User login
HM17 session summary: CT to PET scans – What every hospitalist needs to know
Presenter
Timothy Kasprzak, MD, MBA
Session summary
“What imaging study should I order for this patient?” is a question that comes up frequently in the hospital. Dr. Kasprzak, the director of abdominopelvic and oncologic imaging at Case Western MetroHealth, Cleveland, offered some practical advice for inpatient clinicians during a rapid-fire session at HM17.
The session also touched on the risks and benefits of contrast media for CT scans and MRIs. As with other tests and treatments in medicine, the use of contrast is always a “risk-benefit.” The main benefit of both forms of contrast is to improve the “conspicuity” of findings on imaging studies – many diagnoses that are visible with contrast (such as vascular lesions, solid organ lesions, or extravasations) are invisible without it.
The risks of both CT and MRI contrast have been re-evaluated over the past several years. More recent evidence is suggesting the prevalence of contrast-induced nephropathy is lower than previously thought, especially with newer non-ionic contrast. Conversely, there is some recent evidence that CT contrast might accentuate radiation-related DNA damage. Regarding MRIs, gadolinium has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, particularly in patients with end-stage renal disease. This appears to be less prevalent with newer gadolinium agents. There are, however, recent reports of gadolinium deposition in the basal ganglia of patients. The clinical significance of this imaging finding is still unknown.
Lastly, Dr. Kasprzak offered advice on the use of PET scans on inpatients. While there are a few indications that would warrant inpatient use (such as evaluation in fever of unknown origin), most PET scans are done for oncologic reasons that do not warrant urgent inpatient use. In addition, some insurance companies don’t reimburse for inpatient PET studies.
Key takeaways for HM
• Utilize appropriate use criteria (such as offered by the ACR) for choosing the most worthwhile imaging study.
• Give relevant clinical history in your order to help the radiologist narrow the differential (and to help prevent the “clinically correlate” phrase as much as possible).
• Consider the risk/benefit of contrast use for all patients getting CT or MRI studies.
• Avoid the use of inpatient PET scans, except for very specific indications (such as obscure infections).
Dr. Sehgal is a hospitalist at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System in San Antonio, an associate professor of medicine at University of Texas Health-San Antonio, and a an editorial board member of The Hospitalist.
Presenter
Timothy Kasprzak, MD, MBA
Session summary
“What imaging study should I order for this patient?” is a question that comes up frequently in the hospital. Dr. Kasprzak, the director of abdominopelvic and oncologic imaging at Case Western MetroHealth, Cleveland, offered some practical advice for inpatient clinicians during a rapid-fire session at HM17.
The session also touched on the risks and benefits of contrast media for CT scans and MRIs. As with other tests and treatments in medicine, the use of contrast is always a “risk-benefit.” The main benefit of both forms of contrast is to improve the “conspicuity” of findings on imaging studies – many diagnoses that are visible with contrast (such as vascular lesions, solid organ lesions, or extravasations) are invisible without it.
The risks of both CT and MRI contrast have been re-evaluated over the past several years. More recent evidence is suggesting the prevalence of contrast-induced nephropathy is lower than previously thought, especially with newer non-ionic contrast. Conversely, there is some recent evidence that CT contrast might accentuate radiation-related DNA damage. Regarding MRIs, gadolinium has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, particularly in patients with end-stage renal disease. This appears to be less prevalent with newer gadolinium agents. There are, however, recent reports of gadolinium deposition in the basal ganglia of patients. The clinical significance of this imaging finding is still unknown.
Lastly, Dr. Kasprzak offered advice on the use of PET scans on inpatients. While there are a few indications that would warrant inpatient use (such as evaluation in fever of unknown origin), most PET scans are done for oncologic reasons that do not warrant urgent inpatient use. In addition, some insurance companies don’t reimburse for inpatient PET studies.
Key takeaways for HM
• Utilize appropriate use criteria (such as offered by the ACR) for choosing the most worthwhile imaging study.
• Give relevant clinical history in your order to help the radiologist narrow the differential (and to help prevent the “clinically correlate” phrase as much as possible).
• Consider the risk/benefit of contrast use for all patients getting CT or MRI studies.
• Avoid the use of inpatient PET scans, except for very specific indications (such as obscure infections).
Dr. Sehgal is a hospitalist at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System in San Antonio, an associate professor of medicine at University of Texas Health-San Antonio, and a an editorial board member of The Hospitalist.
Presenter
Timothy Kasprzak, MD, MBA
Session summary
“What imaging study should I order for this patient?” is a question that comes up frequently in the hospital. Dr. Kasprzak, the director of abdominopelvic and oncologic imaging at Case Western MetroHealth, Cleveland, offered some practical advice for inpatient clinicians during a rapid-fire session at HM17.
The session also touched on the risks and benefits of contrast media for CT scans and MRIs. As with other tests and treatments in medicine, the use of contrast is always a “risk-benefit.” The main benefit of both forms of contrast is to improve the “conspicuity” of findings on imaging studies – many diagnoses that are visible with contrast (such as vascular lesions, solid organ lesions, or extravasations) are invisible without it.
The risks of both CT and MRI contrast have been re-evaluated over the past several years. More recent evidence is suggesting the prevalence of contrast-induced nephropathy is lower than previously thought, especially with newer non-ionic contrast. Conversely, there is some recent evidence that CT contrast might accentuate radiation-related DNA damage. Regarding MRIs, gadolinium has been associated with nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, particularly in patients with end-stage renal disease. This appears to be less prevalent with newer gadolinium agents. There are, however, recent reports of gadolinium deposition in the basal ganglia of patients. The clinical significance of this imaging finding is still unknown.
Lastly, Dr. Kasprzak offered advice on the use of PET scans on inpatients. While there are a few indications that would warrant inpatient use (such as evaluation in fever of unknown origin), most PET scans are done for oncologic reasons that do not warrant urgent inpatient use. In addition, some insurance companies don’t reimburse for inpatient PET studies.
Key takeaways for HM
• Utilize appropriate use criteria (such as offered by the ACR) for choosing the most worthwhile imaging study.
• Give relevant clinical history in your order to help the radiologist narrow the differential (and to help prevent the “clinically correlate” phrase as much as possible).
• Consider the risk/benefit of contrast use for all patients getting CT or MRI studies.
• Avoid the use of inpatient PET scans, except for very specific indications (such as obscure infections).
Dr. Sehgal is a hospitalist at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System in San Antonio, an associate professor of medicine at University of Texas Health-San Antonio, and a an editorial board member of The Hospitalist.
Spironolactone’s HFpEF benefit happens mostly in women
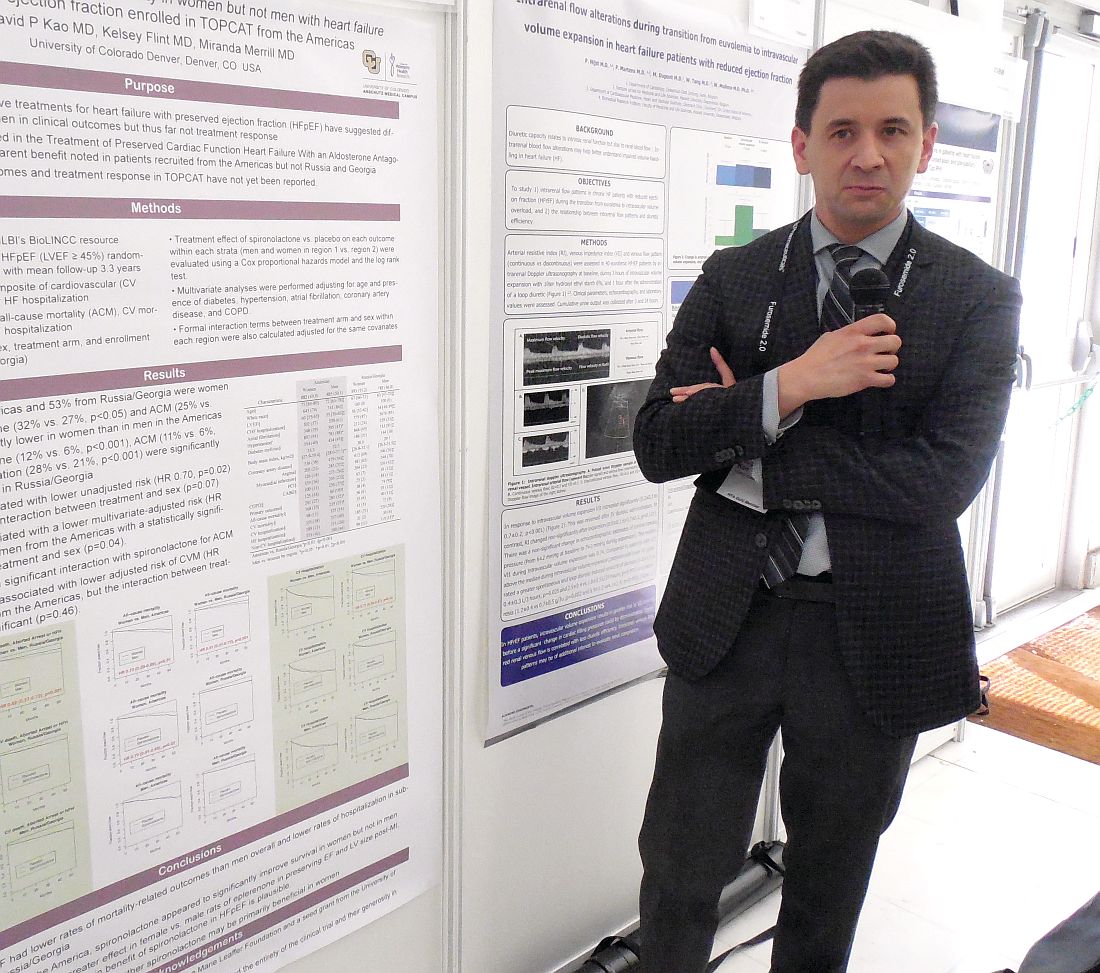
PARIS – Just when the aldosterone receptor antagonists spironolactone and eplerenone received official recognition in the 2017 U.S. heart failure guidelines as the only drug class that benefits patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a new post-hoc analysis of the pivotal evidence suggests the benefit is mostly in women, with little benefit to men.
The new analysis used data collected from TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist), which randomized patients with HFpEF to treatment with spironolactone or placebo. Results from the overall study were neutral for the primary outcome of cardiovascular death, aborted cardiac arrest, and heart failure hospitalization (N Engl J Med. 2014 April 10;370[15]:1383-92). However, a series of post-hoc analyses showed that a high percentage of patients enrolled at centers in Russia or Georgia did not match the expected HFpEF profile, and these patients had poor responses to spironolactone. In contrast, patients enrolled at centers in the Americas more frequently matched the study’s target HFpEF profile, and they showed significant improvement for the primary endpoint (Circulation. 2015 Jan 6;131[1]:34-42).
“The observation that most of the benefit [from spironolactone treatment] may have been in women is interesting, but I don’t think that it would stop me from using [an aldosterone receptor antagonist] in men,” said Dr. Kao while presenting his report. The outcomes in both men and women “head in the same direction. It’s just that the mortality benefit is much clearer in women,” said Dr. Kao, a cardiologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Among the patients enrolled at centers in North and South America, 882 were women, and 885 were men. Dr. Kao used the data collected in TOPCAT to calculate the impact of spironolactone treatment relative to placebo on outcomes just among women in the Americas and just among men.
The difference in all-cause mortality associated with spironolactone treatment had an even sharper sex disparity that in the primary outcome. Overall, all-cause mortality was 28% less common among women, compared with men, in the Americas. Among women, spironolactone treatment linked with a 30% reduced all-cause mortality rate, compared with placebo. Among men, the survival curves of those on spironolactone or placebo superimposed.
Dr. Kao said that published study results in rats had suggested that eplerenone (Inspra), an aldosterone receptor antagonist like spironolactone, had a more potent effect in females rats, compared with male rats, for preserving left ventricular function and size following myocardial damage. In addition, women with HFpEF often have more left ventricular hypertrophy, while men often have more diastolic dysfunction, and prior findings had suggested that aldosterone plays a role in left ventricular hypertrophy.
TOPCAT received no commercial funding. Dr. Kao had no disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
PARIS – Just when the aldosterone receptor antagonists spironolactone and eplerenone received official recognition in the 2017 U.S. heart failure guidelines as the only drug class that benefits patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a new post-hoc analysis of the pivotal evidence suggests the benefit is mostly in women, with little benefit to men.
The new analysis used data collected from TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist), which randomized patients with HFpEF to treatment with spironolactone or placebo. Results from the overall study were neutral for the primary outcome of cardiovascular death, aborted cardiac arrest, and heart failure hospitalization (N Engl J Med. 2014 April 10;370[15]:1383-92). However, a series of post-hoc analyses showed that a high percentage of patients enrolled at centers in Russia or Georgia did not match the expected HFpEF profile, and these patients had poor responses to spironolactone. In contrast, patients enrolled at centers in the Americas more frequently matched the study’s target HFpEF profile, and they showed significant improvement for the primary endpoint (Circulation. 2015 Jan 6;131[1]:34-42).
“The observation that most of the benefit [from spironolactone treatment] may have been in women is interesting, but I don’t think that it would stop me from using [an aldosterone receptor antagonist] in men,” said Dr. Kao while presenting his report. The outcomes in both men and women “head in the same direction. It’s just that the mortality benefit is much clearer in women,” said Dr. Kao, a cardiologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Among the patients enrolled at centers in North and South America, 882 were women, and 885 were men. Dr. Kao used the data collected in TOPCAT to calculate the impact of spironolactone treatment relative to placebo on outcomes just among women in the Americas and just among men.
The difference in all-cause mortality associated with spironolactone treatment had an even sharper sex disparity that in the primary outcome. Overall, all-cause mortality was 28% less common among women, compared with men, in the Americas. Among women, spironolactone treatment linked with a 30% reduced all-cause mortality rate, compared with placebo. Among men, the survival curves of those on spironolactone or placebo superimposed.
Dr. Kao said that published study results in rats had suggested that eplerenone (Inspra), an aldosterone receptor antagonist like spironolactone, had a more potent effect in females rats, compared with male rats, for preserving left ventricular function and size following myocardial damage. In addition, women with HFpEF often have more left ventricular hypertrophy, while men often have more diastolic dysfunction, and prior findings had suggested that aldosterone plays a role in left ventricular hypertrophy.
TOPCAT received no commercial funding. Dr. Kao had no disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
PARIS – Just when the aldosterone receptor antagonists spironolactone and eplerenone received official recognition in the 2017 U.S. heart failure guidelines as the only drug class that benefits patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), a new post-hoc analysis of the pivotal evidence suggests the benefit is mostly in women, with little benefit to men.
The new analysis used data collected from TOPCAT (Treatment of Preserved Cardiac Function Heart Failure with an Aldosterone Antagonist), which randomized patients with HFpEF to treatment with spironolactone or placebo. Results from the overall study were neutral for the primary outcome of cardiovascular death, aborted cardiac arrest, and heart failure hospitalization (N Engl J Med. 2014 April 10;370[15]:1383-92). However, a series of post-hoc analyses showed that a high percentage of patients enrolled at centers in Russia or Georgia did not match the expected HFpEF profile, and these patients had poor responses to spironolactone. In contrast, patients enrolled at centers in the Americas more frequently matched the study’s target HFpEF profile, and they showed significant improvement for the primary endpoint (Circulation. 2015 Jan 6;131[1]:34-42).
“The observation that most of the benefit [from spironolactone treatment] may have been in women is interesting, but I don’t think that it would stop me from using [an aldosterone receptor antagonist] in men,” said Dr. Kao while presenting his report. The outcomes in both men and women “head in the same direction. It’s just that the mortality benefit is much clearer in women,” said Dr. Kao, a cardiologist at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
Among the patients enrolled at centers in North and South America, 882 were women, and 885 were men. Dr. Kao used the data collected in TOPCAT to calculate the impact of spironolactone treatment relative to placebo on outcomes just among women in the Americas and just among men.
The difference in all-cause mortality associated with spironolactone treatment had an even sharper sex disparity that in the primary outcome. Overall, all-cause mortality was 28% less common among women, compared with men, in the Americas. Among women, spironolactone treatment linked with a 30% reduced all-cause mortality rate, compared with placebo. Among men, the survival curves of those on spironolactone or placebo superimposed.
Dr. Kao said that published study results in rats had suggested that eplerenone (Inspra), an aldosterone receptor antagonist like spironolactone, had a more potent effect in females rats, compared with male rats, for preserving left ventricular function and size following myocardial damage. In addition, women with HFpEF often have more left ventricular hypertrophy, while men often have more diastolic dysfunction, and prior findings had suggested that aldosterone plays a role in left ventricular hypertrophy.
TOPCAT received no commercial funding. Dr. Kao had no disclosures.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
AT HEART FAILURE 2017
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Women from the Americas in TOPCAT had an 18% lower rate of primary endpoint events, compared with men in the trial.
Data source: TOPCAT, a multicenter, randomized study with 3,445 patients.
Disclosures: TOPCAT received no commercial funding. Dr. Kao had no disclosures.
HM17 session summary: The hospitalist’s role in the opioid epidemic
Presenters
Shoshana J. Herzig, MD, MPH, and Hillary J. Mosher, MFA, MD, FHM
Summary
The growth in opiate prescribing and associated increases in adverse events has created unique challenges for hospitalists, including how best to assess pain and opiate use disorders and how to safely prescribe opiates during hospitalization and at discharge.
These challenges are compounded by patient and system factors and a paucity of evidence-based guidelines to help guide safe administration of opiates in hospitalized patients. This can mean frustration for hospitalists and harm for patients.
Key takeaways for HM
- When assessing patients’ pain, it is crucial to differentiate between acute and chronic pain (or both) and whether it is nociceptive or neuropathic. Misclassification of pain contributes to inappropriate exposure and escalation of opiate therapy during hospitalization.
- Always consider nonopioid analgesics such as NSAIDs first and pair them with opiates. Studies in a variety of conditions have demonstrated that these are equally, if not more, effective, even for severe pain, such as with renal colic. Reserve opiates for moderate to severe pain.
- Always assess whether the benefits of initiating or continuing opioid therapy outweigh the risks for individual patients. There is no validated tool to predict risk for adverse events and/or opioid abuse disorder but a careful review of patient history can identify established risk factors (such as a history of mental illness or substance abuse disorders, renal impairment, or other comorbidities). In addition, nearly all states now have Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs, and hospitalists should consult these routinely when prescribing opiates.
- Always clearly discuss expectations and risks of opioid therapy, including the potential for development of opioid use disorders with hospitalized patients prior to initiation. Emphasize pain reduction rather than elimination and focus on functional goals such as improved mobility. Also, set expectations for stepping down treatment up front.
- Use the lowest effective dose of immediate-release opioids (preferably oral route) for shortest duration possible. Long acting opiates are associated with increased risk of adverse events, and their initiation should generally be avoided in hospitalized patients with noncancer pain.
- Minimize risk by avoiding concurrent administration of other medications with sedative properties, especially benzodiazepines, which have been found to significantly increase the risk of adverse events, including overdose.
- Recognize that chronic opioid use often begins with treatment of acute pain during hospitalization. Adopt best practice for discharge, including prescribing shorter courses whenever possible, discussing initiation, and changes or modifications in opiate therapy with patients’ primary care provider, and ensure timely postdischarge follow-up. Also consider coprescription of naloxone at discharge for higher risk patients.
Dr. Stella is a hospitalist in Denver and an editorial board member of The Hospitalist.
Presenters
Shoshana J. Herzig, MD, MPH, and Hillary J. Mosher, MFA, MD, FHM
Summary
The growth in opiate prescribing and associated increases in adverse events has created unique challenges for hospitalists, including how best to assess pain and opiate use disorders and how to safely prescribe opiates during hospitalization and at discharge.
These challenges are compounded by patient and system factors and a paucity of evidence-based guidelines to help guide safe administration of opiates in hospitalized patients. This can mean frustration for hospitalists and harm for patients.
Key takeaways for HM
- When assessing patients’ pain, it is crucial to differentiate between acute and chronic pain (or both) and whether it is nociceptive or neuropathic. Misclassification of pain contributes to inappropriate exposure and escalation of opiate therapy during hospitalization.
- Always consider nonopioid analgesics such as NSAIDs first and pair them with opiates. Studies in a variety of conditions have demonstrated that these are equally, if not more, effective, even for severe pain, such as with renal colic. Reserve opiates for moderate to severe pain.
- Always assess whether the benefits of initiating or continuing opioid therapy outweigh the risks for individual patients. There is no validated tool to predict risk for adverse events and/or opioid abuse disorder but a careful review of patient history can identify established risk factors (such as a history of mental illness or substance abuse disorders, renal impairment, or other comorbidities). In addition, nearly all states now have Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs, and hospitalists should consult these routinely when prescribing opiates.
- Always clearly discuss expectations and risks of opioid therapy, including the potential for development of opioid use disorders with hospitalized patients prior to initiation. Emphasize pain reduction rather than elimination and focus on functional goals such as improved mobility. Also, set expectations for stepping down treatment up front.
- Use the lowest effective dose of immediate-release opioids (preferably oral route) for shortest duration possible. Long acting opiates are associated with increased risk of adverse events, and their initiation should generally be avoided in hospitalized patients with noncancer pain.
- Minimize risk by avoiding concurrent administration of other medications with sedative properties, especially benzodiazepines, which have been found to significantly increase the risk of adverse events, including overdose.
- Recognize that chronic opioid use often begins with treatment of acute pain during hospitalization. Adopt best practice for discharge, including prescribing shorter courses whenever possible, discussing initiation, and changes or modifications in opiate therapy with patients’ primary care provider, and ensure timely postdischarge follow-up. Also consider coprescription of naloxone at discharge for higher risk patients.
Dr. Stella is a hospitalist in Denver and an editorial board member of The Hospitalist.
Presenters
Shoshana J. Herzig, MD, MPH, and Hillary J. Mosher, MFA, MD, FHM
Summary
The growth in opiate prescribing and associated increases in adverse events has created unique challenges for hospitalists, including how best to assess pain and opiate use disorders and how to safely prescribe opiates during hospitalization and at discharge.
These challenges are compounded by patient and system factors and a paucity of evidence-based guidelines to help guide safe administration of opiates in hospitalized patients. This can mean frustration for hospitalists and harm for patients.
Key takeaways for HM
- When assessing patients’ pain, it is crucial to differentiate between acute and chronic pain (or both) and whether it is nociceptive or neuropathic. Misclassification of pain contributes to inappropriate exposure and escalation of opiate therapy during hospitalization.
- Always consider nonopioid analgesics such as NSAIDs first and pair them with opiates. Studies in a variety of conditions have demonstrated that these are equally, if not more, effective, even for severe pain, such as with renal colic. Reserve opiates for moderate to severe pain.
- Always assess whether the benefits of initiating or continuing opioid therapy outweigh the risks for individual patients. There is no validated tool to predict risk for adverse events and/or opioid abuse disorder but a careful review of patient history can identify established risk factors (such as a history of mental illness or substance abuse disorders, renal impairment, or other comorbidities). In addition, nearly all states now have Prescription Drug Monitoring Programs, and hospitalists should consult these routinely when prescribing opiates.
- Always clearly discuss expectations and risks of opioid therapy, including the potential for development of opioid use disorders with hospitalized patients prior to initiation. Emphasize pain reduction rather than elimination and focus on functional goals such as improved mobility. Also, set expectations for stepping down treatment up front.
- Use the lowest effective dose of immediate-release opioids (preferably oral route) for shortest duration possible. Long acting opiates are associated with increased risk of adverse events, and their initiation should generally be avoided in hospitalized patients with noncancer pain.
- Minimize risk by avoiding concurrent administration of other medications with sedative properties, especially benzodiazepines, which have been found to significantly increase the risk of adverse events, including overdose.
- Recognize that chronic opioid use often begins with treatment of acute pain during hospitalization. Adopt best practice for discharge, including prescribing shorter courses whenever possible, discussing initiation, and changes or modifications in opiate therapy with patients’ primary care provider, and ensure timely postdischarge follow-up. Also consider coprescription of naloxone at discharge for higher risk patients.
Dr. Stella is a hospitalist in Denver and an editorial board member of The Hospitalist.
Infections up the risk for pregnancy-associated stroke in preeclampsia
A host of factors, some of them preventable or treatable, increase the risk of pregnancy-related stroke among women hospitalized for preeclampsia, according to findings from a case-control study of nearly 800 preeclamptic women in New York.
Women who experienced a stroke were roughly seven times more likely to have severe preeclampsia or eclampsia, and about three to four times more likely to have an infection, a prothrombotic state, a coagulopathy, or chronic hypertension, according to the findings (Stroke. 2017 May 25. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017374).
“Prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and develop interventions aimed at preventing strokes in this uniquely vulnerable group,” they added.
For the study, the investigators used billing data from the 2003-2012 New York State Department of Health inpatient database to identify women aged 12-55 years admitted with preeclampsia.
They matched each woman who experienced pregnancy-associated stroke with three randomly selected controls of the same age, race/ethnicity, and insurance status. They then compared the groups on a set of predefined risk factors.
Results showed that of 88,857 women admitted for preeclampsia during the study period, 0.2% experienced pregnancy-associated stroke, translating to a cumulative incidence of 222 per 100,000 preeclamptic women, a value more than six times that seen in the general pregnant population, the investigators noted.
The majority of strokes occurred post partum (66.5%), but more than a quarter occurred before delivery (27.9%). The single most common type of stroke was hemorrhagic (46.7%).
The 197 women with preeclampsia who experienced pregnancy-associated stroke had a sharply higher rate of in-hospital mortality (13.2%), compared with the 591 controls (0.2%).
In multivariate analysis, women with preeclampsia experiencing stroke were more likely to have severe preeclampsia or eclampsia (odds ratio, 7.2; 95% confidence interval, 4.6-11.3), or infections at the time of admission (OR, 3.0; 95% CI, 1.6-5.8), predominantly genitourinary infections.
Other risk factors for pregnancy-associated stroke included prothrombotic states (OR, 3.5; 95% CI, 1.3-9.2), coagulopathies (OR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.3-7.1), or chronic hypertension (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.8-5.5).
The findings were similar when women were matched by the severity of preeclampsia, when women with eclampsia were excluded, or when women with only postpartum stroke were included.
Heart disease, multiple gestation, and previous pregnancies were not significantly independently associated with the risk of pregnancy-associated stroke.
“The ethnic and regional diversity of New York State increases the generalizability of our findings,” the investigators wrote. “Matching of cases and controls allowed for nuanced analysis of other risk factors.”
But the study may have missed some cases of preeclampsia not formally diagnosed, and the timing of infections relative to stroke was unknown, they acknowledged. Additionally, they noted that causality cannot be inferred from the observational study, and therefore the results should be interpreted cautiously.
The investigators reported research support from the National Institutes of Health. They had no other financial disclosures.
A host of factors, some of them preventable or treatable, increase the risk of pregnancy-related stroke among women hospitalized for preeclampsia, according to findings from a case-control study of nearly 800 preeclamptic women in New York.
Women who experienced a stroke were roughly seven times more likely to have severe preeclampsia or eclampsia, and about three to four times more likely to have an infection, a prothrombotic state, a coagulopathy, or chronic hypertension, according to the findings (Stroke. 2017 May 25. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017374).
“Prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and develop interventions aimed at preventing strokes in this uniquely vulnerable group,” they added.
For the study, the investigators used billing data from the 2003-2012 New York State Department of Health inpatient database to identify women aged 12-55 years admitted with preeclampsia.
They matched each woman who experienced pregnancy-associated stroke with three randomly selected controls of the same age, race/ethnicity, and insurance status. They then compared the groups on a set of predefined risk factors.
Results showed that of 88,857 women admitted for preeclampsia during the study period, 0.2% experienced pregnancy-associated stroke, translating to a cumulative incidence of 222 per 100,000 preeclamptic women, a value more than six times that seen in the general pregnant population, the investigators noted.
The majority of strokes occurred post partum (66.5%), but more than a quarter occurred before delivery (27.9%). The single most common type of stroke was hemorrhagic (46.7%).
The 197 women with preeclampsia who experienced pregnancy-associated stroke had a sharply higher rate of in-hospital mortality (13.2%), compared with the 591 controls (0.2%).
In multivariate analysis, women with preeclampsia experiencing stroke were more likely to have severe preeclampsia or eclampsia (odds ratio, 7.2; 95% confidence interval, 4.6-11.3), or infections at the time of admission (OR, 3.0; 95% CI, 1.6-5.8), predominantly genitourinary infections.
Other risk factors for pregnancy-associated stroke included prothrombotic states (OR, 3.5; 95% CI, 1.3-9.2), coagulopathies (OR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.3-7.1), or chronic hypertension (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.8-5.5).
The findings were similar when women were matched by the severity of preeclampsia, when women with eclampsia were excluded, or when women with only postpartum stroke were included.
Heart disease, multiple gestation, and previous pregnancies were not significantly independently associated with the risk of pregnancy-associated stroke.
“The ethnic and regional diversity of New York State increases the generalizability of our findings,” the investigators wrote. “Matching of cases and controls allowed for nuanced analysis of other risk factors.”
But the study may have missed some cases of preeclampsia not formally diagnosed, and the timing of infections relative to stroke was unknown, they acknowledged. Additionally, they noted that causality cannot be inferred from the observational study, and therefore the results should be interpreted cautiously.
The investigators reported research support from the National Institutes of Health. They had no other financial disclosures.
A host of factors, some of them preventable or treatable, increase the risk of pregnancy-related stroke among women hospitalized for preeclampsia, according to findings from a case-control study of nearly 800 preeclamptic women in New York.
Women who experienced a stroke were roughly seven times more likely to have severe preeclampsia or eclampsia, and about three to four times more likely to have an infection, a prothrombotic state, a coagulopathy, or chronic hypertension, according to the findings (Stroke. 2017 May 25. doi: 10.1161/STROKEAHA.117.017374).
“Prospective studies are needed to confirm these findings and develop interventions aimed at preventing strokes in this uniquely vulnerable group,” they added.
For the study, the investigators used billing data from the 2003-2012 New York State Department of Health inpatient database to identify women aged 12-55 years admitted with preeclampsia.
They matched each woman who experienced pregnancy-associated stroke with three randomly selected controls of the same age, race/ethnicity, and insurance status. They then compared the groups on a set of predefined risk factors.
Results showed that of 88,857 women admitted for preeclampsia during the study period, 0.2% experienced pregnancy-associated stroke, translating to a cumulative incidence of 222 per 100,000 preeclamptic women, a value more than six times that seen in the general pregnant population, the investigators noted.
The majority of strokes occurred post partum (66.5%), but more than a quarter occurred before delivery (27.9%). The single most common type of stroke was hemorrhagic (46.7%).
The 197 women with preeclampsia who experienced pregnancy-associated stroke had a sharply higher rate of in-hospital mortality (13.2%), compared with the 591 controls (0.2%).
In multivariate analysis, women with preeclampsia experiencing stroke were more likely to have severe preeclampsia or eclampsia (odds ratio, 7.2; 95% confidence interval, 4.6-11.3), or infections at the time of admission (OR, 3.0; 95% CI, 1.6-5.8), predominantly genitourinary infections.
Other risk factors for pregnancy-associated stroke included prothrombotic states (OR, 3.5; 95% CI, 1.3-9.2), coagulopathies (OR, 3.1; 95% CI, 1.3-7.1), or chronic hypertension (OR, 3.2; 95% CI, 1.8-5.5).
The findings were similar when women were matched by the severity of preeclampsia, when women with eclampsia were excluded, or when women with only postpartum stroke were included.
Heart disease, multiple gestation, and previous pregnancies were not significantly independently associated with the risk of pregnancy-associated stroke.
“The ethnic and regional diversity of New York State increases the generalizability of our findings,” the investigators wrote. “Matching of cases and controls allowed for nuanced analysis of other risk factors.”
But the study may have missed some cases of preeclampsia not formally diagnosed, and the timing of infections relative to stroke was unknown, they acknowledged. Additionally, they noted that causality cannot be inferred from the observational study, and therefore the results should be interpreted cautiously.
The investigators reported research support from the National Institutes of Health. They had no other financial disclosures.
FROM STROKE
Key clinical point:
Major finding: Independent risk factors for pregnancy-associated stroke were severe preeclampsia or eclampsia (OR, 7.2), infections (OR, 3.0), prothrombotic states (OR, 3.5), coagulopathies (OR, 3.1), or chronic hypertension (OR, 3.2).
Data source: A matched, case-control study of 788 women from a New York inpatient database who were hospitalized for preeclampsia.
Disclosures: The investigators reported research support from the National Institutes of Health. They had no other financial disclosures.
Consider switch to clopidogrel for DAPT early post ACS
PARIS – A strategy of switching from prasugrel or ticagrelor to clopidogrel 1 month after percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome is superior to the guideline-recommended full 12 months of dual-antiplatelet therapy with either of the newer P2Y12 inhibitors, according to Thomas Cuisset, MD.
In the randomized TOPIC (Timing of Platelet Inhibition After Acute Coronary Syndrome) trial, this switch strategy resulted in a marked reduction in bleeding without an increased risk of ischemic events, compared with a full 12 months of standard dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) using prasugrel (Effient) or ticagrelor (Brilinta).
He added that the cost savings of this switch strategy would be enormous, since generic clopidogrel is vastly less expensive than prasugrel or ticagrelor.
Twelve months of DAPT with aspirin plus either prasugrel or ticagrelor is the guideline-recommended DAPT regimen following PCI for ACS on the strength of the TRITON and PLATO trials, respectively, which showed that those agents were more effective than clopidogrel for the prevention of thrombotic events. But Dr. Cuisset and his coinvestigators noted that the risk of ischemic events was highest in the first month or so following ACS, while the risk of DAPT-related serious bleeding increased after the first month and continued for the duration.
“We need to use the new drugs, and we need to go for 1 year with DAPT. But does that mean we need to go for 1 year with the new drugs?” he asked.
This question was the impetus for TOPIC, an open-label, single-center randomized trial that included 646 ACS patients who were free of major adverse cardiovascular events during their first month on DAPT with prasugrel or ticagrelor. At that point they were randomized to remain on their standard regimen or switch to aspirin at 75 mg/day plus clopidogrel at 75 mg/day for months 2-12. The switch strategy is similar to the way pulmonary embolism is managed: an early phase of high-intensity therapy followed by a backing off to a less intensive regimen, said Dr. Cuisset, a cardiologist at Aix-Marseille University, Provence, France.
The primary endpoint in TOPIC was the cumulative 1-year rate of a composite of all-cause mortality, stroke, urgent revascularization, or clinically significant bleeding as reflected in a Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) grade 2 or greater bleeding. The primary endpoint occurred in 13.4% of the switch group, a 52% relative risk reduction, compared with the 26.3% cumulative incidence with standard DAPT.
This difference wasn’t due to any between-group disparity in ischemic events, but rather to a 70% reduction in the risk of BARC grade 2 or greater bleeding in the switch group: 4.0% vs. 14.9%.
Some physicians have already been switching to clopidogrel for DAPT after ACS, either because of safety or cost concerns. Now their practice is evidence based, Dr. Cuisset noted.
Asked why TOPIC didn’t use the more stringent bleeding endpoint of BARC grade 3-5 bleeding, the cardiologist replied that it would have required a larger trial to show a significant difference. Besides, he added, BARC grade 2 bleeding is clinically important because it has a negative impact on quality of life and can cause patients to discontinue DAPT, thereby increasing their risk of thrombosis.
The TOPIC protocol didn’t utilize a loading dose of clopidogrel when making the switch. Investigators started clopidogrel the day after stopping prasugrel and at least 12 hours after the final dose of ticagrelor.
Ideally, the novel TOPIC findings should be confirmed in a much larger, randomized, double-blind clinical trial capable of detecting any small differences in stent thrombosis or MI rates before physicians adopt a change in practice, but discussant Chaim Lotan, MD, director of the Heart Institute at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem, dismissed that prospect as unlikely.
“I tried myself to do a similar study and found I got a lot of opposition from the pharma companies as well as from physicians who said, ‘How can you go against the guidelines?’ ” he said.
“I want to congratulate your team because I think this is a groundbreaking study that is going to dictate a changing of the guidelines,” he told Dr. Cuisset.
Dr. Cuisset reported having no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
Simultaneous with his presentation in Paris, the TOPIC findings were published online (Eur Heart J. 2017 May 16. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx175).
Dr. Cuisset reported no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
[email protected]
PARIS – A strategy of switching from prasugrel or ticagrelor to clopidogrel 1 month after percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome is superior to the guideline-recommended full 12 months of dual-antiplatelet therapy with either of the newer P2Y12 inhibitors, according to Thomas Cuisset, MD.
In the randomized TOPIC (Timing of Platelet Inhibition After Acute Coronary Syndrome) trial, this switch strategy resulted in a marked reduction in bleeding without an increased risk of ischemic events, compared with a full 12 months of standard dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) using prasugrel (Effient) or ticagrelor (Brilinta).
He added that the cost savings of this switch strategy would be enormous, since generic clopidogrel is vastly less expensive than prasugrel or ticagrelor.
Twelve months of DAPT with aspirin plus either prasugrel or ticagrelor is the guideline-recommended DAPT regimen following PCI for ACS on the strength of the TRITON and PLATO trials, respectively, which showed that those agents were more effective than clopidogrel for the prevention of thrombotic events. But Dr. Cuisset and his coinvestigators noted that the risk of ischemic events was highest in the first month or so following ACS, while the risk of DAPT-related serious bleeding increased after the first month and continued for the duration.
“We need to use the new drugs, and we need to go for 1 year with DAPT. But does that mean we need to go for 1 year with the new drugs?” he asked.
This question was the impetus for TOPIC, an open-label, single-center randomized trial that included 646 ACS patients who were free of major adverse cardiovascular events during their first month on DAPT with prasugrel or ticagrelor. At that point they were randomized to remain on their standard regimen or switch to aspirin at 75 mg/day plus clopidogrel at 75 mg/day for months 2-12. The switch strategy is similar to the way pulmonary embolism is managed: an early phase of high-intensity therapy followed by a backing off to a less intensive regimen, said Dr. Cuisset, a cardiologist at Aix-Marseille University, Provence, France.
The primary endpoint in TOPIC was the cumulative 1-year rate of a composite of all-cause mortality, stroke, urgent revascularization, or clinically significant bleeding as reflected in a Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) grade 2 or greater bleeding. The primary endpoint occurred in 13.4% of the switch group, a 52% relative risk reduction, compared with the 26.3% cumulative incidence with standard DAPT.
This difference wasn’t due to any between-group disparity in ischemic events, but rather to a 70% reduction in the risk of BARC grade 2 or greater bleeding in the switch group: 4.0% vs. 14.9%.
Some physicians have already been switching to clopidogrel for DAPT after ACS, either because of safety or cost concerns. Now their practice is evidence based, Dr. Cuisset noted.
Asked why TOPIC didn’t use the more stringent bleeding endpoint of BARC grade 3-5 bleeding, the cardiologist replied that it would have required a larger trial to show a significant difference. Besides, he added, BARC grade 2 bleeding is clinically important because it has a negative impact on quality of life and can cause patients to discontinue DAPT, thereby increasing their risk of thrombosis.
The TOPIC protocol didn’t utilize a loading dose of clopidogrel when making the switch. Investigators started clopidogrel the day after stopping prasugrel and at least 12 hours after the final dose of ticagrelor.
Ideally, the novel TOPIC findings should be confirmed in a much larger, randomized, double-blind clinical trial capable of detecting any small differences in stent thrombosis or MI rates before physicians adopt a change in practice, but discussant Chaim Lotan, MD, director of the Heart Institute at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem, dismissed that prospect as unlikely.
“I tried myself to do a similar study and found I got a lot of opposition from the pharma companies as well as from physicians who said, ‘How can you go against the guidelines?’ ” he said.
“I want to congratulate your team because I think this is a groundbreaking study that is going to dictate a changing of the guidelines,” he told Dr. Cuisset.
Dr. Cuisset reported having no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
Simultaneous with his presentation in Paris, the TOPIC findings were published online (Eur Heart J. 2017 May 16. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx175).
Dr. Cuisset reported no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
[email protected]
PARIS – A strategy of switching from prasugrel or ticagrelor to clopidogrel 1 month after percutaneous coronary intervention for acute coronary syndrome is superior to the guideline-recommended full 12 months of dual-antiplatelet therapy with either of the newer P2Y12 inhibitors, according to Thomas Cuisset, MD.
In the randomized TOPIC (Timing of Platelet Inhibition After Acute Coronary Syndrome) trial, this switch strategy resulted in a marked reduction in bleeding without an increased risk of ischemic events, compared with a full 12 months of standard dual-antiplatelet therapy (DAPT) using prasugrel (Effient) or ticagrelor (Brilinta).
He added that the cost savings of this switch strategy would be enormous, since generic clopidogrel is vastly less expensive than prasugrel or ticagrelor.
Twelve months of DAPT with aspirin plus either prasugrel or ticagrelor is the guideline-recommended DAPT regimen following PCI for ACS on the strength of the TRITON and PLATO trials, respectively, which showed that those agents were more effective than clopidogrel for the prevention of thrombotic events. But Dr. Cuisset and his coinvestigators noted that the risk of ischemic events was highest in the first month or so following ACS, while the risk of DAPT-related serious bleeding increased after the first month and continued for the duration.
“We need to use the new drugs, and we need to go for 1 year with DAPT. But does that mean we need to go for 1 year with the new drugs?” he asked.
This question was the impetus for TOPIC, an open-label, single-center randomized trial that included 646 ACS patients who were free of major adverse cardiovascular events during their first month on DAPT with prasugrel or ticagrelor. At that point they were randomized to remain on their standard regimen or switch to aspirin at 75 mg/day plus clopidogrel at 75 mg/day for months 2-12. The switch strategy is similar to the way pulmonary embolism is managed: an early phase of high-intensity therapy followed by a backing off to a less intensive regimen, said Dr. Cuisset, a cardiologist at Aix-Marseille University, Provence, France.
The primary endpoint in TOPIC was the cumulative 1-year rate of a composite of all-cause mortality, stroke, urgent revascularization, or clinically significant bleeding as reflected in a Bleeding Academic Research Consortium (BARC) grade 2 or greater bleeding. The primary endpoint occurred in 13.4% of the switch group, a 52% relative risk reduction, compared with the 26.3% cumulative incidence with standard DAPT.
This difference wasn’t due to any between-group disparity in ischemic events, but rather to a 70% reduction in the risk of BARC grade 2 or greater bleeding in the switch group: 4.0% vs. 14.9%.
Some physicians have already been switching to clopidogrel for DAPT after ACS, either because of safety or cost concerns. Now their practice is evidence based, Dr. Cuisset noted.
Asked why TOPIC didn’t use the more stringent bleeding endpoint of BARC grade 3-5 bleeding, the cardiologist replied that it would have required a larger trial to show a significant difference. Besides, he added, BARC grade 2 bleeding is clinically important because it has a negative impact on quality of life and can cause patients to discontinue DAPT, thereby increasing their risk of thrombosis.
The TOPIC protocol didn’t utilize a loading dose of clopidogrel when making the switch. Investigators started clopidogrel the day after stopping prasugrel and at least 12 hours after the final dose of ticagrelor.
Ideally, the novel TOPIC findings should be confirmed in a much larger, randomized, double-blind clinical trial capable of detecting any small differences in stent thrombosis or MI rates before physicians adopt a change in practice, but discussant Chaim Lotan, MD, director of the Heart Institute at Hadassah Medical Center in Jerusalem, dismissed that prospect as unlikely.
“I tried myself to do a similar study and found I got a lot of opposition from the pharma companies as well as from physicians who said, ‘How can you go against the guidelines?’ ” he said.
“I want to congratulate your team because I think this is a groundbreaking study that is going to dictate a changing of the guidelines,” he told Dr. Cuisset.
Dr. Cuisset reported having no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
Simultaneous with his presentation in Paris, the TOPIC findings were published online (Eur Heart J. 2017 May 16. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehx175).
Dr. Cuisset reported no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
[email protected]
AT EuroPCR
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The cumulative 1-year incidence of all-cause mortality, stroke, urgent revascularization, or clinically significant bleeding was 13.4% in acute coronary syndrome patients who switched to clopidogrel after 1 month on prasugrel or ticagrelor for dual-antiplatelet therapy, compared with 26.3% in those who didn’t switch.
Data source: An open-label, single-center, randomized trial including 646 ACS patients.
Disclosures: The presenter reported no financial conflicts regarding this investigator-driven study funded without commercial support.
HM17 session summary: Focus on POCUS – Introduction to Point-of-Care Ultrasound for pediatric hospitalists
Presenters
Nilam Soni, MD, FHM; Thomas Conlon, MD; Ria Dancel, MD, FAAP, FHM; Daniel Schnobrich, MD
Summary
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly gaining acceptance in the medical community as a goal-directed examination that answers a specific diagnostic question or guides a bedside invasive procedure. Adoption by pediatric hospitalists is increasing, aided by multiple training pathways, opportunities for scholarship, and organization development.
The use of POCUS is increasing among nonradiologist physicians due to the expectation for perfection, desire for improved patient experience, and increased availability of ultrasound machines. POCUS is rapid and safe, and can be used serially to monitor, provide procedural guidance, and lead to initiation of appropriate therapies.
Training in POCUS in limited applications is possible in short periods of time. One recent study showed that approximately 40% of POCUS cases led to new findings or alteration of treatment. However, POCUS requires training, monitoring for competence, transparency of training/competence, and a QA process that supports the training. One solution at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia was to use American College of Emergency Physician guidelines for POCUS training.
Pediatric applications include guidance of bladder catheterization, identifying occult abscesses, diagnosis of pneumonia and associated parapneumonic effusion, and IV placement. More advanced applications include diagnosis of appendicitis, intussusception, and increased intracranial pressure. Novel applications conceived by nonradiologist physicians have included sinus ultrasound.
Initial training can be provided by “in-house experts,” such as pediatric ED physicians and PICU physicians. Alternatively, an on-site commercial course can be arranged for larger groups. Consideration should be given to mentorship, with comparison to formal imaging and/or clinical progression. Relationships with traditional imagers should be cultivated, as POCUS can potentially be misunderstood. In fact, formal US utilization has been found to increase once clinicals begin to use POCUS.
Key takeaways for HM
- Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly being adopted by pediatric hospitalists.
- Pediatric applications are still being developed, but include guidance of bladder catheterization, identifying occult abscesses, diagnosis of pneumonia/associated effusions, and IV placement.
- Initial training can be provided by pediatric ED physicians/PICU physicians or an on-site commercial course can be arranged for larger groups.
- Relationships with radiologists should be established at the outset to avoid misunderstanding of POCUS.
Dr. Chang is a pediatric hospitalist at Baystate Children’s Hospital and is the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist.
Presenters
Nilam Soni, MD, FHM; Thomas Conlon, MD; Ria Dancel, MD, FAAP, FHM; Daniel Schnobrich, MD
Summary
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly gaining acceptance in the medical community as a goal-directed examination that answers a specific diagnostic question or guides a bedside invasive procedure. Adoption by pediatric hospitalists is increasing, aided by multiple training pathways, opportunities for scholarship, and organization development.
The use of POCUS is increasing among nonradiologist physicians due to the expectation for perfection, desire for improved patient experience, and increased availability of ultrasound machines. POCUS is rapid and safe, and can be used serially to monitor, provide procedural guidance, and lead to initiation of appropriate therapies.
Training in POCUS in limited applications is possible in short periods of time. One recent study showed that approximately 40% of POCUS cases led to new findings or alteration of treatment. However, POCUS requires training, monitoring for competence, transparency of training/competence, and a QA process that supports the training. One solution at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia was to use American College of Emergency Physician guidelines for POCUS training.
Pediatric applications include guidance of bladder catheterization, identifying occult abscesses, diagnosis of pneumonia and associated parapneumonic effusion, and IV placement. More advanced applications include diagnosis of appendicitis, intussusception, and increased intracranial pressure. Novel applications conceived by nonradiologist physicians have included sinus ultrasound.
Initial training can be provided by “in-house experts,” such as pediatric ED physicians and PICU physicians. Alternatively, an on-site commercial course can be arranged for larger groups. Consideration should be given to mentorship, with comparison to formal imaging and/or clinical progression. Relationships with traditional imagers should be cultivated, as POCUS can potentially be misunderstood. In fact, formal US utilization has been found to increase once clinicals begin to use POCUS.
Key takeaways for HM
- Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly being adopted by pediatric hospitalists.
- Pediatric applications are still being developed, but include guidance of bladder catheterization, identifying occult abscesses, diagnosis of pneumonia/associated effusions, and IV placement.
- Initial training can be provided by pediatric ED physicians/PICU physicians or an on-site commercial course can be arranged for larger groups.
- Relationships with radiologists should be established at the outset to avoid misunderstanding of POCUS.
Dr. Chang is a pediatric hospitalist at Baystate Children’s Hospital and is the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist.
Presenters
Nilam Soni, MD, FHM; Thomas Conlon, MD; Ria Dancel, MD, FAAP, FHM; Daniel Schnobrich, MD
Summary
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly gaining acceptance in the medical community as a goal-directed examination that answers a specific diagnostic question or guides a bedside invasive procedure. Adoption by pediatric hospitalists is increasing, aided by multiple training pathways, opportunities for scholarship, and organization development.
The use of POCUS is increasing among nonradiologist physicians due to the expectation for perfection, desire for improved patient experience, and increased availability of ultrasound machines. POCUS is rapid and safe, and can be used serially to monitor, provide procedural guidance, and lead to initiation of appropriate therapies.
Training in POCUS in limited applications is possible in short periods of time. One recent study showed that approximately 40% of POCUS cases led to new findings or alteration of treatment. However, POCUS requires training, monitoring for competence, transparency of training/competence, and a QA process that supports the training. One solution at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia was to use American College of Emergency Physician guidelines for POCUS training.
Pediatric applications include guidance of bladder catheterization, identifying occult abscesses, diagnosis of pneumonia and associated parapneumonic effusion, and IV placement. More advanced applications include diagnosis of appendicitis, intussusception, and increased intracranial pressure. Novel applications conceived by nonradiologist physicians have included sinus ultrasound.
Initial training can be provided by “in-house experts,” such as pediatric ED physicians and PICU physicians. Alternatively, an on-site commercial course can be arranged for larger groups. Consideration should be given to mentorship, with comparison to formal imaging and/or clinical progression. Relationships with traditional imagers should be cultivated, as POCUS can potentially be misunderstood. In fact, formal US utilization has been found to increase once clinicals begin to use POCUS.
Key takeaways for HM
- Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) is rapidly being adopted by pediatric hospitalists.
- Pediatric applications are still being developed, but include guidance of bladder catheterization, identifying occult abscesses, diagnosis of pneumonia/associated effusions, and IV placement.
- Initial training can be provided by pediatric ED physicians/PICU physicians or an on-site commercial course can be arranged for larger groups.
- Relationships with radiologists should be established at the outset to avoid misunderstanding of POCUS.
Dr. Chang is a pediatric hospitalist at Baystate Children’s Hospital and is the pediatric editor of The Hospitalist.
Improve your glycemic control efforts with SHM’s GC eQUIPS program
Inpatient hyperglycemia is a very common condition, affecting approximately 38% of patients in the non–intensive care unit setting.
Enhance the efficiency and reliability of your quality improvement efforts to close the gap between best practices and methods for caring for inpatients with hyperglycemia with SHM’s Glycemic Control (GC) Electronic Quality Improvement Program (eQUIPS). The GC eQUIPS program supports the development and implementation of GC programs at hospitals nationwide.
- Gaining understanding in the principles of glycemic control
- Improving glycemic control data collection/analysis/and reporting
- Building and obtaining approval for protocols/policies for glycemic control
- Creating a culture for change and change management
When you enroll in the Glycemic Control eQUIPS, you’ll receive:
- Data center for performance tracking. Helps track performance on project milestones and outcomes, and benchmark performance against comparison groups at your institution and other participating facilities.
- Implementation toolkit. Provides stepwise instruction for improving glycemic control, preventing hypoglycemia and optimizing care of the inpatient with hyperglycemia and diabetes.
- Online glycemic control toolkit. Includes clinical tools and interventions, research materials and literature review, informational papers and case studies, teaching slide sets, and more.
- Online community and collaborative:
– Glycemic Control Library of site-created tools and documents allows you to view sample order sets and protocols, awareness campaigns, patient education materials, and various articles.
– National Discussion Forum lets you share professional questions and discuss topics related to the planning, implementation and evaluation of glycemic control interventions.
– Access to on-demand webinar, facilitated by national experts, topics include IV Insulin Management Strategies, Change Management and Introduction to Glycemic Control.
Join the webinar on June 28 from 1–2 p.m., ET, to receive additional information about SHM’s GC programs. Visit hospitalmedicine.org/gc to register or learn more. If you have questions on the program, please email Sara Platt at [email protected].
Brett Radler is communications specialist at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Inpatient hyperglycemia is a very common condition, affecting approximately 38% of patients in the non–intensive care unit setting.
Enhance the efficiency and reliability of your quality improvement efforts to close the gap between best practices and methods for caring for inpatients with hyperglycemia with SHM’s Glycemic Control (GC) Electronic Quality Improvement Program (eQUIPS). The GC eQUIPS program supports the development and implementation of GC programs at hospitals nationwide.
- Gaining understanding in the principles of glycemic control
- Improving glycemic control data collection/analysis/and reporting
- Building and obtaining approval for protocols/policies for glycemic control
- Creating a culture for change and change management
When you enroll in the Glycemic Control eQUIPS, you’ll receive:
- Data center for performance tracking. Helps track performance on project milestones and outcomes, and benchmark performance against comparison groups at your institution and other participating facilities.
- Implementation toolkit. Provides stepwise instruction for improving glycemic control, preventing hypoglycemia and optimizing care of the inpatient with hyperglycemia and diabetes.
- Online glycemic control toolkit. Includes clinical tools and interventions, research materials and literature review, informational papers and case studies, teaching slide sets, and more.
- Online community and collaborative:
– Glycemic Control Library of site-created tools and documents allows you to view sample order sets and protocols, awareness campaigns, patient education materials, and various articles.
– National Discussion Forum lets you share professional questions and discuss topics related to the planning, implementation and evaluation of glycemic control interventions.
– Access to on-demand webinar, facilitated by national experts, topics include IV Insulin Management Strategies, Change Management and Introduction to Glycemic Control.
Join the webinar on June 28 from 1–2 p.m., ET, to receive additional information about SHM’s GC programs. Visit hospitalmedicine.org/gc to register or learn more. If you have questions on the program, please email Sara Platt at [email protected].
Brett Radler is communications specialist at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
Inpatient hyperglycemia is a very common condition, affecting approximately 38% of patients in the non–intensive care unit setting.
Enhance the efficiency and reliability of your quality improvement efforts to close the gap between best practices and methods for caring for inpatients with hyperglycemia with SHM’s Glycemic Control (GC) Electronic Quality Improvement Program (eQUIPS). The GC eQUIPS program supports the development and implementation of GC programs at hospitals nationwide.
- Gaining understanding in the principles of glycemic control
- Improving glycemic control data collection/analysis/and reporting
- Building and obtaining approval for protocols/policies for glycemic control
- Creating a culture for change and change management
When you enroll in the Glycemic Control eQUIPS, you’ll receive:
- Data center for performance tracking. Helps track performance on project milestones and outcomes, and benchmark performance against comparison groups at your institution and other participating facilities.
- Implementation toolkit. Provides stepwise instruction for improving glycemic control, preventing hypoglycemia and optimizing care of the inpatient with hyperglycemia and diabetes.
- Online glycemic control toolkit. Includes clinical tools and interventions, research materials and literature review, informational papers and case studies, teaching slide sets, and more.
- Online community and collaborative:
– Glycemic Control Library of site-created tools and documents allows you to view sample order sets and protocols, awareness campaigns, patient education materials, and various articles.
– National Discussion Forum lets you share professional questions and discuss topics related to the planning, implementation and evaluation of glycemic control interventions.
– Access to on-demand webinar, facilitated by national experts, topics include IV Insulin Management Strategies, Change Management and Introduction to Glycemic Control.
Join the webinar on June 28 from 1–2 p.m., ET, to receive additional information about SHM’s GC programs. Visit hospitalmedicine.org/gc to register or learn more. If you have questions on the program, please email Sara Platt at [email protected].
Brett Radler is communications specialist at the Society of Hospital Medicine.
New heart failure guidelines prioritize prevention
The latest update to U.S. guidelines for heart failure management, released at the end of April , puts unprecedented emphasis on heart failure prevention and also shines a brighter light on patients at risk for developing heart failure – people with hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease.
“We have embraced the fact that heart failure can be prevented and that the progression of heart failure can be interrupted, and we articulated how we can use biomarkers to screen patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction,” said Clyde W. Yancy, MD, chair of the writing group that issued the 2017 focused update to the heart failure management guidelines on behalf of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Failure Society of America. (Circulation. 2017 Apr 28. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000509).
This means that, for the first time, these guidelines focus on stage A heart failure patients, those without symptoms or detectable left ventricular dysfunction but at risk for heart failure, a heart failure subgroup that was ignored in the past. Prevention is most immediate for stage A patients. The new guidelines cite the stage A definition from the 2009 guidelines: patients with “risk factors that clearly predispose toward the development of heart failure. For example, patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes mellitus who do not yet demonstrate impaired left ventricular function.”
The number of patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes is pretty large. The new heart failure guidelines apply to many people.
“The mindset [on heart failure] has been on treatment, not prevention. There is far more focus [in the new guidelines] on prevention than ever before,” commented Javed Butler, MD, professor and chief of cardiology at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and a member of the guideline writing panel.
“One reason why heart failure prevention has not been a focus was because people thought that, if you prevented coronary artery disease, you prevented heart failure. What we’ve learned is that a lot of heart failure is not ischemic and not from overt coronary disease, especially age-related HFpEF [heart failure with preserved ejection fraction]. Hopefully, these guidelines will spur more interest in prevention and risk factor control,” Dr. Butler said in an interview.
It starts with blood pressure
The guidelines contain an entirely new section devoted to blood pressure, and, while part of the section deals with a target blood pressure for symptomatic (stage C) heart failure patients (a goal systolic pressure of less than 130 mm Hg for patients with either a preserved or reduced ejection fraction), the first entry is a target blood pressure of less than 130/80 mm Hg for all stage A heart failure patients.
Because stage A is defined to include any adult with hypertension, the new heart failure guidelines set a new blood pressure treatment goal for all U.S. adults with hypertension at a time when the long-awaited revision to U.S. hypertension management guidelines from the ACC and AHA are still pending. Until the new hypertension guidelines come out – they’re expected later this year – the blood pressure target set in the heart failure guidelines will have to suffice.
Indeed, the less than 130/80-mm Hg target for on-treatment blood pressure set for heart failure prevention in the new guidelines was picked to “harmonize” with the guidelines that the ACC and AHA hypertension panel will soon release, Dr. Jessup said in an interview.
The main evidence for this target, lower than in most prior U.S. hypertension guidelines, comes from SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial) (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2103-16). In that trial, the goal blood pressure that linked with the best outcomes was less than 120/80 mm Hg, although the average achieved systolic blood pressure was above that goal with a mean systolic pressure of 121.5 mm Hg. One reason for setting a higher goal systolic pressure for practice was that analyses have shown that blood pressure measurement in SPRINT did not perform like conventional measurements in routine practice. SPRINT patients appeared to have lower measured pressures than they would have recorded had they been measured by more conventional means (Hypertension. 2017 January;69[1]:15-9).
“The way that blood pressures were measured in SPRINT, a pressure of 120/80 mm Hg in the trial was akin to a pressure of 130/80 mm Hg in an office,” Dr. Yancy, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “To avoid dangerous hypotension and to approximate SPRINT, an office pressure of less than 130 mm Hg is a reasonable number.”
New role for BNP screening
Stage A patients are more than just the target for more aggressive hypertension control. They are now also potential candidates for screening for an elevated blood level of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal (NT)–proBNP. The guidelines panel makes this a level IIa recommendation, saying that a screening BNP test in patients at risk for developing heart failure can be useful if followed by team-based care and optimized guideline directed medical therapy.
This guideline follows the lead of two successful controlled trials that focused more aggressive preventive treatments on stage A patients with an elevated level of BNP or NT-proBNP – the STOP-HF (JAMA. 2013 July 3;310[1]:66-74) and PONTIAC (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct;62[15]:1365-72) trials. The target population for some type of BNP screening are patients with cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, diabetes, obesity, or hypertension, Dr. Yancy said. “It was evident in STOP-HF that, if you screened and intervened, you could make a difference” in the development of heart failure.
The STOP-HF intervention included “optimal risk factor management” and “coaching by a specialist nurse who emphasized individual risk status and the importance of adherence to medication and healthy lifestyle behaviors.”
The guidelines aren’t clear on which patients at risk for developing heart failure, stage A patients, should get screened with BNP or NT-proBNP. Dr. Jessup said that it’s for patients in whom a positive result would trigger more aggressive management.
Getting a BNP on a suspect patient can raise a red flag to the patient, as well as to the physician, that more intervention is needed. “It’s easy for a physician to ignore a high-risk patient who looks okay and feels okay.” A BNP or NT-proBNP test can pick out the patients who shouldn’t be ignored, Dr. Januzzi said.
HFpEF treatment now possible
Another groundbreaking change in the guidelines is inclusion, for the first time, of a medical treatment specific for HFpEF. The aldosterone receptor antagonists (ARAs) spironolactone and eplerenone received a class IIb recommendation: An ARA might be considered to decrease hospitalizations in patients with HFpEF with an ejection fraction of at least 45%, an elevated BNP or recent hospitalization, and good renal function and potassium level.
The “might be considered” recommendation is guarded but understandable given that the evidence comes from the somewhat controversial, post-hoc analysis of data from the pivotal TOPCAT trial (N Engl J Med. 2014 Apr 10;370[15]:1383-92) that focused on just the roughly half of patients seen at centers in North or South America (Circulation. 2015 Jan 6;131[1]:34-42).
“It would be irresponsible to overlook the potential that [ARAs] may help patients who looks like the ones enrolled in TOPCAT in the Americas,” said Dr. Yancy. “We blended evidence and pragmatism and said that the field needs this” treatment. He said that an ARA was a reasonable option for HFpEF patients with symptoms of heart failure and a positive biomarker test result.
Dr. Butler largely agreed. ARA treatment is for HFpEF patients with symptomatic heart failure and either a history of hospitalization or a high BNP level, he said.
“I was surprised by how strongly the committee felt there was a reasonable signal of help from ARAs in HFpEF,” said Dr. Jessup. “I believe in them too,” she added.
Dr. Jessup suggested targeting an ARA to a HFpEF patient with some hypertension, some volume problem, some peripheral edema, and a lot of breathlessness but with no underlying ischemia. “I use an ARA on these patients pretty quickly,” Dr. Jessup said. It’s best to start with a low dosage and see how the patient responds. “The best responders have a really stiff heart” and are usually not the more elderly HFpEF patients. ARA treatment also provides more steady volume control, superior to furosemide, she said.
Yet more additions
The revised guidelines contain even more changes. “We say that checking for anemia is important and how iron is an intervention that might make a difference,” said Dr. Jessup. Also, primary care physicians and cardiologists “should look for obstructive sleep apnea” in heart failure patients for whom “intervention with weight loss might help,” she said.
Another feature is the focus on tailored treatment, with many treatment elements that need customizing to each different type of heart failure patient. “Not every drug needs to be given to every patient,” Dr. Yancy warned.
The specifics of how to orchestrate all the guidelines into a coherent management plan may become clearer later this year, when the ACC/AHA group will release a follow-up “Heart Failure Pathways” document, aimed at bridging the gap between guidelines and actual clinical practice, Dr. Yancy said. “We want more value from writing the guidelines. The biggest obstacle is how to implement them,” and that’s what the pathways follow-up will address.
“The biggest challenge the societies have is how to motivate physicians and nurses to more aggressively treat heart failure,” said Dr. Butler.
Dr. Yancy and Dr. Jessup had no disclosures. Dr. Butler has been a consultant to 11 companies. Dr. Januzzi has been a consultant to Critical Diagnostics, Novartis, Phillips, Roche Diagnostics, and Sphingotec, and he has received research support from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, and Prevencio.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
The latest update to U.S. guidelines for heart failure management, released at the end of April , puts unprecedented emphasis on heart failure prevention and also shines a brighter light on patients at risk for developing heart failure – people with hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease.
“We have embraced the fact that heart failure can be prevented and that the progression of heart failure can be interrupted, and we articulated how we can use biomarkers to screen patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction,” said Clyde W. Yancy, MD, chair of the writing group that issued the 2017 focused update to the heart failure management guidelines on behalf of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Failure Society of America. (Circulation. 2017 Apr 28. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000509).
This means that, for the first time, these guidelines focus on stage A heart failure patients, those without symptoms or detectable left ventricular dysfunction but at risk for heart failure, a heart failure subgroup that was ignored in the past. Prevention is most immediate for stage A patients. The new guidelines cite the stage A definition from the 2009 guidelines: patients with “risk factors that clearly predispose toward the development of heart failure. For example, patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes mellitus who do not yet demonstrate impaired left ventricular function.”
The number of patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes is pretty large. The new heart failure guidelines apply to many people.
“The mindset [on heart failure] has been on treatment, not prevention. There is far more focus [in the new guidelines] on prevention than ever before,” commented Javed Butler, MD, professor and chief of cardiology at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and a member of the guideline writing panel.
“One reason why heart failure prevention has not been a focus was because people thought that, if you prevented coronary artery disease, you prevented heart failure. What we’ve learned is that a lot of heart failure is not ischemic and not from overt coronary disease, especially age-related HFpEF [heart failure with preserved ejection fraction]. Hopefully, these guidelines will spur more interest in prevention and risk factor control,” Dr. Butler said in an interview.
It starts with blood pressure
The guidelines contain an entirely new section devoted to blood pressure, and, while part of the section deals with a target blood pressure for symptomatic (stage C) heart failure patients (a goal systolic pressure of less than 130 mm Hg for patients with either a preserved or reduced ejection fraction), the first entry is a target blood pressure of less than 130/80 mm Hg for all stage A heart failure patients.
Because stage A is defined to include any adult with hypertension, the new heart failure guidelines set a new blood pressure treatment goal for all U.S. adults with hypertension at a time when the long-awaited revision to U.S. hypertension management guidelines from the ACC and AHA are still pending. Until the new hypertension guidelines come out – they’re expected later this year – the blood pressure target set in the heart failure guidelines will have to suffice.
Indeed, the less than 130/80-mm Hg target for on-treatment blood pressure set for heart failure prevention in the new guidelines was picked to “harmonize” with the guidelines that the ACC and AHA hypertension panel will soon release, Dr. Jessup said in an interview.
The main evidence for this target, lower than in most prior U.S. hypertension guidelines, comes from SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial) (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2103-16). In that trial, the goal blood pressure that linked with the best outcomes was less than 120/80 mm Hg, although the average achieved systolic blood pressure was above that goal with a mean systolic pressure of 121.5 mm Hg. One reason for setting a higher goal systolic pressure for practice was that analyses have shown that blood pressure measurement in SPRINT did not perform like conventional measurements in routine practice. SPRINT patients appeared to have lower measured pressures than they would have recorded had they been measured by more conventional means (Hypertension. 2017 January;69[1]:15-9).
“The way that blood pressures were measured in SPRINT, a pressure of 120/80 mm Hg in the trial was akin to a pressure of 130/80 mm Hg in an office,” Dr. Yancy, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “To avoid dangerous hypotension and to approximate SPRINT, an office pressure of less than 130 mm Hg is a reasonable number.”
New role for BNP screening
Stage A patients are more than just the target for more aggressive hypertension control. They are now also potential candidates for screening for an elevated blood level of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal (NT)–proBNP. The guidelines panel makes this a level IIa recommendation, saying that a screening BNP test in patients at risk for developing heart failure can be useful if followed by team-based care and optimized guideline directed medical therapy.
This guideline follows the lead of two successful controlled trials that focused more aggressive preventive treatments on stage A patients with an elevated level of BNP or NT-proBNP – the STOP-HF (JAMA. 2013 July 3;310[1]:66-74) and PONTIAC (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct;62[15]:1365-72) trials. The target population for some type of BNP screening are patients with cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, diabetes, obesity, or hypertension, Dr. Yancy said. “It was evident in STOP-HF that, if you screened and intervened, you could make a difference” in the development of heart failure.
The STOP-HF intervention included “optimal risk factor management” and “coaching by a specialist nurse who emphasized individual risk status and the importance of adherence to medication and healthy lifestyle behaviors.”
The guidelines aren’t clear on which patients at risk for developing heart failure, stage A patients, should get screened with BNP or NT-proBNP. Dr. Jessup said that it’s for patients in whom a positive result would trigger more aggressive management.
Getting a BNP on a suspect patient can raise a red flag to the patient, as well as to the physician, that more intervention is needed. “It’s easy for a physician to ignore a high-risk patient who looks okay and feels okay.” A BNP or NT-proBNP test can pick out the patients who shouldn’t be ignored, Dr. Januzzi said.
HFpEF treatment now possible
Another groundbreaking change in the guidelines is inclusion, for the first time, of a medical treatment specific for HFpEF. The aldosterone receptor antagonists (ARAs) spironolactone and eplerenone received a class IIb recommendation: An ARA might be considered to decrease hospitalizations in patients with HFpEF with an ejection fraction of at least 45%, an elevated BNP or recent hospitalization, and good renal function and potassium level.
The “might be considered” recommendation is guarded but understandable given that the evidence comes from the somewhat controversial, post-hoc analysis of data from the pivotal TOPCAT trial (N Engl J Med. 2014 Apr 10;370[15]:1383-92) that focused on just the roughly half of patients seen at centers in North or South America (Circulation. 2015 Jan 6;131[1]:34-42).
“It would be irresponsible to overlook the potential that [ARAs] may help patients who looks like the ones enrolled in TOPCAT in the Americas,” said Dr. Yancy. “We blended evidence and pragmatism and said that the field needs this” treatment. He said that an ARA was a reasonable option for HFpEF patients with symptoms of heart failure and a positive biomarker test result.
Dr. Butler largely agreed. ARA treatment is for HFpEF patients with symptomatic heart failure and either a history of hospitalization or a high BNP level, he said.
“I was surprised by how strongly the committee felt there was a reasonable signal of help from ARAs in HFpEF,” said Dr. Jessup. “I believe in them too,” she added.
Dr. Jessup suggested targeting an ARA to a HFpEF patient with some hypertension, some volume problem, some peripheral edema, and a lot of breathlessness but with no underlying ischemia. “I use an ARA on these patients pretty quickly,” Dr. Jessup said. It’s best to start with a low dosage and see how the patient responds. “The best responders have a really stiff heart” and are usually not the more elderly HFpEF patients. ARA treatment also provides more steady volume control, superior to furosemide, she said.
Yet more additions
The revised guidelines contain even more changes. “We say that checking for anemia is important and how iron is an intervention that might make a difference,” said Dr. Jessup. Also, primary care physicians and cardiologists “should look for obstructive sleep apnea” in heart failure patients for whom “intervention with weight loss might help,” she said.
Another feature is the focus on tailored treatment, with many treatment elements that need customizing to each different type of heart failure patient. “Not every drug needs to be given to every patient,” Dr. Yancy warned.
The specifics of how to orchestrate all the guidelines into a coherent management plan may become clearer later this year, when the ACC/AHA group will release a follow-up “Heart Failure Pathways” document, aimed at bridging the gap between guidelines and actual clinical practice, Dr. Yancy said. “We want more value from writing the guidelines. The biggest obstacle is how to implement them,” and that’s what the pathways follow-up will address.
“The biggest challenge the societies have is how to motivate physicians and nurses to more aggressively treat heart failure,” said Dr. Butler.
Dr. Yancy and Dr. Jessup had no disclosures. Dr. Butler has been a consultant to 11 companies. Dr. Januzzi has been a consultant to Critical Diagnostics, Novartis, Phillips, Roche Diagnostics, and Sphingotec, and he has received research support from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, and Prevencio.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
The latest update to U.S. guidelines for heart failure management, released at the end of April , puts unprecedented emphasis on heart failure prevention and also shines a brighter light on patients at risk for developing heart failure – people with hypertension, diabetes, or coronary artery disease.
“We have embraced the fact that heart failure can be prevented and that the progression of heart failure can be interrupted, and we articulated how we can use biomarkers to screen patients with asymptomatic left ventricular dysfunction,” said Clyde W. Yancy, MD, chair of the writing group that issued the 2017 focused update to the heart failure management guidelines on behalf of the American College of Cardiology, the American Heart Association, and the Heart Failure Society of America. (Circulation. 2017 Apr 28. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000509).
This means that, for the first time, these guidelines focus on stage A heart failure patients, those without symptoms or detectable left ventricular dysfunction but at risk for heart failure, a heart failure subgroup that was ignored in the past. Prevention is most immediate for stage A patients. The new guidelines cite the stage A definition from the 2009 guidelines: patients with “risk factors that clearly predispose toward the development of heart failure. For example, patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes mellitus who do not yet demonstrate impaired left ventricular function.”
The number of patients with coronary artery disease, hypertension, or diabetes is pretty large. The new heart failure guidelines apply to many people.
“The mindset [on heart failure] has been on treatment, not prevention. There is far more focus [in the new guidelines] on prevention than ever before,” commented Javed Butler, MD, professor and chief of cardiology at Stony Brook (N.Y.) University and a member of the guideline writing panel.
“One reason why heart failure prevention has not been a focus was because people thought that, if you prevented coronary artery disease, you prevented heart failure. What we’ve learned is that a lot of heart failure is not ischemic and not from overt coronary disease, especially age-related HFpEF [heart failure with preserved ejection fraction]. Hopefully, these guidelines will spur more interest in prevention and risk factor control,” Dr. Butler said in an interview.
It starts with blood pressure
The guidelines contain an entirely new section devoted to blood pressure, and, while part of the section deals with a target blood pressure for symptomatic (stage C) heart failure patients (a goal systolic pressure of less than 130 mm Hg for patients with either a preserved or reduced ejection fraction), the first entry is a target blood pressure of less than 130/80 mm Hg for all stage A heart failure patients.
Because stage A is defined to include any adult with hypertension, the new heart failure guidelines set a new blood pressure treatment goal for all U.S. adults with hypertension at a time when the long-awaited revision to U.S. hypertension management guidelines from the ACC and AHA are still pending. Until the new hypertension guidelines come out – they’re expected later this year – the blood pressure target set in the heart failure guidelines will have to suffice.
Indeed, the less than 130/80-mm Hg target for on-treatment blood pressure set for heart failure prevention in the new guidelines was picked to “harmonize” with the guidelines that the ACC and AHA hypertension panel will soon release, Dr. Jessup said in an interview.
The main evidence for this target, lower than in most prior U.S. hypertension guidelines, comes from SPRINT (Systolic Blood Pressure Intervention Trial) (N Engl J Med. 2015 Nov 26;373[22]:2103-16). In that trial, the goal blood pressure that linked with the best outcomes was less than 120/80 mm Hg, although the average achieved systolic blood pressure was above that goal with a mean systolic pressure of 121.5 mm Hg. One reason for setting a higher goal systolic pressure for practice was that analyses have shown that blood pressure measurement in SPRINT did not perform like conventional measurements in routine practice. SPRINT patients appeared to have lower measured pressures than they would have recorded had they been measured by more conventional means (Hypertension. 2017 January;69[1]:15-9).
“The way that blood pressures were measured in SPRINT, a pressure of 120/80 mm Hg in the trial was akin to a pressure of 130/80 mm Hg in an office,” Dr. Yancy, chief of cardiology at Northwestern University, Chicago, said in an interview. “To avoid dangerous hypotension and to approximate SPRINT, an office pressure of less than 130 mm Hg is a reasonable number.”
New role for BNP screening
Stage A patients are more than just the target for more aggressive hypertension control. They are now also potential candidates for screening for an elevated blood level of brain natriuretic peptide (BNP) or N-terminal (NT)–proBNP. The guidelines panel makes this a level IIa recommendation, saying that a screening BNP test in patients at risk for developing heart failure can be useful if followed by team-based care and optimized guideline directed medical therapy.
This guideline follows the lead of two successful controlled trials that focused more aggressive preventive treatments on stage A patients with an elevated level of BNP or NT-proBNP – the STOP-HF (JAMA. 2013 July 3;310[1]:66-74) and PONTIAC (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Oct;62[15]:1365-72) trials. The target population for some type of BNP screening are patients with cardiovascular disease, vascular disease, diabetes, obesity, or hypertension, Dr. Yancy said. “It was evident in STOP-HF that, if you screened and intervened, you could make a difference” in the development of heart failure.
The STOP-HF intervention included “optimal risk factor management” and “coaching by a specialist nurse who emphasized individual risk status and the importance of adherence to medication and healthy lifestyle behaviors.”
The guidelines aren’t clear on which patients at risk for developing heart failure, stage A patients, should get screened with BNP or NT-proBNP. Dr. Jessup said that it’s for patients in whom a positive result would trigger more aggressive management.
Getting a BNP on a suspect patient can raise a red flag to the patient, as well as to the physician, that more intervention is needed. “It’s easy for a physician to ignore a high-risk patient who looks okay and feels okay.” A BNP or NT-proBNP test can pick out the patients who shouldn’t be ignored, Dr. Januzzi said.
HFpEF treatment now possible
Another groundbreaking change in the guidelines is inclusion, for the first time, of a medical treatment specific for HFpEF. The aldosterone receptor antagonists (ARAs) spironolactone and eplerenone received a class IIb recommendation: An ARA might be considered to decrease hospitalizations in patients with HFpEF with an ejection fraction of at least 45%, an elevated BNP or recent hospitalization, and good renal function and potassium level.
The “might be considered” recommendation is guarded but understandable given that the evidence comes from the somewhat controversial, post-hoc analysis of data from the pivotal TOPCAT trial (N Engl J Med. 2014 Apr 10;370[15]:1383-92) that focused on just the roughly half of patients seen at centers in North or South America (Circulation. 2015 Jan 6;131[1]:34-42).
“It would be irresponsible to overlook the potential that [ARAs] may help patients who looks like the ones enrolled in TOPCAT in the Americas,” said Dr. Yancy. “We blended evidence and pragmatism and said that the field needs this” treatment. He said that an ARA was a reasonable option for HFpEF patients with symptoms of heart failure and a positive biomarker test result.
Dr. Butler largely agreed. ARA treatment is for HFpEF patients with symptomatic heart failure and either a history of hospitalization or a high BNP level, he said.
“I was surprised by how strongly the committee felt there was a reasonable signal of help from ARAs in HFpEF,” said Dr. Jessup. “I believe in them too,” she added.
Dr. Jessup suggested targeting an ARA to a HFpEF patient with some hypertension, some volume problem, some peripheral edema, and a lot of breathlessness but with no underlying ischemia. “I use an ARA on these patients pretty quickly,” Dr. Jessup said. It’s best to start with a low dosage and see how the patient responds. “The best responders have a really stiff heart” and are usually not the more elderly HFpEF patients. ARA treatment also provides more steady volume control, superior to furosemide, she said.
Yet more additions
The revised guidelines contain even more changes. “We say that checking for anemia is important and how iron is an intervention that might make a difference,” said Dr. Jessup. Also, primary care physicians and cardiologists “should look for obstructive sleep apnea” in heart failure patients for whom “intervention with weight loss might help,” she said.
Another feature is the focus on tailored treatment, with many treatment elements that need customizing to each different type of heart failure patient. “Not every drug needs to be given to every patient,” Dr. Yancy warned.
The specifics of how to orchestrate all the guidelines into a coherent management plan may become clearer later this year, when the ACC/AHA group will release a follow-up “Heart Failure Pathways” document, aimed at bridging the gap between guidelines and actual clinical practice, Dr. Yancy said. “We want more value from writing the guidelines. The biggest obstacle is how to implement them,” and that’s what the pathways follow-up will address.
“The biggest challenge the societies have is how to motivate physicians and nurses to more aggressively treat heart failure,” said Dr. Butler.
Dr. Yancy and Dr. Jessup had no disclosures. Dr. Butler has been a consultant to 11 companies. Dr. Januzzi has been a consultant to Critical Diagnostics, Novartis, Phillips, Roche Diagnostics, and Sphingotec, and he has received research support from Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, and Prevencio.
[email protected]
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
Sneak Peek: Journal of Hospital Medicine
BACKGROUND: Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) have been advocated to improve antimicrobial utilization, but program implementation is variable.
OBJECTIVE: To determine associations of ASPs with facility characteristics and inpatient antimicrobial utilization measures in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system in 2012.
SETTING: All 130 VA facilities with acute care services.
RESULTS: Variables associated with at least three favorable changes in antimicrobial utilization included presence of postgraduate physician/pharmacy training programs, number of antimicrobial-specific order sets, frequency of systematic de-escalation review, presence of pharmacists and/or infectious diseases (ID) attendings on acute care ward teams, and formal ID training of the lead ASP pharmacist. Variables associated with two unfavorable measures included bed size, the level of engagement with VA Antimicrobial Stewardship Task Force online resources, and utilization of antimicrobial stop orders.
CONCLUSIONS: Formalization of ASP processes and presence of pharmacy and ID expertise are associated with favorable utilization. Systematic de-escalation review and order set establishment may be high-yield interventions.
Also in JHM
High prevalence of inappropriate benzodiazepine and sedative hypnotic prescriptions among hospitalized older adults
AUTHORS: Elisabeth Anna Pek, MD, Andrew Remfry, MD, Ciara Pendrith, MSc, Chris Fan-Lun, BScPhm, R. Sacha Bhatia, MD, and Christine Soong, MD, MSc, SFHM
Incidence, predictors, and outcomes of hospital-acquired anemia
AUTHORS: Anil N. Makam, MD, MAS, Oanh K. Nguyen, MD, MAS, Christopher Clark, MPA, and Ethan A. Halm, MD, MPH
Association between radiologic incidental findings and resource utilization in patients admitted with chest pain in an urban medical center
AUTHORS: Venkat P. Gundareddy, MD, MPH, SFHM, Nisa M. Maruthur, MD, MHS, Abednego Chibungu, MD, Preetam Bollampally, MD, Regina Landis, MS, abd Shaker M. Eid, MD, MBA
Clinical utility of routine CBC testing in patients with community-acquired pneumonia
AUTHORS: Neelaysh Vukkadala, BS, and Andrew Auerbach, MD, MPH, SFHM
Overuse of troponin? A comprehensive evaluation of testing in a large hospital system
AUTHORS: Gibbs Wilson, MD, Kyler Barkley, MD, Kipp Slicker, DO, Robert Kowal, MD, PhD, Brandon Pope, PhD, and Jeffrey Michel, MD
BACKGROUND: Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) have been advocated to improve antimicrobial utilization, but program implementation is variable.
OBJECTIVE: To determine associations of ASPs with facility characteristics and inpatient antimicrobial utilization measures in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system in 2012.
SETTING: All 130 VA facilities with acute care services.
RESULTS: Variables associated with at least three favorable changes in antimicrobial utilization included presence of postgraduate physician/pharmacy training programs, number of antimicrobial-specific order sets, frequency of systematic de-escalation review, presence of pharmacists and/or infectious diseases (ID) attendings on acute care ward teams, and formal ID training of the lead ASP pharmacist. Variables associated with two unfavorable measures included bed size, the level of engagement with VA Antimicrobial Stewardship Task Force online resources, and utilization of antimicrobial stop orders.
CONCLUSIONS: Formalization of ASP processes and presence of pharmacy and ID expertise are associated with favorable utilization. Systematic de-escalation review and order set establishment may be high-yield interventions.
Also in JHM
High prevalence of inappropriate benzodiazepine and sedative hypnotic prescriptions among hospitalized older adults
AUTHORS: Elisabeth Anna Pek, MD, Andrew Remfry, MD, Ciara Pendrith, MSc, Chris Fan-Lun, BScPhm, R. Sacha Bhatia, MD, and Christine Soong, MD, MSc, SFHM
Incidence, predictors, and outcomes of hospital-acquired anemia
AUTHORS: Anil N. Makam, MD, MAS, Oanh K. Nguyen, MD, MAS, Christopher Clark, MPA, and Ethan A. Halm, MD, MPH
Association between radiologic incidental findings and resource utilization in patients admitted with chest pain in an urban medical center
AUTHORS: Venkat P. Gundareddy, MD, MPH, SFHM, Nisa M. Maruthur, MD, MHS, Abednego Chibungu, MD, Preetam Bollampally, MD, Regina Landis, MS, abd Shaker M. Eid, MD, MBA
Clinical utility of routine CBC testing in patients with community-acquired pneumonia
AUTHORS: Neelaysh Vukkadala, BS, and Andrew Auerbach, MD, MPH, SFHM
Overuse of troponin? A comprehensive evaluation of testing in a large hospital system
AUTHORS: Gibbs Wilson, MD, Kyler Barkley, MD, Kipp Slicker, DO, Robert Kowal, MD, PhD, Brandon Pope, PhD, and Jeffrey Michel, MD
BACKGROUND: Antimicrobial stewardship programs (ASPs) have been advocated to improve antimicrobial utilization, but program implementation is variable.
OBJECTIVE: To determine associations of ASPs with facility characteristics and inpatient antimicrobial utilization measures in the Veterans Affairs (VA) system in 2012.
SETTING: All 130 VA facilities with acute care services.
RESULTS: Variables associated with at least three favorable changes in antimicrobial utilization included presence of postgraduate physician/pharmacy training programs, number of antimicrobial-specific order sets, frequency of systematic de-escalation review, presence of pharmacists and/or infectious diseases (ID) attendings on acute care ward teams, and formal ID training of the lead ASP pharmacist. Variables associated with two unfavorable measures included bed size, the level of engagement with VA Antimicrobial Stewardship Task Force online resources, and utilization of antimicrobial stop orders.
CONCLUSIONS: Formalization of ASP processes and presence of pharmacy and ID expertise are associated with favorable utilization. Systematic de-escalation review and order set establishment may be high-yield interventions.
Also in JHM
High prevalence of inappropriate benzodiazepine and sedative hypnotic prescriptions among hospitalized older adults
AUTHORS: Elisabeth Anna Pek, MD, Andrew Remfry, MD, Ciara Pendrith, MSc, Chris Fan-Lun, BScPhm, R. Sacha Bhatia, MD, and Christine Soong, MD, MSc, SFHM
Incidence, predictors, and outcomes of hospital-acquired anemia
AUTHORS: Anil N. Makam, MD, MAS, Oanh K. Nguyen, MD, MAS, Christopher Clark, MPA, and Ethan A. Halm, MD, MPH
Association between radiologic incidental findings and resource utilization in patients admitted with chest pain in an urban medical center
AUTHORS: Venkat P. Gundareddy, MD, MPH, SFHM, Nisa M. Maruthur, MD, MHS, Abednego Chibungu, MD, Preetam Bollampally, MD, Regina Landis, MS, abd Shaker M. Eid, MD, MBA
Clinical utility of routine CBC testing in patients with community-acquired pneumonia
AUTHORS: Neelaysh Vukkadala, BS, and Andrew Auerbach, MD, MPH, SFHM
Overuse of troponin? A comprehensive evaluation of testing in a large hospital system
AUTHORS: Gibbs Wilson, MD, Kyler Barkley, MD, Kipp Slicker, DO, Robert Kowal, MD, PhD, Brandon Pope, PhD, and Jeffrey Michel, MD
Oral iron of no benefit in heart failure with iron deficiency
High-dose oral iron therapy doesn’t improve exercise capacity in the estimated 50% of patients with symptomatic heart failure who also have iron deficiency, according to a report published online May 16 in JAMA.
Iron deficiency in patients with HF, regardless of their hemoglobin status, is associated with reduced functional capacity, poorer quality of life, and increased mortality. Iron plays a crucial role in the delivery and utilization of oxygen, and “cells with high-energy demands, including skeletal and cardiac myocytes, are particularly sensitive to depleted iron stores,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, of the pulmonary critical care unit of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and his associates.
The IRONOUT study was conducted at 23 U.S. medical centers, where outcomes after 16 weeks of oral iron therapy (150 mg twice daily) were compared against matching placebo in 225 patients. The median patient age was 63 years, and the median duration of HF was 5.7 years. Ischemic heart disease was the primary cause of HF in 78% of the study participants.
These patients had low LVEF and poor exercise capacity, despite having high rates of guideline-directed treatment with medications.
The primary endpoint was a change in peak oxygen uptake (peak VO2) at the conclusion of treatment, a measure that “reflects the multiple mechanisms by which iron repletion is expected to improve systemic oxygen delivery and utilization.” Change in peak VO2 was not significantly different between the 111 participants who took oral iron supplements (+23 mL/min) and the 114 who took placebo (–2 mL/min), the investigators wrote (JAMA Pediatr. 2017 May 16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.5427).
In subgroup analyses, oral iron also failed to improve peak VO2 in any subgroup of patients: neither men nor women; neither those with decreased hemoglobin nor those with normal hemoglobin levels; nor patients with or without venous congestion at baseline. Oral iron also failed to improve secondary endpoints including 6-minute walk distance, quality of life scores, NT-proBNP levels, and ventilatory efficiency.
In contrast to previous studies of IV iron repletion, oral iron supplementation “produced minimal improvement in iron stores, implicating the route of administration rather than the strategy of iron repletion in the lack of clinical benefit,” Dr. Lewis and his associates said.
This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, which also conceived, designed, and conducted the trial. Dr. Lewis reported ties to Abbott, Novartis, Shape Systems, Stealth Bio Therapeutics, Ironwood, Cheetah Medical, Luitpold, and SoniVie. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
High-dose oral iron therapy doesn’t improve exercise capacity in the estimated 50% of patients with symptomatic heart failure who also have iron deficiency, according to a report published online May 16 in JAMA.
Iron deficiency in patients with HF, regardless of their hemoglobin status, is associated with reduced functional capacity, poorer quality of life, and increased mortality. Iron plays a crucial role in the delivery and utilization of oxygen, and “cells with high-energy demands, including skeletal and cardiac myocytes, are particularly sensitive to depleted iron stores,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, of the pulmonary critical care unit of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and his associates.
The IRONOUT study was conducted at 23 U.S. medical centers, where outcomes after 16 weeks of oral iron therapy (150 mg twice daily) were compared against matching placebo in 225 patients. The median patient age was 63 years, and the median duration of HF was 5.7 years. Ischemic heart disease was the primary cause of HF in 78% of the study participants.
These patients had low LVEF and poor exercise capacity, despite having high rates of guideline-directed treatment with medications.
The primary endpoint was a change in peak oxygen uptake (peak VO2) at the conclusion of treatment, a measure that “reflects the multiple mechanisms by which iron repletion is expected to improve systemic oxygen delivery and utilization.” Change in peak VO2 was not significantly different between the 111 participants who took oral iron supplements (+23 mL/min) and the 114 who took placebo (–2 mL/min), the investigators wrote (JAMA Pediatr. 2017 May 16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.5427).
In subgroup analyses, oral iron also failed to improve peak VO2 in any subgroup of patients: neither men nor women; neither those with decreased hemoglobin nor those with normal hemoglobin levels; nor patients with or without venous congestion at baseline. Oral iron also failed to improve secondary endpoints including 6-minute walk distance, quality of life scores, NT-proBNP levels, and ventilatory efficiency.
In contrast to previous studies of IV iron repletion, oral iron supplementation “produced minimal improvement in iron stores, implicating the route of administration rather than the strategy of iron repletion in the lack of clinical benefit,” Dr. Lewis and his associates said.
This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, which also conceived, designed, and conducted the trial. Dr. Lewis reported ties to Abbott, Novartis, Shape Systems, Stealth Bio Therapeutics, Ironwood, Cheetah Medical, Luitpold, and SoniVie. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
High-dose oral iron therapy doesn’t improve exercise capacity in the estimated 50% of patients with symptomatic heart failure who also have iron deficiency, according to a report published online May 16 in JAMA.
Iron deficiency in patients with HF, regardless of their hemoglobin status, is associated with reduced functional capacity, poorer quality of life, and increased mortality. Iron plays a crucial role in the delivery and utilization of oxygen, and “cells with high-energy demands, including skeletal and cardiac myocytes, are particularly sensitive to depleted iron stores,” said Gregory D. Lewis, MD, of the pulmonary critical care unit of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, and his associates.
The IRONOUT study was conducted at 23 U.S. medical centers, where outcomes after 16 weeks of oral iron therapy (150 mg twice daily) were compared against matching placebo in 225 patients. The median patient age was 63 years, and the median duration of HF was 5.7 years. Ischemic heart disease was the primary cause of HF in 78% of the study participants.
These patients had low LVEF and poor exercise capacity, despite having high rates of guideline-directed treatment with medications.
The primary endpoint was a change in peak oxygen uptake (peak VO2) at the conclusion of treatment, a measure that “reflects the multiple mechanisms by which iron repletion is expected to improve systemic oxygen delivery and utilization.” Change in peak VO2 was not significantly different between the 111 participants who took oral iron supplements (+23 mL/min) and the 114 who took placebo (–2 mL/min), the investigators wrote (JAMA Pediatr. 2017 May 16. doi: 10.1001/jama.2017.5427).
In subgroup analyses, oral iron also failed to improve peak VO2 in any subgroup of patients: neither men nor women; neither those with decreased hemoglobin nor those with normal hemoglobin levels; nor patients with or without venous congestion at baseline. Oral iron also failed to improve secondary endpoints including 6-minute walk distance, quality of life scores, NT-proBNP levels, and ventilatory efficiency.
In contrast to previous studies of IV iron repletion, oral iron supplementation “produced minimal improvement in iron stores, implicating the route of administration rather than the strategy of iron repletion in the lack of clinical benefit,” Dr. Lewis and his associates said.
This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute, which also conceived, designed, and conducted the trial. Dr. Lewis reported ties to Abbott, Novartis, Shape Systems, Stealth Bio Therapeutics, Ironwood, Cheetah Medical, Luitpold, and SoniVie. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.
Key clinical point: High-dose oral iron therapy doesn’t improve exercise capacity in the estimated 50% of patients with symptomatic heart failure and iron deficiency.
Major finding: Change in peak VO2 was not significantly different between the 111 participants who took oral iron supplements (+23 mL/min) and the 114 who took placebo (–2 mL/min).
Data source: A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled phase II trial involving 225 patients treated for 16 weeks.
Disclosures: This study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NCT02188784), which also conceived, designed, and conducted the trial. Dr. Lewis reported ties to Abbott, Novartis, Shape Systems, Stealth Bio Therapeutics, Ironwood, Cheetah Medical, Luitpold, and SoniVie. His associates reported ties to numerous industry sources.