User login
POP AGE shakes up DAPT in elderly
PARIS – Older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome who were assigned to 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel experienced significantly less major and minor bleeding than with ticagrelor or prasugrel and were similarly protected from thrombotic events in the prospective randomized POPular AGE trial, Marieke E. Gimbel, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Therefore, we consider clopidogrel the preferred treatment in patients age 70 or older with non-ST-elevation ACS,” said Dr. Gimbel, a cardiologist at St. Antonius Hospital in Nieuwegein, The Netherlands.
This stance is contrary to both the current ESC and U.S. guidelines on management of non-ST-elevation ACS, which preferentially recommend ticagrelor and prasugrel over clopidogrel, chiefly on the basis of the large PLATO (N Engl J Med 2009;361:1045-57) and TRITON TIMI 38 (N Engl J Med 2007;357:2001-15) randomized trials. Those studies from the previous decade reported significantly lower rates of the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, acute MI, or stroke in patients on ticagrelor or prasugrel, respectively, than with clopidogrel. But this benefit came at a cost of significantly higher rates of TIMI major bleeding than with clopidogrel, and multiple studies have shown that major bleeding in ACS patients is associated with a sharply increased risk of death.
Bleeding is an issue of particular concern in the elderly. But older patients were greatly underrepresented in PLATO and TRITON, where they comprised just 13%-15% of participants, even though registry studies would suggest older individuals make up about 35% of all patients with non-ST-elevation ACS. Selective inclusion of elderly patients in the major trials means those study results can’t legitimately be extrapolated to the entire elderly patient population.
“The best course of action in the elderly has been unclear,” Dr. Gimbel argued.
The POPular AGE (POP AGE) trial was an open-label study featuring independent blinded adjudication of clinical events. The median age of participants was 77 years, and about one-quarter had a prior MI. It was basically an all-comers study in which 1,003 non-ST-elevation ACS patients age 70 or older at 11 Dutch medical centers were randomized within 3 days of hospital admission to 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy with either ticagrelor or one of the two more potent antiplatelet agents. Although the choice of ticagrelor or prasugrel was left to the physician, it’s noteworthy that 94% of patients in the high-potency P2Y12 inhibitor study arm were discharged on ticagrelor. At 12 months, the adherence rate to the assigned regimen was 76% in the clopidogrel group and just 51% in what was essentially the ticagrelor arm. Bleeding was the number-one reason for the much higher discontinuation rate in the ticagrelor group, followed by initiation of oral anticoagulation and dyspnea.
The primary safety endpoint in POP AGE was the rate of major and minor bleeding as defined in the PLATO study. The rate was 17.6% with clopidogrel, compared with 23.1% in the ticagrelor group, for a highly significant 26% reduction in relative risk. Of note, the PLATO major bleeding rate was 4.4% with clopidogrel, versus 8% with ticagrelor/prasugrel.
The coprimary endpoint was net clinical benefit, defined as a composite of all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, and PLATO major and minor bleeding. The rate was 30.7% with ticagrelor and 27.3% in the clopidogrel group, for an absolute 3.4% risk difference favoring clopidogrel, which barely missed the prespecified cutoff for noninferiority. Indeed, even though the 12-month follow-up was 99.6% complete, Dr. Gimbel raised the possibility that when the results come in for the final 0.4% of the study population, the difference in net clinical benefit may reach significance.
In any case, she noted there was no between-group difference in the key secondary endpoint of death, MI, or stroke, with rates of 12.8% and 12.5% in the clopidogrel and ticagrelor groups, respectively.
“One might expect a higher ischemic event rate with clopidogrel compared to ticagrelor. However, in these elderly patients there was no difference between the two treatment strategies,” the cardiologist observed.
POP AGE is hailed as ‘a wake up call’
In an interview, Freek Verheugt, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of cardiology at Radboud University in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, called POP AGE “a very important study.”
“The problem with most studies in the elderly is that they are post hoc analyses from huge trials like PLATO and TRITON, and also the thrombolysis and primary PCI studies. The elderly do very well in those studies, because only the very fit elderly are included in the megatrials. It’s much more important to do a prospective randomized trial in the elderly only, and this is one of the very few done so far,” he observed.
Bleeding is a major problem in the elderly with ACS. It leads to more MIs, strokes, and increased mortality.
“Even minor bleeding is an issue,” Dr. Verheugt added. “Minor bleeding is a major problem, because patients who encounter minor bleeding – nose bleeds, gum bleeds, or even in their underwear – they do away with all drugs. They stop their antithrombotic, but they also stop their statin, their ACE inhibitor – their lifesavers – and that’s why they die.”
So is POP AGE a practice-changing study?
“No, of course not,” the cardiologist scoffed. “To be practice-changing you need several trials going in the same direction. But I think if there are more data prospectively accrued in the elderly alone, showing the same, then POP AGE would be practice-changing.”
“In my personal view, this study is a wake-up call. If you have an elderly, frail patient presenting with ACS, strongly consider good, old clopidogrel. Although people say that 30% of patients on clopidogrel don’t have appropriate platelet inhibition, that’s a laboratory finding. It’s not a clinical finding. POP AGE gave us a clinical finding showing that they do quite well,” he said.
Dr. Verheugt was on the independent data safety monitoring board for POP AGE, funded by ZonMw, a Dutch governmental research organization. Neither Dr. Verheugt nor Dr. Gimbel reported having any financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gimbel ME. ESC 2019, Abstract 84.
PARIS – Older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome who were assigned to 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel experienced significantly less major and minor bleeding than with ticagrelor or prasugrel and were similarly protected from thrombotic events in the prospective randomized POPular AGE trial, Marieke E. Gimbel, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Therefore, we consider clopidogrel the preferred treatment in patients age 70 or older with non-ST-elevation ACS,” said Dr. Gimbel, a cardiologist at St. Antonius Hospital in Nieuwegein, The Netherlands.
This stance is contrary to both the current ESC and U.S. guidelines on management of non-ST-elevation ACS, which preferentially recommend ticagrelor and prasugrel over clopidogrel, chiefly on the basis of the large PLATO (N Engl J Med 2009;361:1045-57) and TRITON TIMI 38 (N Engl J Med 2007;357:2001-15) randomized trials. Those studies from the previous decade reported significantly lower rates of the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, acute MI, or stroke in patients on ticagrelor or prasugrel, respectively, than with clopidogrel. But this benefit came at a cost of significantly higher rates of TIMI major bleeding than with clopidogrel, and multiple studies have shown that major bleeding in ACS patients is associated with a sharply increased risk of death.
Bleeding is an issue of particular concern in the elderly. But older patients were greatly underrepresented in PLATO and TRITON, where they comprised just 13%-15% of participants, even though registry studies would suggest older individuals make up about 35% of all patients with non-ST-elevation ACS. Selective inclusion of elderly patients in the major trials means those study results can’t legitimately be extrapolated to the entire elderly patient population.
“The best course of action in the elderly has been unclear,” Dr. Gimbel argued.
The POPular AGE (POP AGE) trial was an open-label study featuring independent blinded adjudication of clinical events. The median age of participants was 77 years, and about one-quarter had a prior MI. It was basically an all-comers study in which 1,003 non-ST-elevation ACS patients age 70 or older at 11 Dutch medical centers were randomized within 3 days of hospital admission to 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy with either ticagrelor or one of the two more potent antiplatelet agents. Although the choice of ticagrelor or prasugrel was left to the physician, it’s noteworthy that 94% of patients in the high-potency P2Y12 inhibitor study arm were discharged on ticagrelor. At 12 months, the adherence rate to the assigned regimen was 76% in the clopidogrel group and just 51% in what was essentially the ticagrelor arm. Bleeding was the number-one reason for the much higher discontinuation rate in the ticagrelor group, followed by initiation of oral anticoagulation and dyspnea.
The primary safety endpoint in POP AGE was the rate of major and minor bleeding as defined in the PLATO study. The rate was 17.6% with clopidogrel, compared with 23.1% in the ticagrelor group, for a highly significant 26% reduction in relative risk. Of note, the PLATO major bleeding rate was 4.4% with clopidogrel, versus 8% with ticagrelor/prasugrel.
The coprimary endpoint was net clinical benefit, defined as a composite of all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, and PLATO major and minor bleeding. The rate was 30.7% with ticagrelor and 27.3% in the clopidogrel group, for an absolute 3.4% risk difference favoring clopidogrel, which barely missed the prespecified cutoff for noninferiority. Indeed, even though the 12-month follow-up was 99.6% complete, Dr. Gimbel raised the possibility that when the results come in for the final 0.4% of the study population, the difference in net clinical benefit may reach significance.
In any case, she noted there was no between-group difference in the key secondary endpoint of death, MI, or stroke, with rates of 12.8% and 12.5% in the clopidogrel and ticagrelor groups, respectively.
“One might expect a higher ischemic event rate with clopidogrel compared to ticagrelor. However, in these elderly patients there was no difference between the two treatment strategies,” the cardiologist observed.
POP AGE is hailed as ‘a wake up call’
In an interview, Freek Verheugt, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of cardiology at Radboud University in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, called POP AGE “a very important study.”
“The problem with most studies in the elderly is that they are post hoc analyses from huge trials like PLATO and TRITON, and also the thrombolysis and primary PCI studies. The elderly do very well in those studies, because only the very fit elderly are included in the megatrials. It’s much more important to do a prospective randomized trial in the elderly only, and this is one of the very few done so far,” he observed.
Bleeding is a major problem in the elderly with ACS. It leads to more MIs, strokes, and increased mortality.
“Even minor bleeding is an issue,” Dr. Verheugt added. “Minor bleeding is a major problem, because patients who encounter minor bleeding – nose bleeds, gum bleeds, or even in their underwear – they do away with all drugs. They stop their antithrombotic, but they also stop their statin, their ACE inhibitor – their lifesavers – and that’s why they die.”
So is POP AGE a practice-changing study?
“No, of course not,” the cardiologist scoffed. “To be practice-changing you need several trials going in the same direction. But I think if there are more data prospectively accrued in the elderly alone, showing the same, then POP AGE would be practice-changing.”
“In my personal view, this study is a wake-up call. If you have an elderly, frail patient presenting with ACS, strongly consider good, old clopidogrel. Although people say that 30% of patients on clopidogrel don’t have appropriate platelet inhibition, that’s a laboratory finding. It’s not a clinical finding. POP AGE gave us a clinical finding showing that they do quite well,” he said.
Dr. Verheugt was on the independent data safety monitoring board for POP AGE, funded by ZonMw, a Dutch governmental research organization. Neither Dr. Verheugt nor Dr. Gimbel reported having any financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gimbel ME. ESC 2019, Abstract 84.
PARIS – Older patients with non-ST-elevation acute coronary syndrome who were assigned to 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy with clopidogrel experienced significantly less major and minor bleeding than with ticagrelor or prasugrel and were similarly protected from thrombotic events in the prospective randomized POPular AGE trial, Marieke E. Gimbel, MD, reported at the annual congress of the European Society of Cardiology.
“Therefore, we consider clopidogrel the preferred treatment in patients age 70 or older with non-ST-elevation ACS,” said Dr. Gimbel, a cardiologist at St. Antonius Hospital in Nieuwegein, The Netherlands.
This stance is contrary to both the current ESC and U.S. guidelines on management of non-ST-elevation ACS, which preferentially recommend ticagrelor and prasugrel over clopidogrel, chiefly on the basis of the large PLATO (N Engl J Med 2009;361:1045-57) and TRITON TIMI 38 (N Engl J Med 2007;357:2001-15) randomized trials. Those studies from the previous decade reported significantly lower rates of the composite endpoint of cardiovascular death, acute MI, or stroke in patients on ticagrelor or prasugrel, respectively, than with clopidogrel. But this benefit came at a cost of significantly higher rates of TIMI major bleeding than with clopidogrel, and multiple studies have shown that major bleeding in ACS patients is associated with a sharply increased risk of death.
Bleeding is an issue of particular concern in the elderly. But older patients were greatly underrepresented in PLATO and TRITON, where they comprised just 13%-15% of participants, even though registry studies would suggest older individuals make up about 35% of all patients with non-ST-elevation ACS. Selective inclusion of elderly patients in the major trials means those study results can’t legitimately be extrapolated to the entire elderly patient population.
“The best course of action in the elderly has been unclear,” Dr. Gimbel argued.
The POPular AGE (POP AGE) trial was an open-label study featuring independent blinded adjudication of clinical events. The median age of participants was 77 years, and about one-quarter had a prior MI. It was basically an all-comers study in which 1,003 non-ST-elevation ACS patients age 70 or older at 11 Dutch medical centers were randomized within 3 days of hospital admission to 12 months of dual antiplatelet therapy with either ticagrelor or one of the two more potent antiplatelet agents. Although the choice of ticagrelor or prasugrel was left to the physician, it’s noteworthy that 94% of patients in the high-potency P2Y12 inhibitor study arm were discharged on ticagrelor. At 12 months, the adherence rate to the assigned regimen was 76% in the clopidogrel group and just 51% in what was essentially the ticagrelor arm. Bleeding was the number-one reason for the much higher discontinuation rate in the ticagrelor group, followed by initiation of oral anticoagulation and dyspnea.
The primary safety endpoint in POP AGE was the rate of major and minor bleeding as defined in the PLATO study. The rate was 17.6% with clopidogrel, compared with 23.1% in the ticagrelor group, for a highly significant 26% reduction in relative risk. Of note, the PLATO major bleeding rate was 4.4% with clopidogrel, versus 8% with ticagrelor/prasugrel.
The coprimary endpoint was net clinical benefit, defined as a composite of all-cause mortality, MI, stroke, and PLATO major and minor bleeding. The rate was 30.7% with ticagrelor and 27.3% in the clopidogrel group, for an absolute 3.4% risk difference favoring clopidogrel, which barely missed the prespecified cutoff for noninferiority. Indeed, even though the 12-month follow-up was 99.6% complete, Dr. Gimbel raised the possibility that when the results come in for the final 0.4% of the study population, the difference in net clinical benefit may reach significance.
In any case, she noted there was no between-group difference in the key secondary endpoint of death, MI, or stroke, with rates of 12.8% and 12.5% in the clopidogrel and ticagrelor groups, respectively.
“One might expect a higher ischemic event rate with clopidogrel compared to ticagrelor. However, in these elderly patients there was no difference between the two treatment strategies,” the cardiologist observed.
POP AGE is hailed as ‘a wake up call’
In an interview, Freek Verheugt, MD, PhD, professor emeritus of cardiology at Radboud University in Nijmegen, The Netherlands, called POP AGE “a very important study.”
“The problem with most studies in the elderly is that they are post hoc analyses from huge trials like PLATO and TRITON, and also the thrombolysis and primary PCI studies. The elderly do very well in those studies, because only the very fit elderly are included in the megatrials. It’s much more important to do a prospective randomized trial in the elderly only, and this is one of the very few done so far,” he observed.
Bleeding is a major problem in the elderly with ACS. It leads to more MIs, strokes, and increased mortality.
“Even minor bleeding is an issue,” Dr. Verheugt added. “Minor bleeding is a major problem, because patients who encounter minor bleeding – nose bleeds, gum bleeds, or even in their underwear – they do away with all drugs. They stop their antithrombotic, but they also stop their statin, their ACE inhibitor – their lifesavers – and that’s why they die.”
So is POP AGE a practice-changing study?
“No, of course not,” the cardiologist scoffed. “To be practice-changing you need several trials going in the same direction. But I think if there are more data prospectively accrued in the elderly alone, showing the same, then POP AGE would be practice-changing.”
“In my personal view, this study is a wake-up call. If you have an elderly, frail patient presenting with ACS, strongly consider good, old clopidogrel. Although people say that 30% of patients on clopidogrel don’t have appropriate platelet inhibition, that’s a laboratory finding. It’s not a clinical finding. POP AGE gave us a clinical finding showing that they do quite well,” he said.
Dr. Verheugt was on the independent data safety monitoring board for POP AGE, funded by ZonMw, a Dutch governmental research organization. Neither Dr. Verheugt nor Dr. Gimbel reported having any financial conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Gimbel ME. ESC 2019, Abstract 84.
AT THE ESC CONGRESS 2019
Key clinical point:
Major finding: The rate of major and minor bleeding was 17.6% with clopidogrel, compared with 23.1% in the ticagrelor group, for a highly significant 26% reduction in relative risk.
Study details: POPular AGE, an 11-center Dutch RCT, included 1,003 patients age 70 or older with non-ST-elevation ACS.
Disclosures: The presenter reported having no financial conflicts regarding the study, funded by the Dutch government.
Source: Gimbel ME. ESC 2019, Abstract 84.
Some HCV medications associated with serious liver injury
Many of the affected patients had signs or symptoms of moderate to severe liver impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C), and given that these medications – glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret), elbasvir/grazoprevir (Zepatier), and sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (Vosevi) – are not indicated for such patients, they should not have been prescribed in the first place, the FDA noted in the drug safety communication. Some cases had other preexisting risk factors, such as liver cancer, alcohol abuse, or serious medical illnesses associated with liver problems.
In most cases, impairment or decompensation occurred within the first 4 weeks of starting treatment, and symptoms resolved or new-onset worsening of liver function improved after stopping. These medicines have been widely used and, among patients with no or mild liver impairment, have been shown to be safe and effective.
Health care professionals should continue prescribing these medicines as indicated; they should assess patients at baseline for severity of liver disease and other risk factors and closely monitor these patients after for signs and symptoms of worsening liver function. Patients should be aware that the risk of injury is rare and continue taking prescribed medicines; if they develop fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, yellow eyes or skin, or light-colored stools, they should talk with their health care professional but should continue taking the medications in question until instructed to do otherwise.
The full communication is available on the FDA website and includes more facts about these drugs and information for patients and health care professionals.
Many of the affected patients had signs or symptoms of moderate to severe liver impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C), and given that these medications – glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret), elbasvir/grazoprevir (Zepatier), and sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (Vosevi) – are not indicated for such patients, they should not have been prescribed in the first place, the FDA noted in the drug safety communication. Some cases had other preexisting risk factors, such as liver cancer, alcohol abuse, or serious medical illnesses associated with liver problems.
In most cases, impairment or decompensation occurred within the first 4 weeks of starting treatment, and symptoms resolved or new-onset worsening of liver function improved after stopping. These medicines have been widely used and, among patients with no or mild liver impairment, have been shown to be safe and effective.
Health care professionals should continue prescribing these medicines as indicated; they should assess patients at baseline for severity of liver disease and other risk factors and closely monitor these patients after for signs and symptoms of worsening liver function. Patients should be aware that the risk of injury is rare and continue taking prescribed medicines; if they develop fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, yellow eyes or skin, or light-colored stools, they should talk with their health care professional but should continue taking the medications in question until instructed to do otherwise.
The full communication is available on the FDA website and includes more facts about these drugs and information for patients and health care professionals.
Many of the affected patients had signs or symptoms of moderate to severe liver impairment (Child-Pugh class B or C), and given that these medications – glecaprevir/pibrentasvir (Mavyret), elbasvir/grazoprevir (Zepatier), and sofosbuvir/velpatasvir/voxilaprevir (Vosevi) – are not indicated for such patients, they should not have been prescribed in the first place, the FDA noted in the drug safety communication. Some cases had other preexisting risk factors, such as liver cancer, alcohol abuse, or serious medical illnesses associated with liver problems.
In most cases, impairment or decompensation occurred within the first 4 weeks of starting treatment, and symptoms resolved or new-onset worsening of liver function improved after stopping. These medicines have been widely used and, among patients with no or mild liver impairment, have been shown to be safe and effective.
Health care professionals should continue prescribing these medicines as indicated; they should assess patients at baseline for severity of liver disease and other risk factors and closely monitor these patients after for signs and symptoms of worsening liver function. Patients should be aware that the risk of injury is rare and continue taking prescribed medicines; if they develop fatigue, weakness, loss of appetite, nausea and vomiting, yellow eyes or skin, or light-colored stools, they should talk with their health care professional but should continue taking the medications in question until instructed to do otherwise.
The full communication is available on the FDA website and includes more facts about these drugs and information for patients and health care professionals.
Additional physical therapy decreases length of stay
Background: The optimal quantity of physical therapy provided to hospitalized patients is unknown. It has been hypothesized that the costs of additional physical therapy might be outweighed by a decrease in length of stay. A prior meta-analysis done by the same authors was inconclusive; subsequently, additional large trials were published, prompting the authors to repeat their meta-analysis.
Study design: Meta-analysis.
Setting: Literature review of English-language studies conducted worldwide.
Synopsis: A total of 24 randomized controlled trials with a total of 3,262 participants was included in this meta-analysis. The primary finding was that additional physical therapy was associated with a 3-day reduction in length of stay in subacute settings (95% confidence interval, –4.6 to –0.9) and a 0.6-day reduction in acute care settings (95% CI, –1.1 to 0.0). Furthermore, additional physical therapy was associated with small improvements in self-care and activities of daily living. One trial included an economic analysis that suggested additional physical therapy was cost effective.
Of note, there was no standard definition of “additional physical therapy” across the heterogeneous group of trials analyzed in this meta-analysis. In all studies, the experimental group received more physical therapy than the control group, either by increased frequency or duration of sessions. Nonetheless, hospitals may consider increasing physical therapy services as a cost-effective means of reducing length of stay.
Bottom line: Additional physical therapy in acute and subacute care settings results in a decreased length of stay and may be cost effective.
Citation: Peiris CL et al. Additional physical therapy services reduce length of stay and improve health outcomes in people with acute and subacute conditions: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2018;99(11):2299-312.
Dr. Huang is a physician adviser and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Background: The optimal quantity of physical therapy provided to hospitalized patients is unknown. It has been hypothesized that the costs of additional physical therapy might be outweighed by a decrease in length of stay. A prior meta-analysis done by the same authors was inconclusive; subsequently, additional large trials were published, prompting the authors to repeat their meta-analysis.
Study design: Meta-analysis.
Setting: Literature review of English-language studies conducted worldwide.
Synopsis: A total of 24 randomized controlled trials with a total of 3,262 participants was included in this meta-analysis. The primary finding was that additional physical therapy was associated with a 3-day reduction in length of stay in subacute settings (95% confidence interval, –4.6 to –0.9) and a 0.6-day reduction in acute care settings (95% CI, –1.1 to 0.0). Furthermore, additional physical therapy was associated with small improvements in self-care and activities of daily living. One trial included an economic analysis that suggested additional physical therapy was cost effective.
Of note, there was no standard definition of “additional physical therapy” across the heterogeneous group of trials analyzed in this meta-analysis. In all studies, the experimental group received more physical therapy than the control group, either by increased frequency or duration of sessions. Nonetheless, hospitals may consider increasing physical therapy services as a cost-effective means of reducing length of stay.
Bottom line: Additional physical therapy in acute and subacute care settings results in a decreased length of stay and may be cost effective.
Citation: Peiris CL et al. Additional physical therapy services reduce length of stay and improve health outcomes in people with acute and subacute conditions: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2018;99(11):2299-312.
Dr. Huang is a physician adviser and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Background: The optimal quantity of physical therapy provided to hospitalized patients is unknown. It has been hypothesized that the costs of additional physical therapy might be outweighed by a decrease in length of stay. A prior meta-analysis done by the same authors was inconclusive; subsequently, additional large trials were published, prompting the authors to repeat their meta-analysis.
Study design: Meta-analysis.
Setting: Literature review of English-language studies conducted worldwide.
Synopsis: A total of 24 randomized controlled trials with a total of 3,262 participants was included in this meta-analysis. The primary finding was that additional physical therapy was associated with a 3-day reduction in length of stay in subacute settings (95% confidence interval, –4.6 to –0.9) and a 0.6-day reduction in acute care settings (95% CI, –1.1 to 0.0). Furthermore, additional physical therapy was associated with small improvements in self-care and activities of daily living. One trial included an economic analysis that suggested additional physical therapy was cost effective.
Of note, there was no standard definition of “additional physical therapy” across the heterogeneous group of trials analyzed in this meta-analysis. In all studies, the experimental group received more physical therapy than the control group, either by increased frequency or duration of sessions. Nonetheless, hospitals may consider increasing physical therapy services as a cost-effective means of reducing length of stay.
Bottom line: Additional physical therapy in acute and subacute care settings results in a decreased length of stay and may be cost effective.
Citation: Peiris CL et al. Additional physical therapy services reduce length of stay and improve health outcomes in people with acute and subacute conditions: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Arch Phys Med Rehab. 2018;99(11):2299-312.
Dr. Huang is a physician adviser and associate clinical professor in the division of hospital medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Use hospital MRSA rates to guide pediatric osteomyelitis treatment
SEATTLE – If your hospital’s methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rate is less than 10%, cefazolin is a reasonable empiric choice for pediatric acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO). It covers the usual suspects: methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella.
Above the 10% mark, coverage should include considerations of MRSA; clindamycin is good option so long as 85% of isolates are susceptible. Above that, it’s time for vancomycin, according to Nivedita Srinivas, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University.
There are no practice guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis and management of AHO in children; Dr. Srinivas and colleagues sought to plug the gaps in a talk at Pediatric Hospitalist Medicine.
Pediatric AHO is more common in children under 5 years old and in boys. Lower extremities are the usual targets. Staphylococcus aureus, group B Streptococcus, and gram negatives are the most common causes in newborns; Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella in older infants and preschoolers; and Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus in older children.
About half the time, treatment remains empiric because nothing grows out on culture, and there are a few clinical pearls to keep in mind in those cases. A family history of boils or spider bites is suspicious for MRSA, and coverage should include Salmonella in children with abnormal hemoglobins and Streptococcus pneumoniae in children without a spleen or with functional asplenia. Pseudomonas has to be kept in mind with puncture wounds, and Brucella in children who drink unpasteurized milk, Dr. Srinivas said.
A switch from IV to oral therapy is appropriate when C-reactive protein (CRP) drops 50% from its peak or below 3 mg/dL, positive cultures – if any – turn negative, fever has been absent for 24 hours, there’s no sign of metastatic disease, and patients have markedly reduced pain and can bear weight on the infected limb, said copresenter Marie Wang, MD, also a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford.
The oral switch, of course, must have similar coverage as the IV antibiotic: high-dose cephalexin for cefazolin, for instance. Children can be sent home on a PICC line to continue IV treatment, but they won’t do any better than children switched to an oral treatment, and the indwelling catheter can cause problems, she said.
Pleuritic or other sudden pain at a distant site suggests septic emboli. “[Staphylococcus aureus] is notorious for going places you don’t” expect it to go “and forming microabscesses, which become larger abscesses” and need to be drained, said the third presenter, Russell McCulloh, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Four weeks of antibiotics are usually enough, so long as there aren’t complications such as septic thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, sickle cell disease, skull involvement, or immunodeficiencies. Source control and good, postdischarge care – including regular CRP and antibiotic toxicity labs – are critical. Monitoring is recommended for a year.
“X-rays are good at looking for longer-term complications, but bony abnormalities are not going to show up for the first 2 weeks,” Dr. McCulloh said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures. The meeting was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
SEATTLE – If your hospital’s methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rate is less than 10%, cefazolin is a reasonable empiric choice for pediatric acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO). It covers the usual suspects: methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella.
Above the 10% mark, coverage should include considerations of MRSA; clindamycin is good option so long as 85% of isolates are susceptible. Above that, it’s time for vancomycin, according to Nivedita Srinivas, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University.
There are no practice guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis and management of AHO in children; Dr. Srinivas and colleagues sought to plug the gaps in a talk at Pediatric Hospitalist Medicine.
Pediatric AHO is more common in children under 5 years old and in boys. Lower extremities are the usual targets. Staphylococcus aureus, group B Streptococcus, and gram negatives are the most common causes in newborns; Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella in older infants and preschoolers; and Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus in older children.
About half the time, treatment remains empiric because nothing grows out on culture, and there are a few clinical pearls to keep in mind in those cases. A family history of boils or spider bites is suspicious for MRSA, and coverage should include Salmonella in children with abnormal hemoglobins and Streptococcus pneumoniae in children without a spleen or with functional asplenia. Pseudomonas has to be kept in mind with puncture wounds, and Brucella in children who drink unpasteurized milk, Dr. Srinivas said.
A switch from IV to oral therapy is appropriate when C-reactive protein (CRP) drops 50% from its peak or below 3 mg/dL, positive cultures – if any – turn negative, fever has been absent for 24 hours, there’s no sign of metastatic disease, and patients have markedly reduced pain and can bear weight on the infected limb, said copresenter Marie Wang, MD, also a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford.
The oral switch, of course, must have similar coverage as the IV antibiotic: high-dose cephalexin for cefazolin, for instance. Children can be sent home on a PICC line to continue IV treatment, but they won’t do any better than children switched to an oral treatment, and the indwelling catheter can cause problems, she said.
Pleuritic or other sudden pain at a distant site suggests septic emboli. “[Staphylococcus aureus] is notorious for going places you don’t” expect it to go “and forming microabscesses, which become larger abscesses” and need to be drained, said the third presenter, Russell McCulloh, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Four weeks of antibiotics are usually enough, so long as there aren’t complications such as septic thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, sickle cell disease, skull involvement, or immunodeficiencies. Source control and good, postdischarge care – including regular CRP and antibiotic toxicity labs – are critical. Monitoring is recommended for a year.
“X-rays are good at looking for longer-term complications, but bony abnormalities are not going to show up for the first 2 weeks,” Dr. McCulloh said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures. The meeting was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
SEATTLE – If your hospital’s methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus rate is less than 10%, cefazolin is a reasonable empiric choice for pediatric acute hematogenous osteomyelitis (AHO). It covers the usual suspects: methicillin-susceptible Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella.
Above the 10% mark, coverage should include considerations of MRSA; clindamycin is good option so long as 85% of isolates are susceptible. Above that, it’s time for vancomycin, according to Nivedita Srinivas, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford (Calif.) University.
There are no practice guidelines in the United States for the diagnosis and management of AHO in children; Dr. Srinivas and colleagues sought to plug the gaps in a talk at Pediatric Hospitalist Medicine.
Pediatric AHO is more common in children under 5 years old and in boys. Lower extremities are the usual targets. Staphylococcus aureus, group B Streptococcus, and gram negatives are the most common causes in newborns; Staphylococcus aureus, group A Streptococcus, and Kingella in older infants and preschoolers; and Staphylococcus aureus and group A Streptococcus in older children.
About half the time, treatment remains empiric because nothing grows out on culture, and there are a few clinical pearls to keep in mind in those cases. A family history of boils or spider bites is suspicious for MRSA, and coverage should include Salmonella in children with abnormal hemoglobins and Streptococcus pneumoniae in children without a spleen or with functional asplenia. Pseudomonas has to be kept in mind with puncture wounds, and Brucella in children who drink unpasteurized milk, Dr. Srinivas said.
A switch from IV to oral therapy is appropriate when C-reactive protein (CRP) drops 50% from its peak or below 3 mg/dL, positive cultures – if any – turn negative, fever has been absent for 24 hours, there’s no sign of metastatic disease, and patients have markedly reduced pain and can bear weight on the infected limb, said copresenter Marie Wang, MD, also a pediatric infectious disease specialist at Stanford.
The oral switch, of course, must have similar coverage as the IV antibiotic: high-dose cephalexin for cefazolin, for instance. Children can be sent home on a PICC line to continue IV treatment, but they won’t do any better than children switched to an oral treatment, and the indwelling catheter can cause problems, she said.
Pleuritic or other sudden pain at a distant site suggests septic emboli. “[Staphylococcus aureus] is notorious for going places you don’t” expect it to go “and forming microabscesses, which become larger abscesses” and need to be drained, said the third presenter, Russell McCulloh, MD, a pediatric infectious disease specialist at the University of Nebraska Medical Center, Omaha.
Four weeks of antibiotics are usually enough, so long as there aren’t complications such as septic thrombophlebitis, endocarditis, sickle cell disease, skull involvement, or immunodeficiencies. Source control and good, postdischarge care – including regular CRP and antibiotic toxicity labs – are critical. Monitoring is recommended for a year.
“X-rays are good at looking for longer-term complications, but bony abnormalities are not going to show up for the first 2 weeks,” Dr. McCulloh said.
The presenters didn’t have any relevant disclosures. The meeting was sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PHM 2019
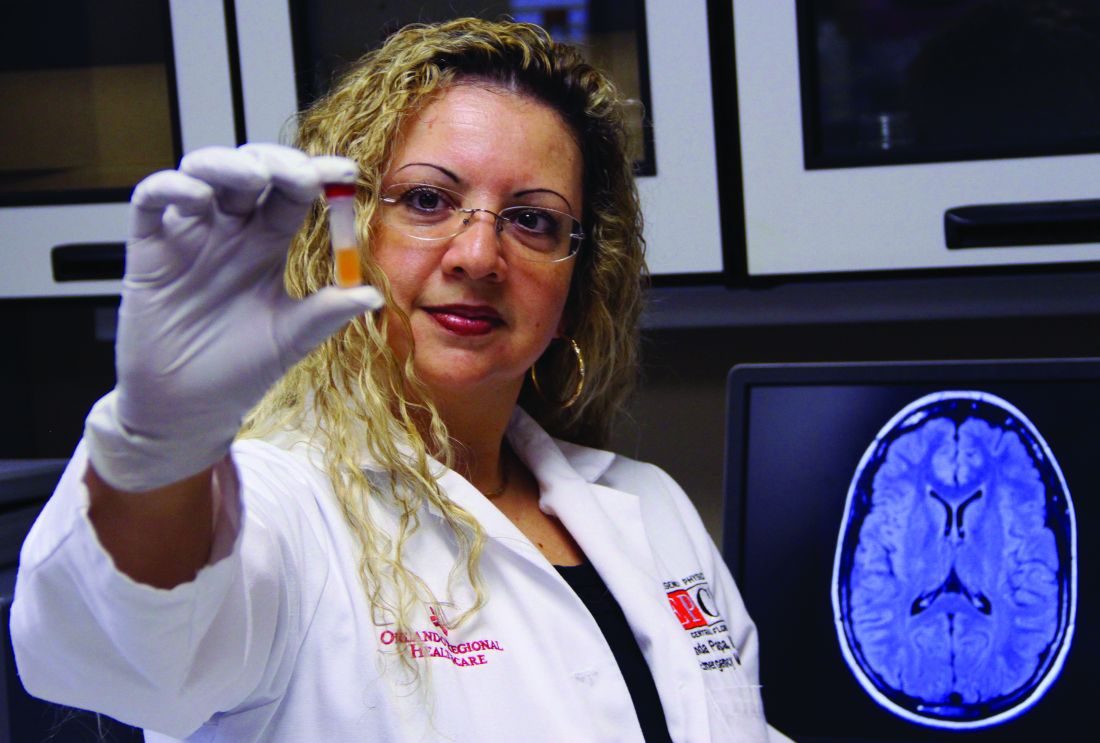
Blood test may reveal brain injury
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
FROM BMJ PAEDIATRICS OPEN
Key clinical point: Levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) are lowest in patients with nonconcussive body trauma, higher in patients with nonconcussive head trauma, and highest in patients with concussion.
Major finding: GFAP was fair to excellent at distinguishing concussion from body trauma, with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves of 0.75-0.89.
Study details: A prospective cohort study of 712 trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. The study included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and presented within 4 hours of injury.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers. Coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
Source: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
FDA’s low-risk TAVR okay set to propel case volume
With the Food and Drug Administration’s approval of two different pairs of transcatheter aortic valve replacement systems for patients at low surgical risk, U.S. case volume for the procedure should markedly rise given that patients at low surgical risk form the largest risk subgroup among patients with aortic stenosis severe enough to warrant valve replacement.
But even as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) now becomes the predominant approach for fixing severely stenotic aortic valves regardless of a patient’s risk level, the procedure remains less optimal than surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in selected patients, putting an onus on clinicians to identify and alert patients for whom the transcatheter approach is questionable.
The anticipated surge in TAVR cases for low-risk patients after the FDA’s Aug. 16, 2019, decision will also likely lead to more hospitals offering TAVR. That development will test whether recently enacted rules from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on procedure-volume minimums for TAVR programs – at least 20 cases a year (or 40 within 2 years) at centers that also perform at least 300 percutaneous coronary interventions annually – lead to outcomes at lower-volume centers that come reasonably close to the outcomes at higher-volume programs for low-risk patients.
“The paradigm has definitely shifted from SAVR as the gold standard to TAVR as the primary treatment for aortic stenosis. This opens TAVR to the vast majority of patients with aortic stenosis,” roughly three-quarters of patients with aortic valve stenosis severe enough to need valve replacement, said Joseph C. Cleveland Jr., MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon and professor of surgery at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
The actual, immediate increase in TAVR patients may not be quite as large as this fraction suggests. That’s in part because many patients in the low-risk category based on their surgical risk score already have been judged to have higher-risk features by heart-valve teams that has allowed such patients to undergo TAVR, said John D. Carroll, MD, professor of medicine and director of interventional cardiology at the University of Colorado.
For several years, U.S. rates of TAVR have exceeded SAVR, he noted, and in 2018 U.S. programs performed roughly 58,000 TAVR procedures and about 25,000 SAVRs, according to data collected by the Transcatheter Valve Therapy (TVT) Registry run by the Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the American College of Cardiology. Dr. Carroll is vice chair of the steering committee for this registry, which was mandated by the FDA in 2011 when the agency first allowed TAVR onto the U.S. market and is designed to capture every TAVR case performed in routine U.S. practice.
Despite this caveat, “there will be substantial growth in TAVR. Going forward, there will be more of a shift from SAVR to TAVR. That is what the results of the low-risk trials did,” Dr. Carroll predicted. In addition, the coming growth in TAVR numbers will stem from more than just low-risk patients whom a month ago would have undergone SAVR but now undergo TAVR instead. The availability of TAVR as an option for a wider range of patients should help boost public awareness that a nonsurgical way exists to treat severe aortic stenosis, plus the aging of baby boomers is on the verge of generating a substantial wave of new patients, a wave so high that Dr. Carroll called it a looming “tsunami” of patients needing TAVR.
How will low-risk TAVR affect lower-volume sites?
More TAVR patients will inevitably mean more U.S. sites offering the procedure, experts agreed. “We anticipate more low-volume programs,” Dr. Carroll said.
“Approval of TAVR for low-risk patients will result in a significant increase in the number of programs offering it. Approximately 1,100 U.S. programs offer SAVR, and as of now about 600 of these programs also offer TAVR. Health systems face the risk of losing patients if they don’t offer TAVR now that low-risk patients can be treated,” observed Sreekanth Vemulapalli, MD, a cardiologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C. who has run several studies using TVT Registry data and serves as liaison between the registry and its analytic center at Duke.
One of these studies, published earlier in 2019, showed that, among more than 96,000 registry patients who underwent transfemoral TAVR during 2015-2017 at 554 U.S. centers, those treated at sites that fell into the bottom quartile for case volume had an adjusted 30-day mortality rate that was 21% higher relative to patients treated at centers in the top quartile, a statistically significant difference (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 27;380[26]:2541-50). The absolute difference in adjusted 30-day mortality between the lowest and highest quartiles was 0.54%, roughly 1 additional death for every 200 patients. The TAVR centers in the lowest-volume quartile performed 5-36 cases/year, averaging 27 TAVRs/year; those in the highest quartile performed 86-371 TAVRs annually with an overall quartile average of 143 procedures/year.
Dr. Vemulapalli and others cautioned that TAVR case volume is currently serving as a surrogate, and imperfect, marker for program quality until TAVR programs generate enough data to allow a directly measured, risk-adjusted, outcome-driven assessment of performance. In the study he and his associates published in June, the 140 TAVR programs in the lowest-volume quartile showed a “high” level of variability in their adjusted mortality rates. Despite this limitation, the prospect that new TAVR programs will soon open to meet growing TAVR demand from low-risk patients poses the question of how these programs will perform during their start-up days (and possibly beyond), when case volumes may be light, especially if sites open in more remote sections of the United States.
“Will the real-world results of TAVR in low-risk patients match the fantastic results in the two low-risk TAVR trials?” wondered Dr. Carroll, referring to the PARTNER 3 (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]:1695-1705) and Evolut Low-Risk Patients trial (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]:1706-15). “It’s unknown whether a site just starting to do TAVRs will get the same results. The sites that participated in the low-risk trials were mostly high-volume sites.” On the other hand, TVT Registry data have shown that patients with surgical risk that was judged prohibitive, high, or intermediate all have had overall real-world outcomes that match what was seen in the relevant TAVR trials.
In addition, some experts view a modest drop in 30-day survival among patients treated at lower-volume TAVR sites as a reasonable trade-off for easier access for patients seeking this life-changing treatment.
“We need to ensure that patients have access to this treatment option,” said Catherine M. Otto, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Heart Valve Clinic at the University of Washington, Seattle. The potentially better outcomes produced at larger TAVR programs “need to be balanced against having a greater number of programs to ensure access for more patients and allow patients to be treated closer to home,” she said in an interview. She suggested that the potential exists to use telemedicine to link larger and more experienced TAVR programs with smaller and newer programs to help boost their performance.
“There is no perfect solution or metric to ensure high quality while also allowing for adequate access. As indications for TAVR expand we need to maintain vigilance and accountability as the therapy is dispersed to more patients at more centers,” said Brian R. Lindman, MD, medical director of the Structural Heat and Valve Center at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “We also need to insure that certain groups of patients have adequate access to this therapy. Adequate access to TAVR and high-quality clinical outcomes are both important goals.”
Plus, “the volume relationship may be less important,” in lower-risk patients, suggested Dr. Cleveland in an interview. Low-risk patients are younger and have fewer comorbidities and less vascular disease. “Low-volume centers should be able to treat these patients,” he said. Despite that, he personally supported the higher volume minimum for TAVR of 50 cases/year that the ACC, STS, and other U.S. professional societies recommended to CMS during public comment on the proposed rules. “We’ll see whether the increased access is worth this volume minimum.”
Who still gets SAVR?
Given the inherent attraction TAVR holds over SAVR for patients, heart-valve teams will need to convey the right message to patients who may be better served with surgical replacement despite the added trauma and recovery time it produces.
“The decision to perform TAVR or SAVR should now be based on a patient’s expected longevity as well as patient preferences and values, and not on the patient’s estimated surgical risk, except for the highest-risk patients in whom TAVR is recommended,” said Dr. Otto. A patient’s age, comorbidities, and overall life expectancy now move to center stage when deciding the TAVR or SAVR question, along with individual anatomic considerations, the possible need for concurrent procedures, and of course what the patient prefers including their willingness and ability to remain on lifelong anticoagulation if they receive a durable mechanical valve. Dr. Otto outlined this new landscape of the heart-valve team’s decision making process in an editorial she recently published (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]: 1769-70) that accompanied publication of PARTNER 3 and the Evolut Low-Risk Patients trial.
“For some patients there will be clear benefit from one approach, but for many patients, particularly those at low surgical risk, both TAVR and SAVR are technically feasible. For these patients it’s essential that the heart-valve team provide unbiased information to guide patients,” Dr. Otto said. The ideal person to provide this unbiased presentation of the pros and cons would be a cardiologist experienced with valve disease but not actively involved in performing valve-replacement procedures.
A big issue younger patients must confront is what remains unknown about long-term durability of TAVR valves. Dr. Otto called this “the most important missing piece of information. We only have robust data out to about 5 years. If TAVR valve will be durable for 15-20 years, then TAVR will become preferred even in younger patients.”
Even after TAVR became available to intermediate-risk patients in 2016, the median age of U.S. patients undergoing TAVR hardly budged, and has recently stood at about 81 years, Dr. Carroll noted. “With low-risk patients, we expect to see this change,” as more patients now who are in their 70s, 60s, and younger start to routinely undergo TAVR. As more younger patients with life expectancies on the order of 30 years consider TAVR, issues of valve durability “enter the discussion,” he said. “We need data to 10, 15 years,” and in its low-risk approval the FDA mandated manufacturers to follow these patients for at least 10 years. Although valve-in-valve replacement of failed TAVR valves is an option, it’s not always a smooth fix with the potential for prosthesis-patient mismatch (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Dec 4;72[22]:2701-11) and resulting hemodynamic problems, Dr. Carroll said.
Bicuspid-valve replacement with TAVR is another big unknown, largely because these patients were excluded from the TAVR trials. A recently published analysis of the 2,726 patients with a bicuspid aortic valve who underwent TAVR anyway in routine U.S. practice between June 2015 and November 2018 and were in the TVT Registry (about 3% of all TAVR patients during this period) showed that these patients had similar mortality, compared with the tricuspid-valve patients, but a significantly increased stroke rate (JAMA. 2019 Jun 11;321[22]:2193-202). The authors concluded that a prospective, randomized study of TAVR, compared with SAVR, is needed for these patients, and many others in the field agree.
As availability of TAVR grows and public awareness increases, heart-valve teams may find it challenging sometimes to help patients understand the upsides of SAVR for their individual clinical needs when TAVR is superficially so much more attractive.
“The desire to avoid the prolonged hospitalization and recovery from SAVR is a huge driver of patient preference,” noted Dr. Carroll.
“It’s hard to tell a 55 year old to think about another procedure they may need when they are 65 or 70 if they undergo TAVR now rather than SAVR. They don’t want open-heart surgery; I hear that all the time,” Dr. Cleveland said. “If I were a 55-year-old aortic valve patient I’d strongly consider TAVR, too.”
Financial consideration at the site performing the interventions can also be a factor. “Differential costs and payments associated with SAVR and TAVR create different financial incentives for health systems between these two procedures,” noted Dr. Vemulapalli. “There likely needs to be a system that creates equal incentives to do SAVR or TAVR so that the decision between them can come down to just the patient and heart-valve team. We need further data and decision aids to help better define which patients will likely do better with SAVR and which with TAVR.”
What now?
Since the first large TAVR trials started in 2007, their main thrust has been to prove the efficacy and safety of TAVR in patients at sequentially less risk of undergoing SAVR. Now that this series of comparisons has ended, where will TAVR research turn its attention?
In addition to the big outstanding issues of TAVR-valve long-term durability, and the efficacy and safety of TAVR for replacing bicuspid valves, other big questions and issues loom. They include the optimal anticoagulant regimen for preventing leaflet thrombosis, reducing the need for pacemakers, reducing strokes, the applicability of TAVR to patients with less severe aortic stenosis, the impact of treating severe but asymptomatic aortic valve obstruction, optimizing valve-in-valve outcomes, and further improvements to valve design, hemodynamics, and delivery. In short, the question of TAVR’s suitability for patients regardless of their surgical risk may have now been answered, but many questions remain about the best way to use and to optimize this technology.
Dr. Cleveland and Dr. Carroll have participated in TAVR trials but had no personal financial disclosures. Dr. Otto had no disclosures. Dr. Vemulapalli has received personal fees from Janssen, Novella, Premiere, and Zafgen, and research funding from Boston Scientific and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Lindman has been a consultant to Medtronic, has served as an advisor to Roche, and has received research funding from Edwards Lifesciences.
With the Food and Drug Administration’s approval of two different pairs of transcatheter aortic valve replacement systems for patients at low surgical risk, U.S. case volume for the procedure should markedly rise given that patients at low surgical risk form the largest risk subgroup among patients with aortic stenosis severe enough to warrant valve replacement.
But even as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) now becomes the predominant approach for fixing severely stenotic aortic valves regardless of a patient’s risk level, the procedure remains less optimal than surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in selected patients, putting an onus on clinicians to identify and alert patients for whom the transcatheter approach is questionable.
The anticipated surge in TAVR cases for low-risk patients after the FDA’s Aug. 16, 2019, decision will also likely lead to more hospitals offering TAVR. That development will test whether recently enacted rules from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on procedure-volume minimums for TAVR programs – at least 20 cases a year (or 40 within 2 years) at centers that also perform at least 300 percutaneous coronary interventions annually – lead to outcomes at lower-volume centers that come reasonably close to the outcomes at higher-volume programs for low-risk patients.
“The paradigm has definitely shifted from SAVR as the gold standard to TAVR as the primary treatment for aortic stenosis. This opens TAVR to the vast majority of patients with aortic stenosis,” roughly three-quarters of patients with aortic valve stenosis severe enough to need valve replacement, said Joseph C. Cleveland Jr., MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon and professor of surgery at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
The actual, immediate increase in TAVR patients may not be quite as large as this fraction suggests. That’s in part because many patients in the low-risk category based on their surgical risk score already have been judged to have higher-risk features by heart-valve teams that has allowed such patients to undergo TAVR, said John D. Carroll, MD, professor of medicine and director of interventional cardiology at the University of Colorado.
For several years, U.S. rates of TAVR have exceeded SAVR, he noted, and in 2018 U.S. programs performed roughly 58,000 TAVR procedures and about 25,000 SAVRs, according to data collected by the Transcatheter Valve Therapy (TVT) Registry run by the Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the American College of Cardiology. Dr. Carroll is vice chair of the steering committee for this registry, which was mandated by the FDA in 2011 when the agency first allowed TAVR onto the U.S. market and is designed to capture every TAVR case performed in routine U.S. practice.
Despite this caveat, “there will be substantial growth in TAVR. Going forward, there will be more of a shift from SAVR to TAVR. That is what the results of the low-risk trials did,” Dr. Carroll predicted. In addition, the coming growth in TAVR numbers will stem from more than just low-risk patients whom a month ago would have undergone SAVR but now undergo TAVR instead. The availability of TAVR as an option for a wider range of patients should help boost public awareness that a nonsurgical way exists to treat severe aortic stenosis, plus the aging of baby boomers is on the verge of generating a substantial wave of new patients, a wave so high that Dr. Carroll called it a looming “tsunami” of patients needing TAVR.
How will low-risk TAVR affect lower-volume sites?
More TAVR patients will inevitably mean more U.S. sites offering the procedure, experts agreed. “We anticipate more low-volume programs,” Dr. Carroll said.
“Approval of TAVR for low-risk patients will result in a significant increase in the number of programs offering it. Approximately 1,100 U.S. programs offer SAVR, and as of now about 600 of these programs also offer TAVR. Health systems face the risk of losing patients if they don’t offer TAVR now that low-risk patients can be treated,” observed Sreekanth Vemulapalli, MD, a cardiologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C. who has run several studies using TVT Registry data and serves as liaison between the registry and its analytic center at Duke.
One of these studies, published earlier in 2019, showed that, among more than 96,000 registry patients who underwent transfemoral TAVR during 2015-2017 at 554 U.S. centers, those treated at sites that fell into the bottom quartile for case volume had an adjusted 30-day mortality rate that was 21% higher relative to patients treated at centers in the top quartile, a statistically significant difference (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 27;380[26]:2541-50). The absolute difference in adjusted 30-day mortality between the lowest and highest quartiles was 0.54%, roughly 1 additional death for every 200 patients. The TAVR centers in the lowest-volume quartile performed 5-36 cases/year, averaging 27 TAVRs/year; those in the highest quartile performed 86-371 TAVRs annually with an overall quartile average of 143 procedures/year.
Dr. Vemulapalli and others cautioned that TAVR case volume is currently serving as a surrogate, and imperfect, marker for program quality until TAVR programs generate enough data to allow a directly measured, risk-adjusted, outcome-driven assessment of performance. In the study he and his associates published in June, the 140 TAVR programs in the lowest-volume quartile showed a “high” level of variability in their adjusted mortality rates. Despite this limitation, the prospect that new TAVR programs will soon open to meet growing TAVR demand from low-risk patients poses the question of how these programs will perform during their start-up days (and possibly beyond), when case volumes may be light, especially if sites open in more remote sections of the United States.
“Will the real-world results of TAVR in low-risk patients match the fantastic results in the two low-risk TAVR trials?” wondered Dr. Carroll, referring to the PARTNER 3 (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]:1695-1705) and Evolut Low-Risk Patients trial (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]:1706-15). “It’s unknown whether a site just starting to do TAVRs will get the same results. The sites that participated in the low-risk trials were mostly high-volume sites.” On the other hand, TVT Registry data have shown that patients with surgical risk that was judged prohibitive, high, or intermediate all have had overall real-world outcomes that match what was seen in the relevant TAVR trials.
In addition, some experts view a modest drop in 30-day survival among patients treated at lower-volume TAVR sites as a reasonable trade-off for easier access for patients seeking this life-changing treatment.
“We need to ensure that patients have access to this treatment option,” said Catherine M. Otto, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Heart Valve Clinic at the University of Washington, Seattle. The potentially better outcomes produced at larger TAVR programs “need to be balanced against having a greater number of programs to ensure access for more patients and allow patients to be treated closer to home,” she said in an interview. She suggested that the potential exists to use telemedicine to link larger and more experienced TAVR programs with smaller and newer programs to help boost their performance.
“There is no perfect solution or metric to ensure high quality while also allowing for adequate access. As indications for TAVR expand we need to maintain vigilance and accountability as the therapy is dispersed to more patients at more centers,” said Brian R. Lindman, MD, medical director of the Structural Heat and Valve Center at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “We also need to insure that certain groups of patients have adequate access to this therapy. Adequate access to TAVR and high-quality clinical outcomes are both important goals.”
Plus, “the volume relationship may be less important,” in lower-risk patients, suggested Dr. Cleveland in an interview. Low-risk patients are younger and have fewer comorbidities and less vascular disease. “Low-volume centers should be able to treat these patients,” he said. Despite that, he personally supported the higher volume minimum for TAVR of 50 cases/year that the ACC, STS, and other U.S. professional societies recommended to CMS during public comment on the proposed rules. “We’ll see whether the increased access is worth this volume minimum.”
Who still gets SAVR?
Given the inherent attraction TAVR holds over SAVR for patients, heart-valve teams will need to convey the right message to patients who may be better served with surgical replacement despite the added trauma and recovery time it produces.
“The decision to perform TAVR or SAVR should now be based on a patient’s expected longevity as well as patient preferences and values, and not on the patient’s estimated surgical risk, except for the highest-risk patients in whom TAVR is recommended,” said Dr. Otto. A patient’s age, comorbidities, and overall life expectancy now move to center stage when deciding the TAVR or SAVR question, along with individual anatomic considerations, the possible need for concurrent procedures, and of course what the patient prefers including their willingness and ability to remain on lifelong anticoagulation if they receive a durable mechanical valve. Dr. Otto outlined this new landscape of the heart-valve team’s decision making process in an editorial she recently published (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]: 1769-70) that accompanied publication of PARTNER 3 and the Evolut Low-Risk Patients trial.
“For some patients there will be clear benefit from one approach, but for many patients, particularly those at low surgical risk, both TAVR and SAVR are technically feasible. For these patients it’s essential that the heart-valve team provide unbiased information to guide patients,” Dr. Otto said. The ideal person to provide this unbiased presentation of the pros and cons would be a cardiologist experienced with valve disease but not actively involved in performing valve-replacement procedures.
A big issue younger patients must confront is what remains unknown about long-term durability of TAVR valves. Dr. Otto called this “the most important missing piece of information. We only have robust data out to about 5 years. If TAVR valve will be durable for 15-20 years, then TAVR will become preferred even in younger patients.”
Even after TAVR became available to intermediate-risk patients in 2016, the median age of U.S. patients undergoing TAVR hardly budged, and has recently stood at about 81 years, Dr. Carroll noted. “With low-risk patients, we expect to see this change,” as more patients now who are in their 70s, 60s, and younger start to routinely undergo TAVR. As more younger patients with life expectancies on the order of 30 years consider TAVR, issues of valve durability “enter the discussion,” he said. “We need data to 10, 15 years,” and in its low-risk approval the FDA mandated manufacturers to follow these patients for at least 10 years. Although valve-in-valve replacement of failed TAVR valves is an option, it’s not always a smooth fix with the potential for prosthesis-patient mismatch (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Dec 4;72[22]:2701-11) and resulting hemodynamic problems, Dr. Carroll said.
Bicuspid-valve replacement with TAVR is another big unknown, largely because these patients were excluded from the TAVR trials. A recently published analysis of the 2,726 patients with a bicuspid aortic valve who underwent TAVR anyway in routine U.S. practice between June 2015 and November 2018 and were in the TVT Registry (about 3% of all TAVR patients during this period) showed that these patients had similar mortality, compared with the tricuspid-valve patients, but a significantly increased stroke rate (JAMA. 2019 Jun 11;321[22]:2193-202). The authors concluded that a prospective, randomized study of TAVR, compared with SAVR, is needed for these patients, and many others in the field agree.
As availability of TAVR grows and public awareness increases, heart-valve teams may find it challenging sometimes to help patients understand the upsides of SAVR for their individual clinical needs when TAVR is superficially so much more attractive.
“The desire to avoid the prolonged hospitalization and recovery from SAVR is a huge driver of patient preference,” noted Dr. Carroll.
“It’s hard to tell a 55 year old to think about another procedure they may need when they are 65 or 70 if they undergo TAVR now rather than SAVR. They don’t want open-heart surgery; I hear that all the time,” Dr. Cleveland said. “If I were a 55-year-old aortic valve patient I’d strongly consider TAVR, too.”
Financial consideration at the site performing the interventions can also be a factor. “Differential costs and payments associated with SAVR and TAVR create different financial incentives for health systems between these two procedures,” noted Dr. Vemulapalli. “There likely needs to be a system that creates equal incentives to do SAVR or TAVR so that the decision between them can come down to just the patient and heart-valve team. We need further data and decision aids to help better define which patients will likely do better with SAVR and which with TAVR.”
What now?
Since the first large TAVR trials started in 2007, their main thrust has been to prove the efficacy and safety of TAVR in patients at sequentially less risk of undergoing SAVR. Now that this series of comparisons has ended, where will TAVR research turn its attention?
In addition to the big outstanding issues of TAVR-valve long-term durability, and the efficacy and safety of TAVR for replacing bicuspid valves, other big questions and issues loom. They include the optimal anticoagulant regimen for preventing leaflet thrombosis, reducing the need for pacemakers, reducing strokes, the applicability of TAVR to patients with less severe aortic stenosis, the impact of treating severe but asymptomatic aortic valve obstruction, optimizing valve-in-valve outcomes, and further improvements to valve design, hemodynamics, and delivery. In short, the question of TAVR’s suitability for patients regardless of their surgical risk may have now been answered, but many questions remain about the best way to use and to optimize this technology.
Dr. Cleveland and Dr. Carroll have participated in TAVR trials but had no personal financial disclosures. Dr. Otto had no disclosures. Dr. Vemulapalli has received personal fees from Janssen, Novella, Premiere, and Zafgen, and research funding from Boston Scientific and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Lindman has been a consultant to Medtronic, has served as an advisor to Roche, and has received research funding from Edwards Lifesciences.
With the Food and Drug Administration’s approval of two different pairs of transcatheter aortic valve replacement systems for patients at low surgical risk, U.S. case volume for the procedure should markedly rise given that patients at low surgical risk form the largest risk subgroup among patients with aortic stenosis severe enough to warrant valve replacement.
But even as transcatheter aortic valve replacement (TAVR) now becomes the predominant approach for fixing severely stenotic aortic valves regardless of a patient’s risk level, the procedure remains less optimal than surgical aortic valve replacement (SAVR) in selected patients, putting an onus on clinicians to identify and alert patients for whom the transcatheter approach is questionable.
The anticipated surge in TAVR cases for low-risk patients after the FDA’s Aug. 16, 2019, decision will also likely lead to more hospitals offering TAVR. That development will test whether recently enacted rules from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services on procedure-volume minimums for TAVR programs – at least 20 cases a year (or 40 within 2 years) at centers that also perform at least 300 percutaneous coronary interventions annually – lead to outcomes at lower-volume centers that come reasonably close to the outcomes at higher-volume programs for low-risk patients.
“The paradigm has definitely shifted from SAVR as the gold standard to TAVR as the primary treatment for aortic stenosis. This opens TAVR to the vast majority of patients with aortic stenosis,” roughly three-quarters of patients with aortic valve stenosis severe enough to need valve replacement, said Joseph C. Cleveland Jr., MD, a cardiothoracic surgeon and professor of surgery at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora.
The actual, immediate increase in TAVR patients may not be quite as large as this fraction suggests. That’s in part because many patients in the low-risk category based on their surgical risk score already have been judged to have higher-risk features by heart-valve teams that has allowed such patients to undergo TAVR, said John D. Carroll, MD, professor of medicine and director of interventional cardiology at the University of Colorado.
For several years, U.S. rates of TAVR have exceeded SAVR, he noted, and in 2018 U.S. programs performed roughly 58,000 TAVR procedures and about 25,000 SAVRs, according to data collected by the Transcatheter Valve Therapy (TVT) Registry run by the Society of Thoracic Surgeons and the American College of Cardiology. Dr. Carroll is vice chair of the steering committee for this registry, which was mandated by the FDA in 2011 when the agency first allowed TAVR onto the U.S. market and is designed to capture every TAVR case performed in routine U.S. practice.
Despite this caveat, “there will be substantial growth in TAVR. Going forward, there will be more of a shift from SAVR to TAVR. That is what the results of the low-risk trials did,” Dr. Carroll predicted. In addition, the coming growth in TAVR numbers will stem from more than just low-risk patients whom a month ago would have undergone SAVR but now undergo TAVR instead. The availability of TAVR as an option for a wider range of patients should help boost public awareness that a nonsurgical way exists to treat severe aortic stenosis, plus the aging of baby boomers is on the verge of generating a substantial wave of new patients, a wave so high that Dr. Carroll called it a looming “tsunami” of patients needing TAVR.
How will low-risk TAVR affect lower-volume sites?
More TAVR patients will inevitably mean more U.S. sites offering the procedure, experts agreed. “We anticipate more low-volume programs,” Dr. Carroll said.
“Approval of TAVR for low-risk patients will result in a significant increase in the number of programs offering it. Approximately 1,100 U.S. programs offer SAVR, and as of now about 600 of these programs also offer TAVR. Health systems face the risk of losing patients if they don’t offer TAVR now that low-risk patients can be treated,” observed Sreekanth Vemulapalli, MD, a cardiologist at Duke University, Durham, N.C. who has run several studies using TVT Registry data and serves as liaison between the registry and its analytic center at Duke.
One of these studies, published earlier in 2019, showed that, among more than 96,000 registry patients who underwent transfemoral TAVR during 2015-2017 at 554 U.S. centers, those treated at sites that fell into the bottom quartile for case volume had an adjusted 30-day mortality rate that was 21% higher relative to patients treated at centers in the top quartile, a statistically significant difference (N Engl J Med. 2019 Jun 27;380[26]:2541-50). The absolute difference in adjusted 30-day mortality between the lowest and highest quartiles was 0.54%, roughly 1 additional death for every 200 patients. The TAVR centers in the lowest-volume quartile performed 5-36 cases/year, averaging 27 TAVRs/year; those in the highest quartile performed 86-371 TAVRs annually with an overall quartile average of 143 procedures/year.
Dr. Vemulapalli and others cautioned that TAVR case volume is currently serving as a surrogate, and imperfect, marker for program quality until TAVR programs generate enough data to allow a directly measured, risk-adjusted, outcome-driven assessment of performance. In the study he and his associates published in June, the 140 TAVR programs in the lowest-volume quartile showed a “high” level of variability in their adjusted mortality rates. Despite this limitation, the prospect that new TAVR programs will soon open to meet growing TAVR demand from low-risk patients poses the question of how these programs will perform during their start-up days (and possibly beyond), when case volumes may be light, especially if sites open in more remote sections of the United States.
“Will the real-world results of TAVR in low-risk patients match the fantastic results in the two low-risk TAVR trials?” wondered Dr. Carroll, referring to the PARTNER 3 (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]:1695-1705) and Evolut Low-Risk Patients trial (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]:1706-15). “It’s unknown whether a site just starting to do TAVRs will get the same results. The sites that participated in the low-risk trials were mostly high-volume sites.” On the other hand, TVT Registry data have shown that patients with surgical risk that was judged prohibitive, high, or intermediate all have had overall real-world outcomes that match what was seen in the relevant TAVR trials.
In addition, some experts view a modest drop in 30-day survival among patients treated at lower-volume TAVR sites as a reasonable trade-off for easier access for patients seeking this life-changing treatment.
“We need to ensure that patients have access to this treatment option,” said Catherine M. Otto, MD, professor of medicine and director of the Heart Valve Clinic at the University of Washington, Seattle. The potentially better outcomes produced at larger TAVR programs “need to be balanced against having a greater number of programs to ensure access for more patients and allow patients to be treated closer to home,” she said in an interview. She suggested that the potential exists to use telemedicine to link larger and more experienced TAVR programs with smaller and newer programs to help boost their performance.
“There is no perfect solution or metric to ensure high quality while also allowing for adequate access. As indications for TAVR expand we need to maintain vigilance and accountability as the therapy is dispersed to more patients at more centers,” said Brian R. Lindman, MD, medical director of the Structural Heat and Valve Center at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn. “We also need to insure that certain groups of patients have adequate access to this therapy. Adequate access to TAVR and high-quality clinical outcomes are both important goals.”
Plus, “the volume relationship may be less important,” in lower-risk patients, suggested Dr. Cleveland in an interview. Low-risk patients are younger and have fewer comorbidities and less vascular disease. “Low-volume centers should be able to treat these patients,” he said. Despite that, he personally supported the higher volume minimum for TAVR of 50 cases/year that the ACC, STS, and other U.S. professional societies recommended to CMS during public comment on the proposed rules. “We’ll see whether the increased access is worth this volume minimum.”
Who still gets SAVR?
Given the inherent attraction TAVR holds over SAVR for patients, heart-valve teams will need to convey the right message to patients who may be better served with surgical replacement despite the added trauma and recovery time it produces.
“The decision to perform TAVR or SAVR should now be based on a patient’s expected longevity as well as patient preferences and values, and not on the patient’s estimated surgical risk, except for the highest-risk patients in whom TAVR is recommended,” said Dr. Otto. A patient’s age, comorbidities, and overall life expectancy now move to center stage when deciding the TAVR or SAVR question, along with individual anatomic considerations, the possible need for concurrent procedures, and of course what the patient prefers including their willingness and ability to remain on lifelong anticoagulation if they receive a durable mechanical valve. Dr. Otto outlined this new landscape of the heart-valve team’s decision making process in an editorial she recently published (N Engl J Med. 2019 May 2;380[18]: 1769-70) that accompanied publication of PARTNER 3 and the Evolut Low-Risk Patients trial.
“For some patients there will be clear benefit from one approach, but for many patients, particularly those at low surgical risk, both TAVR and SAVR are technically feasible. For these patients it’s essential that the heart-valve team provide unbiased information to guide patients,” Dr. Otto said. The ideal person to provide this unbiased presentation of the pros and cons would be a cardiologist experienced with valve disease but not actively involved in performing valve-replacement procedures.
A big issue younger patients must confront is what remains unknown about long-term durability of TAVR valves. Dr. Otto called this “the most important missing piece of information. We only have robust data out to about 5 years. If TAVR valve will be durable for 15-20 years, then TAVR will become preferred even in younger patients.”
Even after TAVR became available to intermediate-risk patients in 2016, the median age of U.S. patients undergoing TAVR hardly budged, and has recently stood at about 81 years, Dr. Carroll noted. “With low-risk patients, we expect to see this change,” as more patients now who are in their 70s, 60s, and younger start to routinely undergo TAVR. As more younger patients with life expectancies on the order of 30 years consider TAVR, issues of valve durability “enter the discussion,” he said. “We need data to 10, 15 years,” and in its low-risk approval the FDA mandated manufacturers to follow these patients for at least 10 years. Although valve-in-valve replacement of failed TAVR valves is an option, it’s not always a smooth fix with the potential for prosthesis-patient mismatch (J Am Coll Cardiol. 2018 Dec 4;72[22]:2701-11) and resulting hemodynamic problems, Dr. Carroll said.
Bicuspid-valve replacement with TAVR is another big unknown, largely because these patients were excluded from the TAVR trials. A recently published analysis of the 2,726 patients with a bicuspid aortic valve who underwent TAVR anyway in routine U.S. practice between June 2015 and November 2018 and were in the TVT Registry (about 3% of all TAVR patients during this period) showed that these patients had similar mortality, compared with the tricuspid-valve patients, but a significantly increased stroke rate (JAMA. 2019 Jun 11;321[22]:2193-202). The authors concluded that a prospective, randomized study of TAVR, compared with SAVR, is needed for these patients, and many others in the field agree.
As availability of TAVR grows and public awareness increases, heart-valve teams may find it challenging sometimes to help patients understand the upsides of SAVR for their individual clinical needs when TAVR is superficially so much more attractive.
“The desire to avoid the prolonged hospitalization and recovery from SAVR is a huge driver of patient preference,” noted Dr. Carroll.
“It’s hard to tell a 55 year old to think about another procedure they may need when they are 65 or 70 if they undergo TAVR now rather than SAVR. They don’t want open-heart surgery; I hear that all the time,” Dr. Cleveland said. “If I were a 55-year-old aortic valve patient I’d strongly consider TAVR, too.”
Financial consideration at the site performing the interventions can also be a factor. “Differential costs and payments associated with SAVR and TAVR create different financial incentives for health systems between these two procedures,” noted Dr. Vemulapalli. “There likely needs to be a system that creates equal incentives to do SAVR or TAVR so that the decision between them can come down to just the patient and heart-valve team. We need further data and decision aids to help better define which patients will likely do better with SAVR and which with TAVR.”
What now?
Since the first large TAVR trials started in 2007, their main thrust has been to prove the efficacy and safety of TAVR in patients at sequentially less risk of undergoing SAVR. Now that this series of comparisons has ended, where will TAVR research turn its attention?
In addition to the big outstanding issues of TAVR-valve long-term durability, and the efficacy and safety of TAVR for replacing bicuspid valves, other big questions and issues loom. They include the optimal anticoagulant regimen for preventing leaflet thrombosis, reducing the need for pacemakers, reducing strokes, the applicability of TAVR to patients with less severe aortic stenosis, the impact of treating severe but asymptomatic aortic valve obstruction, optimizing valve-in-valve outcomes, and further improvements to valve design, hemodynamics, and delivery. In short, the question of TAVR’s suitability for patients regardless of their surgical risk may have now been answered, but many questions remain about the best way to use and to optimize this technology.
Dr. Cleveland and Dr. Carroll have participated in TAVR trials but had no personal financial disclosures. Dr. Otto had no disclosures. Dr. Vemulapalli has received personal fees from Janssen, Novella, Premiere, and Zafgen, and research funding from Boston Scientific and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Lindman has been a consultant to Medtronic, has served as an advisor to Roche, and has received research funding from Edwards Lifesciences.
CPAP safety for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floor
SEATTLE – Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego has been doing continuous positive airway pressure for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floors safely and with no problems for nearly 20 years, according to a presentation at Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
It’s newsworthy because “very, very few” hospitals do bronchiolitis continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) outside of the ICU. “The perception is that there are complications, and you might miss kids that are really sick if you keep them on the floor.” However, “we have been doing it safely for so long that no one thinks twice about it,” said Christiane Lenzen, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Rady and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
It doesn’t matter if children have congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, or other problems, she said, “if they are stable enough for the floor, we will see if it’s okay.”
Rady’s hand was forced on the issue because it has a large catchment area but limited ICU beds, so for practical reasons and within certain limits, CPAP moved to the floors. One of Dr. Lenzen’s colleagues noted that, as long as there’s nurse and respiratory leadership buy in, “it’s actually quite easy to pull off in a very safe manner.”
Rady has a significant advantage over community hospitals and other places considering the approach, because it has onsite pediatric ICU services for when things head south. Over the past 3 or so years, 52% of the children the pediatric hospital medicine service started on CPAP (168/324) had to be transferred to the ICU; 17% were ultimately intubated.
Many of those transfers were caused by comorbidities, not CPAP failure, but other times children needed greater respiratory support; in general, the floor CPAP limit is 6 cm H2O and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50%. Also, sometimes children needed to be sedated for CPAP, which isn’t done on the floor.
With the 52% transfer rate, “I would worry about patients who are sick enough to need CPAP staying” in a hospital without quick access to ICU services, Dr. Lenzen said at the meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Even so, among 324 children who at least initially were treated with CPAP on the floor – out of 2,424 admitted to the pediatric hospital medicine service with bronchiolitis – there hasn’t been a single pneumothorax, aspiration event, or CPAP equipment–related injury, she said.
CPAP on the floor has several benefits. ICU resources are conserved, patient handoffs and the work of transfers into and out of the ICU are avoided, families don’t have to get used to a new treatment team, and infants aren’t subjected to the jarring ICU environment.
For it to work, though, staff “really need to be on top of this,” and “it needs to be very tightly controlled” with order sets and other measures, the presenters said. There’s regular training at Rady for nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists on CPAP equipment, airway management, monitoring, troubleshooting, and other essentials.
Almost all children on the pediatric floors have a trial of high-flow nasal cannula with an upper limit of 8 L/min. If the Respiratory Assessment Score hasn’t improved in an hour, CPAP is considered. If a child is admitted with a score above 10 and they seem to be worsening, they go straight to CPAP.
Children alternate between nasal prongs and nasal masks to prevent pressure necrosis, and are kept nil per os while on CPAP. They are on continual pulse oximetry and cardiorespiratory monitoring. Vital signs and respiratory scores are checked frequently, more so for children who are struggling.
The patient-to-nurse ratio drops from the usual 4:1 to 3:1 when a child goes on CPAP, and to 2:1 if necessary. Traveling nurses aren’t allowed to take CPAP cases.
The presenters didn’t report any disclosures.
This article was updated 8/27/19.
SEATTLE – Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego has been doing continuous positive airway pressure for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floors safely and with no problems for nearly 20 years, according to a presentation at Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
It’s newsworthy because “very, very few” hospitals do bronchiolitis continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) outside of the ICU. “The perception is that there are complications, and you might miss kids that are really sick if you keep them on the floor.” However, “we have been doing it safely for so long that no one thinks twice about it,” said Christiane Lenzen, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Rady and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
It doesn’t matter if children have congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, or other problems, she said, “if they are stable enough for the floor, we will see if it’s okay.”
Rady’s hand was forced on the issue because it has a large catchment area but limited ICU beds, so for practical reasons and within certain limits, CPAP moved to the floors. One of Dr. Lenzen’s colleagues noted that, as long as there’s nurse and respiratory leadership buy in, “it’s actually quite easy to pull off in a very safe manner.”
Rady has a significant advantage over community hospitals and other places considering the approach, because it has onsite pediatric ICU services for when things head south. Over the past 3 or so years, 52% of the children the pediatric hospital medicine service started on CPAP (168/324) had to be transferred to the ICU; 17% were ultimately intubated.
Many of those transfers were caused by comorbidities, not CPAP failure, but other times children needed greater respiratory support; in general, the floor CPAP limit is 6 cm H2O and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50%. Also, sometimes children needed to be sedated for CPAP, which isn’t done on the floor.
With the 52% transfer rate, “I would worry about patients who are sick enough to need CPAP staying” in a hospital without quick access to ICU services, Dr. Lenzen said at the meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Even so, among 324 children who at least initially were treated with CPAP on the floor – out of 2,424 admitted to the pediatric hospital medicine service with bronchiolitis – there hasn’t been a single pneumothorax, aspiration event, or CPAP equipment–related injury, she said.
CPAP on the floor has several benefits. ICU resources are conserved, patient handoffs and the work of transfers into and out of the ICU are avoided, families don’t have to get used to a new treatment team, and infants aren’t subjected to the jarring ICU environment.
For it to work, though, staff “really need to be on top of this,” and “it needs to be very tightly controlled” with order sets and other measures, the presenters said. There’s regular training at Rady for nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists on CPAP equipment, airway management, monitoring, troubleshooting, and other essentials.
Almost all children on the pediatric floors have a trial of high-flow nasal cannula with an upper limit of 8 L/min. If the Respiratory Assessment Score hasn’t improved in an hour, CPAP is considered. If a child is admitted with a score above 10 and they seem to be worsening, they go straight to CPAP.
Children alternate between nasal prongs and nasal masks to prevent pressure necrosis, and are kept nil per os while on CPAP. They are on continual pulse oximetry and cardiorespiratory monitoring. Vital signs and respiratory scores are checked frequently, more so for children who are struggling.
The patient-to-nurse ratio drops from the usual 4:1 to 3:1 when a child goes on CPAP, and to 2:1 if necessary. Traveling nurses aren’t allowed to take CPAP cases.
The presenters didn’t report any disclosures.
This article was updated 8/27/19.
SEATTLE – Rady Children’s Hospital in San Diego has been doing continuous positive airway pressure for infants with bronchiolitis on the general pediatrics floors safely and with no problems for nearly 20 years, according to a presentation at Pediatric Hospital Medicine.
It’s newsworthy because “very, very few” hospitals do bronchiolitis continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) outside of the ICU. “The perception is that there are complications, and you might miss kids that are really sick if you keep them on the floor.” However, “we have been doing it safely for so long that no one thinks twice about it,” said Christiane Lenzen, MD, a pediatric hospitalist at Rady and an assistant clinical professor of pediatrics at the University of California, San Diego.
It doesn’t matter if children have congenital heart disease, chronic lung disease, or other problems, she said, “if they are stable enough for the floor, we will see if it’s okay.”
Rady’s hand was forced on the issue because it has a large catchment area but limited ICU beds, so for practical reasons and within certain limits, CPAP moved to the floors. One of Dr. Lenzen’s colleagues noted that, as long as there’s nurse and respiratory leadership buy in, “it’s actually quite easy to pull off in a very safe manner.”
Rady has a significant advantage over community hospitals and other places considering the approach, because it has onsite pediatric ICU services for when things head south. Over the past 3 or so years, 52% of the children the pediatric hospital medicine service started on CPAP (168/324) had to be transferred to the ICU; 17% were ultimately intubated.
Many of those transfers were caused by comorbidities, not CPAP failure, but other times children needed greater respiratory support; in general, the floor CPAP limit is 6 cm H2O and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 50%. Also, sometimes children needed to be sedated for CPAP, which isn’t done on the floor.
With the 52% transfer rate, “I would worry about patients who are sick enough to need CPAP staying” in a hospital without quick access to ICU services, Dr. Lenzen said at the meeting sponsored by the Society of Hospital Medicine, the American Academy of Pediatrics, and the Academic Pediatric Association.
Even so, among 324 children who at least initially were treated with CPAP on the floor – out of 2,424 admitted to the pediatric hospital medicine service with bronchiolitis – there hasn’t been a single pneumothorax, aspiration event, or CPAP equipment–related injury, she said.
CPAP on the floor has several benefits. ICU resources are conserved, patient handoffs and the work of transfers into and out of the ICU are avoided, families don’t have to get used to a new treatment team, and infants aren’t subjected to the jarring ICU environment.
For it to work, though, staff “really need to be on top of this,” and “it needs to be very tightly controlled” with order sets and other measures, the presenters said. There’s regular training at Rady for nurses, respiratory therapists, and hospitalists on CPAP equipment, airway management, monitoring, troubleshooting, and other essentials.
Almost all children on the pediatric floors have a trial of high-flow nasal cannula with an upper limit of 8 L/min. If the Respiratory Assessment Score hasn’t improved in an hour, CPAP is considered. If a child is admitted with a score above 10 and they seem to be worsening, they go straight to CPAP.
Children alternate between nasal prongs and nasal masks to prevent pressure necrosis, and are kept nil per os while on CPAP. They are on continual pulse oximetry and cardiorespiratory monitoring. Vital signs and respiratory scores are checked frequently, more so for children who are struggling.
The patient-to-nurse ratio drops from the usual 4:1 to 3:1 when a child goes on CPAP, and to 2:1 if necessary. Traveling nurses aren’t allowed to take CPAP cases.
The presenters didn’t report any disclosures.
This article was updated 8/27/19.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM PHM 2019
Anticoagulant therapy for AFib in patients with end-stage renal disease
Warfarin or apixaban are sensible options
Case
A 78-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is hospitalized with cellulitis and is incidentally found to be in atrial fibrillation. She does not have a history of mitral stenosis, nor does she have a prosthetic valve. She does have a history of hypertension, diabetes, and prior stroke without residual deficits.
After counseling her about the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation (AFib) she makes it clear she is interested in pharmacologic therapy to minimize her risk of stroke and asks what medication you would recommend for anticoagulation.
Brief overview of the issue
Anticoagulation for AFib is indicated for stroke prophylaxis in patients with an elevated risk of stroke. The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful in calculating an individual patient’s risk of stroke and as a decision tool to determine who would benefit from anticoagulation, and it is recommended in the American Heart Association guidelines.1
Low-risk patients (CHA2DS2-VASc score of 0 in men or 1 in women) should not be started on anticoagulation for stroke prophylaxis. For anyone with a risk factor, other than being female, anticoagulation is indicated and should be considered.
The guideline recommends anticoagulant therapy, not antiplatelet agents. For most of the recent past, this has meant a vitamin K antagonist (warfarin) or sometimes a low-molecular-weight heparin injected subcutaneously. Over the past decade, however, with the approval of multiple direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), nonwarfarin oral anticoagulation has grown in popularity as the prophylactic medication of choice.2
While the data for patients with preserved renal function is robust, there is far less data to guide decision making for patients with end-stage renal disease.
Overview of the data
Until the introduction of DOACs, warfarin was the main agent used for stroke prophylaxis in patients with end-stage kidney disease and AFib. Professional guidelines favored warfarin for these patients who were mostly excluded from DOAC trials. Specialized conferences also looked at this issue.
The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference, which reviewed chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias, noted that there were no randomized controlled trials that examined the efficacy and safety of anticoagulation in chronic kidney disease patients with estimated creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min. They remarked that there was insufficient high-quality evidence to recommend warfarin for the prevention of stroke in patients with AFib and dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease.
Since, according to other trials, DOACs had better safety profiles in other populations, the conference noted that lower-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily) or rivaroxaban (15 mg daily) may be considered in this population until clinical safety data were available. Furthermore, the conference recommended that these patients be treated with a multidisciplinary approach in regards to anticoagulation and have an annual reevaluation of treatment goals, along with a risk-benefit assessment.3
Since the publication of the 2018 AHA guidelines and the guidance document that resulted from the KDIGO conference, additional research has been published comparing anticoagulation with a DOAC versus warfarin for AFib in patients with ESRD.
“Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States” was an observational, retrospective, cohort study that compared outcomes in dialysis patients who took warfarin for AFib with those who took apixaban.4 Patients’ data was taken from the U.S. Renal Data System database and were included in the final analysis if they had ESRD, a recent diagnosis of AFib or atrial flutter, and a new prescription for either warfarin or apixaban. Outcome measures were stroke or systemic embolism, major bleeding (critical site, transfusion, or death), gastrointestinal bleeding, intracranial bleeding, or death. Drug usage and compliance were assessed using Medicare Part D prescription information.
A total of 25,523 patients met the inclusion/exclusion criteria and had taken either warfarin (n = 23,172) or apixaban (n = 2,351). To account for selection bias in these cohorts, a subset of the warfarin patients was selected based on prognostic score matching. The prognostic score was calculated from the baseline characteristics (which included age, stroke history, diabetes, smoking, antiplatelet medication, liver disease, prior bleeding, and CHA2DS2-VASc score). Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analysis were used to give hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals for each outcome measure. Prespecified subgroup analyses were conducted to compare apixaban doses, where 44% were prescribed 5 mg b.i.d. and 56% were prescribed 2.5 mg b.i.d..
In the study, patients in the apixaban group had a significantly lower risk of major bleeding as compared with the warfarin group (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.59-0.87; P less than .001) with overall high rates of major bleeding in both groups at 19.7 and 22.9 per 100 patient-years in the apixaban group and warfarin group, respectively. There was no difference in the rate of stroke/systemic embolism between patients receiving apixaban and warfarin (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.69-1.12; P = .29). There was a nonsignificant trend toward decreased risk of GI bleeding in the apixaban group and no significant differences between the groups in the rates of intracranial bleeding. Apixaban was also associated with a nonsignificant trend toward lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.71-1.01; P = .06).
Notably, censoring rates because of expired prescriptions or a 1-month gap between prescriptions were high in both groups and the majority of censoring occurred within the first 12 months. Additionally, in dose specific analyses, patients receiving the 5-mg, twice-daily dose were found to have statistically significant decreases in risk of stroke/systemic embolism (P = .035) and mortality (P = .005) as compared with the 2.5-mg, twice-daily dose without significant differences in GI or intracranial bleeding.
There are three ongoing, open-label, randomized, controlled trials examining anticoagulation for nonvalvular AFib in patients with ESRD on hemodialysis with two comparing apixaban to warfarin (or derivative) and the other warfarin versus no anticoagulation.5 All trials are in adult patients with documented AFib and CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2. AKADIA (Germany based) plans to enroll 222 patients and compares a vitamin K antagonist (INR goal, 2-3) with 2.5-mg b.i.d. apixaban patients with ESRD on hemodialysis for at least 3 months with primary outcome of major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding and secondary outcome of thromboembolic events, as well as apixaban levels pre- and post hemodialysis.
RENAL-AF (U.S. based) plans to enrolled 762 patients and compares 5-mg b.i.d. apixaban (with 2.5 mg for selected patients) with warfarin in people of chronic hemodialysis with primary outcome of days to first major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding event and secondary outcome of stroke, systemic embolism, mortality, adherence and plasma apixaban levels. AVKDIAL (France based) plans to enroll 855 patients and compares no anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists in patients on hemodialysis for at least 1 month, with primary outcome of cumulative incidence of severe bleeding and thrombosis.
Application of the data to our original case
Our patient is Medicare age with ESRD and newly diagnosed nonvalvular AFib. Recent data suggests apixaban could be used for stroke prevention instead of the prior standard of care, warfarin. This approach is supported in the 2019 guidelines.1
Patients with ESRD have an increased risk of bleeding and apixaban was shown to have less bleeding complications than warfarin in this analysis. However, only standard-dose apixaban was associated with a statistically significant lower risk of stroke/systemic embolism, major bleeding, and death. Reduced-dose apixaban had a lower risk of major bleeding but no difference for stroke/systemic embolism or death. Reduced-dose apixaban is used for patients who have two out of the following three criteria: aged at least 80 years, weight of at least 60 kg, and creatinine of at least 1.5 mg/dL. Therefore, many Medicare-age patients with ESRD would not be indicated for the dose of apixaban that was shown to improve the most important outcomes of stroke/SE and death.
It may still be beneficial to use apixaban in this patient since it appears to work as well as warfarin for stroke/systemic embolism prevention with less bleeding complications.
Bottom line
For patients who have decided to pursue an anticoagulation strategy for stroke prevention in AFib and have end-stage renal disease, either warfarin or apixaban are sensible options.
Dr. Farber is a medical instructor at Duke University Health System in Durham, N.C. Dr. Stafford is a medical instructor at Duke University. Dr. Sata is assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Abdo and Dr. Menon are hospitalists at Duke University. Dr. Brooks is assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Wachter is associate medical director at Duke Regional Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Sharma is associate medical director for clinical education in hospital medicine at Duke Regional Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University.
References
1. January CT et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2019;139. doi: 1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
2. Lippi G et al. Direct oral anticoagulants: Analysis of worldwide use and popularity using Google Trends. Ann Transl Med. 2017 Aug; 5(16):322. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.06.65.
3. Turakhia MP et al. Chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Eur Heart J. 2018 Jun 21;39(24):2314-25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy060.
4. Siontis KC et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1519-29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035418.
5. Nigwekar SU et al. Long-term anticoagulation for patient receiving dialysis: Tilting the benefit-to-risk ratio? Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1530-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037091.
Key points
- According to 2019 American Heart Association guidelines, warfarin or apixaban are reasonable options for stroke prevention for patients who have end-stage renal disease and who plan for anticoagulation because of atrial fibrillation.
- Recent observational data suggests that apixaban may be safer than warfarin in this population.
- Several randomized, controlled trials are ongoing that may help determine the optimal agent to use in this setting.
- Until more definitive data is available, a reasonable approach is to discuss the risks and benefits of various treatment strategies with patients, and engage a multidisciplinary team (cardiologist, nephrologist, primary care provider, pharmacist) in the decision making process.
Additional reading
January CT et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2019;139. doi: 1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
Nigwekar SU et al. Long-term anticoagulation for patient receiving dialysis: Tilting the benefit to risk ratio? Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1530-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037091.
Garlo KG et al. Demystifying the benefits and harms of anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2019;14:125-36. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06430518.
Quiz
Two days ago you admitted a 72-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease on dialysis who had developed new-onset atrial fibrillation causing a mild acute diastolic congestive heart failure exacerbation. Transthoracic ECG showed a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction and no significant valvular disease. After two sessions of dialysis in the hospital and initiation of a beta-blocker for control of her heart rate, she is stable and ready for discharge. Her discharge weight is 75 kg.
Which of the following recommendations should you make to this patient regarding anticoagulation for prevention of stroke and systemic embolism from atrial fibrillation?
A. Take warfarin with a international normalized ratio goal of 2.5.
B. Take apixaban 2.5 mg twice a day.
C. Take apixaban 5 mg twice a day.
D. Discuss the risks/benefits of various treatment approaches with the patient, and involve the hospital pharmacist as well as the patient’s nephrologist, cardiologist, and/or primary care provider in the decision making process to reach a consensus and to ensure a safe follow-up plan.
The best answer is D. While A, B, and C are all reasonable approaches based on the available data and current guidelines, the best approach is to involve the patient and the multidisciplinary team in the decision making process. When more clinical trial data becomes available in the future, the optimal approach to managing patients such as this one may become clearer, but until then it makes sense to take into account individual patient characteristics and patient preferences.
Warfarin or apixaban are sensible options
Warfarin or apixaban are sensible options
Case
A 78-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is hospitalized with cellulitis and is incidentally found to be in atrial fibrillation. She does not have a history of mitral stenosis, nor does she have a prosthetic valve. She does have a history of hypertension, diabetes, and prior stroke without residual deficits.
After counseling her about the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation (AFib) she makes it clear she is interested in pharmacologic therapy to minimize her risk of stroke and asks what medication you would recommend for anticoagulation.
Brief overview of the issue
Anticoagulation for AFib is indicated for stroke prophylaxis in patients with an elevated risk of stroke. The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful in calculating an individual patient’s risk of stroke and as a decision tool to determine who would benefit from anticoagulation, and it is recommended in the American Heart Association guidelines.1
Low-risk patients (CHA2DS2-VASc score of 0 in men or 1 in women) should not be started on anticoagulation for stroke prophylaxis. For anyone with a risk factor, other than being female, anticoagulation is indicated and should be considered.
The guideline recommends anticoagulant therapy, not antiplatelet agents. For most of the recent past, this has meant a vitamin K antagonist (warfarin) or sometimes a low-molecular-weight heparin injected subcutaneously. Over the past decade, however, with the approval of multiple direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), nonwarfarin oral anticoagulation has grown in popularity as the prophylactic medication of choice.2
While the data for patients with preserved renal function is robust, there is far less data to guide decision making for patients with end-stage renal disease.
Overview of the data
Until the introduction of DOACs, warfarin was the main agent used for stroke prophylaxis in patients with end-stage kidney disease and AFib. Professional guidelines favored warfarin for these patients who were mostly excluded from DOAC trials. Specialized conferences also looked at this issue.
The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference, which reviewed chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias, noted that there were no randomized controlled trials that examined the efficacy and safety of anticoagulation in chronic kidney disease patients with estimated creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min. They remarked that there was insufficient high-quality evidence to recommend warfarin for the prevention of stroke in patients with AFib and dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease.
Since, according to other trials, DOACs had better safety profiles in other populations, the conference noted that lower-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily) or rivaroxaban (15 mg daily) may be considered in this population until clinical safety data were available. Furthermore, the conference recommended that these patients be treated with a multidisciplinary approach in regards to anticoagulation and have an annual reevaluation of treatment goals, along with a risk-benefit assessment.3
Since the publication of the 2018 AHA guidelines and the guidance document that resulted from the KDIGO conference, additional research has been published comparing anticoagulation with a DOAC versus warfarin for AFib in patients with ESRD.
“Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States” was an observational, retrospective, cohort study that compared outcomes in dialysis patients who took warfarin for AFib with those who took apixaban.4 Patients’ data was taken from the U.S. Renal Data System database and were included in the final analysis if they had ESRD, a recent diagnosis of AFib or atrial flutter, and a new prescription for either warfarin or apixaban. Outcome measures were stroke or systemic embolism, major bleeding (critical site, transfusion, or death), gastrointestinal bleeding, intracranial bleeding, or death. Drug usage and compliance were assessed using Medicare Part D prescription information.
A total of 25,523 patients met the inclusion/exclusion criteria and had taken either warfarin (n = 23,172) or apixaban (n = 2,351). To account for selection bias in these cohorts, a subset of the warfarin patients was selected based on prognostic score matching. The prognostic score was calculated from the baseline characteristics (which included age, stroke history, diabetes, smoking, antiplatelet medication, liver disease, prior bleeding, and CHA2DS2-VASc score). Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analysis were used to give hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals for each outcome measure. Prespecified subgroup analyses were conducted to compare apixaban doses, where 44% were prescribed 5 mg b.i.d. and 56% were prescribed 2.5 mg b.i.d..
In the study, patients in the apixaban group had a significantly lower risk of major bleeding as compared with the warfarin group (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.59-0.87; P less than .001) with overall high rates of major bleeding in both groups at 19.7 and 22.9 per 100 patient-years in the apixaban group and warfarin group, respectively. There was no difference in the rate of stroke/systemic embolism between patients receiving apixaban and warfarin (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.69-1.12; P = .29). There was a nonsignificant trend toward decreased risk of GI bleeding in the apixaban group and no significant differences between the groups in the rates of intracranial bleeding. Apixaban was also associated with a nonsignificant trend toward lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.71-1.01; P = .06).
Notably, censoring rates because of expired prescriptions or a 1-month gap between prescriptions were high in both groups and the majority of censoring occurred within the first 12 months. Additionally, in dose specific analyses, patients receiving the 5-mg, twice-daily dose were found to have statistically significant decreases in risk of stroke/systemic embolism (P = .035) and mortality (P = .005) as compared with the 2.5-mg, twice-daily dose without significant differences in GI or intracranial bleeding.
There are three ongoing, open-label, randomized, controlled trials examining anticoagulation for nonvalvular AFib in patients with ESRD on hemodialysis with two comparing apixaban to warfarin (or derivative) and the other warfarin versus no anticoagulation.5 All trials are in adult patients with documented AFib and CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2. AKADIA (Germany based) plans to enroll 222 patients and compares a vitamin K antagonist (INR goal, 2-3) with 2.5-mg b.i.d. apixaban patients with ESRD on hemodialysis for at least 3 months with primary outcome of major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding and secondary outcome of thromboembolic events, as well as apixaban levels pre- and post hemodialysis.
RENAL-AF (U.S. based) plans to enrolled 762 patients and compares 5-mg b.i.d. apixaban (with 2.5 mg for selected patients) with warfarin in people of chronic hemodialysis with primary outcome of days to first major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding event and secondary outcome of stroke, systemic embolism, mortality, adherence and plasma apixaban levels. AVKDIAL (France based) plans to enroll 855 patients and compares no anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists in patients on hemodialysis for at least 1 month, with primary outcome of cumulative incidence of severe bleeding and thrombosis.
Application of the data to our original case
Our patient is Medicare age with ESRD and newly diagnosed nonvalvular AFib. Recent data suggests apixaban could be used for stroke prevention instead of the prior standard of care, warfarin. This approach is supported in the 2019 guidelines.1
Patients with ESRD have an increased risk of bleeding and apixaban was shown to have less bleeding complications than warfarin in this analysis. However, only standard-dose apixaban was associated with a statistically significant lower risk of stroke/systemic embolism, major bleeding, and death. Reduced-dose apixaban had a lower risk of major bleeding but no difference for stroke/systemic embolism or death. Reduced-dose apixaban is used for patients who have two out of the following three criteria: aged at least 80 years, weight of at least 60 kg, and creatinine of at least 1.5 mg/dL. Therefore, many Medicare-age patients with ESRD would not be indicated for the dose of apixaban that was shown to improve the most important outcomes of stroke/SE and death.
It may still be beneficial to use apixaban in this patient since it appears to work as well as warfarin for stroke/systemic embolism prevention with less bleeding complications.
Bottom line
For patients who have decided to pursue an anticoagulation strategy for stroke prevention in AFib and have end-stage renal disease, either warfarin or apixaban are sensible options.
Dr. Farber is a medical instructor at Duke University Health System in Durham, N.C. Dr. Stafford is a medical instructor at Duke University. Dr. Sata is assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Abdo and Dr. Menon are hospitalists at Duke University. Dr. Brooks is assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Wachter is associate medical director at Duke Regional Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Sharma is associate medical director for clinical education in hospital medicine at Duke Regional Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University.
References
1. January CT et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2019;139. doi: 1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
2. Lippi G et al. Direct oral anticoagulants: Analysis of worldwide use and popularity using Google Trends. Ann Transl Med. 2017 Aug; 5(16):322. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.06.65.
3. Turakhia MP et al. Chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Eur Heart J. 2018 Jun 21;39(24):2314-25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy060.
4. Siontis KC et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1519-29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035418.
5. Nigwekar SU et al. Long-term anticoagulation for patient receiving dialysis: Tilting the benefit-to-risk ratio? Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1530-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037091.
Key points
- According to 2019 American Heart Association guidelines, warfarin or apixaban are reasonable options for stroke prevention for patients who have end-stage renal disease and who plan for anticoagulation because of atrial fibrillation.
- Recent observational data suggests that apixaban may be safer than warfarin in this population.
- Several randomized, controlled trials are ongoing that may help determine the optimal agent to use in this setting.
- Until more definitive data is available, a reasonable approach is to discuss the risks and benefits of various treatment strategies with patients, and engage a multidisciplinary team (cardiologist, nephrologist, primary care provider, pharmacist) in the decision making process.
Additional reading
January CT et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2019;139. doi: 1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
Nigwekar SU et al. Long-term anticoagulation for patient receiving dialysis: Tilting the benefit to risk ratio? Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1530-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037091.
Garlo KG et al. Demystifying the benefits and harms of anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2019;14:125-36. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06430518.
Quiz
Two days ago you admitted a 72-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease on dialysis who had developed new-onset atrial fibrillation causing a mild acute diastolic congestive heart failure exacerbation. Transthoracic ECG showed a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction and no significant valvular disease. After two sessions of dialysis in the hospital and initiation of a beta-blocker for control of her heart rate, she is stable and ready for discharge. Her discharge weight is 75 kg.
Which of the following recommendations should you make to this patient regarding anticoagulation for prevention of stroke and systemic embolism from atrial fibrillation?
A. Take warfarin with a international normalized ratio goal of 2.5.
B. Take apixaban 2.5 mg twice a day.
C. Take apixaban 5 mg twice a day.
D. Discuss the risks/benefits of various treatment approaches with the patient, and involve the hospital pharmacist as well as the patient’s nephrologist, cardiologist, and/or primary care provider in the decision making process to reach a consensus and to ensure a safe follow-up plan.
The best answer is D. While A, B, and C are all reasonable approaches based on the available data and current guidelines, the best approach is to involve the patient and the multidisciplinary team in the decision making process. When more clinical trial data becomes available in the future, the optimal approach to managing patients such as this one may become clearer, but until then it makes sense to take into account individual patient characteristics and patient preferences.
Case
A 78-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease (ESRD) is hospitalized with cellulitis and is incidentally found to be in atrial fibrillation. She does not have a history of mitral stenosis, nor does she have a prosthetic valve. She does have a history of hypertension, diabetes, and prior stroke without residual deficits.
After counseling her about the risk of stroke associated with atrial fibrillation (AFib) she makes it clear she is interested in pharmacologic therapy to minimize her risk of stroke and asks what medication you would recommend for anticoagulation.
Brief overview of the issue
Anticoagulation for AFib is indicated for stroke prophylaxis in patients with an elevated risk of stroke. The CHA2DS2-VASc score is useful in calculating an individual patient’s risk of stroke and as a decision tool to determine who would benefit from anticoagulation, and it is recommended in the American Heart Association guidelines.1
Low-risk patients (CHA2DS2-VASc score of 0 in men or 1 in women) should not be started on anticoagulation for stroke prophylaxis. For anyone with a risk factor, other than being female, anticoagulation is indicated and should be considered.
The guideline recommends anticoagulant therapy, not antiplatelet agents. For most of the recent past, this has meant a vitamin K antagonist (warfarin) or sometimes a low-molecular-weight heparin injected subcutaneously. Over the past decade, however, with the approval of multiple direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs), nonwarfarin oral anticoagulation has grown in popularity as the prophylactic medication of choice.2
While the data for patients with preserved renal function is robust, there is far less data to guide decision making for patients with end-stage renal disease.
Overview of the data
Until the introduction of DOACs, warfarin was the main agent used for stroke prophylaxis in patients with end-stage kidney disease and AFib. Professional guidelines favored warfarin for these patients who were mostly excluded from DOAC trials. Specialized conferences also looked at this issue.
The Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference, which reviewed chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias, noted that there were no randomized controlled trials that examined the efficacy and safety of anticoagulation in chronic kidney disease patients with estimated creatinine clearance less than 30 mL/min. They remarked that there was insufficient high-quality evidence to recommend warfarin for the prevention of stroke in patients with AFib and dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease.
Since, according to other trials, DOACs had better safety profiles in other populations, the conference noted that lower-dose apixaban (2.5 mg orally twice daily) or rivaroxaban (15 mg daily) may be considered in this population until clinical safety data were available. Furthermore, the conference recommended that these patients be treated with a multidisciplinary approach in regards to anticoagulation and have an annual reevaluation of treatment goals, along with a risk-benefit assessment.3
Since the publication of the 2018 AHA guidelines and the guidance document that resulted from the KDIGO conference, additional research has been published comparing anticoagulation with a DOAC versus warfarin for AFib in patients with ESRD.
“Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States” was an observational, retrospective, cohort study that compared outcomes in dialysis patients who took warfarin for AFib with those who took apixaban.4 Patients’ data was taken from the U.S. Renal Data System database and were included in the final analysis if they had ESRD, a recent diagnosis of AFib or atrial flutter, and a new prescription for either warfarin or apixaban. Outcome measures were stroke or systemic embolism, major bleeding (critical site, transfusion, or death), gastrointestinal bleeding, intracranial bleeding, or death. Drug usage and compliance were assessed using Medicare Part D prescription information.
A total of 25,523 patients met the inclusion/exclusion criteria and had taken either warfarin (n = 23,172) or apixaban (n = 2,351). To account for selection bias in these cohorts, a subset of the warfarin patients was selected based on prognostic score matching. The prognostic score was calculated from the baseline characteristics (which included age, stroke history, diabetes, smoking, antiplatelet medication, liver disease, prior bleeding, and CHA2DS2-VASc score). Kaplan-Meier and Cox regression analysis were used to give hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals for each outcome measure. Prespecified subgroup analyses were conducted to compare apixaban doses, where 44% were prescribed 5 mg b.i.d. and 56% were prescribed 2.5 mg b.i.d..
In the study, patients in the apixaban group had a significantly lower risk of major bleeding as compared with the warfarin group (HR, 0.72; 95% CI, 0.59-0.87; P less than .001) with overall high rates of major bleeding in both groups at 19.7 and 22.9 per 100 patient-years in the apixaban group and warfarin group, respectively. There was no difference in the rate of stroke/systemic embolism between patients receiving apixaban and warfarin (HR, 0.88; 95% CI, 0.69-1.12; P = .29). There was a nonsignificant trend toward decreased risk of GI bleeding in the apixaban group and no significant differences between the groups in the rates of intracranial bleeding. Apixaban was also associated with a nonsignificant trend toward lower risk of mortality (HR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.71-1.01; P = .06).
Notably, censoring rates because of expired prescriptions or a 1-month gap between prescriptions were high in both groups and the majority of censoring occurred within the first 12 months. Additionally, in dose specific analyses, patients receiving the 5-mg, twice-daily dose were found to have statistically significant decreases in risk of stroke/systemic embolism (P = .035) and mortality (P = .005) as compared with the 2.5-mg, twice-daily dose without significant differences in GI or intracranial bleeding.
There are three ongoing, open-label, randomized, controlled trials examining anticoagulation for nonvalvular AFib in patients with ESRD on hemodialysis with two comparing apixaban to warfarin (or derivative) and the other warfarin versus no anticoagulation.5 All trials are in adult patients with documented AFib and CHA2DS2-VASc score of at least 2. AKADIA (Germany based) plans to enroll 222 patients and compares a vitamin K antagonist (INR goal, 2-3) with 2.5-mg b.i.d. apixaban patients with ESRD on hemodialysis for at least 3 months with primary outcome of major and clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding and secondary outcome of thromboembolic events, as well as apixaban levels pre- and post hemodialysis.
RENAL-AF (U.S. based) plans to enrolled 762 patients and compares 5-mg b.i.d. apixaban (with 2.5 mg for selected patients) with warfarin in people of chronic hemodialysis with primary outcome of days to first major or clinically relevant nonmajor bleeding event and secondary outcome of stroke, systemic embolism, mortality, adherence and plasma apixaban levels. AVKDIAL (France based) plans to enroll 855 patients and compares no anticoagulation with vitamin K antagonists in patients on hemodialysis for at least 1 month, with primary outcome of cumulative incidence of severe bleeding and thrombosis.
Application of the data to our original case
Our patient is Medicare age with ESRD and newly diagnosed nonvalvular AFib. Recent data suggests apixaban could be used for stroke prevention instead of the prior standard of care, warfarin. This approach is supported in the 2019 guidelines.1
Patients with ESRD have an increased risk of bleeding and apixaban was shown to have less bleeding complications than warfarin in this analysis. However, only standard-dose apixaban was associated with a statistically significant lower risk of stroke/systemic embolism, major bleeding, and death. Reduced-dose apixaban had a lower risk of major bleeding but no difference for stroke/systemic embolism or death. Reduced-dose apixaban is used for patients who have two out of the following three criteria: aged at least 80 years, weight of at least 60 kg, and creatinine of at least 1.5 mg/dL. Therefore, many Medicare-age patients with ESRD would not be indicated for the dose of apixaban that was shown to improve the most important outcomes of stroke/SE and death.
It may still be beneficial to use apixaban in this patient since it appears to work as well as warfarin for stroke/systemic embolism prevention with less bleeding complications.
Bottom line
For patients who have decided to pursue an anticoagulation strategy for stroke prevention in AFib and have end-stage renal disease, either warfarin or apixaban are sensible options.
Dr. Farber is a medical instructor at Duke University Health System in Durham, N.C. Dr. Stafford is a medical instructor at Duke University. Dr. Sata is assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Abdo and Dr. Menon are hospitalists at Duke University. Dr. Brooks is assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Wachter is associate medical director at Duke Regional Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University. Dr. Sharma is associate medical director for clinical education in hospital medicine at Duke Regional Hospital and assistant professor of medicine at Duke University.
References
1. January CT et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2019;139. doi: 1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
2. Lippi G et al. Direct oral anticoagulants: Analysis of worldwide use and popularity using Google Trends. Ann Transl Med. 2017 Aug; 5(16):322. doi: 10.21037/atm.2017.06.65.
3. Turakhia MP et al. Chronic kidney disease and arrhythmias: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Controversies Conference. Eur Heart J. 2018 Jun 21;39(24):2314-25. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehy060.
4. Siontis KC et al. Outcomes associated with apixaban use in patients with end-stage kidney disease and atrial fibrillation in the United States. Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1519-29. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.035418.
5. Nigwekar SU et al. Long-term anticoagulation for patient receiving dialysis: Tilting the benefit-to-risk ratio? Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1530-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037091.
Key points
- According to 2019 American Heart Association guidelines, warfarin or apixaban are reasonable options for stroke prevention for patients who have end-stage renal disease and who plan for anticoagulation because of atrial fibrillation.
- Recent observational data suggests that apixaban may be safer than warfarin in this population.
- Several randomized, controlled trials are ongoing that may help determine the optimal agent to use in this setting.
- Until more definitive data is available, a reasonable approach is to discuss the risks and benefits of various treatment strategies with patients, and engage a multidisciplinary team (cardiologist, nephrologist, primary care provider, pharmacist) in the decision making process.
Additional reading
January CT et al. 2019 AHA/ACC/HRS focused update of the 2014 AHA/ACC/HRS guideline for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: A report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines and the Heart Rhythm Society. Circulation. 2019;139. doi: 1161/CIR.0000000000000665.
Nigwekar SU et al. Long-term anticoagulation for patient receiving dialysis: Tilting the benefit to risk ratio? Circulation. 2018 Oct 9;138(15):1530-3. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.037091.
Garlo KG et al. Demystifying the benefits and harms of anticoagulation for atrial fibrillation in chronic kidney disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 2019;14:125-36. doi: 10.2215/CJN.06430518.
Quiz
Two days ago you admitted a 72-year-old woman with end-stage renal disease on dialysis who had developed new-onset atrial fibrillation causing a mild acute diastolic congestive heart failure exacerbation. Transthoracic ECG showed a preserved left ventricular ejection fraction and no significant valvular disease. After two sessions of dialysis in the hospital and initiation of a beta-blocker for control of her heart rate, she is stable and ready for discharge. Her discharge weight is 75 kg.
Which of the following recommendations should you make to this patient regarding anticoagulation for prevention of stroke and systemic embolism from atrial fibrillation?
A. Take warfarin with a international normalized ratio goal of 2.5.
B. Take apixaban 2.5 mg twice a day.
C. Take apixaban 5 mg twice a day.
D. Discuss the risks/benefits of various treatment approaches with the patient, and involve the hospital pharmacist as well as the patient’s nephrologist, cardiologist, and/or primary care provider in the decision making process to reach a consensus and to ensure a safe follow-up plan.
The best answer is D. While A, B, and C are all reasonable approaches based on the available data and current guidelines, the best approach is to involve the patient and the multidisciplinary team in the decision making process. When more clinical trial data becomes available in the future, the optimal approach to managing patients such as this one may become clearer, but until then it makes sense to take into account individual patient characteristics and patient preferences.
FUO, pneumonia often distinguishes influenza from RSV in hospitalized young children
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – as the cause of hospitalization in infants and young children, Cihan Papan, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Papan, a pediatrician at University Children’s Hospital Mannheim (Germany) and Heidelberg (Germany) University, presented a retrospective single-center study of all 573 children aged under 2 years hospitalized over the course of several seasons for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or influenza as confirmed by rapid antigen testing. Even though these are two of the leading causes of hospitalization among young children, there is surprisingly sparse data comparing the two in terms of disease severity and hospital resource utilization, including antibiotic consumption. That information gap provided the basis for this study.
There were 476 children with confirmed RSV, 96 with influenza, and 1 RSV/influenza coinfection. Notably, even though the RSV group had lower temperatures and C-reactive protein levels, they were nevertheless more likely to be treated with antibiotics, by a margin of 29% to 23%.
“These findings open new possibilities for antimicrobial stewardship in these groups of virally infected children,” observed Dr. Papan.
Fever of unknown origin was present in 68.8% of the influenza-positive patients, compared with just 0.2% of the RSV-positive children. In contrast, 50.2% of the RSV group had pneumonia and 49.6% had bronchitis or bronchiolitis, versus just 22.9% and 6.3% of the influenza patients, respectively. A larger proportion of the young children with RSV infection presented in a severely ill–looking condition. Children with RSV infection also were significantly younger.
Dr. Papan reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – as the cause of hospitalization in infants and young children, Cihan Papan, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Papan, a pediatrician at University Children’s Hospital Mannheim (Germany) and Heidelberg (Germany) University, presented a retrospective single-center study of all 573 children aged under 2 years hospitalized over the course of several seasons for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or influenza as confirmed by rapid antigen testing. Even though these are two of the leading causes of hospitalization among young children, there is surprisingly sparse data comparing the two in terms of disease severity and hospital resource utilization, including antibiotic consumption. That information gap provided the basis for this study.
There were 476 children with confirmed RSV, 96 with influenza, and 1 RSV/influenza coinfection. Notably, even though the RSV group had lower temperatures and C-reactive protein levels, they were nevertheless more likely to be treated with antibiotics, by a margin of 29% to 23%.
“These findings open new possibilities for antimicrobial stewardship in these groups of virally infected children,” observed Dr. Papan.
Fever of unknown origin was present in 68.8% of the influenza-positive patients, compared with just 0.2% of the RSV-positive children. In contrast, 50.2% of the RSV group had pneumonia and 49.6% had bronchitis or bronchiolitis, versus just 22.9% and 6.3% of the influenza patients, respectively. A larger proportion of the young children with RSV infection presented in a severely ill–looking condition. Children with RSV infection also were significantly younger.
Dr. Papan reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
LJUBLJANA, SLOVENIA – as the cause of hospitalization in infants and young children, Cihan Papan, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the European Society for Paediatric Infectious Diseases.
Dr. Papan, a pediatrician at University Children’s Hospital Mannheim (Germany) and Heidelberg (Germany) University, presented a retrospective single-center study of all 573 children aged under 2 years hospitalized over the course of several seasons for respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) or influenza as confirmed by rapid antigen testing. Even though these are two of the leading causes of hospitalization among young children, there is surprisingly sparse data comparing the two in terms of disease severity and hospital resource utilization, including antibiotic consumption. That information gap provided the basis for this study.
There were 476 children with confirmed RSV, 96 with influenza, and 1 RSV/influenza coinfection. Notably, even though the RSV group had lower temperatures and C-reactive protein levels, they were nevertheless more likely to be treated with antibiotics, by a margin of 29% to 23%.
“These findings open new possibilities for antimicrobial stewardship in these groups of virally infected children,” observed Dr. Papan.
Fever of unknown origin was present in 68.8% of the influenza-positive patients, compared with just 0.2% of the RSV-positive children. In contrast, 50.2% of the RSV group had pneumonia and 49.6% had bronchitis or bronchiolitis, versus just 22.9% and 6.3% of the influenza patients, respectively. A larger proportion of the young children with RSV infection presented in a severely ill–looking condition. Children with RSV infection also were significantly younger.
Dr. Papan reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study.
REPORTING FROM ESPID 2019
Treating children with Kawasaki disease and coronary enlargement
IVIG plus steroids or infliximab, or IVIG alone?
Clinical question
Does use of corticosteroids or infliximab in addition to intravenous immunoglobulin improve cardiac outcomes in children with Kawasaki disease and enlarged coronary arteries?
Background
Kawasaki disease is a medium-vessel vasculitis primarily of young children. While the underlying cause remains unknown, treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) substantially lowers the risk of coronary artery aneurysms (CAA), the most serious sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Recent studies have suggested that – in cases of high-risk or treatment-resistant Kawasaki disease – using an immunomodulator, such as a corticosteroid or a TNF-alpha blocker, may improve outcomes, though these studies involved relatively small and homogeneous patient populations. It is unknown if these medications could prevent progression of CAA.
Study design
Retrospective multicenter study.
Setting
Two freestanding children’s hospitals and one mother-child hospital.
Synopsis
The study identified 121 children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease with CAA (z score 2.5-10) from 2008 through 2017 treated at the three study hospitals. Children with giant CAA at the time of diagnosis (z score greater than 10) or significant preexisting congenital heart disease were excluded.
All study hospitals had protocols for treatment of Kawasaki disease: Center 1 used IVIG and corticosteroids, Center 2 used IVIG and infliximab, and Center 3 used IVIG alone. Patients at all centers also received aspirin. Center 1 used methylprednisolone IV initially, changing to oral prednisolone after clinical improvement. The researchers reviewed the charts of each patient and classified them as having complete or incomplete Kawasaki disease. They assigned z scores for CAA size based on both initial and follow-up echocardiograms. The primary outcome was change in z score of CAA over the first year.
The population of patients treated at each center was significantly different. Center 1 reported older patients (median age 2.6 vs. 2.0 and 1.1), as well as a higher rate of male patients (83% vs. 77% and 58%). However, there was no difference in baseline z scores between centers. Patients who initially received IVIG and corticosteroids were less likely to require additional therapy because of persistent fever versus those receiving IVIG only, or IVIG and infliximab (0% vs. 21% vs. 14%, P = .03).
Patients receiving IVIG and corticosteroids, or IVIG and infliximab, were less likely to have progression of CAA size, with 23% and 24% having an increase in z score of more than 1 versus 58% of those who received IVIG alone. No group had significant differences in maximum z score, the rate of giant aneurysms, or the rate of regression of CAA.
Bottom line
Using IVIG + corticosteroids or IVIG + infliximab versus IVIG alone for children with Kawasaki disease with coronary artery aneurysms decreases the rate of aneurysm enlargement.
Citation
Dionne A et al. Treatment intensification in patients with Kawasaki disease and coronary aneurysm at diagnosis. Pediatrics. May 2019:e20183341. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3341.
Dr. Stubblefield is a pediatric hospitalist at Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del., and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
IVIG plus steroids or infliximab, or IVIG alone?
IVIG plus steroids or infliximab, or IVIG alone?
Clinical question
Does use of corticosteroids or infliximab in addition to intravenous immunoglobulin improve cardiac outcomes in children with Kawasaki disease and enlarged coronary arteries?
Background
Kawasaki disease is a medium-vessel vasculitis primarily of young children. While the underlying cause remains unknown, treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) substantially lowers the risk of coronary artery aneurysms (CAA), the most serious sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Recent studies have suggested that – in cases of high-risk or treatment-resistant Kawasaki disease – using an immunomodulator, such as a corticosteroid or a TNF-alpha blocker, may improve outcomes, though these studies involved relatively small and homogeneous patient populations. It is unknown if these medications could prevent progression of CAA.
Study design
Retrospective multicenter study.
Setting
Two freestanding children’s hospitals and one mother-child hospital.
Synopsis
The study identified 121 children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease with CAA (z score 2.5-10) from 2008 through 2017 treated at the three study hospitals. Children with giant CAA at the time of diagnosis (z score greater than 10) or significant preexisting congenital heart disease were excluded.
All study hospitals had protocols for treatment of Kawasaki disease: Center 1 used IVIG and corticosteroids, Center 2 used IVIG and infliximab, and Center 3 used IVIG alone. Patients at all centers also received aspirin. Center 1 used methylprednisolone IV initially, changing to oral prednisolone after clinical improvement. The researchers reviewed the charts of each patient and classified them as having complete or incomplete Kawasaki disease. They assigned z scores for CAA size based on both initial and follow-up echocardiograms. The primary outcome was change in z score of CAA over the first year.
The population of patients treated at each center was significantly different. Center 1 reported older patients (median age 2.6 vs. 2.0 and 1.1), as well as a higher rate of male patients (83% vs. 77% and 58%). However, there was no difference in baseline z scores between centers. Patients who initially received IVIG and corticosteroids were less likely to require additional therapy because of persistent fever versus those receiving IVIG only, or IVIG and infliximab (0% vs. 21% vs. 14%, P = .03).
Patients receiving IVIG and corticosteroids, or IVIG and infliximab, were less likely to have progression of CAA size, with 23% and 24% having an increase in z score of more than 1 versus 58% of those who received IVIG alone. No group had significant differences in maximum z score, the rate of giant aneurysms, or the rate of regression of CAA.
Bottom line
Using IVIG + corticosteroids or IVIG + infliximab versus IVIG alone for children with Kawasaki disease with coronary artery aneurysms decreases the rate of aneurysm enlargement.
Citation
Dionne A et al. Treatment intensification in patients with Kawasaki disease and coronary aneurysm at diagnosis. Pediatrics. May 2019:e20183341. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3341.
Dr. Stubblefield is a pediatric hospitalist at Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del., and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.
Clinical question
Does use of corticosteroids or infliximab in addition to intravenous immunoglobulin improve cardiac outcomes in children with Kawasaki disease and enlarged coronary arteries?
Background
Kawasaki disease is a medium-vessel vasculitis primarily of young children. While the underlying cause remains unknown, treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) substantially lowers the risk of coronary artery aneurysms (CAA), the most serious sequelae of Kawasaki disease. Recent studies have suggested that – in cases of high-risk or treatment-resistant Kawasaki disease – using an immunomodulator, such as a corticosteroid or a TNF-alpha blocker, may improve outcomes, though these studies involved relatively small and homogeneous patient populations. It is unknown if these medications could prevent progression of CAA.
Study design
Retrospective multicenter study.
Setting
Two freestanding children’s hospitals and one mother-child hospital.
Synopsis
The study identified 121 children diagnosed with Kawasaki disease with CAA (z score 2.5-10) from 2008 through 2017 treated at the three study hospitals. Children with giant CAA at the time of diagnosis (z score greater than 10) or significant preexisting congenital heart disease were excluded.
All study hospitals had protocols for treatment of Kawasaki disease: Center 1 used IVIG and corticosteroids, Center 2 used IVIG and infliximab, and Center 3 used IVIG alone. Patients at all centers also received aspirin. Center 1 used methylprednisolone IV initially, changing to oral prednisolone after clinical improvement. The researchers reviewed the charts of each patient and classified them as having complete or incomplete Kawasaki disease. They assigned z scores for CAA size based on both initial and follow-up echocardiograms. The primary outcome was change in z score of CAA over the first year.
The population of patients treated at each center was significantly different. Center 1 reported older patients (median age 2.6 vs. 2.0 and 1.1), as well as a higher rate of male patients (83% vs. 77% and 58%). However, there was no difference in baseline z scores between centers. Patients who initially received IVIG and corticosteroids were less likely to require additional therapy because of persistent fever versus those receiving IVIG only, or IVIG and infliximab (0% vs. 21% vs. 14%, P = .03).
Patients receiving IVIG and corticosteroids, or IVIG and infliximab, were less likely to have progression of CAA size, with 23% and 24% having an increase in z score of more than 1 versus 58% of those who received IVIG alone. No group had significant differences in maximum z score, the rate of giant aneurysms, or the rate of regression of CAA.
Bottom line
Using IVIG + corticosteroids or IVIG + infliximab versus IVIG alone for children with Kawasaki disease with coronary artery aneurysms decreases the rate of aneurysm enlargement.
Citation
Dionne A et al. Treatment intensification in patients with Kawasaki disease and coronary aneurysm at diagnosis. Pediatrics. May 2019:e20183341. doi: 10.1542/peds.2018-3341.
Dr. Stubblefield is a pediatric hospitalist at Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del., and clinical assistant professor of pediatrics at Sidney Kimmel Medical College at Thomas Jefferson University in Philadelphia.