User login
FDA approves rituximab biosimilar for cancer, autoimmune disorders
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rituximab-pvvr (Ruxience) for adults with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. It is the first biosimilar approved to treat these two rare autoimmune conditions.
Specifically, the biosimilar product is approved as single-agent therapy for relapsed or refractory, low grade or follicular, CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; in combination with chemotherapy for other types of previously untreated CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; and as a single agent for nonprogressing, low-grade, CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma after first-line chemotherapy treatment. It is also approved for both previously untreated and previously treated CD20-positive CLL in combination with chemotherapy. And it is approved for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis in combination with glucocorticoids.
The approval is based on demonstration that rituximab-pvvr had no clinically meaningful differences in safety or efficacy when compared with the reference drug, rituximab (Rituxan), according to a release from the biosimilar’s developer. As with rituximab, rituximab-pvvr’s label comes with an FDA boxed warning. In the biosimilar’s case, it warns against fatal infusion-related reactions, severe mucocutaneous reactions, hepatitis B virus reactivation, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Other adverse reactions include fever, headache, neutropenia, and lymphopenia.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rituximab-pvvr (Ruxience) for adults with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. It is the first biosimilar approved to treat these two rare autoimmune conditions.
Specifically, the biosimilar product is approved as single-agent therapy for relapsed or refractory, low grade or follicular, CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; in combination with chemotherapy for other types of previously untreated CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; and as a single agent for nonprogressing, low-grade, CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma after first-line chemotherapy treatment. It is also approved for both previously untreated and previously treated CD20-positive CLL in combination with chemotherapy. And it is approved for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis in combination with glucocorticoids.
The approval is based on demonstration that rituximab-pvvr had no clinically meaningful differences in safety or efficacy when compared with the reference drug, rituximab (Rituxan), according to a release from the biosimilar’s developer. As with rituximab, rituximab-pvvr’s label comes with an FDA boxed warning. In the biosimilar’s case, it warns against fatal infusion-related reactions, severe mucocutaneous reactions, hepatitis B virus reactivation, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Other adverse reactions include fever, headache, neutropenia, and lymphopenia.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved rituximab-pvvr (Ruxience) for adults with non-Hodgkin lymphoma, chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), and granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis. It is the first biosimilar approved to treat these two rare autoimmune conditions.
Specifically, the biosimilar product is approved as single-agent therapy for relapsed or refractory, low grade or follicular, CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; in combination with chemotherapy for other types of previously untreated CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma; and as a single agent for nonprogressing, low-grade, CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin lymphoma after first-line chemotherapy treatment. It is also approved for both previously untreated and previously treated CD20-positive CLL in combination with chemotherapy. And it is approved for granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis in combination with glucocorticoids.
The approval is based on demonstration that rituximab-pvvr had no clinically meaningful differences in safety or efficacy when compared with the reference drug, rituximab (Rituxan), according to a release from the biosimilar’s developer. As with rituximab, rituximab-pvvr’s label comes with an FDA boxed warning. In the biosimilar’s case, it warns against fatal infusion-related reactions, severe mucocutaneous reactions, hepatitis B virus reactivation, and progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Other adverse reactions include fever, headache, neutropenia, and lymphopenia.
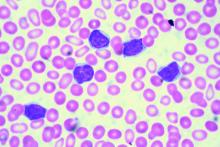
Ibrutinib-venetoclax found highly active in hard-to-treat CLL
The strategy of simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and reactivating apoptosis can eradicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a large share of patients, suggest results from the phase 2 CLARITY trial.
“Both ibrutinib and venetoclax are active in CLL with improved survival; however, as monotherapies, both currently are given until disease progression,” wrote Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, England, and his colleagues.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the investigators treated 53 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with combination ibrutinib (Imbruvica), a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax (Venclexta), a small molecule inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. The primary endpoint was MRD negativity, defined as presence of fewer than one CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes, after 12 months of combination therapy.
Results reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that the combination was highly active, with 53% of patients achieving MRD negativity in the blood and 36% achieving MRD negativity in the marrow.
Most patients, 89%, had a treatment response, and slightly more than half, 51%, achieved a complete remission. With a median 21.1-month follow-up, only a single patient experienced progression and all were still alive.
Adverse effects were generally manageable. Grade 3-4 adverse events of special interest included 34 cases of neutropenia and 1 case of biochemical tumor lysis syndrome that was managed by delaying venetoclax.
“We have demonstrated promising efficacy that indicates potent synergy between ibrutinib and venetoclax for inducing MRD-negative responses with manageable adverse effects,” the investigators wrote. “The observation that a significant proportion of patients experience MRD-negative remission indicates that this combination can be given for a limited period and then stopped after patients achieve a deep remission.”
Whether the combination leads to permanent disease eradication in certain patients is still unclear, the investigators added.
The trial was supported by Bloodwise under the Trials Acceleration Programme, by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Clinical Research Facility, and by an unrestricted educational grant from Janssen-Cilag and AbbVie. Ibrutinib was provided free of charge by Janssen-Cilag, and venetoclax was provided free of charge by AbbVie. Dr. Hillman reported financial relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Roche, Pharmacyclics, and Gilead Sciences.
SOURCE: Hillmen P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00894.
The strategy of simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and reactivating apoptosis can eradicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a large share of patients, suggest results from the phase 2 CLARITY trial.
“Both ibrutinib and venetoclax are active in CLL with improved survival; however, as monotherapies, both currently are given until disease progression,” wrote Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, England, and his colleagues.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the investigators treated 53 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with combination ibrutinib (Imbruvica), a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax (Venclexta), a small molecule inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. The primary endpoint was MRD negativity, defined as presence of fewer than one CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes, after 12 months of combination therapy.
Results reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that the combination was highly active, with 53% of patients achieving MRD negativity in the blood and 36% achieving MRD negativity in the marrow.
Most patients, 89%, had a treatment response, and slightly more than half, 51%, achieved a complete remission. With a median 21.1-month follow-up, only a single patient experienced progression and all were still alive.
Adverse effects were generally manageable. Grade 3-4 adverse events of special interest included 34 cases of neutropenia and 1 case of biochemical tumor lysis syndrome that was managed by delaying venetoclax.
“We have demonstrated promising efficacy that indicates potent synergy between ibrutinib and venetoclax for inducing MRD-negative responses with manageable adverse effects,” the investigators wrote. “The observation that a significant proportion of patients experience MRD-negative remission indicates that this combination can be given for a limited period and then stopped after patients achieve a deep remission.”
Whether the combination leads to permanent disease eradication in certain patients is still unclear, the investigators added.
The trial was supported by Bloodwise under the Trials Acceleration Programme, by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Clinical Research Facility, and by an unrestricted educational grant from Janssen-Cilag and AbbVie. Ibrutinib was provided free of charge by Janssen-Cilag, and venetoclax was provided free of charge by AbbVie. Dr. Hillman reported financial relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Roche, Pharmacyclics, and Gilead Sciences.
SOURCE: Hillmen P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00894.
The strategy of simultaneously inhibiting proliferation and reactivating apoptosis can eradicate chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) in a large share of patients, suggest results from the phase 2 CLARITY trial.
“Both ibrutinib and venetoclax are active in CLL with improved survival; however, as monotherapies, both currently are given until disease progression,” wrote Peter Hillmen, MBChB, PhD, St. James’s University Hospital, Leeds, England, and his colleagues.
In the single-arm, open-label trial, the investigators treated 53 patients with relapsed or refractory CLL with combination ibrutinib (Imbruvica), a small-molecule inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax (Venclexta), a small molecule inhibitor of the anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2. The primary endpoint was MRD negativity, defined as presence of fewer than one CLL cell in 10,000 leukocytes, after 12 months of combination therapy.
Results reported in the Journal of Clinical Oncology showed that the combination was highly active, with 53% of patients achieving MRD negativity in the blood and 36% achieving MRD negativity in the marrow.
Most patients, 89%, had a treatment response, and slightly more than half, 51%, achieved a complete remission. With a median 21.1-month follow-up, only a single patient experienced progression and all were still alive.
Adverse effects were generally manageable. Grade 3-4 adverse events of special interest included 34 cases of neutropenia and 1 case of biochemical tumor lysis syndrome that was managed by delaying venetoclax.
“We have demonstrated promising efficacy that indicates potent synergy between ibrutinib and venetoclax for inducing MRD-negative responses with manageable adverse effects,” the investigators wrote. “The observation that a significant proportion of patients experience MRD-negative remission indicates that this combination can be given for a limited period and then stopped after patients achieve a deep remission.”
Whether the combination leads to permanent disease eradication in certain patients is still unclear, the investigators added.
The trial was supported by Bloodwise under the Trials Acceleration Programme, by the National Institute for Health Research Leeds Clinical Research Facility, and by an unrestricted educational grant from Janssen-Cilag and AbbVie. Ibrutinib was provided free of charge by Janssen-Cilag, and venetoclax was provided free of charge by AbbVie. Dr. Hillman reported financial relationships with Janssen, AbbVie, Roche, Pharmacyclics, and Gilead Sciences.
SOURCE: Hillmen P et al. J Clin Oncol. 2019 Jul 11. doi: 10.1200/JCO.19.00894.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL ONCOLOGY
Potential improvements in convenience, tolerability of hematologic treatment
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I highlight two recent presentations regarding potential improvements in the convenience and tolerability of treatment for two hematologic malignancies: multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL).
SC-Dara in myeloma
At the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Maria-Victoria Mateos, MD, PhD, and colleagues, reported the results of COLUMBA, a phase 3 evaluation in 522 patients with multiple myeloma who were randomized to subcutaneous daratumumab (SC-Dara) or standard intravenous infusions of daratumumab (IV-Dara). A previous phase 1b study (Blood. 2017;130:838) had suggested comparable efficacy from the more convenient SC regime. Whereas conventional infusions of IV-Dara (16 mg/kg) take several hours, the SC formulation (1,800 mg–flat dose) is delivered in minutes. In COLUMBA, patients were randomized between SC- and IV-Dara weekly (cycles 1-2), then every 2 weeks (cycles 3-6), then every 4 weeks until disease progression.
Among the IV-Dara patients, the median duration of the first infusion was 421 minutes in cycle 1, 255 minutes in cycle 2, and 205 minutes in subsequent cycles – compatible with standard practice in the United States. As reported, at a median follow-up of 7.46 months, the efficacy (overall response rate, complete response rate, stringent-complete response rate, very good-partial response rate, progression-free survival, and 6-month overall survival) and safety profile were non-inferior for SC-Dara. SC-Dara patients also reported higher satisfaction with therapy.
What this means in practice
It is always a good idea to await publication of the manuscript because there may be study details and statistical nuances that make SC-Dara appear better than it will prove to be. For example, patient characteristics were slightly different between the two arms. Peer review of the final manuscript could be important in placing these results in context.
However, for treatments that demand frequent office visits over many months, reducing treatment burden for patients has value. Based on COLUMBA, it appears likely that SC-Dara will be a major convenience for patients, without obvious drawbacks in efficacy or toxicity. Meanwhile, flat dosing will be a time-saver for physicians, nursing, and pharmacy staff. If the price of the SC formulation is not exorbitant, I would expect a “win-win” that will support converting from IV- to SC-Dara as standard practice.
Acalabrutinib in CLL/SLL
Preclinical studies have shown acalabrutinib (Acala) to be more selective for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib, with less off-target kinase inhibition. As reported at the 2019 annual congress of the European Hematology Association by Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, and colleagues in the phase 3 ASCEND trial, 310 patients with previously treated CLL were randomized between oral Acala twice daily and treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) – either idelalisib plus rituximab (maximum of seven infusions) or bendamustine plus rituximab (maximum of six cycles).
Progression-free survival was the primary endpoint. At a median of 16.1 months, progression-free survival had not been reached for Acala, in comparison with 16.5 months for TPC. Significant benefit of Acala was observed in all prognostic subsets.
Although there was no difference in overall survival at a median follow-up of about 16 months, 85% of Acala patients had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of TPC patients. Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients treated with Acala, with 45% being grade 3-4 toxicities and six treatment-related deaths.
What this means in practice
The vast majority of CLL/SLL patients will relapse after primary therapy and will require further treatment, so the progression-free survival improvement associated with Acala in ASCEND is eye-catching. However, there are important considerations that demand closer scrutiny.
With oral agents administered until progression or unacceptable toxicity, low-grade toxicities can influence patient adherence, quality of life, and potentially the need for dose reduction or treatment interruptions. Regimens of finite duration and easy adherence monitoring may be, on balance, preferred by patients and providers – especially if the oral agent can be given in later-line with comparable overall survival.
With ibrutinib (Blood. 2017;129:2612-5), Paul M. Barr, MD, and colleagues demonstrated that higher dose intensity was associated with improved progression-free survival and that holds were associated with worsened progression-free survival. Acala’s promise of high efficacy and lower off-target toxicity will be solidified if the large (more than 500 patients) phase 3 ACE-CL-006 study (Acala vs. ibrutinib) demonstrates its relative benefit from efficacy, toxicity, and adherence perspectives, in comparison with a standard therapy that similarly demands adherence until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I highlight two recent presentations regarding potential improvements in the convenience and tolerability of treatment for two hematologic malignancies: multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL).
SC-Dara in myeloma
At the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Maria-Victoria Mateos, MD, PhD, and colleagues, reported the results of COLUMBA, a phase 3 evaluation in 522 patients with multiple myeloma who were randomized to subcutaneous daratumumab (SC-Dara) or standard intravenous infusions of daratumumab (IV-Dara). A previous phase 1b study (Blood. 2017;130:838) had suggested comparable efficacy from the more convenient SC regime. Whereas conventional infusions of IV-Dara (16 mg/kg) take several hours, the SC formulation (1,800 mg–flat dose) is delivered in minutes. In COLUMBA, patients were randomized between SC- and IV-Dara weekly (cycles 1-2), then every 2 weeks (cycles 3-6), then every 4 weeks until disease progression.
Among the IV-Dara patients, the median duration of the first infusion was 421 minutes in cycle 1, 255 minutes in cycle 2, and 205 minutes in subsequent cycles – compatible with standard practice in the United States. As reported, at a median follow-up of 7.46 months, the efficacy (overall response rate, complete response rate, stringent-complete response rate, very good-partial response rate, progression-free survival, and 6-month overall survival) and safety profile were non-inferior for SC-Dara. SC-Dara patients also reported higher satisfaction with therapy.
What this means in practice
It is always a good idea to await publication of the manuscript because there may be study details and statistical nuances that make SC-Dara appear better than it will prove to be. For example, patient characteristics were slightly different between the two arms. Peer review of the final manuscript could be important in placing these results in context.
However, for treatments that demand frequent office visits over many months, reducing treatment burden for patients has value. Based on COLUMBA, it appears likely that SC-Dara will be a major convenience for patients, without obvious drawbacks in efficacy or toxicity. Meanwhile, flat dosing will be a time-saver for physicians, nursing, and pharmacy staff. If the price of the SC formulation is not exorbitant, I would expect a “win-win” that will support converting from IV- to SC-Dara as standard practice.
Acalabrutinib in CLL/SLL
Preclinical studies have shown acalabrutinib (Acala) to be more selective for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib, with less off-target kinase inhibition. As reported at the 2019 annual congress of the European Hematology Association by Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, and colleagues in the phase 3 ASCEND trial, 310 patients with previously treated CLL were randomized between oral Acala twice daily and treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) – either idelalisib plus rituximab (maximum of seven infusions) or bendamustine plus rituximab (maximum of six cycles).
Progression-free survival was the primary endpoint. At a median of 16.1 months, progression-free survival had not been reached for Acala, in comparison with 16.5 months for TPC. Significant benefit of Acala was observed in all prognostic subsets.
Although there was no difference in overall survival at a median follow-up of about 16 months, 85% of Acala patients had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of TPC patients. Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients treated with Acala, with 45% being grade 3-4 toxicities and six treatment-related deaths.
What this means in practice
The vast majority of CLL/SLL patients will relapse after primary therapy and will require further treatment, so the progression-free survival improvement associated with Acala in ASCEND is eye-catching. However, there are important considerations that demand closer scrutiny.
With oral agents administered until progression or unacceptable toxicity, low-grade toxicities can influence patient adherence, quality of life, and potentially the need for dose reduction or treatment interruptions. Regimens of finite duration and easy adherence monitoring may be, on balance, preferred by patients and providers – especially if the oral agent can be given in later-line with comparable overall survival.
With ibrutinib (Blood. 2017;129:2612-5), Paul M. Barr, MD, and colleagues demonstrated that higher dose intensity was associated with improved progression-free survival and that holds were associated with worsened progression-free survival. Acala’s promise of high efficacy and lower off-target toxicity will be solidified if the large (more than 500 patients) phase 3 ACE-CL-006 study (Acala vs. ibrutinib) demonstrates its relative benefit from efficacy, toxicity, and adherence perspectives, in comparison with a standard therapy that similarly demands adherence until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I highlight two recent presentations regarding potential improvements in the convenience and tolerability of treatment for two hematologic malignancies: multiple myeloma and chronic lymphocytic leukemia/small lymphocytic lymphoma (CLL/SLL).
SC-Dara in myeloma
At the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, Maria-Victoria Mateos, MD, PhD, and colleagues, reported the results of COLUMBA, a phase 3 evaluation in 522 patients with multiple myeloma who were randomized to subcutaneous daratumumab (SC-Dara) or standard intravenous infusions of daratumumab (IV-Dara). A previous phase 1b study (Blood. 2017;130:838) had suggested comparable efficacy from the more convenient SC regime. Whereas conventional infusions of IV-Dara (16 mg/kg) take several hours, the SC formulation (1,800 mg–flat dose) is delivered in minutes. In COLUMBA, patients were randomized between SC- and IV-Dara weekly (cycles 1-2), then every 2 weeks (cycles 3-6), then every 4 weeks until disease progression.
Among the IV-Dara patients, the median duration of the first infusion was 421 minutes in cycle 1, 255 minutes in cycle 2, and 205 minutes in subsequent cycles – compatible with standard practice in the United States. As reported, at a median follow-up of 7.46 months, the efficacy (overall response rate, complete response rate, stringent-complete response rate, very good-partial response rate, progression-free survival, and 6-month overall survival) and safety profile were non-inferior for SC-Dara. SC-Dara patients also reported higher satisfaction with therapy.
What this means in practice
It is always a good idea to await publication of the manuscript because there may be study details and statistical nuances that make SC-Dara appear better than it will prove to be. For example, patient characteristics were slightly different between the two arms. Peer review of the final manuscript could be important in placing these results in context.
However, for treatments that demand frequent office visits over many months, reducing treatment burden for patients has value. Based on COLUMBA, it appears likely that SC-Dara will be a major convenience for patients, without obvious drawbacks in efficacy or toxicity. Meanwhile, flat dosing will be a time-saver for physicians, nursing, and pharmacy staff. If the price of the SC formulation is not exorbitant, I would expect a “win-win” that will support converting from IV- to SC-Dara as standard practice.
Acalabrutinib in CLL/SLL
Preclinical studies have shown acalabrutinib (Acala) to be more selective for Bruton’s tyrosine kinase (BTK) than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib, with less off-target kinase inhibition. As reported at the 2019 annual congress of the European Hematology Association by Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, and colleagues in the phase 3 ASCEND trial, 310 patients with previously treated CLL were randomized between oral Acala twice daily and treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) – either idelalisib plus rituximab (maximum of seven infusions) or bendamustine plus rituximab (maximum of six cycles).
Progression-free survival was the primary endpoint. At a median of 16.1 months, progression-free survival had not been reached for Acala, in comparison with 16.5 months for TPC. Significant benefit of Acala was observed in all prognostic subsets.
Although there was no difference in overall survival at a median follow-up of about 16 months, 85% of Acala patients had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of TPC patients. Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients treated with Acala, with 45% being grade 3-4 toxicities and six treatment-related deaths.
What this means in practice
The vast majority of CLL/SLL patients will relapse after primary therapy and will require further treatment, so the progression-free survival improvement associated with Acala in ASCEND is eye-catching. However, there are important considerations that demand closer scrutiny.
With oral agents administered until progression or unacceptable toxicity, low-grade toxicities can influence patient adherence, quality of life, and potentially the need for dose reduction or treatment interruptions. Regimens of finite duration and easy adherence monitoring may be, on balance, preferred by patients and providers – especially if the oral agent can be given in later-line with comparable overall survival.
With ibrutinib (Blood. 2017;129:2612-5), Paul M. Barr, MD, and colleagues demonstrated that higher dose intensity was associated with improved progression-free survival and that holds were associated with worsened progression-free survival. Acala’s promise of high efficacy and lower off-target toxicity will be solidified if the large (more than 500 patients) phase 3 ACE-CL-006 study (Acala vs. ibrutinib) demonstrates its relative benefit from efficacy, toxicity, and adherence perspectives, in comparison with a standard therapy that similarly demands adherence until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
Acalabrutinib extends PFS in advanced CLL
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
AMSTERDAM – For patients with relapsed or refractory chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), monotherapy with the Bruton tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor acalabrutinib (Calquence) was associated with better progression-free survival and a more tolerable safety profile than rituximab combined with either idelalisib (Zydelig) or bendamustine, an interim analysis from the phase 3 ASCEND trial showed.
Among 310 patients with previously treated CLL followed for a median of 16.1 months, the primary endpoint of median progression-free survival (PFS), as assessed by independent reviewers, had not been reached for patients treated with acalabrutinib, compared with 16.5 months for patients treated with idelalisib and rituximab (IdR) or bendamustine and rituximab (BR), reported Paolo Ghia, MD, PhD, from Università Vita-Salute San Raffaele in Milan.
“We show that acalabrutinib improved progression-free survival across all groups, including those with high-risk features,” he said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
Acalabrutinib is approved in the United States for treatment of mantle cell lymphoma that has progressed on at least one prior therapy. It has been shown in preclinical studies to be more selective for BTK than the first-in-class agent ibrutinib (Imbruvica), with less off-target kinase inhibition, Dr. Ghia said.
ASCEND was designed to see whether acalabrutinib monotherapy could offer superior PFS to IdR or BR in patients with CLL who had progressed or were refractory to at least one prior line of therapy.
Patients were randomly assigned, with 155 patients in each arm, to either acalabrutinib 100 mg orally twice daily or the investigator’s choice of either idelalisib 150 mg orally twice daily plus IV rituximab at an initial dose of 375 mg/m2, followed by up to seven doses at 500 mg/m2 delivered every 2 weeks for four infusions, then every 4 weeks for the remaining three infusions or IV bendamustine 70 mg/m2 on days 1 and 2 of each cycle, plus rituximab at the 375 mg/m2 dose on day 1 for the first cycle, followed by 500 mg/m2 for up to six total cycles.
Dr. Ghia presented results of an interim analysis planned for when two-thirds of the predicted PFS events (approximately 79) had occurred.
The baseline patient characteristics were generally similar, with a median age of 68 years in the acalabrutinib arm and 67 years in the comparison arm. Almost half of all patients in each arm had bulky disease, defined as 5 cm or greater. The majority of patients had two or more prior lines of therapy.
The primary endpoint of PFS as assessed by independent review favored acalabrutinib, with a hazard ratio of 0.31 (P less than .0001). Results were similar when acalabrutinib was compared with each of the regimens in the comparison arm (HR, 0.29 vs. IdR, 0.36 vs. BR; P less than .001 for each comparison).
Acalabrutinib was also superior in patients with high-risk cytogenetic features, compared with the other two regimens combined (HR, 0.27; P less than .001).
The benefit of the BTK inhibitor was consistent across all subgroups, including age, sex, performance status, Rai stage at screening, bulky/nonbulky disease, number of prior therapies, presence or absence of deletion 17p or TP53 mutation, mutated or unmutated immunoglobulin heavy chain, and complex/noncomplex karyotype.
Reviewer-assessed objective response rates were similar, occurring in 81% of patients on acalabrutinib and 76% of patients on other regimens.
There were no complete responses in the acalabrutinib arm, compared with two complete responses in the comparison arm. The majority of responses in each arm were partial responses (81% and 74%, respectively).
The median duration of response was not reached with acalabrutinib, compared with 13.6 months with the other therapies (HR, 0.33; P less than .0001).
In all, 85% of patients on acalabrutinib had a response lasting at least 12 months, compared with 60% of patients on the other regimens. There was no difference in overall survival at the 16.1-month median follow-up.
Adverse events of any grade occurred in 94% of patients on acalabrutinib, 99% on IdR, and 80% on BR; the respective incidences of serious adverse events were 29%, 56%, and 26%. Grade 3-4 adverse events occurred in 45%, 86%, and 43% of patients, respectively.
There were 13 treatment-related deaths. Six deaths in the acalabrutinib arm were caused by brain neoplasm, cachexia, cerebral ischemia, malignant lung tumor, neuroendocrine carcinoma, and sepsis. Five deaths among IdR-treated patients included chronic heart failure, cardiopulmonary disease, interstitial lung disease, MI, and pseudomonal pneumonia. Two deaths in BR-treated patients were attributed to acute cardiac failure and a gastric neoplasm.
The results show that “acalabrutinib has demonstrated efficacy in previously untreated and relapsed/refractory CLL and may be considered as an option in the future treatment paradigm,” Dr. Ghia said.
Acalabrutinib monotherapy is currently being compared with ibrutinib monotherapy in patients with relapsed/refractory CLL; in addition, the phase 3 ELEVATE-TN study investigating acalabrutinib in combination with obinutuzumab (Gazyva) versus obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil has reached its primary PFS endpoint and will be reported soon, Dr. Ghia said.
The ASCEND trial is sponsored by Acerta Pharma; AstraZeneca holds majority shares in the company. Dr. Ghia reported consulting fees and honoraria from AstraZeneca and other companies, and research funding from several different companies.
SOURCE: Ghia P et al. EHA Congress, Abstract LB2606.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
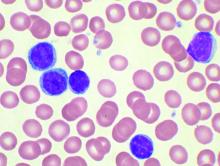
Ibrutinib tops chlorambucil against CLL
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
AMSTERDAM – After 5 years, a large majority of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with front-line ibrutinib (Imbruvica) have not experienced disease progression, and the median progression-free survival has still not been reached, long-term follow-up from the RESONATE-2 shows.
The 5-year estimated progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 70% for patients who had been randomized to receive ibrutinib monotherapy, compared with 12% for patients randomized to chlorambucil, reported Alessandra Tedeschi, MD, from Azienda Ospedaliera Niguarda Ca’ Granda in Milan.
Ibrutinib was also associated with a halving of risk for death, compared with chlorambucil, she said at the annual congress of the European Hematology Association.
“Importantly, the rate of progression during ibrutinib treatment was very low; only 8 – that is, 6% of patients” – experienced disease progression while receiving ibrutinib, she noted.
In the RESONATE-2 (PCYC-1115) trial, investigators enrolled 269 adults aged 65 years and older with previously untreated CLL/small lymphocytic lymphoma (SLL). Patients at the younger end of the age range (65-69 years) had to have comorbidities that would have made them ineligible for the FCR chemotherapy regimen (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab). Additionally, patients with the deleterious 17p deletion were excluded.
Patients were stratified by performance status and Rai stage and then randomized to receive either ibrutinib 420 mg once daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity (136 patients) or chlorambucil 0.5 mg/kg to a maximum of 0.8 mg/kg for up to 12 cycles (133 patients). The trial also had an extension study for patients who had disease progression as confirmed by an independent review committee or who had completed the RESONATE-2 trial. Of the 133 patients in the chlorambucil arm, 76 (57% of the intention-to-treat population) were crossed over to ibrutinib following disease progression.
The median duration of ibrutinib treatment was 57.1 months, with 73% of patients being on it for more than 3 years, 65% for more than 4 years, and 27% for more than 5 years. As of the data cutoff, 79 patients (58%) were continuing with ibrutinib on study.
At 5 years, 70% of ibrutinib-treated patients and 12% of chlorambucil-treated patients were estimated to be progression-free and alive (hazard ratio for PFS with ibrutinib 0.146 (95% confidence interval, 0.10-0.22). The benefit of ibrutinib was consistent for patients with high-risk genomic features, including the 11q deletion and unmutated immunoglobulin heavy-chain variable genes.
Estimated 5-year overall survival was also better with ibrutinib, at 83% vs. 68% (hazard ratio, 0.45; 95% CI, 0.266-0.761).
The most common grade 3 or greater adverse events occurring with ibrutinib were neutropenia (13%), pneumonia (12%), hypertension (8%), anemia (7%), hyponatremia (6%), atrial fibrillation (5%), and cataract (5%). The rates of most adverse events decreased over time, and dose reductions because of adverse events also diminished over time, from 5% of patients in the first year down to zero in years 4 through 5.
Patients responded to subsequent CLL therapies following ibrutinib discontinuation, including chemoimmunotherapy and other kinase inhibitors, Dr. Tedeschi said.
The trial was sponsored by Pharmacyclics with collaboration from Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Tedeschi reported advisory board activities with Janssen, AbbVie, and BeiGene.
SOURCE: Tedeschi A et al. EHA Congress, Abstract S107.
REPORTING FROM EHA CONGRESS
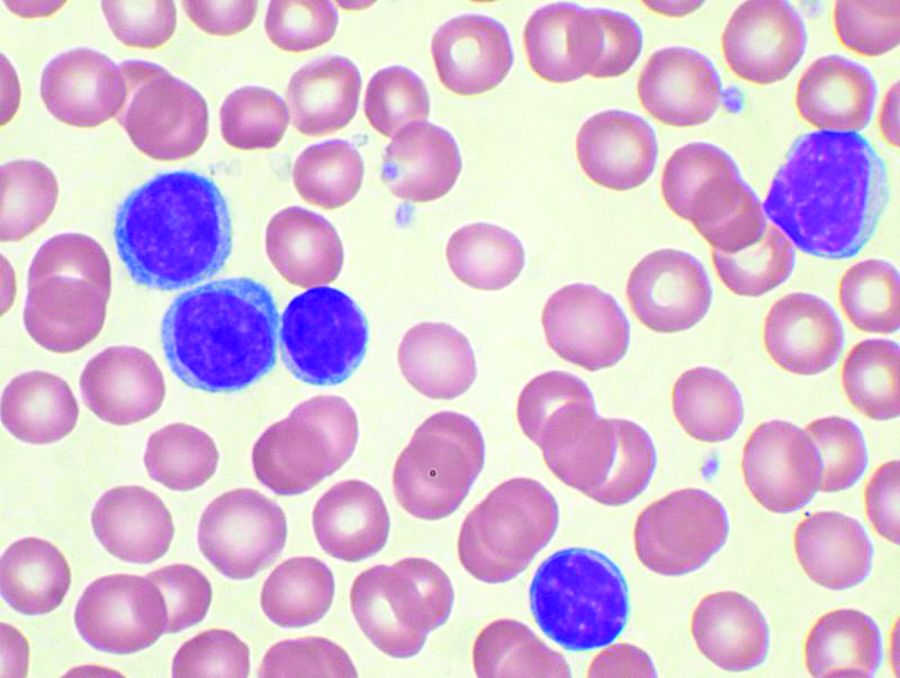
Hedgehog signaling offers prognostic, therapeutic potential in CLL
Activation of hedgehog (Hh) signaling could predict early disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and offer a new therapeutic target, according to investigators.
Approximately 11% of treatment-naive patients had mutations associated with Hh signaling, reported lead author Emanuela M. Ghia, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. In addition to early progression, Hh signaling was associated with expression of GLI1, which could be a future therapeutic target. In support of this possibility, in vitro experimentation with a GLI1 inhibitor showed high cytotoxicity for GLI1-positive CLL cells.
“Targeting GLI1 could block ligand-independent and ligand-dependent Hh pathway activation and perhaps overcome the apparent resistance to SMO inhibitors,” the investigators wrote in Blood.
Using the HALT Pan-Leukemia Gene Panel, which includes 103 genes, the investigators tested for mutations in cell samples from 841 patients with treatment-naive CLL. Specifically, the investigators focused on mutations that did not map to seven well-known signaling/metabolic pathways, such as Wnt and Notch.
This strategy revealed that 89 patients (11%) had nonsynonymous mutations in genes that drive Hh signaling. These mutations were highly associated with GLI1 expression (x2 test; P less than .0001), which stands to reason, as GLI1 is the main effector of the Hh signaling pathway. Of note, 62 of the 161 patients (38%) who did not test positive for an Hh pathway mutation still tested positive for GLI1, suggesting that they had Hh pathway activation, albeit without an identifiable mutational cause.
These findings are clinically significant, as GLI1 overexpression has been linked to numerous types of cancer and is an adverse prognostic indicator for acute myeloid leukemia and several carcinomas, the investigators wrote.
Considering these associations with other cancer types, the investigators looked for a relationship between GLI1 expression and outcomes in CLL. Comparing 103 patients with GLI1-positive disease with 107 GLI-negative patients revealed that GLI1 positivity was significantly associated with shorter median treatment-free survival (4.7 vs. 6.4 years; P = .002). Additional analysis showed that this prognostic relationship was present regardless of IgVH mutational status.
Based on these findings, the investigators concluded that “[a]ctivation of the Hh pathway can strongly influence disease progression in CLL.”
Two additional tests showed that GLI1-positivity was associated with cell survival. First, silencing GLI1 with a GLI1-specific small interfering RNA led to decreased cell viability. Second, GANT61, a small molecule inhibitor of GLI1, was highly cytotoxic for GLI1-positive cells. According to the investigators, these findings suggest that GLI1 could be a future therapeutic target.
“[T]his report shows that the Hh pathway frequently is activated in CLL and associated with relatively rapid disease progression, while identifying a new avenue for therapeutic intervention for patients with this disease,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Stem Cell Consortium, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, and other groups. The investigators reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ghia EM et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 20;133(25):2651-63.
Activation of hedgehog (Hh) signaling could predict early disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and offer a new therapeutic target, according to investigators.
Approximately 11% of treatment-naive patients had mutations associated with Hh signaling, reported lead author Emanuela M. Ghia, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. In addition to early progression, Hh signaling was associated with expression of GLI1, which could be a future therapeutic target. In support of this possibility, in vitro experimentation with a GLI1 inhibitor showed high cytotoxicity for GLI1-positive CLL cells.
“Targeting GLI1 could block ligand-independent and ligand-dependent Hh pathway activation and perhaps overcome the apparent resistance to SMO inhibitors,” the investigators wrote in Blood.
Using the HALT Pan-Leukemia Gene Panel, which includes 103 genes, the investigators tested for mutations in cell samples from 841 patients with treatment-naive CLL. Specifically, the investigators focused on mutations that did not map to seven well-known signaling/metabolic pathways, such as Wnt and Notch.
This strategy revealed that 89 patients (11%) had nonsynonymous mutations in genes that drive Hh signaling. These mutations were highly associated with GLI1 expression (x2 test; P less than .0001), which stands to reason, as GLI1 is the main effector of the Hh signaling pathway. Of note, 62 of the 161 patients (38%) who did not test positive for an Hh pathway mutation still tested positive for GLI1, suggesting that they had Hh pathway activation, albeit without an identifiable mutational cause.
These findings are clinically significant, as GLI1 overexpression has been linked to numerous types of cancer and is an adverse prognostic indicator for acute myeloid leukemia and several carcinomas, the investigators wrote.
Considering these associations with other cancer types, the investigators looked for a relationship between GLI1 expression and outcomes in CLL. Comparing 103 patients with GLI1-positive disease with 107 GLI-negative patients revealed that GLI1 positivity was significantly associated with shorter median treatment-free survival (4.7 vs. 6.4 years; P = .002). Additional analysis showed that this prognostic relationship was present regardless of IgVH mutational status.
Based on these findings, the investigators concluded that “[a]ctivation of the Hh pathway can strongly influence disease progression in CLL.”
Two additional tests showed that GLI1-positivity was associated with cell survival. First, silencing GLI1 with a GLI1-specific small interfering RNA led to decreased cell viability. Second, GANT61, a small molecule inhibitor of GLI1, was highly cytotoxic for GLI1-positive cells. According to the investigators, these findings suggest that GLI1 could be a future therapeutic target.
“[T]his report shows that the Hh pathway frequently is activated in CLL and associated with relatively rapid disease progression, while identifying a new avenue for therapeutic intervention for patients with this disease,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Stem Cell Consortium, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, and other groups. The investigators reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ghia EM et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 20;133(25):2651-63.
Activation of hedgehog (Hh) signaling could predict early disease progression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and offer a new therapeutic target, according to investigators.
Approximately 11% of treatment-naive patients had mutations associated with Hh signaling, reported lead author Emanuela M. Ghia, PhD, of the University of California, San Diego, and colleagues. In addition to early progression, Hh signaling was associated with expression of GLI1, which could be a future therapeutic target. In support of this possibility, in vitro experimentation with a GLI1 inhibitor showed high cytotoxicity for GLI1-positive CLL cells.
“Targeting GLI1 could block ligand-independent and ligand-dependent Hh pathway activation and perhaps overcome the apparent resistance to SMO inhibitors,” the investigators wrote in Blood.
Using the HALT Pan-Leukemia Gene Panel, which includes 103 genes, the investigators tested for mutations in cell samples from 841 patients with treatment-naive CLL. Specifically, the investigators focused on mutations that did not map to seven well-known signaling/metabolic pathways, such as Wnt and Notch.
This strategy revealed that 89 patients (11%) had nonsynonymous mutations in genes that drive Hh signaling. These mutations were highly associated with GLI1 expression (x2 test; P less than .0001), which stands to reason, as GLI1 is the main effector of the Hh signaling pathway. Of note, 62 of the 161 patients (38%) who did not test positive for an Hh pathway mutation still tested positive for GLI1, suggesting that they had Hh pathway activation, albeit without an identifiable mutational cause.
These findings are clinically significant, as GLI1 overexpression has been linked to numerous types of cancer and is an adverse prognostic indicator for acute myeloid leukemia and several carcinomas, the investigators wrote.
Considering these associations with other cancer types, the investigators looked for a relationship between GLI1 expression and outcomes in CLL. Comparing 103 patients with GLI1-positive disease with 107 GLI-negative patients revealed that GLI1 positivity was significantly associated with shorter median treatment-free survival (4.7 vs. 6.4 years; P = .002). Additional analysis showed that this prognostic relationship was present regardless of IgVH mutational status.
Based on these findings, the investigators concluded that “[a]ctivation of the Hh pathway can strongly influence disease progression in CLL.”
Two additional tests showed that GLI1-positivity was associated with cell survival. First, silencing GLI1 with a GLI1-specific small interfering RNA led to decreased cell viability. Second, GANT61, a small molecule inhibitor of GLI1, was highly cytotoxic for GLI1-positive cells. According to the investigators, these findings suggest that GLI1 could be a future therapeutic target.
“[T]his report shows that the Hh pathway frequently is activated in CLL and associated with relatively rapid disease progression, while identifying a new avenue for therapeutic intervention for patients with this disease,” they concluded.
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health, the Cancer Stem Cell Consortium, the Canadian Institutes of Health Research, the Ontario Institute for Cancer Research, and other groups. The investigators reported having no competing financial interests.
SOURCE: Ghia EM et al. Blood. 2019 Jun 20;133(25):2651-63.
FROM BLOOD
Fixed-duration venetoclax-obinutuzumab superior to standard CLL therapy
CHICAGO – A fixed-duration venetoclax-obinutuzumab regimen is safe and provides a superior outcome versus standard chlorambucil-obinutuzumab in elderly patients with untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and comorbidities, results of a randomized phase 3 trial showed.
At 24 months, progression-free survival was 88.2% for the venetoclax-obinutuzumab regimen, versus 64.1% for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.53; P less than .0001) in CLL-14, an open-label, multinational trial presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The regimen, given for just 12 28-day cycles, also achieved the highest rate of minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative responses ever seen in a randomized prospective CLL study, according to investigator Kirsten Fischer, MD, of the University of Cologne in Germany.
“We really think that these unprecedented MRD negativity levels will eventually translate into an improved overall survival,” Dr. Fischer said during an oral abstract presentation.
Matthew Steven Davids, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Medical School, Boston, said venetoclax plus obinutuzumab offers the potential for 1-year, time-limited therapy, which limits concerns over long-term adherence and has the potential for cost savings, should the therapy prove to be highly durable with further follow-up.
“A limitation of the study is that the comparator arm – chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab – is directly applicable to only a relatively small subset of our older and frailer CLL patients,” Dr. Davids said during a podium discussion of the results.
“But nonetheless, venetoclax plus obinutuzumab is a promising, time-limited regimen, and CLL14 is an immediately practice-changing study for frontline CLL treatment,” he added.
The regimen stands in contrast to ibrutinib, which offers durable responses but requires continuous dosing, and FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab), a time-limited therapy with curative potential that is restricted to younger patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, according to Dr. Davids.
In CLL-14, 432 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive venetoclax-obinutuzumab for six cycles followed by venetoclax for six cycles, or chlorambucil-obinutuzumab for six cycles followed by chlorambucil for six cycles. The median age was 72 years in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab arm and 71 years in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm.
The overall response rate was 85% for venetoclax-obinutuzumab and 71% for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (P = .0007), Dr. Fischer reported at the meeting.
The improvement in progression-free survival seen in the overall study population was also seen in patients with TP53 deletions or mutations, and in those with unmutated IGHV, Dr. Fischer reported.
Rates of MRD negativity in peripheral blood were 76% versus 35% for the venetoclax- and chlorambucil-containing combinations, respectively (P less than .001), and similarly, MRD negativity in bone marrow was 57% versus 17% (P less than .001), she said.
There were no significant differences in the rates of grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, which occurred in 52.8% of the venetoclax–obinutuzumab treated patients and 48.1% of the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab treated patients, or in grade 3 or 4 infections, which occurred in 17.5% and 15.0%, respectively, according to a report, published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;380:2225-36).
Likewise, all-cause mortality was not significantly different between the arms, at 9.3% and 7.9%, respectively.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche and AbbVie supported the study. Dr. Fischer reported travel, accommodations, or expenses from Roche in her abstract disclosure.
SOURCE: Fischer K et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7502.
CHICAGO – A fixed-duration venetoclax-obinutuzumab regimen is safe and provides a superior outcome versus standard chlorambucil-obinutuzumab in elderly patients with untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and comorbidities, results of a randomized phase 3 trial showed.
At 24 months, progression-free survival was 88.2% for the venetoclax-obinutuzumab regimen, versus 64.1% for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.53; P less than .0001) in CLL-14, an open-label, multinational trial presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The regimen, given for just 12 28-day cycles, also achieved the highest rate of minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative responses ever seen in a randomized prospective CLL study, according to investigator Kirsten Fischer, MD, of the University of Cologne in Germany.
“We really think that these unprecedented MRD negativity levels will eventually translate into an improved overall survival,” Dr. Fischer said during an oral abstract presentation.
Matthew Steven Davids, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Medical School, Boston, said venetoclax plus obinutuzumab offers the potential for 1-year, time-limited therapy, which limits concerns over long-term adherence and has the potential for cost savings, should the therapy prove to be highly durable with further follow-up.
“A limitation of the study is that the comparator arm – chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab – is directly applicable to only a relatively small subset of our older and frailer CLL patients,” Dr. Davids said during a podium discussion of the results.
“But nonetheless, venetoclax plus obinutuzumab is a promising, time-limited regimen, and CLL14 is an immediately practice-changing study for frontline CLL treatment,” he added.
The regimen stands in contrast to ibrutinib, which offers durable responses but requires continuous dosing, and FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab), a time-limited therapy with curative potential that is restricted to younger patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, according to Dr. Davids.
In CLL-14, 432 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive venetoclax-obinutuzumab for six cycles followed by venetoclax for six cycles, or chlorambucil-obinutuzumab for six cycles followed by chlorambucil for six cycles. The median age was 72 years in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab arm and 71 years in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm.
The overall response rate was 85% for venetoclax-obinutuzumab and 71% for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (P = .0007), Dr. Fischer reported at the meeting.
The improvement in progression-free survival seen in the overall study population was also seen in patients with TP53 deletions or mutations, and in those with unmutated IGHV, Dr. Fischer reported.
Rates of MRD negativity in peripheral blood were 76% versus 35% for the venetoclax- and chlorambucil-containing combinations, respectively (P less than .001), and similarly, MRD negativity in bone marrow was 57% versus 17% (P less than .001), she said.
There were no significant differences in the rates of grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, which occurred in 52.8% of the venetoclax–obinutuzumab treated patients and 48.1% of the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab treated patients, or in grade 3 or 4 infections, which occurred in 17.5% and 15.0%, respectively, according to a report, published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;380:2225-36).
Likewise, all-cause mortality was not significantly different between the arms, at 9.3% and 7.9%, respectively.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche and AbbVie supported the study. Dr. Fischer reported travel, accommodations, or expenses from Roche in her abstract disclosure.
SOURCE: Fischer K et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7502.
CHICAGO – A fixed-duration venetoclax-obinutuzumab regimen is safe and provides a superior outcome versus standard chlorambucil-obinutuzumab in elderly patients with untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and comorbidities, results of a randomized phase 3 trial showed.
At 24 months, progression-free survival was 88.2% for the venetoclax-obinutuzumab regimen, versus 64.1% for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (hazard ratio, 0.35; 95% confidence interval, 0.23-0.53; P less than .0001) in CLL-14, an open-label, multinational trial presented at the annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
The regimen, given for just 12 28-day cycles, also achieved the highest rate of minimal residual disease (MRD)-negative responses ever seen in a randomized prospective CLL study, according to investigator Kirsten Fischer, MD, of the University of Cologne in Germany.
“We really think that these unprecedented MRD negativity levels will eventually translate into an improved overall survival,” Dr. Fischer said during an oral abstract presentation.
Matthew Steven Davids, MD, of Dana-Farber Cancer Institute/Harvard Medical School, Boston, said venetoclax plus obinutuzumab offers the potential for 1-year, time-limited therapy, which limits concerns over long-term adherence and has the potential for cost savings, should the therapy prove to be highly durable with further follow-up.
“A limitation of the study is that the comparator arm – chlorambucil plus obinutuzumab – is directly applicable to only a relatively small subset of our older and frailer CLL patients,” Dr. Davids said during a podium discussion of the results.
“But nonetheless, venetoclax plus obinutuzumab is a promising, time-limited regimen, and CLL14 is an immediately practice-changing study for frontline CLL treatment,” he added.
The regimen stands in contrast to ibrutinib, which offers durable responses but requires continuous dosing, and FCR (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab), a time-limited therapy with curative potential that is restricted to younger patients with IGHV-mutated CLL, according to Dr. Davids.
In CLL-14, 432 patients were randomized 1:1 to receive venetoclax-obinutuzumab for six cycles followed by venetoclax for six cycles, or chlorambucil-obinutuzumab for six cycles followed by chlorambucil for six cycles. The median age was 72 years in the venetoclax-obinutuzumab arm and 71 years in the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab arm.
The overall response rate was 85% for venetoclax-obinutuzumab and 71% for chlorambucil-obinutuzumab (P = .0007), Dr. Fischer reported at the meeting.
The improvement in progression-free survival seen in the overall study population was also seen in patients with TP53 deletions or mutations, and in those with unmutated IGHV, Dr. Fischer reported.
Rates of MRD negativity in peripheral blood were 76% versus 35% for the venetoclax- and chlorambucil-containing combinations, respectively (P less than .001), and similarly, MRD negativity in bone marrow was 57% versus 17% (P less than .001), she said.
There were no significant differences in the rates of grade 3 or 4 neutropenia, which occurred in 52.8% of the venetoclax–obinutuzumab treated patients and 48.1% of the chlorambucil-obinutuzumab treated patients, or in grade 3 or 4 infections, which occurred in 17.5% and 15.0%, respectively, according to a report, published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine (2019;380:2225-36).
Likewise, all-cause mortality was not significantly different between the arms, at 9.3% and 7.9%, respectively.
F. Hoffmann-La Roche and AbbVie supported the study. Dr. Fischer reported travel, accommodations, or expenses from Roche in her abstract disclosure.
SOURCE: Fischer K et al. ASCO 2019, Abstract 7502.
REPORTING FROM ASCO 2019
Venetoclax plus ibrutinib appears to suit elderly and high-risk patients with CLL
A combination of venetoclax and ibrutinib may be a safe and effective treatment option for previously untreated elderly and high-risk patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to investigators of a phase 2 trial of the combination.
About 88% of patients achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery after 12 cycles of treatment, reported lead author Nitin Jain, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues.
There were no new safety signals for the combination of ibrutinib, an irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 protein inhibitor, the investigators noted.
“This combination was reported to be safe and active in patients with mantle cell lymphoma,” they wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine. “Given the clinically complementary activity, preclinical synergism, and nonoverlapping toxic effects, we examined the safety and efficacy of combined ibrutinib and venetoclax treatment in previously untreated patients with CLL.”
In particular, the investigators recruited older patients, as this is a common population that can be challenging to treat. “Because CLL typically occurs in older adults, the majority of patients who need treatment are older than 65 years of age,” the investigators wrote. “This group of patients often has unacceptable side effects and has a lower rate of complete remission and undetectable minimal residual disease with chemoimmunotherapy than younger patients.”
The open-label, phase 2 trial enrolled 80 elderly and high-risk patients with previously untreated CLL. Eligibility required an age of at least 65 years or presence of at least one high-risk genetic feature; namely, mutated TP53, unmutated IgVH, or chromosome 11q deletion.
In order to reduce the risk of tumor lysis syndrome, ibrutinib (420 mg once daily) was given as monotherapy for three 28-day cycles. From the fourth cycle onward, venetoclax was also given, with weekly dose escalations to a target dose of 400 mg once daily. The combination was given for 24 cycles, with treatment continuation offered to patients who were still positive for minimal residual disease.
The median patient age was 65 years, with 30% of the population aged 70 years or older. A large majority (92%) had at least one high-risk genetic feature.
Following initiation with three cycles of ibrutinib, most patients had partial responses, the investigators wrote; however, with the addition of venetoclax, responses improved over time. Of all 80 patients, 59 (74%) had a best response of complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery.
After six cycles, 51 out of 70 patients (73%) achieved this marker. After 12 cycles, 29 of 33 patients (88%) had this response, with 61% of the same group demonstrating undetectable minimal residual disease in bone marrow.
After 18 cycles, 25 of 26 patients (96%) had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery, 18 of which (69%) were negative for minimal residual disease. Three patients completed 24 cycles of combined therapy, all of whom achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery and undetectable minimal residual disease.
Focusing on patients aged 65 years or older, 74% had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery after six cycles of therapy and nearly half (44%) had undetectable minimal residual disease. After 12 cycles, these rates increased to 94% and 76%, respectively. Responses were also seen across genetically high-risk subgroups.
One patient died from a cryptococcal infection of the central nervous system; this was deemed unrelated to treatment, as symptoms began prior to initiation of treatment and only one dose of ibrutinib was given.
The estimated 1-year progression-free survival rate was 98% and the estimated overall survival rate was 99%. At the time of publication, no patients had disease progression.
Among all patients, 60% experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, the most common being neutropenia (48%).
Almost half of the patient population (44%) required dose reductions of ibrutinib, most commonly because of atrial fibrillation, and 24% required dose reductions of venetoclax, most often because of neutropenia.
“Our data showed that combination therapy with ibrutinib and venetoclax was effective in patients with CLL, with no new toxic effects from the combination that were not reported previously for the individual agents,” the investigators wrote, adding that the efficacy findings were also “substantially better” than what has been reported with monotherapy for each of the agents in patients with CLL.
The study was funded by AbbVie, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Moon Shot program, the Andrew Sabin Family Foundation, and the CLL Global Research Foundation. The investigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Incyte, Celgene, and other companies.
SOURCE: Jain N et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2095-103.
In addition to noting the “impressive” results from combining venetoclax and ibrutinib as frontline CLL therapy, Adrian Wiestner, MD, PhD, highlighted the lack of a Kaplan-Meier curve in the paper published by Jain et al. in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Here, assessment of minimal residual disease has replaced the progression-free survival curve of old, indicating a possible shift in focus away from traditional clinical trial endpoints and toward even more stringent measures of clinical efficacy that may be central to regulatory decisions,” Dr. Wiestner wrote.
Dr. Wiestner of the National Institutes of Health made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1904362). He reported grants from with Merck, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie company), and Acerta Pharma.
In addition to noting the “impressive” results from combining venetoclax and ibrutinib as frontline CLL therapy, Adrian Wiestner, MD, PhD, highlighted the lack of a Kaplan-Meier curve in the paper published by Jain et al. in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Here, assessment of minimal residual disease has replaced the progression-free survival curve of old, indicating a possible shift in focus away from traditional clinical trial endpoints and toward even more stringent measures of clinical efficacy that may be central to regulatory decisions,” Dr. Wiestner wrote.
Dr. Wiestner of the National Institutes of Health made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1904362). He reported grants from with Merck, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie company), and Acerta Pharma.
In addition to noting the “impressive” results from combining venetoclax and ibrutinib as frontline CLL therapy, Adrian Wiestner, MD, PhD, highlighted the lack of a Kaplan-Meier curve in the paper published by Jain et al. in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Here, assessment of minimal residual disease has replaced the progression-free survival curve of old, indicating a possible shift in focus away from traditional clinical trial endpoints and toward even more stringent measures of clinical efficacy that may be central to regulatory decisions,” Dr. Wiestner wrote.
Dr. Wiestner of the National Institutes of Health made his remarks in an accompanying editorial (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 29. doi: 10.1056/NEJMe1904362). He reported grants from with Merck, Pharmacyclics (an AbbVie company), and Acerta Pharma.
A combination of venetoclax and ibrutinib may be a safe and effective treatment option for previously untreated elderly and high-risk patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to investigators of a phase 2 trial of the combination.
About 88% of patients achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery after 12 cycles of treatment, reported lead author Nitin Jain, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues.
There were no new safety signals for the combination of ibrutinib, an irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 protein inhibitor, the investigators noted.
“This combination was reported to be safe and active in patients with mantle cell lymphoma,” they wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine. “Given the clinically complementary activity, preclinical synergism, and nonoverlapping toxic effects, we examined the safety and efficacy of combined ibrutinib and venetoclax treatment in previously untreated patients with CLL.”
In particular, the investigators recruited older patients, as this is a common population that can be challenging to treat. “Because CLL typically occurs in older adults, the majority of patients who need treatment are older than 65 years of age,” the investigators wrote. “This group of patients often has unacceptable side effects and has a lower rate of complete remission and undetectable minimal residual disease with chemoimmunotherapy than younger patients.”
The open-label, phase 2 trial enrolled 80 elderly and high-risk patients with previously untreated CLL. Eligibility required an age of at least 65 years or presence of at least one high-risk genetic feature; namely, mutated TP53, unmutated IgVH, or chromosome 11q deletion.
In order to reduce the risk of tumor lysis syndrome, ibrutinib (420 mg once daily) was given as monotherapy for three 28-day cycles. From the fourth cycle onward, venetoclax was also given, with weekly dose escalations to a target dose of 400 mg once daily. The combination was given for 24 cycles, with treatment continuation offered to patients who were still positive for minimal residual disease.
The median patient age was 65 years, with 30% of the population aged 70 years or older. A large majority (92%) had at least one high-risk genetic feature.
Following initiation with three cycles of ibrutinib, most patients had partial responses, the investigators wrote; however, with the addition of venetoclax, responses improved over time. Of all 80 patients, 59 (74%) had a best response of complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery.
After six cycles, 51 out of 70 patients (73%) achieved this marker. After 12 cycles, 29 of 33 patients (88%) had this response, with 61% of the same group demonstrating undetectable minimal residual disease in bone marrow.
After 18 cycles, 25 of 26 patients (96%) had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery, 18 of which (69%) were negative for minimal residual disease. Three patients completed 24 cycles of combined therapy, all of whom achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery and undetectable minimal residual disease.
Focusing on patients aged 65 years or older, 74% had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery after six cycles of therapy and nearly half (44%) had undetectable minimal residual disease. After 12 cycles, these rates increased to 94% and 76%, respectively. Responses were also seen across genetically high-risk subgroups.
One patient died from a cryptococcal infection of the central nervous system; this was deemed unrelated to treatment, as symptoms began prior to initiation of treatment and only one dose of ibrutinib was given.
The estimated 1-year progression-free survival rate was 98% and the estimated overall survival rate was 99%. At the time of publication, no patients had disease progression.
Among all patients, 60% experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, the most common being neutropenia (48%).
Almost half of the patient population (44%) required dose reductions of ibrutinib, most commonly because of atrial fibrillation, and 24% required dose reductions of venetoclax, most often because of neutropenia.
“Our data showed that combination therapy with ibrutinib and venetoclax was effective in patients with CLL, with no new toxic effects from the combination that were not reported previously for the individual agents,” the investigators wrote, adding that the efficacy findings were also “substantially better” than what has been reported with monotherapy for each of the agents in patients with CLL.
The study was funded by AbbVie, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Moon Shot program, the Andrew Sabin Family Foundation, and the CLL Global Research Foundation. The investigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Incyte, Celgene, and other companies.
SOURCE: Jain N et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2095-103.
A combination of venetoclax and ibrutinib may be a safe and effective treatment option for previously untreated elderly and high-risk patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), according to investigators of a phase 2 trial of the combination.
About 88% of patients achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery after 12 cycles of treatment, reported lead author Nitin Jain, MD, of the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston, and colleagues.
There were no new safety signals for the combination of ibrutinib, an irreversible inhibitor of Bruton’s tyrosine kinase, and venetoclax, a B-cell lymphoma 2 protein inhibitor, the investigators noted.
“This combination was reported to be safe and active in patients with mantle cell lymphoma,” they wrote in the New England Journal of Medicine. “Given the clinically complementary activity, preclinical synergism, and nonoverlapping toxic effects, we examined the safety and efficacy of combined ibrutinib and venetoclax treatment in previously untreated patients with CLL.”
In particular, the investigators recruited older patients, as this is a common population that can be challenging to treat. “Because CLL typically occurs in older adults, the majority of patients who need treatment are older than 65 years of age,” the investigators wrote. “This group of patients often has unacceptable side effects and has a lower rate of complete remission and undetectable minimal residual disease with chemoimmunotherapy than younger patients.”
The open-label, phase 2 trial enrolled 80 elderly and high-risk patients with previously untreated CLL. Eligibility required an age of at least 65 years or presence of at least one high-risk genetic feature; namely, mutated TP53, unmutated IgVH, or chromosome 11q deletion.
In order to reduce the risk of tumor lysis syndrome, ibrutinib (420 mg once daily) was given as monotherapy for three 28-day cycles. From the fourth cycle onward, venetoclax was also given, with weekly dose escalations to a target dose of 400 mg once daily. The combination was given for 24 cycles, with treatment continuation offered to patients who were still positive for minimal residual disease.
The median patient age was 65 years, with 30% of the population aged 70 years or older. A large majority (92%) had at least one high-risk genetic feature.
Following initiation with three cycles of ibrutinib, most patients had partial responses, the investigators wrote; however, with the addition of venetoclax, responses improved over time. Of all 80 patients, 59 (74%) had a best response of complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery.
After six cycles, 51 out of 70 patients (73%) achieved this marker. After 12 cycles, 29 of 33 patients (88%) had this response, with 61% of the same group demonstrating undetectable minimal residual disease in bone marrow.
After 18 cycles, 25 of 26 patients (96%) had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery, 18 of which (69%) were negative for minimal residual disease. Three patients completed 24 cycles of combined therapy, all of whom achieved complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery and undetectable minimal residual disease.
Focusing on patients aged 65 years or older, 74% had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery after six cycles of therapy and nearly half (44%) had undetectable minimal residual disease. After 12 cycles, these rates increased to 94% and 76%, respectively. Responses were also seen across genetically high-risk subgroups.
One patient died from a cryptococcal infection of the central nervous system; this was deemed unrelated to treatment, as symptoms began prior to initiation of treatment and only one dose of ibrutinib was given.
The estimated 1-year progression-free survival rate was 98% and the estimated overall survival rate was 99%. At the time of publication, no patients had disease progression.
Among all patients, 60% experienced grade 3 or higher adverse events, the most common being neutropenia (48%).
Almost half of the patient population (44%) required dose reductions of ibrutinib, most commonly because of atrial fibrillation, and 24% required dose reductions of venetoclax, most often because of neutropenia.
“Our data showed that combination therapy with ibrutinib and venetoclax was effective in patients with CLL, with no new toxic effects from the combination that were not reported previously for the individual agents,” the investigators wrote, adding that the efficacy findings were also “substantially better” than what has been reported with monotherapy for each of the agents in patients with CLL.
The study was funded by AbbVie, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Moon Shot program, the Andrew Sabin Family Foundation, and the CLL Global Research Foundation. The investigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Incyte, Celgene, and other companies.
SOURCE: Jain N et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2095-103.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: After 12 cycles of treatment with venetoclax and ibrutinib, 88% of patients had complete remission or complete remission with incomplete count recovery.
Study details: A randomized, open-label, phase 2 study involving 80 elderly and high-risk patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia.
Disclosures: The study was funded by AbbVie, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Moon Shot program, the Andrew Sabin Family Foundation, and the CLL Global Research Foundation. The investigators reported relationships with AbbVie, Incyte, Celgene, and other companies.
Source: Jain N et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;380:2095-103.
Genetic analysis identifies prognostic markers in CLL
A genetic analysis of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with frontline, rituximab-based regimens found that deletion 11q22 and unmutated IgVH status may predict worse prognosis.
Michaela Spunarova, MD, of Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, and colleagues conducted a genetic analysis of 177 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The results of the analysis were published in Leukemia Research.
The study focused on patients with CLL with an intact TP53 gene, looking at recurrently muted genes in CLL, genomic aberrations by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and IgVH status, according to the researchers.
The team analyzed the effects of these mutations on progression-free survival (PFS) following frontline treatment with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) or fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Spunarova and colleagues used next-generation sequencing to analyze DNA from the patient samples. Data on 11q22, 13q14, trisomy 12, and IgVH mutation status were also considered in the analyses of PFS.
After analysis, the researchers validated that unmutated IgVH status is an indicator of poor prognosis in CLL patients with wild-type TP53 treated with frontline FCR.
When looking at both BR and FCR regimens, a single 11q22 deletion, lacking an ATM mutation on the other allele, resulted in the shortest PFS, at a median of just 16 months.
“Based on our data, special attention should be given to CLL patients harboring a sole 11q22 deletion, with no ATM mutation on the other allele, who manifest particularly short PFS,” they noted.
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the small sample size. As a result, the results should be interpreted in a careful manner.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Spunarova M et al. Leuk Res. 2019 Jun;81:75-81.
A genetic analysis of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with frontline, rituximab-based regimens found that deletion 11q22 and unmutated IgVH status may predict worse prognosis.
Michaela Spunarova, MD, of Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, and colleagues conducted a genetic analysis of 177 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The results of the analysis were published in Leukemia Research.
The study focused on patients with CLL with an intact TP53 gene, looking at recurrently muted genes in CLL, genomic aberrations by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and IgVH status, according to the researchers.
The team analyzed the effects of these mutations on progression-free survival (PFS) following frontline treatment with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) or fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Spunarova and colleagues used next-generation sequencing to analyze DNA from the patient samples. Data on 11q22, 13q14, trisomy 12, and IgVH mutation status were also considered in the analyses of PFS.
After analysis, the researchers validated that unmutated IgVH status is an indicator of poor prognosis in CLL patients with wild-type TP53 treated with frontline FCR.
When looking at both BR and FCR regimens, a single 11q22 deletion, lacking an ATM mutation on the other allele, resulted in the shortest PFS, at a median of just 16 months.
“Based on our data, special attention should be given to CLL patients harboring a sole 11q22 deletion, with no ATM mutation on the other allele, who manifest particularly short PFS,” they noted.
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the small sample size. As a result, the results should be interpreted in a careful manner.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Spunarova M et al. Leuk Res. 2019 Jun;81:75-81.
A genetic analysis of patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia treated with frontline, rituximab-based regimens found that deletion 11q22 and unmutated IgVH status may predict worse prognosis.
Michaela Spunarova, MD, of Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, and colleagues conducted a genetic analysis of 177 patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL). The results of the analysis were published in Leukemia Research.
The study focused on patients with CLL with an intact TP53 gene, looking at recurrently muted genes in CLL, genomic aberrations by fluorescence in situ hybridization, and IgVH status, according to the researchers.
The team analyzed the effects of these mutations on progression-free survival (PFS) following frontline treatment with bendamustine and rituximab (BR) or fludarabine, cyclophosphamide, and rituximab (FCR) therapeutic regimens.
Dr. Spunarova and colleagues used next-generation sequencing to analyze DNA from the patient samples. Data on 11q22, 13q14, trisomy 12, and IgVH mutation status were also considered in the analyses of PFS.
After analysis, the researchers validated that unmutated IgVH status is an indicator of poor prognosis in CLL patients with wild-type TP53 treated with frontline FCR.
When looking at both BR and FCR regimens, a single 11q22 deletion, lacking an ATM mutation on the other allele, resulted in the shortest PFS, at a median of just 16 months.
“Based on our data, special attention should be given to CLL patients harboring a sole 11q22 deletion, with no ATM mutation on the other allele, who manifest particularly short PFS,” they noted.
The researchers acknowledged a key limitation of the study was the small sample size. As a result, the results should be interpreted in a careful manner.
The study was funded by the Ministry of Health of the Czech Republic. The authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Spunarova M et al. Leuk Res. 2019 Jun;81:75-81.
FROM LEUKEMIA RESEARCH
FDA approves venetoclax/obinutuzumab combo for CLL
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the combination of venetoclax (Venclexta) plus obinutuzumab (Gazyva) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The approval provides a chemotherapy-free, fixed duration treatment. The FDA based the approval on the results of the phase 3 CLL14 trial, which will be presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers randomized 432 patients to either a 12-month duration of venetoclax with a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab or to a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil and another 6-month duration of chlorambucil.
The newly approved combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death (progression-free survival as assessed by an independent review committee) by 67%, compared with obinutuzumab/chlorambucil (hazard ratio, 0.33; P less than .0001).
Venetoclax/obinutuzumab also had a higher rate of minimal residual disease negativity in bone marrow and peripheral blood, compared to the other combination, according to Genentech.
The most common adverse reactions of any grade reported for venetoclax/obinutuzumab were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, anemia, and upper respiratory tract infection.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the combination of venetoclax (Venclexta) plus obinutuzumab (Gazyva) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The approval provides a chemotherapy-free, fixed duration treatment. The FDA based the approval on the results of the phase 3 CLL14 trial, which will be presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers randomized 432 patients to either a 12-month duration of venetoclax with a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab or to a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil and another 6-month duration of chlorambucil.
The newly approved combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death (progression-free survival as assessed by an independent review committee) by 67%, compared with obinutuzumab/chlorambucil (hazard ratio, 0.33; P less than .0001).
Venetoclax/obinutuzumab also had a higher rate of minimal residual disease negativity in bone marrow and peripheral blood, compared to the other combination, according to Genentech.
The most common adverse reactions of any grade reported for venetoclax/obinutuzumab were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, anemia, and upper respiratory tract infection.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the combination of venetoclax (Venclexta) plus obinutuzumab (Gazyva) for patients with previously untreated chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) or small lymphocytic lymphoma.
The approval provides a chemotherapy-free, fixed duration treatment. The FDA based the approval on the results of the phase 3 CLL14 trial, which will be presented at the 2019 annual meeting of the American Society of Clinical Oncology.
Researchers randomized 432 patients to either a 12-month duration of venetoclax with a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab or to a 6-month duration of obinutuzumab plus chlorambucil and another 6-month duration of chlorambucil.
The newly approved combination reduced the risk of disease progression or death (progression-free survival as assessed by an independent review committee) by 67%, compared with obinutuzumab/chlorambucil (hazard ratio, 0.33; P less than .0001).
Venetoclax/obinutuzumab also had a higher rate of minimal residual disease negativity in bone marrow and peripheral blood, compared to the other combination, according to Genentech.
The most common adverse reactions of any grade reported for venetoclax/obinutuzumab were neutropenia, diarrhea, fatigue, nausea, anemia, and upper respiratory tract infection.