User login
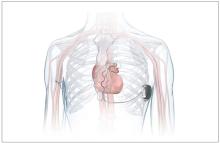
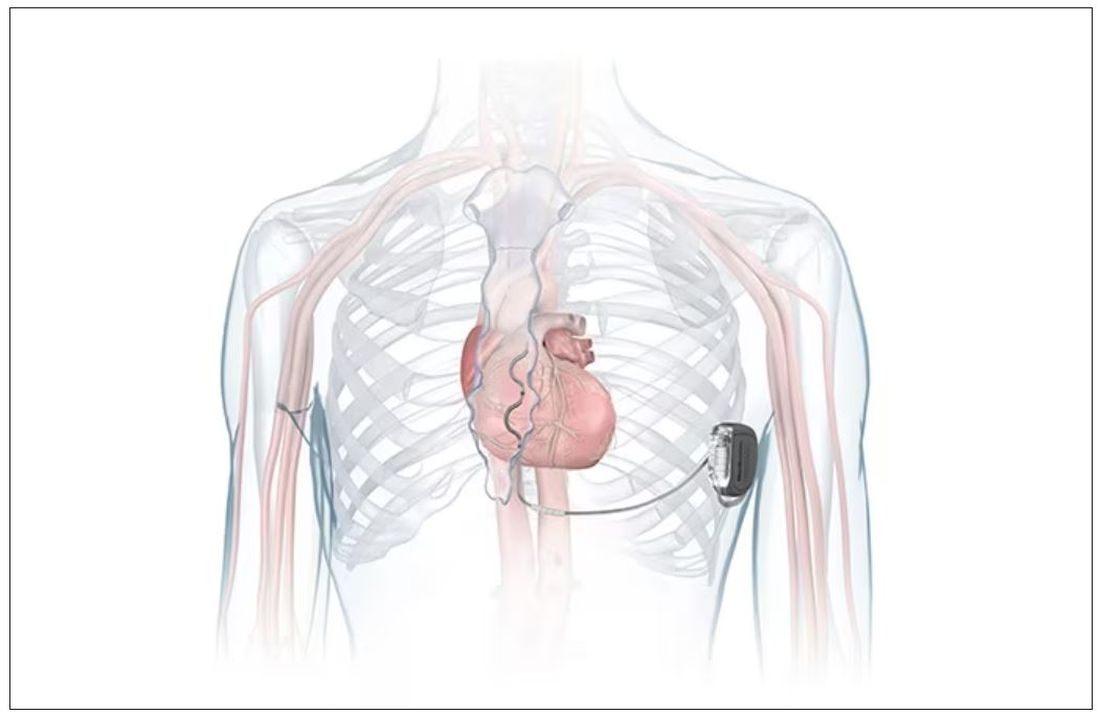
FDA okays first extravascular ICD system
which uses a single lead implanted substernally to allow antitachycardia pacing and low-energy defibrillation while avoiding the vascular space for lead placement.
“The Aurora EV-ICD system is a tremendous step forward in implantable defibrillator technology,” Bradley P. Knight, MD, medical director of electrophysiology at Northwestern Medicine Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute, Chicago, said in a company news release.
“Placing the leads outside of the heart, rather than inside the heart and veins, reduces the risk of long-term complications, ultimately allowing us to further evolve safe and effective ICD technology,” said Dr. Knight, who was involved in the pivotal trial that led to U.S. approval.
The approval, which includes the system’s proprietary procedure implant tools, was supported by results from a global pivotal study that demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of the system.
Results of the study were presented at the annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology in 2022.
The study enrolled 356 patients who were at risk of sudden cardiac death and who had a class I or IIa indication for ICD. Participants were enrolled at 46 sites in 17 countries.
The device’s effectiveness in delivering defibrillation therapy at implant (primary efficacy endpoint) was 98.7%, compared with a prespecified target of 88%.
There were no major intraprocedural complications, nor were any unique complications observed that were related to the EV ICD procedure or system, compared with transvenous and subcutaneous ICDs.
Additionally, 33 defibrillation shocks were avoided by having antitachycardia pacing programmed “on.”
At 6 months, 92.6% of patients (Kaplan-Meier estimate) were free from major system- and/or procedure-related major complications, such as hospitalization, system revision, or death.
The Aurora EV-ICD system is indicated for patients who are at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, who have not previously undergone sternotomy, and who do not need long-term bradycardia pacing.
The Aurora EV-ICD system is similar in size, shape, and longevity to traditional transvenous ICDs.
Medtronic said the Aurora EV-ICD system will be commercially available on a limited basis in the United States in the coming weeks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
which uses a single lead implanted substernally to allow antitachycardia pacing and low-energy defibrillation while avoiding the vascular space for lead placement.
“The Aurora EV-ICD system is a tremendous step forward in implantable defibrillator technology,” Bradley P. Knight, MD, medical director of electrophysiology at Northwestern Medicine Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute, Chicago, said in a company news release.
“Placing the leads outside of the heart, rather than inside the heart and veins, reduces the risk of long-term complications, ultimately allowing us to further evolve safe and effective ICD technology,” said Dr. Knight, who was involved in the pivotal trial that led to U.S. approval.
The approval, which includes the system’s proprietary procedure implant tools, was supported by results from a global pivotal study that demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of the system.
Results of the study were presented at the annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology in 2022.
The study enrolled 356 patients who were at risk of sudden cardiac death and who had a class I or IIa indication for ICD. Participants were enrolled at 46 sites in 17 countries.
The device’s effectiveness in delivering defibrillation therapy at implant (primary efficacy endpoint) was 98.7%, compared with a prespecified target of 88%.
There were no major intraprocedural complications, nor were any unique complications observed that were related to the EV ICD procedure or system, compared with transvenous and subcutaneous ICDs.
Additionally, 33 defibrillation shocks were avoided by having antitachycardia pacing programmed “on.”
At 6 months, 92.6% of patients (Kaplan-Meier estimate) were free from major system- and/or procedure-related major complications, such as hospitalization, system revision, or death.
The Aurora EV-ICD system is indicated for patients who are at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, who have not previously undergone sternotomy, and who do not need long-term bradycardia pacing.
The Aurora EV-ICD system is similar in size, shape, and longevity to traditional transvenous ICDs.
Medtronic said the Aurora EV-ICD system will be commercially available on a limited basis in the United States in the coming weeks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
which uses a single lead implanted substernally to allow antitachycardia pacing and low-energy defibrillation while avoiding the vascular space for lead placement.
“The Aurora EV-ICD system is a tremendous step forward in implantable defibrillator technology,” Bradley P. Knight, MD, medical director of electrophysiology at Northwestern Medicine Bluhm Cardiovascular Institute, Chicago, said in a company news release.
“Placing the leads outside of the heart, rather than inside the heart and veins, reduces the risk of long-term complications, ultimately allowing us to further evolve safe and effective ICD technology,” said Dr. Knight, who was involved in the pivotal trial that led to U.S. approval.
The approval, which includes the system’s proprietary procedure implant tools, was supported by results from a global pivotal study that demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of the system.
Results of the study were presented at the annual meeting of the European Society of Cardiology in 2022.
The study enrolled 356 patients who were at risk of sudden cardiac death and who had a class I or IIa indication for ICD. Participants were enrolled at 46 sites in 17 countries.
The device’s effectiveness in delivering defibrillation therapy at implant (primary efficacy endpoint) was 98.7%, compared with a prespecified target of 88%.
There were no major intraprocedural complications, nor were any unique complications observed that were related to the EV ICD procedure or system, compared with transvenous and subcutaneous ICDs.
Additionally, 33 defibrillation shocks were avoided by having antitachycardia pacing programmed “on.”
At 6 months, 92.6% of patients (Kaplan-Meier estimate) were free from major system- and/or procedure-related major complications, such as hospitalization, system revision, or death.
The Aurora EV-ICD system is indicated for patients who are at risk of life-threatening arrhythmias, who have not previously undergone sternotomy, and who do not need long-term bradycardia pacing.
The Aurora EV-ICD system is similar in size, shape, and longevity to traditional transvenous ICDs.
Medtronic said the Aurora EV-ICD system will be commercially available on a limited basis in the United States in the coming weeks.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves subcutaneous infliximab for IBD
Infliximab-dyyb is a subcutaneous formulation of Celltrion’s infliximab. The FDA approval provides an alternative administration option for delivering the drug, which blocks the action of tumor necrosis factor alpha.
The new formulation was approved based on phase 3 pivotal trials that evaluated the safety and efficacy of infliximab-dyyb as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active UC (LIBERTY-UC) and CD (LIBERTY-CD).
In both 54-week trials, infliximab-dyyb demonstrated superiority to placebo in the primary endpoints of clinical remission (UC and CD) and endoscopic response (CD) when given as maintenance therapy after induction therapy with IV infliximab.
The overall safety profile of infliximab-dyyb was similar to that of the placebo during the maintenance period in both studies, with no new safety signals seen.
In the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind LIBERTY-UC study, 438 patients with moderately to severely active UC after induction therapy with IV infliximab were randomly assigned at week 10. The rate of clinical remission at week 54 was significantly greater with infliximab-dyyb (43.2%), compared with placebo (20.8%).
The most common adverse events were COVID-19, anemia, arthralgia, injection site reaction, increased alanine aminotransferase, and abdominal pain.
In the similarly designed LIBERTY-CD study, 343 patients with moderately to severely active CD after induction therapy were randomly assigned at week 10. At week 54, the clinical remission rate was greater with infliximab-dyyb (62.3%) than with placebo (32.1%).
In parallel, the endoscopic response rate at week 54 was also greater in the infliximab-dyyb arm than in the placebo arm (51.1% vs. 17.9%, respectively).
The safety profile during the maintenance phase was generally comparable between the two trial arms. The most common adverse events were COVID-19, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, injection site reaction, diarrhea, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, neutropenia, hypertension, urinary tract infection, dizziness, and leukopenia.
Full prescribing information is available online.
“As someone dedicated to improving the lives of patients with IBD, I am excited to see data supporting the efficacy and safety of a new formulation offering convenience and improved access to a well-known and proven drug,” Andres Yarur, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in a news release.
The data “validate a convenient treatment option that could allow more patients in the United States to have greater control of their disease management,” added Jean-Frederic Colombel, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infliximab-dyyb is a subcutaneous formulation of Celltrion’s infliximab. The FDA approval provides an alternative administration option for delivering the drug, which blocks the action of tumor necrosis factor alpha.
The new formulation was approved based on phase 3 pivotal trials that evaluated the safety and efficacy of infliximab-dyyb as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active UC (LIBERTY-UC) and CD (LIBERTY-CD).
In both 54-week trials, infliximab-dyyb demonstrated superiority to placebo in the primary endpoints of clinical remission (UC and CD) and endoscopic response (CD) when given as maintenance therapy after induction therapy with IV infliximab.
The overall safety profile of infliximab-dyyb was similar to that of the placebo during the maintenance period in both studies, with no new safety signals seen.
In the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind LIBERTY-UC study, 438 patients with moderately to severely active UC after induction therapy with IV infliximab were randomly assigned at week 10. The rate of clinical remission at week 54 was significantly greater with infliximab-dyyb (43.2%), compared with placebo (20.8%).
The most common adverse events were COVID-19, anemia, arthralgia, injection site reaction, increased alanine aminotransferase, and abdominal pain.
In the similarly designed LIBERTY-CD study, 343 patients with moderately to severely active CD after induction therapy were randomly assigned at week 10. At week 54, the clinical remission rate was greater with infliximab-dyyb (62.3%) than with placebo (32.1%).
In parallel, the endoscopic response rate at week 54 was also greater in the infliximab-dyyb arm than in the placebo arm (51.1% vs. 17.9%, respectively).
The safety profile during the maintenance phase was generally comparable between the two trial arms. The most common adverse events were COVID-19, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, injection site reaction, diarrhea, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, neutropenia, hypertension, urinary tract infection, dizziness, and leukopenia.
Full prescribing information is available online.
“As someone dedicated to improving the lives of patients with IBD, I am excited to see data supporting the efficacy and safety of a new formulation offering convenience and improved access to a well-known and proven drug,” Andres Yarur, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in a news release.
The data “validate a convenient treatment option that could allow more patients in the United States to have greater control of their disease management,” added Jean-Frederic Colombel, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Infliximab-dyyb is a subcutaneous formulation of Celltrion’s infliximab. The FDA approval provides an alternative administration option for delivering the drug, which blocks the action of tumor necrosis factor alpha.
The new formulation was approved based on phase 3 pivotal trials that evaluated the safety and efficacy of infliximab-dyyb as maintenance therapy in patients with moderately to severely active UC (LIBERTY-UC) and CD (LIBERTY-CD).
In both 54-week trials, infliximab-dyyb demonstrated superiority to placebo in the primary endpoints of clinical remission (UC and CD) and endoscopic response (CD) when given as maintenance therapy after induction therapy with IV infliximab.
The overall safety profile of infliximab-dyyb was similar to that of the placebo during the maintenance period in both studies, with no new safety signals seen.
In the randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind LIBERTY-UC study, 438 patients with moderately to severely active UC after induction therapy with IV infliximab were randomly assigned at week 10. The rate of clinical remission at week 54 was significantly greater with infliximab-dyyb (43.2%), compared with placebo (20.8%).
The most common adverse events were COVID-19, anemia, arthralgia, injection site reaction, increased alanine aminotransferase, and abdominal pain.
In the similarly designed LIBERTY-CD study, 343 patients with moderately to severely active CD after induction therapy were randomly assigned at week 10. At week 54, the clinical remission rate was greater with infliximab-dyyb (62.3%) than with placebo (32.1%).
In parallel, the endoscopic response rate at week 54 was also greater in the infliximab-dyyb arm than in the placebo arm (51.1% vs. 17.9%, respectively).
The safety profile during the maintenance phase was generally comparable between the two trial arms. The most common adverse events were COVID-19, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, injection site reaction, diarrhea, increased alanine aminotransferase, increased blood creatine phosphokinase, neutropenia, hypertension, urinary tract infection, dizziness, and leukopenia.
Full prescribing information is available online.
“As someone dedicated to improving the lives of patients with IBD, I am excited to see data supporting the efficacy and safety of a new formulation offering convenience and improved access to a well-known and proven drug,” Andres Yarur, MD, of Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, said in a news release.
The data “validate a convenient treatment option that could allow more patients in the United States to have greater control of their disease management,” added Jean-Frederic Colombel, MD, of Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New meningococcal vaccine wins FDA approval
The new formulation called Penbraya is manufactured by Pfizer and combines the components from two existing meningococcal vaccines, Trumenba the group B vaccine and Nimenrix groups A, C, W-135, and Y conjugate vaccine.
This is the first pentavalent vaccine for meningococcal disease and is approved for use in people aged 10-25.
“Today marks an important step forward in the prevention of meningococcal disease in the U.S.,” Annaliesa Anderson, PhD, head of vaccine research and development at Pfizer, said in a news release. “In a single vaccine, Penbraya has the potential to protect more adolescents and young adults from this severe and unpredictable disease by providing the broadest meningococcal coverage in the fewest shots.”
One shot, five common types
“Incomplete protection against invasive meningococcal disease,” is common, added Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist from Upstate Golisano Children’s Hospital in Syracuse, N.Y. Reducing the number of shots is important because streamlining the vaccination process should help increase the number of young people who get fully vaccinated against meningococcal disease.
Rates are low in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and in 2021 there were around 210 cases reported. But a statewide outbreak has been going on in Virginia since June 2022, with 29 confirmed cases and 6 deaths.
The FDA’s decision is based on the positive results from phase 2 and phase 3 trials, including a randomized, active-controlled and observer-blinded phase 3 trial assessing the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of the pentavalent vaccine candidate, compared with currently licensed meningococcal vaccines. The phase 3 trial evaluated more than 2,400 patients from the United States and Europe.
The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices is meeting on Oct. 25 to discuss recommendations for the appropriate use of Penbraya in young people.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new formulation called Penbraya is manufactured by Pfizer and combines the components from two existing meningococcal vaccines, Trumenba the group B vaccine and Nimenrix groups A, C, W-135, and Y conjugate vaccine.
This is the first pentavalent vaccine for meningococcal disease and is approved for use in people aged 10-25.
“Today marks an important step forward in the prevention of meningococcal disease in the U.S.,” Annaliesa Anderson, PhD, head of vaccine research and development at Pfizer, said in a news release. “In a single vaccine, Penbraya has the potential to protect more adolescents and young adults from this severe and unpredictable disease by providing the broadest meningococcal coverage in the fewest shots.”
One shot, five common types
“Incomplete protection against invasive meningococcal disease,” is common, added Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist from Upstate Golisano Children’s Hospital in Syracuse, N.Y. Reducing the number of shots is important because streamlining the vaccination process should help increase the number of young people who get fully vaccinated against meningococcal disease.
Rates are low in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and in 2021 there were around 210 cases reported. But a statewide outbreak has been going on in Virginia since June 2022, with 29 confirmed cases and 6 deaths.
The FDA’s decision is based on the positive results from phase 2 and phase 3 trials, including a randomized, active-controlled and observer-blinded phase 3 trial assessing the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of the pentavalent vaccine candidate, compared with currently licensed meningococcal vaccines. The phase 3 trial evaluated more than 2,400 patients from the United States and Europe.
The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices is meeting on Oct. 25 to discuss recommendations for the appropriate use of Penbraya in young people.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The new formulation called Penbraya is manufactured by Pfizer and combines the components from two existing meningococcal vaccines, Trumenba the group B vaccine and Nimenrix groups A, C, W-135, and Y conjugate vaccine.
This is the first pentavalent vaccine for meningococcal disease and is approved for use in people aged 10-25.
“Today marks an important step forward in the prevention of meningococcal disease in the U.S.,” Annaliesa Anderson, PhD, head of vaccine research and development at Pfizer, said in a news release. “In a single vaccine, Penbraya has the potential to protect more adolescents and young adults from this severe and unpredictable disease by providing the broadest meningococcal coverage in the fewest shots.”
One shot, five common types
“Incomplete protection against invasive meningococcal disease,” is common, added Jana Shaw, MD, MPH, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist from Upstate Golisano Children’s Hospital in Syracuse, N.Y. Reducing the number of shots is important because streamlining the vaccination process should help increase the number of young people who get fully vaccinated against meningococcal disease.
Rates are low in the United States, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and in 2021 there were around 210 cases reported. But a statewide outbreak has been going on in Virginia since June 2022, with 29 confirmed cases and 6 deaths.
The FDA’s decision is based on the positive results from phase 2 and phase 3 trials, including a randomized, active-controlled and observer-blinded phase 3 trial assessing the safety, tolerability, and immunogenicity of the pentavalent vaccine candidate, compared with currently licensed meningococcal vaccines. The phase 3 trial evaluated more than 2,400 patients from the United States and Europe.
The CDC Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices is meeting on Oct. 25 to discuss recommendations for the appropriate use of Penbraya in young people.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Approximately 20% of U.S. adults are diagnosed with arthritis
TOPLINE:
The prevalence of reported diagnosed arthritis in the United States is highest overall in older adults with comorbid chronic conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) from 2019 to 2021 to update the prevalence of self-reported arthritis in the United States.
- The sample sizes for the 2019, 2020, and 2021 NHIS were 31,997, 21,153, and 29,482, with survey response rates of 59.1%, 48.9%, and 50.9%, respectively.
- The unadjusted and age-standardized prevalence estimates were calculated for adults aged 18 years and older and based on self-reported health and demographic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, arthritis was diagnosed in 53.2 million adults aged 18 years and older in the United States; of these, 88.3% were aged 45 years and older and 48.3% were 65 years and older.
- Age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher in women vs men and among veterans vs nonveterans (20.9% vs 16.3% and 24.2% vs 18.5%, respectively).
- When categorized by race, age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher among non-Hispanic White individuals, compared with Hispanic or Latino individuals or non-Hispanic Asian individuals (20.1%, 14.7%, and 10.3%, respectively).
- The prevalence of arthritis also was higher among individuals with self-reported diagnosis of chronic conditions including dementia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer than in those without these conditions; approximately half of adults aged 65 years and older with arthritis reported at least one of these conditions.
IN PRACTICE:
“These prevalence estimates can be used to guide public health policies and activities to increase equitable access to physical activity opportunities within the built environment and other community-based, arthritis-appropriate, evidence-based interventions,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Elizabeth A. Fallon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. The data were published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design prevented conclusions of causality between individual characteristics and arthritis diagnosis; other limitations included the reliance on self-reports, possible response bias, and the inability to calculate prevalence of arthritis subtypes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The prevalence of reported diagnosed arthritis in the United States is highest overall in older adults with comorbid chronic conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) from 2019 to 2021 to update the prevalence of self-reported arthritis in the United States.
- The sample sizes for the 2019, 2020, and 2021 NHIS were 31,997, 21,153, and 29,482, with survey response rates of 59.1%, 48.9%, and 50.9%, respectively.
- The unadjusted and age-standardized prevalence estimates were calculated for adults aged 18 years and older and based on self-reported health and demographic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, arthritis was diagnosed in 53.2 million adults aged 18 years and older in the United States; of these, 88.3% were aged 45 years and older and 48.3% were 65 years and older.
- Age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher in women vs men and among veterans vs nonveterans (20.9% vs 16.3% and 24.2% vs 18.5%, respectively).
- When categorized by race, age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher among non-Hispanic White individuals, compared with Hispanic or Latino individuals or non-Hispanic Asian individuals (20.1%, 14.7%, and 10.3%, respectively).
- The prevalence of arthritis also was higher among individuals with self-reported diagnosis of chronic conditions including dementia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer than in those without these conditions; approximately half of adults aged 65 years and older with arthritis reported at least one of these conditions.
IN PRACTICE:
“These prevalence estimates can be used to guide public health policies and activities to increase equitable access to physical activity opportunities within the built environment and other community-based, arthritis-appropriate, evidence-based interventions,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Elizabeth A. Fallon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. The data were published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design prevented conclusions of causality between individual characteristics and arthritis diagnosis; other limitations included the reliance on self-reports, possible response bias, and the inability to calculate prevalence of arthritis subtypes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE:
The prevalence of reported diagnosed arthritis in the United States is highest overall in older adults with comorbid chronic conditions.
METHODOLOGY:
- Researchers reviewed data from the National Health Interview Survey (NHIS) from 2019 to 2021 to update the prevalence of self-reported arthritis in the United States.
- The sample sizes for the 2019, 2020, and 2021 NHIS were 31,997, 21,153, and 29,482, with survey response rates of 59.1%, 48.9%, and 50.9%, respectively.
- The unadjusted and age-standardized prevalence estimates were calculated for adults aged 18 years and older and based on self-reported health and demographic data.
TAKEAWAY:
- Overall, arthritis was diagnosed in 53.2 million adults aged 18 years and older in the United States; of these, 88.3% were aged 45 years and older and 48.3% were 65 years and older.
- Age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher in women vs men and among veterans vs nonveterans (20.9% vs 16.3% and 24.2% vs 18.5%, respectively).
- When categorized by race, age-standardized prevalence of arthritis was higher among non-Hispanic White individuals, compared with Hispanic or Latino individuals or non-Hispanic Asian individuals (20.1%, 14.7%, and 10.3%, respectively).
- The prevalence of arthritis also was higher among individuals with self-reported diagnosis of chronic conditions including dementia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, stroke, heart disease, diabetes, and cancer than in those without these conditions; approximately half of adults aged 65 years and older with arthritis reported at least one of these conditions.
IN PRACTICE:
“These prevalence estimates can be used to guide public health policies and activities to increase equitable access to physical activity opportunities within the built environment and other community-based, arthritis-appropriate, evidence-based interventions,” the authors write.
SOURCE:
The study was led by Elizabeth A. Fallon, PhD, of the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, Atlanta, Georgia. The data were published online in the CDC’s Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report.
LIMITATIONS:
The cross-sectional design prevented conclusions of causality between individual characteristics and arthritis diagnosis; other limitations included the reliance on self-reports, possible response bias, and the inability to calculate prevalence of arthritis subtypes.
DISCLOSURES:
The study received no outside funding. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves new drug for ulcerative colitis
Pfizer announced on Oct. 13.
Etrasimod is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor that binds with high affinity to receptors 1, 4, and 5. The approved recommended dose is 2 mg once daily.
Etrasimod is the second agent in the S1P class approved for UC in the United States. The other agent, ozanimod (Zeposia, Bristol-Myers Squibb), received FDA approval for moderately to severely active UC in May 2021.
The approval of etrasimod was based on safety and efficacy data from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials: ELEVATE UC 52 trial and the ELEVATE UC 12 trial. The Lancet published full results from the two trials in March.
Both trials enrolled patients with UC who had previously failed or were intolerant of at least one conventional, biologic, or Janus kinase inhibitor therapy.
In ELEVATE UC 52, clinical remission at 12 weeks occurred in 27% of patients taking etrasimod versus 7% of patients taking a placebo (20% difference; P < .001). At week 52, remission rates were 32% with active treatment verus 7% with placebo (26% difference; P < .001).
In ELEVATE UC 12, clinical remission was achieved among 26% of patients who received etrasimod versus 15.0% of patients who received placebo (11% difference; P < .05).
Statistically significant improvements were also observed with etrasimod (vs. placebo) on all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement and mucosal healing at weeks 12 and 52, and corticosteroid-free remission and sustained clinical remission at week 52.
The most common side effects of etrasimod were found to be headache, elevated values on liver tests, worsening of UC, SARS-CoV-2 infection, dizziness, pyrexia, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea. Full prescribing information is available online.
Etrasimod is “a proven advanced treatment with a favorable benefit-risk profile,” Michael Chiorean, MD, codirector of the IBD Center at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, who is an investigator in the ELEVATE studies, said in a Pfizer news release.
“UC can affect patients differently and many people living with this disease struggle with ongoing symptoms. The introduction of a new treatment for UC could increase options for patients, and we look forward to seeing the impact of Velsipity for patients across the U.S.,” added Michael Osso, president and CEO of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer announced on Oct. 13.
Etrasimod is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor that binds with high affinity to receptors 1, 4, and 5. The approved recommended dose is 2 mg once daily.
Etrasimod is the second agent in the S1P class approved for UC in the United States. The other agent, ozanimod (Zeposia, Bristol-Myers Squibb), received FDA approval for moderately to severely active UC in May 2021.
The approval of etrasimod was based on safety and efficacy data from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials: ELEVATE UC 52 trial and the ELEVATE UC 12 trial. The Lancet published full results from the two trials in March.
Both trials enrolled patients with UC who had previously failed or were intolerant of at least one conventional, biologic, or Janus kinase inhibitor therapy.
In ELEVATE UC 52, clinical remission at 12 weeks occurred in 27% of patients taking etrasimod versus 7% of patients taking a placebo (20% difference; P < .001). At week 52, remission rates were 32% with active treatment verus 7% with placebo (26% difference; P < .001).
In ELEVATE UC 12, clinical remission was achieved among 26% of patients who received etrasimod versus 15.0% of patients who received placebo (11% difference; P < .05).
Statistically significant improvements were also observed with etrasimod (vs. placebo) on all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement and mucosal healing at weeks 12 and 52, and corticosteroid-free remission and sustained clinical remission at week 52.
The most common side effects of etrasimod were found to be headache, elevated values on liver tests, worsening of UC, SARS-CoV-2 infection, dizziness, pyrexia, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea. Full prescribing information is available online.
Etrasimod is “a proven advanced treatment with a favorable benefit-risk profile,” Michael Chiorean, MD, codirector of the IBD Center at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, who is an investigator in the ELEVATE studies, said in a Pfizer news release.
“UC can affect patients differently and many people living with this disease struggle with ongoing symptoms. The introduction of a new treatment for UC could increase options for patients, and we look forward to seeing the impact of Velsipity for patients across the U.S.,” added Michael Osso, president and CEO of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Pfizer announced on Oct. 13.
Etrasimod is an oral sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) receptor that binds with high affinity to receptors 1, 4, and 5. The approved recommended dose is 2 mg once daily.
Etrasimod is the second agent in the S1P class approved for UC in the United States. The other agent, ozanimod (Zeposia, Bristol-Myers Squibb), received FDA approval for moderately to severely active UC in May 2021.
The approval of etrasimod was based on safety and efficacy data from two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase 3 trials: ELEVATE UC 52 trial and the ELEVATE UC 12 trial. The Lancet published full results from the two trials in March.
Both trials enrolled patients with UC who had previously failed or were intolerant of at least one conventional, biologic, or Janus kinase inhibitor therapy.
In ELEVATE UC 52, clinical remission at 12 weeks occurred in 27% of patients taking etrasimod versus 7% of patients taking a placebo (20% difference; P < .001). At week 52, remission rates were 32% with active treatment verus 7% with placebo (26% difference; P < .001).
In ELEVATE UC 12, clinical remission was achieved among 26% of patients who received etrasimod versus 15.0% of patients who received placebo (11% difference; P < .05).
Statistically significant improvements were also observed with etrasimod (vs. placebo) on all key secondary endpoints, including endoscopic improvement and mucosal healing at weeks 12 and 52, and corticosteroid-free remission and sustained clinical remission at week 52.
The most common side effects of etrasimod were found to be headache, elevated values on liver tests, worsening of UC, SARS-CoV-2 infection, dizziness, pyrexia, arthralgia, abdominal pain, and nausea. Full prescribing information is available online.
Etrasimod is “a proven advanced treatment with a favorable benefit-risk profile,” Michael Chiorean, MD, codirector of the IBD Center at Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, who is an investigator in the ELEVATE studies, said in a Pfizer news release.
“UC can affect patients differently and many people living with this disease struggle with ongoing symptoms. The introduction of a new treatment for UC could increase options for patients, and we look forward to seeing the impact of Velsipity for patients across the U.S.,” added Michael Osso, president and CEO of the Crohn’s & Colitis Foundation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA denies approval for patisiran in ATTR cardiomyopathy, despite panel nod
the company has announced.
ATTR amyloidosis is an underdiagnosed, rapidly progressive, debilitating, fatal disease caused by misfolded TTR proteins, which accumulate as amyloid deposits in various parts of the body, including the heart.
In September, the FDA Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee voted 9 to 3 that the benefits of patisiran outweigh the risks for the treatment of ATTR amyloidosis cardiomyopathy on the basis of the results of the APOLLO-B phase 3 study.
However, many panel members questioned whether the benefits are clinically meaningful – a view shared by the FDA in a complete response letter (CRL) the FDA sent to Alnylam.
According to the company, the FDA indicated in the letter that the clinical meaningfulness of patisiran’s treatment effects for the cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis have “not been established,” and therefore, the supplemental new drug application for patisiran “could not be approved in its present form.”
The FDA did not identify any issues with respect to clinical safety, study conduct, drug quality, or manufacturing.
Nonetheless, as a result of the CRL, the company said it will no longer pursue an expanded indication for patisiran in cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis in the United States.
The company said it will continue to make patisiran available for patients with cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis who are enrolled in the open-label extension period of the APOLLO-B study and the patisiran expanded access protocol.
The company also said it will continue to focus on the HELIOS-B phase 3 study of vutrisiran, an investigational RNAi therapeutic in development for the treatment of cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis.
“We remain confident in the HELIOS-B phase 3 study of vutrisiran and look forward to sharing topline results in early 2024. If successful, we believe vutrisiran will offer convenient, quarterly subcutaneous dosing with a therapeutic profile that may potentially include cardiovascular outcome benefits,” Alnylam CEO Yvonne Greenstreet, MBChB, said in the statement.
Intravenously administered patisiran is already approved in the United States and Canada for the treatment of polyneuropathy of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis in adults.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the company has announced.
ATTR amyloidosis is an underdiagnosed, rapidly progressive, debilitating, fatal disease caused by misfolded TTR proteins, which accumulate as amyloid deposits in various parts of the body, including the heart.
In September, the FDA Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee voted 9 to 3 that the benefits of patisiran outweigh the risks for the treatment of ATTR amyloidosis cardiomyopathy on the basis of the results of the APOLLO-B phase 3 study.
However, many panel members questioned whether the benefits are clinically meaningful – a view shared by the FDA in a complete response letter (CRL) the FDA sent to Alnylam.
According to the company, the FDA indicated in the letter that the clinical meaningfulness of patisiran’s treatment effects for the cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis have “not been established,” and therefore, the supplemental new drug application for patisiran “could not be approved in its present form.”
The FDA did not identify any issues with respect to clinical safety, study conduct, drug quality, or manufacturing.
Nonetheless, as a result of the CRL, the company said it will no longer pursue an expanded indication for patisiran in cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis in the United States.
The company said it will continue to make patisiran available for patients with cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis who are enrolled in the open-label extension period of the APOLLO-B study and the patisiran expanded access protocol.
The company also said it will continue to focus on the HELIOS-B phase 3 study of vutrisiran, an investigational RNAi therapeutic in development for the treatment of cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis.
“We remain confident in the HELIOS-B phase 3 study of vutrisiran and look forward to sharing topline results in early 2024. If successful, we believe vutrisiran will offer convenient, quarterly subcutaneous dosing with a therapeutic profile that may potentially include cardiovascular outcome benefits,” Alnylam CEO Yvonne Greenstreet, MBChB, said in the statement.
Intravenously administered patisiran is already approved in the United States and Canada for the treatment of polyneuropathy of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis in adults.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
the company has announced.
ATTR amyloidosis is an underdiagnosed, rapidly progressive, debilitating, fatal disease caused by misfolded TTR proteins, which accumulate as amyloid deposits in various parts of the body, including the heart.
In September, the FDA Cardiovascular and Renal Drugs Advisory Committee voted 9 to 3 that the benefits of patisiran outweigh the risks for the treatment of ATTR amyloidosis cardiomyopathy on the basis of the results of the APOLLO-B phase 3 study.
However, many panel members questioned whether the benefits are clinically meaningful – a view shared by the FDA in a complete response letter (CRL) the FDA sent to Alnylam.
According to the company, the FDA indicated in the letter that the clinical meaningfulness of patisiran’s treatment effects for the cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis have “not been established,” and therefore, the supplemental new drug application for patisiran “could not be approved in its present form.”
The FDA did not identify any issues with respect to clinical safety, study conduct, drug quality, or manufacturing.
Nonetheless, as a result of the CRL, the company said it will no longer pursue an expanded indication for patisiran in cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis in the United States.
The company said it will continue to make patisiran available for patients with cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis who are enrolled in the open-label extension period of the APOLLO-B study and the patisiran expanded access protocol.
The company also said it will continue to focus on the HELIOS-B phase 3 study of vutrisiran, an investigational RNAi therapeutic in development for the treatment of cardiomyopathy of ATTR amyloidosis.
“We remain confident in the HELIOS-B phase 3 study of vutrisiran and look forward to sharing topline results in early 2024. If successful, we believe vutrisiran will offer convenient, quarterly subcutaneous dosing with a therapeutic profile that may potentially include cardiovascular outcome benefits,” Alnylam CEO Yvonne Greenstreet, MBChB, said in the statement.
Intravenously administered patisiran is already approved in the United States and Canada for the treatment of polyneuropathy of hereditary ATTR amyloidosis in adults.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Intravenous formulation of secukinumab gets FDA approval
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved an intravenous (IV) formulation of secukinumab (Cosentyx) for the treatment of adults with psoriatic arthritis (PsA), ankylosing spondylitis (AS), and nonradiographic axial spondyloarthritis (nr-axSpA).
Secukinumab is the only treatment approved in an IV formulation that specifically targets and blocks interleukin-17A and the only non–tumor necrosis factor alpha IV option available to treat the three indications of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA, according to a press release from the drug’s manufacturer, Novartis.
The approval marks the first new IV treatment in 6 years for these three conditions. The drug was first approved in 2015 and up to now has been available only as a subcutaneous injection.
The new formulation is also approved for secukinumab’s other indications of plaque psoriasis in people aged 6 years or older, children aged 2 years or older with PsA, and enthesitis-related arthritis in patients aged 4 years or older.
“A significant portion of the millions of PsA, AS, and nr-axSpA patients in the United States require treatment through IV infusions for a variety of reasons, including not being comfortable with self-injections or simply preferring to have treatments administered in their health care provider’s office,” Philip J. Mease, MD, clinical professor at the University of Washington, Seattle, and director of rheumatology research at the Swedish Medical Center, Seattle, said in the press release. “The approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation is an important milestone for patients because it expands the treatment options available to them with a different mechanism of action than existing biologic IV therapies, along with the comfort and familiarity of an established treatment.”
This IV formulation is administered monthly in a 30-minute, weight-based dosing regimen. This new option will become available before the end of the year, Novartis said.
“With this approval of Cosentyx as an IV formulation, along with the subcutaneous formulation, we can broaden the use of Cosentyx to help more patients manage their condition with a medicine backed by more than a decade of clinical research and 8 years of real-world experience,” said Christy Siegel, vice president and head of immunology, Novartis U.S.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves ninth Humira biosimilar, with interchangeability
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has granted an interchangeability designation to adalimumab-afzb (Abrilada), according to an announcement from Pfizer.
This is the second adalimumab biosimilar granted interchangeability. The first, adalimumab-adbm (Cyltezo), became available in July.
Biosimilars introduce market competition that can help lower drug prices. Adalimumab-afzb is one of nine approved biosimilars for Humira, and the last to launch in 2023.
Adalimumab-afzb is indicated for:
- Adults with rheumatoid arthritis.
- Polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis in patients 2 years of age and older.
- Adults with psoriatic arthritis.
- Adults with ankylosing spondylitis.
- Crohn’s disease in adults and children 6 years of age and older.
- Adults with ulcerative colitis.
- Adults with plaque psoriasis.
- Adults with hidradenitis suppurativa.
- Adults with noninfectious intermediate and posterior uveitis and panuveitis.
“With this designation, Abrilada is now both biosimilar to and interchangeable with Humira, reinforcing confidence among physicians and pharmacists that there is no decrease in effectiveness or increase in safety risk associated with switching between Abrilada and the reference product,” Roy Fleischmann, MD, clinical professor of medicine, University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, said in Pfizer’s statement.
An interchangeability designation allows pharmacists to substitute the biosimilar for the reference product without involving the prescribing clinician (according to state law). To achieve this designation, Pfizer submitted data from a phase 3 study led by Dr. Fleischmann that evaluated adalimumab-afzb in patients with RA. Patients who were switched three times between the biosimilar and the reference product had outcomes similar to those of patients continuously treated with the reference product.
Adalimumab-afzb will be available later in October at a 5% discount from Humira’s price. Later this year, the drug will launch at a second price, a 60% discount from Humira.
Full prescribing information for adalimumab-afzb is available here.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA approves first tocilizumab biosimilar
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar tocilizumab-bavi (Tofidence), Biogen, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on Sept. 29.
It is the first tocilizumab biosimilar approved by the FDA. The reference product, Actemra (Genentech), was first approved by the agency in 2010.
“The approval of Tofidence in the U.S. marks another positive step toward helping more people with chronic autoimmune conditions gain access to leading therapies,” Ian Henshaw, global head of biosimilars at Biogen, said in a statement. “With the increasing numbers of approved biosimilars, we expect increased savings and sustainability for health care systems and an increase in physician choice and patient access to biologics.”
Biogen’s pricing for tocilizumab-bavi will be available closer to the product’s launch date, which has yet to be determined, a company spokesman said. The U.S. average monthly cost of Actemra for rheumatoid arthritis, administered intravenously, is $2,134-$4,268 depending on dosage, according to a Genentech spokesperson.
Tocilizumab-bavi is an intravenous formulation (20 mg/mL) indicated for treatment of moderately to severely active RA, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (PJIA), and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA). The medication is administered every 4 weeks in RA and PJIA and every 8 weeks in SJIA as a single intravenous drip infusion over 1 hour.
The European Commission approved its first tocilizumab biosimilar, Tyenne (Fresenius Kabi), earlier in 2023 in both subcutaneous and intravenous formulations. Biogen did not comment on whether the company is working on a subcutaneous formulation for tocilizumab-bavi.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar tocilizumab-bavi (Tofidence), Biogen, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on Sept. 29.
It is the first tocilizumab biosimilar approved by the FDA. The reference product, Actemra (Genentech), was first approved by the agency in 2010.
“The approval of Tofidence in the U.S. marks another positive step toward helping more people with chronic autoimmune conditions gain access to leading therapies,” Ian Henshaw, global head of biosimilars at Biogen, said in a statement. “With the increasing numbers of approved biosimilars, we expect increased savings and sustainability for health care systems and an increase in physician choice and patient access to biologics.”
Biogen’s pricing for tocilizumab-bavi will be available closer to the product’s launch date, which has yet to be determined, a company spokesman said. The U.S. average monthly cost of Actemra for rheumatoid arthritis, administered intravenously, is $2,134-$4,268 depending on dosage, according to a Genentech spokesperson.
Tocilizumab-bavi is an intravenous formulation (20 mg/mL) indicated for treatment of moderately to severely active RA, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (PJIA), and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA). The medication is administered every 4 weeks in RA and PJIA and every 8 weeks in SJIA as a single intravenous drip infusion over 1 hour.
The European Commission approved its first tocilizumab biosimilar, Tyenne (Fresenius Kabi), earlier in 2023 in both subcutaneous and intravenous formulations. Biogen did not comment on whether the company is working on a subcutaneous formulation for tocilizumab-bavi.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the biosimilar tocilizumab-bavi (Tofidence), Biogen, the drug’s manufacturer, announced on Sept. 29.
It is the first tocilizumab biosimilar approved by the FDA. The reference product, Actemra (Genentech), was first approved by the agency in 2010.
“The approval of Tofidence in the U.S. marks another positive step toward helping more people with chronic autoimmune conditions gain access to leading therapies,” Ian Henshaw, global head of biosimilars at Biogen, said in a statement. “With the increasing numbers of approved biosimilars, we expect increased savings and sustainability for health care systems and an increase in physician choice and patient access to biologics.”
Biogen’s pricing for tocilizumab-bavi will be available closer to the product’s launch date, which has yet to be determined, a company spokesman said. The U.S. average monthly cost of Actemra for rheumatoid arthritis, administered intravenously, is $2,134-$4,268 depending on dosage, according to a Genentech spokesperson.
Tocilizumab-bavi is an intravenous formulation (20 mg/mL) indicated for treatment of moderately to severely active RA, polyarticular juvenile idiopathic arthritis (PJIA), and systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis (SJIA). The medication is administered every 4 weeks in RA and PJIA and every 8 weeks in SJIA as a single intravenous drip infusion over 1 hour.
The European Commission approved its first tocilizumab biosimilar, Tyenne (Fresenius Kabi), earlier in 2023 in both subcutaneous and intravenous formulations. Biogen did not comment on whether the company is working on a subcutaneous formulation for tocilizumab-bavi.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA OKs subcutaneous vedolizumab for UC maintenance therapy
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the subcutaneous administration of vedolizumab (Entyvio SC, Takeda) for maintenance therapy in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) following induction therapy with intravenous administration of vedolizumab.
The FDA approved the intravenous formulation of the biologic in 2014 for patients with moderate to severe UC and Crohn’s disease who failed or cannot tolerate other therapies.
The approval of subcutaneous (SC) vedolizumab was based on results from the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled VISIBLE 1 trial.
The trial assessed the safety and efficacy of maintenance therapy with SC vedolizumab in adult patients with moderately to severely active UC who achieved clinical response at week 6 following two doses of intravenous vedolizumab.
At week 6, 162 patients were randomly allocated (2:1) to vedolizumab or placebo by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was clinical remission at week 52, defined as a total Mayo score of 2 or less and no individual subscore greater than 1.
At week 52, nearly half (46%) of patients who received vedolizumab SC maintenance therapy achieved clinical remission, compared with 14% of those who received placebo SC (P < .001).
The safety profile of SC vedolizumab was “generally consistent” with that of intravenous vedolizumab, with the addition of injection-site reactions, the drugmaker, Takeda, said in a news release.
The most common adverse reactions with intravenous vedolizumab are nasopharyngitis, headache, arthralgia, nausea, pyrexia (fever), upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, bronchitis, influenza, back pain, rash, pruritus, sinusitis, oropharyngeal pain, and pain in the extremities.
SC vedolizumab “can provide physicians with an additional administration option for achieving remission in their moderate to severe ulcerative colitis patients,” according to Bruce E. Sands, MD, AGAF, chief of gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. He provided a statement in the Takeda news release.
“I appreciate now having a subcutaneous administration option that provides a clinical profile consistent with Entyvio intravenous while also giving me and my appropriate UC patients a choice of how they receive their maintenance therapy,” Dr. Sands said.
The FDA is currently reviewing Takeda’s biologics license application for subcutaneous administration of vedolizumab in the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease.
Dr. Sands is a paid consultant of Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the subcutaneous administration of vedolizumab (Entyvio SC, Takeda) for maintenance therapy in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) following induction therapy with intravenous administration of vedolizumab.
The FDA approved the intravenous formulation of the biologic in 2014 for patients with moderate to severe UC and Crohn’s disease who failed or cannot tolerate other therapies.
The approval of subcutaneous (SC) vedolizumab was based on results from the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled VISIBLE 1 trial.
The trial assessed the safety and efficacy of maintenance therapy with SC vedolizumab in adult patients with moderately to severely active UC who achieved clinical response at week 6 following two doses of intravenous vedolizumab.
At week 6, 162 patients were randomly allocated (2:1) to vedolizumab or placebo by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was clinical remission at week 52, defined as a total Mayo score of 2 or less and no individual subscore greater than 1.
At week 52, nearly half (46%) of patients who received vedolizumab SC maintenance therapy achieved clinical remission, compared with 14% of those who received placebo SC (P < .001).
The safety profile of SC vedolizumab was “generally consistent” with that of intravenous vedolizumab, with the addition of injection-site reactions, the drugmaker, Takeda, said in a news release.
The most common adverse reactions with intravenous vedolizumab are nasopharyngitis, headache, arthralgia, nausea, pyrexia (fever), upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, bronchitis, influenza, back pain, rash, pruritus, sinusitis, oropharyngeal pain, and pain in the extremities.
SC vedolizumab “can provide physicians with an additional administration option for achieving remission in their moderate to severe ulcerative colitis patients,” according to Bruce E. Sands, MD, AGAF, chief of gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. He provided a statement in the Takeda news release.
“I appreciate now having a subcutaneous administration option that provides a clinical profile consistent with Entyvio intravenous while also giving me and my appropriate UC patients a choice of how they receive their maintenance therapy,” Dr. Sands said.
The FDA is currently reviewing Takeda’s biologics license application for subcutaneous administration of vedolizumab in the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease.
Dr. Sands is a paid consultant of Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration has approved the subcutaneous administration of vedolizumab (Entyvio SC, Takeda) for maintenance therapy in adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis (UC) following induction therapy with intravenous administration of vedolizumab.
The FDA approved the intravenous formulation of the biologic in 2014 for patients with moderate to severe UC and Crohn’s disease who failed or cannot tolerate other therapies.
The approval of subcutaneous (SC) vedolizumab was based on results from the phase 3, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled VISIBLE 1 trial.
The trial assessed the safety and efficacy of maintenance therapy with SC vedolizumab in adult patients with moderately to severely active UC who achieved clinical response at week 6 following two doses of intravenous vedolizumab.
At week 6, 162 patients were randomly allocated (2:1) to vedolizumab or placebo by subcutaneous injection every 2 weeks. The primary endpoint was clinical remission at week 52, defined as a total Mayo score of 2 or less and no individual subscore greater than 1.
At week 52, nearly half (46%) of patients who received vedolizumab SC maintenance therapy achieved clinical remission, compared with 14% of those who received placebo SC (P < .001).
The safety profile of SC vedolizumab was “generally consistent” with that of intravenous vedolizumab, with the addition of injection-site reactions, the drugmaker, Takeda, said in a news release.
The most common adverse reactions with intravenous vedolizumab are nasopharyngitis, headache, arthralgia, nausea, pyrexia (fever), upper respiratory tract infection, fatigue, cough, bronchitis, influenza, back pain, rash, pruritus, sinusitis, oropharyngeal pain, and pain in the extremities.
SC vedolizumab “can provide physicians with an additional administration option for achieving remission in their moderate to severe ulcerative colitis patients,” according to Bruce E. Sands, MD, AGAF, chief of gastroenterology at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. He provided a statement in the Takeda news release.
“I appreciate now having a subcutaneous administration option that provides a clinical profile consistent with Entyvio intravenous while also giving me and my appropriate UC patients a choice of how they receive their maintenance therapy,” Dr. Sands said.
The FDA is currently reviewing Takeda’s biologics license application for subcutaneous administration of vedolizumab in the treatment of adults with moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease.
Dr. Sands is a paid consultant of Takeda.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.