelong effects on their cardiovascular system, as well as infertility.”
Dr. Zaenglein is a member of the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) Acne Guidelines work group, the immediate past president of the American Acne and Rosacea Society, a member of the AAD iPLEDGE work group, co–editor in chief of Pediatric Dermatology, an advisory board member of Ortho Dermatologics, and a consultant for Church & Dwight. Dr. Maguiness had no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Several Skin Conditions More Likely in Children With Obesity
TORONTO — results of new research show.
The retrospective cohort study found markedly higher rates of skin infections, atopic dermatitis (AD), and acanthosis nigricans among children with overweight, compared with children with average weight.
“Many conditions associated with obesity are strong predictors of cardiovascular mortality as these children age, so doctors can play a key role in advocating for weight loss strategies in this population,” lead study author Samantha Epstein, third-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview. The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Previous research has linked obesity, a chronic inflammatory condition, to psoriasis, AD, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), acne vulgaris, infections, and rosacea in adults. However, there’s scant research exploring the connection between obesity and cutaneous conditions in children.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index, which is weight in kg divided by the square of height in m2, at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 years or older.
For the study, Ms. Epstein and coauthor Sonal D. Shah, MD, associate professor, Department of Dermatology, Case Western Reserve University, and a board-certified pediatric dermatologist accessed a large national research database and used diagnostic codes to identify over 1 million children (mean age, 8.5 years). Most (about 44%) were White; about one-quarter were Black. The groups were propensity matched, so there were about equal numbers of youngsters with and without obesity and of boys and girls.
They collected data on AD, HS, rosacea, psoriasis, and acanthosis nigricans (a thickened purplish discoloration typically found in body folds around the armpits, groin, and neck). They also gathered information on comorbidities.
Acanthosis nigricans, which is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance , was more prevalent among children with obesity (20,885 cases in the with-obesity group and 336 in the without-obesity group, for a relative risk [RR] of 62.16 and an odds ratio [OR] of 64.38).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue infections were also more common among those with obesity (14,795 cases) vs 4720 cases among those without obesity (RR, 3.14; OR, 3.2). As for AD, there were 11,892 cases in the with-obesity group and 2983 in the without-obesity group (RR, 3.99; OR, 4.06). There were 1166 cases of psoriasis among those with obesity and 408 among those without obesity (RR, 2.86; OR, 2.88).
HS (587 cases in the with-obesity group and 70 in the without-obesity group; RR, 8.39; OR, 8.39) and rosacea (351 in the with-obesity group and 138 in the without-obesity group; RR, 2.54; OR, 2.55) were the least common skin conditions.
Higher Comorbidity Rates
Compared with their average-weight counterparts, the children with obesity had higher rates of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes. Ms. Epstein noted that children with diabetes and obesity had increased risks for every skin condition except for infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue when compared with children without obesity.
Such infections were the most common skin conditions among children without obesity. “This was expected just due to the fact that children are outside, they’re playing in the grass and the dirt, and they get infected,” said Ms. Epstein. Still, these infections were three times more common in youngsters with obesity.
Although acanthosis nigricans is “highly correlated” with type 2 diabetes, “not as many children as we would expect in this population have developed type 2 diabetes,” said Ms. Epstein. This might make some sense, though, because these children are still quite young. “When dermatologists recognize this skin condition, they can advocate for weight loss management to try to prevent it.”
Other conditions seen more often in the overweight children with overweight included: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, polycystic ovarian syndrome, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, depressive episodes, and anxiety (all P < .001).
Commenting on the results, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview that the study reflects trends that she and her colleagues see in clinic: There are more common skin conditions in their patients with obesity.
She agreed that it offers an opening for education. “The results of this study highlight the opportunity we have as pediatric dermatologists to provide additional counseling on obesity and offer referrals to our colleagues in endocrinology, gastroenterology, and nutrition if needed.”
No conflicts of interest were reported.
TORONTO — results of new research show.
The retrospective cohort study found markedly higher rates of skin infections, atopic dermatitis (AD), and acanthosis nigricans among children with overweight, compared with children with average weight.
“Many conditions associated with obesity are strong predictors of cardiovascular mortality as these children age, so doctors can play a key role in advocating for weight loss strategies in this population,” lead study author Samantha Epstein, third-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview. The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Previous research has linked obesity, a chronic inflammatory condition, to psoriasis, AD, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), acne vulgaris, infections, and rosacea in adults. However, there’s scant research exploring the connection between obesity and cutaneous conditions in children.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index, which is weight in kg divided by the square of height in m2, at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 years or older.
For the study, Ms. Epstein and coauthor Sonal D. Shah, MD, associate professor, Department of Dermatology, Case Western Reserve University, and a board-certified pediatric dermatologist accessed a large national research database and used diagnostic codes to identify over 1 million children (mean age, 8.5 years). Most (about 44%) were White; about one-quarter were Black. The groups were propensity matched, so there were about equal numbers of youngsters with and without obesity and of boys and girls.
They collected data on AD, HS, rosacea, psoriasis, and acanthosis nigricans (a thickened purplish discoloration typically found in body folds around the armpits, groin, and neck). They also gathered information on comorbidities.
Acanthosis nigricans, which is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance , was more prevalent among children with obesity (20,885 cases in the with-obesity group and 336 in the without-obesity group, for a relative risk [RR] of 62.16 and an odds ratio [OR] of 64.38).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue infections were also more common among those with obesity (14,795 cases) vs 4720 cases among those without obesity (RR, 3.14; OR, 3.2). As for AD, there were 11,892 cases in the with-obesity group and 2983 in the without-obesity group (RR, 3.99; OR, 4.06). There were 1166 cases of psoriasis among those with obesity and 408 among those without obesity (RR, 2.86; OR, 2.88).
HS (587 cases in the with-obesity group and 70 in the without-obesity group; RR, 8.39; OR, 8.39) and rosacea (351 in the with-obesity group and 138 in the without-obesity group; RR, 2.54; OR, 2.55) were the least common skin conditions.
Higher Comorbidity Rates
Compared with their average-weight counterparts, the children with obesity had higher rates of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes. Ms. Epstein noted that children with diabetes and obesity had increased risks for every skin condition except for infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue when compared with children without obesity.
Such infections were the most common skin conditions among children without obesity. “This was expected just due to the fact that children are outside, they’re playing in the grass and the dirt, and they get infected,” said Ms. Epstein. Still, these infections were three times more common in youngsters with obesity.
Although acanthosis nigricans is “highly correlated” with type 2 diabetes, “not as many children as we would expect in this population have developed type 2 diabetes,” said Ms. Epstein. This might make some sense, though, because these children are still quite young. “When dermatologists recognize this skin condition, they can advocate for weight loss management to try to prevent it.”
Other conditions seen more often in the overweight children with overweight included: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, polycystic ovarian syndrome, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, depressive episodes, and anxiety (all P < .001).
Commenting on the results, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview that the study reflects trends that she and her colleagues see in clinic: There are more common skin conditions in their patients with obesity.
She agreed that it offers an opening for education. “The results of this study highlight the opportunity we have as pediatric dermatologists to provide additional counseling on obesity and offer referrals to our colleagues in endocrinology, gastroenterology, and nutrition if needed.”
No conflicts of interest were reported.
TORONTO — results of new research show.
The retrospective cohort study found markedly higher rates of skin infections, atopic dermatitis (AD), and acanthosis nigricans among children with overweight, compared with children with average weight.
“Many conditions associated with obesity are strong predictors of cardiovascular mortality as these children age, so doctors can play a key role in advocating for weight loss strategies in this population,” lead study author Samantha Epstein, third-year medical student at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, Ohio, said in an interview. The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
Previous research has linked obesity, a chronic inflammatory condition, to psoriasis, AD, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), acne vulgaris, infections, and rosacea in adults. However, there’s scant research exploring the connection between obesity and cutaneous conditions in children.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, childhood obesity is defined as a body mass index, which is weight in kg divided by the square of height in m2, at or above the 95th percentile for age and sex in children aged 2 years or older.
For the study, Ms. Epstein and coauthor Sonal D. Shah, MD, associate professor, Department of Dermatology, Case Western Reserve University, and a board-certified pediatric dermatologist accessed a large national research database and used diagnostic codes to identify over 1 million children (mean age, 8.5 years). Most (about 44%) were White; about one-quarter were Black. The groups were propensity matched, so there were about equal numbers of youngsters with and without obesity and of boys and girls.
They collected data on AD, HS, rosacea, psoriasis, and acanthosis nigricans (a thickened purplish discoloration typically found in body folds around the armpits, groin, and neck). They also gathered information on comorbidities.
Acanthosis nigricans, which is linked to metabolic syndrome, type 2 diabetes, and insulin resistance , was more prevalent among children with obesity (20,885 cases in the with-obesity group and 336 in the without-obesity group, for a relative risk [RR] of 62.16 and an odds ratio [OR] of 64.38).
Skin and subcutaneous tissue infections were also more common among those with obesity (14,795 cases) vs 4720 cases among those without obesity (RR, 3.14; OR, 3.2). As for AD, there were 11,892 cases in the with-obesity group and 2983 in the without-obesity group (RR, 3.99; OR, 4.06). There were 1166 cases of psoriasis among those with obesity and 408 among those without obesity (RR, 2.86; OR, 2.88).
HS (587 cases in the with-obesity group and 70 in the without-obesity group; RR, 8.39; OR, 8.39) and rosacea (351 in the with-obesity group and 138 in the without-obesity group; RR, 2.54; OR, 2.55) were the least common skin conditions.
Higher Comorbidity Rates
Compared with their average-weight counterparts, the children with obesity had higher rates of comorbidities, including type 2 diabetes. Ms. Epstein noted that children with diabetes and obesity had increased risks for every skin condition except for infections of the skin and subcutaneous tissue when compared with children without obesity.
Such infections were the most common skin conditions among children without obesity. “This was expected just due to the fact that children are outside, they’re playing in the grass and the dirt, and they get infected,” said Ms. Epstein. Still, these infections were three times more common in youngsters with obesity.
Although acanthosis nigricans is “highly correlated” with type 2 diabetes, “not as many children as we would expect in this population have developed type 2 diabetes,” said Ms. Epstein. This might make some sense, though, because these children are still quite young. “When dermatologists recognize this skin condition, they can advocate for weight loss management to try to prevent it.”
Other conditions seen more often in the overweight children with overweight included: hypertension, hyperlipidemia, obstructive sleep apnea, polycystic ovarian syndrome, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder, major depressive disorder, depressive episodes, and anxiety (all P < .001).
Commenting on the results, Sonia Havele, MD, a pediatrician and dermatology resident at Children’s Mercy Hospital, Kansas City, Missouri, said in an interview that the study reflects trends that she and her colleagues see in clinic: There are more common skin conditions in their patients with obesity.
She agreed that it offers an opening for education. “The results of this study highlight the opportunity we have as pediatric dermatologists to provide additional counseling on obesity and offer referrals to our colleagues in endocrinology, gastroenterology, and nutrition if needed.”
No conflicts of interest were reported.
FROM SPD 2024
Topical Ruxolitinib: Analysis Finds Repigmentation Rates in Adolescents with Vitiligo
data showed.
“We consider repigmenting vitiligo a two-step process, where the overactive immune system needs to be calmed down and then the melanocytes need to repopulate to the white areas,” one of the study investigators, David Rosmarin, MD, chair of the Department of Dermatology at Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study results were presented during a poster session. “In younger patients, it may be that the melanocytes are more rapidly repigmenting the patches, which is why we see this effect.”
Ruxolitinib, 1.5% cream (Opzelura) is a Janus kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older. Dr. Rosmarin and colleagues sought to evaluate differences in rates of complete or near-complete repigmentation and repigmentation by body region between adolescents 12-17 years of age and adults 18 years of age and older who applied ruxolitinib cream twice daily. The researchers evaluated patients who were initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream, 1.5% in the pivotal TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies and applied it for up to 104 weeks. Complete facial improvement was defined as 100% improvement on the Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI 100) from baseline, and near-total improvement was categorized as a ≥ 75% or ≥ 90% improvement from baseline on the Total body VASI (T-VASI). Responses for each of six body regions, excluding the face, were assessed by the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline on the T-VASI.
Compared with adults, a greater proportion of adolescents achieved F-VASI 100 at week 24 (5.7% [3/53] vs 2.9% [10/341], respectively), but there were no differences between the two groups at week 52 (8.0% [4/50] vs 8.0% [24/300]). Response rates were greater among adolescents vs adults for T-VASI 75 at weeks 24 (13.2% [7/53] vs 5.6% [19/341]) and 52 (22.0% [11/50] vs 20.3% [61/300]), as well as T-VASI 90 at weeks 24 (3.8% [2/53] vs 0.3% [1/341]) and 52 (12.0% [6/50] vs 4.0% [12/300]).
The researchers observed that VASI 50 responses by body region were generally similar between adolescents and adults, but a greater proportion of adolescents achieved a VASI 50 in lower extremities (67.3% [33/49] vs 51.8% [118/228]) and feet (37.5% [12/32] vs 27.9% [51/183]) at week 52.
“Adolescents repigmented more rapidly than adults, so that at 24 weeks, more teens had complete facial repigmentation and T-VASI 75 and T-VASI 90 results,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “With continued use of ruxolitinib cream, both more adults and adolescents achieved greater repigmentation.” He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was only vehicle controlled up through 24 weeks and that, after week 52, there were fewer patients who completed the long-term extension.
“The take-home message is that ruxolitinib cream can effectively and safely help many patients repigment, including adolescents,” he said.
The study was funded by topical ruxolitinib manufacturer Incyte. Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he has consulted, spoken for, or conducted trials for AbbVie, Abcuro, Almirall, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena, Astria, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant Sciences, Dermira, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Merck, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, RAPT, Regeneron, Recludix Pharma, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Viela Bio, and Zura.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
data showed.
“We consider repigmenting vitiligo a two-step process, where the overactive immune system needs to be calmed down and then the melanocytes need to repopulate to the white areas,” one of the study investigators, David Rosmarin, MD, chair of the Department of Dermatology at Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study results were presented during a poster session. “In younger patients, it may be that the melanocytes are more rapidly repigmenting the patches, which is why we see this effect.”
Ruxolitinib, 1.5% cream (Opzelura) is a Janus kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older. Dr. Rosmarin and colleagues sought to evaluate differences in rates of complete or near-complete repigmentation and repigmentation by body region between adolescents 12-17 years of age and adults 18 years of age and older who applied ruxolitinib cream twice daily. The researchers evaluated patients who were initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream, 1.5% in the pivotal TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies and applied it for up to 104 weeks. Complete facial improvement was defined as 100% improvement on the Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI 100) from baseline, and near-total improvement was categorized as a ≥ 75% or ≥ 90% improvement from baseline on the Total body VASI (T-VASI). Responses for each of six body regions, excluding the face, were assessed by the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline on the T-VASI.
Compared with adults, a greater proportion of adolescents achieved F-VASI 100 at week 24 (5.7% [3/53] vs 2.9% [10/341], respectively), but there were no differences between the two groups at week 52 (8.0% [4/50] vs 8.0% [24/300]). Response rates were greater among adolescents vs adults for T-VASI 75 at weeks 24 (13.2% [7/53] vs 5.6% [19/341]) and 52 (22.0% [11/50] vs 20.3% [61/300]), as well as T-VASI 90 at weeks 24 (3.8% [2/53] vs 0.3% [1/341]) and 52 (12.0% [6/50] vs 4.0% [12/300]).
The researchers observed that VASI 50 responses by body region were generally similar between adolescents and adults, but a greater proportion of adolescents achieved a VASI 50 in lower extremities (67.3% [33/49] vs 51.8% [118/228]) and feet (37.5% [12/32] vs 27.9% [51/183]) at week 52.
“Adolescents repigmented more rapidly than adults, so that at 24 weeks, more teens had complete facial repigmentation and T-VASI 75 and T-VASI 90 results,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “With continued use of ruxolitinib cream, both more adults and adolescents achieved greater repigmentation.” He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was only vehicle controlled up through 24 weeks and that, after week 52, there were fewer patients who completed the long-term extension.
“The take-home message is that ruxolitinib cream can effectively and safely help many patients repigment, including adolescents,” he said.
The study was funded by topical ruxolitinib manufacturer Incyte. Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he has consulted, spoken for, or conducted trials for AbbVie, Abcuro, Almirall, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena, Astria, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant Sciences, Dermira, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Merck, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, RAPT, Regeneron, Recludix Pharma, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Viela Bio, and Zura.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
data showed.
“We consider repigmenting vitiligo a two-step process, where the overactive immune system needs to be calmed down and then the melanocytes need to repopulate to the white areas,” one of the study investigators, David Rosmarin, MD, chair of the Department of Dermatology at Indiana University School of Medicine, Indianapolis, said in an interview in advance of the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology, where the study results were presented during a poster session. “In younger patients, it may be that the melanocytes are more rapidly repigmenting the patches, which is why we see this effect.”
Ruxolitinib, 1.5% cream (Opzelura) is a Janus kinase inhibitor approved for the treatment of nonsegmental vitiligo in patients 12 years of age and older. Dr. Rosmarin and colleagues sought to evaluate differences in rates of complete or near-complete repigmentation and repigmentation by body region between adolescents 12-17 years of age and adults 18 years of age and older who applied ruxolitinib cream twice daily. The researchers evaluated patients who were initially randomized to ruxolitinib cream, 1.5% in the pivotal TRuE-V1 and TRuE-V2 studies and applied it for up to 104 weeks. Complete facial improvement was defined as 100% improvement on the Facial Vitiligo Area Scoring Index (F-VASI 100) from baseline, and near-total improvement was categorized as a ≥ 75% or ≥ 90% improvement from baseline on the Total body VASI (T-VASI). Responses for each of six body regions, excluding the face, were assessed by the proportion of patients who achieved at least a 50% improvement from baseline on the T-VASI.
Compared with adults, a greater proportion of adolescents achieved F-VASI 100 at week 24 (5.7% [3/53] vs 2.9% [10/341], respectively), but there were no differences between the two groups at week 52 (8.0% [4/50] vs 8.0% [24/300]). Response rates were greater among adolescents vs adults for T-VASI 75 at weeks 24 (13.2% [7/53] vs 5.6% [19/341]) and 52 (22.0% [11/50] vs 20.3% [61/300]), as well as T-VASI 90 at weeks 24 (3.8% [2/53] vs 0.3% [1/341]) and 52 (12.0% [6/50] vs 4.0% [12/300]).
The researchers observed that VASI 50 responses by body region were generally similar between adolescents and adults, but a greater proportion of adolescents achieved a VASI 50 in lower extremities (67.3% [33/49] vs 51.8% [118/228]) and feet (37.5% [12/32] vs 27.9% [51/183]) at week 52.
“Adolescents repigmented more rapidly than adults, so that at 24 weeks, more teens had complete facial repigmentation and T-VASI 75 and T-VASI 90 results,” Dr. Rosmarin said. “With continued use of ruxolitinib cream, both more adults and adolescents achieved greater repigmentation.” He acknowledged certain limitations of the study, including the fact that it was only vehicle controlled up through 24 weeks and that, after week 52, there were fewer patients who completed the long-term extension.
“The take-home message is that ruxolitinib cream can effectively and safely help many patients repigment, including adolescents,” he said.
The study was funded by topical ruxolitinib manufacturer Incyte. Dr. Rosmarin disclosed that he has consulted, spoken for, or conducted trials for AbbVie, Abcuro, Almirall, AltruBio, Amgen, Arena, Astria, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Meyers Squibb, Celgene, Concert, CSL Behring, Dermavant Sciences, Dermira, Galderma, Incyte, Janssen, Kyowa Kirin, Lilly, Merck, Nektar, Novartis, Pfizer, RAPT, Regeneron, Recludix Pharma, Revolo Biotherapeutics, Sanofi, Sun Pharmaceuticals, UCB, Viela Bio, and Zura.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM SPD 2024
Mysteries Persist About Tissue Resident Memory T Cells in Psoriasis
SEATTLE — In fact, flare-ups often recur at the same site, a phenomenon that might be driven by these resident memory cells, according to Liv Eidsmo, MD, PhD.
This has led to their use as biomarkers in clinical trials for new therapies, but TRM T cells have a complex biology that is far from fully understood, Dr. Eidsmo said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. “With time, we’re understanding that the regulation of the functionality is more complicated than we thought, so following these cells as a positive outcome of a clinical trial is a little bit premature,” said Dr. Eidsmo, who is a consultant dermatologist at the University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Treatment strategies focus on inhibition of interleukin (IL)-23, which is an activator of TRM T cells and probably keeps them alive, according to Dr. Eidsmo. “The hope is that these cells can be silenced by IL-23 inhibition, which is a great idea, and it probably works. It’s just a matter of what is the readout of long-term remission, because the big challenge in the clinical world is when do we stop these expensive biological treatments? When can we feel secure that patients are in deep remission?” she asked.
TRM cells are also far from the only immune cells involved in psoriasis. Others include keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, and fibroblasts. Dr. Eidsmo referenced a recent spatial analysis that used single-cell and spatial RNA sequencing to identify the localization of specific cell populations and inflammatory pathways within psoriasis lesions and epidermal compartments as well as also suggested crosstalk links between cell types. Epigenetic changes in stem cells may also maintain a lower threshold for tissue inflammation.
Dr. Eidsmo advised caution in eliminating TRM T cells, which play a key role in protecting against melanoma and other cancers, especially later in life. “We don’t want to get rid of them. We want to have the right balance.”
She noted a study in her own lab that mapped TRM T cells in healthy epidermis and found that they could be renewed from both circulating precursors and cells within the epidermis. “So getting rid of the mature TRM T cells will most likely just lead to a new generation of the same subset.”
Other data show that there are a wide range of subsets of TRM T cells, and she recommended focusing on the functionality of TRM T cells rather than sheer numbers. “This is something we’re working on now: Can we change the functionality [of TRM T cells], rather than eradicate them and hope for the best in the next generation? Can we change the functionality of the T cells we already have in the skin?”
There is also epigenetic data in TRM T cells, keratinocytes, stem cells, and other cells thus suggesting complexity and plasticity in the system that remains poorly understood.
Taken together, the research is at too early of a stage to be clinically useful, said Dr. Eidsmo. “We need to go back to the drawing board and just realize what we need to measure, and with the new techniques coming out, maybe spatial [measurement] at a high resolution, we can find biomarkers that better dictate the future of this. Be a little bit wary when you read the outcomes from the clinical trials that are ongoing, because right now, it’s a bit of a race between different biologics. These cells are used as a readout of efficacy of the treatments, and we’re not quite there yet.”
During the Q&A session after the presentation, one audience member asked about the heterogeneity of cells found within the skin of patients with psoriasis and pointed out that many proinflammatory cells likely play a role in tumor control. Dr. Eidsmo responded that her group’s analysis of a large database of patients with metastatic melanoma found that a factor that is important to the development of TRM T cells was strongly correlated to survival in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving immune checkpoint blockade. “So we really don’t want to eradicate them,” she said.
Also during the Q&A, Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, commented about the need to understand the previous events that drove the creation of memory T cells. “For me, the question is about the hierarchy, the primacy of what really drives the memory. In the infectious world, we’re trained to think [that memory responses] are T cell driven memory, but I wonder whether you have an idea of whether the T cell is responding to other memories, particularly in the stroma. Because certainly in the arthropathies, we have really good evidence now of epigenetic change in the synovial stroma and subsets,” said Dr. McInnes, who is director of the Institute of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, Glasgow, Scotland.
Dr. Eidsmo responded that she believes responses are different among different individuals. “We know too little about how these two systems interact with one another. I think the TRM T cells are very good at amplifying the stroma to recruit cells in. I think we need to think of two-step therapies. You need to normalize this [stromal] environment. How you can do that, I don’t know.”
Dr. McInnes agreed. “As a myeloid doctor, I strongly believe that perpetuators are innate and the adaptive is following on. But how do we test that? That’s really hard,” he said.
Dr. Eidsmo did not list any disclosures. Dr. McInnes has financial relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer, Compugen, Cabaletta, Causeway, Dextera, Eli Lilly, Celgene, MoonLake, Pfizer, Novartis, Janssen, Roche, Versus Arthritis, MRC, and UCB.
SEATTLE — In fact, flare-ups often recur at the same site, a phenomenon that might be driven by these resident memory cells, according to Liv Eidsmo, MD, PhD.
This has led to their use as biomarkers in clinical trials for new therapies, but TRM T cells have a complex biology that is far from fully understood, Dr. Eidsmo said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. “With time, we’re understanding that the regulation of the functionality is more complicated than we thought, so following these cells as a positive outcome of a clinical trial is a little bit premature,” said Dr. Eidsmo, who is a consultant dermatologist at the University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Treatment strategies focus on inhibition of interleukin (IL)-23, which is an activator of TRM T cells and probably keeps them alive, according to Dr. Eidsmo. “The hope is that these cells can be silenced by IL-23 inhibition, which is a great idea, and it probably works. It’s just a matter of what is the readout of long-term remission, because the big challenge in the clinical world is when do we stop these expensive biological treatments? When can we feel secure that patients are in deep remission?” she asked.
TRM cells are also far from the only immune cells involved in psoriasis. Others include keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, and fibroblasts. Dr. Eidsmo referenced a recent spatial analysis that used single-cell and spatial RNA sequencing to identify the localization of specific cell populations and inflammatory pathways within psoriasis lesions and epidermal compartments as well as also suggested crosstalk links between cell types. Epigenetic changes in stem cells may also maintain a lower threshold for tissue inflammation.
Dr. Eidsmo advised caution in eliminating TRM T cells, which play a key role in protecting against melanoma and other cancers, especially later in life. “We don’t want to get rid of them. We want to have the right balance.”
She noted a study in her own lab that mapped TRM T cells in healthy epidermis and found that they could be renewed from both circulating precursors and cells within the epidermis. “So getting rid of the mature TRM T cells will most likely just lead to a new generation of the same subset.”
Other data show that there are a wide range of subsets of TRM T cells, and she recommended focusing on the functionality of TRM T cells rather than sheer numbers. “This is something we’re working on now: Can we change the functionality [of TRM T cells], rather than eradicate them and hope for the best in the next generation? Can we change the functionality of the T cells we already have in the skin?”
There is also epigenetic data in TRM T cells, keratinocytes, stem cells, and other cells thus suggesting complexity and plasticity in the system that remains poorly understood.
Taken together, the research is at too early of a stage to be clinically useful, said Dr. Eidsmo. “We need to go back to the drawing board and just realize what we need to measure, and with the new techniques coming out, maybe spatial [measurement] at a high resolution, we can find biomarkers that better dictate the future of this. Be a little bit wary when you read the outcomes from the clinical trials that are ongoing, because right now, it’s a bit of a race between different biologics. These cells are used as a readout of efficacy of the treatments, and we’re not quite there yet.”
During the Q&A session after the presentation, one audience member asked about the heterogeneity of cells found within the skin of patients with psoriasis and pointed out that many proinflammatory cells likely play a role in tumor control. Dr. Eidsmo responded that her group’s analysis of a large database of patients with metastatic melanoma found that a factor that is important to the development of TRM T cells was strongly correlated to survival in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving immune checkpoint blockade. “So we really don’t want to eradicate them,” she said.
Also during the Q&A, Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, commented about the need to understand the previous events that drove the creation of memory T cells. “For me, the question is about the hierarchy, the primacy of what really drives the memory. In the infectious world, we’re trained to think [that memory responses] are T cell driven memory, but I wonder whether you have an idea of whether the T cell is responding to other memories, particularly in the stroma. Because certainly in the arthropathies, we have really good evidence now of epigenetic change in the synovial stroma and subsets,” said Dr. McInnes, who is director of the Institute of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, Glasgow, Scotland.
Dr. Eidsmo responded that she believes responses are different among different individuals. “We know too little about how these two systems interact with one another. I think the TRM T cells are very good at amplifying the stroma to recruit cells in. I think we need to think of two-step therapies. You need to normalize this [stromal] environment. How you can do that, I don’t know.”
Dr. McInnes agreed. “As a myeloid doctor, I strongly believe that perpetuators are innate and the adaptive is following on. But how do we test that? That’s really hard,” he said.
Dr. Eidsmo did not list any disclosures. Dr. McInnes has financial relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer, Compugen, Cabaletta, Causeway, Dextera, Eli Lilly, Celgene, MoonLake, Pfizer, Novartis, Janssen, Roche, Versus Arthritis, MRC, and UCB.
SEATTLE — In fact, flare-ups often recur at the same site, a phenomenon that might be driven by these resident memory cells, according to Liv Eidsmo, MD, PhD.
This has led to their use as biomarkers in clinical trials for new therapies, but TRM T cells have a complex biology that is far from fully understood, Dr. Eidsmo said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis. “With time, we’re understanding that the regulation of the functionality is more complicated than we thought, so following these cells as a positive outcome of a clinical trial is a little bit premature,” said Dr. Eidsmo, who is a consultant dermatologist at the University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark.
Treatment strategies focus on inhibition of interleukin (IL)-23, which is an activator of TRM T cells and probably keeps them alive, according to Dr. Eidsmo. “The hope is that these cells can be silenced by IL-23 inhibition, which is a great idea, and it probably works. It’s just a matter of what is the readout of long-term remission, because the big challenge in the clinical world is when do we stop these expensive biological treatments? When can we feel secure that patients are in deep remission?” she asked.
TRM cells are also far from the only immune cells involved in psoriasis. Others include keratinocytes, Langerhans cells, and fibroblasts. Dr. Eidsmo referenced a recent spatial analysis that used single-cell and spatial RNA sequencing to identify the localization of specific cell populations and inflammatory pathways within psoriasis lesions and epidermal compartments as well as also suggested crosstalk links between cell types. Epigenetic changes in stem cells may also maintain a lower threshold for tissue inflammation.
Dr. Eidsmo advised caution in eliminating TRM T cells, which play a key role in protecting against melanoma and other cancers, especially later in life. “We don’t want to get rid of them. We want to have the right balance.”
She noted a study in her own lab that mapped TRM T cells in healthy epidermis and found that they could be renewed from both circulating precursors and cells within the epidermis. “So getting rid of the mature TRM T cells will most likely just lead to a new generation of the same subset.”
Other data show that there are a wide range of subsets of TRM T cells, and she recommended focusing on the functionality of TRM T cells rather than sheer numbers. “This is something we’re working on now: Can we change the functionality [of TRM T cells], rather than eradicate them and hope for the best in the next generation? Can we change the functionality of the T cells we already have in the skin?”
There is also epigenetic data in TRM T cells, keratinocytes, stem cells, and other cells thus suggesting complexity and plasticity in the system that remains poorly understood.
Taken together, the research is at too early of a stage to be clinically useful, said Dr. Eidsmo. “We need to go back to the drawing board and just realize what we need to measure, and with the new techniques coming out, maybe spatial [measurement] at a high resolution, we can find biomarkers that better dictate the future of this. Be a little bit wary when you read the outcomes from the clinical trials that are ongoing, because right now, it’s a bit of a race between different biologics. These cells are used as a readout of efficacy of the treatments, and we’re not quite there yet.”
During the Q&A session after the presentation, one audience member asked about the heterogeneity of cells found within the skin of patients with psoriasis and pointed out that many proinflammatory cells likely play a role in tumor control. Dr. Eidsmo responded that her group’s analysis of a large database of patients with metastatic melanoma found that a factor that is important to the development of TRM T cells was strongly correlated to survival in patients with metastatic melanoma receiving immune checkpoint blockade. “So we really don’t want to eradicate them,” she said.
Also during the Q&A, Iain McInnes, MD, PhD, commented about the need to understand the previous events that drove the creation of memory T cells. “For me, the question is about the hierarchy, the primacy of what really drives the memory. In the infectious world, we’re trained to think [that memory responses] are T cell driven memory, but I wonder whether you have an idea of whether the T cell is responding to other memories, particularly in the stroma. Because certainly in the arthropathies, we have really good evidence now of epigenetic change in the synovial stroma and subsets,” said Dr. McInnes, who is director of the Institute of Infection, Immunity, and Inflammation at the University of Glasgow, Glasgow, Scotland.
Dr. Eidsmo responded that she believes responses are different among different individuals. “We know too little about how these two systems interact with one another. I think the TRM T cells are very good at amplifying the stroma to recruit cells in. I think we need to think of two-step therapies. You need to normalize this [stromal] environment. How you can do that, I don’t know.”
Dr. McInnes agreed. “As a myeloid doctor, I strongly believe that perpetuators are innate and the adaptive is following on. But how do we test that? That’s really hard,” he said.
Dr. Eidsmo did not list any disclosures. Dr. McInnes has financial relationships with AbbVie, AstraZeneca, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Boehringer, Compugen, Cabaletta, Causeway, Dextera, Eli Lilly, Celgene, MoonLake, Pfizer, Novartis, Janssen, Roche, Versus Arthritis, MRC, and UCB.
FROM GRAPPA 2024