User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack nav-ce-stack__large-screen')]
header[@id='header']
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
Brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation predict COPD rehabilitation success
In an experimental medicine study of D-cycloserine given during chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) rehabilitation, only models including brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation successfully predicted Dyspnea-12 score improvement. D-cycloserine was independently associated with breathlessness improvement, according to original research published in Thorax.
Chronic breathlessness persisting despite maximal medical therapy is a key feature of COPD. While pulmonary rehabilitation is the best treatment for chronic breathlessness in COPD, responses to treatment are variable, with 30% deriving no clinical benefit, Sarah L. Finnegan, PhD, with the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford (England), and colleagues wrote.
While recent research has shown fear and anxiety to be key components of the expectation that plays an important role in the mechanisms and maintenance of breathlessness, expectation-related effects have not previously been considered in prediction studies of pulmonary rehabilitation outcomes. The authors’ prior research showed a clear correlation between improvements in breathlessness through pulmonary rehabilitation and expectation-related brain activity in areas that include the anterior insula, anterior cingulate cortex, and prefrontal cortex. That research methodology, however, did not attempt to predict individual responses.
The current study focused on brain activity changes within preselected regions associated with breathlessness-expectation and body and symptom perception. Its purpose was to predict improvements in breathlessness during pulmonary rehabilitation by analyzing baseline data from a longitudinal experimental medicine study of D-cycloserine on breathlessness during pulmonary rehabilitation. D-cycloserine, a partial agonist of brain N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, was chosen because of its effects on neural plasticity and influence on brain expectation mechanisms associated with cognitive behavioral therapies. The authors hypothesized that baseline brain activity in response to breathlessness-related expectation would predict improvement in breathlessness through pulmonary rehabilitation, with D-cycloserine emerging as a significant factor in the prediction model.
The researchers recruited 71 participants (18 women, median age 71 years [46-85 years]) with mild to moderate COPD immediately prior to enrollment in a National Health Service–prescribed course of pulmonary rehabilitation. They were randomized double-blind to receive either 250 mg oral D-cycloserine or a matched placebo. Participants received a single dose on four occasions 30 minutes prior to the onset of the first four pulmonary rehabilitation sessions.
Baseline variables, including brain-activity, self-report questionnaires responses, clinical measures of respiratory function, and drug allocation were used to train three machine-learning models to predict the outcome, a minimally clinically relevant change in the Dyspnea-12 score.
Improvements in Dyspnea-12 score occurred only in the two models including brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation (sensitivity 0.88, specificity 0.77). The model that combined brain and behavior metrics produced the best classification performance (accuracy, 0.83 [95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.90]; sensitivity, 0.88; specificity, 0.77; P < 0.001). While the brain-only model was able to correctly categorize participants with statistically significant likelihood (accuracy, 0.70 [95% CI, 0.58-0.81]), it demonstrated poor goodness of fit, a measure of how well sample data fit a distribution from a population with a normal distribution. “By enriching the brain-only models with questionnaires and physiology measures improved performance considerably,” the researchers stated.
“Our findings demonstrate the first predictive model of change in breathlessness across pulmonary rehabilitation and, for the first time, the clinical relevance of expectation-related brain activity as a therapeutic target in the treatment of breathlessness. ... This was achieved using sensitive brain imaging techniques in order to capture personalized responses to breathlessness-expectation which has, until recently remained relatively unexplored.”
“This study raises interesting questions about breathlessness-expectations,” commented assistant professor of medicine Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, director pulmonary hypertension service, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, in an interview. “There is much more to be understood about expectations pathways as to how these pathways are built upon prior experience and pave the way for reaction to future experiences. There is need for a similar study with larger sample size and clarification of the role of the effect of the agent D-cycloserine on breathlessness-expectation.”
The researchers noted their study’s limitations, pointing out that the small sample size precluded holding out a proportion of the original data to create an external validation dataset.
Dr. Finnegan and Dr. Farmer declared no disclosures relevant to this study. This work was supported by the JABBS Foundation and Dunhill Medical Trust. This research was funded in whole, or in part, by the Wellcome Trust.
In an experimental medicine study of D-cycloserine given during chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) rehabilitation, only models including brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation successfully predicted Dyspnea-12 score improvement. D-cycloserine was independently associated with breathlessness improvement, according to original research published in Thorax.
Chronic breathlessness persisting despite maximal medical therapy is a key feature of COPD. While pulmonary rehabilitation is the best treatment for chronic breathlessness in COPD, responses to treatment are variable, with 30% deriving no clinical benefit, Sarah L. Finnegan, PhD, with the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford (England), and colleagues wrote.
While recent research has shown fear and anxiety to be key components of the expectation that plays an important role in the mechanisms and maintenance of breathlessness, expectation-related effects have not previously been considered in prediction studies of pulmonary rehabilitation outcomes. The authors’ prior research showed a clear correlation between improvements in breathlessness through pulmonary rehabilitation and expectation-related brain activity in areas that include the anterior insula, anterior cingulate cortex, and prefrontal cortex. That research methodology, however, did not attempt to predict individual responses.
The current study focused on brain activity changes within preselected regions associated with breathlessness-expectation and body and symptom perception. Its purpose was to predict improvements in breathlessness during pulmonary rehabilitation by analyzing baseline data from a longitudinal experimental medicine study of D-cycloserine on breathlessness during pulmonary rehabilitation. D-cycloserine, a partial agonist of brain N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, was chosen because of its effects on neural plasticity and influence on brain expectation mechanisms associated with cognitive behavioral therapies. The authors hypothesized that baseline brain activity in response to breathlessness-related expectation would predict improvement in breathlessness through pulmonary rehabilitation, with D-cycloserine emerging as a significant factor in the prediction model.
The researchers recruited 71 participants (18 women, median age 71 years [46-85 years]) with mild to moderate COPD immediately prior to enrollment in a National Health Service–prescribed course of pulmonary rehabilitation. They were randomized double-blind to receive either 250 mg oral D-cycloserine or a matched placebo. Participants received a single dose on four occasions 30 minutes prior to the onset of the first four pulmonary rehabilitation sessions.
Baseline variables, including brain-activity, self-report questionnaires responses, clinical measures of respiratory function, and drug allocation were used to train three machine-learning models to predict the outcome, a minimally clinically relevant change in the Dyspnea-12 score.
Improvements in Dyspnea-12 score occurred only in the two models including brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation (sensitivity 0.88, specificity 0.77). The model that combined brain and behavior metrics produced the best classification performance (accuracy, 0.83 [95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.90]; sensitivity, 0.88; specificity, 0.77; P < 0.001). While the brain-only model was able to correctly categorize participants with statistically significant likelihood (accuracy, 0.70 [95% CI, 0.58-0.81]), it demonstrated poor goodness of fit, a measure of how well sample data fit a distribution from a population with a normal distribution. “By enriching the brain-only models with questionnaires and physiology measures improved performance considerably,” the researchers stated.
“Our findings demonstrate the first predictive model of change in breathlessness across pulmonary rehabilitation and, for the first time, the clinical relevance of expectation-related brain activity as a therapeutic target in the treatment of breathlessness. ... This was achieved using sensitive brain imaging techniques in order to capture personalized responses to breathlessness-expectation which has, until recently remained relatively unexplored.”
“This study raises interesting questions about breathlessness-expectations,” commented assistant professor of medicine Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, director pulmonary hypertension service, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, in an interview. “There is much more to be understood about expectations pathways as to how these pathways are built upon prior experience and pave the way for reaction to future experiences. There is need for a similar study with larger sample size and clarification of the role of the effect of the agent D-cycloserine on breathlessness-expectation.”
The researchers noted their study’s limitations, pointing out that the small sample size precluded holding out a proportion of the original data to create an external validation dataset.
Dr. Finnegan and Dr. Farmer declared no disclosures relevant to this study. This work was supported by the JABBS Foundation and Dunhill Medical Trust. This research was funded in whole, or in part, by the Wellcome Trust.
In an experimental medicine study of D-cycloserine given during chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) rehabilitation, only models including brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation successfully predicted Dyspnea-12 score improvement. D-cycloserine was independently associated with breathlessness improvement, according to original research published in Thorax.
Chronic breathlessness persisting despite maximal medical therapy is a key feature of COPD. While pulmonary rehabilitation is the best treatment for chronic breathlessness in COPD, responses to treatment are variable, with 30% deriving no clinical benefit, Sarah L. Finnegan, PhD, with the Nuffield Department of Clinical Neurosciences, University of Oxford (England), and colleagues wrote.
While recent research has shown fear and anxiety to be key components of the expectation that plays an important role in the mechanisms and maintenance of breathlessness, expectation-related effects have not previously been considered in prediction studies of pulmonary rehabilitation outcomes. The authors’ prior research showed a clear correlation between improvements in breathlessness through pulmonary rehabilitation and expectation-related brain activity in areas that include the anterior insula, anterior cingulate cortex, and prefrontal cortex. That research methodology, however, did not attempt to predict individual responses.
The current study focused on brain activity changes within preselected regions associated with breathlessness-expectation and body and symptom perception. Its purpose was to predict improvements in breathlessness during pulmonary rehabilitation by analyzing baseline data from a longitudinal experimental medicine study of D-cycloserine on breathlessness during pulmonary rehabilitation. D-cycloserine, a partial agonist of brain N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors, was chosen because of its effects on neural plasticity and influence on brain expectation mechanisms associated with cognitive behavioral therapies. The authors hypothesized that baseline brain activity in response to breathlessness-related expectation would predict improvement in breathlessness through pulmonary rehabilitation, with D-cycloserine emerging as a significant factor in the prediction model.
The researchers recruited 71 participants (18 women, median age 71 years [46-85 years]) with mild to moderate COPD immediately prior to enrollment in a National Health Service–prescribed course of pulmonary rehabilitation. They were randomized double-blind to receive either 250 mg oral D-cycloserine or a matched placebo. Participants received a single dose on four occasions 30 minutes prior to the onset of the first four pulmonary rehabilitation sessions.
Baseline variables, including brain-activity, self-report questionnaires responses, clinical measures of respiratory function, and drug allocation were used to train three machine-learning models to predict the outcome, a minimally clinically relevant change in the Dyspnea-12 score.
Improvements in Dyspnea-12 score occurred only in the two models including brain imaging markers of breathlessness-expectation (sensitivity 0.88, specificity 0.77). The model that combined brain and behavior metrics produced the best classification performance (accuracy, 0.83 [95% confidence interval, 0.75-0.90]; sensitivity, 0.88; specificity, 0.77; P < 0.001). While the brain-only model was able to correctly categorize participants with statistically significant likelihood (accuracy, 0.70 [95% CI, 0.58-0.81]), it demonstrated poor goodness of fit, a measure of how well sample data fit a distribution from a population with a normal distribution. “By enriching the brain-only models with questionnaires and physiology measures improved performance considerably,” the researchers stated.
“Our findings demonstrate the first predictive model of change in breathlessness across pulmonary rehabilitation and, for the first time, the clinical relevance of expectation-related brain activity as a therapeutic target in the treatment of breathlessness. ... This was achieved using sensitive brain imaging techniques in order to capture personalized responses to breathlessness-expectation which has, until recently remained relatively unexplored.”
“This study raises interesting questions about breathlessness-expectations,” commented assistant professor of medicine Mary Jo S. Farmer, MD, PhD, director pulmonary hypertension service, University of Massachusetts, Worcester, in an interview. “There is much more to be understood about expectations pathways as to how these pathways are built upon prior experience and pave the way for reaction to future experiences. There is need for a similar study with larger sample size and clarification of the role of the effect of the agent D-cycloserine on breathlessness-expectation.”
The researchers noted their study’s limitations, pointing out that the small sample size precluded holding out a proportion of the original data to create an external validation dataset.
Dr. Finnegan and Dr. Farmer declared no disclosures relevant to this study. This work was supported by the JABBS Foundation and Dunhill Medical Trust. This research was funded in whole, or in part, by the Wellcome Trust.
FROM THORAX
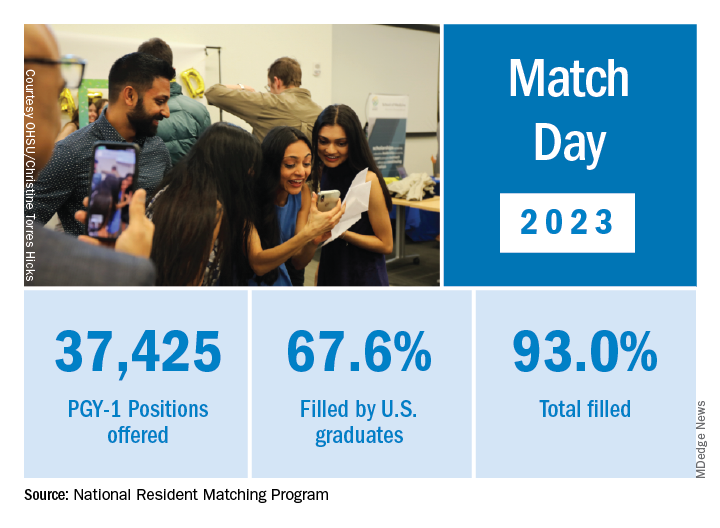
Match Day: Record number of residencies offered
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.
NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Baily Nagle, vice president of her graduating class at Harvard Medical School, Boston, celebrated “the luck of the Irish” on St. Patrick’s Day that allowed her to match into her chosen specialty and top choice of residency programs: anesthesia at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
“I am feeling very excited and relieved – I matched,” she said in an interview upon hearing her good fortune on Match Monday, March 13. She had a similar reaction on Match Day, March 17. “After a lot of long nights and hard work, happy to have it pay off.”
Ms. Nagle was so determined to match into her specialty that she didn’t have any other specialties in mind as a backup.
The annual process of matching medical school graduates with compatible residency programs is an emotional roller coaster for all applicants, their personal March Madness, so to speak. But Ms. Nagle was one of the more fortunate applicants. She didn’t have to confront the heartbreak other applicants felt when the National Resident Matching Program (NRMP) announced results of the main residency match and the Supplemental Offer and Acceptance Program (SOAP), which offers alternate programs for unfilled positions or unmatched applicants.
During the 2023 Match process, this news organization has been following a handful of students, checking in with them periodically for updates on their progress. Most of them matched successfully, but at least one international medical graduate (IMG) did not. What the others have in common is that their hearts were set on a chosen specialty. Like Ms. Nagle, another student banked on landing his chosen specialty without a backup plan, whereas another said that she’d continue through the SOAP if she didn’t match successfully.
Overall, Match Day resulted in a record number of residency positions offered, most notably in primary care, which “hit an all-time high,” according to NRMP President and CEO Donna L. Lamb, DHSc, MBA, BSN. The number of positions has “consistently increased over the past 5 years, and most importantly the fill rate for primary care has remained steady,” Dr.. Lamb noted in the NRMP release of Match Day results. The release coincided with students learning through emails at noon Eastern Time to which residency or supplemental programs they were matched.
Though more applicants registered for the Match in 2023 than in 2022 – driven primarily by non-U.S. IMGs – the NRMP stated that it was surprised by the decrease in U.S. MD senior applicants.
U.S. MD seniors had a nearly 94% Match rate, a small increase over 2022. U.S. citizen IMGs saw a nearly 68% Match rate, which NRMP reported as an “all-time high” and about six percentage points over in 2022, whereas non-U.S. IMGs had a nearly 60% Match rate, a 1.3 percentage point increase over 2022.
Among the specialties that filled all available positions in 2023 were orthopedic surgery, plastic surgery (integrated), and radiology – diagnostic and thoracic surgery.
Not everyone matches
On March 13, the American College of Emergency Physicians issued a joint statement with other emergency medicine (EM) organizations about a high rate of unfilled EM positions expected in 2023.

NRMP acknowledged March 17 that 554 positions remained unfilled, an increase of 335 more unfilled positions than 2022. NRMP attributed the increase in unfilled positions in part to a decrease in the number of U.S. MD and U.S. DO seniors who submitted ranks for the specialty, which “could reflect changing applicant interests or projections about workforce opportunities post residency.”
Applicants who didn’t match usually try to obtain an unfilled position through SOAP. In 2023, 2,685 positions were unfilled after the matching algorithm was processed, an increase of nearly 19% over 2022. The vast majority of those positions were placed in SOAP, an increase of 17.5% over 2022.
Asim Ansari was one of the unlucky ones. Mr. Ansari was trying to match for the fifth time. He was unsuccessful in doing so again in 2023 in the Match and SOAP. Still, he was offered and accepted a child and adolescent psychiatry fellowship at Kansas University Medical Center in Kansas City. Psychiatry was his chosen specialty, so he was “feeling good. It’s a nice place to go to do the next 2 years.”
Mr. Ansari, who started the #MatchMadness support group for unmatched doctors on Twitter Spaces, was quick to cheer on his fellow matching peers on March 13 while revealing his own fate: “Congratulations to everyone who matched!!! Y’all are amazing. So proud of each one of you!!! I didn’t.”
Soon after the results, #MatchMadness held a #Soap2023 support session, and Mr. Ansari sought advice for those willing to review SOAP applications. Elsewhere on Twitter Match Day threads, a few doctors offered their support to those who planned to SOAP, students announced their matches, and others either congratulated or encouraged those still trying to match.
Couples match
Not everyone who matched considered the alternative. Before March 13, William Boyer said that he hadn’t given much thought to what would happen if he didn’t match because he was “optimistically confident” he would match into his chosen EM specialty. But he did and got his top choice of programs: Yale New Haven (Conn.) Hospital.
“I feel great,” he said in an interview. “I was definitely nervous opening the envelope” that revealed his residency program, “but there was a rush of relief” when he saw he landed Yale.
Earlier in the match cycle, he said in an interview that he “interviewed at a few ‘reach’ programs, so I hope I don’t match lower than expected on my rank list.”
Mr. Boyer considers himself “a mature applicant,” entering the University of South Carolina, Columbia, after 4 years as an insurance broker.
“I am celebrating today by playing pickleball with a few close medical friends who also matched this morning,” Mr. Boyer said on March 13. “I definitely had periods of nervousness leading up to this morning though that quickly turned into joy and relief” after learning he matched.
Mr. Boyer believes that his professional experience in the insurance industry and health care lobbying efforts with the National Association of Health Underwriters set him apart from other applicants.
“I changed careers to pursue this aspiration, which demonstrates my full dedication to the medical profession.”
He applied to 48 programs and was offered interviews to nearly half. Mr. Boyer visited the majority of those virtually. He said he targeted programs close to where his and his partner’s families are located: Massachusetts, North Carolina, and Texas. “My partner, who I met in medical school, matched into ortho as well so the whole household is very happy,” Mr. Boyer said.
She matched into her top choice as well on March 17, though a distance away at UT Health in San Antonio, he said. “We are both ecstatic. We both got our no. 1 choice. That was the plan going into it. We will make it work. I have 4 weeks of vacation.”
In his program choices, Mr. Boyer prioritized access to nature, minimal leadership turnover, a mix of clinical training sites, and adequate elective rotations and fellowship opportunities, such as in wilderness medicine and health policy.
NRMP reported that there were 1,239 couples participating in the Match; 1,095 had both partners match, and 114 had one partner match to residency training programs for a match rate of 93%.
Like Mr. Boyer, Hannah Hedriana matched into EM, one of the more popular despite the reported unfilled positions. In the past few years, it has consistently been one of the fastest-growing specialties, according to the NRMP.
Still Ms. Hedriana had a fall-back plan. “If I don’t match, then I do plan on going through SOAP. With the number of EM spots that were unfilled in 2022, there’s a chance I could still be an EM physician, but if not, then that’s okay with me.”
Her reaction on March 13, after learning she matched? “Super excited, celebrating with my friends right now.” On Match Day, she said she was “ecstatic” to be matched into Lakeland (Fla.) Regional Health. “This was my first choice so now I can stay close to family and friends,” she said in an interview soon after the results were released.
A first-generation, Filipino American student from the University of South Florida, Tampa, Ms. Hedriana comes from a family of health care professionals. Her father is a respiratory therapist turned physical therapist; her mother a registered nurse. Her sister is a patient care technician applying to nursing school.
Ms. Hedriana applied to 70 programs and interviewed mostly online with 24. Her goal was to stay on the East Coast.
“My partner is a licensed dentist in the state of Florida, and so for his career it would be more practical to stay in state, rather than get relicensed in another state, which could take months,” she said earlier in the matching cycle. “However, when we discussed choosing a residency program, he ultimately left it up to me and wanted me to pick where I thought I’d flourish best,” Ms. Hedriana said, adding that her family lives in Florida, too.
She said she sought a residency program that values family and teamwork.
“A program gets more points in my book if they have sites at nonprofit hospitals or has residents that regularly volunteer throughout their communities or participate in DEI [diversity, equity, and inclusion] initiatives.”
Ms. Hedriana noted that some specialties exclusively offered virtual interviews in 2023, whereas other specialties favored in-person interviews. “This year, many of my classmates were able to do multiple away rotations, which they saw as a positive regarding their chances of matching.” During COVID, in-person visits were limited.
“However, I’ve noticed that many of my classmates are not fond of the signaling aspect that was present for this year’s cycle,” she said. Signaling is a relatively new process that allows applicants to indicate interest in a limited number of residency programs. Not all residencies participate, but it’s growing in popularity among specialties, according to the American Medical Association.
‘Extremely competitive’
Ms. Nagle, a second lieutenant in the U.S. Air Force, applied to 12 programs and interviewed with half of them online. She said that she wasn’t targeting any specific type of program through the match.
“I believe you can get phenomenal training anywhere where you mesh with the residents and leadership. My ultimate priority is to (1) be near good people, (2) be near good food (Indian and Thai are a must), and (3) be near an international airport so I can flee the country during breaks.”
Meanwhile, she said that she found the application process, in which students have to articulate their entire medical school experience, extremely competitive. “I think this process is so easy to get wound up in and the anxiety can be palpable,” Ms. Nagle said. “People around you match your energy. So if you are a ball of anxiety then so are your attendings and residents – and that doesn’t bode well for passing the ‘do I want to be on call with them’ test.”
Looking back at medical school, Ms. Nagle recalled having a baby named after her during her first anesthesia rotation and being featured on The Kelly Clarkson Show. Ms. Nagle said that she had walked into the delivery room where new parents had been debating names of babies beginning with the letter B. “And when I introduced myself, they looked at each other and said, ‘Yep, that’s the one.’”
Mr. Boyer recounted how the majority of his medical school experience involved online education. “Roughly two-thirds of my first year was in-person prior to the pandemic. However, from spring break first year to in-person clinical rotations at the beginning of third year, we were all virtual. While I missed interacting with my classmates, I benefited from the virtual learning environment as I learn more efficiently from reading and visual aids than auditory lectures.”
Ms. Hedriana cited the friends and memories she made while learning to be a doctor. “Medical school was hard, but I wouldn’t have changed a thing.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Older men more at risk as dangerous falls rise for all seniors
When Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.) fell recently at a dinner event in Washington, he unfortunately joined a large group of his senior citizen peers.
This wasn’t the first tumble the 81-year-old has taken. In 2019, he fell in his home, fracturing his shoulder. This time, he got a concussion and was recently released to an in-patient rehabilitation facility. While Sen. McConnell didn’t fracture his skull, in falling and hitting his head, he became part of an emerging statistic: One that reveals falls are more dangerous for senior men than senior women.
This new research, which appeared in the American Journal of Emergency Medicine, came as a surprise to lead researcher Scott Alter, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton.
“We always hear about lower bone density rates among females, so we didn’t expect to see males with more skull fractures,” he said.
Dr. Alter said that as a clinician in a southern Florida facility, his emergency department was the perfect study grounds to evaluate incoming geriatric patients due to falls. Older “patients are at higher risk of skull fractures and intercranial bleeding, and we wanted to look at any patient presenting with a head injury. Some 80% were fall related, however.”
The statistics bear out the fact that falls of all types are common among the elderly: Some 800,000 seniors wind up in the hospital each year because of falls.
The numbers show death rates from falls are on the rise in the senior citizen age group, too, up 30% from 2007 to 2016. Falls account for 70% of accidental deaths in people 75 and older. They are the leading cause of injury-related visits to emergency departments in the country, too.
Jennifer Stevens, MD, a gerontologist and executive director at Florida-based Abbey Delray South, is aware of the dire numbers and sees their consequences regularly. “The reasons seniors are at a high fall risk are many,” she said. “They include balance issues, declining strength, diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, side effects of their medications, and more.”
In addition, many seniors live in spaces that are not necessarily equipped for their limitations, and hazards exist all over their homes. Put together, and the risks for falls are everywhere. But there are steps seniors, their families, and even middle-aged people can take to mitigate and hopefully prevent dangerous falls.
Starting early
While in many cases the journey to lessen fall risks begins after a fall, the time to begin addressing the issue is long before you hit your senior years. Mary Therese Cole, a physical therapist and certified dementia practitioner at Manual Edge Physical Therapy in Colorado Springs, Colo., says that age 50 is a good time to start paying attention and addressing physical declines.
“This is an age where your vision might begin deteriorating,” she said. “It’s a big reason why elderly people trip and fall.”
As our brains begin to age in our middle years, the neural pathways from brain to extremities start to decline, too. The result is that many people stop picking up their feet as well as they used to do, making them more likely to trip.
“You’re not elderly yet, but you’re not a spring chicken, either,” Ms. Cole said. “Any issues you have now will only get worse if you’re not working on them.”
A good starting point in middle age, then, is to work on both strength training and balance exercises. A certified personal trainer or physical therapist can help get you on a program to ward off many of these declines.
If you’ve reached your later years, however, and are experiencing physical declines, it’s smart to check in with your primary care doctor for an assessment. “He or she can get your started on regular PT to evaluate any shortcomings and then address them,” Ms. Cole said.
She noted that when she’s working with senior patients, she’ll test their strength getting into and out of a chair, do a manual strength test to check on lower extremities, check their walking stride, and ask about conditions such as diabetes, former surgeries, and other conditions.
From there, Ms. Cole said she can write up a plan for the patient. Likewise, Dr. Stevens uses a program called Be Active that allows her to test seniors on a variety of measurements, including flexibility, balance, hand strength, and more.
“Then we match them with classes to address their shortcomings,” she said. “It’s critical that seniors have the ability to recover and not fall if they get knocked off balance.”
Beyond working on your physical limitations, taking a good look at your home is essential, too. “You can have an occupational therapist come to your home and do an evaluation,” Dr. Stevens said. “They can help you rearrange and reorganize for a safer environment.”
Big, common household fall hazards include throw rugs, lack of nightlights for middle-of-the-night visits to the bathroom, a lack of grab bars in the shower/bathtub, and furniture that blocks pathways.
For his part, Dr. Alter likes to point seniors and their doctors to the CDC’s STEADI program, which is aimed at stopping elderly accidents, deaths, and injuries.
“It includes screening for fall risk, assessing factors you can modify or improve, and more tools,” he said.
Dr. Alter also recommended seniors talk to their doctors about medications, particularly blood thinners.
“At a certain point, you need to weigh the benefits of disease prevention with the risk of injury if you fall,” he said. “The bleeding risk might be too high if the patient is at a high risk of falls.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.) fell recently at a dinner event in Washington, he unfortunately joined a large group of his senior citizen peers.
This wasn’t the first tumble the 81-year-old has taken. In 2019, he fell in his home, fracturing his shoulder. This time, he got a concussion and was recently released to an in-patient rehabilitation facility. While Sen. McConnell didn’t fracture his skull, in falling and hitting his head, he became part of an emerging statistic: One that reveals falls are more dangerous for senior men than senior women.
This new research, which appeared in the American Journal of Emergency Medicine, came as a surprise to lead researcher Scott Alter, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton.
“We always hear about lower bone density rates among females, so we didn’t expect to see males with more skull fractures,” he said.
Dr. Alter said that as a clinician in a southern Florida facility, his emergency department was the perfect study grounds to evaluate incoming geriatric patients due to falls. Older “patients are at higher risk of skull fractures and intercranial bleeding, and we wanted to look at any patient presenting with a head injury. Some 80% were fall related, however.”
The statistics bear out the fact that falls of all types are common among the elderly: Some 800,000 seniors wind up in the hospital each year because of falls.
The numbers show death rates from falls are on the rise in the senior citizen age group, too, up 30% from 2007 to 2016. Falls account for 70% of accidental deaths in people 75 and older. They are the leading cause of injury-related visits to emergency departments in the country, too.
Jennifer Stevens, MD, a gerontologist and executive director at Florida-based Abbey Delray South, is aware of the dire numbers and sees their consequences regularly. “The reasons seniors are at a high fall risk are many,” she said. “They include balance issues, declining strength, diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, side effects of their medications, and more.”
In addition, many seniors live in spaces that are not necessarily equipped for their limitations, and hazards exist all over their homes. Put together, and the risks for falls are everywhere. But there are steps seniors, their families, and even middle-aged people can take to mitigate and hopefully prevent dangerous falls.
Starting early
While in many cases the journey to lessen fall risks begins after a fall, the time to begin addressing the issue is long before you hit your senior years. Mary Therese Cole, a physical therapist and certified dementia practitioner at Manual Edge Physical Therapy in Colorado Springs, Colo., says that age 50 is a good time to start paying attention and addressing physical declines.
“This is an age where your vision might begin deteriorating,” she said. “It’s a big reason why elderly people trip and fall.”
As our brains begin to age in our middle years, the neural pathways from brain to extremities start to decline, too. The result is that many people stop picking up their feet as well as they used to do, making them more likely to trip.
“You’re not elderly yet, but you’re not a spring chicken, either,” Ms. Cole said. “Any issues you have now will only get worse if you’re not working on them.”
A good starting point in middle age, then, is to work on both strength training and balance exercises. A certified personal trainer or physical therapist can help get you on a program to ward off many of these declines.
If you’ve reached your later years, however, and are experiencing physical declines, it’s smart to check in with your primary care doctor for an assessment. “He or she can get your started on regular PT to evaluate any shortcomings and then address them,” Ms. Cole said.
She noted that when she’s working with senior patients, she’ll test their strength getting into and out of a chair, do a manual strength test to check on lower extremities, check their walking stride, and ask about conditions such as diabetes, former surgeries, and other conditions.
From there, Ms. Cole said she can write up a plan for the patient. Likewise, Dr. Stevens uses a program called Be Active that allows her to test seniors on a variety of measurements, including flexibility, balance, hand strength, and more.
“Then we match them with classes to address their shortcomings,” she said. “It’s critical that seniors have the ability to recover and not fall if they get knocked off balance.”
Beyond working on your physical limitations, taking a good look at your home is essential, too. “You can have an occupational therapist come to your home and do an evaluation,” Dr. Stevens said. “They can help you rearrange and reorganize for a safer environment.”
Big, common household fall hazards include throw rugs, lack of nightlights for middle-of-the-night visits to the bathroom, a lack of grab bars in the shower/bathtub, and furniture that blocks pathways.
For his part, Dr. Alter likes to point seniors and their doctors to the CDC’s STEADI program, which is aimed at stopping elderly accidents, deaths, and injuries.
“It includes screening for fall risk, assessing factors you can modify or improve, and more tools,” he said.
Dr. Alter also recommended seniors talk to their doctors about medications, particularly blood thinners.
“At a certain point, you need to weigh the benefits of disease prevention with the risk of injury if you fall,” he said. “The bleeding risk might be too high if the patient is at a high risk of falls.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
When Senate Minority Leader Mitch McConnell (R-Ky.) fell recently at a dinner event in Washington, he unfortunately joined a large group of his senior citizen peers.
This wasn’t the first tumble the 81-year-old has taken. In 2019, he fell in his home, fracturing his shoulder. This time, he got a concussion and was recently released to an in-patient rehabilitation facility. While Sen. McConnell didn’t fracture his skull, in falling and hitting his head, he became part of an emerging statistic: One that reveals falls are more dangerous for senior men than senior women.
This new research, which appeared in the American Journal of Emergency Medicine, came as a surprise to lead researcher Scott Alter, MD, associate professor of emergency medicine at the Florida Atlantic University, Boca Raton.
“We always hear about lower bone density rates among females, so we didn’t expect to see males with more skull fractures,” he said.
Dr. Alter said that as a clinician in a southern Florida facility, his emergency department was the perfect study grounds to evaluate incoming geriatric patients due to falls. Older “patients are at higher risk of skull fractures and intercranial bleeding, and we wanted to look at any patient presenting with a head injury. Some 80% were fall related, however.”
The statistics bear out the fact that falls of all types are common among the elderly: Some 800,000 seniors wind up in the hospital each year because of falls.
The numbers show death rates from falls are on the rise in the senior citizen age group, too, up 30% from 2007 to 2016. Falls account for 70% of accidental deaths in people 75 and older. They are the leading cause of injury-related visits to emergency departments in the country, too.
Jennifer Stevens, MD, a gerontologist and executive director at Florida-based Abbey Delray South, is aware of the dire numbers and sees their consequences regularly. “The reasons seniors are at a high fall risk are many,” she said. “They include balance issues, declining strength, diseases like Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s, side effects of their medications, and more.”
In addition, many seniors live in spaces that are not necessarily equipped for their limitations, and hazards exist all over their homes. Put together, and the risks for falls are everywhere. But there are steps seniors, their families, and even middle-aged people can take to mitigate and hopefully prevent dangerous falls.
Starting early
While in many cases the journey to lessen fall risks begins after a fall, the time to begin addressing the issue is long before you hit your senior years. Mary Therese Cole, a physical therapist and certified dementia practitioner at Manual Edge Physical Therapy in Colorado Springs, Colo., says that age 50 is a good time to start paying attention and addressing physical declines.
“This is an age where your vision might begin deteriorating,” she said. “It’s a big reason why elderly people trip and fall.”
As our brains begin to age in our middle years, the neural pathways from brain to extremities start to decline, too. The result is that many people stop picking up their feet as well as they used to do, making them more likely to trip.
“You’re not elderly yet, but you’re not a spring chicken, either,” Ms. Cole said. “Any issues you have now will only get worse if you’re not working on them.”
A good starting point in middle age, then, is to work on both strength training and balance exercises. A certified personal trainer or physical therapist can help get you on a program to ward off many of these declines.
If you’ve reached your later years, however, and are experiencing physical declines, it’s smart to check in with your primary care doctor for an assessment. “He or she can get your started on regular PT to evaluate any shortcomings and then address them,” Ms. Cole said.
She noted that when she’s working with senior patients, she’ll test their strength getting into and out of a chair, do a manual strength test to check on lower extremities, check their walking stride, and ask about conditions such as diabetes, former surgeries, and other conditions.
From there, Ms. Cole said she can write up a plan for the patient. Likewise, Dr. Stevens uses a program called Be Active that allows her to test seniors on a variety of measurements, including flexibility, balance, hand strength, and more.
“Then we match them with classes to address their shortcomings,” she said. “It’s critical that seniors have the ability to recover and not fall if they get knocked off balance.”
Beyond working on your physical limitations, taking a good look at your home is essential, too. “You can have an occupational therapist come to your home and do an evaluation,” Dr. Stevens said. “They can help you rearrange and reorganize for a safer environment.”
Big, common household fall hazards include throw rugs, lack of nightlights for middle-of-the-night visits to the bathroom, a lack of grab bars in the shower/bathtub, and furniture that blocks pathways.
For his part, Dr. Alter likes to point seniors and their doctors to the CDC’s STEADI program, which is aimed at stopping elderly accidents, deaths, and injuries.
“It includes screening for fall risk, assessing factors you can modify or improve, and more tools,” he said.
Dr. Alter also recommended seniors talk to their doctors about medications, particularly blood thinners.
“At a certain point, you need to weigh the benefits of disease prevention with the risk of injury if you fall,” he said. “The bleeding risk might be too high if the patient is at a high risk of falls.”
A version of this article originally appeared on WebMD.com.
How to become wise
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. – Socrates
At what age is one supposed to be wise? I feel like I’m falling behind. I’ve crossed the middle of life and can check the prerequisite experiences: Joy, tragedy, love, adventure, love again. I lived a jetsetter life with an overnight bag always packed. I’ve sported the “Dad AF” tee with a fully loaded dad-pack. I’ve seen the 50 states and had my picture wrapped on a city bus (super-weird when you pull up next to one). Yet, when a moment arrives to pop in pithy advice for a resident or drop a few reassuring lines for a grieving friend, I’m often unable to find the words. If life were a video game, I’ve not earned the wisdom level yet.
Who are the wise men and women in your life? It’s difficult to list them. This is because it’s a complex attribute and hard to explain. It’s also because the wise who walk among us are rare. Wise is more than being brilliant at bullous diseases or knowing how to sleep train a baby. Nor is wise the buddy who purchased $1,000 of Bitcoin in 2010 (although stay close with him, he probably owns a jet). Neither content experts nor lucky friends rise to the appellation. Both experience and empathy.
The ancients considered wisdom to be one of the vital virtues. It was personified in high-profile gods like Apollo and Athena. It’s rare and important enough to be seen as spiritual. It features heavily in the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, the Meditations of Marcus Aurelius. In some cultures the wise are called elders or sages. In all cultures they are helpful, respected, sought after, appreciated. We need more wise people in this game of life. I want to be one. But there’s no Coursera for it.
To become wise you have to pass through many levels, put in a lot of reps, suffer through many sleepless nights. Like the third molar, also known as the wisdom tooth, it takes years. You also have to emerge stronger and smarter through those experiences. FDR would not have become one of the wisest presidents in history had it not been for his trials, and victories, over polio. Osler missed Cushing syndrome multiple times before he got it right. It seems you have to go to the mountain, like Batman, and fight a few battles to realize your full wisdom potential.
You must also reflect on your experiences and hone your insight. The management sage Peter Drucker would write what he expected to happen after a decision. Then he’d return to it to hone his intuition and judgment.
Lastly, you have to use your powers for good. Using insight to win your NCAA bracket pool isn’t wisdom. Helping a friend whose marriage is falling apart or colleague whose patient is suing them or a resident whose excision hit an arteriole surely is.
I’ve got a ways to go before anyone puts me on their wise friend list. I’m working on it though. Perhaps you will too – we are desperately short-staffed in this area. For now, I can start with writing better condolences.
“Who maintains that it is not a heavy blow? But it is part of being human.” – Seneca
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. – Socrates
At what age is one supposed to be wise? I feel like I’m falling behind. I’ve crossed the middle of life and can check the prerequisite experiences: Joy, tragedy, love, adventure, love again. I lived a jetsetter life with an overnight bag always packed. I’ve sported the “Dad AF” tee with a fully loaded dad-pack. I’ve seen the 50 states and had my picture wrapped on a city bus (super-weird when you pull up next to one). Yet, when a moment arrives to pop in pithy advice for a resident or drop a few reassuring lines for a grieving friend, I’m often unable to find the words. If life were a video game, I’ve not earned the wisdom level yet.
Who are the wise men and women in your life? It’s difficult to list them. This is because it’s a complex attribute and hard to explain. It’s also because the wise who walk among us are rare. Wise is more than being brilliant at bullous diseases or knowing how to sleep train a baby. Nor is wise the buddy who purchased $1,000 of Bitcoin in 2010 (although stay close with him, he probably owns a jet). Neither content experts nor lucky friends rise to the appellation. Both experience and empathy.
The ancients considered wisdom to be one of the vital virtues. It was personified in high-profile gods like Apollo and Athena. It’s rare and important enough to be seen as spiritual. It features heavily in the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, the Meditations of Marcus Aurelius. In some cultures the wise are called elders or sages. In all cultures they are helpful, respected, sought after, appreciated. We need more wise people in this game of life. I want to be one. But there’s no Coursera for it.
To become wise you have to pass through many levels, put in a lot of reps, suffer through many sleepless nights. Like the third molar, also known as the wisdom tooth, it takes years. You also have to emerge stronger and smarter through those experiences. FDR would not have become one of the wisest presidents in history had it not been for his trials, and victories, over polio. Osler missed Cushing syndrome multiple times before he got it right. It seems you have to go to the mountain, like Batman, and fight a few battles to realize your full wisdom potential.
You must also reflect on your experiences and hone your insight. The management sage Peter Drucker would write what he expected to happen after a decision. Then he’d return to it to hone his intuition and judgment.
Lastly, you have to use your powers for good. Using insight to win your NCAA bracket pool isn’t wisdom. Helping a friend whose marriage is falling apart or colleague whose patient is suing them or a resident whose excision hit an arteriole surely is.
I’ve got a ways to go before anyone puts me on their wise friend list. I’m working on it though. Perhaps you will too – we are desperately short-staffed in this area. For now, I can start with writing better condolences.
“Who maintains that it is not a heavy blow? But it is part of being human.” – Seneca
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
The only true wisdom is in knowing you know nothing. – Socrates
At what age is one supposed to be wise? I feel like I’m falling behind. I’ve crossed the middle of life and can check the prerequisite experiences: Joy, tragedy, love, adventure, love again. I lived a jetsetter life with an overnight bag always packed. I’ve sported the “Dad AF” tee with a fully loaded dad-pack. I’ve seen the 50 states and had my picture wrapped on a city bus (super-weird when you pull up next to one). Yet, when a moment arrives to pop in pithy advice for a resident or drop a few reassuring lines for a grieving friend, I’m often unable to find the words. If life were a video game, I’ve not earned the wisdom level yet.
Who are the wise men and women in your life? It’s difficult to list them. This is because it’s a complex attribute and hard to explain. It’s also because the wise who walk among us are rare. Wise is more than being brilliant at bullous diseases or knowing how to sleep train a baby. Nor is wise the buddy who purchased $1,000 of Bitcoin in 2010 (although stay close with him, he probably owns a jet). Neither content experts nor lucky friends rise to the appellation. Both experience and empathy.
The ancients considered wisdom to be one of the vital virtues. It was personified in high-profile gods like Apollo and Athena. It’s rare and important enough to be seen as spiritual. It features heavily in the Bible, the Bhagavad Gita, the Meditations of Marcus Aurelius. In some cultures the wise are called elders or sages. In all cultures they are helpful, respected, sought after, appreciated. We need more wise people in this game of life. I want to be one. But there’s no Coursera for it.
To become wise you have to pass through many levels, put in a lot of reps, suffer through many sleepless nights. Like the third molar, also known as the wisdom tooth, it takes years. You also have to emerge stronger and smarter through those experiences. FDR would not have become one of the wisest presidents in history had it not been for his trials, and victories, over polio. Osler missed Cushing syndrome multiple times before he got it right. It seems you have to go to the mountain, like Batman, and fight a few battles to realize your full wisdom potential.
You must also reflect on your experiences and hone your insight. The management sage Peter Drucker would write what he expected to happen after a decision. Then he’d return to it to hone his intuition and judgment.
Lastly, you have to use your powers for good. Using insight to win your NCAA bracket pool isn’t wisdom. Helping a friend whose marriage is falling apart or colleague whose patient is suing them or a resident whose excision hit an arteriole surely is.
I’ve got a ways to go before anyone puts me on their wise friend list. I’m working on it though. Perhaps you will too – we are desperately short-staffed in this area. For now, I can start with writing better condolences.
“Who maintains that it is not a heavy blow? But it is part of being human.” – Seneca
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. Write to him at [email protected].
What’s driving the "world’s fastest-growing brain disease"?
An international team of researchers reviewed previous research and cited data that suggest the chemical trichloroethylene (TCE) is associated with as much as a 500% increased risk for Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Lead investigator Ray Dorsey, MD, professor of neurology, University of Rochester, N.Y., called PD “the world’s fastest-growing brain disease,” and told this news organization that it “may be largely preventable.”
“Countless people have died over generations from cancer and other disease linked to TCE [and] Parkinson’s may be the latest,” he said. “Banning these chemicals, containing contaminated sites, and protecting homes, schools, and buildings at risk may all create a world where Parkinson’s is increasingly rare, not common.”
The paper was published online in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
Invisible, ubiquitous
TCE was first synthesized in a lab in 1864, with commercial production beginning in 1920, the researchers noted.
“Because of its unique properties, TCE has had countless industrial, commercial, military, and medical applications,” including producing refrigerants, cleaning electronics, and degreasing engine parts.
In addition, it’s been used in dry cleaning, although a similar chemical (perchloroethylene [PCE]) is currently more widely used for that purpose. Nevertheless, the authors noted, in anaerobic conditions, perchloroethylene often transforms into TCE “and their toxicity may be similar.”
Consumer products in which TCE is found include typewriter correction fluid, paint removers, gun cleaners, and aerosol cleaning products. Up until the 1970s, it was used to decaffeinate coffee.
TCE exposure isn’t confined to those who work with it. It also pollutes outdoor air, taints groundwater, and contaminates indoor air. It’s present in a substantial amount of groundwater in the United States and it “evaporates from underlying soil and groundwater and enters homes, workplaces, or schools, often undetected,” the researchers noted.
“Exposure can come via occupation or the environment and is often largely unknown at the time it occurs,” Dr. Dorsey said.
He noted that the rapid increase in PD incidence cannot be explained by genetic factors alone, which affect only about 15% of patients with PD, nor can it be explained by aging alone. “Certain pesticides ... are likely causes but would not explain the high prevalence of PD in urban areas, as is the case in the U.S.” Rather, “other factors” are involved, and “TCE is likely one such factor.”
Yet, “despite widespread contamination and increasing industrial, commercial, and military use, clinical investigations of TCE and PD have been limited.”
To fill this knowledge gap, Dr. Dorsey and his coauthors of the book, “Ending Parkinson’s Disease: A Prescription for Action,” took a deep dive into studies focusing on the potential association of TCE and PD and presented seven cases to illustrate the association.
“Like many genetic mutations (e.g., Parkin) and other environmental toxicants ... TCE damages the energy-producing parts of cells, i.e., the mitochondria,” said Dr. Dorsey.
TCE and PCE “likely mediate their toxicity through a common metabolite.” Because both are lipophilic, they “readily distribute in the brain and body tissues and appear to cause mitochondrial dysfunction at high doses,” the researchers hypothesized.
Dopaminergic neurons are particularly sensitive to mitochondrial neurotoxicants, so this might “partially explain the link to PD.”
Animal studies have shown that TCE “caused selective loss of dopaminergic neurons.” Moreover, PD-related neuropathology was found in the substantia nigra of rodents exposed to TCE over time. In addition, studies as early as 1960 were showing an association between TCE and parkinsonism.
The authors describe TCE as “ubiquitous” in the 1970s, with 10 million Americans working with the chemical or other organic solvents daily. The review details an extensive list of industries and occupations in which TCE exposure continues to occur.
People working with TCE might inhale it or touch it; but “millions more encounter the chemical unknowingly through outdoor air, contaminated groundwater, and indoor air pollution.”
They noted that TCE contaminates up to one-third of U.S. drinking water, has polluted the groundwater in more than 20 different countries on five continents, and is found in half of the 1,300 most toxic “Superfund” sites that are “part of a federal clean-up program, including 15 in California’s Silicon Valley, where TCE was used to clean electronics.”
Although the U.S. military stopped using TCE, numerous sites have been contaminated, including Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune in North Carolina, where TCE and PCE were found in drinking water at 280 times the recommended safety standards.
The researchers highlighted seven cases of individuals who developed PD after likely exposure to TCE, including NBA basketball player Brian Grant, who developed symptoms of PD in 2006 at the age of 34.
Mr. Grant and his family had lived in Camp Lejeune when he was a child, during which time he drank, bathed, and swam in contaminated water, “unaware of its toxicity.” His father also died of esophageal cancer, “which is linked to TCE,” the authors of the study wrote. Mr. Grant has created a foundation to inspire and support patients with PD.
All of the individuals either grew up in or spent time in an area where they were extensively exposed to TCE, PCE, or other chemicals, or experienced occupational exposure.
The authors acknowledged that the role of TCE in PD, as illustrated by the cases, is “far from definitive.” For example, exposure to TCE is often combined with exposure to other toxins, or with unmeasured genetic risk factors.
They highlighted the need for more research and called for cleaning and containing contaminated sites, monitoring TCE levels, and publicly communicating risk and a ban on TCE.
Recall bias?
Commenting for this news organization, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA), noted that the authors “are very frank about the limitations of this approach [illustrative cases] as proof of causation between PD and TCE exposure.”
Another limitation is that TCE exposure is very common, “as argued in the paper.” But “most people with exposure do not develop PD,” Dr. Gilbert pointed out. “By probing the TCE exposure of those who already have PD, there is a danger of recall bias.”
Dr. Gilbert, associate professor of neurology at NYU Langone Health, who was not involved with the study, acknowledged that the authors “present their work as hypothesis and clearly state that more work is needed to understand the connection between TCE and PD.”
In the meantime, however, there are “well-established health risks of TCE exposure, including development of various cancers,” she said. Therefore, the authors’ goals appear to be educating the public about known health risks, working to clean up known sites of contamination, and advocating to ban future use of TCE.
These goals “do not need to wait for [proof of] firm causation between TCE and PD,” she stated.
Dr. Dorsey reported he has received honoraria for speaking at the American Academy of Neurology and at multiple other societies and foundations and has received compensation for consulting services from pharmaceutical companies, foundations, medical education companies, and medical publications; he owns stock in several companies. The other authors’ disclosures can be found in the original paper. Dr. Gilbert is employed by the American Parkinson Disease Association and Bellevue Hospital Center in New York City.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An international team of researchers reviewed previous research and cited data that suggest the chemical trichloroethylene (TCE) is associated with as much as a 500% increased risk for Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Lead investigator Ray Dorsey, MD, professor of neurology, University of Rochester, N.Y., called PD “the world’s fastest-growing brain disease,” and told this news organization that it “may be largely preventable.”
“Countless people have died over generations from cancer and other disease linked to TCE [and] Parkinson’s may be the latest,” he said. “Banning these chemicals, containing contaminated sites, and protecting homes, schools, and buildings at risk may all create a world where Parkinson’s is increasingly rare, not common.”
The paper was published online in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
Invisible, ubiquitous
TCE was first synthesized in a lab in 1864, with commercial production beginning in 1920, the researchers noted.
“Because of its unique properties, TCE has had countless industrial, commercial, military, and medical applications,” including producing refrigerants, cleaning electronics, and degreasing engine parts.
In addition, it’s been used in dry cleaning, although a similar chemical (perchloroethylene [PCE]) is currently more widely used for that purpose. Nevertheless, the authors noted, in anaerobic conditions, perchloroethylene often transforms into TCE “and their toxicity may be similar.”
Consumer products in which TCE is found include typewriter correction fluid, paint removers, gun cleaners, and aerosol cleaning products. Up until the 1970s, it was used to decaffeinate coffee.
TCE exposure isn’t confined to those who work with it. It also pollutes outdoor air, taints groundwater, and contaminates indoor air. It’s present in a substantial amount of groundwater in the United States and it “evaporates from underlying soil and groundwater and enters homes, workplaces, or schools, often undetected,” the researchers noted.
“Exposure can come via occupation or the environment and is often largely unknown at the time it occurs,” Dr. Dorsey said.
He noted that the rapid increase in PD incidence cannot be explained by genetic factors alone, which affect only about 15% of patients with PD, nor can it be explained by aging alone. “Certain pesticides ... are likely causes but would not explain the high prevalence of PD in urban areas, as is the case in the U.S.” Rather, “other factors” are involved, and “TCE is likely one such factor.”
Yet, “despite widespread contamination and increasing industrial, commercial, and military use, clinical investigations of TCE and PD have been limited.”
To fill this knowledge gap, Dr. Dorsey and his coauthors of the book, “Ending Parkinson’s Disease: A Prescription for Action,” took a deep dive into studies focusing on the potential association of TCE and PD and presented seven cases to illustrate the association.
“Like many genetic mutations (e.g., Parkin) and other environmental toxicants ... TCE damages the energy-producing parts of cells, i.e., the mitochondria,” said Dr. Dorsey.
TCE and PCE “likely mediate their toxicity through a common metabolite.” Because both are lipophilic, they “readily distribute in the brain and body tissues and appear to cause mitochondrial dysfunction at high doses,” the researchers hypothesized.
Dopaminergic neurons are particularly sensitive to mitochondrial neurotoxicants, so this might “partially explain the link to PD.”
Animal studies have shown that TCE “caused selective loss of dopaminergic neurons.” Moreover, PD-related neuropathology was found in the substantia nigra of rodents exposed to TCE over time. In addition, studies as early as 1960 were showing an association between TCE and parkinsonism.
The authors describe TCE as “ubiquitous” in the 1970s, with 10 million Americans working with the chemical or other organic solvents daily. The review details an extensive list of industries and occupations in which TCE exposure continues to occur.
People working with TCE might inhale it or touch it; but “millions more encounter the chemical unknowingly through outdoor air, contaminated groundwater, and indoor air pollution.”
They noted that TCE contaminates up to one-third of U.S. drinking water, has polluted the groundwater in more than 20 different countries on five continents, and is found in half of the 1,300 most toxic “Superfund” sites that are “part of a federal clean-up program, including 15 in California’s Silicon Valley, where TCE was used to clean electronics.”
Although the U.S. military stopped using TCE, numerous sites have been contaminated, including Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune in North Carolina, where TCE and PCE were found in drinking water at 280 times the recommended safety standards.
The researchers highlighted seven cases of individuals who developed PD after likely exposure to TCE, including NBA basketball player Brian Grant, who developed symptoms of PD in 2006 at the age of 34.
Mr. Grant and his family had lived in Camp Lejeune when he was a child, during which time he drank, bathed, and swam in contaminated water, “unaware of its toxicity.” His father also died of esophageal cancer, “which is linked to TCE,” the authors of the study wrote. Mr. Grant has created a foundation to inspire and support patients with PD.
All of the individuals either grew up in or spent time in an area where they were extensively exposed to TCE, PCE, or other chemicals, or experienced occupational exposure.
The authors acknowledged that the role of TCE in PD, as illustrated by the cases, is “far from definitive.” For example, exposure to TCE is often combined with exposure to other toxins, or with unmeasured genetic risk factors.
They highlighted the need for more research and called for cleaning and containing contaminated sites, monitoring TCE levels, and publicly communicating risk and a ban on TCE.
Recall bias?
Commenting for this news organization, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA), noted that the authors “are very frank about the limitations of this approach [illustrative cases] as proof of causation between PD and TCE exposure.”
Another limitation is that TCE exposure is very common, “as argued in the paper.” But “most people with exposure do not develop PD,” Dr. Gilbert pointed out. “By probing the TCE exposure of those who already have PD, there is a danger of recall bias.”
Dr. Gilbert, associate professor of neurology at NYU Langone Health, who was not involved with the study, acknowledged that the authors “present their work as hypothesis and clearly state that more work is needed to understand the connection between TCE and PD.”
In the meantime, however, there are “well-established health risks of TCE exposure, including development of various cancers,” she said. Therefore, the authors’ goals appear to be educating the public about known health risks, working to clean up known sites of contamination, and advocating to ban future use of TCE.
These goals “do not need to wait for [proof of] firm causation between TCE and PD,” she stated.
Dr. Dorsey reported he has received honoraria for speaking at the American Academy of Neurology and at multiple other societies and foundations and has received compensation for consulting services from pharmaceutical companies, foundations, medical education companies, and medical publications; he owns stock in several companies. The other authors’ disclosures can be found in the original paper. Dr. Gilbert is employed by the American Parkinson Disease Association and Bellevue Hospital Center in New York City.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
An international team of researchers reviewed previous research and cited data that suggest the chemical trichloroethylene (TCE) is associated with as much as a 500% increased risk for Parkinson’s disease (PD).
Lead investigator Ray Dorsey, MD, professor of neurology, University of Rochester, N.Y., called PD “the world’s fastest-growing brain disease,” and told this news organization that it “may be largely preventable.”
“Countless people have died over generations from cancer and other disease linked to TCE [and] Parkinson’s may be the latest,” he said. “Banning these chemicals, containing contaminated sites, and protecting homes, schools, and buildings at risk may all create a world where Parkinson’s is increasingly rare, not common.”
The paper was published online in the Journal of Parkinson’s Disease.
Invisible, ubiquitous
TCE was first synthesized in a lab in 1864, with commercial production beginning in 1920, the researchers noted.
“Because of its unique properties, TCE has had countless industrial, commercial, military, and medical applications,” including producing refrigerants, cleaning electronics, and degreasing engine parts.
In addition, it’s been used in dry cleaning, although a similar chemical (perchloroethylene [PCE]) is currently more widely used for that purpose. Nevertheless, the authors noted, in anaerobic conditions, perchloroethylene often transforms into TCE “and their toxicity may be similar.”
Consumer products in which TCE is found include typewriter correction fluid, paint removers, gun cleaners, and aerosol cleaning products. Up until the 1970s, it was used to decaffeinate coffee.
TCE exposure isn’t confined to those who work with it. It also pollutes outdoor air, taints groundwater, and contaminates indoor air. It’s present in a substantial amount of groundwater in the United States and it “evaporates from underlying soil and groundwater and enters homes, workplaces, or schools, often undetected,” the researchers noted.
“Exposure can come via occupation or the environment and is often largely unknown at the time it occurs,” Dr. Dorsey said.
He noted that the rapid increase in PD incidence cannot be explained by genetic factors alone, which affect only about 15% of patients with PD, nor can it be explained by aging alone. “Certain pesticides ... are likely causes but would not explain the high prevalence of PD in urban areas, as is the case in the U.S.” Rather, “other factors” are involved, and “TCE is likely one such factor.”
Yet, “despite widespread contamination and increasing industrial, commercial, and military use, clinical investigations of TCE and PD have been limited.”
To fill this knowledge gap, Dr. Dorsey and his coauthors of the book, “Ending Parkinson’s Disease: A Prescription for Action,” took a deep dive into studies focusing on the potential association of TCE and PD and presented seven cases to illustrate the association.
“Like many genetic mutations (e.g., Parkin) and other environmental toxicants ... TCE damages the energy-producing parts of cells, i.e., the mitochondria,” said Dr. Dorsey.
TCE and PCE “likely mediate their toxicity through a common metabolite.” Because both are lipophilic, they “readily distribute in the brain and body tissues and appear to cause mitochondrial dysfunction at high doses,” the researchers hypothesized.
Dopaminergic neurons are particularly sensitive to mitochondrial neurotoxicants, so this might “partially explain the link to PD.”
Animal studies have shown that TCE “caused selective loss of dopaminergic neurons.” Moreover, PD-related neuropathology was found in the substantia nigra of rodents exposed to TCE over time. In addition, studies as early as 1960 were showing an association between TCE and parkinsonism.
The authors describe TCE as “ubiquitous” in the 1970s, with 10 million Americans working with the chemical or other organic solvents daily. The review details an extensive list of industries and occupations in which TCE exposure continues to occur.
People working with TCE might inhale it or touch it; but “millions more encounter the chemical unknowingly through outdoor air, contaminated groundwater, and indoor air pollution.”
They noted that TCE contaminates up to one-third of U.S. drinking water, has polluted the groundwater in more than 20 different countries on five continents, and is found in half of the 1,300 most toxic “Superfund” sites that are “part of a federal clean-up program, including 15 in California’s Silicon Valley, where TCE was used to clean electronics.”
Although the U.S. military stopped using TCE, numerous sites have been contaminated, including Marine Corps Base Camp Lejeune in North Carolina, where TCE and PCE were found in drinking water at 280 times the recommended safety standards.
The researchers highlighted seven cases of individuals who developed PD after likely exposure to TCE, including NBA basketball player Brian Grant, who developed symptoms of PD in 2006 at the age of 34.
Mr. Grant and his family had lived in Camp Lejeune when he was a child, during which time he drank, bathed, and swam in contaminated water, “unaware of its toxicity.” His father also died of esophageal cancer, “which is linked to TCE,” the authors of the study wrote. Mr. Grant has created a foundation to inspire and support patients with PD.
All of the individuals either grew up in or spent time in an area where they were extensively exposed to TCE, PCE, or other chemicals, or experienced occupational exposure.
The authors acknowledged that the role of TCE in PD, as illustrated by the cases, is “far from definitive.” For example, exposure to TCE is often combined with exposure to other toxins, or with unmeasured genetic risk factors.
They highlighted the need for more research and called for cleaning and containing contaminated sites, monitoring TCE levels, and publicly communicating risk and a ban on TCE.
Recall bias?
Commenting for this news organization, Rebecca Gilbert, MD, PhD, chief scientific officer, American Parkinson Disease Association (APDA), noted that the authors “are very frank about the limitations of this approach [illustrative cases] as proof of causation between PD and TCE exposure.”
Another limitation is that TCE exposure is very common, “as argued in the paper.” But “most people with exposure do not develop PD,” Dr. Gilbert pointed out. “By probing the TCE exposure of those who already have PD, there is a danger of recall bias.”
Dr. Gilbert, associate professor of neurology at NYU Langone Health, who was not involved with the study, acknowledged that the authors “present their work as hypothesis and clearly state that more work is needed to understand the connection between TCE and PD.”
In the meantime, however, there are “well-established health risks of TCE exposure, including development of various cancers,” she said. Therefore, the authors’ goals appear to be educating the public about known health risks, working to clean up known sites of contamination, and advocating to ban future use of TCE.
These goals “do not need to wait for [proof of] firm causation between TCE and PD,” she stated.
Dr. Dorsey reported he has received honoraria for speaking at the American Academy of Neurology and at multiple other societies and foundations and has received compensation for consulting services from pharmaceutical companies, foundations, medical education companies, and medical publications; he owns stock in several companies. The other authors’ disclosures can be found in the original paper. Dr. Gilbert is employed by the American Parkinson Disease Association and Bellevue Hospital Center in New York City.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF PARKINSON’S DISEASE
Cutting social media to 1 hour a day boosts self-image in young adults
“Youth spend, on average, between 6 and 8 hours per day on screens, much of it on social media,” said senior study author Gary S. Goldfield, PhD, senior scientist at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute in Ottawa, Canada. “Social media provides exposure to so many photo-edited pictures – including those of models, celebrities, and fitness instructors – that perpetuate an unattainable beauty standard that gets internalized by impressionable youth and young adults, leading to body dissatisfaction.”
Plenty of research has linked frequent social media use with body image issues and even eating disorders. But crucial gaps in our knowledge remain, Dr. Goldfield said.
Much of that research “is correlational,” Dr. Goldfield added. And studies don’t always focus on individuals who may be more vulnerable to social media’s harmful effects, such as those with ruminative or brooding cognitive styles, affecting results.
And none have explored an obvious question: Can cutting down on social media use also diminish its potential harms?
Dr. Goldfield and his colleagues found an answer: Yes, it can.
Limiting social media use to 1 hour per day helped older teens and young adults feel much better about their weight and appearance after only 3 weeks, according to the study in Psychology of Popular Media, a journal of the American Psychological Association.
“Our randomized controlled design allowed us to show a stronger causal link between social media use and body image in youth, compared to previous research,” Dr. Goldfield said. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that social media use reduction leads to enhanced body image.”
Nancy Lee Zucker, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and director of the Duke Center for Eating Disorders, said the results provide needed data that could help guide young people and parents on optimal social media use. Dr. Zucker was not involved in the study.
What the researchers did
For the study, Dr. Goldfield and colleagues recruited undergraduate psychology students aged 17-25 who averaged at least 2 hours per day of social media use on smartphones, and who had symptoms of depression or anxiety.
Participants were not told the purpose of the study, and their social media use was monitored by a screen time tracking program. At the beginning and end of the study, they answered questions such as “I’m pretty happy about the way I look,” and “I am satisfied with my weight,” on a 1 (never) to 5 (always) Likert scale.
During the first week, all 220 participants (76% female, 23% male, and 1% other) were told to use social media on their smartphones as they usually do. Over the next 3 weeks, 117 students were told to limit their social media use to 1 hour per day, while the rest were instructed to carry on as usual. In both groups, over 70% of participants were between age 17 and 19.
The first group cut their social media use by about 50%, from a mean of around 168 minutes per day during week 1 to around 78 minutes per day by the end of week 4, while the unrestricted group went from around 181 minutes per day to 189.
Cutting use by around half yielded quick, significant improvements
The students who curbed their social media use saw significant improvements in their “appearance esteem” (from 2.95 to 3.15 points; P <.001) and their “weight esteem” (from 3.16 to 3.32 points; P < .001), whereas those who used social media freely saw no such changes (from 2.72 to 2.76; P = .992 and 3.01 to 3.02; P = .654, respectively). No gender differences between the groups were found.
The researchers are now studying possible reasons for these findings.
The changes in appearance scores “represent a small- to medium-effect size,” said child psychologist Sara R. Gould, PhD, director of the Eating Disorders Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City in Missouri, who was not associated with the research.“ As such, these are clinically meaningful results, particularly since they were achieved in only 3 weeks. Even small impacts can be added to other changes to create larger impacts or have the potential to grow over time.”
The push to limit social media
As more and more experts scrutinize the impact of social media on young people’s mental health, social media companies have responded with features designed to limit the time young users spend on their platforms.
Just this year, Instagram rolled out “quiet mode,” which lets users shut down their direct messages (DMs) for a specified amount of time. To turn on quiet mode, users can navigate to their profiles, and select the triple line icon, “settings,” “notifications,” and “quiet mode.” Another option: Tap the triple line icon, “your activity,” and “time spent” to set reminders to take breaks after 10, 20, or 30 minutes of use.
TikTok users under 18 will soon have their accounts defaulted to a 1-hour daily screen-time limit, TikTok has announced. Unlike other similar features, it will require users to turn it off rather than turn it on.
Leveraging built-in controls is “a good start to being more intentional about your screen time,” suggested lead author Helen Thai, a PhD student in clinical psychology at McGill University in Montreal. “Unfortunately, users can easily bypass these settings.”
One reason for social’s magnetic pull: “FOMO – fear of missing out – on what friends are doing can make cutting back on social media use difficult,” said Dr. Zucker. To help prevent FOMO, parents may consider talking to parents of their children’s friends about reducing usage for all the children, Dr. Zucker suggested.
Mary E. Romano, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics-adolescent medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., urges parents “to have very clear rules and expectations about social media use.”
Dr. Romano, also not involved in the study, recommended the website Wait Until 8th to help parents band together to commit to delaying smartphone access until at least eighth grade.
Dr. Gould recommended the Family Media Plan, a tool from the American Academy of Pediatrics that lets users create a customized plan, complete with guidance tailored to each person’s age and the family’s goals. Sample tips: Designate a basket for holding devices during meals, and switch to audiobooks or relaxing music instead of videos to fall asleep at night.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Youth spend, on average, between 6 and 8 hours per day on screens, much of it on social media,” said senior study author Gary S. Goldfield, PhD, senior scientist at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute in Ottawa, Canada. “Social media provides exposure to so many photo-edited pictures – including those of models, celebrities, and fitness instructors – that perpetuate an unattainable beauty standard that gets internalized by impressionable youth and young adults, leading to body dissatisfaction.”
Plenty of research has linked frequent social media use with body image issues and even eating disorders. But crucial gaps in our knowledge remain, Dr. Goldfield said.
Much of that research “is correlational,” Dr. Goldfield added. And studies don’t always focus on individuals who may be more vulnerable to social media’s harmful effects, such as those with ruminative or brooding cognitive styles, affecting results.
And none have explored an obvious question: Can cutting down on social media use also diminish its potential harms?
Dr. Goldfield and his colleagues found an answer: Yes, it can.
Limiting social media use to 1 hour per day helped older teens and young adults feel much better about their weight and appearance after only 3 weeks, according to the study in Psychology of Popular Media, a journal of the American Psychological Association.
“Our randomized controlled design allowed us to show a stronger causal link between social media use and body image in youth, compared to previous research,” Dr. Goldfield said. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that social media use reduction leads to enhanced body image.”
Nancy Lee Zucker, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and director of the Duke Center for Eating Disorders, said the results provide needed data that could help guide young people and parents on optimal social media use. Dr. Zucker was not involved in the study.
What the researchers did
For the study, Dr. Goldfield and colleagues recruited undergraduate psychology students aged 17-25 who averaged at least 2 hours per day of social media use on smartphones, and who had symptoms of depression or anxiety.
Participants were not told the purpose of the study, and their social media use was monitored by a screen time tracking program. At the beginning and end of the study, they answered questions such as “I’m pretty happy about the way I look,” and “I am satisfied with my weight,” on a 1 (never) to 5 (always) Likert scale.
During the first week, all 220 participants (76% female, 23% male, and 1% other) were told to use social media on their smartphones as they usually do. Over the next 3 weeks, 117 students were told to limit their social media use to 1 hour per day, while the rest were instructed to carry on as usual. In both groups, over 70% of participants were between age 17 and 19.
The first group cut their social media use by about 50%, from a mean of around 168 minutes per day during week 1 to around 78 minutes per day by the end of week 4, while the unrestricted group went from around 181 minutes per day to 189.
Cutting use by around half yielded quick, significant improvements
The students who curbed their social media use saw significant improvements in their “appearance esteem” (from 2.95 to 3.15 points; P <.001) and their “weight esteem” (from 3.16 to 3.32 points; P < .001), whereas those who used social media freely saw no such changes (from 2.72 to 2.76; P = .992 and 3.01 to 3.02; P = .654, respectively). No gender differences between the groups were found.
The researchers are now studying possible reasons for these findings.
The changes in appearance scores “represent a small- to medium-effect size,” said child psychologist Sara R. Gould, PhD, director of the Eating Disorders Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City in Missouri, who was not associated with the research.“ As such, these are clinically meaningful results, particularly since they were achieved in only 3 weeks. Even small impacts can be added to other changes to create larger impacts or have the potential to grow over time.”
The push to limit social media
As more and more experts scrutinize the impact of social media on young people’s mental health, social media companies have responded with features designed to limit the time young users spend on their platforms.
Just this year, Instagram rolled out “quiet mode,” which lets users shut down their direct messages (DMs) for a specified amount of time. To turn on quiet mode, users can navigate to their profiles, and select the triple line icon, “settings,” “notifications,” and “quiet mode.” Another option: Tap the triple line icon, “your activity,” and “time spent” to set reminders to take breaks after 10, 20, or 30 minutes of use.
TikTok users under 18 will soon have their accounts defaulted to a 1-hour daily screen-time limit, TikTok has announced. Unlike other similar features, it will require users to turn it off rather than turn it on.
Leveraging built-in controls is “a good start to being more intentional about your screen time,” suggested lead author Helen Thai, a PhD student in clinical psychology at McGill University in Montreal. “Unfortunately, users can easily bypass these settings.”
One reason for social’s magnetic pull: “FOMO – fear of missing out – on what friends are doing can make cutting back on social media use difficult,” said Dr. Zucker. To help prevent FOMO, parents may consider talking to parents of their children’s friends about reducing usage for all the children, Dr. Zucker suggested.
Mary E. Romano, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics-adolescent medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., urges parents “to have very clear rules and expectations about social media use.”
Dr. Romano, also not involved in the study, recommended the website Wait Until 8th to help parents band together to commit to delaying smartphone access until at least eighth grade.
Dr. Gould recommended the Family Media Plan, a tool from the American Academy of Pediatrics that lets users create a customized plan, complete with guidance tailored to each person’s age and the family’s goals. Sample tips: Designate a basket for holding devices during meals, and switch to audiobooks or relaxing music instead of videos to fall asleep at night.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“Youth spend, on average, between 6 and 8 hours per day on screens, much of it on social media,” said senior study author Gary S. Goldfield, PhD, senior scientist at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario Research Institute in Ottawa, Canada. “Social media provides exposure to so many photo-edited pictures – including those of models, celebrities, and fitness instructors – that perpetuate an unattainable beauty standard that gets internalized by impressionable youth and young adults, leading to body dissatisfaction.”
Plenty of research has linked frequent social media use with body image issues and even eating disorders. But crucial gaps in our knowledge remain, Dr. Goldfield said.
Much of that research “is correlational,” Dr. Goldfield added. And studies don’t always focus on individuals who may be more vulnerable to social media’s harmful effects, such as those with ruminative or brooding cognitive styles, affecting results.
And none have explored an obvious question: Can cutting down on social media use also diminish its potential harms?
Dr. Goldfield and his colleagues found an answer: Yes, it can.
Limiting social media use to 1 hour per day helped older teens and young adults feel much better about their weight and appearance after only 3 weeks, according to the study in Psychology of Popular Media, a journal of the American Psychological Association.
“Our randomized controlled design allowed us to show a stronger causal link between social media use and body image in youth, compared to previous research,” Dr. Goldfield said. “To our knowledge, this is the first study to show that social media use reduction leads to enhanced body image.”
Nancy Lee Zucker, PhD, professor of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University, Durham, N.C., and director of the Duke Center for Eating Disorders, said the results provide needed data that could help guide young people and parents on optimal social media use. Dr. Zucker was not involved in the study.
What the researchers did
For the study, Dr. Goldfield and colleagues recruited undergraduate psychology students aged 17-25 who averaged at least 2 hours per day of social media use on smartphones, and who had symptoms of depression or anxiety.
Participants were not told the purpose of the study, and their social media use was monitored by a screen time tracking program. At the beginning and end of the study, they answered questions such as “I’m pretty happy about the way I look,” and “I am satisfied with my weight,” on a 1 (never) to 5 (always) Likert scale.
During the first week, all 220 participants (76% female, 23% male, and 1% other) were told to use social media on their smartphones as they usually do. Over the next 3 weeks, 117 students were told to limit their social media use to 1 hour per day, while the rest were instructed to carry on as usual. In both groups, over 70% of participants were between age 17 and 19.
The first group cut their social media use by about 50%, from a mean of around 168 minutes per day during week 1 to around 78 minutes per day by the end of week 4, while the unrestricted group went from around 181 minutes per day to 189.
Cutting use by around half yielded quick, significant improvements
The students who curbed their social media use saw significant improvements in their “appearance esteem” (from 2.95 to 3.15 points; P <.001) and their “weight esteem” (from 3.16 to 3.32 points; P < .001), whereas those who used social media freely saw no such changes (from 2.72 to 2.76; P = .992 and 3.01 to 3.02; P = .654, respectively). No gender differences between the groups were found.
The researchers are now studying possible reasons for these findings.
The changes in appearance scores “represent a small- to medium-effect size,” said child psychologist Sara R. Gould, PhD, director of the Eating Disorders Center at Children’s Mercy Kansas City in Missouri, who was not associated with the research.“ As such, these are clinically meaningful results, particularly since they were achieved in only 3 weeks. Even small impacts can be added to other changes to create larger impacts or have the potential to grow over time.”
The push to limit social media
As more and more experts scrutinize the impact of social media on young people’s mental health, social media companies have responded with features designed to limit the time young users spend on their platforms.
Just this year, Instagram rolled out “quiet mode,” which lets users shut down their direct messages (DMs) for a specified amount of time. To turn on quiet mode, users can navigate to their profiles, and select the triple line icon, “settings,” “notifications,” and “quiet mode.” Another option: Tap the triple line icon, “your activity,” and “time spent” to set reminders to take breaks after 10, 20, or 30 minutes of use.
TikTok users under 18 will soon have their accounts defaulted to a 1-hour daily screen-time limit, TikTok has announced. Unlike other similar features, it will require users to turn it off rather than turn it on.
Leveraging built-in controls is “a good start to being more intentional about your screen time,” suggested lead author Helen Thai, a PhD student in clinical psychology at McGill University in Montreal. “Unfortunately, users can easily bypass these settings.”
One reason for social’s magnetic pull: “FOMO – fear of missing out – on what friends are doing can make cutting back on social media use difficult,” said Dr. Zucker. To help prevent FOMO, parents may consider talking to parents of their children’s friends about reducing usage for all the children, Dr. Zucker suggested.
Mary E. Romano, MD, MPH, associate professor of pediatrics-adolescent medicine at Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tenn., urges parents “to have very clear rules and expectations about social media use.”
Dr. Romano, also not involved in the study, recommended the website Wait Until 8th to help parents band together to commit to delaying smartphone access until at least eighth grade.
Dr. Gould recommended the Family Media Plan, a tool from the American Academy of Pediatrics that lets users create a customized plan, complete with guidance tailored to each person’s age and the family’s goals. Sample tips: Designate a basket for holding devices during meals, and switch to audiobooks or relaxing music instead of videos to fall asleep at night.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM PSYCHOLOGY OF POPULAR MEDIA
Which recommendations on screening, diagnosing, and treating eating disorders are most helpful?
Most medical professionals would agree that people with eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and binge-eating disorder (BED), have serious diseases that result in greater morbidity and mortality compared with those in the general population. Although these do not represent the entire spectrum of eating disorders, these are the ones with the most available research data.
Eating disorders were previously thought to be diseases of affluent white females. Over the past few years, however, it has become more widely accepted that eating disorders may be found across people of a variety of identities and socioeconomic statuses. Clinicians have also become concerned that the incidence of eating disorders has increased and that part of this occurred during the COVID pandemic.
APA’s guideline
In February 2023, the American Psychiatric Association released its first update to the Guideline of Treatment of Patients with Eating Disorders. This is the first update to the guideline since 2006. The guideline was updated with the additional evidence that is now available as further studies have been published since the last update. The 2023 guideline provides nine recommendations for assessment and determination of a treatment plan. It then provides three recommendations specifically for AN and two recommendations each for BN and BED. The introduction acknowledges an unsuccessful attempt to provide recommendations for avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder due to the paucity of evidence on this disease.
The first recommendation within the guidelines indicates “the clinician should be sure to ask all patients about the presence of eating disorder symptoms as part of their standard psychiatric evaluation.” This recommendation is provided as there are many with normal or elevated BMI who may have eating disorders and the identification could provide the prevention of significant morbidity and mortality. It includes screening questions that can be used and standardized screening questionnaires.
Other recommendations go on to describe further evaluation for diagnosis, aspects of the history that should be obtained, and specific treatment modalities that can be used, including cognitive behavioral therapy and oral medications that have been approved for use in eating disorder treatments.1
AAP’s clinical report
These guidelines add to the recommendations provided by the American Academy of Pediatrics, which published a clinical report on the Identification and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents in January 2021. In this guidance document, the AAP recommends screening for eating disorders in any children or adolescents with “reported dieting, body image dissatisfaction, experiences of weight-based stigma, or changes in eating or exercise” and those with weight loss or rapid weight fluctuations.
If there are concerns, then a full assessment is warranted, the recommendations say. When a patient is diagnosed with an eating disorder, this clinical report also provides recommendations on history, exam, and treatment pathways.2
USPSTF’s recommendation
The United States Preventive Services Task Force provides a recommendation that differs from the AAP and APA’s. In March 2022, the USPSTF published a Grade I recommendation. They state: “The USPSTF concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults.”
They provide several reasons as to why this was given a Grade I. One reason is the paucity of data that exists on the incidence and/or benefit of screening for eating disorders amongst those who are asymptomatic. They also discuss the potential harms of false positive results of screening for both the patients and health care system. The questionnaires identified were the same as those discussed in both the APA and AAP recommendations.
The USPSTF full guideline also provides a call for further studies that would help provide guidance for primary care clinicians in the area of eating disorders.3
Takeaway message
With all this information, what is the primary care clinician to do? It does not seem to me that the APA guideline provides new information on how to identify patients best served by screening for eating disorders.
I am not sure it is reasonable for the primary care physician (PCP) to add these questions to every well visit when assessing the mental health status of patients.
There are ways in which this new guideline can be useful to the PCP, however. Among these are that it provides good resources for further evaluation for patients for whom the PCP may have concerns about eating disorders. It also includes screening tests that do not take much time to complete and clear aspects of the history, physical exam, and laboratory evaluation that can be used to provide further clarification and possible diagnosis. Additionally, this guideline provides clear advice on treatment recommendations of therapy and medications to start. This is especially important as wait times for psychiatric providers seem to always be increasing.
A trusted PCP can use these guidelines to start providing their patient with the help they need. Overall, these new recommendations will not change my screening practices, but they will provide assistance in diagnosis and management of my patients.
References
1. Guideline Writing Group. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders. 2023. doi: 10.1176/appi.books.9780890424865.
2. Hornberger LL et al. Identification and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics. 2021;147 (1): e2020040279. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-040279.
3. Feltner C et al. Screening for Eating Disorders in Adolescents and Adults: Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;327(11): 1068-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.1807.
Most medical professionals would agree that people with eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and binge-eating disorder (BED), have serious diseases that result in greater morbidity and mortality compared with those in the general population. Although these do not represent the entire spectrum of eating disorders, these are the ones with the most available research data.
Eating disorders were previously thought to be diseases of affluent white females. Over the past few years, however, it has become more widely accepted that eating disorders may be found across people of a variety of identities and socioeconomic statuses. Clinicians have also become concerned that the incidence of eating disorders has increased and that part of this occurred during the COVID pandemic.
APA’s guideline
In February 2023, the American Psychiatric Association released its first update to the Guideline of Treatment of Patients with Eating Disorders. This is the first update to the guideline since 2006. The guideline was updated with the additional evidence that is now available as further studies have been published since the last update. The 2023 guideline provides nine recommendations for assessment and determination of a treatment plan. It then provides three recommendations specifically for AN and two recommendations each for BN and BED. The introduction acknowledges an unsuccessful attempt to provide recommendations for avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder due to the paucity of evidence on this disease.
The first recommendation within the guidelines indicates “the clinician should be sure to ask all patients about the presence of eating disorder symptoms as part of their standard psychiatric evaluation.” This recommendation is provided as there are many with normal or elevated BMI who may have eating disorders and the identification could provide the prevention of significant morbidity and mortality. It includes screening questions that can be used and standardized screening questionnaires.
Other recommendations go on to describe further evaluation for diagnosis, aspects of the history that should be obtained, and specific treatment modalities that can be used, including cognitive behavioral therapy and oral medications that have been approved for use in eating disorder treatments.1
AAP’s clinical report
These guidelines add to the recommendations provided by the American Academy of Pediatrics, which published a clinical report on the Identification and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents in January 2021. In this guidance document, the AAP recommends screening for eating disorders in any children or adolescents with “reported dieting, body image dissatisfaction, experiences of weight-based stigma, or changes in eating or exercise” and those with weight loss or rapid weight fluctuations.
If there are concerns, then a full assessment is warranted, the recommendations say. When a patient is diagnosed with an eating disorder, this clinical report also provides recommendations on history, exam, and treatment pathways.2
USPSTF’s recommendation
The United States Preventive Services Task Force provides a recommendation that differs from the AAP and APA’s. In March 2022, the USPSTF published a Grade I recommendation. They state: “The USPSTF concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults.”
They provide several reasons as to why this was given a Grade I. One reason is the paucity of data that exists on the incidence and/or benefit of screening for eating disorders amongst those who are asymptomatic. They also discuss the potential harms of false positive results of screening for both the patients and health care system. The questionnaires identified were the same as those discussed in both the APA and AAP recommendations.
The USPSTF full guideline also provides a call for further studies that would help provide guidance for primary care clinicians in the area of eating disorders.3
Takeaway message
With all this information, what is the primary care clinician to do? It does not seem to me that the APA guideline provides new information on how to identify patients best served by screening for eating disorders.
I am not sure it is reasonable for the primary care physician (PCP) to add these questions to every well visit when assessing the mental health status of patients.
There are ways in which this new guideline can be useful to the PCP, however. Among these are that it provides good resources for further evaluation for patients for whom the PCP may have concerns about eating disorders. It also includes screening tests that do not take much time to complete and clear aspects of the history, physical exam, and laboratory evaluation that can be used to provide further clarification and possible diagnosis. Additionally, this guideline provides clear advice on treatment recommendations of therapy and medications to start. This is especially important as wait times for psychiatric providers seem to always be increasing.
A trusted PCP can use these guidelines to start providing their patient with the help they need. Overall, these new recommendations will not change my screening practices, but they will provide assistance in diagnosis and management of my patients.
References
1. Guideline Writing Group. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders. 2023. doi: 10.1176/appi.books.9780890424865.
2. Hornberger LL et al. Identification and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics. 2021;147 (1): e2020040279. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-040279.
3. Feltner C et al. Screening for Eating Disorders in Adolescents and Adults: Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;327(11): 1068-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.1807.
Most medical professionals would agree that people with eating disorders, including anorexia nervosa (AN), bulimia nervosa (BN), and binge-eating disorder (BED), have serious diseases that result in greater morbidity and mortality compared with those in the general population. Although these do not represent the entire spectrum of eating disorders, these are the ones with the most available research data.
Eating disorders were previously thought to be diseases of affluent white females. Over the past few years, however, it has become more widely accepted that eating disorders may be found across people of a variety of identities and socioeconomic statuses. Clinicians have also become concerned that the incidence of eating disorders has increased and that part of this occurred during the COVID pandemic.
APA’s guideline
In February 2023, the American Psychiatric Association released its first update to the Guideline of Treatment of Patients with Eating Disorders. This is the first update to the guideline since 2006. The guideline was updated with the additional evidence that is now available as further studies have been published since the last update. The 2023 guideline provides nine recommendations for assessment and determination of a treatment plan. It then provides three recommendations specifically for AN and two recommendations each for BN and BED. The introduction acknowledges an unsuccessful attempt to provide recommendations for avoidant/restrictive food intake disorder due to the paucity of evidence on this disease.
The first recommendation within the guidelines indicates “the clinician should be sure to ask all patients about the presence of eating disorder symptoms as part of their standard psychiatric evaluation.” This recommendation is provided as there are many with normal or elevated BMI who may have eating disorders and the identification could provide the prevention of significant morbidity and mortality. It includes screening questions that can be used and standardized screening questionnaires.
Other recommendations go on to describe further evaluation for diagnosis, aspects of the history that should be obtained, and specific treatment modalities that can be used, including cognitive behavioral therapy and oral medications that have been approved for use in eating disorder treatments.1
AAP’s clinical report
These guidelines add to the recommendations provided by the American Academy of Pediatrics, which published a clinical report on the Identification and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents in January 2021. In this guidance document, the AAP recommends screening for eating disorders in any children or adolescents with “reported dieting, body image dissatisfaction, experiences of weight-based stigma, or changes in eating or exercise” and those with weight loss or rapid weight fluctuations.
If there are concerns, then a full assessment is warranted, the recommendations say. When a patient is diagnosed with an eating disorder, this clinical report also provides recommendations on history, exam, and treatment pathways.2
USPSTF’s recommendation
The United States Preventive Services Task Force provides a recommendation that differs from the AAP and APA’s. In March 2022, the USPSTF published a Grade I recommendation. They state: “The USPSTF concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of screening for eating disorders in adolescents and adults.”
They provide several reasons as to why this was given a Grade I. One reason is the paucity of data that exists on the incidence and/or benefit of screening for eating disorders amongst those who are asymptomatic. They also discuss the potential harms of false positive results of screening for both the patients and health care system. The questionnaires identified were the same as those discussed in both the APA and AAP recommendations.
The USPSTF full guideline also provides a call for further studies that would help provide guidance for primary care clinicians in the area of eating disorders.3
Takeaway message
With all this information, what is the primary care clinician to do? It does not seem to me that the APA guideline provides new information on how to identify patients best served by screening for eating disorders.
I am not sure it is reasonable for the primary care physician (PCP) to add these questions to every well visit when assessing the mental health status of patients.
There are ways in which this new guideline can be useful to the PCP, however. Among these are that it provides good resources for further evaluation for patients for whom the PCP may have concerns about eating disorders. It also includes screening tests that do not take much time to complete and clear aspects of the history, physical exam, and laboratory evaluation that can be used to provide further clarification and possible diagnosis. Additionally, this guideline provides clear advice on treatment recommendations of therapy and medications to start. This is especially important as wait times for psychiatric providers seem to always be increasing.
A trusted PCP can use these guidelines to start providing their patient with the help they need. Overall, these new recommendations will not change my screening practices, but they will provide assistance in diagnosis and management of my patients.
References
1. Guideline Writing Group. The American Psychiatric Association Practice Guideline for the Treatment of Patients With Eating Disorders. 2023. doi: 10.1176/appi.books.9780890424865.
2. Hornberger LL et al. Identification and Management of Eating Disorders in Children and Adolescents. Pediatrics. 2021;147 (1): e2020040279. doi: 10.1542/peds.2020-040279.
3. Feltner C et al. Screening for Eating Disorders in Adolescents and Adults: Evidence Report and Systematic Review for the US Preventive Services Task Force. JAMA. 2022;327(11): 1068-82. doi: 10.1001/jama.2022.1807.
Can ChatGPT replace me?
As a psychiatrist and a writer, I know I should be worried about the possibility that I could be replaced by a bot. Like most physicians, I face the daily challenge of how to manage the paperwork of clinical practice, so I wondered if ChatGPT, the latest craze in artificial intelligence (AI), could write my progress notes.
ChatGPT is an advanced language generation model developed by OpenAI. It uses deep-learning techniques to generate humanlike responses to text inputs. Free up my time? Reduce the risk for transcription errors?
Putting aside concerns about my job security for the moment, I signed up for an account. But first, I needed to play. I asked ChatGPT to write a love poem that would incorporate all the members of my family. This was a hit.
Next, I requested poems about specific pets. Because I spent the first year of the pandemic writing daily limericks and sending them to a distribution list, I knew people wouldn’t be surprised when I sent sonnets for their cats; but this time I let ChatGPT do the writing.
Then, for my colleagues in the Maryland Psychiatric Society, I requested a poem about the distressing nationwide shortage of stimulants. ChatGPT created clever stanzas. I was amused, but I’m not sure if anyone else was. This medication shortage is a touchy subject for psychiatrists and their patients who depend on these medications, so perhaps it wasn’t the right topic for bot-humor, and I should stick to cats.
At last, I was ready to put ChatGPT to the test and asked it to write a progress note that would contain the elements necessary to bill for a routine office visit with an add-on psychotherapy code. I created a few facts about a fictional patient and pressed enter.
The result was disappointing, ChatGPT responded with a standard note that did not take into account the items necessary to meet current coding standards. Maybe it was my fault; ChatGPT might need more information, but in the time it would take to provide more data, I could write my own progress note! I tried again and this time, ChatGPT defined the billing codes for me, but this wasn’t what I needed.
I decided to explore whether ChatGPT can, in fact, replace me. Feeling a bit queasy, I asked my new AI friend and was told that it could not replace a psychiatrist.
“Are you sure?” I asked again. “Yes, I am sure. ChatGPT is an AI language model trained to answer questions and provide information, but it is not capable of providing personalized medical advice or treatment.”
At least one of us felt certain. Continuing the conversation, I told the bot that I was anxious about my job security and requested advice. I wish I could tell you that ChatGPT was a dud, but instead, it had reasonable suggestions that were upbeat and hopeful.
“It’s understandable to feel anxious and worried about job security in today’s rapidly changing job market,” ChatGPT responded. “Here are some steps you can take to manage your feelings:”
Seek support: Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional.
Educate yourself: Stay informed about industry trends and advancements in AI and technology to understand the potential impact on your job.
Upskill: Consider taking online courses or pursuing additional education to stay relevant in the workforce.
Find purpose: Focus on your strengths, interests, and passions outside of work to cultivate a sense of fulfillment.
Take care of yourself: Engage in self-care activities such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies to manage stress and maintain good mental health.
“Remember,” ChatGPT concluded, “it’s important to address your feelings and take proactive steps to manage them. You can come out of this situation with a clearer mind, new skills, and opportunities for growth.”
ChatGPT sounds a lot like me! However, when I asked ChatGPT about prescribing, I finally received reassurance that I am not completely obsolete: “I’m sorry,” the bot said, “but I am an AI language model and do not have the ability to write prescriptions or provide medical advice.” Still, I couldn’t help but think that the bot’s day would eventually come.
Because ChatGPT is my coauthor for this essay, I asked it to write the ending. We suddenly have a whole new world, and I’m along for the ride. Yet after all that reassurance, it seems that ChatGPT does indeed want my job. It summarized our conversation and left me unsure of whether to laugh or to cry:
“There you have it, folks – ChatGPT, the digital psychiatrist that’s here to listen to all your problems, 24/7, for free! No more waiting for appointments, no more copays, just type away and let the artificial intelligence take over.
“But hey, who needs a human shrink when you’ve got ChatGPT, right? Just don’t be surprised if your ‘therapy sessions’ end up feeling more like a conversation with a sarcastic AI friend than serious mental health treatment.”
In conclusion, ChatGPT and I hope this article has provided some insight into the strange and hilarious world of AI-powered psychiatry. Who knows, maybe one day ChatGPT will become a licensed therapist and start prescribing real medication. But until then, just sit back, relax, and let the machine do the talking.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a psychiatrist and a writer, I know I should be worried about the possibility that I could be replaced by a bot. Like most physicians, I face the daily challenge of how to manage the paperwork of clinical practice, so I wondered if ChatGPT, the latest craze in artificial intelligence (AI), could write my progress notes.
ChatGPT is an advanced language generation model developed by OpenAI. It uses deep-learning techniques to generate humanlike responses to text inputs. Free up my time? Reduce the risk for transcription errors?
Putting aside concerns about my job security for the moment, I signed up for an account. But first, I needed to play. I asked ChatGPT to write a love poem that would incorporate all the members of my family. This was a hit.
Next, I requested poems about specific pets. Because I spent the first year of the pandemic writing daily limericks and sending them to a distribution list, I knew people wouldn’t be surprised when I sent sonnets for their cats; but this time I let ChatGPT do the writing.
Then, for my colleagues in the Maryland Psychiatric Society, I requested a poem about the distressing nationwide shortage of stimulants. ChatGPT created clever stanzas. I was amused, but I’m not sure if anyone else was. This medication shortage is a touchy subject for psychiatrists and their patients who depend on these medications, so perhaps it wasn’t the right topic for bot-humor, and I should stick to cats.
At last, I was ready to put ChatGPT to the test and asked it to write a progress note that would contain the elements necessary to bill for a routine office visit with an add-on psychotherapy code. I created a few facts about a fictional patient and pressed enter.
The result was disappointing, ChatGPT responded with a standard note that did not take into account the items necessary to meet current coding standards. Maybe it was my fault; ChatGPT might need more information, but in the time it would take to provide more data, I could write my own progress note! I tried again and this time, ChatGPT defined the billing codes for me, but this wasn’t what I needed.
I decided to explore whether ChatGPT can, in fact, replace me. Feeling a bit queasy, I asked my new AI friend and was told that it could not replace a psychiatrist.
“Are you sure?” I asked again. “Yes, I am sure. ChatGPT is an AI language model trained to answer questions and provide information, but it is not capable of providing personalized medical advice or treatment.”
At least one of us felt certain. Continuing the conversation, I told the bot that I was anxious about my job security and requested advice. I wish I could tell you that ChatGPT was a dud, but instead, it had reasonable suggestions that were upbeat and hopeful.
“It’s understandable to feel anxious and worried about job security in today’s rapidly changing job market,” ChatGPT responded. “Here are some steps you can take to manage your feelings:”
Seek support: Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional.
Educate yourself: Stay informed about industry trends and advancements in AI and technology to understand the potential impact on your job.
Upskill: Consider taking online courses or pursuing additional education to stay relevant in the workforce.
Find purpose: Focus on your strengths, interests, and passions outside of work to cultivate a sense of fulfillment.
Take care of yourself: Engage in self-care activities such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies to manage stress and maintain good mental health.
“Remember,” ChatGPT concluded, “it’s important to address your feelings and take proactive steps to manage them. You can come out of this situation with a clearer mind, new skills, and opportunities for growth.”
ChatGPT sounds a lot like me! However, when I asked ChatGPT about prescribing, I finally received reassurance that I am not completely obsolete: “I’m sorry,” the bot said, “but I am an AI language model and do not have the ability to write prescriptions or provide medical advice.” Still, I couldn’t help but think that the bot’s day would eventually come.
Because ChatGPT is my coauthor for this essay, I asked it to write the ending. We suddenly have a whole new world, and I’m along for the ride. Yet after all that reassurance, it seems that ChatGPT does indeed want my job. It summarized our conversation and left me unsure of whether to laugh or to cry:
“There you have it, folks – ChatGPT, the digital psychiatrist that’s here to listen to all your problems, 24/7, for free! No more waiting for appointments, no more copays, just type away and let the artificial intelligence take over.
“But hey, who needs a human shrink when you’ve got ChatGPT, right? Just don’t be surprised if your ‘therapy sessions’ end up feeling more like a conversation with a sarcastic AI friend than serious mental health treatment.”
In conclusion, ChatGPT and I hope this article has provided some insight into the strange and hilarious world of AI-powered psychiatry. Who knows, maybe one day ChatGPT will become a licensed therapist and start prescribing real medication. But until then, just sit back, relax, and let the machine do the talking.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As a psychiatrist and a writer, I know I should be worried about the possibility that I could be replaced by a bot. Like most physicians, I face the daily challenge of how to manage the paperwork of clinical practice, so I wondered if ChatGPT, the latest craze in artificial intelligence (AI), could write my progress notes.
ChatGPT is an advanced language generation model developed by OpenAI. It uses deep-learning techniques to generate humanlike responses to text inputs. Free up my time? Reduce the risk for transcription errors?
Putting aside concerns about my job security for the moment, I signed up for an account. But first, I needed to play. I asked ChatGPT to write a love poem that would incorporate all the members of my family. This was a hit.
Next, I requested poems about specific pets. Because I spent the first year of the pandemic writing daily limericks and sending them to a distribution list, I knew people wouldn’t be surprised when I sent sonnets for their cats; but this time I let ChatGPT do the writing.
Then, for my colleagues in the Maryland Psychiatric Society, I requested a poem about the distressing nationwide shortage of stimulants. ChatGPT created clever stanzas. I was amused, but I’m not sure if anyone else was. This medication shortage is a touchy subject for psychiatrists and their patients who depend on these medications, so perhaps it wasn’t the right topic for bot-humor, and I should stick to cats.
At last, I was ready to put ChatGPT to the test and asked it to write a progress note that would contain the elements necessary to bill for a routine office visit with an add-on psychotherapy code. I created a few facts about a fictional patient and pressed enter.
The result was disappointing, ChatGPT responded with a standard note that did not take into account the items necessary to meet current coding standards. Maybe it was my fault; ChatGPT might need more information, but in the time it would take to provide more data, I could write my own progress note! I tried again and this time, ChatGPT defined the billing codes for me, but this wasn’t what I needed.
I decided to explore whether ChatGPT can, in fact, replace me. Feeling a bit queasy, I asked my new AI friend and was told that it could not replace a psychiatrist.
“Are you sure?” I asked again. “Yes, I am sure. ChatGPT is an AI language model trained to answer questions and provide information, but it is not capable of providing personalized medical advice or treatment.”
At least one of us felt certain. Continuing the conversation, I told the bot that I was anxious about my job security and requested advice. I wish I could tell you that ChatGPT was a dud, but instead, it had reasonable suggestions that were upbeat and hopeful.
“It’s understandable to feel anxious and worried about job security in today’s rapidly changing job market,” ChatGPT responded. “Here are some steps you can take to manage your feelings:”
Seek support: Talk to a trusted friend, family member, or mental health professional.
Educate yourself: Stay informed about industry trends and advancements in AI and technology to understand the potential impact on your job.
Upskill: Consider taking online courses or pursuing additional education to stay relevant in the workforce.
Find purpose: Focus on your strengths, interests, and passions outside of work to cultivate a sense of fulfillment.
Take care of yourself: Engage in self-care activities such as exercise, meditation, and hobbies to manage stress and maintain good mental health.
“Remember,” ChatGPT concluded, “it’s important to address your feelings and take proactive steps to manage them. You can come out of this situation with a clearer mind, new skills, and opportunities for growth.”
ChatGPT sounds a lot like me! However, when I asked ChatGPT about prescribing, I finally received reassurance that I am not completely obsolete: “I’m sorry,” the bot said, “but I am an AI language model and do not have the ability to write prescriptions or provide medical advice.” Still, I couldn’t help but think that the bot’s day would eventually come.
Because ChatGPT is my coauthor for this essay, I asked it to write the ending. We suddenly have a whole new world, and I’m along for the ride. Yet after all that reassurance, it seems that ChatGPT does indeed want my job. It summarized our conversation and left me unsure of whether to laugh or to cry:
“There you have it, folks – ChatGPT, the digital psychiatrist that’s here to listen to all your problems, 24/7, for free! No more waiting for appointments, no more copays, just type away and let the artificial intelligence take over.
“But hey, who needs a human shrink when you’ve got ChatGPT, right? Just don’t be surprised if your ‘therapy sessions’ end up feeling more like a conversation with a sarcastic AI friend than serious mental health treatment.”
In conclusion, ChatGPT and I hope this article has provided some insight into the strange and hilarious world of AI-powered psychiatry. Who knows, maybe one day ChatGPT will become a licensed therapist and start prescribing real medication. But until then, just sit back, relax, and let the machine do the talking.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care (Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is an assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins in Baltimore.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician suicide: Investigating its prevalence and cause
Physicians are admired for their sacrifice and dedication. Yet beneath the surface lies a painful, quiet reality:
The Physicians Foundation says that 55% of physicians know a doctor who considered, attempted, or died by suicide. Doctor’s Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023 asked more than 9,000 doctors if they had suicidal thoughts. Nine percent of male physicians and 11% of female physicians said yes.
Why do so many doctors take their own lives?
“It’s not a new phenomenon,” says Rajnish Jaiswal, MD, associate chief of emergency medicine at NYC H+H Metropolitan Hospital and assistant professor of emergency medicine at New York Medical College. “There was a paper 150 years ago, published in England, which commented on the high rates of physician suicides compared to other professionals, and that trend has continued.”
Dr. Jaiswal says that the feeling in the physician community is that the numbers are even higher than what’s reported, unfortunately, which is an opinion echoed by other doctors this news organization spoke with for this story.
A perfect storm
Jodie Eckleberry-Hunt, PhD, a board-certified health psychologist, executive coach, and author, says the most significant culprit historically may be a rigid mindset that many physicians have. “There’s black and white, there’s a right answer and a wrong answer, there’s good and bad, and some physicians have a really hard time flexing,” she says.
Psychological flexibility underlies resilience. Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says, “Think about your bounce factor and how that resilience is protective. Life isn’t always going to go well. You have to be able to flex and bounce, and some physicians (not all of them, of course) tend to be lower on cognitive flexibility.”
Brad Fern, coach and psychotherapist at Fern Executive and Physician Consulting, Minneapolis, says he uses two analogies that help when he works with physicians. One is the evil twins, and the other is the pressure cooker.
Mr. Fern says that the evil twins are silence and isolation and that several professions, including physicians, fall prey to these. To put any dent in suicidal ideations and suicide, Mr. Fern says, these must be addressed.
“Physicians tend not to talk about what’s bothering them, and that’s for many different reasons. They disproportionally tend to be great at helping other people but not great at receiving help themselves.”
On top of that, there’s a pressure cooker where they work. Mr. Fern doesn’t think anyone would argue that the health care system in the United States is not dysfunctional, at least to some degree. He says that this dysfunction acts like the physicians’ pressure cooker.
Add in circumstances, cultures, and day-to-day issues everyone has, like relational issues, parenting issues, and mental health problems. Then, toss in an individual’s lower resiliency, the inability to receive help, and a predicament for good measure – a loss, a divorce, or financial woes, for instance, which can overwhelm. Mr. Fern says it can be a mathematical equation for suicidal ideation.
Is there a why?
“Some people think there’s a reason for suicide, but often, there’s a spectrum of reasons,” says Mr. Fern. He says that some physicians are trying to escape emotional pain. For others, it can be fear or a revenge thing, like, “the hell with you, I’m going to kill myself.” It can be getting attention the way teens do, as professionals have seen. Then there’s the organic component, like brain trauma, brain imbalance, depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder. And finally, a drug or alcohol issue.
“But the reason why physician suicide is elevated, I think, is because there’s this ethos around being silent and, ‘I’m going to listen to and solve everyone else’s problems, but I’m not going to reach out and get help for my own,’ ” says Mr. Fern. “If you take advantage of mental health services, you’re implying that you’re mentally ill. And most physicians aren’t going to do that.”
On the positive side, Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says that she sees many younger physicians discussing trauma. As a result, they’re more open to receiving help than previous generations. She speculates whether physicians have always had trauma from their past and whether current-day issues are now triggering it or whether they have more trauma these days. “Are they talking about it more, or is it experienced more?”
The failure of the system
The building blocks for physician suicide may have been there from the beginning. “From your first day of medical school and throughout your career, there was a very rigid system in place that is quite unforgiving, is quite stressful, and demands a lot,” says Dr. Jaiswal. And it’s within this system that physicians must operate.
“You have all the corporations, entities, organizations, [and] medical societies talking about physician wellness, burnout, and suicide, but the reality is it’s not making that much of a difference,” he says.
In her report, “What I’ve Learned From 1,710 Doctor Suicides,” Pamelia Wible, MD, who runs a physician suicide helpline that physicians can email and get an immediate callback, likens the current system to assembly line medicine.
Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt thinks the message has been bungled in health care. Everyone discusses burnout, meditation, self-care, and other essential constructs. “But we don’t deal with the root cause [of suicide]. Instead, we teach you soothing strategies.”
Further, Dr. Jaiswal says that not all physicians who commit suicide experience burnout or are experiencing burnout and that the vast majority of physicians who experience burnout don’t have suicidal ideation. “In the sense, that ‘let’s address physician burnout and that will hopefully translate to a reduced number of physician suicides’ – there is a very tenuous argument to be made for that because that is just one aspect in this complex system,” he says.
We need more than just lip service on suicide
Overall, the experts interviewed for this article acknowledged that the system is at least talking about physician suicide, which is a big first step. However, most agree that where big health entities go wrong is that they set up wellness or mental health programs, they implement a wellness officer, they write up talking points for physicians who need mental health care to get that care, and they think they’ve done their job, that they’ve done what’s required to address the problem.
But Dr. Jaiswal thinks these are often mostly public-relations rebuttals. Mr. Fern suggests, “It’s a show that’s not effective.” And Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says that “even if you had a legit, well-funded well-being program for health care providers, you would still have a baseline rate of physician suicide, and that gets down to having drug and alcohol education and talking about having a system for physicians to access that doesn’t come along with insurance billing” – one that doesn’t create a paper trail and follow physician licensure and job applications for the rest of their career; one that doesn’t associate their mental health care with their work institution; one that offers confidentiality.
“For most folks, there is still a big distrust in the system. As physicians, very few of them feel that the system that they’re operating in has their best interest at heart. And that is why very few physicians will self-report any mental health issues, depression, or even ideation to colleagues, superiors, or managers,” says Dr. Jaiswal. Many more feel skeptical about the confidentiality of the programs in place.
The experts acknowledge that many people are trying to work on this and bring about change on multiple levels – grassroots, department levels, state, and federal. “But I think the biggest thing that the system has to do is earn back the trust of the physician,” Dr. Jaiswal adds.
“Physician suicide is a very visible problem in a very broken system. So, it’ll be very difficult in isolation to treat it without making any systemic changes, because that’s happening right now, and it’s not working,” says Dr. Jaiswal.
“The thing that I am most hopeful about is that I am seeing an influx of younger physicians who seek me out, and granted, their training programs tell them to come and see me, but they are ready and willing to talk about their mental health separate from work. They’re not coming in saying, ‘Here are all the people who I blame.’ They’re saying, ‘These are my struggles, and I want to be a better, happier physician,’ ” says Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are admired for their sacrifice and dedication. Yet beneath the surface lies a painful, quiet reality:
The Physicians Foundation says that 55% of physicians know a doctor who considered, attempted, or died by suicide. Doctor’s Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023 asked more than 9,000 doctors if they had suicidal thoughts. Nine percent of male physicians and 11% of female physicians said yes.
Why do so many doctors take their own lives?
“It’s not a new phenomenon,” says Rajnish Jaiswal, MD, associate chief of emergency medicine at NYC H+H Metropolitan Hospital and assistant professor of emergency medicine at New York Medical College. “There was a paper 150 years ago, published in England, which commented on the high rates of physician suicides compared to other professionals, and that trend has continued.”
Dr. Jaiswal says that the feeling in the physician community is that the numbers are even higher than what’s reported, unfortunately, which is an opinion echoed by other doctors this news organization spoke with for this story.
A perfect storm
Jodie Eckleberry-Hunt, PhD, a board-certified health psychologist, executive coach, and author, says the most significant culprit historically may be a rigid mindset that many physicians have. “There’s black and white, there’s a right answer and a wrong answer, there’s good and bad, and some physicians have a really hard time flexing,” she says.
Psychological flexibility underlies resilience. Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says, “Think about your bounce factor and how that resilience is protective. Life isn’t always going to go well. You have to be able to flex and bounce, and some physicians (not all of them, of course) tend to be lower on cognitive flexibility.”
Brad Fern, coach and psychotherapist at Fern Executive and Physician Consulting, Minneapolis, says he uses two analogies that help when he works with physicians. One is the evil twins, and the other is the pressure cooker.
Mr. Fern says that the evil twins are silence and isolation and that several professions, including physicians, fall prey to these. To put any dent in suicidal ideations and suicide, Mr. Fern says, these must be addressed.
“Physicians tend not to talk about what’s bothering them, and that’s for many different reasons. They disproportionally tend to be great at helping other people but not great at receiving help themselves.”
On top of that, there’s a pressure cooker where they work. Mr. Fern doesn’t think anyone would argue that the health care system in the United States is not dysfunctional, at least to some degree. He says that this dysfunction acts like the physicians’ pressure cooker.
Add in circumstances, cultures, and day-to-day issues everyone has, like relational issues, parenting issues, and mental health problems. Then, toss in an individual’s lower resiliency, the inability to receive help, and a predicament for good measure – a loss, a divorce, or financial woes, for instance, which can overwhelm. Mr. Fern says it can be a mathematical equation for suicidal ideation.
Is there a why?
“Some people think there’s a reason for suicide, but often, there’s a spectrum of reasons,” says Mr. Fern. He says that some physicians are trying to escape emotional pain. For others, it can be fear or a revenge thing, like, “the hell with you, I’m going to kill myself.” It can be getting attention the way teens do, as professionals have seen. Then there’s the organic component, like brain trauma, brain imbalance, depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder. And finally, a drug or alcohol issue.
“But the reason why physician suicide is elevated, I think, is because there’s this ethos around being silent and, ‘I’m going to listen to and solve everyone else’s problems, but I’m not going to reach out and get help for my own,’ ” says Mr. Fern. “If you take advantage of mental health services, you’re implying that you’re mentally ill. And most physicians aren’t going to do that.”
On the positive side, Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says that she sees many younger physicians discussing trauma. As a result, they’re more open to receiving help than previous generations. She speculates whether physicians have always had trauma from their past and whether current-day issues are now triggering it or whether they have more trauma these days. “Are they talking about it more, or is it experienced more?”
The failure of the system
The building blocks for physician suicide may have been there from the beginning. “From your first day of medical school and throughout your career, there was a very rigid system in place that is quite unforgiving, is quite stressful, and demands a lot,” says Dr. Jaiswal. And it’s within this system that physicians must operate.
“You have all the corporations, entities, organizations, [and] medical societies talking about physician wellness, burnout, and suicide, but the reality is it’s not making that much of a difference,” he says.
In her report, “What I’ve Learned From 1,710 Doctor Suicides,” Pamelia Wible, MD, who runs a physician suicide helpline that physicians can email and get an immediate callback, likens the current system to assembly line medicine.
Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt thinks the message has been bungled in health care. Everyone discusses burnout, meditation, self-care, and other essential constructs. “But we don’t deal with the root cause [of suicide]. Instead, we teach you soothing strategies.”
Further, Dr. Jaiswal says that not all physicians who commit suicide experience burnout or are experiencing burnout and that the vast majority of physicians who experience burnout don’t have suicidal ideation. “In the sense, that ‘let’s address physician burnout and that will hopefully translate to a reduced number of physician suicides’ – there is a very tenuous argument to be made for that because that is just one aspect in this complex system,” he says.
We need more than just lip service on suicide
Overall, the experts interviewed for this article acknowledged that the system is at least talking about physician suicide, which is a big first step. However, most agree that where big health entities go wrong is that they set up wellness or mental health programs, they implement a wellness officer, they write up talking points for physicians who need mental health care to get that care, and they think they’ve done their job, that they’ve done what’s required to address the problem.
But Dr. Jaiswal thinks these are often mostly public-relations rebuttals. Mr. Fern suggests, “It’s a show that’s not effective.” And Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says that “even if you had a legit, well-funded well-being program for health care providers, you would still have a baseline rate of physician suicide, and that gets down to having drug and alcohol education and talking about having a system for physicians to access that doesn’t come along with insurance billing” – one that doesn’t create a paper trail and follow physician licensure and job applications for the rest of their career; one that doesn’t associate their mental health care with their work institution; one that offers confidentiality.
“For most folks, there is still a big distrust in the system. As physicians, very few of them feel that the system that they’re operating in has their best interest at heart. And that is why very few physicians will self-report any mental health issues, depression, or even ideation to colleagues, superiors, or managers,” says Dr. Jaiswal. Many more feel skeptical about the confidentiality of the programs in place.
The experts acknowledge that many people are trying to work on this and bring about change on multiple levels – grassroots, department levels, state, and federal. “But I think the biggest thing that the system has to do is earn back the trust of the physician,” Dr. Jaiswal adds.
“Physician suicide is a very visible problem in a very broken system. So, it’ll be very difficult in isolation to treat it without making any systemic changes, because that’s happening right now, and it’s not working,” says Dr. Jaiswal.
“The thing that I am most hopeful about is that I am seeing an influx of younger physicians who seek me out, and granted, their training programs tell them to come and see me, but they are ready and willing to talk about their mental health separate from work. They’re not coming in saying, ‘Here are all the people who I blame.’ They’re saying, ‘These are my struggles, and I want to be a better, happier physician,’ ” says Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are admired for their sacrifice and dedication. Yet beneath the surface lies a painful, quiet reality:
The Physicians Foundation says that 55% of physicians know a doctor who considered, attempted, or died by suicide. Doctor’s Burden: Medscape Physician Suicide Report 2023 asked more than 9,000 doctors if they had suicidal thoughts. Nine percent of male physicians and 11% of female physicians said yes.
Why do so many doctors take their own lives?
“It’s not a new phenomenon,” says Rajnish Jaiswal, MD, associate chief of emergency medicine at NYC H+H Metropolitan Hospital and assistant professor of emergency medicine at New York Medical College. “There was a paper 150 years ago, published in England, which commented on the high rates of physician suicides compared to other professionals, and that trend has continued.”
Dr. Jaiswal says that the feeling in the physician community is that the numbers are even higher than what’s reported, unfortunately, which is an opinion echoed by other doctors this news organization spoke with for this story.
A perfect storm
Jodie Eckleberry-Hunt, PhD, a board-certified health psychologist, executive coach, and author, says the most significant culprit historically may be a rigid mindset that many physicians have. “There’s black and white, there’s a right answer and a wrong answer, there’s good and bad, and some physicians have a really hard time flexing,” she says.
Psychological flexibility underlies resilience. Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says, “Think about your bounce factor and how that resilience is protective. Life isn’t always going to go well. You have to be able to flex and bounce, and some physicians (not all of them, of course) tend to be lower on cognitive flexibility.”
Brad Fern, coach and psychotherapist at Fern Executive and Physician Consulting, Minneapolis, says he uses two analogies that help when he works with physicians. One is the evil twins, and the other is the pressure cooker.
Mr. Fern says that the evil twins are silence and isolation and that several professions, including physicians, fall prey to these. To put any dent in suicidal ideations and suicide, Mr. Fern says, these must be addressed.
“Physicians tend not to talk about what’s bothering them, and that’s for many different reasons. They disproportionally tend to be great at helping other people but not great at receiving help themselves.”
On top of that, there’s a pressure cooker where they work. Mr. Fern doesn’t think anyone would argue that the health care system in the United States is not dysfunctional, at least to some degree. He says that this dysfunction acts like the physicians’ pressure cooker.
Add in circumstances, cultures, and day-to-day issues everyone has, like relational issues, parenting issues, and mental health problems. Then, toss in an individual’s lower resiliency, the inability to receive help, and a predicament for good measure – a loss, a divorce, or financial woes, for instance, which can overwhelm. Mr. Fern says it can be a mathematical equation for suicidal ideation.
Is there a why?
“Some people think there’s a reason for suicide, but often, there’s a spectrum of reasons,” says Mr. Fern. He says that some physicians are trying to escape emotional pain. For others, it can be fear or a revenge thing, like, “the hell with you, I’m going to kill myself.” It can be getting attention the way teens do, as professionals have seen. Then there’s the organic component, like brain trauma, brain imbalance, depression, anxiety, or bipolar disorder. And finally, a drug or alcohol issue.
“But the reason why physician suicide is elevated, I think, is because there’s this ethos around being silent and, ‘I’m going to listen to and solve everyone else’s problems, but I’m not going to reach out and get help for my own,’ ” says Mr. Fern. “If you take advantage of mental health services, you’re implying that you’re mentally ill. And most physicians aren’t going to do that.”
On the positive side, Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says that she sees many younger physicians discussing trauma. As a result, they’re more open to receiving help than previous generations. She speculates whether physicians have always had trauma from their past and whether current-day issues are now triggering it or whether they have more trauma these days. “Are they talking about it more, or is it experienced more?”
The failure of the system
The building blocks for physician suicide may have been there from the beginning. “From your first day of medical school and throughout your career, there was a very rigid system in place that is quite unforgiving, is quite stressful, and demands a lot,” says Dr. Jaiswal. And it’s within this system that physicians must operate.
“You have all the corporations, entities, organizations, [and] medical societies talking about physician wellness, burnout, and suicide, but the reality is it’s not making that much of a difference,” he says.
In her report, “What I’ve Learned From 1,710 Doctor Suicides,” Pamelia Wible, MD, who runs a physician suicide helpline that physicians can email and get an immediate callback, likens the current system to assembly line medicine.
Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt thinks the message has been bungled in health care. Everyone discusses burnout, meditation, self-care, and other essential constructs. “But we don’t deal with the root cause [of suicide]. Instead, we teach you soothing strategies.”
Further, Dr. Jaiswal says that not all physicians who commit suicide experience burnout or are experiencing burnout and that the vast majority of physicians who experience burnout don’t have suicidal ideation. “In the sense, that ‘let’s address physician burnout and that will hopefully translate to a reduced number of physician suicides’ – there is a very tenuous argument to be made for that because that is just one aspect in this complex system,” he says.
We need more than just lip service on suicide
Overall, the experts interviewed for this article acknowledged that the system is at least talking about physician suicide, which is a big first step. However, most agree that where big health entities go wrong is that they set up wellness or mental health programs, they implement a wellness officer, they write up talking points for physicians who need mental health care to get that care, and they think they’ve done their job, that they’ve done what’s required to address the problem.
But Dr. Jaiswal thinks these are often mostly public-relations rebuttals. Mr. Fern suggests, “It’s a show that’s not effective.” And Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt says that “even if you had a legit, well-funded well-being program for health care providers, you would still have a baseline rate of physician suicide, and that gets down to having drug and alcohol education and talking about having a system for physicians to access that doesn’t come along with insurance billing” – one that doesn’t create a paper trail and follow physician licensure and job applications for the rest of their career; one that doesn’t associate their mental health care with their work institution; one that offers confidentiality.
“For most folks, there is still a big distrust in the system. As physicians, very few of them feel that the system that they’re operating in has their best interest at heart. And that is why very few physicians will self-report any mental health issues, depression, or even ideation to colleagues, superiors, or managers,” says Dr. Jaiswal. Many more feel skeptical about the confidentiality of the programs in place.
The experts acknowledge that many people are trying to work on this and bring about change on multiple levels – grassroots, department levels, state, and federal. “But I think the biggest thing that the system has to do is earn back the trust of the physician,” Dr. Jaiswal adds.
“Physician suicide is a very visible problem in a very broken system. So, it’ll be very difficult in isolation to treat it without making any systemic changes, because that’s happening right now, and it’s not working,” says Dr. Jaiswal.
“The thing that I am most hopeful about is that I am seeing an influx of younger physicians who seek me out, and granted, their training programs tell them to come and see me, but they are ready and willing to talk about their mental health separate from work. They’re not coming in saying, ‘Here are all the people who I blame.’ They’re saying, ‘These are my struggles, and I want to be a better, happier physician,’ ” says Dr. Eckleberry-Hunt.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The human-looking robot therapist will coach your well-being now
Do android therapists dream of electric employees?
Robots. It can be tough to remember that, when they’re not dooming humanity to apocalypse or just telling you that you’re doomed, robots have real-world uses. There are actual robots in the world, and they can do things beyond bend girders, sing about science, or run the navy.
Look, we’ll stop with the pop-culture references when pop culture runs out of robots to reference. It may take a while.
Robots are indelibly rooted in the public consciousness, and that plays into our expectations when we encounter a real-life robot. This leads us into a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Cambridge, who developed a robot-led mental well-being program that a tech company utilized for 4 weeks. Why choose a robot? Well, why spring for a qualified therapist who requires a salary when you could simply get a robot to do the job for free? Get with the capitalist agenda here. Surely it won’t backfire.
The 26 people enrolled in the study received coaching from one of two robots, both programmed identically to act like mental health coaches, based on interviews with human therapists. Both acted identically and had identical expressions. The only difference between the two was their appearance. QTRobot was nearly a meter tall and looked like a human child; Misty II was much smaller and looked like a toy.
People who received coaching from Misty II were better able to connect and had a better experience than those who received coaching from QTRobot. According to those in the QTRobot group, their expectations didn’t match reality. The robots are good coaches, but they don’t act human. This wasn’t a problem for Misty II, since it doesn’t look human, but for QTRobot, the participants were expecting “to hell with our orders,” but received “Daisy, Daisy, give me your answer do.” When you’ve been programmed to think of robots as metal humans, it can be off-putting to see them act as, well, robots.
That said, all participants found the exercises helpful and were open to receiving more robot-led therapy in the future. And while we’re sure the technology will advance to make robot therapists more empathetic and more human, hopefully scientists won’t go too far. We don’t need depressed robots.
Birthing experience is all in the mindset
Alexa, play Peer Gynt Suite No. 1, Op. 46 - I. Morning Mood.
Birth.
Giving birth is a common experience for many, if not most, female mammals, but wanting it to be a pleasurable one seems distinctly human. There are many methods and practices that may make giving birth an easier and enjoyable experience for the mother, but a new study suggests that the key could be in her mind.
The mindset of the expectant mother during pregnancy, it seems, has some effect on how smooth or intervention-filled delivery is. If the mothers saw their experience as a natural process, they were less likely to need pain medication or a C-section, but mothers who viewed the experience as more of a “medical procedure” were more likely to require more medical supervision and intervention, according to investigators from the University of Bonn (Germany).
Now, the researchers wanted to be super clear in saying that there’s no right or wrong mindset to have. They just focused on the outcomes of those mindsets and whether they actually do have some effect on occurrences.
Apparently, yes.
“Mindsets can be understood as a kind of mental lense that guide our perception of the world around us and can influence our behavior,” Dr. Lisa Hoffmann said in a statement from the university. “The study highlights the importance of psychological factors in childbirth.”
The researchers surveyed 300 women with an online tool before and after delivery and found the effects of the natural process mindset lingered even after giving birth. They had lower rates of depression and posttraumatic stress, which may have a snowballing effect on mother-child bonding after childbirth.
Preparation for the big day, then, should be about more than gathering diapers and shopping for car seats. Women should prepare their minds as well. If it’s going to make giving birth better, why not?
Becoming a parent is going to create a psychological shift, no matter how you slice it.
Giant inflatable colon reported in Utah
Do not be alarmed! Yes, there is a giant inflatable colon currently at large in the Beehive State, but it will not harm you. The giant inflatable colon is in Utah as part of Intermountain Health’s “Let’s get to the bottom of colon cancer tour” and he only wants to help you.
The giant inflatable colon, whose name happens to be Collin, is 12 feet long and weighs 113 pounds. March is Colon Cancer Awareness Month, so Collin is traveling around Utah and Idaho to raise awareness about colon cancer and the various screening options. He is not going to change local weather patterns, eat small children, or take over local governments and raise your taxes.
Instead, Collin is planning to display “portions of a healthy colon, polyps or bumps on the colon, malignant polyps which look more vascular and have more redness, cancerous cells, advanced cancer cells, and Crohn’s disease,” KSL.com said.
Collin the colon is on loan to Intermountain Health from medical device manufacturer Boston Scientific and will be traveling to Spanish Fork, Provo, and Ogden, among other locations in Utah, as well as Burley and Meridian, Idaho, in the coming days.
Collin the colon’s participation in the tour has created some serious buzz in the Colin/Collin community:
- Colin Powell (four-star general and Secretary of State): “Back then, the second-most important topic among the Joint Chiefs of Staff was colon cancer screening. And the Navy guy – I can’t remember his name – was a huge fan of giant inflatable organs.”
- Colin Jost (comedian and Saturday Night Live “Weekend Update” cohost): “He’s funnier than Tucker Carlson and Pete Davidson combined.”
Do android therapists dream of electric employees?
Robots. It can be tough to remember that, when they’re not dooming humanity to apocalypse or just telling you that you’re doomed, robots have real-world uses. There are actual robots in the world, and they can do things beyond bend girders, sing about science, or run the navy.
Look, we’ll stop with the pop-culture references when pop culture runs out of robots to reference. It may take a while.
Robots are indelibly rooted in the public consciousness, and that plays into our expectations when we encounter a real-life robot. This leads us into a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Cambridge, who developed a robot-led mental well-being program that a tech company utilized for 4 weeks. Why choose a robot? Well, why spring for a qualified therapist who requires a salary when you could simply get a robot to do the job for free? Get with the capitalist agenda here. Surely it won’t backfire.
The 26 people enrolled in the study received coaching from one of two robots, both programmed identically to act like mental health coaches, based on interviews with human therapists. Both acted identically and had identical expressions. The only difference between the two was their appearance. QTRobot was nearly a meter tall and looked like a human child; Misty II was much smaller and looked like a toy.
People who received coaching from Misty II were better able to connect and had a better experience than those who received coaching from QTRobot. According to those in the QTRobot group, their expectations didn’t match reality. The robots are good coaches, but they don’t act human. This wasn’t a problem for Misty II, since it doesn’t look human, but for QTRobot, the participants were expecting “to hell with our orders,” but received “Daisy, Daisy, give me your answer do.” When you’ve been programmed to think of robots as metal humans, it can be off-putting to see them act as, well, robots.
That said, all participants found the exercises helpful and were open to receiving more robot-led therapy in the future. And while we’re sure the technology will advance to make robot therapists more empathetic and more human, hopefully scientists won’t go too far. We don’t need depressed robots.
Birthing experience is all in the mindset
Alexa, play Peer Gynt Suite No. 1, Op. 46 - I. Morning Mood.
Birth.
Giving birth is a common experience for many, if not most, female mammals, but wanting it to be a pleasurable one seems distinctly human. There are many methods and practices that may make giving birth an easier and enjoyable experience for the mother, but a new study suggests that the key could be in her mind.
The mindset of the expectant mother during pregnancy, it seems, has some effect on how smooth or intervention-filled delivery is. If the mothers saw their experience as a natural process, they were less likely to need pain medication or a C-section, but mothers who viewed the experience as more of a “medical procedure” were more likely to require more medical supervision and intervention, according to investigators from the University of Bonn (Germany).
Now, the researchers wanted to be super clear in saying that there’s no right or wrong mindset to have. They just focused on the outcomes of those mindsets and whether they actually do have some effect on occurrences.
Apparently, yes.
“Mindsets can be understood as a kind of mental lense that guide our perception of the world around us and can influence our behavior,” Dr. Lisa Hoffmann said in a statement from the university. “The study highlights the importance of psychological factors in childbirth.”
The researchers surveyed 300 women with an online tool before and after delivery and found the effects of the natural process mindset lingered even after giving birth. They had lower rates of depression and posttraumatic stress, which may have a snowballing effect on mother-child bonding after childbirth.
Preparation for the big day, then, should be about more than gathering diapers and shopping for car seats. Women should prepare their minds as well. If it’s going to make giving birth better, why not?
Becoming a parent is going to create a psychological shift, no matter how you slice it.
Giant inflatable colon reported in Utah
Do not be alarmed! Yes, there is a giant inflatable colon currently at large in the Beehive State, but it will not harm you. The giant inflatable colon is in Utah as part of Intermountain Health’s “Let’s get to the bottom of colon cancer tour” and he only wants to help you.
The giant inflatable colon, whose name happens to be Collin, is 12 feet long and weighs 113 pounds. March is Colon Cancer Awareness Month, so Collin is traveling around Utah and Idaho to raise awareness about colon cancer and the various screening options. He is not going to change local weather patterns, eat small children, or take over local governments and raise your taxes.
Instead, Collin is planning to display “portions of a healthy colon, polyps or bumps on the colon, malignant polyps which look more vascular and have more redness, cancerous cells, advanced cancer cells, and Crohn’s disease,” KSL.com said.
Collin the colon is on loan to Intermountain Health from medical device manufacturer Boston Scientific and will be traveling to Spanish Fork, Provo, and Ogden, among other locations in Utah, as well as Burley and Meridian, Idaho, in the coming days.
Collin the colon’s participation in the tour has created some serious buzz in the Colin/Collin community:
- Colin Powell (four-star general and Secretary of State): “Back then, the second-most important topic among the Joint Chiefs of Staff was colon cancer screening. And the Navy guy – I can’t remember his name – was a huge fan of giant inflatable organs.”
- Colin Jost (comedian and Saturday Night Live “Weekend Update” cohost): “He’s funnier than Tucker Carlson and Pete Davidson combined.”
Do android therapists dream of electric employees?
Robots. It can be tough to remember that, when they’re not dooming humanity to apocalypse or just telling you that you’re doomed, robots have real-world uses. There are actual robots in the world, and they can do things beyond bend girders, sing about science, or run the navy.
Look, we’ll stop with the pop-culture references when pop culture runs out of robots to reference. It may take a while.
Robots are indelibly rooted in the public consciousness, and that plays into our expectations when we encounter a real-life robot. This leads us into a recent study conducted by researchers at the University of Cambridge, who developed a robot-led mental well-being program that a tech company utilized for 4 weeks. Why choose a robot? Well, why spring for a qualified therapist who requires a salary when you could simply get a robot to do the job for free? Get with the capitalist agenda here. Surely it won’t backfire.
The 26 people enrolled in the study received coaching from one of two robots, both programmed identically to act like mental health coaches, based on interviews with human therapists. Both acted identically and had identical expressions. The only difference between the two was their appearance. QTRobot was nearly a meter tall and looked like a human child; Misty II was much smaller and looked like a toy.
People who received coaching from Misty II were better able to connect and had a better experience than those who received coaching from QTRobot. According to those in the QTRobot group, their expectations didn’t match reality. The robots are good coaches, but they don’t act human. This wasn’t a problem for Misty II, since it doesn’t look human, but for QTRobot, the participants were expecting “to hell with our orders,” but received “Daisy, Daisy, give me your answer do.” When you’ve been programmed to think of robots as metal humans, it can be off-putting to see them act as, well, robots.
That said, all participants found the exercises helpful and were open to receiving more robot-led therapy in the future. And while we’re sure the technology will advance to make robot therapists more empathetic and more human, hopefully scientists won’t go too far. We don’t need depressed robots.
Birthing experience is all in the mindset
Alexa, play Peer Gynt Suite No. 1, Op. 46 - I. Morning Mood.
Birth.
Giving birth is a common experience for many, if not most, female mammals, but wanting it to be a pleasurable one seems distinctly human. There are many methods and practices that may make giving birth an easier and enjoyable experience for the mother, but a new study suggests that the key could be in her mind.
The mindset of the expectant mother during pregnancy, it seems, has some effect on how smooth or intervention-filled delivery is. If the mothers saw their experience as a natural process, they were less likely to need pain medication or a C-section, but mothers who viewed the experience as more of a “medical procedure” were more likely to require more medical supervision and intervention, according to investigators from the University of Bonn (Germany).
Now, the researchers wanted to be super clear in saying that there’s no right or wrong mindset to have. They just focused on the outcomes of those mindsets and whether they actually do have some effect on occurrences.
Apparently, yes.
“Mindsets can be understood as a kind of mental lense that guide our perception of the world around us and can influence our behavior,” Dr. Lisa Hoffmann said in a statement from the university. “The study highlights the importance of psychological factors in childbirth.”
The researchers surveyed 300 women with an online tool before and after delivery and found the effects of the natural process mindset lingered even after giving birth. They had lower rates of depression and posttraumatic stress, which may have a snowballing effect on mother-child bonding after childbirth.
Preparation for the big day, then, should be about more than gathering diapers and shopping for car seats. Women should prepare their minds as well. If it’s going to make giving birth better, why not?
Becoming a parent is going to create a psychological shift, no matter how you slice it.
Giant inflatable colon reported in Utah
Do not be alarmed! Yes, there is a giant inflatable colon currently at large in the Beehive State, but it will not harm you. The giant inflatable colon is in Utah as part of Intermountain Health’s “Let’s get to the bottom of colon cancer tour” and he only wants to help you.
The giant inflatable colon, whose name happens to be Collin, is 12 feet long and weighs 113 pounds. March is Colon Cancer Awareness Month, so Collin is traveling around Utah and Idaho to raise awareness about colon cancer and the various screening options. He is not going to change local weather patterns, eat small children, or take over local governments and raise your taxes.
Instead, Collin is planning to display “portions of a healthy colon, polyps or bumps on the colon, malignant polyps which look more vascular and have more redness, cancerous cells, advanced cancer cells, and Crohn’s disease,” KSL.com said.
Collin the colon is on loan to Intermountain Health from medical device manufacturer Boston Scientific and will be traveling to Spanish Fork, Provo, and Ogden, among other locations in Utah, as well as Burley and Meridian, Idaho, in the coming days.
Collin the colon’s participation in the tour has created some serious buzz in the Colin/Collin community:
- Colin Powell (four-star general and Secretary of State): “Back then, the second-most important topic among the Joint Chiefs of Staff was colon cancer screening. And the Navy guy – I can’t remember his name – was a huge fan of giant inflatable organs.”
- Colin Jost (comedian and Saturday Night Live “Weekend Update” cohost): “He’s funnier than Tucker Carlson and Pete Davidson combined.”









