User login
Asthma Across a Woman’s Lifespan
1. Chowdhury NU et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2021;30(162):210067. doi:10.1183/16000617.0067-2021
2. Perikleous EP et al. J Pers Med. 2022;12(6):999. doi:10.3390/jpm12060999
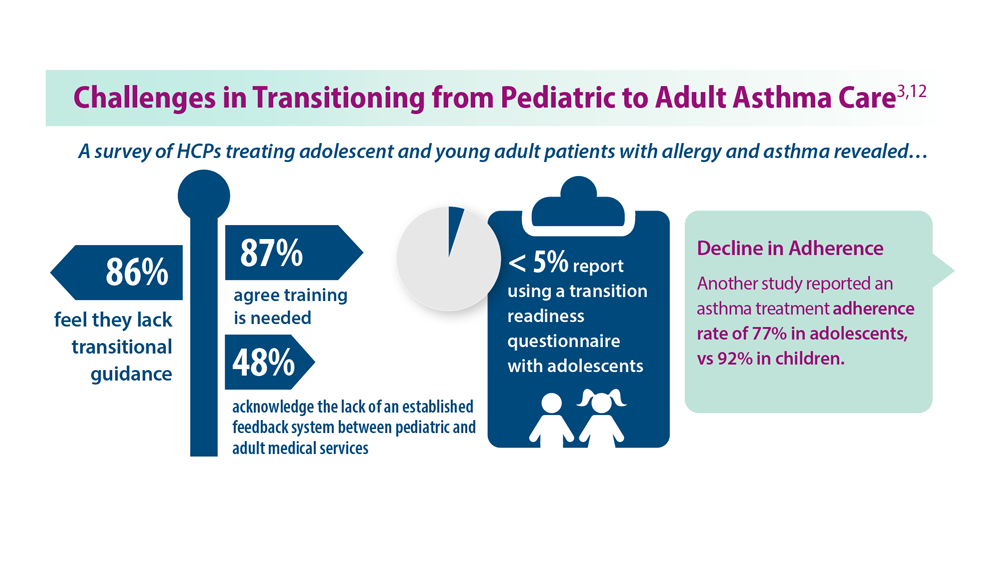
3. Khaleva E et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2020;10:40. doi:10.1186/s13601-020-00340-z
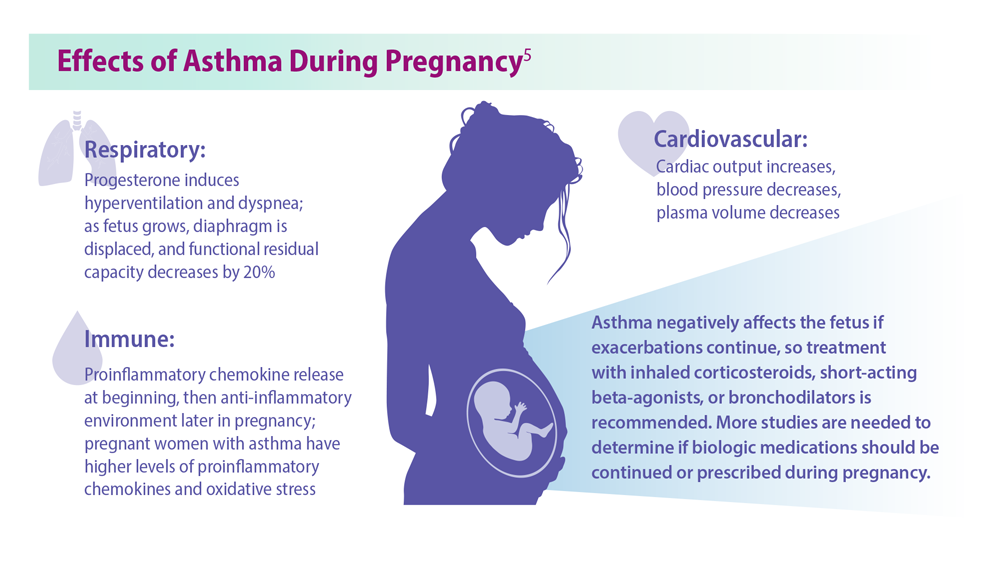
4. Robijn AL et al. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2019;25(1):11-17. doi:10.1097/MCP.0000000000000538
5. Bravo-Solarte DC et al. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2023;44(1):24-34. doi:10.2500/aap.2023.44.220077
6. Wang G et al. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014;27(9):934-942. doi:10.3109/14767058.2013.847080
7. Hough KP et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:191. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00191
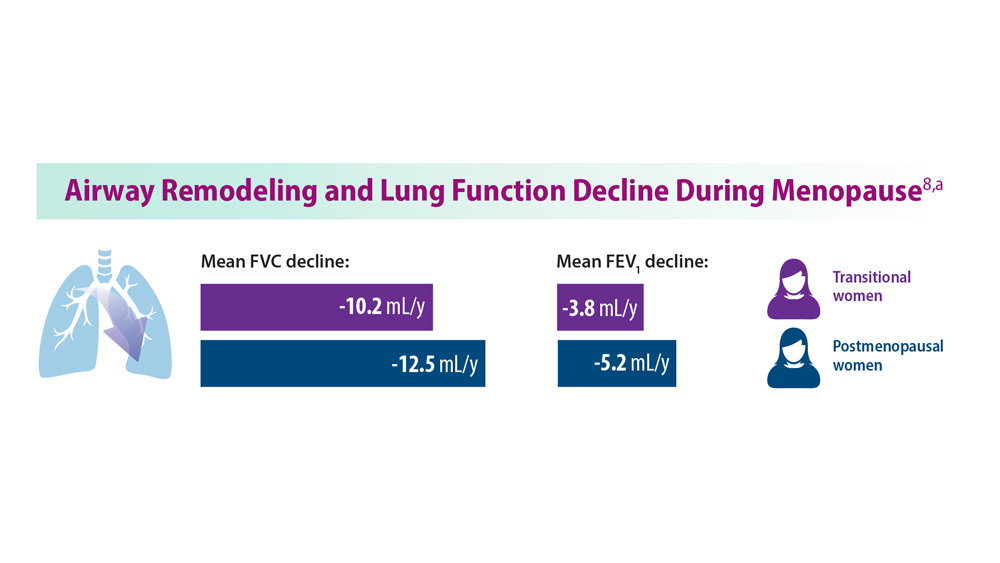
8. Triebner K et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(8):1058-1065. doi:10.1164/rccm.201605-0968OC
9. Bacharier LB, Jackson DJ. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023;151(3):581-589. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.002
10. An amazing journey: how young lungs develop. American Lung Association. Published May 11, 2018. Accessed June 28, 2023. https://www.lung.org/blog/how-young-lungs-develop
11. Strunk RC et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118(5):1040-1047. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2006.07.053
12. Kaplan A, Price D. J Asthma Allergy. 2020;13:39-49. doi:10.2147/JAA.S233268
1. Chowdhury NU et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2021;30(162):210067. doi:10.1183/16000617.0067-2021
2. Perikleous EP et al. J Pers Med. 2022;12(6):999. doi:10.3390/jpm12060999
3. Khaleva E et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2020;10:40. doi:10.1186/s13601-020-00340-z
4. Robijn AL et al. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2019;25(1):11-17. doi:10.1097/MCP.0000000000000538
5. Bravo-Solarte DC et al. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2023;44(1):24-34. doi:10.2500/aap.2023.44.220077
6. Wang G et al. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014;27(9):934-942. doi:10.3109/14767058.2013.847080
7. Hough KP et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:191. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00191
8. Triebner K et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(8):1058-1065. doi:10.1164/rccm.201605-0968OC
9. Bacharier LB, Jackson DJ. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023;151(3):581-589. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.002
10. An amazing journey: how young lungs develop. American Lung Association. Published May 11, 2018. Accessed June 28, 2023. https://www.lung.org/blog/how-young-lungs-develop
11. Strunk RC et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118(5):1040-1047. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2006.07.053
12. Kaplan A, Price D. J Asthma Allergy. 2020;13:39-49. doi:10.2147/JAA.S233268
1. Chowdhury NU et al. Eur Respir Rev. 2021;30(162):210067. doi:10.1183/16000617.0067-2021
2. Perikleous EP et al. J Pers Med. 2022;12(6):999. doi:10.3390/jpm12060999
3. Khaleva E et al. Clin Transl Allergy. 2020;10:40. doi:10.1186/s13601-020-00340-z
4. Robijn AL et al. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2019;25(1):11-17. doi:10.1097/MCP.0000000000000538
5. Bravo-Solarte DC et al. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2023;44(1):24-34. doi:10.2500/aap.2023.44.220077
6. Wang G et al. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014;27(9):934-942. doi:10.3109/14767058.2013.847080
7. Hough KP et al. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:191. doi:10.3389/fmed.2020.00191
8. Triebner K et al. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2017;195(8):1058-1065. doi:10.1164/rccm.201605-0968OC
9. Bacharier LB, Jackson DJ. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023;151(3):581-589. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2023.01.002
10. An amazing journey: how young lungs develop. American Lung Association. Published May 11, 2018. Accessed June 28, 2023. https://www.lung.org/blog/how-young-lungs-develop
11. Strunk RC et al. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2006;118(5):1040-1047. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2006.07.053
12. Kaplan A, Price D. J Asthma Allergy. 2020;13:39-49. doi:10.2147/JAA.S233268
It’s back to school for asthma, too
The years go by, and nothing much changes: The first 2 weeks of the new school year have brought with them a rise in emergency department (ED) admissions for asthma in patients under age 15 years. A more relaxed approach to maintenance therapy for the condition over the summer holidays, exposure to allergens at school, and the surge in viral respiratory infections that accompanies the return to group settings explain this trend, which can be foreseen.
According to Public Health France, which has just relaunched its epidemiological monitoring, these cases reach their peak around 2 weeks after the start of the new term.
In its first weekly review on Aug. 22, 2023, the authority reported a slight uptick in cases in its Indian Ocean overseas departments, and the calm before the storm in mainland France.
Last year, between weeks 35 and 36, the increases were 82% for SOS Médecins (the French home doctor visit service), 169% for EDs, and 33% for hospital admissions.
These data are similar to the figures obtained over the past 3 years. The authors of this monitoring, using the SurSaUD system, France’s program for monitoring emergency cases and deaths, attribute these increases to the surge in viral respiratory infections seen after the return to group settings after the school summer holidays.
Indeed, viral-induced exacerbations are mostly caused by rhinoviruses, which circulate throughout the year, but more so during the autumn and winter months. These are probably the main culprits behind the epidemics seen once schools have reopened. Yet relaxation of maintenance asthma treatment (inhaled corticosteroids alone or in combination with long-acting bronchodilators) during the summer holidays also plays a significant role in this yearly recurrence.
Compliance ends with school
Flore Amat, MD, PhD, pediatric respiratory and allergy specialist and coordinating doctor at the Zephyr asthma clinic (Robert-Debré Hospital, Paris Public Hospitals) acknowledged, “The summer holidays are often a time when compliance with maintenance therapy is relaxed.” Aware of this fact, doctors prefer to strike a deal with their young patients. “For some of our young and teenage asthma patients, we support their relaxed approach to medication during the summer holidays,” she admitted. “In July and August, there are fewer viruses circulating, and the weather is often dry, which limits the risk of an asthma attack, meaning we can ease off the maintenance therapy, or even stop taking it altogether. We tell parents and children to start taking them again 2 weeks before school starts; 2 weeks being the minimum time needed for inhaled corticosteroids to start taking effect again.” Unsurprisingly, some forget to do so or simply don’t.
Two other things contribute to the rise in asthma attacks in children in early September. The first relates to exposure to allergens, especially dust mites. “Ninety percent of asthmatic children are allergic,” said Frédéric le Guillou, MD, respiratory medicine specialist and chair of the French Society for Respiratory Health, an organization aimed at patients and health care professionals. “Don’t forget that asthma is the leading chronic condition in childhood, with a prevalence estimated at between 8% and 10% of children and adolescents. So, we’re talking about considerable numbers of children being affected.”
Although dust mites are a year-round problem, their peak period of reproduction mainly occurs during the wetter months (March to April and September to November). This means that there is a risk of relapse in asthmatic children who are allergic to dust mites when school starts again after the summer holidays. “In such children, any signs of unmanageable allergic rhinitis should be examined,” said Dr. Amat, “these signs being permanent nasal congestion, runny nose, et cetera.”
Finally, we can also add “the stress and anxiety generated by the school setting and settling back into a routine” to the list of likely explanations for this peak in asthma attacks, Dr. Amat concluded.
Check-up time
Children and teenagers with asthma should have a check-up with their respiratory medicine specialists at the start of the new term to confirm that their condition is under control and to determine whether any changes need to be made to their maintenance therapy. “Looking back at previous Septembers and winters is informative in adapting a patient’s treatment plan,” said Dr. Amat. “If maintenance therapy has been stopped during the summer, take the opportunity to represcribe it or modify it if, for example, the dose of inhaled corticosteroids has not been enough to prevent attacks in years gone by. Adequate control of symptoms over the summer months suggests that treatment should be bolstered with preventive therapy to cope with the autumn and winter months. Finally, the factors aggravating poor management of asthma should be dealt with, such as intranasal antihistamines and corticosteroids in allergic rhinitis, specific immunotherapy in patients with controlled asthma but with significant allergy symptoms.”
The start-of-term visit to the doctor’s office is also the perfect opportunity to carry out respiratory function testing (RFT), if this has not been done for over a year in patients whose asthma is well managed. “RFT is indicated in the 3 months following any changes to maintenance therapy, every 3 to 6 months in patients with poorly controlled asthma, and after stopping maintenance therapy or when considering stopping treatment permanently or for an extended period of time,” noted Dr. Amat.
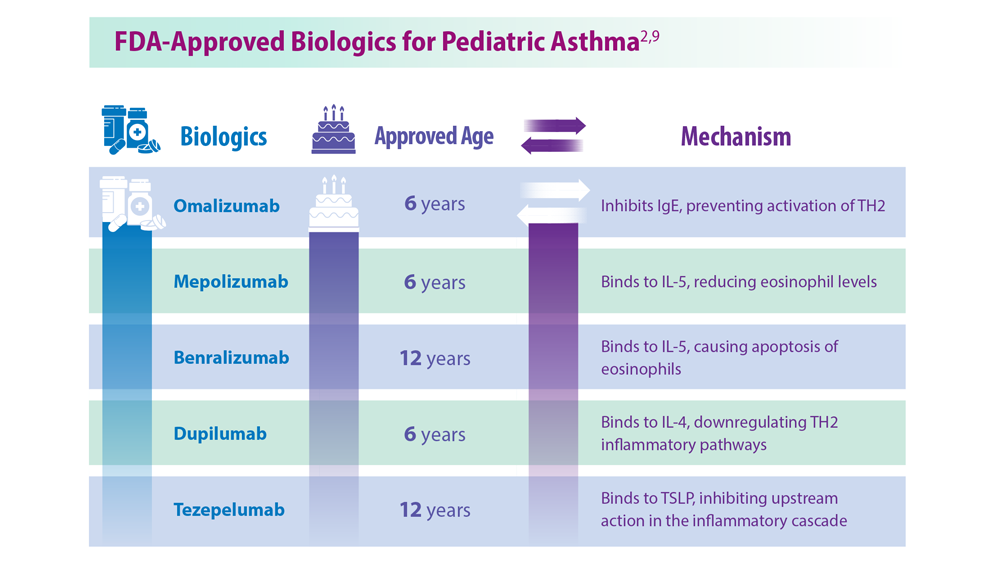
The distinction between difficult asthma (suboptimal treatment plan, poor compliance, persisting allergen exposure, etc.) and severe asthma may be made during this back-to-school asthma review. In specialist clinics, children with severe asthma (not controlled by combined treatment with maximum-dose corticosteroids and maximum-dose bronchodilators) may, like adults, benefit from some biotherapies.
Commentary from Madiha Ellaffi, MD, respiratory medicine specialist
When children experience relatively calm summers without seasonal summer allergies to certain pollens or molds (such as Alternaria, some grasses, etc.) that require maintenance therapy to be continued, we know full well that compliance is often left up to the child. What would be better would be striking a “deal” with these young people: Maintenance treatment can be stopped over the summer, providing that their usual dose is quite low or their asthma is considered mild to moderate, but it must be restarted before going back to school in September. An action plan should be discussed in the event of an asthma attack, and treatment bolstered to overcome this hurdle, should it occur, such as double inhaled corticosteroid doses, etc. Indeed, this period is conducive to asthma exacerbations due to stress, the return of students to confined classrooms, pollutants released by the deep cleaning of school buildings that occurs at the start of term (particularly the release of volatile organic compounds that irritate the airways), and the lack of ventilation in classrooms, which is conducive to the spread of viruses that can cause worsening asthma symptoms. I’d also like to remind parents of the importance of detecting early symptoms (such as wheezing, cough, bronchitis, itchy throat and nose, etc.) in warding off asthma attacks or severe symptoms. I insist on basic measures, such as nasal irrigation, treating allergic rhinitis, which can exacerbate asthma, and ensuring good habits at home to prevent dust mites and mold, such as vacuuming, airing houses, etc. It is sensible to assess the risk of asthma attacks at the start of term according to the child’s allergy profile and their previous history, like starting treatment for allergic rhinitis if not already being taken.
This article was translated from Medscape’s French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The years go by, and nothing much changes: The first 2 weeks of the new school year have brought with them a rise in emergency department (ED) admissions for asthma in patients under age 15 years. A more relaxed approach to maintenance therapy for the condition over the summer holidays, exposure to allergens at school, and the surge in viral respiratory infections that accompanies the return to group settings explain this trend, which can be foreseen.
According to Public Health France, which has just relaunched its epidemiological monitoring, these cases reach their peak around 2 weeks after the start of the new term.
In its first weekly review on Aug. 22, 2023, the authority reported a slight uptick in cases in its Indian Ocean overseas departments, and the calm before the storm in mainland France.
Last year, between weeks 35 and 36, the increases were 82% for SOS Médecins (the French home doctor visit service), 169% for EDs, and 33% for hospital admissions.
These data are similar to the figures obtained over the past 3 years. The authors of this monitoring, using the SurSaUD system, France’s program for monitoring emergency cases and deaths, attribute these increases to the surge in viral respiratory infections seen after the return to group settings after the school summer holidays.
Indeed, viral-induced exacerbations are mostly caused by rhinoviruses, which circulate throughout the year, but more so during the autumn and winter months. These are probably the main culprits behind the epidemics seen once schools have reopened. Yet relaxation of maintenance asthma treatment (inhaled corticosteroids alone or in combination with long-acting bronchodilators) during the summer holidays also plays a significant role in this yearly recurrence.
Compliance ends with school
Flore Amat, MD, PhD, pediatric respiratory and allergy specialist and coordinating doctor at the Zephyr asthma clinic (Robert-Debré Hospital, Paris Public Hospitals) acknowledged, “The summer holidays are often a time when compliance with maintenance therapy is relaxed.” Aware of this fact, doctors prefer to strike a deal with their young patients. “For some of our young and teenage asthma patients, we support their relaxed approach to medication during the summer holidays,” she admitted. “In July and August, there are fewer viruses circulating, and the weather is often dry, which limits the risk of an asthma attack, meaning we can ease off the maintenance therapy, or even stop taking it altogether. We tell parents and children to start taking them again 2 weeks before school starts; 2 weeks being the minimum time needed for inhaled corticosteroids to start taking effect again.” Unsurprisingly, some forget to do so or simply don’t.
Two other things contribute to the rise in asthma attacks in children in early September. The first relates to exposure to allergens, especially dust mites. “Ninety percent of asthmatic children are allergic,” said Frédéric le Guillou, MD, respiratory medicine specialist and chair of the French Society for Respiratory Health, an organization aimed at patients and health care professionals. “Don’t forget that asthma is the leading chronic condition in childhood, with a prevalence estimated at between 8% and 10% of children and adolescents. So, we’re talking about considerable numbers of children being affected.”
Although dust mites are a year-round problem, their peak period of reproduction mainly occurs during the wetter months (March to April and September to November). This means that there is a risk of relapse in asthmatic children who are allergic to dust mites when school starts again after the summer holidays. “In such children, any signs of unmanageable allergic rhinitis should be examined,” said Dr. Amat, “these signs being permanent nasal congestion, runny nose, et cetera.”
Finally, we can also add “the stress and anxiety generated by the school setting and settling back into a routine” to the list of likely explanations for this peak in asthma attacks, Dr. Amat concluded.
Check-up time
Children and teenagers with asthma should have a check-up with their respiratory medicine specialists at the start of the new term to confirm that their condition is under control and to determine whether any changes need to be made to their maintenance therapy. “Looking back at previous Septembers and winters is informative in adapting a patient’s treatment plan,” said Dr. Amat. “If maintenance therapy has been stopped during the summer, take the opportunity to represcribe it or modify it if, for example, the dose of inhaled corticosteroids has not been enough to prevent attacks in years gone by. Adequate control of symptoms over the summer months suggests that treatment should be bolstered with preventive therapy to cope with the autumn and winter months. Finally, the factors aggravating poor management of asthma should be dealt with, such as intranasal antihistamines and corticosteroids in allergic rhinitis, specific immunotherapy in patients with controlled asthma but with significant allergy symptoms.”
The start-of-term visit to the doctor’s office is also the perfect opportunity to carry out respiratory function testing (RFT), if this has not been done for over a year in patients whose asthma is well managed. “RFT is indicated in the 3 months following any changes to maintenance therapy, every 3 to 6 months in patients with poorly controlled asthma, and after stopping maintenance therapy or when considering stopping treatment permanently or for an extended period of time,” noted Dr. Amat.
The distinction between difficult asthma (suboptimal treatment plan, poor compliance, persisting allergen exposure, etc.) and severe asthma may be made during this back-to-school asthma review. In specialist clinics, children with severe asthma (not controlled by combined treatment with maximum-dose corticosteroids and maximum-dose bronchodilators) may, like adults, benefit from some biotherapies.
Commentary from Madiha Ellaffi, MD, respiratory medicine specialist
When children experience relatively calm summers without seasonal summer allergies to certain pollens or molds (such as Alternaria, some grasses, etc.) that require maintenance therapy to be continued, we know full well that compliance is often left up to the child. What would be better would be striking a “deal” with these young people: Maintenance treatment can be stopped over the summer, providing that their usual dose is quite low or their asthma is considered mild to moderate, but it must be restarted before going back to school in September. An action plan should be discussed in the event of an asthma attack, and treatment bolstered to overcome this hurdle, should it occur, such as double inhaled corticosteroid doses, etc. Indeed, this period is conducive to asthma exacerbations due to stress, the return of students to confined classrooms, pollutants released by the deep cleaning of school buildings that occurs at the start of term (particularly the release of volatile organic compounds that irritate the airways), and the lack of ventilation in classrooms, which is conducive to the spread of viruses that can cause worsening asthma symptoms. I’d also like to remind parents of the importance of detecting early symptoms (such as wheezing, cough, bronchitis, itchy throat and nose, etc.) in warding off asthma attacks or severe symptoms. I insist on basic measures, such as nasal irrigation, treating allergic rhinitis, which can exacerbate asthma, and ensuring good habits at home to prevent dust mites and mold, such as vacuuming, airing houses, etc. It is sensible to assess the risk of asthma attacks at the start of term according to the child’s allergy profile and their previous history, like starting treatment for allergic rhinitis if not already being taken.
This article was translated from Medscape’s French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The years go by, and nothing much changes: The first 2 weeks of the new school year have brought with them a rise in emergency department (ED) admissions for asthma in patients under age 15 years. A more relaxed approach to maintenance therapy for the condition over the summer holidays, exposure to allergens at school, and the surge in viral respiratory infections that accompanies the return to group settings explain this trend, which can be foreseen.
According to Public Health France, which has just relaunched its epidemiological monitoring, these cases reach their peak around 2 weeks after the start of the new term.
In its first weekly review on Aug. 22, 2023, the authority reported a slight uptick in cases in its Indian Ocean overseas departments, and the calm before the storm in mainland France.
Last year, between weeks 35 and 36, the increases were 82% for SOS Médecins (the French home doctor visit service), 169% for EDs, and 33% for hospital admissions.
These data are similar to the figures obtained over the past 3 years. The authors of this monitoring, using the SurSaUD system, France’s program for monitoring emergency cases and deaths, attribute these increases to the surge in viral respiratory infections seen after the return to group settings after the school summer holidays.
Indeed, viral-induced exacerbations are mostly caused by rhinoviruses, which circulate throughout the year, but more so during the autumn and winter months. These are probably the main culprits behind the epidemics seen once schools have reopened. Yet relaxation of maintenance asthma treatment (inhaled corticosteroids alone or in combination with long-acting bronchodilators) during the summer holidays also plays a significant role in this yearly recurrence.
Compliance ends with school
Flore Amat, MD, PhD, pediatric respiratory and allergy specialist and coordinating doctor at the Zephyr asthma clinic (Robert-Debré Hospital, Paris Public Hospitals) acknowledged, “The summer holidays are often a time when compliance with maintenance therapy is relaxed.” Aware of this fact, doctors prefer to strike a deal with their young patients. “For some of our young and teenage asthma patients, we support their relaxed approach to medication during the summer holidays,” she admitted. “In July and August, there are fewer viruses circulating, and the weather is often dry, which limits the risk of an asthma attack, meaning we can ease off the maintenance therapy, or even stop taking it altogether. We tell parents and children to start taking them again 2 weeks before school starts; 2 weeks being the minimum time needed for inhaled corticosteroids to start taking effect again.” Unsurprisingly, some forget to do so or simply don’t.
Two other things contribute to the rise in asthma attacks in children in early September. The first relates to exposure to allergens, especially dust mites. “Ninety percent of asthmatic children are allergic,” said Frédéric le Guillou, MD, respiratory medicine specialist and chair of the French Society for Respiratory Health, an organization aimed at patients and health care professionals. “Don’t forget that asthma is the leading chronic condition in childhood, with a prevalence estimated at between 8% and 10% of children and adolescents. So, we’re talking about considerable numbers of children being affected.”
Although dust mites are a year-round problem, their peak period of reproduction mainly occurs during the wetter months (March to April and September to November). This means that there is a risk of relapse in asthmatic children who are allergic to dust mites when school starts again after the summer holidays. “In such children, any signs of unmanageable allergic rhinitis should be examined,” said Dr. Amat, “these signs being permanent nasal congestion, runny nose, et cetera.”
Finally, we can also add “the stress and anxiety generated by the school setting and settling back into a routine” to the list of likely explanations for this peak in asthma attacks, Dr. Amat concluded.
Check-up time
Children and teenagers with asthma should have a check-up with their respiratory medicine specialists at the start of the new term to confirm that their condition is under control and to determine whether any changes need to be made to their maintenance therapy. “Looking back at previous Septembers and winters is informative in adapting a patient’s treatment plan,” said Dr. Amat. “If maintenance therapy has been stopped during the summer, take the opportunity to represcribe it or modify it if, for example, the dose of inhaled corticosteroids has not been enough to prevent attacks in years gone by. Adequate control of symptoms over the summer months suggests that treatment should be bolstered with preventive therapy to cope with the autumn and winter months. Finally, the factors aggravating poor management of asthma should be dealt with, such as intranasal antihistamines and corticosteroids in allergic rhinitis, specific immunotherapy in patients with controlled asthma but with significant allergy symptoms.”
The start-of-term visit to the doctor’s office is also the perfect opportunity to carry out respiratory function testing (RFT), if this has not been done for over a year in patients whose asthma is well managed. “RFT is indicated in the 3 months following any changes to maintenance therapy, every 3 to 6 months in patients with poorly controlled asthma, and after stopping maintenance therapy or when considering stopping treatment permanently or for an extended period of time,” noted Dr. Amat.
The distinction between difficult asthma (suboptimal treatment plan, poor compliance, persisting allergen exposure, etc.) and severe asthma may be made during this back-to-school asthma review. In specialist clinics, children with severe asthma (not controlled by combined treatment with maximum-dose corticosteroids and maximum-dose bronchodilators) may, like adults, benefit from some biotherapies.
Commentary from Madiha Ellaffi, MD, respiratory medicine specialist
When children experience relatively calm summers without seasonal summer allergies to certain pollens or molds (such as Alternaria, some grasses, etc.) that require maintenance therapy to be continued, we know full well that compliance is often left up to the child. What would be better would be striking a “deal” with these young people: Maintenance treatment can be stopped over the summer, providing that their usual dose is quite low or their asthma is considered mild to moderate, but it must be restarted before going back to school in September. An action plan should be discussed in the event of an asthma attack, and treatment bolstered to overcome this hurdle, should it occur, such as double inhaled corticosteroid doses, etc. Indeed, this period is conducive to asthma exacerbations due to stress, the return of students to confined classrooms, pollutants released by the deep cleaning of school buildings that occurs at the start of term (particularly the release of volatile organic compounds that irritate the airways), and the lack of ventilation in classrooms, which is conducive to the spread of viruses that can cause worsening asthma symptoms. I’d also like to remind parents of the importance of detecting early symptoms (such as wheezing, cough, bronchitis, itchy throat and nose, etc.) in warding off asthma attacks or severe symptoms. I insist on basic measures, such as nasal irrigation, treating allergic rhinitis, which can exacerbate asthma, and ensuring good habits at home to prevent dust mites and mold, such as vacuuming, airing houses, etc. It is sensible to assess the risk of asthma attacks at the start of term according to the child’s allergy profile and their previous history, like starting treatment for allergic rhinitis if not already being taken.
This article was translated from Medscape’s French edition. A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Navigating chronic cough in primary care
Chronic cough took center stage at the European Respiratory Society Congress session titled “Conditions We Are Just Dealing With the Tip of the Iceberg in Primary Care: Frequently Mismanaged Conditions in Primary Health Care.”
“When it comes to chronic cough, general practitioners often feel lost,” Miguel Román Rodríguez, family doctor and an associate professor of family medicine at the University of the Balearic Islands, Palma, Mallorca, Spain, and one of the chairs of the session, said to this news organization.
“GPs are central in diagnosing conditions like chronic cough. We bring something that the specialists don’t bring: the knowledge of the context, of the family, the longitudinal history,” echoed the second chair of the session, Hilary Pinnock, family physician and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at the University of Edinburgh.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic cough
Imran Satia, an assistant professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., guided attendees at the Milan, Italy, meeting through a comprehensive exploration of chronic cough. The first issue he addressed was the definition of the condition, emphasizing that it is defined by its duration, with chronic cough typically lasting for more than 8 weeks. Prof. Satia pointed out common associations of chronic cough, including asthma, nasal disease, and reflux disease.
Delving into epidemiology, he cited a meta-analysis indicating a global prevalence of approximately 10% in the adult population, with significant regional variability: from 18.1% in Australia to 2.3% in Africa. Notably, the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging found an overall prevalence of 16% at baseline. “The most common risk factor was smoke, but even in nonsmokers the prevalence reached 10%,” Prof. Satia added, highlighting that it increased with age and changed depending on location. “The most common associated comorbidities were heart failure and hypertension, but also conditions related to chronic pain, mood, and anxiety,” he explained.
Mental health was identified as a crucial factor in chronic cough, with psychological distress and depressive symptoms emerging as risk factors for developing chronic cough over the next 3 years, contributing to a 20% increased risk.
Effective management strategies
Prof. Satia proposed the use of algorithms to aid in the management of patients with chronic cough in primary care. He introduced a Canadian algorithm that offers specific recommendations for both primary and secondary care.
The algorithm’s primary care assessment, step 1, includes a comprehensive evaluation of the cough history (duration, severity, triggers, nature, location); cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, and nasal symptoms; and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and smoking status. Essential diagnostic tests, such as chest radiography (to check for structural disease), complete blood cell count, and spirometry (with or without bronchodilator reversibility), were emphasized. Urgent referral criteria encompassed symptoms like hemoptysis, weight loss, fever, or abnormal chest radiography findings.
“When checking for cough history, GPs should always consider factors like the presence of dry or productive cough, mental health, presence of chronic pain, stroke, and swallowing,” said Prof. Satia, stressing the importance of documenting the impact of chronic cough on quality of life, work life, social life, and family life. “This is something that doctors sometimes do not ask about. They may think that these are not major problems, but acknowledging their importance can help the patient,” he added.
Step 2 of the algorithm focuses on treatment options tailored to specific diagnoses, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prof. Satia urged caution, emphasizing that treatment should only be initiated when evidence of these conditions is present. Additionally, he encouraged early consideration of cough hypersensitivity syndrome when patients exhibit coughing in response to low levels of mechanical stimulation.
Current treatments and future prospects
Prof. Satia presented an overview of existing treatments for chronic cough, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. For instance, speech therapy is a patient-led approach with no side effects but entails challenges related to access, costs, and patient motivation. On the other hand, low-dose morphine offers rapid relief but is associated with issues like nausea, stigma, and constipation.
Looking ahead, Prof. Satia shared the results of COUGH-1 and COUGH-2, pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating the oral, peripherally acting P2X3-receptor antagonist gefapixant. This drug, currently approved in Switzerland and Japan, demonstrated a significant reduction in cough frequency, compared with placebo, with rapid and sustained effects. “The estimated relative reduction for 45 mg was 18.45% in COUGH-1 (12 weeks) and 14.64% in COUGH-2 (24 weeks). Of note, cough reduction is very quick and sustained with gefapixant, but a 40% reduction is observed in the placebo arm,” commented Prof. Satia.
Experts unanimously stressed the importance for specialists and GPs of effective communication in managing chronic cough, involving both patients and their families.
“As GPs, we are crucial to manage the common problems, but we are also crucial to spot the needle in the haystack: this is extremely difficult and challenging, and we need support from our colleagues,” Dr. Pinnock concluded.
Prof. Satia reported funding from Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK; consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Merck MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic cough took center stage at the European Respiratory Society Congress session titled “Conditions We Are Just Dealing With the Tip of the Iceberg in Primary Care: Frequently Mismanaged Conditions in Primary Health Care.”
“When it comes to chronic cough, general practitioners often feel lost,” Miguel Román Rodríguez, family doctor and an associate professor of family medicine at the University of the Balearic Islands, Palma, Mallorca, Spain, and one of the chairs of the session, said to this news organization.
“GPs are central in diagnosing conditions like chronic cough. We bring something that the specialists don’t bring: the knowledge of the context, of the family, the longitudinal history,” echoed the second chair of the session, Hilary Pinnock, family physician and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at the University of Edinburgh.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic cough
Imran Satia, an assistant professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., guided attendees at the Milan, Italy, meeting through a comprehensive exploration of chronic cough. The first issue he addressed was the definition of the condition, emphasizing that it is defined by its duration, with chronic cough typically lasting for more than 8 weeks. Prof. Satia pointed out common associations of chronic cough, including asthma, nasal disease, and reflux disease.
Delving into epidemiology, he cited a meta-analysis indicating a global prevalence of approximately 10% in the adult population, with significant regional variability: from 18.1% in Australia to 2.3% in Africa. Notably, the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging found an overall prevalence of 16% at baseline. “The most common risk factor was smoke, but even in nonsmokers the prevalence reached 10%,” Prof. Satia added, highlighting that it increased with age and changed depending on location. “The most common associated comorbidities were heart failure and hypertension, but also conditions related to chronic pain, mood, and anxiety,” he explained.
Mental health was identified as a crucial factor in chronic cough, with psychological distress and depressive symptoms emerging as risk factors for developing chronic cough over the next 3 years, contributing to a 20% increased risk.
Effective management strategies
Prof. Satia proposed the use of algorithms to aid in the management of patients with chronic cough in primary care. He introduced a Canadian algorithm that offers specific recommendations for both primary and secondary care.
The algorithm’s primary care assessment, step 1, includes a comprehensive evaluation of the cough history (duration, severity, triggers, nature, location); cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, and nasal symptoms; and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and smoking status. Essential diagnostic tests, such as chest radiography (to check for structural disease), complete blood cell count, and spirometry (with or without bronchodilator reversibility), were emphasized. Urgent referral criteria encompassed symptoms like hemoptysis, weight loss, fever, or abnormal chest radiography findings.
“When checking for cough history, GPs should always consider factors like the presence of dry or productive cough, mental health, presence of chronic pain, stroke, and swallowing,” said Prof. Satia, stressing the importance of documenting the impact of chronic cough on quality of life, work life, social life, and family life. “This is something that doctors sometimes do not ask about. They may think that these are not major problems, but acknowledging their importance can help the patient,” he added.
Step 2 of the algorithm focuses on treatment options tailored to specific diagnoses, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prof. Satia urged caution, emphasizing that treatment should only be initiated when evidence of these conditions is present. Additionally, he encouraged early consideration of cough hypersensitivity syndrome when patients exhibit coughing in response to low levels of mechanical stimulation.
Current treatments and future prospects
Prof. Satia presented an overview of existing treatments for chronic cough, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. For instance, speech therapy is a patient-led approach with no side effects but entails challenges related to access, costs, and patient motivation. On the other hand, low-dose morphine offers rapid relief but is associated with issues like nausea, stigma, and constipation.
Looking ahead, Prof. Satia shared the results of COUGH-1 and COUGH-2, pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating the oral, peripherally acting P2X3-receptor antagonist gefapixant. This drug, currently approved in Switzerland and Japan, demonstrated a significant reduction in cough frequency, compared with placebo, with rapid and sustained effects. “The estimated relative reduction for 45 mg was 18.45% in COUGH-1 (12 weeks) and 14.64% in COUGH-2 (24 weeks). Of note, cough reduction is very quick and sustained with gefapixant, but a 40% reduction is observed in the placebo arm,” commented Prof. Satia.
Experts unanimously stressed the importance for specialists and GPs of effective communication in managing chronic cough, involving both patients and their families.
“As GPs, we are crucial to manage the common problems, but we are also crucial to spot the needle in the haystack: this is extremely difficult and challenging, and we need support from our colleagues,” Dr. Pinnock concluded.
Prof. Satia reported funding from Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK; consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Merck MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic cough took center stage at the European Respiratory Society Congress session titled “Conditions We Are Just Dealing With the Tip of the Iceberg in Primary Care: Frequently Mismanaged Conditions in Primary Health Care.”
“When it comes to chronic cough, general practitioners often feel lost,” Miguel Román Rodríguez, family doctor and an associate professor of family medicine at the University of the Balearic Islands, Palma, Mallorca, Spain, and one of the chairs of the session, said to this news organization.
“GPs are central in diagnosing conditions like chronic cough. We bring something that the specialists don’t bring: the knowledge of the context, of the family, the longitudinal history,” echoed the second chair of the session, Hilary Pinnock, family physician and professor of primary care respiratory medicine at the University of Edinburgh.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of chronic cough
Imran Satia, an assistant professor at McMaster University, Hamilton, Ont., guided attendees at the Milan, Italy, meeting through a comprehensive exploration of chronic cough. The first issue he addressed was the definition of the condition, emphasizing that it is defined by its duration, with chronic cough typically lasting for more than 8 weeks. Prof. Satia pointed out common associations of chronic cough, including asthma, nasal disease, and reflux disease.
Delving into epidemiology, he cited a meta-analysis indicating a global prevalence of approximately 10% in the adult population, with significant regional variability: from 18.1% in Australia to 2.3% in Africa. Notably, the Canadian Longitudinal Study on Aging found an overall prevalence of 16% at baseline. “The most common risk factor was smoke, but even in nonsmokers the prevalence reached 10%,” Prof. Satia added, highlighting that it increased with age and changed depending on location. “The most common associated comorbidities were heart failure and hypertension, but also conditions related to chronic pain, mood, and anxiety,” he explained.
Mental health was identified as a crucial factor in chronic cough, with psychological distress and depressive symptoms emerging as risk factors for developing chronic cough over the next 3 years, contributing to a 20% increased risk.
Effective management strategies
Prof. Satia proposed the use of algorithms to aid in the management of patients with chronic cough in primary care. He introduced a Canadian algorithm that offers specific recommendations for both primary and secondary care.
The algorithm’s primary care assessment, step 1, includes a comprehensive evaluation of the cough history (duration, severity, triggers, nature, location); cardiorespiratory, gastrointestinal, and nasal symptoms; and use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors and smoking status. Essential diagnostic tests, such as chest radiography (to check for structural disease), complete blood cell count, and spirometry (with or without bronchodilator reversibility), were emphasized. Urgent referral criteria encompassed symptoms like hemoptysis, weight loss, fever, or abnormal chest radiography findings.
“When checking for cough history, GPs should always consider factors like the presence of dry or productive cough, mental health, presence of chronic pain, stroke, and swallowing,” said Prof. Satia, stressing the importance of documenting the impact of chronic cough on quality of life, work life, social life, and family life. “This is something that doctors sometimes do not ask about. They may think that these are not major problems, but acknowledging their importance can help the patient,” he added.
Step 2 of the algorithm focuses on treatment options tailored to specific diagnoses, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Prof. Satia urged caution, emphasizing that treatment should only be initiated when evidence of these conditions is present. Additionally, he encouraged early consideration of cough hypersensitivity syndrome when patients exhibit coughing in response to low levels of mechanical stimulation.
Current treatments and future prospects
Prof. Satia presented an overview of existing treatments for chronic cough, outlining their respective advantages and disadvantages. For instance, speech therapy is a patient-led approach with no side effects but entails challenges related to access, costs, and patient motivation. On the other hand, low-dose morphine offers rapid relief but is associated with issues like nausea, stigma, and constipation.
Looking ahead, Prof. Satia shared the results of COUGH-1 and COUGH-2, pivotal phase 3 trials evaluating the oral, peripherally acting P2X3-receptor antagonist gefapixant. This drug, currently approved in Switzerland and Japan, demonstrated a significant reduction in cough frequency, compared with placebo, with rapid and sustained effects. “The estimated relative reduction for 45 mg was 18.45% in COUGH-1 (12 weeks) and 14.64% in COUGH-2 (24 weeks). Of note, cough reduction is very quick and sustained with gefapixant, but a 40% reduction is observed in the placebo arm,” commented Prof. Satia.
Experts unanimously stressed the importance for specialists and GPs of effective communication in managing chronic cough, involving both patients and their families.
“As GPs, we are crucial to manage the common problems, but we are also crucial to spot the needle in the haystack: this is extremely difficult and challenging, and we need support from our colleagues,” Dr. Pinnock concluded.
Prof. Satia reported funding from Merck MSD, AstraZeneca, and GSK; consulting fees from Merck MSD, Genentech, and Respiplus; and speaker fees from AstraZeneca, GSK, and Merck MSD.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ERS 2023
The surprising way to fight asthma symptoms
Asthma is a sneaky foe.
a professor of nursing at Columbia University and a spokesperson for the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America.
But that doesn’t mean exercise should be avoided, she said.
Exercise, in fact, is one of the best ways to reduce asthma symptoms. Research over the past 2 decades has shown that physical activity can help improve lung function and boost quality of life for someone with asthma.
As their fitness improves, asthma patients report better sleep, reduced stress, improved weight control, and more days without symptoms. In some cases, they’re able to cut down their medication doses.
Exercise reduces inflammatory cytokines and increases anti-inflammatory cytokines, according to a 2023 review by researchers in the United Kingdom. That could help calm chronic airway inflammation, easing symptoms of asthma.
A few simple guidelines can help patients reap those benefits while staying safe.
Make sure the first steps aren’t the last steps
For someone who’s new to exercise, there’s only one way to begin: Carefully.
The Global Initiative for Asthma recommends twice-weekly cardio and strength training.
“You always start low and slow,” said Spencer Nadolsky, DO, a board-certified obesity and lipid specialist and medical director of Sequence, a comprehensive weight management program.
“Low” means light loads in the weight room. “Slow” means short, easy walks.
Many have been put “through the wringer” when starting out, discouraging them from continuing, Dr. Nadolsky said. “They were too sore, and it felt more like punishment.”
An even bigger concern is triggering an asthma attack. Patients should take steps to lower the risk by carrying their rescue inhalers and keeping up on medications, he added.
“A health care professional should be consulted” before the start of a new activity or ramping up a program, or anytime asthma interferes with a workout, Dr. George said.
Those who exercise outside need to be aware of the air quality, especially at a time when smoke and particulates from a wildfires in Canada can trigger asthma symptoms in people thousands of miles away.
The harder one works, the higher one’s “ventilation” – taking more air into the lungs, and potentially more allergens and pollutants.
Temperature and humidity also become risky at the extremes. Cold, dry air can dehydrate and constrict the airways, making it hard to breathe.
How to choose the best type of exercise
Step 1: Be realistic. People with asthma often have less exercise capacity than those who don’t – understandable when shortness of breath is the default setting.
Second, allow for plenty of time to warm up. A solid warm-up routine – particularly one with a mix of lower- and higher-intensity exercises – may help prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction causing shortness of breath and wheezing.
For example, warming up on a treadmill or exercise bike could be mixed with a few short bursts of faster running or cycling, with a couple of minutes of recovery at a slower pace in between.
That concept can be expanded into a full-blown workout.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a promising option for people with asthma. A 2021 study showed that three 20-minute interval workouts per week significantly improved asthma control.
“The benefit of HIIT is that ventilation is able to recover intermittently,” said Carley O’Neill, PhD, an exercise scientist at Acadia University in Nova Scotia and the study’s lead author.
That’s a key difference from conventional cardio, where the constant exertion can evaporate water from the lungs faster than your body can replenish it. “Dehydrating of the airways can, in some, trigger exercise-induced asthma,” Dr. O’Neill said.
HIIT, conversely, allows the airways to recover and rehydrate between exercise bouts.
Another recent study found that people with asthma who did HIIT workouts had fewer breathing problems and felt less fatigued, compared with a matched group who did cardio training at a constant pace. (Both types of cardio led to similar improvements in aerobic fitness.)
Individuals can choose other types of intermittent exercise as well. Strength training, for example, requires relatively short periods of exertion, with plenty of rest in between.
The one choice you don’t want to make
While there are lots of good exercise options for someone with asthma, there’s one clearly bad choice, according to Dr. George: “Avoiding exercise.”
Being inactive puts one at higher risk for obesity and all the health problems that go with it. And allowing one’s fitness level to decline makes it much harder to move when one needs or wants to.
Any choice is better than that one.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Asthma is a sneaky foe.
a professor of nursing at Columbia University and a spokesperson for the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America.
But that doesn’t mean exercise should be avoided, she said.
Exercise, in fact, is one of the best ways to reduce asthma symptoms. Research over the past 2 decades has shown that physical activity can help improve lung function and boost quality of life for someone with asthma.
As their fitness improves, asthma patients report better sleep, reduced stress, improved weight control, and more days without symptoms. In some cases, they’re able to cut down their medication doses.
Exercise reduces inflammatory cytokines and increases anti-inflammatory cytokines, according to a 2023 review by researchers in the United Kingdom. That could help calm chronic airway inflammation, easing symptoms of asthma.
A few simple guidelines can help patients reap those benefits while staying safe.
Make sure the first steps aren’t the last steps
For someone who’s new to exercise, there’s only one way to begin: Carefully.
The Global Initiative for Asthma recommends twice-weekly cardio and strength training.
“You always start low and slow,” said Spencer Nadolsky, DO, a board-certified obesity and lipid specialist and medical director of Sequence, a comprehensive weight management program.
“Low” means light loads in the weight room. “Slow” means short, easy walks.
Many have been put “through the wringer” when starting out, discouraging them from continuing, Dr. Nadolsky said. “They were too sore, and it felt more like punishment.”
An even bigger concern is triggering an asthma attack. Patients should take steps to lower the risk by carrying their rescue inhalers and keeping up on medications, he added.
“A health care professional should be consulted” before the start of a new activity or ramping up a program, or anytime asthma interferes with a workout, Dr. George said.
Those who exercise outside need to be aware of the air quality, especially at a time when smoke and particulates from a wildfires in Canada can trigger asthma symptoms in people thousands of miles away.
The harder one works, the higher one’s “ventilation” – taking more air into the lungs, and potentially more allergens and pollutants.
Temperature and humidity also become risky at the extremes. Cold, dry air can dehydrate and constrict the airways, making it hard to breathe.
How to choose the best type of exercise
Step 1: Be realistic. People with asthma often have less exercise capacity than those who don’t – understandable when shortness of breath is the default setting.
Second, allow for plenty of time to warm up. A solid warm-up routine – particularly one with a mix of lower- and higher-intensity exercises – may help prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction causing shortness of breath and wheezing.
For example, warming up on a treadmill or exercise bike could be mixed with a few short bursts of faster running or cycling, with a couple of minutes of recovery at a slower pace in between.
That concept can be expanded into a full-blown workout.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a promising option for people with asthma. A 2021 study showed that three 20-minute interval workouts per week significantly improved asthma control.
“The benefit of HIIT is that ventilation is able to recover intermittently,” said Carley O’Neill, PhD, an exercise scientist at Acadia University in Nova Scotia and the study’s lead author.
That’s a key difference from conventional cardio, where the constant exertion can evaporate water from the lungs faster than your body can replenish it. “Dehydrating of the airways can, in some, trigger exercise-induced asthma,” Dr. O’Neill said.
HIIT, conversely, allows the airways to recover and rehydrate between exercise bouts.
Another recent study found that people with asthma who did HIIT workouts had fewer breathing problems and felt less fatigued, compared with a matched group who did cardio training at a constant pace. (Both types of cardio led to similar improvements in aerobic fitness.)
Individuals can choose other types of intermittent exercise as well. Strength training, for example, requires relatively short periods of exertion, with plenty of rest in between.
The one choice you don’t want to make
While there are lots of good exercise options for someone with asthma, there’s one clearly bad choice, according to Dr. George: “Avoiding exercise.”
Being inactive puts one at higher risk for obesity and all the health problems that go with it. And allowing one’s fitness level to decline makes it much harder to move when one needs or wants to.
Any choice is better than that one.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Asthma is a sneaky foe.
a professor of nursing at Columbia University and a spokesperson for the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America.
But that doesn’t mean exercise should be avoided, she said.
Exercise, in fact, is one of the best ways to reduce asthma symptoms. Research over the past 2 decades has shown that physical activity can help improve lung function and boost quality of life for someone with asthma.
As their fitness improves, asthma patients report better sleep, reduced stress, improved weight control, and more days without symptoms. In some cases, they’re able to cut down their medication doses.
Exercise reduces inflammatory cytokines and increases anti-inflammatory cytokines, according to a 2023 review by researchers in the United Kingdom. That could help calm chronic airway inflammation, easing symptoms of asthma.
A few simple guidelines can help patients reap those benefits while staying safe.
Make sure the first steps aren’t the last steps
For someone who’s new to exercise, there’s only one way to begin: Carefully.
The Global Initiative for Asthma recommends twice-weekly cardio and strength training.
“You always start low and slow,” said Spencer Nadolsky, DO, a board-certified obesity and lipid specialist and medical director of Sequence, a comprehensive weight management program.
“Low” means light loads in the weight room. “Slow” means short, easy walks.
Many have been put “through the wringer” when starting out, discouraging them from continuing, Dr. Nadolsky said. “They were too sore, and it felt more like punishment.”
An even bigger concern is triggering an asthma attack. Patients should take steps to lower the risk by carrying their rescue inhalers and keeping up on medications, he added.
“A health care professional should be consulted” before the start of a new activity or ramping up a program, or anytime asthma interferes with a workout, Dr. George said.
Those who exercise outside need to be aware of the air quality, especially at a time when smoke and particulates from a wildfires in Canada can trigger asthma symptoms in people thousands of miles away.
The harder one works, the higher one’s “ventilation” – taking more air into the lungs, and potentially more allergens and pollutants.
Temperature and humidity also become risky at the extremes. Cold, dry air can dehydrate and constrict the airways, making it hard to breathe.
How to choose the best type of exercise
Step 1: Be realistic. People with asthma often have less exercise capacity than those who don’t – understandable when shortness of breath is the default setting.
Second, allow for plenty of time to warm up. A solid warm-up routine – particularly one with a mix of lower- and higher-intensity exercises – may help prevent exercise-induced bronchoconstriction causing shortness of breath and wheezing.
For example, warming up on a treadmill or exercise bike could be mixed with a few short bursts of faster running or cycling, with a couple of minutes of recovery at a slower pace in between.
That concept can be expanded into a full-blown workout.
High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is a promising option for people with asthma. A 2021 study showed that three 20-minute interval workouts per week significantly improved asthma control.
“The benefit of HIIT is that ventilation is able to recover intermittently,” said Carley O’Neill, PhD, an exercise scientist at Acadia University in Nova Scotia and the study’s lead author.
That’s a key difference from conventional cardio, where the constant exertion can evaporate water from the lungs faster than your body can replenish it. “Dehydrating of the airways can, in some, trigger exercise-induced asthma,” Dr. O’Neill said.
HIIT, conversely, allows the airways to recover and rehydrate between exercise bouts.
Another recent study found that people with asthma who did HIIT workouts had fewer breathing problems and felt less fatigued, compared with a matched group who did cardio training at a constant pace. (Both types of cardio led to similar improvements in aerobic fitness.)
Individuals can choose other types of intermittent exercise as well. Strength training, for example, requires relatively short periods of exertion, with plenty of rest in between.
The one choice you don’t want to make
While there are lots of good exercise options for someone with asthma, there’s one clearly bad choice, according to Dr. George: “Avoiding exercise.”
Being inactive puts one at higher risk for obesity and all the health problems that go with it. And allowing one’s fitness level to decline makes it much harder to move when one needs or wants to.
Any choice is better than that one.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Mepolizumab improves asthma after 1 year despite comorbidities
Adults with asthma who were newly prescribed mepolizumab showed significant improvement in symptoms after 1 year regardless of comorbidities, based on data from 822 individuals.
Comorbidities including chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps (CRSwNP), gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD), anxiety and depression, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) are common in patients with severe asthma and add to the disease burden, wrote Mark C. Liu, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
“Some comorbidities, such as CRSwNP, share pathophysiological mechanisms with severe asthma, with interleukin-5 (IL-5),” and treatments targeting IL-5 could improve outcomes, they said.
In the real-world REALITI-A study, mepolizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets IL-5, significantly reduced asthma exacerbation and oral corticosteroid use in severe asthma patients, they said.
To assess the impact of mepolizumab on patients with comorbidities, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of 822 adults with severe asthma, including 321 with CRSwNP, 309 with GERD, 203 with depression/anxiety, and 81 with COPD. The findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
The main outcomes were the rate of clinically significant asthma exacerbations (CSEs) between the 12 months before and after mepolizumab initiation, and the changes from baseline in the daily maintenance use of oral corticosteroids (OCS).
Across all comorbidities, the rate of CSEs decreased significantly from the pretreatment period to the follow-up period, from 4.28 events per year to 1.23 events per year.
“A numerically greater reduction in the rate of CSEs was reported for patients with versus without CRSwNP, whereas the reverse was reported for patients with versus without COPD and depression/anxiety, although the confidence intervals were large for the with COPD subgroup,” the researchers wrote.
The median maintenance dose of oral corticosteroids decreased by at least 50% across all comorbidities after mepolizumab treatment; patients with CRSwNP had the greatest reduction (83%).
In addition, scores on the Asthma Control Questionnaire–5 decreased by at least 0.63 points, and least squared (LS) mean changes in forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1) increased from baseline across all comorbidities after mepolizumab treatment by at least 74 mL.
Although patients with versus without CRSwNP had greater improvements, patients without GERD, depression/anxiety, and COPD had greater improvements than did those without the respective conditions with the exception of greater FEV1 improvement in patients with vs. without COPD.
“Patients with severe asthma and comorbid CRSwNP are recognized as having a high disease burden, as demonstrated by more frequent exacerbations,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Mepolizumab may serve to reduce the disease burden of this high-risk group by targeting the common pathophysiological pathway of IL-5 and eosinophilic-driven inflammation because it has proven clinical benefits in treating asthma and CRSwNP separately and together,” and the current study findings support the use of mepolizumab for this population in particular, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the incomplete data for voluntary assessments, the post hoc design and relatively small numbers of patients in various subgroups, notably COPD, and the potential inaccurate diagnosis of COPD, the researchers noted.
“Nevertheless, because the amount of improvement in each outcome following mepolizumab treatment differed depending on the comorbidity in question, our findings highlight the impact that comorbidities and their prevalence and severity have on outcomes,” and the overall success of mepolizumab across clinical characteristics and comorbidities supports the generalizability of the findings to the larger population of adults with severe asthma, they concluded.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Liu disclosed research funding from GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Gossamer Bio, and participation on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK, and Gossamer Bio.
Adults with asthma who were newly prescribed mepolizumab showed significant improvement in symptoms after 1 year regardless of comorbidities, based on data from 822 individuals.
Comorbidities including chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps (CRSwNP), gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD), anxiety and depression, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) are common in patients with severe asthma and add to the disease burden, wrote Mark C. Liu, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
“Some comorbidities, such as CRSwNP, share pathophysiological mechanisms with severe asthma, with interleukin-5 (IL-5),” and treatments targeting IL-5 could improve outcomes, they said.
In the real-world REALITI-A study, mepolizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets IL-5, significantly reduced asthma exacerbation and oral corticosteroid use in severe asthma patients, they said.
To assess the impact of mepolizumab on patients with comorbidities, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of 822 adults with severe asthma, including 321 with CRSwNP, 309 with GERD, 203 with depression/anxiety, and 81 with COPD. The findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
The main outcomes were the rate of clinically significant asthma exacerbations (CSEs) between the 12 months before and after mepolizumab initiation, and the changes from baseline in the daily maintenance use of oral corticosteroids (OCS).
Across all comorbidities, the rate of CSEs decreased significantly from the pretreatment period to the follow-up period, from 4.28 events per year to 1.23 events per year.
“A numerically greater reduction in the rate of CSEs was reported for patients with versus without CRSwNP, whereas the reverse was reported for patients with versus without COPD and depression/anxiety, although the confidence intervals were large for the with COPD subgroup,” the researchers wrote.
The median maintenance dose of oral corticosteroids decreased by at least 50% across all comorbidities after mepolizumab treatment; patients with CRSwNP had the greatest reduction (83%).
In addition, scores on the Asthma Control Questionnaire–5 decreased by at least 0.63 points, and least squared (LS) mean changes in forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1) increased from baseline across all comorbidities after mepolizumab treatment by at least 74 mL.
Although patients with versus without CRSwNP had greater improvements, patients without GERD, depression/anxiety, and COPD had greater improvements than did those without the respective conditions with the exception of greater FEV1 improvement in patients with vs. without COPD.
“Patients with severe asthma and comorbid CRSwNP are recognized as having a high disease burden, as demonstrated by more frequent exacerbations,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Mepolizumab may serve to reduce the disease burden of this high-risk group by targeting the common pathophysiological pathway of IL-5 and eosinophilic-driven inflammation because it has proven clinical benefits in treating asthma and CRSwNP separately and together,” and the current study findings support the use of mepolizumab for this population in particular, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the incomplete data for voluntary assessments, the post hoc design and relatively small numbers of patients in various subgroups, notably COPD, and the potential inaccurate diagnosis of COPD, the researchers noted.
“Nevertheless, because the amount of improvement in each outcome following mepolizumab treatment differed depending on the comorbidity in question, our findings highlight the impact that comorbidities and their prevalence and severity have on outcomes,” and the overall success of mepolizumab across clinical characteristics and comorbidities supports the generalizability of the findings to the larger population of adults with severe asthma, they concluded.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Liu disclosed research funding from GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Gossamer Bio, and participation on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK, and Gossamer Bio.
Adults with asthma who were newly prescribed mepolizumab showed significant improvement in symptoms after 1 year regardless of comorbidities, based on data from 822 individuals.
Comorbidities including chronic rhinosinusitis with polyps (CRSwNP), gastroesophageal reflux disease GERD), anxiety and depression, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) are common in patients with severe asthma and add to the disease burden, wrote Mark C. Liu, MD, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and colleagues.
“Some comorbidities, such as CRSwNP, share pathophysiological mechanisms with severe asthma, with interleukin-5 (IL-5),” and treatments targeting IL-5 could improve outcomes, they said.
In the real-world REALITI-A study, mepolizumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets IL-5, significantly reduced asthma exacerbation and oral corticosteroid use in severe asthma patients, they said.
To assess the impact of mepolizumab on patients with comorbidities, the researchers conducted a post hoc analysis of 822 adults with severe asthma, including 321 with CRSwNP, 309 with GERD, 203 with depression/anxiety, and 81 with COPD. The findings were published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice.
The main outcomes were the rate of clinically significant asthma exacerbations (CSEs) between the 12 months before and after mepolizumab initiation, and the changes from baseline in the daily maintenance use of oral corticosteroids (OCS).
Across all comorbidities, the rate of CSEs decreased significantly from the pretreatment period to the follow-up period, from 4.28 events per year to 1.23 events per year.
“A numerically greater reduction in the rate of CSEs was reported for patients with versus without CRSwNP, whereas the reverse was reported for patients with versus without COPD and depression/anxiety, although the confidence intervals were large for the with COPD subgroup,” the researchers wrote.
The median maintenance dose of oral corticosteroids decreased by at least 50% across all comorbidities after mepolizumab treatment; patients with CRSwNP had the greatest reduction (83%).
In addition, scores on the Asthma Control Questionnaire–5 decreased by at least 0.63 points, and least squared (LS) mean changes in forced expiratory volume per second (FEV1) increased from baseline across all comorbidities after mepolizumab treatment by at least 74 mL.
Although patients with versus without CRSwNP had greater improvements, patients without GERD, depression/anxiety, and COPD had greater improvements than did those without the respective conditions with the exception of greater FEV1 improvement in patients with vs. without COPD.
“Patients with severe asthma and comorbid CRSwNP are recognized as having a high disease burden, as demonstrated by more frequent exacerbations,” the researchers wrote in their discussion. “Mepolizumab may serve to reduce the disease burden of this high-risk group by targeting the common pathophysiological pathway of IL-5 and eosinophilic-driven inflammation because it has proven clinical benefits in treating asthma and CRSwNP separately and together,” and the current study findings support the use of mepolizumab for this population in particular, they said.
The findings were limited by several factors including the incomplete data for voluntary assessments, the post hoc design and relatively small numbers of patients in various subgroups, notably COPD, and the potential inaccurate diagnosis of COPD, the researchers noted.
“Nevertheless, because the amount of improvement in each outcome following mepolizumab treatment differed depending on the comorbidity in question, our findings highlight the impact that comorbidities and their prevalence and severity have on outcomes,” and the overall success of mepolizumab across clinical characteristics and comorbidities supports the generalizability of the findings to the larger population of adults with severe asthma, they concluded.
The study was supported by GlaxoSmithKline. Dr. Liu disclosed research funding from GSK, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Gossamer Bio, and participation on advisory boards for AstraZeneca, GSK, and Gossamer Bio.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY: IN PRACTICE
Generic inhalers for COPD support hold their own
Sometimes we get what we pay for. Other times we pay too much.
That’s the message of a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, which finds that a generic maintenance inhaler is as effective at managing symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) as a pricier branded alternative.
In 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved Wixela Inhub (the combination corticosteroid/long-acting beta2 adrenergic agonist fluticasone-salmeterol; Viatris) as a generic dry powder inhaler for managing symptoms of COPD. This approval was based on evidence of the generic’s effectiveness against asthma, although COPD also was on the product label. The study authors compared Wixela’s effectiveness in controlling symptoms of COPD with that of the brand name inhaler Advair Diskus (fluticasone-salmeterol; GlaxoSmithKline), which uses the same active ingredients.
The result: “The generic looks to be as safe and effective as the brand name. I don’t see a clinical reason why one would ever need to get the brand name over the generic version,” said study author William Feldman, MD, DPhil, MPH, a health services researcher and pulmonologist at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Same types of patients, different inhalers, same outcomes
Dr. Feldman and colleagues compared the medical records of 10,000 patients with COPD who began using the branded inhaler to the records of another 10,000 patients with COPD who opted for the generic alternative. Participants in the two groups were evenly matched by age, sex, race, and ethnicity, region, severity of COPD, and presence of other comorbidities, according to the researchers. Participants were all older than age 40, and the average age in both groups was 72 years.
The researchers looked for a difference in a first episode of a moderate exacerbation of COPD, defined as requiring a course of prednisone for 5-14 days. They also looked for cases of severe COPD exacerbation requiring hospitalization in the year after people began using either the generic or brand name inhaler. And they looked for differences across 1 year in rates of hospitalization for pneumonia.
For none of those outcomes, however, did the type of inhaler appear to matter. Compared with the brand-name drug, using the generic was associated with nearly identical rates of moderate or severe COPD exacerbation (hazard ratio, 0.97; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.04. The same was true for the proportion of people who went to the hospital for pneumonia at least once (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.86-1.15).
“To get through the FDA as an interchangeable generic, the generic firms have to show that their product can be used in just the same way as the brand-name version,” Dr. Feldman said, which may explain why the generic and brand-name versions of the inhaler performed so similarly.
Dr. Feldman cautioned that the price savings for patients who opt for the generic over the branded product are hard to determine, given the vagaries of different insurance plans and potential rebates when using the branded project. As a general matter, having a single generic competitor will not lower costs much, Dr. Feldman noted, pointing to 2017 research from Harvard that found a profusion of generic competitors is needed to significantly lower health care costs.
“I don’t want to in any way underestimate the importance of getting that first generic onto the market, because it sets the stage for future generics,” Dr. Feldman said.
“There are very few generic options for patients with COPD,” said Surya Bhatt, MD, director of the Pulmonary Function and Exercise Physiology Lab at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Even the rescue inhalers that people with COPD use to manage acute episodes of the condition are usually branded at this time, Dr. Bhatt noted, with few generic options.*
“The results are quite compelling,” said Dr. Bhatt, who was not involved in the research. Although the trial was not randomized, he commended the researchers for stratifying participants in the two groups to be as comparable as possible.
Dr. Bhatt noted that the FDA’s 2019 approval – given that the agency requires bioequivalence studies between branded and generic products – was enough to cause him to begin prescribing the generic inhaler. The fact that this approval was based on asthma but not also COPD is not a concern.
“There are so many similarities between asthma, COPD, and some obstructive lung diseases,” Dr. Bhatt noted.
In his experience, the only time someone with COPD continues using the branded inhaler – now that a potentially cheaper generic is available – is when their insurance plan makes their out-of-pocket cost minimal. Otherwise, brand loyalty does not exist.
“Patients are generally okay with being on a generic for inhalers, just because of the high cost,” Dr. Bhatt said.
The study was primarily supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Feldman reported funding from Arnold Ventures, the Commonwealth Fund, and the FDA, and consulting relationships with Alosa Health and Aetion. Dr. Bhatt reported no relevant financial relationships.
*Correction, 8/16/23: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized Dr. Bhatt's comments on the availability of generic options.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sometimes we get what we pay for. Other times we pay too much.
That’s the message of a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, which finds that a generic maintenance inhaler is as effective at managing symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) as a pricier branded alternative.
In 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved Wixela Inhub (the combination corticosteroid/long-acting beta2 adrenergic agonist fluticasone-salmeterol; Viatris) as a generic dry powder inhaler for managing symptoms of COPD. This approval was based on evidence of the generic’s effectiveness against asthma, although COPD also was on the product label. The study authors compared Wixela’s effectiveness in controlling symptoms of COPD with that of the brand name inhaler Advair Diskus (fluticasone-salmeterol; GlaxoSmithKline), which uses the same active ingredients.
The result: “The generic looks to be as safe and effective as the brand name. I don’t see a clinical reason why one would ever need to get the brand name over the generic version,” said study author William Feldman, MD, DPhil, MPH, a health services researcher and pulmonologist at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Same types of patients, different inhalers, same outcomes
Dr. Feldman and colleagues compared the medical records of 10,000 patients with COPD who began using the branded inhaler to the records of another 10,000 patients with COPD who opted for the generic alternative. Participants in the two groups were evenly matched by age, sex, race, and ethnicity, region, severity of COPD, and presence of other comorbidities, according to the researchers. Participants were all older than age 40, and the average age in both groups was 72 years.
The researchers looked for a difference in a first episode of a moderate exacerbation of COPD, defined as requiring a course of prednisone for 5-14 days. They also looked for cases of severe COPD exacerbation requiring hospitalization in the year after people began using either the generic or brand name inhaler. And they looked for differences across 1 year in rates of hospitalization for pneumonia.
For none of those outcomes, however, did the type of inhaler appear to matter. Compared with the brand-name drug, using the generic was associated with nearly identical rates of moderate or severe COPD exacerbation (hazard ratio, 0.97; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.04. The same was true for the proportion of people who went to the hospital for pneumonia at least once (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.86-1.15).
“To get through the FDA as an interchangeable generic, the generic firms have to show that their product can be used in just the same way as the brand-name version,” Dr. Feldman said, which may explain why the generic and brand-name versions of the inhaler performed so similarly.
Dr. Feldman cautioned that the price savings for patients who opt for the generic over the branded product are hard to determine, given the vagaries of different insurance plans and potential rebates when using the branded project. As a general matter, having a single generic competitor will not lower costs much, Dr. Feldman noted, pointing to 2017 research from Harvard that found a profusion of generic competitors is needed to significantly lower health care costs.
“I don’t want to in any way underestimate the importance of getting that first generic onto the market, because it sets the stage for future generics,” Dr. Feldman said.
“There are very few generic options for patients with COPD,” said Surya Bhatt, MD, director of the Pulmonary Function and Exercise Physiology Lab at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Even the rescue inhalers that people with COPD use to manage acute episodes of the condition are usually branded at this time, Dr. Bhatt noted, with few generic options.*
“The results are quite compelling,” said Dr. Bhatt, who was not involved in the research. Although the trial was not randomized, he commended the researchers for stratifying participants in the two groups to be as comparable as possible.
Dr. Bhatt noted that the FDA’s 2019 approval – given that the agency requires bioequivalence studies between branded and generic products – was enough to cause him to begin prescribing the generic inhaler. The fact that this approval was based on asthma but not also COPD is not a concern.
“There are so many similarities between asthma, COPD, and some obstructive lung diseases,” Dr. Bhatt noted.
In his experience, the only time someone with COPD continues using the branded inhaler – now that a potentially cheaper generic is available – is when their insurance plan makes their out-of-pocket cost minimal. Otherwise, brand loyalty does not exist.
“Patients are generally okay with being on a generic for inhalers, just because of the high cost,” Dr. Bhatt said.
The study was primarily supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Feldman reported funding from Arnold Ventures, the Commonwealth Fund, and the FDA, and consulting relationships with Alosa Health and Aetion. Dr. Bhatt reported no relevant financial relationships.
*Correction, 8/16/23: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized Dr. Bhatt's comments on the availability of generic options.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sometimes we get what we pay for. Other times we pay too much.
That’s the message of a study published in Annals of Internal Medicine, which finds that a generic maintenance inhaler is as effective at managing symptoms of chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder (COPD) as a pricier branded alternative.
In 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved Wixela Inhub (the combination corticosteroid/long-acting beta2 adrenergic agonist fluticasone-salmeterol; Viatris) as a generic dry powder inhaler for managing symptoms of COPD. This approval was based on evidence of the generic’s effectiveness against asthma, although COPD also was on the product label. The study authors compared Wixela’s effectiveness in controlling symptoms of COPD with that of the brand name inhaler Advair Diskus (fluticasone-salmeterol; GlaxoSmithKline), which uses the same active ingredients.
The result: “The generic looks to be as safe and effective as the brand name. I don’t see a clinical reason why one would ever need to get the brand name over the generic version,” said study author William Feldman, MD, DPhil, MPH, a health services researcher and pulmonologist at Harvard Medical School and Brigham and Women’s Hospital, both in Boston.
Same types of patients, different inhalers, same outcomes
Dr. Feldman and colleagues compared the medical records of 10,000 patients with COPD who began using the branded inhaler to the records of another 10,000 patients with COPD who opted for the generic alternative. Participants in the two groups were evenly matched by age, sex, race, and ethnicity, region, severity of COPD, and presence of other comorbidities, according to the researchers. Participants were all older than age 40, and the average age in both groups was 72 years.
The researchers looked for a difference in a first episode of a moderate exacerbation of COPD, defined as requiring a course of prednisone for 5-14 days. They also looked for cases of severe COPD exacerbation requiring hospitalization in the year after people began using either the generic or brand name inhaler. And they looked for differences across 1 year in rates of hospitalization for pneumonia.
For none of those outcomes, however, did the type of inhaler appear to matter. Compared with the brand-name drug, using the generic was associated with nearly identical rates of moderate or severe COPD exacerbation (hazard ratio, 0.97; 95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.04. The same was true for the proportion of people who went to the hospital for pneumonia at least once (HR, 0.99; 95% CI, 0.86-1.15).
“To get through the FDA as an interchangeable generic, the generic firms have to show that their product can be used in just the same way as the brand-name version,” Dr. Feldman said, which may explain why the generic and brand-name versions of the inhaler performed so similarly.
Dr. Feldman cautioned that the price savings for patients who opt for the generic over the branded product are hard to determine, given the vagaries of different insurance plans and potential rebates when using the branded project. As a general matter, having a single generic competitor will not lower costs much, Dr. Feldman noted, pointing to 2017 research from Harvard that found a profusion of generic competitors is needed to significantly lower health care costs.
“I don’t want to in any way underestimate the importance of getting that first generic onto the market, because it sets the stage for future generics,” Dr. Feldman said.
“There are very few generic options for patients with COPD,” said Surya Bhatt, MD, director of the Pulmonary Function and Exercise Physiology Lab at the University of Alabama at Birmingham. Even the rescue inhalers that people with COPD use to manage acute episodes of the condition are usually branded at this time, Dr. Bhatt noted, with few generic options.*
“The results are quite compelling,” said Dr. Bhatt, who was not involved in the research. Although the trial was not randomized, he commended the researchers for stratifying participants in the two groups to be as comparable as possible.
Dr. Bhatt noted that the FDA’s 2019 approval – given that the agency requires bioequivalence studies between branded and generic products – was enough to cause him to begin prescribing the generic inhaler. The fact that this approval was based on asthma but not also COPD is not a concern.
“There are so many similarities between asthma, COPD, and some obstructive lung diseases,” Dr. Bhatt noted.
In his experience, the only time someone with COPD continues using the branded inhaler – now that a potentially cheaper generic is available – is when their insurance plan makes their out-of-pocket cost minimal. Otherwise, brand loyalty does not exist.
“Patients are generally okay with being on a generic for inhalers, just because of the high cost,” Dr. Bhatt said.
The study was primarily supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. Dr. Feldman reported funding from Arnold Ventures, the Commonwealth Fund, and the FDA, and consulting relationships with Alosa Health and Aetion. Dr. Bhatt reported no relevant financial relationships.
*Correction, 8/16/23: An earlier version of this article mischaracterized Dr. Bhatt's comments on the availability of generic options.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Asthma severity, exacerbations increase with RV infection
TOPLINE:
Immunological and quantitative mRNA assays support a pathogenesis role for histamine-releasing factor (HRF), its interaction with HRF-reactive immunoglobulin E and rhinovirus (RV) in asthma severity and exacerbation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Clinical data for healthy controls (HCs) were compared with data from patients with asthma for three distinct cohorts recruited from programs located in Pittsburg, Boston, and Virginia.
- Cohorts differed primarily by total number of participants, median age, description of asthma severity, RV status, and longitudinal follow-up.
- Enzyme-linked immunoassay tests quantified for comparisons total IgE, IgGs, and IgG1 levels occurring in human sera samples and for HRF-reactive IgE, IgG1, and IgG2b in sera from mice inoculated with mouse .
- Anti-IgE stimulation experiments characterized bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell supernatants for tryptase and PGD2 by ELISA and the mRNAs for tryptase and FCER1A
- Effect of inoculated RV infections and/or house dust mite allergen on stimulating HRF secretion from respiratory epithelial cells and in vitro–grown lung BEAS-2B cells was evaluated by Western blots.
TAKEAWAY:
- HRF-reactive IgGs and IgG1 levels in serum were lower in people with asthma than in HCs.
- People with asthma with high HRF-reactive IgE, compared with those with low levels, tended to release more tryptase prostaglandin D2 with anti-IgE stimulation of BAL cells.
- RV infection induced HFR secretions from both in vivo– and in vitro–grown respiratory epithelial cells and was associated with higher levels of HRF-IgE at the time of asthma exacerbations, compared with after resolution.
IN PRACTICE:
Inhibiting HRF and HRF-reactive IgE interactions “can be a preventative/therapeutic target” for severe and RV-induced exacerbated asthma conditions.
SOURCE:
The study led by Yu Kawakami, MD, of La Jolla Institute for Allergy & Immunology, California, and colleagues was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
LIMITATIONS:
Small sample sizes, large median age differences between cohorts, and lack of data for other demographic traits and variant asthma phenotypes or endotypes in some cohorts are noted limitations that may affect result extrapolations and conclusions.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report there are no conflicts of interest directly related to this study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Immunological and quantitative mRNA assays support a pathogenesis role for histamine-releasing factor (HRF), its interaction with HRF-reactive immunoglobulin E and rhinovirus (RV) in asthma severity and exacerbation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Clinical data for healthy controls (HCs) were compared with data from patients with asthma for three distinct cohorts recruited from programs located in Pittsburg, Boston, and Virginia.
- Cohorts differed primarily by total number of participants, median age, description of asthma severity, RV status, and longitudinal follow-up.
- Enzyme-linked immunoassay tests quantified for comparisons total IgE, IgGs, and IgG1 levels occurring in human sera samples and for HRF-reactive IgE, IgG1, and IgG2b in sera from mice inoculated with mouse .
- Anti-IgE stimulation experiments characterized bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell supernatants for tryptase and PGD2 by ELISA and the mRNAs for tryptase and FCER1A
- Effect of inoculated RV infections and/or house dust mite allergen on stimulating HRF secretion from respiratory epithelial cells and in vitro–grown lung BEAS-2B cells was evaluated by Western blots.
TAKEAWAY:
- HRF-reactive IgGs and IgG1 levels in serum were lower in people with asthma than in HCs.
- People with asthma with high HRF-reactive IgE, compared with those with low levels, tended to release more tryptase prostaglandin D2 with anti-IgE stimulation of BAL cells.
- RV infection induced HFR secretions from both in vivo– and in vitro–grown respiratory epithelial cells and was associated with higher levels of HRF-IgE at the time of asthma exacerbations, compared with after resolution.
IN PRACTICE:
Inhibiting HRF and HRF-reactive IgE interactions “can be a preventative/therapeutic target” for severe and RV-induced exacerbated asthma conditions.
SOURCE:
The study led by Yu Kawakami, MD, of La Jolla Institute for Allergy & Immunology, California, and colleagues was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
LIMITATIONS:
Small sample sizes, large median age differences between cohorts, and lack of data for other demographic traits and variant asthma phenotypes or endotypes in some cohorts are noted limitations that may affect result extrapolations and conclusions.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report there are no conflicts of interest directly related to this study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
Immunological and quantitative mRNA assays support a pathogenesis role for histamine-releasing factor (HRF), its interaction with HRF-reactive immunoglobulin E and rhinovirus (RV) in asthma severity and exacerbation.
METHODOLOGY:
- Clinical data for healthy controls (HCs) were compared with data from patients with asthma for three distinct cohorts recruited from programs located in Pittsburg, Boston, and Virginia.
- Cohorts differed primarily by total number of participants, median age, description of asthma severity, RV status, and longitudinal follow-up.
- Enzyme-linked immunoassay tests quantified for comparisons total IgE, IgGs, and IgG1 levels occurring in human sera samples and for HRF-reactive IgE, IgG1, and IgG2b in sera from mice inoculated with mouse .
- Anti-IgE stimulation experiments characterized bronchoalveolar lavage (BAL) cell supernatants for tryptase and PGD2 by ELISA and the mRNAs for tryptase and FCER1A
- Effect of inoculated RV infections and/or house dust mite allergen on stimulating HRF secretion from respiratory epithelial cells and in vitro–grown lung BEAS-2B cells was evaluated by Western blots.
TAKEAWAY:
- HRF-reactive IgGs and IgG1 levels in serum were lower in people with asthma than in HCs.
- People with asthma with high HRF-reactive IgE, compared with those with low levels, tended to release more tryptase prostaglandin D2 with anti-IgE stimulation of BAL cells.
- RV infection induced HFR secretions from both in vivo– and in vitro–grown respiratory epithelial cells and was associated with higher levels of HRF-IgE at the time of asthma exacerbations, compared with after resolution.
IN PRACTICE:
Inhibiting HRF and HRF-reactive IgE interactions “can be a preventative/therapeutic target” for severe and RV-induced exacerbated asthma conditions.
SOURCE:
The study led by Yu Kawakami, MD, of La Jolla Institute for Allergy & Immunology, California, and colleagues was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology
LIMITATIONS:
Small sample sizes, large median age differences between cohorts, and lack of data for other demographic traits and variant asthma phenotypes or endotypes in some cohorts are noted limitations that may affect result extrapolations and conclusions.
DISCLOSURES:
The authors report there are no conflicts of interest directly related to this study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New German guidelines change the paradigm for asthma
Asthma has long been associated with the use of inhalers to control symptoms. The new S2K guideline on the management of asthma, compiled by experts and published in March 2023, aims to change this. “For decades, we have known about medication that can be used to put asthma into remission. The patient can go out or travel on vacation without an inhaler. This is possible. This is a symptom-prevention approach,” said the guideline coordinator Marek Lommatzsch, MD, PhD, head senior physician of the pulmonology department at the University Medicine Rostock, Germany, in an interview.
The guideline was created by the German Respiratory Society, and a further 11 professional societies from Germany and Austria were involved in the update. The authors comprehensively revised the guideline from 2017, and the evidence-based national disease management guideline (NVL) for general asthma care from 2020 was amended.
Erika von Mutius, MD, PhD, pediatrician and professor of pediatric allergology and pulmonology at the Dr. Von Hauner Children’s Hospital, Munich, and director of the Institute of Asthma and Allergy Prevention at Helmholtz Munich, was not directly involved in the guideline. She said,
Anti-inflammatory therapy
The significance of anti-inflammatory therapy was stressed in the NVL from 2020. The new guideline holds that anti-inflammatory therapy should be considered the primary therapeutic option. “We are making a U-turn: only treat the respiratory inflammation. Salbutamol should still only be given in exceptional cases as required,” according to Dr. Lommatzsch.
In the guideline, asthma therapy is described using an updated step-by-step plan. Inhaled glucocorticoids (ICS) represent the most important pillar of therapy. ICS can be used as permanent therapy or as as-needed therapy in fixed combination with formoterol, which rapidly dilates the airways.
Allergen immunotherapy, also known as hyposensitization, and biologics are also effective anti-inflammatory treatments, Dr. Lommatzsch added. “We must ensure that these anti-inflammatory medicines are also used effectively. Mild to moderate forms of asthma can be treated easily by a primary care physician,” he said. Basic diagnostics in the form of a blood sample are required. A somewhat more comprehensive medical history is also needed. “It takes a little more time and involves more than just taking the inhaler out of the cupboard.”
The situation regarding children, however, is a little different with regard to anti-inflammatory therapy, Dr. Von Mutius explained. “Childhood asthma has many forms, and confirming the diagnosis is not always straightforward, especially in infancy. If needed, salbutamol can be prescribed. However, the anti-inflammatory medication should usually also be administered.”
She emphasized that the guideline has been designed in a sophisticated way that offers the option of “using medical experience to see what is suitable for this family or better for this patient. This is still always subject to medical judgment and responsibility. I find this really successful.”
Diagnostics using biomarkers
The previous guideline concentrated on measuring lung function as a way of diagnosing asthmatic illness. Three biomarkers were brought to the fore:
- Eosinophils in the blood.
- IgE levels.
- The FeNO test (proportion of nitrogen monoxide in exhaled air).
Slightly amended, the guideline now states that the FeNO test is implemented as “an integral component of specialist diagnosis.”
The test measures the nitrogen monoxide content of exhaled air as an indicator of inflammation in the airways. However, this test must often be paid for by the patient. “In this respect, we want to give a nudge in the direction of the political decision-makers,” emphasized Dr. Lommatzsch.
Dr. Von Mutius added that use of the FeNO test has not been established in many practices and outpatient clinics. The inflammatory marker is also subject to fluctuations. “This is an update to the guideline where we must wait to see the political response.”
Which biologic?
Despite treatment with the established therapies, the symptoms of asthma can persist in some people with severe forms of the condition. Biologics are highly effective for these patients and are preferable in the last stage of therapy to long-term therapy with oral steroids, which have numerous side effects. The current guideline provides an overview diagram to help decide which biologic is suitable for which patient.
“There are six biologics that can be used to treat severe asthma. Officially, almost any biologic can be taken into consideration for a patient, since the approvals overlap. Nevertheless, we know that certain patients benefit hugely from certain biologics. A targeted choice should therefore be made,” explained Dr. Lommatzsch.
Biologics were mentioned in the 2020 NVL but not to the great extent that they are in the latest version. “For the first time, we have created an overview diagram for the individual choice of biologic. With it, we have now set a standard,” said Dr. Lommatzsch.
Therapy with biologics has brought about rapid progress for adults. Dr. Von Mutius anticipates challenges in approving such therapeutics for pediatric treatment. “As is often the case, these therapies are not approved for young children. Meanwhile, dupilumab is approved for children aged 6 months and older; unfortunately, the indication for this is actually atopic dermatitis,” she explains.
When using this therapy for pediatric patients, it is therefore important to explain the options to parents and to inform them of side effects. Severe forms of asthma are rare in children; they are uncommon in adults but are more prevalent than in children.
Children and adolescents
One new chapter in the guideline describes giving medical advice to adolescents choosing a career. A table has been compiled that contains information regarding jobs and their respective allergy and asthma risk. The table is designed to be displayed in a medical practice.
Another chapter characterizes the interrelation between asthma and mental health. It differentiates between psychiatric comorbidities for which the patient requires professional help and the stress caused by the asthmatic illness itself. Many patients do not have a mental illness but do suffer under the everyday strain of having asthma, said Dr. Lommatzsch. Therefore, it is important to educate patients and their relatives on how to make a strength out of this supposed weakness – the asthmatic illness. “We have established a procedure for this and have summarized its key points in the guideline,” said Dr. Lommatzsch.
Other updates to the guideline cover asthma in different contexts, such as in pregnant women. The updates address adrenal insufficiency as a side effect of the use of steroids over many years. In addition, the guideline contains a chapter on digital apps that can help with diagnostics and medical history.
Dr. Lommatzsch highlighted a new tool. “By using 15 key points summarized in a table, the guideline displays the essential differences between COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disease] and asthma in terms of the symptoms and the findings. It is the most modern table available in Germany that differentiates between the two diseases.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
Asthma has long been associated with the use of inhalers to control symptoms. The new S2K guideline on the management of asthma, compiled by experts and published in March 2023, aims to change this. “For decades, we have known about medication that can be used to put asthma into remission. The patient can go out or travel on vacation without an inhaler. This is possible. This is a symptom-prevention approach,” said the guideline coordinator Marek Lommatzsch, MD, PhD, head senior physician of the pulmonology department at the University Medicine Rostock, Germany, in an interview.
The guideline was created by the German Respiratory Society, and a further 11 professional societies from Germany and Austria were involved in the update. The authors comprehensively revised the guideline from 2017, and the evidence-based national disease management guideline (NVL) for general asthma care from 2020 was amended.
Erika von Mutius, MD, PhD, pediatrician and professor of pediatric allergology and pulmonology at the Dr. Von Hauner Children’s Hospital, Munich, and director of the Institute of Asthma and Allergy Prevention at Helmholtz Munich, was not directly involved in the guideline. She said,
Anti-inflammatory therapy
The significance of anti-inflammatory therapy was stressed in the NVL from 2020. The new guideline holds that anti-inflammatory therapy should be considered the primary therapeutic option. “We are making a U-turn: only treat the respiratory inflammation. Salbutamol should still only be given in exceptional cases as required,” according to Dr. Lommatzsch.
In the guideline, asthma therapy is described using an updated step-by-step plan. Inhaled glucocorticoids (ICS) represent the most important pillar of therapy. ICS can be used as permanent therapy or as as-needed therapy in fixed combination with formoterol, which rapidly dilates the airways.
Allergen immunotherapy, also known as hyposensitization, and biologics are also effective anti-inflammatory treatments, Dr. Lommatzsch added. “We must ensure that these anti-inflammatory medicines are also used effectively. Mild to moderate forms of asthma can be treated easily by a primary care physician,” he said. Basic diagnostics in the form of a blood sample are required. A somewhat more comprehensive medical history is also needed. “It takes a little more time and involves more than just taking the inhaler out of the cupboard.”
The situation regarding children, however, is a little different with regard to anti-inflammatory therapy, Dr. Von Mutius explained. “Childhood asthma has many forms, and confirming the diagnosis is not always straightforward, especially in infancy. If needed, salbutamol can be prescribed. However, the anti-inflammatory medication should usually also be administered.”
She emphasized that the guideline has been designed in a sophisticated way that offers the option of “using medical experience to see what is suitable for this family or better for this patient. This is still always subject to medical judgment and responsibility. I find this really successful.”
Diagnostics using biomarkers
The previous guideline concentrated on measuring lung function as a way of diagnosing asthmatic illness. Three biomarkers were brought to the fore:
- Eosinophils in the blood.
- IgE levels.
- The FeNO test (proportion of nitrogen monoxide in exhaled air).
Slightly amended, the guideline now states that the FeNO test is implemented as “an integral component of specialist diagnosis.”
The test measures the nitrogen monoxide content of exhaled air as an indicator of inflammation in the airways. However, this test must often be paid for by the patient. “In this respect, we want to give a nudge in the direction of the political decision-makers,” emphasized Dr. Lommatzsch.
Dr. Von Mutius added that use of the FeNO test has not been established in many practices and outpatient clinics. The inflammatory marker is also subject to fluctuations. “This is an update to the guideline where we must wait to see the political response.”
Which biologic?
Despite treatment with the established therapies, the symptoms of asthma can persist in some people with severe forms of the condition. Biologics are highly effective for these patients and are preferable in the last stage of therapy to long-term therapy with oral steroids, which have numerous side effects. The current guideline provides an overview diagram to help decide which biologic is suitable for which patient.
“There are six biologics that can be used to treat severe asthma. Officially, almost any biologic can be taken into consideration for a patient, since the approvals overlap. Nevertheless, we know that certain patients benefit hugely from certain biologics. A targeted choice should therefore be made,” explained Dr. Lommatzsch.
Biologics were mentioned in the 2020 NVL but not to the great extent that they are in the latest version. “For the first time, we have created an overview diagram for the individual choice of biologic. With it, we have now set a standard,” said Dr. Lommatzsch.
Therapy with biologics has brought about rapid progress for adults. Dr. Von Mutius anticipates challenges in approving such therapeutics for pediatric treatment. “As is often the case, these therapies are not approved for young children. Meanwhile, dupilumab is approved for children aged 6 months and older; unfortunately, the indication for this is actually atopic dermatitis,” she explains.
When using this therapy for pediatric patients, it is therefore important to explain the options to parents and to inform them of side effects. Severe forms of asthma are rare in children; they are uncommon in adults but are more prevalent than in children.
Children and adolescents
One new chapter in the guideline describes giving medical advice to adolescents choosing a career. A table has been compiled that contains information regarding jobs and their respective allergy and asthma risk. The table is designed to be displayed in a medical practice.
Another chapter characterizes the interrelation between asthma and mental health. It differentiates between psychiatric comorbidities for which the patient requires professional help and the stress caused by the asthmatic illness itself. Many patients do not have a mental illness but do suffer under the everyday strain of having asthma, said Dr. Lommatzsch. Therefore, it is important to educate patients and their relatives on how to make a strength out of this supposed weakness – the asthmatic illness. “We have established a procedure for this and have summarized its key points in the guideline,” said Dr. Lommatzsch.
Other updates to the guideline cover asthma in different contexts, such as in pregnant women. The updates address adrenal insufficiency as a side effect of the use of steroids over many years. In addition, the guideline contains a chapter on digital apps that can help with diagnostics and medical history.
Dr. Lommatzsch highlighted a new tool. “By using 15 key points summarized in a table, the guideline displays the essential differences between COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disease] and asthma in terms of the symptoms and the findings. It is the most modern table available in Germany that differentiates between the two diseases.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
Asthma has long been associated with the use of inhalers to control symptoms. The new S2K guideline on the management of asthma, compiled by experts and published in March 2023, aims to change this. “For decades, we have known about medication that can be used to put asthma into remission. The patient can go out or travel on vacation without an inhaler. This is possible. This is a symptom-prevention approach,” said the guideline coordinator Marek Lommatzsch, MD, PhD, head senior physician of the pulmonology department at the University Medicine Rostock, Germany, in an interview.
The guideline was created by the German Respiratory Society, and a further 11 professional societies from Germany and Austria were involved in the update. The authors comprehensively revised the guideline from 2017, and the evidence-based national disease management guideline (NVL) for general asthma care from 2020 was amended.
Erika von Mutius, MD, PhD, pediatrician and professor of pediatric allergology and pulmonology at the Dr. Von Hauner Children’s Hospital, Munich, and director of the Institute of Asthma and Allergy Prevention at Helmholtz Munich, was not directly involved in the guideline. She said,
Anti-inflammatory therapy
The significance of anti-inflammatory therapy was stressed in the NVL from 2020. The new guideline holds that anti-inflammatory therapy should be considered the primary therapeutic option. “We are making a U-turn: only treat the respiratory inflammation. Salbutamol should still only be given in exceptional cases as required,” according to Dr. Lommatzsch.
In the guideline, asthma therapy is described using an updated step-by-step plan. Inhaled glucocorticoids (ICS) represent the most important pillar of therapy. ICS can be used as permanent therapy or as as-needed therapy in fixed combination with formoterol, which rapidly dilates the airways.
Allergen immunotherapy, also known as hyposensitization, and biologics are also effective anti-inflammatory treatments, Dr. Lommatzsch added. “We must ensure that these anti-inflammatory medicines are also used effectively. Mild to moderate forms of asthma can be treated easily by a primary care physician,” he said. Basic diagnostics in the form of a blood sample are required. A somewhat more comprehensive medical history is also needed. “It takes a little more time and involves more than just taking the inhaler out of the cupboard.”
The situation regarding children, however, is a little different with regard to anti-inflammatory therapy, Dr. Von Mutius explained. “Childhood asthma has many forms, and confirming the diagnosis is not always straightforward, especially in infancy. If needed, salbutamol can be prescribed. However, the anti-inflammatory medication should usually also be administered.”
She emphasized that the guideline has been designed in a sophisticated way that offers the option of “using medical experience to see what is suitable for this family or better for this patient. This is still always subject to medical judgment and responsibility. I find this really successful.”
Diagnostics using biomarkers
The previous guideline concentrated on measuring lung function as a way of diagnosing asthmatic illness. Three biomarkers were brought to the fore:
- Eosinophils in the blood.
- IgE levels.
- The FeNO test (proportion of nitrogen monoxide in exhaled air).
Slightly amended, the guideline now states that the FeNO test is implemented as “an integral component of specialist diagnosis.”
The test measures the nitrogen monoxide content of exhaled air as an indicator of inflammation in the airways. However, this test must often be paid for by the patient. “In this respect, we want to give a nudge in the direction of the political decision-makers,” emphasized Dr. Lommatzsch.
Dr. Von Mutius added that use of the FeNO test has not been established in many practices and outpatient clinics. The inflammatory marker is also subject to fluctuations. “This is an update to the guideline where we must wait to see the political response.”
Which biologic?
Despite treatment with the established therapies, the symptoms of asthma can persist in some people with severe forms of the condition. Biologics are highly effective for these patients and are preferable in the last stage of therapy to long-term therapy with oral steroids, which have numerous side effects. The current guideline provides an overview diagram to help decide which biologic is suitable for which patient.
“There are six biologics that can be used to treat severe asthma. Officially, almost any biologic can be taken into consideration for a patient, since the approvals overlap. Nevertheless, we know that certain patients benefit hugely from certain biologics. A targeted choice should therefore be made,” explained Dr. Lommatzsch.
Biologics were mentioned in the 2020 NVL but not to the great extent that they are in the latest version. “For the first time, we have created an overview diagram for the individual choice of biologic. With it, we have now set a standard,” said Dr. Lommatzsch.
Therapy with biologics has brought about rapid progress for adults. Dr. Von Mutius anticipates challenges in approving such therapeutics for pediatric treatment. “As is often the case, these therapies are not approved for young children. Meanwhile, dupilumab is approved for children aged 6 months and older; unfortunately, the indication for this is actually atopic dermatitis,” she explains.
When using this therapy for pediatric patients, it is therefore important to explain the options to parents and to inform them of side effects. Severe forms of asthma are rare in children; they are uncommon in adults but are more prevalent than in children.
Children and adolescents
One new chapter in the guideline describes giving medical advice to adolescents choosing a career. A table has been compiled that contains information regarding jobs and their respective allergy and asthma risk. The table is designed to be displayed in a medical practice.
Another chapter characterizes the interrelation between asthma and mental health. It differentiates between psychiatric comorbidities for which the patient requires professional help and the stress caused by the asthmatic illness itself. Many patients do not have a mental illness but do suffer under the everyday strain of having asthma, said Dr. Lommatzsch. Therefore, it is important to educate patients and their relatives on how to make a strength out of this supposed weakness – the asthmatic illness. “We have established a procedure for this and have summarized its key points in the guideline,” said Dr. Lommatzsch.
Other updates to the guideline cover asthma in different contexts, such as in pregnant women. The updates address adrenal insufficiency as a side effect of the use of steroids over many years. In addition, the guideline contains a chapter on digital apps that can help with diagnostics and medical history.
Dr. Lommatzsch highlighted a new tool. “By using 15 key points summarized in a table, the guideline displays the essential differences between COPD [chronic obstructive pulmonary disease] and asthma in terms of the symptoms and the findings. It is the most modern table available in Germany that differentiates between the two diseases.”
This article was translated from the Medscape German Edition and a version appeared on Medscape.com.
Real-world study extends benralizumab asthma benefit
The real-world Zephyr 2 study, which assessed benralizumab for effectiveness in treating severe eosinophilic asthma, was extended with an analysis of a larger population stratified into three cohorts of participants who were aged 12 years or older.
Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies designed to block specific inflammatory pathways is a recommended add-on treatment option for adults to manage severe, uncontrolled eosinophilic-dependent (> 150 cells/µl) and corticosteroid-dependent asthma. One such biologic, benralizumab, targets the interleukin-5 receptor alpha chain (IL-5Rα).
For asthma patients who had previously been treated with benralizumab, there were significant reductions in exacerbation rates in the ZEPHYR 1 study. However, information regarding benefit associated with specific profiles was limited, warranting a larger study to address effectiveness when considering various blood eosinophil counts, prior treatments with other biologics, or benralizumab use for up to 24 months, Donna Carstens, MD, of AstraZeneca, Wilmington, Del., and colleagues write.
Study details
In the retrospective cohort Zephyr 2 study, which was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, the researchers retrieved deidentified patient information from medical, laboratory, and pharmacy U.S. insurance claims records from the PatientSource and DiagnosticSource databases and compared asthma exacerbation rates before and after treatment with benralizumab.
Age, asthma diagnosis, number of exacerbations, and number of benralizumab treatment records within specified periods were used to identify a total of 1,795 participants for inclusion in the study. The index date for establishing before-treatment and after-treatment index time intervals of 12 months each was defined as the day after the initial benralizumab treatment occurring between November 2017 and June 2019.
The cohort was stratified into three nonmutually exclusive groups consisting of 349 patients who had switched primarily from either omalizumab or mepolizumab biologics to benralizumab; 429 patients subdivided by closest to the index date blood eosinophil counts of less than 150, greater than or equal to 150, 150-299, less than 300, and greater than or equal to 300, and 419 patients with post data collection extended beyond 12 months to 18 or 24 months.
Similarities in baseline patient characteristics that were were observed across the three cohorts included a mean age range of 51-53 years, preponderance of women (67%-69%), obesity diagnosis (31.5%-32.9%), and a mean Charlson Comorbidity Index of 1.47-1.52. Allergic rhinitis was the most frequently reported (60%-67%) comorbidity, followed by hypertension and gastroesophageal reflex.
Effectiveness
Benralizumab was found to be a significantly effective treatment for managing severe eosinophilic asthma for all three evaluated cohorts, as evidenced by reductions in asthma exacerbations post-index, compared with pre-index. Specifically, the exacerbation rate for all five subgroups of the blood eosinophil cohort significantly decreased from the pre-index 3.10-3.55 person per year (PPY) rate to a 1.11-1.72 PPY post-index rate, equivalent to a 52%-64% decrease in exacerbations (P < .001 for all pre-index vs. post-index comparisons).
Comparable reductions also occurred with the cohort in which the biologic treatment was changed to benralizumab. A greater effect was observed when the switch was made from omalizumab to benralizumab with a pre-post PPY rate reduction of 3.25-1.25 (62%) than when the switch was made from mepolizumab (pre-post PPY rate reduction was 3.81-1.78 [53%], but both resulted in significant post-treatment improvements (P < .001).
Results from the extended follow-up analysis cohort showed consistency for significant exacerbation rate decline going from a pre-index rate of 3.38 PPY down to 1.34 PPY (60% rate reduction vs. pre-index) in the first 12 post-index months, continuing to decline to 1.18 PPY (65% reduction) over the following six months (both significant at P < .001).
Likewise, the results from the extended follow-up 24-month subgroup presented significant down trending exacerbation rates from pre-index 3.38 PPY to 1.38 (comparative 59% reduction) for the first 12 months continuing down to 1.08 PPY (68% reduction) over the 12-24 month post-index period (both P < .001). In the first and second 12 post-index months for the 24-month subgroup, 39% and 49% of the patients, respectively, experienced no exacerbations.
Following treatment with benralizumab, in addition to the observed decline in asthma exacerbation rates, the need for concomitant asthma medications was also significantly reduced for all three cohorts.
This retrospective ZEPHYR 2 study contributes evidence supporting the significant effectiveness of benralizumab in improving disease management for “specific subsets of severe asthma patients that are frequently seen in real-world practice and may be excluded from clinical trials,” according to the authors. The treatment resulted in reduced rates of asthma exacerbations with defined standards for hospitalizations, visits to emergency department or urgent care, or outpatient visits with separate exacerbations occurring at greater than or equal to 14 days, as reported in database records. Reduction in the rate of asthma exacerbations when benralizumab is switched for another biologic increases the disease management options for achieving optimal patient care, the authors add.
The authors have financial relationships with AstraZeneca, the source of funding for the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The real-world Zephyr 2 study, which assessed benralizumab for effectiveness in treating severe eosinophilic asthma, was extended with an analysis of a larger population stratified into three cohorts of participants who were aged 12 years or older.
Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies designed to block specific inflammatory pathways is a recommended add-on treatment option for adults to manage severe, uncontrolled eosinophilic-dependent (> 150 cells/µl) and corticosteroid-dependent asthma. One such biologic, benralizumab, targets the interleukin-5 receptor alpha chain (IL-5Rα).
For asthma patients who had previously been treated with benralizumab, there were significant reductions in exacerbation rates in the ZEPHYR 1 study. However, information regarding benefit associated with specific profiles was limited, warranting a larger study to address effectiveness when considering various blood eosinophil counts, prior treatments with other biologics, or benralizumab use for up to 24 months, Donna Carstens, MD, of AstraZeneca, Wilmington, Del., and colleagues write.
Study details
In the retrospective cohort Zephyr 2 study, which was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, the researchers retrieved deidentified patient information from medical, laboratory, and pharmacy U.S. insurance claims records from the PatientSource and DiagnosticSource databases and compared asthma exacerbation rates before and after treatment with benralizumab.
Age, asthma diagnosis, number of exacerbations, and number of benralizumab treatment records within specified periods were used to identify a total of 1,795 participants for inclusion in the study. The index date for establishing before-treatment and after-treatment index time intervals of 12 months each was defined as the day after the initial benralizumab treatment occurring between November 2017 and June 2019.
The cohort was stratified into three nonmutually exclusive groups consisting of 349 patients who had switched primarily from either omalizumab or mepolizumab biologics to benralizumab; 429 patients subdivided by closest to the index date blood eosinophil counts of less than 150, greater than or equal to 150, 150-299, less than 300, and greater than or equal to 300, and 419 patients with post data collection extended beyond 12 months to 18 or 24 months.
Similarities in baseline patient characteristics that were were observed across the three cohorts included a mean age range of 51-53 years, preponderance of women (67%-69%), obesity diagnosis (31.5%-32.9%), and a mean Charlson Comorbidity Index of 1.47-1.52. Allergic rhinitis was the most frequently reported (60%-67%) comorbidity, followed by hypertension and gastroesophageal reflex.
Effectiveness
Benralizumab was found to be a significantly effective treatment for managing severe eosinophilic asthma for all three evaluated cohorts, as evidenced by reductions in asthma exacerbations post-index, compared with pre-index. Specifically, the exacerbation rate for all five subgroups of the blood eosinophil cohort significantly decreased from the pre-index 3.10-3.55 person per year (PPY) rate to a 1.11-1.72 PPY post-index rate, equivalent to a 52%-64% decrease in exacerbations (P < .001 for all pre-index vs. post-index comparisons).
Comparable reductions also occurred with the cohort in which the biologic treatment was changed to benralizumab. A greater effect was observed when the switch was made from omalizumab to benralizumab with a pre-post PPY rate reduction of 3.25-1.25 (62%) than when the switch was made from mepolizumab (pre-post PPY rate reduction was 3.81-1.78 [53%], but both resulted in significant post-treatment improvements (P < .001).
Results from the extended follow-up analysis cohort showed consistency for significant exacerbation rate decline going from a pre-index rate of 3.38 PPY down to 1.34 PPY (60% rate reduction vs. pre-index) in the first 12 post-index months, continuing to decline to 1.18 PPY (65% reduction) over the following six months (both significant at P < .001).
Likewise, the results from the extended follow-up 24-month subgroup presented significant down trending exacerbation rates from pre-index 3.38 PPY to 1.38 (comparative 59% reduction) for the first 12 months continuing down to 1.08 PPY (68% reduction) over the 12-24 month post-index period (both P < .001). In the first and second 12 post-index months for the 24-month subgroup, 39% and 49% of the patients, respectively, experienced no exacerbations.
Following treatment with benralizumab, in addition to the observed decline in asthma exacerbation rates, the need for concomitant asthma medications was also significantly reduced for all three cohorts.
This retrospective ZEPHYR 2 study contributes evidence supporting the significant effectiveness of benralizumab in improving disease management for “specific subsets of severe asthma patients that are frequently seen in real-world practice and may be excluded from clinical trials,” according to the authors. The treatment resulted in reduced rates of asthma exacerbations with defined standards for hospitalizations, visits to emergency department or urgent care, or outpatient visits with separate exacerbations occurring at greater than or equal to 14 days, as reported in database records. Reduction in the rate of asthma exacerbations when benralizumab is switched for another biologic increases the disease management options for achieving optimal patient care, the authors add.
The authors have financial relationships with AstraZeneca, the source of funding for the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The real-world Zephyr 2 study, which assessed benralizumab for effectiveness in treating severe eosinophilic asthma, was extended with an analysis of a larger population stratified into three cohorts of participants who were aged 12 years or older.
Immunotherapy with monoclonal antibodies designed to block specific inflammatory pathways is a recommended add-on treatment option for adults to manage severe, uncontrolled eosinophilic-dependent (> 150 cells/µl) and corticosteroid-dependent asthma. One such biologic, benralizumab, targets the interleukin-5 receptor alpha chain (IL-5Rα).
For asthma patients who had previously been treated with benralizumab, there were significant reductions in exacerbation rates in the ZEPHYR 1 study. However, information regarding benefit associated with specific profiles was limited, warranting a larger study to address effectiveness when considering various blood eosinophil counts, prior treatments with other biologics, or benralizumab use for up to 24 months, Donna Carstens, MD, of AstraZeneca, Wilmington, Del., and colleagues write.
Study details
In the retrospective cohort Zephyr 2 study, which was published in the Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology: In Practice, the researchers retrieved deidentified patient information from medical, laboratory, and pharmacy U.S. insurance claims records from the PatientSource and DiagnosticSource databases and compared asthma exacerbation rates before and after treatment with benralizumab.
Age, asthma diagnosis, number of exacerbations, and number of benralizumab treatment records within specified periods were used to identify a total of 1,795 participants for inclusion in the study. The index date for establishing before-treatment and after-treatment index time intervals of 12 months each was defined as the day after the initial benralizumab treatment occurring between November 2017 and June 2019.
The cohort was stratified into three nonmutually exclusive groups consisting of 349 patients who had switched primarily from either omalizumab or mepolizumab biologics to benralizumab; 429 patients subdivided by closest to the index date blood eosinophil counts of less than 150, greater than or equal to 150, 150-299, less than 300, and greater than or equal to 300, and 419 patients with post data collection extended beyond 12 months to 18 or 24 months.
Similarities in baseline patient characteristics that were were observed across the three cohorts included a mean age range of 51-53 years, preponderance of women (67%-69%), obesity diagnosis (31.5%-32.9%), and a mean Charlson Comorbidity Index of 1.47-1.52. Allergic rhinitis was the most frequently reported (60%-67%) comorbidity, followed by hypertension and gastroesophageal reflex.
Effectiveness
Benralizumab was found to be a significantly effective treatment for managing severe eosinophilic asthma for all three evaluated cohorts, as evidenced by reductions in asthma exacerbations post-index, compared with pre-index. Specifically, the exacerbation rate for all five subgroups of the blood eosinophil cohort significantly decreased from the pre-index 3.10-3.55 person per year (PPY) rate to a 1.11-1.72 PPY post-index rate, equivalent to a 52%-64% decrease in exacerbations (P < .001 for all pre-index vs. post-index comparisons).
Comparable reductions also occurred with the cohort in which the biologic treatment was changed to benralizumab. A greater effect was observed when the switch was made from omalizumab to benralizumab with a pre-post PPY rate reduction of 3.25-1.25 (62%) than when the switch was made from mepolizumab (pre-post PPY rate reduction was 3.81-1.78 [53%], but both resulted in significant post-treatment improvements (P < .001).
Results from the extended follow-up analysis cohort showed consistency for significant exacerbation rate decline going from a pre-index rate of 3.38 PPY down to 1.34 PPY (60% rate reduction vs. pre-index) in the first 12 post-index months, continuing to decline to 1.18 PPY (65% reduction) over the following six months (both significant at P < .001).
Likewise, the results from the extended follow-up 24-month subgroup presented significant down trending exacerbation rates from pre-index 3.38 PPY to 1.38 (comparative 59% reduction) for the first 12 months continuing down to 1.08 PPY (68% reduction) over the 12-24 month post-index period (both P < .001). In the first and second 12 post-index months for the 24-month subgroup, 39% and 49% of the patients, respectively, experienced no exacerbations.
Following treatment with benralizumab, in addition to the observed decline in asthma exacerbation rates, the need for concomitant asthma medications was also significantly reduced for all three cohorts.
This retrospective ZEPHYR 2 study contributes evidence supporting the significant effectiveness of benralizumab in improving disease management for “specific subsets of severe asthma patients that are frequently seen in real-world practice and may be excluded from clinical trials,” according to the authors. The treatment resulted in reduced rates of asthma exacerbations with defined standards for hospitalizations, visits to emergency department or urgent care, or outpatient visits with separate exacerbations occurring at greater than or equal to 14 days, as reported in database records. Reduction in the rate of asthma exacerbations when benralizumab is switched for another biologic increases the disease management options for achieving optimal patient care, the authors add.
The authors have financial relationships with AstraZeneca, the source of funding for the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALLERGY AND CLINICAL IMMUNOLOGY: IN PRACTICE
Enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis linked to dupilumab use for atopic dermatitis
Around 5% of patients treated with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis experience musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, according to the results of a descriptive study.
The main MSK symptom seen in the observational cohort was enthesitis, but some patients also experienced arthritis and tenosynovitis a median of 17 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment. Together these symptoms represent a new MSK syndrome, say researchers from the United Kingdom.
“The pattern of MSK symptoms and signs is characteristic of psoriatic arthritis/peripheral spondyloarthritis,” Bruce Kirkham, MD, and collaborators report in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“We started a few years ago and have been following the patients for quite a long time,” Dr. Kirkham, a consultant rheumatologist at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, told this news organization.
“We’re still seeing patients with the same type of syndrome presenting occasionally. It’s not a very common adverse event, but we think it continues,” he observed.
“Most of them don’t have very severe problems, and a lot of them can be treated with quite simple drugs or, alternatively, reducing the frequency of the injection,” Dr. Kirkham added.
Characterizing the MSK symptoms
Of 470 patients with atopic dermatitis who started treatment with dupilumab at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between October 2018 and February 2021, 36 (7.65%) developed rheumatic symptoms and were referred to the rheumatology department. These individuals had their family history assessed and thorough MSK evaluations, which included antibody and inflammatory markers, ultrasound of the peripheral small joints, and MRI of the large joints and spine.
A total of 26 (5.5%) patients – 14 of whom were male – had inflammatory enthesitis, arthritis, and/or tenosynovitis. Of the others, seven had osteoarthritis and three had degenerative spine disease.
Enthesitis was the most common finding in those with rheumatic symptoms, occurring on its own in 11 patients, with arthritis in three patients, and tenosynovitis in two patients.
These symptoms appeared 2-48 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment and were categorized as mild in 16 (61%) cases, moderate in six cases, and severe in four cases.
No specific predictors of the MSK symptoms seen were noted. Patient age, sex, duration of their atopic dermatitis, or how their skin condition had been previously treated did not help identify those who might develop rheumatic problems.
Conservative management approach
All patients had “outstanding” responses to treatment, Dr. Kirkham noted: The mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score before dupilumab treatment was 21, falling to 4.2 with treatment, indicating a mean 80% improvement.
Co-author Joseph Nathan, MBChB, of London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, who collaborated on the research while working within Dr. Kirkham’s group, said separately: “The concern that patients have is that when they start a medication and develop a side effect is that the medication is going to be stopped.”
Clinicians treating the patients took a conservative approach, prescribing NSAIDs such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors or altering the frequency with which dupilumab was given.
With this approach, MSK symptoms resolved in 15 patients who remained on treatment and in seven who had to stop dupilumab. There were four patients, however, who had unresolved symptoms even once dupilumab treatment had been stopped.
Altering the local cytokine balance
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. This results in blocking the function of not only IL-4 but also IL-13.
Dr. Kirkham and colleagues think this might not only alter the balance of cytokines in the skin but also in the joints and entheses with IL-17, IL-23, or even tumor necrosis factor playing a possible role. Another thought is that many circulating T-cells in the skin move to the joints and entheses to trigger symptoms.
IL-13 inhibition does seem to be important, as another British research team, from the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis at the University of Manchester (England), has found.
At the recent annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology, Sizheng Steven Zhao, MBChB, PhD, and colleagues reported that among people who carried a genetic variant predisposing them to having low IL-13 function, there was a higher risk for inflammatory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and other spondyloarthropathy-related diseases.
Indeed, when the single nucleotide polymorphism rs20541 was present, the odds for having psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis were higher than when it was not.
The findings are consistent with the idea that IL-4 and IL-13 may be acting as a restraint towards MSK diseases in some patients, Dr. Zhao and co-authors suggest.
“The genetic data supports what [Dr. Kirkham and team] have said from a mechanistic point of view,” Dr. Zhao said in an interview. “What you’re observing has a genetic basis.”
Dermatology perspective
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017, dupilumab has since been hailed as a “breakthrough” in atopic dermatitis treatment. Given as a subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, it provides a much-needed option for people who have moderate-to-severe disease and have tried other available treatments, including corticosteroids.
Dupilumab has since also been approved for asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis and is used off-label for other skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and alopecia areata.
“Dupilumab, like a lot of medications for atopic dermatitis, is a relatively new drug, and we are still learning about its safety,” Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Inflammatory arthritis has been reported in patients treated with dupilumab, and this new study provides some useful estimates,” added Dr. Gelfand, who is a professor of dermatology and epidemiology and directs the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, Philadelphia.
“There was no control group,” Dr. Gelfand said, so “a causal relationship cannot be well established based on these data alone. The mechanism is not known but may result from a shifting of the immune system.”
Dr. Zhao observed: “We don’t know what the natural history of these adverse events is. We don’t know if stopping the drug early will prevent long-term adverse events. So, we don’t know if people will ultimately develop permanent psoriatic arthritis if we don’t intervene quick enough when we observe an adverse event.”
Being aware of the possibility of rheumatic side effects occurring with dupilumab and similar agents is key, Dr. Gelfand and Dr. Kirkham both said independently.
“I have personally seen this entity in my practice,” Dr. Gelfand said. “It is important to clinicians prescribing dupilumab to alert patients about this potential side effect and ask about joint symptoms in follow-up.”
Dr. Kirkham said: “Prescribers need to be aware of it, because up until now it’s been just very vaguely discussed as sort of aches and pains, arthralgias, and it’s a much more specific of a kind of syndrome of enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis – a little like psoriatic arthritis.”
Not everyone has come across these side effects, however, as Steven Daveluy, MD, associate professor and dermatology program director at Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
“This article and the other case series both noted the musculoskeletal symptoms occurred in about 5% of patients, which surprised me since I haven’t seen it in my practice and have enough patients being treated with dupilumab that I would expect to see a case at that rate,” Dr. Daveluy said.
“The majority of cases are mild and respond to treatment with anti-inflammatories like naproxen, which is available over the counter. It’s likely that patients with a mild case could simply treat their pain with naproxen that’s already in their medicine cabinet until it resolves, never bringing it to the doctor’s attention,” he suggested.
“Dupilumab is still a safe and effective medication that can change the lives of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis,” he said.
“Awareness of this potential side effect can help dermatologists recognize it early and work together with patients to determine the best course of action.”
All research mentioned in this article was independently supported. Dr. Kirkham, Mr. Nathan, Dr. Zhao, and Dr. Daveluy report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gelfand has served as a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and receives research grants from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. He is a co-patent holder of resiquimod for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around 5% of patients treated with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis experience musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, according to the results of a descriptive study.
The main MSK symptom seen in the observational cohort was enthesitis, but some patients also experienced arthritis and tenosynovitis a median of 17 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment. Together these symptoms represent a new MSK syndrome, say researchers from the United Kingdom.
“The pattern of MSK symptoms and signs is characteristic of psoriatic arthritis/peripheral spondyloarthritis,” Bruce Kirkham, MD, and collaborators report in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“We started a few years ago and have been following the patients for quite a long time,” Dr. Kirkham, a consultant rheumatologist at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, told this news organization.
“We’re still seeing patients with the same type of syndrome presenting occasionally. It’s not a very common adverse event, but we think it continues,” he observed.
“Most of them don’t have very severe problems, and a lot of them can be treated with quite simple drugs or, alternatively, reducing the frequency of the injection,” Dr. Kirkham added.
Characterizing the MSK symptoms
Of 470 patients with atopic dermatitis who started treatment with dupilumab at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between October 2018 and February 2021, 36 (7.65%) developed rheumatic symptoms and were referred to the rheumatology department. These individuals had their family history assessed and thorough MSK evaluations, which included antibody and inflammatory markers, ultrasound of the peripheral small joints, and MRI of the large joints and spine.
A total of 26 (5.5%) patients – 14 of whom were male – had inflammatory enthesitis, arthritis, and/or tenosynovitis. Of the others, seven had osteoarthritis and three had degenerative spine disease.
Enthesitis was the most common finding in those with rheumatic symptoms, occurring on its own in 11 patients, with arthritis in three patients, and tenosynovitis in two patients.
These symptoms appeared 2-48 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment and were categorized as mild in 16 (61%) cases, moderate in six cases, and severe in four cases.
No specific predictors of the MSK symptoms seen were noted. Patient age, sex, duration of their atopic dermatitis, or how their skin condition had been previously treated did not help identify those who might develop rheumatic problems.
Conservative management approach
All patients had “outstanding” responses to treatment, Dr. Kirkham noted: The mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score before dupilumab treatment was 21, falling to 4.2 with treatment, indicating a mean 80% improvement.
Co-author Joseph Nathan, MBChB, of London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, who collaborated on the research while working within Dr. Kirkham’s group, said separately: “The concern that patients have is that when they start a medication and develop a side effect is that the medication is going to be stopped.”
Clinicians treating the patients took a conservative approach, prescribing NSAIDs such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors or altering the frequency with which dupilumab was given.
With this approach, MSK symptoms resolved in 15 patients who remained on treatment and in seven who had to stop dupilumab. There were four patients, however, who had unresolved symptoms even once dupilumab treatment had been stopped.
Altering the local cytokine balance
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. This results in blocking the function of not only IL-4 but also IL-13.
Dr. Kirkham and colleagues think this might not only alter the balance of cytokines in the skin but also in the joints and entheses with IL-17, IL-23, or even tumor necrosis factor playing a possible role. Another thought is that many circulating T-cells in the skin move to the joints and entheses to trigger symptoms.
IL-13 inhibition does seem to be important, as another British research team, from the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis at the University of Manchester (England), has found.
At the recent annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology, Sizheng Steven Zhao, MBChB, PhD, and colleagues reported that among people who carried a genetic variant predisposing them to having low IL-13 function, there was a higher risk for inflammatory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and other spondyloarthropathy-related diseases.
Indeed, when the single nucleotide polymorphism rs20541 was present, the odds for having psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis were higher than when it was not.
The findings are consistent with the idea that IL-4 and IL-13 may be acting as a restraint towards MSK diseases in some patients, Dr. Zhao and co-authors suggest.
“The genetic data supports what [Dr. Kirkham and team] have said from a mechanistic point of view,” Dr. Zhao said in an interview. “What you’re observing has a genetic basis.”
Dermatology perspective
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017, dupilumab has since been hailed as a “breakthrough” in atopic dermatitis treatment. Given as a subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, it provides a much-needed option for people who have moderate-to-severe disease and have tried other available treatments, including corticosteroids.
Dupilumab has since also been approved for asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis and is used off-label for other skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and alopecia areata.
“Dupilumab, like a lot of medications for atopic dermatitis, is a relatively new drug, and we are still learning about its safety,” Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Inflammatory arthritis has been reported in patients treated with dupilumab, and this new study provides some useful estimates,” added Dr. Gelfand, who is a professor of dermatology and epidemiology and directs the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, Philadelphia.
“There was no control group,” Dr. Gelfand said, so “a causal relationship cannot be well established based on these data alone. The mechanism is not known but may result from a shifting of the immune system.”
Dr. Zhao observed: “We don’t know what the natural history of these adverse events is. We don’t know if stopping the drug early will prevent long-term adverse events. So, we don’t know if people will ultimately develop permanent psoriatic arthritis if we don’t intervene quick enough when we observe an adverse event.”
Being aware of the possibility of rheumatic side effects occurring with dupilumab and similar agents is key, Dr. Gelfand and Dr. Kirkham both said independently.
“I have personally seen this entity in my practice,” Dr. Gelfand said. “It is important to clinicians prescribing dupilumab to alert patients about this potential side effect and ask about joint symptoms in follow-up.”
Dr. Kirkham said: “Prescribers need to be aware of it, because up until now it’s been just very vaguely discussed as sort of aches and pains, arthralgias, and it’s a much more specific of a kind of syndrome of enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis – a little like psoriatic arthritis.”
Not everyone has come across these side effects, however, as Steven Daveluy, MD, associate professor and dermatology program director at Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
“This article and the other case series both noted the musculoskeletal symptoms occurred in about 5% of patients, which surprised me since I haven’t seen it in my practice and have enough patients being treated with dupilumab that I would expect to see a case at that rate,” Dr. Daveluy said.
“The majority of cases are mild and respond to treatment with anti-inflammatories like naproxen, which is available over the counter. It’s likely that patients with a mild case could simply treat their pain with naproxen that’s already in their medicine cabinet until it resolves, never bringing it to the doctor’s attention,” he suggested.
“Dupilumab is still a safe and effective medication that can change the lives of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis,” he said.
“Awareness of this potential side effect can help dermatologists recognize it early and work together with patients to determine the best course of action.”
All research mentioned in this article was independently supported. Dr. Kirkham, Mr. Nathan, Dr. Zhao, and Dr. Daveluy report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gelfand has served as a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and receives research grants from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. He is a co-patent holder of resiquimod for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Around 5% of patients treated with dupilumab (Dupixent) for moderate-to-severe atopic dermatitis experience musculoskeletal (MSK) symptoms, according to the results of a descriptive study.
The main MSK symptom seen in the observational cohort was enthesitis, but some patients also experienced arthritis and tenosynovitis a median of 17 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment. Together these symptoms represent a new MSK syndrome, say researchers from the United Kingdom.
“The pattern of MSK symptoms and signs is characteristic of psoriatic arthritis/peripheral spondyloarthritis,” Bruce Kirkham, MD, and collaborators report in Arthritis & Rheumatology.
“We started a few years ago and have been following the patients for quite a long time,” Dr. Kirkham, a consultant rheumatologist at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust, London, told this news organization.
“We’re still seeing patients with the same type of syndrome presenting occasionally. It’s not a very common adverse event, but we think it continues,” he observed.
“Most of them don’t have very severe problems, and a lot of them can be treated with quite simple drugs or, alternatively, reducing the frequency of the injection,” Dr. Kirkham added.
Characterizing the MSK symptoms
Of 470 patients with atopic dermatitis who started treatment with dupilumab at Guy’s and St. Thomas’ NHS Foundation Trust between October 2018 and February 2021, 36 (7.65%) developed rheumatic symptoms and were referred to the rheumatology department. These individuals had their family history assessed and thorough MSK evaluations, which included antibody and inflammatory markers, ultrasound of the peripheral small joints, and MRI of the large joints and spine.
A total of 26 (5.5%) patients – 14 of whom were male – had inflammatory enthesitis, arthritis, and/or tenosynovitis. Of the others, seven had osteoarthritis and three had degenerative spine disease.
Enthesitis was the most common finding in those with rheumatic symptoms, occurring on its own in 11 patients, with arthritis in three patients, and tenosynovitis in two patients.
These symptoms appeared 2-48 weeks after starting dupilumab treatment and were categorized as mild in 16 (61%) cases, moderate in six cases, and severe in four cases.
No specific predictors of the MSK symptoms seen were noted. Patient age, sex, duration of their atopic dermatitis, or how their skin condition had been previously treated did not help identify those who might develop rheumatic problems.
Conservative management approach
All patients had “outstanding” responses to treatment, Dr. Kirkham noted: The mean Eczema Area and Severity Index score before dupilumab treatment was 21, falling to 4.2 with treatment, indicating a mean 80% improvement.
Co-author Joseph Nathan, MBChB, of London North West Healthcare NHS Trust, who collaborated on the research while working within Dr. Kirkham’s group, said separately: “The concern that patients have is that when they start a medication and develop a side effect is that the medication is going to be stopped.”
Clinicians treating the patients took a conservative approach, prescribing NSAIDs such as cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitors or altering the frequency with which dupilumab was given.
With this approach, MSK symptoms resolved in 15 patients who remained on treatment and in seven who had to stop dupilumab. There were four patients, however, who had unresolved symptoms even once dupilumab treatment had been stopped.
Altering the local cytokine balance
Dupilumab is a monoclonal antibody that binds to the alpha subunit of the interleukin-4 receptor. This results in blocking the function of not only IL-4 but also IL-13.
Dr. Kirkham and colleagues think this might not only alter the balance of cytokines in the skin but also in the joints and entheses with IL-17, IL-23, or even tumor necrosis factor playing a possible role. Another thought is that many circulating T-cells in the skin move to the joints and entheses to trigger symptoms.
IL-13 inhibition does seem to be important, as another British research team, from the Centre for Epidemiology Versus Arthritis at the University of Manchester (England), has found.
At the recent annual meeting of the British Society for Rheumatology, Sizheng Steven Zhao, MBChB, PhD, and colleagues reported that among people who carried a genetic variant predisposing them to having low IL-13 function, there was a higher risk for inflammatory diseases such as psoriatic arthritis and other spondyloarthropathy-related diseases.
Indeed, when the single nucleotide polymorphism rs20541 was present, the odds for having psoriatic arthritis and psoriasis were higher than when it was not.
The findings are consistent with the idea that IL-4 and IL-13 may be acting as a restraint towards MSK diseases in some patients, Dr. Zhao and co-authors suggest.
“The genetic data supports what [Dr. Kirkham and team] have said from a mechanistic point of view,” Dr. Zhao said in an interview. “What you’re observing has a genetic basis.”
Dermatology perspective
Approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration in 2017, dupilumab has since been hailed as a “breakthrough” in atopic dermatitis treatment. Given as a subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks, it provides a much-needed option for people who have moderate-to-severe disease and have tried other available treatments, including corticosteroids.
Dupilumab has since also been approved for asthma, chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis, eosinophilic esophagitis, and prurigo nodularis and is used off-label for other skin conditions such as contact dermatitis, chronic spontaneous urticaria, and alopecia areata.
“Dupilumab, like a lot of medications for atopic dermatitis, is a relatively new drug, and we are still learning about its safety,” Joel M. Gelfand, MD, MSCE, of the University of Pennsylvania Perelman School of Medicine, Philadelphia, told this news organization.
“Inflammatory arthritis has been reported in patients treated with dupilumab, and this new study provides some useful estimates,” added Dr. Gelfand, who is a professor of dermatology and epidemiology and directs the Psoriasis and Phototherapy Treatment Center, Philadelphia.
“There was no control group,” Dr. Gelfand said, so “a causal relationship cannot be well established based on these data alone. The mechanism is not known but may result from a shifting of the immune system.”
Dr. Zhao observed: “We don’t know what the natural history of these adverse events is. We don’t know if stopping the drug early will prevent long-term adverse events. So, we don’t know if people will ultimately develop permanent psoriatic arthritis if we don’t intervene quick enough when we observe an adverse event.”
Being aware of the possibility of rheumatic side effects occurring with dupilumab and similar agents is key, Dr. Gelfand and Dr. Kirkham both said independently.
“I have personally seen this entity in my practice,” Dr. Gelfand said. “It is important to clinicians prescribing dupilumab to alert patients about this potential side effect and ask about joint symptoms in follow-up.”
Dr. Kirkham said: “Prescribers need to be aware of it, because up until now it’s been just very vaguely discussed as sort of aches and pains, arthralgias, and it’s a much more specific of a kind of syndrome of enthesitis, arthritis, tenosynovitis – a little like psoriatic arthritis.”
Not everyone has come across these side effects, however, as Steven Daveluy, MD, associate professor and dermatology program director at Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
“This article and the other case series both noted the musculoskeletal symptoms occurred in about 5% of patients, which surprised me since I haven’t seen it in my practice and have enough patients being treated with dupilumab that I would expect to see a case at that rate,” Dr. Daveluy said.
“The majority of cases are mild and respond to treatment with anti-inflammatories like naproxen, which is available over the counter. It’s likely that patients with a mild case could simply treat their pain with naproxen that’s already in their medicine cabinet until it resolves, never bringing it to the doctor’s attention,” he suggested.
“Dupilumab is still a safe and effective medication that can change the lives of patients suffering from atopic dermatitis,” he said.
“Awareness of this potential side effect can help dermatologists recognize it early and work together with patients to determine the best course of action.”
All research mentioned in this article was independently supported. Dr. Kirkham, Mr. Nathan, Dr. Zhao, and Dr. Daveluy report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Gelfand has served as a consultant for numerous pharmaceutical companies and receives research grants from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, and Pfizer. He is a co-patent holder of resiquimod for treatment of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ARTHRITIS & RHEUMATOLOGY