User login
FDA approves Primatene Mist return
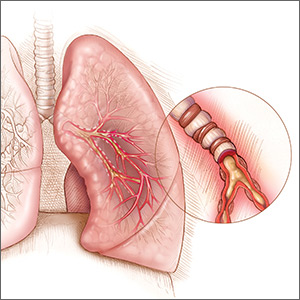
After a long absence, Primatene Mist, an over-the-counter asthma inhaler removed from the market in 2011, is being reintroduced in a metered-dose inhaler with a new, environmentally friendly propellant.
But the inhaler’s comeback may prove as controversial as its removal. Respiratory medicine associations have taken issue with the Food and Drug Administration’s decision, warning patients that asthma is not a “do-it-yourself” disease that can be managed with over-the-counter medications.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, American College of Chest Physicians, American Lung Association, American Thoracic Society, and the American Association of Asthma Educators have each individually protested the decision, and together sent a joint resolution to FDA decrying it. At the core of their protest are the facts that epinephrine is a symptomatic, not therapeutic, asthma treatment and that racemic epinephrine is not a not a recommended asthma treatment under the National Institutes of Health’s “Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma.”
CHEST has published the following statement: “The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) is disappointed with the FDA’s decision to approve over-the counter epinephrine (Primatene® Mist HFA) for the treatment of asthma. CHEST is a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing best patient outcomes. Our membership of more than 19,000 members from around the world provides patient care in pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine.
Asthma is a serious and chronic condition with associated high health-care burden. Care for ALL patients with asthma should be under the guidance of a health-care provider. The majority of asthma patients requires treatment with a controller medication, which is only available by prescription. Frequent rescue inhaler use has been associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Over the counter availability of a reliever medication like Primatene Mist can endanger a patient’s wellbeing by providing temporary relief in symptoms, resulting in delay in seeking medical care.”
The inhaler was pulled from sales as part of an international pact to reduce ozone-depleting substances. The 1989 Montreal Protocol of Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer and the Clean Air Act of 1990 targeted chlorofluorocarbons among those substances, and epinephrine inhalers that contained CFCs were phased out.
The new Primatene Mist HFA (Amphastar Pharmaceuticals) contains hydrofluoroalkane (HFA) propellants, which are permitted under current international and U.S. law. This puts Primatene in the same category with other inhalers, including albuterol and levalbuterol, which also use HFAs as propellants. Each dose delivers 125 mcg of epinephrine.
The inhaler itself has also been redesigned, according to Theresa Michele, MD, director of the FDA’s Division of Nonprescription Drug Products in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. The active ingredient is still epinephrine, albeit a smaller dose than found in the original 200-mcg mist. However, the inhaler needs to be activated before first use and cleaned every day after use to prevent a medication buildup. Like other metered-dose inhalers, it requires a priming spray before the inhalation dose, Dr. Michele noted in her online column.
“The inhaler also needs to be shaken and then sprayed once into the air before each use. It may seem strange to shake and spray the inhaler into the air each time before using it. But these two steps are critical to ensure that the medicine is properly mixed before each dose,” Dr. Michele wrote.
A public statement by FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, and Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, asserted that the inhaler fills a clinical gap for patients with mild to moderate intermittent asthma.
“The scientific information we reviewed to approve the new version of OTC Primatene Mist shows there is a narrow population of those diagnosed with asthma that may benefit from having access to this type of OTC asthma inhaler. But the product has certain cautions. Making sure that patients can understand and apply the instructions for use was a critical consideration for the FDA. The new product is only appropriate for those with a diagnosis of mild, intermittent asthma. Patients with more severe asthma should not rely on it. Instead, they should be working with their health care provider to ensure an appropriate treatment plan for their condition.”
Before this approval, Amphastar had unsuccessfully brought the reformulated Primatene before FDA several times. The move to finally reinstate it comes after a long, and sometimes contentious, debate among patients and FDA’s Nonprescription Drugs and Pulmonary-Allergy Drugs advisory committee. A quick Internet or Facebook search brings up dozens of stories from patients who say they effectively managed their mild to moderate asthma for years with Primatene. Typically, the stories describe changing to prescription asthma medications that, for some, run into the hundreds of dollars per month. Supporters often negatively compare decades of using the inexpensive Primatene with no ill effects to their recent experiences using prescription corticosteroid inhalers.
It was 4 years ago when Amphastar first appeared before the advisory committee with the reformulated inhaler and positive safety and efficacy data. Although agreeing with the efficacy data, the advisory committee voted against approval, because some felt that asthma should always be managed by a physician; an OTC bronchodilator encouraged self-medicating and discouraged patients from seeking medical care, they said.
“On the one hand, it has been stated that a quick-relief medication available OTC is needed for use in low-income, elderly, and uninsured individuals who might otherwise not have access to treatment or be able to see a health care practitioner,” FDA documents noted. “In contrast, there is also a concern that because asthma is a potentially life-threatening condition that should be diagnosed and treated by a health care professional, availability of an OTC bronchodilator product may discourage consumers from seeking appropriate care, resulting in worse asthma outcomes.”
Two years later, the company received another blow to Primatene program. FDA’s Complete Response Letter required Amphastar to make additional changes to the packaging and run a consumer product safety study, intended to show that people could learn to use the metered-dose inhaler correctly.
In Amphastar’s 2018 first-quarter report, however, company CEO Jack Zhang, PhD, finally shared some good news. “We are pleased to announce that we have resubmitted our NDA for Primatene Mist after receiving good results from our recent human factors study. While we don’t have a Prescription Free User Drug Act [PDUFA] date yet, we plan to begin producing inventory in preparation for a launch.”
That day arrived on Nov. 8, when the PDUFA was granted. In their public letter, Dr. Gottlieb and Dr. Woodcock acknowledged the long and difficult approval path and offered reassurance that Primatene is safe and effective.
“For the right patient, our analysis of the data, including new information that was developed since this product was previously on the market, shows that there are no serious safety concerns when Primatene Mist is used as directed. The product is appropriate for mild symptoms of intermittent asthma, however, even patients with mild asthma can have severe exacerbations – so it’s still important to consult a health care provider about appropriate care and have their condition reassessed. And, of course, all patients who experience severe exacerbations should go to the emergency room right away.”
Primatene Mist HFA is intended for the temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma (wheezing, tightness of chest, shortness of breath) in patients aged 12 years and older. It should not be considered a replacement for prescription asthma medications. It should be available in stores early next year.
After a long absence, Primatene Mist, an over-the-counter asthma inhaler removed from the market in 2011, is being reintroduced in a metered-dose inhaler with a new, environmentally friendly propellant.
But the inhaler’s comeback may prove as controversial as its removal. Respiratory medicine associations have taken issue with the Food and Drug Administration’s decision, warning patients that asthma is not a “do-it-yourself” disease that can be managed with over-the-counter medications.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, American College of Chest Physicians, American Lung Association, American Thoracic Society, and the American Association of Asthma Educators have each individually protested the decision, and together sent a joint resolution to FDA decrying it. At the core of their protest are the facts that epinephrine is a symptomatic, not therapeutic, asthma treatment and that racemic epinephrine is not a not a recommended asthma treatment under the National Institutes of Health’s “Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma.”
CHEST has published the following statement: “The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) is disappointed with the FDA’s decision to approve over-the counter epinephrine (Primatene® Mist HFA) for the treatment of asthma. CHEST is a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing best patient outcomes. Our membership of more than 19,000 members from around the world provides patient care in pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine.
Asthma is a serious and chronic condition with associated high health-care burden. Care for ALL patients with asthma should be under the guidance of a health-care provider. The majority of asthma patients requires treatment with a controller medication, which is only available by prescription. Frequent rescue inhaler use has been associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Over the counter availability of a reliever medication like Primatene Mist can endanger a patient’s wellbeing by providing temporary relief in symptoms, resulting in delay in seeking medical care.”
The inhaler was pulled from sales as part of an international pact to reduce ozone-depleting substances. The 1989 Montreal Protocol of Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer and the Clean Air Act of 1990 targeted chlorofluorocarbons among those substances, and epinephrine inhalers that contained CFCs were phased out.
The new Primatene Mist HFA (Amphastar Pharmaceuticals) contains hydrofluoroalkane (HFA) propellants, which are permitted under current international and U.S. law. This puts Primatene in the same category with other inhalers, including albuterol and levalbuterol, which also use HFAs as propellants. Each dose delivers 125 mcg of epinephrine.
The inhaler itself has also been redesigned, according to Theresa Michele, MD, director of the FDA’s Division of Nonprescription Drug Products in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. The active ingredient is still epinephrine, albeit a smaller dose than found in the original 200-mcg mist. However, the inhaler needs to be activated before first use and cleaned every day after use to prevent a medication buildup. Like other metered-dose inhalers, it requires a priming spray before the inhalation dose, Dr. Michele noted in her online column.
“The inhaler also needs to be shaken and then sprayed once into the air before each use. It may seem strange to shake and spray the inhaler into the air each time before using it. But these two steps are critical to ensure that the medicine is properly mixed before each dose,” Dr. Michele wrote.
A public statement by FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, and Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, asserted that the inhaler fills a clinical gap for patients with mild to moderate intermittent asthma.
“The scientific information we reviewed to approve the new version of OTC Primatene Mist shows there is a narrow population of those diagnosed with asthma that may benefit from having access to this type of OTC asthma inhaler. But the product has certain cautions. Making sure that patients can understand and apply the instructions for use was a critical consideration for the FDA. The new product is only appropriate for those with a diagnosis of mild, intermittent asthma. Patients with more severe asthma should not rely on it. Instead, they should be working with their health care provider to ensure an appropriate treatment plan for their condition.”
Before this approval, Amphastar had unsuccessfully brought the reformulated Primatene before FDA several times. The move to finally reinstate it comes after a long, and sometimes contentious, debate among patients and FDA’s Nonprescription Drugs and Pulmonary-Allergy Drugs advisory committee. A quick Internet or Facebook search brings up dozens of stories from patients who say they effectively managed their mild to moderate asthma for years with Primatene. Typically, the stories describe changing to prescription asthma medications that, for some, run into the hundreds of dollars per month. Supporters often negatively compare decades of using the inexpensive Primatene with no ill effects to their recent experiences using prescription corticosteroid inhalers.
It was 4 years ago when Amphastar first appeared before the advisory committee with the reformulated inhaler and positive safety and efficacy data. Although agreeing with the efficacy data, the advisory committee voted against approval, because some felt that asthma should always be managed by a physician; an OTC bronchodilator encouraged self-medicating and discouraged patients from seeking medical care, they said.
“On the one hand, it has been stated that a quick-relief medication available OTC is needed for use in low-income, elderly, and uninsured individuals who might otherwise not have access to treatment or be able to see a health care practitioner,” FDA documents noted. “In contrast, there is also a concern that because asthma is a potentially life-threatening condition that should be diagnosed and treated by a health care professional, availability of an OTC bronchodilator product may discourage consumers from seeking appropriate care, resulting in worse asthma outcomes.”
Two years later, the company received another blow to Primatene program. FDA’s Complete Response Letter required Amphastar to make additional changes to the packaging and run a consumer product safety study, intended to show that people could learn to use the metered-dose inhaler correctly.
In Amphastar’s 2018 first-quarter report, however, company CEO Jack Zhang, PhD, finally shared some good news. “We are pleased to announce that we have resubmitted our NDA for Primatene Mist after receiving good results from our recent human factors study. While we don’t have a Prescription Free User Drug Act [PDUFA] date yet, we plan to begin producing inventory in preparation for a launch.”
That day arrived on Nov. 8, when the PDUFA was granted. In their public letter, Dr. Gottlieb and Dr. Woodcock acknowledged the long and difficult approval path and offered reassurance that Primatene is safe and effective.
“For the right patient, our analysis of the data, including new information that was developed since this product was previously on the market, shows that there are no serious safety concerns when Primatene Mist is used as directed. The product is appropriate for mild symptoms of intermittent asthma, however, even patients with mild asthma can have severe exacerbations – so it’s still important to consult a health care provider about appropriate care and have their condition reassessed. And, of course, all patients who experience severe exacerbations should go to the emergency room right away.”
Primatene Mist HFA is intended for the temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma (wheezing, tightness of chest, shortness of breath) in patients aged 12 years and older. It should not be considered a replacement for prescription asthma medications. It should be available in stores early next year.
After a long absence, Primatene Mist, an over-the-counter asthma inhaler removed from the market in 2011, is being reintroduced in a metered-dose inhaler with a new, environmentally friendly propellant.
But the inhaler’s comeback may prove as controversial as its removal. Respiratory medicine associations have taken issue with the Food and Drug Administration’s decision, warning patients that asthma is not a “do-it-yourself” disease that can be managed with over-the-counter medications.
The American College of Allergy, Asthma, and Immunology, American College of Chest Physicians, American Lung Association, American Thoracic Society, and the American Association of Asthma Educators have each individually protested the decision, and together sent a joint resolution to FDA decrying it. At the core of their protest are the facts that epinephrine is a symptomatic, not therapeutic, asthma treatment and that racemic epinephrine is not a not a recommended asthma treatment under the National Institutes of Health’s “Guidelines for the Diagnosis and Management of Asthma.”
CHEST has published the following statement: “The American College of Chest Physicians (CHEST) is disappointed with the FDA’s decision to approve over-the counter epinephrine (Primatene® Mist HFA) for the treatment of asthma. CHEST is a nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing best patient outcomes. Our membership of more than 19,000 members from around the world provides patient care in pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine.
Asthma is a serious and chronic condition with associated high health-care burden. Care for ALL patients with asthma should be under the guidance of a health-care provider. The majority of asthma patients requires treatment with a controller medication, which is only available by prescription. Frequent rescue inhaler use has been associated with increased morbidity and mortality. Over the counter availability of a reliever medication like Primatene Mist can endanger a patient’s wellbeing by providing temporary relief in symptoms, resulting in delay in seeking medical care.”
The inhaler was pulled from sales as part of an international pact to reduce ozone-depleting substances. The 1989 Montreal Protocol of Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer and the Clean Air Act of 1990 targeted chlorofluorocarbons among those substances, and epinephrine inhalers that contained CFCs were phased out.
The new Primatene Mist HFA (Amphastar Pharmaceuticals) contains hydrofluoroalkane (HFA) propellants, which are permitted under current international and U.S. law. This puts Primatene in the same category with other inhalers, including albuterol and levalbuterol, which also use HFAs as propellants. Each dose delivers 125 mcg of epinephrine.
The inhaler itself has also been redesigned, according to Theresa Michele, MD, director of the FDA’s Division of Nonprescription Drug Products in the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research. The active ingredient is still epinephrine, albeit a smaller dose than found in the original 200-mcg mist. However, the inhaler needs to be activated before first use and cleaned every day after use to prevent a medication buildup. Like other metered-dose inhalers, it requires a priming spray before the inhalation dose, Dr. Michele noted in her online column.
“The inhaler also needs to be shaken and then sprayed once into the air before each use. It may seem strange to shake and spray the inhaler into the air each time before using it. But these two steps are critical to ensure that the medicine is properly mixed before each dose,” Dr. Michele wrote.
A public statement by FDA Commissioner Scott Gottlieb, MD, and Janet Woodcock, MD, director of the Center for Drug Evaluation and Research, asserted that the inhaler fills a clinical gap for patients with mild to moderate intermittent asthma.
“The scientific information we reviewed to approve the new version of OTC Primatene Mist shows there is a narrow population of those diagnosed with asthma that may benefit from having access to this type of OTC asthma inhaler. But the product has certain cautions. Making sure that patients can understand and apply the instructions for use was a critical consideration for the FDA. The new product is only appropriate for those with a diagnosis of mild, intermittent asthma. Patients with more severe asthma should not rely on it. Instead, they should be working with their health care provider to ensure an appropriate treatment plan for their condition.”
Before this approval, Amphastar had unsuccessfully brought the reformulated Primatene before FDA several times. The move to finally reinstate it comes after a long, and sometimes contentious, debate among patients and FDA’s Nonprescription Drugs and Pulmonary-Allergy Drugs advisory committee. A quick Internet or Facebook search brings up dozens of stories from patients who say they effectively managed their mild to moderate asthma for years with Primatene. Typically, the stories describe changing to prescription asthma medications that, for some, run into the hundreds of dollars per month. Supporters often negatively compare decades of using the inexpensive Primatene with no ill effects to their recent experiences using prescription corticosteroid inhalers.
It was 4 years ago when Amphastar first appeared before the advisory committee with the reformulated inhaler and positive safety and efficacy data. Although agreeing with the efficacy data, the advisory committee voted against approval, because some felt that asthma should always be managed by a physician; an OTC bronchodilator encouraged self-medicating and discouraged patients from seeking medical care, they said.
“On the one hand, it has been stated that a quick-relief medication available OTC is needed for use in low-income, elderly, and uninsured individuals who might otherwise not have access to treatment or be able to see a health care practitioner,” FDA documents noted. “In contrast, there is also a concern that because asthma is a potentially life-threatening condition that should be diagnosed and treated by a health care professional, availability of an OTC bronchodilator product may discourage consumers from seeking appropriate care, resulting in worse asthma outcomes.”
Two years later, the company received another blow to Primatene program. FDA’s Complete Response Letter required Amphastar to make additional changes to the packaging and run a consumer product safety study, intended to show that people could learn to use the metered-dose inhaler correctly.
In Amphastar’s 2018 first-quarter report, however, company CEO Jack Zhang, PhD, finally shared some good news. “We are pleased to announce that we have resubmitted our NDA for Primatene Mist after receiving good results from our recent human factors study. While we don’t have a Prescription Free User Drug Act [PDUFA] date yet, we plan to begin producing inventory in preparation for a launch.”
That day arrived on Nov. 8, when the PDUFA was granted. In their public letter, Dr. Gottlieb and Dr. Woodcock acknowledged the long and difficult approval path and offered reassurance that Primatene is safe and effective.
“For the right patient, our analysis of the data, including new information that was developed since this product was previously on the market, shows that there are no serious safety concerns when Primatene Mist is used as directed. The product is appropriate for mild symptoms of intermittent asthma, however, even patients with mild asthma can have severe exacerbations – so it’s still important to consult a health care provider about appropriate care and have their condition reassessed. And, of course, all patients who experience severe exacerbations should go to the emergency room right away.”
Primatene Mist HFA is intended for the temporary relief of mild symptoms of intermittent asthma (wheezing, tightness of chest, shortness of breath) in patients aged 12 years and older. It should not be considered a replacement for prescription asthma medications. It should be available in stores early next year.
Pneumonia, COPD most common emergency care–sensitive conditions
SAN DIEGO – Emergency care–sensitive conditions – those for which timely access to high-quality emergency care impact morbidity and mortality—account for 14% of all ED visits, results from a large analysis of national data showed.
In previously published work, an eight-member expert panel identified 51 condition groups as emergency care–sensitive conditions (ECSCs), including asthma, cardiac arrest, cerebral infarction, and pneumonia. The purpose of the current study, published in Annals of Emergency Medicine and presented by Anita Vashi, MD, MPH, at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians, was to provide the first national estimates of acute care utilization and the demographic characteristics of adults experiencing ECSCs, compare ECSC and non-ECSC ED visits, and assess patient- and hospital-level characteristics predictive of an ECSC-related ED visit.
Using the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample data set, Dr. Vashi, a physician investigator at the Center for Innovation to Implementation at the VA Palo Alto Health Care System, and her colleagues retrospectively evaluated all ED visits for patients aged 18 years and older from 2009 to 2014. The researchers used summary statistics to compare population characteristics across groups and multivariable logistic regression models to assess the odds of an ECSC-related ED visit with patient- and hospital-level characteristics.
Of the 622,725,542 estimated ED visits evaluated during the study period, 86,577,041 (14%) were ECSCs. Among these ECSC visits, 58% of patients were admitted for an average length of 3.2 days and an average charge of $2,240. The most frequent ECSC-related visits were for pneumonia (9%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (9%), asthma (7%), heart failure (7%), and sepsis (5%), but varied by age group.
Dr. Vashi and her colleagues found that ECSCs were more common among older adults, males, those who reside in low-income areas, those who reside in the South, and among metropolitan-based hospitals and nontrauma center hospitals. ECSCs also accounted for about 45% of all inpatient admissions.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of having an ECSC-related visit was highest among patients aged 65 years and older (odds ratio, 3.84), those on Medicare (OR, 1.37), those who resided in rural counties (OR, 1.21), and those who reside in the Western portion of the United States (OR, 1.11). Significant hospital-related factors related to ECSC visits included trauma centers (OR, 1.09), nonteaching hospitals (OR, 1.04), and EDs located in the wealthiest counties (OR, 1.02).
The researchers also found that 40% of patients who made ECSC-related ED visits were treated and discharged back to the community. “There is evidence of regional variability, suggesting the need for future research,” said Dr. Vashi, who also holds a faculty position in the department of emergency medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “We found no consistent relationship between insurance, income, and ED use for ECSC-related conditions. This suggests that ECSCs are not significantly influenced by socioeconomic factor and can serve as a reliable marker for acuity.”
The next steps in this research area, she added, are to create condition-specific measures related to morbidity, mortality, and posthospital events, as well as to analyze regional and hospital variations including correlation across conditions, and to compare performance across conditions and hospitals.
Dr. Vashi reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Vashi A et al. Ann Emerg Med. 2018 Oct;72;4:S38. doi. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.08.091.
SAN DIEGO – Emergency care–sensitive conditions – those for which timely access to high-quality emergency care impact morbidity and mortality—account for 14% of all ED visits, results from a large analysis of national data showed.
In previously published work, an eight-member expert panel identified 51 condition groups as emergency care–sensitive conditions (ECSCs), including asthma, cardiac arrest, cerebral infarction, and pneumonia. The purpose of the current study, published in Annals of Emergency Medicine and presented by Anita Vashi, MD, MPH, at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians, was to provide the first national estimates of acute care utilization and the demographic characteristics of adults experiencing ECSCs, compare ECSC and non-ECSC ED visits, and assess patient- and hospital-level characteristics predictive of an ECSC-related ED visit.
Using the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample data set, Dr. Vashi, a physician investigator at the Center for Innovation to Implementation at the VA Palo Alto Health Care System, and her colleagues retrospectively evaluated all ED visits for patients aged 18 years and older from 2009 to 2014. The researchers used summary statistics to compare population characteristics across groups and multivariable logistic regression models to assess the odds of an ECSC-related ED visit with patient- and hospital-level characteristics.
Of the 622,725,542 estimated ED visits evaluated during the study period, 86,577,041 (14%) were ECSCs. Among these ECSC visits, 58% of patients were admitted for an average length of 3.2 days and an average charge of $2,240. The most frequent ECSC-related visits were for pneumonia (9%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (9%), asthma (7%), heart failure (7%), and sepsis (5%), but varied by age group.
Dr. Vashi and her colleagues found that ECSCs were more common among older adults, males, those who reside in low-income areas, those who reside in the South, and among metropolitan-based hospitals and nontrauma center hospitals. ECSCs also accounted for about 45% of all inpatient admissions.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of having an ECSC-related visit was highest among patients aged 65 years and older (odds ratio, 3.84), those on Medicare (OR, 1.37), those who resided in rural counties (OR, 1.21), and those who reside in the Western portion of the United States (OR, 1.11). Significant hospital-related factors related to ECSC visits included trauma centers (OR, 1.09), nonteaching hospitals (OR, 1.04), and EDs located in the wealthiest counties (OR, 1.02).
The researchers also found that 40% of patients who made ECSC-related ED visits were treated and discharged back to the community. “There is evidence of regional variability, suggesting the need for future research,” said Dr. Vashi, who also holds a faculty position in the department of emergency medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “We found no consistent relationship between insurance, income, and ED use for ECSC-related conditions. This suggests that ECSCs are not significantly influenced by socioeconomic factor and can serve as a reliable marker for acuity.”
The next steps in this research area, she added, are to create condition-specific measures related to morbidity, mortality, and posthospital events, as well as to analyze regional and hospital variations including correlation across conditions, and to compare performance across conditions and hospitals.
Dr. Vashi reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Vashi A et al. Ann Emerg Med. 2018 Oct;72;4:S38. doi. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.08.091.
SAN DIEGO – Emergency care–sensitive conditions – those for which timely access to high-quality emergency care impact morbidity and mortality—account for 14% of all ED visits, results from a large analysis of national data showed.
In previously published work, an eight-member expert panel identified 51 condition groups as emergency care–sensitive conditions (ECSCs), including asthma, cardiac arrest, cerebral infarction, and pneumonia. The purpose of the current study, published in Annals of Emergency Medicine and presented by Anita Vashi, MD, MPH, at the annual meeting of the American College of Emergency Physicians, was to provide the first national estimates of acute care utilization and the demographic characteristics of adults experiencing ECSCs, compare ECSC and non-ECSC ED visits, and assess patient- and hospital-level characteristics predictive of an ECSC-related ED visit.
Using the Nationwide Emergency Department Sample data set, Dr. Vashi, a physician investigator at the Center for Innovation to Implementation at the VA Palo Alto Health Care System, and her colleagues retrospectively evaluated all ED visits for patients aged 18 years and older from 2009 to 2014. The researchers used summary statistics to compare population characteristics across groups and multivariable logistic regression models to assess the odds of an ECSC-related ED visit with patient- and hospital-level characteristics.
Of the 622,725,542 estimated ED visits evaluated during the study period, 86,577,041 (14%) were ECSCs. Among these ECSC visits, 58% of patients were admitted for an average length of 3.2 days and an average charge of $2,240. The most frequent ECSC-related visits were for pneumonia (9%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (9%), asthma (7%), heart failure (7%), and sepsis (5%), but varied by age group.
Dr. Vashi and her colleagues found that ECSCs were more common among older adults, males, those who reside in low-income areas, those who reside in the South, and among metropolitan-based hospitals and nontrauma center hospitals. ECSCs also accounted for about 45% of all inpatient admissions.
Multivariate logistic regression analysis revealed that the odds of having an ECSC-related visit was highest among patients aged 65 years and older (odds ratio, 3.84), those on Medicare (OR, 1.37), those who resided in rural counties (OR, 1.21), and those who reside in the Western portion of the United States (OR, 1.11). Significant hospital-related factors related to ECSC visits included trauma centers (OR, 1.09), nonteaching hospitals (OR, 1.04), and EDs located in the wealthiest counties (OR, 1.02).
The researchers also found that 40% of patients who made ECSC-related ED visits were treated and discharged back to the community. “There is evidence of regional variability, suggesting the need for future research,” said Dr. Vashi, who also holds a faculty position in the department of emergency medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University. “We found no consistent relationship between insurance, income, and ED use for ECSC-related conditions. This suggests that ECSCs are not significantly influenced by socioeconomic factor and can serve as a reliable marker for acuity.”
The next steps in this research area, she added, are to create condition-specific measures related to morbidity, mortality, and posthospital events, as well as to analyze regional and hospital variations including correlation across conditions, and to compare performance across conditions and hospitals.
Dr. Vashi reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Vashi A et al. Ann Emerg Med. 2018 Oct;72;4:S38. doi. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.08.091.
REPORTING FROM ACEP18
Key clinical point: Emergency care–sensitive conditions (ECSCs) make up a significant proportion of ED visits.
Major finding: The most common ECSC-related visits were for pneumonia (9%), chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (9%), and asthma (7%).
Study details: A retrospective cohort study of more than 86.5 million ECSC-related ED visits.
Disclosures: Dr. Vashi reported having no financial disclosures.
Source: Vashi A et al. Ann Emerg Med. 2018 Oct;72;4:S38. doi. 10.1016/j.annemergmed.2018.08.091.
Should you reassess your patient’s asthma diagnosis?
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 45-year-old woman presents to your office for a yearly visit. Two years ago she was started on an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) and a bronchodilator rescue inhaler after being diagnosed with asthma based on her history and physical exam findings. She has had no exacerbations since then. Should you consider weaning her off the inhalers?
Asthma is a prevalent problem; 8% of adults ages 18 to 64 years have the chronic lung disease.2 Diagnosis can be challenging, partially because it requires measurement of transient airway resistance. And treatment entails significant costs and possible adverse effects. Without some sort of pulmonary function measurements or trials off medication, there is no clinical way to differentiate patients with well-controlled asthma from those who are being treated unnecessarily. Not surprisingly, studies have shown that ruling out active asthma and reducing medication usage is cost effective.3,4 This study followed a cohort of patients to see how many could be weaned off their asthma medications, and how they did in the subsequent year.
STUDY SUMMARY
About one-third of adults with asthma are “undiagnosed” within 5 years
The researchers recruited participants from the general population of the 10 largest cities and surrounding areas in Canada by randomly dialing cellular and landline phone numbers and asking about adult household members with asthma.1 The researchers focused on people with a recent (<5 years) asthma diagnosis, so as to represent contemporary diagnostic practice and to make it easier to collect medical records. Participants lived within 90 minutes of 10 medical centers in Canada. Patients were excluded if they were using long-term oral steroids, pregnant or breastfeeding, unable to tolerate spirometry or methacholine challenges, or had a history of more than 10 pack-years of smoking.
Of the 701 patients enrolled, 613 (87.4%) completed all study assessments. Patients progressed through a series of spirometry tests and were then tapered off their asthma-controlling medications.
The initial spirometry test confirmed asthma if bronchodilators caused a significant improvement in forced expiratory volume in the first second of expiration (FEV1). If there was no improvement, the patient took a methacholine challenge 1 week later; if they did well, their maintenance medications were reduced by half. If the patient did well with another methacholine challenge about 1 month later, maintenance medications were stopped, and the patient underwent a third methacholine challenge 3 weeks later.
Asthma was confirmed at any methacholine challenge if there was a 20% decrease in FEV1 from baseline at a methacholine concentration of ≤8 mg/mL; these patients were restarted on appropriate medications. If current asthma was ruled out, follow-up bronchial challenges were repeated at 6 and 12 months.
Results. Among the adults with physician-diagnosed asthma, 33.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 29.4%-36.8%) no longer met criteria for an asthma diagnosis. Of those who no longer had asthma, 44% had previously undergone objective testing of airflow limitation. The investigators also found 12 patients (2%) had other serious cardiorespiratory conditions instead of asthma, including ischemic heart disease, subglottic stenosis, and bronchiectasis.
Continue to: During the 1-year follow-up period...
During the 1-year follow-up period, 22 (10.8%) of the 203 patients who were initially judged to no longer have asthma had a positive bronchial challenge test; 16 had no symptoms and continued to do well off all asthma medications. Six (3%) presented with respiratory symptoms and resumed treatment with asthma medications, but only 1 (0.5%) required oral corticosteroid therapy.
WHAT’S NEW?
Asthma meds are of no benefit for about one-third of patients taking them
This study found that one-third of patients with asthma diagnosed in the last 5 years no longer had symptoms or spirometry results consistent with asthma and did well in the subsequent year. For those patients, there appears to be no benefit to using asthma medications. The Global Institute for Asthma recommends stepping down treatment in adults with asthma that is well controlled for 3 months or more.5 While patients with objectively confirmed asthma diagnoses were more likely to still have asthma in this study, over 40% of patients who no longer had asthma were objectively proven to have had asthma at their original diagnosis.
CAVEATS
High level of rigor and the absence of a randomized trial
This study used a very structured protocol for tapering patients off their medications, including multiple spirometry tests, most including methacholine challenges, as well as oversight by pulmonologists. It is unclear whether this level of rigor is necessary for weaning in other clinical settings.
Also, this study was not a randomized trial, which is the gold standard for withdrawal of therapy. However, a cohort study is adequate to assess diagnostic testing, and this could be considered a trial of “undiagnosing” asthma in adults. The results here are consistent with those of a study that looked at asthma disappearance in groups of patients with and without obesity. In that study, approximately 30% of both groups of patients no longer had a diagnosis of asthma.6
Using random dialing is likely to have broadened the pool of patients this study drew upon. Also, there is a possibility that the patients who were lost to follow-up in this study represented those who had worsening symptoms. Some patients with mild asthma may have a waxing and waning course; it is possible that the study period was not long enough to capture this. In this study, only about 3% of patients who had their medications stopped reported worsening of symptoms.
Continue to: CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
“Undiagnosis” is unusual
Using objective testing may provide some logistical or financial challenges for patients. Furthermore, “undiagnosing” a chronic disease like asthma is not a physician’s typical work, and it may take some time and effort to educate and monitor patients through the process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, FitzGerald JM, et al. Reevaluation of diagnosis in adults with physician-diagnosed asthma. JAMA. 2017;317:269-279.
2. QuickStats: percentage of adults aged 18-64 years with current asthma,* by state - National Health Interview Survey,† 2014-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:590.
3. Pakhale S, Sumner A, Coyle D, et al. (Correcting) misdiagnoses of asthma: a cost effectiveness analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2011;11:27.
4. Rank MA, Liesinger JT, Branda ME, et al. Comparative safety and costs of stepping down asthma medications in patients with controlled asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:1373-1379.
5. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2018. https://ginasthma.org. Accessed June 15, 2018.
6. Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, Boulet LP, et al. Overdiagnosis of asthma in obese and nonobese adults. CMAJ. 2008;179:1121-1131.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 45-year-old woman presents to your office for a yearly visit. Two years ago she was started on an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) and a bronchodilator rescue inhaler after being diagnosed with asthma based on her history and physical exam findings. She has had no exacerbations since then. Should you consider weaning her off the inhalers?
Asthma is a prevalent problem; 8% of adults ages 18 to 64 years have the chronic lung disease.2 Diagnosis can be challenging, partially because it requires measurement of transient airway resistance. And treatment entails significant costs and possible adverse effects. Without some sort of pulmonary function measurements or trials off medication, there is no clinical way to differentiate patients with well-controlled asthma from those who are being treated unnecessarily. Not surprisingly, studies have shown that ruling out active asthma and reducing medication usage is cost effective.3,4 This study followed a cohort of patients to see how many could be weaned off their asthma medications, and how they did in the subsequent year.
STUDY SUMMARY
About one-third of adults with asthma are “undiagnosed” within 5 years
The researchers recruited participants from the general population of the 10 largest cities and surrounding areas in Canada by randomly dialing cellular and landline phone numbers and asking about adult household members with asthma.1 The researchers focused on people with a recent (<5 years) asthma diagnosis, so as to represent contemporary diagnostic practice and to make it easier to collect medical records. Participants lived within 90 minutes of 10 medical centers in Canada. Patients were excluded if they were using long-term oral steroids, pregnant or breastfeeding, unable to tolerate spirometry or methacholine challenges, or had a history of more than 10 pack-years of smoking.
Of the 701 patients enrolled, 613 (87.4%) completed all study assessments. Patients progressed through a series of spirometry tests and were then tapered off their asthma-controlling medications.
The initial spirometry test confirmed asthma if bronchodilators caused a significant improvement in forced expiratory volume in the first second of expiration (FEV1). If there was no improvement, the patient took a methacholine challenge 1 week later; if they did well, their maintenance medications were reduced by half. If the patient did well with another methacholine challenge about 1 month later, maintenance medications were stopped, and the patient underwent a third methacholine challenge 3 weeks later.
Asthma was confirmed at any methacholine challenge if there was a 20% decrease in FEV1 from baseline at a methacholine concentration of ≤8 mg/mL; these patients were restarted on appropriate medications. If current asthma was ruled out, follow-up bronchial challenges were repeated at 6 and 12 months.
Results. Among the adults with physician-diagnosed asthma, 33.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 29.4%-36.8%) no longer met criteria for an asthma diagnosis. Of those who no longer had asthma, 44% had previously undergone objective testing of airflow limitation. The investigators also found 12 patients (2%) had other serious cardiorespiratory conditions instead of asthma, including ischemic heart disease, subglottic stenosis, and bronchiectasis.
Continue to: During the 1-year follow-up period...
During the 1-year follow-up period, 22 (10.8%) of the 203 patients who were initially judged to no longer have asthma had a positive bronchial challenge test; 16 had no symptoms and continued to do well off all asthma medications. Six (3%) presented with respiratory symptoms and resumed treatment with asthma medications, but only 1 (0.5%) required oral corticosteroid therapy.
WHAT’S NEW?
Asthma meds are of no benefit for about one-third of patients taking them
This study found that one-third of patients with asthma diagnosed in the last 5 years no longer had symptoms or spirometry results consistent with asthma and did well in the subsequent year. For those patients, there appears to be no benefit to using asthma medications. The Global Institute for Asthma recommends stepping down treatment in adults with asthma that is well controlled for 3 months or more.5 While patients with objectively confirmed asthma diagnoses were more likely to still have asthma in this study, over 40% of patients who no longer had asthma were objectively proven to have had asthma at their original diagnosis.
CAVEATS
High level of rigor and the absence of a randomized trial
This study used a very structured protocol for tapering patients off their medications, including multiple spirometry tests, most including methacholine challenges, as well as oversight by pulmonologists. It is unclear whether this level of rigor is necessary for weaning in other clinical settings.
Also, this study was not a randomized trial, which is the gold standard for withdrawal of therapy. However, a cohort study is adequate to assess diagnostic testing, and this could be considered a trial of “undiagnosing” asthma in adults. The results here are consistent with those of a study that looked at asthma disappearance in groups of patients with and without obesity. In that study, approximately 30% of both groups of patients no longer had a diagnosis of asthma.6
Using random dialing is likely to have broadened the pool of patients this study drew upon. Also, there is a possibility that the patients who were lost to follow-up in this study represented those who had worsening symptoms. Some patients with mild asthma may have a waxing and waning course; it is possible that the study period was not long enough to capture this. In this study, only about 3% of patients who had their medications stopped reported worsening of symptoms.
Continue to: CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
“Undiagnosis” is unusual
Using objective testing may provide some logistical or financial challenges for patients. Furthermore, “undiagnosing” a chronic disease like asthma is not a physician’s typical work, and it may take some time and effort to educate and monitor patients through the process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
ILLUSTRATIVE CASE
A 45-year-old woman presents to your office for a yearly visit. Two years ago she was started on an inhaled corticosteroid (ICS) and a bronchodilator rescue inhaler after being diagnosed with asthma based on her history and physical exam findings. She has had no exacerbations since then. Should you consider weaning her off the inhalers?
Asthma is a prevalent problem; 8% of adults ages 18 to 64 years have the chronic lung disease.2 Diagnosis can be challenging, partially because it requires measurement of transient airway resistance. And treatment entails significant costs and possible adverse effects. Without some sort of pulmonary function measurements or trials off medication, there is no clinical way to differentiate patients with well-controlled asthma from those who are being treated unnecessarily. Not surprisingly, studies have shown that ruling out active asthma and reducing medication usage is cost effective.3,4 This study followed a cohort of patients to see how many could be weaned off their asthma medications, and how they did in the subsequent year.
STUDY SUMMARY
About one-third of adults with asthma are “undiagnosed” within 5 years
The researchers recruited participants from the general population of the 10 largest cities and surrounding areas in Canada by randomly dialing cellular and landline phone numbers and asking about adult household members with asthma.1 The researchers focused on people with a recent (<5 years) asthma diagnosis, so as to represent contemporary diagnostic practice and to make it easier to collect medical records. Participants lived within 90 minutes of 10 medical centers in Canada. Patients were excluded if they were using long-term oral steroids, pregnant or breastfeeding, unable to tolerate spirometry or methacholine challenges, or had a history of more than 10 pack-years of smoking.
Of the 701 patients enrolled, 613 (87.4%) completed all study assessments. Patients progressed through a series of spirometry tests and were then tapered off their asthma-controlling medications.
The initial spirometry test confirmed asthma if bronchodilators caused a significant improvement in forced expiratory volume in the first second of expiration (FEV1). If there was no improvement, the patient took a methacholine challenge 1 week later; if they did well, their maintenance medications were reduced by half. If the patient did well with another methacholine challenge about 1 month later, maintenance medications were stopped, and the patient underwent a third methacholine challenge 3 weeks later.
Asthma was confirmed at any methacholine challenge if there was a 20% decrease in FEV1 from baseline at a methacholine concentration of ≤8 mg/mL; these patients were restarted on appropriate medications. If current asthma was ruled out, follow-up bronchial challenges were repeated at 6 and 12 months.
Results. Among the adults with physician-diagnosed asthma, 33.1% (95% confidence interval [CI], 29.4%-36.8%) no longer met criteria for an asthma diagnosis. Of those who no longer had asthma, 44% had previously undergone objective testing of airflow limitation. The investigators also found 12 patients (2%) had other serious cardiorespiratory conditions instead of asthma, including ischemic heart disease, subglottic stenosis, and bronchiectasis.
Continue to: During the 1-year follow-up period...
During the 1-year follow-up period, 22 (10.8%) of the 203 patients who were initially judged to no longer have asthma had a positive bronchial challenge test; 16 had no symptoms and continued to do well off all asthma medications. Six (3%) presented with respiratory symptoms and resumed treatment with asthma medications, but only 1 (0.5%) required oral corticosteroid therapy.
WHAT’S NEW?
Asthma meds are of no benefit for about one-third of patients taking them
This study found that one-third of patients with asthma diagnosed in the last 5 years no longer had symptoms or spirometry results consistent with asthma and did well in the subsequent year. For those patients, there appears to be no benefit to using asthma medications. The Global Institute for Asthma recommends stepping down treatment in adults with asthma that is well controlled for 3 months or more.5 While patients with objectively confirmed asthma diagnoses were more likely to still have asthma in this study, over 40% of patients who no longer had asthma were objectively proven to have had asthma at their original diagnosis.
CAVEATS
High level of rigor and the absence of a randomized trial
This study used a very structured protocol for tapering patients off their medications, including multiple spirometry tests, most including methacholine challenges, as well as oversight by pulmonologists. It is unclear whether this level of rigor is necessary for weaning in other clinical settings.
Also, this study was not a randomized trial, which is the gold standard for withdrawal of therapy. However, a cohort study is adequate to assess diagnostic testing, and this could be considered a trial of “undiagnosing” asthma in adults. The results here are consistent with those of a study that looked at asthma disappearance in groups of patients with and without obesity. In that study, approximately 30% of both groups of patients no longer had a diagnosis of asthma.6
Using random dialing is likely to have broadened the pool of patients this study drew upon. Also, there is a possibility that the patients who were lost to follow-up in this study represented those who had worsening symptoms. Some patients with mild asthma may have a waxing and waning course; it is possible that the study period was not long enough to capture this. In this study, only about 3% of patients who had their medications stopped reported worsening of symptoms.
Continue to: CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
CHALLENGES TO IMPLEMENTATION
“Undiagnosis” is unusual
Using objective testing may provide some logistical or financial challenges for patients. Furthermore, “undiagnosing” a chronic disease like asthma is not a physician’s typical work, and it may take some time and effort to educate and monitor patients through the process.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENT
The PURLs Surveillance System was supported in part by Grant Number UL1RR024999 from the National Center For Research Resources, a Clinical Translational Science Award to the University of Chicago. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Center For Research Resources or the National Institutes of Health.
1. Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, FitzGerald JM, et al. Reevaluation of diagnosis in adults with physician-diagnosed asthma. JAMA. 2017;317:269-279.
2. QuickStats: percentage of adults aged 18-64 years with current asthma,* by state - National Health Interview Survey,† 2014-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:590.
3. Pakhale S, Sumner A, Coyle D, et al. (Correcting) misdiagnoses of asthma: a cost effectiveness analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2011;11:27.
4. Rank MA, Liesinger JT, Branda ME, et al. Comparative safety and costs of stepping down asthma medications in patients with controlled asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:1373-1379.
5. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2018. https://ginasthma.org. Accessed June 15, 2018.
6. Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, Boulet LP, et al. Overdiagnosis of asthma in obese and nonobese adults. CMAJ. 2008;179:1121-1131.
1. Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, FitzGerald JM, et al. Reevaluation of diagnosis in adults with physician-diagnosed asthma. JAMA. 2017;317:269-279.
2. QuickStats: percentage of adults aged 18-64 years with current asthma,* by state - National Health Interview Survey,† 2014-2016. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2018;67:590.
3. Pakhale S, Sumner A, Coyle D, et al. (Correcting) misdiagnoses of asthma: a cost effectiveness analysis. BMC Pulm Med. 2011;11:27.
4. Rank MA, Liesinger JT, Branda ME, et al. Comparative safety and costs of stepping down asthma medications in patients with controlled asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2016;137:1373-1379.
5. Global Initiative for Asthma. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention. 2018. https://ginasthma.org. Accessed June 15, 2018.
6. Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, Boulet LP, et al. Overdiagnosis of asthma in obese and nonobese adults. CMAJ. 2008;179:1121-1131.
PRACTICE CHANGER
Consider tapering medications and retesting spirometry in adults with well-controlled asthma, as many may no longer have the disease.1
STRENGTH OF RECOMMENDATION
A: Based on a high-quality prospective cohort study and consistent findings in other studies.
Aaron SD, Vandemheen KL, FitzGerald JM, et al. Reevaluation of diagnosis in adults with physician-diagnosed asthma. JAMA. 2017;317:269-279.
Two-thirds of COPD patients not using inhalers correctly
SAN ANTONIO – Two-thirds of U.S. adults with (MDIs), according to new research. About half of patients failed to inhale slowly and deeply to ensure they received the appropriate dose, and about 40% of patients failed to hold their breath for 5-10 seconds afterward so that the medication made its way to their lungs, the findings show.
“There’s a need to educate patients on proper inhalation technique to optimize the appropriate delivery of medication,” Maryam Navaie, DrPH, of Advance Health Solutions in New York told attendees at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. She also urged practitioners to think more carefully about what devices to prescribe to patients based on their own personal attributes.
“Nebulizer devices may be a better consideration for patients who have difficulty performing the necessary steps required by handheld inhalers,” Dr. Navaie said.
She and fellow researchers conducted a systematic review to gain more insights into the errors and difficulties experienced by U.S. adults using MDIs for COPD or asthma. They combed through PubMed, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases for English language studies about MDI-related errors in U.S. adult COPD or asthma patients published between January 2003 and February 2017.
The researchers included only randomized controlled trials and cross-sectional and observational studies, and they excluded studies with combined error rates across multiple devices so they could better parse out the data. They also used baseline rates only in studies that involved an intervention to reduce errors.
The researchers defined the proportion of overall MDI errors as “the percentage of patients who made errors in equal to or greater than 20% of inhalation steps.” They computed pooled estimates and created forest plots for both overall errors and for errors according to each step in using an MDI.
The eight studies they identified involved 1,221 patients, with ages ranging from a mean 48 to 82 years, 53% of whom were female. Nearly two-thirds of the patients had COPD (63.6%) while 36.4% had asthma. Most of the devices studied were MDIs alone (68.8%), while 31.2% included a spacer.
The pooled weighted average revealed a 66.5% error rate, that is, two-thirds of all the patients were making at least two errors during the 10 steps involved in using their device. The researchers then used individual error rates data in five studies to calculate the overall error rate for each step in using MDIs. The most common error, made by 73.8% of people in those five studies, was failing to attach the inhaler to the spacer. In addition, 68.7% of patients were failing to exhale fully and away from the inhaler before inhaling, and 47.8% were inhaling too fast instead of inhaling deeply.
“So these [findings] actually give you [some specific] ideas of how we could help improve patients’ ability to use the device properly,” Dr. Navaie told attendees, adding that these data can inform patient education needs and interventions.
Based on the data from those five studies, the error rates for all 10 steps to using an MDI were as follows:
- Failed to shake inhaler before use (37.9%).
- Failed to attach inhaler to spacer (73.8%).
- Failed to exhale fully and away from inhaler before inhalation (68.7%).
- Failed to place mouthpiece between teeth and sealed lips (7.4%).
- Failed to actuate once during inhalation (24.4%).
- Inhalation too fast, not deep (47.8%).
- Failed to hold breath for 5-10 seconds (40.1%).
- Failed to remove the inhaler/spacer from mouth (11.3%).
- Failed to exhale after inhalation (33.2%).
- Failed to repeat steps for second puff (36.7%).
Dr. Navaie also noted the investigators were surprised to learn that physicians themselves sometimes make several of these errors in explaining to patients how to use their devices.
“I think for the reps and other people who go out and visit doctors, it’s important to think about making sure the clinicians are using the devices properly,” Dr. Navaie said. She pointed out the potential for patients to forget steps between visits.
“One of the things a lot of our clinicians and key opinion leaders told us during the course of this study is that you shouldn’t just educate the patient at the time you are scripting the device but repeatedly because patients forget,” she said. She recommended having patients demonstrate their use of the device at each visit. If patients continue to struggle, it may be worth considering other therapies, such as a nebulizer, for patients unable to regularly use their devices correctly.
The meta-analysis was limited by the sparse research available in general on MDI errors in the U.S. adult population, so the data on error rates for each individual step may not be broadly generalizable. The studies also did not distinguish between rates among users with asthma vs. users with COPD. Further, too few data exist on associations between MDI errors and health outcomes to have a clear picture of the clinical implications of regularly making multiple errors in MDI use.
Dr. Navaie is employed by Advance Health Solutions, which received Sunovion Pharmaceuticals funding for the study.
SOURCE: Navaie M et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.705.
SAN ANTONIO – Two-thirds of U.S. adults with (MDIs), according to new research. About half of patients failed to inhale slowly and deeply to ensure they received the appropriate dose, and about 40% of patients failed to hold their breath for 5-10 seconds afterward so that the medication made its way to their lungs, the findings show.
“There’s a need to educate patients on proper inhalation technique to optimize the appropriate delivery of medication,” Maryam Navaie, DrPH, of Advance Health Solutions in New York told attendees at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. She also urged practitioners to think more carefully about what devices to prescribe to patients based on their own personal attributes.
“Nebulizer devices may be a better consideration for patients who have difficulty performing the necessary steps required by handheld inhalers,” Dr. Navaie said.
She and fellow researchers conducted a systematic review to gain more insights into the errors and difficulties experienced by U.S. adults using MDIs for COPD or asthma. They combed through PubMed, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases for English language studies about MDI-related errors in U.S. adult COPD or asthma patients published between January 2003 and February 2017.
The researchers included only randomized controlled trials and cross-sectional and observational studies, and they excluded studies with combined error rates across multiple devices so they could better parse out the data. They also used baseline rates only in studies that involved an intervention to reduce errors.
The researchers defined the proportion of overall MDI errors as “the percentage of patients who made errors in equal to or greater than 20% of inhalation steps.” They computed pooled estimates and created forest plots for both overall errors and for errors according to each step in using an MDI.
The eight studies they identified involved 1,221 patients, with ages ranging from a mean 48 to 82 years, 53% of whom were female. Nearly two-thirds of the patients had COPD (63.6%) while 36.4% had asthma. Most of the devices studied were MDIs alone (68.8%), while 31.2% included a spacer.
The pooled weighted average revealed a 66.5% error rate, that is, two-thirds of all the patients were making at least two errors during the 10 steps involved in using their device. The researchers then used individual error rates data in five studies to calculate the overall error rate for each step in using MDIs. The most common error, made by 73.8% of people in those five studies, was failing to attach the inhaler to the spacer. In addition, 68.7% of patients were failing to exhale fully and away from the inhaler before inhaling, and 47.8% were inhaling too fast instead of inhaling deeply.
“So these [findings] actually give you [some specific] ideas of how we could help improve patients’ ability to use the device properly,” Dr. Navaie told attendees, adding that these data can inform patient education needs and interventions.
Based on the data from those five studies, the error rates for all 10 steps to using an MDI were as follows:
- Failed to shake inhaler before use (37.9%).
- Failed to attach inhaler to spacer (73.8%).
- Failed to exhale fully and away from inhaler before inhalation (68.7%).
- Failed to place mouthpiece between teeth and sealed lips (7.4%).
- Failed to actuate once during inhalation (24.4%).
- Inhalation too fast, not deep (47.8%).
- Failed to hold breath for 5-10 seconds (40.1%).
- Failed to remove the inhaler/spacer from mouth (11.3%).
- Failed to exhale after inhalation (33.2%).
- Failed to repeat steps for second puff (36.7%).
Dr. Navaie also noted the investigators were surprised to learn that physicians themselves sometimes make several of these errors in explaining to patients how to use their devices.
“I think for the reps and other people who go out and visit doctors, it’s important to think about making sure the clinicians are using the devices properly,” Dr. Navaie said. She pointed out the potential for patients to forget steps between visits.
“One of the things a lot of our clinicians and key opinion leaders told us during the course of this study is that you shouldn’t just educate the patient at the time you are scripting the device but repeatedly because patients forget,” she said. She recommended having patients demonstrate their use of the device at each visit. If patients continue to struggle, it may be worth considering other therapies, such as a nebulizer, for patients unable to regularly use their devices correctly.
The meta-analysis was limited by the sparse research available in general on MDI errors in the U.S. adult population, so the data on error rates for each individual step may not be broadly generalizable. The studies also did not distinguish between rates among users with asthma vs. users with COPD. Further, too few data exist on associations between MDI errors and health outcomes to have a clear picture of the clinical implications of regularly making multiple errors in MDI use.
Dr. Navaie is employed by Advance Health Solutions, which received Sunovion Pharmaceuticals funding for the study.
SOURCE: Navaie M et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.705.
SAN ANTONIO – Two-thirds of U.S. adults with (MDIs), according to new research. About half of patients failed to inhale slowly and deeply to ensure they received the appropriate dose, and about 40% of patients failed to hold their breath for 5-10 seconds afterward so that the medication made its way to their lungs, the findings show.
“There’s a need to educate patients on proper inhalation technique to optimize the appropriate delivery of medication,” Maryam Navaie, DrPH, of Advance Health Solutions in New York told attendees at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians. She also urged practitioners to think more carefully about what devices to prescribe to patients based on their own personal attributes.
“Nebulizer devices may be a better consideration for patients who have difficulty performing the necessary steps required by handheld inhalers,” Dr. Navaie said.
She and fellow researchers conducted a systematic review to gain more insights into the errors and difficulties experienced by U.S. adults using MDIs for COPD or asthma. They combed through PubMed, EMBASE, PsycINFO, Cochrane, and Google Scholar databases for English language studies about MDI-related errors in U.S. adult COPD or asthma patients published between January 2003 and February 2017.
The researchers included only randomized controlled trials and cross-sectional and observational studies, and they excluded studies with combined error rates across multiple devices so they could better parse out the data. They also used baseline rates only in studies that involved an intervention to reduce errors.
The researchers defined the proportion of overall MDI errors as “the percentage of patients who made errors in equal to or greater than 20% of inhalation steps.” They computed pooled estimates and created forest plots for both overall errors and for errors according to each step in using an MDI.
The eight studies they identified involved 1,221 patients, with ages ranging from a mean 48 to 82 years, 53% of whom were female. Nearly two-thirds of the patients had COPD (63.6%) while 36.4% had asthma. Most of the devices studied were MDIs alone (68.8%), while 31.2% included a spacer.
The pooled weighted average revealed a 66.5% error rate, that is, two-thirds of all the patients were making at least two errors during the 10 steps involved in using their device. The researchers then used individual error rates data in five studies to calculate the overall error rate for each step in using MDIs. The most common error, made by 73.8% of people in those five studies, was failing to attach the inhaler to the spacer. In addition, 68.7% of patients were failing to exhale fully and away from the inhaler before inhaling, and 47.8% were inhaling too fast instead of inhaling deeply.
“So these [findings] actually give you [some specific] ideas of how we could help improve patients’ ability to use the device properly,” Dr. Navaie told attendees, adding that these data can inform patient education needs and interventions.
Based on the data from those five studies, the error rates for all 10 steps to using an MDI were as follows:
- Failed to shake inhaler before use (37.9%).
- Failed to attach inhaler to spacer (73.8%).
- Failed to exhale fully and away from inhaler before inhalation (68.7%).
- Failed to place mouthpiece between teeth and sealed lips (7.4%).
- Failed to actuate once during inhalation (24.4%).
- Inhalation too fast, not deep (47.8%).
- Failed to hold breath for 5-10 seconds (40.1%).
- Failed to remove the inhaler/spacer from mouth (11.3%).
- Failed to exhale after inhalation (33.2%).
- Failed to repeat steps for second puff (36.7%).
Dr. Navaie also noted the investigators were surprised to learn that physicians themselves sometimes make several of these errors in explaining to patients how to use their devices.
“I think for the reps and other people who go out and visit doctors, it’s important to think about making sure the clinicians are using the devices properly,” Dr. Navaie said. She pointed out the potential for patients to forget steps between visits.
“One of the things a lot of our clinicians and key opinion leaders told us during the course of this study is that you shouldn’t just educate the patient at the time you are scripting the device but repeatedly because patients forget,” she said. She recommended having patients demonstrate their use of the device at each visit. If patients continue to struggle, it may be worth considering other therapies, such as a nebulizer, for patients unable to regularly use their devices correctly.
The meta-analysis was limited by the sparse research available in general on MDI errors in the U.S. adult population, so the data on error rates for each individual step may not be broadly generalizable. The studies also did not distinguish between rates among users with asthma vs. users with COPD. Further, too few data exist on associations between MDI errors and health outcomes to have a clear picture of the clinical implications of regularly making multiple errors in MDI use.
Dr. Navaie is employed by Advance Health Solutions, which received Sunovion Pharmaceuticals funding for the study.
SOURCE: Navaie M et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.705.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2018
Key clinical point: 67% of US adult patients with COPD or asthma report making errors in using metered-dose inhalers.
Major finding: 69% of patients do not exhale fully and away from the inhaler before inhalation; 50% do not inhale slowly and deeply.
Study details: Meta-analysis of eight studies involving 1,221 U.S. adult patients with COPD or asthma who use metered-dose inhalers.
Disclosures: Dr. Navaie is employed by Advance Health Solutions, which received Sunovion Pharmaceuticals funding for the study.
Source: Navaie M et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.705.
Dupilumab offers extra benefits to asthmatic teens
SAN ANTONIO – For adolescents with asthma, treatment with the biologic agent dupilumab provided benefits that were at least comparable with what was seen in adults, results from a retrospective analysis of a randomized, phase 3 study suggest.
Adolescents had reduced asthma exacerbations in line with what was seen in adults and had improvements in lung function that were at a greater magnitude than adults, according to study coauthor Neil M.H. Graham, MD, of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Tarrytown, N.Y.
“We think, overall, it’s a very good treatment response from this drug in this high-risk population, and it is generally well tolerated, as we’ve seen in other studies,” Dr. Graham said in a podium presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Dr. Graham presented results of an analysis of the 1,902-patient, phase 3 Liberty Asthma QUEST trial, published in May 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Top-line results of QUEST showed that treatment with dupilumab, a fully human anti–IL-4Ra monoclonal antibody, resulted in significantly lower rates of severe asthma exacerbation, along with improved lung function, in patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe asthma.
Now, this retrospective analysis shows that, in adolescents, improvements from baseline to week 12 in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) were significant and at a greater magnitude than in adults, according to Dr. Graham and his coinvestigators.
The improvement over 12 weeks in FEV1 for adolescents was 0.36 L and 0.27 L, respectively, for the 200- and 300-mg doses of dupilumab (P less than .05 vs. placebo for both), Dr. Graham and his coinvestigators reported. In adults, the improvement was 0.12 L.
The annualized exacerbation rate dropped by 46.4% for those adolescents who received 200 mg dupilumab, though there was no treatment effect versus placebo for dupilumab 300 mg; the investigators said the lack of effect in this retrospective analysis could have been caused by imbalances in prior event rates or the small sample size.
A total of 107 out of 1,902 patients in QUEST were adolescents, and of those, 68 were randomly assigned to dupilumab, according to the report. Injection site reaction was the most common adverse event in adolescents in both dosing groups.
Dr. Graham reported disclosures related to his employment with Regeneron. Study coauthors reported disclosures related to Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Genentech, and others.
SOURCE: Graham NMH et al. CHEST. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.022.
SAN ANTONIO – For adolescents with asthma, treatment with the biologic agent dupilumab provided benefits that were at least comparable with what was seen in adults, results from a retrospective analysis of a randomized, phase 3 study suggest.
Adolescents had reduced asthma exacerbations in line with what was seen in adults and had improvements in lung function that were at a greater magnitude than adults, according to study coauthor Neil M.H. Graham, MD, of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Tarrytown, N.Y.
“We think, overall, it’s a very good treatment response from this drug in this high-risk population, and it is generally well tolerated, as we’ve seen in other studies,” Dr. Graham said in a podium presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Dr. Graham presented results of an analysis of the 1,902-patient, phase 3 Liberty Asthma QUEST trial, published in May 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Top-line results of QUEST showed that treatment with dupilumab, a fully human anti–IL-4Ra monoclonal antibody, resulted in significantly lower rates of severe asthma exacerbation, along with improved lung function, in patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe asthma.
Now, this retrospective analysis shows that, in adolescents, improvements from baseline to week 12 in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) were significant and at a greater magnitude than in adults, according to Dr. Graham and his coinvestigators.
The improvement over 12 weeks in FEV1 for adolescents was 0.36 L and 0.27 L, respectively, for the 200- and 300-mg doses of dupilumab (P less than .05 vs. placebo for both), Dr. Graham and his coinvestigators reported. In adults, the improvement was 0.12 L.
The annualized exacerbation rate dropped by 46.4% for those adolescents who received 200 mg dupilumab, though there was no treatment effect versus placebo for dupilumab 300 mg; the investigators said the lack of effect in this retrospective analysis could have been caused by imbalances in prior event rates or the small sample size.
A total of 107 out of 1,902 patients in QUEST were adolescents, and of those, 68 were randomly assigned to dupilumab, according to the report. Injection site reaction was the most common adverse event in adolescents in both dosing groups.
Dr. Graham reported disclosures related to his employment with Regeneron. Study coauthors reported disclosures related to Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Genentech, and others.
SOURCE: Graham NMH et al. CHEST. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.022.
SAN ANTONIO – For adolescents with asthma, treatment with the biologic agent dupilumab provided benefits that were at least comparable with what was seen in adults, results from a retrospective analysis of a randomized, phase 3 study suggest.
Adolescents had reduced asthma exacerbations in line with what was seen in adults and had improvements in lung function that were at a greater magnitude than adults, according to study coauthor Neil M.H. Graham, MD, of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Tarrytown, N.Y.
“We think, overall, it’s a very good treatment response from this drug in this high-risk population, and it is generally well tolerated, as we’ve seen in other studies,” Dr. Graham said in a podium presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Dr. Graham presented results of an analysis of the 1,902-patient, phase 3 Liberty Asthma QUEST trial, published in May 2018 in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Top-line results of QUEST showed that treatment with dupilumab, a fully human anti–IL-4Ra monoclonal antibody, resulted in significantly lower rates of severe asthma exacerbation, along with improved lung function, in patients aged 12 years and older with moderate to severe asthma.
Now, this retrospective analysis shows that, in adolescents, improvements from baseline to week 12 in forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) were significant and at a greater magnitude than in adults, according to Dr. Graham and his coinvestigators.
The improvement over 12 weeks in FEV1 for adolescents was 0.36 L and 0.27 L, respectively, for the 200- and 300-mg doses of dupilumab (P less than .05 vs. placebo for both), Dr. Graham and his coinvestigators reported. In adults, the improvement was 0.12 L.
The annualized exacerbation rate dropped by 46.4% for those adolescents who received 200 mg dupilumab, though there was no treatment effect versus placebo for dupilumab 300 mg; the investigators said the lack of effect in this retrospective analysis could have been caused by imbalances in prior event rates or the small sample size.
A total of 107 out of 1,902 patients in QUEST were adolescents, and of those, 68 were randomly assigned to dupilumab, according to the report. Injection site reaction was the most common adverse event in adolescents in both dosing groups.
Dr. Graham reported disclosures related to his employment with Regeneron. Study coauthors reported disclosures related to Regeneron, AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, Genentech, and others.
SOURCE: Graham NMH et al. CHEST. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.022.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2018
Key clinical point: Dupilumab’s benefits in adolescents with moderate to severe asthma are at least comparable with what has been reported in adults.
Major finding: The improvement over 12 weeks in forced expiratory volume in 1 second for adolescents was 0.36 L and 0.27 L, respectively, for the 200- and 300-mg doses of dupilumab versus 0.12 L for adults.
Study details: A retrospective analysis of 1,902 patients (including 107 adolescents) in Liberty Asthma QUEST, a recently reported randomized, phase 3 trial.
Disclosures: Several study coauthors reported employment with Regeneron. Dr. Graham reported disclosures related to his employment with Regeneron. Other reported disclosures were related to AstraZeneca, Sanofi, Teva Pharmaceutical, GlaxoSmithKline, Boehringer Ingelheim, Merck, and Genentech, among other entities.
Source: Graham NMH et al. CHEST. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j/chest.2018.08.002.
COPD: Triple trumps dual therapy regardless of baseline reversibility
SAN ANTONIO – Regardless of COPD patients’ bronchodilator reversibility at baseline, versus dual therapies, according to a recent retrospective analysis of a randomized, double-blind study.
FF/UMEC/VI, a triple-therapy combination of an inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist (ICS/LAMA/LABA), was superior to both LAMA/LABA and ICS/LABA combinations in reducing the rate of moderate to severe exacerbation and lung function, the analysis showed.
The ICS/LAMA/LABA combination, compared with LAMA/LABA, also significantly reduced the rate of severe exacerbations and time to first moderate to severe exacerbations in both reversible and nonreversible patients, Robert Wise, MD, FCCP, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The analysis was based on data from IMPACT, an international, randomized, 52-week study that included more than 10,000 patients with symptomatic COPD, of whom 18% demonstrated reversibility at screening.
“The results across both reversibility subgroups are consistent with those observed in the intention-to-treat or overall study population and show a similar benefit-to-risk profile of the triple therapy across different subtypes based on bronchodilator reversibility,” Dr. Wise told attendees in a podium presentation.
Reversibility was defined as a difference between pre- and postalbuterol assessment of FEV1 of equal to or greater than 12% and equal to or greater than 200 mL at screening, Dr. Wise said.
Reversible patients had a 40% reduction in the rate of moderate to severe exacerbations for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI, while nonreversible patients had a 21% reduction, according to data reported in the meeting abstract.
Severe exacerbation rates dropped by 44% and 31%, respectively, in the reversible and nonreversible patients for triple versus dual therapy, he added.
Triple therapy reduced time to first moderate to severe exacerbation versus dual therapy by 25.6% in reversible and 13.6% in nonreversible COPD patients, the data showed.
The FF/UMEC/VI combination also demonstrated improvements versus UMEC/VI in time to first severe exacerbation for both the reversible and nonreversible groups, as well as improved quality of life in both groups as measured by the St. George Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) in both groups.
Results were somewhat different when comparing the FF/UMEC/VI combination with the FF/VI – the ICS/LABA combination – in this post hoc analysis.
Triple therapy did reduce moderate to severe exacerbations and improved lung function regardless of baseline reversibility. However, for the reversible patients, ICS/LAMA/LABA versus ICS/LABA did not significantly reduce risk specifically of severe exacerbations, time to first moderate to severe exacerbation, or increase odds of being an SGRQ responder, Dr. Wise said.
Nonetheless, these findings taken together imply that this ICS/LAMA/LABA combination provides clinically relevant improvements versus dual therapy across a range of important outcomes regardless of baseline reversibility, according to Dr. Wise and colleagues.
Dr. Wise and coinvestigators provided disclosures related to Boehringer Ingelheim, BTG, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Mereo, Novartis, PneumRx, Prometic, and Pulmonx.
SOURCE: Wise R et al. Chest. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.662
SAN ANTONIO – Regardless of COPD patients’ bronchodilator reversibility at baseline, versus dual therapies, according to a recent retrospective analysis of a randomized, double-blind study.
FF/UMEC/VI, a triple-therapy combination of an inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist (ICS/LAMA/LABA), was superior to both LAMA/LABA and ICS/LABA combinations in reducing the rate of moderate to severe exacerbation and lung function, the analysis showed.
The ICS/LAMA/LABA combination, compared with LAMA/LABA, also significantly reduced the rate of severe exacerbations and time to first moderate to severe exacerbations in both reversible and nonreversible patients, Robert Wise, MD, FCCP, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The analysis was based on data from IMPACT, an international, randomized, 52-week study that included more than 10,000 patients with symptomatic COPD, of whom 18% demonstrated reversibility at screening.
“The results across both reversibility subgroups are consistent with those observed in the intention-to-treat or overall study population and show a similar benefit-to-risk profile of the triple therapy across different subtypes based on bronchodilator reversibility,” Dr. Wise told attendees in a podium presentation.
Reversibility was defined as a difference between pre- and postalbuterol assessment of FEV1 of equal to or greater than 12% and equal to or greater than 200 mL at screening, Dr. Wise said.
Reversible patients had a 40% reduction in the rate of moderate to severe exacerbations for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI, while nonreversible patients had a 21% reduction, according to data reported in the meeting abstract.
Severe exacerbation rates dropped by 44% and 31%, respectively, in the reversible and nonreversible patients for triple versus dual therapy, he added.
Triple therapy reduced time to first moderate to severe exacerbation versus dual therapy by 25.6% in reversible and 13.6% in nonreversible COPD patients, the data showed.
The FF/UMEC/VI combination also demonstrated improvements versus UMEC/VI in time to first severe exacerbation for both the reversible and nonreversible groups, as well as improved quality of life in both groups as measured by the St. George Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) in both groups.
Results were somewhat different when comparing the FF/UMEC/VI combination with the FF/VI – the ICS/LABA combination – in this post hoc analysis.
Triple therapy did reduce moderate to severe exacerbations and improved lung function regardless of baseline reversibility. However, for the reversible patients, ICS/LAMA/LABA versus ICS/LABA did not significantly reduce risk specifically of severe exacerbations, time to first moderate to severe exacerbation, or increase odds of being an SGRQ responder, Dr. Wise said.
Nonetheless, these findings taken together imply that this ICS/LAMA/LABA combination provides clinically relevant improvements versus dual therapy across a range of important outcomes regardless of baseline reversibility, according to Dr. Wise and colleagues.
Dr. Wise and coinvestigators provided disclosures related to Boehringer Ingelheim, BTG, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Mereo, Novartis, PneumRx, Prometic, and Pulmonx.
SOURCE: Wise R et al. Chest. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.662
SAN ANTONIO – Regardless of COPD patients’ bronchodilator reversibility at baseline, versus dual therapies, according to a recent retrospective analysis of a randomized, double-blind study.
FF/UMEC/VI, a triple-therapy combination of an inhaled corticosteroid, long-acting muscarinic antagonist, and long-acting beta2 agonist (ICS/LAMA/LABA), was superior to both LAMA/LABA and ICS/LABA combinations in reducing the rate of moderate to severe exacerbation and lung function, the analysis showed.
The ICS/LAMA/LABA combination, compared with LAMA/LABA, also significantly reduced the rate of severe exacerbations and time to first moderate to severe exacerbations in both reversible and nonreversible patients, Robert Wise, MD, FCCP, of Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The analysis was based on data from IMPACT, an international, randomized, 52-week study that included more than 10,000 patients with symptomatic COPD, of whom 18% demonstrated reversibility at screening.
“The results across both reversibility subgroups are consistent with those observed in the intention-to-treat or overall study population and show a similar benefit-to-risk profile of the triple therapy across different subtypes based on bronchodilator reversibility,” Dr. Wise told attendees in a podium presentation.
Reversibility was defined as a difference between pre- and postalbuterol assessment of FEV1 of equal to or greater than 12% and equal to or greater than 200 mL at screening, Dr. Wise said.
Reversible patients had a 40% reduction in the rate of moderate to severe exacerbations for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI, while nonreversible patients had a 21% reduction, according to data reported in the meeting abstract.
Severe exacerbation rates dropped by 44% and 31%, respectively, in the reversible and nonreversible patients for triple versus dual therapy, he added.
Triple therapy reduced time to first moderate to severe exacerbation versus dual therapy by 25.6% in reversible and 13.6% in nonreversible COPD patients, the data showed.
The FF/UMEC/VI combination also demonstrated improvements versus UMEC/VI in time to first severe exacerbation for both the reversible and nonreversible groups, as well as improved quality of life in both groups as measured by the St. George Respiratory Questionnaire (SGRQ) in both groups.
Results were somewhat different when comparing the FF/UMEC/VI combination with the FF/VI – the ICS/LABA combination – in this post hoc analysis.
Triple therapy did reduce moderate to severe exacerbations and improved lung function regardless of baseline reversibility. However, for the reversible patients, ICS/LAMA/LABA versus ICS/LABA did not significantly reduce risk specifically of severe exacerbations, time to first moderate to severe exacerbation, or increase odds of being an SGRQ responder, Dr. Wise said.
Nonetheless, these findings taken together imply that this ICS/LAMA/LABA combination provides clinically relevant improvements versus dual therapy across a range of important outcomes regardless of baseline reversibility, according to Dr. Wise and colleagues.
Dr. Wise and coinvestigators provided disclosures related to Boehringer Ingelheim, BTG, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Mereo, Novartis, PneumRx, Prometic, and Pulmonx.
SOURCE: Wise R et al. Chest. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.662
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2018
Key clinical point: Triple therapy with fluticasone furoate, umeclidinium, and vilanterol (FF/UMEC/VI) is superior to UMEC/VI in COPD patients regardless of baseline bronchodilator reversibility.
Major finding: Reversible patients had a 40% reduction in the rate of moderate to severe exacerbations for FF/UMEC/VI versus UMEC/VI, while nonreversible patients had a 21% reduction.
Study details: Retrospective analysis of IMPACT, an international, randomized, 52-week study that included more than 10,000 patients with symptomatic COPD, of whom 18% demonstrated reversibility at screening.
Disclosures: Study authors reported disclosures related to Boehringer Ingelheim, BTG, Chiesi, GlaxoSmithKline, Mereo, Novartis, PneumRx, Prometic, and Pulmonx.
Source: Wise R et al. Chest. 2018 Oct. doi: 10.1016/j/chest.2018.08.662.
Managing asthma in children: Pets don’t always have to go
SAN ANTONIO – It may not always be necessary to tell parents of children with asthma to get rid of the household pet, a recent study suggests.
Children with had significant improvements in a variety of asthma measures, regardless of whether parents reported pets or smoking at home, according to results of the 4-year, 471-patient prospective study.
Those results suggest that clinicians should be working to make sure the guidelines are being closely followed before, for example, telling parents they need to consider getting rid of the family pet, said Shahid Sheikh, MD, FCCP, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
“As the guidelines still work, we need to focus and develop the connections with the family to make sure the patients are on the right treatment, and that they’re getting the medications,” Dr. Sheikh said in an interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The prospective cohort study by Dr. Sheikh and his colleagues, presented in a poster session, included children referred to a pediatric asthma center with the diagnosis of uncontrolled asthma. All patients received asthma care according to National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 guidelines.
Medications were changed as needed, and the asthma action plan was revised accordingly and reviewed with the family at each visit, Dr. Sheikh reported. After a baseline evaluation, clinic visits for the study occurred at 3 months, 6 months, and then at 1, 2, 3, and 4 years.
Out of 471 patients, 258 had pets, and 125 were in homes where smoking took place, according to parent reports.
Asthma control test scores were 15.1 at baseline for children in no-pet households, and 16.5 for those with pets; by the 3-month visit, scores increased to 20.1 and 20.3 for the no-pet and pet groups, and at 4 years, those scores had edged up to 22.2 and 22.7 (P = .371), Dr. Sheikh reported.
Similarly, after care was started, there was no significant difference between the no-pet and pet groups in mean percent of predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), wheezing, nighttime cough, albuterol use, and other factors over the 4 years of follow-up, he said.
Likewise, looking at the data by nonsmoking vs. smoking households, asthma control test scores at baseline were 16.1 and 15.1, respectively, and at 4 years they were 22.2 and 22.3 (P = .078), with a similar lack of difference in predicted FEV1, wheezing, and all other factors evaluated.
Getting rid of the family pet may need to be a consideration for some families, but based on these data, that might not be necessary for the majority of families, Dr. Sheikh said in the interview.
“On the other hand, we are not saying that if you are smoking, you should continue to smoke,” he added.
“What we are saying is that smoking is bad, but if your child is not getting better, I don’t want to blame your smoking for it. There may be something else which may be more important than smoking which we are missing – the child may not be getting the medicine, or may not be on the right medicine, or may have other comorbidities.”
Dr. Sheikh and his coinvestigators disclosed that they had no relationships relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Sheikh S et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.666.
SAN ANTONIO – It may not always be necessary to tell parents of children with asthma to get rid of the household pet, a recent study suggests.
Children with had significant improvements in a variety of asthma measures, regardless of whether parents reported pets or smoking at home, according to results of the 4-year, 471-patient prospective study.
Those results suggest that clinicians should be working to make sure the guidelines are being closely followed before, for example, telling parents they need to consider getting rid of the family pet, said Shahid Sheikh, MD, FCCP, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
“As the guidelines still work, we need to focus and develop the connections with the family to make sure the patients are on the right treatment, and that they’re getting the medications,” Dr. Sheikh said in an interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The prospective cohort study by Dr. Sheikh and his colleagues, presented in a poster session, included children referred to a pediatric asthma center with the diagnosis of uncontrolled asthma. All patients received asthma care according to National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 guidelines.
Medications were changed as needed, and the asthma action plan was revised accordingly and reviewed with the family at each visit, Dr. Sheikh reported. After a baseline evaluation, clinic visits for the study occurred at 3 months, 6 months, and then at 1, 2, 3, and 4 years.
Out of 471 patients, 258 had pets, and 125 were in homes where smoking took place, according to parent reports.
Asthma control test scores were 15.1 at baseline for children in no-pet households, and 16.5 for those with pets; by the 3-month visit, scores increased to 20.1 and 20.3 for the no-pet and pet groups, and at 4 years, those scores had edged up to 22.2 and 22.7 (P = .371), Dr. Sheikh reported.
Similarly, after care was started, there was no significant difference between the no-pet and pet groups in mean percent of predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), wheezing, nighttime cough, albuterol use, and other factors over the 4 years of follow-up, he said.
Likewise, looking at the data by nonsmoking vs. smoking households, asthma control test scores at baseline were 16.1 and 15.1, respectively, and at 4 years they were 22.2 and 22.3 (P = .078), with a similar lack of difference in predicted FEV1, wheezing, and all other factors evaluated.
Getting rid of the family pet may need to be a consideration for some families, but based on these data, that might not be necessary for the majority of families, Dr. Sheikh said in the interview.
“On the other hand, we are not saying that if you are smoking, you should continue to smoke,” he added.
“What we are saying is that smoking is bad, but if your child is not getting better, I don’t want to blame your smoking for it. There may be something else which may be more important than smoking which we are missing – the child may not be getting the medicine, or may not be on the right medicine, or may have other comorbidities.”
Dr. Sheikh and his coinvestigators disclosed that they had no relationships relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Sheikh S et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.666.
SAN ANTONIO – It may not always be necessary to tell parents of children with asthma to get rid of the household pet, a recent study suggests.
Children with had significant improvements in a variety of asthma measures, regardless of whether parents reported pets or smoking at home, according to results of the 4-year, 471-patient prospective study.
Those results suggest that clinicians should be working to make sure the guidelines are being closely followed before, for example, telling parents they need to consider getting rid of the family pet, said Shahid Sheikh, MD, FCCP, of Nationwide Children’s Hospital, Columbus, Ohio.
“As the guidelines still work, we need to focus and develop the connections with the family to make sure the patients are on the right treatment, and that they’re getting the medications,” Dr. Sheikh said in an interview at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
The prospective cohort study by Dr. Sheikh and his colleagues, presented in a poster session, included children referred to a pediatric asthma center with the diagnosis of uncontrolled asthma. All patients received asthma care according to National Asthma Education and Prevention Program Expert Panel Report 3 guidelines.
Medications were changed as needed, and the asthma action plan was revised accordingly and reviewed with the family at each visit, Dr. Sheikh reported. After a baseline evaluation, clinic visits for the study occurred at 3 months, 6 months, and then at 1, 2, 3, and 4 years.
Out of 471 patients, 258 had pets, and 125 were in homes where smoking took place, according to parent reports.
Asthma control test scores were 15.1 at baseline for children in no-pet households, and 16.5 for those with pets; by the 3-month visit, scores increased to 20.1 and 20.3 for the no-pet and pet groups, and at 4 years, those scores had edged up to 22.2 and 22.7 (P = .371), Dr. Sheikh reported.
Similarly, after care was started, there was no significant difference between the no-pet and pet groups in mean percent of predicted forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), wheezing, nighttime cough, albuterol use, and other factors over the 4 years of follow-up, he said.
Likewise, looking at the data by nonsmoking vs. smoking households, asthma control test scores at baseline were 16.1 and 15.1, respectively, and at 4 years they were 22.2 and 22.3 (P = .078), with a similar lack of difference in predicted FEV1, wheezing, and all other factors evaluated.
Getting rid of the family pet may need to be a consideration for some families, but based on these data, that might not be necessary for the majority of families, Dr. Sheikh said in the interview.
“On the other hand, we are not saying that if you are smoking, you should continue to smoke,” he added.
“What we are saying is that smoking is bad, but if your child is not getting better, I don’t want to blame your smoking for it. There may be something else which may be more important than smoking which we are missing – the child may not be getting the medicine, or may not be on the right medicine, or may have other comorbidities.”
Dr. Sheikh and his coinvestigators disclosed that they had no relationships relevant to the study.
SOURCE: Sheikh S et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.666.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2018
Key clinical point: Exposure to pets and tobacco smoke may have very little effect on the improvement of asthma in children who are being managed according to guidelines.
Major finding: ACT scores were 15.1 and 16.5 at baseline for children in no-pet and pet households, respectively, and were 22.2 and 22.7 at the 4-year evaluation.
Study details: A 4-year prospective cohort study of 471 children with uncontrolled asthma seen in a pediatric asthma center.
Disclosures: The study authors had no disclosures.
Source: Sheikh S et al. CHEST 2018. doi: 10.1016/j.chest.2018.08.666.
Reducing asthma, COPD exacerbations in obese patients
SAN ANTONIO – Interventions that address variations in inflammation type and metabolism unique to might prove useful for improving their management, Cherry Wongtrakool, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Obese patients with asthma or COPD typically have metabolic and inflammatory profiles that differ from those of nonobese patients with the disorders. Obesity is associated with the development of asthma as well as its severity and the risk for exacerbations. Obese patients with asthma are less likely to have controlled disease or to respond to medication.
The variations in asthma related to obesity even can be traced to infancy for some. Children with rapid weight gain after birth, for example, have an increased risk for developing asthma. In the recently published Boston Birth Cohort study, more than 500 babies from urban, low income families were followed from birth until age 16. Babies with rapid weight gain at 4 months and at 24 months had an increased risk for developing asthma by age 16. Even after adjusting for multiple risk factors, the increased risk for developing asthma persisted in these obese infants.
Higher BMIs during infancy may affect lung development, which continues up to age 5-8 years, Dr. Wongtrakool said. Obesity may affect immune system development. Asthma may develop when persistent inflammation during infancy gets a second hit from genetic factors or from risk factors such as atopy or maternal smoking.
Dr. Wongtrakool noted that obese patients with asthma, unlike nonobese asthma patients, tend to have non-TH2 inflammation. Their TH1/TH2 ratio in stimulated T cells is higher and is directly associated with insulin resistance. Similar to obese patients without asthma, they have higher levels of circulating TNF-alpha, interferon-gamma inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). They are more likely to have insulin resistance, low high-density lipid levels, differences in gut microbiota, increased leptin, decreased adiponectin, increased asymmetric dimethylarginine, and decreased exhaled nitrous oxide (NO).
In broncheoalveolar lavage samples, obese asthma patients have more cells that secrete interleukin-17, Dr. Wontrakool said. TH17-associated inflammation also has an influence in asthma with obesity. A recent study of 30 obese and lean asthma patients found a difference in metabolites measured in breath samples of obese people with asthma, compared with lean people with asthma and obese people without asthma.
In terms of metabolites in their breath, obese asthma patients clustered together and differed from lean patients with asthma and obese patients without asthma.
Obese people with asthma also differ in their gut microbiota, having more firmicutes species and decreased bacteroides species. Studies in mice indicate that these species have a role in body weight and that altering gut microbiota via fecal transplant was associated with weight loss when obese mice received fecal transplants from lean mice, and vice versa.
In the Supplemental Nutrition in Asthma Control (SNAC) study, preadolescents with asthma were given a nutrition bar designed by researchers at the Children’s Hospital Oakland (Calif.) Research Institute. The children also received asthma education and exercise classes, but the intervention was not designed to reduce weight. FVC and FEV1 improved in all study participants, but those participants in the low inflammation subgroup had the most pronounced improvements in FVC and FEV1 after 2 months.
Dr. Wongtrakool called the study “intriguing,” as it indicates asthma patients with lower level inflammation appear more likely to benefit from nutritional supplementation.
In another study of 55 obese adult asthma patients, a hypocaloric diet, access to a nutritionist and psychologist, and exercise classes were associated with improved asthma control and an improved inflammatory and metabolic profile.
In a British registry of the outcomes of bariatric surgery for obesity, patients who also had asthma had a decrease in asthma prevalence in the year after surgery that persisted over 5 years.
The association of COPD with obesity has been less studied than asthma and COPD, but metabolic syndrome appears to be on the rise in these patients. In a study performed over a decade ago, 47% of COPD patients met the definition of metabolic syndrome; a more recent study found 77% of COPD patients met the standard.
Admission glucose levels also have been found to influence the severity of COPD exacerbation. With higher blood glucose levels, there was a higher risk of mortality—from 12% in those with glucose levels of less than 6.0 mmol/l to 31% among those with glucose levels exceeding 9.0 mmol/l, one study showed.
Bariatric surgery may reduce the risk of acute exacerbations of COPD in obese patients, another recent study found. In a study of 480 obese patients with COPD who underwent bariatric surgery, their 28% presurgical risk of acute exacerbations of COPD was cut in half by 12 months after surgery, and the reduction persisted at 24 months.
SAN ANTONIO – Interventions that address variations in inflammation type and metabolism unique to might prove useful for improving their management, Cherry Wongtrakool, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Obese patients with asthma or COPD typically have metabolic and inflammatory profiles that differ from those of nonobese patients with the disorders. Obesity is associated with the development of asthma as well as its severity and the risk for exacerbations. Obese patients with asthma are less likely to have controlled disease or to respond to medication.
The variations in asthma related to obesity even can be traced to infancy for some. Children with rapid weight gain after birth, for example, have an increased risk for developing asthma. In the recently published Boston Birth Cohort study, more than 500 babies from urban, low income families were followed from birth until age 16. Babies with rapid weight gain at 4 months and at 24 months had an increased risk for developing asthma by age 16. Even after adjusting for multiple risk factors, the increased risk for developing asthma persisted in these obese infants.
Higher BMIs during infancy may affect lung development, which continues up to age 5-8 years, Dr. Wongtrakool said. Obesity may affect immune system development. Asthma may develop when persistent inflammation during infancy gets a second hit from genetic factors or from risk factors such as atopy or maternal smoking.
Dr. Wongtrakool noted that obese patients with asthma, unlike nonobese asthma patients, tend to have non-TH2 inflammation. Their TH1/TH2 ratio in stimulated T cells is higher and is directly associated with insulin resistance. Similar to obese patients without asthma, they have higher levels of circulating TNF-alpha, interferon-gamma inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). They are more likely to have insulin resistance, low high-density lipid levels, differences in gut microbiota, increased leptin, decreased adiponectin, increased asymmetric dimethylarginine, and decreased exhaled nitrous oxide (NO).
In broncheoalveolar lavage samples, obese asthma patients have more cells that secrete interleukin-17, Dr. Wontrakool said. TH17-associated inflammation also has an influence in asthma with obesity. A recent study of 30 obese and lean asthma patients found a difference in metabolites measured in breath samples of obese people with asthma, compared with lean people with asthma and obese people without asthma.
In terms of metabolites in their breath, obese asthma patients clustered together and differed from lean patients with asthma and obese patients without asthma.
Obese people with asthma also differ in their gut microbiota, having more firmicutes species and decreased bacteroides species. Studies in mice indicate that these species have a role in body weight and that altering gut microbiota via fecal transplant was associated with weight loss when obese mice received fecal transplants from lean mice, and vice versa.
In the Supplemental Nutrition in Asthma Control (SNAC) study, preadolescents with asthma were given a nutrition bar designed by researchers at the Children’s Hospital Oakland (Calif.) Research Institute. The children also received asthma education and exercise classes, but the intervention was not designed to reduce weight. FVC and FEV1 improved in all study participants, but those participants in the low inflammation subgroup had the most pronounced improvements in FVC and FEV1 after 2 months.
Dr. Wongtrakool called the study “intriguing,” as it indicates asthma patients with lower level inflammation appear more likely to benefit from nutritional supplementation.
In another study of 55 obese adult asthma patients, a hypocaloric diet, access to a nutritionist and psychologist, and exercise classes were associated with improved asthma control and an improved inflammatory and metabolic profile.
In a British registry of the outcomes of bariatric surgery for obesity, patients who also had asthma had a decrease in asthma prevalence in the year after surgery that persisted over 5 years.
The association of COPD with obesity has been less studied than asthma and COPD, but metabolic syndrome appears to be on the rise in these patients. In a study performed over a decade ago, 47% of COPD patients met the definition of metabolic syndrome; a more recent study found 77% of COPD patients met the standard.
Admission glucose levels also have been found to influence the severity of COPD exacerbation. With higher blood glucose levels, there was a higher risk of mortality—from 12% in those with glucose levels of less than 6.0 mmol/l to 31% among those with glucose levels exceeding 9.0 mmol/l, one study showed.
Bariatric surgery may reduce the risk of acute exacerbations of COPD in obese patients, another recent study found. In a study of 480 obese patients with COPD who underwent bariatric surgery, their 28% presurgical risk of acute exacerbations of COPD was cut in half by 12 months after surgery, and the reduction persisted at 24 months.
SAN ANTONIO – Interventions that address variations in inflammation type and metabolism unique to might prove useful for improving their management, Cherry Wongtrakool, MD, of Emory University, Atlanta, said in a presentation at the annual meeting of the American College of Chest Physicians.
Obese patients with asthma or COPD typically have metabolic and inflammatory profiles that differ from those of nonobese patients with the disorders. Obesity is associated with the development of asthma as well as its severity and the risk for exacerbations. Obese patients with asthma are less likely to have controlled disease or to respond to medication.
The variations in asthma related to obesity even can be traced to infancy for some. Children with rapid weight gain after birth, for example, have an increased risk for developing asthma. In the recently published Boston Birth Cohort study, more than 500 babies from urban, low income families were followed from birth until age 16. Babies with rapid weight gain at 4 months and at 24 months had an increased risk for developing asthma by age 16. Even after adjusting for multiple risk factors, the increased risk for developing asthma persisted in these obese infants.
Higher BMIs during infancy may affect lung development, which continues up to age 5-8 years, Dr. Wongtrakool said. Obesity may affect immune system development. Asthma may develop when persistent inflammation during infancy gets a second hit from genetic factors or from risk factors such as atopy or maternal smoking.
Dr. Wongtrakool noted that obese patients with asthma, unlike nonobese asthma patients, tend to have non-TH2 inflammation. Their TH1/TH2 ratio in stimulated T cells is higher and is directly associated with insulin resistance. Similar to obese patients without asthma, they have higher levels of circulating TNF-alpha, interferon-gamma inducible protein 10, and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1). They are more likely to have insulin resistance, low high-density lipid levels, differences in gut microbiota, increased leptin, decreased adiponectin, increased asymmetric dimethylarginine, and decreased exhaled nitrous oxide (NO).
In broncheoalveolar lavage samples, obese asthma patients have more cells that secrete interleukin-17, Dr. Wontrakool said. TH17-associated inflammation also has an influence in asthma with obesity. A recent study of 30 obese and lean asthma patients found a difference in metabolites measured in breath samples of obese people with asthma, compared with lean people with asthma and obese people without asthma.
In terms of metabolites in their breath, obese asthma patients clustered together and differed from lean patients with asthma and obese patients without asthma.
Obese people with asthma also differ in their gut microbiota, having more firmicutes species and decreased bacteroides species. Studies in mice indicate that these species have a role in body weight and that altering gut microbiota via fecal transplant was associated with weight loss when obese mice received fecal transplants from lean mice, and vice versa.
In the Supplemental Nutrition in Asthma Control (SNAC) study, preadolescents with asthma were given a nutrition bar designed by researchers at the Children’s Hospital Oakland (Calif.) Research Institute. The children also received asthma education and exercise classes, but the intervention was not designed to reduce weight. FVC and FEV1 improved in all study participants, but those participants in the low inflammation subgroup had the most pronounced improvements in FVC and FEV1 after 2 months.
Dr. Wongtrakool called the study “intriguing,” as it indicates asthma patients with lower level inflammation appear more likely to benefit from nutritional supplementation.
In another study of 55 obese adult asthma patients, a hypocaloric diet, access to a nutritionist and psychologist, and exercise classes were associated with improved asthma control and an improved inflammatory and metabolic profile.
In a British registry of the outcomes of bariatric surgery for obesity, patients who also had asthma had a decrease in asthma prevalence in the year after surgery that persisted over 5 years.
The association of COPD with obesity has been less studied than asthma and COPD, but metabolic syndrome appears to be on the rise in these patients. In a study performed over a decade ago, 47% of COPD patients met the definition of metabolic syndrome; a more recent study found 77% of COPD patients met the standard.
Admission glucose levels also have been found to influence the severity of COPD exacerbation. With higher blood glucose levels, there was a higher risk of mortality—from 12% in those with glucose levels of less than 6.0 mmol/l to 31% among those with glucose levels exceeding 9.0 mmol/l, one study showed.
Bariatric surgery may reduce the risk of acute exacerbations of COPD in obese patients, another recent study found. In a study of 480 obese patients with COPD who underwent bariatric surgery, their 28% presurgical risk of acute exacerbations of COPD was cut in half by 12 months after surgery, and the reduction persisted at 24 months.
REPORTING FROM CHEST 2018
Refill disruptions for inhaled corticosteroids may mean more exacerbations
Interruptions of patients’ refills for combination inhaled corticosteroid medication caused by the Medicare Part D formulary switch may have resulted in increased exacerbations and hospitalizations, according to a study that will be presented at the CHEST 2018 annual meeting.
Katie Devane, PhD, and her colleagues examined pharmacy records of 44,832 patients aged 12 years and older who had received a combination inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide/formoterol) and a long-acting beta-agonist medication in 2016-2017. They were followed to track their refills, medication switches, and use of other medications such as oral corticosteroids, antibiotics, and rescue inhalers.
After the Medicare Part D formulary switch on Jan. 1, 2017, many of these patients experienced disruption of their refills. About half of the patients attempted to get a refill of their inhaled corticosteroid prescription but only 46% were approved. One-third of the patients studied did not replace their medication, 12% switched to monotherapy, and 17% had no inhaled medication, the study found.
The investigators concluded that the formulary block resulted in many patients going without optimal medication and potentially led to more exacerbations and ER visits.
View the study abstract here: https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(18)31877-4/fulltext
The study will be presented in the session Improving Care in COPD, Monday, Oct. 8, 2:15 p.m., Convention Center Room 207A.
Interruptions of patients’ refills for combination inhaled corticosteroid medication caused by the Medicare Part D formulary switch may have resulted in increased exacerbations and hospitalizations, according to a study that will be presented at the CHEST 2018 annual meeting.
Katie Devane, PhD, and her colleagues examined pharmacy records of 44,832 patients aged 12 years and older who had received a combination inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide/formoterol) and a long-acting beta-agonist medication in 2016-2017. They were followed to track their refills, medication switches, and use of other medications such as oral corticosteroids, antibiotics, and rescue inhalers.
After the Medicare Part D formulary switch on Jan. 1, 2017, many of these patients experienced disruption of their refills. About half of the patients attempted to get a refill of their inhaled corticosteroid prescription but only 46% were approved. One-third of the patients studied did not replace their medication, 12% switched to monotherapy, and 17% had no inhaled medication, the study found.
The investigators concluded that the formulary block resulted in many patients going without optimal medication and potentially led to more exacerbations and ER visits.
View the study abstract here: https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(18)31877-4/fulltext
The study will be presented in the session Improving Care in COPD, Monday, Oct. 8, 2:15 p.m., Convention Center Room 207A.
Interruptions of patients’ refills for combination inhaled corticosteroid medication caused by the Medicare Part D formulary switch may have resulted in increased exacerbations and hospitalizations, according to a study that will be presented at the CHEST 2018 annual meeting.
Katie Devane, PhD, and her colleagues examined pharmacy records of 44,832 patients aged 12 years and older who had received a combination inhaled corticosteroid (budesonide/formoterol) and a long-acting beta-agonist medication in 2016-2017. They were followed to track their refills, medication switches, and use of other medications such as oral corticosteroids, antibiotics, and rescue inhalers.
After the Medicare Part D formulary switch on Jan. 1, 2017, many of these patients experienced disruption of their refills. About half of the patients attempted to get a refill of their inhaled corticosteroid prescription but only 46% were approved. One-third of the patients studied did not replace their medication, 12% switched to monotherapy, and 17% had no inhaled medication, the study found.
The investigators concluded that the formulary block resulted in many patients going without optimal medication and potentially led to more exacerbations and ER visits.
View the study abstract here: https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(18)31877-4/fulltext
The study will be presented in the session Improving Care in COPD, Monday, Oct. 8, 2:15 p.m., Convention Center Room 207A.
Treatment adherence may trump environmental factors for children with asthma
Children with asthma who are provided with care and medication per National Asthma Education and Prevention Program guidelines can improve over time, despite the presence of environmental factors such as second-hand tobacco smoke and domestic pets, according to a study presented at the CHEST 2018 annual meeting.
A study conducted at the Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, included 395 children aged 2-17 years with a diagnosis of uncontrolled asthma. These children were then treated using the NAEPP guidelines for acute care needs and symptom control. In this sample of patients, 25% were exposed to second-hand smoke, and 55% had a cat or dog in the home.
The investigators followed these patients and observed improvement of symptoms. But in a comparison of those with and without the potentially problematic environmental factors, improvement was independent of the presence of these factors. The findings suggest that NAEPP-recommended treatment of asthma is more important than are some environmental factors.
View the study abstract here: https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(18)31862-2/fulltext.
The findings will be presented in the session on Obstructive Lung Diseases, Wednesday, Oct. 10, at 1:00 p.m.
Children with asthma who are provided with care and medication per National Asthma Education and Prevention Program guidelines can improve over time, despite the presence of environmental factors such as second-hand tobacco smoke and domestic pets, according to a study presented at the CHEST 2018 annual meeting.
A study conducted at the Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, included 395 children aged 2-17 years with a diagnosis of uncontrolled asthma. These children were then treated using the NAEPP guidelines for acute care needs and symptom control. In this sample of patients, 25% were exposed to second-hand smoke, and 55% had a cat or dog in the home.
The investigators followed these patients and observed improvement of symptoms. But in a comparison of those with and without the potentially problematic environmental factors, improvement was independent of the presence of these factors. The findings suggest that NAEPP-recommended treatment of asthma is more important than are some environmental factors.
View the study abstract here: https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(18)31862-2/fulltext.
The findings will be presented in the session on Obstructive Lung Diseases, Wednesday, Oct. 10, at 1:00 p.m.
Children with asthma who are provided with care and medication per National Asthma Education and Prevention Program guidelines can improve over time, despite the presence of environmental factors such as second-hand tobacco smoke and domestic pets, according to a study presented at the CHEST 2018 annual meeting.
A study conducted at the Nationwide Children’s Hospital in Columbus, Ohio, included 395 children aged 2-17 years with a diagnosis of uncontrolled asthma. These children were then treated using the NAEPP guidelines for acute care needs and symptom control. In this sample of patients, 25% were exposed to second-hand smoke, and 55% had a cat or dog in the home.
The investigators followed these patients and observed improvement of symptoms. But in a comparison of those with and without the potentially problematic environmental factors, improvement was independent of the presence of these factors. The findings suggest that NAEPP-recommended treatment of asthma is more important than are some environmental factors.
View the study abstract here: https://journal.chestnet.org/article/S0012-3692(18)31862-2/fulltext.
The findings will be presented in the session on Obstructive Lung Diseases, Wednesday, Oct. 10, at 1:00 p.m.