User login
PJP prophylaxis may be unnecessary for CLL patients on BTK inhibitors
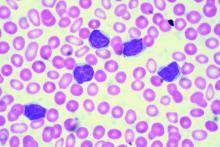
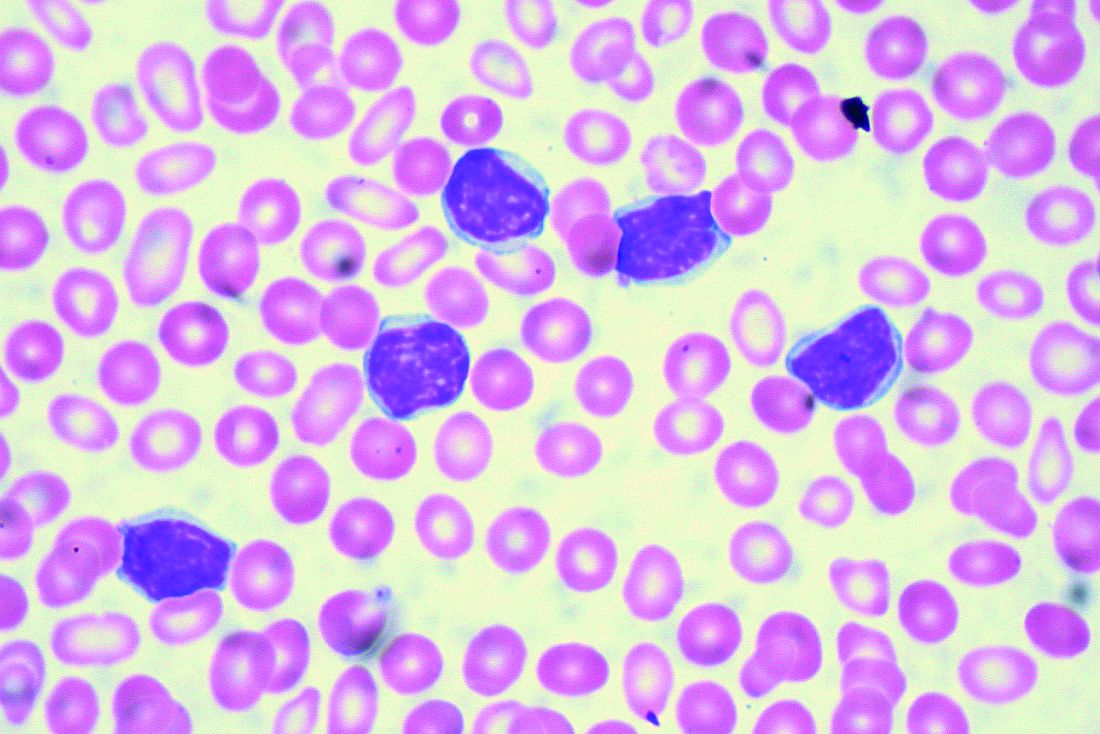
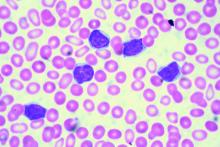
EDINBURGH – Routine empiric prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) may be unwarranted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients initiating Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor therapy, a retrospective chart review suggests.
Among 212 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib either as monotherapy or as part of a combination regimen for at least 30 days between Jan. 1, 2010, and Feb. 1, 2019, at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, 125 (59%) received PJP prophylaxis, including either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (74%) or atovaquone (26%), Christine Ryan, MD, reported at the International Workshop on CLL.
Two PJP cases occurred in the 120 patients on single-agent ibrutinib, including one in a previously untreated patient and one in a patient with relapsed/refractory CLL. Neither patient had received PJP prophylaxis, said Dr. Ryan, a senior resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
No PJP cases occurred in the 21 patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy or in the 14 patients who received acalabrutinib combination therapy, and 1 occurred in a trial cohort of 57 patients receiving frontline ibrutinib plus fludarabine-based chemotherapy (FCR). The latter had been prescribed PJP prophylaxis, but “unfortunately self-discontinued the prophylaxis” 2 months prior to the infection, Dr. Ryan said.
“The overall prevalence of PJP in patients not on prophylaxis was 3.4%, there were no cases of PJP in patients on prophylaxis, and the incidence rate in patients not on prophylaxis was 1.9 per 100 person-years, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 case of PJP calculated to be 42 patients,” she said.
In addition to PJP, three cases of proven or probable invasive fungal infections (IFI) occurred, including one case of pulmonary histoplasmosis in the ibrutinib plus FCR trial cohort and two cases of aspergillosis, including a pulmonary case and a brain abscess, in an ibrutinib plus umbralisib trial cohort.
“The overall prevalence of aspergillosis or histoplasmosis in our entire cohort was 1.4%, and notably there were no cases of IFI in the single-agent therapy cohort, but the prevalence in the ibrutinib-combination therapy patients was 4.2%,” Dr. Ryan said.
Patients included in the review were adults with a median age of 64.8 years, and 64% were men. The median duration of BTK inhibitor therapy was 23.2 months.
“We know that CLL patients treated with fludarabine have an increased risk of PJP,” she said. “As such, it is routinely recommended that patients receiving fludarabine-containing chemotherapy regimens are prescribed PJP prophylaxis.”
Additionally, the increasing use of oral BTK inhibitors has raised concerns about the potential risk of PJP or other IFIs in patients on those agents, Dr. Ryan explained, noting that existing case reports and case series looking at PJP have shown varying prevalence rates, and little is known about the effects of prophylaxis.
“At present, there are no international guidelines regarding the use of antimicrobial prophylaxis in CLL patients treated with BTK inhibitors, and prophylaxis practices vary widely across countries and institutions,” she said.
The findings of the current study demonstrate that such variation exists “even within our own institution,” Dr. Ryan added.
The findings also show an overall low PJP prevalence of 3.4% in patients not receiving prophylaxis, which falls below the “commonly accepted threshold of 5%, above which routine prophylaxis becomes recommended,” she said.
“Overall, our data suggest that routine PJP or IFI prophylaxis in patients receiving BTK inhibitors may not be needed, but this is definitely an area that requires further study, ideally with a prospective trial with a larger sample size and multiple institutions, to support the development of consensus guidelines on this issue,” she said.
Dr. Ryan reported having no financial disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Routine empiric prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) may be unwarranted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients initiating Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor therapy, a retrospective chart review suggests.
Among 212 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib either as monotherapy or as part of a combination regimen for at least 30 days between Jan. 1, 2010, and Feb. 1, 2019, at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, 125 (59%) received PJP prophylaxis, including either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (74%) or atovaquone (26%), Christine Ryan, MD, reported at the International Workshop on CLL.
Two PJP cases occurred in the 120 patients on single-agent ibrutinib, including one in a previously untreated patient and one in a patient with relapsed/refractory CLL. Neither patient had received PJP prophylaxis, said Dr. Ryan, a senior resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
No PJP cases occurred in the 21 patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy or in the 14 patients who received acalabrutinib combination therapy, and 1 occurred in a trial cohort of 57 patients receiving frontline ibrutinib plus fludarabine-based chemotherapy (FCR). The latter had been prescribed PJP prophylaxis, but “unfortunately self-discontinued the prophylaxis” 2 months prior to the infection, Dr. Ryan said.
“The overall prevalence of PJP in patients not on prophylaxis was 3.4%, there were no cases of PJP in patients on prophylaxis, and the incidence rate in patients not on prophylaxis was 1.9 per 100 person-years, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 case of PJP calculated to be 42 patients,” she said.
In addition to PJP, three cases of proven or probable invasive fungal infections (IFI) occurred, including one case of pulmonary histoplasmosis in the ibrutinib plus FCR trial cohort and two cases of aspergillosis, including a pulmonary case and a brain abscess, in an ibrutinib plus umbralisib trial cohort.
“The overall prevalence of aspergillosis or histoplasmosis in our entire cohort was 1.4%, and notably there were no cases of IFI in the single-agent therapy cohort, but the prevalence in the ibrutinib-combination therapy patients was 4.2%,” Dr. Ryan said.
Patients included in the review were adults with a median age of 64.8 years, and 64% were men. The median duration of BTK inhibitor therapy was 23.2 months.
“We know that CLL patients treated with fludarabine have an increased risk of PJP,” she said. “As such, it is routinely recommended that patients receiving fludarabine-containing chemotherapy regimens are prescribed PJP prophylaxis.”
Additionally, the increasing use of oral BTK inhibitors has raised concerns about the potential risk of PJP or other IFIs in patients on those agents, Dr. Ryan explained, noting that existing case reports and case series looking at PJP have shown varying prevalence rates, and little is known about the effects of prophylaxis.
“At present, there are no international guidelines regarding the use of antimicrobial prophylaxis in CLL patients treated with BTK inhibitors, and prophylaxis practices vary widely across countries and institutions,” she said.
The findings of the current study demonstrate that such variation exists “even within our own institution,” Dr. Ryan added.
The findings also show an overall low PJP prevalence of 3.4% in patients not receiving prophylaxis, which falls below the “commonly accepted threshold of 5%, above which routine prophylaxis becomes recommended,” she said.
“Overall, our data suggest that routine PJP or IFI prophylaxis in patients receiving BTK inhibitors may not be needed, but this is definitely an area that requires further study, ideally with a prospective trial with a larger sample size and multiple institutions, to support the development of consensus guidelines on this issue,” she said.
Dr. Ryan reported having no financial disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Routine empiric prophylaxis against pneumocystis jiroveci pneumonia (PJP) may be unwarranted in chronic lymphocytic leukemia patients initiating Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor therapy, a retrospective chart review suggests.
Among 212 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who were treated with ibrutinib or acalabrutinib either as monotherapy or as part of a combination regimen for at least 30 days between Jan. 1, 2010, and Feb. 1, 2019, at Dana-Farber Cancer Institute and Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, 125 (59%) received PJP prophylaxis, including either trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole (74%) or atovaquone (26%), Christine Ryan, MD, reported at the International Workshop on CLL.
Two PJP cases occurred in the 120 patients on single-agent ibrutinib, including one in a previously untreated patient and one in a patient with relapsed/refractory CLL. Neither patient had received PJP prophylaxis, said Dr. Ryan, a senior resident at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
No PJP cases occurred in the 21 patients who received acalabrutinib monotherapy or in the 14 patients who received acalabrutinib combination therapy, and 1 occurred in a trial cohort of 57 patients receiving frontline ibrutinib plus fludarabine-based chemotherapy (FCR). The latter had been prescribed PJP prophylaxis, but “unfortunately self-discontinued the prophylaxis” 2 months prior to the infection, Dr. Ryan said.
“The overall prevalence of PJP in patients not on prophylaxis was 3.4%, there were no cases of PJP in patients on prophylaxis, and the incidence rate in patients not on prophylaxis was 1.9 per 100 person-years, with a number needed to treat to prevent 1 case of PJP calculated to be 42 patients,” she said.
In addition to PJP, three cases of proven or probable invasive fungal infections (IFI) occurred, including one case of pulmonary histoplasmosis in the ibrutinib plus FCR trial cohort and two cases of aspergillosis, including a pulmonary case and a brain abscess, in an ibrutinib plus umbralisib trial cohort.
“The overall prevalence of aspergillosis or histoplasmosis in our entire cohort was 1.4%, and notably there were no cases of IFI in the single-agent therapy cohort, but the prevalence in the ibrutinib-combination therapy patients was 4.2%,” Dr. Ryan said.
Patients included in the review were adults with a median age of 64.8 years, and 64% were men. The median duration of BTK inhibitor therapy was 23.2 months.
“We know that CLL patients treated with fludarabine have an increased risk of PJP,” she said. “As such, it is routinely recommended that patients receiving fludarabine-containing chemotherapy regimens are prescribed PJP prophylaxis.”
Additionally, the increasing use of oral BTK inhibitors has raised concerns about the potential risk of PJP or other IFIs in patients on those agents, Dr. Ryan explained, noting that existing case reports and case series looking at PJP have shown varying prevalence rates, and little is known about the effects of prophylaxis.
“At present, there are no international guidelines regarding the use of antimicrobial prophylaxis in CLL patients treated with BTK inhibitors, and prophylaxis practices vary widely across countries and institutions,” she said.
The findings of the current study demonstrate that such variation exists “even within our own institution,” Dr. Ryan added.
The findings also show an overall low PJP prevalence of 3.4% in patients not receiving prophylaxis, which falls below the “commonly accepted threshold of 5%, above which routine prophylaxis becomes recommended,” she said.
“Overall, our data suggest that routine PJP or IFI prophylaxis in patients receiving BTK inhibitors may not be needed, but this is definitely an area that requires further study, ideally with a prospective trial with a larger sample size and multiple institutions, to support the development of consensus guidelines on this issue,” she said.
Dr. Ryan reported having no financial disclosures.
REPORTING FROM IWCLL 2019
Targeted agents vs. chemoimmunotherapy as first-line treatment of CLL
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
SAN FRANCISCO – Should targeted agents replace chemoimmunotherapy (CIT) as first-line treatment for chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL)? A recent debate suggests there’s no consensus.
William G. Wierda, MD, PhD, of The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center in Houston, and Jennifer R. Brown, MD, PhD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, debated the topic at the National Comprehensive Cancer Network Hematologic Malignancies Annual Congress.
Dr. Wierda argued that CLL patients should receive a BTK inhibitor or BCL2 inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab, as first-line therapy because these targeted agents have been shown to provide better progression-free survival (PFS) than CIT, and the targeted therapies may prolong overall survival (OS) as well.
Dr. Brown countered that targeted agents don’t improve PFS for all CLL patients, improved PFS doesn’t always translate to improved OS, and targeted agents cost more than CIT.
No role for CIT as first-line treatment
“We have two approaches right now, with nonchemoimmunotherapy-based treatment,” Dr. Wierda said. “One approach, with small-molecule inhibitors, is to have a sustained and durable period of disease control, particularly with BTK inhibitors. The other strategy that has emerged is deep remissions with fixed-duration treatment with BCL2 small-molecule inhibitor-based therapy, which, I would argue, is better than being exposed to genotoxic chemoimmunotherapy.”
Dr. Wierda went on to explain that the BTK inhibitor ibrutinib has been shown to improve PFS, compared with CIT, in phase 3 trials.
In the iLLUMINATE trial, researchers compared ibrutinib plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab as first-line treatment in CLL. At a median follow-up of 31.3 months, the median PFS was not reached in the ibrutinib arm and was 19 months in the chlorambucil arm (P less than .0001; Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56).
In the A041202 study, researchers compared ibrutinib alone (Ib) or in combination with rituximab (Ib-R) to bendamustine plus rituximab (BR) in untreated, older patients with CLL. The 2-year PFS estimates were 74% in the BR arm, 87% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (P less than .001 for BR vs. Ib or Ib-R; N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the E1912 trial, researchers compared Ib-R to fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) in younger, untreated CLL patients. The 3-year PFS was 89.4% with Ib-R and 72.9% with FCR (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43).
Dr. Wierda noted that the E1912 trial also showed superior OS with Ib-R. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% with Ib-R and 91.5% with FCR (P less than .001). However, there was no significant difference in OS between the treatment arms in the A041202 trial or the iLLUMINATE trial.
“But I would argue that is, in part, because of short follow-up,” Dr. Wierda said. “The trials were all designed to look at progression-free survival, not overall survival. With longer follow-up, we may see differences in overall survival emerging.”
Dr. Wierda went on to say that fixed‐duration treatment with the BCL2 inhibitor venetoclax can improve PFS over CIT.
In the phase 3 CLL14 trial, researchers compared fixed-duration treatment with venetoclax plus obinutuzumab to chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated CLL patients with comorbidities. The estimated PFS at 2 years was 88.2% in the venetoclax group and 64.1% in the chlorambucil group (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
“[There was] no difference in overall survival,” Dr. Wierda noted. “But, again, I would argue ... that follow-up is relatively limited. We may ultimately see a difference in overall survival.”
Based on these findings, Dr. Wierda made the following treatment recommendations:
- Any CLL patient with del(17p) or TP53 mutation, and older, unfit patients with unmutated IGHV should receive a BTK inhibitor, with or without obinutuzumab.
- All young, fit patients, and older, unfit patients with mutated IGHV should receive a BCL2 inhibitor plus obinutuzumab.
Dr. Wierda also noted that ibrutinib and venetoclax in combination have shown early promise for patients with previously untreated CLL (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2095-2103).
CIT still has a role as first-line treatment
Dr. Brown suggested that a PFS benefit may not be enough to recommend targeted agents over CIT. For one thing, the PFS benefit doesn’t apply to all patients, as the IGHV-mutated subgroup does equally well with CIT and targeted agents.
In the IGHV-mutated group from the E1912 trial, the 3-year PFS was 88% for patients who received Ib-R and those who received FCR (N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). In the A041202 study, the 2-year PFS among IGHV-mutated patients was 87% in the BR arm, 86% in the Ib arm, and 88% in the Ib-R arm (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28).
In the CLL14 trial, PFS rates were similar among IGHV-mutated patients who received chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab and IGHV-mutated or unmutated patients who received venetoclax and obinutuzumab (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
Dr. Brown also noted that the overall improvement in PFS observed with ibrutinib and venetoclax doesn’t always translate to improved OS.
In the A041202 study, there was no significant difference in OS between the Ib, Ib-R, and BR arms (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2517-28). There was no significant difference in OS between the ibrutinib and chlorambucil arms in the iLLUMINATE trial (Lancet Oncol. 2019 Jan;20[1]:43-56). And there was no significant difference in OS between the venetoclax and chlorambucil arms in the CLL14 trial (N Engl J Med. 2019; 380:2225-36).
However, in the RESONATE-2 trial, ibrutinib provided an OS benefit over chlorambucil. The 2-year OS was 95% and 84%, respectively (P = .0145; Haematologica. Sept 2018;103:1502-10). Dr. Brown said the OS advantage in this study was due to the “very poor comparator of chlorambucil and very limited crossover.”
As Dr. Wierda mentioned, the OS rate was higher with Ib-R than with FCR in the E1912 trial. The 3-year OS rate was 98.8% and 91.5%, respectively (P less than .001; N Engl J Med. 2019 Aug 1;381:432-43). Dr. Brown noted, however, that there were few deaths in this study, and many of them “were not clearly related to the disease or its treatment.”
Dr. Brown also pointed out that FCR has been shown to have curative potential in IGHV-mutated CLL in both the FCR300 trial (Blood. 2016 127:303-9) and the CLL8 trial (Blood. 2016 127:208-15).
Another factor to consider is the greater cost of targeted agents. One analysis suggested the per-patient lifetime cost of CLL treatment in the United States will increase from $147,000 to $604,000 as targeted therapies overtake CIT as first-line treatment (J Clin Oncol. 2017 Jan 10;35[2]:166-174).
“Given all of the above, chemoimmunotherapy is going to remain part of the treatment repertoire for CLL,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s our only known potential cure for the fit, mutated patients ... and can also result in prolonged treatment-free intervals for patients who are older. As we manage CLL as a chronic disease over a lifetime, we need to continue to have this in our armamentarium.”
Specifically, Dr. Brown said CIT is appropriate for patients who don’t have del(17p) or mutated TP53. FCR should be given to young, fit patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, and FCR or BR should be given to older patients and young, fit patients with IGHV-unmutated CLL.
Dr. Brown and Dr. Wierda reported financial ties to multiple pharmaceutical companies, including makers of CLL treatments.
REPORTING FROM NCCN HEMATOLOGIC MALIGNANCIES
German CLLM1 study: 4-year data raise concerns about lenalidomide maintenance
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Lenalidomide maintenance therapy after chemoimmunotherapy in high-risk chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) improved progression- and event-free survival, but not overall survival, and was associated with three unexpected cases of B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), according to 4-year follow-up in the German, phase 3 CLLM1 study.
Given these findings, and in particular the B-ALL cases, lenalidomide cannot be generally recommended as maintenance therapy in high-risk CLL, Moritz Fürstenau, MD, of the University of Cologne, reported in a poster at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
At a median follow-up of 47.6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment was 54.7 months in 60 patients randomized to receive lenalidomide maintenance therapy, compared with 23.2 months for 29 who received placebo (hazard ratio, 0.22), and median event-free survival (EFS) was 46.2 months vs. 14.6 months in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.24), Dr. Fürstenau said during an oral poster presentation at the conference.
“So ... after 4 years of observation, we still see improvement in PFS, EFS, and time to next treatment,” he said, also noting that minimal residual disease (MRD) negativity was achieved by eight patients in the lenalidomide group, and in none of the patients in the placebo group.
However, overall survival was 79% and 87% in the lenalidomide and placebo groups, respectively (HR, 1.53). In total, 12 patients died, including 9 in the lenalidomide group from fatal infections, concomitant disease, CLL progression, or unknown causes. Three patients in the placebo group died from CLL progression or fatal infection.
In the lenalidomide group, hematological and solid tumor second primary malignancies were reported in three and four patients, respectively (5% and 7%), compared with zero and two patients, respectively (0% and 7%), in the placebo group.
The CLLM1 study of the German CLL Study Group evaluated maintenance with lenalidomide vs. placebo in patients with high risk of progression after first-line chemoimmunotherapy. Previously reported results also favored lenalidomide maintenance for PFS, but not OS, Dr. Fürstenau said, adding that the study was unblinded at a median follow-up of 17.9 months, and in November 2017 treatment was stopped when two cases of B-ALL were observed. A third case was reported in 2018.
The current analysis includes data available through December 2018, and the findings warrant further investigation to analyze the unexpectedly high incidence of B-ALL, he said.
The CLLM1 study was funded by Celgene.
[email protected]
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
ICLL-07 trial: MRD-driven strategy yields prolonged survival
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
EDINBURGH – Treatment induction with obinutuzumab and ibrutinib followed by a minimal residual disease (MRD)–driven treatment strategy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) yields a high long-term complete response rate and prolonged progression-free and overall survival, according to findings from the phase 2 ICLL-07 trial.
The intent-to-treat (ITT) complete response rate at 16 months in 135 patients who were treated with this strategy was 62%, Anne-Sophie Michallet, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
Patients in the multicenter, open-label trial conducted by the French Innovative Leukemia Organization (FILO) were previously untreated, medically fit patients with CLL and no 17p deletion. They were enrolled between November 2015 and May 2017 to receive eight 1,000 mg IV doses of obinutuzumab over six 4-week cycles along with oral Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib at a dose of 420 mg daily for 9 months.
Ten patients (7.7%) achieved complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% (undetectable) at 9 months and, by study protocol, continued on only the ibrutinib for 6 additional months. The remaining 120 evaluable patients received four 4-week cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide along with the obinutuzumab and ibrutinib for 6 additional months, explained Dr. Michallet of Centre Léon Bérard, Lyon, France.
The ITT rate at 16 months – the primary endpoint of the study – was achieved with no more than four cycles of fludarabine/cyclophosphamide and obinutuzumab, and exceeded the primary objective of demonstrating a 30% or higher rate of complete response with bone marrow MRD less than 0.01% at the month 16 ITT analysis, she said.
“The ... strategy yielded an overall response rate of 100%, a complete response rate, according to iwCLL [criteria], of 73%, a bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 79% [in the ITT population],” she said, adding that the primary objective was achieved with a complete response with a peripheral blood and bone marrow MRD–undetectable rate of 62%.
Response assessments at months 9 and 16 involved whole-body computed tomography scans with tumor measurements and bone marrow trephine biopsy for patients in clinical complete response. MRD testing was performed by eight-color flow cytometry in both peripheral blood and bone marrow.
After month 16, response was clinically assessed every 3 months, and peripheral blood MRD was assessed every 6 months until month 40.
“With a median follow-up of 26.3 months, the 2-year progression-free survival and overall survival were, respectively, 97% and 97.5%,” Dr. Michallet said, noting that the longitudinal follow-up of peripheral blood MRD in the entire cohort showed durability of a deep response. The rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at 22 months was 77% in the 10 patients who received only ibrutinib after the 9-month assessment, and 93% in those who received fludarabine/cyclophosphamide after the 9-month assessment.
In patients with immunoglobulin heavy gene variable (IGHV) mutations, the rate of peripheral blood MRD less than 0.01% at month 22 was 96%, and in those without IGHV mutations, the rate was 77%, she noted.
The findings demonstrate that the approach has merit in medically fit, treatment-naive patients with CLL and no 17p deletion, she said, explaining that the fixed-duration, MRD-driven strategy used in this study was developed to “avoid or at least reduce chemotherapy exposure” in the first-line treatment of such patients.
Indeed, the approach was associated with “a high [complete response] rate, a high level of undetectable bone marrow MRD, an acceptable safety profile, and a sustained MRD negativity rate at 12 months after the end of the treatment,” she said.
“This highly effective strategy combining a BTK inhibitor and abbreviated immunochemotherapy deserves further investigation with randomized trials,” she concluded.
ICLL-07 FILO was funded by Roche and Janssen. Dr. Michallet reported having no disclosures.
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
GALACTIC CLL trial: Obinutuzumab consolidation helps eradicate MRD
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
[email protected]
EDINBURGH – Consolidation therapy with obinutuzumab after chemoimmunotherapy for B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia (B-CLL) was highly effective for eradicating minimal residual disease (MRD) within 6 months following randomization in the seamless phase 2/3 GALACTIC trial.
Of 14 patients who were MRD positive after chemoimmunotherapy and randomized to consolidation with the type II monoclonal antibody targeting the CD20 antigen, 10 achieved MRD negativity in the bone marrow by 6 months, and 13 achieved MRD negativity in the peripheral blood by 6 months, Talha Munir, MD, reported at the International Workshop on Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia.
“And that translated into [progression-free survival] improvement in the consolidation arm,” said Dr. Munir of St. James’s University, Leeds, England.
The median progression-free survival in that arm was not reached, whereas progression-free survival in 15 MRD-positive patients randomized to the nonconsolidation arm was 16.6 months, he said.
Further, no difference was seen in median progression-free survival, overall survival, or MRD duration between the consolidation arm and 19 patients who were not randomized because of MRD negativity after chemoimmunotherapy, he noted.
Achieving MRD negativity in CLL confers a survival advantage, and obinutuzumab has shown greater efficacy with respect to MRD in CLL when compared with previous anti-CD20 antibodies, and it is less immune suppressive than the anti-CD52 antibody alemtuzumab, he explained.
The GALACTIC trial was designed to assess the safety and efficacy of obinutuzumab consolidation for eradicating MRD and whether its effects would prolong progression-free survival in patients with B-CLL who recently responded to chemoimmunotherapy. Those achieving complete response or partial response at 3-24 months after chemoimmunotherapy, and who remained MRD-positive, were eligible for randomization.
The planned sample size was 188 patients, but the trial was closed early in February 2017 because of poor recruitment; a total of 48 patients were enrolled, including the 19 nonrandomized, MRD-negative patients.
Patients randomized to consolidation received 1,000 mg of obinutuzumab weekly for the first four doses, and then every other week for four additional doses.
Obinutuzumab was well tolerated with minimal infusion-related reactions and toxicity, Dr. Munir said.
Despite the low recruitment, both the phase 2 and 3 endpoints were assessed as positive, because the consolidation strategy was so efficacious, Dr. Munir noted, concluding that the findings provide further evidence of the value of MRD negativity for improving outcomes in CLL.
The GALACTIC trial was developed by the GALACTIC Trial Management Group with the support of the UKCLL/NCRI CLL Clinical Trials Subgroup. The trial is funded by Cancer Research UK and Roche and sponsored by the University of Leeds. Dr. Munir reported having no disclosures.
[email protected]
REPORTING FROM iwCLL 2019
CK doesn’t seem to affect OS in CLL patients taking idelalisib
The presence of complex karyotype (CK) does not affect survival in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are treated with idelalisib, according to a new analysis.
Researchers analyzed data from two clinical trials of idelalisib, given alone or in combination with rituximab, and found no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with and without CK.
Karl-Anton Kreuzer, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany), and colleagues described these findings in a letter to Leukemia.
The researchers evaluated patients with previously treated CLL who were enrolled in a phase 3 trial and received either idelalisib plus rituximab or rituximab plus placebo. Patients from either treatment arm could enroll in an extension study of idelalisib monotherapy.
There were 220 patients randomized to idelalisib plus rituximab (n = 110) or placebo plus rituximab (n = 110) in the primary study, and 161 of these patients were enrolled in the extension study.
The final analysis included 120 patients who were successfully karyotyped – 63 from the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 57 from the placebo-rituximab arm. Less than half of patients in each arm were CK-positive – 41% (26/63) of the idelalisib arm and 42% (24/57) of the placebo arm.
The researchers wrote that baseline characteristics were “mostly balanced” between the CK-positive and CK-negative groups in each treatment arm. The only significant difference was that fewer CK-positive patients in the placebo arm had a creatinine clearance of 30-59 mL/min (P = .0324).
Results
There were no significant differences in outcomes between CK-positive and CK-negative patients who received idelalisib and rituximab. The overall response rate was 81% in CK-positive patients and 89% in CK-negative patients (P = .3509). The median progression-free survival was 20.9 months and 19.4 months, respectively (P = .5848).
The median OS was 28.3 months in the CK-positive group and 49.7 months in the CK-negative group (P = .2099). The copresence of CK and del(17p), TP53 mutation, or del(11q) didn’t significantly affect OS, the researchers noted.
Among all CK-positive patients, the median OS was 28.3 months in the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 9.2 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (P = .0412).
“Our analysis suggests that CK-positive patients treated with idelalisib/rituximab did not exhibit a significantly shortened survival compared with those who were CK negative,” the researchers wrote. “In addition, the primary beneficial effect of adding idelalisib to rituximab treatment in [relapsed/refractory] CLL patients with CK was reflected in OS prolongation compared to those who received only rituximab.”
The researchers noted that this study has limitations, so prospective clinical trials are needed to guide treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and CK.
Both trials of idelalisib were sponsored by Gilead. The researchers reported relationships, including employment, with Gilead and other companies. They also disclosed funding from the German government and from nonprofit organizations in Germany.
SOURCE: Kreuzer K-A et al. Leukemia. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0533-6.
The presence of complex karyotype (CK) does not affect survival in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are treated with idelalisib, according to a new analysis.
Researchers analyzed data from two clinical trials of idelalisib, given alone or in combination with rituximab, and found no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with and without CK.
Karl-Anton Kreuzer, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany), and colleagues described these findings in a letter to Leukemia.
The researchers evaluated patients with previously treated CLL who were enrolled in a phase 3 trial and received either idelalisib plus rituximab or rituximab plus placebo. Patients from either treatment arm could enroll in an extension study of idelalisib monotherapy.
There were 220 patients randomized to idelalisib plus rituximab (n = 110) or placebo plus rituximab (n = 110) in the primary study, and 161 of these patients were enrolled in the extension study.
The final analysis included 120 patients who were successfully karyotyped – 63 from the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 57 from the placebo-rituximab arm. Less than half of patients in each arm were CK-positive – 41% (26/63) of the idelalisib arm and 42% (24/57) of the placebo arm.
The researchers wrote that baseline characteristics were “mostly balanced” between the CK-positive and CK-negative groups in each treatment arm. The only significant difference was that fewer CK-positive patients in the placebo arm had a creatinine clearance of 30-59 mL/min (P = .0324).
Results
There were no significant differences in outcomes between CK-positive and CK-negative patients who received idelalisib and rituximab. The overall response rate was 81% in CK-positive patients and 89% in CK-negative patients (P = .3509). The median progression-free survival was 20.9 months and 19.4 months, respectively (P = .5848).
The median OS was 28.3 months in the CK-positive group and 49.7 months in the CK-negative group (P = .2099). The copresence of CK and del(17p), TP53 mutation, or del(11q) didn’t significantly affect OS, the researchers noted.
Among all CK-positive patients, the median OS was 28.3 months in the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 9.2 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (P = .0412).
“Our analysis suggests that CK-positive patients treated with idelalisib/rituximab did not exhibit a significantly shortened survival compared with those who were CK negative,” the researchers wrote. “In addition, the primary beneficial effect of adding idelalisib to rituximab treatment in [relapsed/refractory] CLL patients with CK was reflected in OS prolongation compared to those who received only rituximab.”
The researchers noted that this study has limitations, so prospective clinical trials are needed to guide treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and CK.
Both trials of idelalisib were sponsored by Gilead. The researchers reported relationships, including employment, with Gilead and other companies. They also disclosed funding from the German government and from nonprofit organizations in Germany.
SOURCE: Kreuzer K-A et al. Leukemia. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0533-6.
The presence of complex karyotype (CK) does not affect survival in patients with relapsed/refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) who are treated with idelalisib, according to a new analysis.
Researchers analyzed data from two clinical trials of idelalisib, given alone or in combination with rituximab, and found no significant difference in overall survival (OS) between patients with and without CK.
Karl-Anton Kreuzer, MD, of the University of Cologne (Germany), and colleagues described these findings in a letter to Leukemia.
The researchers evaluated patients with previously treated CLL who were enrolled in a phase 3 trial and received either idelalisib plus rituximab or rituximab plus placebo. Patients from either treatment arm could enroll in an extension study of idelalisib monotherapy.
There were 220 patients randomized to idelalisib plus rituximab (n = 110) or placebo plus rituximab (n = 110) in the primary study, and 161 of these patients were enrolled in the extension study.
The final analysis included 120 patients who were successfully karyotyped – 63 from the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 57 from the placebo-rituximab arm. Less than half of patients in each arm were CK-positive – 41% (26/63) of the idelalisib arm and 42% (24/57) of the placebo arm.
The researchers wrote that baseline characteristics were “mostly balanced” between the CK-positive and CK-negative groups in each treatment arm. The only significant difference was that fewer CK-positive patients in the placebo arm had a creatinine clearance of 30-59 mL/min (P = .0324).
Results
There were no significant differences in outcomes between CK-positive and CK-negative patients who received idelalisib and rituximab. The overall response rate was 81% in CK-positive patients and 89% in CK-negative patients (P = .3509). The median progression-free survival was 20.9 months and 19.4 months, respectively (P = .5848).
The median OS was 28.3 months in the CK-positive group and 49.7 months in the CK-negative group (P = .2099). The copresence of CK and del(17p), TP53 mutation, or del(11q) didn’t significantly affect OS, the researchers noted.
Among all CK-positive patients, the median OS was 28.3 months in the idelalisib-rituximab arm and 9.2 months in the placebo-rituximab arm (P = .0412).
“Our analysis suggests that CK-positive patients treated with idelalisib/rituximab did not exhibit a significantly shortened survival compared with those who were CK negative,” the researchers wrote. “In addition, the primary beneficial effect of adding idelalisib to rituximab treatment in [relapsed/refractory] CLL patients with CK was reflected in OS prolongation compared to those who received only rituximab.”
The researchers noted that this study has limitations, so prospective clinical trials are needed to guide treatment of patients with relapsed/refractory CLL and CK.
Both trials of idelalisib were sponsored by Gilead. The researchers reported relationships, including employment, with Gilead and other companies. They also disclosed funding from the German government and from nonprofit organizations in Germany.
SOURCE: Kreuzer K-A et al. Leukemia. 2019 Aug 19. doi: 10.1038/s41375-019-0533-6.
FROM LEUKEMIA
Calquence earns breakthrough designation for CLL monotherapy
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor is already approved for the treatment of adults with mantle cell lymphoma who have received at least one prior therapy, and multiple trials are underway to evaluate the drug’s use in a variety of B-cell malignancies, according to the drug’s sponsor, AstraZeneca.
The current designation was based on preliminary results from two phase 3 trials – ELEVATE-TN and ASCEND. In the three-arm ELEVATE-TN trial, researchers evaluated acalabrutinib alone or in combination with obinutuzumab versus chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab in previously untreated patients with CLL. In the two-arm ASCEND trial, previously treated patients with CLL were randomized to receive acalabrutinib monotherapy or the physician’s choice of either rituximab plus idelalisib or rituximab plus bendamustine.
Interim analyses of the two trials showed that acalabrutinib alone, or in combination, significantly improved progression-free survival without raising safety concerns.
Breakthrough therapy designation allows for an expedited review by the FDA for treatments aimed at treating serious conditions where there is preliminary clinical evidence showing a substantial improvement over an available therapy or a clinically significant endpoint.
Zanubrutinib may be poised to challenge ibrutinib for CLL
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor zanubrutinib appears safe and effective for patients with B-cell malignancies, according to results from a phase 1 trial.
Among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), the overall response rate was 96.2%, reported Constantine Si Lun Tam, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne and colleagues.
“Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a highly specific next-generation BTK inhibitor with favorable oral bioavailability, as shown in preclinical studies,” the investigators wrote in Blood. “Compared with ibrutinib, zanubrutinib has shown greater selectivity for BTK and fewer off-target effects in multiple in vitro enzymatic and cell-based assays.”
The current, open-label trial involved 144 patients with B-cell malignancies. To determine optimal dosing, the investigators recruited 17 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies who had received at least one prior therapy. The dose expansion part of the study assessed responses in multiple cohorts, including patients with CLL/SLL, mantle cell lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, including maximum tolerated dose. Efficacy findings were also reported.
During dose escalation, no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, so the highest dose – 320 mg once daily or 160 mg twice daily – was selected for further testing.
The investigators highlighted efficacy and safety findings from 94 patients with CLL/SLL who were involved in dose expansion. Although nearly one-quarter (23.4%) were treatment-naive, the median number of prior therapies was two, and some patients had high-risk features, such as adverse cytogenetics, including 19.1% with a TP53 mutation and 23.3% with a 17p deletion. After a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 94.7% of these patients were still undergoing treatment.
Out of the initial 94 patients with CLL/SLL, 78 were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 96.2%, including two (2.6%) complete responses, 63 (80.8%) partial responses, and 10 (12.8%) partial responses with lymphocytosis. The median progression-free survival had not been reached, and the 12-month estimated progression-free survival was 100%.
In regard to safety, the most common adverse events were contusion (35.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (33.0%), cough (25.5%), diarrhea (21.3%), fatigue (19.1%), back pain (14.9%), hematuria (14.9%), headache (13.8%), nausea (13.8%), rash (12.8%), arthralgia (11.7%), muscle spasms (11.7%), and urinary tract infection (10.6%).
A number of other adverse events were reported, although these occurred in less than 10% of patients.
More than one-third of patients (36.2%) experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, with neutropenia being most common (6.4%), followed by pneumonia , hypertension, and anemia, which each occurred in 2.1% of patients, and less commonly, back pain, nausea, urinary tract infection, purpura, cellulitis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which each occurred in 1.1% of patients.
“In this first-in-human study, zanubrutinib demonstrated encouraging activity in patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naive CLL/SLL, with good tolerability,” the investigators concluded. “Two ongoing randomized studies of zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (NCT03053440 and NCT03734016) aim to determine whether consistent, continuous BTK blockade with a selective inhibitor results in fewer off-target effects and translates into improvements in disease control.”
The study was funded by BeiGene USA, which is developing the drug. The investigators reported relationships with the study sponsor, as well as Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and others.
SOURCE: Tam CSL et al. Blood. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor zanubrutinib appears safe and effective for patients with B-cell malignancies, according to results from a phase 1 trial.
Among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), the overall response rate was 96.2%, reported Constantine Si Lun Tam, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne and colleagues.
“Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a highly specific next-generation BTK inhibitor with favorable oral bioavailability, as shown in preclinical studies,” the investigators wrote in Blood. “Compared with ibrutinib, zanubrutinib has shown greater selectivity for BTK and fewer off-target effects in multiple in vitro enzymatic and cell-based assays.”
The current, open-label trial involved 144 patients with B-cell malignancies. To determine optimal dosing, the investigators recruited 17 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies who had received at least one prior therapy. The dose expansion part of the study assessed responses in multiple cohorts, including patients with CLL/SLL, mantle cell lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, including maximum tolerated dose. Efficacy findings were also reported.
During dose escalation, no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, so the highest dose – 320 mg once daily or 160 mg twice daily – was selected for further testing.
The investigators highlighted efficacy and safety findings from 94 patients with CLL/SLL who were involved in dose expansion. Although nearly one-quarter (23.4%) were treatment-naive, the median number of prior therapies was two, and some patients had high-risk features, such as adverse cytogenetics, including 19.1% with a TP53 mutation and 23.3% with a 17p deletion. After a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 94.7% of these patients were still undergoing treatment.
Out of the initial 94 patients with CLL/SLL, 78 were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 96.2%, including two (2.6%) complete responses, 63 (80.8%) partial responses, and 10 (12.8%) partial responses with lymphocytosis. The median progression-free survival had not been reached, and the 12-month estimated progression-free survival was 100%.
In regard to safety, the most common adverse events were contusion (35.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (33.0%), cough (25.5%), diarrhea (21.3%), fatigue (19.1%), back pain (14.9%), hematuria (14.9%), headache (13.8%), nausea (13.8%), rash (12.8%), arthralgia (11.7%), muscle spasms (11.7%), and urinary tract infection (10.6%).
A number of other adverse events were reported, although these occurred in less than 10% of patients.
More than one-third of patients (36.2%) experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, with neutropenia being most common (6.4%), followed by pneumonia , hypertension, and anemia, which each occurred in 2.1% of patients, and less commonly, back pain, nausea, urinary tract infection, purpura, cellulitis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which each occurred in 1.1% of patients.
“In this first-in-human study, zanubrutinib demonstrated encouraging activity in patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naive CLL/SLL, with good tolerability,” the investigators concluded. “Two ongoing randomized studies of zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (NCT03053440 and NCT03734016) aim to determine whether consistent, continuous BTK blockade with a selective inhibitor results in fewer off-target effects and translates into improvements in disease control.”
The study was funded by BeiGene USA, which is developing the drug. The investigators reported relationships with the study sponsor, as well as Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and others.
SOURCE: Tam CSL et al. Blood. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160.
The Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor zanubrutinib appears safe and effective for patients with B-cell malignancies, according to results from a phase 1 trial.
Among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL), the overall response rate was 96.2%, reported Constantine Si Lun Tam, MD, of Peter MacCallum Cancer Centre in Melbourne and colleagues.
“Zanubrutinib (BGB-3111) is a highly specific next-generation BTK inhibitor with favorable oral bioavailability, as shown in preclinical studies,” the investigators wrote in Blood. “Compared with ibrutinib, zanubrutinib has shown greater selectivity for BTK and fewer off-target effects in multiple in vitro enzymatic and cell-based assays.”
The current, open-label trial involved 144 patients with B-cell malignancies. To determine optimal dosing, the investigators recruited 17 patients with relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies who had received at least one prior therapy. The dose expansion part of the study assessed responses in multiple cohorts, including patients with CLL/SLL, mantle cell lymphoma, and Waldenström macroglobulinemia. The primary endpoints were safety and tolerability, including maximum tolerated dose. Efficacy findings were also reported.
During dose escalation, no dose-limiting toxicities were observed, so the highest dose – 320 mg once daily or 160 mg twice daily – was selected for further testing.
The investigators highlighted efficacy and safety findings from 94 patients with CLL/SLL who were involved in dose expansion. Although nearly one-quarter (23.4%) were treatment-naive, the median number of prior therapies was two, and some patients had high-risk features, such as adverse cytogenetics, including 19.1% with a TP53 mutation and 23.3% with a 17p deletion. After a median follow-up of 13.7 months, 94.7% of these patients were still undergoing treatment.
Out of the initial 94 patients with CLL/SLL, 78 were evaluable for efficacy. The overall response rate was 96.2%, including two (2.6%) complete responses, 63 (80.8%) partial responses, and 10 (12.8%) partial responses with lymphocytosis. The median progression-free survival had not been reached, and the 12-month estimated progression-free survival was 100%.
In regard to safety, the most common adverse events were contusion (35.1%), upper respiratory tract infection (33.0%), cough (25.5%), diarrhea (21.3%), fatigue (19.1%), back pain (14.9%), hematuria (14.9%), headache (13.8%), nausea (13.8%), rash (12.8%), arthralgia (11.7%), muscle spasms (11.7%), and urinary tract infection (10.6%).
A number of other adverse events were reported, although these occurred in less than 10% of patients.
More than one-third of patients (36.2%) experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, with neutropenia being most common (6.4%), followed by pneumonia , hypertension, and anemia, which each occurred in 2.1% of patients, and less commonly, back pain, nausea, urinary tract infection, purpura, cellulitis, and squamous cell carcinoma of the skin, which each occurred in 1.1% of patients.
“In this first-in-human study, zanubrutinib demonstrated encouraging activity in patients with relapsed/refractory and treatment-naive CLL/SLL, with good tolerability,” the investigators concluded. “Two ongoing randomized studies of zanubrutinib versus ibrutinib (NCT03053440 and NCT03734016) aim to determine whether consistent, continuous BTK blockade with a selective inhibitor results in fewer off-target effects and translates into improvements in disease control.”
The study was funded by BeiGene USA, which is developing the drug. The investigators reported relationships with the study sponsor, as well as Janssen, Pharmacyclics, AbbVie, and others.
SOURCE: Tam CSL et al. Blood. 2019 Jul 24. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019001160.
FROM BLOOD
ICYMI: Ibrutinib/rituximab combo improves CLL survival
Patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) aged 70 years or younger who received ibrutinib/rituximab therapy experienced significantly greater progression-free survival, compared with those who received standard chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (89.4% vs. 72.9% at 3 years; hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.56; P less than .001), according to results from a randomized, phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:432-43).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Find our coverage at the link below.
Patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) aged 70 years or younger who received ibrutinib/rituximab therapy experienced significantly greater progression-free survival, compared with those who received standard chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (89.4% vs. 72.9% at 3 years; hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.56; P less than .001), according to results from a randomized, phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:432-43).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Find our coverage at the link below.
Patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) aged 70 years or younger who received ibrutinib/rituximab therapy experienced significantly greater progression-free survival, compared with those who received standard chemotherapy with fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (89.4% vs. 72.9% at 3 years; hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.22-0.56; P less than .001), according to results from a randomized, phase 3 trial published in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;381:432-43).
We first reported on the results of this trial when they were presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Hematology. Find our coverage at the link below.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
BTK mutations linked to CLL progression on ibrutinib
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
Mutations in Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) are associated with progression of chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in patients taking ibrutinib, according to a new study.
Researchers analyzed a “real-life” cohort of CLL patients taking ibrutinib for about 3 years and found that patients with BTK mutations were significantly more likely to progress (P = .0005).
“Our findings support that mutational analysis should be considered in patients receiving ibrutinib who have residual clonal lymphocytosis, and that clinical trials are needed to evaluate whether patients with a BTK mutation may benefit from an early switch to another treatment,” wrote Anne Quinquenel, MD, PhD, of Hôpital Robert Debré, Université Reims (France) Champagne-Ardenne, and colleagues. Their report is in Blood.
The researchers studied 57 CLL patients who were still on ibrutinib after at least 3 years and provided fresh blood samples. The median time between the start of ibrutinib and sample collection was 3.5 years.
All 57 patients had minimal residual disease at baseline. Of the 55 patients with response data available, 48 had a partial response, and 7 had a partial response with lymphocytosis.
Mutational profiling was possible in 30 patients who had a CLL clone greater than or equal to 0.5 x 109/L.
BTK mutations were present in 17 of the 30 patients (57%). There were 20 BTK mutations in total, all were at C481, and 14 were at C481S.
The researchers also identified 15 patients with TP53 mutations and 4 patients with phospholipase Cg2 (PLCG2) mutations. All 4 patients with PLCG2 mutations also had a BTK mutation and a TP53 mutation.
However, there were no significant associations between BTK mutations and other mutations. BTK mutations were not associated with the number of previous therapies a patient received or the need for ibrutinib dose interruptions or reductions.
The researchers assessed CLL progression at median of 8.5 months from sample collection and found the presence of a BTK mutation was significantly associated with progression (P = .0005).
Of the 17 patients with a BTK mutation, 14 progressed with one case of Richter’s syndrome. Three patients who progressed were still on ibrutinib, nine patients received venetoclax, and two patients died without further treatment.
Of the 13 patients without BTK mutations, just two patients progressed. One patient died without further treatment, and the other received venetoclax.
The event-free survival was significantly shorter in patients with a BTK mutation than in those without (P = .0380), but there was no significant difference in overall survival.
This research was supported by Sunesis Pharmaceuticals and the Force Hemato (fonds de recherche clinique en hématologie) foundation. The researchers reported relationships with Janssen, Gilead, Roche, and AbbVie.
SOURCE: Quinquenel A et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 26. doi: 10.1182/blood.2019000854.
FROM BLOOD