User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]
div[contains(@class, 'medstat-accordion-set article-series')]
Immunocompromised patients should receive fourth COVID shot: CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention contacted pharmacies on Jan. 26 to reinforce the message that people with moderate to severe immune suppression should receive a fourth COVID-19 vaccine, according to Kaiser Health News.
The conference call came a day after the news outlet reported that immunocompromised people were being turned away by pharmacies. White House officials also emphasized on Jan. 26 that immunocompromised people should receive an additional shot.
During the call, the CDC “reiterated the recommendations, running through case examples,” Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates for the American Pharmacists Association, told KHN.
While on the call, Mr. Rothholz asked for a “prepared document” with the CDC’s recommendations “so we can clearly and consistently communicate the message.” The CDC officials on the call said they would create a document but “don’t know how long that will take,” Mr. Rothholz told KHN.
The CDC recommends an additional shot -– or a fourth shot – for those who have weak immune systems, which makes them more at risk for severe COVID-19 and death. About 7 million American adults are considered immunocompromised, KHN reported, which includes people who have certain medical conditions that impair their immune response or who take immune-suppressing drugs because of organ transplants, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
The CDC first recommended fourth shots for immunocompromised people in October. This month, the CDC shortened the time for booster shots from 6 months to 5 months, and some immunocompromised people who are due for another shot have begun to seek them. The agency has been educating pharmacists and other health providers since then, a CDC spokesperson told KHN.
While patients don’t need to provide proof that they are immunocompromised, according to the CDC, some have been turned away, KHN reported.
To improve communication with the public, large pharmacies could issue news releases and update their websites “explicitly stating that they are offering fourth doses” to immunocompromised people, Ameet Kini, MD, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago, told KHN.
Pharmacies should also update their patient portals and provide “clear guidance for their pharmacists,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention contacted pharmacies on Jan. 26 to reinforce the message that people with moderate to severe immune suppression should receive a fourth COVID-19 vaccine, according to Kaiser Health News.
The conference call came a day after the news outlet reported that immunocompromised people were being turned away by pharmacies. White House officials also emphasized on Jan. 26 that immunocompromised people should receive an additional shot.
During the call, the CDC “reiterated the recommendations, running through case examples,” Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates for the American Pharmacists Association, told KHN.
While on the call, Mr. Rothholz asked for a “prepared document” with the CDC’s recommendations “so we can clearly and consistently communicate the message.” The CDC officials on the call said they would create a document but “don’t know how long that will take,” Mr. Rothholz told KHN.
The CDC recommends an additional shot -– or a fourth shot – for those who have weak immune systems, which makes them more at risk for severe COVID-19 and death. About 7 million American adults are considered immunocompromised, KHN reported, which includes people who have certain medical conditions that impair their immune response or who take immune-suppressing drugs because of organ transplants, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
The CDC first recommended fourth shots for immunocompromised people in October. This month, the CDC shortened the time for booster shots from 6 months to 5 months, and some immunocompromised people who are due for another shot have begun to seek them. The agency has been educating pharmacists and other health providers since then, a CDC spokesperson told KHN.
While patients don’t need to provide proof that they are immunocompromised, according to the CDC, some have been turned away, KHN reported.
To improve communication with the public, large pharmacies could issue news releases and update their websites “explicitly stating that they are offering fourth doses” to immunocompromised people, Ameet Kini, MD, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago, told KHN.
Pharmacies should also update their patient portals and provide “clear guidance for their pharmacists,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention contacted pharmacies on Jan. 26 to reinforce the message that people with moderate to severe immune suppression should receive a fourth COVID-19 vaccine, according to Kaiser Health News.
The conference call came a day after the news outlet reported that immunocompromised people were being turned away by pharmacies. White House officials also emphasized on Jan. 26 that immunocompromised people should receive an additional shot.
During the call, the CDC “reiterated the recommendations, running through case examples,” Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates for the American Pharmacists Association, told KHN.
While on the call, Mr. Rothholz asked for a “prepared document” with the CDC’s recommendations “so we can clearly and consistently communicate the message.” The CDC officials on the call said they would create a document but “don’t know how long that will take,” Mr. Rothholz told KHN.
The CDC recommends an additional shot -– or a fourth shot – for those who have weak immune systems, which makes them more at risk for severe COVID-19 and death. About 7 million American adults are considered immunocompromised, KHN reported, which includes people who have certain medical conditions that impair their immune response or who take immune-suppressing drugs because of organ transplants, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
The CDC first recommended fourth shots for immunocompromised people in October. This month, the CDC shortened the time for booster shots from 6 months to 5 months, and some immunocompromised people who are due for another shot have begun to seek them. The agency has been educating pharmacists and other health providers since then, a CDC spokesperson told KHN.
While patients don’t need to provide proof that they are immunocompromised, according to the CDC, some have been turned away, KHN reported.
To improve communication with the public, large pharmacies could issue news releases and update their websites “explicitly stating that they are offering fourth doses” to immunocompromised people, Ameet Kini, MD, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago, told KHN.
Pharmacies should also update their patient portals and provide “clear guidance for their pharmacists,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Get free masks at grocery stores and pharmacies starting Jan. 28
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another winter for our discontent
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
'The whitest specialty,' revisited
A recent STAT article by Usha Lee McFarling identified orthopedic surgery as “the whitest specialty.” That’s a problem many, perhaps most, orthopedic surgeons are aware of. But seeing it stated so bluntly is jolting. It’s disconcerting to think that the orthopedic community is making so little progress toward achieving the principal ideal articulated in our country’s fundamental declaration of moral values: that all people are created equal and that they have inalienable rights – in our case, that everyone, Black, brown, as well as White, has the right to the same high level of medical care.
Unfortunately, as study after study has shown, minorities do not enjoy the right to equitable care. Instead, they are subject to disparities in treatment and outcomes that speak to the prejudices that are built into the health care system and are present – sometimes consciously, but most often subconsciously – in the minds of physicians. One important contributing element to these disparities is the paucity of minority practitioners. Studies have also shown that Black patients, for example, respond better to Black physicians, who so often share a psychological and cultural sympathy unavailable to most White physicians. It’s for that reason that being identified as “the whitest specialty” is so immensely troubling.
In researching her STAT article, Ms. McFarling spoke with American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons leaders, practicing surgeons, residents, and med students about the dearth of minority and female orthopedic surgeons. What she heard was perplexity and frustration about why better progress hasn’t been made toward correcting the gross underrepresentation of everyone other than White men. The AAOS, she noted, was one of the first specialties to recognize the lack of diversity and over the years has put in great effort to address the problem, creating task forces, committees, and diversity awards and sponsoring conferences and discussions. Yet progress has been glacial, at best.
From her respondents, Ms. McFarling heard an array of reasons for this. Black, Hispanic, and Native American persons are underrepresented in medical schools, so the pool of potential applicants for orthopedic residencies is shallow to begin with. STEM studies are notoriously inadequate in poorer primary and secondary schools, in which so many minority students are educated. The MCAT and USMLE Step 1 test, which play a role in acceptance to residencies, have been shown to be biased. The specialty has few Black or brown role models and, consequently, few advocates and a lack of mentorship. Overt bias may be fairly rare (though microaggressions are still a common and ongoing problem), but most minority and female orthopedic surgeons feel strongly that implicit or subconscious bias is entrenched and works against acceptance to residencies, success in residencies, and advancement in the field.
One of this article’s authors (AW) saw all these factors at work as a resident, then as an admissions committee member at both Yale and Harvard. But the fact is that other medical specialties face exactly these problems and barriers, and yet have been substantially more successful in overcoming them.
What seems to be distinctive about orthopedics is that the mindset which perpetuated (and still perpetuates) In this regard, Kristy Weber, MD, the first female president of the AAOS, told Ms. McFarling that the critical first step to bringing in more women or people of color is changing the culture. There seems to be a consensus about that.
So, what does that mean, given that the AAOS has made serious efforts in that regard that have clearly been less than effective?
The answer, as we see it, is first – to not give in to frustration. The time frames involved in changing customary states of mind are typically elongated, and the deeper the habituation, the longer transformation takes. Deep changes always mean a long, hard slog. For transformations of this sort to take place, the requirements are a general agreement on the value of the transformation, exposure to the destructive consequences of the customary modus operandi, and persuasion for why change needs to happen.
In orthopedics, the first requirement has been met. The AAOS espouses diversity and inclusion as a high-level value. In terms of the second two requirements – exposure and persuasion – orthopedic surgeons have been witness to events, campaigns, conferences, et cetera. But these have not been enough, which means that efforts need to be focused, enlarged, sustained, determined, and innovative.
Does the orthopedic surgery community have the ability to do that?
The answer is: Yes, it does.
Currently the orthopedic surgeon community boasts a number of organizations, groups, and individuals pushing for change, in addition to the AAOS’s Diversity Advisory Board. The predominantly African American J. Robert Gladden Orthopaedic Society, the Ruth Jackson Orthopaedic Society of female orthopedic physicians, and the Association of Latino Orthopaedic Surgeons are all energetic advocates, as is Nth Dimensions, the Perry Initiative, and various ad hoc and individual endeavors.
These are all strong proponents for their own groups in their own way. But history has shown in so many cases that concerted rather than individual action empowers advocacy, and what orthopedic surgery needs in its current situation of gross underrepresentation of minorities and women is an enhanced campaign to raise awareness and redouble persuasion.
One of many examples of the power of collective action is the Association of Minority Health Professions Schools founded by Dr. Louis Sullivan in 1977.* Dr. Sullivan (later secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services) was at that time the founding dean of Morehouse School of Medicine. Morehouse had been launched on a shoestring and needed funding urgently. Other Black health schools, such as Meharry Medical College and Tuskegee College of Veterinary Medicine, were in even more pressing financial need. The coalition of schools that Dr. Sullivan organized became a powerful force in Congress and the National Institutes of Health, magnitudes more effective in raising funds from government and other sources than the best individual efforts of the separate institutions.
Dr. Sullivan’s association is only one of a multitude of historical examples of the effectiveness of unified action. AAOS currently has no single officer charged with bringing together the efforts of the change assets that already exist. It could, perhaps should, have someone in that position. AAOS could invest that same office with a mandate to survey the other medical specialties and bring to bear the most effective diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) practices in their arsenals.
Finally, despite the attention AAOS has brought to DEI needs, a look at the organization’s strategic goals, its core values, and its “key enablers” finds not a single mention of diversity or inclusion. Given the country’s current focus on the need for equality, given the poor performance of the orthopedic surgery specialty in terms of inclusion, the obvious question is: Should there not be an official declaration positing diversity as a primary AAOS desideratum?
There is recent precedent for this in the American College of Physicians/American Board of Internal Medicine’s Physician Charter on Professionalism, which includes “social justice” as a primary goal of medical practice. This highlights and reinforces the humanitarian strivings of the profession. In light of the paralysis illuminated by Ms. McFarling’s STAT article, a clear, concise declaration by the AAOS of the value and need for DEI as a central component of the organization’s values should be high on the AAOS order of business. A commitment in that form would serve as a powerful catalyst for bringing orthopedic surgery into step with its sister specialties, as well as affirming the core egalitarian principle that underlies all of medical care.
Dr. White is the Ellen and Melvin Gordon Distinguished Professor of Medical Education and Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Chanoff is a founding board member of the Augustus A. White III Institute for Healthcare Equity. Neither Dr. White nor Dr. Chanoff reported any conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 2/1/22: An earlier version of this article omitted the title of "Dr." before Dr. Louis Sullivan's name.
A recent STAT article by Usha Lee McFarling identified orthopedic surgery as “the whitest specialty.” That’s a problem many, perhaps most, orthopedic surgeons are aware of. But seeing it stated so bluntly is jolting. It’s disconcerting to think that the orthopedic community is making so little progress toward achieving the principal ideal articulated in our country’s fundamental declaration of moral values: that all people are created equal and that they have inalienable rights – in our case, that everyone, Black, brown, as well as White, has the right to the same high level of medical care.
Unfortunately, as study after study has shown, minorities do not enjoy the right to equitable care. Instead, they are subject to disparities in treatment and outcomes that speak to the prejudices that are built into the health care system and are present – sometimes consciously, but most often subconsciously – in the minds of physicians. One important contributing element to these disparities is the paucity of minority practitioners. Studies have also shown that Black patients, for example, respond better to Black physicians, who so often share a psychological and cultural sympathy unavailable to most White physicians. It’s for that reason that being identified as “the whitest specialty” is so immensely troubling.
In researching her STAT article, Ms. McFarling spoke with American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons leaders, practicing surgeons, residents, and med students about the dearth of minority and female orthopedic surgeons. What she heard was perplexity and frustration about why better progress hasn’t been made toward correcting the gross underrepresentation of everyone other than White men. The AAOS, she noted, was one of the first specialties to recognize the lack of diversity and over the years has put in great effort to address the problem, creating task forces, committees, and diversity awards and sponsoring conferences and discussions. Yet progress has been glacial, at best.
From her respondents, Ms. McFarling heard an array of reasons for this. Black, Hispanic, and Native American persons are underrepresented in medical schools, so the pool of potential applicants for orthopedic residencies is shallow to begin with. STEM studies are notoriously inadequate in poorer primary and secondary schools, in which so many minority students are educated. The MCAT and USMLE Step 1 test, which play a role in acceptance to residencies, have been shown to be biased. The specialty has few Black or brown role models and, consequently, few advocates and a lack of mentorship. Overt bias may be fairly rare (though microaggressions are still a common and ongoing problem), but most minority and female orthopedic surgeons feel strongly that implicit or subconscious bias is entrenched and works against acceptance to residencies, success in residencies, and advancement in the field.
One of this article’s authors (AW) saw all these factors at work as a resident, then as an admissions committee member at both Yale and Harvard. But the fact is that other medical specialties face exactly these problems and barriers, and yet have been substantially more successful in overcoming them.
What seems to be distinctive about orthopedics is that the mindset which perpetuated (and still perpetuates) In this regard, Kristy Weber, MD, the first female president of the AAOS, told Ms. McFarling that the critical first step to bringing in more women or people of color is changing the culture. There seems to be a consensus about that.
So, what does that mean, given that the AAOS has made serious efforts in that regard that have clearly been less than effective?
The answer, as we see it, is first – to not give in to frustration. The time frames involved in changing customary states of mind are typically elongated, and the deeper the habituation, the longer transformation takes. Deep changes always mean a long, hard slog. For transformations of this sort to take place, the requirements are a general agreement on the value of the transformation, exposure to the destructive consequences of the customary modus operandi, and persuasion for why change needs to happen.
In orthopedics, the first requirement has been met. The AAOS espouses diversity and inclusion as a high-level value. In terms of the second two requirements – exposure and persuasion – orthopedic surgeons have been witness to events, campaigns, conferences, et cetera. But these have not been enough, which means that efforts need to be focused, enlarged, sustained, determined, and innovative.
Does the orthopedic surgery community have the ability to do that?
The answer is: Yes, it does.
Currently the orthopedic surgeon community boasts a number of organizations, groups, and individuals pushing for change, in addition to the AAOS’s Diversity Advisory Board. The predominantly African American J. Robert Gladden Orthopaedic Society, the Ruth Jackson Orthopaedic Society of female orthopedic physicians, and the Association of Latino Orthopaedic Surgeons are all energetic advocates, as is Nth Dimensions, the Perry Initiative, and various ad hoc and individual endeavors.
These are all strong proponents for their own groups in their own way. But history has shown in so many cases that concerted rather than individual action empowers advocacy, and what orthopedic surgery needs in its current situation of gross underrepresentation of minorities and women is an enhanced campaign to raise awareness and redouble persuasion.
One of many examples of the power of collective action is the Association of Minority Health Professions Schools founded by Dr. Louis Sullivan in 1977.* Dr. Sullivan (later secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services) was at that time the founding dean of Morehouse School of Medicine. Morehouse had been launched on a shoestring and needed funding urgently. Other Black health schools, such as Meharry Medical College and Tuskegee College of Veterinary Medicine, were in even more pressing financial need. The coalition of schools that Dr. Sullivan organized became a powerful force in Congress and the National Institutes of Health, magnitudes more effective in raising funds from government and other sources than the best individual efforts of the separate institutions.
Dr. Sullivan’s association is only one of a multitude of historical examples of the effectiveness of unified action. AAOS currently has no single officer charged with bringing together the efforts of the change assets that already exist. It could, perhaps should, have someone in that position. AAOS could invest that same office with a mandate to survey the other medical specialties and bring to bear the most effective diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) practices in their arsenals.
Finally, despite the attention AAOS has brought to DEI needs, a look at the organization’s strategic goals, its core values, and its “key enablers” finds not a single mention of diversity or inclusion. Given the country’s current focus on the need for equality, given the poor performance of the orthopedic surgery specialty in terms of inclusion, the obvious question is: Should there not be an official declaration positing diversity as a primary AAOS desideratum?
There is recent precedent for this in the American College of Physicians/American Board of Internal Medicine’s Physician Charter on Professionalism, which includes “social justice” as a primary goal of medical practice. This highlights and reinforces the humanitarian strivings of the profession. In light of the paralysis illuminated by Ms. McFarling’s STAT article, a clear, concise declaration by the AAOS of the value and need for DEI as a central component of the organization’s values should be high on the AAOS order of business. A commitment in that form would serve as a powerful catalyst for bringing orthopedic surgery into step with its sister specialties, as well as affirming the core egalitarian principle that underlies all of medical care.
Dr. White is the Ellen and Melvin Gordon Distinguished Professor of Medical Education and Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Chanoff is a founding board member of the Augustus A. White III Institute for Healthcare Equity. Neither Dr. White nor Dr. Chanoff reported any conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 2/1/22: An earlier version of this article omitted the title of "Dr." before Dr. Louis Sullivan's name.
A recent STAT article by Usha Lee McFarling identified orthopedic surgery as “the whitest specialty.” That’s a problem many, perhaps most, orthopedic surgeons are aware of. But seeing it stated so bluntly is jolting. It’s disconcerting to think that the orthopedic community is making so little progress toward achieving the principal ideal articulated in our country’s fundamental declaration of moral values: that all people are created equal and that they have inalienable rights – in our case, that everyone, Black, brown, as well as White, has the right to the same high level of medical care.
Unfortunately, as study after study has shown, minorities do not enjoy the right to equitable care. Instead, they are subject to disparities in treatment and outcomes that speak to the prejudices that are built into the health care system and are present – sometimes consciously, but most often subconsciously – in the minds of physicians. One important contributing element to these disparities is the paucity of minority practitioners. Studies have also shown that Black patients, for example, respond better to Black physicians, who so often share a psychological and cultural sympathy unavailable to most White physicians. It’s for that reason that being identified as “the whitest specialty” is so immensely troubling.
In researching her STAT article, Ms. McFarling spoke with American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons leaders, practicing surgeons, residents, and med students about the dearth of minority and female orthopedic surgeons. What she heard was perplexity and frustration about why better progress hasn’t been made toward correcting the gross underrepresentation of everyone other than White men. The AAOS, she noted, was one of the first specialties to recognize the lack of diversity and over the years has put in great effort to address the problem, creating task forces, committees, and diversity awards and sponsoring conferences and discussions. Yet progress has been glacial, at best.
From her respondents, Ms. McFarling heard an array of reasons for this. Black, Hispanic, and Native American persons are underrepresented in medical schools, so the pool of potential applicants for orthopedic residencies is shallow to begin with. STEM studies are notoriously inadequate in poorer primary and secondary schools, in which so many minority students are educated. The MCAT and USMLE Step 1 test, which play a role in acceptance to residencies, have been shown to be biased. The specialty has few Black or brown role models and, consequently, few advocates and a lack of mentorship. Overt bias may be fairly rare (though microaggressions are still a common and ongoing problem), but most minority and female orthopedic surgeons feel strongly that implicit or subconscious bias is entrenched and works against acceptance to residencies, success in residencies, and advancement in the field.
One of this article’s authors (AW) saw all these factors at work as a resident, then as an admissions committee member at both Yale and Harvard. But the fact is that other medical specialties face exactly these problems and barriers, and yet have been substantially more successful in overcoming them.
What seems to be distinctive about orthopedics is that the mindset which perpetuated (and still perpetuates) In this regard, Kristy Weber, MD, the first female president of the AAOS, told Ms. McFarling that the critical first step to bringing in more women or people of color is changing the culture. There seems to be a consensus about that.
So, what does that mean, given that the AAOS has made serious efforts in that regard that have clearly been less than effective?
The answer, as we see it, is first – to not give in to frustration. The time frames involved in changing customary states of mind are typically elongated, and the deeper the habituation, the longer transformation takes. Deep changes always mean a long, hard slog. For transformations of this sort to take place, the requirements are a general agreement on the value of the transformation, exposure to the destructive consequences of the customary modus operandi, and persuasion for why change needs to happen.
In orthopedics, the first requirement has been met. The AAOS espouses diversity and inclusion as a high-level value. In terms of the second two requirements – exposure and persuasion – orthopedic surgeons have been witness to events, campaigns, conferences, et cetera. But these have not been enough, which means that efforts need to be focused, enlarged, sustained, determined, and innovative.
Does the orthopedic surgery community have the ability to do that?
The answer is: Yes, it does.
Currently the orthopedic surgeon community boasts a number of organizations, groups, and individuals pushing for change, in addition to the AAOS’s Diversity Advisory Board. The predominantly African American J. Robert Gladden Orthopaedic Society, the Ruth Jackson Orthopaedic Society of female orthopedic physicians, and the Association of Latino Orthopaedic Surgeons are all energetic advocates, as is Nth Dimensions, the Perry Initiative, and various ad hoc and individual endeavors.
These are all strong proponents for their own groups in their own way. But history has shown in so many cases that concerted rather than individual action empowers advocacy, and what orthopedic surgery needs in its current situation of gross underrepresentation of minorities and women is an enhanced campaign to raise awareness and redouble persuasion.
One of many examples of the power of collective action is the Association of Minority Health Professions Schools founded by Dr. Louis Sullivan in 1977.* Dr. Sullivan (later secretary of the Department of Health & Human Services) was at that time the founding dean of Morehouse School of Medicine. Morehouse had been launched on a shoestring and needed funding urgently. Other Black health schools, such as Meharry Medical College and Tuskegee College of Veterinary Medicine, were in even more pressing financial need. The coalition of schools that Dr. Sullivan organized became a powerful force in Congress and the National Institutes of Health, magnitudes more effective in raising funds from government and other sources than the best individual efforts of the separate institutions.
Dr. Sullivan’s association is only one of a multitude of historical examples of the effectiveness of unified action. AAOS currently has no single officer charged with bringing together the efforts of the change assets that already exist. It could, perhaps should, have someone in that position. AAOS could invest that same office with a mandate to survey the other medical specialties and bring to bear the most effective diversity, equity, and inclusion (DEI) practices in their arsenals.
Finally, despite the attention AAOS has brought to DEI needs, a look at the organization’s strategic goals, its core values, and its “key enablers” finds not a single mention of diversity or inclusion. Given the country’s current focus on the need for equality, given the poor performance of the orthopedic surgery specialty in terms of inclusion, the obvious question is: Should there not be an official declaration positing diversity as a primary AAOS desideratum?
There is recent precedent for this in the American College of Physicians/American Board of Internal Medicine’s Physician Charter on Professionalism, which includes “social justice” as a primary goal of medical practice. This highlights and reinforces the humanitarian strivings of the profession. In light of the paralysis illuminated by Ms. McFarling’s STAT article, a clear, concise declaration by the AAOS of the value and need for DEI as a central component of the organization’s values should be high on the AAOS order of business. A commitment in that form would serve as a powerful catalyst for bringing orthopedic surgery into step with its sister specialties, as well as affirming the core egalitarian principle that underlies all of medical care.
Dr. White is the Ellen and Melvin Gordon Distinguished Professor of Medical Education and Professor of Orthopedic Surgery at Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Chanoff is a founding board member of the Augustus A. White III Institute for Healthcare Equity. Neither Dr. White nor Dr. Chanoff reported any conflicts of interest. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Correction, 2/1/22: An earlier version of this article omitted the title of "Dr." before Dr. Louis Sullivan's name.
FDA approves risankizumab (Skyrizi) for psoriatic arthritis
The Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 21 approved risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) for a second indication – treating adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) – making it the second anti–interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody available to treat PsA, according to an announcement from manufacturer AbbVie.
The agency previously approved risankizumab in April 2019 for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
The dosing regimen for PsA is the same as it is for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a single 150-mg subcutaneous injection four times a year (after two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4), and it can be administered alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Two phase 3 trials, KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, were the basis for the approval. These two trials tested the biologic agent in adults with active PsA, including those who had responded inadequately or were intolerant to biologic therapy and/or nonbiologic DMARDs. Fulfillment of the trials’ primary endpoint of at least a 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at 24 weeks occurred in 51.3%-57.3% of patients, compared with 26.5%-33.5% of placebo-treated patients.
Those on risankizumab also achieved significantly higher rates of ACR50 and ACR70 responses than those on placebo. In addition, patients with preexisting dactylitis and enthesitis experienced improvements in these PsA manifestations. Risankizumab was also associated with an improvement in physical function at 24 weeks on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, bettering placebo by a mean difference of 0.16-0.20 points in the two trials. A significantly higher percentage of patients who had psoriatic skin lesions experienced at least 90% improvement with risankizumab on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, compared with placebo.
AbbVie said that the safety profile of risankizumab in patients with PsA has been generally consistent with its effects in patients with plaque psoriasis.
The KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies are ongoing, and patients in the long-term extensions of the trials remain blinded to the original randomized allocation for the duration of the studies.
Phase 3 trials of risankizumab are also ongoing in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 21 approved risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) for a second indication – treating adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) – making it the second anti–interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody available to treat PsA, according to an announcement from manufacturer AbbVie.
The agency previously approved risankizumab in April 2019 for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
The dosing regimen for PsA is the same as it is for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a single 150-mg subcutaneous injection four times a year (after two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4), and it can be administered alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Two phase 3 trials, KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, were the basis for the approval. These two trials tested the biologic agent in adults with active PsA, including those who had responded inadequately or were intolerant to biologic therapy and/or nonbiologic DMARDs. Fulfillment of the trials’ primary endpoint of at least a 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at 24 weeks occurred in 51.3%-57.3% of patients, compared with 26.5%-33.5% of placebo-treated patients.
Those on risankizumab also achieved significantly higher rates of ACR50 and ACR70 responses than those on placebo. In addition, patients with preexisting dactylitis and enthesitis experienced improvements in these PsA manifestations. Risankizumab was also associated with an improvement in physical function at 24 weeks on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, bettering placebo by a mean difference of 0.16-0.20 points in the two trials. A significantly higher percentage of patients who had psoriatic skin lesions experienced at least 90% improvement with risankizumab on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, compared with placebo.
AbbVie said that the safety profile of risankizumab in patients with PsA has been generally consistent with its effects in patients with plaque psoriasis.
The KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies are ongoing, and patients in the long-term extensions of the trials remain blinded to the original randomized allocation for the duration of the studies.
Phase 3 trials of risankizumab are also ongoing in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The Food and Drug Administration on Jan. 21 approved risankizumab-rzaa (Skyrizi) for a second indication – treating adults with active psoriatic arthritis (PsA) – making it the second anti–interleukin-23 monoclonal antibody available to treat PsA, according to an announcement from manufacturer AbbVie.
The agency previously approved risankizumab in April 2019 for adults with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis.
The dosing regimen for PsA is the same as it is for patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis: a single 150-mg subcutaneous injection four times a year (after two starter doses at weeks 0 and 4), and it can be administered alone or in combination with disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs).
Two phase 3 trials, KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2, were the basis for the approval. These two trials tested the biologic agent in adults with active PsA, including those who had responded inadequately or were intolerant to biologic therapy and/or nonbiologic DMARDs. Fulfillment of the trials’ primary endpoint of at least a 20% improvement in American College of Rheumatology response criteria at 24 weeks occurred in 51.3%-57.3% of patients, compared with 26.5%-33.5% of placebo-treated patients.
Those on risankizumab also achieved significantly higher rates of ACR50 and ACR70 responses than those on placebo. In addition, patients with preexisting dactylitis and enthesitis experienced improvements in these PsA manifestations. Risankizumab was also associated with an improvement in physical function at 24 weeks on the Health Assessment Questionnaire–Disability Index, bettering placebo by a mean difference of 0.16-0.20 points in the two trials. A significantly higher percentage of patients who had psoriatic skin lesions experienced at least 90% improvement with risankizumab on the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index, compared with placebo.
AbbVie said that the safety profile of risankizumab in patients with PsA has been generally consistent with its effects in patients with plaque psoriasis.
The KEEPsAKE 1 and KEEPsAKE 2 studies are ongoing, and patients in the long-term extensions of the trials remain blinded to the original randomized allocation for the duration of the studies.
Phase 3 trials of risankizumab are also ongoing in patients with Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
We’re dying to tell you about fatigability
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
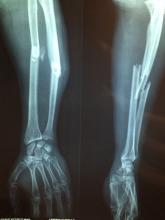
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
35% of employers to proceed with vaccine mandate, poll shows
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: RA February 2022
Several recent RA studies have addressed aspects of systemic illness other than joint pain and inflammation, including sleep, fatigue, psychosocial burden, and well-being. A cohort study by Lyne et al1 evaluated sleep duration and quality in 3,265 patients in the Swedish EIRA registry from 1-12 years after RA diagnosis. About 40% had problems in at least one sleep domain and the frequency of sleep problems increased somewhat with disease duration, but the strongest correlations with poor sleep were pain and functional impairment, suggesting that the overall activity of the RA was most important. Further research on improving sleep quality with improved control of disease activity would be helpful in supporting this hypothesis.
A systematic review by Shamail et al2 examined mental health outcomes in patients with RA taking Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, limiting the review to studies reporting SF-36 mental health outcomes. The resulting 19 studies encompassed over 14,000 patients and did demonstrate clinically meaningful changes in SF-36 scores compared to baseline in patients treated with JAK inhibitors. When compared to changes with placebo or disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment, JAK inhibitors appeared to have a benefit, though few studies showed a clinically meaningful difference. Given that other studies have shown improvement in mental health outcomes with other classes of RA treatments, it is not clear that this is an effect of the JAK inhibitor class rather than related to overall improvement in quality of life.
Fatigue is a prevalent concern among patients with RA and may significantly impact quality of life; its origins in RA are not well-understood but thought to be related to inflammation. A UK study of an inception cohort by Ifeseman et al3 examines fatigue in early RA; about 75% of participants reported a decreased vitality score compared to the mean in the UK general population. Of the approximately 729 study participants in the longitudinal analysis, trajectory modeling was used to identify two groups of people: one with an “average” vitality score and another with a score that was significantly reduced compared to average. This group had worse disease activity scores, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) scores, and pain, though as with the other studies mentioned above, it is not clear if fatigue is a feature of worse control of RA or related to ongoing central sensitization or “non-inflammatory” mechanisms.
Doumen et al4 analyzed interaction between psychosocial variables and disease activity in an early RA cohort and found that better baseline short form-36 (SF-36) scores as well as other measures of psychosocial burden and coping were associated with sustained Disease Activity Score 28 for Rheumatoid Arthritis with C-Reactive Protein (DAS-28-CRP) remission, while negative illness perception was associated with lower probability of sustained remission. Of the 287 patients who achieved DAS-28-CRP remission at week 16, the 231 patients who had a low psychosocial burden were more likely to remain in remission. Causality and direction are not established in this small study, so while evaluating psychosocial needs is relevant, as with the other studies mentioned above, caution must be used in attributing lack of improvement in disease activity to psychosocial burden or mood disorders.
References
- Lyne L et al. Sleep problems in rheumatoid arthritis over 12 years from diagnosis: results from the Swedish EIRA study. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001800 (Jan 5).
- Shamail GMH et al. Association between janus kinase inhibitors therapy and mental health outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 (Dec 13).
- Ifesemen OS et al. Fatigue in early rheumatoid arthritis: data from the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab861 (Dec 27).
- Doumen M et al. Psychosocial burden predicts sustained remission in early rheumatoid arthritis: unraveling the complex interplay of wellbeing and disease activity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 (Dec 20).
Several recent RA studies have addressed aspects of systemic illness other than joint pain and inflammation, including sleep, fatigue, psychosocial burden, and well-being. A cohort study by Lyne et al1 evaluated sleep duration and quality in 3,265 patients in the Swedish EIRA registry from 1-12 years after RA diagnosis. About 40% had problems in at least one sleep domain and the frequency of sleep problems increased somewhat with disease duration, but the strongest correlations with poor sleep were pain and functional impairment, suggesting that the overall activity of the RA was most important. Further research on improving sleep quality with improved control of disease activity would be helpful in supporting this hypothesis.
A systematic review by Shamail et al2 examined mental health outcomes in patients with RA taking Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, limiting the review to studies reporting SF-36 mental health outcomes. The resulting 19 studies encompassed over 14,000 patients and did demonstrate clinically meaningful changes in SF-36 scores compared to baseline in patients treated with JAK inhibitors. When compared to changes with placebo or disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment, JAK inhibitors appeared to have a benefit, though few studies showed a clinically meaningful difference. Given that other studies have shown improvement in mental health outcomes with other classes of RA treatments, it is not clear that this is an effect of the JAK inhibitor class rather than related to overall improvement in quality of life.
Fatigue is a prevalent concern among patients with RA and may significantly impact quality of life; its origins in RA are not well-understood but thought to be related to inflammation. A UK study of an inception cohort by Ifeseman et al3 examines fatigue in early RA; about 75% of participants reported a decreased vitality score compared to the mean in the UK general population. Of the approximately 729 study participants in the longitudinal analysis, trajectory modeling was used to identify two groups of people: one with an “average” vitality score and another with a score that was significantly reduced compared to average. This group had worse disease activity scores, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) scores, and pain, though as with the other studies mentioned above, it is not clear if fatigue is a feature of worse control of RA or related to ongoing central sensitization or “non-inflammatory” mechanisms.
Doumen et al4 analyzed interaction between psychosocial variables and disease activity in an early RA cohort and found that better baseline short form-36 (SF-36) scores as well as other measures of psychosocial burden and coping were associated with sustained Disease Activity Score 28 for Rheumatoid Arthritis with C-Reactive Protein (DAS-28-CRP) remission, while negative illness perception was associated with lower probability of sustained remission. Of the 287 patients who achieved DAS-28-CRP remission at week 16, the 231 patients who had a low psychosocial burden were more likely to remain in remission. Causality and direction are not established in this small study, so while evaluating psychosocial needs is relevant, as with the other studies mentioned above, caution must be used in attributing lack of improvement in disease activity to psychosocial burden or mood disorders.
References
- Lyne L et al. Sleep problems in rheumatoid arthritis over 12 years from diagnosis: results from the Swedish EIRA study. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001800 (Jan 5).
- Shamail GMH et al. Association between janus kinase inhibitors therapy and mental health outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 (Dec 13).
- Ifesemen OS et al. Fatigue in early rheumatoid arthritis: data from the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab861 (Dec 27).
- Doumen M et al. Psychosocial burden predicts sustained remission in early rheumatoid arthritis: unraveling the complex interplay of wellbeing and disease activity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 (Dec 20).
Several recent RA studies have addressed aspects of systemic illness other than joint pain and inflammation, including sleep, fatigue, psychosocial burden, and well-being. A cohort study by Lyne et al1 evaluated sleep duration and quality in 3,265 patients in the Swedish EIRA registry from 1-12 years after RA diagnosis. About 40% had problems in at least one sleep domain and the frequency of sleep problems increased somewhat with disease duration, but the strongest correlations with poor sleep were pain and functional impairment, suggesting that the overall activity of the RA was most important. Further research on improving sleep quality with improved control of disease activity would be helpful in supporting this hypothesis.
A systematic review by Shamail et al2 examined mental health outcomes in patients with RA taking Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors, limiting the review to studies reporting SF-36 mental health outcomes. The resulting 19 studies encompassed over 14,000 patients and did demonstrate clinically meaningful changes in SF-36 scores compared to baseline in patients treated with JAK inhibitors. When compared to changes with placebo or disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD) treatment, JAK inhibitors appeared to have a benefit, though few studies showed a clinically meaningful difference. Given that other studies have shown improvement in mental health outcomes with other classes of RA treatments, it is not clear that this is an effect of the JAK inhibitor class rather than related to overall improvement in quality of life.
Fatigue is a prevalent concern among patients with RA and may significantly impact quality of life; its origins in RA are not well-understood but thought to be related to inflammation. A UK study of an inception cohort by Ifeseman et al3 examines fatigue in early RA; about 75% of participants reported a decreased vitality score compared to the mean in the UK general population. Of the approximately 729 study participants in the longitudinal analysis, trajectory modeling was used to identify two groups of people: one with an “average” vitality score and another with a score that was significantly reduced compared to average. This group had worse disease activity scores, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ) scores, and pain, though as with the other studies mentioned above, it is not clear if fatigue is a feature of worse control of RA or related to ongoing central sensitization or “non-inflammatory” mechanisms.
Doumen et al4 analyzed interaction between psychosocial variables and disease activity in an early RA cohort and found that better baseline short form-36 (SF-36) scores as well as other measures of psychosocial burden and coping were associated with sustained Disease Activity Score 28 for Rheumatoid Arthritis with C-Reactive Protein (DAS-28-CRP) remission, while negative illness perception was associated with lower probability of sustained remission. Of the 287 patients who achieved DAS-28-CRP remission at week 16, the 231 patients who had a low psychosocial burden were more likely to remain in remission. Causality and direction are not established in this small study, so while evaluating psychosocial needs is relevant, as with the other studies mentioned above, caution must be used in attributing lack of improvement in disease activity to psychosocial burden or mood disorders.
References
- Lyne L et al. Sleep problems in rheumatoid arthritis over 12 years from diagnosis: results from the Swedish EIRA study. RMD Open. 2022;8:e001800 (Jan 5).
- Shamail GMH et al. Association between janus kinase inhibitors therapy and mental health outcome in rheumatoid arthritis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rheumatol Ther. 2021 (Dec 13).
- Ifesemen OS et al. Fatigue in early rheumatoid arthritis: data from the Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Network. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021;keab861 (Dec 27).
- Doumen M et al. Psychosocial burden predicts sustained remission in early rheumatoid arthritis: unraveling the complex interplay of wellbeing and disease activity. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2021 (Dec 20).
Clinical Edge Journal Scan Commentary: PsA February 2022
Identifying risk factors associated with transition from cutaneous psoriasis to arthritic psoriasis remains a hot area of research. In a retrospective nested case-control study using the resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project, Karmacharya et al1 identified 164 patients with incident PsA between 2000 and 2017. Among the 158 total patients satisfying study criteria, 64 (41%) had concurrent psoriasis and PsA and 94 (59%) had onset of psoriasis before PsA. The median time from psoriasis diagnosis to the incidence of PsA was 35.5 months with age at psoriasis onset (odds ratio [OR] per 10-year decrease 1.63; 95% CI 1.26-2.11) and its severity (OR for severe vs. mild 3.65; 95% CI 1.18-11.32) being associated with having a psoriasis diagnosis >1 year prior to incident PsA. Early onset as well as severe psoriasis is associated with the HLA- C*06 allele as is longer psoriasis-PsA latency. Although not evaluated in this study, this genetic factor, or other factors such as detection bias, may underly these observations.
Once diagnosed, stratification of PsA severity is important for planning treatment. Towards this goal, Dubash et al2 demonstrated that the presence of dactylitis indicates a more severe PsA phenotype. In a study of 177 disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive patients with early PsA, they found that those with dactylitis (46%) had significantly higher tender and swollen joint counts and C-reactive protein than those with non-dactylitic PsA. Ultrasound synovitis and erosions were also significantly more prevalent in dactylitic PsA. Thus, the presence of dactylitis indicates a more severe phenotype, and patients with dactylitis should be treated aggressively to improve long-term outcomes.
Novel therapies are being frequently evaluated in PsA and a recent target is interleukin (IL)-23, a key cytokine in the T-helper 17 (Th17) pathway and in the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease. Risankizumab is a novel monoclonal antibody targeting IL-23. In the double-blind phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 study including 964 patients with active PsA and inadequate response to one or more conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. They were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg risankizumab or placebo, Kristensen et al3 demonstrated that, at week 24, at least a 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score (ACR20) was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab vs. placebo (57.3% vs. 33.5%; P < .001). Treatment-emergent adverse events were mild-to-moderate and reported at similar frequencies in the risankizumab (40.4%) and placebo (38.7%) groups. Thus, risankizumab was efficacious in reducing clinical manifestations of PsA in patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs with no new adverse events. An important question when treating patients with PsA with targeted therapies is the need for concomitant therapy with csDMARDs. In a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 non-biologic (nb) DMARDs or biologic DMARDs were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks, Nash et al4 demonstrated that at week 12, ACR20 response was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar between monotherapy and combination therapy. Although, we don’t have information regarding the sustainability of the response, these data indicate that upadacitinib may be used without concomitant csDMARDs in PsA.
References
- Karmacharya P et al. Time to transition from psoriasis to psoriatic arthritis: A population-based study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021(Dec 31):S0049-0172(21)00230-4.
- Dubash S et al. Dactylitis is an indicator of a more severe phenotype independently associated with greater SJC, CRP, ultrasound synovitis and erosive damage in DMARD-naive early psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021(Dec 10):annrheumdis-2021-220964.
- Kristensen LE et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab for active psoriatic arthritis: 24-week results from the randomised, double-blind, phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022(Feb);81(2):225-231.
- Nash P et al. Upadacitinib as monotherapy and in combination with non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021(Dec 3):keab905.
Identifying risk factors associated with transition from cutaneous psoriasis to arthritic psoriasis remains a hot area of research. In a retrospective nested case-control study using the resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project, Karmacharya et al1 identified 164 patients with incident PsA between 2000 and 2017. Among the 158 total patients satisfying study criteria, 64 (41%) had concurrent psoriasis and PsA and 94 (59%) had onset of psoriasis before PsA. The median time from psoriasis diagnosis to the incidence of PsA was 35.5 months with age at psoriasis onset (odds ratio [OR] per 10-year decrease 1.63; 95% CI 1.26-2.11) and its severity (OR for severe vs. mild 3.65; 95% CI 1.18-11.32) being associated with having a psoriasis diagnosis >1 year prior to incident PsA. Early onset as well as severe psoriasis is associated with the HLA- C*06 allele as is longer psoriasis-PsA latency. Although not evaluated in this study, this genetic factor, or other factors such as detection bias, may underly these observations.
Once diagnosed, stratification of PsA severity is important for planning treatment. Towards this goal, Dubash et al2 demonstrated that the presence of dactylitis indicates a more severe PsA phenotype. In a study of 177 disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive patients with early PsA, they found that those with dactylitis (46%) had significantly higher tender and swollen joint counts and C-reactive protein than those with non-dactylitic PsA. Ultrasound synovitis and erosions were also significantly more prevalent in dactylitic PsA. Thus, the presence of dactylitis indicates a more severe phenotype, and patients with dactylitis should be treated aggressively to improve long-term outcomes.
Novel therapies are being frequently evaluated in PsA and a recent target is interleukin (IL)-23, a key cytokine in the T-helper 17 (Th17) pathway and in the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease. Risankizumab is a novel monoclonal antibody targeting IL-23. In the double-blind phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 study including 964 patients with active PsA and inadequate response to one or more conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. They were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg risankizumab or placebo, Kristensen et al3 demonstrated that, at week 24, at least a 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score (ACR20) was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab vs. placebo (57.3% vs. 33.5%; P < .001). Treatment-emergent adverse events were mild-to-moderate and reported at similar frequencies in the risankizumab (40.4%) and placebo (38.7%) groups. Thus, risankizumab was efficacious in reducing clinical manifestations of PsA in patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs with no new adverse events. An important question when treating patients with PsA with targeted therapies is the need for concomitant therapy with csDMARDs. In a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 non-biologic (nb) DMARDs or biologic DMARDs were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks, Nash et al4 demonstrated that at week 12, ACR20 response was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar between monotherapy and combination therapy. Although, we don’t have information regarding the sustainability of the response, these data indicate that upadacitinib may be used without concomitant csDMARDs in PsA.
References
- Karmacharya P et al. Time to transition from psoriasis to psoriatic arthritis: A population-based study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021(Dec 31):S0049-0172(21)00230-4.
- Dubash S et al. Dactylitis is an indicator of a more severe phenotype independently associated with greater SJC, CRP, ultrasound synovitis and erosive damage in DMARD-naive early psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021(Dec 10):annrheumdis-2021-220964.
- Kristensen LE et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab for active psoriatic arthritis: 24-week results from the randomised, double-blind, phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022(Feb);81(2):225-231.
- Nash P et al. Upadacitinib as monotherapy and in combination with non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021(Dec 3):keab905.
Identifying risk factors associated with transition from cutaneous psoriasis to arthritic psoriasis remains a hot area of research. In a retrospective nested case-control study using the resources of the Rochester Epidemiology Project, Karmacharya et al1 identified 164 patients with incident PsA between 2000 and 2017. Among the 158 total patients satisfying study criteria, 64 (41%) had concurrent psoriasis and PsA and 94 (59%) had onset of psoriasis before PsA. The median time from psoriasis diagnosis to the incidence of PsA was 35.5 months with age at psoriasis onset (odds ratio [OR] per 10-year decrease 1.63; 95% CI 1.26-2.11) and its severity (OR for severe vs. mild 3.65; 95% CI 1.18-11.32) being associated with having a psoriasis diagnosis >1 year prior to incident PsA. Early onset as well as severe psoriasis is associated with the HLA- C*06 allele as is longer psoriasis-PsA latency. Although not evaluated in this study, this genetic factor, or other factors such as detection bias, may underly these observations.
Once diagnosed, stratification of PsA severity is important for planning treatment. Towards this goal, Dubash et al2 demonstrated that the presence of dactylitis indicates a more severe PsA phenotype. In a study of 177 disease-modifying antirheumatic drug (DMARD)-naive patients with early PsA, they found that those with dactylitis (46%) had significantly higher tender and swollen joint counts and C-reactive protein than those with non-dactylitic PsA. Ultrasound synovitis and erosions were also significantly more prevalent in dactylitic PsA. Thus, the presence of dactylitis indicates a more severe phenotype, and patients with dactylitis should be treated aggressively to improve long-term outcomes.
Novel therapies are being frequently evaluated in PsA and a recent target is interleukin (IL)-23, a key cytokine in the T-helper 17 (Th17) pathway and in the pathogenesis of psoriatic disease. Risankizumab is a novel monoclonal antibody targeting IL-23. In the double-blind phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 study including 964 patients with active PsA and inadequate response to one or more conventional synthetic (cs) DMARDs. They were randomly assigned to receive 150 mg risankizumab or placebo, Kristensen et al3 demonstrated that, at week 24, at least a 20% improvement in the American College of Rheumatology score (ACR20) was achieved by a significantly higher proportion of patients receiving risankizumab vs. placebo (57.3% vs. 33.5%; P < .001). Treatment-emergent adverse events were mild-to-moderate and reported at similar frequencies in the risankizumab (40.4%) and placebo (38.7%) groups. Thus, risankizumab was efficacious in reducing clinical manifestations of PsA in patients with inadequate response to csDMARDs with no new adverse events. An important question when treating patients with PsA with targeted therapies is the need for concomitant therapy with csDMARDs. In a pooled analysis of 2 phase 3 trials, SELECT-PsA 1 and SELECT-PsA 2, 1,916 patients with active PsA with an inadequate response to ≥1 non-biologic (nb) DMARDs or biologic DMARDs were randomly assigned to placebo, 15 mg upadacitinib, or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy or in combination with ≤2 nbDMARDs for 24 weeks, Nash et al4 demonstrated that at week 12, ACR20 response was achieved by a similar proportion of patients receiving 15 mg upadacitinib or 30 mg upadacitinib as monotherapy (15 mg: 33.7%; 95% CI 24.4%-43.1%; 30 mg: 45.7%; 95% CI 36.9%-54.5%) or combination therapy (15 mg: 34.0%; 95% CI 27.9%-40.1%; 30 mg: 39.6%; 95% CI 33.7%-45.5%). Adverse events were generally similar between monotherapy and combination therapy. Although, we don’t have information regarding the sustainability of the response, these data indicate that upadacitinib may be used without concomitant csDMARDs in PsA.
References
- Karmacharya P et al. Time to transition from psoriasis to psoriatic arthritis: A population-based study. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2021(Dec 31):S0049-0172(21)00230-4.
- Dubash S et al. Dactylitis is an indicator of a more severe phenotype independently associated with greater SJC, CRP, ultrasound synovitis and erosive damage in DMARD-naive early psoriatic arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2021(Dec 10):annrheumdis-2021-220964.
- Kristensen LE et al. Efficacy and safety of risankizumab for active psoriatic arthritis: 24-week results from the randomised, double-blind, phase 3 KEEPsAKE 1 trial. Ann Rheum Dis. 2022(Feb);81(2):225-231.
- Nash P et al. Upadacitinib as monotherapy and in combination with non-biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs for psoriatic arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2021(Dec 3):keab905.
Omicron survives longer on plastic, skin than other COVID variants
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, one possible explanation for why Omicron has spread so rapidly around the world.
In a lab experiment, samples of different variants were applied to pieces of plastic and human skin collected from autopsies, researchers from Kyoto Prefectural University of Medicine wrote in bioRxiv. A variant “survived” until it could no longer be detected on the surface.
“This study showed that the Omicron variant also has the highest environmental stability among VOCs (variants of concern), which suggests that this high stability might also be one of the factors that have allowed the Omicron variant to replace the Delta variant and spread rapidly,” the researchers wrote.
On plastic, the Omicron variant samples survived an average of 193.5 hours, a little more than 8 days. By comparison, the other survival times on plastic were 56 hours for the original COVID strain, 191.3 hours for Alpha, 156.6 hours for Beta, 59.3 hours for Gamma, and 114 hours for Delta.
On skin samples, the Omicron samples survived an average of 21.1 hours. The other variants had these average survival times on skin: 8.6 hours for the original version, 19.6 hours for Alpha, 19.1 hours for Beta, 11 hours for Gamma, and 16.8 hours for Delta.
The study found that the variants had more resistance to ethanol than the original strain of COVID. That said, all COVID samples were inactivated after being exposed to alcohol-based hand sanitizers for 15 seconds.
“Therefore, it is highly recommended that current infection control (hand hygiene) practices use disinfectants ... as proposed by the World Health Organization,” the researchers said.
The study has not been peer-reviewed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.