User login
Ablation at an early stage of fibrosis appears critical to improved AFib control
No benefit observed if fibrosis advanced
The addition of image-guided atrial fibrosis ablation did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrence relative to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) alone in patients with treatment-resistant atrial fibrillation (AFib), according to results of an intention-to-treat analysis of the randomized DECAAF II trial.
However, there was a significant advantage for the addition of image-guided ablation in the subgroup of patients with stage I or II fibrosis, and this is a clinically meaningful finding, Nassir F. Marrouche, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Patients at early stages [of fibrosis] appear to do well if you do a good job covering the myopathy [with scar formation], and that is an important message,” said Dr. Marrouche, the principal investigator.
The underlying hypothesis of the DECAAF trial was that ablation guided with MRI imaging would prove superior to PVI alone in the treatment of resistant AF. There were 843 participants randomized at 44 centers. At baseline, all underwent a late gadolinium-enhancement MRI, a technique that allows detection of fibrotic tissue.
After randomization, those in the control group underwent standard of care PVI alone. Those in the intervention group underwent ablation of areas of the atrium revealed to be fibrotic on the MRI scan in addition to PVI.
Five percent risk reduction not significant
After a median follow-up of 12 months, recurrence of AFib, which was the primary endpoint, was observed in 43% in the intervention group and 46.1% in the control group. The relative 5% reduction for treatment was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.778-1.17; P = .63).
As part of the study protocol, MRI was repeated 3 months after treatment in all patients. This permitted the investigators to evaluate the degree of scar formation in relation to the fibrosis covered in the intervention group. Independent reviewers rated this coverage on levels from 1 to 5, with 5 representing complete coverage.
In this analysis, it was found that ablation resulted in higher levels of lesion formation in those with early stages of disease, defined as stage I or II fibrosis, but lower levels in advanced stages.
“The more myopathy, the more disease, the less likelihood of lesion formation,” reported Dr. Marrouche, professor of medicine in the section of cardiology at Tulane University, New Orleans.
Attributed to the greater levels of fibrosis coverage, the risk of AF recurrence over the course of follow-up was significantly reduced in the intervention relative to the control group on as-treated analysis in patients who had stage I or II fibrosis at baseline. (HR 0.841, 95% CI, 0.732-0.968; P < .05).
Subgroup data called clinically meaningful
“This has huge implications going forward,” Dr. Marrouche maintained. In the context of a series of previous trials, including DECAAF I, which associated advanced fibrosis with higher risk of failing ablation, DECAAF II provides the groundwork for “where and how to ablate.”
Taken together, the DECAAF data suggest that there is no value in ablating advanced fibrosis. Due to the poor scar formation needed to reduce risk of AF recurrence, there are no benefits to outweigh the slightly greater risk of strokes and other adverse events observed among the intervention group in the DECAAF II trial, according to Dr. Marrouche.
“If the fibrosis is advanced, do PVI only,” he said.
However, if fibrosis remains at an early stage, defined by these data as stage II or lower, the data from DECAAF indicated that there is a benefit, according to Dr. Marrouche.
“DECAAF tells you to target early disease,” he said. Asked if he would now apply these data to treatment of patients with early fibrosis, he replied, “Yes, that’s what I am concluding.”
Several aspects of the design of DECAAF II, such as the use of a follow-up MRI to assess ablation at 3 months, were praised by Paul J. Wang, MD, director, Stanford Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, Stanford (Calif.) University, but he did not agree with Dr. Marrouche’s interpretation. This included the contention that scar formation was easier to achieve in patients with less atrial fibrosis.
DECAAF II is not a positive trial
Based on his reading of the correlation coefficients, expressed as an r value, which were 0.237 and 0.493 for the low- and high-fibrosis groups, respectively, “the difference in lesion formation in low- and high-fibrosis groups seems difficult to prove,” Dr. Wang pointed out.
In addition, “the authors suggest that the failure to achieve a good ablation lesion may account for the AFib recurrence,” said Dr. Wang, editor-in-chief of the American Heart Association’s Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology. However, due to the many other potential variables influencing this risk, “this is difficult to show.”
Ultimately, despite a benefit observed among patients with a low level of fibrosis that was identified in an as-treated subgroup, “DECAAF II joins the numerous studies [evaluating the addition of an intervention relative to PVI alone] that have not achieved the primary endpoint,” Dr. Wang concluded.
An ESC-invited discussant, Christophe Leclercq, MD, chief of cardiology at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Rennes, France, made the same point. He said several previous studies have made the concept of achieving greater ablation to reduce AF recurrence “attractive,” but this “was not confirmed in DECAAF II.”
He also would not endorse MRI-guided ablation in resistant AFib among patients with early disease.
“There was a positive result observed in those with a low stage of fibrosis, but there were also more complications in those undergoing MRI-guided ablation,” he said.
Dr. Marrouche reports financial relationships with Abbott, which provided funding for this study. Dr. Wang had no disclosures. Dr. Leclercq reported financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Sorin Group, and St. Jude Medical.
No benefit observed if fibrosis advanced
No benefit observed if fibrosis advanced
The addition of image-guided atrial fibrosis ablation did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrence relative to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) alone in patients with treatment-resistant atrial fibrillation (AFib), according to results of an intention-to-treat analysis of the randomized DECAAF II trial.
However, there was a significant advantage for the addition of image-guided ablation in the subgroup of patients with stage I or II fibrosis, and this is a clinically meaningful finding, Nassir F. Marrouche, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Patients at early stages [of fibrosis] appear to do well if you do a good job covering the myopathy [with scar formation], and that is an important message,” said Dr. Marrouche, the principal investigator.
The underlying hypothesis of the DECAAF trial was that ablation guided with MRI imaging would prove superior to PVI alone in the treatment of resistant AF. There were 843 participants randomized at 44 centers. At baseline, all underwent a late gadolinium-enhancement MRI, a technique that allows detection of fibrotic tissue.
After randomization, those in the control group underwent standard of care PVI alone. Those in the intervention group underwent ablation of areas of the atrium revealed to be fibrotic on the MRI scan in addition to PVI.
Five percent risk reduction not significant
After a median follow-up of 12 months, recurrence of AFib, which was the primary endpoint, was observed in 43% in the intervention group and 46.1% in the control group. The relative 5% reduction for treatment was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.778-1.17; P = .63).
As part of the study protocol, MRI was repeated 3 months after treatment in all patients. This permitted the investigators to evaluate the degree of scar formation in relation to the fibrosis covered in the intervention group. Independent reviewers rated this coverage on levels from 1 to 5, with 5 representing complete coverage.
In this analysis, it was found that ablation resulted in higher levels of lesion formation in those with early stages of disease, defined as stage I or II fibrosis, but lower levels in advanced stages.
“The more myopathy, the more disease, the less likelihood of lesion formation,” reported Dr. Marrouche, professor of medicine in the section of cardiology at Tulane University, New Orleans.
Attributed to the greater levels of fibrosis coverage, the risk of AF recurrence over the course of follow-up was significantly reduced in the intervention relative to the control group on as-treated analysis in patients who had stage I or II fibrosis at baseline. (HR 0.841, 95% CI, 0.732-0.968; P < .05).
Subgroup data called clinically meaningful
“This has huge implications going forward,” Dr. Marrouche maintained. In the context of a series of previous trials, including DECAAF I, which associated advanced fibrosis with higher risk of failing ablation, DECAAF II provides the groundwork for “where and how to ablate.”
Taken together, the DECAAF data suggest that there is no value in ablating advanced fibrosis. Due to the poor scar formation needed to reduce risk of AF recurrence, there are no benefits to outweigh the slightly greater risk of strokes and other adverse events observed among the intervention group in the DECAAF II trial, according to Dr. Marrouche.
“If the fibrosis is advanced, do PVI only,” he said.
However, if fibrosis remains at an early stage, defined by these data as stage II or lower, the data from DECAAF indicated that there is a benefit, according to Dr. Marrouche.
“DECAAF tells you to target early disease,” he said. Asked if he would now apply these data to treatment of patients with early fibrosis, he replied, “Yes, that’s what I am concluding.”
Several aspects of the design of DECAAF II, such as the use of a follow-up MRI to assess ablation at 3 months, were praised by Paul J. Wang, MD, director, Stanford Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, Stanford (Calif.) University, but he did not agree with Dr. Marrouche’s interpretation. This included the contention that scar formation was easier to achieve in patients with less atrial fibrosis.
DECAAF II is not a positive trial
Based on his reading of the correlation coefficients, expressed as an r value, which were 0.237 and 0.493 for the low- and high-fibrosis groups, respectively, “the difference in lesion formation in low- and high-fibrosis groups seems difficult to prove,” Dr. Wang pointed out.
In addition, “the authors suggest that the failure to achieve a good ablation lesion may account for the AFib recurrence,” said Dr. Wang, editor-in-chief of the American Heart Association’s Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology. However, due to the many other potential variables influencing this risk, “this is difficult to show.”
Ultimately, despite a benefit observed among patients with a low level of fibrosis that was identified in an as-treated subgroup, “DECAAF II joins the numerous studies [evaluating the addition of an intervention relative to PVI alone] that have not achieved the primary endpoint,” Dr. Wang concluded.
An ESC-invited discussant, Christophe Leclercq, MD, chief of cardiology at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Rennes, France, made the same point. He said several previous studies have made the concept of achieving greater ablation to reduce AF recurrence “attractive,” but this “was not confirmed in DECAAF II.”
He also would not endorse MRI-guided ablation in resistant AFib among patients with early disease.
“There was a positive result observed in those with a low stage of fibrosis, but there were also more complications in those undergoing MRI-guided ablation,” he said.
Dr. Marrouche reports financial relationships with Abbott, which provided funding for this study. Dr. Wang had no disclosures. Dr. Leclercq reported financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Sorin Group, and St. Jude Medical.
The addition of image-guided atrial fibrosis ablation did not significantly reduce the risk of recurrence relative to pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) alone in patients with treatment-resistant atrial fibrillation (AFib), according to results of an intention-to-treat analysis of the randomized DECAAF II trial.
However, there was a significant advantage for the addition of image-guided ablation in the subgroup of patients with stage I or II fibrosis, and this is a clinically meaningful finding, Nassir F. Marrouche, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Patients at early stages [of fibrosis] appear to do well if you do a good job covering the myopathy [with scar formation], and that is an important message,” said Dr. Marrouche, the principal investigator.
The underlying hypothesis of the DECAAF trial was that ablation guided with MRI imaging would prove superior to PVI alone in the treatment of resistant AF. There were 843 participants randomized at 44 centers. At baseline, all underwent a late gadolinium-enhancement MRI, a technique that allows detection of fibrotic tissue.
After randomization, those in the control group underwent standard of care PVI alone. Those in the intervention group underwent ablation of areas of the atrium revealed to be fibrotic on the MRI scan in addition to PVI.
Five percent risk reduction not significant
After a median follow-up of 12 months, recurrence of AFib, which was the primary endpoint, was observed in 43% in the intervention group and 46.1% in the control group. The relative 5% reduction for treatment was not statistically significant (hazard ratio, 0.95; 95% confidence interval, 0.778-1.17; P = .63).
As part of the study protocol, MRI was repeated 3 months after treatment in all patients. This permitted the investigators to evaluate the degree of scar formation in relation to the fibrosis covered in the intervention group. Independent reviewers rated this coverage on levels from 1 to 5, with 5 representing complete coverage.
In this analysis, it was found that ablation resulted in higher levels of lesion formation in those with early stages of disease, defined as stage I or II fibrosis, but lower levels in advanced stages.
“The more myopathy, the more disease, the less likelihood of lesion formation,” reported Dr. Marrouche, professor of medicine in the section of cardiology at Tulane University, New Orleans.
Attributed to the greater levels of fibrosis coverage, the risk of AF recurrence over the course of follow-up was significantly reduced in the intervention relative to the control group on as-treated analysis in patients who had stage I or II fibrosis at baseline. (HR 0.841, 95% CI, 0.732-0.968; P < .05).
Subgroup data called clinically meaningful
“This has huge implications going forward,” Dr. Marrouche maintained. In the context of a series of previous trials, including DECAAF I, which associated advanced fibrosis with higher risk of failing ablation, DECAAF II provides the groundwork for “where and how to ablate.”
Taken together, the DECAAF data suggest that there is no value in ablating advanced fibrosis. Due to the poor scar formation needed to reduce risk of AF recurrence, there are no benefits to outweigh the slightly greater risk of strokes and other adverse events observed among the intervention group in the DECAAF II trial, according to Dr. Marrouche.
“If the fibrosis is advanced, do PVI only,” he said.
However, if fibrosis remains at an early stage, defined by these data as stage II or lower, the data from DECAAF indicated that there is a benefit, according to Dr. Marrouche.
“DECAAF tells you to target early disease,” he said. Asked if he would now apply these data to treatment of patients with early fibrosis, he replied, “Yes, that’s what I am concluding.”
Several aspects of the design of DECAAF II, such as the use of a follow-up MRI to assess ablation at 3 months, were praised by Paul J. Wang, MD, director, Stanford Cardiac Arrhythmia Service, Stanford (Calif.) University, but he did not agree with Dr. Marrouche’s interpretation. This included the contention that scar formation was easier to achieve in patients with less atrial fibrosis.
DECAAF II is not a positive trial
Based on his reading of the correlation coefficients, expressed as an r value, which were 0.237 and 0.493 for the low- and high-fibrosis groups, respectively, “the difference in lesion formation in low- and high-fibrosis groups seems difficult to prove,” Dr. Wang pointed out.
In addition, “the authors suggest that the failure to achieve a good ablation lesion may account for the AFib recurrence,” said Dr. Wang, editor-in-chief of the American Heart Association’s Circulation: Arrhythmia and Electrophysiology. However, due to the many other potential variables influencing this risk, “this is difficult to show.”
Ultimately, despite a benefit observed among patients with a low level of fibrosis that was identified in an as-treated subgroup, “DECAAF II joins the numerous studies [evaluating the addition of an intervention relative to PVI alone] that have not achieved the primary endpoint,” Dr. Wang concluded.
An ESC-invited discussant, Christophe Leclercq, MD, chief of cardiology at Centre Hospitalier Universitaire, Rennes, France, made the same point. He said several previous studies have made the concept of achieving greater ablation to reduce AF recurrence “attractive,” but this “was not confirmed in DECAAF II.”
He also would not endorse MRI-guided ablation in resistant AFib among patients with early disease.
“There was a positive result observed in those with a low stage of fibrosis, but there were also more complications in those undergoing MRI-guided ablation,” he said.
Dr. Marrouche reports financial relationships with Abbott, which provided funding for this study. Dr. Wang had no disclosures. Dr. Leclercq reported financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Sorin Group, and St. Jude Medical.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
Dapagliflozin in HFrEF may cut arrhythmias, sudden death: DAPA-HF
Dapagliflozin might reduce the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-HF trial suggests.
The addition of dapagliflozin to standard therapy reduced the relative risk for the primary composite endpoint of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or sudden death by 21%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99). The absolute risk reduction was 1.5% (5.9% vs. 7.4%).
The benefit was consistent in a competing-risks analysis that included all-cause mortality (HR, 0.80; P = .043) and across the individual components of the composite outcome, James Curtain, MD, Cardiovascular Research Centre of Glasgow, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
As previously reported from the main trial, treatment with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor cut the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by 26% among 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class 2-4.
Cochair of the late-breaking science session, Lars Lund, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, pointed out that dapagliflozin reduced sudden cardiac deaths and related events to an extent similar to that observed for cardiovascular deaths, total mortality, and the main trial’s primary endpoint.
“So does that mean it has any particular effect on arrhythmic events or does it mean, such as a beta-blocker, for example, [it] reduces calcium transience and improves handling of calcium, or does it have an effect simply by improving heart failure?” he asked.
Dr. Curtain replied they are still trying to understand the effects of this new class of drug but that studies have shown dapagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors have favorable effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, which contributes to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia. They’ve also been shown to reduce cardiac chamber size, left ventricular hypertrophy, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels over time, consistent with a reduction in myocardial wall stress. “So it could indeed be one of several mechanisms by which they may exert a beneficial cardiac effect.”
Speaking with this news organization, Dr. Curtain pointed out that the Kaplan-Meier curves for the composite outcome began to separate early on, but that the clearest separation was after 9 months, suggestive of a positive action on adverse cardiac remodeling over time.
“This would improve the patients’ heart failure situation, but also thick ventricles are a key risk factor for the occurrence of sudden death and ventricular arrhythmias,” he said. “The effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, given its plausibility in terms of our Kaplan-Meier curves, are one [mechanism] that I’d look to in the first instance, but I’m sure there are more than one actions at play.”
According to the new analysis, the primary outcome occurred in 315 (6.6%) patients; there were 203 adjudicated sudden deaths (64%), 104 investigator-reported ventricular arrhythmias (33%), and 8 resuscitated cardiac arrests (3%). Independent predictors of the primary outcome were higher NT-proBNP levels (odds ratio, 1.54), previous ventricular arrhythmia (OR, 1.93), previous myocardial infarction (OR, 1.42), male sex (OR, 1.53), and higher body mass index (OR, 1.03).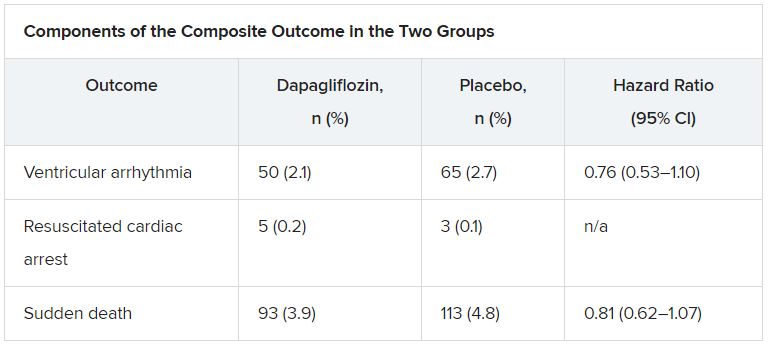
The effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent in several sensitivity analyses and “generally consistent” across key subgroups, Dr. Curtain said.
During a discussion of the results, session cochair Mitja Lainscak, MD, General Hospital Murska Sobota, Slovenia, called out two exceptions. “With regard to patients with implanted ICDs, the effect was neutral, and in the patients without diabetes, the benefit was less than in diabetic patients. Any explanations for that?”
Dr. Curtain responded that “it’s important to note that in the subgroup analyses the point estimates were all on the side favoring dapagliflozin and the interaction test was not significant in that subgroup. The numbers of patients who were in the defibrillator group were modest, and there was a relatively smaller number of events, so it may be harder to show benefit in that group.”
In the dapagliflozin and placebo groups, the event rates per 100 person-years were 3.9 and 5.8, respectively, in patients with diabetes, and 4.1 and 4.7, respectively, in those without diabetes (P for interaction = .273).
Event rates per 100 person-years were 5.8 and 5.9, respectively, in patients with a defibrillator at baseline, and 3.5 and 4.9, respectively, in those without a defibrillator (P for interaction = .174).
Asked to comment on the study, which was simultaneously published in the European Heart Journal, Milton Packer, MD, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, said he had “very little confidence” in the findings.
“This was entirely post hoc and the investigators combined events – with markedly different levels of clinical importance – in order to achieve a P value less than 0.05,” he told this news organization. “If one takes asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias out of the analysis, the effect is no longer statistically significant. Furthermore, half of sudden deaths in patients with heart failure are not related to a ventricular arrhythmia.”
The authors note in their report that the analysis was not prespecified and the findings should be regarded as “hypothesis generating and require confirmation,” but also point out that a recent meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitor use was associated with a lower risk for ventricular tachycardia. Other limitations to the post hoc analysis are that adverse-event reporting likely underestimated the true prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias, and that these events were not adjudicated.
DAPA-HF was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Curtain reports no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the coauthors are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dapagliflozin might reduce the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-HF trial suggests.
The addition of dapagliflozin to standard therapy reduced the relative risk for the primary composite endpoint of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or sudden death by 21%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99). The absolute risk reduction was 1.5% (5.9% vs. 7.4%).
The benefit was consistent in a competing-risks analysis that included all-cause mortality (HR, 0.80; P = .043) and across the individual components of the composite outcome, James Curtain, MD, Cardiovascular Research Centre of Glasgow, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
As previously reported from the main trial, treatment with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor cut the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by 26% among 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class 2-4.
Cochair of the late-breaking science session, Lars Lund, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, pointed out that dapagliflozin reduced sudden cardiac deaths and related events to an extent similar to that observed for cardiovascular deaths, total mortality, and the main trial’s primary endpoint.
“So does that mean it has any particular effect on arrhythmic events or does it mean, such as a beta-blocker, for example, [it] reduces calcium transience and improves handling of calcium, or does it have an effect simply by improving heart failure?” he asked.
Dr. Curtain replied they are still trying to understand the effects of this new class of drug but that studies have shown dapagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors have favorable effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, which contributes to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia. They’ve also been shown to reduce cardiac chamber size, left ventricular hypertrophy, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels over time, consistent with a reduction in myocardial wall stress. “So it could indeed be one of several mechanisms by which they may exert a beneficial cardiac effect.”
Speaking with this news organization, Dr. Curtain pointed out that the Kaplan-Meier curves for the composite outcome began to separate early on, but that the clearest separation was after 9 months, suggestive of a positive action on adverse cardiac remodeling over time.
“This would improve the patients’ heart failure situation, but also thick ventricles are a key risk factor for the occurrence of sudden death and ventricular arrhythmias,” he said. “The effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, given its plausibility in terms of our Kaplan-Meier curves, are one [mechanism] that I’d look to in the first instance, but I’m sure there are more than one actions at play.”
According to the new analysis, the primary outcome occurred in 315 (6.6%) patients; there were 203 adjudicated sudden deaths (64%), 104 investigator-reported ventricular arrhythmias (33%), and 8 resuscitated cardiac arrests (3%). Independent predictors of the primary outcome were higher NT-proBNP levels (odds ratio, 1.54), previous ventricular arrhythmia (OR, 1.93), previous myocardial infarction (OR, 1.42), male sex (OR, 1.53), and higher body mass index (OR, 1.03).
The effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent in several sensitivity analyses and “generally consistent” across key subgroups, Dr. Curtain said.
During a discussion of the results, session cochair Mitja Lainscak, MD, General Hospital Murska Sobota, Slovenia, called out two exceptions. “With regard to patients with implanted ICDs, the effect was neutral, and in the patients without diabetes, the benefit was less than in diabetic patients. Any explanations for that?”
Dr. Curtain responded that “it’s important to note that in the subgroup analyses the point estimates were all on the side favoring dapagliflozin and the interaction test was not significant in that subgroup. The numbers of patients who were in the defibrillator group were modest, and there was a relatively smaller number of events, so it may be harder to show benefit in that group.”
In the dapagliflozin and placebo groups, the event rates per 100 person-years were 3.9 and 5.8, respectively, in patients with diabetes, and 4.1 and 4.7, respectively, in those without diabetes (P for interaction = .273).
Event rates per 100 person-years were 5.8 and 5.9, respectively, in patients with a defibrillator at baseline, and 3.5 and 4.9, respectively, in those without a defibrillator (P for interaction = .174).
Asked to comment on the study, which was simultaneously published in the European Heart Journal, Milton Packer, MD, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, said he had “very little confidence” in the findings.
“This was entirely post hoc and the investigators combined events – with markedly different levels of clinical importance – in order to achieve a P value less than 0.05,” he told this news organization. “If one takes asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias out of the analysis, the effect is no longer statistically significant. Furthermore, half of sudden deaths in patients with heart failure are not related to a ventricular arrhythmia.”
The authors note in their report that the analysis was not prespecified and the findings should be regarded as “hypothesis generating and require confirmation,” but also point out that a recent meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitor use was associated with a lower risk for ventricular tachycardia. Other limitations to the post hoc analysis are that adverse-event reporting likely underestimated the true prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias, and that these events were not adjudicated.
DAPA-HF was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Curtain reports no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the coauthors are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Dapagliflozin might reduce the risk for ventricular arrhythmias and sudden death in patients with heart failure and reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), a post hoc analysis of the DAPA-HF trial suggests.
The addition of dapagliflozin to standard therapy reduced the relative risk for the primary composite endpoint of any serious ventricular arrhythmia, resuscitated cardiac arrest, or sudden death by 21%, compared with placebo (hazard ratio, 0.79; 95% confidence interval, 0.63-0.99). The absolute risk reduction was 1.5% (5.9% vs. 7.4%).
The benefit was consistent in a competing-risks analysis that included all-cause mortality (HR, 0.80; P = .043) and across the individual components of the composite outcome, James Curtain, MD, Cardiovascular Research Centre of Glasgow, said at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
As previously reported from the main trial, treatment with the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor cut the primary endpoint of cardiovascular death or worsening heart failure by 26% among 4,744 patients with HFrEF and in New York Heart Association functional class 2-4.
Cochair of the late-breaking science session, Lars Lund, MD, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, pointed out that dapagliflozin reduced sudden cardiac deaths and related events to an extent similar to that observed for cardiovascular deaths, total mortality, and the main trial’s primary endpoint.
“So does that mean it has any particular effect on arrhythmic events or does it mean, such as a beta-blocker, for example, [it] reduces calcium transience and improves handling of calcium, or does it have an effect simply by improving heart failure?” he asked.
Dr. Curtain replied they are still trying to understand the effects of this new class of drug but that studies have shown dapagliflozin and other SGLT2 inhibitors have favorable effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, which contributes to sudden death and ventricular arrhythmia. They’ve also been shown to reduce cardiac chamber size, left ventricular hypertrophy, and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) levels over time, consistent with a reduction in myocardial wall stress. “So it could indeed be one of several mechanisms by which they may exert a beneficial cardiac effect.”
Speaking with this news organization, Dr. Curtain pointed out that the Kaplan-Meier curves for the composite outcome began to separate early on, but that the clearest separation was after 9 months, suggestive of a positive action on adverse cardiac remodeling over time.
“This would improve the patients’ heart failure situation, but also thick ventricles are a key risk factor for the occurrence of sudden death and ventricular arrhythmias,” he said. “The effects on adverse cardiac remodeling, given its plausibility in terms of our Kaplan-Meier curves, are one [mechanism] that I’d look to in the first instance, but I’m sure there are more than one actions at play.”
According to the new analysis, the primary outcome occurred in 315 (6.6%) patients; there were 203 adjudicated sudden deaths (64%), 104 investigator-reported ventricular arrhythmias (33%), and 8 resuscitated cardiac arrests (3%). Independent predictors of the primary outcome were higher NT-proBNP levels (odds ratio, 1.54), previous ventricular arrhythmia (OR, 1.93), previous myocardial infarction (OR, 1.42), male sex (OR, 1.53), and higher body mass index (OR, 1.03).
The effect of dapagliflozin on the primary outcome was consistent in several sensitivity analyses and “generally consistent” across key subgroups, Dr. Curtain said.
During a discussion of the results, session cochair Mitja Lainscak, MD, General Hospital Murska Sobota, Slovenia, called out two exceptions. “With regard to patients with implanted ICDs, the effect was neutral, and in the patients without diabetes, the benefit was less than in diabetic patients. Any explanations for that?”
Dr. Curtain responded that “it’s important to note that in the subgroup analyses the point estimates were all on the side favoring dapagliflozin and the interaction test was not significant in that subgroup. The numbers of patients who were in the defibrillator group were modest, and there was a relatively smaller number of events, so it may be harder to show benefit in that group.”
In the dapagliflozin and placebo groups, the event rates per 100 person-years were 3.9 and 5.8, respectively, in patients with diabetes, and 4.1 and 4.7, respectively, in those without diabetes (P for interaction = .273).
Event rates per 100 person-years were 5.8 and 5.9, respectively, in patients with a defibrillator at baseline, and 3.5 and 4.9, respectively, in those without a defibrillator (P for interaction = .174).
Asked to comment on the study, which was simultaneously published in the European Heart Journal, Milton Packer, MD, Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, said he had “very little confidence” in the findings.
“This was entirely post hoc and the investigators combined events – with markedly different levels of clinical importance – in order to achieve a P value less than 0.05,” he told this news organization. “If one takes asymptomatic ventricular arrhythmias out of the analysis, the effect is no longer statistically significant. Furthermore, half of sudden deaths in patients with heart failure are not related to a ventricular arrhythmia.”
The authors note in their report that the analysis was not prespecified and the findings should be regarded as “hypothesis generating and require confirmation,” but also point out that a recent meta-analysis showed that SGLT2 inhibitor use was associated with a lower risk for ventricular tachycardia. Other limitations to the post hoc analysis are that adverse-event reporting likely underestimated the true prevalence of ventricular arrhythmias, and that these events were not adjudicated.
DAPA-HF was funded by AstraZeneca. Dr. Curtain reports no relevant financial relationships. Disclosures for the coauthors are listed in the paper.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
ICMs detect serious arrhythmias in high-risk post-MI patients: SMART-MI
Prevention strategies may be next
After a myocardial infarction, implantable cardiac monitors (ICMs) are sensitive for detecting serious arrhythmias in patients with cardiac autonomic dysfunction but only moderately reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), according to results of the randomized SMART-MI trial.
When remote monitoring with the ICM was compared with conventional follow-up in this group of patients, serious arrhythmic events were detected at a nearly sixfold greater rate, reported Axel Bauer, MD, at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The study further showed that these events were closely associated with subsequent major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).
“SMART-MI is the first study to test an implantable device in high-risk MI patients with a LVEF greater than 35%,” reported Dr. Bauer, a cardiologist and director of the internal medicine clinic, University of Innsbruck (Austria). It showed that the types and frequency of arrhythmias were “comparable to those of post-MI patients with reduced LVEF.”
The ability to assess risk is potentially significant because “the majority of cardiovascular complications, including sudden death, occur in patients with only moderately reduced LVEF,” explained Dr. Bauer.
Despite the greater risk, “there are no preventive strategies so far” currently available for this group, he said.
The SMART-MI study confirms the need for treatments, confirms a method for monitoring risk, and might provide the basis for trials designed to test treatments to modify this risk, he added.
ECG used to define autonomic dysfunction
In the SMART MI protocol, 1,305 survivors of MI with LVEF of 36%-50% at 33 participating centers in Austria and Germany were evaluated with a 20-minute high resolution electrocardiogram. They were enrolled and randomized if they demonstrated cardiac autonomic dysfunction on at least two validated ECG biomarkers.
The 400 participants were randomized to implantation of a ICM, which transmitted daily reports to a ICM core laboratory, or to conventional follow-up.
After a median follow-up of 21 months, serious events were detected in 60 of the 201 patients in the ICM group and 12 of the 199 patients in the control group (29% vs. 6%). Serious adverse events were defined as those that would typically warrant therapy, such as prolonged atrial fibrillation (at least 6 minutes) high-degree atrioventricular block, and sustained ventricular tachycardia.
The difference in the detection rate, which was the primary endpoint, was highly significant (P < .0001), but the study was also able to confirm that these events predicted MACCE, a secondary study endpoint. In those with a serious arrhythmia, the hazard ratio for subsequent MACCE was approximately sevenfold greater relative to those without a serious arrhythmia. This was true of those in the ICM group (HR, 6.8; P < .001) and controls (HR 7.3; P < .001).
Arrhythmias warn of impending complications
“The data show that the prognostic impact of detecting a serious arrhythmia does not depend on the mode of detection,” Dr. Bauer reported. The data also confirm that “subclinical serious arrhythmia events are a warning signal for an impending complication.”
Although more interventions – including pacemakers, catheter ablations, and oral anticoagulants – were offered to patients in the experimental arm, “the study was not powered to show differences in outcomes,” and, in fact, no significant differences were observed, according to Dr. Bauer. However, the evidence that ICM is effective for detecting arrhythmias does provide a structure on which to build clinical trials.
“We now need the trials to see if ICM can change practice and improve outcomes,” said Carlos Aguiar, MD, a staff cardiologist at the Hospital Santa Cruz, Lisbon. He acknowledged that this study proves that ICM can detect serious arrhythmias in patients with moderate left ventricular dysfunction, but “we need to develop and test treatment paths.”
Dr. Aguiar considers SMART-MI an important study that “goes to the heart” of a common clinical dilemma.
“In clinical practice, we see patients with LVEF that is not that suppressed and so do not have a class I indication for ICM, but there are often features that might have you concerned and make you think it would be great if the LVEF was 35% or lower [to justify intervention],” Dr. Aguiar said.
Data provide insight on unaddressed risk group
SMART-MI confirms earlier evidence that post-MI patients with cardiac autonomic dysfunction are at high risk. Currently, this relative increase in risk goes “unaddressed,” according to Dr. Bauer. Although he contended that the risk itself “could be an indication for ICM in a high-risk patient group without classically defined left ventricular dysfunction,” he agreed that the ultimate value of this trial might be that it “opens a window” for a rationale to test preventive strategies.
An invited ESC discussant, Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD, praised the study for drawing attention to the risk of events in a subset of post-MI patients with LVEF of 35% or greater. However, he suggested that criteria other than those based on ECG might be more sensitive for selecting patients who might benefit from intervention.
“We do not know whether additional methods of establishing risk, such as imaging, might be valuable,” said Dr. Hindricks, chief of the department of arrhythmology in the Heart Institute of the University of Leipzig (Germany). He believes work in this area is needed to ensure appropriate entry criteria for interventional trials designed to modify risk in post-MI patients who do not meet the traditional definition of reduced ejection fraction.
Dr. Bauer reports financial relationships with Medtronic, which sponsored this study, as well as Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards, and Novartis. Dr. Aguiar reports no relevant financial conflicts.
Prevention strategies may be next
Prevention strategies may be next
After a myocardial infarction, implantable cardiac monitors (ICMs) are sensitive for detecting serious arrhythmias in patients with cardiac autonomic dysfunction but only moderately reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), according to results of the randomized SMART-MI trial.
When remote monitoring with the ICM was compared with conventional follow-up in this group of patients, serious arrhythmic events were detected at a nearly sixfold greater rate, reported Axel Bauer, MD, at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The study further showed that these events were closely associated with subsequent major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).
“SMART-MI is the first study to test an implantable device in high-risk MI patients with a LVEF greater than 35%,” reported Dr. Bauer, a cardiologist and director of the internal medicine clinic, University of Innsbruck (Austria). It showed that the types and frequency of arrhythmias were “comparable to those of post-MI patients with reduced LVEF.”
The ability to assess risk is potentially significant because “the majority of cardiovascular complications, including sudden death, occur in patients with only moderately reduced LVEF,” explained Dr. Bauer.
Despite the greater risk, “there are no preventive strategies so far” currently available for this group, he said.
The SMART-MI study confirms the need for treatments, confirms a method for monitoring risk, and might provide the basis for trials designed to test treatments to modify this risk, he added.
ECG used to define autonomic dysfunction
In the SMART MI protocol, 1,305 survivors of MI with LVEF of 36%-50% at 33 participating centers in Austria and Germany were evaluated with a 20-minute high resolution electrocardiogram. They were enrolled and randomized if they demonstrated cardiac autonomic dysfunction on at least two validated ECG biomarkers.
The 400 participants were randomized to implantation of a ICM, which transmitted daily reports to a ICM core laboratory, or to conventional follow-up.
After a median follow-up of 21 months, serious events were detected in 60 of the 201 patients in the ICM group and 12 of the 199 patients in the control group (29% vs. 6%). Serious adverse events were defined as those that would typically warrant therapy, such as prolonged atrial fibrillation (at least 6 minutes) high-degree atrioventricular block, and sustained ventricular tachycardia.
The difference in the detection rate, which was the primary endpoint, was highly significant (P < .0001), but the study was also able to confirm that these events predicted MACCE, a secondary study endpoint. In those with a serious arrhythmia, the hazard ratio for subsequent MACCE was approximately sevenfold greater relative to those without a serious arrhythmia. This was true of those in the ICM group (HR, 6.8; P < .001) and controls (HR 7.3; P < .001).
Arrhythmias warn of impending complications
“The data show that the prognostic impact of detecting a serious arrhythmia does not depend on the mode of detection,” Dr. Bauer reported. The data also confirm that “subclinical serious arrhythmia events are a warning signal for an impending complication.”
Although more interventions – including pacemakers, catheter ablations, and oral anticoagulants – were offered to patients in the experimental arm, “the study was not powered to show differences in outcomes,” and, in fact, no significant differences were observed, according to Dr. Bauer. However, the evidence that ICM is effective for detecting arrhythmias does provide a structure on which to build clinical trials.
“We now need the trials to see if ICM can change practice and improve outcomes,” said Carlos Aguiar, MD, a staff cardiologist at the Hospital Santa Cruz, Lisbon. He acknowledged that this study proves that ICM can detect serious arrhythmias in patients with moderate left ventricular dysfunction, but “we need to develop and test treatment paths.”
Dr. Aguiar considers SMART-MI an important study that “goes to the heart” of a common clinical dilemma.
“In clinical practice, we see patients with LVEF that is not that suppressed and so do not have a class I indication for ICM, but there are often features that might have you concerned and make you think it would be great if the LVEF was 35% or lower [to justify intervention],” Dr. Aguiar said.
Data provide insight on unaddressed risk group
SMART-MI confirms earlier evidence that post-MI patients with cardiac autonomic dysfunction are at high risk. Currently, this relative increase in risk goes “unaddressed,” according to Dr. Bauer. Although he contended that the risk itself “could be an indication for ICM in a high-risk patient group without classically defined left ventricular dysfunction,” he agreed that the ultimate value of this trial might be that it “opens a window” for a rationale to test preventive strategies.
An invited ESC discussant, Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD, praised the study for drawing attention to the risk of events in a subset of post-MI patients with LVEF of 35% or greater. However, he suggested that criteria other than those based on ECG might be more sensitive for selecting patients who might benefit from intervention.
“We do not know whether additional methods of establishing risk, such as imaging, might be valuable,” said Dr. Hindricks, chief of the department of arrhythmology in the Heart Institute of the University of Leipzig (Germany). He believes work in this area is needed to ensure appropriate entry criteria for interventional trials designed to modify risk in post-MI patients who do not meet the traditional definition of reduced ejection fraction.
Dr. Bauer reports financial relationships with Medtronic, which sponsored this study, as well as Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards, and Novartis. Dr. Aguiar reports no relevant financial conflicts.
After a myocardial infarction, implantable cardiac monitors (ICMs) are sensitive for detecting serious arrhythmias in patients with cardiac autonomic dysfunction but only moderately reduced left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF), according to results of the randomized SMART-MI trial.
When remote monitoring with the ICM was compared with conventional follow-up in this group of patients, serious arrhythmic events were detected at a nearly sixfold greater rate, reported Axel Bauer, MD, at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The study further showed that these events were closely associated with subsequent major adverse cardiac and cerebrovascular events (MACCE).
“SMART-MI is the first study to test an implantable device in high-risk MI patients with a LVEF greater than 35%,” reported Dr. Bauer, a cardiologist and director of the internal medicine clinic, University of Innsbruck (Austria). It showed that the types and frequency of arrhythmias were “comparable to those of post-MI patients with reduced LVEF.”
The ability to assess risk is potentially significant because “the majority of cardiovascular complications, including sudden death, occur in patients with only moderately reduced LVEF,” explained Dr. Bauer.
Despite the greater risk, “there are no preventive strategies so far” currently available for this group, he said.
The SMART-MI study confirms the need for treatments, confirms a method for monitoring risk, and might provide the basis for trials designed to test treatments to modify this risk, he added.
ECG used to define autonomic dysfunction
In the SMART MI protocol, 1,305 survivors of MI with LVEF of 36%-50% at 33 participating centers in Austria and Germany were evaluated with a 20-minute high resolution electrocardiogram. They were enrolled and randomized if they demonstrated cardiac autonomic dysfunction on at least two validated ECG biomarkers.
The 400 participants were randomized to implantation of a ICM, which transmitted daily reports to a ICM core laboratory, or to conventional follow-up.
After a median follow-up of 21 months, serious events were detected in 60 of the 201 patients in the ICM group and 12 of the 199 patients in the control group (29% vs. 6%). Serious adverse events were defined as those that would typically warrant therapy, such as prolonged atrial fibrillation (at least 6 minutes) high-degree atrioventricular block, and sustained ventricular tachycardia.
The difference in the detection rate, which was the primary endpoint, was highly significant (P < .0001), but the study was also able to confirm that these events predicted MACCE, a secondary study endpoint. In those with a serious arrhythmia, the hazard ratio for subsequent MACCE was approximately sevenfold greater relative to those without a serious arrhythmia. This was true of those in the ICM group (HR, 6.8; P < .001) and controls (HR 7.3; P < .001).
Arrhythmias warn of impending complications
“The data show that the prognostic impact of detecting a serious arrhythmia does not depend on the mode of detection,” Dr. Bauer reported. The data also confirm that “subclinical serious arrhythmia events are a warning signal for an impending complication.”
Although more interventions – including pacemakers, catheter ablations, and oral anticoagulants – were offered to patients in the experimental arm, “the study was not powered to show differences in outcomes,” and, in fact, no significant differences were observed, according to Dr. Bauer. However, the evidence that ICM is effective for detecting arrhythmias does provide a structure on which to build clinical trials.
“We now need the trials to see if ICM can change practice and improve outcomes,” said Carlos Aguiar, MD, a staff cardiologist at the Hospital Santa Cruz, Lisbon. He acknowledged that this study proves that ICM can detect serious arrhythmias in patients with moderate left ventricular dysfunction, but “we need to develop and test treatment paths.”
Dr. Aguiar considers SMART-MI an important study that “goes to the heart” of a common clinical dilemma.
“In clinical practice, we see patients with LVEF that is not that suppressed and so do not have a class I indication for ICM, but there are often features that might have you concerned and make you think it would be great if the LVEF was 35% or lower [to justify intervention],” Dr. Aguiar said.
Data provide insight on unaddressed risk group
SMART-MI confirms earlier evidence that post-MI patients with cardiac autonomic dysfunction are at high risk. Currently, this relative increase in risk goes “unaddressed,” according to Dr. Bauer. Although he contended that the risk itself “could be an indication for ICM in a high-risk patient group without classically defined left ventricular dysfunction,” he agreed that the ultimate value of this trial might be that it “opens a window” for a rationale to test preventive strategies.
An invited ESC discussant, Gerhard Hindricks, MD, PhD, praised the study for drawing attention to the risk of events in a subset of post-MI patients with LVEF of 35% or greater. However, he suggested that criteria other than those based on ECG might be more sensitive for selecting patients who might benefit from intervention.
“We do not know whether additional methods of establishing risk, such as imaging, might be valuable,” said Dr. Hindricks, chief of the department of arrhythmology in the Heart Institute of the University of Leipzig (Germany). He believes work in this area is needed to ensure appropriate entry criteria for interventional trials designed to modify risk in post-MI patients who do not meet the traditional definition of reduced ejection fraction.
Dr. Bauer reports financial relationships with Medtronic, which sponsored this study, as well as Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Edwards, and Novartis. Dr. Aguiar reports no relevant financial conflicts.
FROM ESC CONGRESS 2021
GUIDE-HF: CardioMEMS-guided meds fall short in mild to moderate heart failure
Medical therapy for heart failure guided by an implanted pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) sensor didn’t improve survival or risk for HF events like hospitalization over a year in a major randomized trial that entered a broad range of patients with mild to moderate disease.
But medical therapy adjustments based on PAP readings from the miniature CardioMEMS (Abbott) implant might well have surpassed conventional HF management for outcomes had the world not been turned upside down by SARS-CoV-2 and the pandemic lockdowns, assert researchers from the GUIDE-HF trial.
Something about the crisis, they concluded – although not without some pushback – led to better outcomes in the standard-care control group, apparently muddling any potential differences from those on PAP-guided management.
Working with regulators, the team conducted a “pre–COVID-19 impact analysis” that compared outcomes before the March 2020 national COVID-19 emergency declaration that forced much of the United States with shelter in place.
By that time, all of the trial’s patients had been followed for at least 3 months, and about three-fourths of its endpoints had already been counted, JoAnn Lindenfeld, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said at a media briefing prior to unveiling GUIDE-HF at the all-virtual European Society of Cardiology Congress 2021.
The pre–COVID-19 analysis, approved several months before the end of the trial – while the data were still blinded – had been “suggested by both regulatory agencies and professional societies in Europe and in the United States,” Dr. Lindenfeld said.
It pointed to a possible benefit for the CardioMEMS-guided strategy, a barely significant 19% drop in risk (P = .049) for the primary endpoint of death, HF hospitalization, or urgent HF hospital visit. The effect was driven by a 24% decline in HF events (P = .014), with no significant contribution from mortality.
“The benefits of hemodynamic monitoring and management in reducing heart failure hospitalizations extended to patients with less severe heart failure”; that is, those in New York Heart Association class 2 and any in NYHA class 3 with “elevated natriuretic peptides but no previous hospitalization,” said Dr. Lindenfeld, who is also lead author on the GUIDE-HF report published in the Lancet.
Such benefits would suggest that CardioMEMS-guided management can improve outcomes in an HF population much broader than the device’s current indication.
But as it happens, the trial’s prospectively defined 12-month primary outcomes were less impressive. A 12% decline in risk for the composite endpoint among patients managed by CardioMEMS failed to reach significance compared with standard management (P = .16).
“Several factors could explain the considerable loss of benefit of hemodynamic-guided management during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the Lancet report explained. They include “improved patient compliance with medical and dietary regimens, reduced respiratory infections, altered health-care provider behavior, changes in disease progression due to COVID-19, or other as yet unknown effects of a major pandemic.”
Expanded population
Importantly, GUIDE-HF had entered 1,000 patients in NYHA class 2-4 and either an HF hospitalization in the previous year or elevated natriuretic peptide levels. About 44% of the entrants in NYHA class 3 did not have a 1-year history of HF hospitalization.
That’s a more heterogeneous and potentially lower-risk cohort than patients in the randomized CHAMPION study of 11 years ago, which led to the implant’s approval on both sides of the Atlantic.
In that trial, CardioMEMS-guided management was followed by 30% drop in risk for HF hospitalization over 6 months (P < .001). But CHAMPION was limited to patients in NYHA class 3 with a history of HF hospitalization, the device’s current indication in both the United States and Europe.
The GUIDE-HF findings “reinforce that patients with class 3 heart failure and prior heart failure hospitalization are those in whom there is the clearest benefit, based on the prior CHAMPION trial. These are the patients where this monitoring strategy may be best targeted,” Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, said in an interview.
Although GUIDE-HF didn’t show a significant benefit for NYHA class 2 patients with elevated biomarkers, who aren’t covered by the device’s current labeling, that group showed “some suggestions of potential benefit,” noted Dr. Fonarow, who isn’t a coauthor on the Lancet report. So, “there may be select patients with class 2 heart failure where monitoring could be considered on a case-by-case basis.”
In an interview, Larry A. Allen, MD, MHS, said that, “while the technology is pretty amazing, the real question is whether it tells us something that we didn’t already know that leads to improved care. Unfortunately, as tested here, it doesn’t, or at least not enough to make a big difference.”
The pre–COVID-19 impact analysis “should be interpreted with caution, and not as the primary finding,” Dr. Allen, from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who is not a GUIDE-HF coauthor, said in an interview.
One might hypothesize, he said, “that, in the setting of limited in-person visits with loss of physical examination, perhaps CardioMEMS would be more – not less – helpful during the pandemic. And yet the opposite was seen.”
The pandemic has “markedly altered all kinds of aspects of patient care and trial conduct, but that doesn’t make the data derived during that period uninformative,” Dr. Allen said. “And as we are increasingly reminded, the future will be a new normal, not a prepandemic normal.”
A third group
The GUIDE-HF trial includes, in addition to the 1,000 randomized patients, a single-group observational cohort of 2,600 patients, whose outcomes will be reported at another time, noted the published report.
But in the randomized comparison, conducted at 118 centers in North America, all patients were implanted with the CardioMEMS device and blinded as to their assigned strategy. Enrollment took place between March 2018 and Dec. 20, 2019.
Of the 1,000 successfully implanted patients, 497 were assigned to the pressure-guided strategy, in which “titration of diuretics was recommended if pulmonary artery pressure provided evidence of excess intravascular volume, and titration of vasodilators was recommended if elevated vascular resistance was evident,” the report stated.
The remaining 503 patients assigned to standard care served as control subjects, for whom “investigators were aware of treatment assignment but did not have access to PAP data.”
The hazard ratio for the primary endpoint in the pressure-guided group, compared with the control group, was 0.88 (95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.05; P = .16) over a median follow-up of 11.7 months.
But in the sensitivity analysis comparing outcomes before and after the COVID-19 lockdowns, using established methodology, the report stated, the primary-endpoint HR was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.66-1.00; P = .049).
The difference is owed to improved outcomes in the control group under pandemic conditions, the researchers concluded. Patients assigned to conventional management –whatever that meant during shelter-in-place – experienced 21% fewer primary-endpoint events than their own rate before the pandemic. After the COVID-19 emergency was declared, there was no significant difference in event rates between the two randomization groups.
In the primary 12-month analysis, the HR for HF events in the guided-therapy was not significant reduced, at 0.85 (95% CI, 0.70-1.03; P = .096). But in the pre-COVID-19 analysis, that risk fell significantly with CardioMEMS-guided management, for an HR of 0.76 (95% CI, 0.61-0.95; P = .014).
An editorial accompanying the GUIDE-HF publication (Lancet. 2021 Aug 27. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[21]01914-0) asserts that the trial “did not enroll an ideal group of patients for showing the efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure monitoring, since many had baseline pressures in the target range with little possibility of short-term gain.”
Also, wrote John G. F. Cleland, MD, PhD, University of Glasgow, and Pierpaolo Pellicori, MD, Imperial College London, “follow-up was too short, and interventions did not substantially change pulmonary artery pressure.”
They continue: “Monitoring alone cannot improve outcome, but consequent actions might. The GUIDE-HF results are encouraging but inconclusive, and should inform further research, possibly a large, simple, open-label trial to investigate a system of care rather than a single technology.”
GUIDE-HF was funded by Abbott. Dr. Lindenfeld disclosed receiving research grants from AstraZeneca, Sensible Medical, and Volumetrix; and consulting for Abbott, Alleviant Medical, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Edwards, Impulse Dynamics, and VWave. Dr. Fonarow reported consulting for Abbott and that his institution has participated in the GUIDE-HF trial; he has elsewhere disclosed consulting for Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions Lifesciences, Janssen, Medtronic, and Novartis. Dr. Allen had elsewhere reported consulting for Abbott, Amgen, Boston Scientific, and Novartis. Dr. Cleland disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbott for serving on an advisory board for the MitraClip device, unrelated to the CardioMEMS device. Dr. Pellicori reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical therapy for heart failure guided by an implanted pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) sensor didn’t improve survival or risk for HF events like hospitalization over a year in a major randomized trial that entered a broad range of patients with mild to moderate disease.
But medical therapy adjustments based on PAP readings from the miniature CardioMEMS (Abbott) implant might well have surpassed conventional HF management for outcomes had the world not been turned upside down by SARS-CoV-2 and the pandemic lockdowns, assert researchers from the GUIDE-HF trial.
Something about the crisis, they concluded – although not without some pushback – led to better outcomes in the standard-care control group, apparently muddling any potential differences from those on PAP-guided management.
Working with regulators, the team conducted a “pre–COVID-19 impact analysis” that compared outcomes before the March 2020 national COVID-19 emergency declaration that forced much of the United States with shelter in place.
By that time, all of the trial’s patients had been followed for at least 3 months, and about three-fourths of its endpoints had already been counted, JoAnn Lindenfeld, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said at a media briefing prior to unveiling GUIDE-HF at the all-virtual European Society of Cardiology Congress 2021.
The pre–COVID-19 analysis, approved several months before the end of the trial – while the data were still blinded – had been “suggested by both regulatory agencies and professional societies in Europe and in the United States,” Dr. Lindenfeld said.
It pointed to a possible benefit for the CardioMEMS-guided strategy, a barely significant 19% drop in risk (P = .049) for the primary endpoint of death, HF hospitalization, or urgent HF hospital visit. The effect was driven by a 24% decline in HF events (P = .014), with no significant contribution from mortality.
“The benefits of hemodynamic monitoring and management in reducing heart failure hospitalizations extended to patients with less severe heart failure”; that is, those in New York Heart Association class 2 and any in NYHA class 3 with “elevated natriuretic peptides but no previous hospitalization,” said Dr. Lindenfeld, who is also lead author on the GUIDE-HF report published in the Lancet.
Such benefits would suggest that CardioMEMS-guided management can improve outcomes in an HF population much broader than the device’s current indication.
But as it happens, the trial’s prospectively defined 12-month primary outcomes were less impressive. A 12% decline in risk for the composite endpoint among patients managed by CardioMEMS failed to reach significance compared with standard management (P = .16).
“Several factors could explain the considerable loss of benefit of hemodynamic-guided management during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the Lancet report explained. They include “improved patient compliance with medical and dietary regimens, reduced respiratory infections, altered health-care provider behavior, changes in disease progression due to COVID-19, or other as yet unknown effects of a major pandemic.”
Expanded population
Importantly, GUIDE-HF had entered 1,000 patients in NYHA class 2-4 and either an HF hospitalization in the previous year or elevated natriuretic peptide levels. About 44% of the entrants in NYHA class 3 did not have a 1-year history of HF hospitalization.
That’s a more heterogeneous and potentially lower-risk cohort than patients in the randomized CHAMPION study of 11 years ago, which led to the implant’s approval on both sides of the Atlantic.
In that trial, CardioMEMS-guided management was followed by 30% drop in risk for HF hospitalization over 6 months (P < .001). But CHAMPION was limited to patients in NYHA class 3 with a history of HF hospitalization, the device’s current indication in both the United States and Europe.
The GUIDE-HF findings “reinforce that patients with class 3 heart failure and prior heart failure hospitalization are those in whom there is the clearest benefit, based on the prior CHAMPION trial. These are the patients where this monitoring strategy may be best targeted,” Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, said in an interview.
Although GUIDE-HF didn’t show a significant benefit for NYHA class 2 patients with elevated biomarkers, who aren’t covered by the device’s current labeling, that group showed “some suggestions of potential benefit,” noted Dr. Fonarow, who isn’t a coauthor on the Lancet report. So, “there may be select patients with class 2 heart failure where monitoring could be considered on a case-by-case basis.”
In an interview, Larry A. Allen, MD, MHS, said that, “while the technology is pretty amazing, the real question is whether it tells us something that we didn’t already know that leads to improved care. Unfortunately, as tested here, it doesn’t, or at least not enough to make a big difference.”
The pre–COVID-19 impact analysis “should be interpreted with caution, and not as the primary finding,” Dr. Allen, from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who is not a GUIDE-HF coauthor, said in an interview.
One might hypothesize, he said, “that, in the setting of limited in-person visits with loss of physical examination, perhaps CardioMEMS would be more – not less – helpful during the pandemic. And yet the opposite was seen.”
The pandemic has “markedly altered all kinds of aspects of patient care and trial conduct, but that doesn’t make the data derived during that period uninformative,” Dr. Allen said. “And as we are increasingly reminded, the future will be a new normal, not a prepandemic normal.”
A third group
The GUIDE-HF trial includes, in addition to the 1,000 randomized patients, a single-group observational cohort of 2,600 patients, whose outcomes will be reported at another time, noted the published report.
But in the randomized comparison, conducted at 118 centers in North America, all patients were implanted with the CardioMEMS device and blinded as to their assigned strategy. Enrollment took place between March 2018 and Dec. 20, 2019.
Of the 1,000 successfully implanted patients, 497 were assigned to the pressure-guided strategy, in which “titration of diuretics was recommended if pulmonary artery pressure provided evidence of excess intravascular volume, and titration of vasodilators was recommended if elevated vascular resistance was evident,” the report stated.
The remaining 503 patients assigned to standard care served as control subjects, for whom “investigators were aware of treatment assignment but did not have access to PAP data.”
The hazard ratio for the primary endpoint in the pressure-guided group, compared with the control group, was 0.88 (95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.05; P = .16) over a median follow-up of 11.7 months.
But in the sensitivity analysis comparing outcomes before and after the COVID-19 lockdowns, using established methodology, the report stated, the primary-endpoint HR was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.66-1.00; P = .049).
The difference is owed to improved outcomes in the control group under pandemic conditions, the researchers concluded. Patients assigned to conventional management –whatever that meant during shelter-in-place – experienced 21% fewer primary-endpoint events than their own rate before the pandemic. After the COVID-19 emergency was declared, there was no significant difference in event rates between the two randomization groups.
In the primary 12-month analysis, the HR for HF events in the guided-therapy was not significant reduced, at 0.85 (95% CI, 0.70-1.03; P = .096). But in the pre-COVID-19 analysis, that risk fell significantly with CardioMEMS-guided management, for an HR of 0.76 (95% CI, 0.61-0.95; P = .014).
An editorial accompanying the GUIDE-HF publication (Lancet. 2021 Aug 27. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[21]01914-0) asserts that the trial “did not enroll an ideal group of patients for showing the efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure monitoring, since many had baseline pressures in the target range with little possibility of short-term gain.”
Also, wrote John G. F. Cleland, MD, PhD, University of Glasgow, and Pierpaolo Pellicori, MD, Imperial College London, “follow-up was too short, and interventions did not substantially change pulmonary artery pressure.”
They continue: “Monitoring alone cannot improve outcome, but consequent actions might. The GUIDE-HF results are encouraging but inconclusive, and should inform further research, possibly a large, simple, open-label trial to investigate a system of care rather than a single technology.”
GUIDE-HF was funded by Abbott. Dr. Lindenfeld disclosed receiving research grants from AstraZeneca, Sensible Medical, and Volumetrix; and consulting for Abbott, Alleviant Medical, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Edwards, Impulse Dynamics, and VWave. Dr. Fonarow reported consulting for Abbott and that his institution has participated in the GUIDE-HF trial; he has elsewhere disclosed consulting for Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions Lifesciences, Janssen, Medtronic, and Novartis. Dr. Allen had elsewhere reported consulting for Abbott, Amgen, Boston Scientific, and Novartis. Dr. Cleland disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbott for serving on an advisory board for the MitraClip device, unrelated to the CardioMEMS device. Dr. Pellicori reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Medical therapy for heart failure guided by an implanted pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) sensor didn’t improve survival or risk for HF events like hospitalization over a year in a major randomized trial that entered a broad range of patients with mild to moderate disease.
But medical therapy adjustments based on PAP readings from the miniature CardioMEMS (Abbott) implant might well have surpassed conventional HF management for outcomes had the world not been turned upside down by SARS-CoV-2 and the pandemic lockdowns, assert researchers from the GUIDE-HF trial.
Something about the crisis, they concluded – although not without some pushback – led to better outcomes in the standard-care control group, apparently muddling any potential differences from those on PAP-guided management.
Working with regulators, the team conducted a “pre–COVID-19 impact analysis” that compared outcomes before the March 2020 national COVID-19 emergency declaration that forced much of the United States with shelter in place.
By that time, all of the trial’s patients had been followed for at least 3 months, and about three-fourths of its endpoints had already been counted, JoAnn Lindenfeld, MD, Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., said at a media briefing prior to unveiling GUIDE-HF at the all-virtual European Society of Cardiology Congress 2021.
The pre–COVID-19 analysis, approved several months before the end of the trial – while the data were still blinded – had been “suggested by both regulatory agencies and professional societies in Europe and in the United States,” Dr. Lindenfeld said.
It pointed to a possible benefit for the CardioMEMS-guided strategy, a barely significant 19% drop in risk (P = .049) for the primary endpoint of death, HF hospitalization, or urgent HF hospital visit. The effect was driven by a 24% decline in HF events (P = .014), with no significant contribution from mortality.
“The benefits of hemodynamic monitoring and management in reducing heart failure hospitalizations extended to patients with less severe heart failure”; that is, those in New York Heart Association class 2 and any in NYHA class 3 with “elevated natriuretic peptides but no previous hospitalization,” said Dr. Lindenfeld, who is also lead author on the GUIDE-HF report published in the Lancet.
Such benefits would suggest that CardioMEMS-guided management can improve outcomes in an HF population much broader than the device’s current indication.
But as it happens, the trial’s prospectively defined 12-month primary outcomes were less impressive. A 12% decline in risk for the composite endpoint among patients managed by CardioMEMS failed to reach significance compared with standard management (P = .16).
“Several factors could explain the considerable loss of benefit of hemodynamic-guided management during the COVID-19 pandemic,” the Lancet report explained. They include “improved patient compliance with medical and dietary regimens, reduced respiratory infections, altered health-care provider behavior, changes in disease progression due to COVID-19, or other as yet unknown effects of a major pandemic.”
Expanded population
Importantly, GUIDE-HF had entered 1,000 patients in NYHA class 2-4 and either an HF hospitalization in the previous year or elevated natriuretic peptide levels. About 44% of the entrants in NYHA class 3 did not have a 1-year history of HF hospitalization.
That’s a more heterogeneous and potentially lower-risk cohort than patients in the randomized CHAMPION study of 11 years ago, which led to the implant’s approval on both sides of the Atlantic.
In that trial, CardioMEMS-guided management was followed by 30% drop in risk for HF hospitalization over 6 months (P < .001). But CHAMPION was limited to patients in NYHA class 3 with a history of HF hospitalization, the device’s current indication in both the United States and Europe.
The GUIDE-HF findings “reinforce that patients with class 3 heart failure and prior heart failure hospitalization are those in whom there is the clearest benefit, based on the prior CHAMPION trial. These are the patients where this monitoring strategy may be best targeted,” Gregg C. Fonarow, MD, University of California Los Angeles Medical Center, said in an interview.
Although GUIDE-HF didn’t show a significant benefit for NYHA class 2 patients with elevated biomarkers, who aren’t covered by the device’s current labeling, that group showed “some suggestions of potential benefit,” noted Dr. Fonarow, who isn’t a coauthor on the Lancet report. So, “there may be select patients with class 2 heart failure where monitoring could be considered on a case-by-case basis.”
In an interview, Larry A. Allen, MD, MHS, said that, “while the technology is pretty amazing, the real question is whether it tells us something that we didn’t already know that leads to improved care. Unfortunately, as tested here, it doesn’t, or at least not enough to make a big difference.”
The pre–COVID-19 impact analysis “should be interpreted with caution, and not as the primary finding,” Dr. Allen, from the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, who is not a GUIDE-HF coauthor, said in an interview.
One might hypothesize, he said, “that, in the setting of limited in-person visits with loss of physical examination, perhaps CardioMEMS would be more – not less – helpful during the pandemic. And yet the opposite was seen.”
The pandemic has “markedly altered all kinds of aspects of patient care and trial conduct, but that doesn’t make the data derived during that period uninformative,” Dr. Allen said. “And as we are increasingly reminded, the future will be a new normal, not a prepandemic normal.”
A third group
The GUIDE-HF trial includes, in addition to the 1,000 randomized patients, a single-group observational cohort of 2,600 patients, whose outcomes will be reported at another time, noted the published report.
But in the randomized comparison, conducted at 118 centers in North America, all patients were implanted with the CardioMEMS device and blinded as to their assigned strategy. Enrollment took place between March 2018 and Dec. 20, 2019.
Of the 1,000 successfully implanted patients, 497 were assigned to the pressure-guided strategy, in which “titration of diuretics was recommended if pulmonary artery pressure provided evidence of excess intravascular volume, and titration of vasodilators was recommended if elevated vascular resistance was evident,” the report stated.
The remaining 503 patients assigned to standard care served as control subjects, for whom “investigators were aware of treatment assignment but did not have access to PAP data.”
The hazard ratio for the primary endpoint in the pressure-guided group, compared with the control group, was 0.88 (95% confidence interval, 0.74-1.05; P = .16) over a median follow-up of 11.7 months.
But in the sensitivity analysis comparing outcomes before and after the COVID-19 lockdowns, using established methodology, the report stated, the primary-endpoint HR was 0.81 (95% CI, 0.66-1.00; P = .049).
The difference is owed to improved outcomes in the control group under pandemic conditions, the researchers concluded. Patients assigned to conventional management –whatever that meant during shelter-in-place – experienced 21% fewer primary-endpoint events than their own rate before the pandemic. After the COVID-19 emergency was declared, there was no significant difference in event rates between the two randomization groups.
In the primary 12-month analysis, the HR for HF events in the guided-therapy was not significant reduced, at 0.85 (95% CI, 0.70-1.03; P = .096). But in the pre-COVID-19 analysis, that risk fell significantly with CardioMEMS-guided management, for an HR of 0.76 (95% CI, 0.61-0.95; P = .014).
An editorial accompanying the GUIDE-HF publication (Lancet. 2021 Aug 27. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736[21]01914-0) asserts that the trial “did not enroll an ideal group of patients for showing the efficacy of pulmonary artery pressure monitoring, since many had baseline pressures in the target range with little possibility of short-term gain.”
Also, wrote John G. F. Cleland, MD, PhD, University of Glasgow, and Pierpaolo Pellicori, MD, Imperial College London, “follow-up was too short, and interventions did not substantially change pulmonary artery pressure.”
They continue: “Monitoring alone cannot improve outcome, but consequent actions might. The GUIDE-HF results are encouraging but inconclusive, and should inform further research, possibly a large, simple, open-label trial to investigate a system of care rather than a single technology.”
GUIDE-HF was funded by Abbott. Dr. Lindenfeld disclosed receiving research grants from AstraZeneca, Sensible Medical, and Volumetrix; and consulting for Abbott, Alleviant Medical, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Boston Scientific, CVRx, Edwards, Impulse Dynamics, and VWave. Dr. Fonarow reported consulting for Abbott and that his institution has participated in the GUIDE-HF trial; he has elsewhere disclosed consulting for Amgen, AstraZeneca, CHF Solutions Lifesciences, Janssen, Medtronic, and Novartis. Dr. Allen had elsewhere reported consulting for Abbott, Amgen, Boston Scientific, and Novartis. Dr. Cleland disclosed receiving personal fees from Abbott for serving on an advisory board for the MitraClip device, unrelated to the CardioMEMS device. Dr. Pellicori reported no relevant conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerobic exercise can reduce AFib frequency, severity: ACTIVE-AF
Patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) gained significant benefits from a 6-month program of supervised and unsupervised moderate exercise versus usual care, new randomized trial results show.
Among 120 AFib patients in the ACTIVE-AF trial, those randomized to the exercise arm had significantly less frequent AFib recurrence and less severe symptoms over a 1-year period, said Adrian Elliott, PhD, who will present this late-breaking research at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021.
The trial “demonstrates that some patients can control their arrhythmia through physical activity, without the need for complex interventions such as ablation or medications to keep their heart in normal rhythm,” Dr. Elliott, from the University of Adelaide, Australia, said in a statement from the ESC.
This is “the largest randomized controlled trial investigating the value of an exercise prescription in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent [AFib],” he told this news organization in an email.
The findings “really provide the evidence needed that recommending aerobic exercise in patients with symptomatic AFib can lower the severity of symptoms and prevent the recurrence of AFib for many patients,” he said. Aerobic exercise should be incorporated into patient treatment, he added, “alongside the use of medications, as guided by a cardiologist, and management of obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea.”
Mina K. Chung, MD, lead author of a Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association on Lifestyle and Risk Factor Modification for Reduction of Atrial Fibrillation, as previously reported, agrees.
The “findings support the AHA Scientific Statement that we should encourage our patients with AFib to include regular moderate exercise to help prevent AFib, reduce AFib burden, and improve AFib-related symptoms and quality of life,” Dr. Chung, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic, summarized in an email.
“Our recommendation is to encourage AFib patients to aim for at least the AHA physical activity guidelines for the general population, which advise 150 minutes each week of moderate-intensity exercise,” Dr. Chung said.
This is a “reasonable” goal, but “some might argue that a slightly higher target of physical activity duration may be considered,” Dr. Elliott commented.
ACTIVE-AF, he noted, suggests that “as a general guide, patients [with AFib] should strive to build up to 3.5 hours per week of aerobic exercise and incorporate some higher intensity activities to improve cardiorespiratory fitness.”
Aim for 3.5 hours a week
A previous observational study showed that patients who improved their cardiorespiratory fitness over a 5-year period were significantly less likely to have AFib recurrences.
And in a randomized trial of 51 patients, 12 weeks of aerobic interval training reduced the time spent in AFib compared to usual care, during a 4-week follow-up.
ACTIVE-AF aimed to investigate the value of exercise in AFib in a larger, longer, randomized trial.
The researchers enrolled 120 patients with an average age of 65 years, of whom 43% were women.
Patients in the treatment group received individualized guided exercise from an exercise physiologist in the cardiology clinic once a week for 3 months, then every second week for the following 3 months along with a physical activity plan to follow at home for the other days – aiming to build up to 3.5 hours of physical activity a week.
The supervised sessions, Dr. Elliott explained, were typically higher intensity to raise cardiorespiratory fitness, while the home-based exercise was a moderate intensity aerobic activity of the patient’s choice, such as walking, indoor cycling, or swimming.
“We certainly cautioned against far exceeding this level,” he added.
Patients in the usual care group received exercise advice but no active intervention.
All patients received usual medical care from their cardiologist, who was blinded to the study group allocation.
The co-primary outcomes were AFib symptom severity score and the percentage of patients with recurrent AFib at 12 months, defined as having an AFib episode that lasted longer than 30 seconds or undergoing ablation or requiring ongoing anti-arrhythmic drug therapy.
At 12 months, the percentage of patients with AFib recurrence was significantly lower in the exercise group than in the control group (60% vs. 80%; hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.78; P = .002).
This means that more patients in the exercise group had a normal heart rhythm without needing an invasive intervention (ablation) or continued use of drugs, Dr. Elliott stressed.
Patients in the exercise group also had significantly less severe symptoms – palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue – than patients in the control group.
“On average, patients were achieving close to 180 minutes [of physical activity] per week by 6 months of the intervention and attended 18 supervised sessions in the clinic,” Dr. Elliott said.
Cost was not a barrier since the sessions with an exercise physiologist were free.
Lack of time was the most common reason for missing the physical activity targets, especially for patients with work and family commitments.
Most patients liked the variety of physical activity options.
The researchers plan to determine any gender differences in ACTIVE-AF.
Further research is needed, Dr. Elliott added, to determine which type of exercise is best, whether exercise plus weight loss is synergistic, and whether exercise leads to better long-term freedom from arrhythmia, reduced hospitalization, and improved survival.
The study was partially supported by the National Heart Foundation of Australia through a postdoctoral fellowship to Dr. Elliott. The researchers and Dr. Chung have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) gained significant benefits from a 6-month program of supervised and unsupervised moderate exercise versus usual care, new randomized trial results show.
Among 120 AFib patients in the ACTIVE-AF trial, those randomized to the exercise arm had significantly less frequent AFib recurrence and less severe symptoms over a 1-year period, said Adrian Elliott, PhD, who will present this late-breaking research at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021.
The trial “demonstrates that some patients can control their arrhythmia through physical activity, without the need for complex interventions such as ablation or medications to keep their heart in normal rhythm,” Dr. Elliott, from the University of Adelaide, Australia, said in a statement from the ESC.
This is “the largest randomized controlled trial investigating the value of an exercise prescription in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent [AFib],” he told this news organization in an email.
The findings “really provide the evidence needed that recommending aerobic exercise in patients with symptomatic AFib can lower the severity of symptoms and prevent the recurrence of AFib for many patients,” he said. Aerobic exercise should be incorporated into patient treatment, he added, “alongside the use of medications, as guided by a cardiologist, and management of obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea.”
Mina K. Chung, MD, lead author of a Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association on Lifestyle and Risk Factor Modification for Reduction of Atrial Fibrillation, as previously reported, agrees.
The “findings support the AHA Scientific Statement that we should encourage our patients with AFib to include regular moderate exercise to help prevent AFib, reduce AFib burden, and improve AFib-related symptoms and quality of life,” Dr. Chung, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic, summarized in an email.
“Our recommendation is to encourage AFib patients to aim for at least the AHA physical activity guidelines for the general population, which advise 150 minutes each week of moderate-intensity exercise,” Dr. Chung said.
This is a “reasonable” goal, but “some might argue that a slightly higher target of physical activity duration may be considered,” Dr. Elliott commented.
ACTIVE-AF, he noted, suggests that “as a general guide, patients [with AFib] should strive to build up to 3.5 hours per week of aerobic exercise and incorporate some higher intensity activities to improve cardiorespiratory fitness.”
Aim for 3.5 hours a week
A previous observational study showed that patients who improved their cardiorespiratory fitness over a 5-year period were significantly less likely to have AFib recurrences.
And in a randomized trial of 51 patients, 12 weeks of aerobic interval training reduced the time spent in AFib compared to usual care, during a 4-week follow-up.
ACTIVE-AF aimed to investigate the value of exercise in AFib in a larger, longer, randomized trial.
The researchers enrolled 120 patients with an average age of 65 years, of whom 43% were women.
Patients in the treatment group received individualized guided exercise from an exercise physiologist in the cardiology clinic once a week for 3 months, then every second week for the following 3 months along with a physical activity plan to follow at home for the other days – aiming to build up to 3.5 hours of physical activity a week.
The supervised sessions, Dr. Elliott explained, were typically higher intensity to raise cardiorespiratory fitness, while the home-based exercise was a moderate intensity aerobic activity of the patient’s choice, such as walking, indoor cycling, or swimming.
“We certainly cautioned against far exceeding this level,” he added.
Patients in the usual care group received exercise advice but no active intervention.
All patients received usual medical care from their cardiologist, who was blinded to the study group allocation.
The co-primary outcomes were AFib symptom severity score and the percentage of patients with recurrent AFib at 12 months, defined as having an AFib episode that lasted longer than 30 seconds or undergoing ablation or requiring ongoing anti-arrhythmic drug therapy.
At 12 months, the percentage of patients with AFib recurrence was significantly lower in the exercise group than in the control group (60% vs. 80%; hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.78; P = .002).
This means that more patients in the exercise group had a normal heart rhythm without needing an invasive intervention (ablation) or continued use of drugs, Dr. Elliott stressed.
Patients in the exercise group also had significantly less severe symptoms – palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue – than patients in the control group.
“On average, patients were achieving close to 180 minutes [of physical activity] per week by 6 months of the intervention and attended 18 supervised sessions in the clinic,” Dr. Elliott said.
Cost was not a barrier since the sessions with an exercise physiologist were free.
Lack of time was the most common reason for missing the physical activity targets, especially for patients with work and family commitments.
Most patients liked the variety of physical activity options.
The researchers plan to determine any gender differences in ACTIVE-AF.
Further research is needed, Dr. Elliott added, to determine which type of exercise is best, whether exercise plus weight loss is synergistic, and whether exercise leads to better long-term freedom from arrhythmia, reduced hospitalization, and improved survival.
The study was partially supported by the National Heart Foundation of Australia through a postdoctoral fellowship to Dr. Elliott. The researchers and Dr. Chung have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib) gained significant benefits from a 6-month program of supervised and unsupervised moderate exercise versus usual care, new randomized trial results show.
Among 120 AFib patients in the ACTIVE-AF trial, those randomized to the exercise arm had significantly less frequent AFib recurrence and less severe symptoms over a 1-year period, said Adrian Elliott, PhD, who will present this late-breaking research at the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) Congress 2021.
The trial “demonstrates that some patients can control their arrhythmia through physical activity, without the need for complex interventions such as ablation or medications to keep their heart in normal rhythm,” Dr. Elliott, from the University of Adelaide, Australia, said in a statement from the ESC.
This is “the largest randomized controlled trial investigating the value of an exercise prescription in patients with symptomatic paroxysmal or persistent [AFib],” he told this news organization in an email.
The findings “really provide the evidence needed that recommending aerobic exercise in patients with symptomatic AFib can lower the severity of symptoms and prevent the recurrence of AFib for many patients,” he said. Aerobic exercise should be incorporated into patient treatment, he added, “alongside the use of medications, as guided by a cardiologist, and management of obesity, hypertension, and sleep apnea.”
Mina K. Chung, MD, lead author of a Scientific Statement from the American Heart Association on Lifestyle and Risk Factor Modification for Reduction of Atrial Fibrillation, as previously reported, agrees.
The “findings support the AHA Scientific Statement that we should encourage our patients with AFib to include regular moderate exercise to help prevent AFib, reduce AFib burden, and improve AFib-related symptoms and quality of life,” Dr. Chung, a cardiologist at the Cleveland Clinic, summarized in an email.
“Our recommendation is to encourage AFib patients to aim for at least the AHA physical activity guidelines for the general population, which advise 150 minutes each week of moderate-intensity exercise,” Dr. Chung said.
This is a “reasonable” goal, but “some might argue that a slightly higher target of physical activity duration may be considered,” Dr. Elliott commented.
ACTIVE-AF, he noted, suggests that “as a general guide, patients [with AFib] should strive to build up to 3.5 hours per week of aerobic exercise and incorporate some higher intensity activities to improve cardiorespiratory fitness.”
Aim for 3.5 hours a week
A previous observational study showed that patients who improved their cardiorespiratory fitness over a 5-year period were significantly less likely to have AFib recurrences.
And in a randomized trial of 51 patients, 12 weeks of aerobic interval training reduced the time spent in AFib compared to usual care, during a 4-week follow-up.
ACTIVE-AF aimed to investigate the value of exercise in AFib in a larger, longer, randomized trial.
The researchers enrolled 120 patients with an average age of 65 years, of whom 43% were women.
Patients in the treatment group received individualized guided exercise from an exercise physiologist in the cardiology clinic once a week for 3 months, then every second week for the following 3 months along with a physical activity plan to follow at home for the other days – aiming to build up to 3.5 hours of physical activity a week.
The supervised sessions, Dr. Elliott explained, were typically higher intensity to raise cardiorespiratory fitness, while the home-based exercise was a moderate intensity aerobic activity of the patient’s choice, such as walking, indoor cycling, or swimming.
“We certainly cautioned against far exceeding this level,” he added.
Patients in the usual care group received exercise advice but no active intervention.
All patients received usual medical care from their cardiologist, who was blinded to the study group allocation.
The co-primary outcomes were AFib symptom severity score and the percentage of patients with recurrent AFib at 12 months, defined as having an AFib episode that lasted longer than 30 seconds or undergoing ablation or requiring ongoing anti-arrhythmic drug therapy.
At 12 months, the percentage of patients with AFib recurrence was significantly lower in the exercise group than in the control group (60% vs. 80%; hazard ratio, 0.50; 95% confidence interval, 0.33-0.78; P = .002).
This means that more patients in the exercise group had a normal heart rhythm without needing an invasive intervention (ablation) or continued use of drugs, Dr. Elliott stressed.
Patients in the exercise group also had significantly less severe symptoms – palpitations, shortness of breath, and fatigue – than patients in the control group.
“On average, patients were achieving close to 180 minutes [of physical activity] per week by 6 months of the intervention and attended 18 supervised sessions in the clinic,” Dr. Elliott said.
Cost was not a barrier since the sessions with an exercise physiologist were free.
Lack of time was the most common reason for missing the physical activity targets, especially for patients with work and family commitments.
Most patients liked the variety of physical activity options.
The researchers plan to determine any gender differences in ACTIVE-AF.
Further research is needed, Dr. Elliott added, to determine which type of exercise is best, whether exercise plus weight loss is synergistic, and whether exercise leads to better long-term freedom from arrhythmia, reduced hospitalization, and improved survival.
The study was partially supported by the National Heart Foundation of Australia through a postdoctoral fellowship to Dr. Elliott. The researchers and Dr. Chung have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Eyes on ESC ‘21: Hope for EMPEROR-Preserved, guidelines remade
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There will be so much more to the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology, which begins Aug. 27 with an all-virtual format, than detailed primary results of EMPEROR-Preserved, a trial that could mark a turning point for heart failure (HF) medical therapy.
Also among the featured Hot Line and Late-Breaking Science sessions are – along with many other studies – explorations of arrhythmia management (ablation or guided by loop recorder); secondary prevention, including by vaccination; oral anticoagulation, notably after transcatheter valve procedures; and colchicine or thrombosis prophylaxis in hospitalized patients with COVID-19.
There will even be a head-to-head comparison of two long-familiar left atrial appendage (LAA) occluders, and a population-based, randomized trial of sodium restriction through wide-scale use of a potassium-based salt substitute.
The congress will also introduce four guideline documents at sessions throughout the Congress, one on each day. They cover new and modified recommendations for heart failure; pacing, including cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT); cardiovascular (CV) disease prevention; and, with cosponsorship from the European Association for Cardio-Thoracic Surgery, valvular heart disease.
The virtues of virtual
That next year’s Congress is slated for Aug. 27-30 in Barcelona should be welcome news for anyone whose “what if” curiosity about all-virtual conferences has already been satisfied. But with experience comes wisdom, as the medical societies have learned that online scientific meetings have some winning qualities that may be worth keeping, as least for a while.
“I think there is no doubt that the digital format will continue, for several reasons. One is that this pandemic is not over,” ESC Congress program committee chair Stephan Windecker, MD, Bern (Switzerland) University Hospital, , told this news organization. “As long as it is not over, the digital format is here to stay.”
But it also appears that people who haven’t been able to attend the congress in person are keen to log in and engage online, Dr. Windecker said. The 2020 all-virtual conference drew a much younger pool of registrants, on average, than did the live conferences before the pandemic.
“I think that’s an indication of people that may be in training, in early stages of their career, or they don’t have the support from departments or from their practice, or other financial means.” But they are able to participate via computer, tablet, or smartphone, he said.
“Another advantage is that the recorded content can be replayed at the convenience of whoever wants to consume it at a later point in time,” he added. “Those are just some examples why the digital format is likely to stay,” on its own or in a new age of hybrid meetings.
New and updated guidelines
Leading off the guideline series is the document on diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic HF, which leveraged the past few busy years of HF clinical trials to arrive at a number of new recommendations and strengthened level-of-evidence ratings. It covers both drug and device therapy of HF with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) and acute decompensated HF, and tweaks and further enshrines the concept of HF with mildly reduced ejection fraction (HFmrEF).
Several updated recommendations for both long-used and novel medications, notably the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 inhibitors, will be included because of the recently appreciated evidence-based impact in HFrEF, Dr. Windecker noted.
“I think it will be particularly interesting to look for the SGLT2 inhibitors as not a completely new class of drugs, but certainly one where there has been a lot of new evidence, to look at how those drugs will be integrated in the overall care pathway.”
A top-line preview of the new HF guideline limited to drug therapy, presented at July’s Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC-HFA), provided a simple answer to a common question in the new, bountiful age of HFrEF medications: Which meds, initiated in what order?
As it happens, the new recommendation for first-line HFrEF drug therapy is not a silver bullet, but a shotgun – prompt initiation of at least four meds, one from each of four drug classes: renin-angiotensin system inhibitors, beta-blockers, mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists (MRA), and SGLT2 inhibitors. Each class, as described in the document, is to be started as soon as safely feasible, in a sequence deemed appropriate for each individual patient.
Spotlight on EMPEROR-Preserved
The world already knows that the trial, which tested the SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin (Jardiance, Boehringer Ingelheim/Eli Lilly) on top of standard therapy, “met” its primary endpoint in almost 6,000 patients with HF with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), who included some with HFmrEF by more contemporary definitions.
That means patients in EMPEROR-Preserved assigned to take empagliflozin showed significantly fewer events that made up the study’s primary endpoint, a composite of CV death or HF hospitalization. It appears to be the first clearly significant overall medical therapy benefit for a clinical primary endpoint in a major randomized HFpEF drug trial.
And that, pending fuller presentation of trial results at the Congress on Aug. 27, could be a huge deal for the half of HF patients with left ventricular ejection fractions (LVEF) higher than the HFrEF range.
Those early top-line results weren’t a decisive bombshell for a field now filled with hope for a practice-changing empagliflozin outcome in EMPEROR-Preserved, which isn’t a certainty. They were more like the “boom” of a mortar launching a rocket of fireworks that may explode into a chrysanthemum or green comet or, sometimes, turn out to be no more than a dud. The promise of the early cursory results critically depends on further details.
“Provided there is a compelling benefit, this is what everyone has been waiting for in this condition for decades,” Mikhail N. Kosiborod, MD, director of cardiometabolic research at Saint Luke’s Mid-America Heart Institute, Kansas City, Mo., said.
“Already knowing that the trial met the primary endpoint is obviously very intriguing and encouraging,” he added. “But there are things we don’t know, such as: What is the magnitude of benefit? And whether that benefit, whatever the magnitude, is driven by reductions in both heart failure hospitalizations and cardiovascular death, or only one of the two.”
For example: “If we see an impressive benefit for reduction of hospitalizations, but not a significant reduction in death, that would still be a huge advance. That’s because, to date, we don’t have any drug for HFpEF that has convincingly demonstrated a compelling reduction in heart failure hospitalization or improvement in symptoms, function, or quality of life,” observed Dr. Kosiborod, who wasn’t part of EMPEROR-Preserved.
There have been “suggestions” from HFrEF trials that empagliflozin and dapagliflozin (Farxiga, AstraZeneca) “have very comparable effects on at least the endpoint of cardiovascular death or hospitalization for heart failure,” he said. “So, my expectation would be that whatever is observed in EMPEROR-Preserved is likely a class effect, as well.”
Following EMPEROR-Preserved on the agenda is EMPEROR-Pooled, a patient-level combined analysis of the EMPEROR series of trials that spans the range of HF, regardless of ejection fraction or diabetes status, primarily exploring the effects of empagliflozin on renal function.
Other offerings, Friday, Aug. 27
Scheduled immediately after EMPEROR-Preserved is a presentation on the SMART-MI trial, which should clarify whether management guided by continuous ambulatory monitoring is effective in patients considered at especially high arrhythmic risk. Entry called for recent myocardial infarction and an LVEF of 36%-50% with evidence of cardiac autonomic dysfunction.
The trial randomly assigned 400 such patients to be or not be implanted with a Reveal LINQ (Medtronic) loop recorder and followed them for up to 18 months, primarily for detection of potentially serious arrhythmic events. Endpoints that involved mortality, hospitalization or other clinical events were secondary.
In a time slot preceding both SMART-MI and EMPEROR-Preserved, the GUIDE-HF trial is following a projected 3,600 patients with HF implanted with a CardioMEMS HF System (Abbott) pulmonary artery (PA) pressure sensor to explore the its value for guiding management.
The trial’s three cohorts, followed for at least 12 months, include randomized sensor-monitored and control groups of patients with New York Heart Association class 2-4 symptoms, as well as a third observational set of patients in NYHA class 3. That’s the indication for which the CardioMEMS monitor gained approval in the United States in 2014 based on the 2011 CHAMPION trial, and which fared just as well in the 2017 CHAMPION Post-Approval Study.
The Friday Hot Lines also include Dal-GenE, which has entered about 6,000 patients with recent MI to test the once-abandoned cholesterol ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor dalcetrapib (DalCor) for any secondary-prevention benefits when used selectively. The trial’s hook: All its patients are confirmed to have the AA genotype of the rs1967309 variant in the ADCY9 gene, which has been associated with a pronounced clinical response to CETP inhibition.
Saturday, Aug. 28
The direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) have largely replaced vitamin K antagonists in patients with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation (AFib). But whether DOACs are similarly preferable in the growing world population of people who have undergone transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR or TAVI), an issue explored with variable results in the ATLANTIS and GALILEO trials, is far from settled.
The ENVISAGE-TAVI AF trial explored the question for the factor X inhibitor edoxaban (Savaysa, Lixiana, Daiichi-Sankyo) in 1,400 patients with AFib and a transfemoral TAVR in the previous 5 days, who were randomly assigned to the DOAC or standard management along with discretionary antiplatelet therapy. They’ve been followed for up to 3 years for a composite endpoint of clinical events – including death, MI, and stroke – and for major bleeding.
The day will also feature MASTER DAPT, a comparison of two dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) regimens in an estimated 4,300 patients considered to be high-risk for bleeding who had received the sirolimus-eluting Ultimaster (Terumo) coronary stent, which has a bioresorbable polymer coating.
Investigators have randomly assigned patients to receive either very-short-duration DAPT, for about a month after stenting, followed by a P2Y12 inhibitor alone for up to a year after the procedure; or a more conventional regimen of a P2Y12 inhibitor for 6-12 months with aspirin maintained for a total of 12 months.
Later that day, investigators from the FIGARO-DKD trial will present their results based on 7,437 patients with type 2 diabetes and chronic kidney disease (CKD), a much fuller version than the top-line findings announced by sponsor Bayer 3 months ago.
Those top-line results suggested that patients assigned to receive the nonsteroidal nonselective mineralocorticoid receptor antagonist (MRA) finerenone (Kerendia) on top of standard care benefited with a drop in risk for the primary endpoint of CV death or nonfatal CV events.
Finerenone was recently approved in the United States for treating patients with both type 2 diabetes and CKD based on the published FIDELIO-DKD trial, which had seen less CKD progression and fewer CV events in such patients who took the novel MRA.
Although similar in design to FIGARO-DKD, FIDELIO-DKD had entered fewer patients with early-stage diabetic kidney disease (DKD). That led researchers to pool the two trials’ populations to create a cohort that spans the spectrum of DKD severity. An analysis of the pooled cohort, dubbed FIDELITY, is on the schedule after FIGARO-DKD.
After FIDELITY is the prospective APAF-CRT trial that is following a projected 1,830 patients with permanent, symptomatic AFib and a recent hospitalization for AFib or HF and who were not good candidates for standard ablation. They were assigned to receive either atrioventricular junctional ablation followed by CRT, with or without a defibrillation, on top of optimal meds – a so-called “ablate-and-pace” strategy – or an implantable cardioverter defibrillator with rate-control drug therapy.
The new analysis represents the trial’s second phase in which mortality was followed for 4 years as the primary endpoint, in contrast to the previously reported initial phase that followed the first 102 patients for 2 years for the composite primary endpoint of death, worsening HF, and HF hospitalization. The first phase had halted enrollment before reaching its planned target of 280 patients after an interim analysis showed a significant benefit for ablate and pace.
Next up: DECAAF 2, a randomized assessment of whether catheter ablation for AFib guided by delayed gadolinium enhancement on MRI, a proxy for scar tissue, can be more effective than standard AFib ablation by pulmonary vein isolation alone. An estimated 900 patients with persistent AFib who had never before undergone ablation for the arrhythmia were randomly assigned to one strategy or the other and followed for AFib recurrence over 18 months.
Sunday, Aug. 29
The TOMAHAWK trial aimed to clarify the optimal timing of invasive coronary angiography for resuscitated patients with non–ST-segment elevation out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, a broad population in a setting for which there is little randomized-trial guidance. Investigators randomly assigned 558 such patients to undergo immediate invasive angiography or to direct intensive care unit admission for initial standard care with discretionary delayed angiography. Patients were followed for all-cause mortality, with other clinical events and neurologic outcomes as secondary endpoints.
Next on the schedule, the RIPCORD-2 trial randomly assigned 1,100 patients with stable known or suspected coronary artery disease (CAD) to undergo conventional angiography alone or with added direct pressure-wire measurement of fractional flow reserve to guide management decisions. Primary outcomes include health care costs and patient-reported quality of life at 1 year.
Slated for later that day, the Asymptomatic Carotid Surgery Trial-2 (ACST-2) has entered an estimated 3600 patients with a substantial carotid artery narrowing not associated with symptoms but for which either carotid endarterectomy (CEA) or carotid artery stenting (CAS) was considered anatomically feasible. There also must have been “substantial uncertainty” regarding the optimal procedure choice.
The trial, conducted in 40 countries primarily in Europe and North America and launched in 2008, randomly assigned the patients to undergo either CEA or CAS, in both cases with appropriate medical therapy, and followed them for periprocedural events and up to 10 years for strokes and stroke-related events.
The LOOP study, which is to directly follow ACST-2, has explored whether screening for AFib using the Medtronic Reveal LINQ monitor in older patients with non-AFib stroke risk factors – with oral anticoagulation prescribed for those who test positive – can lower their risk for stroke or systemic embolism. It randomly assigned 6,000 such patients to care guided by the loop recorder or to standard care.
On a somewhat larger scale, the Salt Substitute and Stroke Study (SSaSS) randomly assigned a total of 20,996 people in about 600 villages across northern China and Tibet to sodium-restriction intervention and control groups by village. All participants had a history of stroke or were aged at least 60 years with uncontrolled hypertension.
As described by the trial’s online portal, participants in villages assigned to the intervention group were given a supply of a low-sodium, potassium-supplementing salt substitute to replace their own salt supplies, along with education on the health benefits of sodium restriction. Participants in control villages continued their normal diets and, at the trial’s beginning, received “advice to reduce their salt intake.” All were required to own a telephone.
Clinical events, including strokes and hospitalizations throughout a 5-year follow-up, were tracked by phone calls made to all participants every 6 months and were documented at follow-up home visits.
Sunday is also to feature a Late-Breaking Trials session with a focus on COVID-19, which leads off with COLCOVID, a test of colchicine in patients hospitalized for suspected SARS-CoV-2 infection and in acute respiratory distress.
The 1,279 participants in Argentina were randomly assigned to receive or not receive the potent anti-inflammatory agent on top of antivirals and other standard management and followed for death or new need for mechanical ventilation. A successful outcome would contrast with the RECOVERY trial, which terminated a colchicine group of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 because of a lack of efficacy earlier this year.
COLCOVID is to be followed by the MICHELLE trial of rivaroxaban (Xarelto, Bayer/Janssen) prophylaxis, compared with no preventive oral anticoagulant, in 320 patients who, when hospitalized with COVID-19, had been on parenteral anticoagulants because of an elevated risk for venous thromboembolism. The trial, conducted in Brazil, called for postdischarge rivaroxaban at a once-daily dosage of 10 mg for about 1 month.
The session also includes a presentation called “Insights into the Effects of the COVID-19 Pandemic: Comprehensive Analysis from the GUIDE-HF Trial,” the primary outcomes of which will be reported on the first day of the Congress.
Following is a presentation on the PREPARE-IT study of icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), given at high dosages intended to be anti-inflammatory, compared with placebo, in an estimated 4,000 adults. The trial has two groups: A prevention group of adults living and circulating in the community; and a treatment group of patients aged at least 40 years with confirmed symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection for whom the need for hospitalization isn’t clear.
Monday, Aug. 30
The final day of the Congress features a trial called Influenza Vaccination after Myocardial Infarction (IAMI), which has tested the secondary preventive effect of influenza vaccination by randomly assigning 2,571 patients to receive a standard vaccine or a saline placebo injection on one occasion.
Entry to the international trial called for a diagnosis of MI with or without ST-segment elevation, or stable CAD and age at least 75 years with other risk factors. The patients were followed for death, MI, stent thrombosis, and a slew of secondary endpoints over 12 months.
Monday offerings continue later in a time block leading off with the STEP trial, which has randomly assigned an estimated 8,000 patients at 40 centers in China who are 60 to 80 years of age with a systolic blood pressure of 140 to <190 mm Hg to be on standard guideline-based therapy or an intensive drug-management strategy.
The systolic BP goals are 130 to <150 mm Hg for standard care and 110 to <130 mm Hg for the intensive regimen. The composite primary endpoint includes death and clinical events related to acute coronary syndromes, HF, revascularization, and stroke.
Following on heels of STEP, the Amulet IDE trial – the first major randomized comparison of two transcatheter LAA closure devices – entered 1,878 patients with nonvalvular AFib who were considered high-risk for bleeding and stroke or systemic embolism.
They were randomly assigned in the noninferiority trial to receive either the AMPLATZER Amulet (Abbott Medical Devices) or the WATCHMAN (Boston Scientific) closure devices and were followed for safety and efficacy for up to 5 years.
Both LAA closure devices, intended to make patients with AFib less reliant on oral anticoagulation, are now available on both sides of the Atlantic – as well as many other countries – after the Amulet’s United States market approval on Aug. 16, based largely on the Amulet IDE trial.
Rounding out the final Hot Line set is one of the latest efforts to show the efficacy and safety of a very short DAPT period after coronary stenting in patients with acute coronary syndromes, the STOPDAPT-2 ACS trial.
The study assigned 3,008 patients in Japan to receive aspirin and clopidogrel for either 1 month or 1 year after implantation with an everolimus-eluting cobalt-chromium stent and followed them for up to 5 years for a composite of MI, CV death, stent thrombosis, stroke, and bleeding.
The trial follows the published STOPDAPT-2 trial that showed superiority for the 1-month DAPT regimen in a predominantly stable-CAD population treated with the same kind of stent.
Program structure and format
A total of 15 online channels are to be available in the morning, European time, their schedules running in parallel. Presentations often are prerecorded, but also include live sessions at 8:00 a.m. Central time and 12 p.m. CET (2:00 a.m. and 6:00 a.m. Eastern time) to liven up the channel offerings, Dr. Windecker observed, and to make them more immediate and potentially interactive.
Many of the parallel channels are devoted throughout the Congress to particular silos of cardiology; for example, arrhythmias and device therapy is on channel 3; CAD and acute care is on 5; HF is on 6; and preventive cardiology is on 9.
Other channels swing across different topics from day to day, such as channel 1, which covers COVID-19 topics on the first and third day of the meeting, “advances in science” on day 2, and “digital health, public health, health economics” on day 4.
The focus each day, starting at 2:00 p.m. CET (8:00 a.m. ET) and continuing into the evening in Europe, shifts over to the Prime Time live program, which features the Hot Line and guideline presentations and many of the live abstract presentations.
Dr. Kosiborod, not a researcher with the EMPEROR trials, is chair of the Dapagliflozin in Preserved Ejection Fraction Heart Failure ( PRESERVED-HF ) trial, which is scheduled for presentation at the September 2021 Heart Failure Society of American meeting.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Chronic kidney disease tied to worse LAAO outcomes
The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is associated with worse in-hospital and short-term outcomes after left atrial appendage (LAA) closure, a nationwide study shows.
Patients with ESRD were particularly vulnerable, having about 6.5-fold higher odds of in-hospital mortality than those without CKD and about 11.5-fold higher odds than those with CKD, even after adjustment for potential confounders.
Patients with CKD had higher rates of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) and more short-term readmissions for bleeding, Keerat Rai Ahuja, MD, Reading Hospital-Tower Health, West Reading, Pennsylvania, and colleagues reported August 16 in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
CKD and ESRD are known to be associated with an increased risk for stroke and bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), yet data are limited on the safety and efficacy of LAA closure for stroke prevention in AFib patients with CKD or ESRD, they note.
“It’s important to know about CKD and understand that there may be an association with worse levels of CKD and worse outcomes, but the data that strikes me is really that for end-stage renal disease,” Matthew Sherwood, MD, MHS, who was not involved with the study, said in an interview.
He noted that data have not been published for patients with CKD and ESRD enrolled in the pivotal PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL trials of Boston Scientific’s Watchman device or from large clinical registries such as EWOLUTION and the company’s continued access protocol registries.
Further, it’s not well understood what the best strategy is to prevent stroke in AFib patients with ESRD and whether they benefit from anticoagulation with warfarin or any of the newer agents. “Thus, it’s hard to then say: ‘Well they have worse outcomes with Watchman,’ which is true as shown in this study, but they may not have any other options based upon the lack of data for oral anticoagulants in end-stage kidney disease patients,” said Dr. Sherwood, from the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Falls Church, Virginia.
The lack of clarity is concerning, given rising atrial fibrillation cases and the prevalence of abnormal renal function in everyday practice. In the present study – involving 21,274 patients undergoing LAA closure between 2016 and 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database – 18.6% of patients had CKD stages I to V and 2.7% had ESRD based on ICD-10 codes.
In-hospital mortality was increased only in patients with ESRD. In all, 3.3% of patients with ESRD and 0.4% of those with no CKD died in hospital (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 6.48), as did 0.5% of patients with CKD (aOR, 11.43; both P <.001).
“These patients represent a sicker population at baseline and have an inherent greater risk for mortality in cardiac interventions, as noted in other studies of structural heart interventions,” Dr. Ahuja and colleagues write.
Patients with CKD had a higher risk for in-hospital stroke or TIA than patients with no CKD (1.8% vs. 1.3%; aOR, 1.35; P = .038) and this risk continued up to 90 days after discharge (1.7% vs. 1.0%; aOR, 1.67; P = .007).
The in-hospital stroke rate was numerically higher in patients with ESRD compared with no CKD (aOR, 1.18; P = .62).
The authors point out that previous LAA closure and CKD studies have reported no differences in in-hospital or subsequent stroke/TIA rates in patients with and without CKD. Possible explanations are that patients with CKD in the present study had higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores than those without CKD (4.18 vs. 3.62) and, second, patients with CKD and AFib are known to have higher risk for thromboembolic events than those with AFib without CKD.
CKD patients were also more likely than those without CKD to experience in-hospital acute kidney injury or hemodialysis (aOR, 5.02; P <.001).
CKD has been shown to be independently associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) after LAA closure. AKI may have long-term thromboembolic consequences, the authors suggest, with one study reporting higher stroke risk at midterm follow-up in patients with AKI.
“As with other cardiac interventions in patients with CKD, efforts should be made to optimize preoperative renal function, minimize contrast volume, and avoid abrupt hemodynamic changes such as hypotension during the procedure to prevent AKI,” Dr. Ahuja and colleagues write.
Patients with CKD and ESRD had longer index length of stay than those without CKD but had similar rates of other in-hospital complications, such as systemic embolization, bleeding/transfusion, vascular complications, and pericardial tamponade requiring intervention.
Among the short-term outcomes, 30- and 90-day all-cause readmissions were increased in patients with CKD and ESRD compared with those without CKD, and 30-day bleeding readmissions were increased within the CKD cohort.
“With Watchman and left atrial appendage closure, what we see is that they have higher rates of readmission and other problems,” Dr. Sherwood said. “I think we understand that that’s probably related not to the procedure itself, not because the Watchman doesn’t work for end-stage kidney disease, but because the patients themselves are likely higher risk.”
Commonly used risk scores for atrial fibrillation, however, don’t take into account advanced kidney disease, he added.
Besides the inherent limitations of observational studies, Dr. Sherwood and the authors point to the lack of laboratory variables and procedural variables in the database, the fact that CKD was defined using ICD-10 codes, that outcomes were not clinically adjudicated, that unmeasured confounders likely still exist, and that long-term follow-up is lacking.
Dr. Sherwood, who wrote an editorial accompanying the study, said that the release of outcomes data from CKD and ESRD patients in the major clinical trials would be helpful going forward, as would possible involvement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes organization.
“One of the main points of this study is that we just need a lot more research diving into this patient population,” he said.
The authors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sherwood reports honoraria from Janssen and Medtronic. Editorial coauthor Sean Pokorney reports research grant support from Gilead, Boston Scientific, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, and the Food and Drug Administration; and advisory board, consulting, and honoraria supports from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Philips, and Zoll.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is associated with worse in-hospital and short-term outcomes after left atrial appendage (LAA) closure, a nationwide study shows.
Patients with ESRD were particularly vulnerable, having about 6.5-fold higher odds of in-hospital mortality than those without CKD and about 11.5-fold higher odds than those with CKD, even after adjustment for potential confounders.
Patients with CKD had higher rates of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) and more short-term readmissions for bleeding, Keerat Rai Ahuja, MD, Reading Hospital-Tower Health, West Reading, Pennsylvania, and colleagues reported August 16 in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
CKD and ESRD are known to be associated with an increased risk for stroke and bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), yet data are limited on the safety and efficacy of LAA closure for stroke prevention in AFib patients with CKD or ESRD, they note.
“It’s important to know about CKD and understand that there may be an association with worse levels of CKD and worse outcomes, but the data that strikes me is really that for end-stage renal disease,” Matthew Sherwood, MD, MHS, who was not involved with the study, said in an interview.
He noted that data have not been published for patients with CKD and ESRD enrolled in the pivotal PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL trials of Boston Scientific’s Watchman device or from large clinical registries such as EWOLUTION and the company’s continued access protocol registries.
Further, it’s not well understood what the best strategy is to prevent stroke in AFib patients with ESRD and whether they benefit from anticoagulation with warfarin or any of the newer agents. “Thus, it’s hard to then say: ‘Well they have worse outcomes with Watchman,’ which is true as shown in this study, but they may not have any other options based upon the lack of data for oral anticoagulants in end-stage kidney disease patients,” said Dr. Sherwood, from the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Falls Church, Virginia.
The lack of clarity is concerning, given rising atrial fibrillation cases and the prevalence of abnormal renal function in everyday practice. In the present study – involving 21,274 patients undergoing LAA closure between 2016 and 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database – 18.6% of patients had CKD stages I to V and 2.7% had ESRD based on ICD-10 codes.
In-hospital mortality was increased only in patients with ESRD. In all, 3.3% of patients with ESRD and 0.4% of those with no CKD died in hospital (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 6.48), as did 0.5% of patients with CKD (aOR, 11.43; both P <.001).
“These patients represent a sicker population at baseline and have an inherent greater risk for mortality in cardiac interventions, as noted in other studies of structural heart interventions,” Dr. Ahuja and colleagues write.
Patients with CKD had a higher risk for in-hospital stroke or TIA than patients with no CKD (1.8% vs. 1.3%; aOR, 1.35; P = .038) and this risk continued up to 90 days after discharge (1.7% vs. 1.0%; aOR, 1.67; P = .007).
The in-hospital stroke rate was numerically higher in patients with ESRD compared with no CKD (aOR, 1.18; P = .62).
The authors point out that previous LAA closure and CKD studies have reported no differences in in-hospital or subsequent stroke/TIA rates in patients with and without CKD. Possible explanations are that patients with CKD in the present study had higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores than those without CKD (4.18 vs. 3.62) and, second, patients with CKD and AFib are known to have higher risk for thromboembolic events than those with AFib without CKD.
CKD patients were also more likely than those without CKD to experience in-hospital acute kidney injury or hemodialysis (aOR, 5.02; P <.001).
CKD has been shown to be independently associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) after LAA closure. AKI may have long-term thromboembolic consequences, the authors suggest, with one study reporting higher stroke risk at midterm follow-up in patients with AKI.
“As with other cardiac interventions in patients with CKD, efforts should be made to optimize preoperative renal function, minimize contrast volume, and avoid abrupt hemodynamic changes such as hypotension during the procedure to prevent AKI,” Dr. Ahuja and colleagues write.
Patients with CKD and ESRD had longer index length of stay than those without CKD but had similar rates of other in-hospital complications, such as systemic embolization, bleeding/transfusion, vascular complications, and pericardial tamponade requiring intervention.
Among the short-term outcomes, 30- and 90-day all-cause readmissions were increased in patients with CKD and ESRD compared with those without CKD, and 30-day bleeding readmissions were increased within the CKD cohort.
“With Watchman and left atrial appendage closure, what we see is that they have higher rates of readmission and other problems,” Dr. Sherwood said. “I think we understand that that’s probably related not to the procedure itself, not because the Watchman doesn’t work for end-stage kidney disease, but because the patients themselves are likely higher risk.”
Commonly used risk scores for atrial fibrillation, however, don’t take into account advanced kidney disease, he added.
Besides the inherent limitations of observational studies, Dr. Sherwood and the authors point to the lack of laboratory variables and procedural variables in the database, the fact that CKD was defined using ICD-10 codes, that outcomes were not clinically adjudicated, that unmeasured confounders likely still exist, and that long-term follow-up is lacking.
Dr. Sherwood, who wrote an editorial accompanying the study, said that the release of outcomes data from CKD and ESRD patients in the major clinical trials would be helpful going forward, as would possible involvement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes organization.
“One of the main points of this study is that we just need a lot more research diving into this patient population,” he said.
The authors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sherwood reports honoraria from Janssen and Medtronic. Editorial coauthor Sean Pokorney reports research grant support from Gilead, Boston Scientific, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, and the Food and Drug Administration; and advisory board, consulting, and honoraria supports from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Philips, and Zoll.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The presence of chronic kidney disease (CKD) or end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is associated with worse in-hospital and short-term outcomes after left atrial appendage (LAA) closure, a nationwide study shows.
Patients with ESRD were particularly vulnerable, having about 6.5-fold higher odds of in-hospital mortality than those without CKD and about 11.5-fold higher odds than those with CKD, even after adjustment for potential confounders.
Patients with CKD had higher rates of stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA) and more short-term readmissions for bleeding, Keerat Rai Ahuja, MD, Reading Hospital-Tower Health, West Reading, Pennsylvania, and colleagues reported August 16 in JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions.
CKD and ESRD are known to be associated with an increased risk for stroke and bleeding in patients with atrial fibrillation (AFib), yet data are limited on the safety and efficacy of LAA closure for stroke prevention in AFib patients with CKD or ESRD, they note.
“It’s important to know about CKD and understand that there may be an association with worse levels of CKD and worse outcomes, but the data that strikes me is really that for end-stage renal disease,” Matthew Sherwood, MD, MHS, who was not involved with the study, said in an interview.
He noted that data have not been published for patients with CKD and ESRD enrolled in the pivotal PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL trials of Boston Scientific’s Watchman device or from large clinical registries such as EWOLUTION and the company’s continued access protocol registries.
Further, it’s not well understood what the best strategy is to prevent stroke in AFib patients with ESRD and whether they benefit from anticoagulation with warfarin or any of the newer agents. “Thus, it’s hard to then say: ‘Well they have worse outcomes with Watchman,’ which is true as shown in this study, but they may not have any other options based upon the lack of data for oral anticoagulants in end-stage kidney disease patients,” said Dr. Sherwood, from the Inova Heart and Vascular Institute, Falls Church, Virginia.
The lack of clarity is concerning, given rising atrial fibrillation cases and the prevalence of abnormal renal function in everyday practice. In the present study – involving 21,274 patients undergoing LAA closure between 2016 and 2017 in the Nationwide Readmissions Database – 18.6% of patients had CKD stages I to V and 2.7% had ESRD based on ICD-10 codes.
In-hospital mortality was increased only in patients with ESRD. In all, 3.3% of patients with ESRD and 0.4% of those with no CKD died in hospital (adjusted odds ratio [aOR], 6.48), as did 0.5% of patients with CKD (aOR, 11.43; both P <.001).
“These patients represent a sicker population at baseline and have an inherent greater risk for mortality in cardiac interventions, as noted in other studies of structural heart interventions,” Dr. Ahuja and colleagues write.
Patients with CKD had a higher risk for in-hospital stroke or TIA than patients with no CKD (1.8% vs. 1.3%; aOR, 1.35; P = .038) and this risk continued up to 90 days after discharge (1.7% vs. 1.0%; aOR, 1.67; P = .007).
The in-hospital stroke rate was numerically higher in patients with ESRD compared with no CKD (aOR, 1.18; P = .62).
The authors point out that previous LAA closure and CKD studies have reported no differences in in-hospital or subsequent stroke/TIA rates in patients with and without CKD. Possible explanations are that patients with CKD in the present study had higher CHA2DS2-VASc scores than those without CKD (4.18 vs. 3.62) and, second, patients with CKD and AFib are known to have higher risk for thromboembolic events than those with AFib without CKD.
CKD patients were also more likely than those without CKD to experience in-hospital acute kidney injury or hemodialysis (aOR, 5.02; P <.001).
CKD has been shown to be independently associated with acute kidney injury (AKI) after LAA closure. AKI may have long-term thromboembolic consequences, the authors suggest, with one study reporting higher stroke risk at midterm follow-up in patients with AKI.
“As with other cardiac interventions in patients with CKD, efforts should be made to optimize preoperative renal function, minimize contrast volume, and avoid abrupt hemodynamic changes such as hypotension during the procedure to prevent AKI,” Dr. Ahuja and colleagues write.
Patients with CKD and ESRD had longer index length of stay than those without CKD but had similar rates of other in-hospital complications, such as systemic embolization, bleeding/transfusion, vascular complications, and pericardial tamponade requiring intervention.
Among the short-term outcomes, 30- and 90-day all-cause readmissions were increased in patients with CKD and ESRD compared with those without CKD, and 30-day bleeding readmissions were increased within the CKD cohort.
“With Watchman and left atrial appendage closure, what we see is that they have higher rates of readmission and other problems,” Dr. Sherwood said. “I think we understand that that’s probably related not to the procedure itself, not because the Watchman doesn’t work for end-stage kidney disease, but because the patients themselves are likely higher risk.”
Commonly used risk scores for atrial fibrillation, however, don’t take into account advanced kidney disease, he added.
Besides the inherent limitations of observational studies, Dr. Sherwood and the authors point to the lack of laboratory variables and procedural variables in the database, the fact that CKD was defined using ICD-10 codes, that outcomes were not clinically adjudicated, that unmeasured confounders likely still exist, and that long-term follow-up is lacking.
Dr. Sherwood, who wrote an editorial accompanying the study, said that the release of outcomes data from CKD and ESRD patients in the major clinical trials would be helpful going forward, as would possible involvement with the Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes organization.
“One of the main points of this study is that we just need a lot more research diving into this patient population,” he said.
The authors report no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Sherwood reports honoraria from Janssen and Medtronic. Editorial coauthor Sean Pokorney reports research grant support from Gilead, Boston Scientific, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Janssen, and the Food and Drug Administration; and advisory board, consulting, and honoraria supports from Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Pfizer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Philips, and Zoll.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves Abbott’s Amplatzer Amulet for AFib
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Amplatzer Amulet left atrial appendage occluder (Abbott) to treat people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation who are at increased risk for stroke and systemic embolism.
The Amulet and its competitor, Boston Scientific’s Watchman, are minimally invasive devices used to close off the left atrial appendage (LAA), an area where blood clots tend to form in people with atrial fibrillation.
Amulet uses dual-seal technology to completely and immediately seal the LAA, the company says, whereas the other minimally invasive solution uses a single component to seal the LAA that requires blood-thinning drugs to heal and additional patient monitoring. The Amulet also has the widest range of occluder sizes on the market and is recapturable and repositionable to ensure optimal placement.
“As the world’s population continues to age, we’re seeing a surge in atrial fibrillation cases, and with that comes increased risk of stroke. The approval of Abbott’s Amulet device provides physicians with a treatment option that reduces the risk of stroke and eliminates the need for blood-thinning medication immediately after the procedure, which is incredibly valuable given the bleeding risks associated with these medicines,” Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute at HCA Midwest Health, Overland Park, Kan., and principal investigator for the study that led to FDA approval, said in a news release from Abbott.
The FDA approval is supported by findings from the global Amulet IDE trial, a head-to-head comparison of the Amulet and Watchman devices in 1,878 participants with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. The results will be presented virtually on Aug. 30 at the 2021 annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The Amplatzer Amulet received CE Mark designation in 2013 and is approved for use in more than 80 countries, including in Australia, Canada, and European countries.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Amplatzer Amulet left atrial appendage occluder (Abbott) to treat people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation who are at increased risk for stroke and systemic embolism.
The Amulet and its competitor, Boston Scientific’s Watchman, are minimally invasive devices used to close off the left atrial appendage (LAA), an area where blood clots tend to form in people with atrial fibrillation.
Amulet uses dual-seal technology to completely and immediately seal the LAA, the company says, whereas the other minimally invasive solution uses a single component to seal the LAA that requires blood-thinning drugs to heal and additional patient monitoring. The Amulet also has the widest range of occluder sizes on the market and is recapturable and repositionable to ensure optimal placement.
“As the world’s population continues to age, we’re seeing a surge in atrial fibrillation cases, and with that comes increased risk of stroke. The approval of Abbott’s Amulet device provides physicians with a treatment option that reduces the risk of stroke and eliminates the need for blood-thinning medication immediately after the procedure, which is incredibly valuable given the bleeding risks associated with these medicines,” Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute at HCA Midwest Health, Overland Park, Kan., and principal investigator for the study that led to FDA approval, said in a news release from Abbott.
The FDA approval is supported by findings from the global Amulet IDE trial, a head-to-head comparison of the Amulet and Watchman devices in 1,878 participants with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. The results will be presented virtually on Aug. 30 at the 2021 annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The Amplatzer Amulet received CE Mark designation in 2013 and is approved for use in more than 80 countries, including in Australia, Canada, and European countries.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the Amplatzer Amulet left atrial appendage occluder (Abbott) to treat people with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation who are at increased risk for stroke and systemic embolism.
The Amulet and its competitor, Boston Scientific’s Watchman, are minimally invasive devices used to close off the left atrial appendage (LAA), an area where blood clots tend to form in people with atrial fibrillation.
Amulet uses dual-seal technology to completely and immediately seal the LAA, the company says, whereas the other minimally invasive solution uses a single component to seal the LAA that requires blood-thinning drugs to heal and additional patient monitoring. The Amulet also has the widest range of occluder sizes on the market and is recapturable and repositionable to ensure optimal placement.
“As the world’s population continues to age, we’re seeing a surge in atrial fibrillation cases, and with that comes increased risk of stroke. The approval of Abbott’s Amulet device provides physicians with a treatment option that reduces the risk of stroke and eliminates the need for blood-thinning medication immediately after the procedure, which is incredibly valuable given the bleeding risks associated with these medicines,” Dhanunjaya Lakkireddy, MD, Kansas City Heart Rhythm Institute at HCA Midwest Health, Overland Park, Kan., and principal investigator for the study that led to FDA approval, said in a news release from Abbott.
The FDA approval is supported by findings from the global Amulet IDE trial, a head-to-head comparison of the Amulet and Watchman devices in 1,878 participants with nonvalvular atrial fibrillation. The results will be presented virtually on Aug. 30 at the 2021 annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
The Amplatzer Amulet received CE Mark designation in 2013 and is approved for use in more than 80 countries, including in Australia, Canada, and European countries.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Striking’ difference in adverse events in women with Watchman LAAO
Women have more in-hospital complications than men and double the risk for major adverse events after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device, according to new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry data.
In-hospital mortality was also twofold higher among women than men and hospital stay was longer. Even after adjustment for potential confounders, these relationships still exist, Douglas Darden, MD, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
“I think this article certainly highlights – specific to a procedure that has gained more popularity and will become more commonplace in cardiovascular practice – that operators and patients need to pay more attention [to the fact] that women may be at more risk for adverse events and mortality,” senior author Jonathan Hsu, MD, also from UCSD, told this news organization.
Possible explanations for the disparities include anatomic differences between the sexes, such as smaller vessel diameter, thinner myocardial wall, and a more friable LLA in women; increased frailty; and clinician inexperience, the authors suggest.
“It could be something as simple or as specific as thinness of tissue or friability of tissue that may predispose women more than men to perforation or other risks that may put them at risk for adverse events specifically,” Dr. Hsu said.
Commenting further, he said, “I think we would be remiss not to mention the fact that part of this association may unfortunately be a disparity in care that women as a specific sex may receive,” he said.
Indeed, postimplantation women had higher adjusted odds of receiving a direct oral anticoagulant only (odds ratio, 1.07, P = .02) and warfarin only (OR, 1.12; P < .001), and lower odds of receiving clinical trial-recommended combined oral anticoagulants plus single antiplatelet therapy (OR, 0.91; P < .001).
“This article highlights the fact that in all aspects we need to pay attention that women receive as high-level, guideline-driven care as men,” Dr. Hsu said.
First author Dr. Darden pointed out in an email that women suffer disproportionately from atrial fibrillation (AFib), compared with men, with worse quality of life and higher risk for stroke. So “it’s only natural to seek further treatment in order to decrease that risk, specifically LAAO with Watchman.”
Despite the fact that women are known to be at greater risk for adverse events after invasive procedures, including AFib ablation and TAVR, little is known about sex differences with LAAO, as the LAAO clinical trials only included about 30% women, he said.
Two 2021 papers zeroing in on these sex differences produced mixed results. An American report in roughly 9,200 patients reported a higher risk for major in-hospital events in women after receipt of Watchman implants, whereas a German report found similar safety and efficacy among 387 consecutive patients, regardless of sex.
The present study involved 20,388 women and 28,969 men implanted with the Watchman device between January 2016 and June 2019 in the NCDR registry, the largest LAAO registry with adjudicated events with participation mandated for Medicare coverage.
The women were older (mean age, 76.5 vs. 75.8 years), had a higher mean CHA2DS2-VASc score (5.3 vs. 4.5), and were more likely to have a high fall risk as an indication for LAAO (39.8% vs. 33.5%).
Furthermore, women were more likely than men to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and uncontrolled hypertension, but less likely to have congestive heart failure, diabetes, and coronary artery disease.
After multivariable adjustment, all but one of the primary outcomes was significantly worse in women versus men:
- Aborted or canceled procedure: 3.0% vs. 2.9% (OR, 1.01; P = .87)
- Any adverse event: 6.3% vs. 3.9% (OR, 1.63; P < .001)
- Major adverse event: 4.1% vs. 2.0% (OR, 2.06; P < .001)
- Hospital stay more than 1 day: 16.0% vs. 11.6% (OR, 1.46; P < .001)
- Death: 58/0.3% vs. 37/0.1% (OR, 2.01; P = .001).
The authors point out that device-related adverse events are lower than in the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL clinical trials of the Watchman, with 0.8% of patients developing a pericardial effusion requiring drainage and 1.2% having major bleeding, down from highs of 4.8% and 3.5%, respectively, in PROTECT-AF.
Although promising overall, adverse events among women were driven by higher rates of both pericardial effusion requiring draining (1.2% vs. 0.5%; P < .001) and major bleeding (1.7% vs. 0.8%; P < .001).
Commenting for this news organization John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Kentucky, expressed concern that despite its increasing popularity, the rate of serious complications appears to be increasing for the preventive procedure. “That’s peculiar because you’d expect increased experience and device iterations to decrease complications. And the NCDR data surely undercounts the real rate of adverse events because it only includes in-hospital complications.”
Based on the current data, he observed that there’s a 3% chance for a major complication overall, with the typical female Watchman patient facing a 6% chance of any adverse event and 4% risk for a major adverse event during her hospital stay alone.
“The striking difference in complications in women is a super important observation because higher upfront risk has an even more negative effect on the harm-benefit calculus of this procedure,” Dr. Mandrola said.
“Some of the increased harm in women may have been due to the slightly higher rate of comorbid conditions, but that is real-life,” he said. “Registry data like this is extremely valuable because, unlike the carefully selected randomized trial, registries reflect what is actually being done in practice.”
Dr. Hsu agreed that the absolute numbers are concerning. Nevertheless, “it doesn’t necessarily sound an alarm that our adverse events are worse in contemporary practice or that adverse events continue to increase. But, in general, it just points to the fact that there is this inherent larger risk in women, compared with men, and that we need to, first, figure out why, and second, we need to figure out how to improve.”
Strategies to mitigate procedural risk included ultrasound-guided venous access, preprocedural imaging, improved proficiency with LAAO devices, and continued development of safer devices, they note.
Despite the more generalizable nature of registry data, “the results of this study should not result in differing sex-based thresholds for LAAO implant,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s NCDR. Dr. Hsu reports financial relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Biotronik, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Altathera Pharmaceuticals, and Zoll Medical and holding equity interest in Acutus Medical and Vektor Medical outside the submitted work. Dr. Darden reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women have more in-hospital complications than men and double the risk for major adverse events after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device, according to new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry data.
In-hospital mortality was also twofold higher among women than men and hospital stay was longer. Even after adjustment for potential confounders, these relationships still exist, Douglas Darden, MD, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
“I think this article certainly highlights – specific to a procedure that has gained more popularity and will become more commonplace in cardiovascular practice – that operators and patients need to pay more attention [to the fact] that women may be at more risk for adverse events and mortality,” senior author Jonathan Hsu, MD, also from UCSD, told this news organization.
Possible explanations for the disparities include anatomic differences between the sexes, such as smaller vessel diameter, thinner myocardial wall, and a more friable LLA in women; increased frailty; and clinician inexperience, the authors suggest.
“It could be something as simple or as specific as thinness of tissue or friability of tissue that may predispose women more than men to perforation or other risks that may put them at risk for adverse events specifically,” Dr. Hsu said.
Commenting further, he said, “I think we would be remiss not to mention the fact that part of this association may unfortunately be a disparity in care that women as a specific sex may receive,” he said.
Indeed, postimplantation women had higher adjusted odds of receiving a direct oral anticoagulant only (odds ratio, 1.07, P = .02) and warfarin only (OR, 1.12; P < .001), and lower odds of receiving clinical trial-recommended combined oral anticoagulants plus single antiplatelet therapy (OR, 0.91; P < .001).
“This article highlights the fact that in all aspects we need to pay attention that women receive as high-level, guideline-driven care as men,” Dr. Hsu said.
First author Dr. Darden pointed out in an email that women suffer disproportionately from atrial fibrillation (AFib), compared with men, with worse quality of life and higher risk for stroke. So “it’s only natural to seek further treatment in order to decrease that risk, specifically LAAO with Watchman.”
Despite the fact that women are known to be at greater risk for adverse events after invasive procedures, including AFib ablation and TAVR, little is known about sex differences with LAAO, as the LAAO clinical trials only included about 30% women, he said.
Two 2021 papers zeroing in on these sex differences produced mixed results. An American report in roughly 9,200 patients reported a higher risk for major in-hospital events in women after receipt of Watchman implants, whereas a German report found similar safety and efficacy among 387 consecutive patients, regardless of sex.
The present study involved 20,388 women and 28,969 men implanted with the Watchman device between January 2016 and June 2019 in the NCDR registry, the largest LAAO registry with adjudicated events with participation mandated for Medicare coverage.
The women were older (mean age, 76.5 vs. 75.8 years), had a higher mean CHA2DS2-VASc score (5.3 vs. 4.5), and were more likely to have a high fall risk as an indication for LAAO (39.8% vs. 33.5%).
Furthermore, women were more likely than men to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and uncontrolled hypertension, but less likely to have congestive heart failure, diabetes, and coronary artery disease.
After multivariable adjustment, all but one of the primary outcomes was significantly worse in women versus men:
- Aborted or canceled procedure: 3.0% vs. 2.9% (OR, 1.01; P = .87)
- Any adverse event: 6.3% vs. 3.9% (OR, 1.63; P < .001)
- Major adverse event: 4.1% vs. 2.0% (OR, 2.06; P < .001)
- Hospital stay more than 1 day: 16.0% vs. 11.6% (OR, 1.46; P < .001)
- Death: 58/0.3% vs. 37/0.1% (OR, 2.01; P = .001).
The authors point out that device-related adverse events are lower than in the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL clinical trials of the Watchman, with 0.8% of patients developing a pericardial effusion requiring drainage and 1.2% having major bleeding, down from highs of 4.8% and 3.5%, respectively, in PROTECT-AF.
Although promising overall, adverse events among women were driven by higher rates of both pericardial effusion requiring draining (1.2% vs. 0.5%; P < .001) and major bleeding (1.7% vs. 0.8%; P < .001).
Commenting for this news organization John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Kentucky, expressed concern that despite its increasing popularity, the rate of serious complications appears to be increasing for the preventive procedure. “That’s peculiar because you’d expect increased experience and device iterations to decrease complications. And the NCDR data surely undercounts the real rate of adverse events because it only includes in-hospital complications.”
Based on the current data, he observed that there’s a 3% chance for a major complication overall, with the typical female Watchman patient facing a 6% chance of any adverse event and 4% risk for a major adverse event during her hospital stay alone.
“The striking difference in complications in women is a super important observation because higher upfront risk has an even more negative effect on the harm-benefit calculus of this procedure,” Dr. Mandrola said.
“Some of the increased harm in women may have been due to the slightly higher rate of comorbid conditions, but that is real-life,” he said. “Registry data like this is extremely valuable because, unlike the carefully selected randomized trial, registries reflect what is actually being done in practice.”
Dr. Hsu agreed that the absolute numbers are concerning. Nevertheless, “it doesn’t necessarily sound an alarm that our adverse events are worse in contemporary practice or that adverse events continue to increase. But, in general, it just points to the fact that there is this inherent larger risk in women, compared with men, and that we need to, first, figure out why, and second, we need to figure out how to improve.”
Strategies to mitigate procedural risk included ultrasound-guided venous access, preprocedural imaging, improved proficiency with LAAO devices, and continued development of safer devices, they note.
Despite the more generalizable nature of registry data, “the results of this study should not result in differing sex-based thresholds for LAAO implant,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s NCDR. Dr. Hsu reports financial relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Biotronik, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Altathera Pharmaceuticals, and Zoll Medical and holding equity interest in Acutus Medical and Vektor Medical outside the submitted work. Dr. Darden reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Women have more in-hospital complications than men and double the risk for major adverse events after left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO) with the Watchman device, according to new National Cardiovascular Data Registry (NCDR) LAAO Registry data.
In-hospital mortality was also twofold higher among women than men and hospital stay was longer. Even after adjustment for potential confounders, these relationships still exist, Douglas Darden, MD, University of California, San Diego, and colleagues reported online in JAMA Cardiology.
“I think this article certainly highlights – specific to a procedure that has gained more popularity and will become more commonplace in cardiovascular practice – that operators and patients need to pay more attention [to the fact] that women may be at more risk for adverse events and mortality,” senior author Jonathan Hsu, MD, also from UCSD, told this news organization.
Possible explanations for the disparities include anatomic differences between the sexes, such as smaller vessel diameter, thinner myocardial wall, and a more friable LLA in women; increased frailty; and clinician inexperience, the authors suggest.
“It could be something as simple or as specific as thinness of tissue or friability of tissue that may predispose women more than men to perforation or other risks that may put them at risk for adverse events specifically,” Dr. Hsu said.
Commenting further, he said, “I think we would be remiss not to mention the fact that part of this association may unfortunately be a disparity in care that women as a specific sex may receive,” he said.
Indeed, postimplantation women had higher adjusted odds of receiving a direct oral anticoagulant only (odds ratio, 1.07, P = .02) and warfarin only (OR, 1.12; P < .001), and lower odds of receiving clinical trial-recommended combined oral anticoagulants plus single antiplatelet therapy (OR, 0.91; P < .001).
“This article highlights the fact that in all aspects we need to pay attention that women receive as high-level, guideline-driven care as men,” Dr. Hsu said.
First author Dr. Darden pointed out in an email that women suffer disproportionately from atrial fibrillation (AFib), compared with men, with worse quality of life and higher risk for stroke. So “it’s only natural to seek further treatment in order to decrease that risk, specifically LAAO with Watchman.”
Despite the fact that women are known to be at greater risk for adverse events after invasive procedures, including AFib ablation and TAVR, little is known about sex differences with LAAO, as the LAAO clinical trials only included about 30% women, he said.
Two 2021 papers zeroing in on these sex differences produced mixed results. An American report in roughly 9,200 patients reported a higher risk for major in-hospital events in women after receipt of Watchman implants, whereas a German report found similar safety and efficacy among 387 consecutive patients, regardless of sex.
The present study involved 20,388 women and 28,969 men implanted with the Watchman device between January 2016 and June 2019 in the NCDR registry, the largest LAAO registry with adjudicated events with participation mandated for Medicare coverage.
The women were older (mean age, 76.5 vs. 75.8 years), had a higher mean CHA2DS2-VASc score (5.3 vs. 4.5), and were more likely to have a high fall risk as an indication for LAAO (39.8% vs. 33.5%).
Furthermore, women were more likely than men to have paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and uncontrolled hypertension, but less likely to have congestive heart failure, diabetes, and coronary artery disease.
After multivariable adjustment, all but one of the primary outcomes was significantly worse in women versus men:
- Aborted or canceled procedure: 3.0% vs. 2.9% (OR, 1.01; P = .87)
- Any adverse event: 6.3% vs. 3.9% (OR, 1.63; P < .001)
- Major adverse event: 4.1% vs. 2.0% (OR, 2.06; P < .001)
- Hospital stay more than 1 day: 16.0% vs. 11.6% (OR, 1.46; P < .001)
- Death: 58/0.3% vs. 37/0.1% (OR, 2.01; P = .001).
The authors point out that device-related adverse events are lower than in the PROTECT-AF and PREVAIL clinical trials of the Watchman, with 0.8% of patients developing a pericardial effusion requiring drainage and 1.2% having major bleeding, down from highs of 4.8% and 3.5%, respectively, in PROTECT-AF.
Although promising overall, adverse events among women were driven by higher rates of both pericardial effusion requiring draining (1.2% vs. 0.5%; P < .001) and major bleeding (1.7% vs. 0.8%; P < .001).
Commenting for this news organization John Mandrola, MD, Baptist Health, Louisville, Kentucky, expressed concern that despite its increasing popularity, the rate of serious complications appears to be increasing for the preventive procedure. “That’s peculiar because you’d expect increased experience and device iterations to decrease complications. And the NCDR data surely undercounts the real rate of adverse events because it only includes in-hospital complications.”
Based on the current data, he observed that there’s a 3% chance for a major complication overall, with the typical female Watchman patient facing a 6% chance of any adverse event and 4% risk for a major adverse event during her hospital stay alone.
“The striking difference in complications in women is a super important observation because higher upfront risk has an even more negative effect on the harm-benefit calculus of this procedure,” Dr. Mandrola said.
“Some of the increased harm in women may have been due to the slightly higher rate of comorbid conditions, but that is real-life,” he said. “Registry data like this is extremely valuable because, unlike the carefully selected randomized trial, registries reflect what is actually being done in practice.”
Dr. Hsu agreed that the absolute numbers are concerning. Nevertheless, “it doesn’t necessarily sound an alarm that our adverse events are worse in contemporary practice or that adverse events continue to increase. But, in general, it just points to the fact that there is this inherent larger risk in women, compared with men, and that we need to, first, figure out why, and second, we need to figure out how to improve.”
Strategies to mitigate procedural risk included ultrasound-guided venous access, preprocedural imaging, improved proficiency with LAAO devices, and continued development of safer devices, they note.
Despite the more generalizable nature of registry data, “the results of this study should not result in differing sex-based thresholds for LAAO implant,” the authors conclude.
The study was supported by the American College of Cardiology Foundation’s NCDR. Dr. Hsu reports financial relationships with Medtronic, Boston Scientific, Abbott, Biotronik, Janssen Pharmaceutical, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, Biosense Webster, Altathera Pharmaceuticals, and Zoll Medical and holding equity interest in Acutus Medical and Vektor Medical outside the submitted work. Dr. Darden reports no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Mandrola is a regular contributor to Medscape Cardiology.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tachycardia syndrome may be distinct marker for long COVID
Tachycardia is commonly reported in patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS), also known as long COVID, authors report in a new article. The researchers say tachycardia syndrome should be considered a distinct phenotype.
The study by Marcus Ståhlberg, MD, PhD, of Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, and colleagues was published online August 11 in The American Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Ståhlberg told this news organization that although much attention has been paid to cases of clotting and perimyocarditis in patients after COVID, relatively little attention has been paid to tachycardia, despite case reports that show that palpitations are a common complaint.
“We have diagnosed a large number of patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome [POTS] and other forms of COVID-related tachycardia at our post-COVID outpatient clinic at Karolinska University Hospital and wanted to highlight this phenomenon,” he said.
Between 25% and 50% of patients at the clinic report tachycardia and/or palpitations that last 12 weeks or longer, the authors report.
“Systematic investigations suggest that 9% of Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome patients report palpitations at six months,” the authors write.
The findings also shed light on potential tests and treatments, he said.
“Physicians should be liberal in performing a basic cardiological workup, including an ECG [electrocardiogram], echocardiography, and Holter ECG monitoring in patients complaining of palpitations and/or chest pain,” Dr. Ståhlberg said.
“If orthostatic intolerance is also reported – such as vertigo, nausea, dyspnea – suspicion of POTS should be raised and a head-up tilt test or at least an active standing test should be performed,” he said.
If POTS is confirmed, he said, patients should be offered a heart rate–lowering drug, such as low-dose propranolol or ivabradine. Compression garments, increased fluid intake, and a structured rehabilitation program also help.
“According to our clinical experience, ivabradine can also reduce symptoms in patients with inappropriate sinus tachycardia and post-COVID,” Dr. Ståhlberg said. “Another finding on Holter-ECG to look out for is frequent premature extrasystoles, which could indicate myocarditis and should warrant a cardiac MRI.”
Dr. Ståhlberg said the researchers think the mechanism underlying the tachycardia is autoimmune and that primary SARS-CoV-2 infections trigger an autoimmune response with formation of autoantibodies that can activate receptors regulating blood pressure and heart rate.
Long-lasting symptoms from COVID are prevalent, the authors note, especially in patients who experienced severe forms of the disease.
In the longest follow-up study to date of patients hospitalized with COVID, more than 60% experienced fatigue or muscle weakness 6 months after hospitalization.
PACS should not be considered a single syndrome; the term denotes an array of subsyndromes and phenotypes, the authors write. Typical symptoms include headache, fatigue, dyspnea, and mental fog but can involve multiple organs and systems.
Tachycardia can also be used as a marker to help gauge the severity of long COVID, the authors write.
“[T]achycardia can be considered a universal and easily obtainable quantitative marker of Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and its severity rather than patient-reported symptoms, blood testing, and thoracic CT-scans,” they write.
An underrecognized complication
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, director of women’s cardiovascular health and associate director of preventive cardiology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview that she has seen many similar symptoms in the long-COVID patients referred to her practice.
Dr. Michos, who is also an associate professor of medicine and epidemiology, said she’s been receiving a “huge number” of referrals of long-COVID patients with postural tachycardia, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and POTS.
“I think this is all in the spectrum of autonomic dysfunction that has been recognized a lot since COVID. POTS has been thought to have [a potentially] viral cause that triggers an autoimmune response. Even before COVID, many patients had POTS triggered by a viral infection. The question is whether COVID-related POTS for long COVID is different from other kinds of POTS.”
She says she treats long-COVID patients who complain of elevated heart rates with many of the cardiac workup procedures the authors list and that she treats them in a way similar to the way she treats patients with POTS.
She recommends checking resting oxygen levels and having patients walk the halls and measure their oxygen levels after walking, because their elevated heart rate may be related to ongoing lung injury from COVID.
Eric Adler, MD, a cardiologist with University of San Diego Health, told this news organization that the findings by Dr. Ståhlberg and colleagues are consistent with what he’s seeing in his clinical practice.
Dr. Adler agrees with the authors that tachycardia is an underrecognized complication of long COVID.
He said the article represents further proof that though people may survive COVID, the threat of long-term symptoms, such as heart palpitations, is real and supports the case for vaccinations.
The authors, Dr. Michos, and Dr. Adler have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tachycardia is commonly reported in patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS), also known as long COVID, authors report in a new article. The researchers say tachycardia syndrome should be considered a distinct phenotype.
The study by Marcus Ståhlberg, MD, PhD, of Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, and colleagues was published online August 11 in The American Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Ståhlberg told this news organization that although much attention has been paid to cases of clotting and perimyocarditis in patients after COVID, relatively little attention has been paid to tachycardia, despite case reports that show that palpitations are a common complaint.
“We have diagnosed a large number of patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome [POTS] and other forms of COVID-related tachycardia at our post-COVID outpatient clinic at Karolinska University Hospital and wanted to highlight this phenomenon,” he said.
Between 25% and 50% of patients at the clinic report tachycardia and/or palpitations that last 12 weeks or longer, the authors report.
“Systematic investigations suggest that 9% of Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome patients report palpitations at six months,” the authors write.
The findings also shed light on potential tests and treatments, he said.
“Physicians should be liberal in performing a basic cardiological workup, including an ECG [electrocardiogram], echocardiography, and Holter ECG monitoring in patients complaining of palpitations and/or chest pain,” Dr. Ståhlberg said.
“If orthostatic intolerance is also reported – such as vertigo, nausea, dyspnea – suspicion of POTS should be raised and a head-up tilt test or at least an active standing test should be performed,” he said.
If POTS is confirmed, he said, patients should be offered a heart rate–lowering drug, such as low-dose propranolol or ivabradine. Compression garments, increased fluid intake, and a structured rehabilitation program also help.
“According to our clinical experience, ivabradine can also reduce symptoms in patients with inappropriate sinus tachycardia and post-COVID,” Dr. Ståhlberg said. “Another finding on Holter-ECG to look out for is frequent premature extrasystoles, which could indicate myocarditis and should warrant a cardiac MRI.”
Dr. Ståhlberg said the researchers think the mechanism underlying the tachycardia is autoimmune and that primary SARS-CoV-2 infections trigger an autoimmune response with formation of autoantibodies that can activate receptors regulating blood pressure and heart rate.
Long-lasting symptoms from COVID are prevalent, the authors note, especially in patients who experienced severe forms of the disease.
In the longest follow-up study to date of patients hospitalized with COVID, more than 60% experienced fatigue or muscle weakness 6 months after hospitalization.
PACS should not be considered a single syndrome; the term denotes an array of subsyndromes and phenotypes, the authors write. Typical symptoms include headache, fatigue, dyspnea, and mental fog but can involve multiple organs and systems.
Tachycardia can also be used as a marker to help gauge the severity of long COVID, the authors write.
“[T]achycardia can be considered a universal and easily obtainable quantitative marker of Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and its severity rather than patient-reported symptoms, blood testing, and thoracic CT-scans,” they write.
An underrecognized complication
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, director of women’s cardiovascular health and associate director of preventive cardiology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview that she has seen many similar symptoms in the long-COVID patients referred to her practice.
Dr. Michos, who is also an associate professor of medicine and epidemiology, said she’s been receiving a “huge number” of referrals of long-COVID patients with postural tachycardia, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and POTS.
“I think this is all in the spectrum of autonomic dysfunction that has been recognized a lot since COVID. POTS has been thought to have [a potentially] viral cause that triggers an autoimmune response. Even before COVID, many patients had POTS triggered by a viral infection. The question is whether COVID-related POTS for long COVID is different from other kinds of POTS.”
She says she treats long-COVID patients who complain of elevated heart rates with many of the cardiac workup procedures the authors list and that she treats them in a way similar to the way she treats patients with POTS.
She recommends checking resting oxygen levels and having patients walk the halls and measure their oxygen levels after walking, because their elevated heart rate may be related to ongoing lung injury from COVID.
Eric Adler, MD, a cardiologist with University of San Diego Health, told this news organization that the findings by Dr. Ståhlberg and colleagues are consistent with what he’s seeing in his clinical practice.
Dr. Adler agrees with the authors that tachycardia is an underrecognized complication of long COVID.
He said the article represents further proof that though people may survive COVID, the threat of long-term symptoms, such as heart palpitations, is real and supports the case for vaccinations.
The authors, Dr. Michos, and Dr. Adler have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Tachycardia is commonly reported in patients with post-acute COVID-19 syndrome (PACS), also known as long COVID, authors report in a new article. The researchers say tachycardia syndrome should be considered a distinct phenotype.
The study by Marcus Ståhlberg, MD, PhD, of Karolinska University Hospital, Stockholm, and colleagues was published online August 11 in The American Journal of Medicine.
Dr. Ståhlberg told this news organization that although much attention has been paid to cases of clotting and perimyocarditis in patients after COVID, relatively little attention has been paid to tachycardia, despite case reports that show that palpitations are a common complaint.
“We have diagnosed a large number of patients with postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome [POTS] and other forms of COVID-related tachycardia at our post-COVID outpatient clinic at Karolinska University Hospital and wanted to highlight this phenomenon,” he said.
Between 25% and 50% of patients at the clinic report tachycardia and/or palpitations that last 12 weeks or longer, the authors report.
“Systematic investigations suggest that 9% of Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome patients report palpitations at six months,” the authors write.
The findings also shed light on potential tests and treatments, he said.
“Physicians should be liberal in performing a basic cardiological workup, including an ECG [electrocardiogram], echocardiography, and Holter ECG monitoring in patients complaining of palpitations and/or chest pain,” Dr. Ståhlberg said.
“If orthostatic intolerance is also reported – such as vertigo, nausea, dyspnea – suspicion of POTS should be raised and a head-up tilt test or at least an active standing test should be performed,” he said.
If POTS is confirmed, he said, patients should be offered a heart rate–lowering drug, such as low-dose propranolol or ivabradine. Compression garments, increased fluid intake, and a structured rehabilitation program also help.
“According to our clinical experience, ivabradine can also reduce symptoms in patients with inappropriate sinus tachycardia and post-COVID,” Dr. Ståhlberg said. “Another finding on Holter-ECG to look out for is frequent premature extrasystoles, which could indicate myocarditis and should warrant a cardiac MRI.”
Dr. Ståhlberg said the researchers think the mechanism underlying the tachycardia is autoimmune and that primary SARS-CoV-2 infections trigger an autoimmune response with formation of autoantibodies that can activate receptors regulating blood pressure and heart rate.
Long-lasting symptoms from COVID are prevalent, the authors note, especially in patients who experienced severe forms of the disease.
In the longest follow-up study to date of patients hospitalized with COVID, more than 60% experienced fatigue or muscle weakness 6 months after hospitalization.
PACS should not be considered a single syndrome; the term denotes an array of subsyndromes and phenotypes, the authors write. Typical symptoms include headache, fatigue, dyspnea, and mental fog but can involve multiple organs and systems.
Tachycardia can also be used as a marker to help gauge the severity of long COVID, the authors write.
“[T]achycardia can be considered a universal and easily obtainable quantitative marker of Post-acute COVID-19 syndrome and its severity rather than patient-reported symptoms, blood testing, and thoracic CT-scans,” they write.
An underrecognized complication
Erin D. Michos, MD, MHS, director of women’s cardiovascular health and associate director of preventive cardiology at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, said in an interview that she has seen many similar symptoms in the long-COVID patients referred to her practice.
Dr. Michos, who is also an associate professor of medicine and epidemiology, said she’s been receiving a “huge number” of referrals of long-COVID patients with postural tachycardia, inappropriate sinus tachycardia, and POTS.
“I think this is all in the spectrum of autonomic dysfunction that has been recognized a lot since COVID. POTS has been thought to have [a potentially] viral cause that triggers an autoimmune response. Even before COVID, many patients had POTS triggered by a viral infection. The question is whether COVID-related POTS for long COVID is different from other kinds of POTS.”
She says she treats long-COVID patients who complain of elevated heart rates with many of the cardiac workup procedures the authors list and that she treats them in a way similar to the way she treats patients with POTS.
She recommends checking resting oxygen levels and having patients walk the halls and measure their oxygen levels after walking, because their elevated heart rate may be related to ongoing lung injury from COVID.
Eric Adler, MD, a cardiologist with University of San Diego Health, told this news organization that the findings by Dr. Ståhlberg and colleagues are consistent with what he’s seeing in his clinical practice.
Dr. Adler agrees with the authors that tachycardia is an underrecognized complication of long COVID.
He said the article represents further proof that though people may survive COVID, the threat of long-term symptoms, such as heart palpitations, is real and supports the case for vaccinations.
The authors, Dr. Michos, and Dr. Adler have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.








