User login
2019 at a glance: Hem-onc U.S. drug approvals
The rapid development and identification of novel drugs has translated into innovative therapies in hematology and oncology. The aim of this piece is to present newly approved drugs and expanded indications to serve as a reference guide for practicing clinicians.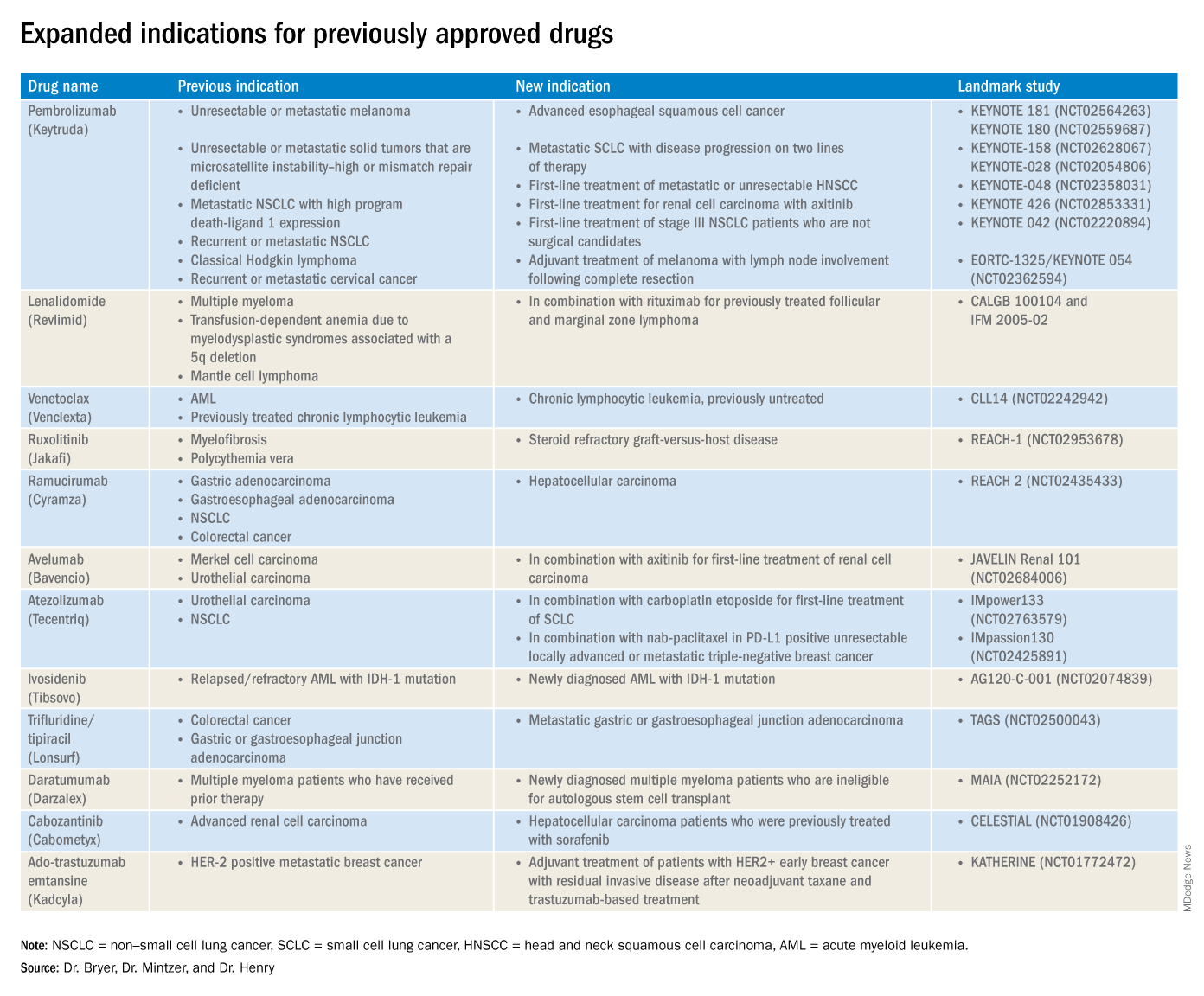
This article reviews therapies that were newly approved so far in 2019, as well as those previously approved whose indications were expanded this past year. The list highlights the most clinically important approvals, as well as adverse events that are unique or especially severe.
New approvals
Fedratinib (Inrebic)
Class: JAK2 and FLT3 selective kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary (postpolycythemia vera or postessential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis.
Dose: 400 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
Adverse events (AEs): Black box warning: Fatal encephalopathy, including Wernicke’s (thiamine level monitoring suggested).
Trials: In JAKARTA (NCT01437787), 37% of patients achieved a 35% or greater reduction in spleen volume and 40% received a 50% or greater reduction in myelofibrosis-related symptoms. In Jakarta-2, there was a 55% spleen response in patients resistant or intolerant to ruxolitinib.
Entrectinib (Rozlytrek)
Class: Tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Solid tumors that have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion and for ROS-1 positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Dose: 600 mg orally once daily.
AEs: Heart failure, QT prolongation, skeletal fractures, hepatotoxicity, central nervous system effects, and hyperuricemia.
Trial: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267): Overall response rate of 57% for NTRK positive patients; response rate of 77% in ROS-1 positive NSCLC.
Pexidartinib (Turalio)
Class: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R.
Disease: Symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor.
Dose: 400 mg orally twice daily without food.
AEs: Black box warning on hepatotoxicity.
Trial: ENLIVEN (NCT02371369): Overall response rate of 38% at 25 weeks, with a 15% complete response rate and a 23% partial response rate.
Darolutamide (Nubeqa)
Class: Androgen receptor inhibitor.
Disease: Nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dose: 600 mg orally twice daily with food with concomitant androgen deprivation therapy.
AEs: Fatigue, extremity pain, and rash.
Trial: ARAMIS (NCT02200614): Median metastasis free survival was 40.4 months for patients with darolutamide, compared with 18.4 months for controls.
Selinexor (Xpovio)
Class: Reversible inhibitor of nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins, growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Indicated for patients who have received at least four prior therapies, including at least two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Dose: 80 mg orally in combination with oral dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
AEs: Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, pancytopenia, and hyponatremia.
Trial: STORM (NCT02336815): Overall response rate 25.3% with a median time to first response of 4 weeks and 3.8-month median duration of response.
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy)
Class: CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Indicated for patients who have had at least two prior therapies.
Dose: 1.8 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product.
AEs: Pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy.
Trial: GO29365 (NCT02257567): Complete response rate was 40% for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq plus bendamustine/rituximab, compared with 18% with bendamustine/rituximab alone.*
Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi)
Class: Monoclonal antibody fragment directed against von Willebrand factor.
Disease: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Dose: 11 mg IV initially, then daily subcutaneously; in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
AEs: Epistaxis, headache, and gingival bleeding.
Trial: Hercules trial (NCT02553317): More rapid normalization of platelets, lower incidence of composite TTP-related death, and lower rate of recurrence when added to plasma exchange and steroids.
Alpelisib (Piqray)
Class: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
Disease: Hormone receptor positive HER2-negative PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Dose: 300 mg orally once daily with food with concomitant fulvestrant.
AEs: Hyperglycemia, pancytopenia.
Trial: SOLAR-1 (NCT02437318): 11-month progression-free survival among patients treated with alpelisib and fulvestrant, compared with 5.7 months in fulvestrant alone control arm; overall response rate of 36% versus 16%, respectively.
Erdafitinib (Balversa)
Class: Fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutations.
Dose: 8 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
AEs: Ocular disorders including retinopathy or retinal detachment.
Trial: BLC2001 (NCT02365597): Objective response rate of 32.2%, with a complete response in 2.3% of patients and partial response in 29.9% of patients.
Biosimilar approvals
Trastuzumab and hyaluronidase-oysk (Herceptin Hylecta)
Biosimilar to: Trastuzumab.
Indication: HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Dr. Bryer is a resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Mintzer is chief of hematology-oncology at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Henry is a hematologist-oncologist at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
*Correction, 11/7/2019: An earlier version of this article misstated the drug combination in the GO29365 trial.
The rapid development and identification of novel drugs has translated into innovative therapies in hematology and oncology. The aim of this piece is to present newly approved drugs and expanded indications to serve as a reference guide for practicing clinicians.
This article reviews therapies that were newly approved so far in 2019, as well as those previously approved whose indications were expanded this past year. The list highlights the most clinically important approvals, as well as adverse events that are unique or especially severe.
New approvals
Fedratinib (Inrebic)
Class: JAK2 and FLT3 selective kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary (postpolycythemia vera or postessential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis.
Dose: 400 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
Adverse events (AEs): Black box warning: Fatal encephalopathy, including Wernicke’s (thiamine level monitoring suggested).
Trials: In JAKARTA (NCT01437787), 37% of patients achieved a 35% or greater reduction in spleen volume and 40% received a 50% or greater reduction in myelofibrosis-related symptoms. In Jakarta-2, there was a 55% spleen response in patients resistant or intolerant to ruxolitinib.
Entrectinib (Rozlytrek)
Class: Tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Solid tumors that have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion and for ROS-1 positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Dose: 600 mg orally once daily.
AEs: Heart failure, QT prolongation, skeletal fractures, hepatotoxicity, central nervous system effects, and hyperuricemia.
Trial: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267): Overall response rate of 57% for NTRK positive patients; response rate of 77% in ROS-1 positive NSCLC.
Pexidartinib (Turalio)
Class: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R.
Disease: Symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor.
Dose: 400 mg orally twice daily without food.
AEs: Black box warning on hepatotoxicity.
Trial: ENLIVEN (NCT02371369): Overall response rate of 38% at 25 weeks, with a 15% complete response rate and a 23% partial response rate.
Darolutamide (Nubeqa)
Class: Androgen receptor inhibitor.
Disease: Nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dose: 600 mg orally twice daily with food with concomitant androgen deprivation therapy.
AEs: Fatigue, extremity pain, and rash.
Trial: ARAMIS (NCT02200614): Median metastasis free survival was 40.4 months for patients with darolutamide, compared with 18.4 months for controls.
Selinexor (Xpovio)
Class: Reversible inhibitor of nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins, growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Indicated for patients who have received at least four prior therapies, including at least two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Dose: 80 mg orally in combination with oral dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
AEs: Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, pancytopenia, and hyponatremia.
Trial: STORM (NCT02336815): Overall response rate 25.3% with a median time to first response of 4 weeks and 3.8-month median duration of response.
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy)
Class: CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Indicated for patients who have had at least two prior therapies.
Dose: 1.8 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product.
AEs: Pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy.
Trial: GO29365 (NCT02257567): Complete response rate was 40% for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq plus bendamustine/rituximab, compared with 18% with bendamustine/rituximab alone.*
Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi)
Class: Monoclonal antibody fragment directed against von Willebrand factor.
Disease: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Dose: 11 mg IV initially, then daily subcutaneously; in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
AEs: Epistaxis, headache, and gingival bleeding.
Trial: Hercules trial (NCT02553317): More rapid normalization of platelets, lower incidence of composite TTP-related death, and lower rate of recurrence when added to plasma exchange and steroids.
Alpelisib (Piqray)
Class: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
Disease: Hormone receptor positive HER2-negative PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Dose: 300 mg orally once daily with food with concomitant fulvestrant.
AEs: Hyperglycemia, pancytopenia.
Trial: SOLAR-1 (NCT02437318): 11-month progression-free survival among patients treated with alpelisib and fulvestrant, compared with 5.7 months in fulvestrant alone control arm; overall response rate of 36% versus 16%, respectively.
Erdafitinib (Balversa)
Class: Fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutations.
Dose: 8 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
AEs: Ocular disorders including retinopathy or retinal detachment.
Trial: BLC2001 (NCT02365597): Objective response rate of 32.2%, with a complete response in 2.3% of patients and partial response in 29.9% of patients.
Biosimilar approvals
Trastuzumab and hyaluronidase-oysk (Herceptin Hylecta)
Biosimilar to: Trastuzumab.
Indication: HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Dr. Bryer is a resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Mintzer is chief of hematology-oncology at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Henry is a hematologist-oncologist at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
*Correction, 11/7/2019: An earlier version of this article misstated the drug combination in the GO29365 trial.
The rapid development and identification of novel drugs has translated into innovative therapies in hematology and oncology. The aim of this piece is to present newly approved drugs and expanded indications to serve as a reference guide for practicing clinicians.
This article reviews therapies that were newly approved so far in 2019, as well as those previously approved whose indications were expanded this past year. The list highlights the most clinically important approvals, as well as adverse events that are unique or especially severe.
New approvals
Fedratinib (Inrebic)
Class: JAK2 and FLT3 selective kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Intermediate or high-risk primary or secondary (postpolycythemia vera or postessential thrombocythemia) myelofibrosis.
Dose: 400 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
Adverse events (AEs): Black box warning: Fatal encephalopathy, including Wernicke’s (thiamine level monitoring suggested).
Trials: In JAKARTA (NCT01437787), 37% of patients achieved a 35% or greater reduction in spleen volume and 40% received a 50% or greater reduction in myelofibrosis-related symptoms. In Jakarta-2, there was a 55% spleen response in patients resistant or intolerant to ruxolitinib.
Entrectinib (Rozlytrek)
Class: Tropomyosin receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Solid tumors that have a neurotrophic tyrosine receptor kinase (NTRK) gene fusion and for ROS-1 positive non–small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Dose: 600 mg orally once daily.
AEs: Heart failure, QT prolongation, skeletal fractures, hepatotoxicity, central nervous system effects, and hyperuricemia.
Trial: ALKA, STARTRK-1 (NCT02097810) and STARTRK-2 (NCT02568267): Overall response rate of 57% for NTRK positive patients; response rate of 77% in ROS-1 positive NSCLC.
Pexidartinib (Turalio)
Class: Small molecule tyrosine kinase inhibitor targeting CSF1R.
Disease: Symptomatic tenosynovial giant cell tumor.
Dose: 400 mg orally twice daily without food.
AEs: Black box warning on hepatotoxicity.
Trial: ENLIVEN (NCT02371369): Overall response rate of 38% at 25 weeks, with a 15% complete response rate and a 23% partial response rate.
Darolutamide (Nubeqa)
Class: Androgen receptor inhibitor.
Disease: Nonmetastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer.
Dose: 600 mg orally twice daily with food with concomitant androgen deprivation therapy.
AEs: Fatigue, extremity pain, and rash.
Trial: ARAMIS (NCT02200614): Median metastasis free survival was 40.4 months for patients with darolutamide, compared with 18.4 months for controls.
Selinexor (Xpovio)
Class: Reversible inhibitor of nuclear export of tumor suppressor proteins, growth regulators, and mRNAs of oncogenic proteins.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory multiple myeloma. Indicated for patients who have received at least four prior therapies, including at least two immunomodulatory agents and an anti-CD38 monoclonal antibody.
Dose: 80 mg orally in combination with oral dexamethasone on days 1 and 3 of each week.
AEs: Thrombocytopenia, fatigue, pancytopenia, and hyponatremia.
Trial: STORM (NCT02336815): Overall response rate 25.3% with a median time to first response of 4 weeks and 3.8-month median duration of response.
Polatuzumab vedotin-piiq (Polivy)
Class: CD79b-directed antibody-drug conjugate.
Disease: Relapsed or refractory diffuse large B-cell lymphoma. Indicated for patients who have had at least two prior therapies.
Dose: 1.8 mg/kg intravenous infusion every 21 days for six cycles in combination with bendamustine and a rituximab product.
AEs: Pancytopenia, peripheral neuropathy.
Trial: GO29365 (NCT02257567): Complete response rate was 40% for polatuzumab vedotin-piiq plus bendamustine/rituximab, compared with 18% with bendamustine/rituximab alone.*
Caplacizumab-yhdp (Cablivi)
Class: Monoclonal antibody fragment directed against von Willebrand factor.
Disease: Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura.
Dose: 11 mg IV initially, then daily subcutaneously; in combination with plasma exchange and immunosuppressive therapy.
AEs: Epistaxis, headache, and gingival bleeding.
Trial: Hercules trial (NCT02553317): More rapid normalization of platelets, lower incidence of composite TTP-related death, and lower rate of recurrence when added to plasma exchange and steroids.
Alpelisib (Piqray)
Class: Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitor.
Disease: Hormone receptor positive HER2-negative PIK3CA-mutated, advanced or metastatic breast cancer.
Dose: 300 mg orally once daily with food with concomitant fulvestrant.
AEs: Hyperglycemia, pancytopenia.
Trial: SOLAR-1 (NCT02437318): 11-month progression-free survival among patients treated with alpelisib and fulvestrant, compared with 5.7 months in fulvestrant alone control arm; overall response rate of 36% versus 16%, respectively.
Erdafitinib (Balversa)
Class: Fibroblast growth factor receptor kinase inhibitor.
Disease: Locally advanced or metastatic urothelial carcinoma with FGFR3 or FGFR2 mutations.
Dose: 8 mg orally once daily, with or without food.
AEs: Ocular disorders including retinopathy or retinal detachment.
Trial: BLC2001 (NCT02365597): Objective response rate of 32.2%, with a complete response in 2.3% of patients and partial response in 29.9% of patients.
Biosimilar approvals
Trastuzumab and hyaluronidase-oysk (Herceptin Hylecta)
Biosimilar to: Trastuzumab.
Indication: HER2-overexpressing breast cancer.
Dr. Bryer is a resident in the department of internal medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia. Dr. Mintzer is chief of hematology-oncology at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. Dr. Henry is a hematologist-oncologist at Pennsylvania Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of Pennsylvania.
*Correction, 11/7/2019: An earlier version of this article misstated the drug combination in the GO29365 trial.
Treat or treat
In Charles M. Schulz’s “It’s the Great Pumpkin, Charlie Brown,” the Peanuts gang goes trick or treating door to door. While everyone else gets candy, chewing gum, and chocolate bars, Charlie Brown just gets a bag of rocks. Everyone got treats except Charlie Brown, who only got tricks. Sometimes it seems that my patients are trick or treating, too. Sadly, the tricks come way too often.

Linus tried to avoid tricks by staking out a sincere pumpkin patch in the hope that the Great Pumpkin would rise and deliver him candy and toys. Alas, our patients sometimes sincerely believe things like alkalinization, naturopathy, and antineoplastons will deliver the treats they need to cure their cancer. They will be similarly disappointed.
Most patients depend on us to skew the treat to trick ratio favorably. They trust us to know what to recommend to lengthen life and reduce suffering. Their faith is both a profound privilege and a daunting responsibility.
My patient was hospitalized with hypercalcemia, the latest complication deriving from a decade of progressive multiple myeloma. He was on his 11th line of therapy complicated by at least a grade 3 neuropathy resulting in an unstable gait, chronic pain requiring opioid analgesia, two hospitalizations in the last year for severe infections, and venous thromboembolism on anticoagulation, all resulting in an ECOG performance status no better than a 2. He stabilized and then we needed to talk about next steps.
A clinical trial would be ideal, but he would be excluded from any that we have open and travel isn’t really an option for him. I could choose to treat him with selinexor. It is approved by the Food and Drug Administration and has about a one-in-four chance of producing a short remission in a population of patients that would not include my patient. It also has a three-in-four chance of significant side effects. I could also create a combination regimen with drugs that he has already been exposed to, knowing that response is unlikely and side effects are certain.
This situation is not unique; in fact it is an all too frequent occurrence. The easiest path forward for me would be to recommend treatment. The patient expects treatment and would readily consent to whatever regimen I proposed. He would bear whatever side effects resulted as an expected consequence of therapy. On the surface, this easy path appears to be the proverbial “treat.” But really, further treatment is the “trick” because it is not known to prolong life and would certainly add side effects. The problem, of course, is knowing both when treats become tricks and how to let patients know this, too.
No one knows exactly when treats become tricks, least of all me. Every month I get a report updating me on the status of a former patient being treated elsewhere. This is someone who I thought had no more treatment options. I am humbled every time a colleague, or fellow, recommends a treatment I had never considered. I am not perfect; I do the best I can. My recommendation might be wrong.
Yet I have watched my patient steadily deteriorate and cognitively decline no matter what treatment I employed, whether or not the monoclonal spike decreased. There is no evidence that treatment under such circumstances benefits the patient at all. Moreover, I have sat through many morbidity and mortality conferences where the conclusion was that we should have consulted hospice sooner. Like so many hematologists and oncologists every day, I needed to have a goals-of-care conversation with my patient knowing that treatment could possibly help, but probably would not.
Crucial conversations like these are difficult for everybody. There are techniques to employ that my palliative care colleagues recommend. I tried to remember them as I started talking to my patient and his wife. He listened and clearly understood the gravity of the situation and the resulting poor prognosis regardless of treatment. I recommended hospice. He declined.
Getting to this point was uncomfortable enough, but then I came to a decision that I am still struggling with – acquiesce to his wishes and treat while feeling that I should not, or decline to treat further and transfer his care to someone more willing? This is not the kind of trick or treat I enjoy.
I look forward to the day when discussions of end of life are less awkward. Small movements have started to bring these conversations into the open. One such movement choreographs a dinner to encourage frank and open discussion of death (https://deathoverdinner.org/). Another reimagines the doula – a childbirth coach – as a coach at the end of life (https://www.agentlerparting.com/). Another provides a step-by-step approach to generating an end-of-life conversation (https://theconversationproject.org/). These, and many other efforts, did not occur in a vacuum. They emerged because of the growing recognition that the modern delivery of health care, and the culture it created, is inadequate for the end of life.
Until our culture changes, though, we are left with tough conversations and tougher decisions with our patients who are at the end of their cancer journey. I wish I could tell my junior colleagues that it gets easier with experience. In many ways it gets worse because of the long relationships we develop. As long as the rewards of treats are greater than the disappointments of tricks, though, I will continue trick or treating in my white coat costume.
Dr. Kalaycio is editor in chief of Hematology News. He is a hematologist-oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute. Contact him at [email protected].
In Charles M. Schulz’s “It’s the Great Pumpkin, Charlie Brown,” the Peanuts gang goes trick or treating door to door. While everyone else gets candy, chewing gum, and chocolate bars, Charlie Brown just gets a bag of rocks. Everyone got treats except Charlie Brown, who only got tricks. Sometimes it seems that my patients are trick or treating, too. Sadly, the tricks come way too often.

Linus tried to avoid tricks by staking out a sincere pumpkin patch in the hope that the Great Pumpkin would rise and deliver him candy and toys. Alas, our patients sometimes sincerely believe things like alkalinization, naturopathy, and antineoplastons will deliver the treats they need to cure their cancer. They will be similarly disappointed.
Most patients depend on us to skew the treat to trick ratio favorably. They trust us to know what to recommend to lengthen life and reduce suffering. Their faith is both a profound privilege and a daunting responsibility.
My patient was hospitalized with hypercalcemia, the latest complication deriving from a decade of progressive multiple myeloma. He was on his 11th line of therapy complicated by at least a grade 3 neuropathy resulting in an unstable gait, chronic pain requiring opioid analgesia, two hospitalizations in the last year for severe infections, and venous thromboembolism on anticoagulation, all resulting in an ECOG performance status no better than a 2. He stabilized and then we needed to talk about next steps.
A clinical trial would be ideal, but he would be excluded from any that we have open and travel isn’t really an option for him. I could choose to treat him with selinexor. It is approved by the Food and Drug Administration and has about a one-in-four chance of producing a short remission in a population of patients that would not include my patient. It also has a three-in-four chance of significant side effects. I could also create a combination regimen with drugs that he has already been exposed to, knowing that response is unlikely and side effects are certain.
This situation is not unique; in fact it is an all too frequent occurrence. The easiest path forward for me would be to recommend treatment. The patient expects treatment and would readily consent to whatever regimen I proposed. He would bear whatever side effects resulted as an expected consequence of therapy. On the surface, this easy path appears to be the proverbial “treat.” But really, further treatment is the “trick” because it is not known to prolong life and would certainly add side effects. The problem, of course, is knowing both when treats become tricks and how to let patients know this, too.
No one knows exactly when treats become tricks, least of all me. Every month I get a report updating me on the status of a former patient being treated elsewhere. This is someone who I thought had no more treatment options. I am humbled every time a colleague, or fellow, recommends a treatment I had never considered. I am not perfect; I do the best I can. My recommendation might be wrong.
Yet I have watched my patient steadily deteriorate and cognitively decline no matter what treatment I employed, whether or not the monoclonal spike decreased. There is no evidence that treatment under such circumstances benefits the patient at all. Moreover, I have sat through many morbidity and mortality conferences where the conclusion was that we should have consulted hospice sooner. Like so many hematologists and oncologists every day, I needed to have a goals-of-care conversation with my patient knowing that treatment could possibly help, but probably would not.
Crucial conversations like these are difficult for everybody. There are techniques to employ that my palliative care colleagues recommend. I tried to remember them as I started talking to my patient and his wife. He listened and clearly understood the gravity of the situation and the resulting poor prognosis regardless of treatment. I recommended hospice. He declined.
Getting to this point was uncomfortable enough, but then I came to a decision that I am still struggling with – acquiesce to his wishes and treat while feeling that I should not, or decline to treat further and transfer his care to someone more willing? This is not the kind of trick or treat I enjoy.
I look forward to the day when discussions of end of life are less awkward. Small movements have started to bring these conversations into the open. One such movement choreographs a dinner to encourage frank and open discussion of death (https://deathoverdinner.org/). Another reimagines the doula – a childbirth coach – as a coach at the end of life (https://www.agentlerparting.com/). Another provides a step-by-step approach to generating an end-of-life conversation (https://theconversationproject.org/). These, and many other efforts, did not occur in a vacuum. They emerged because of the growing recognition that the modern delivery of health care, and the culture it created, is inadequate for the end of life.
Until our culture changes, though, we are left with tough conversations and tougher decisions with our patients who are at the end of their cancer journey. I wish I could tell my junior colleagues that it gets easier with experience. In many ways it gets worse because of the long relationships we develop. As long as the rewards of treats are greater than the disappointments of tricks, though, I will continue trick or treating in my white coat costume.
Dr. Kalaycio is editor in chief of Hematology News. He is a hematologist-oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute. Contact him at [email protected].
In Charles M. Schulz’s “It’s the Great Pumpkin, Charlie Brown,” the Peanuts gang goes trick or treating door to door. While everyone else gets candy, chewing gum, and chocolate bars, Charlie Brown just gets a bag of rocks. Everyone got treats except Charlie Brown, who only got tricks. Sometimes it seems that my patients are trick or treating, too. Sadly, the tricks come way too often.

Linus tried to avoid tricks by staking out a sincere pumpkin patch in the hope that the Great Pumpkin would rise and deliver him candy and toys. Alas, our patients sometimes sincerely believe things like alkalinization, naturopathy, and antineoplastons will deliver the treats they need to cure their cancer. They will be similarly disappointed.
Most patients depend on us to skew the treat to trick ratio favorably. They trust us to know what to recommend to lengthen life and reduce suffering. Their faith is both a profound privilege and a daunting responsibility.
My patient was hospitalized with hypercalcemia, the latest complication deriving from a decade of progressive multiple myeloma. He was on his 11th line of therapy complicated by at least a grade 3 neuropathy resulting in an unstable gait, chronic pain requiring opioid analgesia, two hospitalizations in the last year for severe infections, and venous thromboembolism on anticoagulation, all resulting in an ECOG performance status no better than a 2. He stabilized and then we needed to talk about next steps.
A clinical trial would be ideal, but he would be excluded from any that we have open and travel isn’t really an option for him. I could choose to treat him with selinexor. It is approved by the Food and Drug Administration and has about a one-in-four chance of producing a short remission in a population of patients that would not include my patient. It also has a three-in-four chance of significant side effects. I could also create a combination regimen with drugs that he has already been exposed to, knowing that response is unlikely and side effects are certain.
This situation is not unique; in fact it is an all too frequent occurrence. The easiest path forward for me would be to recommend treatment. The patient expects treatment and would readily consent to whatever regimen I proposed. He would bear whatever side effects resulted as an expected consequence of therapy. On the surface, this easy path appears to be the proverbial “treat.” But really, further treatment is the “trick” because it is not known to prolong life and would certainly add side effects. The problem, of course, is knowing both when treats become tricks and how to let patients know this, too.
No one knows exactly when treats become tricks, least of all me. Every month I get a report updating me on the status of a former patient being treated elsewhere. This is someone who I thought had no more treatment options. I am humbled every time a colleague, or fellow, recommends a treatment I had never considered. I am not perfect; I do the best I can. My recommendation might be wrong.
Yet I have watched my patient steadily deteriorate and cognitively decline no matter what treatment I employed, whether or not the monoclonal spike decreased. There is no evidence that treatment under such circumstances benefits the patient at all. Moreover, I have sat through many morbidity and mortality conferences where the conclusion was that we should have consulted hospice sooner. Like so many hematologists and oncologists every day, I needed to have a goals-of-care conversation with my patient knowing that treatment could possibly help, but probably would not.
Crucial conversations like these are difficult for everybody. There are techniques to employ that my palliative care colleagues recommend. I tried to remember them as I started talking to my patient and his wife. He listened and clearly understood the gravity of the situation and the resulting poor prognosis regardless of treatment. I recommended hospice. He declined.
Getting to this point was uncomfortable enough, but then I came to a decision that I am still struggling with – acquiesce to his wishes and treat while feeling that I should not, or decline to treat further and transfer his care to someone more willing? This is not the kind of trick or treat I enjoy.
I look forward to the day when discussions of end of life are less awkward. Small movements have started to bring these conversations into the open. One such movement choreographs a dinner to encourage frank and open discussion of death (https://deathoverdinner.org/). Another reimagines the doula – a childbirth coach – as a coach at the end of life (https://www.agentlerparting.com/). Another provides a step-by-step approach to generating an end-of-life conversation (https://theconversationproject.org/). These, and many other efforts, did not occur in a vacuum. They emerged because of the growing recognition that the modern delivery of health care, and the culture it created, is inadequate for the end of life.
Until our culture changes, though, we are left with tough conversations and tougher decisions with our patients who are at the end of their cancer journey. I wish I could tell my junior colleagues that it gets easier with experience. In many ways it gets worse because of the long relationships we develop. As long as the rewards of treats are greater than the disappointments of tricks, though, I will continue trick or treating in my white coat costume.
Dr. Kalaycio is editor in chief of Hematology News. He is a hematologist-oncologist at the Cleveland Clinic Taussig Cancer Institute. Contact him at [email protected].
‘Time lost is brain lost’
Question: Which of the following statements regarding “common knowledge” is correct?
A. In any negligence action absent common knowledge, expert testimony is then required to prove requisite standard of care and causation.
B.
C. An expert is needed in the first place to establish whether something constitutes common knowledge.
D. The jury is the one who determines whether a plaintiff can invoke the common knowledge exception.
E. An example of common knowledge in malpractice law is where a delay in stroke diagnosis results in loss of brain function.
Answer: B. The judge, not the jury or anyone else, makes the decision regarding res ipsa loquitur (the thing speaks for itself) or common knowledge, which exempts a plaintiff from producing an expert witness to testify as to the standard of care and causation. However, this is only true in actions arising out of professional negligence such as medical malpractice, whereas most common negligence actions – for example, slips and falls – do not require expert testimony.
Only a professional, duly qualified by the court as an expert witness, is allowed to offer medical testimony, while the plaintiff will typically be disqualified from playing this role because of the complexity of issues involved unless there is common knowledge. In general, courts are reluctant to grant this exception, which favors the plaintiff.
The best example of res ipsa loquitur is where a surgeon inadvertently leaves behind a sponge or instrument inside a body cavity. Other successfully litigated examples include cardiac arrest in the operating room, hypoxia in the recovery room, burns to the buttock, gangrene after the accidental injection of penicillin into an artery, air trapped subcutaneously from a displaced needle, and a pierced eyeball during a procedure. The factual circumstances of each case are critical to its outcome. For example, in a 2013 New York case, the plaintiff was barred from using the res doctrine.1 The defendant doctor had left a guide wire in the plaintiff’s chest following a biopsy and retrieved it 2 months later. The plaintiff did not call any expert witness, relying instead on the “foreign object” basis for invoking the res doctrine. However, the Court of Appeals reasoned that the object was left behind deliberately, not unintentionally, and that under the circumstances of the case, an expert witness was needed to set out the applicable standard of care, without which a jury could not determine whether the doctor’s professional judgment breached the requisite standard.
The Supreme Court of Kentucky recently rejected the use of common knowledge in a stroke case.2 In 2010, David Shackelford’s rheumatologist referred him to Paul Lewis, MD, an interventional radiologist, for a four-vessel cerebral angiogram to assist with diagnosing the cause of Mr. Shackelford’s chronic headaches. The procedure itself was uneventful, but while in the recovery room, Mr. Shackelford reported a frontal headache and scotoma, which resolved on its own. The headache improved with medication, and the patient experienced no other symptoms. There were no other visual changes, weakness, slurred speech, or facial palsies. Mr. Shackelford was discharged but had to return to the hospital the next morning via ambulance after becoming disoriented at his home. An MRI indicated multiple scattered small infarcts, and he was left with residual short-term memory loss and visual problems.
There was no allegation that the stroke itself was caused by negligence; rather, Mr. Shackelford alleged that the failure to examine and diagnose the stroke after the angiogram was negligent and caused injury greater than that which the stroke would have caused with earlier intervention. To support his claims, Mr. Shackelford’s expert, Michael David Khoury, MD, a vascular surgeon, criticized Dr. Lewis’s failure to examine Mr. Shackelford when his symptoms were consistent with a stroke. However, Dr. Khoury did not opine that Dr. Lewis could have limited the effects of the stroke through earlier intervention. When asked specifically whether he could state within a reasonable degree of medical probability that Dr. Lewis’s postprocedure care was a substantial factor in causing harm to Mr. Shackelford, Dr. Khoury responded that it was “impossible to tell.”
Based largely upon Dr. Khoury’s deposition testimony, the defendants successfully moved for summary judgment on the basis that the expert had failed to opine that the alleged negligence caused any injury to Mr. Shackelford. As a result, Mr. Shackelford could not prove an essential element of his medical malpractice claim. Defense expert Peter J. Pema, MD, a neuroradiologist, acknowledged the general proposition that strokes require timely diagnosis and treatment but did not provide an opinion on causation under the specific facts of this case. Another defense expert, Gregory Postal, MD, opined that Mr. Shackelford began to present symptoms of a stroke after leaving the hospital.
Notwithstanding the lower court’s ruling to summarily dismiss the case, the Court of Appeals found that, in this case, the issue of causation did not require expert medical testimony. It explained that given the ubiquity of information regarding stroke symptom identification and the necessity of prompt treatment, it had become common knowledge that “time lost is brain lost” as to timely medical intervention. In other words, a jury of laymen with this general knowledge could resolve the causation issue without the aid of expert testimony.
However, the Supreme Court of Kentucky held otherwise, writing: “We disagree with the Court of Appeals’ analysis. Although public service campaigns have increased public awareness and knowledge about stroke symptoms and timely intervention, that general information cannot provide the medical expertise necessary to evaluate this particular claim of medical malpractice. In other words, the question is not simply whether ‘time lost is brain lost.’ Rather, the specific facts and circumstances of this case play a significant role in determining whether the alleged negligent conduct was a substantial factor in Shackelford’s injuries, and to what extent. For example, as Dr. Lewis’s deposition testimony illustrates, a variety of factors influenced his diagnosis and treatment of Shackelford, including Shackelford’s medical history and history of cluster headaches; the common side effects of the angiogram procedure, including headache and scotoma; and the manner in which Shackelford’s headache and scotoma presented, as well as their timing. The complexities of these factors and how they affected Dr. Lewis’s evaluation of Shackelford may have also influenced the severity of the injury. These matters are clearly relevant to the determination of an alleged breach of the standard of care. Despite public perception about timely intervention, the average layperson cannot properly weigh such complex medical evidence without the aid of expert opinion. … To conclude otherwise is to drastically expand the res ipsa loquitor exception and to virtually eliminate the need for expert opinion evidence in similar medical malpractice actions that involve common or highly publicized conditions (e.g., stroke, heart attack, and even some cancers).”
Dr. Tan is professor emeritus of medicine and former adjunct professor of law at the University of Hawaii, Honolulu. This article is meant to be educational and does not constitute medical, ethical or legal advice. The author published an earlier version of this topic in the April 19, 2016, issue of Internal Medicine News, available at https://www.mdedge.com/internalmedicine/law-medicine. For additional information, readers may contact the author at [email protected].
References
1. James v. Wormuth, 997 N.E.2d 133 (N.Y. 2013).
2. Lewis/Ashland Hospital v. Shackelford, Supreme Court of Kentucky, Opinion of the Court by Justice Keller, rendered August 29, 2019.
Question: Which of the following statements regarding “common knowledge” is correct?
A. In any negligence action absent common knowledge, expert testimony is then required to prove requisite standard of care and causation.
B.
C. An expert is needed in the first place to establish whether something constitutes common knowledge.
D. The jury is the one who determines whether a plaintiff can invoke the common knowledge exception.
E. An example of common knowledge in malpractice law is where a delay in stroke diagnosis results in loss of brain function.
Answer: B. The judge, not the jury or anyone else, makes the decision regarding res ipsa loquitur (the thing speaks for itself) or common knowledge, which exempts a plaintiff from producing an expert witness to testify as to the standard of care and causation. However, this is only true in actions arising out of professional negligence such as medical malpractice, whereas most common negligence actions – for example, slips and falls – do not require expert testimony.
Only a professional, duly qualified by the court as an expert witness, is allowed to offer medical testimony, while the plaintiff will typically be disqualified from playing this role because of the complexity of issues involved unless there is common knowledge. In general, courts are reluctant to grant this exception, which favors the plaintiff.
The best example of res ipsa loquitur is where a surgeon inadvertently leaves behind a sponge or instrument inside a body cavity. Other successfully litigated examples include cardiac arrest in the operating room, hypoxia in the recovery room, burns to the buttock, gangrene after the accidental injection of penicillin into an artery, air trapped subcutaneously from a displaced needle, and a pierced eyeball during a procedure. The factual circumstances of each case are critical to its outcome. For example, in a 2013 New York case, the plaintiff was barred from using the res doctrine.1 The defendant doctor had left a guide wire in the plaintiff’s chest following a biopsy and retrieved it 2 months later. The plaintiff did not call any expert witness, relying instead on the “foreign object” basis for invoking the res doctrine. However, the Court of Appeals reasoned that the object was left behind deliberately, not unintentionally, and that under the circumstances of the case, an expert witness was needed to set out the applicable standard of care, without which a jury could not determine whether the doctor’s professional judgment breached the requisite standard.
The Supreme Court of Kentucky recently rejected the use of common knowledge in a stroke case.2 In 2010, David Shackelford’s rheumatologist referred him to Paul Lewis, MD, an interventional radiologist, for a four-vessel cerebral angiogram to assist with diagnosing the cause of Mr. Shackelford’s chronic headaches. The procedure itself was uneventful, but while in the recovery room, Mr. Shackelford reported a frontal headache and scotoma, which resolved on its own. The headache improved with medication, and the patient experienced no other symptoms. There were no other visual changes, weakness, slurred speech, or facial palsies. Mr. Shackelford was discharged but had to return to the hospital the next morning via ambulance after becoming disoriented at his home. An MRI indicated multiple scattered small infarcts, and he was left with residual short-term memory loss and visual problems.
There was no allegation that the stroke itself was caused by negligence; rather, Mr. Shackelford alleged that the failure to examine and diagnose the stroke after the angiogram was negligent and caused injury greater than that which the stroke would have caused with earlier intervention. To support his claims, Mr. Shackelford’s expert, Michael David Khoury, MD, a vascular surgeon, criticized Dr. Lewis’s failure to examine Mr. Shackelford when his symptoms were consistent with a stroke. However, Dr. Khoury did not opine that Dr. Lewis could have limited the effects of the stroke through earlier intervention. When asked specifically whether he could state within a reasonable degree of medical probability that Dr. Lewis’s postprocedure care was a substantial factor in causing harm to Mr. Shackelford, Dr. Khoury responded that it was “impossible to tell.”
Based largely upon Dr. Khoury’s deposition testimony, the defendants successfully moved for summary judgment on the basis that the expert had failed to opine that the alleged negligence caused any injury to Mr. Shackelford. As a result, Mr. Shackelford could not prove an essential element of his medical malpractice claim. Defense expert Peter J. Pema, MD, a neuroradiologist, acknowledged the general proposition that strokes require timely diagnosis and treatment but did not provide an opinion on causation under the specific facts of this case. Another defense expert, Gregory Postal, MD, opined that Mr. Shackelford began to present symptoms of a stroke after leaving the hospital.
Notwithstanding the lower court’s ruling to summarily dismiss the case, the Court of Appeals found that, in this case, the issue of causation did not require expert medical testimony. It explained that given the ubiquity of information regarding stroke symptom identification and the necessity of prompt treatment, it had become common knowledge that “time lost is brain lost” as to timely medical intervention. In other words, a jury of laymen with this general knowledge could resolve the causation issue without the aid of expert testimony.
However, the Supreme Court of Kentucky held otherwise, writing: “We disagree with the Court of Appeals’ analysis. Although public service campaigns have increased public awareness and knowledge about stroke symptoms and timely intervention, that general information cannot provide the medical expertise necessary to evaluate this particular claim of medical malpractice. In other words, the question is not simply whether ‘time lost is brain lost.’ Rather, the specific facts and circumstances of this case play a significant role in determining whether the alleged negligent conduct was a substantial factor in Shackelford’s injuries, and to what extent. For example, as Dr. Lewis’s deposition testimony illustrates, a variety of factors influenced his diagnosis and treatment of Shackelford, including Shackelford’s medical history and history of cluster headaches; the common side effects of the angiogram procedure, including headache and scotoma; and the manner in which Shackelford’s headache and scotoma presented, as well as their timing. The complexities of these factors and how they affected Dr. Lewis’s evaluation of Shackelford may have also influenced the severity of the injury. These matters are clearly relevant to the determination of an alleged breach of the standard of care. Despite public perception about timely intervention, the average layperson cannot properly weigh such complex medical evidence without the aid of expert opinion. … To conclude otherwise is to drastically expand the res ipsa loquitor exception and to virtually eliminate the need for expert opinion evidence in similar medical malpractice actions that involve common or highly publicized conditions (e.g., stroke, heart attack, and even some cancers).”
Dr. Tan is professor emeritus of medicine and former adjunct professor of law at the University of Hawaii, Honolulu. This article is meant to be educational and does not constitute medical, ethical or legal advice. The author published an earlier version of this topic in the April 19, 2016, issue of Internal Medicine News, available at https://www.mdedge.com/internalmedicine/law-medicine. For additional information, readers may contact the author at [email protected].
References
1. James v. Wormuth, 997 N.E.2d 133 (N.Y. 2013).
2. Lewis/Ashland Hospital v. Shackelford, Supreme Court of Kentucky, Opinion of the Court by Justice Keller, rendered August 29, 2019.
Question: Which of the following statements regarding “common knowledge” is correct?
A. In any negligence action absent common knowledge, expert testimony is then required to prove requisite standard of care and causation.
B.
C. An expert is needed in the first place to establish whether something constitutes common knowledge.
D. The jury is the one who determines whether a plaintiff can invoke the common knowledge exception.
E. An example of common knowledge in malpractice law is where a delay in stroke diagnosis results in loss of brain function.
Answer: B. The judge, not the jury or anyone else, makes the decision regarding res ipsa loquitur (the thing speaks for itself) or common knowledge, which exempts a plaintiff from producing an expert witness to testify as to the standard of care and causation. However, this is only true in actions arising out of professional negligence such as medical malpractice, whereas most common negligence actions – for example, slips and falls – do not require expert testimony.
Only a professional, duly qualified by the court as an expert witness, is allowed to offer medical testimony, while the plaintiff will typically be disqualified from playing this role because of the complexity of issues involved unless there is common knowledge. In general, courts are reluctant to grant this exception, which favors the plaintiff.
The best example of res ipsa loquitur is where a surgeon inadvertently leaves behind a sponge or instrument inside a body cavity. Other successfully litigated examples include cardiac arrest in the operating room, hypoxia in the recovery room, burns to the buttock, gangrene after the accidental injection of penicillin into an artery, air trapped subcutaneously from a displaced needle, and a pierced eyeball during a procedure. The factual circumstances of each case are critical to its outcome. For example, in a 2013 New York case, the plaintiff was barred from using the res doctrine.1 The defendant doctor had left a guide wire in the plaintiff’s chest following a biopsy and retrieved it 2 months later. The plaintiff did not call any expert witness, relying instead on the “foreign object” basis for invoking the res doctrine. However, the Court of Appeals reasoned that the object was left behind deliberately, not unintentionally, and that under the circumstances of the case, an expert witness was needed to set out the applicable standard of care, without which a jury could not determine whether the doctor’s professional judgment breached the requisite standard.
The Supreme Court of Kentucky recently rejected the use of common knowledge in a stroke case.2 In 2010, David Shackelford’s rheumatologist referred him to Paul Lewis, MD, an interventional radiologist, for a four-vessel cerebral angiogram to assist with diagnosing the cause of Mr. Shackelford’s chronic headaches. The procedure itself was uneventful, but while in the recovery room, Mr. Shackelford reported a frontal headache and scotoma, which resolved on its own. The headache improved with medication, and the patient experienced no other symptoms. There were no other visual changes, weakness, slurred speech, or facial palsies. Mr. Shackelford was discharged but had to return to the hospital the next morning via ambulance after becoming disoriented at his home. An MRI indicated multiple scattered small infarcts, and he was left with residual short-term memory loss and visual problems.
There was no allegation that the stroke itself was caused by negligence; rather, Mr. Shackelford alleged that the failure to examine and diagnose the stroke after the angiogram was negligent and caused injury greater than that which the stroke would have caused with earlier intervention. To support his claims, Mr. Shackelford’s expert, Michael David Khoury, MD, a vascular surgeon, criticized Dr. Lewis’s failure to examine Mr. Shackelford when his symptoms were consistent with a stroke. However, Dr. Khoury did not opine that Dr. Lewis could have limited the effects of the stroke through earlier intervention. When asked specifically whether he could state within a reasonable degree of medical probability that Dr. Lewis’s postprocedure care was a substantial factor in causing harm to Mr. Shackelford, Dr. Khoury responded that it was “impossible to tell.”
Based largely upon Dr. Khoury’s deposition testimony, the defendants successfully moved for summary judgment on the basis that the expert had failed to opine that the alleged negligence caused any injury to Mr. Shackelford. As a result, Mr. Shackelford could not prove an essential element of his medical malpractice claim. Defense expert Peter J. Pema, MD, a neuroradiologist, acknowledged the general proposition that strokes require timely diagnosis and treatment but did not provide an opinion on causation under the specific facts of this case. Another defense expert, Gregory Postal, MD, opined that Mr. Shackelford began to present symptoms of a stroke after leaving the hospital.
Notwithstanding the lower court’s ruling to summarily dismiss the case, the Court of Appeals found that, in this case, the issue of causation did not require expert medical testimony. It explained that given the ubiquity of information regarding stroke symptom identification and the necessity of prompt treatment, it had become common knowledge that “time lost is brain lost” as to timely medical intervention. In other words, a jury of laymen with this general knowledge could resolve the causation issue without the aid of expert testimony.
However, the Supreme Court of Kentucky held otherwise, writing: “We disagree with the Court of Appeals’ analysis. Although public service campaigns have increased public awareness and knowledge about stroke symptoms and timely intervention, that general information cannot provide the medical expertise necessary to evaluate this particular claim of medical malpractice. In other words, the question is not simply whether ‘time lost is brain lost.’ Rather, the specific facts and circumstances of this case play a significant role in determining whether the alleged negligent conduct was a substantial factor in Shackelford’s injuries, and to what extent. For example, as Dr. Lewis’s deposition testimony illustrates, a variety of factors influenced his diagnosis and treatment of Shackelford, including Shackelford’s medical history and history of cluster headaches; the common side effects of the angiogram procedure, including headache and scotoma; and the manner in which Shackelford’s headache and scotoma presented, as well as their timing. The complexities of these factors and how they affected Dr. Lewis’s evaluation of Shackelford may have also influenced the severity of the injury. These matters are clearly relevant to the determination of an alleged breach of the standard of care. Despite public perception about timely intervention, the average layperson cannot properly weigh such complex medical evidence without the aid of expert opinion. … To conclude otherwise is to drastically expand the res ipsa loquitor exception and to virtually eliminate the need for expert opinion evidence in similar medical malpractice actions that involve common or highly publicized conditions (e.g., stroke, heart attack, and even some cancers).”
Dr. Tan is professor emeritus of medicine and former adjunct professor of law at the University of Hawaii, Honolulu. This article is meant to be educational and does not constitute medical, ethical or legal advice. The author published an earlier version of this topic in the April 19, 2016, issue of Internal Medicine News, available at https://www.mdedge.com/internalmedicine/law-medicine. For additional information, readers may contact the author at [email protected].
References
1. James v. Wormuth, 997 N.E.2d 133 (N.Y. 2013).
2. Lewis/Ashland Hospital v. Shackelford, Supreme Court of Kentucky, Opinion of the Court by Justice Keller, rendered August 29, 2019.
USPSTF recommendations on risk assessment, genetic counseling, and genetic testing for BRCA-related cancer
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.
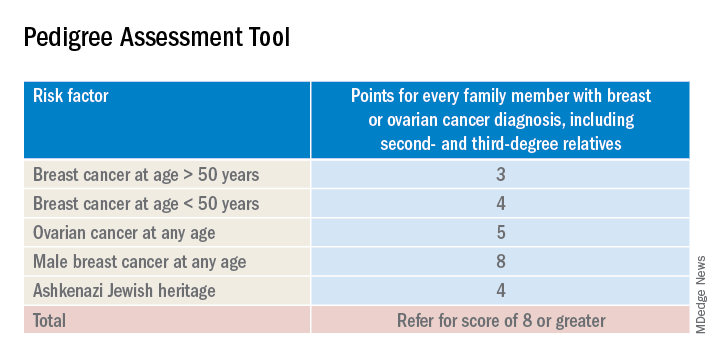
A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.

A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
Breast cancer screening recommendations have evolved over the past decade. BRCA1/2 genes are tumor-suppressor genes. Mutations in these genes place women at an increased risk for developing breast, ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. Detection of BRCA1/2 mutations through genetic screening can provide patients with more information about their cancer risk and can lead to discussion of prophylactic therapies. This includes increased screening frequency, medical therapy, and surgical interventions.
New USPSTF recommendations address who is at an increased risk for BRCA1/2 mutations. They recommend using screening tools focusing on family history that primary care physicians can utilize to determine who should be referred for genetic counseling to discuss the risks and benefits of genetic screening. The following are the task force’s two primary recommendations:
The USPSTF recommends that primary care clinicians assess women with a personal or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or who have an ancestry associated with BRCA1/2 gene mutations with an appropriate brief familial risk assessment tool. Women with a positive result on the risk assessment tool should receive genetic counseling and, if indicated after counseling, genetic testing. (B recommendation)
The USPSTF recommends against routine risk assessment, genetic counseling, or genetic testing for women whose personal or family history or ancestry is not associated with potentially harmful BRCA1/2 gene mutations. (D recommendation)
Breast cancer is the second leading cause of cancer and cancer death for women in the United States. Ovarian cancer ranks fifth in cancer deaths for women in the U.S. By age 70, women with BRCA1/2 mutations have a 45%-65% cumulative lifetime risk of developing breast cancer.
Mutations in BRCA1, specifically, are associated with a 39% lifetime risk for ovarian, fallopian tube, and peritoneal cancer. In contrast, mutations in BRCA2 are associated with a 10%-17% lifetime risk.
The USPSTF also underscores the increased prevalence of BRCA1/2 mutations in the Ashkenazi Jewish population. Three out of seven familial risk assessment tools inquire about Jewish ancestry. This is because the Ashkenazi Jewish population have a higher prevalence of three founder mutations in the BRCA1/2 gene. A member of this population has a 1 in 40 chance of carrying one of these three mutations, whereas the general population has a 1 in 300 chance.
The USPSTF recommends a multistep process of screening. The first step is taking a family history of cancer. For women who have a family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or a personal history of these cancers, a brief familial risk assessment tool should be used to determine the need for referral for in-depth genetic counseling to determine the need for genetic testing.
It is important to recognize that the validated tools recommended by the USPSTF are specific for genetic risk assessment. General breast cancer risk assessment tools, including the National Cancer Institute Breast Cancer Risk Assessment Tool, which is based on the Gail model, are not recommended.
The sensitivity of the tools recommended by the USPSTF range between 77% and 100%. A number of tools are given as an option with no one tool being better than the other. Perhaps the easiest to implement of the validated tools recommended is the Pedigree Assessment Tool. For this tool, points are assigned for every family member with breast or ovarian cancer as indicated in the table below.

A positive result on a screening tool will lead primary care physicians to appropriately refer patients for genetic counseling. Genetic testing for BRCA1/2 mutations should be limited to those individuals whose personal and/or family history reflects an increased risk for gene mutations after detailed genetic assessment and counseling. The results of the genetic screening should assist a patient in their decision making.
Prophylactic treatment for BRCA1/2 mutation carriers are outside the scope of this recommendation. However the guidelines briefly review risk-reducing therapies including screening, medical, and surgical options. Medical therapy for patients who have BRCA1/2 mutations include the use of tamoxifen, raloxifene, and aromatase inhibitors. Surgical interventions include bilateral mastectomy and salpingo-oopherectomy.
Screening options include earlier and more frequent mammograms and breast MRIs. Screening is largely based on family history and the USPSTF acknowledges their uncertainty when screening women with an unknown family history. Male breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, prostate cancer, and melanoma are also associated with BRCA1/2 mutations. They are not included in this recommendation.
The bottom line
USPSTF recommended that primary care physicians should use familial risk assessment tools to screen women for BRCA1/2 mutations. This includes women with a personal and/or family history of breast, ovarian, tubal, or peritoneal cancer or women with a family history of BRCA1/2 gene mutations. Patients who test positive through one of the suggested screening tools should be referred for genetic counseling. This could lead to genetic testing and subsequent prophylactic therapies and/or increased screenings if the patient so desires. It is of importance to note the USPSTF recommends against routine screening of BRCA1/2 gene mutations for women who do not meet the above requirements.
Reference
USPSTF Recommendation: Assessment, counseling, and testing for BRCA-related cancer. JAMA. 2019;322(7):652-65. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.10987.
Dr. Style is a second-year resident in the Family Medicine Residency Program at Abington (Pa.) Jefferson Health. Dr. Skolnik is professor of family and community medicine at Jefferson Medical College, Philadelphia, and an associate director of the family medicine residency program at Abington Jefferson Health.
CBD: What physicians need to know about it
Cannabidiol is a derivative of marijuana that is sold everywhere from medical marijuana stores to health food markets to gas stations. While this chemical is derived from marijuana plants, it can be sold in many states as a supplement and is largely unregulated. The ubiquity of cannabidiol (CBD) and its potential benefits means that doctors need to be able to counsel patients about what we know, what we don’t, and how to use it safely. For conditions such as chronic pain and addiction, where we have few safe and effective alternatives, CBD may be reasonable to recommend.
To find out what physicians need to know about CBD, Elisabeth Poorman, MD, a general internist at a University of Washington neighborhood clinic in Kent and member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, interviewed Peter Grinspoon, MD, who provides free consultation to primary care patients on the benefits and risks of using various forms of cannabis, including CBD. Dr. Grinspoon is an internist at Massachusetts General Hospital Chelsea Healthcare Center and is an instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He has contributed to the Harvard Health Blog on the topic of medical marijuana, delivered grand rounds on cannabis at Massachusetts General Hospital, and lectured at the American College of Physicians. Dr. Grinspoon is also medical director for Galenas, a medical marijuana company.
Dr. Grinspoon is the son of Lester Grinspoon, MD, associate professor emeritus of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, who researched the medicinal legitimacy of marijuana prohibition and has authored books on the medical benefits of marijuana.
and his knowledge of CBD’s efficacy for various medical conditions. Below are excerpts from that conversation.
Dr. Poorman: How do you explain the difference between THC and CBD to patients?
Dr. Grinspoon: Cannabis contains at least a hundred different chemicals called cannabinoids, of which tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD are the most prevalent. THC is the one that gets you high and can be used recreationally and medically. The CBD molecule is not intoxicating, and people use it for a variety of medical purposes, most commonly to treat anxiety, insomnia, and pain.
Dr. Poorman: There are a lot of gaps in what we now about CBD’s potential benefits. Why don’t we know more?
Dr. Grinspoon: CBD has no abuse liability according to the World Health Organization, but because it is a cannabinoid, it is still technically a schedule I substance under the Controlled Substances Act, and that makes it difficult to study.
Dr. Poorman: What kinds of conditions can CBD treat?
Dr. Grinspoon: In anxiety, the enthusiasm has outpaced the science; there’s no question about that. And most of the studies have done in animals. That said, some studies have shown that CBD helps treat components of anxiety, like public speaking. Unlike THC, it is nonintoxicating and non–habit forming. But we don’t have the wealth of randomized controlled trials that we have for official psychiatric medications.
CBD’s benefits have been most extensively studied in pediatric epilepsy. The one Food and Drug Administration–approved drug derived from cannabis is Epidiolex, used to treat rare forms of childhood epilepsy. There is some evidence that as an adjunct, it can be used for glioblastoma multiforme in patients receiving other appropriate therapy. There is also some preliminary evidence that it can be used for addiction, including to opioids, cannabis, tobacco, and stimulants.
Most of the evidence for using CBD in chronic pain comes from animal studies, including a study published in the European Journal of Pain in 2016. Among my patients to whom I have suggested CBD for chronic pain, a few have noticed great benefit, a few have noticed some benefit, and a lot have noticed no benefit. For those who have said they noticed benefit it is unclear whether that benefit was just the placebo effect.
In insomnia, I usually have them take CBD under the tongue half an hour time before bedtime, or if it’s an edible, an hour before bedtime. I start with a lower dose and slowly try higher doses. I also encourage them to do the other sleep hygiene things, like no screens, increasing exercise, and decreasing caffeine. It seems that CBD helps them fall asleep, though it’s hard to know if it’s the CBD or the fact that they have started taking something, and have simultaneously made various lifestyle changes.
Dr. Poorman: Can CBD interfere with your normal sleep architecture, the way benzodiazepines and Benadryl can?
Dr. Grinspoon: We know that THC affects your sleep architecture and affects what percentage of REM sleep you have. But I don’t know if the effects of CBD on sleep architecture have been studied.
Dr. Poorman: What harms do you counsel patients about when discussing CBD?
Dr. Grinspoon: There are four main harms. The first is the price. It’s overpriced, and the doses are very low. In most animal studies, the doses are about 20 milligrams per kilogram of weight. And you go to the market, and it’s like a dollar for a hundredth of that.
Number two is that it’s not regulated; it’s a supplement. A few years ago, the government tested a bunch of samples of CBD, and some didn’t actually contain CBD, some didn’t have the right amount; and worse, some contained THC that had not been disclosed in the packaging. So you can’t just go to a roadside gas station and assume that if you buy CBD, it’s actually that. You want a place that has a certificate of assurance. Make sure third-party testing was done, including testing for pesticides and other heavy metals.
The third thing is drug interactions. It affects the body like grapefruit and inhibits the cytochrome P450 system. The medications doctors should be most concerned about are blood thinners like Coumadin. And if you’re on blood thinners, you definitely want to tell your doctor that you are on CBD and he or she might want to check your blood levels more frequently than they usually do.
The fourth concern is liver inflammation. In the childhood epilepsy studies, a bump in some liver enzymes was seen, although I haven’t heard of any clinically significant cases of chemical hepatitis related to CBD. But if someone has liver disease you want to keep an eye on their liver enzymes.
Dr. Poorman: What methods of ingestion do you recommend or not recommend?
Dr. Grinspoon: It’s basically trial and error, but I usually recommend oral form. If people feel comfortable taking a gummy bear, or a pill, I’m not particular about that. If the product being taken contains less than 0.3% THC, it won’t get you high.
The topical form probably works better for treating chronic pain if it contains some THC, suggests a review article published in the Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. Topical THC is nonintoxicating, unless you managed to sit in a bathtub for 8 hours after applying it.
I don’t recommend smoking CBD, and right now, I don’t recommend vaping anything.
If people have severe pain, like moderately severe arthritis, CBD may not be enough, whereas medical cannabis with THC could help, a report suggests.
Dr. Poorman: Do you ever encourage patients to stop using CBD products?
Dr. Grinspoon: I work in a low-income area, and my patients don’t have a ton of disposable income. If it’s not working, I worry about the expense.
Dr. Poorman: The CBD industry is growing quickly. What changes are you seeing in what products are out there, and what changes would you like to see?
Dr. Grinspoon: CBD is being put in everything, and it’s comical. On the one hand, you can say if people want to waste their money on a CBD emitting pillowcase, that’s fine. On the other hand, you can say that certainly seems like misleading advertising, because a CBD emitting pillowcase isn’t going to help you sleep any better.
I think the purported benefits are far beyond what we can say scientifically. We do know that CBD has anti-inflammatory characteristics. But that doesn’t mean that putting CBD in all skin products is good for your skin. It’s bad for your pocketbook, though. I would like there to be less of a gap between the claims and the science.
Dr. Elisabeth Poorman has no conflicts to disclose.
Cannabidiol is a derivative of marijuana that is sold everywhere from medical marijuana stores to health food markets to gas stations. While this chemical is derived from marijuana plants, it can be sold in many states as a supplement and is largely unregulated. The ubiquity of cannabidiol (CBD) and its potential benefits means that doctors need to be able to counsel patients about what we know, what we don’t, and how to use it safely. For conditions such as chronic pain and addiction, where we have few safe and effective alternatives, CBD may be reasonable to recommend.
To find out what physicians need to know about CBD, Elisabeth Poorman, MD, a general internist at a University of Washington neighborhood clinic in Kent and member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, interviewed Peter Grinspoon, MD, who provides free consultation to primary care patients on the benefits and risks of using various forms of cannabis, including CBD. Dr. Grinspoon is an internist at Massachusetts General Hospital Chelsea Healthcare Center and is an instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He has contributed to the Harvard Health Blog on the topic of medical marijuana, delivered grand rounds on cannabis at Massachusetts General Hospital, and lectured at the American College of Physicians. Dr. Grinspoon is also medical director for Galenas, a medical marijuana company.
Dr. Grinspoon is the son of Lester Grinspoon, MD, associate professor emeritus of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, who researched the medicinal legitimacy of marijuana prohibition and has authored books on the medical benefits of marijuana.
and his knowledge of CBD’s efficacy for various medical conditions. Below are excerpts from that conversation.
Dr. Poorman: How do you explain the difference between THC and CBD to patients?
Dr. Grinspoon: Cannabis contains at least a hundred different chemicals called cannabinoids, of which tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD are the most prevalent. THC is the one that gets you high and can be used recreationally and medically. The CBD molecule is not intoxicating, and people use it for a variety of medical purposes, most commonly to treat anxiety, insomnia, and pain.
Dr. Poorman: There are a lot of gaps in what we now about CBD’s potential benefits. Why don’t we know more?
Dr. Grinspoon: CBD has no abuse liability according to the World Health Organization, but because it is a cannabinoid, it is still technically a schedule I substance under the Controlled Substances Act, and that makes it difficult to study.
Dr. Poorman: What kinds of conditions can CBD treat?
Dr. Grinspoon: In anxiety, the enthusiasm has outpaced the science; there’s no question about that. And most of the studies have done in animals. That said, some studies have shown that CBD helps treat components of anxiety, like public speaking. Unlike THC, it is nonintoxicating and non–habit forming. But we don’t have the wealth of randomized controlled trials that we have for official psychiatric medications.
CBD’s benefits have been most extensively studied in pediatric epilepsy. The one Food and Drug Administration–approved drug derived from cannabis is Epidiolex, used to treat rare forms of childhood epilepsy. There is some evidence that as an adjunct, it can be used for glioblastoma multiforme in patients receiving other appropriate therapy. There is also some preliminary evidence that it can be used for addiction, including to opioids, cannabis, tobacco, and stimulants.
Most of the evidence for using CBD in chronic pain comes from animal studies, including a study published in the European Journal of Pain in 2016. Among my patients to whom I have suggested CBD for chronic pain, a few have noticed great benefit, a few have noticed some benefit, and a lot have noticed no benefit. For those who have said they noticed benefit it is unclear whether that benefit was just the placebo effect.
In insomnia, I usually have them take CBD under the tongue half an hour time before bedtime, or if it’s an edible, an hour before bedtime. I start with a lower dose and slowly try higher doses. I also encourage them to do the other sleep hygiene things, like no screens, increasing exercise, and decreasing caffeine. It seems that CBD helps them fall asleep, though it’s hard to know if it’s the CBD or the fact that they have started taking something, and have simultaneously made various lifestyle changes.
Dr. Poorman: Can CBD interfere with your normal sleep architecture, the way benzodiazepines and Benadryl can?
Dr. Grinspoon: We know that THC affects your sleep architecture and affects what percentage of REM sleep you have. But I don’t know if the effects of CBD on sleep architecture have been studied.
Dr. Poorman: What harms do you counsel patients about when discussing CBD?
Dr. Grinspoon: There are four main harms. The first is the price. It’s overpriced, and the doses are very low. In most animal studies, the doses are about 20 milligrams per kilogram of weight. And you go to the market, and it’s like a dollar for a hundredth of that.
Number two is that it’s not regulated; it’s a supplement. A few years ago, the government tested a bunch of samples of CBD, and some didn’t actually contain CBD, some didn’t have the right amount; and worse, some contained THC that had not been disclosed in the packaging. So you can’t just go to a roadside gas station and assume that if you buy CBD, it’s actually that. You want a place that has a certificate of assurance. Make sure third-party testing was done, including testing for pesticides and other heavy metals.
The third thing is drug interactions. It affects the body like grapefruit and inhibits the cytochrome P450 system. The medications doctors should be most concerned about are blood thinners like Coumadin. And if you’re on blood thinners, you definitely want to tell your doctor that you are on CBD and he or she might want to check your blood levels more frequently than they usually do.
The fourth concern is liver inflammation. In the childhood epilepsy studies, a bump in some liver enzymes was seen, although I haven’t heard of any clinically significant cases of chemical hepatitis related to CBD. But if someone has liver disease you want to keep an eye on their liver enzymes.
Dr. Poorman: What methods of ingestion do you recommend or not recommend?
Dr. Grinspoon: It’s basically trial and error, but I usually recommend oral form. If people feel comfortable taking a gummy bear, or a pill, I’m not particular about that. If the product being taken contains less than 0.3% THC, it won’t get you high.
The topical form probably works better for treating chronic pain if it contains some THC, suggests a review article published in the Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. Topical THC is nonintoxicating, unless you managed to sit in a bathtub for 8 hours after applying it.
I don’t recommend smoking CBD, and right now, I don’t recommend vaping anything.
If people have severe pain, like moderately severe arthritis, CBD may not be enough, whereas medical cannabis with THC could help, a report suggests.
Dr. Poorman: Do you ever encourage patients to stop using CBD products?
Dr. Grinspoon: I work in a low-income area, and my patients don’t have a ton of disposable income. If it’s not working, I worry about the expense.
Dr. Poorman: The CBD industry is growing quickly. What changes are you seeing in what products are out there, and what changes would you like to see?
Dr. Grinspoon: CBD is being put in everything, and it’s comical. On the one hand, you can say if people want to waste their money on a CBD emitting pillowcase, that’s fine. On the other hand, you can say that certainly seems like misleading advertising, because a CBD emitting pillowcase isn’t going to help you sleep any better.
I think the purported benefits are far beyond what we can say scientifically. We do know that CBD has anti-inflammatory characteristics. But that doesn’t mean that putting CBD in all skin products is good for your skin. It’s bad for your pocketbook, though. I would like there to be less of a gap between the claims and the science.
Dr. Elisabeth Poorman has no conflicts to disclose.
Cannabidiol is a derivative of marijuana that is sold everywhere from medical marijuana stores to health food markets to gas stations. While this chemical is derived from marijuana plants, it can be sold in many states as a supplement and is largely unregulated. The ubiquity of cannabidiol (CBD) and its potential benefits means that doctors need to be able to counsel patients about what we know, what we don’t, and how to use it safely. For conditions such as chronic pain and addiction, where we have few safe and effective alternatives, CBD may be reasonable to recommend.
To find out what physicians need to know about CBD, Elisabeth Poorman, MD, a general internist at a University of Washington neighborhood clinic in Kent and member of the editorial advisory board of Internal Medicine News, interviewed Peter Grinspoon, MD, who provides free consultation to primary care patients on the benefits and risks of using various forms of cannabis, including CBD. Dr. Grinspoon is an internist at Massachusetts General Hospital Chelsea Healthcare Center and is an instructor at Harvard Medical School, Boston. He has contributed to the Harvard Health Blog on the topic of medical marijuana, delivered grand rounds on cannabis at Massachusetts General Hospital, and lectured at the American College of Physicians. Dr. Grinspoon is also medical director for Galenas, a medical marijuana company.
Dr. Grinspoon is the son of Lester Grinspoon, MD, associate professor emeritus of psychiatry at Harvard Medical School, who researched the medicinal legitimacy of marijuana prohibition and has authored books on the medical benefits of marijuana.
and his knowledge of CBD’s efficacy for various medical conditions. Below are excerpts from that conversation.
Dr. Poorman: How do you explain the difference between THC and CBD to patients?
Dr. Grinspoon: Cannabis contains at least a hundred different chemicals called cannabinoids, of which tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and CBD are the most prevalent. THC is the one that gets you high and can be used recreationally and medically. The CBD molecule is not intoxicating, and people use it for a variety of medical purposes, most commonly to treat anxiety, insomnia, and pain.
Dr. Poorman: There are a lot of gaps in what we now about CBD’s potential benefits. Why don’t we know more?
Dr. Grinspoon: CBD has no abuse liability according to the World Health Organization, but because it is a cannabinoid, it is still technically a schedule I substance under the Controlled Substances Act, and that makes it difficult to study.
Dr. Poorman: What kinds of conditions can CBD treat?
Dr. Grinspoon: In anxiety, the enthusiasm has outpaced the science; there’s no question about that. And most of the studies have done in animals. That said, some studies have shown that CBD helps treat components of anxiety, like public speaking. Unlike THC, it is nonintoxicating and non–habit forming. But we don’t have the wealth of randomized controlled trials that we have for official psychiatric medications.
CBD’s benefits have been most extensively studied in pediatric epilepsy. The one Food and Drug Administration–approved drug derived from cannabis is Epidiolex, used to treat rare forms of childhood epilepsy. There is some evidence that as an adjunct, it can be used for glioblastoma multiforme in patients receiving other appropriate therapy. There is also some preliminary evidence that it can be used for addiction, including to opioids, cannabis, tobacco, and stimulants.
Most of the evidence for using CBD in chronic pain comes from animal studies, including a study published in the European Journal of Pain in 2016. Among my patients to whom I have suggested CBD for chronic pain, a few have noticed great benefit, a few have noticed some benefit, and a lot have noticed no benefit. For those who have said they noticed benefit it is unclear whether that benefit was just the placebo effect.
In insomnia, I usually have them take CBD under the tongue half an hour time before bedtime, or if it’s an edible, an hour before bedtime. I start with a lower dose and slowly try higher doses. I also encourage them to do the other sleep hygiene things, like no screens, increasing exercise, and decreasing caffeine. It seems that CBD helps them fall asleep, though it’s hard to know if it’s the CBD or the fact that they have started taking something, and have simultaneously made various lifestyle changes.
Dr. Poorman: Can CBD interfere with your normal sleep architecture, the way benzodiazepines and Benadryl can?
Dr. Grinspoon: We know that THC affects your sleep architecture and affects what percentage of REM sleep you have. But I don’t know if the effects of CBD on sleep architecture have been studied.
Dr. Poorman: What harms do you counsel patients about when discussing CBD?
Dr. Grinspoon: There are four main harms. The first is the price. It’s overpriced, and the doses are very low. In most animal studies, the doses are about 20 milligrams per kilogram of weight. And you go to the market, and it’s like a dollar for a hundredth of that.
Number two is that it’s not regulated; it’s a supplement. A few years ago, the government tested a bunch of samples of CBD, and some didn’t actually contain CBD, some didn’t have the right amount; and worse, some contained THC that had not been disclosed in the packaging. So you can’t just go to a roadside gas station and assume that if you buy CBD, it’s actually that. You want a place that has a certificate of assurance. Make sure third-party testing was done, including testing for pesticides and other heavy metals.
The third thing is drug interactions. It affects the body like grapefruit and inhibits the cytochrome P450 system. The medications doctors should be most concerned about are blood thinners like Coumadin. And if you’re on blood thinners, you definitely want to tell your doctor that you are on CBD and he or she might want to check your blood levels more frequently than they usually do.
The fourth concern is liver inflammation. In the childhood epilepsy studies, a bump in some liver enzymes was seen, although I haven’t heard of any clinically significant cases of chemical hepatitis related to CBD. But if someone has liver disease you want to keep an eye on their liver enzymes.
Dr. Poorman: What methods of ingestion do you recommend or not recommend?
Dr. Grinspoon: It’s basically trial and error, but I usually recommend oral form. If people feel comfortable taking a gummy bear, or a pill, I’m not particular about that. If the product being taken contains less than 0.3% THC, it won’t get you high.
The topical form probably works better for treating chronic pain if it contains some THC, suggests a review article published in the Cleveland Clinic Journal of Medicine. Topical THC is nonintoxicating, unless you managed to sit in a bathtub for 8 hours after applying it.
I don’t recommend smoking CBD, and right now, I don’t recommend vaping anything.
If people have severe pain, like moderately severe arthritis, CBD may not be enough, whereas medical cannabis with THC could help, a report suggests.
Dr. Poorman: Do you ever encourage patients to stop using CBD products?
Dr. Grinspoon: I work in a low-income area, and my patients don’t have a ton of disposable income. If it’s not working, I worry about the expense.
Dr. Poorman: The CBD industry is growing quickly. What changes are you seeing in what products are out there, and what changes would you like to see?
Dr. Grinspoon: CBD is being put in everything, and it’s comical. On the one hand, you can say if people want to waste their money on a CBD emitting pillowcase, that’s fine. On the other hand, you can say that certainly seems like misleading advertising, because a CBD emitting pillowcase isn’t going to help you sleep any better.
I think the purported benefits are far beyond what we can say scientifically. We do know that CBD has anti-inflammatory characteristics. But that doesn’t mean that putting CBD in all skin products is good for your skin. It’s bad for your pocketbook, though. I would like there to be less of a gap between the claims and the science.
Dr. Elisabeth Poorman has no conflicts to disclose.
Is it time to expand the use of PARP inhibitors?
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I review two recent presentations at the European Society of Medical Oncology Congress regarding the expanded use of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) in patients with advanced solid tumors, potentially broadening the indications for this important class of agents.
Metastatic CRPC
Perhaps 25% of prostate cancer patients have loss-of-function mutations – BRCA1, BRCA2, and ATM – or alterations in homologous recombinant repair (HRR) genes. In the PROfound trial, men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) who had progressed on either abiraterone or enzalutamide and who had DNA-repair mutations were randomized to either olaparib (300 mg b.i.d.) or treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) with either abiraterone or enzalutamide plus prednisone (Hussain M et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA-12).
Two cohorts were enrolled. Cohort A included 245 men with BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM mutations, and cohort B included 142 men with other alterations (BARD1, BIRP1, CDK12, CHEK1, CHEK2, FANCL, PALB2, PPP2R2A, RAD15B, RAD15C, RAD15D, or RAD54L). After disease progression, patients could cross over to receive PARPi, which more than 80% of patients eventually did.
Median radiographic progression-free survival (PFS) in cohort A was 7.39 months with PARPi, compared with 3.55 months with TPC, for a hazard ratio for progression on PARPi of 0.34 (P less than .0001). A significant benefit was seen for PARPi in the overall population (both cohorts), with a median radiographic PFS of 5.82 months va. 3.52 months, respectively (HR, 0.49; P less than .0001).
Among patients in cohort A, the objective response rate (ORR) was 33.3% with PARPi, compared with 2.3% for TPC, resulting in an odds ratio for ORR of 20.86 (P less than .0001).
PARPi demonstrated a longer time to pain progression in cohort A, with the median not reached, compared with 9.92 months with TPC (HR, 0.44; P = .0192). Perhaps because of the high proportion of TPC patients who eventually received PARPi, no statistically significant differences in overall survival have yet been seen.
What this means in practice
During my fellowship, a mentor taught that “because quality of life is generally better before progression than afterwards, PFS is a worthy endpoint in its own right.” For that reason, although I would have liked to see the data for cohort B alone, it appears worthwhile for physicians to make every effort to obtain PARPi. The difference in ORR, pain progression, and PFS at 12 months is clinically dramatic.
Of equal significance, however, is that PROfound is the first positive phase 3 biomarker-selected study evaluating a targeted treatment in patients with mCRPC. For prostate cancer – as for breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and several other cancers – the molecular biology and genetic background of our patients dictates the other tumors for which they and their family members are at risk, and expands the treatment armamentarium for them.
For those clinicians who needed to be convinced that “precision medicine” for prostate cancer patients was worthwhile, the PROfound trial should have a profound impact.
Advanced ovarian cancer
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 PAOLA-1/ENGOT-ov25 trial studied patients with stage III-IV ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had surgery, platinum-taxane chemotherapy, and at least 3 months of bevacizumab. Patients were randomized to maintenance treatment with an additional 12 months of bevacizumab plus 24 months of PARPi with olaparib or placebo. Germline BRCA mutations were not required (Ray-Coquard I et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA2).
As reported at ESMO, adding PARPi to bevacizumab maintenance provided a clinically meaningful PFS benefit of 22.1 months, in comparison with 16.6 months for bevacizumab alone. The difference was statistically significant.
For patients with tumor BRCA mutations (tBRCAm), PFS was 37.2 months with olaparib vs. 21.7 months for placebo (HR, 0.31). The PFS benefit was even more impressive for homologous recombination deficient (HRD)–positive patients, inclusive of those with tBRCAm (PFS 37.2 months for PARPi vs. 17.7 months for placebo; and in the 152 HRD-positive patients without tBRCAm, (median PFS 28.1 months vs. 16.6 months; HR, 0.43).
The improved PFS in patients with tBRCAm is similar to that reported in the SOLO1 trial of olaparib monotherapy vs. chemotherapy in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2495-2505), but the PFS in the control arm was longer in PAOLA-1 than in SOLO1, perhaps because of the use of bevacizumab in PAOLA-1. PARPi did not affect tolerance to bevacizumab.
In PAOLA-1, the HRD-positive patients who lacked tBRCAm and, by extension, lacked germline BRCA mutations – a new population of patients – was identified who benefited substantially from maintenance PARPi in the first-line setting.
What this means in practice
PAOLA-1 demonstrates that PARPi can improve outcomes in first-line treatment – and in patients beyond those with germline BRCA mutations. As a result, PAOLA-1 potentially changes the standard of care for initial treatment of the respectable fraction of patients with previously untreated, advanced müllerian cancers who have either tBRCAm or HRD positive tumors.
Importantly, PAOLA-1 is one of many published trials that stimulates the discussion of cost vs. value for combinations of biologics. The incremental benefit from the second biologic (in this case PARPi) is almost never completely additive or supra-additive to the benefit associated with the first biologic (in this case, bevacizumab). In that regard, despite the fact that PARPi showed a PFS benefit in the intent-to-treat population overall, precisely defining the patient population that has the greatest benefit will facilitate the goal of getting the treatments of greatest “value for cost” to our patients in the most responsible way.
Additional research will hopefully define the relative contribution of bevacizumab to PARPi in patients who benefited so dramatically from PARPi in PAOLA-1.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I review two recent presentations at the European Society of Medical Oncology Congress regarding the expanded use of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) in patients with advanced solid tumors, potentially broadening the indications for this important class of agents.
Metastatic CRPC
Perhaps 25% of prostate cancer patients have loss-of-function mutations – BRCA1, BRCA2, and ATM – or alterations in homologous recombinant repair (HRR) genes. In the PROfound trial, men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) who had progressed on either abiraterone or enzalutamide and who had DNA-repair mutations were randomized to either olaparib (300 mg b.i.d.) or treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) with either abiraterone or enzalutamide plus prednisone (Hussain M et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA-12).
Two cohorts were enrolled. Cohort A included 245 men with BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM mutations, and cohort B included 142 men with other alterations (BARD1, BIRP1, CDK12, CHEK1, CHEK2, FANCL, PALB2, PPP2R2A, RAD15B, RAD15C, RAD15D, or RAD54L). After disease progression, patients could cross over to receive PARPi, which more than 80% of patients eventually did.
Median radiographic progression-free survival (PFS) in cohort A was 7.39 months with PARPi, compared with 3.55 months with TPC, for a hazard ratio for progression on PARPi of 0.34 (P less than .0001). A significant benefit was seen for PARPi in the overall population (both cohorts), with a median radiographic PFS of 5.82 months va. 3.52 months, respectively (HR, 0.49; P less than .0001).
Among patients in cohort A, the objective response rate (ORR) was 33.3% with PARPi, compared with 2.3% for TPC, resulting in an odds ratio for ORR of 20.86 (P less than .0001).
PARPi demonstrated a longer time to pain progression in cohort A, with the median not reached, compared with 9.92 months with TPC (HR, 0.44; P = .0192). Perhaps because of the high proportion of TPC patients who eventually received PARPi, no statistically significant differences in overall survival have yet been seen.
What this means in practice
During my fellowship, a mentor taught that “because quality of life is generally better before progression than afterwards, PFS is a worthy endpoint in its own right.” For that reason, although I would have liked to see the data for cohort B alone, it appears worthwhile for physicians to make every effort to obtain PARPi. The difference in ORR, pain progression, and PFS at 12 months is clinically dramatic.
Of equal significance, however, is that PROfound is the first positive phase 3 biomarker-selected study evaluating a targeted treatment in patients with mCRPC. For prostate cancer – as for breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and several other cancers – the molecular biology and genetic background of our patients dictates the other tumors for which they and their family members are at risk, and expands the treatment armamentarium for them.
For those clinicians who needed to be convinced that “precision medicine” for prostate cancer patients was worthwhile, the PROfound trial should have a profound impact.
Advanced ovarian cancer
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 PAOLA-1/ENGOT-ov25 trial studied patients with stage III-IV ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had surgery, platinum-taxane chemotherapy, and at least 3 months of bevacizumab. Patients were randomized to maintenance treatment with an additional 12 months of bevacizumab plus 24 months of PARPi with olaparib or placebo. Germline BRCA mutations were not required (Ray-Coquard I et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA2).
As reported at ESMO, adding PARPi to bevacizumab maintenance provided a clinically meaningful PFS benefit of 22.1 months, in comparison with 16.6 months for bevacizumab alone. The difference was statistically significant.
For patients with tumor BRCA mutations (tBRCAm), PFS was 37.2 months with olaparib vs. 21.7 months for placebo (HR, 0.31). The PFS benefit was even more impressive for homologous recombination deficient (HRD)–positive patients, inclusive of those with tBRCAm (PFS 37.2 months for PARPi vs. 17.7 months for placebo; and in the 152 HRD-positive patients without tBRCAm, (median PFS 28.1 months vs. 16.6 months; HR, 0.43).
The improved PFS in patients with tBRCAm is similar to that reported in the SOLO1 trial of olaparib monotherapy vs. chemotherapy in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2495-2505), but the PFS in the control arm was longer in PAOLA-1 than in SOLO1, perhaps because of the use of bevacizumab in PAOLA-1. PARPi did not affect tolerance to bevacizumab.
In PAOLA-1, the HRD-positive patients who lacked tBRCAm and, by extension, lacked germline BRCA mutations – a new population of patients – was identified who benefited substantially from maintenance PARPi in the first-line setting.
What this means in practice
PAOLA-1 demonstrates that PARPi can improve outcomes in first-line treatment – and in patients beyond those with germline BRCA mutations. As a result, PAOLA-1 potentially changes the standard of care for initial treatment of the respectable fraction of patients with previously untreated, advanced müllerian cancers who have either tBRCAm or HRD positive tumors.
Importantly, PAOLA-1 is one of many published trials that stimulates the discussion of cost vs. value for combinations of biologics. The incremental benefit from the second biologic (in this case PARPi) is almost never completely additive or supra-additive to the benefit associated with the first biologic (in this case, bevacizumab). In that regard, despite the fact that PARPi showed a PFS benefit in the intent-to-treat population overall, precisely defining the patient population that has the greatest benefit will facilitate the goal of getting the treatments of greatest “value for cost” to our patients in the most responsible way.
Additional research will hopefully define the relative contribution of bevacizumab to PARPi in patients who benefited so dramatically from PARPi in PAOLA-1.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
In this edition of “How I will treat my next patient,” I review two recent presentations at the European Society of Medical Oncology Congress regarding the expanded use of poly (adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase inhibitors (PARPi) in patients with advanced solid tumors, potentially broadening the indications for this important class of agents.
Metastatic CRPC
Perhaps 25% of prostate cancer patients have loss-of-function mutations – BRCA1, BRCA2, and ATM – or alterations in homologous recombinant repair (HRR) genes. In the PROfound trial, men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (mCRPC) who had progressed on either abiraterone or enzalutamide and who had DNA-repair mutations were randomized to either olaparib (300 mg b.i.d.) or treatment of physician’s choice (TPC) with either abiraterone or enzalutamide plus prednisone (Hussain M et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA-12).
Two cohorts were enrolled. Cohort A included 245 men with BRCA1, BRCA2, or ATM mutations, and cohort B included 142 men with other alterations (BARD1, BIRP1, CDK12, CHEK1, CHEK2, FANCL, PALB2, PPP2R2A, RAD15B, RAD15C, RAD15D, or RAD54L). After disease progression, patients could cross over to receive PARPi, which more than 80% of patients eventually did.
Median radiographic progression-free survival (PFS) in cohort A was 7.39 months with PARPi, compared with 3.55 months with TPC, for a hazard ratio for progression on PARPi of 0.34 (P less than .0001). A significant benefit was seen for PARPi in the overall population (both cohorts), with a median radiographic PFS of 5.82 months va. 3.52 months, respectively (HR, 0.49; P less than .0001).
Among patients in cohort A, the objective response rate (ORR) was 33.3% with PARPi, compared with 2.3% for TPC, resulting in an odds ratio for ORR of 20.86 (P less than .0001).
PARPi demonstrated a longer time to pain progression in cohort A, with the median not reached, compared with 9.92 months with TPC (HR, 0.44; P = .0192). Perhaps because of the high proportion of TPC patients who eventually received PARPi, no statistically significant differences in overall survival have yet been seen.
What this means in practice
During my fellowship, a mentor taught that “because quality of life is generally better before progression than afterwards, PFS is a worthy endpoint in its own right.” For that reason, although I would have liked to see the data for cohort B alone, it appears worthwhile for physicians to make every effort to obtain PARPi. The difference in ORR, pain progression, and PFS at 12 months is clinically dramatic.
Of equal significance, however, is that PROfound is the first positive phase 3 biomarker-selected study evaluating a targeted treatment in patients with mCRPC. For prostate cancer – as for breast, ovarian, pancreatic, and several other cancers – the molecular biology and genetic background of our patients dictates the other tumors for which they and their family members are at risk, and expands the treatment armamentarium for them.
For those clinicians who needed to be convinced that “precision medicine” for prostate cancer patients was worthwhile, the PROfound trial should have a profound impact.
Advanced ovarian cancer
The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 PAOLA-1/ENGOT-ov25 trial studied patients with stage III-IV ovarian, fallopian tube, or primary peritoneal cancer who had surgery, platinum-taxane chemotherapy, and at least 3 months of bevacizumab. Patients were randomized to maintenance treatment with an additional 12 months of bevacizumab plus 24 months of PARPi with olaparib or placebo. Germline BRCA mutations were not required (Ray-Coquard I et al. ESMO 2019, Abstract LBA2).
As reported at ESMO, adding PARPi to bevacizumab maintenance provided a clinically meaningful PFS benefit of 22.1 months, in comparison with 16.6 months for bevacizumab alone. The difference was statistically significant.
For patients with tumor BRCA mutations (tBRCAm), PFS was 37.2 months with olaparib vs. 21.7 months for placebo (HR, 0.31). The PFS benefit was even more impressive for homologous recombination deficient (HRD)–positive patients, inclusive of those with tBRCAm (PFS 37.2 months for PARPi vs. 17.7 months for placebo; and in the 152 HRD-positive patients without tBRCAm, (median PFS 28.1 months vs. 16.6 months; HR, 0.43).
The improved PFS in patients with tBRCAm is similar to that reported in the SOLO1 trial of olaparib monotherapy vs. chemotherapy in newly diagnosed advanced ovarian cancer (N Engl J Med. 2018; 379:2495-2505), but the PFS in the control arm was longer in PAOLA-1 than in SOLO1, perhaps because of the use of bevacizumab in PAOLA-1. PARPi did not affect tolerance to bevacizumab.
In PAOLA-1, the HRD-positive patients who lacked tBRCAm and, by extension, lacked germline BRCA mutations – a new population of patients – was identified who benefited substantially from maintenance PARPi in the first-line setting.
What this means in practice
PAOLA-1 demonstrates that PARPi can improve outcomes in first-line treatment – and in patients beyond those with germline BRCA mutations. As a result, PAOLA-1 potentially changes the standard of care for initial treatment of the respectable fraction of patients with previously untreated, advanced müllerian cancers who have either tBRCAm or HRD positive tumors.
Importantly, PAOLA-1 is one of many published trials that stimulates the discussion of cost vs. value for combinations of biologics. The incremental benefit from the second biologic (in this case PARPi) is almost never completely additive or supra-additive to the benefit associated with the first biologic (in this case, bevacizumab). In that regard, despite the fact that PARPi showed a PFS benefit in the intent-to-treat population overall, precisely defining the patient population that has the greatest benefit will facilitate the goal of getting the treatments of greatest “value for cost” to our patients in the most responsible way.
Additional research will hopefully define the relative contribution of bevacizumab to PARPi in patients who benefited so dramatically from PARPi in PAOLA-1.
Dr. Lyss has been a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years, practicing in St. Louis. His clinical and research interests are in the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of breast and lung cancers and in expanding access to clinical trials to medically underserved populations.
When patient autonomy gets in the way
“Why didn’t you see that patient?”
The hospitalist on the phone was angry. He’d wanted the patient seen by neurology and cleared for discharge. Apparently, I hadn’t complied.
Actually, that isn’t true. I was on call, so I had dutifully dragged myself in (with the help of some coffee), reviewed the chart, and gone in to see the fellow.
The patient, however, had other ideas. He said he was sick of doctors, didn’t like them, didn’t want to see me, and asked me to leave. So I did.
This threw off the hospitalist’s well-choreographed day of admissions and discharges. Without me seeing the patient, he had to either discharge him on his own decision or find another neurologist who would do it.
Sorry, but I’m not going to force this issue. If a patient doesn’t want to see me, it’s not worth fighting over. Believe me, I get paid to see patients, so I don’t have much incentive to just walk away.
But at the same time I have to respect patients’ decisions. While a neurology consult is pretty noninvasive, it’s still a part of medicine. If a patient doesn’t want to see me, I’m not going to force them to.
Granted, there are exceptions. Obviously, if the patient is fairly demented or otherwise not mentally competent to make such a decision, I’ll see them. In those cases, their deteriorating mental status is likely the reason for the consult.
But the fellow that day seemed alert and reasonable, and there was nothing in the chart about confusion. So I’m going to assume he knew what he was doing when he told me to go away.
The hospitalist didn’t see this as an issue, but I did. I’m sorry if it messes up the discharge planning, but that’s not my fault. It’s the patient’s decision.
While I may disagree at times with patients’ decisions, their autonomy is still central to medicine. I respect and believe in that, even if it makes things more difficult for those around them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Why didn’t you see that patient?”
The hospitalist on the phone was angry. He’d wanted the patient seen by neurology and cleared for discharge. Apparently, I hadn’t complied.
Actually, that isn’t true. I was on call, so I had dutifully dragged myself in (with the help of some coffee), reviewed the chart, and gone in to see the fellow.
The patient, however, had other ideas. He said he was sick of doctors, didn’t like them, didn’t want to see me, and asked me to leave. So I did.
This threw off the hospitalist’s well-choreographed day of admissions and discharges. Without me seeing the patient, he had to either discharge him on his own decision or find another neurologist who would do it.
Sorry, but I’m not going to force this issue. If a patient doesn’t want to see me, it’s not worth fighting over. Believe me, I get paid to see patients, so I don’t have much incentive to just walk away.
But at the same time I have to respect patients’ decisions. While a neurology consult is pretty noninvasive, it’s still a part of medicine. If a patient doesn’t want to see me, I’m not going to force them to.
Granted, there are exceptions. Obviously, if the patient is fairly demented or otherwise not mentally competent to make such a decision, I’ll see them. In those cases, their deteriorating mental status is likely the reason for the consult.
But the fellow that day seemed alert and reasonable, and there was nothing in the chart about confusion. So I’m going to assume he knew what he was doing when he told me to go away.
The hospitalist didn’t see this as an issue, but I did. I’m sorry if it messes up the discharge planning, but that’s not my fault. It’s the patient’s decision.
While I may disagree at times with patients’ decisions, their autonomy is still central to medicine. I respect and believe in that, even if it makes things more difficult for those around them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
“Why didn’t you see that patient?”
The hospitalist on the phone was angry. He’d wanted the patient seen by neurology and cleared for discharge. Apparently, I hadn’t complied.
Actually, that isn’t true. I was on call, so I had dutifully dragged myself in (with the help of some coffee), reviewed the chart, and gone in to see the fellow.
The patient, however, had other ideas. He said he was sick of doctors, didn’t like them, didn’t want to see me, and asked me to leave. So I did.
This threw off the hospitalist’s well-choreographed day of admissions and discharges. Without me seeing the patient, he had to either discharge him on his own decision or find another neurologist who would do it.
Sorry, but I’m not going to force this issue. If a patient doesn’t want to see me, it’s not worth fighting over. Believe me, I get paid to see patients, so I don’t have much incentive to just walk away.
But at the same time I have to respect patients’ decisions. While a neurology consult is pretty noninvasive, it’s still a part of medicine. If a patient doesn’t want to see me, I’m not going to force them to.
Granted, there are exceptions. Obviously, if the patient is fairly demented or otherwise not mentally competent to make such a decision, I’ll see them. In those cases, their deteriorating mental status is likely the reason for the consult.
But the fellow that day seemed alert and reasonable, and there was nothing in the chart about confusion. So I’m going to assume he knew what he was doing when he told me to go away.
The hospitalist didn’t see this as an issue, but I did. I’m sorry if it messes up the discharge planning, but that’s not my fault. It’s the patient’s decision.
While I may disagree at times with patients’ decisions, their autonomy is still central to medicine. I respect and believe in that, even if it makes things more difficult for those around them.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz.
Supporting elimination of nonmedical vaccine exemptions
Let’s suppose your first patient of the morning is a 2-month-old you have never seen before. The family arrives 10 minutes late because they are still getting the dressing-undressing-diaper change-car seat–adjusting thing worked out. Father is a computer programmer. Mother lists her occupation as nutrition counselor. The child is gaining. Breastfeeding seems to come naturally to the dyad.
As the visit draws to a close, you take the matter-of-fact approach and say, “The nurse will be in shortly with the vaccines do you have any questions.” Well ... it turns out the parents don’t feel comfortable with vaccines. They claim to understand the science and feel that vaccines make sense for some families. But they feel that for themselves, with a healthy lifestyle and God’s benevolence their son will be protected without having to introduce a host of foreign substances into his body.
What word best describes your reaction? Anger? Frustration? Disappointment (in our education system)? Maybe you’re angry at yourself for failing to make it clear in your office pamphlet and social media feeds that to protect your other patients, you no longer accept families who refuse immunizations for the common childhood diseases.
The American Academy of Pediatrics says it feels your pain, and its Annual Leadership Forum made eliminating nonmedical vaccine exemption laws its top priority in 2019. As part of its effort to help, the AAP Board of Directors was asked to advocate for the creation of a toolkit of strategies for Academy chapters facing the challenge of nonmedical exemptions. As an initial step to this process, three physicians in the department of pediatrics at the Denver Health Medical Center have begun interviewing religious leaders in hopes of developing “clergy-specific vaccine educational materials and deriv[ing] best practices for engaging them as vaccination advocates.” The investigators describe their plan and initial findings in Pediatrics (2019 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0933). Although they acknowledged that their efforts may not provide a quick solution to the nonmedical exemption problem, they hope that including more stakeholders and engendering trust will help future discussions.
Fourteen pages deeper into that issue of Pediatrics is the runner-up submission of this year’s Section on Pediatric Trainees essay competition titled “What I Learned From the Antivaccine Movement” (2019 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2384). Alana C. Ju, MD, describes the 2-hour ordeal she endured to testify at the California State Capitol in support of a state Senate bill aimed at tightening the regulations for vaccine medical exemptions. Totally unprepared for the “level of vitriol” aimed at her and other supporters of the bill, she was “accused of violating her duty as” a pediatrician because she was failing to protect children. The supporters were called “greedy, ignorant, and negligent.”
To her credit, Dr. Ju was able to step back from this assault and began looking at the faces of her accusers and learned that, “they too, felt strongly about children’s health.” She realized that “focusing on perceived ignorance is counterproductive.” She now hopes that by focusing on the shared goal of what is best for children, “we can all be better advocates.”
Both of these articles have a warm sort of kumbaya feel about them. It never is a bad idea to learn more about those with whom we disagree. But before huddling up too close to the campfire, we must realize that there is good evidence that sharing the scientific data with vaccine-hesitant parents doesn’t convert them into vaccine acceptors. In fact, it may strengthen their resolve to resist (Nyhan et al. “Effective Messages in Vaccine Promotion: A Randomized Trial,” Pediatrics. 2014 Apr;133[4] e835-42).
We are unlikely to convert many anti-vaxxers by sitting down together. Our target audience needs to be legislators and the majority of people who do vaccinate their children. These are the voters who will support legislation to eliminate nonmedical vaccine exemptions. To characterize anti-vaxxers as despicable ignorants is untrue and serves no purpose. We all do care about the health of children. However,
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
*This article has been updated 1/22/2020.
Let’s suppose your first patient of the morning is a 2-month-old you have never seen before. The family arrives 10 minutes late because they are still getting the dressing-undressing-diaper change-car seat–adjusting thing worked out. Father is a computer programmer. Mother lists her occupation as nutrition counselor. The child is gaining. Breastfeeding seems to come naturally to the dyad.
As the visit draws to a close, you take the matter-of-fact approach and say, “The nurse will be in shortly with the vaccines do you have any questions.” Well ... it turns out the parents don’t feel comfortable with vaccines. They claim to understand the science and feel that vaccines make sense for some families. But they feel that for themselves, with a healthy lifestyle and God’s benevolence their son will be protected without having to introduce a host of foreign substances into his body.
What word best describes your reaction? Anger? Frustration? Disappointment (in our education system)? Maybe you’re angry at yourself for failing to make it clear in your office pamphlet and social media feeds that to protect your other patients, you no longer accept families who refuse immunizations for the common childhood diseases.
The American Academy of Pediatrics says it feels your pain, and its Annual Leadership Forum made eliminating nonmedical vaccine exemption laws its top priority in 2019. As part of its effort to help, the AAP Board of Directors was asked to advocate for the creation of a toolkit of strategies for Academy chapters facing the challenge of nonmedical exemptions. As an initial step to this process, three physicians in the department of pediatrics at the Denver Health Medical Center have begun interviewing religious leaders in hopes of developing “clergy-specific vaccine educational materials and deriv[ing] best practices for engaging them as vaccination advocates.” The investigators describe their plan and initial findings in Pediatrics (2019 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0933). Although they acknowledged that their efforts may not provide a quick solution to the nonmedical exemption problem, they hope that including more stakeholders and engendering trust will help future discussions.
Fourteen pages deeper into that issue of Pediatrics is the runner-up submission of this year’s Section on Pediatric Trainees essay competition titled “What I Learned From the Antivaccine Movement” (2019 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2384). Alana C. Ju, MD, describes the 2-hour ordeal she endured to testify at the California State Capitol in support of a state Senate bill aimed at tightening the regulations for vaccine medical exemptions. Totally unprepared for the “level of vitriol” aimed at her and other supporters of the bill, she was “accused of violating her duty as” a pediatrician because she was failing to protect children. The supporters were called “greedy, ignorant, and negligent.”
To her credit, Dr. Ju was able to step back from this assault and began looking at the faces of her accusers and learned that, “they too, felt strongly about children’s health.” She realized that “focusing on perceived ignorance is counterproductive.” She now hopes that by focusing on the shared goal of what is best for children, “we can all be better advocates.”
Both of these articles have a warm sort of kumbaya feel about them. It never is a bad idea to learn more about those with whom we disagree. But before huddling up too close to the campfire, we must realize that there is good evidence that sharing the scientific data with vaccine-hesitant parents doesn’t convert them into vaccine acceptors. In fact, it may strengthen their resolve to resist (Nyhan et al. “Effective Messages in Vaccine Promotion: A Randomized Trial,” Pediatrics. 2014 Apr;133[4] e835-42).
We are unlikely to convert many anti-vaxxers by sitting down together. Our target audience needs to be legislators and the majority of people who do vaccinate their children. These are the voters who will support legislation to eliminate nonmedical vaccine exemptions. To characterize anti-vaxxers as despicable ignorants is untrue and serves no purpose. We all do care about the health of children. However,
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
*This article has been updated 1/22/2020.
Let’s suppose your first patient of the morning is a 2-month-old you have never seen before. The family arrives 10 minutes late because they are still getting the dressing-undressing-diaper change-car seat–adjusting thing worked out. Father is a computer programmer. Mother lists her occupation as nutrition counselor. The child is gaining. Breastfeeding seems to come naturally to the dyad.
As the visit draws to a close, you take the matter-of-fact approach and say, “The nurse will be in shortly with the vaccines do you have any questions.” Well ... it turns out the parents don’t feel comfortable with vaccines. They claim to understand the science and feel that vaccines make sense for some families. But they feel that for themselves, with a healthy lifestyle and God’s benevolence their son will be protected without having to introduce a host of foreign substances into his body.
What word best describes your reaction? Anger? Frustration? Disappointment (in our education system)? Maybe you’re angry at yourself for failing to make it clear in your office pamphlet and social media feeds that to protect your other patients, you no longer accept families who refuse immunizations for the common childhood diseases.
The American Academy of Pediatrics says it feels your pain, and its Annual Leadership Forum made eliminating nonmedical vaccine exemption laws its top priority in 2019. As part of its effort to help, the AAP Board of Directors was asked to advocate for the creation of a toolkit of strategies for Academy chapters facing the challenge of nonmedical exemptions. As an initial step to this process, three physicians in the department of pediatrics at the Denver Health Medical Center have begun interviewing religious leaders in hopes of developing “clergy-specific vaccine educational materials and deriv[ing] best practices for engaging them as vaccination advocates.” The investigators describe their plan and initial findings in Pediatrics (2019 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-0933). Although they acknowledged that their efforts may not provide a quick solution to the nonmedical exemption problem, they hope that including more stakeholders and engendering trust will help future discussions.
Fourteen pages deeper into that issue of Pediatrics is the runner-up submission of this year’s Section on Pediatric Trainees essay competition titled “What I Learned From the Antivaccine Movement” (2019 Oct. doi: 10.1542/peds.2019-2384). Alana C. Ju, MD, describes the 2-hour ordeal she endured to testify at the California State Capitol in support of a state Senate bill aimed at tightening the regulations for vaccine medical exemptions. Totally unprepared for the “level of vitriol” aimed at her and other supporters of the bill, she was “accused of violating her duty as” a pediatrician because she was failing to protect children. The supporters were called “greedy, ignorant, and negligent.”
To her credit, Dr. Ju was able to step back from this assault and began looking at the faces of her accusers and learned that, “they too, felt strongly about children’s health.” She realized that “focusing on perceived ignorance is counterproductive.” She now hopes that by focusing on the shared goal of what is best for children, “we can all be better advocates.”
Both of these articles have a warm sort of kumbaya feel about them. It never is a bad idea to learn more about those with whom we disagree. But before huddling up too close to the campfire, we must realize that there is good evidence that sharing the scientific data with vaccine-hesitant parents doesn’t convert them into vaccine acceptors. In fact, it may strengthen their resolve to resist (Nyhan et al. “Effective Messages in Vaccine Promotion: A Randomized Trial,” Pediatrics. 2014 Apr;133[4] e835-42).
We are unlikely to convert many anti-vaxxers by sitting down together. Our target audience needs to be legislators and the majority of people who do vaccinate their children. These are the voters who will support legislation to eliminate nonmedical vaccine exemptions. To characterize anti-vaxxers as despicable ignorants is untrue and serves no purpose. We all do care about the health of children. However,
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Email him at [email protected].
*This article has been updated 1/22/2020.
Climate change, health systems, and hospital medicine
Working toward carbon neutrality
I have always enjoyed talking with my patients from coastal Louisiana. They enjoy life, embrace their environment, and give me a perspective which is both similar and different than that of residents of New Orleans where I practice hospital medicine.
Their hospitalization is often a reflective moment in their lives. Lately I have been asking them about their advice to their children concerning the future of southern Louisiana in reference to sea rise, global warming, and increasing climatic events. More often than not, they have been telling their children it is time to move away.
These are a people who have strong devotion to family, but they are also practical. More than anything they would like their children to stay and preserve their heritage, but concern for their children’s future outweighs that. They have not come to this conclusion by scientific reports, but rather by what is happening before them. This group of people doesn’t alarm easily, but they see the unrelenting evidence of land loss and sea rise before them with little reason to believe it will change.
I am normally not one to speak out about climate change. Like most I have listened to the continuous alarms sounded by experts but have always assumed someone more qualified than myself should lead the efforts. But when I see the tangible effects of climate change both in my own life and the lives of my patients, I feel a sense of urgency.
12 years
Twelve years. That is the time we have to significantly reduce carbon emissions before catastrophic and potentially irreversible events will occur. This evidence is according to the authors of the landmark report by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released in October 2018. The report states urgent and unprecedented changes are needed to limit temperature elevations of 1.5°C and 2°C, as compared with the preindustrial era. Exceeding a 2°C elevation will likely lead to global adverse events at an unprecedented level.1
The events forecast by the U.N. report are not abstract, particularly as they relate to public health. With high confidence, the report outlines with high specificity: increases in extreme heat, floods, crop failures, and a multitude of economic and social stressors which will affect the care of our most vulnerable patients.1
This statement by Dr. Dana Hanson, president of the World Medical Association, summarizes the effects of climate change on the delivery of health care: “Climate change represents an inevitable massive threat to global health that will likely eclipse the major pandemics as a leading cause of death in the 21st century.”
So, what does the health care system have to do with climate change and its primary driver, carbon emissions? More than I realized, as the U.S. health care industry produces 10% of the nation’s carbon emissions.2 If the U.S. health care system was a country it would be ranked seventh, ahead of the United Kingdom; 10% of all smog and 9% of all particulate-related respiratory disease can be attributed to the carbon emissions of the health care industry. This breaks down to possibly 20,000 premature deaths per year.2 Our current health care industry is a significant driver of environmentally related disease and will continue to be so, unless major change occurs.
Although much of it is behind the scenes, providing health care 24/7 is a highly energy-intensive and waste-producing endeavor. Many of the innovations to reduce carbon emissions that have been seen in other industries have lagged behind in health care, as we have focused on other issues.
But the health care system is transitioning. It strives to address the whole person, including where they live, work, and play. A key component of this will be addressing our impact on the environments we serve. How can we make that argument if we don’t first address our own impact on the climate?
Carbon-neutral health care
Health care is one of the few industries that has the economic clout, the scientific basis, the community engagement, and perhaps most importantly the motivations to “first, do no harm” that could lead a national (if not a global) transformation in environmental stewardship among all industries.
Many agree that action is needed, but is essential that we set specific meaningful goals that take into account the urgency of the situation. One possible solution is to encourage every health care system to begin the process of becoming carbon neutral. Simply defined, carbon neutrality is balancing the activities that result in carbon emissions with activities that reduce carbon emissions. Carbon neutrality has become the standard by which an industry’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions is measured. The measurement is standardized and achievable, and the basic concept is understood by most. It results not only in long-term benefits to climate change, but immediate improvement of air quality in the local community. In addition, achieving carbon neutrality serves as a catalyst of new desired industries, improves employee morale, and aids in recruitment.3
So, what would a carbon-neutral health care system look like? In short, sustainability should be considered in all of its actions. Risks and benefits would be contemplated, as we do with all treatments, except now environmental risks would be brought into the equation. This includes the obvious, such as purchasing and supporting the development of renewable energy, but also transportation of patients and employees, food supply chains, and even the use of virtual visits to reduce the environmental impact of patient transportation.
I am optimistic that carbon neutrality is achievable in the health care sector. It can drive economic development and engage the community in environmental stewardship efforts. But time is of the essence and leaders for these efforts are needed now. As hospitalists, we are on the front lines of the health care system. We see the direct impact of social, economic, and environmental issues on our patients. We have credibility with both our patients and hospital administration. Among all industries, there need to be champions of environmental sustainability efforts. Hospitalists are uniquely positioned to fill that role.
My concern is that 12 years is right around the corner. We are at an inflection point on our efforts to reduce carbon emissions and that is good, but time has become our enemy. The difference between terrible and unlivable will be our, and the world’s, response to reducing carbon emissions.
It is time for bold action from us, the health care community. It is our moment and our place to lead those efforts, so let’s take advantage of both this challenge and this opportunity. Consider leading those efforts in your health care system.
Dr. Conrad is medical director of community affairs and health policy at Ochsner Health Systems in New Orleans.
References
1. Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C. Incheon [Republic of Korea]: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 7 Oct 2018.
2. Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. PLoS ONE. 11(6):e0157014.
3. McCunn LJ, Gifford R. Do green offices affect employee engagement and environmental attitudes? Archit Sci Rev. 55:2;128-34. doi: 10.1080/00038628.2012.667939.
Working toward carbon neutrality
Working toward carbon neutrality
I have always enjoyed talking with my patients from coastal Louisiana. They enjoy life, embrace their environment, and give me a perspective which is both similar and different than that of residents of New Orleans where I practice hospital medicine.
Their hospitalization is often a reflective moment in their lives. Lately I have been asking them about their advice to their children concerning the future of southern Louisiana in reference to sea rise, global warming, and increasing climatic events. More often than not, they have been telling their children it is time to move away.
These are a people who have strong devotion to family, but they are also practical. More than anything they would like their children to stay and preserve their heritage, but concern for their children’s future outweighs that. They have not come to this conclusion by scientific reports, but rather by what is happening before them. This group of people doesn’t alarm easily, but they see the unrelenting evidence of land loss and sea rise before them with little reason to believe it will change.
I am normally not one to speak out about climate change. Like most I have listened to the continuous alarms sounded by experts but have always assumed someone more qualified than myself should lead the efforts. But when I see the tangible effects of climate change both in my own life and the lives of my patients, I feel a sense of urgency.
12 years
Twelve years. That is the time we have to significantly reduce carbon emissions before catastrophic and potentially irreversible events will occur. This evidence is according to the authors of the landmark report by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released in October 2018. The report states urgent and unprecedented changes are needed to limit temperature elevations of 1.5°C and 2°C, as compared with the preindustrial era. Exceeding a 2°C elevation will likely lead to global adverse events at an unprecedented level.1
The events forecast by the U.N. report are not abstract, particularly as they relate to public health. With high confidence, the report outlines with high specificity: increases in extreme heat, floods, crop failures, and a multitude of economic and social stressors which will affect the care of our most vulnerable patients.1
This statement by Dr. Dana Hanson, president of the World Medical Association, summarizes the effects of climate change on the delivery of health care: “Climate change represents an inevitable massive threat to global health that will likely eclipse the major pandemics as a leading cause of death in the 21st century.”
So, what does the health care system have to do with climate change and its primary driver, carbon emissions? More than I realized, as the U.S. health care industry produces 10% of the nation’s carbon emissions.2 If the U.S. health care system was a country it would be ranked seventh, ahead of the United Kingdom; 10% of all smog and 9% of all particulate-related respiratory disease can be attributed to the carbon emissions of the health care industry. This breaks down to possibly 20,000 premature deaths per year.2 Our current health care industry is a significant driver of environmentally related disease and will continue to be so, unless major change occurs.
Although much of it is behind the scenes, providing health care 24/7 is a highly energy-intensive and waste-producing endeavor. Many of the innovations to reduce carbon emissions that have been seen in other industries have lagged behind in health care, as we have focused on other issues.
But the health care system is transitioning. It strives to address the whole person, including where they live, work, and play. A key component of this will be addressing our impact on the environments we serve. How can we make that argument if we don’t first address our own impact on the climate?
Carbon-neutral health care
Health care is one of the few industries that has the economic clout, the scientific basis, the community engagement, and perhaps most importantly the motivations to “first, do no harm” that could lead a national (if not a global) transformation in environmental stewardship among all industries.
Many agree that action is needed, but is essential that we set specific meaningful goals that take into account the urgency of the situation. One possible solution is to encourage every health care system to begin the process of becoming carbon neutral. Simply defined, carbon neutrality is balancing the activities that result in carbon emissions with activities that reduce carbon emissions. Carbon neutrality has become the standard by which an industry’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions is measured. The measurement is standardized and achievable, and the basic concept is understood by most. It results not only in long-term benefits to climate change, but immediate improvement of air quality in the local community. In addition, achieving carbon neutrality serves as a catalyst of new desired industries, improves employee morale, and aids in recruitment.3
So, what would a carbon-neutral health care system look like? In short, sustainability should be considered in all of its actions. Risks and benefits would be contemplated, as we do with all treatments, except now environmental risks would be brought into the equation. This includes the obvious, such as purchasing and supporting the development of renewable energy, but also transportation of patients and employees, food supply chains, and even the use of virtual visits to reduce the environmental impact of patient transportation.
I am optimistic that carbon neutrality is achievable in the health care sector. It can drive economic development and engage the community in environmental stewardship efforts. But time is of the essence and leaders for these efforts are needed now. As hospitalists, we are on the front lines of the health care system. We see the direct impact of social, economic, and environmental issues on our patients. We have credibility with both our patients and hospital administration. Among all industries, there need to be champions of environmental sustainability efforts. Hospitalists are uniquely positioned to fill that role.
My concern is that 12 years is right around the corner. We are at an inflection point on our efforts to reduce carbon emissions and that is good, but time has become our enemy. The difference between terrible and unlivable will be our, and the world’s, response to reducing carbon emissions.
It is time for bold action from us, the health care community. It is our moment and our place to lead those efforts, so let’s take advantage of both this challenge and this opportunity. Consider leading those efforts in your health care system.
Dr. Conrad is medical director of community affairs and health policy at Ochsner Health Systems in New Orleans.
References
1. Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C. Incheon [Republic of Korea]: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 7 Oct 2018.
2. Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. PLoS ONE. 11(6):e0157014.
3. McCunn LJ, Gifford R. Do green offices affect employee engagement and environmental attitudes? Archit Sci Rev. 55:2;128-34. doi: 10.1080/00038628.2012.667939.
I have always enjoyed talking with my patients from coastal Louisiana. They enjoy life, embrace their environment, and give me a perspective which is both similar and different than that of residents of New Orleans where I practice hospital medicine.
Their hospitalization is often a reflective moment in their lives. Lately I have been asking them about their advice to their children concerning the future of southern Louisiana in reference to sea rise, global warming, and increasing climatic events. More often than not, they have been telling their children it is time to move away.
These are a people who have strong devotion to family, but they are also practical. More than anything they would like their children to stay and preserve their heritage, but concern for their children’s future outweighs that. They have not come to this conclusion by scientific reports, but rather by what is happening before them. This group of people doesn’t alarm easily, but they see the unrelenting evidence of land loss and sea rise before them with little reason to believe it will change.
I am normally not one to speak out about climate change. Like most I have listened to the continuous alarms sounded by experts but have always assumed someone more qualified than myself should lead the efforts. But when I see the tangible effects of climate change both in my own life and the lives of my patients, I feel a sense of urgency.
12 years
Twelve years. That is the time we have to significantly reduce carbon emissions before catastrophic and potentially irreversible events will occur. This evidence is according to the authors of the landmark report by the UN Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change released in October 2018. The report states urgent and unprecedented changes are needed to limit temperature elevations of 1.5°C and 2°C, as compared with the preindustrial era. Exceeding a 2°C elevation will likely lead to global adverse events at an unprecedented level.1
The events forecast by the U.N. report are not abstract, particularly as they relate to public health. With high confidence, the report outlines with high specificity: increases in extreme heat, floods, crop failures, and a multitude of economic and social stressors which will affect the care of our most vulnerable patients.1
This statement by Dr. Dana Hanson, president of the World Medical Association, summarizes the effects of climate change on the delivery of health care: “Climate change represents an inevitable massive threat to global health that will likely eclipse the major pandemics as a leading cause of death in the 21st century.”
So, what does the health care system have to do with climate change and its primary driver, carbon emissions? More than I realized, as the U.S. health care industry produces 10% of the nation’s carbon emissions.2 If the U.S. health care system was a country it would be ranked seventh, ahead of the United Kingdom; 10% of all smog and 9% of all particulate-related respiratory disease can be attributed to the carbon emissions of the health care industry. This breaks down to possibly 20,000 premature deaths per year.2 Our current health care industry is a significant driver of environmentally related disease and will continue to be so, unless major change occurs.
Although much of it is behind the scenes, providing health care 24/7 is a highly energy-intensive and waste-producing endeavor. Many of the innovations to reduce carbon emissions that have been seen in other industries have lagged behind in health care, as we have focused on other issues.
But the health care system is transitioning. It strives to address the whole person, including where they live, work, and play. A key component of this will be addressing our impact on the environments we serve. How can we make that argument if we don’t first address our own impact on the climate?
Carbon-neutral health care
Health care is one of the few industries that has the economic clout, the scientific basis, the community engagement, and perhaps most importantly the motivations to “first, do no harm” that could lead a national (if not a global) transformation in environmental stewardship among all industries.
Many agree that action is needed, but is essential that we set specific meaningful goals that take into account the urgency of the situation. One possible solution is to encourage every health care system to begin the process of becoming carbon neutral. Simply defined, carbon neutrality is balancing the activities that result in carbon emissions with activities that reduce carbon emissions. Carbon neutrality has become the standard by which an industry’s commitment to reducing carbon emissions is measured. The measurement is standardized and achievable, and the basic concept is understood by most. It results not only in long-term benefits to climate change, but immediate improvement of air quality in the local community. In addition, achieving carbon neutrality serves as a catalyst of new desired industries, improves employee morale, and aids in recruitment.3
So, what would a carbon-neutral health care system look like? In short, sustainability should be considered in all of its actions. Risks and benefits would be contemplated, as we do with all treatments, except now environmental risks would be brought into the equation. This includes the obvious, such as purchasing and supporting the development of renewable energy, but also transportation of patients and employees, food supply chains, and even the use of virtual visits to reduce the environmental impact of patient transportation.
I am optimistic that carbon neutrality is achievable in the health care sector. It can drive economic development and engage the community in environmental stewardship efforts. But time is of the essence and leaders for these efforts are needed now. As hospitalists, we are on the front lines of the health care system. We see the direct impact of social, economic, and environmental issues on our patients. We have credibility with both our patients and hospital administration. Among all industries, there need to be champions of environmental sustainability efforts. Hospitalists are uniquely positioned to fill that role.
My concern is that 12 years is right around the corner. We are at an inflection point on our efforts to reduce carbon emissions and that is good, but time has become our enemy. The difference between terrible and unlivable will be our, and the world’s, response to reducing carbon emissions.
It is time for bold action from us, the health care community. It is our moment and our place to lead those efforts, so let’s take advantage of both this challenge and this opportunity. Consider leading those efforts in your health care system.
Dr. Conrad is medical director of community affairs and health policy at Ochsner Health Systems in New Orleans.
References
1. Special Report on Global Warming of 1.5°C. Incheon [Republic of Korea]: Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. 7 Oct 2018.
2. Eckelman MJ, Sherman J. Environmental Impacts of the U.S. Health Care System and Effects on Public Health. PLoS ONE. 11(6):e0157014.
3. McCunn LJ, Gifford R. Do green offices affect employee engagement and environmental attitudes? Archit Sci Rev. 55:2;128-34. doi: 10.1080/00038628.2012.667939.
Antituberculosis drugs in pregnancy and lactation
Tuberculosis is one of the top ten causes of death worldwide and the leading cause from a single infectious agent. In the 2012-2017 period, there were more than 9,000 cases of TB each year in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that untreated TB is a greater hazard to a pregnant woman and her fetus than its treatment.
In the material below, the molecular weights, rounded to the nearest whole number, are shown in parentheses after the drug name. Those less than 1,000 or so suggest that the drug will cross the placenta throughout pregnancy. In the second half of pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, nearly all drugs will cross regardless of their molecular weight.
Para-aminosalicylic acid (Paser) (153) is most frequently used in combination with other agents for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis; multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB) is defined as being caused by TB bacteria that is resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampin, the two most potent TB drugs. The drug has been associated with a marked increased risk of birth defects in some, but not all, studies. Because of this potential risk, the drug is best avoided in the first trimester. The drug is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Bedaquiline (Sirturo) (556) is used in combination therapy for patents with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. One report describing the use of this drug during human pregnancy has been located. Treatment was started in the last 3 weeks of pregnancy and no abnormalities were noted in the child at birth and for 2 years after birth (Emerg Infect Dis. 2017. doi: 10.3201/eid2310.161398). The CDC states that the drug should be used only in a minimum four-drug treatment regimen and administered by direct observation (MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013 Oct 25;62[RR-09]:1-12). The drug probably is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Capreomycin (Capastat) (653-669) is a polypeptide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces capreolus that is given intramuscularly. The human pregnancy data are limited to three reports. The toxicity of capreomycin is similar to aminoglycosides (e.g., cranial nerve VIII and renal) and it should not be used with these agents. The CDC has classified the drug as contraindicated in pregnancy. The drug probably is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Cycloserine (Seromycin) (102) is a broad spectrum antibiotic. The human pregnancy data are limited but have not shown embryo-fetal harm. Although the best course is to avoid the drug during gestation, it should not be withheld because of pregnancy if the maternal condition requires the antibiotic. The American Academy of Pediatrics classified cycloserine as compatible with breastfeeding.
Ethambutol (Myambutol) (205) should be used in conjunction with other antituberculosis drugs. The human pregnancy data do not suggest an embryo-fetal risk. A frequently used regimen is ethambutol + isoniazid + rifampin. The American Academy of Pediatrics classified ethambutol as compatible with breastfeeding.
Ethionamide (Trecator) (166) is indicated when Mycobacterium tuberculosis is resistant to isoniazid or rifampin, or when the patient is intolerant to other drugs. Although the animal reproductive data suggest risk, the limited human data suggest that the risk is probably low. If indicated, the drug should not be withheld because of pregnancy. Although the molecular weight suggests that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, no reports describing the amount in milk have been located.
Isoniazid (137) is compatible in pregnancy, even though the molecular weight suggests that it will cross the placenta, because the maternal benefit is much greater than the potential embryo-fetal risk. Although the human data are limited, the molecular weight also suggests that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, but it can be considered probably compatible during breastfeeding. No reports of isoniazid-induced effects in the nursing infant have been located, but the potential for interference with nucleic acid function and for hepatotoxicity may exist.
Pyrazinamide (123) is metabolized to an active metabolite. The molecular weight, low plasma protein binding (10%), and prolonged elimination half-life (9-10 hours) suggest that the drug will cross the placenta throughout pregnancy. The drug has been used in human pregnancy without causing embryo-fetal harm. Similar results, although limited, were reported when the drug was used during breastfeeding.
Rifabutin (Mycobutin) (847) has no reported human pregnancy data, but the animal data suggest low risk. The drug probably crosses the placenta throughout pregnancy. The maternal benefit appears to outweigh the unknown risk to the embryo-fetus, so therapy should not be withheld because of pregnancy. The drug probably is excreted into breast milk.
Rifampin (Rifadin) (823) appears to be compatible in pregnancy. Several reviews and reports have concluded that the drug was not a teratogen and recommended use of the drug with isoniazid and ethambutol. However, prophylactic vitamin K1 has been recommended to prevent drug-induced hemorrhagic disease of the newborn. There are no data regarding its use during breastfeeding, but it is probably compatible.
Rifapentine (Priftin) (877) was toxic and teratogenic in two animal species at doses close to those used in humans. In a 2018 study, however, the rates of fetal loss in pregnancies of less than 20 weeks (8/54, 15%) and congenital anomalies in live births (1/37, 3%) were within the expected background rates (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 May;15[4]:570-80). There are no data regarding its use during breastfeeding, but it is probably compatible.
The CDC classifies four antituberculosis and one class of drugs as contraindicated in pregnancy. In addition to capreomycin mentioned above, they are amikacin, fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin, moxifloxacin, ofloxacin), kanamycin, and streptomycin. These ten agents are discussed in the 11th edition of my book “Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation,” (Wolters Kluwer Health: Riverwood, Il., 2017). If they have to be used, checking this source will provide information that has to be discussed with the patient.
Mr. Briggs is clinical professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco, and adjunct professor of pharmacy at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, as well as at Washington State University, Spokane. Mr. Briggs had no disclosures, except for his book. Email him at [email protected].
Tuberculosis is one of the top ten causes of death worldwide and the leading cause from a single infectious agent. In the 2012-2017 period, there were more than 9,000 cases of TB each year in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that untreated TB is a greater hazard to a pregnant woman and her fetus than its treatment.
In the material below, the molecular weights, rounded to the nearest whole number, are shown in parentheses after the drug name. Those less than 1,000 or so suggest that the drug will cross the placenta throughout pregnancy. In the second half of pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, nearly all drugs will cross regardless of their molecular weight.
Para-aminosalicylic acid (Paser) (153) is most frequently used in combination with other agents for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis; multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB) is defined as being caused by TB bacteria that is resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampin, the two most potent TB drugs. The drug has been associated with a marked increased risk of birth defects in some, but not all, studies. Because of this potential risk, the drug is best avoided in the first trimester. The drug is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Bedaquiline (Sirturo) (556) is used in combination therapy for patents with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. One report describing the use of this drug during human pregnancy has been located. Treatment was started in the last 3 weeks of pregnancy and no abnormalities were noted in the child at birth and for 2 years after birth (Emerg Infect Dis. 2017. doi: 10.3201/eid2310.161398). The CDC states that the drug should be used only in a minimum four-drug treatment regimen and administered by direct observation (MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013 Oct 25;62[RR-09]:1-12). The drug probably is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Capreomycin (Capastat) (653-669) is a polypeptide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces capreolus that is given intramuscularly. The human pregnancy data are limited to three reports. The toxicity of capreomycin is similar to aminoglycosides (e.g., cranial nerve VIII and renal) and it should not be used with these agents. The CDC has classified the drug as contraindicated in pregnancy. The drug probably is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Cycloserine (Seromycin) (102) is a broad spectrum antibiotic. The human pregnancy data are limited but have not shown embryo-fetal harm. Although the best course is to avoid the drug during gestation, it should not be withheld because of pregnancy if the maternal condition requires the antibiotic. The American Academy of Pediatrics classified cycloserine as compatible with breastfeeding.
Ethambutol (Myambutol) (205) should be used in conjunction with other antituberculosis drugs. The human pregnancy data do not suggest an embryo-fetal risk. A frequently used regimen is ethambutol + isoniazid + rifampin. The American Academy of Pediatrics classified ethambutol as compatible with breastfeeding.
Ethionamide (Trecator) (166) is indicated when Mycobacterium tuberculosis is resistant to isoniazid or rifampin, or when the patient is intolerant to other drugs. Although the animal reproductive data suggest risk, the limited human data suggest that the risk is probably low. If indicated, the drug should not be withheld because of pregnancy. Although the molecular weight suggests that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, no reports describing the amount in milk have been located.
Isoniazid (137) is compatible in pregnancy, even though the molecular weight suggests that it will cross the placenta, because the maternal benefit is much greater than the potential embryo-fetal risk. Although the human data are limited, the molecular weight also suggests that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, but it can be considered probably compatible during breastfeeding. No reports of isoniazid-induced effects in the nursing infant have been located, but the potential for interference with nucleic acid function and for hepatotoxicity may exist.
Pyrazinamide (123) is metabolized to an active metabolite. The molecular weight, low plasma protein binding (10%), and prolonged elimination half-life (9-10 hours) suggest that the drug will cross the placenta throughout pregnancy. The drug has been used in human pregnancy without causing embryo-fetal harm. Similar results, although limited, were reported when the drug was used during breastfeeding.
Rifabutin (Mycobutin) (847) has no reported human pregnancy data, but the animal data suggest low risk. The drug probably crosses the placenta throughout pregnancy. The maternal benefit appears to outweigh the unknown risk to the embryo-fetus, so therapy should not be withheld because of pregnancy. The drug probably is excreted into breast milk.
Rifampin (Rifadin) (823) appears to be compatible in pregnancy. Several reviews and reports have concluded that the drug was not a teratogen and recommended use of the drug with isoniazid and ethambutol. However, prophylactic vitamin K1 has been recommended to prevent drug-induced hemorrhagic disease of the newborn. There are no data regarding its use during breastfeeding, but it is probably compatible.
Rifapentine (Priftin) (877) was toxic and teratogenic in two animal species at doses close to those used in humans. In a 2018 study, however, the rates of fetal loss in pregnancies of less than 20 weeks (8/54, 15%) and congenital anomalies in live births (1/37, 3%) were within the expected background rates (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 May;15[4]:570-80). There are no data regarding its use during breastfeeding, but it is probably compatible.
The CDC classifies four antituberculosis and one class of drugs as contraindicated in pregnancy. In addition to capreomycin mentioned above, they are amikacin, fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin, moxifloxacin, ofloxacin), kanamycin, and streptomycin. These ten agents are discussed in the 11th edition of my book “Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation,” (Wolters Kluwer Health: Riverwood, Il., 2017). If they have to be used, checking this source will provide information that has to be discussed with the patient.
Mr. Briggs is clinical professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco, and adjunct professor of pharmacy at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, as well as at Washington State University, Spokane. Mr. Briggs had no disclosures, except for his book. Email him at [email protected].
Tuberculosis is one of the top ten causes of death worldwide and the leading cause from a single infectious agent. In the 2012-2017 period, there were more than 9,000 cases of TB each year in the United States. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention states that untreated TB is a greater hazard to a pregnant woman and her fetus than its treatment.
In the material below, the molecular weights, rounded to the nearest whole number, are shown in parentheses after the drug name. Those less than 1,000 or so suggest that the drug will cross the placenta throughout pregnancy. In the second half of pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, nearly all drugs will cross regardless of their molecular weight.
Para-aminosalicylic acid (Paser) (153) is most frequently used in combination with other agents for the treatment of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis; multidrug-resistant TB (MDR TB) is defined as being caused by TB bacteria that is resistant to at least isoniazid and rifampin, the two most potent TB drugs. The drug has been associated with a marked increased risk of birth defects in some, but not all, studies. Because of this potential risk, the drug is best avoided in the first trimester. The drug is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Bedaquiline (Sirturo) (556) is used in combination therapy for patents with multidrug-resistant tuberculosis. One report describing the use of this drug during human pregnancy has been located. Treatment was started in the last 3 weeks of pregnancy and no abnormalities were noted in the child at birth and for 2 years after birth (Emerg Infect Dis. 2017. doi: 10.3201/eid2310.161398). The CDC states that the drug should be used only in a minimum four-drug treatment regimen and administered by direct observation (MMWR Recomm Rep. 2013 Oct 25;62[RR-09]:1-12). The drug probably is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Capreomycin (Capastat) (653-669) is a polypeptide antibiotic isolated from Streptomyces capreolus that is given intramuscularly. The human pregnancy data are limited to three reports. The toxicity of capreomycin is similar to aminoglycosides (e.g., cranial nerve VIII and renal) and it should not be used with these agents. The CDC has classified the drug as contraindicated in pregnancy. The drug probably is excreted into breast milk, but there are no reports of its use during breastfeeding.
Cycloserine (Seromycin) (102) is a broad spectrum antibiotic. The human pregnancy data are limited but have not shown embryo-fetal harm. Although the best course is to avoid the drug during gestation, it should not be withheld because of pregnancy if the maternal condition requires the antibiotic. The American Academy of Pediatrics classified cycloserine as compatible with breastfeeding.
Ethambutol (Myambutol) (205) should be used in conjunction with other antituberculosis drugs. The human pregnancy data do not suggest an embryo-fetal risk. A frequently used regimen is ethambutol + isoniazid + rifampin. The American Academy of Pediatrics classified ethambutol as compatible with breastfeeding.
Ethionamide (Trecator) (166) is indicated when Mycobacterium tuberculosis is resistant to isoniazid or rifampin, or when the patient is intolerant to other drugs. Although the animal reproductive data suggest risk, the limited human data suggest that the risk is probably low. If indicated, the drug should not be withheld because of pregnancy. Although the molecular weight suggests that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, no reports describing the amount in milk have been located.
Isoniazid (137) is compatible in pregnancy, even though the molecular weight suggests that it will cross the placenta, because the maternal benefit is much greater than the potential embryo-fetal risk. Although the human data are limited, the molecular weight also suggests that the drug will be excreted into breast milk, but it can be considered probably compatible during breastfeeding. No reports of isoniazid-induced effects in the nursing infant have been located, but the potential for interference with nucleic acid function and for hepatotoxicity may exist.
Pyrazinamide (123) is metabolized to an active metabolite. The molecular weight, low plasma protein binding (10%), and prolonged elimination half-life (9-10 hours) suggest that the drug will cross the placenta throughout pregnancy. The drug has been used in human pregnancy without causing embryo-fetal harm. Similar results, although limited, were reported when the drug was used during breastfeeding.
Rifabutin (Mycobutin) (847) has no reported human pregnancy data, but the animal data suggest low risk. The drug probably crosses the placenta throughout pregnancy. The maternal benefit appears to outweigh the unknown risk to the embryo-fetus, so therapy should not be withheld because of pregnancy. The drug probably is excreted into breast milk.
Rifampin (Rifadin) (823) appears to be compatible in pregnancy. Several reviews and reports have concluded that the drug was not a teratogen and recommended use of the drug with isoniazid and ethambutol. However, prophylactic vitamin K1 has been recommended to prevent drug-induced hemorrhagic disease of the newborn. There are no data regarding its use during breastfeeding, but it is probably compatible.
Rifapentine (Priftin) (877) was toxic and teratogenic in two animal species at doses close to those used in humans. In a 2018 study, however, the rates of fetal loss in pregnancies of less than 20 weeks (8/54, 15%) and congenital anomalies in live births (1/37, 3%) were within the expected background rates (Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2018 May;15[4]:570-80). There are no data regarding its use during breastfeeding, but it is probably compatible.
The CDC classifies four antituberculosis and one class of drugs as contraindicated in pregnancy. In addition to capreomycin mentioned above, they are amikacin, fluoroquinolones (ciprofloxacin, gemifloxacin, levofloxacin, lomefloxacin, moxifloxacin, ofloxacin), kanamycin, and streptomycin. These ten agents are discussed in the 11th edition of my book “Drugs in Pregnancy and Lactation,” (Wolters Kluwer Health: Riverwood, Il., 2017). If they have to be used, checking this source will provide information that has to be discussed with the patient.
Mr. Briggs is clinical professor of pharmacy at the University of California, San Francisco, and adjunct professor of pharmacy at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, as well as at Washington State University, Spokane. Mr. Briggs had no disclosures, except for his book. Email him at [email protected].