User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Can too much sleep raise the risk of cancer?
The findings reveal that sleeping 10-plus hours may increase a woman’s risk of getting cancer and both men and women’s risk of dying from cancer.
The researchers say their findings may help refine sleep recommendations in Japan, which currently advise working, middle-aged adults to sleep “as long as they can.”
Based on the new findings, a sleep duration of 6-8 hours for men and 6-9 hours for women “may be the safest” regarding cancer incidence and mortality risk among Japanese adults, the authors conclude.
The findings were published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
The literature on sleep time and cancer risk is mixed. A trio of meta-analyses conducted between 2016 and 2019 found that long sleep duration, but not short, was associated with a slightly elevated risk of all cancer mortality in Asians.
A separate meta-analysis conducted in 2018 found that both short and long sleep durations were not related to cancer incidence. But in the stratified analysis, shorter sleep time was associated with 36% increased cancer risk among Asians.
To investigate further, the researchers pooled data from six population-based cohorts that included 271,694 adults – 126,930 men and 144,764 women – with 40,751 total incident cancer cases and 18,323 total cancer deaths during a follow-up lasting about 5.9 million person-years.
In the multivariable analysis, longer sleep duration was not associated with total cancer incidence in men. In women, however, sleeping 10 or more hours vs. 7 was associated with a 19% increased risk of cancer.
In addition, sleeping 10 or more hours was associated with an increased risk of dying from cancer in women (hazard ratio, 1.44) and men (HR, 1.18).
Sleeping for 5 hours or fewer, compared with 7, was not associated with cancer incidence and mortality. However, among postmenopausal women, shorter sleep durations did increase the risk of dying from cancer (HR, 1.15).
The authors highlight several strengths of the analysis, including a large sample size as well as stratification of the results by body mass index and menopause status, which has rarely been done in previous studies.
Limitations include self-reported sleep durations and lack of data on sleep quality. The researchers note that the mechanism by which sleep time may influence cancer incidence and mortality is unclear but likely to be complex and cancer site specific.
It’s also possible that reverse causation could explain associations between sleep duration and cancer occurrence and mortality – with pain from cancer, for instance, impairing sleep duration and quality. However, the sensitivity analysis found no evidence of reverse causality or other confounding factors.
Based on these findings, the researchers say sleep duration “may be an important variable to include in cancer incidence and mortality risk prediction models.”
The study had no specific funding. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings reveal that sleeping 10-plus hours may increase a woman’s risk of getting cancer and both men and women’s risk of dying from cancer.
The researchers say their findings may help refine sleep recommendations in Japan, which currently advise working, middle-aged adults to sleep “as long as they can.”
Based on the new findings, a sleep duration of 6-8 hours for men and 6-9 hours for women “may be the safest” regarding cancer incidence and mortality risk among Japanese adults, the authors conclude.
The findings were published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
The literature on sleep time and cancer risk is mixed. A trio of meta-analyses conducted between 2016 and 2019 found that long sleep duration, but not short, was associated with a slightly elevated risk of all cancer mortality in Asians.
A separate meta-analysis conducted in 2018 found that both short and long sleep durations were not related to cancer incidence. But in the stratified analysis, shorter sleep time was associated with 36% increased cancer risk among Asians.
To investigate further, the researchers pooled data from six population-based cohorts that included 271,694 adults – 126,930 men and 144,764 women – with 40,751 total incident cancer cases and 18,323 total cancer deaths during a follow-up lasting about 5.9 million person-years.
In the multivariable analysis, longer sleep duration was not associated with total cancer incidence in men. In women, however, sleeping 10 or more hours vs. 7 was associated with a 19% increased risk of cancer.
In addition, sleeping 10 or more hours was associated with an increased risk of dying from cancer in women (hazard ratio, 1.44) and men (HR, 1.18).
Sleeping for 5 hours or fewer, compared with 7, was not associated with cancer incidence and mortality. However, among postmenopausal women, shorter sleep durations did increase the risk of dying from cancer (HR, 1.15).
The authors highlight several strengths of the analysis, including a large sample size as well as stratification of the results by body mass index and menopause status, which has rarely been done in previous studies.
Limitations include self-reported sleep durations and lack of data on sleep quality. The researchers note that the mechanism by which sleep time may influence cancer incidence and mortality is unclear but likely to be complex and cancer site specific.
It’s also possible that reverse causation could explain associations between sleep duration and cancer occurrence and mortality – with pain from cancer, for instance, impairing sleep duration and quality. However, the sensitivity analysis found no evidence of reverse causality or other confounding factors.
Based on these findings, the researchers say sleep duration “may be an important variable to include in cancer incidence and mortality risk prediction models.”
The study had no specific funding. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The findings reveal that sleeping 10-plus hours may increase a woman’s risk of getting cancer and both men and women’s risk of dying from cancer.
The researchers say their findings may help refine sleep recommendations in Japan, which currently advise working, middle-aged adults to sleep “as long as they can.”
Based on the new findings, a sleep duration of 6-8 hours for men and 6-9 hours for women “may be the safest” regarding cancer incidence and mortality risk among Japanese adults, the authors conclude.
The findings were published online in the International Journal of Cancer.
The literature on sleep time and cancer risk is mixed. A trio of meta-analyses conducted between 2016 and 2019 found that long sleep duration, but not short, was associated with a slightly elevated risk of all cancer mortality in Asians.
A separate meta-analysis conducted in 2018 found that both short and long sleep durations were not related to cancer incidence. But in the stratified analysis, shorter sleep time was associated with 36% increased cancer risk among Asians.
To investigate further, the researchers pooled data from six population-based cohorts that included 271,694 adults – 126,930 men and 144,764 women – with 40,751 total incident cancer cases and 18,323 total cancer deaths during a follow-up lasting about 5.9 million person-years.
In the multivariable analysis, longer sleep duration was not associated with total cancer incidence in men. In women, however, sleeping 10 or more hours vs. 7 was associated with a 19% increased risk of cancer.
In addition, sleeping 10 or more hours was associated with an increased risk of dying from cancer in women (hazard ratio, 1.44) and men (HR, 1.18).
Sleeping for 5 hours or fewer, compared with 7, was not associated with cancer incidence and mortality. However, among postmenopausal women, shorter sleep durations did increase the risk of dying from cancer (HR, 1.15).
The authors highlight several strengths of the analysis, including a large sample size as well as stratification of the results by body mass index and menopause status, which has rarely been done in previous studies.
Limitations include self-reported sleep durations and lack of data on sleep quality. The researchers note that the mechanism by which sleep time may influence cancer incidence and mortality is unclear but likely to be complex and cancer site specific.
It’s also possible that reverse causation could explain associations between sleep duration and cancer occurrence and mortality – with pain from cancer, for instance, impairing sleep duration and quality. However, the sensitivity analysis found no evidence of reverse causality or other confounding factors.
Based on these findings, the researchers say sleep duration “may be an important variable to include in cancer incidence and mortality risk prediction models.”
The study had no specific funding. The authors declared no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF CANCER
Findings raise questions about migraine and sleep
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – What may be the largest case-based study of patients with migraine and sleep-disordered breathing to date has found that, counter to prevailing thought, they may not be at higher risk of having obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than nonmigraine patients, although further prospective studies are needed to validate that finding.
“This in no way for me changes the fact that, for patients that complain of headaches, sleep apnea remains to be something that should be considered as possible cause of their headaches,” neurologist and Cleveland Clinic postdoctoral fellow Eric Gruenthal, MD, said in an interview after he presented his results at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
The study suggested that patients with migraine may have an OSA risk that “may be a little lower” than their nonmigraine counterparts, Dr. Gruenthal said. “But we have really yet to determine whether that’s true or not.”
Large case-based study
The retrospective case study included 4,783 migraine cases from the Cleveland Clinic electronic health record database who were case matched on a 1:3 basis with 14,287 controls. Patients with migraine had an average age of 47.5 years (±13.3) and body mass index of 33.7 kg/m2 (±8.6), and 76.4% were White. All patients had polysomnography (PSG) at a Cleveland Clinic facility from 1998 to 2021.
The analysis evaluated the collected data in two domains: sleep architecture, consisting of arousal index (AI), total sleep time (TST) and percentage of sleep stage time; and sleep-disordered breathing, including apnea hypopnea index (AHI) and mean oxygen saturation. The key findings of the migraine patients versus controls include:
- Lower AI, 19.6 (95% confidence interval, 12.8-30.9) versus 22.6 (95% CI, 14.7-34.9; P < .001).
- Shorter TST, 359 (95% CI, 307-421) versus 363 (95% CI, 306-432.5) minutes (P = .01).
- With regard to sleep stage, the percentage of N2 sleep was higher, 67.8% (95% CI, 59.6%-75.6%) versus 67% (95% CI, 58.4%-74.8%; P < .001); but the percentage of REM was lower at 16.7% (95% CI, 10%-22%) versus 17% (95% CI, 11.1%-22.2%; P = .012).
- Lower AHI, 7.4 (95% CI, 2.6-17) versus 9.5 (95% CI, 3.7-22.1, P < .001).
- Higher mean oxygen saturation, 93.7 (±2.4) versus 93.3% (±2.6; P < .001).
“Also,” Dr. Gruenthal added, “we found that the percentage of sleep time with oxygen saturation below 90% was lower among patients with migraine, at 1.3% versus 2.4%” (P < .001).
A unique profile?
The goal of the study was to determine whether migraine patients would have a unique PSG profile, Dr. Gruenthal said. “We were trying to overcome some of the limitations of previous studies, most notably those that use small sample sizes, and in some cases a lack of controls.”
The findings that migraine patients would have higher AI and elevated AHI ran counter to the study’s hypotheses, but fell in line with the expectation that they would have reduced TST, Dr. Gruenthal said.
Patients with migraine “may, in fact, exhibit a lower burden of sleep-disordered breathing, and that’s based on our findings such as the lower AHI and decreased burden of hypoxemia,” he said. “We theorized that this may be related to patients with migraine having a unique CGRP [calcitonin gene-related peptide] and serotonin physiology.” He noted that previously published research has shown that sleep CGRP and serotonin have a central role in causing arousal in response to rising CO2 levels during sleep, which can occur during apneas and hypopneas.
Dr. Gruenthal noted that the researchers are still analyzing the findings. “We theorized that possible indication bias may be present in our study,” he said. “It may be the case that patients with migraine are more likely to get their PSG done because of their headache and not for things like snoring and witnessed apneas, which may be more predictive of significant sleep apnea.” They’re also evaluating the “question of medicine confounding.”
Dr. Gruenthal added that “the big unanswered question out there is, if you have a patient with migraine who also has sleep apnea, by treating the sleep apnea will that improve their migraine?”
More questions than answers
Commenting on the study, Donald Bliwise, PhD, professor of neurology at Emory Sleep Center, Atlanta, said the study findings shouldn’t change how clinicians approach migraine in relation to sleep.
“It’s a case series, it’s retrospective,” said Dr. Bliwise, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the largest study that I know of that has ever looked at the diagnosis of migraine in relation to polysomnographic measures of sleep, but it’s imprecise to the extent that migraine is a clinical diagnosis, so not everyone that carries the diagnosis of migraine has the diagnosis made by a neurologist.”
The study raises more questions than it answers, he said, “but that’s not necessarily a bad thing. I think we need more prospective studies.” Those studies should be more granular in how they analyze sleep in migraine patients “Since migraine is an intermittent event, and sleep quality and length, and percentage of REM sleep and even sleep apnea can vary from night to night, it would be fascinating to look at headaches over a month in relation to sleep over a month.”
Dr. Gruenthal and Dr. Bliwise have no disclosures. The Association of Migraine Disorders provided funding for the study.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – What may be the largest case-based study of patients with migraine and sleep-disordered breathing to date has found that, counter to prevailing thought, they may not be at higher risk of having obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than nonmigraine patients, although further prospective studies are needed to validate that finding.
“This in no way for me changes the fact that, for patients that complain of headaches, sleep apnea remains to be something that should be considered as possible cause of their headaches,” neurologist and Cleveland Clinic postdoctoral fellow Eric Gruenthal, MD, said in an interview after he presented his results at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
The study suggested that patients with migraine may have an OSA risk that “may be a little lower” than their nonmigraine counterparts, Dr. Gruenthal said. “But we have really yet to determine whether that’s true or not.”
Large case-based study
The retrospective case study included 4,783 migraine cases from the Cleveland Clinic electronic health record database who were case matched on a 1:3 basis with 14,287 controls. Patients with migraine had an average age of 47.5 years (±13.3) and body mass index of 33.7 kg/m2 (±8.6), and 76.4% were White. All patients had polysomnography (PSG) at a Cleveland Clinic facility from 1998 to 2021.
The analysis evaluated the collected data in two domains: sleep architecture, consisting of arousal index (AI), total sleep time (TST) and percentage of sleep stage time; and sleep-disordered breathing, including apnea hypopnea index (AHI) and mean oxygen saturation. The key findings of the migraine patients versus controls include:
- Lower AI, 19.6 (95% confidence interval, 12.8-30.9) versus 22.6 (95% CI, 14.7-34.9; P < .001).
- Shorter TST, 359 (95% CI, 307-421) versus 363 (95% CI, 306-432.5) minutes (P = .01).
- With regard to sleep stage, the percentage of N2 sleep was higher, 67.8% (95% CI, 59.6%-75.6%) versus 67% (95% CI, 58.4%-74.8%; P < .001); but the percentage of REM was lower at 16.7% (95% CI, 10%-22%) versus 17% (95% CI, 11.1%-22.2%; P = .012).
- Lower AHI, 7.4 (95% CI, 2.6-17) versus 9.5 (95% CI, 3.7-22.1, P < .001).
- Higher mean oxygen saturation, 93.7 (±2.4) versus 93.3% (±2.6; P < .001).
“Also,” Dr. Gruenthal added, “we found that the percentage of sleep time with oxygen saturation below 90% was lower among patients with migraine, at 1.3% versus 2.4%” (P < .001).
A unique profile?
The goal of the study was to determine whether migraine patients would have a unique PSG profile, Dr. Gruenthal said. “We were trying to overcome some of the limitations of previous studies, most notably those that use small sample sizes, and in some cases a lack of controls.”
The findings that migraine patients would have higher AI and elevated AHI ran counter to the study’s hypotheses, but fell in line with the expectation that they would have reduced TST, Dr. Gruenthal said.
Patients with migraine “may, in fact, exhibit a lower burden of sleep-disordered breathing, and that’s based on our findings such as the lower AHI and decreased burden of hypoxemia,” he said. “We theorized that this may be related to patients with migraine having a unique CGRP [calcitonin gene-related peptide] and serotonin physiology.” He noted that previously published research has shown that sleep CGRP and serotonin have a central role in causing arousal in response to rising CO2 levels during sleep, which can occur during apneas and hypopneas.
Dr. Gruenthal noted that the researchers are still analyzing the findings. “We theorized that possible indication bias may be present in our study,” he said. “It may be the case that patients with migraine are more likely to get their PSG done because of their headache and not for things like snoring and witnessed apneas, which may be more predictive of significant sleep apnea.” They’re also evaluating the “question of medicine confounding.”
Dr. Gruenthal added that “the big unanswered question out there is, if you have a patient with migraine who also has sleep apnea, by treating the sleep apnea will that improve their migraine?”
More questions than answers
Commenting on the study, Donald Bliwise, PhD, professor of neurology at Emory Sleep Center, Atlanta, said the study findings shouldn’t change how clinicians approach migraine in relation to sleep.
“It’s a case series, it’s retrospective,” said Dr. Bliwise, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the largest study that I know of that has ever looked at the diagnosis of migraine in relation to polysomnographic measures of sleep, but it’s imprecise to the extent that migraine is a clinical diagnosis, so not everyone that carries the diagnosis of migraine has the diagnosis made by a neurologist.”
The study raises more questions than it answers, he said, “but that’s not necessarily a bad thing. I think we need more prospective studies.” Those studies should be more granular in how they analyze sleep in migraine patients “Since migraine is an intermittent event, and sleep quality and length, and percentage of REM sleep and even sleep apnea can vary from night to night, it would be fascinating to look at headaches over a month in relation to sleep over a month.”
Dr. Gruenthal and Dr. Bliwise have no disclosures. The Association of Migraine Disorders provided funding for the study.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – What may be the largest case-based study of patients with migraine and sleep-disordered breathing to date has found that, counter to prevailing thought, they may not be at higher risk of having obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) than nonmigraine patients, although further prospective studies are needed to validate that finding.
“This in no way for me changes the fact that, for patients that complain of headaches, sleep apnea remains to be something that should be considered as possible cause of their headaches,” neurologist and Cleveland Clinic postdoctoral fellow Eric Gruenthal, MD, said in an interview after he presented his results at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
The study suggested that patients with migraine may have an OSA risk that “may be a little lower” than their nonmigraine counterparts, Dr. Gruenthal said. “But we have really yet to determine whether that’s true or not.”
Large case-based study
The retrospective case study included 4,783 migraine cases from the Cleveland Clinic electronic health record database who were case matched on a 1:3 basis with 14,287 controls. Patients with migraine had an average age of 47.5 years (±13.3) and body mass index of 33.7 kg/m2 (±8.6), and 76.4% were White. All patients had polysomnography (PSG) at a Cleveland Clinic facility from 1998 to 2021.
The analysis evaluated the collected data in two domains: sleep architecture, consisting of arousal index (AI), total sleep time (TST) and percentage of sleep stage time; and sleep-disordered breathing, including apnea hypopnea index (AHI) and mean oxygen saturation. The key findings of the migraine patients versus controls include:
- Lower AI, 19.6 (95% confidence interval, 12.8-30.9) versus 22.6 (95% CI, 14.7-34.9; P < .001).
- Shorter TST, 359 (95% CI, 307-421) versus 363 (95% CI, 306-432.5) minutes (P = .01).
- With regard to sleep stage, the percentage of N2 sleep was higher, 67.8% (95% CI, 59.6%-75.6%) versus 67% (95% CI, 58.4%-74.8%; P < .001); but the percentage of REM was lower at 16.7% (95% CI, 10%-22%) versus 17% (95% CI, 11.1%-22.2%; P = .012).
- Lower AHI, 7.4 (95% CI, 2.6-17) versus 9.5 (95% CI, 3.7-22.1, P < .001).
- Higher mean oxygen saturation, 93.7 (±2.4) versus 93.3% (±2.6; P < .001).
“Also,” Dr. Gruenthal added, “we found that the percentage of sleep time with oxygen saturation below 90% was lower among patients with migraine, at 1.3% versus 2.4%” (P < .001).
A unique profile?
The goal of the study was to determine whether migraine patients would have a unique PSG profile, Dr. Gruenthal said. “We were trying to overcome some of the limitations of previous studies, most notably those that use small sample sizes, and in some cases a lack of controls.”
The findings that migraine patients would have higher AI and elevated AHI ran counter to the study’s hypotheses, but fell in line with the expectation that they would have reduced TST, Dr. Gruenthal said.
Patients with migraine “may, in fact, exhibit a lower burden of sleep-disordered breathing, and that’s based on our findings such as the lower AHI and decreased burden of hypoxemia,” he said. “We theorized that this may be related to patients with migraine having a unique CGRP [calcitonin gene-related peptide] and serotonin physiology.” He noted that previously published research has shown that sleep CGRP and serotonin have a central role in causing arousal in response to rising CO2 levels during sleep, which can occur during apneas and hypopneas.
Dr. Gruenthal noted that the researchers are still analyzing the findings. “We theorized that possible indication bias may be present in our study,” he said. “It may be the case that patients with migraine are more likely to get their PSG done because of their headache and not for things like snoring and witnessed apneas, which may be more predictive of significant sleep apnea.” They’re also evaluating the “question of medicine confounding.”
Dr. Gruenthal added that “the big unanswered question out there is, if you have a patient with migraine who also has sleep apnea, by treating the sleep apnea will that improve their migraine?”
More questions than answers
Commenting on the study, Donald Bliwise, PhD, professor of neurology at Emory Sleep Center, Atlanta, said the study findings shouldn’t change how clinicians approach migraine in relation to sleep.
“It’s a case series, it’s retrospective,” said Dr. Bliwise, who was not involved in the study. “It’s the largest study that I know of that has ever looked at the diagnosis of migraine in relation to polysomnographic measures of sleep, but it’s imprecise to the extent that migraine is a clinical diagnosis, so not everyone that carries the diagnosis of migraine has the diagnosis made by a neurologist.”
The study raises more questions than it answers, he said, “but that’s not necessarily a bad thing. I think we need more prospective studies.” Those studies should be more granular in how they analyze sleep in migraine patients “Since migraine is an intermittent event, and sleep quality and length, and percentage of REM sleep and even sleep apnea can vary from night to night, it would be fascinating to look at headaches over a month in relation to sleep over a month.”
Dr. Gruenthal and Dr. Bliwise have no disclosures. The Association of Migraine Disorders provided funding for the study.
AT SLEEP 2022
Long-term erratic sleep may foretell cognitive problems
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Erratic sleep patterns over years or even decades, along with a patient’s age and history of depression, may be harbingers of cognitive impairment later in life, an analysis of decades of data from a large sleep study has found.
“What we were a little surprised to find in this model was that sleep duration, whether short, long or average, was not significant, but the sleep variability – the change in sleep across those time measurements—was significantly impacting the incidence of cognitive impairment,” Samantha Keil, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Washington, Seattle, reported at the at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
The researchers analyzed sleep and cognition data collected over decades on 1,104 adults who participated in the Seattle Longitudinal Study. Study participants ranged from age 55 to over 100, with almost 80% of the study cohort aged 65 and older.
The Seattle Longitudinal Study first started gathering data in the 1950s. Participants in the study cohort underwent an extensive cognitive battery, which was added to the study in 1984 and gathered every 5-7 years, and completed a health behavioral questionnaire (HBQ), which was added in 1993 and administered every 3-5 years, Dr. Keil said. The HBQ included a question on average nightly sleep duration.
The study used a multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression model to evaluate the overall effect of average sleep duration and changes in sleep duration over time on cognitive impairment. Covariates used in the model included apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) genotype, gender, years of education, ethnicity, and depression.
Dr. Keil said the model found, as expected, that the demographic variables of education, APOE status, and depression were significantly associated with cognitive impairment (hazard ratios of 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.21; P = .01; and 2.08; 95% CI, 1.31-3.31; P < .005; and 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.13; P < .005, respectively). Importantly, when evaluating the duration, change and variability of sleep, the researchers found that increased sleep variability was significantly associated with cognitive impairment (HR, 3.15; 95% CI, 1.69-5.87; P < .005).
Under this analysis, “sleep variability over time and not median sleep duration was associated with cognitive impairment,” she said. When sleep variability was added into the model, it improved the concordance score – a value that reflects the ability of a model to predict an outcome better than random chance – from .63 to .73 (a value of .5 indicates the model is no better at predicting an outcome than a random chance model; a value of .7 or greater indicates a good model).
Identification of sleep variability as a sleep pattern of interest in longitudinal studies is important, Dr. Keil said, because simply evaluating mean or median sleep duration across time might not account for a subject’s variable sleep phenotype. Most importantly, further evaluation of sleep variability with a linear regression prediction analysis (F statistic 8.796, P < .0001, adjusted R-squared .235) found that increased age, depression, and sleep variability significantly predicted cognitive impairment 10 years downstream. “Longitudinal sleep variability is perhaps for the first time being reported as significantly associated with the development of downstream cognitive impairment,” Dr. Keil said.
What makes this study unique, Dr. Keil said in an interview, is that it used self-reported longitudinal data gathered at 3- to 5-year intervals for up to 25 years, allowing for the assessment of variation of sleep duration across this entire time frame. “If you could use that shift in sleep duration as a point of therapeutic intervention, that would be really exciting,” she said.
Future research will evaluate how sleep variability and cognitive function are impacted by other variables gathered in the Seattle Longitudinal Study over the years, including factors such as diabetes and hypertension status, diet, alcohol and tobacco use, and marital and family status. Follow-up studies will be investigating the impact of sleep variability on neuropathologic disease progression and lymphatic system impairment, Dr. Keil said.
A newer approach
By linking sleep variability and daytime functioning, the study employs a “newer approach,” said Joseph M. Dzierzewski, PhD, director of behavioral medicine concentration in the department of psychology at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond. “While some previous work has examined night-to-night fluctuation in various sleep characteristics and cognitive functioning, what differentiates the present study from these previous works is the duration of the investigation,” he said. The “richness of data” in the Seattle Longitudinal Study and how it tracks sleep and cognition over years make it “quite unique and novel.”
Future studies, he said, should be deliberate in how they evaluate sleep and neurocognitive function across years. “Disentangling short-term moment-to-moment and day-to-day fluctuation, which may be more reversible in nature, from long-term, enduring month-to-month or year-to-year fluctuation, which may be more permanent, will be important for continuing to advance our understanding of these complex phenomena,” Dr. Dzierzewski said. “An additional important area of future investigation would be to continue the hunt for a common biological factor underpinning both sleep variability and Alzheimer’s disease.” That, he said, may help identify potential intervention targets.
Dr. Keil and Dr. Dzierzewski have no relevant disclosures.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Erratic sleep patterns over years or even decades, along with a patient’s age and history of depression, may be harbingers of cognitive impairment later in life, an analysis of decades of data from a large sleep study has found.
“What we were a little surprised to find in this model was that sleep duration, whether short, long or average, was not significant, but the sleep variability – the change in sleep across those time measurements—was significantly impacting the incidence of cognitive impairment,” Samantha Keil, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Washington, Seattle, reported at the at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
The researchers analyzed sleep and cognition data collected over decades on 1,104 adults who participated in the Seattle Longitudinal Study. Study participants ranged from age 55 to over 100, with almost 80% of the study cohort aged 65 and older.
The Seattle Longitudinal Study first started gathering data in the 1950s. Participants in the study cohort underwent an extensive cognitive battery, which was added to the study in 1984 and gathered every 5-7 years, and completed a health behavioral questionnaire (HBQ), which was added in 1993 and administered every 3-5 years, Dr. Keil said. The HBQ included a question on average nightly sleep duration.
The study used a multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression model to evaluate the overall effect of average sleep duration and changes in sleep duration over time on cognitive impairment. Covariates used in the model included apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) genotype, gender, years of education, ethnicity, and depression.
Dr. Keil said the model found, as expected, that the demographic variables of education, APOE status, and depression were significantly associated with cognitive impairment (hazard ratios of 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.21; P = .01; and 2.08; 95% CI, 1.31-3.31; P < .005; and 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.13; P < .005, respectively). Importantly, when evaluating the duration, change and variability of sleep, the researchers found that increased sleep variability was significantly associated with cognitive impairment (HR, 3.15; 95% CI, 1.69-5.87; P < .005).
Under this analysis, “sleep variability over time and not median sleep duration was associated with cognitive impairment,” she said. When sleep variability was added into the model, it improved the concordance score – a value that reflects the ability of a model to predict an outcome better than random chance – from .63 to .73 (a value of .5 indicates the model is no better at predicting an outcome than a random chance model; a value of .7 or greater indicates a good model).
Identification of sleep variability as a sleep pattern of interest in longitudinal studies is important, Dr. Keil said, because simply evaluating mean or median sleep duration across time might not account for a subject’s variable sleep phenotype. Most importantly, further evaluation of sleep variability with a linear regression prediction analysis (F statistic 8.796, P < .0001, adjusted R-squared .235) found that increased age, depression, and sleep variability significantly predicted cognitive impairment 10 years downstream. “Longitudinal sleep variability is perhaps for the first time being reported as significantly associated with the development of downstream cognitive impairment,” Dr. Keil said.
What makes this study unique, Dr. Keil said in an interview, is that it used self-reported longitudinal data gathered at 3- to 5-year intervals for up to 25 years, allowing for the assessment of variation of sleep duration across this entire time frame. “If you could use that shift in sleep duration as a point of therapeutic intervention, that would be really exciting,” she said.
Future research will evaluate how sleep variability and cognitive function are impacted by other variables gathered in the Seattle Longitudinal Study over the years, including factors such as diabetes and hypertension status, diet, alcohol and tobacco use, and marital and family status. Follow-up studies will be investigating the impact of sleep variability on neuropathologic disease progression and lymphatic system impairment, Dr. Keil said.
A newer approach
By linking sleep variability and daytime functioning, the study employs a “newer approach,” said Joseph M. Dzierzewski, PhD, director of behavioral medicine concentration in the department of psychology at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond. “While some previous work has examined night-to-night fluctuation in various sleep characteristics and cognitive functioning, what differentiates the present study from these previous works is the duration of the investigation,” he said. The “richness of data” in the Seattle Longitudinal Study and how it tracks sleep and cognition over years make it “quite unique and novel.”
Future studies, he said, should be deliberate in how they evaluate sleep and neurocognitive function across years. “Disentangling short-term moment-to-moment and day-to-day fluctuation, which may be more reversible in nature, from long-term, enduring month-to-month or year-to-year fluctuation, which may be more permanent, will be important for continuing to advance our understanding of these complex phenomena,” Dr. Dzierzewski said. “An additional important area of future investigation would be to continue the hunt for a common biological factor underpinning both sleep variability and Alzheimer’s disease.” That, he said, may help identify potential intervention targets.
Dr. Keil and Dr. Dzierzewski have no relevant disclosures.
CHARLOTTE, N.C. – Erratic sleep patterns over years or even decades, along with a patient’s age and history of depression, may be harbingers of cognitive impairment later in life, an analysis of decades of data from a large sleep study has found.
“What we were a little surprised to find in this model was that sleep duration, whether short, long or average, was not significant, but the sleep variability – the change in sleep across those time measurements—was significantly impacting the incidence of cognitive impairment,” Samantha Keil, PhD, a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Washington, Seattle, reported at the at the annual meeting of the Associated Professional Sleep Societies.
The researchers analyzed sleep and cognition data collected over decades on 1,104 adults who participated in the Seattle Longitudinal Study. Study participants ranged from age 55 to over 100, with almost 80% of the study cohort aged 65 and older.
The Seattle Longitudinal Study first started gathering data in the 1950s. Participants in the study cohort underwent an extensive cognitive battery, which was added to the study in 1984 and gathered every 5-7 years, and completed a health behavioral questionnaire (HBQ), which was added in 1993 and administered every 3-5 years, Dr. Keil said. The HBQ included a question on average nightly sleep duration.
The study used a multivariable Cox proportional hazard regression model to evaluate the overall effect of average sleep duration and changes in sleep duration over time on cognitive impairment. Covariates used in the model included apolipoprotein E4 (APOE4) genotype, gender, years of education, ethnicity, and depression.
Dr. Keil said the model found, as expected, that the demographic variables of education, APOE status, and depression were significantly associated with cognitive impairment (hazard ratios of 1.11; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.02-1.21; P = .01; and 2.08; 95% CI, 1.31-3.31; P < .005; and 1.08; 95% CI, 1.04-1.13; P < .005, respectively). Importantly, when evaluating the duration, change and variability of sleep, the researchers found that increased sleep variability was significantly associated with cognitive impairment (HR, 3.15; 95% CI, 1.69-5.87; P < .005).
Under this analysis, “sleep variability over time and not median sleep duration was associated with cognitive impairment,” she said. When sleep variability was added into the model, it improved the concordance score – a value that reflects the ability of a model to predict an outcome better than random chance – from .63 to .73 (a value of .5 indicates the model is no better at predicting an outcome than a random chance model; a value of .7 or greater indicates a good model).
Identification of sleep variability as a sleep pattern of interest in longitudinal studies is important, Dr. Keil said, because simply evaluating mean or median sleep duration across time might not account for a subject’s variable sleep phenotype. Most importantly, further evaluation of sleep variability with a linear regression prediction analysis (F statistic 8.796, P < .0001, adjusted R-squared .235) found that increased age, depression, and sleep variability significantly predicted cognitive impairment 10 years downstream. “Longitudinal sleep variability is perhaps for the first time being reported as significantly associated with the development of downstream cognitive impairment,” Dr. Keil said.
What makes this study unique, Dr. Keil said in an interview, is that it used self-reported longitudinal data gathered at 3- to 5-year intervals for up to 25 years, allowing for the assessment of variation of sleep duration across this entire time frame. “If you could use that shift in sleep duration as a point of therapeutic intervention, that would be really exciting,” she said.
Future research will evaluate how sleep variability and cognitive function are impacted by other variables gathered in the Seattle Longitudinal Study over the years, including factors such as diabetes and hypertension status, diet, alcohol and tobacco use, and marital and family status. Follow-up studies will be investigating the impact of sleep variability on neuropathologic disease progression and lymphatic system impairment, Dr. Keil said.
A newer approach
By linking sleep variability and daytime functioning, the study employs a “newer approach,” said Joseph M. Dzierzewski, PhD, director of behavioral medicine concentration in the department of psychology at Virginia Commonwealth University in Richmond. “While some previous work has examined night-to-night fluctuation in various sleep characteristics and cognitive functioning, what differentiates the present study from these previous works is the duration of the investigation,” he said. The “richness of data” in the Seattle Longitudinal Study and how it tracks sleep and cognition over years make it “quite unique and novel.”
Future studies, he said, should be deliberate in how they evaluate sleep and neurocognitive function across years. “Disentangling short-term moment-to-moment and day-to-day fluctuation, which may be more reversible in nature, from long-term, enduring month-to-month or year-to-year fluctuation, which may be more permanent, will be important for continuing to advance our understanding of these complex phenomena,” Dr. Dzierzewski said. “An additional important area of future investigation would be to continue the hunt for a common biological factor underpinning both sleep variability and Alzheimer’s disease.” That, he said, may help identify potential intervention targets.
Dr. Keil and Dr. Dzierzewski have no relevant disclosures.
AT SLEEP 2022
New onset-depression after RA diagnosis raises mortality risk ‘more than sixfold’
The development of depression after a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis increased the risk for death “more than sixfold” when compared with having no depression at diagnosis, according to Danish researchers.
Cumulative mortality at 10 years was approximately 37% in patients with comorbid RA and depression versus around 13.5% of RA patients with no depression, Jens Kristian Pedersen, MD, PhD, of Odense (Denmark) University Hospital–Svendborg Hospital and the department of clinical research at the University of Southern Denmark, also in Odense, reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“According to [antidepressant] exposure status, the cumulative mortality followed two clearly different paths,” Dr. Pedersen said. “The mortality curves separated early and already within the first and second year of follow-up.”
RA, depression, and mortality
Rates of depression in patients with RA are high, Dr. Pedersen said, and while it’s previously been reported that their coexistence can increase mortality, this is the first time that the link has been investigated in a population newly diagnosed with RA.
In this study, Dr. Pedersen and collaborators wanted to look at the association in incident RA and defined depression as the first filling of an antidepressant prescription.
“Although antidepressants are used for different indications, we have recently described that in RA the most frequent indication for filling antidepressants is depression,” he explained. Moreover, that research found that “the frequency of filling coincides with the occurrence of depressive disorder previously reported in the scientific literature.”
Data sourced from multiple Danish registers
To examine the mortality risk associated with newly diagnosed RA and new-onset depression, Dr. Pedersen described how five different Danish registers were used.
First, data from the DANBIO register were used to identify patients with incident RA living in Denmark over a 10-year period ending in December 2018. Although perhaps widely known as a biologics register, DANBIO is required by the Danish National Board of Health to collect information on all patients with RA, regardless of their treatment.
Next, the Danish National Prescription Register and Danish National Patient Register were consulted to obtain data on patients who had a first prescription for antidepressant treatment and information on those who developed a diagnosis of depression. Demographic, vital status, and socioeconomic data were collated from the Danish Civil Registration System and Statistics Denmark databases.
To be sure they were looking at incident cases of RA and new cases of depression, the researchers excluded anyone with an existing prescription of antidepressants or methotrexate, or who had a confirmed diagnosis of either disorder 3 years prior to the index date of Jan. 1, 2008.
This meant that, from a total population of 18,000 patients in the DANBIO database, there were just over 11,000 who could be included in the analyses.
Overall, the median age at RA diagnosis was 61 years, two-thirds were female, and two-thirds had seropositive disease.
New-onset depression in incident RA
“During follow-up, about 10% filled a prescription of antidepressants,” said Dr. Pedersen, adding that there were 671 deaths, representing around 57,000 person-years at risk.
“The majority died from natural causes,” he said, although the cause of death was unknown in 30% of cases.
Comparing those who did and did not have a prescription for antidepressants, there were some differences in the age at which death occurred, the percentage of females to males, the presence of other comorbidities, and levels of higher education and income. These were all adjusted for in the analyses.
Adjusted hazard rate ratios were calculated to look at the mortality risk in patients who had antidepressant exposure. The highest HRR for mortality with antidepressant use was seen in patients aged 55 years or younger at 6.66, with the next highest HRRs being for male gender (3.70) and seropositive RA (3.45).
But HRRs for seronegative RA, female gender, and age 55-70 years or older than 75 years were all still around 3.0.
Depression definition questioned
“My only concern is about the definition of depression in your analysis,” said a member of the audience at the congress.
“You used antidepressant use as a proxy of depression diagnosis, but it might be that most or many patients have taken [medication] like duloxetine for pain control, and you are just seeing higher disease activity and more aggressive RA.”
Dr. Pedersen responded: “After the EULAR 2022 submission deadline, we reanalyzed our data using two other measures of depression.
“First, we use treatment with antidepressants with a positive indication of depression, according to the prescribing physician, and secondly, we used first diagnosis with depression according to ICD-10 Code F32 – ‘depressive episode after discharge from hospital as an outpatient,’ ” he said.
“All definitions end up with a hazard rate ratio of about three. So, in my opinion, it doesn’t matter whether you focus on one measure of depression or the other.”
David Isenberg, MD, FRCP, professor of rheumatology at University College London, wanted to know more about the antecedent history of depression and whether people who had been depressed maybe a decade or 2 decades before, were more likely to get RA.
That calculation has not been done, Dr. Pedersen said, adding that the study also can’t account for people who may have had recurrent depression. Depression treatment guidelines often recommend nonpharmacologic intervention in the first instance, “so we do not necessarily get the right picture of recurrent depression if we look further back.”
Pointing out that the sixfold increase in mortality was impressive, another delegate asked about whether it was because of a higher disease activity or joint damage and if the mortality risk might be lower in patients who are in remission.
“We don’t know that yet,” Dr. Pedersen answered. “We haven’t done the calculations, but there is the issue of residual confounding if we don’t take all relevant covariates into account. So, we need to do that calculation as well.”
The study was supported by the Danish Rheumatism Association. Dr. Pedersen had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
The development of depression after a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis increased the risk for death “more than sixfold” when compared with having no depression at diagnosis, according to Danish researchers.
Cumulative mortality at 10 years was approximately 37% in patients with comorbid RA and depression versus around 13.5% of RA patients with no depression, Jens Kristian Pedersen, MD, PhD, of Odense (Denmark) University Hospital–Svendborg Hospital and the department of clinical research at the University of Southern Denmark, also in Odense, reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“According to [antidepressant] exposure status, the cumulative mortality followed two clearly different paths,” Dr. Pedersen said. “The mortality curves separated early and already within the first and second year of follow-up.”
RA, depression, and mortality
Rates of depression in patients with RA are high, Dr. Pedersen said, and while it’s previously been reported that their coexistence can increase mortality, this is the first time that the link has been investigated in a population newly diagnosed with RA.
In this study, Dr. Pedersen and collaborators wanted to look at the association in incident RA and defined depression as the first filling of an antidepressant prescription.
“Although antidepressants are used for different indications, we have recently described that in RA the most frequent indication for filling antidepressants is depression,” he explained. Moreover, that research found that “the frequency of filling coincides with the occurrence of depressive disorder previously reported in the scientific literature.”
Data sourced from multiple Danish registers
To examine the mortality risk associated with newly diagnosed RA and new-onset depression, Dr. Pedersen described how five different Danish registers were used.
First, data from the DANBIO register were used to identify patients with incident RA living in Denmark over a 10-year period ending in December 2018. Although perhaps widely known as a biologics register, DANBIO is required by the Danish National Board of Health to collect information on all patients with RA, regardless of their treatment.
Next, the Danish National Prescription Register and Danish National Patient Register were consulted to obtain data on patients who had a first prescription for antidepressant treatment and information on those who developed a diagnosis of depression. Demographic, vital status, and socioeconomic data were collated from the Danish Civil Registration System and Statistics Denmark databases.
To be sure they were looking at incident cases of RA and new cases of depression, the researchers excluded anyone with an existing prescription of antidepressants or methotrexate, or who had a confirmed diagnosis of either disorder 3 years prior to the index date of Jan. 1, 2008.
This meant that, from a total population of 18,000 patients in the DANBIO database, there were just over 11,000 who could be included in the analyses.
Overall, the median age at RA diagnosis was 61 years, two-thirds were female, and two-thirds had seropositive disease.
New-onset depression in incident RA
“During follow-up, about 10% filled a prescription of antidepressants,” said Dr. Pedersen, adding that there were 671 deaths, representing around 57,000 person-years at risk.
“The majority died from natural causes,” he said, although the cause of death was unknown in 30% of cases.
Comparing those who did and did not have a prescription for antidepressants, there were some differences in the age at which death occurred, the percentage of females to males, the presence of other comorbidities, and levels of higher education and income. These were all adjusted for in the analyses.
Adjusted hazard rate ratios were calculated to look at the mortality risk in patients who had antidepressant exposure. The highest HRR for mortality with antidepressant use was seen in patients aged 55 years or younger at 6.66, with the next highest HRRs being for male gender (3.70) and seropositive RA (3.45).
But HRRs for seronegative RA, female gender, and age 55-70 years or older than 75 years were all still around 3.0.
Depression definition questioned
“My only concern is about the definition of depression in your analysis,” said a member of the audience at the congress.
“You used antidepressant use as a proxy of depression diagnosis, but it might be that most or many patients have taken [medication] like duloxetine for pain control, and you are just seeing higher disease activity and more aggressive RA.”
Dr. Pedersen responded: “After the EULAR 2022 submission deadline, we reanalyzed our data using two other measures of depression.
“First, we use treatment with antidepressants with a positive indication of depression, according to the prescribing physician, and secondly, we used first diagnosis with depression according to ICD-10 Code F32 – ‘depressive episode after discharge from hospital as an outpatient,’ ” he said.
“All definitions end up with a hazard rate ratio of about three. So, in my opinion, it doesn’t matter whether you focus on one measure of depression or the other.”
David Isenberg, MD, FRCP, professor of rheumatology at University College London, wanted to know more about the antecedent history of depression and whether people who had been depressed maybe a decade or 2 decades before, were more likely to get RA.
That calculation has not been done, Dr. Pedersen said, adding that the study also can’t account for people who may have had recurrent depression. Depression treatment guidelines often recommend nonpharmacologic intervention in the first instance, “so we do not necessarily get the right picture of recurrent depression if we look further back.”
Pointing out that the sixfold increase in mortality was impressive, another delegate asked about whether it was because of a higher disease activity or joint damage and if the mortality risk might be lower in patients who are in remission.
“We don’t know that yet,” Dr. Pedersen answered. “We haven’t done the calculations, but there is the issue of residual confounding if we don’t take all relevant covariates into account. So, we need to do that calculation as well.”
The study was supported by the Danish Rheumatism Association. Dr. Pedersen had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
The development of depression after a rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis increased the risk for death “more than sixfold” when compared with having no depression at diagnosis, according to Danish researchers.
Cumulative mortality at 10 years was approximately 37% in patients with comorbid RA and depression versus around 13.5% of RA patients with no depression, Jens Kristian Pedersen, MD, PhD, of Odense (Denmark) University Hospital–Svendborg Hospital and the department of clinical research at the University of Southern Denmark, also in Odense, reported at the annual European Congress of Rheumatology.
“According to [antidepressant] exposure status, the cumulative mortality followed two clearly different paths,” Dr. Pedersen said. “The mortality curves separated early and already within the first and second year of follow-up.”
RA, depression, and mortality
Rates of depression in patients with RA are high, Dr. Pedersen said, and while it’s previously been reported that their coexistence can increase mortality, this is the first time that the link has been investigated in a population newly diagnosed with RA.
In this study, Dr. Pedersen and collaborators wanted to look at the association in incident RA and defined depression as the first filling of an antidepressant prescription.
“Although antidepressants are used for different indications, we have recently described that in RA the most frequent indication for filling antidepressants is depression,” he explained. Moreover, that research found that “the frequency of filling coincides with the occurrence of depressive disorder previously reported in the scientific literature.”
Data sourced from multiple Danish registers
To examine the mortality risk associated with newly diagnosed RA and new-onset depression, Dr. Pedersen described how five different Danish registers were used.
First, data from the DANBIO register were used to identify patients with incident RA living in Denmark over a 10-year period ending in December 2018. Although perhaps widely known as a biologics register, DANBIO is required by the Danish National Board of Health to collect information on all patients with RA, regardless of their treatment.
Next, the Danish National Prescription Register and Danish National Patient Register were consulted to obtain data on patients who had a first prescription for antidepressant treatment and information on those who developed a diagnosis of depression. Demographic, vital status, and socioeconomic data were collated from the Danish Civil Registration System and Statistics Denmark databases.
To be sure they were looking at incident cases of RA and new cases of depression, the researchers excluded anyone with an existing prescription of antidepressants or methotrexate, or who had a confirmed diagnosis of either disorder 3 years prior to the index date of Jan. 1, 2008.
This meant that, from a total population of 18,000 patients in the DANBIO database, there were just over 11,000 who could be included in the analyses.
Overall, the median age at RA diagnosis was 61 years, two-thirds were female, and two-thirds had seropositive disease.
New-onset depression in incident RA
“During follow-up, about 10% filled a prescription of antidepressants,” said Dr. Pedersen, adding that there were 671 deaths, representing around 57,000 person-years at risk.
“The majority died from natural causes,” he said, although the cause of death was unknown in 30% of cases.
Comparing those who did and did not have a prescription for antidepressants, there were some differences in the age at which death occurred, the percentage of females to males, the presence of other comorbidities, and levels of higher education and income. These were all adjusted for in the analyses.
Adjusted hazard rate ratios were calculated to look at the mortality risk in patients who had antidepressant exposure. The highest HRR for mortality with antidepressant use was seen in patients aged 55 years or younger at 6.66, with the next highest HRRs being for male gender (3.70) and seropositive RA (3.45).
But HRRs for seronegative RA, female gender, and age 55-70 years or older than 75 years were all still around 3.0.
Depression definition questioned
“My only concern is about the definition of depression in your analysis,” said a member of the audience at the congress.
“You used antidepressant use as a proxy of depression diagnosis, but it might be that most or many patients have taken [medication] like duloxetine for pain control, and you are just seeing higher disease activity and more aggressive RA.”
Dr. Pedersen responded: “After the EULAR 2022 submission deadline, we reanalyzed our data using two other measures of depression.
“First, we use treatment with antidepressants with a positive indication of depression, according to the prescribing physician, and secondly, we used first diagnosis with depression according to ICD-10 Code F32 – ‘depressive episode after discharge from hospital as an outpatient,’ ” he said.
“All definitions end up with a hazard rate ratio of about three. So, in my opinion, it doesn’t matter whether you focus on one measure of depression or the other.”
David Isenberg, MD, FRCP, professor of rheumatology at University College London, wanted to know more about the antecedent history of depression and whether people who had been depressed maybe a decade or 2 decades before, were more likely to get RA.
That calculation has not been done, Dr. Pedersen said, adding that the study also can’t account for people who may have had recurrent depression. Depression treatment guidelines often recommend nonpharmacologic intervention in the first instance, “so we do not necessarily get the right picture of recurrent depression if we look further back.”
Pointing out that the sixfold increase in mortality was impressive, another delegate asked about whether it was because of a higher disease activity or joint damage and if the mortality risk might be lower in patients who are in remission.
“We don’t know that yet,” Dr. Pedersen answered. “We haven’t done the calculations, but there is the issue of residual confounding if we don’t take all relevant covariates into account. So, we need to do that calculation as well.”
The study was supported by the Danish Rheumatism Association. Dr. Pedersen had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM THE EULAR 2022 CONGRESS
Adjunctive psychotherapy may offer no benefit in severe depression
Results of a cross-sectional, naturalistic, multicenter European study showed there were no significant differences in response rates between patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) who received combination treatment with psychotherapy and antidepressant medication in comparison with those who received antidepressant monotherapy, even when comparing different types of psychotherapy.
This “might emphasize the fundamental role of the underlying complex biological interrelationships in MDD and its treatment,” said study investigator Lucie Bartova, MD, PhD, Clinical Division of General Psychiatry, Medical University of Vienna.
However, she noted that patients who received psychotherapy in combination with antidepressants also had “beneficial sociodemographic and clinical characteristics,” which might reflect poorer access to “psychotherapeutic techniques for patients who are more severely ill and have less socioeconomic privilege.”
The resulting selection bias may cause patients with more severe illness to “fall by the wayside,” Dr. Bartova said.
Lead researcher Siegfried Kasper, MD, also from the Medical University of Vienna, agreed, saying in a press release that, by implication, “additional psychotherapy tends to be given to more highly educated and healthier patients, which may reflect the greater availability of psychotherapy to more socially and economically advantaged patients.”
The findings, some of which were previously published in the Journal of Psychiatry Research, were presented at the virtual European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Inconsistent guidelines
During her presentation, Dr. Bartova said that while “numerous effective antidepressant strategies are available for the treatment of MDD, many patients do not achieve a satisfactory treatment response,” which often leads to further management refinement and the use of off-label treatments.
She continued, saying that the “most obvious” approach in these situations is to try the available treatment options in a “systematic and individualized” manner, ideally by following recommended treatment algorithms.
Meta-analyses have suggested that standardized psychotherapy with fixed, regular sessions that follows an established rationale and is based on a defined school of thought is effective in MDD, “with at least moderate effects.”
Among the psychotherapy approaches, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is the “best and most investigated,” Dr. Bartova said, but international clinical practice guidelines “lack consistency” regarding recommendations for psychotherapy.
To examine the use and impact of psychotherapy for MDD patients, the researchers studied 1,410 adult inpatients and outpatients from 10 centers in eight countries who were surveyed between 2011 and 2016 by the European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression.
Participants were assessed via the Mini–International Neuropsychiatric Interview, the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale.
Results showed that among 1,279 MDD patients who were included in the final analysis, 880 (68.8%) received only antidepressants, while 399 (31.2%) received some form of structured psychotherapy as part of their treatment.
These patients included 22.8% who received CBT, 3.4% who underwent psychoanalytic psychotherapy, and 1.3% who received systemic psychotherapy. The additional psychotherapy was not specified for 3.8%.
Dr. Bartova explained that the use of psychotherapy in combination pharmacologic treatment was significantly associated with younger age, higher educational attainment, and ongoing employment in comparison with antidepressant use alone (P < .001 for all).
In addition, combination therapy was associated with an earlier average age of MDD onset, lower severity of current depressive symptoms, a lower risk of suicidality, higher rates of additional melancholic features in the patients’ symptomatology, and higher rates of comorbid asthma and migraine (P < .001 for all).
There was also a significant association between the use of psychotherapy plus pharmacologic treatment and lower average daily doses of first-line antidepressant medication (P < .001), as well as more frequent administration of agomelatine (P < .001) and a trend toward greater use of vortioxetine (P = .006).
In contrast, among patients who received antidepressants alone, there was a trend toward higher rates of additional psychotic features (P = .054), and the patients were more likely to have received selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as their first-line antidepressant medication (P < .001).
The researchers found there was no significant difference in rates of response, nonresponse, and treatment-resistant depression (TRD) between patients who received combination psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy and those who received antidepressants alone (P = .369).
Dr. Bartova showed that 25.8% of MDD patients who received combination therapy were classified as responders, compared with 23.5% of those given only antidepressants. Nonresponse was identified in 35.6% and 33.8% of patients, respectively, while 38.6% versus 42.7% had TRD.
Dr. Bartova and colleagues performed an additional analysis to determine whether there was any difference in response depending on the type of psychotherapy.
They divided patients who received combination therapy into those who had received CBT and those who had been given another form of psychotherapy.
Again, there were no significant differences in response, nonresponse, and TRD (P = .256). The response rate was 27.1% among patients given combination CBT, versus 22.4% among those who received another psychotherapy.
“Despite clinical guidelines and studies which advocate for psychotherapy and combining psychotherapy with antidepressants, this study shows that in real life, no added value can be demonstrated for psychotherapy in those already treated with antidepressants for severe depression,” Livia De Picker, MD, PhD, Collaborative Antwerp Psychiatric Research Institute, University of Antwerp, Belgium, said in the press release.
“This doesn’t necessarily mean that psychotherapy is not useful, but it is a clear sign that the way we are currently managing these depressed patients with psychotherapy is not effective and needs critical evaluation,” added Dr. De Picker, who was not involved in the research.
However, Michael E. Thase, MD, professor of psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the current study “is a secondary analysis of a naturalistic study.”
Consequently, it is not possible to account for the “dose and duration, and quality, of the psychotherapy provided.”
Therefore, the findings simply suggest that “the kinds of psychotherapy provided to these patients was not so powerful that people who received it consistently did better than those who did not,” Dr. Thase said.
The European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression obtained an unrestricted grant sponsored by Lundbeck A/S. Dr. Bartova has relationships with AOP Orphan, Medizin Medien Austria, Universimed, Vertretungsnetz, Dialectica, Diagnosia, Schwabe, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Angelini. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a cross-sectional, naturalistic, multicenter European study showed there were no significant differences in response rates between patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) who received combination treatment with psychotherapy and antidepressant medication in comparison with those who received antidepressant monotherapy, even when comparing different types of psychotherapy.
This “might emphasize the fundamental role of the underlying complex biological interrelationships in MDD and its treatment,” said study investigator Lucie Bartova, MD, PhD, Clinical Division of General Psychiatry, Medical University of Vienna.
However, she noted that patients who received psychotherapy in combination with antidepressants also had “beneficial sociodemographic and clinical characteristics,” which might reflect poorer access to “psychotherapeutic techniques for patients who are more severely ill and have less socioeconomic privilege.”
The resulting selection bias may cause patients with more severe illness to “fall by the wayside,” Dr. Bartova said.
Lead researcher Siegfried Kasper, MD, also from the Medical University of Vienna, agreed, saying in a press release that, by implication, “additional psychotherapy tends to be given to more highly educated and healthier patients, which may reflect the greater availability of psychotherapy to more socially and economically advantaged patients.”
The findings, some of which were previously published in the Journal of Psychiatry Research, were presented at the virtual European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Inconsistent guidelines
During her presentation, Dr. Bartova said that while “numerous effective antidepressant strategies are available for the treatment of MDD, many patients do not achieve a satisfactory treatment response,” which often leads to further management refinement and the use of off-label treatments.
She continued, saying that the “most obvious” approach in these situations is to try the available treatment options in a “systematic and individualized” manner, ideally by following recommended treatment algorithms.
Meta-analyses have suggested that standardized psychotherapy with fixed, regular sessions that follows an established rationale and is based on a defined school of thought is effective in MDD, “with at least moderate effects.”
Among the psychotherapy approaches, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is the “best and most investigated,” Dr. Bartova said, but international clinical practice guidelines “lack consistency” regarding recommendations for psychotherapy.
To examine the use and impact of psychotherapy for MDD patients, the researchers studied 1,410 adult inpatients and outpatients from 10 centers in eight countries who were surveyed between 2011 and 2016 by the European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression.
Participants were assessed via the Mini–International Neuropsychiatric Interview, the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale.
Results showed that among 1,279 MDD patients who were included in the final analysis, 880 (68.8%) received only antidepressants, while 399 (31.2%) received some form of structured psychotherapy as part of their treatment.
These patients included 22.8% who received CBT, 3.4% who underwent psychoanalytic psychotherapy, and 1.3% who received systemic psychotherapy. The additional psychotherapy was not specified for 3.8%.
Dr. Bartova explained that the use of psychotherapy in combination pharmacologic treatment was significantly associated with younger age, higher educational attainment, and ongoing employment in comparison with antidepressant use alone (P < .001 for all).
In addition, combination therapy was associated with an earlier average age of MDD onset, lower severity of current depressive symptoms, a lower risk of suicidality, higher rates of additional melancholic features in the patients’ symptomatology, and higher rates of comorbid asthma and migraine (P < .001 for all).
There was also a significant association between the use of psychotherapy plus pharmacologic treatment and lower average daily doses of first-line antidepressant medication (P < .001), as well as more frequent administration of agomelatine (P < .001) and a trend toward greater use of vortioxetine (P = .006).
In contrast, among patients who received antidepressants alone, there was a trend toward higher rates of additional psychotic features (P = .054), and the patients were more likely to have received selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as their first-line antidepressant medication (P < .001).
The researchers found there was no significant difference in rates of response, nonresponse, and treatment-resistant depression (TRD) between patients who received combination psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy and those who received antidepressants alone (P = .369).
Dr. Bartova showed that 25.8% of MDD patients who received combination therapy were classified as responders, compared with 23.5% of those given only antidepressants. Nonresponse was identified in 35.6% and 33.8% of patients, respectively, while 38.6% versus 42.7% had TRD.
Dr. Bartova and colleagues performed an additional analysis to determine whether there was any difference in response depending on the type of psychotherapy.
They divided patients who received combination therapy into those who had received CBT and those who had been given another form of psychotherapy.
Again, there were no significant differences in response, nonresponse, and TRD (P = .256). The response rate was 27.1% among patients given combination CBT, versus 22.4% among those who received another psychotherapy.
“Despite clinical guidelines and studies which advocate for psychotherapy and combining psychotherapy with antidepressants, this study shows that in real life, no added value can be demonstrated for psychotherapy in those already treated with antidepressants for severe depression,” Livia De Picker, MD, PhD, Collaborative Antwerp Psychiatric Research Institute, University of Antwerp, Belgium, said in the press release.
“This doesn’t necessarily mean that psychotherapy is not useful, but it is a clear sign that the way we are currently managing these depressed patients with psychotherapy is not effective and needs critical evaluation,” added Dr. De Picker, who was not involved in the research.
However, Michael E. Thase, MD, professor of psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the current study “is a secondary analysis of a naturalistic study.”
Consequently, it is not possible to account for the “dose and duration, and quality, of the psychotherapy provided.”
Therefore, the findings simply suggest that “the kinds of psychotherapy provided to these patients was not so powerful that people who received it consistently did better than those who did not,” Dr. Thase said.
The European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression obtained an unrestricted grant sponsored by Lundbeck A/S. Dr. Bartova has relationships with AOP Orphan, Medizin Medien Austria, Universimed, Vertretungsnetz, Dialectica, Diagnosia, Schwabe, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Angelini. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Results of a cross-sectional, naturalistic, multicenter European study showed there were no significant differences in response rates between patients with major depressive disorder (MDD) who received combination treatment with psychotherapy and antidepressant medication in comparison with those who received antidepressant monotherapy, even when comparing different types of psychotherapy.
This “might emphasize the fundamental role of the underlying complex biological interrelationships in MDD and its treatment,” said study investigator Lucie Bartova, MD, PhD, Clinical Division of General Psychiatry, Medical University of Vienna.
However, she noted that patients who received psychotherapy in combination with antidepressants also had “beneficial sociodemographic and clinical characteristics,” which might reflect poorer access to “psychotherapeutic techniques for patients who are more severely ill and have less socioeconomic privilege.”
The resulting selection bias may cause patients with more severe illness to “fall by the wayside,” Dr. Bartova said.
Lead researcher Siegfried Kasper, MD, also from the Medical University of Vienna, agreed, saying in a press release that, by implication, “additional psychotherapy tends to be given to more highly educated and healthier patients, which may reflect the greater availability of psychotherapy to more socially and economically advantaged patients.”
The findings, some of which were previously published in the Journal of Psychiatry Research, were presented at the virtual European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Inconsistent guidelines
During her presentation, Dr. Bartova said that while “numerous effective antidepressant strategies are available for the treatment of MDD, many patients do not achieve a satisfactory treatment response,” which often leads to further management refinement and the use of off-label treatments.
She continued, saying that the “most obvious” approach in these situations is to try the available treatment options in a “systematic and individualized” manner, ideally by following recommended treatment algorithms.
Meta-analyses have suggested that standardized psychotherapy with fixed, regular sessions that follows an established rationale and is based on a defined school of thought is effective in MDD, “with at least moderate effects.”
Among the psychotherapy approaches, cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is the “best and most investigated,” Dr. Bartova said, but international clinical practice guidelines “lack consistency” regarding recommendations for psychotherapy.
To examine the use and impact of psychotherapy for MDD patients, the researchers studied 1,410 adult inpatients and outpatients from 10 centers in eight countries who were surveyed between 2011 and 2016 by the European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression.
Participants were assessed via the Mini–International Neuropsychiatric Interview, the Montgomery-Åsberg Depression Rating Scale, and the Hamilton Depression Rating Scale.
Results showed that among 1,279 MDD patients who were included in the final analysis, 880 (68.8%) received only antidepressants, while 399 (31.2%) received some form of structured psychotherapy as part of their treatment.
These patients included 22.8% who received CBT, 3.4% who underwent psychoanalytic psychotherapy, and 1.3% who received systemic psychotherapy. The additional psychotherapy was not specified for 3.8%.
Dr. Bartova explained that the use of psychotherapy in combination pharmacologic treatment was significantly associated with younger age, higher educational attainment, and ongoing employment in comparison with antidepressant use alone (P < .001 for all).
In addition, combination therapy was associated with an earlier average age of MDD onset, lower severity of current depressive symptoms, a lower risk of suicidality, higher rates of additional melancholic features in the patients’ symptomatology, and higher rates of comorbid asthma and migraine (P < .001 for all).
There was also a significant association between the use of psychotherapy plus pharmacologic treatment and lower average daily doses of first-line antidepressant medication (P < .001), as well as more frequent administration of agomelatine (P < .001) and a trend toward greater use of vortioxetine (P = .006).
In contrast, among patients who received antidepressants alone, there was a trend toward higher rates of additional psychotic features (P = .054), and the patients were more likely to have received selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors as their first-line antidepressant medication (P < .001).
The researchers found there was no significant difference in rates of response, nonresponse, and treatment-resistant depression (TRD) between patients who received combination psychotherapy and pharmacotherapy and those who received antidepressants alone (P = .369).
Dr. Bartova showed that 25.8% of MDD patients who received combination therapy were classified as responders, compared with 23.5% of those given only antidepressants. Nonresponse was identified in 35.6% and 33.8% of patients, respectively, while 38.6% versus 42.7% had TRD.
Dr. Bartova and colleagues performed an additional analysis to determine whether there was any difference in response depending on the type of psychotherapy.
They divided patients who received combination therapy into those who had received CBT and those who had been given another form of psychotherapy.
Again, there were no significant differences in response, nonresponse, and TRD (P = .256). The response rate was 27.1% among patients given combination CBT, versus 22.4% among those who received another psychotherapy.
“Despite clinical guidelines and studies which advocate for psychotherapy and combining psychotherapy with antidepressants, this study shows that in real life, no added value can be demonstrated for psychotherapy in those already treated with antidepressants for severe depression,” Livia De Picker, MD, PhD, Collaborative Antwerp Psychiatric Research Institute, University of Antwerp, Belgium, said in the press release.
“This doesn’t necessarily mean that psychotherapy is not useful, but it is a clear sign that the way we are currently managing these depressed patients with psychotherapy is not effective and needs critical evaluation,” added Dr. De Picker, who was not involved in the research.
However, Michael E. Thase, MD, professor of psychiatry, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, told this news organization that the current study “is a secondary analysis of a naturalistic study.”
Consequently, it is not possible to account for the “dose and duration, and quality, of the psychotherapy provided.”
Therefore, the findings simply suggest that “the kinds of psychotherapy provided to these patients was not so powerful that people who received it consistently did better than those who did not,” Dr. Thase said.
The European Group for the Study of Resistant Depression obtained an unrestricted grant sponsored by Lundbeck A/S. Dr. Bartova has relationships with AOP Orphan, Medizin Medien Austria, Universimed, Vertretungsnetz, Dialectica, Diagnosia, Schwabe, Janssen, Lundbeck, and Angelini. No other relevant financial relationships have been disclosed.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EPA 2022
Synthetic opioid use up almost 800% nationwide
The results of a national urine drug test (UDT) study come as the United States is reporting a record-high number of drug overdose deaths – more than 80% of which involved fentanyl or other synthetic opioids and prompting a push for better surveillance models.
Researchers found that UDTs can be used to accurately identify which drugs are circulating in a community, revealing in just a matter of days critically important drug use trends that current surveillance methods take a month or longer to report.
The faster turnaround could potentially allow clinicians and public health officials to be more proactive with targeted overdose prevention and harm-reduction strategies such as distribution of naloxone and fentanyl test strips.
“We’re talking about trying to come up with an early-warning system,” study author Steven Passik, PhD, vice president for scientific affairs for Millennium Health, San Diego, Calif., told this news organization. “We’re trying to find out if we can let people in the harm reduction and treatment space know about what might be coming weeks or a month or more in advance so that some interventions could be marshaled.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Call for better surveillance
More than 100,000 people in the United States died of an unintended drug overdose in 2021, a record high and a 15% increase over 2020 figures, which also set a record.
Part of the federal government’s plan to address the crisis includes strengthening epidemiologic efforts by better collection and mining of public health surveillance data.
Sources currently used to detect drug use trends include mortality data, poison control centers, emergency departments, electronic health records, and crime laboratories. But analysis of these sources can take weeks or more.
“One of the real challenges in addressing and reducing overdose deaths has been the relative lack of accessible real-time data that can support agile responses to deployment of resources in a specific geographic region,” study coauthor Rebecca Jackson, MD, professor and associate dean for clinical and translational research at Ohio State University in Columbus, said in an interview.
Ohio State researchers partnered with scientists at Millennium Health, one of the largest urine test labs in the United States, on a cross-sectional study to find out if UDTs could be an accurate and speedier tool for drug surveillance.
They analyzed 500,000 unique urine samples from patients in substance use disorder (SUD) treatment facilities in all 50 states from 2013 to 2020, comparing levels of cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, synthetic opioids, and other opioids found in the samples to levels of the same drugs from overdose mortality data at the national, state, and county level from the National Vital Statistics System.
On a national level, synthetic opioids and methamphetamine were highly correlated with overdose mortality data (Spearman’s rho = .96 for both). When synthetic opioids were coinvolved, methamphetamine (rho = .98), heroin (rho = .78), cocaine (rho = .94), and other opioids (rho = .83) were also highly correlated with overdose mortality data.
Similar correlations were found when examining state-level data from 24 states and at the county level upon analysis of 19 counties in Ohio.
A changing landscape
Researchers said the strong correlation between overdose deaths and UDT results for synthetic opioids and methamphetamine are likely explained by the drugs’ availability and lethality.
“The most important thing that we found was just the strength of the correlation, which goes right to the heart of why we considered correlation to be so critical,” lead author Penn Whitley, senior director of bioinformatics for Millennium Health, told this news organization. “We needed to demonstrate that there was a strong correlation of just the UDT positivity rates with mortality – in this case, fatal drug overdose rates – as a steppingstone to build out tools that could utilize UDT as a real-time data source.”
While the main goal of the study was to establish correlation between UDT results and national mortality data, the study also offers a view of a changing landscape in the opioid epidemic.
Overall, UDT positivity for total synthetic opioids increased from 2.1% in 2013 to 19.1% in 2020 (a 792.5% increase). Positivity rates for all included drug categories increased when synthetic opioids were present.
However, in the absence of synthetic opioids, UDT positivity decreased for almost all drug categories from 2013 to 2020 (from 7.7% to 4.7% for cocaine; 3.9% to 1.6% for heroin; 20.5% to 6.9% for other opioids).
Only methamphetamine positivity increased with or without involvement of synthetic opioids. With synthetic opioids, meth positivity rose from 0.1% in 2013 to 7.9% in 2020. Without them, meth positivity rates still rose, from 2.1% in 2013 to 13.1% in 2020.
The findings track with an earlier study showing methamphetamine-involved overdose deaths rose sharply between 2011 and 2018.
“The data from this manuscript support that the opioid epidemic is transitioning from an opioid epidemic to a polysubstance epidemic where illicit synthetic opioids, largely fentanyl, in combination with other substances are now responsible for upwards of 80% of OD deaths,” Dr. Jackson said.
In an accompanying editorial Jeffrey Brent, MD, PhD, clinical professor in internal medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and Stephanie T. Weiss, MD, PhD, staff clinician in the Translational Addiction Medicine Branch at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Baltimore, note that as new agents emerge, different harm-reduction strategies will be needed, adding that having a real-time tool to identify the trends will be key to preventing deaths.
“Surveillance systems are an integral component of reducing morbidity and mortality associated with illicit drug use. On local, regional, and national levels, information of this type is needed to most efficiently allocate limited resources to maximize benefit and save lives,” Dr. Brent and Dr. Weiss write.
The study was funded by Millennium Health and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Full disclosures are included in the original articles, but no sources reported conflicts related to the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results of a national urine drug test (UDT) study come as the United States is reporting a record-high number of drug overdose deaths – more than 80% of which involved fentanyl or other synthetic opioids and prompting a push for better surveillance models.
Researchers found that UDTs can be used to accurately identify which drugs are circulating in a community, revealing in just a matter of days critically important drug use trends that current surveillance methods take a month or longer to report.
The faster turnaround could potentially allow clinicians and public health officials to be more proactive with targeted overdose prevention and harm-reduction strategies such as distribution of naloxone and fentanyl test strips.
“We’re talking about trying to come up with an early-warning system,” study author Steven Passik, PhD, vice president for scientific affairs for Millennium Health, San Diego, Calif., told this news organization. “We’re trying to find out if we can let people in the harm reduction and treatment space know about what might be coming weeks or a month or more in advance so that some interventions could be marshaled.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Call for better surveillance
More than 100,000 people in the United States died of an unintended drug overdose in 2021, a record high and a 15% increase over 2020 figures, which also set a record.
Part of the federal government’s plan to address the crisis includes strengthening epidemiologic efforts by better collection and mining of public health surveillance data.
Sources currently used to detect drug use trends include mortality data, poison control centers, emergency departments, electronic health records, and crime laboratories. But analysis of these sources can take weeks or more.
“One of the real challenges in addressing and reducing overdose deaths has been the relative lack of accessible real-time data that can support agile responses to deployment of resources in a specific geographic region,” study coauthor Rebecca Jackson, MD, professor and associate dean for clinical and translational research at Ohio State University in Columbus, said in an interview.
Ohio State researchers partnered with scientists at Millennium Health, one of the largest urine test labs in the United States, on a cross-sectional study to find out if UDTs could be an accurate and speedier tool for drug surveillance.
They analyzed 500,000 unique urine samples from patients in substance use disorder (SUD) treatment facilities in all 50 states from 2013 to 2020, comparing levels of cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, synthetic opioids, and other opioids found in the samples to levels of the same drugs from overdose mortality data at the national, state, and county level from the National Vital Statistics System.
On a national level, synthetic opioids and methamphetamine were highly correlated with overdose mortality data (Spearman’s rho = .96 for both). When synthetic opioids were coinvolved, methamphetamine (rho = .98), heroin (rho = .78), cocaine (rho = .94), and other opioids (rho = .83) were also highly correlated with overdose mortality data.
Similar correlations were found when examining state-level data from 24 states and at the county level upon analysis of 19 counties in Ohio.
A changing landscape
Researchers said the strong correlation between overdose deaths and UDT results for synthetic opioids and methamphetamine are likely explained by the drugs’ availability and lethality.
“The most important thing that we found was just the strength of the correlation, which goes right to the heart of why we considered correlation to be so critical,” lead author Penn Whitley, senior director of bioinformatics for Millennium Health, told this news organization. “We needed to demonstrate that there was a strong correlation of just the UDT positivity rates with mortality – in this case, fatal drug overdose rates – as a steppingstone to build out tools that could utilize UDT as a real-time data source.”
While the main goal of the study was to establish correlation between UDT results and national mortality data, the study also offers a view of a changing landscape in the opioid epidemic.
Overall, UDT positivity for total synthetic opioids increased from 2.1% in 2013 to 19.1% in 2020 (a 792.5% increase). Positivity rates for all included drug categories increased when synthetic opioids were present.
However, in the absence of synthetic opioids, UDT positivity decreased for almost all drug categories from 2013 to 2020 (from 7.7% to 4.7% for cocaine; 3.9% to 1.6% for heroin; 20.5% to 6.9% for other opioids).
Only methamphetamine positivity increased with or without involvement of synthetic opioids. With synthetic opioids, meth positivity rose from 0.1% in 2013 to 7.9% in 2020. Without them, meth positivity rates still rose, from 2.1% in 2013 to 13.1% in 2020.
The findings track with an earlier study showing methamphetamine-involved overdose deaths rose sharply between 2011 and 2018.
“The data from this manuscript support that the opioid epidemic is transitioning from an opioid epidemic to a polysubstance epidemic where illicit synthetic opioids, largely fentanyl, in combination with other substances are now responsible for upwards of 80% of OD deaths,” Dr. Jackson said.
In an accompanying editorial Jeffrey Brent, MD, PhD, clinical professor in internal medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and Stephanie T. Weiss, MD, PhD, staff clinician in the Translational Addiction Medicine Branch at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Baltimore, note that as new agents emerge, different harm-reduction strategies will be needed, adding that having a real-time tool to identify the trends will be key to preventing deaths.
“Surveillance systems are an integral component of reducing morbidity and mortality associated with illicit drug use. On local, regional, and national levels, information of this type is needed to most efficiently allocate limited resources to maximize benefit and save lives,” Dr. Brent and Dr. Weiss write.
The study was funded by Millennium Health and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Full disclosures are included in the original articles, but no sources reported conflicts related to the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The results of a national urine drug test (UDT) study come as the United States is reporting a record-high number of drug overdose deaths – more than 80% of which involved fentanyl or other synthetic opioids and prompting a push for better surveillance models.
Researchers found that UDTs can be used to accurately identify which drugs are circulating in a community, revealing in just a matter of days critically important drug use trends that current surveillance methods take a month or longer to report.
The faster turnaround could potentially allow clinicians and public health officials to be more proactive with targeted overdose prevention and harm-reduction strategies such as distribution of naloxone and fentanyl test strips.
“We’re talking about trying to come up with an early-warning system,” study author Steven Passik, PhD, vice president for scientific affairs for Millennium Health, San Diego, Calif., told this news organization. “We’re trying to find out if we can let people in the harm reduction and treatment space know about what might be coming weeks or a month or more in advance so that some interventions could be marshaled.”
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Call for better surveillance
More than 100,000 people in the United States died of an unintended drug overdose in 2021, a record high and a 15% increase over 2020 figures, which also set a record.
Part of the federal government’s plan to address the crisis includes strengthening epidemiologic efforts by better collection and mining of public health surveillance data.
Sources currently used to detect drug use trends include mortality data, poison control centers, emergency departments, electronic health records, and crime laboratories. But analysis of these sources can take weeks or more.
“One of the real challenges in addressing and reducing overdose deaths has been the relative lack of accessible real-time data that can support agile responses to deployment of resources in a specific geographic region,” study coauthor Rebecca Jackson, MD, professor and associate dean for clinical and translational research at Ohio State University in Columbus, said in an interview.
Ohio State researchers partnered with scientists at Millennium Health, one of the largest urine test labs in the United States, on a cross-sectional study to find out if UDTs could be an accurate and speedier tool for drug surveillance.
They analyzed 500,000 unique urine samples from patients in substance use disorder (SUD) treatment facilities in all 50 states from 2013 to 2020, comparing levels of cocaine, heroin, methamphetamine, synthetic opioids, and other opioids found in the samples to levels of the same drugs from overdose mortality data at the national, state, and county level from the National Vital Statistics System.
On a national level, synthetic opioids and methamphetamine were highly correlated with overdose mortality data (Spearman’s rho = .96 for both). When synthetic opioids were coinvolved, methamphetamine (rho = .98), heroin (rho = .78), cocaine (rho = .94), and other opioids (rho = .83) were also highly correlated with overdose mortality data.
Similar correlations were found when examining state-level data from 24 states and at the county level upon analysis of 19 counties in Ohio.
A changing landscape
Researchers said the strong correlation between overdose deaths and UDT results for synthetic opioids and methamphetamine are likely explained by the drugs’ availability and lethality.
“The most important thing that we found was just the strength of the correlation, which goes right to the heart of why we considered correlation to be so critical,” lead author Penn Whitley, senior director of bioinformatics for Millennium Health, told this news organization. “We needed to demonstrate that there was a strong correlation of just the UDT positivity rates with mortality – in this case, fatal drug overdose rates – as a steppingstone to build out tools that could utilize UDT as a real-time data source.”
While the main goal of the study was to establish correlation between UDT results and national mortality data, the study also offers a view of a changing landscape in the opioid epidemic.
Overall, UDT positivity for total synthetic opioids increased from 2.1% in 2013 to 19.1% in 2020 (a 792.5% increase). Positivity rates for all included drug categories increased when synthetic opioids were present.
However, in the absence of synthetic opioids, UDT positivity decreased for almost all drug categories from 2013 to 2020 (from 7.7% to 4.7% for cocaine; 3.9% to 1.6% for heroin; 20.5% to 6.9% for other opioids).
Only methamphetamine positivity increased with or without involvement of synthetic opioids. With synthetic opioids, meth positivity rose from 0.1% in 2013 to 7.9% in 2020. Without them, meth positivity rates still rose, from 2.1% in 2013 to 13.1% in 2020.
The findings track with an earlier study showing methamphetamine-involved overdose deaths rose sharply between 2011 and 2018.
“The data from this manuscript support that the opioid epidemic is transitioning from an opioid epidemic to a polysubstance epidemic where illicit synthetic opioids, largely fentanyl, in combination with other substances are now responsible for upwards of 80% of OD deaths,” Dr. Jackson said.
In an accompanying editorial Jeffrey Brent, MD, PhD, clinical professor in internal medicine at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, and Stephanie T. Weiss, MD, PhD, staff clinician in the Translational Addiction Medicine Branch at the National Institute on Drug Abuse, Baltimore, note that as new agents emerge, different harm-reduction strategies will be needed, adding that having a real-time tool to identify the trends will be key to preventing deaths.
“Surveillance systems are an integral component of reducing morbidity and mortality associated with illicit drug use. On local, regional, and national levels, information of this type is needed to most efficiently allocate limited resources to maximize benefit and save lives,” Dr. Brent and Dr. Weiss write.
The study was funded by Millennium Health and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences. Full disclosures are included in the original articles, but no sources reported conflicts related to the study.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A ‘crisis’ of suicidal thoughts, attempts in transgender youth
Transgender youth are significantly more likely to consider suicide and attempt it, compared with their cisgender peers, new research shows.
In a large population-based study, investigators found the increased risk of suicidality is partly because of bullying and cyberbullying experienced by transgender teens.
The findings are “extremely concerning and should be a wake-up call,” Ian Colman, PhD, with the University of Ottawa School of Epidemiology and Public Health, said in an interview.
Young people who are exploring their sexual identities may suffer from depression and anxiety, both about the reactions of their peers and families, as well as their own sense of self.
“These youth are highly marginalized and stigmatized in many corners of our society, and these findings highlight just how distressing these experiences can be,” Dr. Colman said.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Sevenfold increased risk of attempted suicide
The risk of suicidal thoughts and actions is not well studied in transgender and nonbinary youth.
To expand the evidence base, the researchers analyzed data for 6,800 adolescents aged 15-17 years from the 2019 Canadian Health Survey on Children and Youth.
The sample included 1,130 (16.5%) adolescents who identified as having some degree of same-gender attraction, 265 (4.3%) who were unsure of their attraction (“questioning”), and 50 (0.6%) who were transgender, meaning they identified as being of a gender different from that assigned at birth.
Overall, 980 (14.0%) adolescents reported having thoughts of suicide in the prior year, and 480 (6.8%) had attempted suicide in their life.
Transgender youth were five times more likely to think about suicide and more than seven times more likely to have ever attempted suicide than cisgender, heterosexual peers.
Among cisgender adolescents, girls who were attracted to girls had 3.6 times the risk of suicidal ideation and 3.3 times the risk of having ever attempted suicide, compared with their heterosexual peers.
Teens attracted to multiple genders had more than twice the risk of suicidal ideation and suicide attempt. Youth who were questioning their sexual orientation had twice the risk of having attempted suicide in their lifetime.
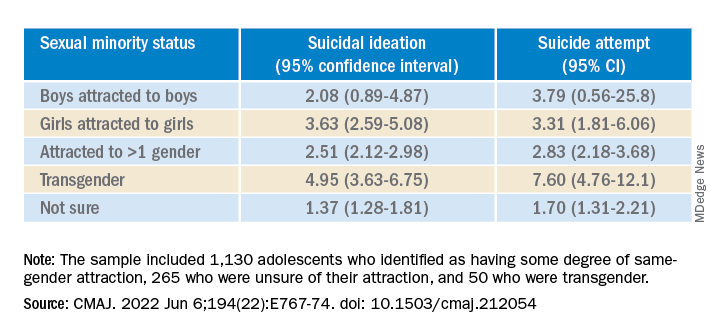
A crisis – with reason for hope
“This is a crisis, and it shows just how much more needs to be done to support transgender young people,” co-author Fae Johnstone, MSW, executive director, Wisdom2Action, who is a trans woman herself, said in the news release.
“Suicide prevention programs specifically targeted to transgender, nonbinary, and sexual minority adolescents, as well as gender-affirming care for transgender adolescents, may help reduce the burden of suicidality among this group,” Ms. Johnstone added.
“The most important thing that parents, teachers, and health care providers can do is to be supportive of these youth,” Dr. Colman told this news organization.
“Providing a safe place where gender and sexual minorities can explore and express themselves is crucial. The first step is to listen and to be compassionate,” Dr. Colman added.
Reached for comment, Jess Ting, MD, director of surgery at the Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, New York, said the data from this study on suicidal thoughts and actions among sexual minority and transgender adolescents “mirror what we see and what we know” about suicidality in trans and nonbinary adults.
“The reasons for this are complex, and it’s hard for someone who doesn’t have a lived experience as a trans or nonbinary person to understand the reasons for suicidality,” he told this news organization.
“But we also know that there are higher rates of anxiety and depression and self-image issues and posttraumatic stress disorder, not to mention outside factors – marginalization, discrimination, violence, abuse. When you add up all these intrinsic and extrinsic factors, it’s not hard to believe that there is a high rate of suicidality,” Dr. Ting said.
“There have been studies that have shown that in children who are supported in their gender identity, the rates of depression and anxiety decreased to almost the same levels as non-trans and nonbinary children, so I think that gives cause for hope,” Dr. Ting added.
The study was funded in part by the Research Council of Norway through its Centres of Excellence funding scheme and by a Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Scholarship Doctoral Award. Ms. Johnstone reports consulting fees from Spectrum Waterloo and volunteer participation with the Youth Suicide Prevention Leadership Committee of Ontario. No other competing interests were declared. Dr. Ting has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transgender youth are significantly more likely to consider suicide and attempt it, compared with their cisgender peers, new research shows.
In a large population-based study, investigators found the increased risk of suicidality is partly because of bullying and cyberbullying experienced by transgender teens.
The findings are “extremely concerning and should be a wake-up call,” Ian Colman, PhD, with the University of Ottawa School of Epidemiology and Public Health, said in an interview.
Young people who are exploring their sexual identities may suffer from depression and anxiety, both about the reactions of their peers and families, as well as their own sense of self.
“These youth are highly marginalized and stigmatized in many corners of our society, and these findings highlight just how distressing these experiences can be,” Dr. Colman said.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Sevenfold increased risk of attempted suicide
The risk of suicidal thoughts and actions is not well studied in transgender and nonbinary youth.
To expand the evidence base, the researchers analyzed data for 6,800 adolescents aged 15-17 years from the 2019 Canadian Health Survey on Children and Youth.
The sample included 1,130 (16.5%) adolescents who identified as having some degree of same-gender attraction, 265 (4.3%) who were unsure of their attraction (“questioning”), and 50 (0.6%) who were transgender, meaning they identified as being of a gender different from that assigned at birth.
Overall, 980 (14.0%) adolescents reported having thoughts of suicide in the prior year, and 480 (6.8%) had attempted suicide in their life.
Transgender youth were five times more likely to think about suicide and more than seven times more likely to have ever attempted suicide than cisgender, heterosexual peers.
Among cisgender adolescents, girls who were attracted to girls had 3.6 times the risk of suicidal ideation and 3.3 times the risk of having ever attempted suicide, compared with their heterosexual peers.
Teens attracted to multiple genders had more than twice the risk of suicidal ideation and suicide attempt. Youth who were questioning their sexual orientation had twice the risk of having attempted suicide in their lifetime.

A crisis – with reason for hope
“This is a crisis, and it shows just how much more needs to be done to support transgender young people,” co-author Fae Johnstone, MSW, executive director, Wisdom2Action, who is a trans woman herself, said in the news release.
“Suicide prevention programs specifically targeted to transgender, nonbinary, and sexual minority adolescents, as well as gender-affirming care for transgender adolescents, may help reduce the burden of suicidality among this group,” Ms. Johnstone added.
“The most important thing that parents, teachers, and health care providers can do is to be supportive of these youth,” Dr. Colman told this news organization.
“Providing a safe place where gender and sexual minorities can explore and express themselves is crucial. The first step is to listen and to be compassionate,” Dr. Colman added.
Reached for comment, Jess Ting, MD, director of surgery at the Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, New York, said the data from this study on suicidal thoughts and actions among sexual minority and transgender adolescents “mirror what we see and what we know” about suicidality in trans and nonbinary adults.
“The reasons for this are complex, and it’s hard for someone who doesn’t have a lived experience as a trans or nonbinary person to understand the reasons for suicidality,” he told this news organization.
“But we also know that there are higher rates of anxiety and depression and self-image issues and posttraumatic stress disorder, not to mention outside factors – marginalization, discrimination, violence, abuse. When you add up all these intrinsic and extrinsic factors, it’s not hard to believe that there is a high rate of suicidality,” Dr. Ting said.
“There have been studies that have shown that in children who are supported in their gender identity, the rates of depression and anxiety decreased to almost the same levels as non-trans and nonbinary children, so I think that gives cause for hope,” Dr. Ting added.
The study was funded in part by the Research Council of Norway through its Centres of Excellence funding scheme and by a Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Scholarship Doctoral Award. Ms. Johnstone reports consulting fees from Spectrum Waterloo and volunteer participation with the Youth Suicide Prevention Leadership Committee of Ontario. No other competing interests were declared. Dr. Ting has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transgender youth are significantly more likely to consider suicide and attempt it, compared with their cisgender peers, new research shows.
In a large population-based study, investigators found the increased risk of suicidality is partly because of bullying and cyberbullying experienced by transgender teens.
The findings are “extremely concerning and should be a wake-up call,” Ian Colman, PhD, with the University of Ottawa School of Epidemiology and Public Health, said in an interview.
Young people who are exploring their sexual identities may suffer from depression and anxiety, both about the reactions of their peers and families, as well as their own sense of self.
“These youth are highly marginalized and stigmatized in many corners of our society, and these findings highlight just how distressing these experiences can be,” Dr. Colman said.
The study was published online in the Canadian Medical Association Journal.
Sevenfold increased risk of attempted suicide
The risk of suicidal thoughts and actions is not well studied in transgender and nonbinary youth.
To expand the evidence base, the researchers analyzed data for 6,800 adolescents aged 15-17 years from the 2019 Canadian Health Survey on Children and Youth.
The sample included 1,130 (16.5%) adolescents who identified as having some degree of same-gender attraction, 265 (4.3%) who were unsure of their attraction (“questioning”), and 50 (0.6%) who were transgender, meaning they identified as being of a gender different from that assigned at birth.
Overall, 980 (14.0%) adolescents reported having thoughts of suicide in the prior year, and 480 (6.8%) had attempted suicide in their life.
Transgender youth were five times more likely to think about suicide and more than seven times more likely to have ever attempted suicide than cisgender, heterosexual peers.
Among cisgender adolescents, girls who were attracted to girls had 3.6 times the risk of suicidal ideation and 3.3 times the risk of having ever attempted suicide, compared with their heterosexual peers.
Teens attracted to multiple genders had more than twice the risk of suicidal ideation and suicide attempt. Youth who were questioning their sexual orientation had twice the risk of having attempted suicide in their lifetime.

A crisis – with reason for hope
“This is a crisis, and it shows just how much more needs to be done to support transgender young people,” co-author Fae Johnstone, MSW, executive director, Wisdom2Action, who is a trans woman herself, said in the news release.
“Suicide prevention programs specifically targeted to transgender, nonbinary, and sexual minority adolescents, as well as gender-affirming care for transgender adolescents, may help reduce the burden of suicidality among this group,” Ms. Johnstone added.
“The most important thing that parents, teachers, and health care providers can do is to be supportive of these youth,” Dr. Colman told this news organization.
“Providing a safe place where gender and sexual minorities can explore and express themselves is crucial. The first step is to listen and to be compassionate,” Dr. Colman added.
Reached for comment, Jess Ting, MD, director of surgery at the Mount Sinai Center for Transgender Medicine and Surgery, New York, said the data from this study on suicidal thoughts and actions among sexual minority and transgender adolescents “mirror what we see and what we know” about suicidality in trans and nonbinary adults.
“The reasons for this are complex, and it’s hard for someone who doesn’t have a lived experience as a trans or nonbinary person to understand the reasons for suicidality,” he told this news organization.
“But we also know that there are higher rates of anxiety and depression and self-image issues and posttraumatic stress disorder, not to mention outside factors – marginalization, discrimination, violence, abuse. When you add up all these intrinsic and extrinsic factors, it’s not hard to believe that there is a high rate of suicidality,” Dr. Ting said.
“There have been studies that have shown that in children who are supported in their gender identity, the rates of depression and anxiety decreased to almost the same levels as non-trans and nonbinary children, so I think that gives cause for hope,” Dr. Ting added.
The study was funded in part by the Research Council of Norway through its Centres of Excellence funding scheme and by a Frederick Banting and Charles Best Canada Graduate Scholarship Doctoral Award. Ms. Johnstone reports consulting fees from Spectrum Waterloo and volunteer participation with the Youth Suicide Prevention Leadership Committee of Ontario. No other competing interests were declared. Dr. Ting has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE CANADIAN MEDICAL ASSOCIATION JOURNAL
New studies show growing number of trans, nonbinary youth in U.S.
Two new studies point to an ever-increasing number of young people in the United States who identify as transgender and nonbinary, with the figures doubling among 18- to 24-year-olds in one institute’s research – from 0.66% of the population in 2016 to 1.3% (398,900) in 2022.
In addition, 1.4% (300,100) of 13- to 17-year-olds identify as trans or nonbinary, according to the report from that group, the Williams Institute at the University of California, Los Angeles, School of Law.
Williams, which conducts independent research on sexual orientation and gender identity law and public policy, did not contain data on 13- to 17-year-olds in its 2016 study, so the growth in that group over the past 5+ years is not as well documented.
Overall, some 1.6 million Americans older than age 13 now identify as transgender, reported the Williams researchers.
And in a new Pew Research Center survey, 2% of adults aged 18-29 identify as transgender and 3% identify as nonbinary, a far greater number than in other age cohorts.
These reports are likely underestimates. The Human Rights Campaign estimates that some 2 million Americans of all ages identify as transgender.
The Pew survey is weighted to be representative but still has limitations, said the organization. The Williams analysis, based on responses to two CDC surveys – the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) – is incomplete, say researchers, because not every state collects data on gender identity.
Transgender identities more predominant among youth
The Williams researchers report that 18.3% of those who identified as trans were 13- to 17-year-olds; that age group makes up 7.6% of the United States population 13 and older.
And despite not having firm figures from earlier reports, they comment: “Youth ages 13-17 comprise a larger share of the transgender-identified population than we previously estimated, currently comprising about 18% of the transgender-identified population in the United State, up from 10% previously.”
About one-quarter of those who identified as trans in the new 2022 report were aged 18-24; that age cohort accounts for 11% of Americans.
The number of older Americans who identify as trans are more proportionate to their representation in the population, according to Williams. Overall, about half of those who said they were trans were aged 25-64; that group accounts for 62% of the overall American population. Some 10% of trans-identified individuals were over age 65. About 20% of Americans are 65 or older, said the researchers.
The Pew research – based on the responses of 10,188 individuals surveyed in May – also found growing numbers of young people who identify as trans. “The share of U.S. adults who are transgender is particularly high among adults younger than 25,” reported Pew in a blog post.
In the 18- to 25-year-old group, 3.1% identified as a trans man or a trans woman, compared with just 0.5% of those ages 25-29.
That compares to 0.3% of those aged 30-49 and 0.2% of those older than 50.
Racial and state-by-state variation
Similar percentages of youth aged 13-17 of all races and ethnicities in the Williams study report they are transgender, ranging from 1% of those who are Asian, to 1.3% of White youth, 1.4% of Black youth, 1.8% of American Indian or Alaska Native, and 1.8% of Latinx youth. The institute reported that 1.5% of biracial and multiracial youth identified as transgender.
The researchers said, however, that “transgender-identified youth and adults appear more likely to report being Latinx and less likely to report being White, as compared to the United States population.”
Transgender individuals live in every state, with the greatest percentage of both youth and adults in the Northeast and West, and lesser percentages in the Midwest and South, reported the Williams Institute.
Williams estimates as many as 3% of 13- to 17-year-olds in New York identify as trans, while just 0.6% of that age group in Wyoming is transgender. A total of 2%-2.5% of those aged 13-17 are transgender in Hawaii, New Mexico, Maryland, and Washington, D.C.
Among the states with higher percentages of trans-identifying 18- to 24-year-olds: Arizona (1.9%), Arkansas (3.6%), Colorado (2%), Delaware (2.4%), Illinois (1.9%), Maryland (1.9%), North Carolina (2.5%), Oklahoma (2.5%), Massachusetts (2.3%), Rhode Island (2.1%), and Washington (2%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two new studies point to an ever-increasing number of young people in the United States who identify as transgender and nonbinary, with the figures doubling among 18- to 24-year-olds in one institute’s research – from 0.66% of the population in 2016 to 1.3% (398,900) in 2022.
In addition, 1.4% (300,100) of 13- to 17-year-olds identify as trans or nonbinary, according to the report from that group, the Williams Institute at the University of California, Los Angeles, School of Law.
Williams, which conducts independent research on sexual orientation and gender identity law and public policy, did not contain data on 13- to 17-year-olds in its 2016 study, so the growth in that group over the past 5+ years is not as well documented.
Overall, some 1.6 million Americans older than age 13 now identify as transgender, reported the Williams researchers.
And in a new Pew Research Center survey, 2% of adults aged 18-29 identify as transgender and 3% identify as nonbinary, a far greater number than in other age cohorts.
These reports are likely underestimates. The Human Rights Campaign estimates that some 2 million Americans of all ages identify as transgender.
The Pew survey is weighted to be representative but still has limitations, said the organization. The Williams analysis, based on responses to two CDC surveys – the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) – is incomplete, say researchers, because not every state collects data on gender identity.
Transgender identities more predominant among youth
The Williams researchers report that 18.3% of those who identified as trans were 13- to 17-year-olds; that age group makes up 7.6% of the United States population 13 and older.
And despite not having firm figures from earlier reports, they comment: “Youth ages 13-17 comprise a larger share of the transgender-identified population than we previously estimated, currently comprising about 18% of the transgender-identified population in the United State, up from 10% previously.”
About one-quarter of those who identified as trans in the new 2022 report were aged 18-24; that age cohort accounts for 11% of Americans.
The number of older Americans who identify as trans are more proportionate to their representation in the population, according to Williams. Overall, about half of those who said they were trans were aged 25-64; that group accounts for 62% of the overall American population. Some 10% of trans-identified individuals were over age 65. About 20% of Americans are 65 or older, said the researchers.
The Pew research – based on the responses of 10,188 individuals surveyed in May – also found growing numbers of young people who identify as trans. “The share of U.S. adults who are transgender is particularly high among adults younger than 25,” reported Pew in a blog post.
In the 18- to 25-year-old group, 3.1% identified as a trans man or a trans woman, compared with just 0.5% of those ages 25-29.
That compares to 0.3% of those aged 30-49 and 0.2% of those older than 50.
Racial and state-by-state variation
Similar percentages of youth aged 13-17 of all races and ethnicities in the Williams study report they are transgender, ranging from 1% of those who are Asian, to 1.3% of White youth, 1.4% of Black youth, 1.8% of American Indian or Alaska Native, and 1.8% of Latinx youth. The institute reported that 1.5% of biracial and multiracial youth identified as transgender.
The researchers said, however, that “transgender-identified youth and adults appear more likely to report being Latinx and less likely to report being White, as compared to the United States population.”
Transgender individuals live in every state, with the greatest percentage of both youth and adults in the Northeast and West, and lesser percentages in the Midwest and South, reported the Williams Institute.
Williams estimates as many as 3% of 13- to 17-year-olds in New York identify as trans, while just 0.6% of that age group in Wyoming is transgender. A total of 2%-2.5% of those aged 13-17 are transgender in Hawaii, New Mexico, Maryland, and Washington, D.C.
Among the states with higher percentages of trans-identifying 18- to 24-year-olds: Arizona (1.9%), Arkansas (3.6%), Colorado (2%), Delaware (2.4%), Illinois (1.9%), Maryland (1.9%), North Carolina (2.5%), Oklahoma (2.5%), Massachusetts (2.3%), Rhode Island (2.1%), and Washington (2%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Two new studies point to an ever-increasing number of young people in the United States who identify as transgender and nonbinary, with the figures doubling among 18- to 24-year-olds in one institute’s research – from 0.66% of the population in 2016 to 1.3% (398,900) in 2022.
In addition, 1.4% (300,100) of 13- to 17-year-olds identify as trans or nonbinary, according to the report from that group, the Williams Institute at the University of California, Los Angeles, School of Law.
Williams, which conducts independent research on sexual orientation and gender identity law and public policy, did not contain data on 13- to 17-year-olds in its 2016 study, so the growth in that group over the past 5+ years is not as well documented.
Overall, some 1.6 million Americans older than age 13 now identify as transgender, reported the Williams researchers.
And in a new Pew Research Center survey, 2% of adults aged 18-29 identify as transgender and 3% identify as nonbinary, a far greater number than in other age cohorts.
These reports are likely underestimates. The Human Rights Campaign estimates that some 2 million Americans of all ages identify as transgender.
The Pew survey is weighted to be representative but still has limitations, said the organization. The Williams analysis, based on responses to two CDC surveys – the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System (BRFSS) and Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS) – is incomplete, say researchers, because not every state collects data on gender identity.
Transgender identities more predominant among youth
The Williams researchers report that 18.3% of those who identified as trans were 13- to 17-year-olds; that age group makes up 7.6% of the United States population 13 and older.
And despite not having firm figures from earlier reports, they comment: “Youth ages 13-17 comprise a larger share of the transgender-identified population than we previously estimated, currently comprising about 18% of the transgender-identified population in the United State, up from 10% previously.”
About one-quarter of those who identified as trans in the new 2022 report were aged 18-24; that age cohort accounts for 11% of Americans.
The number of older Americans who identify as trans are more proportionate to their representation in the population, according to Williams. Overall, about half of those who said they were trans were aged 25-64; that group accounts for 62% of the overall American population. Some 10% of trans-identified individuals were over age 65. About 20% of Americans are 65 or older, said the researchers.
The Pew research – based on the responses of 10,188 individuals surveyed in May – also found growing numbers of young people who identify as trans. “The share of U.S. adults who are transgender is particularly high among adults younger than 25,” reported Pew in a blog post.
In the 18- to 25-year-old group, 3.1% identified as a trans man or a trans woman, compared with just 0.5% of those ages 25-29.
That compares to 0.3% of those aged 30-49 and 0.2% of those older than 50.
Racial and state-by-state variation
Similar percentages of youth aged 13-17 of all races and ethnicities in the Williams study report they are transgender, ranging from 1% of those who are Asian, to 1.3% of White youth, 1.4% of Black youth, 1.8% of American Indian or Alaska Native, and 1.8% of Latinx youth. The institute reported that 1.5% of biracial and multiracial youth identified as transgender.
The researchers said, however, that “transgender-identified youth and adults appear more likely to report being Latinx and less likely to report being White, as compared to the United States population.”
Transgender individuals live in every state, with the greatest percentage of both youth and adults in the Northeast and West, and lesser percentages in the Midwest and South, reported the Williams Institute.
Williams estimates as many as 3% of 13- to 17-year-olds in New York identify as trans, while just 0.6% of that age group in Wyoming is transgender. A total of 2%-2.5% of those aged 13-17 are transgender in Hawaii, New Mexico, Maryland, and Washington, D.C.
Among the states with higher percentages of trans-identifying 18- to 24-year-olds: Arizona (1.9%), Arkansas (3.6%), Colorado (2%), Delaware (2.4%), Illinois (1.9%), Maryland (1.9%), North Carolina (2.5%), Oklahoma (2.5%), Massachusetts (2.3%), Rhode Island (2.1%), and Washington (2%).
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hormonal contraceptives protective against suicide?
Contrary to previous analyses, new research suggests.
In a study of more than 800 women younger than age 50 who attempted suicide and more than 3,000 age-matched peers, results showed those who took hormonal contraceptives had a 27% reduced risk for attempted suicide.
Further analysis showed this was confined to women without a history of psychiatric illness and the reduction in risk rose to 43% among those who took combined hormonal contraceptives rather than progestin-only versions.
The protective effect against attempted suicide increased further to 46% if ethinyl estradiol (EE)–containing preparations were used. Moreover, the beneficial effect of contraceptive use increased over time.
The main message is the “current use of hormonal contraceptives is not associated with an increased risk of attempted suicide in our population,” study presenter Elena Toffol, MD, PhD, department of public health, University of Helsinki, told meeting attendees at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Age range differences
Dr. Toffol said there could be “several reasons” why the results are different from those in previous studies, including that the researchers included a “larger age range.” She noted it is known that “older women have a lower rate of attempted suicide and use different types of contraceptives.”
Dr. Toffol said in an interview that, although it’s “hard to estimate any causality” because this is an observational study, it is “tempting to speculate, and it is plausible, that hormones partly play a role with some, but not all, women being more sensitive to hormonal influences.”
However, the results “may also reflect life choices or a protective life status; for example, more stable relationships or more conscious and health-focused behaviors,” she said.
“It may also be that the underlying characteristics of women who are prescribed or opt for certain types of contraceptives are somehow related to their suicidal risk,” she added.
In 2019, the global age-standardized suicide rate was 9.0 per 100,000, which translates into more than 700,000 deaths every year, Dr. Toffol noted.
However, she emphasized the World Health Organization has calculated that, for every adult who dies by suicide, more than 20 people attempt suicide. In addition, data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate that attempted suicides are three times more common among young women than in men.
“What are the reasons for this gender gap?” Dr. Toffol asked during her presentation.
“It is known that the major risk factor for suicidal behavior is a psychiatric disorder, and in particular depression and mood disorders. And depression and mood disorders are more common in women than in men,” she said.
However, there is also “growing interest into the role of biological factors” in the risk for suicide, including hormones and hormonal contraception. Some studies have also suggested that there is an increased risk for depression and “both completed and attempted suicide” after starting hormonal contraception.
Dr. Toffol added that about 70% of European women use some form of contraception and, among Finnish women, 40% choose a hormonal contraceptive.
Nested analysis
The researchers conducted a nested case-control analysis combining 2017 national prescription data on 587,823 women aged 15-49 years with information from general and primary healthcare registers for the years 2018 to 2019.
They were able to identify 818 cases of attempted suicide among the women. These were matched 4:1 with 3,272 age-matched healthy women who acted as the control group. Use of hormonal contraceptives in the previous 180 days was determined for the whole cohort.
Among users of hormonal contraceptives, there were 344 attempted suicides in 2017, at an incidence rate of 0.59 per 1,000 person-years. This compared with 474 attempted suicides among nonusers, at an incidence rate of 0.81 per 1000 person-years.
Kaplan-Meier analysis showed there was a significant difference in rates for attempted suicide among hormonal contraceptive users versus nonusers, at an incidence rate ratio of 0.73 (P < .0001) – and the difference increased over time.
In addition, the incidence of attempted suicide decreased with increasing age, with the highest incidence rate in women aged 15-19 years (1.62 per 1,000 person-years).
Conditional logistic regression analysis that controlled for education, marital status, chronic disease, recent psychiatric hospitalization, and current use of psychotropic medication showed hormonal contraceptive use was not linked to an increased risk of attempted suicide overall, at an odds ratio of 0.79 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-1.11).
However, when they looked specifically at women without a history of psychiatric illness, the association became significant, at an OR of 0.73 for attempted suicide among hormonal contraceptive users (95% CI, 0.58-0.91), while the relationship remained nonsignificant in women with a history of psychiatric disorders.
Further analysis suggested the significant association was confined to women taking combined hormonal contraceptives, at an OR of 0.57 for suicide attempt versus nonusers (95% CI, 0.44-0.75), and those use EE-containing preparations (OR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.40-0.73).
There was a suggestion in the data that hormonal contraceptives containing desogestrel or drospirenone alongside EE may offer the greatest reduction in attempted suicide risk, but that did not survive multivariate analysis.
Dr. Toffol also noted that they were not able to capture data on use of intrauterine devices in their analysis.
“There is a growing number of municipalities in Finland that are providing free-of-charge contraception to young women” that is often an intrauterine device, she said. The researchers hope to include these women in a future analysis.
‘Age matters’
Commenting on the findings, Alexis C. Edwards, PhD, Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the current study’s findings “made a lot of sense.” Dr. Edwards wasn’t involved with this study but conducted a previous study of 216,702 Swedish women aged 15-22 years that showed use of combination or progestin-only oral contraceptives was associated with an increased risk for suicidal behavior.
She agreed with Dr. Toffol that the “much larger age range” in the new study may have played a role in showing the opposite result.
“The trajectory that we saw if we had been able to continue following the women for longer – which we couldn’t, due to limitations of the registries – [was that] using hormonal contraceptives was going to end up being protective, so I do think that it matters what age you’re looking at,” she said.
Dr. Edwards noted the takeaway from both studies “is that, even if there is a slight increase in risk from using hormonal contraceptives, it’s short lived and it’s probably specific to young women, which is important.”
She suggested the hormonal benefit from extended contraceptive use could come from the regulation of mood, as it offers a “more stable hormonal course than what their body might be putting them through in the absence of using the pill.”
Overall, it is “really lovely to see very well-executed studies on this, providing more empirical evidence on this question, because it is something that’s relevant to anyone who’s potentially going to be using hormonal contraception,” Dr. Edwards said.
Clinical implications?
Andrea Fiorillo, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli,” Naples, Italy, said in a press release that the “striking” findings of the current study need “careful evaluation.”
They also need to be replicated in “different cohorts of women and controlled for the impact of several psychosocial stressors, such as economic upheavals, social insecurity, and uncertainty due to the COVID pandemic,” said Dr. Fiorillo, who was not involved with the research.
Nevertheless, she believes the “clinical implications of the study are obvious and may help to destigmatize the use of hormonal contraceptives.”
The study was funded by the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Avohoidon Tsukimis äätiö (Foundation for Primary Care Research), the Yrj ö Jahnsson Foundation, and the Finnish Cultural Foundation. No relevant financial relationships were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contrary to previous analyses, new research suggests.
In a study of more than 800 women younger than age 50 who attempted suicide and more than 3,000 age-matched peers, results showed those who took hormonal contraceptives had a 27% reduced risk for attempted suicide.
Further analysis showed this was confined to women without a history of psychiatric illness and the reduction in risk rose to 43% among those who took combined hormonal contraceptives rather than progestin-only versions.
The protective effect against attempted suicide increased further to 46% if ethinyl estradiol (EE)–containing preparations were used. Moreover, the beneficial effect of contraceptive use increased over time.
The main message is the “current use of hormonal contraceptives is not associated with an increased risk of attempted suicide in our population,” study presenter Elena Toffol, MD, PhD, department of public health, University of Helsinki, told meeting attendees at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Age range differences
Dr. Toffol said there could be “several reasons” why the results are different from those in previous studies, including that the researchers included a “larger age range.” She noted it is known that “older women have a lower rate of attempted suicide and use different types of contraceptives.”
Dr. Toffol said in an interview that, although it’s “hard to estimate any causality” because this is an observational study, it is “tempting to speculate, and it is plausible, that hormones partly play a role with some, but not all, women being more sensitive to hormonal influences.”
However, the results “may also reflect life choices or a protective life status; for example, more stable relationships or more conscious and health-focused behaviors,” she said.
“It may also be that the underlying characteristics of women who are prescribed or opt for certain types of contraceptives are somehow related to their suicidal risk,” she added.
In 2019, the global age-standardized suicide rate was 9.0 per 100,000, which translates into more than 700,000 deaths every year, Dr. Toffol noted.
However, she emphasized the World Health Organization has calculated that, for every adult who dies by suicide, more than 20 people attempt suicide. In addition, data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate that attempted suicides are three times more common among young women than in men.
“What are the reasons for this gender gap?” Dr. Toffol asked during her presentation.
“It is known that the major risk factor for suicidal behavior is a psychiatric disorder, and in particular depression and mood disorders. And depression and mood disorders are more common in women than in men,” she said.
However, there is also “growing interest into the role of biological factors” in the risk for suicide, including hormones and hormonal contraception. Some studies have also suggested that there is an increased risk for depression and “both completed and attempted suicide” after starting hormonal contraception.
Dr. Toffol added that about 70% of European women use some form of contraception and, among Finnish women, 40% choose a hormonal contraceptive.
Nested analysis
The researchers conducted a nested case-control analysis combining 2017 national prescription data on 587,823 women aged 15-49 years with information from general and primary healthcare registers for the years 2018 to 2019.
They were able to identify 818 cases of attempted suicide among the women. These were matched 4:1 with 3,272 age-matched healthy women who acted as the control group. Use of hormonal contraceptives in the previous 180 days was determined for the whole cohort.
Among users of hormonal contraceptives, there were 344 attempted suicides in 2017, at an incidence rate of 0.59 per 1,000 person-years. This compared with 474 attempted suicides among nonusers, at an incidence rate of 0.81 per 1000 person-years.
Kaplan-Meier analysis showed there was a significant difference in rates for attempted suicide among hormonal contraceptive users versus nonusers, at an incidence rate ratio of 0.73 (P < .0001) – and the difference increased over time.
In addition, the incidence of attempted suicide decreased with increasing age, with the highest incidence rate in women aged 15-19 years (1.62 per 1,000 person-years).
Conditional logistic regression analysis that controlled for education, marital status, chronic disease, recent psychiatric hospitalization, and current use of psychotropic medication showed hormonal contraceptive use was not linked to an increased risk of attempted suicide overall, at an odds ratio of 0.79 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-1.11).
However, when they looked specifically at women without a history of psychiatric illness, the association became significant, at an OR of 0.73 for attempted suicide among hormonal contraceptive users (95% CI, 0.58-0.91), while the relationship remained nonsignificant in women with a history of psychiatric disorders.
Further analysis suggested the significant association was confined to women taking combined hormonal contraceptives, at an OR of 0.57 for suicide attempt versus nonusers (95% CI, 0.44-0.75), and those use EE-containing preparations (OR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.40-0.73).
There was a suggestion in the data that hormonal contraceptives containing desogestrel or drospirenone alongside EE may offer the greatest reduction in attempted suicide risk, but that did not survive multivariate analysis.
Dr. Toffol also noted that they were not able to capture data on use of intrauterine devices in their analysis.
“There is a growing number of municipalities in Finland that are providing free-of-charge contraception to young women” that is often an intrauterine device, she said. The researchers hope to include these women in a future analysis.
‘Age matters’
Commenting on the findings, Alexis C. Edwards, PhD, Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the current study’s findings “made a lot of sense.” Dr. Edwards wasn’t involved with this study but conducted a previous study of 216,702 Swedish women aged 15-22 years that showed use of combination or progestin-only oral contraceptives was associated with an increased risk for suicidal behavior.
She agreed with Dr. Toffol that the “much larger age range” in the new study may have played a role in showing the opposite result.
“The trajectory that we saw if we had been able to continue following the women for longer – which we couldn’t, due to limitations of the registries – [was that] using hormonal contraceptives was going to end up being protective, so I do think that it matters what age you’re looking at,” she said.
Dr. Edwards noted the takeaway from both studies “is that, even if there is a slight increase in risk from using hormonal contraceptives, it’s short lived and it’s probably specific to young women, which is important.”
She suggested the hormonal benefit from extended contraceptive use could come from the regulation of mood, as it offers a “more stable hormonal course than what their body might be putting them through in the absence of using the pill.”
Overall, it is “really lovely to see very well-executed studies on this, providing more empirical evidence on this question, because it is something that’s relevant to anyone who’s potentially going to be using hormonal contraception,” Dr. Edwards said.
Clinical implications?
Andrea Fiorillo, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli,” Naples, Italy, said in a press release that the “striking” findings of the current study need “careful evaluation.”
They also need to be replicated in “different cohorts of women and controlled for the impact of several psychosocial stressors, such as economic upheavals, social insecurity, and uncertainty due to the COVID pandemic,” said Dr. Fiorillo, who was not involved with the research.
Nevertheless, she believes the “clinical implications of the study are obvious and may help to destigmatize the use of hormonal contraceptives.”
The study was funded by the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Avohoidon Tsukimis äätiö (Foundation for Primary Care Research), the Yrj ö Jahnsson Foundation, and the Finnish Cultural Foundation. No relevant financial relationships were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Contrary to previous analyses, new research suggests.
In a study of more than 800 women younger than age 50 who attempted suicide and more than 3,000 age-matched peers, results showed those who took hormonal contraceptives had a 27% reduced risk for attempted suicide.
Further analysis showed this was confined to women without a history of psychiatric illness and the reduction in risk rose to 43% among those who took combined hormonal contraceptives rather than progestin-only versions.
The protective effect against attempted suicide increased further to 46% if ethinyl estradiol (EE)–containing preparations were used. Moreover, the beneficial effect of contraceptive use increased over time.
The main message is the “current use of hormonal contraceptives is not associated with an increased risk of attempted suicide in our population,” study presenter Elena Toffol, MD, PhD, department of public health, University of Helsinki, told meeting attendees at the European Psychiatric Association 2022 Congress.
Age range differences
Dr. Toffol said there could be “several reasons” why the results are different from those in previous studies, including that the researchers included a “larger age range.” She noted it is known that “older women have a lower rate of attempted suicide and use different types of contraceptives.”
Dr. Toffol said in an interview that, although it’s “hard to estimate any causality” because this is an observational study, it is “tempting to speculate, and it is plausible, that hormones partly play a role with some, but not all, women being more sensitive to hormonal influences.”
However, the results “may also reflect life choices or a protective life status; for example, more stable relationships or more conscious and health-focused behaviors,” she said.
“It may also be that the underlying characteristics of women who are prescribed or opt for certain types of contraceptives are somehow related to their suicidal risk,” she added.
In 2019, the global age-standardized suicide rate was 9.0 per 100,000, which translates into more than 700,000 deaths every year, Dr. Toffol noted.
However, she emphasized the World Health Organization has calculated that, for every adult who dies by suicide, more than 20 people attempt suicide. In addition, data from the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention indicate that attempted suicides are three times more common among young women than in men.
“What are the reasons for this gender gap?” Dr. Toffol asked during her presentation.
“It is known that the major risk factor for suicidal behavior is a psychiatric disorder, and in particular depression and mood disorders. And depression and mood disorders are more common in women than in men,” she said.
However, there is also “growing interest into the role of biological factors” in the risk for suicide, including hormones and hormonal contraception. Some studies have also suggested that there is an increased risk for depression and “both completed and attempted suicide” after starting hormonal contraception.
Dr. Toffol added that about 70% of European women use some form of contraception and, among Finnish women, 40% choose a hormonal contraceptive.
Nested analysis
The researchers conducted a nested case-control analysis combining 2017 national prescription data on 587,823 women aged 15-49 years with information from general and primary healthcare registers for the years 2018 to 2019.
They were able to identify 818 cases of attempted suicide among the women. These were matched 4:1 with 3,272 age-matched healthy women who acted as the control group. Use of hormonal contraceptives in the previous 180 days was determined for the whole cohort.
Among users of hormonal contraceptives, there were 344 attempted suicides in 2017, at an incidence rate of 0.59 per 1,000 person-years. This compared with 474 attempted suicides among nonusers, at an incidence rate of 0.81 per 1000 person-years.
Kaplan-Meier analysis showed there was a significant difference in rates for attempted suicide among hormonal contraceptive users versus nonusers, at an incidence rate ratio of 0.73 (P < .0001) – and the difference increased over time.
In addition, the incidence of attempted suicide decreased with increasing age, with the highest incidence rate in women aged 15-19 years (1.62 per 1,000 person-years).
Conditional logistic regression analysis that controlled for education, marital status, chronic disease, recent psychiatric hospitalization, and current use of psychotropic medication showed hormonal contraceptive use was not linked to an increased risk of attempted suicide overall, at an odds ratio of 0.79 (95% confidence interval, 0.56-1.11).
However, when they looked specifically at women without a history of psychiatric illness, the association became significant, at an OR of 0.73 for attempted suicide among hormonal contraceptive users (95% CI, 0.58-0.91), while the relationship remained nonsignificant in women with a history of psychiatric disorders.
Further analysis suggested the significant association was confined to women taking combined hormonal contraceptives, at an OR of 0.57 for suicide attempt versus nonusers (95% CI, 0.44-0.75), and those use EE-containing preparations (OR, 0.54; 95% CI, 0.40-0.73).
There was a suggestion in the data that hormonal contraceptives containing desogestrel or drospirenone alongside EE may offer the greatest reduction in attempted suicide risk, but that did not survive multivariate analysis.
Dr. Toffol also noted that they were not able to capture data on use of intrauterine devices in their analysis.
“There is a growing number of municipalities in Finland that are providing free-of-charge contraception to young women” that is often an intrauterine device, she said. The researchers hope to include these women in a future analysis.
‘Age matters’
Commenting on the findings, Alexis C. Edwards, PhD, Virginia Institute for Psychiatric and Behavioral Genetics, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, said the current study’s findings “made a lot of sense.” Dr. Edwards wasn’t involved with this study but conducted a previous study of 216,702 Swedish women aged 15-22 years that showed use of combination or progestin-only oral contraceptives was associated with an increased risk for suicidal behavior.
She agreed with Dr. Toffol that the “much larger age range” in the new study may have played a role in showing the opposite result.
“The trajectory that we saw if we had been able to continue following the women for longer – which we couldn’t, due to limitations of the registries – [was that] using hormonal contraceptives was going to end up being protective, so I do think that it matters what age you’re looking at,” she said.
Dr. Edwards noted the takeaway from both studies “is that, even if there is a slight increase in risk from using hormonal contraceptives, it’s short lived and it’s probably specific to young women, which is important.”
She suggested the hormonal benefit from extended contraceptive use could come from the regulation of mood, as it offers a “more stable hormonal course than what their body might be putting them through in the absence of using the pill.”
Overall, it is “really lovely to see very well-executed studies on this, providing more empirical evidence on this question, because it is something that’s relevant to anyone who’s potentially going to be using hormonal contraception,” Dr. Edwards said.
Clinical implications?
Andrea Fiorillo, MD, PhD, department of psychiatry, University of Campania “Luigi Vanvitelli,” Naples, Italy, said in a press release that the “striking” findings of the current study need “careful evaluation.”
They also need to be replicated in “different cohorts of women and controlled for the impact of several psychosocial stressors, such as economic upheavals, social insecurity, and uncertainty due to the COVID pandemic,” said Dr. Fiorillo, who was not involved with the research.
Nevertheless, she believes the “clinical implications of the study are obvious and may help to destigmatize the use of hormonal contraceptives.”
The study was funded by the Jane and Aatos Erkko Foundation, the Avohoidon Tsukimis äätiö (Foundation for Primary Care Research), the Yrj ö Jahnsson Foundation, and the Finnish Cultural Foundation. No relevant financial relationships were reported.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM EPA 2022
When suffering defies diagnosis
I still remember the woman who came to my office that day, years ago. She was struggling and uncomfortable, and she wanted “something” for stress. She described her life, and to me, it sounded stressful. She lived in a blended family and she described the chaos that one might expect to find in a household with four teens, their friends, their activities, and all it took to keep the household going. I spent 2 hours evaluating the patient, and I could not find a diagnosis that fit this problem nor – I believed – a pill that would fix it. She didn’t “meet criteria” for a psychiatric disorder, but she insisted she was uncomfortable and she wanted to try medication. I admit, I relented and I gave her a prescription for fluoxetine.
When she returned a few weeks later, my patient said she felt better, and what I remember decades later was her statement: “Now I can see dishes in the sink and be okay with it.” Perhaps she had downplayed her anxiety during our first meeting, but what I took from this was that some people are uncomfortable in ways that our lexicon does not capture, and sometimes medication helps with this discomfort.
The APA’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders attempts to capture the problems of emotional and behavioral distress and classify them into discrete syndromes that can be validated and reliably diagnosed by different evaluators. Our disorders are syndromic; they are defined by clusters of symptoms that occur together, and not by a single symptom, lab value, or radiologic finding. The DSM is rewritten periodically so that what is or is not a disorder can bend with new discoveries and with a changing culture. And for better or for worse, when there is an available medication that can alleviate a problem, this may influence what once was a variant of normal into becoming a disorder.
Our illnesses often lie along a spectrum, so there is no precise point where someone who is easily distracted is a person with attention deficit disorder as opposed to being a mentally healthy person who is easily distracted, or a shy person is someone with social anxiety disorder. whether they want to address this with medications, and whether their distress warrants taking a chance that they might have side effects or an adverse reaction to a medication.
When we look at our criteria, sometimes we fall short. One needs to have at least five symptoms out of nine options, to be present for 2 weeks to be diagnosed with major depression, yet I don’t know a single psychiatrist who would not offer medication to a patient who ascribed to feeling profoundly sad with thoughts of suicide in the absence of other symptoms of depression. These issues have come to the forefront with the recent inclusion of prolonged grief in the DSM, as a disorder that is distinct from both normal grieving and from major depression.
In recent weeks, mass murder has been on everyone’s mind as we mourn those lost in Uvalde, Buffalo, and unfortunately, in so many other places. Absolutely no one thinks that someone who shoots strangers is “normal” or emotionally well. Yet psychiatry is often tasked with figuring out if someone is mad (mentally ill), bad (evil), or both. We don’t have a clear path for how to treat and manage people who commit horrendous acts of violence unless they meet criteria for another illness. Yet no one would argue that a person who informs others that he is thinking of killing strangers is in need of some type of intervention, regardless of his motive. We struggle too, with how to manage people who have more regular angry outbursts or emotional dysregulation. Perhaps we diagnose intermittent explosive disorder, or irritability caused by a mood disorder, but we don’t always know how to help people to control their tempers and modulate their emotions. And our semantics to describe psychic pain and anguish are surprisingly limited – sometimes we can only assume that someone who lashes out must be in turmoil.
Psychiatry continues to struggle with our relationship with human suffering. Suffering is part of life, not necessarily a sign of illness, and in his iconic memoir, “Man’s Search for Meaning,” psychiatrist Viktor Frankl, MD, wrote of the atrocities he endured in a Nazi concentration camp. It was through his suffering that Dr. Frankl found meaning and he used these harrowing experiences to fuel positive emotions later in life. Dr. Frankl wrote: “If there is a meaning in life at all, then there must be a meaning in suffering. Suffering is an ineradicable part of life, even as fate and death. Without suffering and death, human life cannot be complete.”
Suffering may be the kindling for acts of violence, or for profound creativity. Would we have music, art, cinema, poetry, or fiction if no one ever suffered? Yet suffering and emotional torment are often what leads people to seek treatment, and what leads us, as healers, to offer any range of therapies. For years, suicide rates have been rising, as have overdose death. And now, in addition to these “deaths of despair,” we are hearing about skyrocketing rates of depression and anxiety in our world that is so full of reasons to be sad and anxious. Access to treatment is limited by so many things, and it is not always clear when one needs psychiatric interventions or when problems will heal on their own, leaving scars or not.
I wrote this article in response to the hundreds of comments that were placed on an article I wrote after the horrors at Uvalde and Buffalo: “Don’t Equate Mass Shootings with Mental Illness.” Many of the commenters suggested I believe the shooter was perfectly sane, and that I am naive (or worse). Many wrote in with their own thoughts about what causes people to become mass murderers. One commenter wrote: “To suggest that random killers do not have mental health issues and their behavior is normal is ridiculous.” I don’t believe that I ever suggested that such behavior was normal, but – for many of these crimes – we as a society have decided to treat the behavior as criminal and not as the product of our current concept of mental disorders. Obviously, people who are well, who are emotionally at peace and comfortable in their own skin, don’t kill strangers.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
I still remember the woman who came to my office that day, years ago. She was struggling and uncomfortable, and she wanted “something” for stress. She described her life, and to me, it sounded stressful. She lived in a blended family and she described the chaos that one might expect to find in a household with four teens, their friends, their activities, and all it took to keep the household going. I spent 2 hours evaluating the patient, and I could not find a diagnosis that fit this problem nor – I believed – a pill that would fix it. She didn’t “meet criteria” for a psychiatric disorder, but she insisted she was uncomfortable and she wanted to try medication. I admit, I relented and I gave her a prescription for fluoxetine.
When she returned a few weeks later, my patient said she felt better, and what I remember decades later was her statement: “Now I can see dishes in the sink and be okay with it.” Perhaps she had downplayed her anxiety during our first meeting, but what I took from this was that some people are uncomfortable in ways that our lexicon does not capture, and sometimes medication helps with this discomfort.
The APA’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders attempts to capture the problems of emotional and behavioral distress and classify them into discrete syndromes that can be validated and reliably diagnosed by different evaluators. Our disorders are syndromic; they are defined by clusters of symptoms that occur together, and not by a single symptom, lab value, or radiologic finding. The DSM is rewritten periodically so that what is or is not a disorder can bend with new discoveries and with a changing culture. And for better or for worse, when there is an available medication that can alleviate a problem, this may influence what once was a variant of normal into becoming a disorder.
Our illnesses often lie along a spectrum, so there is no precise point where someone who is easily distracted is a person with attention deficit disorder as opposed to being a mentally healthy person who is easily distracted, or a shy person is someone with social anxiety disorder. whether they want to address this with medications, and whether their distress warrants taking a chance that they might have side effects or an adverse reaction to a medication.
When we look at our criteria, sometimes we fall short. One needs to have at least five symptoms out of nine options, to be present for 2 weeks to be diagnosed with major depression, yet I don’t know a single psychiatrist who would not offer medication to a patient who ascribed to feeling profoundly sad with thoughts of suicide in the absence of other symptoms of depression. These issues have come to the forefront with the recent inclusion of prolonged grief in the DSM, as a disorder that is distinct from both normal grieving and from major depression.
In recent weeks, mass murder has been on everyone’s mind as we mourn those lost in Uvalde, Buffalo, and unfortunately, in so many other places. Absolutely no one thinks that someone who shoots strangers is “normal” or emotionally well. Yet psychiatry is often tasked with figuring out if someone is mad (mentally ill), bad (evil), or both. We don’t have a clear path for how to treat and manage people who commit horrendous acts of violence unless they meet criteria for another illness. Yet no one would argue that a person who informs others that he is thinking of killing strangers is in need of some type of intervention, regardless of his motive. We struggle too, with how to manage people who have more regular angry outbursts or emotional dysregulation. Perhaps we diagnose intermittent explosive disorder, or irritability caused by a mood disorder, but we don’t always know how to help people to control their tempers and modulate their emotions. And our semantics to describe psychic pain and anguish are surprisingly limited – sometimes we can only assume that someone who lashes out must be in turmoil.
Psychiatry continues to struggle with our relationship with human suffering. Suffering is part of life, not necessarily a sign of illness, and in his iconic memoir, “Man’s Search for Meaning,” psychiatrist Viktor Frankl, MD, wrote of the atrocities he endured in a Nazi concentration camp. It was through his suffering that Dr. Frankl found meaning and he used these harrowing experiences to fuel positive emotions later in life. Dr. Frankl wrote: “If there is a meaning in life at all, then there must be a meaning in suffering. Suffering is an ineradicable part of life, even as fate and death. Without suffering and death, human life cannot be complete.”
Suffering may be the kindling for acts of violence, or for profound creativity. Would we have music, art, cinema, poetry, or fiction if no one ever suffered? Yet suffering and emotional torment are often what leads people to seek treatment, and what leads us, as healers, to offer any range of therapies. For years, suicide rates have been rising, as have overdose death. And now, in addition to these “deaths of despair,” we are hearing about skyrocketing rates of depression and anxiety in our world that is so full of reasons to be sad and anxious. Access to treatment is limited by so many things, and it is not always clear when one needs psychiatric interventions or when problems will heal on their own, leaving scars or not.
I wrote this article in response to the hundreds of comments that were placed on an article I wrote after the horrors at Uvalde and Buffalo: “Don’t Equate Mass Shootings with Mental Illness.” Many of the commenters suggested I believe the shooter was perfectly sane, and that I am naive (or worse). Many wrote in with their own thoughts about what causes people to become mass murderers. One commenter wrote: “To suggest that random killers do not have mental health issues and their behavior is normal is ridiculous.” I don’t believe that I ever suggested that such behavior was normal, but – for many of these crimes – we as a society have decided to treat the behavior as criminal and not as the product of our current concept of mental disorders. Obviously, people who are well, who are emotionally at peace and comfortable in their own skin, don’t kill strangers.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
I still remember the woman who came to my office that day, years ago. She was struggling and uncomfortable, and she wanted “something” for stress. She described her life, and to me, it sounded stressful. She lived in a blended family and she described the chaos that one might expect to find in a household with four teens, their friends, their activities, and all it took to keep the household going. I spent 2 hours evaluating the patient, and I could not find a diagnosis that fit this problem nor – I believed – a pill that would fix it. She didn’t “meet criteria” for a psychiatric disorder, but she insisted she was uncomfortable and she wanted to try medication. I admit, I relented and I gave her a prescription for fluoxetine.
When she returned a few weeks later, my patient said she felt better, and what I remember decades later was her statement: “Now I can see dishes in the sink and be okay with it.” Perhaps she had downplayed her anxiety during our first meeting, but what I took from this was that some people are uncomfortable in ways that our lexicon does not capture, and sometimes medication helps with this discomfort.
The APA’s Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders attempts to capture the problems of emotional and behavioral distress and classify them into discrete syndromes that can be validated and reliably diagnosed by different evaluators. Our disorders are syndromic; they are defined by clusters of symptoms that occur together, and not by a single symptom, lab value, or radiologic finding. The DSM is rewritten periodically so that what is or is not a disorder can bend with new discoveries and with a changing culture. And for better or for worse, when there is an available medication that can alleviate a problem, this may influence what once was a variant of normal into becoming a disorder.
Our illnesses often lie along a spectrum, so there is no precise point where someone who is easily distracted is a person with attention deficit disorder as opposed to being a mentally healthy person who is easily distracted, or a shy person is someone with social anxiety disorder. whether they want to address this with medications, and whether their distress warrants taking a chance that they might have side effects or an adverse reaction to a medication.
When we look at our criteria, sometimes we fall short. One needs to have at least five symptoms out of nine options, to be present for 2 weeks to be diagnosed with major depression, yet I don’t know a single psychiatrist who would not offer medication to a patient who ascribed to feeling profoundly sad with thoughts of suicide in the absence of other symptoms of depression. These issues have come to the forefront with the recent inclusion of prolonged grief in the DSM, as a disorder that is distinct from both normal grieving and from major depression.
In recent weeks, mass murder has been on everyone’s mind as we mourn those lost in Uvalde, Buffalo, and unfortunately, in so many other places. Absolutely no one thinks that someone who shoots strangers is “normal” or emotionally well. Yet psychiatry is often tasked with figuring out if someone is mad (mentally ill), bad (evil), or both. We don’t have a clear path for how to treat and manage people who commit horrendous acts of violence unless they meet criteria for another illness. Yet no one would argue that a person who informs others that he is thinking of killing strangers is in need of some type of intervention, regardless of his motive. We struggle too, with how to manage people who have more regular angry outbursts or emotional dysregulation. Perhaps we diagnose intermittent explosive disorder, or irritability caused by a mood disorder, but we don’t always know how to help people to control their tempers and modulate their emotions. And our semantics to describe psychic pain and anguish are surprisingly limited – sometimes we can only assume that someone who lashes out must be in turmoil.
Psychiatry continues to struggle with our relationship with human suffering. Suffering is part of life, not necessarily a sign of illness, and in his iconic memoir, “Man’s Search for Meaning,” psychiatrist Viktor Frankl, MD, wrote of the atrocities he endured in a Nazi concentration camp. It was through his suffering that Dr. Frankl found meaning and he used these harrowing experiences to fuel positive emotions later in life. Dr. Frankl wrote: “If there is a meaning in life at all, then there must be a meaning in suffering. Suffering is an ineradicable part of life, even as fate and death. Without suffering and death, human life cannot be complete.”
Suffering may be the kindling for acts of violence, or for profound creativity. Would we have music, art, cinema, poetry, or fiction if no one ever suffered? Yet suffering and emotional torment are often what leads people to seek treatment, and what leads us, as healers, to offer any range of therapies. For years, suicide rates have been rising, as have overdose death. And now, in addition to these “deaths of despair,” we are hearing about skyrocketing rates of depression and anxiety in our world that is so full of reasons to be sad and anxious. Access to treatment is limited by so many things, and it is not always clear when one needs psychiatric interventions or when problems will heal on their own, leaving scars or not.
I wrote this article in response to the hundreds of comments that were placed on an article I wrote after the horrors at Uvalde and Buffalo: “Don’t Equate Mass Shootings with Mental Illness.” Many of the commenters suggested I believe the shooter was perfectly sane, and that I am naive (or worse). Many wrote in with their own thoughts about what causes people to become mass murderers. One commenter wrote: “To suggest that random killers do not have mental health issues and their behavior is normal is ridiculous.” I don’t believe that I ever suggested that such behavior was normal, but – for many of these crimes – we as a society have decided to treat the behavior as criminal and not as the product of our current concept of mental disorders. Obviously, people who are well, who are emotionally at peace and comfortable in their own skin, don’t kill strangers.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.

















