User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
How could this happen? Judge forces doctors to give ivermectin
The judge’s order was a major affront to many clinical ethicists. A county judge in Ohio ordered a hospital to give ivermectin to a COVID-19 patient on a ventilator. This order occurred against the advice and judgment of the local physicians. It occurred in spite of the hospital’s lawyers fighting the order. How could such a situation occur?
This column is not the appropriate forum to debate the use of ivermectin. The Food and Drug Administration has not approved the drug for treating COVID-19. Indeed, the FDA has specifically recommended against its use.1 So has the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.2 Poison control centers report a large uptick in exposures this summer because of self-medication, sometimes from veterinary sources.3
Fortunately for this case, the judge who overruled the order, Judge Michael A. Oster, wrote in his decision a summary of facts presented by both sides. The topic here is how a judge could order a medical institution and its staff to provide care against medical judgment. A key tenet of clinical ethics consultation is that the consultant needs to do their own investigation. Most veteran consultants have a litany of anecdotes wherein the initial story changed markedly as new facts were uncovered. The more outrageous the initial story, the more likely a major distortion is found. Therefore, most clinical ethics consultants are reluctant to discuss case studies based solely on publicly available information. Often, it is nearly impossible to obtain further information. One side of the story may be gagged by privacy laws. However, cases must sometimes be discussed based on the limited information available because, without that discussion, egregious violations of medical ethics would not be brought to light.
Fortunately for this case, Judge Osler’s decision contains a summary of facts presented by both sides. In August 2021, a 51-year-old patient with severe COVID-19 is in an Ohio intensive care unit on a ventilator. His wife seeks and obtains a prescription for ivermectin from a physician who has an Ohio state medical license but lives elsewhere, has no clinical privileges at the involved hospital, and has never examined the patient. The wife, as a surrogate decision maker, demands her husband receive the medication. The medical staff involved do not consider it a valid treatment. The wife seeks an injunction. A county judge orders the hospital to administer a specified dose of ivermectin daily for 21 days.4 That judge further grants an emergency preliminary injunction for 14 days that orders administration of the medication while legal appeals are made. Two weeks later, a second county judge hearing the case rules that the wife has not presented convincing evidence that she is likely to ultimately win the case on the merits.5 Therefore, the second judge reverses the preliminary injunction. The hospital need not continue to give the medication while further legal proceedings take place.
Cases like this are uncommon. Judges generally defer the authority for medical decisions to physicians. Various attitudes combine to make such an event happen. The judge may view the hospital as a local monopoly of health care and the patient may be too unstable to transport elsewhere. A judge in that situation, combined with a “the consumer is always right” mentality, and a sympathetic plaintiff, may seek to make miracles happen.
Judges overriding science are more likely to manifest when they see the science as ambiguous. Scientists have lost some of the gravitas they had when men walked on the moon. The spectacular success of the mRNA vaccines has surprisingly not reversed that loss. Science has been tainted by mercenary scientists, biased researchers seeking publications, and the large volume of published medical research that is false.
But there is more going on here. In the United States there has been a significant rebellion against any form of expertise and any form of authority. The echo chambers of misinformation on social media have led to polarization, conspiracy theories, and loyalty to political tribe rather than truth; hence the battle over masks and vaccines. This breakdown in authority is accompanied by losses in virtues such as civic duty and loving one’s neighbor. This is a failure of modern moral institutions. When major medical journals print opinion pieces portraying physicians as interchangeable automatons,6 it should not be surprising to see judges tempted by similar imagery.
One part of the solution is accountability in peer review. With 30,000 county judges scattered in 50 states, there will always be a few rogue and maverick attitudes among judges. The judiciary has a means of reassigning rebels to less impactful tasks. Similarly, if the physician who counseled the wife to use ivermectin had privileges at the admitting hospital, then peer review and credential committees could discipline behaviors that were too far outside accepted norms. Even when a consensus on best practice is hard to establish, damage can be mitigated by creating consequences for promoting aberrant care.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. “Why you should not use ivermectin to treat or prevent COVID-19,” FDA Consumer Updates, Sept. 3, 2021.
2. “Rapid increase in ivermectin prescriptions and reports of severe illness associated with use of products containing ivermectin to prevent or treat COVID-19,” CDC Health Advisory, Aug. 26, 2021.
3. National Poison Data System Bulletin: COVID-19 (Ivermectin), American Association of Poison Control Centers, 2021.
4. Smith v West Chester Hosptial, LLC, DBA West Chester Hospital, Butler County Clerk of Courts, Aug. 23, 2021.
5. Smith v West Chester Hosptial, LLC, Decision denying plaintiff’s action for a preliminary injunction, Butler County Clerk of Courts, Sept. 6, 2021.
6. “Conscientious objection in medicine,” BMJ 2006 Feb 2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.332.7536.294.
The judge’s order was a major affront to many clinical ethicists. A county judge in Ohio ordered a hospital to give ivermectin to a COVID-19 patient on a ventilator. This order occurred against the advice and judgment of the local physicians. It occurred in spite of the hospital’s lawyers fighting the order. How could such a situation occur?
This column is not the appropriate forum to debate the use of ivermectin. The Food and Drug Administration has not approved the drug for treating COVID-19. Indeed, the FDA has specifically recommended against its use.1 So has the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.2 Poison control centers report a large uptick in exposures this summer because of self-medication, sometimes from veterinary sources.3
Fortunately for this case, the judge who overruled the order, Judge Michael A. Oster, wrote in his decision a summary of facts presented by both sides. The topic here is how a judge could order a medical institution and its staff to provide care against medical judgment. A key tenet of clinical ethics consultation is that the consultant needs to do their own investigation. Most veteran consultants have a litany of anecdotes wherein the initial story changed markedly as new facts were uncovered. The more outrageous the initial story, the more likely a major distortion is found. Therefore, most clinical ethics consultants are reluctant to discuss case studies based solely on publicly available information. Often, it is nearly impossible to obtain further information. One side of the story may be gagged by privacy laws. However, cases must sometimes be discussed based on the limited information available because, without that discussion, egregious violations of medical ethics would not be brought to light.
Fortunately for this case, Judge Osler’s decision contains a summary of facts presented by both sides. In August 2021, a 51-year-old patient with severe COVID-19 is in an Ohio intensive care unit on a ventilator. His wife seeks and obtains a prescription for ivermectin from a physician who has an Ohio state medical license but lives elsewhere, has no clinical privileges at the involved hospital, and has never examined the patient. The wife, as a surrogate decision maker, demands her husband receive the medication. The medical staff involved do not consider it a valid treatment. The wife seeks an injunction. A county judge orders the hospital to administer a specified dose of ivermectin daily for 21 days.4 That judge further grants an emergency preliminary injunction for 14 days that orders administration of the medication while legal appeals are made. Two weeks later, a second county judge hearing the case rules that the wife has not presented convincing evidence that she is likely to ultimately win the case on the merits.5 Therefore, the second judge reverses the preliminary injunction. The hospital need not continue to give the medication while further legal proceedings take place.
Cases like this are uncommon. Judges generally defer the authority for medical decisions to physicians. Various attitudes combine to make such an event happen. The judge may view the hospital as a local monopoly of health care and the patient may be too unstable to transport elsewhere. A judge in that situation, combined with a “the consumer is always right” mentality, and a sympathetic plaintiff, may seek to make miracles happen.
Judges overriding science are more likely to manifest when they see the science as ambiguous. Scientists have lost some of the gravitas they had when men walked on the moon. The spectacular success of the mRNA vaccines has surprisingly not reversed that loss. Science has been tainted by mercenary scientists, biased researchers seeking publications, and the large volume of published medical research that is false.
But there is more going on here. In the United States there has been a significant rebellion against any form of expertise and any form of authority. The echo chambers of misinformation on social media have led to polarization, conspiracy theories, and loyalty to political tribe rather than truth; hence the battle over masks and vaccines. This breakdown in authority is accompanied by losses in virtues such as civic duty and loving one’s neighbor. This is a failure of modern moral institutions. When major medical journals print opinion pieces portraying physicians as interchangeable automatons,6 it should not be surprising to see judges tempted by similar imagery.
One part of the solution is accountability in peer review. With 30,000 county judges scattered in 50 states, there will always be a few rogue and maverick attitudes among judges. The judiciary has a means of reassigning rebels to less impactful tasks. Similarly, if the physician who counseled the wife to use ivermectin had privileges at the admitting hospital, then peer review and credential committees could discipline behaviors that were too far outside accepted norms. Even when a consensus on best practice is hard to establish, damage can be mitigated by creating consequences for promoting aberrant care.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. “Why you should not use ivermectin to treat or prevent COVID-19,” FDA Consumer Updates, Sept. 3, 2021.
2. “Rapid increase in ivermectin prescriptions and reports of severe illness associated with use of products containing ivermectin to prevent or treat COVID-19,” CDC Health Advisory, Aug. 26, 2021.
3. National Poison Data System Bulletin: COVID-19 (Ivermectin), American Association of Poison Control Centers, 2021.
4. Smith v West Chester Hosptial, LLC, DBA West Chester Hospital, Butler County Clerk of Courts, Aug. 23, 2021.
5. Smith v West Chester Hosptial, LLC, Decision denying plaintiff’s action for a preliminary injunction, Butler County Clerk of Courts, Sept. 6, 2021.
6. “Conscientious objection in medicine,” BMJ 2006 Feb 2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.332.7536.294.
The judge’s order was a major affront to many clinical ethicists. A county judge in Ohio ordered a hospital to give ivermectin to a COVID-19 patient on a ventilator. This order occurred against the advice and judgment of the local physicians. It occurred in spite of the hospital’s lawyers fighting the order. How could such a situation occur?
This column is not the appropriate forum to debate the use of ivermectin. The Food and Drug Administration has not approved the drug for treating COVID-19. Indeed, the FDA has specifically recommended against its use.1 So has the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.2 Poison control centers report a large uptick in exposures this summer because of self-medication, sometimes from veterinary sources.3
Fortunately for this case, the judge who overruled the order, Judge Michael A. Oster, wrote in his decision a summary of facts presented by both sides. The topic here is how a judge could order a medical institution and its staff to provide care against medical judgment. A key tenet of clinical ethics consultation is that the consultant needs to do their own investigation. Most veteran consultants have a litany of anecdotes wherein the initial story changed markedly as new facts were uncovered. The more outrageous the initial story, the more likely a major distortion is found. Therefore, most clinical ethics consultants are reluctant to discuss case studies based solely on publicly available information. Often, it is nearly impossible to obtain further information. One side of the story may be gagged by privacy laws. However, cases must sometimes be discussed based on the limited information available because, without that discussion, egregious violations of medical ethics would not be brought to light.
Fortunately for this case, Judge Osler’s decision contains a summary of facts presented by both sides. In August 2021, a 51-year-old patient with severe COVID-19 is in an Ohio intensive care unit on a ventilator. His wife seeks and obtains a prescription for ivermectin from a physician who has an Ohio state medical license but lives elsewhere, has no clinical privileges at the involved hospital, and has never examined the patient. The wife, as a surrogate decision maker, demands her husband receive the medication. The medical staff involved do not consider it a valid treatment. The wife seeks an injunction. A county judge orders the hospital to administer a specified dose of ivermectin daily for 21 days.4 That judge further grants an emergency preliminary injunction for 14 days that orders administration of the medication while legal appeals are made. Two weeks later, a second county judge hearing the case rules that the wife has not presented convincing evidence that she is likely to ultimately win the case on the merits.5 Therefore, the second judge reverses the preliminary injunction. The hospital need not continue to give the medication while further legal proceedings take place.
Cases like this are uncommon. Judges generally defer the authority for medical decisions to physicians. Various attitudes combine to make such an event happen. The judge may view the hospital as a local monopoly of health care and the patient may be too unstable to transport elsewhere. A judge in that situation, combined with a “the consumer is always right” mentality, and a sympathetic plaintiff, may seek to make miracles happen.
Judges overriding science are more likely to manifest when they see the science as ambiguous. Scientists have lost some of the gravitas they had when men walked on the moon. The spectacular success of the mRNA vaccines has surprisingly not reversed that loss. Science has been tainted by mercenary scientists, biased researchers seeking publications, and the large volume of published medical research that is false.
But there is more going on here. In the United States there has been a significant rebellion against any form of expertise and any form of authority. The echo chambers of misinformation on social media have led to polarization, conspiracy theories, and loyalty to political tribe rather than truth; hence the battle over masks and vaccines. This breakdown in authority is accompanied by losses in virtues such as civic duty and loving one’s neighbor. This is a failure of modern moral institutions. When major medical journals print opinion pieces portraying physicians as interchangeable automatons,6 it should not be surprising to see judges tempted by similar imagery.
One part of the solution is accountability in peer review. With 30,000 county judges scattered in 50 states, there will always be a few rogue and maverick attitudes among judges. The judiciary has a means of reassigning rebels to less impactful tasks. Similarly, if the physician who counseled the wife to use ivermectin had privileges at the admitting hospital, then peer review and credential committees could discipline behaviors that were too far outside accepted norms. Even when a consensus on best practice is hard to establish, damage can be mitigated by creating consequences for promoting aberrant care.
Dr. Powell is a retired pediatric hospitalist and clinical ethics consultant living in St. Louis. Email him at [email protected].
References
1. “Why you should not use ivermectin to treat or prevent COVID-19,” FDA Consumer Updates, Sept. 3, 2021.
2. “Rapid increase in ivermectin prescriptions and reports of severe illness associated with use of products containing ivermectin to prevent or treat COVID-19,” CDC Health Advisory, Aug. 26, 2021.
3. National Poison Data System Bulletin: COVID-19 (Ivermectin), American Association of Poison Control Centers, 2021.
4. Smith v West Chester Hosptial, LLC, DBA West Chester Hospital, Butler County Clerk of Courts, Aug. 23, 2021.
5. Smith v West Chester Hosptial, LLC, Decision denying plaintiff’s action for a preliminary injunction, Butler County Clerk of Courts, Sept. 6, 2021.
6. “Conscientious objection in medicine,” BMJ 2006 Feb 2. doi: 10.1136/bmj.332.7536.294.
Gut microbiome could make weight loss easier for some
Researchers found that the gut microbiome – the bacteria that help digest food and absorb nutrients in the intestines – can influence attempts at weight loss.
They identified genes within these bacteria that determine how quickly the bacteria grow, how well people can take advantage of nutrients in food, and whether starches and fiber, in particular, get broken down into sugars too quickly to aid weight loss.
“Some people have a harder time losing weight than others,” study author Sean Gibbons, PhD, told this news organization. “For example, some people are able to control their weight through basic lifestyle interventions, while others may not.”
Furthermore, it is difficult to predict which individuals will respond to changes in diet or exercise and who might require more intense strategies.
The study, which was published online September 14 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, could bring us closer to an answer.
“We’ve identified specific genetic signatures in the gut microbiome that were predictive of weight loss response in a small cohort of patients following a healthy lifestyle intervention,” explained Dr. Gibbons, Washington Research Foundation distinguished investigator and assistant professor at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle.
Weight loss takes guts?
Differences in 31 functional genes emerged from the gut microbiome in 48 people who lost 1% or more of their weight each month compared with 57 others whose weight remained the same. These findings came from stool samples taken 6 to 12 months after people started a commercial weight loss coaching program.
In contrast, lead author Christian Diener, PhD, also of the Institute for Systems Biology, and colleagues found only one factor in the blood that differed between the weight loss and weight maintenance groups. (They specifically evaluated proteins associated with obesity in the blood and genetic data from stool samples in a subset of 25 participants.)
Their findings align with previous research showing different types of bacteria in the gut microbiome can affect the success of weight loss interventions, but they took it a step further to determine how this works.
“We know that the gut microbiome plays an important role in weight management and can also influence a response to weight loss interventions. However, specific gut microbiome features that can explain this observation in more detail are still to be discovered,” Hana Kahleova, MD, PhD, MBA, director of clinical research at the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine in Washington, D.C., told this news organization when asked for comment.
Good versus bad players
On the plus side, genes that help bacteria grow more rapidly were associated with weight loss. These bacteria take more of the nutrients in food for themselves, leaving less to go toward human weight gain compared with slower growing bacteria.
In fact, prior evidence points to a particular gut bacteria, Prevotella, as being beneficial for weight loss. “In our study,” Dr. Gibbons said, “we found that some of the fastest-growing microbes in the weight-loss responder group were from the genus Prevotella.”
On the other hand, bacteria that produce more enzymes to breakdown starches or fiber quickly into sugars, for example, were linked with making people more resistant to weight loss.
“By understanding these functional patterns, we may one day be able to engineer resistant microbiomes to be more permissive to weight loss,” Dr. Gibbons said.
Dr. Kahleova agreed. “These findings expand our understanding of the specific features of the gut microbiome that play a role in weight loss,” she said.
Moving beyond BMI
Interestingly, the researchers controlled for baseline body mass index (BMI) and other factors that could affect weight loss. People who start off with a higher BMI tend to lose more weight than others, a phenomenon known as ‘regression to the mean.” This factor confounded some earlier research, they noted.
“The vast majority of features associated with weight loss, independent of BMI, were functional genes within the gut metagenome,” Dr. Gibbons said.
“This tells us that the gut microbiome is an important modulator of weight loss, independent of your underlying metabolic health state, baseline diet, or BMI status.”
“This study described several metagenomic functional features that were associated with weight loss after controlling for potential confounders, such as age, sex, and baseline BMI,” Dr. Kahleova said. “These findings ... may help optimize the weight-loss protocols in future studies.”
Fecal microbiota transplants?
What do the findings mean for people willing to adjust their diet – or undergo a fecal transplant – to include more of the gut bacteria that facilitate weight loss?
It could be too soon for such interventions, Dr. Gibbons said. “It is still very difficult to rationally engineer your gut microbiome.”
“Interestingly, a recent study suggests that fecal transplants from a high-Prevotella donor may be able to flip low-Prevotella recipients to high-Prevotella,” Dr. Gibbons said.
More research is required, however, to understand whether or not these fecal microbial transplant-flipped individuals are also more capable of weight loss, he added.
Beyond that, “I can’t give any specific recommendations, other than that [people] should eat more fiber-rich, plant-based, whole foods and reduce their consumption of red meat. That’s well-supported.”
“Also, prepare your own meals, rather than relying on sugar and sodium-rich processed foods,” Dr. Gibbons said.
Dr. Gibbons and his team hope to validate their work in larger human studies “and perhaps develop clinical diagnostics or interventions for people trying to lose weight.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers found that the gut microbiome – the bacteria that help digest food and absorb nutrients in the intestines – can influence attempts at weight loss.
They identified genes within these bacteria that determine how quickly the bacteria grow, how well people can take advantage of nutrients in food, and whether starches and fiber, in particular, get broken down into sugars too quickly to aid weight loss.
“Some people have a harder time losing weight than others,” study author Sean Gibbons, PhD, told this news organization. “For example, some people are able to control their weight through basic lifestyle interventions, while others may not.”
Furthermore, it is difficult to predict which individuals will respond to changes in diet or exercise and who might require more intense strategies.
The study, which was published online September 14 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, could bring us closer to an answer.
“We’ve identified specific genetic signatures in the gut microbiome that were predictive of weight loss response in a small cohort of patients following a healthy lifestyle intervention,” explained Dr. Gibbons, Washington Research Foundation distinguished investigator and assistant professor at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle.
Weight loss takes guts?
Differences in 31 functional genes emerged from the gut microbiome in 48 people who lost 1% or more of their weight each month compared with 57 others whose weight remained the same. These findings came from stool samples taken 6 to 12 months after people started a commercial weight loss coaching program.
In contrast, lead author Christian Diener, PhD, also of the Institute for Systems Biology, and colleagues found only one factor in the blood that differed between the weight loss and weight maintenance groups. (They specifically evaluated proteins associated with obesity in the blood and genetic data from stool samples in a subset of 25 participants.)
Their findings align with previous research showing different types of bacteria in the gut microbiome can affect the success of weight loss interventions, but they took it a step further to determine how this works.
“We know that the gut microbiome plays an important role in weight management and can also influence a response to weight loss interventions. However, specific gut microbiome features that can explain this observation in more detail are still to be discovered,” Hana Kahleova, MD, PhD, MBA, director of clinical research at the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine in Washington, D.C., told this news organization when asked for comment.
Good versus bad players
On the plus side, genes that help bacteria grow more rapidly were associated with weight loss. These bacteria take more of the nutrients in food for themselves, leaving less to go toward human weight gain compared with slower growing bacteria.
In fact, prior evidence points to a particular gut bacteria, Prevotella, as being beneficial for weight loss. “In our study,” Dr. Gibbons said, “we found that some of the fastest-growing microbes in the weight-loss responder group were from the genus Prevotella.”
On the other hand, bacteria that produce more enzymes to breakdown starches or fiber quickly into sugars, for example, were linked with making people more resistant to weight loss.
“By understanding these functional patterns, we may one day be able to engineer resistant microbiomes to be more permissive to weight loss,” Dr. Gibbons said.
Dr. Kahleova agreed. “These findings expand our understanding of the specific features of the gut microbiome that play a role in weight loss,” she said.
Moving beyond BMI
Interestingly, the researchers controlled for baseline body mass index (BMI) and other factors that could affect weight loss. People who start off with a higher BMI tend to lose more weight than others, a phenomenon known as ‘regression to the mean.” This factor confounded some earlier research, they noted.
“The vast majority of features associated with weight loss, independent of BMI, were functional genes within the gut metagenome,” Dr. Gibbons said.
“This tells us that the gut microbiome is an important modulator of weight loss, independent of your underlying metabolic health state, baseline diet, or BMI status.”
“This study described several metagenomic functional features that were associated with weight loss after controlling for potential confounders, such as age, sex, and baseline BMI,” Dr. Kahleova said. “These findings ... may help optimize the weight-loss protocols in future studies.”
Fecal microbiota transplants?
What do the findings mean for people willing to adjust their diet – or undergo a fecal transplant – to include more of the gut bacteria that facilitate weight loss?
It could be too soon for such interventions, Dr. Gibbons said. “It is still very difficult to rationally engineer your gut microbiome.”
“Interestingly, a recent study suggests that fecal transplants from a high-Prevotella donor may be able to flip low-Prevotella recipients to high-Prevotella,” Dr. Gibbons said.
More research is required, however, to understand whether or not these fecal microbial transplant-flipped individuals are also more capable of weight loss, he added.
Beyond that, “I can’t give any specific recommendations, other than that [people] should eat more fiber-rich, plant-based, whole foods and reduce their consumption of red meat. That’s well-supported.”
“Also, prepare your own meals, rather than relying on sugar and sodium-rich processed foods,” Dr. Gibbons said.
Dr. Gibbons and his team hope to validate their work in larger human studies “and perhaps develop clinical diagnostics or interventions for people trying to lose weight.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers found that the gut microbiome – the bacteria that help digest food and absorb nutrients in the intestines – can influence attempts at weight loss.
They identified genes within these bacteria that determine how quickly the bacteria grow, how well people can take advantage of nutrients in food, and whether starches and fiber, in particular, get broken down into sugars too quickly to aid weight loss.
“Some people have a harder time losing weight than others,” study author Sean Gibbons, PhD, told this news organization. “For example, some people are able to control their weight through basic lifestyle interventions, while others may not.”
Furthermore, it is difficult to predict which individuals will respond to changes in diet or exercise and who might require more intense strategies.
The study, which was published online September 14 in mSystems, a journal of the American Society for Microbiology, could bring us closer to an answer.
“We’ve identified specific genetic signatures in the gut microbiome that were predictive of weight loss response in a small cohort of patients following a healthy lifestyle intervention,” explained Dr. Gibbons, Washington Research Foundation distinguished investigator and assistant professor at the Institute for Systems Biology in Seattle.
Weight loss takes guts?
Differences in 31 functional genes emerged from the gut microbiome in 48 people who lost 1% or more of their weight each month compared with 57 others whose weight remained the same. These findings came from stool samples taken 6 to 12 months after people started a commercial weight loss coaching program.
In contrast, lead author Christian Diener, PhD, also of the Institute for Systems Biology, and colleagues found only one factor in the blood that differed between the weight loss and weight maintenance groups. (They specifically evaluated proteins associated with obesity in the blood and genetic data from stool samples in a subset of 25 participants.)
Their findings align with previous research showing different types of bacteria in the gut microbiome can affect the success of weight loss interventions, but they took it a step further to determine how this works.
“We know that the gut microbiome plays an important role in weight management and can also influence a response to weight loss interventions. However, specific gut microbiome features that can explain this observation in more detail are still to be discovered,” Hana Kahleova, MD, PhD, MBA, director of clinical research at the Physicians Committee for Responsible Medicine in Washington, D.C., told this news organization when asked for comment.
Good versus bad players
On the plus side, genes that help bacteria grow more rapidly were associated with weight loss. These bacteria take more of the nutrients in food for themselves, leaving less to go toward human weight gain compared with slower growing bacteria.
In fact, prior evidence points to a particular gut bacteria, Prevotella, as being beneficial for weight loss. “In our study,” Dr. Gibbons said, “we found that some of the fastest-growing microbes in the weight-loss responder group were from the genus Prevotella.”
On the other hand, bacteria that produce more enzymes to breakdown starches or fiber quickly into sugars, for example, were linked with making people more resistant to weight loss.
“By understanding these functional patterns, we may one day be able to engineer resistant microbiomes to be more permissive to weight loss,” Dr. Gibbons said.
Dr. Kahleova agreed. “These findings expand our understanding of the specific features of the gut microbiome that play a role in weight loss,” she said.
Moving beyond BMI
Interestingly, the researchers controlled for baseline body mass index (BMI) and other factors that could affect weight loss. People who start off with a higher BMI tend to lose more weight than others, a phenomenon known as ‘regression to the mean.” This factor confounded some earlier research, they noted.
“The vast majority of features associated with weight loss, independent of BMI, were functional genes within the gut metagenome,” Dr. Gibbons said.
“This tells us that the gut microbiome is an important modulator of weight loss, independent of your underlying metabolic health state, baseline diet, or BMI status.”
“This study described several metagenomic functional features that were associated with weight loss after controlling for potential confounders, such as age, sex, and baseline BMI,” Dr. Kahleova said. “These findings ... may help optimize the weight-loss protocols in future studies.”
Fecal microbiota transplants?
What do the findings mean for people willing to adjust their diet – or undergo a fecal transplant – to include more of the gut bacteria that facilitate weight loss?
It could be too soon for such interventions, Dr. Gibbons said. “It is still very difficult to rationally engineer your gut microbiome.”
“Interestingly, a recent study suggests that fecal transplants from a high-Prevotella donor may be able to flip low-Prevotella recipients to high-Prevotella,” Dr. Gibbons said.
More research is required, however, to understand whether or not these fecal microbial transplant-flipped individuals are also more capable of weight loss, he added.
Beyond that, “I can’t give any specific recommendations, other than that [people] should eat more fiber-rich, plant-based, whole foods and reduce their consumption of red meat. That’s well-supported.”
“Also, prepare your own meals, rather than relying on sugar and sodium-rich processed foods,” Dr. Gibbons said.
Dr. Gibbons and his team hope to validate their work in larger human studies “and perhaps develop clinical diagnostics or interventions for people trying to lose weight.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hormone agonist therapy disrupts bone density in transgender youth
The use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists has a negative effect on bone mass in transgender youth, according to data from 172 individuals.
The onset of puberty and pubertal hormones contributes to the development of bone mass and body composition in adolescence, wrote Behdad Navabi, MD, and colleagues at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, Canada. Although the safety and efficacy of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) has been described in short-term studies of youth with gender dysphoria, concerns persist about suppression of bone mass accrual from extended use of GnRHas in this population, they noted.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 172 youth younger than 18 years of age who were treated with GNRHa and underwent at least one baseline dual-energy radiograph absorptiometry (DXA) measurement between January 2006 and April 2017 at a single center. The standard treatment protocol started with three doses of 7.5 mg leuprolide acetate, given intramuscularly every 4 weeks, followed by 11.25 mg intramuscularly every 12 weeks after puberty suppression was confirmed both clinically and biochemically. Areal bone mineral density (aBMD) measurement z scores were based on birth-assigned sex, age, and ethnicity, and assessed at baseline and every 12 months. In addition, volumetric bone mineral density was calculated as bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) at the lower spine, and the z score based on age-matched, birth-assigned gender BMAD.
Overall, 55.2% of the youth were vitamin D deficient or insufficient at baseline, but 87.3% were sufficient by the time of a third follow-up visit after treatment with 1,000-2,000 IU of vitamin D daily; no cases of vitamin D toxicity were reported.
At baseline, transgender females had lower z scores for the LS aBMD and BMAD compared to transgender males, reflecting a difference seen in previous studies of transgender youth and adult females, the researchers noted.
The researchers analyzed pre- and posttreatment DXA data in a subgroup of 36 transgender females and 80 transgender males to identify any changes associated with GnRHa. The average time between the DXA scans was 407 days. In this population, aBMD z scores at the lower lumbar spine (LS), left total hip (LTH), and total body less head (TBLH) decreased significantly from baseline in transgender males and females.
Among transgender males, LS bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) z scores also decreased significantly from baseline, but no such change occurred among transgender females. The most significant decrease in z scores occurred in the LS aBMD and BMAD of transgender males, with changes that reflect findings from previous studies and may be explained by decreased estrogen, the researchers wrote.
In terms of body composition, no significant changes occurred in body mass index z score from baseline to follow-up in transgender males or females, the researchers noted, and changes in both gynoid and android fat percentages were consistent with the individuals’ affirmed genders. No vertebral fractures were detected.
However, GnRHa was significantly associated with a decrease in total body fat percentage and a decrease in lean body mass (LBM) in transgender females.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of consistent baseline physical activity records, and limited analysis at follow-up of the possible role of physical activity in bone health and body composition, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the relatively large study population with baseline assessments, and by the pre- and posttreatment analysis, they added.
“Evidence on GnRHa-associated changes in body composition and BMD will help health care professionals involved in the care of youth with GD [gender dysphoria] to counsel appropriately and optimize their bone health,” the researchers said. “Given the absence of vertebral fractures detected in those with significant decreases in their LS z scores, the significance of BMD effects of GnRHa in transgender youth needs further study, as well as whether future spine radiographs are needed on the basis of BMD trajectory,” they concluded.
Balance bone health concerns with potential benefits
The effect of estrogen and testosterone on bone geometry in puberty varies, and the increase in the use of GnRHa as part of a multidisciplinary gender transition plan makes research on the skeletal impact of this therapy in transgender youth a top priority, Laura K. Bachrach, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and Catherine M. Gordon of Harvard Medical School, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The decrease in areal bone mineral density and in bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) z scores in the current study is not unexpected, but the key question is how much bone density recovers once the suppression therapy ends and transgender sex steroid use begins, they said. “Follow-up studies of young adults treated with GnRHa for precocious puberty in childhood are reassuring,” they wrote. “It is premature, however, to extrapolate from these findings to transgender youth,” because the impact of gender-affirming sex steroid therapy on the skeleton at older ages and stages of maturity are unclear, they emphasized.
In the absence of definitive answers, the editorial authors advised clinicians treating youth with gender dysphoria to provide a balanced view of the risks and benefits of hormone therapy, and encourage adequate intake of dietary vitamin D and calcium, along with weight-bearing physical activity, to promote general bone health. “Transgender teenagers and their parents should be reassured that some recovery from decreases in aBMD during pubertal suppression with GnRHa is likely,” the authors noted. Bone health should be monitored throughout all stages of treatment in transgender youth, but concerns about transient bone loss should not discourage gender transition therapy, they emphasized. “In this patient group, providing a pause in pubertal development offers a life-changing and, for some, a life-saving intervention,” they concluded.
Comparison to cisgender controls would add value
“This study is important because one of the major side effects of GnRH agonists is decreased bone density, especially the longer that patients are on them,” M. Brett Cooper, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, said in an interview. The findings add to existing data to underscore the importance of screening for low bone density and low vitamin D levels, Dr. Cooper added.
Dr. Cooper said that he was not surprised by the study findings. “I think that this study supported what clinicians already knew, which is that GnRH agonists do potentially cause a decline in bone mineral density and thus, you need to support these patients as best you can with calcium, vitamin D, and weight-bearing exercise,” he noted.
Dr. Cooper emphasized two main take-home points from the study. “First, clinicians who prescribe GnRH agonists need to ensure that they are checking bone density and vitamin D measurements, and then optimizing these appropriately,” he said. “Second, when a bone density is found to be low or a vitamin level is low, clinicians need to ensure that they are monitored and treated appropriately.” Clinicians need to use these data when deciding when to start gender-affirming hormones so their patients have the best chance to recover bone density, he added.
“I think one confounding factor on this study is the ranges they used for vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Cooper noted. “This study was done in Canada, and the scale used was in nmol/L, while most labs in the U.S. use ng/mL,” he said. “Most pediatric and adolescent societies in the United States use < 20 ng/mL as an indicator of vitamin D deficient and between 20 and 29 ng/mL as insufficient,” he explained, citing the position statement on recommended vitamin D intake for adolescents published by The Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. In this study, the results converted to < 12 ng/mL as deficient and between 12 and 20 ng/mL as insufficient, respectively, on the U.S. scale, said Dr. Cooper.
“Therefore, I can see that there are cases where someone may have been labeled vitamin D insufficient in this study using their range, whereas in the U.S. these patients would be labeled as vitamin D deficient and treated with higher-dose supplementation,” he said. In addition, individuals with levels between 20 ng/mL and 29 ng/mL in the U.S. would still be treated with vitamin D supplementation, “whereas in their study those individuals would have been labeled as normal,” he noted.
As for future research, it would be useful to study whether bone mass in transgender young people differs from age- and gender-matched controls who are not gender diverse (cisgender), Dr. Cooper added. “It may be possible that the youth in this study are not different from their peers and maybe the GnRH agonist is not the culprit,” he said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, editorial authors, and Dr. Cooper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists has a negative effect on bone mass in transgender youth, according to data from 172 individuals.
The onset of puberty and pubertal hormones contributes to the development of bone mass and body composition in adolescence, wrote Behdad Navabi, MD, and colleagues at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, Canada. Although the safety and efficacy of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) has been described in short-term studies of youth with gender dysphoria, concerns persist about suppression of bone mass accrual from extended use of GnRHas in this population, they noted.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 172 youth younger than 18 years of age who were treated with GNRHa and underwent at least one baseline dual-energy radiograph absorptiometry (DXA) measurement between January 2006 and April 2017 at a single center. The standard treatment protocol started with three doses of 7.5 mg leuprolide acetate, given intramuscularly every 4 weeks, followed by 11.25 mg intramuscularly every 12 weeks after puberty suppression was confirmed both clinically and biochemically. Areal bone mineral density (aBMD) measurement z scores were based on birth-assigned sex, age, and ethnicity, and assessed at baseline and every 12 months. In addition, volumetric bone mineral density was calculated as bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) at the lower spine, and the z score based on age-matched, birth-assigned gender BMAD.
Overall, 55.2% of the youth were vitamin D deficient or insufficient at baseline, but 87.3% were sufficient by the time of a third follow-up visit after treatment with 1,000-2,000 IU of vitamin D daily; no cases of vitamin D toxicity were reported.
At baseline, transgender females had lower z scores for the LS aBMD and BMAD compared to transgender males, reflecting a difference seen in previous studies of transgender youth and adult females, the researchers noted.
The researchers analyzed pre- and posttreatment DXA data in a subgroup of 36 transgender females and 80 transgender males to identify any changes associated with GnRHa. The average time between the DXA scans was 407 days. In this population, aBMD z scores at the lower lumbar spine (LS), left total hip (LTH), and total body less head (TBLH) decreased significantly from baseline in transgender males and females.
Among transgender males, LS bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) z scores also decreased significantly from baseline, but no such change occurred among transgender females. The most significant decrease in z scores occurred in the LS aBMD and BMAD of transgender males, with changes that reflect findings from previous studies and may be explained by decreased estrogen, the researchers wrote.
In terms of body composition, no significant changes occurred in body mass index z score from baseline to follow-up in transgender males or females, the researchers noted, and changes in both gynoid and android fat percentages were consistent with the individuals’ affirmed genders. No vertebral fractures were detected.
However, GnRHa was significantly associated with a decrease in total body fat percentage and a decrease in lean body mass (LBM) in transgender females.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of consistent baseline physical activity records, and limited analysis at follow-up of the possible role of physical activity in bone health and body composition, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the relatively large study population with baseline assessments, and by the pre- and posttreatment analysis, they added.
“Evidence on GnRHa-associated changes in body composition and BMD will help health care professionals involved in the care of youth with GD [gender dysphoria] to counsel appropriately and optimize their bone health,” the researchers said. “Given the absence of vertebral fractures detected in those with significant decreases in their LS z scores, the significance of BMD effects of GnRHa in transgender youth needs further study, as well as whether future spine radiographs are needed on the basis of BMD trajectory,” they concluded.
Balance bone health concerns with potential benefits
The effect of estrogen and testosterone on bone geometry in puberty varies, and the increase in the use of GnRHa as part of a multidisciplinary gender transition plan makes research on the skeletal impact of this therapy in transgender youth a top priority, Laura K. Bachrach, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and Catherine M. Gordon of Harvard Medical School, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The decrease in areal bone mineral density and in bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) z scores in the current study is not unexpected, but the key question is how much bone density recovers once the suppression therapy ends and transgender sex steroid use begins, they said. “Follow-up studies of young adults treated with GnRHa for precocious puberty in childhood are reassuring,” they wrote. “It is premature, however, to extrapolate from these findings to transgender youth,” because the impact of gender-affirming sex steroid therapy on the skeleton at older ages and stages of maturity are unclear, they emphasized.
In the absence of definitive answers, the editorial authors advised clinicians treating youth with gender dysphoria to provide a balanced view of the risks and benefits of hormone therapy, and encourage adequate intake of dietary vitamin D and calcium, along with weight-bearing physical activity, to promote general bone health. “Transgender teenagers and their parents should be reassured that some recovery from decreases in aBMD during pubertal suppression with GnRHa is likely,” the authors noted. Bone health should be monitored throughout all stages of treatment in transgender youth, but concerns about transient bone loss should not discourage gender transition therapy, they emphasized. “In this patient group, providing a pause in pubertal development offers a life-changing and, for some, a life-saving intervention,” they concluded.
Comparison to cisgender controls would add value
“This study is important because one of the major side effects of GnRH agonists is decreased bone density, especially the longer that patients are on them,” M. Brett Cooper, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, said in an interview. The findings add to existing data to underscore the importance of screening for low bone density and low vitamin D levels, Dr. Cooper added.
Dr. Cooper said that he was not surprised by the study findings. “I think that this study supported what clinicians already knew, which is that GnRH agonists do potentially cause a decline in bone mineral density and thus, you need to support these patients as best you can with calcium, vitamin D, and weight-bearing exercise,” he noted.
Dr. Cooper emphasized two main take-home points from the study. “First, clinicians who prescribe GnRH agonists need to ensure that they are checking bone density and vitamin D measurements, and then optimizing these appropriately,” he said. “Second, when a bone density is found to be low or a vitamin level is low, clinicians need to ensure that they are monitored and treated appropriately.” Clinicians need to use these data when deciding when to start gender-affirming hormones so their patients have the best chance to recover bone density, he added.
“I think one confounding factor on this study is the ranges they used for vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Cooper noted. “This study was done in Canada, and the scale used was in nmol/L, while most labs in the U.S. use ng/mL,” he said. “Most pediatric and adolescent societies in the United States use < 20 ng/mL as an indicator of vitamin D deficient and between 20 and 29 ng/mL as insufficient,” he explained, citing the position statement on recommended vitamin D intake for adolescents published by The Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. In this study, the results converted to < 12 ng/mL as deficient and between 12 and 20 ng/mL as insufficient, respectively, on the U.S. scale, said Dr. Cooper.
“Therefore, I can see that there are cases where someone may have been labeled vitamin D insufficient in this study using their range, whereas in the U.S. these patients would be labeled as vitamin D deficient and treated with higher-dose supplementation,” he said. In addition, individuals with levels between 20 ng/mL and 29 ng/mL in the U.S. would still be treated with vitamin D supplementation, “whereas in their study those individuals would have been labeled as normal,” he noted.
As for future research, it would be useful to study whether bone mass in transgender young people differs from age- and gender-matched controls who are not gender diverse (cisgender), Dr. Cooper added. “It may be possible that the youth in this study are not different from their peers and maybe the GnRH agonist is not the culprit,” he said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, editorial authors, and Dr. Cooper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
The use of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists has a negative effect on bone mass in transgender youth, according to data from 172 individuals.
The onset of puberty and pubertal hormones contributes to the development of bone mass and body composition in adolescence, wrote Behdad Navabi, MD, and colleagues at Children’s Hospital of Eastern Ontario, Canada. Although the safety and efficacy of gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists (GnRHa) has been described in short-term studies of youth with gender dysphoria, concerns persist about suppression of bone mass accrual from extended use of GnRHas in this population, they noted.
In a study published in Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 172 youth younger than 18 years of age who were treated with GNRHa and underwent at least one baseline dual-energy radiograph absorptiometry (DXA) measurement between January 2006 and April 2017 at a single center. The standard treatment protocol started with three doses of 7.5 mg leuprolide acetate, given intramuscularly every 4 weeks, followed by 11.25 mg intramuscularly every 12 weeks after puberty suppression was confirmed both clinically and biochemically. Areal bone mineral density (aBMD) measurement z scores were based on birth-assigned sex, age, and ethnicity, and assessed at baseline and every 12 months. In addition, volumetric bone mineral density was calculated as bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) at the lower spine, and the z score based on age-matched, birth-assigned gender BMAD.
Overall, 55.2% of the youth were vitamin D deficient or insufficient at baseline, but 87.3% were sufficient by the time of a third follow-up visit after treatment with 1,000-2,000 IU of vitamin D daily; no cases of vitamin D toxicity were reported.
At baseline, transgender females had lower z scores for the LS aBMD and BMAD compared to transgender males, reflecting a difference seen in previous studies of transgender youth and adult females, the researchers noted.
The researchers analyzed pre- and posttreatment DXA data in a subgroup of 36 transgender females and 80 transgender males to identify any changes associated with GnRHa. The average time between the DXA scans was 407 days. In this population, aBMD z scores at the lower lumbar spine (LS), left total hip (LTH), and total body less head (TBLH) decreased significantly from baseline in transgender males and females.
Among transgender males, LS bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) z scores also decreased significantly from baseline, but no such change occurred among transgender females. The most significant decrease in z scores occurred in the LS aBMD and BMAD of transgender males, with changes that reflect findings from previous studies and may be explained by decreased estrogen, the researchers wrote.
In terms of body composition, no significant changes occurred in body mass index z score from baseline to follow-up in transgender males or females, the researchers noted, and changes in both gynoid and android fat percentages were consistent with the individuals’ affirmed genders. No vertebral fractures were detected.
However, GnRHa was significantly associated with a decrease in total body fat percentage and a decrease in lean body mass (LBM) in transgender females.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the lack of consistent baseline physical activity records, and limited analysis at follow-up of the possible role of physical activity in bone health and body composition, the researchers noted. However, the results were strengthened by the relatively large study population with baseline assessments, and by the pre- and posttreatment analysis, they added.
“Evidence on GnRHa-associated changes in body composition and BMD will help health care professionals involved in the care of youth with GD [gender dysphoria] to counsel appropriately and optimize their bone health,” the researchers said. “Given the absence of vertebral fractures detected in those with significant decreases in their LS z scores, the significance of BMD effects of GnRHa in transgender youth needs further study, as well as whether future spine radiographs are needed on the basis of BMD trajectory,” they concluded.
Balance bone health concerns with potential benefits
The effect of estrogen and testosterone on bone geometry in puberty varies, and the increase in the use of GnRHa as part of a multidisciplinary gender transition plan makes research on the skeletal impact of this therapy in transgender youth a top priority, Laura K. Bachrach, MD, of Stanford (Calif.) University, and Catherine M. Gordon of Harvard Medical School, Boston, wrote in an accompanying editorial.
The decrease in areal bone mineral density and in bone mineral apparent density (BMAD) z scores in the current study is not unexpected, but the key question is how much bone density recovers once the suppression therapy ends and transgender sex steroid use begins, they said. “Follow-up studies of young adults treated with GnRHa for precocious puberty in childhood are reassuring,” they wrote. “It is premature, however, to extrapolate from these findings to transgender youth,” because the impact of gender-affirming sex steroid therapy on the skeleton at older ages and stages of maturity are unclear, they emphasized.
In the absence of definitive answers, the editorial authors advised clinicians treating youth with gender dysphoria to provide a balanced view of the risks and benefits of hormone therapy, and encourage adequate intake of dietary vitamin D and calcium, along with weight-bearing physical activity, to promote general bone health. “Transgender teenagers and their parents should be reassured that some recovery from decreases in aBMD during pubertal suppression with GnRHa is likely,” the authors noted. Bone health should be monitored throughout all stages of treatment in transgender youth, but concerns about transient bone loss should not discourage gender transition therapy, they emphasized. “In this patient group, providing a pause in pubertal development offers a life-changing and, for some, a life-saving intervention,” they concluded.
Comparison to cisgender controls would add value
“This study is important because one of the major side effects of GnRH agonists is decreased bone density, especially the longer that patients are on them,” M. Brett Cooper, MD, of UT Southwestern Medical Center, said in an interview. The findings add to existing data to underscore the importance of screening for low bone density and low vitamin D levels, Dr. Cooper added.
Dr. Cooper said that he was not surprised by the study findings. “I think that this study supported what clinicians already knew, which is that GnRH agonists do potentially cause a decline in bone mineral density and thus, you need to support these patients as best you can with calcium, vitamin D, and weight-bearing exercise,” he noted.
Dr. Cooper emphasized two main take-home points from the study. “First, clinicians who prescribe GnRH agonists need to ensure that they are checking bone density and vitamin D measurements, and then optimizing these appropriately,” he said. “Second, when a bone density is found to be low or a vitamin level is low, clinicians need to ensure that they are monitored and treated appropriately.” Clinicians need to use these data when deciding when to start gender-affirming hormones so their patients have the best chance to recover bone density, he added.
“I think one confounding factor on this study is the ranges they used for vitamin D deficiency,” Dr. Cooper noted. “This study was done in Canada, and the scale used was in nmol/L, while most labs in the U.S. use ng/mL,” he said. “Most pediatric and adolescent societies in the United States use < 20 ng/mL as an indicator of vitamin D deficient and between 20 and 29 ng/mL as insufficient,” he explained, citing the position statement on recommended vitamin D intake for adolescents published by The Society for Adolescent Health and Medicine. In this study, the results converted to < 12 ng/mL as deficient and between 12 and 20 ng/mL as insufficient, respectively, on the U.S. scale, said Dr. Cooper.
“Therefore, I can see that there are cases where someone may have been labeled vitamin D insufficient in this study using their range, whereas in the U.S. these patients would be labeled as vitamin D deficient and treated with higher-dose supplementation,” he said. In addition, individuals with levels between 20 ng/mL and 29 ng/mL in the U.S. would still be treated with vitamin D supplementation, “whereas in their study those individuals would have been labeled as normal,” he noted.
As for future research, it would be useful to study whether bone mass in transgender young people differs from age- and gender-matched controls who are not gender diverse (cisgender), Dr. Cooper added. “It may be possible that the youth in this study are not different from their peers and maybe the GnRH agonist is not the culprit,” he said.
The study received no outside funding. The researchers, editorial authors, and Dr. Cooper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
FROM PEDIATRICS
Researchers warn young adults are at highest risk of obesity
Individuals aged 18-24 years are at the highest risk of weight gain and developing overweight or obesity over the next 10 years, compared with all other adults, and should be a target for obesity prevention policies, say U.K. researchers.
The research, published online Sept. 2, 2021, in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, showed that factors more traditionally associated with obesity – such as socioeconomic status and ethnicity – play less of a role than age.
“Our results show clearly that age is the most important sociodemographic factor for BMI [body mass index] change,” lead author Michail Katsoulis, PhD, Institute of Health Informatics, University College London, said in a press release.
Cosenior author Claudia Langenberg, PhD, agreed, adding young people “go through big life changes. They may start work, go to university, or leave home for the first time,” and the habits formed during these years “may stick through adulthood.”
Current obesity prevention guidelines are mainly directed at individuals who already have obesity, the researchers said in their article.
“As the evidence presented in our study suggests, the opportunity to modify weight gain is greatest in individuals who are young and do not yet have obesity,” they observed.
“If we are serious about preventing obesity, then we should develop interventions that can be targeted and are relevant for young adults,” added Dr. Langenberg, of the MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge, (England), and Berlin Institute of Health.
Risks for higher BMI substantially greater in the youngest adults
The researchers gathered data on more than 2 million adults aged 18-74 years registered with general practitioners in England. Participants had BMI and weight measurements recorded between Jan. 1, 1998, and June 30, 2016, with at least 1 year of follow-up. Overall, 58% were women, 76% were White, 9% had prevalent cardiovascular disease, and 4% had prevalent cancer.
Changes in BMI were assessed at 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years.
At 10 years, adults aged 18-24 years had the highest risk of transitioning from normal weight to overweight or obesity, compared with adults aged 65-74 years, at a greatest absolute risk of 37% versus 24% (odds ratio, 4.22).
Moreover, the results showed that adults aged 18-24 years who were already overweight or obese had a greater risk of transitioning to a higher BMI category during follow-up versus the oldest participants.
They had an absolute risk of 42% versus 18% of transitioning from overweight to class 1 and 2 obesity (OR, 4.60), and an absolute risk of transitioning from class 1 and 2 obesity to class 3 obesity of 22% versus 5% (OR, 5.87).
Online risk calculator and YouTube video help explain findings
While factors other than age were associated with transitioning to a higher BMI category, the association was less pronounced.
For example, the OR of transitioning from normal weight to overweight or obesity in the most socially deprived versus the least deprived areas was 1.23 in men and 1.12 in women. The OR for making the same transition in Black versus White individuals was 1.13.
The findings allowed the researchers to develop a series of nomograms to determine an individual’s absolute risk of transitioning to a higher BMI category over 10 years based on their baseline BMI category, age, sex, and Index of Multiple Deprivation quintile.
“We show that, within each stratum, the risks for transitioning to higher BMI categories were substantially higher in the youngest adult age group than in older age groups,” the team writes.
From this, they developed an open-access online risk calculator to help individuals calculate their risk of weight change over the next 1, 5, and 10 years. The calculator takes into account current weight, height, age, sex, ethnicity, and socioeconomic-area characteristics.
They have also posted a video on YouTube to help explain their findings.
COVID and obesity pandemics collide
Cosenior author Harry Hemingway, MD, PhD, also of University College London, believes that focusing on this young age group is especially critical now because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Calculating personal risk of transitioning to a higher weight category is important” as COVID-19 “collides with the obesity pandemic,” he said, noting that “people are exercising less and finding it harder to eat healthy diets during lockdowns.
“Health systems like the NHS [National Health Service] need to identify new ways to prevent obesity and its consequences,” he continued. “This study demonstrates that NHS data collected over time in primary care holds an important key to unlocking new insights for public health action.”
The study was funded by the British Heart Foundation, Health Data Research UK, the UK Medical Research Council, and the National Institute for Health Research. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals aged 18-24 years are at the highest risk of weight gain and developing overweight or obesity over the next 10 years, compared with all other adults, and should be a target for obesity prevention policies, say U.K. researchers.
The research, published online Sept. 2, 2021, in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, showed that factors more traditionally associated with obesity – such as socioeconomic status and ethnicity – play less of a role than age.
“Our results show clearly that age is the most important sociodemographic factor for BMI [body mass index] change,” lead author Michail Katsoulis, PhD, Institute of Health Informatics, University College London, said in a press release.
Cosenior author Claudia Langenberg, PhD, agreed, adding young people “go through big life changes. They may start work, go to university, or leave home for the first time,” and the habits formed during these years “may stick through adulthood.”
Current obesity prevention guidelines are mainly directed at individuals who already have obesity, the researchers said in their article.
“As the evidence presented in our study suggests, the opportunity to modify weight gain is greatest in individuals who are young and do not yet have obesity,” they observed.
“If we are serious about preventing obesity, then we should develop interventions that can be targeted and are relevant for young adults,” added Dr. Langenberg, of the MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge, (England), and Berlin Institute of Health.
Risks for higher BMI substantially greater in the youngest adults
The researchers gathered data on more than 2 million adults aged 18-74 years registered with general practitioners in England. Participants had BMI and weight measurements recorded between Jan. 1, 1998, and June 30, 2016, with at least 1 year of follow-up. Overall, 58% were women, 76% were White, 9% had prevalent cardiovascular disease, and 4% had prevalent cancer.
Changes in BMI were assessed at 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years.
At 10 years, adults aged 18-24 years had the highest risk of transitioning from normal weight to overweight or obesity, compared with adults aged 65-74 years, at a greatest absolute risk of 37% versus 24% (odds ratio, 4.22).
Moreover, the results showed that adults aged 18-24 years who were already overweight or obese had a greater risk of transitioning to a higher BMI category during follow-up versus the oldest participants.
They had an absolute risk of 42% versus 18% of transitioning from overweight to class 1 and 2 obesity (OR, 4.60), and an absolute risk of transitioning from class 1 and 2 obesity to class 3 obesity of 22% versus 5% (OR, 5.87).
Online risk calculator and YouTube video help explain findings
While factors other than age were associated with transitioning to a higher BMI category, the association was less pronounced.
For example, the OR of transitioning from normal weight to overweight or obesity in the most socially deprived versus the least deprived areas was 1.23 in men and 1.12 in women. The OR for making the same transition in Black versus White individuals was 1.13.
The findings allowed the researchers to develop a series of nomograms to determine an individual’s absolute risk of transitioning to a higher BMI category over 10 years based on their baseline BMI category, age, sex, and Index of Multiple Deprivation quintile.
“We show that, within each stratum, the risks for transitioning to higher BMI categories were substantially higher in the youngest adult age group than in older age groups,” the team writes.
From this, they developed an open-access online risk calculator to help individuals calculate their risk of weight change over the next 1, 5, and 10 years. The calculator takes into account current weight, height, age, sex, ethnicity, and socioeconomic-area characteristics.
They have also posted a video on YouTube to help explain their findings.
COVID and obesity pandemics collide
Cosenior author Harry Hemingway, MD, PhD, also of University College London, believes that focusing on this young age group is especially critical now because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Calculating personal risk of transitioning to a higher weight category is important” as COVID-19 “collides with the obesity pandemic,” he said, noting that “people are exercising less and finding it harder to eat healthy diets during lockdowns.
“Health systems like the NHS [National Health Service] need to identify new ways to prevent obesity and its consequences,” he continued. “This study demonstrates that NHS data collected over time in primary care holds an important key to unlocking new insights for public health action.”
The study was funded by the British Heart Foundation, Health Data Research UK, the UK Medical Research Council, and the National Institute for Health Research. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals aged 18-24 years are at the highest risk of weight gain and developing overweight or obesity over the next 10 years, compared with all other adults, and should be a target for obesity prevention policies, say U.K. researchers.
The research, published online Sept. 2, 2021, in The Lancet Diabetes and Endocrinology, showed that factors more traditionally associated with obesity – such as socioeconomic status and ethnicity – play less of a role than age.
“Our results show clearly that age is the most important sociodemographic factor for BMI [body mass index] change,” lead author Michail Katsoulis, PhD, Institute of Health Informatics, University College London, said in a press release.
Cosenior author Claudia Langenberg, PhD, agreed, adding young people “go through big life changes. They may start work, go to university, or leave home for the first time,” and the habits formed during these years “may stick through adulthood.”
Current obesity prevention guidelines are mainly directed at individuals who already have obesity, the researchers said in their article.
“As the evidence presented in our study suggests, the opportunity to modify weight gain is greatest in individuals who are young and do not yet have obesity,” they observed.
“If we are serious about preventing obesity, then we should develop interventions that can be targeted and are relevant for young adults,” added Dr. Langenberg, of the MRC Epidemiology Unit, University of Cambridge, (England), and Berlin Institute of Health.
Risks for higher BMI substantially greater in the youngest adults
The researchers gathered data on more than 2 million adults aged 18-74 years registered with general practitioners in England. Participants had BMI and weight measurements recorded between Jan. 1, 1998, and June 30, 2016, with at least 1 year of follow-up. Overall, 58% were women, 76% were White, 9% had prevalent cardiovascular disease, and 4% had prevalent cancer.
Changes in BMI were assessed at 1 year, 5 years, and 10 years.
At 10 years, adults aged 18-24 years had the highest risk of transitioning from normal weight to overweight or obesity, compared with adults aged 65-74 years, at a greatest absolute risk of 37% versus 24% (odds ratio, 4.22).
Moreover, the results showed that adults aged 18-24 years who were already overweight or obese had a greater risk of transitioning to a higher BMI category during follow-up versus the oldest participants.
They had an absolute risk of 42% versus 18% of transitioning from overweight to class 1 and 2 obesity (OR, 4.60), and an absolute risk of transitioning from class 1 and 2 obesity to class 3 obesity of 22% versus 5% (OR, 5.87).
Online risk calculator and YouTube video help explain findings
While factors other than age were associated with transitioning to a higher BMI category, the association was less pronounced.
For example, the OR of transitioning from normal weight to overweight or obesity in the most socially deprived versus the least deprived areas was 1.23 in men and 1.12 in women. The OR for making the same transition in Black versus White individuals was 1.13.
The findings allowed the researchers to develop a series of nomograms to determine an individual’s absolute risk of transitioning to a higher BMI category over 10 years based on their baseline BMI category, age, sex, and Index of Multiple Deprivation quintile.
“We show that, within each stratum, the risks for transitioning to higher BMI categories were substantially higher in the youngest adult age group than in older age groups,” the team writes.
From this, they developed an open-access online risk calculator to help individuals calculate their risk of weight change over the next 1, 5, and 10 years. The calculator takes into account current weight, height, age, sex, ethnicity, and socioeconomic-area characteristics.
They have also posted a video on YouTube to help explain their findings.
COVID and obesity pandemics collide
Cosenior author Harry Hemingway, MD, PhD, also of University College London, believes that focusing on this young age group is especially critical now because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
“Calculating personal risk of transitioning to a higher weight category is important” as COVID-19 “collides with the obesity pandemic,” he said, noting that “people are exercising less and finding it harder to eat healthy diets during lockdowns.
“Health systems like the NHS [National Health Service] need to identify new ways to prevent obesity and its consequences,” he continued. “This study demonstrates that NHS data collected over time in primary care holds an important key to unlocking new insights for public health action.”
The study was funded by the British Heart Foundation, Health Data Research UK, the UK Medical Research Council, and the National Institute for Health Research. The authors reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New Moderna vaccine data ‘support’ booster shot after 8 months
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Moderna has released new data that it said support the argument for COVID-19 booster shots – specifically showing that people who received a first shot of their mRNA vaccine a median of 13 months ago are more likely to experience a breakthrough infection compared to individuals who received a first shot a median of 8 months ago.
The findings come from the ongoing phase 3 COVE clinical trial, the results of which the Food and Drug Administration considered in granting emergency use authorization for the vaccine. In the initial stage of the trial, people were randomly assigned to receive the company’s mRNA vaccine or placebo.
according to the analysis of the open-label extension of the study during which placebo participants could cross over and get immunized as well.
The updated COVE trial data show that 88 breakthrough cases of COVID-19 occurred among 11,431 participants vaccinated between December 2020 and March 2021 (49.0 cases per 1,000 person-years).
In contrast, there were 162 breakthrough cases among 14,746 people vaccinated between July and October 2020 (77.1 cases per 1,000 person-years).
The breakthrough infections include 19 severe cases. Although not statically different, there was a trend toward fewer severe cases among the more recently vaccinated, at a rate of 3.3 per 1,000 person-years, compared with 6.2 per 1,000 person-years in the group vaccinated in 2020
The findings were posted as a preprint to the medRxiv server and have not yet been peer reviewed.
“The increased risk of breakthrough infections in COVE study participants who were vaccinated last year compared to more recently illustrates the impact of waning immunity and supports the need for a booster to maintain high levels of protection,” Moderna CEO Stéphane Bancel said in a company statement.
An FDA advisory committee is meeting Sept. 17 to look at the available evidence on boosters to help the agency decide whether the additional shots are warranted.
There is still a lot of debate in the medical community about the need for boosters. U.S. physicians and nurses are divided about the need for them and about how the country should prioritize its vaccine supplies, according to a Medscape poll of more than 1,700 clinicians that collected responses from Aug. 25 to Sept. 6, 2020.
The research was funded by Moderna, and also supported by the Office of the Assistant Secretary for Preparedness and Response, Biomedical Advanced Research and Development Authority, and by the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID vaccine preprint study prompts Twitter outrage
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A preprint study finding that the Pfizer-BioNTech mRNA COVID vaccine is associated with an increased risk for cardiac adverse events in teenage boys has elicited a firestorm on Twitter. Although some people issued thoughtful critiques, others lobbed insults against the authors, and still others accused them of either being antivaccine or stoking the fires of the vaccine skeptic movement.
The controversy began soon after the study was posted online September 8 on medRxiv. The authors conclude that for boys, the risk for a cardiac adverse event or hospitalization after the second dose of the Pfizer mRNA vaccine was “considerably higher” than the 120-day risk for hospitalization for COVID-19, “even at times of peak disease prevalence.” This was especially true for those aged 12 to 15 years and even those with no underlying health conditions.
The conclusion – as well as the paper’s source, the Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS), and its methodology, modeled after the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention assessment of the database – did not sit well with many.
“Your methodology hugely overestimates risk, which many commentators who are specialists in the field have highlighted,” tweeted Deepti Gurdasani, senior lecturer in epidemiology at Queen Mary University of London. “Why make this claim when you must know it’s wrong?”
“The authors don’t know what they are doing and they are following their own ideology,” tweeted Boback Ziaeian, MD, PhD, assistant professor of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles, in the cardiology division. Dr. Ziaeian also tweeted, “I believe the CDC is doing honest work and not dredging slop like you are.”
“Holy shit. Truly terrible methods in that paper,” tweeted Michael Mina, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and immunologist at the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, more bluntly.
Some pointed out that VAERS is often used by vaccine skeptics to spread misinformation. “‘Dumpster diving’ describes studies using #VAERS by authors (almost always antivaxxers) who don’t understand its limitations,” tweeted David Gorski, MD, PhD, the editor of Science-Based Medicine, who says in his Twitter bio that he “exposes quackery.”
Added Dr. Gorski: “Doctors fell into this trap with their study suggesting #CovidVaccine is more dangerous to children than #COVID19.”
Dr. Gorski said he did not think that the authors were antivaccine. But, he tweeted, “I’d argue that at least one of the authors (Stevenson) is grossly unqualified to analyze the data. Mandrola? Marginal. The other two *might* be qualified in public health/epi, but they clearly either had no clue about #VAERS limitations or didn’t take them seriously enough.”
Two of the authors, John Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist who is also a columnist for Medscape, and Tracy Beth Hoeg, MD, PhD, an epidemiologist and sports medicine specialist, told this news organization that their estimates are not definitive, owing to the nature of the VAERS database.
“I want to emphasize that our signal is hypothesis-generating,” said Dr. Mandrola. “There’s obviously more research that needs to be done.”
“I don’t think it should be used to establish a for-certain rate,” said Dr. Hoeg, about the study. “It’s not a perfect way of establishing what the rate of cardiac adverse events was, but it gives you an estimate, and generally with VAERS, it’s a significant underestimate.”
Both Dr. Hoeg and Dr. Mandrola said their analysis showed enough of a signal that it warranted a rush to publish. “We felt that it was super time-sensitive,” Dr. Mandrola said.
Vaccine risks versus COVID harm
The authors searched the VAERS system for children aged 12 to 17 years who had received one or two doses of an mRNA vaccine and had symptoms of myocarditis, pericarditis, myopericarditis, or chest pain, and also troponin levels available in the lab data.
Of the 257 patients they examined, 211 had peak troponin values available for analysis. All but one received the Pfizer vaccine. Results were stratified by age and sex.
The authors found that the rates of cardiac adverse events (CAEs) after dose 1 were 12.0 per million for 12- to 15-year-old boys and 8.2 per million for 16- and 17-year-old boys, compared with 0.0 per million and 2.0 per million for girls the same ages.
The estimates for the 12- to 15-year-old boys were 22% to 150% higher than what the CDC had previously reported.
After the second dose, the rate of CAEs for boys 12 to 15 years was 162.2 per million (143% to 280% higher than the CDC estimate) and for boys 16 and 17 years, it was 94.0 per million, or 30% to 40% higher than CDC estimate.
Dr. Mandrola said he and his colleagues found potentially more cases by using slightly broader search terms than those employed by the CDC but agreed with some critics that a limitation was that they did not call the reporting physicians, as is typical with CDC follow-up on VAERS reports.
The authors point to troponin levels as valid indicators of myocardial damage. Peak troponin levels exceeded 2 ng/mL in 71% of the 12- to 15-year-olds and 82% of 16- and 17-year-olds.
The study shows that for boys 12 to 15 years with no comorbidities, the risk for a CAE after the second dose would be 22.8 times higher than the risk for hospitalization for COVID-19 during periods of low disease burden, 6.0 times higher during periods of moderate transmission, and 4.3 times higher during periods of high transmission.
The authors acknowledge in the paper that their analysis “does not take into account any benefits the vaccine provides against transmission to others, long-term COVID-19 disease risk, or protection from nonsevere COVID-19 symptoms.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg told this news organization that they are currently recalculating their estimates because of the rising numbers of pediatric hospitalizations from the Delta variant surge.
Paper rejected by journals
Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that the paper went through peer-review at three journals but was rejected by all three, for reasons that were not made clear.
She and the other authors incorporated the reviewers’ feedback at each turn and included all of their suggestions in the paper that was ultimately uploaded to medRxiv, said Dr. Hoeg.
They decided to put it out as a preprint after the U.S. Food and Drug Administration issued its data and then a warning on June 25 about myocarditis with use of the Pfizer vaccine in children 12 to 15 years of age.
The preprint study was picked up by some media outlets, including The Telegraph and The Guardian newspapers, and tweeted out by vaccine skeptics like Robert W. Malone, MD.
Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Georgia), an outspoken vaccine skeptic, tweeted out the Guardian story saying that the findings mean “there is every reason to stop the covid vaccine mandates.”
Dr. Gorski noted in tweets and in a blog post that one of the paper’s coauthors, Josh Stevenson, is part of Rational Ground, a group that supports the Great Barrington Declaration and is against lockdowns and mask mandates.
Mr. Stevenson did not disclose his affiliation in the paper, and Dr. Hoeg said in an interview that she was unaware of the group and Mr. Stevenson’s association with it and that she did not have the impression that he was altering the data to show any bias.
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they are provaccine and that they were dismayed to find their work being used to support any agenda. “It’s very frustrating,” said Dr. Hoeg, adding that she understands that “when you publish research on a controversial topic, people are going to take it and use it for their agendas.”
Some on Twitter blamed the open and free-wheeling nature of preprints.
Harlan Krumholz, MD, SM, the Harold H. Hines, junior professor of medicine and public health at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., which oversees medRxiv, tweeted, “Do you get that the discussion about the preprint is exactly the purpose of #preprints. So that way when someone claims something, you can look at the source and experts can comment.”
But Dr. Ziaeian tweeted back, “Preprints like this one can be weaponized to stir anti-vaccine lies and damage public health.”
In turn, the Yale physician replied, “Unfortunately these days, almost anything can be weaponized, distorted, misunderstood.” Dr. Krumholz added: “There is no question that this preprint is worthy of deep vetting and discussion. But there is a #preprint artifact to examine.”
Measured support
Some clinicians signaled their support for open debate and the preprint’s findings.
“I’ve been very critical of preprints that are too quickly disseminated in the media, and this one is no exception,” tweeted Walid Gellad, MD, MPH, associate professor of medicine at the University of Pittsburgh. “On the other hand, I think the vitriol directed at these authors is wrong,” he added.
“Like it or not, the issue of myocarditis in kids is an issue. Other countries have made vaccination decisions because of this issue, not because they’re driven by some ideology,” he tweeted.
Dr. Gellad also notes that the FDA has estimated the risk could be as high as one in 5,000 and that the preprint numbers could actually be underestimates.
In a long thread, Frank Han, MD, an adult congenital and pediatric cardiologist at the University of Illinois, tweets that relying on the VAERS reports might be faulty and that advanced cardiac imaging – guided by strict criteria – is the best way to determine myocarditis. And, he tweeted, “Physician review of VAERS reports really matters.”
Dr. Han concluded that vaccination “trades in a significant risk with a much smaller risk. That’s what counts in the end.”
In a response, Dr. Mandrola called Han’s tweets “reasoned criticism of our analysis.” He adds that his and Dr. Hoeg’s study have limits, but “our point is not to avoid protecting kids, but how to do so most safely.”
Both Dr. Mandrola and Dr. Hoeg said they welcomed critiques, but they felt blindsided by the vehemence of some of the Twitter debate.
“Some of the vitriol was surprising,” Dr. Mandrola said. “I kind of have this naive notion that people would assume that we’re not bad people,” he added.
However, Dr. Mandrola is known on Twitter for sometimes being highly critical of other researchers’ work, referring to some studies as “howlers,” and has in the past called out others for citing those papers.
Dr. Hoeg said she found critiques about weaknesses in the methods to be helpful. But she said many tweets were “attacking us as people, or not really attacking anything about our study, but just attacking the finding,” which does not help anyone “figure out what we should do about the safety signal or how we can research it further.”
Said Dr. Mandrola: “Why would we just ignore that and go forward with two-shot vaccination as a mandate when other countries are looking at other strategies?”
He noted that the United Kingdom has announced that children 12 to 15 years of age should receive just one shot of the mRNA vaccines instead of two because of the risk for myocarditis. Sixteen- to 18-year-olds have already been advised to get only one dose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Three ‘bad news’ payment changes coming soon for physicians
Physicians are bracing for upcoming changes in reimbursement that may start within a few months. As doctors gear up for another wave of COVID, payment trends may not be the top priority, but some “uh oh” announcements in the fall of 2021 could have far-reaching implications that could affect your future.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a proposed rule in the summer covering key aspects of physician payment. Although the rule contained some small bright lights, the most important changes proposed were far from welcome.
Here’s what could be in store:
1. The highly anticipated Medicare Physician Fee Schedule ruling confirmed a sweeping payment cut. The drive to maintain budget neutrality forced the federal agency to reduce Medicare payments, on average, by nearly 4%. Many physicians are outraged at the proposed cut.
2. More bad news for 2022: Sequestration will be back. Sequestration is the mandatory, pesky, negative 2% adjustment on all Medicare payments. It had been put on hold and is set to return at the beginning of 2022.
Essentially, sequestration reduces what Medicare pays its providers for health services, but Medicare beneficiaries bear no responsibility for the cost difference. To prevent further debt, CMS imposes financially on hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers.
The Health Resources and Services Administration has funds remaining to reimburse for all COVID-related testing, treatment, and vaccines provided to uninsured individuals. You can apply and be reimbursed at Medicare rates for these services when COVID is the primary diagnosis (or secondary in the case of pregnancy). Patients need not be American citizens for you to get paid.
3. Down to a nail-biter: The final ruling is expected in early November. The situation smacks of earlier days when physicians clung to a precipice, waiting in anticipation for a legislative body to save them from the dreaded income plunge. Indeed, we are slipping back to the decade-long period when Congress kept coming to the rescue simply to maintain the status quo.
Many anticipate a last-minute Congressional intervention to save the day, particularly in the midst of another COVID spike. The promises of a stable reimbursement system made possible by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act have been far from realized, and there are signs that the payment landscape is in the midst of a fundamental transformation.
Other changes proposed in the 1,747-page ruling include:
Positive:
- More telehealth services will be covered by Medicare, including home visits.
- Tele–mental health services got a big boost; many restrictions were removed so that now the patient’s home is considered a permissible originating site. It also allows for audio-only (no visual required) encounters; the audio-only allowance will extend to opioid use disorder treatment services. Phone treatment is covered.
- Permanent adoption of G2252: The 11- to 20-minute virtual check-in code wasn’t just a one-time payment but will be reimbursed in perpetuity.
- Boosts in reimbursement for chronic care and principal care management codes, which range on the basis of service but indicate a commitment to pay for care coordination.
- Clarification of roles and billing opportunities for split/shared visits, which occur if a physician and advanced practice provider see the same patient on a particular day. Prepare for new coding rules to include a modifier. Previously, the rules for billing were muddled, so transparency helps guide payment opportunities.
- Delay of the appropriate use criteria for advanced imaging for 1 (more) year, a welcome postponement of the ruling that carries a significant administrative burden.
- Physician assistants will be able to bill Medicare directly, and referrals to be made to medical nutrition therapy by a nontreating physician.
- A new approach to patient cost-sharing for colorectal cancer screenings will be phased in. This area has caused problems in the past when the physician identifies a need for additional services (for example, polyp removal by a gastroenterologist during routine colonoscopy).
Not positive:
- Which specialties benefit and which get zapped? The anticipated impact by specialty ranges from hits to interventional radiologists (–9%) and vascular surgeons (–8%), to increases for family practitioners, hand surgeons, endocrinologists, and geriatricians, each estimated to gain a modest 2%. (The exception is portable x-ray supplier, with an estimated increase of 10%.) All other specialties fall in between.
- The proposed conversion factor for 2022 is $33.58, a 3.75% drop from the 2021 conversion factor of $34.89.
The proposed ruling also covered the Quality Payment Program, the overarching program of which the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the main track for participation. The proposal incorporates additional episode-based cost measures as well as updates to quality indicators and improvement activities.
MIPS penalties. The stakes are higher now, with 9% penalties on the table for nonparticipants. The government offers physicians the ability to officially get out of the program in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby staving off the steep penalty. The option, which is available through the end of the year, requires a simple application that can be completed on behalf of the entire practice. If you want out, now is the time to find and fill out that application.
Exempt from technology requirements. If the proposal is accepted, small practices – defined by CMS as 15 eligible clinicians or fewer – won’t have to file an annual application to reweight the “promoting interoperability” portion of the program. If acknowledged, small practices will automatically be exempt from the program’s technology section. That’s a big plus, as one of the many chief complaints from small practices is the onus of meeting the technology requirements, which include a security risk analysis, bi-directional health information exchange, public health reporting, and patient access to health information. Meeting the requirements is no small feat. That will only affect future years, so be sure to apply in 2021 if applicable for your practice.
Changes in MIPS. MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) are anticipated for 2023, with the government releasing details about proposed models for heart disease, rheumatology, joint repair, and more. The MVPs are slated to take over the traditional MIPS by 2027.
The program will shift to 30% of your score coming from the “cost” category, which is based on the government’s analysis of a physician’s claims – and, if attributed, the claims of the patients for whom you care. This area is tricky to manage, but recognize that the costs under scrutiny are the expenses paid by Medicare on behalf of its patients.
In essence, Medicare is measuring the cost of your patients as compared with your colleagues’ costs (in the form of specialty-based benchmarks). Therefore, if you’re referring, or ordering, a more costly set of diagnostic tests, assessments, or interventions than your peers, you’ll be dinged.
However, physicians are more likely this year to flat out reject participation in the federal payment program. Payouts have been paltry and dismal to date, and the buzz is that physicians just don’t consider it worth the effort. Of course, clearing the threshold (which is proposed at 70 points next year) is a must to avoid the penalty, but don’t go crazy to get a perfect score as it won’t count for much. 2022 is the final year that there are any monies for exceptional performance.
Considering that the payouts for exceptional performance have been less than 2% for several years now, it’s hard to justify dedicating resources to achieve perfection. Experts believe that even exceptional performance will only be worth pennies in bonus payments.
The fear of the stick, therefore, may be the only motivation. And that is subjective, as physicians weigh the effort required versus just taking the hit on the penalty. But the penalty is substantial, and so even without the incentive, it’s important to participate at least at the threshold.
Fewer cost-sharing waivers. While the federal government’s payment policies have a major impact on reimbursement, other forces may have broader implications. Commercial payers have rolled back cost-sharing waivers, bringing to light the significant financial responsibility that patients have for their health care in the form of deductibles, coinsurance, and so forth.
More than a third of Americans had trouble paying their health care bills before the pandemic; as patients catch up with services that were postponed or delayed because of the pandemic, this may expose challenges for you. Patients with unpaid bills translate into your financial burden.
Virtual-first health plans. Patients may be seeking alternatives to avoid the frustrating cycle of unpaid medical bills. This may be a factor propelling another trend: Lower-cost virtual-first health plans such as Alignment Health have taken hold in the market. As the name implies, insurance coverage features telehealth that extends to in-person services if necessary.
These disruptors may have their hands at least somewhat tied, however. The market may not be able to fully embrace telemedicine until state licensure is addressed. Despite the federal regulatory relaxations, states still control the distribution of medical care through licensure requirements. Many are rolling back their pandemic-based emergency orders and only allowing licensed physicians to see patients in their state, even over telemedicine.
While seemingly frustrating for physicians who want to see patients over state lines, the delays imposed by states may actually have a welcome effect. If licensure migrates to the federal level, there are many implications. For the purposes of this article, the competitive landscape will become incredibly aggressive. You will need to compete with Amazon Care, Walmart, Cigna, and many other well-funded national players that would love nothing more than to launch a campaign to target the entire nation. Investors are eager to capture part of the nearly quarter-trillion-dollar market, with telemedicine at 38 times prepandemic levels and no signs of abating.
Increased competition for insurers. While the proposed drop in Medicare reimbursement is frustrating, keep a pulse on the fact that your patients may soon be lured by vendors like Amazon and others eager to gain access to physician payments. Instead of analyzing Federal Registers in the future, we may be assessing stock prices.
Consider, therefore, how to ensure that your digital front door is at least available, if not wide open, in the meantime. The nature of physician payments is surely changing.
Ms. Woodcock is president of Woodcock & Associates, Atlanta. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are bracing for upcoming changes in reimbursement that may start within a few months. As doctors gear up for another wave of COVID, payment trends may not be the top priority, but some “uh oh” announcements in the fall of 2021 could have far-reaching implications that could affect your future.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a proposed rule in the summer covering key aspects of physician payment. Although the rule contained some small bright lights, the most important changes proposed were far from welcome.
Here’s what could be in store:
1. The highly anticipated Medicare Physician Fee Schedule ruling confirmed a sweeping payment cut. The drive to maintain budget neutrality forced the federal agency to reduce Medicare payments, on average, by nearly 4%. Many physicians are outraged at the proposed cut.
2. More bad news for 2022: Sequestration will be back. Sequestration is the mandatory, pesky, negative 2% adjustment on all Medicare payments. It had been put on hold and is set to return at the beginning of 2022.
Essentially, sequestration reduces what Medicare pays its providers for health services, but Medicare beneficiaries bear no responsibility for the cost difference. To prevent further debt, CMS imposes financially on hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers.
The Health Resources and Services Administration has funds remaining to reimburse for all COVID-related testing, treatment, and vaccines provided to uninsured individuals. You can apply and be reimbursed at Medicare rates for these services when COVID is the primary diagnosis (or secondary in the case of pregnancy). Patients need not be American citizens for you to get paid.
3. Down to a nail-biter: The final ruling is expected in early November. The situation smacks of earlier days when physicians clung to a precipice, waiting in anticipation for a legislative body to save them from the dreaded income plunge. Indeed, we are slipping back to the decade-long period when Congress kept coming to the rescue simply to maintain the status quo.
Many anticipate a last-minute Congressional intervention to save the day, particularly in the midst of another COVID spike. The promises of a stable reimbursement system made possible by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act have been far from realized, and there are signs that the payment landscape is in the midst of a fundamental transformation.
Other changes proposed in the 1,747-page ruling include:
Positive:
- More telehealth services will be covered by Medicare, including home visits.
- Tele–mental health services got a big boost; many restrictions were removed so that now the patient’s home is considered a permissible originating site. It also allows for audio-only (no visual required) encounters; the audio-only allowance will extend to opioid use disorder treatment services. Phone treatment is covered.
- Permanent adoption of G2252: The 11- to 20-minute virtual check-in code wasn’t just a one-time payment but will be reimbursed in perpetuity.
- Boosts in reimbursement for chronic care and principal care management codes, which range on the basis of service but indicate a commitment to pay for care coordination.
- Clarification of roles and billing opportunities for split/shared visits, which occur if a physician and advanced practice provider see the same patient on a particular day. Prepare for new coding rules to include a modifier. Previously, the rules for billing were muddled, so transparency helps guide payment opportunities.
- Delay of the appropriate use criteria for advanced imaging for 1 (more) year, a welcome postponement of the ruling that carries a significant administrative burden.
- Physician assistants will be able to bill Medicare directly, and referrals to be made to medical nutrition therapy by a nontreating physician.
- A new approach to patient cost-sharing for colorectal cancer screenings will be phased in. This area has caused problems in the past when the physician identifies a need for additional services (for example, polyp removal by a gastroenterologist during routine colonoscopy).
Not positive:
- Which specialties benefit and which get zapped? The anticipated impact by specialty ranges from hits to interventional radiologists (–9%) and vascular surgeons (–8%), to increases for family practitioners, hand surgeons, endocrinologists, and geriatricians, each estimated to gain a modest 2%. (The exception is portable x-ray supplier, with an estimated increase of 10%.) All other specialties fall in between.
- The proposed conversion factor for 2022 is $33.58, a 3.75% drop from the 2021 conversion factor of $34.89.
The proposed ruling also covered the Quality Payment Program, the overarching program of which the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the main track for participation. The proposal incorporates additional episode-based cost measures as well as updates to quality indicators and improvement activities.
MIPS penalties. The stakes are higher now, with 9% penalties on the table for nonparticipants. The government offers physicians the ability to officially get out of the program in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby staving off the steep penalty. The option, which is available through the end of the year, requires a simple application that can be completed on behalf of the entire practice. If you want out, now is the time to find and fill out that application.
Exempt from technology requirements. If the proposal is accepted, small practices – defined by CMS as 15 eligible clinicians or fewer – won’t have to file an annual application to reweight the “promoting interoperability” portion of the program. If acknowledged, small practices will automatically be exempt from the program’s technology section. That’s a big plus, as one of the many chief complaints from small practices is the onus of meeting the technology requirements, which include a security risk analysis, bi-directional health information exchange, public health reporting, and patient access to health information. Meeting the requirements is no small feat. That will only affect future years, so be sure to apply in 2021 if applicable for your practice.
Changes in MIPS. MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) are anticipated for 2023, with the government releasing details about proposed models for heart disease, rheumatology, joint repair, and more. The MVPs are slated to take over the traditional MIPS by 2027.
The program will shift to 30% of your score coming from the “cost” category, which is based on the government’s analysis of a physician’s claims – and, if attributed, the claims of the patients for whom you care. This area is tricky to manage, but recognize that the costs under scrutiny are the expenses paid by Medicare on behalf of its patients.
In essence, Medicare is measuring the cost of your patients as compared with your colleagues’ costs (in the form of specialty-based benchmarks). Therefore, if you’re referring, or ordering, a more costly set of diagnostic tests, assessments, or interventions than your peers, you’ll be dinged.
However, physicians are more likely this year to flat out reject participation in the federal payment program. Payouts have been paltry and dismal to date, and the buzz is that physicians just don’t consider it worth the effort. Of course, clearing the threshold (which is proposed at 70 points next year) is a must to avoid the penalty, but don’t go crazy to get a perfect score as it won’t count for much. 2022 is the final year that there are any monies for exceptional performance.
Considering that the payouts for exceptional performance have been less than 2% for several years now, it’s hard to justify dedicating resources to achieve perfection. Experts believe that even exceptional performance will only be worth pennies in bonus payments.
The fear of the stick, therefore, may be the only motivation. And that is subjective, as physicians weigh the effort required versus just taking the hit on the penalty. But the penalty is substantial, and so even without the incentive, it’s important to participate at least at the threshold.
Fewer cost-sharing waivers. While the federal government’s payment policies have a major impact on reimbursement, other forces may have broader implications. Commercial payers have rolled back cost-sharing waivers, bringing to light the significant financial responsibility that patients have for their health care in the form of deductibles, coinsurance, and so forth.
More than a third of Americans had trouble paying their health care bills before the pandemic; as patients catch up with services that were postponed or delayed because of the pandemic, this may expose challenges for you. Patients with unpaid bills translate into your financial burden.
Virtual-first health plans. Patients may be seeking alternatives to avoid the frustrating cycle of unpaid medical bills. This may be a factor propelling another trend: Lower-cost virtual-first health plans such as Alignment Health have taken hold in the market. As the name implies, insurance coverage features telehealth that extends to in-person services if necessary.
These disruptors may have their hands at least somewhat tied, however. The market may not be able to fully embrace telemedicine until state licensure is addressed. Despite the federal regulatory relaxations, states still control the distribution of medical care through licensure requirements. Many are rolling back their pandemic-based emergency orders and only allowing licensed physicians to see patients in their state, even over telemedicine.
While seemingly frustrating for physicians who want to see patients over state lines, the delays imposed by states may actually have a welcome effect. If licensure migrates to the federal level, there are many implications. For the purposes of this article, the competitive landscape will become incredibly aggressive. You will need to compete with Amazon Care, Walmart, Cigna, and many other well-funded national players that would love nothing more than to launch a campaign to target the entire nation. Investors are eager to capture part of the nearly quarter-trillion-dollar market, with telemedicine at 38 times prepandemic levels and no signs of abating.
Increased competition for insurers. While the proposed drop in Medicare reimbursement is frustrating, keep a pulse on the fact that your patients may soon be lured by vendors like Amazon and others eager to gain access to physician payments. Instead of analyzing Federal Registers in the future, we may be assessing stock prices.
Consider, therefore, how to ensure that your digital front door is at least available, if not wide open, in the meantime. The nature of physician payments is surely changing.
Ms. Woodcock is president of Woodcock & Associates, Atlanta. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physicians are bracing for upcoming changes in reimbursement that may start within a few months. As doctors gear up for another wave of COVID, payment trends may not be the top priority, but some “uh oh” announcements in the fall of 2021 could have far-reaching implications that could affect your future.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services issued a proposed rule in the summer covering key aspects of physician payment. Although the rule contained some small bright lights, the most important changes proposed were far from welcome.
Here’s what could be in store:
1. The highly anticipated Medicare Physician Fee Schedule ruling confirmed a sweeping payment cut. The drive to maintain budget neutrality forced the federal agency to reduce Medicare payments, on average, by nearly 4%. Many physicians are outraged at the proposed cut.
2. More bad news for 2022: Sequestration will be back. Sequestration is the mandatory, pesky, negative 2% adjustment on all Medicare payments. It had been put on hold and is set to return at the beginning of 2022.
Essentially, sequestration reduces what Medicare pays its providers for health services, but Medicare beneficiaries bear no responsibility for the cost difference. To prevent further debt, CMS imposes financially on hospitals, physicians, and other health care providers.
The Health Resources and Services Administration has funds remaining to reimburse for all COVID-related testing, treatment, and vaccines provided to uninsured individuals. You can apply and be reimbursed at Medicare rates for these services when COVID is the primary diagnosis (or secondary in the case of pregnancy). Patients need not be American citizens for you to get paid.
3. Down to a nail-biter: The final ruling is expected in early November. The situation smacks of earlier days when physicians clung to a precipice, waiting in anticipation for a legislative body to save them from the dreaded income plunge. Indeed, we are slipping back to the decade-long period when Congress kept coming to the rescue simply to maintain the status quo.
Many anticipate a last-minute Congressional intervention to save the day, particularly in the midst of another COVID spike. The promises of a stable reimbursement system made possible by the Medicare Access and CHIP Reauthorization Act have been far from realized, and there are signs that the payment landscape is in the midst of a fundamental transformation.
Other changes proposed in the 1,747-page ruling include:
Positive:
- More telehealth services will be covered by Medicare, including home visits.
- Tele–mental health services got a big boost; many restrictions were removed so that now the patient’s home is considered a permissible originating site. It also allows for audio-only (no visual required) encounters; the audio-only allowance will extend to opioid use disorder treatment services. Phone treatment is covered.
- Permanent adoption of G2252: The 11- to 20-minute virtual check-in code wasn’t just a one-time payment but will be reimbursed in perpetuity.
- Boosts in reimbursement for chronic care and principal care management codes, which range on the basis of service but indicate a commitment to pay for care coordination.
- Clarification of roles and billing opportunities for split/shared visits, which occur if a physician and advanced practice provider see the same patient on a particular day. Prepare for new coding rules to include a modifier. Previously, the rules for billing were muddled, so transparency helps guide payment opportunities.
- Delay of the appropriate use criteria for advanced imaging for 1 (more) year, a welcome postponement of the ruling that carries a significant administrative burden.
- Physician assistants will be able to bill Medicare directly, and referrals to be made to medical nutrition therapy by a nontreating physician.
- A new approach to patient cost-sharing for colorectal cancer screenings will be phased in. This area has caused problems in the past when the physician identifies a need for additional services (for example, polyp removal by a gastroenterologist during routine colonoscopy).
Not positive:
- Which specialties benefit and which get zapped? The anticipated impact by specialty ranges from hits to interventional radiologists (–9%) and vascular surgeons (–8%), to increases for family practitioners, hand surgeons, endocrinologists, and geriatricians, each estimated to gain a modest 2%. (The exception is portable x-ray supplier, with an estimated increase of 10%.) All other specialties fall in between.
- The proposed conversion factor for 2022 is $33.58, a 3.75% drop from the 2021 conversion factor of $34.89.
The proposed ruling also covered the Quality Payment Program, the overarching program of which the Merit-based Incentive Payment System (MIPS) is the main track for participation. The proposal incorporates additional episode-based cost measures as well as updates to quality indicators and improvement activities.
MIPS penalties. The stakes are higher now, with 9% penalties on the table for nonparticipants. The government offers physicians the ability to officially get out of the program in 2021 because of the COVID-19 pandemic, thereby staving off the steep penalty. The option, which is available through the end of the year, requires a simple application that can be completed on behalf of the entire practice. If you want out, now is the time to find and fill out that application.
Exempt from technology requirements. If the proposal is accepted, small practices – defined by CMS as 15 eligible clinicians or fewer – won’t have to file an annual application to reweight the “promoting interoperability” portion of the program. If acknowledged, small practices will automatically be exempt from the program’s technology section. That’s a big plus, as one of the many chief complaints from small practices is the onus of meeting the technology requirements, which include a security risk analysis, bi-directional health information exchange, public health reporting, and patient access to health information. Meeting the requirements is no small feat. That will only affect future years, so be sure to apply in 2021 if applicable for your practice.
Changes in MIPS. MIPS Value Pathways (MVPs) are anticipated for 2023, with the government releasing details about proposed models for heart disease, rheumatology, joint repair, and more. The MVPs are slated to take over the traditional MIPS by 2027.
The program will shift to 30% of your score coming from the “cost” category, which is based on the government’s analysis of a physician’s claims – and, if attributed, the claims of the patients for whom you care. This area is tricky to manage, but recognize that the costs under scrutiny are the expenses paid by Medicare on behalf of its patients.
In essence, Medicare is measuring the cost of your patients as compared with your colleagues’ costs (in the form of specialty-based benchmarks). Therefore, if you’re referring, or ordering, a more costly set of diagnostic tests, assessments, or interventions than your peers, you’ll be dinged.
However, physicians are more likely this year to flat out reject participation in the federal payment program. Payouts have been paltry and dismal to date, and the buzz is that physicians just don’t consider it worth the effort. Of course, clearing the threshold (which is proposed at 70 points next year) is a must to avoid the penalty, but don’t go crazy to get a perfect score as it won’t count for much. 2022 is the final year that there are any monies for exceptional performance.
Considering that the payouts for exceptional performance have been less than 2% for several years now, it’s hard to justify dedicating resources to achieve perfection. Experts believe that even exceptional performance will only be worth pennies in bonus payments.
The fear of the stick, therefore, may be the only motivation. And that is subjective, as physicians weigh the effort required versus just taking the hit on the penalty. But the penalty is substantial, and so even without the incentive, it’s important to participate at least at the threshold.
Fewer cost-sharing waivers. While the federal government’s payment policies have a major impact on reimbursement, other forces may have broader implications. Commercial payers have rolled back cost-sharing waivers, bringing to light the significant financial responsibility that patients have for their health care in the form of deductibles, coinsurance, and so forth.
More than a third of Americans had trouble paying their health care bills before the pandemic; as patients catch up with services that were postponed or delayed because of the pandemic, this may expose challenges for you. Patients with unpaid bills translate into your financial burden.
Virtual-first health plans. Patients may be seeking alternatives to avoid the frustrating cycle of unpaid medical bills. This may be a factor propelling another trend: Lower-cost virtual-first health plans such as Alignment Health have taken hold in the market. As the name implies, insurance coverage features telehealth that extends to in-person services if necessary.
These disruptors may have their hands at least somewhat tied, however. The market may not be able to fully embrace telemedicine until state licensure is addressed. Despite the federal regulatory relaxations, states still control the distribution of medical care through licensure requirements. Many are rolling back their pandemic-based emergency orders and only allowing licensed physicians to see patients in their state, even over telemedicine.
While seemingly frustrating for physicians who want to see patients over state lines, the delays imposed by states may actually have a welcome effect. If licensure migrates to the federal level, there are many implications. For the purposes of this article, the competitive landscape will become incredibly aggressive. You will need to compete with Amazon Care, Walmart, Cigna, and many other well-funded national players that would love nothing more than to launch a campaign to target the entire nation. Investors are eager to capture part of the nearly quarter-trillion-dollar market, with telemedicine at 38 times prepandemic levels and no signs of abating.
Increased competition for insurers. While the proposed drop in Medicare reimbursement is frustrating, keep a pulse on the fact that your patients may soon be lured by vendors like Amazon and others eager to gain access to physician payments. Instead of analyzing Federal Registers in the future, we may be assessing stock prices.
Consider, therefore, how to ensure that your digital front door is at least available, if not wide open, in the meantime. The nature of physician payments is surely changing.
Ms. Woodcock is president of Woodcock & Associates, Atlanta. She has disclosed no relevant financial relationships. A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID wars, part nine: The rise of iodine
Onions and iodine and COVID, oh my!
As surely as the sun rises, anti-vaxxers will come up with some wacky and dangerous new idea to prevent COVID. While perhaps nothing will top horse medication, gargling iodine (or spraying it into the nose) is also not a great idea.
Multiple social media posts have extolled the virtues of gargling Betadine (povidone iodine), which is a TOPICAL disinfectant commonly used in EDs and operating rooms. One post cited a paper by a Bangladeshi plastic surgeon who hypothesized on the subject, and if that’s not a peer-reviewed, rigorously researched source, we don’t know what is.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, actual medical experts do not recommend using Betadine to prevent COVID. Ingesting it can cause iodine poisoning and plenty of nasty GI side effects; while Betadine does make a diluted product safe for gargling use (used for the treatment of sore throats), it has not shown any effectiveness against viruses or COVID in particular.
A New York ED doctor summed it up best in the Rolling Stone article when he was told anti-vaxxers were gargling iodine: He offered a choice four-letter expletive, then said, “Of course they are.”
But wait! We’ve got a two-for-one deal on dubious COVID cures this week. Health experts in Myanmar (Burma to all the “Seinfeld” fans) and Thailand have been combating social media posts claiming that onion fumes will cure COVID. All you need to do is slice an onion in half, sniff it for a while, then chew on a second onion, and your COVID will be cured!
In what is surely the most radical understatement of the year, a professor in the department of preventive and social medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, said in the AFP article that there is “no solid evidence” to support onion sniffing from “any clinical research.”
We’re just going to assume the expletives that surely followed were kept off the record.
Pro-Trump state governor encourages vaccination
Clearly, the politics of COVID-19 have been working against the science of COVID-19. Politicians can’t, or won’t, agree on what to do about it, and many prominent Republicans have been actively resisting vaccine and mask mandates.
There is at least one Republican governor who has wholeheartedly encouraged vaccination in his pro-Trump state. We’re talking about Gov. Jim Justice of West Virginia, and not for the first time.
The Washington Post has detailed his efforts to promote the COVID vaccine, and we would like to share a couple of examples.
In June he suggested that people who didn’t get vaccinated were “entering the death drawing.” He followed that by saying, “If I knew for certain that there was going to be eight or nine people die by next Tuesday, and I could be one of them if I don’t take the vaccine ... What in the world do you think I would do? I mean, I would run over top of somebody.”
More recently, Gov. Justice took on vaccine conspiracy theories.
“For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the very same people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Nuff said.
Jet lag may be a gut feeling
After a week-long vacation halfway around the world, it’s time to go back to your usual routine and time zone. But don’t forget about that free souvenir, jet lag. A disrupted circadian rhythm can be a real bummer, but researchers may have found the fix in your belly.
In a study funded by the U.S. Navy, researchers at the University of Colorado, Boulder, looked into how the presence of a prebiotic in one’s diet can have on the disrupted biological clocks. They’re not the same as probiotics, which help you stay regular in another way. Prebiotics work as food to help the good gut bacteria you already have. An earlier study had suggested that prebiotics may have a positive effect on the brain.
To test the theory, the researchers gave one group of rats their regular food while another group received food with two different prebiotics. After manipulating the rats’ light-dark cycle for 8 weeks to give the illusion of traveling to a time zone 12 hours ahead every week, they found that the rats who ate the prebiotics were able to bounce back faster.
The possibility of ingesting something to keep your body clock regular sounds like a dream, but the researchers don’t really advise you to snatch all the supplements you can at your local pharmacy just yet.
“If you know you are going to come into a challenge, you could take a look at some of the prebiotics that are available. Just realize that they are not customized yet, so it might work for you but it won’t work for your neighbor,” said senior author Monika Fleshner.
Until there’s more conclusive research, just be good to your bacteria.
How to make stuff up and influence people
You’ve probably heard that we use only 10% of our brain. It’s right up there with “the Earth is flat” and “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
The idea that we use only 10% of our brains can probably be traced back to the early 1900s, suggests Discover magazine, when psychologist William James wrote, “Compared with what we ought to be, we are only half awake. Our fires are damped, our drafts are checked. We are making use of only a small part of our possible mental and physical resources.”
There are many different takes on it, but it is indeed a myth that we use only 10% of our brains. Dale Carnegie, the public speaking teacher, seems to be the one who put the specific number of 10% on James’ idea in his 1936 book, “How to Win Friends and Influence People.”
“We think that people are excited by this pseudo fact because it’s very optimistic,” neuroscientist Sandra Aamodt told Discover. “Wouldn’t we all love to think our brains had some giant pool of untapped potential that we’re not using?”
The reality is, we do use our whole brain. Functional MRI shows that different parts of the brain are used for different things such as language and memories. “Not all at the same time, of course. But every part of the brain has a job to do,” the Discover article explained.
There are many things we don’t know about how the brain works, but at least you know you use more than 10%. After all, a brain just told you so.
Onions and iodine and COVID, oh my!
As surely as the sun rises, anti-vaxxers will come up with some wacky and dangerous new idea to prevent COVID. While perhaps nothing will top horse medication, gargling iodine (or spraying it into the nose) is also not a great idea.
Multiple social media posts have extolled the virtues of gargling Betadine (povidone iodine), which is a TOPICAL disinfectant commonly used in EDs and operating rooms. One post cited a paper by a Bangladeshi plastic surgeon who hypothesized on the subject, and if that’s not a peer-reviewed, rigorously researched source, we don’t know what is.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, actual medical experts do not recommend using Betadine to prevent COVID. Ingesting it can cause iodine poisoning and plenty of nasty GI side effects; while Betadine does make a diluted product safe for gargling use (used for the treatment of sore throats), it has not shown any effectiveness against viruses or COVID in particular.
A New York ED doctor summed it up best in the Rolling Stone article when he was told anti-vaxxers were gargling iodine: He offered a choice four-letter expletive, then said, “Of course they are.”
But wait! We’ve got a two-for-one deal on dubious COVID cures this week. Health experts in Myanmar (Burma to all the “Seinfeld” fans) and Thailand have been combating social media posts claiming that onion fumes will cure COVID. All you need to do is slice an onion in half, sniff it for a while, then chew on a second onion, and your COVID will be cured!
In what is surely the most radical understatement of the year, a professor in the department of preventive and social medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, said in the AFP article that there is “no solid evidence” to support onion sniffing from “any clinical research.”
We’re just going to assume the expletives that surely followed were kept off the record.
Pro-Trump state governor encourages vaccination
Clearly, the politics of COVID-19 have been working against the science of COVID-19. Politicians can’t, or won’t, agree on what to do about it, and many prominent Republicans have been actively resisting vaccine and mask mandates.
There is at least one Republican governor who has wholeheartedly encouraged vaccination in his pro-Trump state. We’re talking about Gov. Jim Justice of West Virginia, and not for the first time.
The Washington Post has detailed his efforts to promote the COVID vaccine, and we would like to share a couple of examples.
In June he suggested that people who didn’t get vaccinated were “entering the death drawing.” He followed that by saying, “If I knew for certain that there was going to be eight or nine people die by next Tuesday, and I could be one of them if I don’t take the vaccine ... What in the world do you think I would do? I mean, I would run over top of somebody.”
More recently, Gov. Justice took on vaccine conspiracy theories.
“For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the very same people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Nuff said.
Jet lag may be a gut feeling
After a week-long vacation halfway around the world, it’s time to go back to your usual routine and time zone. But don’t forget about that free souvenir, jet lag. A disrupted circadian rhythm can be a real bummer, but researchers may have found the fix in your belly.
In a study funded by the U.S. Navy, researchers at the University of Colorado, Boulder, looked into how the presence of a prebiotic in one’s diet can have on the disrupted biological clocks. They’re not the same as probiotics, which help you stay regular in another way. Prebiotics work as food to help the good gut bacteria you already have. An earlier study had suggested that prebiotics may have a positive effect on the brain.
To test the theory, the researchers gave one group of rats their regular food while another group received food with two different prebiotics. After manipulating the rats’ light-dark cycle for 8 weeks to give the illusion of traveling to a time zone 12 hours ahead every week, they found that the rats who ate the prebiotics were able to bounce back faster.
The possibility of ingesting something to keep your body clock regular sounds like a dream, but the researchers don’t really advise you to snatch all the supplements you can at your local pharmacy just yet.
“If you know you are going to come into a challenge, you could take a look at some of the prebiotics that are available. Just realize that they are not customized yet, so it might work for you but it won’t work for your neighbor,” said senior author Monika Fleshner.
Until there’s more conclusive research, just be good to your bacteria.
How to make stuff up and influence people
You’ve probably heard that we use only 10% of our brain. It’s right up there with “the Earth is flat” and “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
The idea that we use only 10% of our brains can probably be traced back to the early 1900s, suggests Discover magazine, when psychologist William James wrote, “Compared with what we ought to be, we are only half awake. Our fires are damped, our drafts are checked. We are making use of only a small part of our possible mental and physical resources.”
There are many different takes on it, but it is indeed a myth that we use only 10% of our brains. Dale Carnegie, the public speaking teacher, seems to be the one who put the specific number of 10% on James’ idea in his 1936 book, “How to Win Friends and Influence People.”
“We think that people are excited by this pseudo fact because it’s very optimistic,” neuroscientist Sandra Aamodt told Discover. “Wouldn’t we all love to think our brains had some giant pool of untapped potential that we’re not using?”
The reality is, we do use our whole brain. Functional MRI shows that different parts of the brain are used for different things such as language and memories. “Not all at the same time, of course. But every part of the brain has a job to do,” the Discover article explained.
There are many things we don’t know about how the brain works, but at least you know you use more than 10%. After all, a brain just told you so.
Onions and iodine and COVID, oh my!
As surely as the sun rises, anti-vaxxers will come up with some wacky and dangerous new idea to prevent COVID. While perhaps nothing will top horse medication, gargling iodine (or spraying it into the nose) is also not a great idea.
Multiple social media posts have extolled the virtues of gargling Betadine (povidone iodine), which is a TOPICAL disinfectant commonly used in EDs and operating rooms. One post cited a paper by a Bangladeshi plastic surgeon who hypothesized on the subject, and if that’s not a peer-reviewed, rigorously researched source, we don’t know what is.
Perhaps unsurprisingly, actual medical experts do not recommend using Betadine to prevent COVID. Ingesting it can cause iodine poisoning and plenty of nasty GI side effects; while Betadine does make a diluted product safe for gargling use (used for the treatment of sore throats), it has not shown any effectiveness against viruses or COVID in particular.
A New York ED doctor summed it up best in the Rolling Stone article when he was told anti-vaxxers were gargling iodine: He offered a choice four-letter expletive, then said, “Of course they are.”
But wait! We’ve got a two-for-one deal on dubious COVID cures this week. Health experts in Myanmar (Burma to all the “Seinfeld” fans) and Thailand have been combating social media posts claiming that onion fumes will cure COVID. All you need to do is slice an onion in half, sniff it for a while, then chew on a second onion, and your COVID will be cured!
In what is surely the most radical understatement of the year, a professor in the department of preventive and social medicine at Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, said in the AFP article that there is “no solid evidence” to support onion sniffing from “any clinical research.”
We’re just going to assume the expletives that surely followed were kept off the record.
Pro-Trump state governor encourages vaccination
Clearly, the politics of COVID-19 have been working against the science of COVID-19. Politicians can’t, or won’t, agree on what to do about it, and many prominent Republicans have been actively resisting vaccine and mask mandates.
There is at least one Republican governor who has wholeheartedly encouraged vaccination in his pro-Trump state. We’re talking about Gov. Jim Justice of West Virginia, and not for the first time.
The Washington Post has detailed his efforts to promote the COVID vaccine, and we would like to share a couple of examples.
In June he suggested that people who didn’t get vaccinated were “entering the death drawing.” He followed that by saying, “If I knew for certain that there was going to be eight or nine people die by next Tuesday, and I could be one of them if I don’t take the vaccine ... What in the world do you think I would do? I mean, I would run over top of somebody.”
More recently, Gov. Justice took on vaccine conspiracy theories.
“For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the very same people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Nuff said.
Jet lag may be a gut feeling
After a week-long vacation halfway around the world, it’s time to go back to your usual routine and time zone. But don’t forget about that free souvenir, jet lag. A disrupted circadian rhythm can be a real bummer, but researchers may have found the fix in your belly.
In a study funded by the U.S. Navy, researchers at the University of Colorado, Boulder, looked into how the presence of a prebiotic in one’s diet can have on the disrupted biological clocks. They’re not the same as probiotics, which help you stay regular in another way. Prebiotics work as food to help the good gut bacteria you already have. An earlier study had suggested that prebiotics may have a positive effect on the brain.
To test the theory, the researchers gave one group of rats their regular food while another group received food with two different prebiotics. After manipulating the rats’ light-dark cycle for 8 weeks to give the illusion of traveling to a time zone 12 hours ahead every week, they found that the rats who ate the prebiotics were able to bounce back faster.
The possibility of ingesting something to keep your body clock regular sounds like a dream, but the researchers don’t really advise you to snatch all the supplements you can at your local pharmacy just yet.
“If you know you are going to come into a challenge, you could take a look at some of the prebiotics that are available. Just realize that they are not customized yet, so it might work for you but it won’t work for your neighbor,” said senior author Monika Fleshner.
Until there’s more conclusive research, just be good to your bacteria.
How to make stuff up and influence people
You’ve probably heard that we use only 10% of our brain. It’s right up there with “the Earth is flat” and “an apple a day keeps the doctor away.”
The idea that we use only 10% of our brains can probably be traced back to the early 1900s, suggests Discover magazine, when psychologist William James wrote, “Compared with what we ought to be, we are only half awake. Our fires are damped, our drafts are checked. We are making use of only a small part of our possible mental and physical resources.”
There are many different takes on it, but it is indeed a myth that we use only 10% of our brains. Dale Carnegie, the public speaking teacher, seems to be the one who put the specific number of 10% on James’ idea in his 1936 book, “How to Win Friends and Influence People.”
“We think that people are excited by this pseudo fact because it’s very optimistic,” neuroscientist Sandra Aamodt told Discover. “Wouldn’t we all love to think our brains had some giant pool of untapped potential that we’re not using?”
The reality is, we do use our whole brain. Functional MRI shows that different parts of the brain are used for different things such as language and memories. “Not all at the same time, of course. But every part of the brain has a job to do,” the Discover article explained.
There are many things we don’t know about how the brain works, but at least you know you use more than 10%. After all, a brain just told you so.
A boy went to a COVID-swamped ER. He waited for hours. Then his appendix burst.
Seth was finally diagnosed with appendicitis more than six hours after arriving at Cleveland Clinic Martin Health North Hospital in late July. Around midnight, he was taken by ambulance to a sister hospital about a half-hour away that was better equipped to perform pediatric emergency surgery, his father said.
But by the time the doctor operated in the early morning hours, Seth’s appendix had burst – a potentially fatal complication.
They, too, need emergency care, but the sheer number of COVID-19 cases is crowding them out. Treatment has often been delayed as ERs scramble to find a bed that may be hundreds of miles away.
Some health officials now worry about looming ethical decisions. Last week, Idaho activated a “crisis standard of care,” which one official described as a “last resort.” It allows overwhelmed hospitals to ration care, including “in rare cases, ventilator (breathing machines) or intensive care unit (ICU) beds may need to be used for those who are most likely to survive, while patients who are not likely to survive may not be able to receive one,” the state’s website said.
The federal government’s latest data shows Alabama is at 100% of its intensive care unit capacity, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi and Arkansas at more than 90% ICU capacity. Florida is just under 90%.
It’s the COVID-19 cases that are dominating. In Georgia, 62% of the ICU beds are now filled with just COVID-19 patients. In Texas, the percentage is nearly half.
To have so many ICU beds pressed into service for a single diagnosis is “unheard of,” said Dr. Hasan Kakli, an emergency room physician at Bellville Medical Center in Bellville, Texas, about an hour from Houston. “It’s approaching apocalyptic.”
In Texas, state data released Monday showed there were only 319 adult and 104 pediatric staffed ICU beds available across a state of 29 million people.
Hospitals need to hold some ICU beds for other patients, such as those recovering from major surgery or other critical conditions such as stroke, trauma or heart failure.
“This is not just a COVID issue,” said Dr. Normaliz Rodriguez, pediatric emergency physician at Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. “This is an everyone issue.”
While the latest hospital crisis echoes previous pandemic spikes, there are troubling differences this time around.
Before, localized COVID-19 hot spots led to bed shortages, but there were usually hospitals in the region not as affected that could accept a transfer.
Now, as the highly contagious delta variant envelops swaths of low-vaccination states all at once, it becomes harder to find nearby hospitals that are not slammed.
“Wait times can now be measured in days,” said Darrell Pile, CEO of the SouthEast Texas Regional Advisory Council, which helps coordinate patient transfers across a 25-county region.
Recently, Dr. Cedric Dark, a Houston emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said he saw a critically ill COVID-19 patient waiting in the emergency room for an ICU bed to open. The doctor worked eight hours, went home and came in the next day. The patient was still waiting.
Holding a seriously ill patient in an emergency room while waiting for an in-patient bed to open is known as boarding. The longer the wait, the more dangerous it can be for the patient, studies have found.
Not only do patients ultimately end up staying in the hospital or the ICU longer, some research suggests that long waits for a bed will worsen their condition and may increase the risk of in-hospital death.
That’s what happened last month in Texas.
On Aug. 21, around 11:30 a.m., Michelle Puget took her adult son, Daniel Wilkinson, to the Bellville Medical Center’s emergency room as a pain in his abdomen became unbearable. “Mama,” he said, “take me to the hospital.”
Wilkinson, a 46-year-old decorated Army veteran who did two tours of duty in Afghanistan, was ushered into an exam room about half an hour later. Kakli, the emergency room physician there, diagnosed gallstone pancreatitis, a serious but treatable condition that required a specialist to perform a surgical procedure and an ICU bed.
In other times, the transfer to a larger facility would be easy. But soon Kakli found himself on a frantic, six-hour quest to find a bed for his patient. Not only did he call hospitals across Texas, but he also tried Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma and Colorado. It was like throwing darts at a map and hoping to get lucky, he told ProPublica. But no one could or would take the transfer.
By 2:30 p.m., Wilkinson’s condition was deteriorating. Kakli told Puget to come back to the hospital. “I have to tell you,” she said he told her, “Your son is a very, very sick man. If he doesn’t get this procedure he will die.” She began to weep.
Two hours later, Wilkinson’s blood pressure was dropping, signaling his organs were failing, she said.
Kakli went on Facebook and posted an all-caps plea to physician groups around the nation: “GETTING REJECTED BY ALL HOSPITALS IN TEXAS DUE TO NO ICU BEDS. PLEASE HELP. MESSAGE ME IF YOU HAVE A BED. PATIENT IS IN ER NOW. I AM THE ER DOC. WILL FLY ANYWHERE.”
The doctor tried Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston for a second time. This time he found a bed.
Around 7 p.m., Wilkinson, still conscious but in grave condition, was flown by helicopter to the hospital. He was put in a medically induced coma. Through the night and into the next morning, medical teams worked to stabilize him enough to perform the procedure. They could not.
Doctors told his family the internal damage was catastrophic. “We made the decision we had to let him go,” Puget said.
Time of death: 1:37 p.m. Aug. 22 – 26 hours after he first arrived in the emergency room.
The story was first reported by CBS News. Kakli told ProPublica last week he still sometimes does the math in his head: It should have been 40 minutes from diagnosis in Bellville to transfer to the ICU in Houston. “If he had 40 minutes to wait instead of six hours, I strongly believe he would have had a different outcome.”
Another difference with the latest surge is how it’s affecting children.
Last year, schools were closed, and children were more protected because they were mostly isolated at home. In fact, children’s hospitals were often so empty during previous spikes they opened beds to adult patients.
Now, families are out more. Schools have reopened, some with mask mandates, some without. Vaccines are not yet available to those under 12. Suddenly the numbers of hospitalized children are on the rise, setting up the same type of competition for resources between young COVID-19 patients and those with other illnesses such as new onset diabetes, trauma, pneumonia or appendicitis.
Dr. Rafael Santiago, a pediatric emergency physician in Central Florida, said at Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center, the average number of children coming into the emergency room is around 130 per day. During the lockdown last spring, that number dropped to 33. Last month – “the busiest month ever” – the average daily number of children in the emergency room was 160.
Pediatric transfers are not yet as fraught as adult ones, Santiago said, but it does take more calls than it once did to secure a bed.
Seth Osborn, the 12-year-old whose appendix burst after a long wait, spent five days and four nights in the hospital as doctors pumped his body full of antibiotics to stave off infection from the rupture. The typical hospitalization for a routine appendectomy is about 24 hours.
The initial hospital bill for the stay came to more than $48,000, Nathaniel Osborn said. Although insurance paid for most of it, he said the family still borrowed against its house to cover the more than $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs so far.
While the hospital system where Seth was treated declined to comment about his case because of patient privacy laws, it did email a statement about the strain the pandemic is creating.
“Since July 2021, we have seen a tremendous spike in COVID-19 patients needing care and hospitalization. In mid-August, we saw the highest number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 across the Cleveland Clinic Florida region, a total of 395 COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. Those hospitals have approximately 1,000 total beds,” the email to ProPublica said. “We strongly encourage vaccination. Approximately 90% of our patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 are unvaccinated.”
On Sunday, The Washington Post reported that a hospital in Alabama called 43 others across three states before finding a bed for Ray DeMonia, a critically ill heart patient who later died. In his obituary his family wrote: “In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies. ... He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Today, Seth is mostly recovered. “Twelve-year-old boys bounce back,” his father said. Still, the experience has left Nathaniel Osborn shaken.
The high school history teacher said he likes to stay upbeat and apolitical in his social media musings, posting about Florida wildlife preservation and favorite books. But on Sept. 7, he tweeted: “My 12-year-old had appendicitis. The ER was overwhelmed with unvaccinated Covid patients and we had to wait 6+ hours. While waiting, his appendix ruptured and had to spend 5 days in hospital. ... So yeah, your decision to not vaccinate does affect others.”
It was retweeted 34,700 times, with 143,000 likes. Most comments were sympathetic and wished his child a speedy recovery. Some, though, went straight to hate, apparently triggered by his last line. He was attacked personally and accused of making up the story: “Good try with the guilt, jerk.”
Osborn, who is vaccinated, as are his wife and son, told ProPublica he only shared Seth’s story on Twitter to encourage vaccinations.
“I have no ill will towards the hospitals or the care received at either hospital,” he said this week, “but had these hospitals not been so crowded with COVID patients, we wouldn’t have had to wait so long and perhaps my son’s appendix would not have burst.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Seth was finally diagnosed with appendicitis more than six hours after arriving at Cleveland Clinic Martin Health North Hospital in late July. Around midnight, he was taken by ambulance to a sister hospital about a half-hour away that was better equipped to perform pediatric emergency surgery, his father said.
But by the time the doctor operated in the early morning hours, Seth’s appendix had burst – a potentially fatal complication.
They, too, need emergency care, but the sheer number of COVID-19 cases is crowding them out. Treatment has often been delayed as ERs scramble to find a bed that may be hundreds of miles away.
Some health officials now worry about looming ethical decisions. Last week, Idaho activated a “crisis standard of care,” which one official described as a “last resort.” It allows overwhelmed hospitals to ration care, including “in rare cases, ventilator (breathing machines) or intensive care unit (ICU) beds may need to be used for those who are most likely to survive, while patients who are not likely to survive may not be able to receive one,” the state’s website said.
The federal government’s latest data shows Alabama is at 100% of its intensive care unit capacity, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi and Arkansas at more than 90% ICU capacity. Florida is just under 90%.
It’s the COVID-19 cases that are dominating. In Georgia, 62% of the ICU beds are now filled with just COVID-19 patients. In Texas, the percentage is nearly half.
To have so many ICU beds pressed into service for a single diagnosis is “unheard of,” said Dr. Hasan Kakli, an emergency room physician at Bellville Medical Center in Bellville, Texas, about an hour from Houston. “It’s approaching apocalyptic.”
In Texas, state data released Monday showed there were only 319 adult and 104 pediatric staffed ICU beds available across a state of 29 million people.
Hospitals need to hold some ICU beds for other patients, such as those recovering from major surgery or other critical conditions such as stroke, trauma or heart failure.
“This is not just a COVID issue,” said Dr. Normaliz Rodriguez, pediatric emergency physician at Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. “This is an everyone issue.”
While the latest hospital crisis echoes previous pandemic spikes, there are troubling differences this time around.
Before, localized COVID-19 hot spots led to bed shortages, but there were usually hospitals in the region not as affected that could accept a transfer.
Now, as the highly contagious delta variant envelops swaths of low-vaccination states all at once, it becomes harder to find nearby hospitals that are not slammed.
“Wait times can now be measured in days,” said Darrell Pile, CEO of the SouthEast Texas Regional Advisory Council, which helps coordinate patient transfers across a 25-county region.
Recently, Dr. Cedric Dark, a Houston emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said he saw a critically ill COVID-19 patient waiting in the emergency room for an ICU bed to open. The doctor worked eight hours, went home and came in the next day. The patient was still waiting.
Holding a seriously ill patient in an emergency room while waiting for an in-patient bed to open is known as boarding. The longer the wait, the more dangerous it can be for the patient, studies have found.
Not only do patients ultimately end up staying in the hospital or the ICU longer, some research suggests that long waits for a bed will worsen their condition and may increase the risk of in-hospital death.
That’s what happened last month in Texas.
On Aug. 21, around 11:30 a.m., Michelle Puget took her adult son, Daniel Wilkinson, to the Bellville Medical Center’s emergency room as a pain in his abdomen became unbearable. “Mama,” he said, “take me to the hospital.”
Wilkinson, a 46-year-old decorated Army veteran who did two tours of duty in Afghanistan, was ushered into an exam room about half an hour later. Kakli, the emergency room physician there, diagnosed gallstone pancreatitis, a serious but treatable condition that required a specialist to perform a surgical procedure and an ICU bed.
In other times, the transfer to a larger facility would be easy. But soon Kakli found himself on a frantic, six-hour quest to find a bed for his patient. Not only did he call hospitals across Texas, but he also tried Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma and Colorado. It was like throwing darts at a map and hoping to get lucky, he told ProPublica. But no one could or would take the transfer.
By 2:30 p.m., Wilkinson’s condition was deteriorating. Kakli told Puget to come back to the hospital. “I have to tell you,” she said he told her, “Your son is a very, very sick man. If he doesn’t get this procedure he will die.” She began to weep.
Two hours later, Wilkinson’s blood pressure was dropping, signaling his organs were failing, she said.
Kakli went on Facebook and posted an all-caps plea to physician groups around the nation: “GETTING REJECTED BY ALL HOSPITALS IN TEXAS DUE TO NO ICU BEDS. PLEASE HELP. MESSAGE ME IF YOU HAVE A BED. PATIENT IS IN ER NOW. I AM THE ER DOC. WILL FLY ANYWHERE.”
The doctor tried Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston for a second time. This time he found a bed.
Around 7 p.m., Wilkinson, still conscious but in grave condition, was flown by helicopter to the hospital. He was put in a medically induced coma. Through the night and into the next morning, medical teams worked to stabilize him enough to perform the procedure. They could not.
Doctors told his family the internal damage was catastrophic. “We made the decision we had to let him go,” Puget said.
Time of death: 1:37 p.m. Aug. 22 – 26 hours after he first arrived in the emergency room.
The story was first reported by CBS News. Kakli told ProPublica last week he still sometimes does the math in his head: It should have been 40 minutes from diagnosis in Bellville to transfer to the ICU in Houston. “If he had 40 minutes to wait instead of six hours, I strongly believe he would have had a different outcome.”
Another difference with the latest surge is how it’s affecting children.
Last year, schools were closed, and children were more protected because they were mostly isolated at home. In fact, children’s hospitals were often so empty during previous spikes they opened beds to adult patients.
Now, families are out more. Schools have reopened, some with mask mandates, some without. Vaccines are not yet available to those under 12. Suddenly the numbers of hospitalized children are on the rise, setting up the same type of competition for resources between young COVID-19 patients and those with other illnesses such as new onset diabetes, trauma, pneumonia or appendicitis.
Dr. Rafael Santiago, a pediatric emergency physician in Central Florida, said at Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center, the average number of children coming into the emergency room is around 130 per day. During the lockdown last spring, that number dropped to 33. Last month – “the busiest month ever” – the average daily number of children in the emergency room was 160.
Pediatric transfers are not yet as fraught as adult ones, Santiago said, but it does take more calls than it once did to secure a bed.
Seth Osborn, the 12-year-old whose appendix burst after a long wait, spent five days and four nights in the hospital as doctors pumped his body full of antibiotics to stave off infection from the rupture. The typical hospitalization for a routine appendectomy is about 24 hours.
The initial hospital bill for the stay came to more than $48,000, Nathaniel Osborn said. Although insurance paid for most of it, he said the family still borrowed against its house to cover the more than $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs so far.
While the hospital system where Seth was treated declined to comment about his case because of patient privacy laws, it did email a statement about the strain the pandemic is creating.
“Since July 2021, we have seen a tremendous spike in COVID-19 patients needing care and hospitalization. In mid-August, we saw the highest number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 across the Cleveland Clinic Florida region, a total of 395 COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. Those hospitals have approximately 1,000 total beds,” the email to ProPublica said. “We strongly encourage vaccination. Approximately 90% of our patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 are unvaccinated.”
On Sunday, The Washington Post reported that a hospital in Alabama called 43 others across three states before finding a bed for Ray DeMonia, a critically ill heart patient who later died. In his obituary his family wrote: “In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies. ... He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Today, Seth is mostly recovered. “Twelve-year-old boys bounce back,” his father said. Still, the experience has left Nathaniel Osborn shaken.
The high school history teacher said he likes to stay upbeat and apolitical in his social media musings, posting about Florida wildlife preservation and favorite books. But on Sept. 7, he tweeted: “My 12-year-old had appendicitis. The ER was overwhelmed with unvaccinated Covid patients and we had to wait 6+ hours. While waiting, his appendix ruptured and had to spend 5 days in hospital. ... So yeah, your decision to not vaccinate does affect others.”
It was retweeted 34,700 times, with 143,000 likes. Most comments were sympathetic and wished his child a speedy recovery. Some, though, went straight to hate, apparently triggered by his last line. He was attacked personally and accused of making up the story: “Good try with the guilt, jerk.”
Osborn, who is vaccinated, as are his wife and son, told ProPublica he only shared Seth’s story on Twitter to encourage vaccinations.
“I have no ill will towards the hospitals or the care received at either hospital,” he said this week, “but had these hospitals not been so crowded with COVID patients, we wouldn’t have had to wait so long and perhaps my son’s appendix would not have burst.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Seth was finally diagnosed with appendicitis more than six hours after arriving at Cleveland Clinic Martin Health North Hospital in late July. Around midnight, he was taken by ambulance to a sister hospital about a half-hour away that was better equipped to perform pediatric emergency surgery, his father said.
But by the time the doctor operated in the early morning hours, Seth’s appendix had burst – a potentially fatal complication.
They, too, need emergency care, but the sheer number of COVID-19 cases is crowding them out. Treatment has often been delayed as ERs scramble to find a bed that may be hundreds of miles away.
Some health officials now worry about looming ethical decisions. Last week, Idaho activated a “crisis standard of care,” which one official described as a “last resort.” It allows overwhelmed hospitals to ration care, including “in rare cases, ventilator (breathing machines) or intensive care unit (ICU) beds may need to be used for those who are most likely to survive, while patients who are not likely to survive may not be able to receive one,” the state’s website said.
The federal government’s latest data shows Alabama is at 100% of its intensive care unit capacity, with Texas, Georgia, Mississippi and Arkansas at more than 90% ICU capacity. Florida is just under 90%.
It’s the COVID-19 cases that are dominating. In Georgia, 62% of the ICU beds are now filled with just COVID-19 patients. In Texas, the percentage is nearly half.
To have so many ICU beds pressed into service for a single diagnosis is “unheard of,” said Dr. Hasan Kakli, an emergency room physician at Bellville Medical Center in Bellville, Texas, about an hour from Houston. “It’s approaching apocalyptic.”
In Texas, state data released Monday showed there were only 319 adult and 104 pediatric staffed ICU beds available across a state of 29 million people.
Hospitals need to hold some ICU beds for other patients, such as those recovering from major surgery or other critical conditions such as stroke, trauma or heart failure.
“This is not just a COVID issue,” said Dr. Normaliz Rodriguez, pediatric emergency physician at Johns Hopkins All Children’s Hospital in St. Petersburg, Florida. “This is an everyone issue.”
While the latest hospital crisis echoes previous pandemic spikes, there are troubling differences this time around.
Before, localized COVID-19 hot spots led to bed shortages, but there were usually hospitals in the region not as affected that could accept a transfer.
Now, as the highly contagious delta variant envelops swaths of low-vaccination states all at once, it becomes harder to find nearby hospitals that are not slammed.
“Wait times can now be measured in days,” said Darrell Pile, CEO of the SouthEast Texas Regional Advisory Council, which helps coordinate patient transfers across a 25-county region.
Recently, Dr. Cedric Dark, a Houston emergency physician and assistant professor of emergency medicine at Baylor College of Medicine, said he saw a critically ill COVID-19 patient waiting in the emergency room for an ICU bed to open. The doctor worked eight hours, went home and came in the next day. The patient was still waiting.
Holding a seriously ill patient in an emergency room while waiting for an in-patient bed to open is known as boarding. The longer the wait, the more dangerous it can be for the patient, studies have found.
Not only do patients ultimately end up staying in the hospital or the ICU longer, some research suggests that long waits for a bed will worsen their condition and may increase the risk of in-hospital death.
That’s what happened last month in Texas.
On Aug. 21, around 11:30 a.m., Michelle Puget took her adult son, Daniel Wilkinson, to the Bellville Medical Center’s emergency room as a pain in his abdomen became unbearable. “Mama,” he said, “take me to the hospital.”
Wilkinson, a 46-year-old decorated Army veteran who did two tours of duty in Afghanistan, was ushered into an exam room about half an hour later. Kakli, the emergency room physician there, diagnosed gallstone pancreatitis, a serious but treatable condition that required a specialist to perform a surgical procedure and an ICU bed.
In other times, the transfer to a larger facility would be easy. But soon Kakli found himself on a frantic, six-hour quest to find a bed for his patient. Not only did he call hospitals across Texas, but he also tried Kansas, Missouri, Oklahoma and Colorado. It was like throwing darts at a map and hoping to get lucky, he told ProPublica. But no one could or would take the transfer.
By 2:30 p.m., Wilkinson’s condition was deteriorating. Kakli told Puget to come back to the hospital. “I have to tell you,” she said he told her, “Your son is a very, very sick man. If he doesn’t get this procedure he will die.” She began to weep.
Two hours later, Wilkinson’s blood pressure was dropping, signaling his organs were failing, she said.
Kakli went on Facebook and posted an all-caps plea to physician groups around the nation: “GETTING REJECTED BY ALL HOSPITALS IN TEXAS DUE TO NO ICU BEDS. PLEASE HELP. MESSAGE ME IF YOU HAVE A BED. PATIENT IS IN ER NOW. I AM THE ER DOC. WILL FLY ANYWHERE.”
The doctor tried Michael E. DeBakey VA Medical Center in Houston for a second time. This time he found a bed.
Around 7 p.m., Wilkinson, still conscious but in grave condition, was flown by helicopter to the hospital. He was put in a medically induced coma. Through the night and into the next morning, medical teams worked to stabilize him enough to perform the procedure. They could not.
Doctors told his family the internal damage was catastrophic. “We made the decision we had to let him go,” Puget said.
Time of death: 1:37 p.m. Aug. 22 – 26 hours after he first arrived in the emergency room.
The story was first reported by CBS News. Kakli told ProPublica last week he still sometimes does the math in his head: It should have been 40 minutes from diagnosis in Bellville to transfer to the ICU in Houston. “If he had 40 minutes to wait instead of six hours, I strongly believe he would have had a different outcome.”
Another difference with the latest surge is how it’s affecting children.
Last year, schools were closed, and children were more protected because they were mostly isolated at home. In fact, children’s hospitals were often so empty during previous spikes they opened beds to adult patients.
Now, families are out more. Schools have reopened, some with mask mandates, some without. Vaccines are not yet available to those under 12. Suddenly the numbers of hospitalized children are on the rise, setting up the same type of competition for resources between young COVID-19 patients and those with other illnesses such as new onset diabetes, trauma, pneumonia or appendicitis.
Dr. Rafael Santiago, a pediatric emergency physician in Central Florida, said at Lakeland Regional Health Medical Center, the average number of children coming into the emergency room is around 130 per day. During the lockdown last spring, that number dropped to 33. Last month – “the busiest month ever” – the average daily number of children in the emergency room was 160.
Pediatric transfers are not yet as fraught as adult ones, Santiago said, but it does take more calls than it once did to secure a bed.
Seth Osborn, the 12-year-old whose appendix burst after a long wait, spent five days and four nights in the hospital as doctors pumped his body full of antibiotics to stave off infection from the rupture. The typical hospitalization for a routine appendectomy is about 24 hours.
The initial hospital bill for the stay came to more than $48,000, Nathaniel Osborn said. Although insurance paid for most of it, he said the family still borrowed against its house to cover the more than $5,000 in out-of-pocket costs so far.
While the hospital system where Seth was treated declined to comment about his case because of patient privacy laws, it did email a statement about the strain the pandemic is creating.
“Since July 2021, we have seen a tremendous spike in COVID-19 patients needing care and hospitalization. In mid-August, we saw the highest number of patients hospitalized with COVID-19 across the Cleveland Clinic Florida region, a total of 395 COVID-19 patients in four hospitals. Those hospitals have approximately 1,000 total beds,” the email to ProPublica said. “We strongly encourage vaccination. Approximately 90% of our patients hospitalized due to COVID-19 are unvaccinated.”
On Sunday, The Washington Post reported that a hospital in Alabama called 43 others across three states before finding a bed for Ray DeMonia, a critically ill heart patient who later died. In his obituary his family wrote: “In honor of Ray, please get vaccinated if you have not, in an effort to free up resources for non COVID related emergencies. ... He would not want any other family to go through what his did.”
Today, Seth is mostly recovered. “Twelve-year-old boys bounce back,” his father said. Still, the experience has left Nathaniel Osborn shaken.
The high school history teacher said he likes to stay upbeat and apolitical in his social media musings, posting about Florida wildlife preservation and favorite books. But on Sept. 7, he tweeted: “My 12-year-old had appendicitis. The ER was overwhelmed with unvaccinated Covid patients and we had to wait 6+ hours. While waiting, his appendix ruptured and had to spend 5 days in hospital. ... So yeah, your decision to not vaccinate does affect others.”
It was retweeted 34,700 times, with 143,000 likes. Most comments were sympathetic and wished his child a speedy recovery. Some, though, went straight to hate, apparently triggered by his last line. He was attacked personally and accused of making up the story: “Good try with the guilt, jerk.”
Osborn, who is vaccinated, as are his wife and son, told ProPublica he only shared Seth’s story on Twitter to encourage vaccinations.
“I have no ill will towards the hospitals or the care received at either hospital,” he said this week, “but had these hospitals not been so crowded with COVID patients, we wouldn’t have had to wait so long and perhaps my son’s appendix would not have burst.”
This story was originally published on ProPublica. ProPublica is a nonprofit newsroom that investigates abuses of power. Sign up to receive their biggest stories as soon as they’re published.
Children and COVID: New cases down slightly from record high
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.
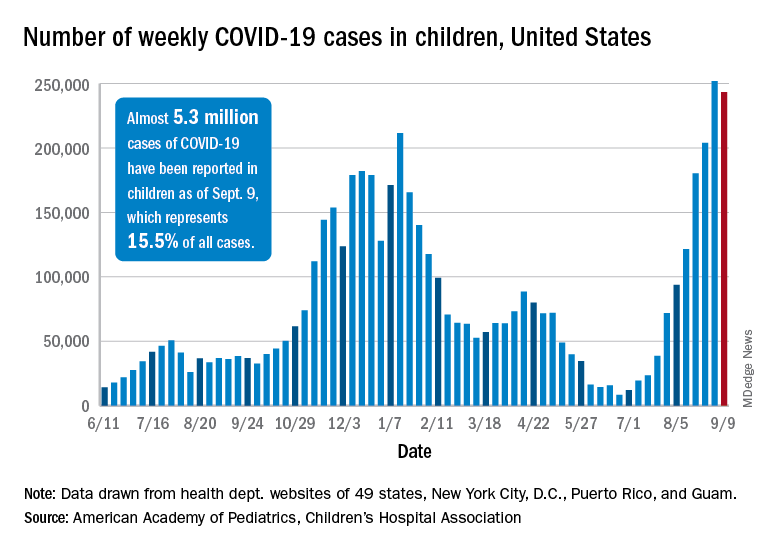
Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).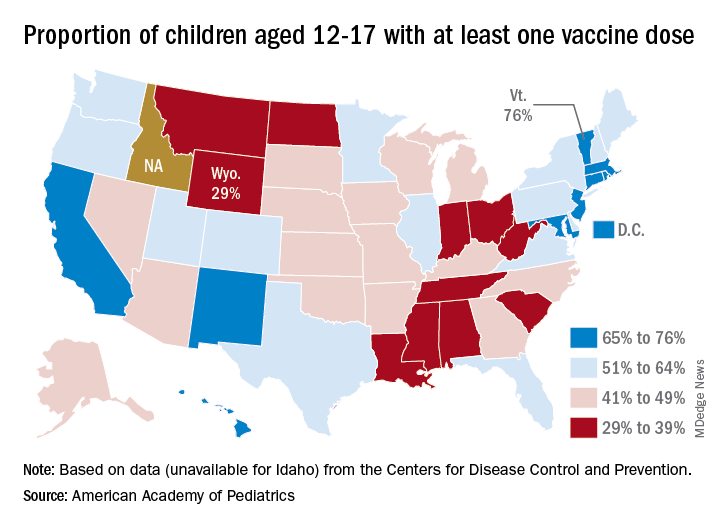
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.
Weekly cases of COVID-19 in children dropped for the first time since June, and daily hospitalizations appear to be falling, even as the pace of vaccinations continues to slow among the youngest eligible recipients, according to new data.

Despite the 3.3% decline from the previous week’s record high, the new-case count still topped 243,000 for the week of Sept. 3-9, putting the total number of cases in children at almost 5.3 million since the pandemic began.
Hospitalizations seem to have peaked on Sept. 4, when the rate for children aged 0-17 years reached 0.51 per 100,000 population. The admission rate for confirmed COVID-19 has dropped steadily since then and was down to 0.45 per 100,000 on Sept. 11, the last day for which preliminary data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention were available.
On the prevention side, fully vaccinated children aged 12-17 years represented 5.5% of all Americans who had completed the vaccine regimen as of Sept. 13. Vaccine initiation, however, has dropped for 5 consecutive weeks in 12- to 15-year-olds and in 4 of the last 5 weeks among 16- and 17-year-olds, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Just under 199,000 children aged 12-15 received their first dose of the COVID-19 vaccine during the week of Sept. 7-13. That’s down by 18.5% from the week before and by 51.6% since Aug. 9, the last week that vaccine initiation increased for the age group. Among 16- and 17-year-olds, the 83,000 new recipients that week was a decrease of 25.7% from the previous week and a decline of 47% since the summer peak of Aug. 9, the CDC data show.
Those newest recipients bring at-least-one-dose status to 52.0% of those aged 12-15 and 59.9% of the 16- and 17-year-olds, while 40.3% and 48.9% were fully vaccinated as of Sept. 13. Corresponding figures for some of the older groups are 61.6%/49.7% (age 18-24 years), 73.8%/63.1% (40-49 years), and 95.1%/84.5% (65-74 years), the CDC said.
Vaccine coverage for children at the state level deviates considerably from the national averages. The highest rates for children aged 12-17 are to be found in Vermont, where 76% have received at least one dose, the AAP reported in a separate analysis. Massachusetts is just below that but also comes in at 76% by virtue of a rounding error. The other states in the top five are Connecticut (74%), Hawaii (73%), and Rhode Island (71%).
The lowest vaccination rate for children comes from Wyoming (29%), which is preceded by North Dakota (33%), West Virginia (33%), Alabama (33%), and Mississippi (34%). the AAP said based on data from the CDC, which does not include Idaho.
In a bit of a side note, West Virginia’s Republican governor, Jim Justice, recently said this about vaccine reluctance in his state: “For God’s sakes a livin’, how difficult is this to understand? Why in the world do we have to come up with these crazy ideas – and they’re crazy ideas – that the vaccine’s got something in it and it’s tracing people wherever they go? And the same very people that are saying that are carrying their cellphones around. I mean, come on. Come on.”
Over the last 3 weeks, the District of Columbia has had the largest increase in children having received at least one dose: 10 percentage points, as it went from 58% to 68%. The next-largest improvement – 7 percentage points – occurred in Georgia (34% to 41%), New Mexico (61% to 68%), New York (55% to 62%), and Washington (57% to 64%), the AAP said in its weekly vaccination trends report.