User login
News and Views that Matter to Pediatricians
The leading independent newspaper covering news and commentary in pediatrics.
WOW! You spend that much time on the EHR?
Unlike many of you, maybe even most of you, I can recall when my office records were handwritten, some would say scribbled, on pieces of paper. They were decipherable by a select few. Some veteran assistants never mastered the skill. Pages were sometimes lavishly illustrated with drawings of body parts, often because I couldn’t remember or spell the correct anatomic term. When I needed to send a referring letter to another provider I typed it myself because dictating never quite suited my personality.
When I joined a small primary care group, the computer-savvy lead physician and a programmer developed our own homegrown EHR. It relied on scanning documents, as so many of us still generated handwritten notes. Even the most vociferous Luddites among us loved the system from day 2.
However, for a variety of reasons, some defensible some just plain bad, our beloved system needed to be replaced after 7 years. We then invested in an off-the-shelf EHR system that promised more capabilities. We were told there would be a learning curve but the plateau would come quickly and we would enjoy our new electronic assistant.
You’ve lived the rest of the story. The learning curve was steep and long and the plateau was a time gobbler. I was probably the most efficient provider in the group, and after 6 months I was leaving the office an hour later than I had been and was seeing the same number of patients. Most of my coworkers were staying and/or working on the computer at home for an extra 2 hours. This change could be easily documented by speaking with our spouses and children. I understand from my colleagues who have stayed in the business that over the ensuing decade and a half since my first experience with the EHR, its insatiable appetite for a clinician’s time has not abated.
The authors of a recent article in Annals of Family Medicine offer up some advice on how this tragic situation might be brought under control. First, the investigators point out that the phenomenon of after-hours EHR work, sometimes referred to as WOW (work outside of work), has not gone unnoticed by health system administrators and vendors who develop and sell the EHRs. However, analyzing the voluminous data necessary is not any easy task and for the most part has resulted in metrics that cannot be easily applied over a variety of practice scenarios. Many health care organizations, even large ones, have simply given up and rely on the WOW data and recommendations provided by the vendors, obviously lending the situation a faint odor of conflict of interest.
The bottom line is that . It would seem to me just asking the spouses and significant others of the clinicians would be sufficient. But, authors of the paper have more specific recommendations. First, they suggest that time working on the computer outside of scheduled time with patients should be separated from any other calculation of EHR usage. They encourage vendors and time-management researchers to develop standardized and validated methods for measuring active EHR use. And, finally they recommend that all EHR work done outside of time scheduled with patients be attributed to WOW. They feel that clearly labeling it work outside of work offers health care organizations a better chance of developing policies that will address the scourge of burnout.
This, unfortunately, is another tragic example of how clinicians have lost control of our work environments. The fact that 20 years have passed and there is still no standardized method for determining how much time we spend on the computer is more evidence we need to raise our voices.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Unlike many of you, maybe even most of you, I can recall when my office records were handwritten, some would say scribbled, on pieces of paper. They were decipherable by a select few. Some veteran assistants never mastered the skill. Pages were sometimes lavishly illustrated with drawings of body parts, often because I couldn’t remember or spell the correct anatomic term. When I needed to send a referring letter to another provider I typed it myself because dictating never quite suited my personality.
When I joined a small primary care group, the computer-savvy lead physician and a programmer developed our own homegrown EHR. It relied on scanning documents, as so many of us still generated handwritten notes. Even the most vociferous Luddites among us loved the system from day 2.
However, for a variety of reasons, some defensible some just plain bad, our beloved system needed to be replaced after 7 years. We then invested in an off-the-shelf EHR system that promised more capabilities. We were told there would be a learning curve but the plateau would come quickly and we would enjoy our new electronic assistant.
You’ve lived the rest of the story. The learning curve was steep and long and the plateau was a time gobbler. I was probably the most efficient provider in the group, and after 6 months I was leaving the office an hour later than I had been and was seeing the same number of patients. Most of my coworkers were staying and/or working on the computer at home for an extra 2 hours. This change could be easily documented by speaking with our spouses and children. I understand from my colleagues who have stayed in the business that over the ensuing decade and a half since my first experience with the EHR, its insatiable appetite for a clinician’s time has not abated.
The authors of a recent article in Annals of Family Medicine offer up some advice on how this tragic situation might be brought under control. First, the investigators point out that the phenomenon of after-hours EHR work, sometimes referred to as WOW (work outside of work), has not gone unnoticed by health system administrators and vendors who develop and sell the EHRs. However, analyzing the voluminous data necessary is not any easy task and for the most part has resulted in metrics that cannot be easily applied over a variety of practice scenarios. Many health care organizations, even large ones, have simply given up and rely on the WOW data and recommendations provided by the vendors, obviously lending the situation a faint odor of conflict of interest.
The bottom line is that . It would seem to me just asking the spouses and significant others of the clinicians would be sufficient. But, authors of the paper have more specific recommendations. First, they suggest that time working on the computer outside of scheduled time with patients should be separated from any other calculation of EHR usage. They encourage vendors and time-management researchers to develop standardized and validated methods for measuring active EHR use. And, finally they recommend that all EHR work done outside of time scheduled with patients be attributed to WOW. They feel that clearly labeling it work outside of work offers health care organizations a better chance of developing policies that will address the scourge of burnout.
This, unfortunately, is another tragic example of how clinicians have lost control of our work environments. The fact that 20 years have passed and there is still no standardized method for determining how much time we spend on the computer is more evidence we need to raise our voices.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
Unlike many of you, maybe even most of you, I can recall when my office records were handwritten, some would say scribbled, on pieces of paper. They were decipherable by a select few. Some veteran assistants never mastered the skill. Pages were sometimes lavishly illustrated with drawings of body parts, often because I couldn’t remember or spell the correct anatomic term. When I needed to send a referring letter to another provider I typed it myself because dictating never quite suited my personality.
When I joined a small primary care group, the computer-savvy lead physician and a programmer developed our own homegrown EHR. It relied on scanning documents, as so many of us still generated handwritten notes. Even the most vociferous Luddites among us loved the system from day 2.
However, for a variety of reasons, some defensible some just plain bad, our beloved system needed to be replaced after 7 years. We then invested in an off-the-shelf EHR system that promised more capabilities. We were told there would be a learning curve but the plateau would come quickly and we would enjoy our new electronic assistant.
You’ve lived the rest of the story. The learning curve was steep and long and the plateau was a time gobbler. I was probably the most efficient provider in the group, and after 6 months I was leaving the office an hour later than I had been and was seeing the same number of patients. Most of my coworkers were staying and/or working on the computer at home for an extra 2 hours. This change could be easily documented by speaking with our spouses and children. I understand from my colleagues who have stayed in the business that over the ensuing decade and a half since my first experience with the EHR, its insatiable appetite for a clinician’s time has not abated.
The authors of a recent article in Annals of Family Medicine offer up some advice on how this tragic situation might be brought under control. First, the investigators point out that the phenomenon of after-hours EHR work, sometimes referred to as WOW (work outside of work), has not gone unnoticed by health system administrators and vendors who develop and sell the EHRs. However, analyzing the voluminous data necessary is not any easy task and for the most part has resulted in metrics that cannot be easily applied over a variety of practice scenarios. Many health care organizations, even large ones, have simply given up and rely on the WOW data and recommendations provided by the vendors, obviously lending the situation a faint odor of conflict of interest.
The bottom line is that . It would seem to me just asking the spouses and significant others of the clinicians would be sufficient. But, authors of the paper have more specific recommendations. First, they suggest that time working on the computer outside of scheduled time with patients should be separated from any other calculation of EHR usage. They encourage vendors and time-management researchers to develop standardized and validated methods for measuring active EHR use. And, finally they recommend that all EHR work done outside of time scheduled with patients be attributed to WOW. They feel that clearly labeling it work outside of work offers health care organizations a better chance of developing policies that will address the scourge of burnout.
This, unfortunately, is another tragic example of how clinicians have lost control of our work environments. The fact that 20 years have passed and there is still no standardized method for determining how much time we spend on the computer is more evidence we need to raise our voices.
Dr. Wilkoff practiced primary care pediatrics in Brunswick, Maine, for nearly 40 years. He has authored several books on behavioral pediatrics, including “How to Say No to Your Toddler.” Other than a Littman stethoscope he accepted as a first-year medical student in 1966, Dr. Wilkoff reports having nothing to disclose. Email him at [email protected].
FDA approves first treatment for constipation in children
The recommended dosage in pediatric patients is 72 mcg orally once daily.
Functional constipation is common in children and adolescents. Symptoms include infrequent bowel movements with hard stools that can be difficult or painful to pass.
There is no known underlying organic cause and there are typically multiple contributing factors, the FDA noted in a statement announcing the approval.
The efficacy of linaclotide in children with functional constipation was demonstrated in a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trial (Trial 7; NCT04026113) and supported by efficacy data from trials in adults with chronic idiopathic constipation, the FDA said.
The FDA first approved linaclotide in 2012 for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) in adults.
Study details
To be eligible for the pediatric clinical trial, patients had to have experienced fewer than three spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs) per week.
They also had to experience one or more of the following at least once weekly, for at least 2 months prior to the trial screening visit:
- History of stool withholding or excessive voluntary stool retention.
- History of painful or hard bowel movements.
- History of large diameter stools that may obstruct the toilet.
- Presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum.
- At least one episode of fecal incontinence per week.
The primary efficacy endpoint was a 12-week change from baseline in SBM frequency rate. Children on linaclotide experienced greater improvement in the average number of SBMs per week than peers given placebo.
SBM frequency improved during the first week and was maintained throughout the remainder of the 12-week treatment period, the FDA said.
The most common adverse reaction is diarrhea. If severe diarrhea occurs, linaclotide should be discontinued and rehydration started.
The product’s boxed warning states that linaclotide is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years. In neonatal mice, linaclotide caused deaths due to dehydration.
Patients with known or suspected mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction should not take linaclotide.
Full prescribing information is available online.
The application for linaclotide in children received priority review.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The recommended dosage in pediatric patients is 72 mcg orally once daily.
Functional constipation is common in children and adolescents. Symptoms include infrequent bowel movements with hard stools that can be difficult or painful to pass.
There is no known underlying organic cause and there are typically multiple contributing factors, the FDA noted in a statement announcing the approval.
The efficacy of linaclotide in children with functional constipation was demonstrated in a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trial (Trial 7; NCT04026113) and supported by efficacy data from trials in adults with chronic idiopathic constipation, the FDA said.
The FDA first approved linaclotide in 2012 for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) in adults.
Study details
To be eligible for the pediatric clinical trial, patients had to have experienced fewer than three spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs) per week.
They also had to experience one or more of the following at least once weekly, for at least 2 months prior to the trial screening visit:
- History of stool withholding or excessive voluntary stool retention.
- History of painful or hard bowel movements.
- History of large diameter stools that may obstruct the toilet.
- Presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum.
- At least one episode of fecal incontinence per week.
The primary efficacy endpoint was a 12-week change from baseline in SBM frequency rate. Children on linaclotide experienced greater improvement in the average number of SBMs per week than peers given placebo.
SBM frequency improved during the first week and was maintained throughout the remainder of the 12-week treatment period, the FDA said.
The most common adverse reaction is diarrhea. If severe diarrhea occurs, linaclotide should be discontinued and rehydration started.
The product’s boxed warning states that linaclotide is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years. In neonatal mice, linaclotide caused deaths due to dehydration.
Patients with known or suspected mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction should not take linaclotide.
Full prescribing information is available online.
The application for linaclotide in children received priority review.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The recommended dosage in pediatric patients is 72 mcg orally once daily.
Functional constipation is common in children and adolescents. Symptoms include infrequent bowel movements with hard stools that can be difficult or painful to pass.
There is no known underlying organic cause and there are typically multiple contributing factors, the FDA noted in a statement announcing the approval.
The efficacy of linaclotide in children with functional constipation was demonstrated in a 12-week double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized, multicenter clinical trial (Trial 7; NCT04026113) and supported by efficacy data from trials in adults with chronic idiopathic constipation, the FDA said.
The FDA first approved linaclotide in 2012 for the treatment of chronic idiopathic constipation and irritable bowel syndrome with constipation (IBS-C) in adults.
Study details
To be eligible for the pediatric clinical trial, patients had to have experienced fewer than three spontaneous bowel movements (SBMs) per week.
They also had to experience one or more of the following at least once weekly, for at least 2 months prior to the trial screening visit:
- History of stool withholding or excessive voluntary stool retention.
- History of painful or hard bowel movements.
- History of large diameter stools that may obstruct the toilet.
- Presence of a large fecal mass in the rectum.
- At least one episode of fecal incontinence per week.
The primary efficacy endpoint was a 12-week change from baseline in SBM frequency rate. Children on linaclotide experienced greater improvement in the average number of SBMs per week than peers given placebo.
SBM frequency improved during the first week and was maintained throughout the remainder of the 12-week treatment period, the FDA said.
The most common adverse reaction is diarrhea. If severe diarrhea occurs, linaclotide should be discontinued and rehydration started.
The product’s boxed warning states that linaclotide is contraindicated in children younger than 2 years. In neonatal mice, linaclotide caused deaths due to dehydration.
Patients with known or suspected mechanical gastrointestinal obstruction should not take linaclotide.
Full prescribing information is available online.
The application for linaclotide in children received priority review.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
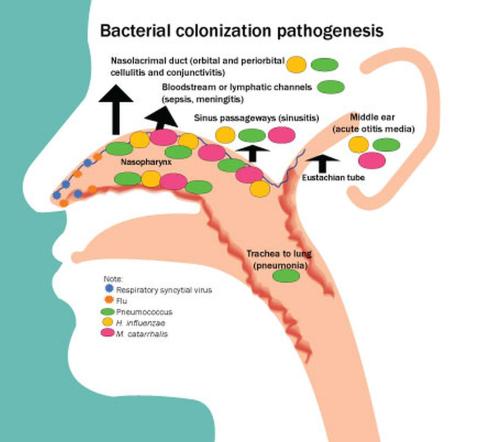
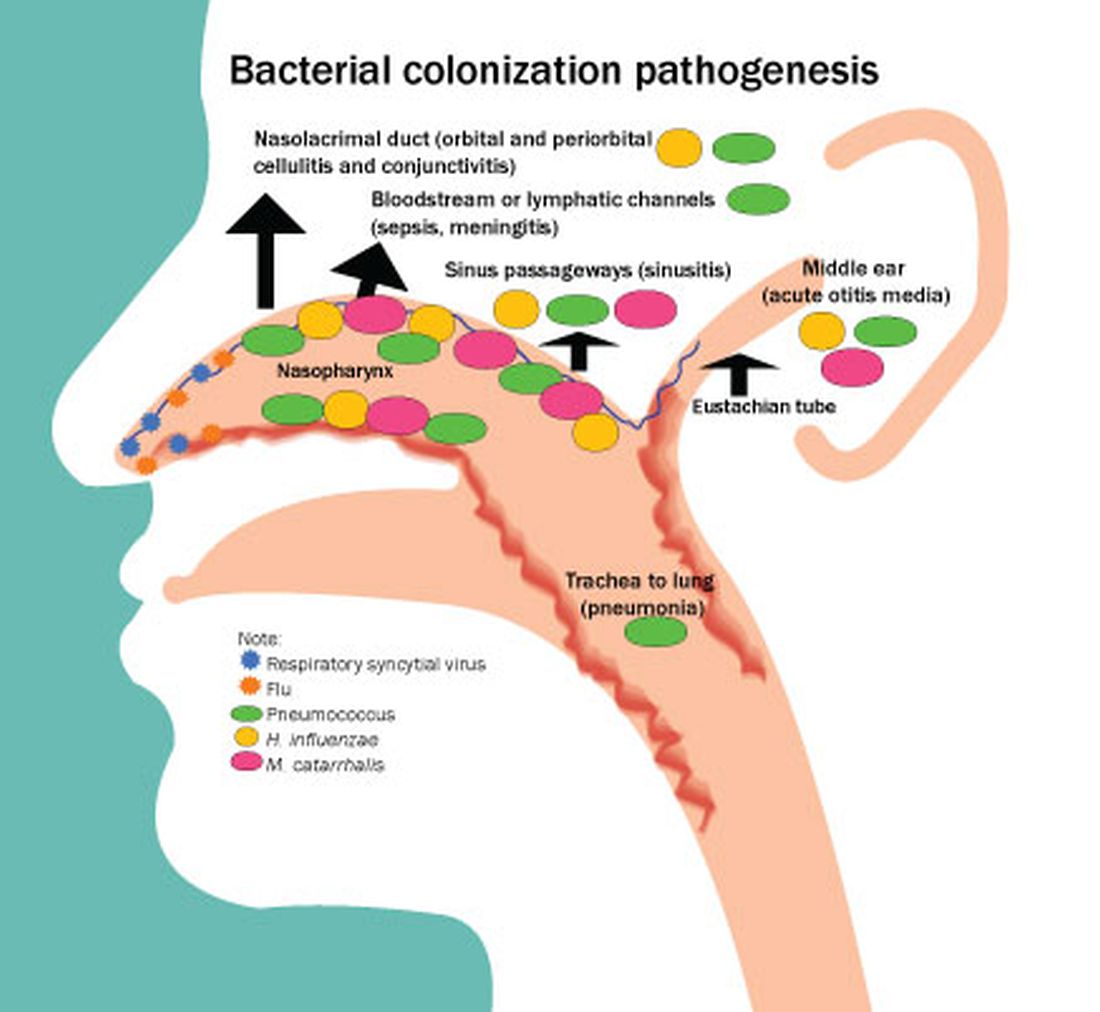
Profile of respiratory bacteria in children younger than 6 months
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
In this column, I will describe the results of a recently published study from my group.1 We sought to profile Streptococcus pneumoniae (pneumococcus), Haemophilus influenzae (Hflu) and Moraxella catarrhalis (Mcat) in the nasopharynx among 13-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV13)-immunized children, with a focus on the first 6 months of life. The rationale was to provide heretofore unreported contemporary data in a highly PCV13-immunized, community-based child population in the United States. A secondary objective was to assess nasopharyngeal bacterial density because higher density associates with greater likelihood of progression to infection. Thirdly, the serotype distribution and antibiotic susceptibility of pneumococci among children seen in primary care settings in the United States had not been evaluated for strains circulating among infants less than 6 months old and they may differ from strains recovered from older children. Therefore, comparisons were made within the same cohort of children to later child age time points.
Risk factors identified
The study was prospective and collected from a cohort of 101 children in Rochester, N.Y., during 2018-2020. Nasopharyngeal swabs were taken for study at age 1, 2 and 3 weeks, then 1, 2, 4, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18 and 24 months. All children had received PCV13 vaccine according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention recommended schedule.
We found two significant risk factors in the first 6 months of life for detection of nasopharyngeal colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat. They were daycare attendance and one or more siblings aged 1-5 years at home.
Colonization by one or more of the three bacteria was detected in only 5% of infants before age 2 months. None of the five children attended daycare but all five had young siblings at home. Pneumococcal colonization was detected in 12%, Hflu in 3%, and Mcat in 21% of nasopharyngeal swabs collected during the first 6 months of life. Nasopharyngeal colonization with the bacteria increased rapidly between age 4 and 6 months of life, coincident with infants going to daycare and other social interaction opportunities. Bacterial density of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat during the first 6 months of life was significantly lower in the nasopharynx compared with bacterial density when samples were collected during child age 7-24 months.
The prevalent pneumococcal serotypes in children up to 6 months old were 23B (17%), 22F (13%), 15B/C (11%), 16F (9%), and 21 (7%), 19F (7%), which differed from those isolated from children age 7-24 months, where serotypes 35B (15%), 21 (10%), 15B (9%), and 23B (7%), 23A (7%) were most commonly observed. Antibiotic resistance among isolates did not significantly differ in comparisons between infants younger than 6 months versus 7- to 24-month-olds.
What is the clinical significance?
Colonization of the nasopharynx is a necessary first step in infection pathogenesis (Figure).
Prevalence of colonization varies among settings and countries, with generally much higher prevalence soon after birth and persisting at high rates in children living in low/middle-income countries versus high-income countries. This is one explanation for higher respiratory infection rates in low/middle-income countries compared with the United States, Europe, and other high-income countries. Environmental risk factors for early life colonization include household crowding, young siblings, no breastfeeding, daycare attendance, antibiotic usage, and passive exposure to smoke.
In a prior study of a different cohort of 358 prospectively-enrolled children, we sought associations between physician-attended illness visits and bacterial colonization in the first 5 years of life.2 We showed that early age of first colonization with pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat was associated with respiratory infection proneness and asthma among the children.
Multiple demographic and risk factors may contribute to early life and high-density colonization that in turn may increase risk of infections. High densities and early life pneumococcal colonization in low/middle-income countries might impact PCV responses by induction of immunity tolerance. While it is appealing to study new vaccines in low/middle-income populations with high infection incidence, there are reasons that infection incidence is higher compared with high-income countries like the United States, among them may be early life nasopharyngeal colonization and density of colonization.
Prevalent pneumococcal serotype appear to differ with age. The most common serotypes in the first 6 months of life for the children were 23B> 22F> 16F and 21=19F, but in children 7-24 months, serotypes 35B> 21>15B>23A=23B were most commonly observed. This difference might be due to the impact of antibiotics.3 Pneumococci expressing serotypes 22F and 16F were oxacillin susceptible and antibiotic exposure in the first 6 months of life is very uncommon in our study cohorts. In contrast, all pneumococci expressing 35B capsule were oxacillin resistant and in our cohorts antibiotic exposures are common among 7- to 24-month-olds.
In conclusion, we determined that children in the first 6 months of life seen in pediatric primary care settings in Rochester, N.Y., have very low prevalence and low-density colonization of pneumococcus, Hflu, and Mcat compared with 7- to 24-month olds. Our results may explain the significantly lower rates of infections caused by pneumococci, Hflu, and Mcat in infants younger than 6 months old compared with low/middle-income countries.
Dr. Pichichero is a specialist in pediatric infectious diseases, Center for Infectious Diseases and Immunology, and director of the Research Institute at Rochester (N.Y.) General Hospital. He has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
References
1. Kaur R and Pichichero M. Colonization, density, and antibiotic resistance of Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus Influenzae, and Moraxella catarrhalis among PCV13 vaccinated infants in the first six months of life in Rochester, New York. J Pediatric Infect Dis Soc. 2023 Apr 18;12(3):135-42.
2. Chapman T et al. Nasopharyngeal colonization with pathobionts is associated with susceptibility to respiratory illnesses in young children. PLoS One. 2020 Dec 11;15(12):e0243942. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243942.
3. Chapman TJ et al. Antibiotic use and vaccine antibody levels. Pediatrics 2022 May 1;149(5):e2021052061. doi: 10.1542/peds.2021-052061.
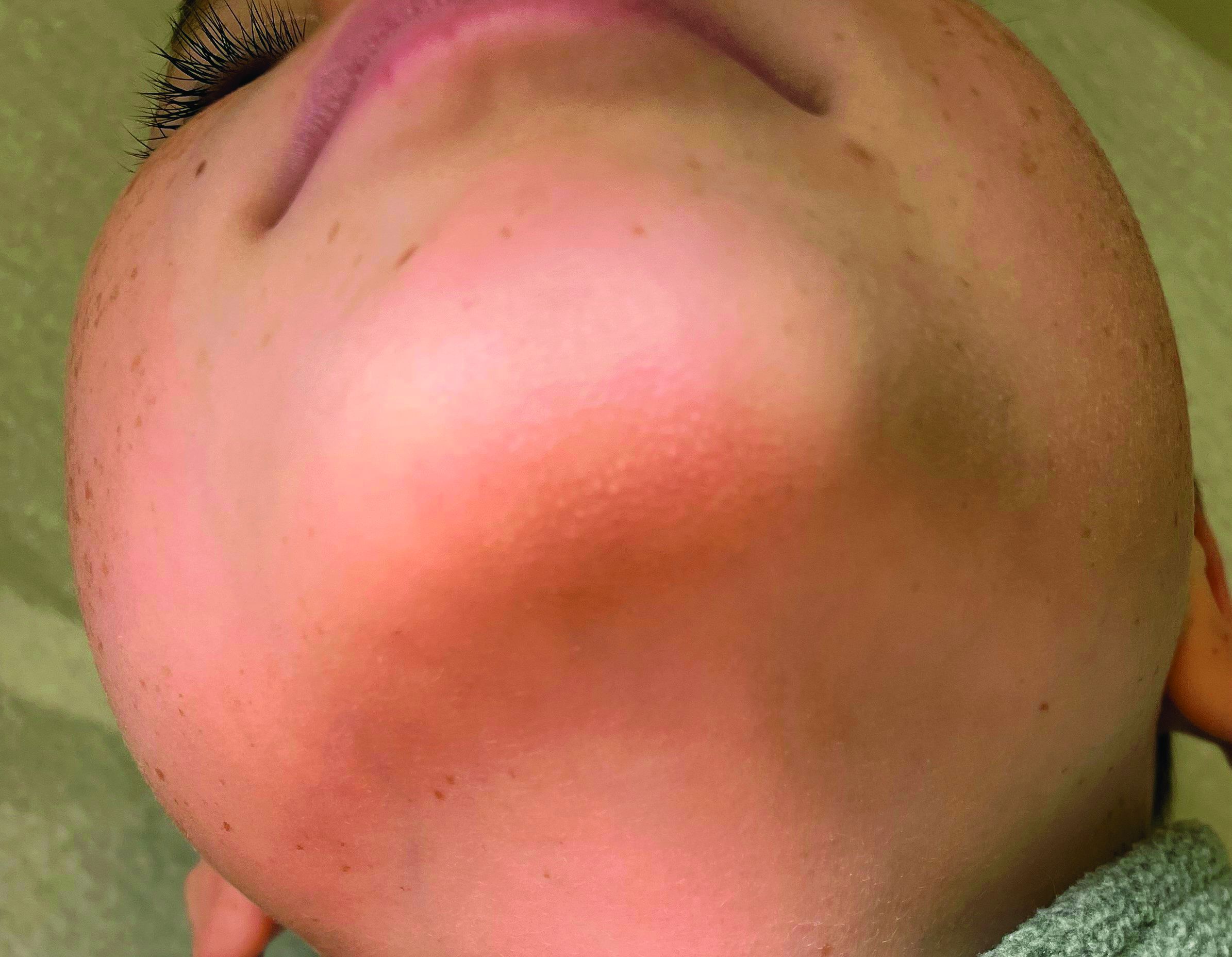
A 7-year-old male has a bumpy rash on the chin for several months
Given the presentation and the unique location of the lesions he was diagnosed with follicular keratosis of the chin (FKC).
This is a rare and poorly understood condition that can be present in older children and young teenagers. In the cases reported by Kanzaki et al.1 were two boys who presented with the condition; it was thought to be associated with rubbing of the chin with their hands when watching TV or reading. The author described improvement with habit change. This condition is usually described in boys, and some cases presented in brothers,2 suggesting a genetic predisposition. Some reports lack a history of rubbing or trauma to the area.
Histopathologic evaluation of the lesions demonstrates dilated hair follicles containing keratotic basophilic material without any signs of inflammation.
The lesions can be confused with keratosis pilaris (KP). Keratosis pilaris can be described in association with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis, which were not present in our patient. The lesions usually present on the sides of the cheeks and lateral region of the arms and legs. Compared with follicular keratosis, KP lesions usually present with associated perifollicular erythema. Our patient did not present with lesions on the cheeks or the sides of the arms or legs. Milia can present on the chin of children, usually if there is history of rubbing or trauma, or on a scar. Milia are micro keratin cysts, usually seen in areas of the face. Lichen spinulous is described as rough small follicular papules that present in oval or circular patches that can grow up to 5 cm and spread rapidly. They usually present on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, neck, abdomen, and knees. These lesions are thought to be secondary to infections, have been associated with atopy, and have been seen in patients with atopic dermatitis. There is a probable genetic predisposition. The lesions are usually treated with gentle soaps and moisturizer containing keratolytics like urea or salicylic acid, and in some cases topical retinoids can also be tried. Follicular mucinosis can also present similarly to keratosis follicularis. The lesions present as scaly plaques or as grouped skin color papules on the face, scalp, or the neck that can also be associated with hair loss. Sometimes a biopsy needs to be done to be able to distinguish it from follicular keratosis. There is an increase of mucin around hair follicles and sebaceous glands with associated inflammation and degeneration of the follicular structures. In patients with primary follicular mucinosis the lesions can resolve spontaneously in a couple of years. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids, oral antibiotics like macrolides or tetracyclines, dapsone, and phototherapy.
KFC can be treated with vitamin D analogues. It is usually unresponsive to corticosteroids, keratolytic lotions, and retinoids. Our patient was prescribed calcipotriene.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego
References
1. Kanzaki T et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(1):134-5.
2. Buechner AA et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Jan 1;154(1):111-2.
Given the presentation and the unique location of the lesions he was diagnosed with follicular keratosis of the chin (FKC).
This is a rare and poorly understood condition that can be present in older children and young teenagers. In the cases reported by Kanzaki et al.1 were two boys who presented with the condition; it was thought to be associated with rubbing of the chin with their hands when watching TV or reading. The author described improvement with habit change. This condition is usually described in boys, and some cases presented in brothers,2 suggesting a genetic predisposition. Some reports lack a history of rubbing or trauma to the area.
Histopathologic evaluation of the lesions demonstrates dilated hair follicles containing keratotic basophilic material without any signs of inflammation.
The lesions can be confused with keratosis pilaris (KP). Keratosis pilaris can be described in association with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis, which were not present in our patient. The lesions usually present on the sides of the cheeks and lateral region of the arms and legs. Compared with follicular keratosis, KP lesions usually present with associated perifollicular erythema. Our patient did not present with lesions on the cheeks or the sides of the arms or legs. Milia can present on the chin of children, usually if there is history of rubbing or trauma, or on a scar. Milia are micro keratin cysts, usually seen in areas of the face. Lichen spinulous is described as rough small follicular papules that present in oval or circular patches that can grow up to 5 cm and spread rapidly. They usually present on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, neck, abdomen, and knees. These lesions are thought to be secondary to infections, have been associated with atopy, and have been seen in patients with atopic dermatitis. There is a probable genetic predisposition. The lesions are usually treated with gentle soaps and moisturizer containing keratolytics like urea or salicylic acid, and in some cases topical retinoids can also be tried. Follicular mucinosis can also present similarly to keratosis follicularis. The lesions present as scaly plaques or as grouped skin color papules on the face, scalp, or the neck that can also be associated with hair loss. Sometimes a biopsy needs to be done to be able to distinguish it from follicular keratosis. There is an increase of mucin around hair follicles and sebaceous glands with associated inflammation and degeneration of the follicular structures. In patients with primary follicular mucinosis the lesions can resolve spontaneously in a couple of years. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids, oral antibiotics like macrolides or tetracyclines, dapsone, and phototherapy.
KFC can be treated with vitamin D analogues. It is usually unresponsive to corticosteroids, keratolytic lotions, and retinoids. Our patient was prescribed calcipotriene.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego
References
1. Kanzaki T et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(1):134-5.
2. Buechner AA et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Jan 1;154(1):111-2.
Given the presentation and the unique location of the lesions he was diagnosed with follicular keratosis of the chin (FKC).
This is a rare and poorly understood condition that can be present in older children and young teenagers. In the cases reported by Kanzaki et al.1 were two boys who presented with the condition; it was thought to be associated with rubbing of the chin with their hands when watching TV or reading. The author described improvement with habit change. This condition is usually described in boys, and some cases presented in brothers,2 suggesting a genetic predisposition. Some reports lack a history of rubbing or trauma to the area.
Histopathologic evaluation of the lesions demonstrates dilated hair follicles containing keratotic basophilic material without any signs of inflammation.
The lesions can be confused with keratosis pilaris (KP). Keratosis pilaris can be described in association with atopic dermatitis and ichthyosis, which were not present in our patient. The lesions usually present on the sides of the cheeks and lateral region of the arms and legs. Compared with follicular keratosis, KP lesions usually present with associated perifollicular erythema. Our patient did not present with lesions on the cheeks or the sides of the arms or legs. Milia can present on the chin of children, usually if there is history of rubbing or trauma, or on a scar. Milia are micro keratin cysts, usually seen in areas of the face. Lichen spinulous is described as rough small follicular papules that present in oval or circular patches that can grow up to 5 cm and spread rapidly. They usually present on the extensor surfaces of the extremities, neck, abdomen, and knees. These lesions are thought to be secondary to infections, have been associated with atopy, and have been seen in patients with atopic dermatitis. There is a probable genetic predisposition. The lesions are usually treated with gentle soaps and moisturizer containing keratolytics like urea or salicylic acid, and in some cases topical retinoids can also be tried. Follicular mucinosis can also present similarly to keratosis follicularis. The lesions present as scaly plaques or as grouped skin color papules on the face, scalp, or the neck that can also be associated with hair loss. Sometimes a biopsy needs to be done to be able to distinguish it from follicular keratosis. There is an increase of mucin around hair follicles and sebaceous glands with associated inflammation and degeneration of the follicular structures. In patients with primary follicular mucinosis the lesions can resolve spontaneously in a couple of years. Lesions can be treated with topical corticosteroids, oral antibiotics like macrolides or tetracyclines, dapsone, and phototherapy.
KFC can be treated with vitamin D analogues. It is usually unresponsive to corticosteroids, keratolytic lotions, and retinoids. Our patient was prescribed calcipotriene.
Dr. Matiz is a pediatric dermatologist at Southern California Permanente Medical Group, San Diego
References
1. Kanzaki T et al. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1992;26(1):134-5.
2. Buechner AA et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2018 Jan 1;154(1):111-2.
He is a healthy child with no past medical history. He is not taking any medications.
On physical exam he has follicular hyperkeratotic papules on the chin. No lesions on the axilla or thighs.
Reach Out and Read redux
When I speak with parents and colleagues about the well-being of today’s youth, the nearly unanimous cry is the negative effects of social media. But then, after a few moments of silence they say, “I don’t know how we can stop it. The genie is out of the bottle.”
The helplessness we as responsible adults and professionals feel about our inability to change this cultural shift to youth fixation on social media and its increasingly clear impact on depression, anxiety, self-esteem, and even suicide is profound. In China the country has “simply” regulated access to the Internet for children to 2 hours per day and blocked many websites. But such universal restriction is not likely in the United States. We need some other solutions.
A solution for all ages
Reach Out and Read, an international program promoting early relational health and literacy by encouraging and modeling reading and handing out books to families with children aged 0-5 years, has significant evidence for improving child development and parent-child interaction.
But why stop promoting reading and the associated parent-child bonding at 5 years old? Academic progress, child mental health and well-being, and family relationships are all currently in trouble and could all benefit from more reading. As pediatric providers for all ages of children and youth we can effectively promote reading as part of preventive care, not just for the youngest.
Reading fluency is a key factor in academic success. A study from 2019, before the pandemic, found that by the end of high school, students were reading 19% slower than were students of a similar age 50 years ago. The possible reasons, among many, include poverty with its effect on vocabulary, modeling and access to books, hours on social media, and less unstructured time to read for pleasure. With less reading comes less practice. Reading then doesn’t feel as comfortable and is avoided.
The pandemic made measures of academic level even worse, with reading fluency in second and third grade now about 30% behind what would be expected. Reading fluency and comprehension become more critical for future academic progress beginning in third grade when “learning to read” shifts to “reading to learn.” Educators are doing their best to catch children up but with limited support resources, and families need strategies to help their children.
Early strategies to promote reading by discussing the benefits with parents of bedtime stories and sharing books seems easy in comparison to encouraging school-aged children and older youth to read. But there are good reasons and strategies to persist.
Reading can help a child’s mental health as well as development. After a day at school, picking up another book may seem to the parent like more homework. But “reading for pleasure” is different. Reading has been shown to lower heart rate and muscle tension and reduce stress by as much as 68% in minutes, even lowering cortisol and activating pleasure centers of the brain. An immersive story can distract one from worries and be a real escape; the opposite of looking at social media online where peer comparisons and a constant stream of nasty comments 24/7 are culprits producing anxiety, depression, eating disorders, and suicide. Books that have characters going through similar struggles as those of the youth provide a sense of not being alone with these stresses and generally include models of problem solving and resolution that can inspire hopefulness. Joining (or starting) a kids’ or parent-child book club offers a chance to socialize with a nonjudgmental shared focus. There are books with content about all sorts of topics that may be areas the child or youth have as life and career goals that may help them gain new ideas and confidence as well as knowledge and skills. Having clear ideas about future roles is a one way to reduce the chance of developing depression and even suicide.
Reading a book, ideally illuminated by a warm colored light, assists in falling asleep, a huge issue for many youth. This is valuable in itself as inadequate sleep is a large contributor to worsening of many mental conditions. In contrast, the blue light from computer screens makes it harder to fall asleep. When reading a book is a bedtime habit, just as for babies and toddlers and whether read to by a parent (no age is too old!) or reading alone, the routine itself helps prepare the brain to transition into sleep.
Encouraging good habits
But how can parents get their children away from scanning the Internet to reading books? The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests setting time blocks for the day designated for school, exercise, homework, media, and sleep with a goal of a healthy balance. Reading could be added to the family’s plan. Making reading in the same room with parents as a regular habit both models reading (as parents have to get offline, too!) and sets up an opportunity to ask questions and converse about the reading materials, thereby building family relationships. Children are notorious for being recalcitrant about talking “about their day” when coming home from school. Having a less personal and intrusive subject to talk about creates a favorable setting for precious parent-child discussions. Some families read aloud to each other. This comes up naturally when reading a clip from a newspaper or magazine. It is especially valuable and inclusive for younger children who may not yet be able to read that level of material.
Getting creative
Some other strategies to promote reading include bringing books, magazines, or even comics with subjects that interest the child or youth into the house and leaving them around without comment. Getting started on a book series (Nancy Drew, Harry Potter, etc.) that is captivating provides extra incentive. Parents can talk about their favorites from their childhood, some of which are timeless! Families may need to be creative and find literature about the online characters from video games or movies that already interest their child, even if those are not seen as ideal learning material. Not commenting on the presence of the reading material takes the pressure off and makes it clear that it is their choice whether to read them or not.
Books need to be seen as a gift rather than a “penalty” for being online. Visiting a bookstore together or giving a gift certificate for books are other ways a parent can support reading while indicating that the youth has choice. There are now more than 150,000 Little Free Library locations worldwide (visible on the app) where books can be obtained 24/7 at no cost. Bringing books to donate or even joining the cause and becoming a steward of one of these pop-up libraries models high valuation of reading but is also a volunteer activity of which the child can be proud. We brought our children’s old books to our pediatric practice and encouraged patients to “bring one and take one.” Of course, the public library is often an option and is free. Another advantage of the library is that librarians and other children there may make suggestions of books that are popular with children their age. There are lots of specific suggestions online as well.
We need to be aware that children who resist reading books may have reading weaknesses. We can assess reading fluency with standard Gray Oral Reading paragraphs or the Wide Range Achievement test in the office or recommend a reading assessment by the school. Parents who already know that their child has a reading problem may be getting advice from teachers or tutors on how to help. But to promote reading that is not onerous for a child with a reading disability, parents can do more reading aloud at home, offer audiobooks or podcasts at home or play them while driving, and aim for books with a lower reading level. Teachers or librarians can make suggestions. It is important for family members to not be judgmental about a child’s choice of reading materials.
We do not need to feel helpless in the face of the Internet – we can recommend more reading!
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
When I speak with parents and colleagues about the well-being of today’s youth, the nearly unanimous cry is the negative effects of social media. But then, after a few moments of silence they say, “I don’t know how we can stop it. The genie is out of the bottle.”
The helplessness we as responsible adults and professionals feel about our inability to change this cultural shift to youth fixation on social media and its increasingly clear impact on depression, anxiety, self-esteem, and even suicide is profound. In China the country has “simply” regulated access to the Internet for children to 2 hours per day and blocked many websites. But such universal restriction is not likely in the United States. We need some other solutions.
A solution for all ages
Reach Out and Read, an international program promoting early relational health and literacy by encouraging and modeling reading and handing out books to families with children aged 0-5 years, has significant evidence for improving child development and parent-child interaction.
But why stop promoting reading and the associated parent-child bonding at 5 years old? Academic progress, child mental health and well-being, and family relationships are all currently in trouble and could all benefit from more reading. As pediatric providers for all ages of children and youth we can effectively promote reading as part of preventive care, not just for the youngest.
Reading fluency is a key factor in academic success. A study from 2019, before the pandemic, found that by the end of high school, students were reading 19% slower than were students of a similar age 50 years ago. The possible reasons, among many, include poverty with its effect on vocabulary, modeling and access to books, hours on social media, and less unstructured time to read for pleasure. With less reading comes less practice. Reading then doesn’t feel as comfortable and is avoided.
The pandemic made measures of academic level even worse, with reading fluency in second and third grade now about 30% behind what would be expected. Reading fluency and comprehension become more critical for future academic progress beginning in third grade when “learning to read” shifts to “reading to learn.” Educators are doing their best to catch children up but with limited support resources, and families need strategies to help their children.
Early strategies to promote reading by discussing the benefits with parents of bedtime stories and sharing books seems easy in comparison to encouraging school-aged children and older youth to read. But there are good reasons and strategies to persist.
Reading can help a child’s mental health as well as development. After a day at school, picking up another book may seem to the parent like more homework. But “reading for pleasure” is different. Reading has been shown to lower heart rate and muscle tension and reduce stress by as much as 68% in minutes, even lowering cortisol and activating pleasure centers of the brain. An immersive story can distract one from worries and be a real escape; the opposite of looking at social media online where peer comparisons and a constant stream of nasty comments 24/7 are culprits producing anxiety, depression, eating disorders, and suicide. Books that have characters going through similar struggles as those of the youth provide a sense of not being alone with these stresses and generally include models of problem solving and resolution that can inspire hopefulness. Joining (or starting) a kids’ or parent-child book club offers a chance to socialize with a nonjudgmental shared focus. There are books with content about all sorts of topics that may be areas the child or youth have as life and career goals that may help them gain new ideas and confidence as well as knowledge and skills. Having clear ideas about future roles is a one way to reduce the chance of developing depression and even suicide.
Reading a book, ideally illuminated by a warm colored light, assists in falling asleep, a huge issue for many youth. This is valuable in itself as inadequate sleep is a large contributor to worsening of many mental conditions. In contrast, the blue light from computer screens makes it harder to fall asleep. When reading a book is a bedtime habit, just as for babies and toddlers and whether read to by a parent (no age is too old!) or reading alone, the routine itself helps prepare the brain to transition into sleep.
Encouraging good habits
But how can parents get their children away from scanning the Internet to reading books? The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests setting time blocks for the day designated for school, exercise, homework, media, and sleep with a goal of a healthy balance. Reading could be added to the family’s plan. Making reading in the same room with parents as a regular habit both models reading (as parents have to get offline, too!) and sets up an opportunity to ask questions and converse about the reading materials, thereby building family relationships. Children are notorious for being recalcitrant about talking “about their day” when coming home from school. Having a less personal and intrusive subject to talk about creates a favorable setting for precious parent-child discussions. Some families read aloud to each other. This comes up naturally when reading a clip from a newspaper or magazine. It is especially valuable and inclusive for younger children who may not yet be able to read that level of material.
Getting creative
Some other strategies to promote reading include bringing books, magazines, or even comics with subjects that interest the child or youth into the house and leaving them around without comment. Getting started on a book series (Nancy Drew, Harry Potter, etc.) that is captivating provides extra incentive. Parents can talk about their favorites from their childhood, some of which are timeless! Families may need to be creative and find literature about the online characters from video games or movies that already interest their child, even if those are not seen as ideal learning material. Not commenting on the presence of the reading material takes the pressure off and makes it clear that it is their choice whether to read them or not.
Books need to be seen as a gift rather than a “penalty” for being online. Visiting a bookstore together or giving a gift certificate for books are other ways a parent can support reading while indicating that the youth has choice. There are now more than 150,000 Little Free Library locations worldwide (visible on the app) where books can be obtained 24/7 at no cost. Bringing books to donate or even joining the cause and becoming a steward of one of these pop-up libraries models high valuation of reading but is also a volunteer activity of which the child can be proud. We brought our children’s old books to our pediatric practice and encouraged patients to “bring one and take one.” Of course, the public library is often an option and is free. Another advantage of the library is that librarians and other children there may make suggestions of books that are popular with children their age. There are lots of specific suggestions online as well.
We need to be aware that children who resist reading books may have reading weaknesses. We can assess reading fluency with standard Gray Oral Reading paragraphs or the Wide Range Achievement test in the office or recommend a reading assessment by the school. Parents who already know that their child has a reading problem may be getting advice from teachers or tutors on how to help. But to promote reading that is not onerous for a child with a reading disability, parents can do more reading aloud at home, offer audiobooks or podcasts at home or play them while driving, and aim for books with a lower reading level. Teachers or librarians can make suggestions. It is important for family members to not be judgmental about a child’s choice of reading materials.
We do not need to feel helpless in the face of the Internet – we can recommend more reading!
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
When I speak with parents and colleagues about the well-being of today’s youth, the nearly unanimous cry is the negative effects of social media. But then, after a few moments of silence they say, “I don’t know how we can stop it. The genie is out of the bottle.”
The helplessness we as responsible adults and professionals feel about our inability to change this cultural shift to youth fixation on social media and its increasingly clear impact on depression, anxiety, self-esteem, and even suicide is profound. In China the country has “simply” regulated access to the Internet for children to 2 hours per day and blocked many websites. But such universal restriction is not likely in the United States. We need some other solutions.
A solution for all ages
Reach Out and Read, an international program promoting early relational health and literacy by encouraging and modeling reading and handing out books to families with children aged 0-5 years, has significant evidence for improving child development and parent-child interaction.
But why stop promoting reading and the associated parent-child bonding at 5 years old? Academic progress, child mental health and well-being, and family relationships are all currently in trouble and could all benefit from more reading. As pediatric providers for all ages of children and youth we can effectively promote reading as part of preventive care, not just for the youngest.
Reading fluency is a key factor in academic success. A study from 2019, before the pandemic, found that by the end of high school, students were reading 19% slower than were students of a similar age 50 years ago. The possible reasons, among many, include poverty with its effect on vocabulary, modeling and access to books, hours on social media, and less unstructured time to read for pleasure. With less reading comes less practice. Reading then doesn’t feel as comfortable and is avoided.
The pandemic made measures of academic level even worse, with reading fluency in second and third grade now about 30% behind what would be expected. Reading fluency and comprehension become more critical for future academic progress beginning in third grade when “learning to read” shifts to “reading to learn.” Educators are doing their best to catch children up but with limited support resources, and families need strategies to help their children.
Early strategies to promote reading by discussing the benefits with parents of bedtime stories and sharing books seems easy in comparison to encouraging school-aged children and older youth to read. But there are good reasons and strategies to persist.
Reading can help a child’s mental health as well as development. After a day at school, picking up another book may seem to the parent like more homework. But “reading for pleasure” is different. Reading has been shown to lower heart rate and muscle tension and reduce stress by as much as 68% in minutes, even lowering cortisol and activating pleasure centers of the brain. An immersive story can distract one from worries and be a real escape; the opposite of looking at social media online where peer comparisons and a constant stream of nasty comments 24/7 are culprits producing anxiety, depression, eating disorders, and suicide. Books that have characters going through similar struggles as those of the youth provide a sense of not being alone with these stresses and generally include models of problem solving and resolution that can inspire hopefulness. Joining (or starting) a kids’ or parent-child book club offers a chance to socialize with a nonjudgmental shared focus. There are books with content about all sorts of topics that may be areas the child or youth have as life and career goals that may help them gain new ideas and confidence as well as knowledge and skills. Having clear ideas about future roles is a one way to reduce the chance of developing depression and even suicide.
Reading a book, ideally illuminated by a warm colored light, assists in falling asleep, a huge issue for many youth. This is valuable in itself as inadequate sleep is a large contributor to worsening of many mental conditions. In contrast, the blue light from computer screens makes it harder to fall asleep. When reading a book is a bedtime habit, just as for babies and toddlers and whether read to by a parent (no age is too old!) or reading alone, the routine itself helps prepare the brain to transition into sleep.
Encouraging good habits
But how can parents get their children away from scanning the Internet to reading books? The American Academy of Pediatrics suggests setting time blocks for the day designated for school, exercise, homework, media, and sleep with a goal of a healthy balance. Reading could be added to the family’s plan. Making reading in the same room with parents as a regular habit both models reading (as parents have to get offline, too!) and sets up an opportunity to ask questions and converse about the reading materials, thereby building family relationships. Children are notorious for being recalcitrant about talking “about their day” when coming home from school. Having a less personal and intrusive subject to talk about creates a favorable setting for precious parent-child discussions. Some families read aloud to each other. This comes up naturally when reading a clip from a newspaper or magazine. It is especially valuable and inclusive for younger children who may not yet be able to read that level of material.
Getting creative
Some other strategies to promote reading include bringing books, magazines, or even comics with subjects that interest the child or youth into the house and leaving them around without comment. Getting started on a book series (Nancy Drew, Harry Potter, etc.) that is captivating provides extra incentive. Parents can talk about their favorites from their childhood, some of which are timeless! Families may need to be creative and find literature about the online characters from video games or movies that already interest their child, even if those are not seen as ideal learning material. Not commenting on the presence of the reading material takes the pressure off and makes it clear that it is their choice whether to read them or not.
Books need to be seen as a gift rather than a “penalty” for being online. Visiting a bookstore together or giving a gift certificate for books are other ways a parent can support reading while indicating that the youth has choice. There are now more than 150,000 Little Free Library locations worldwide (visible on the app) where books can be obtained 24/7 at no cost. Bringing books to donate or even joining the cause and becoming a steward of one of these pop-up libraries models high valuation of reading but is also a volunteer activity of which the child can be proud. We brought our children’s old books to our pediatric practice and encouraged patients to “bring one and take one.” Of course, the public library is often an option and is free. Another advantage of the library is that librarians and other children there may make suggestions of books that are popular with children their age. There are lots of specific suggestions online as well.
We need to be aware that children who resist reading books may have reading weaknesses. We can assess reading fluency with standard Gray Oral Reading paragraphs or the Wide Range Achievement test in the office or recommend a reading assessment by the school. Parents who already know that their child has a reading problem may be getting advice from teachers or tutors on how to help. But to promote reading that is not onerous for a child with a reading disability, parents can do more reading aloud at home, offer audiobooks or podcasts at home or play them while driving, and aim for books with a lower reading level. Teachers or librarians can make suggestions. It is important for family members to not be judgmental about a child’s choice of reading materials.
We do not need to feel helpless in the face of the Internet – we can recommend more reading!
Dr. Howard is assistant professor of pediatrics at The Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, and creator of CHADIS. She had no other relevant disclosures. Dr. Howard’s contribution to this publication was as a paid expert to MDedge News. E-mail her at [email protected].
Burnout threatens primary care workforce and doctors’ mental health
CHARLESTON, S.C. – Melanie Gray Miller, a 30-year-old physician, wiped away tears as she described the isolation she felt after losing a beloved patient.
“It was at the end of a night shift, when it seems like bad things always happen,” said Dr. Miller, who is training to become a pediatrician.
The infant had been sick for months in the Medical University of South Carolina’s pediatric intensive care unit and the possibility that he might not improve was obvious, Dr. Miller recalled during an April meeting with physicians and hospital administrators. But the suddenness of his death still caught her off guard.
“I have family and friends that I talk to about things,” she said. “But no one truly understands.”
Doctors don’t typically take time to grieve at work. But during that recent meeting, Dr. Miller and her colleagues opened up about the insomnia, emotional exhaustion, trauma, and burnout they experienced from their time in the pediatric ICU.
“This is not a normal place,” Grant Goodrich, the hospital system’s director of ethics, said to the group, acknowledging an occupational hazard the industry often downplays. “Most people don’t see kids die.”
The recurring conversation, scheduled for early-career doctors coming off month-long pediatric ICU rotations, is one way the hospital helps staffers cope with stress, according to Alyssa Rheingold, a licensed clinical psychologist who leads its resiliency program.
“Often the focus is to teach somebody how to do yoga and take a bath,” she said. “That’s not at all what well-being is about.”
Dr. Miller says working in the hospital’s pediatric intensive care unit can be tough. “In medicine, we’re just expected to be resilient 24/7,” she says. The trauma and stress from patients dying can be particularly hard to process.
Burnout in the health care industry is a widespread problem that long predates the COVID-19 pandemic, though the chaos introduced by the coronavirus’s spread made things worse, physicians and psychologists said. Health systems across the country are trying to boost morale and keep clinicians from quitting or retiring early, but the stakes are higher than workforce shortages.
Rates of physician suicide, partly fueled by burnout, have been a concern for decades.
“Why go into primary care when you can make twice the money doing something with half the stress?” said Daniel Crummett, a retired primary care doctor who lives in North Carolina. “I don’t know why anyone would go into primary care.”
Doctors say they are fed up with demands imposed by hospital administrators and health insurance companies, and they’re concerned about the notoriously grueling shifts assigned to medical residents during the early years of their careers. A long-standing stigma keeps physicians from prioritizing their own mental health, while their jobs require them to routinely grapple with death, grief, and trauma. The culture of medicine encourages them to simply bear it.
“Resiliency is a cringe word for me,” Dr. Miller said. “In medicine, we’re just expected to be resilient 24/7. I don’t love that culture.”
And though the pipeline of physicians entering the profession is strong, the ranks of doctors in the United States aren’t growing fast enough to meet future demand, according to the American Medical Association. That’s why burnout exacerbates workforce shortages and, if it continues, may limit the ability of some patients to access even basic care. A 2021 report published by the Association of American Medical Colleges projects the United States will be short as many as 48,000 primary care physicians by 2034, a higher number than any other single medical specialty.
A survey published last year by The Physicians Foundation, a nonprofit focused on improving health care, found more than half of the 1,501 responding doctors didn›t have positive feelings about the current or future state of the medical profession. More than 20% said they wanted to retire within a year.
Similarly, in a 2022 AMA survey of 11,000 doctors and other medical professionals, more than half reported feeling burned out and indicated they were experiencing a great deal of stress.
Those numbers appear to be even higher in primary care. Even before the pandemic, 70% of primary care providers and 89% of primary care residents reported feelings of burnout.
“Everyone in health care feels overworked,” said Gregg Coodley, a primary care physician in Portland, Ore., and author of the book “Patients in Peril: The Demise of Primary Care in America”
“I’m not saying there aren’t issues for other specialists, too, but in primary care, it’s the worst problem,” he said.
The high level of student debt most medical school graduates carry, combined with salaries more than four times as high as the average, deter many physicians from quitting medicine midcareer. Even primary care doctors, whose salaries are among the lowest of all medical specialties, are paid significantly more than the average American worker. That's why, instead of leaving the profession in their 30s or 40s, doctors often stay in their jobs but retire early.
“We go into medicine to help people, to take care of people, to do good in the world,” said Dr. Crummett, who retired from the Duke University hospital system in 2020 when he turned 65.
Dr. Crummett said he would have enjoyed working until he was 70, if not for the bureaucratic burdens of practicing medicine, including needing to get prior authorization from insurance companies before providing care, navigating cumbersome electronic health record platforms, and logging hours of administrative work outside the exam room.
“I enjoyed seeing patients. I really enjoyed my coworkers,” he said. “The administration was certainly a major factor in burnout.”
Jean Antonucci, a primary care doctor in rural Maine who retired from full-time work at 66, said she, too, would have kept working if not for the hassle of dealing with hospital administrators and insurance companies.
Once, Dr. Antonucci said, she had to call an insurance company – by landline and cellphone simultaneously, with one phone on each ear – to get prior authorization to conduct a CT scan, while her patient in need of an appendectomy waited in pain. The hospital wouldn’t conduct the scan without insurance approval.
“It was just infuriating,” said Dr. Antonucci, who now practices medicine only 1 day a week. “I could have kept working. I just got tired.”
Providers’ collective exhaustion is a crisis kept hidden by design, said Whitney Marvin, a pediatrician who works in the pediatric ICU at the Medical University of South Carolina. She said hospital culture implicitly teaches doctors to tamp down their emotions and to “keep moving.”
“I’m not supposed to be weak, and I’m not supposed to cry, and I’m not supposed to have all these emotions, because then maybe I’m not good enough at my job,” said Dr. Marvin, describing the way doctors have historically thought about their mental health.
This mentality prevents many doctors from seeking the help they need, which can lead to burnout – and much worse. An estimated 300 physicians die by suicide every year, according to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. The problem is particularly pronounced among female physicians, who die by suicide at a significantly higher rate than women in other professions.
A March report from this news organization found, of more than 9,000 doctors surveyed, 9% of male physicians and 11% of female physicians said they have had suicidal thoughts. But the problem isn’t new, the report noted. Elevated rates of suicide among physicians have been documented for 150 years.
“Ironically, it’s happening to a group of people who should have the easiest access to mental health care,” said Gary Price, a Connecticut surgeon and president of The Physicians Foundation.
But the reluctance to seek help isn’t unfounded, said Corey Feist, president of the Dr. Lorna Breen Heroes’ Foundation .
“There’s something known in residency as the ‘silent curriculum,’ ” Mr. Feist said in describing an often-unspoken understanding among doctors that seeking mental health treatment could jeopardize their livelihood.
Mr. Feist’s sister-in-law, emergency room physician Lorna Breen, died by suicide during the early months of the pandemic. Dr. Breen sought inpatient treatment for mental health once, Mr. Feist said, but feared that her medical license could be revoked for doing so.
The foundation works to change laws across the country to prohibit medical boards and hospitals from asking doctors invasive mental health questions on employment or license applications.
“These people need to be taken care of by us, because really, no one’s looking out for them,” Mr. Feist said.
In Charleston, psychologists are made available to physicians during group meetings like the one Dr. Miller attended, as part of the resiliency program.
But fixing the burnout problem also requires a cultural change, especially among older physicians.
“They had it worse and we know that. But it’s still not good,” Dr. Miller said. “Until that changes, we’re just going to continue burning out physicians within the first 3 years of their career.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.
CHARLESTON, S.C. – Melanie Gray Miller, a 30-year-old physician, wiped away tears as she described the isolation she felt after losing a beloved patient.
“It was at the end of a night shift, when it seems like bad things always happen,” said Dr. Miller, who is training to become a pediatrician.
The infant had been sick for months in the Medical University of South Carolina’s pediatric intensive care unit and the possibility that he might not improve was obvious, Dr. Miller recalled during an April meeting with physicians and hospital administrators. But the suddenness of his death still caught her off guard.
“I have family and friends that I talk to about things,” she said. “But no one truly understands.”
Doctors don’t typically take time to grieve at work. But during that recent meeting, Dr. Miller and her colleagues opened up about the insomnia, emotional exhaustion, trauma, and burnout they experienced from their time in the pediatric ICU.
“This is not a normal place,” Grant Goodrich, the hospital system’s director of ethics, said to the group, acknowledging an occupational hazard the industry often downplays. “Most people don’t see kids die.”
The recurring conversation, scheduled for early-career doctors coming off month-long pediatric ICU rotations, is one way the hospital helps staffers cope with stress, according to Alyssa Rheingold, a licensed clinical psychologist who leads its resiliency program.
“Often the focus is to teach somebody how to do yoga and take a bath,” she said. “That’s not at all what well-being is about.”
Dr. Miller says working in the hospital’s pediatric intensive care unit can be tough. “In medicine, we’re just expected to be resilient 24/7,” she says. The trauma and stress from patients dying can be particularly hard to process.
Burnout in the health care industry is a widespread problem that long predates the COVID-19 pandemic, though the chaos introduced by the coronavirus’s spread made things worse, physicians and psychologists said. Health systems across the country are trying to boost morale and keep clinicians from quitting or retiring early, but the stakes are higher than workforce shortages.
Rates of physician suicide, partly fueled by burnout, have been a concern for decades.
“Why go into primary care when you can make twice the money doing something with half the stress?” said Daniel Crummett, a retired primary care doctor who lives in North Carolina. “I don’t know why anyone would go into primary care.”
Doctors say they are fed up with demands imposed by hospital administrators and health insurance companies, and they’re concerned about the notoriously grueling shifts assigned to medical residents during the early years of their careers. A long-standing stigma keeps physicians from prioritizing their own mental health, while their jobs require them to routinely grapple with death, grief, and trauma. The culture of medicine encourages them to simply bear it.
“Resiliency is a cringe word for me,” Dr. Miller said. “In medicine, we’re just expected to be resilient 24/7. I don’t love that culture.”
And though the pipeline of physicians entering the profession is strong, the ranks of doctors in the United States aren’t growing fast enough to meet future demand, according to the American Medical Association. That’s why burnout exacerbates workforce shortages and, if it continues, may limit the ability of some patients to access even basic care. A 2021 report published by the Association of American Medical Colleges projects the United States will be short as many as 48,000 primary care physicians by 2034, a higher number than any other single medical specialty.
A survey published last year by The Physicians Foundation, a nonprofit focused on improving health care, found more than half of the 1,501 responding doctors didn›t have positive feelings about the current or future state of the medical profession. More than 20% said they wanted to retire within a year.
Similarly, in a 2022 AMA survey of 11,000 doctors and other medical professionals, more than half reported feeling burned out and indicated they were experiencing a great deal of stress.
Those numbers appear to be even higher in primary care. Even before the pandemic, 70% of primary care providers and 89% of primary care residents reported feelings of burnout.
“Everyone in health care feels overworked,” said Gregg Coodley, a primary care physician in Portland, Ore., and author of the book “Patients in Peril: The Demise of Primary Care in America”
“I’m not saying there aren’t issues for other specialists, too, but in primary care, it’s the worst problem,” he said.
The high level of student debt most medical school graduates carry, combined with salaries more than four times as high as the average, deter many physicians from quitting medicine midcareer. Even primary care doctors, whose salaries are among the lowest of all medical specialties, are paid significantly more than the average American worker. That's why, instead of leaving the profession in their 30s or 40s, doctors often stay in their jobs but retire early.
“We go into medicine to help people, to take care of people, to do good in the world,” said Dr. Crummett, who retired from the Duke University hospital system in 2020 when he turned 65.
Dr. Crummett said he would have enjoyed working until he was 70, if not for the bureaucratic burdens of practicing medicine, including needing to get prior authorization from insurance companies before providing care, navigating cumbersome electronic health record platforms, and logging hours of administrative work outside the exam room.
“I enjoyed seeing patients. I really enjoyed my coworkers,” he said. “The administration was certainly a major factor in burnout.”
Jean Antonucci, a primary care doctor in rural Maine who retired from full-time work at 66, said she, too, would have kept working if not for the hassle of dealing with hospital administrators and insurance companies.
Once, Dr. Antonucci said, she had to call an insurance company – by landline and cellphone simultaneously, with one phone on each ear – to get prior authorization to conduct a CT scan, while her patient in need of an appendectomy waited in pain. The hospital wouldn’t conduct the scan without insurance approval.
“It was just infuriating,” said Dr. Antonucci, who now practices medicine only 1 day a week. “I could have kept working. I just got tired.”
Providers’ collective exhaustion is a crisis kept hidden by design, said Whitney Marvin, a pediatrician who works in the pediatric ICU at the Medical University of South Carolina. She said hospital culture implicitly teaches doctors to tamp down their emotions and to “keep moving.”
“I’m not supposed to be weak, and I’m not supposed to cry, and I’m not supposed to have all these emotions, because then maybe I’m not good enough at my job,” said Dr. Marvin, describing the way doctors have historically thought about their mental health.
This mentality prevents many doctors from seeking the help they need, which can lead to burnout – and much worse. An estimated 300 physicians die by suicide every year, according to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. The problem is particularly pronounced among female physicians, who die by suicide at a significantly higher rate than women in other professions.
A March report from this news organization found, of more than 9,000 doctors surveyed, 9% of male physicians and 11% of female physicians said they have had suicidal thoughts. But the problem isn’t new, the report noted. Elevated rates of suicide among physicians have been documented for 150 years.
“Ironically, it’s happening to a group of people who should have the easiest access to mental health care,” said Gary Price, a Connecticut surgeon and president of The Physicians Foundation.
But the reluctance to seek help isn’t unfounded, said Corey Feist, president of the Dr. Lorna Breen Heroes’ Foundation .
“There’s something known in residency as the ‘silent curriculum,’ ” Mr. Feist said in describing an often-unspoken understanding among doctors that seeking mental health treatment could jeopardize their livelihood.
Mr. Feist’s sister-in-law, emergency room physician Lorna Breen, died by suicide during the early months of the pandemic. Dr. Breen sought inpatient treatment for mental health once, Mr. Feist said, but feared that her medical license could be revoked for doing so.
The foundation works to change laws across the country to prohibit medical boards and hospitals from asking doctors invasive mental health questions on employment or license applications.
“These people need to be taken care of by us, because really, no one’s looking out for them,” Mr. Feist said.
In Charleston, psychologists are made available to physicians during group meetings like the one Dr. Miller attended, as part of the resiliency program.
But fixing the burnout problem also requires a cultural change, especially among older physicians.
“They had it worse and we know that. But it’s still not good,” Dr. Miller said. “Until that changes, we’re just going to continue burning out physicians within the first 3 years of their career.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.
CHARLESTON, S.C. – Melanie Gray Miller, a 30-year-old physician, wiped away tears as she described the isolation she felt after losing a beloved patient.
“It was at the end of a night shift, when it seems like bad things always happen,” said Dr. Miller, who is training to become a pediatrician.
The infant had been sick for months in the Medical University of South Carolina’s pediatric intensive care unit and the possibility that he might not improve was obvious, Dr. Miller recalled during an April meeting with physicians and hospital administrators. But the suddenness of his death still caught her off guard.
“I have family and friends that I talk to about things,” she said. “But no one truly understands.”
Doctors don’t typically take time to grieve at work. But during that recent meeting, Dr. Miller and her colleagues opened up about the insomnia, emotional exhaustion, trauma, and burnout they experienced from their time in the pediatric ICU.
“This is not a normal place,” Grant Goodrich, the hospital system’s director of ethics, said to the group, acknowledging an occupational hazard the industry often downplays. “Most people don’t see kids die.”
The recurring conversation, scheduled for early-career doctors coming off month-long pediatric ICU rotations, is one way the hospital helps staffers cope with stress, according to Alyssa Rheingold, a licensed clinical psychologist who leads its resiliency program.
“Often the focus is to teach somebody how to do yoga and take a bath,” she said. “That’s not at all what well-being is about.”
Dr. Miller says working in the hospital’s pediatric intensive care unit can be tough. “In medicine, we’re just expected to be resilient 24/7,” she says. The trauma and stress from patients dying can be particularly hard to process.
Burnout in the health care industry is a widespread problem that long predates the COVID-19 pandemic, though the chaos introduced by the coronavirus’s spread made things worse, physicians and psychologists said. Health systems across the country are trying to boost morale and keep clinicians from quitting or retiring early, but the stakes are higher than workforce shortages.
Rates of physician suicide, partly fueled by burnout, have been a concern for decades.
“Why go into primary care when you can make twice the money doing something with half the stress?” said Daniel Crummett, a retired primary care doctor who lives in North Carolina. “I don’t know why anyone would go into primary care.”
Doctors say they are fed up with demands imposed by hospital administrators and health insurance companies, and they’re concerned about the notoriously grueling shifts assigned to medical residents during the early years of their careers. A long-standing stigma keeps physicians from prioritizing their own mental health, while their jobs require them to routinely grapple with death, grief, and trauma. The culture of medicine encourages them to simply bear it.
“Resiliency is a cringe word for me,” Dr. Miller said. “In medicine, we’re just expected to be resilient 24/7. I don’t love that culture.”
And though the pipeline of physicians entering the profession is strong, the ranks of doctors in the United States aren’t growing fast enough to meet future demand, according to the American Medical Association. That’s why burnout exacerbates workforce shortages and, if it continues, may limit the ability of some patients to access even basic care. A 2021 report published by the Association of American Medical Colleges projects the United States will be short as many as 48,000 primary care physicians by 2034, a higher number than any other single medical specialty.
A survey published last year by The Physicians Foundation, a nonprofit focused on improving health care, found more than half of the 1,501 responding doctors didn›t have positive feelings about the current or future state of the medical profession. More than 20% said they wanted to retire within a year.
Similarly, in a 2022 AMA survey of 11,000 doctors and other medical professionals, more than half reported feeling burned out and indicated they were experiencing a great deal of stress.
Those numbers appear to be even higher in primary care. Even before the pandemic, 70% of primary care providers and 89% of primary care residents reported feelings of burnout.
“Everyone in health care feels overworked,” said Gregg Coodley, a primary care physician in Portland, Ore., and author of the book “Patients in Peril: The Demise of Primary Care in America”
“I’m not saying there aren’t issues for other specialists, too, but in primary care, it’s the worst problem,” he said.
The high level of student debt most medical school graduates carry, combined with salaries more than four times as high as the average, deter many physicians from quitting medicine midcareer. Even primary care doctors, whose salaries are among the lowest of all medical specialties, are paid significantly more than the average American worker. That's why, instead of leaving the profession in their 30s or 40s, doctors often stay in their jobs but retire early.
“We go into medicine to help people, to take care of people, to do good in the world,” said Dr. Crummett, who retired from the Duke University hospital system in 2020 when he turned 65.
Dr. Crummett said he would have enjoyed working until he was 70, if not for the bureaucratic burdens of practicing medicine, including needing to get prior authorization from insurance companies before providing care, navigating cumbersome electronic health record platforms, and logging hours of administrative work outside the exam room.
“I enjoyed seeing patients. I really enjoyed my coworkers,” he said. “The administration was certainly a major factor in burnout.”
Jean Antonucci, a primary care doctor in rural Maine who retired from full-time work at 66, said she, too, would have kept working if not for the hassle of dealing with hospital administrators and insurance companies.
Once, Dr. Antonucci said, she had to call an insurance company – by landline and cellphone simultaneously, with one phone on each ear – to get prior authorization to conduct a CT scan, while her patient in need of an appendectomy waited in pain. The hospital wouldn’t conduct the scan without insurance approval.
“It was just infuriating,” said Dr. Antonucci, who now practices medicine only 1 day a week. “I could have kept working. I just got tired.”
Providers’ collective exhaustion is a crisis kept hidden by design, said Whitney Marvin, a pediatrician who works in the pediatric ICU at the Medical University of South Carolina. She said hospital culture implicitly teaches doctors to tamp down their emotions and to “keep moving.”
“I’m not supposed to be weak, and I’m not supposed to cry, and I’m not supposed to have all these emotions, because then maybe I’m not good enough at my job,” said Dr. Marvin, describing the way doctors have historically thought about their mental health.
This mentality prevents many doctors from seeking the help they need, which can lead to burnout – and much worse. An estimated 300 physicians die by suicide every year, according to the American Foundation for Suicide Prevention. The problem is particularly pronounced among female physicians, who die by suicide at a significantly higher rate than women in other professions.
A March report from this news organization found, of more than 9,000 doctors surveyed, 9% of male physicians and 11% of female physicians said they have had suicidal thoughts. But the problem isn’t new, the report noted. Elevated rates of suicide among physicians have been documented for 150 years.
“Ironically, it’s happening to a group of people who should have the easiest access to mental health care,” said Gary Price, a Connecticut surgeon and president of The Physicians Foundation.
But the reluctance to seek help isn’t unfounded, said Corey Feist, president of the Dr. Lorna Breen Heroes’ Foundation .
“There’s something known in residency as the ‘silent curriculum,’ ” Mr. Feist said in describing an often-unspoken understanding among doctors that seeking mental health treatment could jeopardize their livelihood.
Mr. Feist’s sister-in-law, emergency room physician Lorna Breen, died by suicide during the early months of the pandemic. Dr. Breen sought inpatient treatment for mental health once, Mr. Feist said, but feared that her medical license could be revoked for doing so.
The foundation works to change laws across the country to prohibit medical boards and hospitals from asking doctors invasive mental health questions on employment or license applications.
“These people need to be taken care of by us, because really, no one’s looking out for them,” Mr. Feist said.
In Charleston, psychologists are made available to physicians during group meetings like the one Dr. Miller attended, as part of the resiliency program.
But fixing the burnout problem also requires a cultural change, especially among older physicians.
“They had it worse and we know that. But it’s still not good,” Dr. Miller said. “Until that changes, we’re just going to continue burning out physicians within the first 3 years of their career.”
KFF Health News is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues and is one of the core operating programs at KFF — the independent source for health policy research, polling, and journalism.
Kangaroo mother care may cut death risk for premature babies by a third
, according to new research published online in BMJ Global Health.
Starting the contact, which involves mothers carrying the newborn in a sling, within 24 hours of birth and continuing it for at least 8 hours a day both appear to amplify the effect on reducing mortality and infection, the paper states.
Sindhu Sivanandan, MD, with the department of neonatology at Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India, and Mari Jeeva Sankar, MD, in the pediatrics department of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, looked at existing studies to compare KMC with conventional care and to compare starting the intervention within 24 hours of birth versus a later start.
Their review looked at 31 trials that included 15,559 low-birthweight and preterm infants collectively. Of the 31 trials, 27 studies compared KMC with conventional care and four compared early with late initiation of KMC.
Mortality risk reduction
Analysis showed that, compared with conventional care, KMC appeared to cut mortality risk by 32% (relative risk, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.86) during birth hospitalization or by 28 days after birth, while it seemed to reduce the risk of severe infection, such as sepsis, by 15% (RR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.76-0.96; low-certainty evidence.)
That mortality-risk reduction was found regardless of gestational age or weight of the child at enrolment, time of starting KMC, and whether the intervention was started in a hospital or community.
The studies that had compared early with late-initiated KMC showed a reduction in neonatal mortality of 33%.
Low- and middle-income countries have the highest rates of premature births (gestational age of less than 37 weeks) and low birthweight (less than 2,500 grams). Premature births and low birthweight both are key causes of death and disability.
The World Health Organization recommends KMC as the standard of care among low birthweight infants after clinical stabilization. The American Academy of Pediatrics also promotes immediate KMC.
Relevance in the U.S.
Grace Chan, MD, MPH, PhD, an epidemiologist and pediatrician with the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, said though the practice is promoted by the WHO and AAP, recommendations to families vary widely by providers.
She said the health benefits for KMC are numerous. One of the biggest is that skin-to-skin contact can help transfer heat to newborns who may have trouble regulating their own temperature. That is especially important in cold climates in places where there may be insufficient indoor heat.
She said it’s well-known that preterm babies are at higher risk for apnea, and listening to a mother’s heartbeat may stimulate the child to breathe regularly.
Additionally with KMC, there’s an inherent benefit of a mother or caregiver being able to see any change in a newborn’s color immediately when the baby is held so closely, as opposed to a nurse watching several babies at a time in a neonatal intensive care unit.
This is evidence that starting KMC right away is important, because the risk of death for premature and low-weight newborns is highest in the first 24 hours of life, Dr. Chan noted.
Barriers of time
There are some barriers, she noted, in that mothers or other caregivers caring for several young children may not have the time to carry a child in a sling for 8 or more hours at a time.
The authors conclude that their findings have policy implications, particularly for low- and middle-income countries: “KMC should be provided to all low birth weight and preterm infants irrespective of the settings – both health facilities and at home,” they wrote.
The authors caution that, “very low birth weight, extremely preterm neonates, and severely unstable neonates were often excluded from studies. More evidence is needed before extrapolating the study results in these high-risk groups.”
The study authors and Dr. Chan report no relevant financial relationships.
, according to new research published online in BMJ Global Health.
Starting the contact, which involves mothers carrying the newborn in a sling, within 24 hours of birth and continuing it for at least 8 hours a day both appear to amplify the effect on reducing mortality and infection, the paper states.
Sindhu Sivanandan, MD, with the department of neonatology at Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India, and Mari Jeeva Sankar, MD, in the pediatrics department of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, looked at existing studies to compare KMC with conventional care and to compare starting the intervention within 24 hours of birth versus a later start.
Their review looked at 31 trials that included 15,559 low-birthweight and preterm infants collectively. Of the 31 trials, 27 studies compared KMC with conventional care and four compared early with late initiation of KMC.
Mortality risk reduction
Analysis showed that, compared with conventional care, KMC appeared to cut mortality risk by 32% (relative risk, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.86) during birth hospitalization or by 28 days after birth, while it seemed to reduce the risk of severe infection, such as sepsis, by 15% (RR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.76-0.96; low-certainty evidence.)
That mortality-risk reduction was found regardless of gestational age or weight of the child at enrolment, time of starting KMC, and whether the intervention was started in a hospital or community.
The studies that had compared early with late-initiated KMC showed a reduction in neonatal mortality of 33%.
Low- and middle-income countries have the highest rates of premature births (gestational age of less than 37 weeks) and low birthweight (less than 2,500 grams). Premature births and low birthweight both are key causes of death and disability.
The World Health Organization recommends KMC as the standard of care among low birthweight infants after clinical stabilization. The American Academy of Pediatrics also promotes immediate KMC.
Relevance in the U.S.
Grace Chan, MD, MPH, PhD, an epidemiologist and pediatrician with the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, said though the practice is promoted by the WHO and AAP, recommendations to families vary widely by providers.
She said the health benefits for KMC are numerous. One of the biggest is that skin-to-skin contact can help transfer heat to newborns who may have trouble regulating their own temperature. That is especially important in cold climates in places where there may be insufficient indoor heat.
She said it’s well-known that preterm babies are at higher risk for apnea, and listening to a mother’s heartbeat may stimulate the child to breathe regularly.
Additionally with KMC, there’s an inherent benefit of a mother or caregiver being able to see any change in a newborn’s color immediately when the baby is held so closely, as opposed to a nurse watching several babies at a time in a neonatal intensive care unit.
This is evidence that starting KMC right away is important, because the risk of death for premature and low-weight newborns is highest in the first 24 hours of life, Dr. Chan noted.
Barriers of time
There are some barriers, she noted, in that mothers or other caregivers caring for several young children may not have the time to carry a child in a sling for 8 or more hours at a time.
The authors conclude that their findings have policy implications, particularly for low- and middle-income countries: “KMC should be provided to all low birth weight and preterm infants irrespective of the settings – both health facilities and at home,” they wrote.
The authors caution that, “very low birth weight, extremely preterm neonates, and severely unstable neonates were often excluded from studies. More evidence is needed before extrapolating the study results in these high-risk groups.”
The study authors and Dr. Chan report no relevant financial relationships.
, according to new research published online in BMJ Global Health.
Starting the contact, which involves mothers carrying the newborn in a sling, within 24 hours of birth and continuing it for at least 8 hours a day both appear to amplify the effect on reducing mortality and infection, the paper states.
Sindhu Sivanandan, MD, with the department of neonatology at Jawaharlal Institute of Postgraduate Medical Education and Research, Puducherry, India, and Mari Jeeva Sankar, MD, in the pediatrics department of the All India Institute of Medical Sciences, New Delhi, looked at existing studies to compare KMC with conventional care and to compare starting the intervention within 24 hours of birth versus a later start.
Their review looked at 31 trials that included 15,559 low-birthweight and preterm infants collectively. Of the 31 trials, 27 studies compared KMC with conventional care and four compared early with late initiation of KMC.
Mortality risk reduction
Analysis showed that, compared with conventional care, KMC appeared to cut mortality risk by 32% (relative risk, 0.68; 95% confidence interval, 0.53-0.86) during birth hospitalization or by 28 days after birth, while it seemed to reduce the risk of severe infection, such as sepsis, by 15% (RR, 0.85; 95% CI, 0.76-0.96; low-certainty evidence.)
That mortality-risk reduction was found regardless of gestational age or weight of the child at enrolment, time of starting KMC, and whether the intervention was started in a hospital or community.
The studies that had compared early with late-initiated KMC showed a reduction in neonatal mortality of 33%.
Low- and middle-income countries have the highest rates of premature births (gestational age of less than 37 weeks) and low birthweight (less than 2,500 grams). Premature births and low birthweight both are key causes of death and disability.
The World Health Organization recommends KMC as the standard of care among low birthweight infants after clinical stabilization. The American Academy of Pediatrics also promotes immediate KMC.
Relevance in the U.S.
Grace Chan, MD, MPH, PhD, an epidemiologist and pediatrician with the Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, said though the practice is promoted by the WHO and AAP, recommendations to families vary widely by providers.
She said the health benefits for KMC are numerous. One of the biggest is that skin-to-skin contact can help transfer heat to newborns who may have trouble regulating their own temperature. That is especially important in cold climates in places where there may be insufficient indoor heat.
She said it’s well-known that preterm babies are at higher risk for apnea, and listening to a mother’s heartbeat may stimulate the child to breathe regularly.
Additionally with KMC, there’s an inherent benefit of a mother or caregiver being able to see any change in a newborn’s color immediately when the baby is held so closely, as opposed to a nurse watching several babies at a time in a neonatal intensive care unit.
This is evidence that starting KMC right away is important, because the risk of death for premature and low-weight newborns is highest in the first 24 hours of life, Dr. Chan noted.
Barriers of time
There are some barriers, she noted, in that mothers or other caregivers caring for several young children may not have the time to carry a child in a sling for 8 or more hours at a time.
The authors conclude that their findings have policy implications, particularly for low- and middle-income countries: “KMC should be provided to all low birth weight and preterm infants irrespective of the settings – both health facilities and at home,” they wrote.
The authors caution that, “very low birth weight, extremely preterm neonates, and severely unstable neonates were often excluded from studies. More evidence is needed before extrapolating the study results in these high-risk groups.”
The study authors and Dr. Chan report no relevant financial relationships.
FROM BMJ GLOBAL HEALTH
Alcohol dependence in teens tied to subsequent depression
TOPLINE
Alcohol dependence, but not consumption, at age 18 years increases the risk for depression at age 24 years.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included 3,902 mostly White adolescents, about 58% female, born in England from April 1991 to December 1992, who were part of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) that examined genetic and environmental determinants of health and development.
- Participants completed the self-report Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) between the ages of 16 and 23 years, a period when average alcohol use increases rapidly.
- The primary outcome was probability for depression at age 24 years, using the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), a self-administered computerized clinical assessment of common mental disorder symptoms during the past week.
- Researchers assessed frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption as well as alcohol dependence.
- Confounders included sex, housing type, maternal education and depressive symptoms, parents’ alcohol use, conduct problems at age 4 years, being bullied, and smoking status.
TAKEAWAYS
- After adjustments, alcohol dependence at age 18 years was associated with depression at age 24 years (unstandardized probit coefficient 0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.02-0.25; P = .019)
- The relationship appeared to persist for alcohol dependence at each age of the growth curve (17-22 years).
- There was no evidence that frequency or quantity of alcohol consumption at age 18 was significantly associated with depression at age 24, suggesting these factors may not increase the risk for later depression unless there are also features of dependency.
IN PRACTICE
“Our findings suggest that preventing alcohol dependence during adolescence, or treating it early, could reduce the risk of depression,” which could have important public health implications, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS
The study was carried out by researchers at the University of Bristol; University College London; Critical Thinking Unit, Public Health Directorate, NHS; University of Nottingham, all in the United Kingdom. It was published online in Lancet Psychiatry
LIMITATIONS
There was substantial attrition in the ALSPAC cohort from birth to age 24 years. The sample was recruited from one U.K. region and most participants were White. Measures of alcohol consumption and dependence excluded some features of abuse. And as this is an observational study, the possibility of residual confounding can’t be excluded.
DISCLOSURES
The investigators report no relevant disclosures. The study received support from the UK Medical Research Council and Alcohol Research UK.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
Alcohol dependence, but not consumption, at age 18 years increases the risk for depression at age 24 years.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included 3,902 mostly White adolescents, about 58% female, born in England from April 1991 to December 1992, who were part of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) that examined genetic and environmental determinants of health and development.
- Participants completed the self-report Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) between the ages of 16 and 23 years, a period when average alcohol use increases rapidly.
- The primary outcome was probability for depression at age 24 years, using the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), a self-administered computerized clinical assessment of common mental disorder symptoms during the past week.
- Researchers assessed frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption as well as alcohol dependence.
- Confounders included sex, housing type, maternal education and depressive symptoms, parents’ alcohol use, conduct problems at age 4 years, being bullied, and smoking status.
TAKEAWAYS
- After adjustments, alcohol dependence at age 18 years was associated with depression at age 24 years (unstandardized probit coefficient 0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.02-0.25; P = .019)
- The relationship appeared to persist for alcohol dependence at each age of the growth curve (17-22 years).
- There was no evidence that frequency or quantity of alcohol consumption at age 18 was significantly associated with depression at age 24, suggesting these factors may not increase the risk for later depression unless there are also features of dependency.
IN PRACTICE
“Our findings suggest that preventing alcohol dependence during adolescence, or treating it early, could reduce the risk of depression,” which could have important public health implications, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS
The study was carried out by researchers at the University of Bristol; University College London; Critical Thinking Unit, Public Health Directorate, NHS; University of Nottingham, all in the United Kingdom. It was published online in Lancet Psychiatry
LIMITATIONS
There was substantial attrition in the ALSPAC cohort from birth to age 24 years. The sample was recruited from one U.K. region and most participants were White. Measures of alcohol consumption and dependence excluded some features of abuse. And as this is an observational study, the possibility of residual confounding can’t be excluded.
DISCLOSURES
The investigators report no relevant disclosures. The study received support from the UK Medical Research Council and Alcohol Research UK.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TOPLINE
Alcohol dependence, but not consumption, at age 18 years increases the risk for depression at age 24 years.
METHODOLOGY
- The study included 3,902 mostly White adolescents, about 58% female, born in England from April 1991 to December 1992, who were part of the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) that examined genetic and environmental determinants of health and development.
- Participants completed the self-report Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT) between the ages of 16 and 23 years, a period when average alcohol use increases rapidly.
- The primary outcome was probability for depression at age 24 years, using the Clinical Interview Schedule Revised (CIS-R), a self-administered computerized clinical assessment of common mental disorder symptoms during the past week.
- Researchers assessed frequency and quantity of alcohol consumption as well as alcohol dependence.
- Confounders included sex, housing type, maternal education and depressive symptoms, parents’ alcohol use, conduct problems at age 4 years, being bullied, and smoking status.
TAKEAWAYS
- After adjustments, alcohol dependence at age 18 years was associated with depression at age 24 years (unstandardized probit coefficient 0.13; 95% confidence interval, 0.02-0.25; P = .019)
- The relationship appeared to persist for alcohol dependence at each age of the growth curve (17-22 years).
- There was no evidence that frequency or quantity of alcohol consumption at age 18 was significantly associated with depression at age 24, suggesting these factors may not increase the risk for later depression unless there are also features of dependency.
IN PRACTICE
“Our findings suggest that preventing alcohol dependence during adolescence, or treating it early, could reduce the risk of depression,” which could have important public health implications, the researchers write.
STUDY DETAILS
The study was carried out by researchers at the University of Bristol; University College London; Critical Thinking Unit, Public Health Directorate, NHS; University of Nottingham, all in the United Kingdom. It was published online in Lancet Psychiatry
LIMITATIONS
There was substantial attrition in the ALSPAC cohort from birth to age 24 years. The sample was recruited from one U.K. region and most participants were White. Measures of alcohol consumption and dependence excluded some features of abuse. And as this is an observational study, the possibility of residual confounding can’t be excluded.
DISCLOSURES
The investigators report no relevant disclosures. The study received support from the UK Medical Research Council and Alcohol Research UK.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
After backlash, publisher to retract article that surveyed parents of children with gender dysphoria, says coauthor
The move is “due to concerns about lack of informed consent,” according to tweets by one of the paper’s authors.
The article, “Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria: Parent Reports on 1655 Possible Cases,” was published in March in the Archives of Sexual Behavior. It has not been cited in the scientific literature, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science, but Altmetric, which tracks the online attention papers receive, ranks the article in the top 1% of all articles of a similar age.
Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria (ROGD) is, the article stated, a “controversial theory” that “common cultural beliefs, values, and preoccupations cause some adolescents (especially female adolescents) to attribute their social problems, feelings, and mental health issues to gender dysphoria,” and that “youth with ROGD falsely believe that they are transgender,” in part due to social influences.
Michael Bailey, a psychology professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the paper’s corresponding author, tweeted:
Bailey told Retraction Watch that he would “respond when [he] can” to our request for comment, following “new developments on our end.” Neither Springer Nature nor Kenneth Zucker, editor in chief of Archives of Sexual Behavior, has responded to similar requests.
The paper reported the results of a survey of parents who contacted the website ParentsofROGDKids.com, with which the first author is affiliated. According to the abstract, the authors found:
“Pre-existing mental health issues were common, and youths with these issues were more likely than those without them to have socially and medically transitioned. Parents reported that they had often felt pressured by clinicians to affirm their AYA [adolescent and young adult] child’s new gender and support their transition. According to the parents, AYA children’s mental health deteriorated considerably after social transition.”
Soon after publication, the paper attracted criticism that its method of gathering study participants was biased, and that the authors ignored information that didn’t support the theory of ROGD.
Archives of Sexual Behavior is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research, which tweeted on April 19:
The episode prompted a May 5 “Open Letter in Support of Dr. Kenneth Zucker and the Need to Promote Robust Scientific Debate” from the Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism that has now been signed by nearly 2000 people.
On May 10, the following publisher’s note was added to the article:
“readers are alerted that concerns have been raised regarding methodology as described in this article. The publisher is currently investigating this matter and a further response will follow the conclusion of this investigation.
Six days later, the publisher removed the article’s supplementary information “due to a lack of documented consent by study participants.”
The story may feel familiar to readers who recall what happened to another paper in 2018. In that paper, Brown University’s Lisa Littman coined the term ROGD. Following a backlash, Brown took down a press release touting the results, and the paper was eventually republished with corrections.
Bailey has been accused of mistreating transgender research participants, but an investigation by bioethicist Alice Dreger found that of the many accusations, “almost none appear to have been legitimate.”
In a post on UnHerd earlier this month, Bailey responded to the reported concerns about the study lacking approval by an Institutional Review Board (IRB), and that the way the participants were recruited biased the results.
IRB approval was not necessary, Bailey wrote, because Suzanna Diaz, the first author who collected the data, was not affiliated with an institution that required it. “Suzanna Diaz” is a pseudonym for “the mother of a gender dysphoric child she believes has ROGD” who wishes to remain anonymous for the sake of her family, Bailey wrote.
The paper included the following statement about its ethical approval:
“The first author and creator of the survey is not affiliated with any university or hospital. Thus, she did not seek approval from an IRB. After seeing a presentation of preliminary survey results by the first author, the second author suggested the data to be analyzed and submitted as an academic article (he was not involved in collecting the data). The second author consulted with his university’s IRB, who declined to certify the study because data were already collected. However, they advised that publishing the results was likely ethical provided data were deidentified. Editor’s note: After I reviewed the manuscript, I concluded that its publication is ethically appropriate, consistent with Springer policy.”
In his UnHerd post, Bailey quoted from the journal’s submission guidelines:
“If a study has not been granted ethics committee approval prior to commencing, retrospective ethics approval usually cannot be obtained and it may not be possible to consider the manuscript for peer review. The decision on whether to proceed to peer review in such cases is at the Editor’s discretion.”
“Regarding the methodological limitations of the study, these were addressed forthrightly and thoroughly in our article,” Bailey wrote.
Adam Marcus, a cofounder of Retraction Watch, is an editor at this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on RetractionWatch.com.
The move is “due to concerns about lack of informed consent,” according to tweets by one of the paper’s authors.
The article, “Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria: Parent Reports on 1655 Possible Cases,” was published in March in the Archives of Sexual Behavior. It has not been cited in the scientific literature, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science, but Altmetric, which tracks the online attention papers receive, ranks the article in the top 1% of all articles of a similar age.
Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria (ROGD) is, the article stated, a “controversial theory” that “common cultural beliefs, values, and preoccupations cause some adolescents (especially female adolescents) to attribute their social problems, feelings, and mental health issues to gender dysphoria,” and that “youth with ROGD falsely believe that they are transgender,” in part due to social influences.
Michael Bailey, a psychology professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the paper’s corresponding author, tweeted:
Bailey told Retraction Watch that he would “respond when [he] can” to our request for comment, following “new developments on our end.” Neither Springer Nature nor Kenneth Zucker, editor in chief of Archives of Sexual Behavior, has responded to similar requests.
The paper reported the results of a survey of parents who contacted the website ParentsofROGDKids.com, with which the first author is affiliated. According to the abstract, the authors found:
“Pre-existing mental health issues were common, and youths with these issues were more likely than those without them to have socially and medically transitioned. Parents reported that they had often felt pressured by clinicians to affirm their AYA [adolescent and young adult] child’s new gender and support their transition. According to the parents, AYA children’s mental health deteriorated considerably after social transition.”
Soon after publication, the paper attracted criticism that its method of gathering study participants was biased, and that the authors ignored information that didn’t support the theory of ROGD.
Archives of Sexual Behavior is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research, which tweeted on April 19:
The episode prompted a May 5 “Open Letter in Support of Dr. Kenneth Zucker and the Need to Promote Robust Scientific Debate” from the Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism that has now been signed by nearly 2000 people.
On May 10, the following publisher’s note was added to the article:
“readers are alerted that concerns have been raised regarding methodology as described in this article. The publisher is currently investigating this matter and a further response will follow the conclusion of this investigation.
Six days later, the publisher removed the article’s supplementary information “due to a lack of documented consent by study participants.”
The story may feel familiar to readers who recall what happened to another paper in 2018. In that paper, Brown University’s Lisa Littman coined the term ROGD. Following a backlash, Brown took down a press release touting the results, and the paper was eventually republished with corrections.
Bailey has been accused of mistreating transgender research participants, but an investigation by bioethicist Alice Dreger found that of the many accusations, “almost none appear to have been legitimate.”
In a post on UnHerd earlier this month, Bailey responded to the reported concerns about the study lacking approval by an Institutional Review Board (IRB), and that the way the participants were recruited biased the results.
IRB approval was not necessary, Bailey wrote, because Suzanna Diaz, the first author who collected the data, was not affiliated with an institution that required it. “Suzanna Diaz” is a pseudonym for “the mother of a gender dysphoric child she believes has ROGD” who wishes to remain anonymous for the sake of her family, Bailey wrote.
The paper included the following statement about its ethical approval:
“The first author and creator of the survey is not affiliated with any university or hospital. Thus, she did not seek approval from an IRB. After seeing a presentation of preliminary survey results by the first author, the second author suggested the data to be analyzed and submitted as an academic article (he was not involved in collecting the data). The second author consulted with his university’s IRB, who declined to certify the study because data were already collected. However, they advised that publishing the results was likely ethical provided data were deidentified. Editor’s note: After I reviewed the manuscript, I concluded that its publication is ethically appropriate, consistent with Springer policy.”
In his UnHerd post, Bailey quoted from the journal’s submission guidelines:
“If a study has not been granted ethics committee approval prior to commencing, retrospective ethics approval usually cannot be obtained and it may not be possible to consider the manuscript for peer review. The decision on whether to proceed to peer review in such cases is at the Editor’s discretion.”
“Regarding the methodological limitations of the study, these were addressed forthrightly and thoroughly in our article,” Bailey wrote.
Adam Marcus, a cofounder of Retraction Watch, is an editor at this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on RetractionWatch.com.
The move is “due to concerns about lack of informed consent,” according to tweets by one of the paper’s authors.
The article, “Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria: Parent Reports on 1655 Possible Cases,” was published in March in the Archives of Sexual Behavior. It has not been cited in the scientific literature, according to Clarivate’s Web of Science, but Altmetric, which tracks the online attention papers receive, ranks the article in the top 1% of all articles of a similar age.
Rapid Onset Gender Dysphoria (ROGD) is, the article stated, a “controversial theory” that “common cultural beliefs, values, and preoccupations cause some adolescents (especially female adolescents) to attribute their social problems, feelings, and mental health issues to gender dysphoria,” and that “youth with ROGD falsely believe that they are transgender,” in part due to social influences.
Michael Bailey, a psychology professor at Northwestern University in Evanston, Ill., and the paper’s corresponding author, tweeted:
Bailey told Retraction Watch that he would “respond when [he] can” to our request for comment, following “new developments on our end.” Neither Springer Nature nor Kenneth Zucker, editor in chief of Archives of Sexual Behavior, has responded to similar requests.
The paper reported the results of a survey of parents who contacted the website ParentsofROGDKids.com, with which the first author is affiliated. According to the abstract, the authors found:
“Pre-existing mental health issues were common, and youths with these issues were more likely than those without them to have socially and medically transitioned. Parents reported that they had often felt pressured by clinicians to affirm their AYA [adolescent and young adult] child’s new gender and support their transition. According to the parents, AYA children’s mental health deteriorated considerably after social transition.”
Soon after publication, the paper attracted criticism that its method of gathering study participants was biased, and that the authors ignored information that didn’t support the theory of ROGD.
Archives of Sexual Behavior is the official publication of the International Academy of Sex Research, which tweeted on April 19:
The episode prompted a May 5 “Open Letter in Support of Dr. Kenneth Zucker and the Need to Promote Robust Scientific Debate” from the Foundation Against Intolerance and Racism that has now been signed by nearly 2000 people.
On May 10, the following publisher’s note was added to the article:
“readers are alerted that concerns have been raised regarding methodology as described in this article. The publisher is currently investigating this matter and a further response will follow the conclusion of this investigation.
Six days later, the publisher removed the article’s supplementary information “due to a lack of documented consent by study participants.”
The story may feel familiar to readers who recall what happened to another paper in 2018. In that paper, Brown University’s Lisa Littman coined the term ROGD. Following a backlash, Brown took down a press release touting the results, and the paper was eventually republished with corrections.
Bailey has been accused of mistreating transgender research participants, but an investigation by bioethicist Alice Dreger found that of the many accusations, “almost none appear to have been legitimate.”
In a post on UnHerd earlier this month, Bailey responded to the reported concerns about the study lacking approval by an Institutional Review Board (IRB), and that the way the participants were recruited biased the results.
IRB approval was not necessary, Bailey wrote, because Suzanna Diaz, the first author who collected the data, was not affiliated with an institution that required it. “Suzanna Diaz” is a pseudonym for “the mother of a gender dysphoric child she believes has ROGD” who wishes to remain anonymous for the sake of her family, Bailey wrote.
The paper included the following statement about its ethical approval:
“The first author and creator of the survey is not affiliated with any university or hospital. Thus, she did not seek approval from an IRB. After seeing a presentation of preliminary survey results by the first author, the second author suggested the data to be analyzed and submitted as an academic article (he was not involved in collecting the data). The second author consulted with his university’s IRB, who declined to certify the study because data were already collected. However, they advised that publishing the results was likely ethical provided data were deidentified. Editor’s note: After I reviewed the manuscript, I concluded that its publication is ethically appropriate, consistent with Springer policy.”
In his UnHerd post, Bailey quoted from the journal’s submission guidelines:
“If a study has not been granted ethics committee approval prior to commencing, retrospective ethics approval usually cannot be obtained and it may not be possible to consider the manuscript for peer review. The decision on whether to proceed to peer review in such cases is at the Editor’s discretion.”
“Regarding the methodological limitations of the study, these were addressed forthrightly and thoroughly in our article,” Bailey wrote.
Adam Marcus, a cofounder of Retraction Watch, is an editor at this news organization.
A version of this article first appeared on RetractionWatch.com.
Cognitive decline risk in adult childhood cancer survivors
Among more than 2,300 adult survivors of childhood cancer and their siblings, who served as controls, new-onset memory impairment emerged more often in survivors decades later.
The increased risk was associated with the cancer treatment that was provided as well as modifiable health behaviors and chronic health conditions.
Even 35 years after being diagnosed, cancer survivors who never received chemotherapies or radiation therapies known to damage the brain reported far greater memory impairment than did their siblings, first author Nicholas Phillips, MD, told this news organization.
What the findings suggest is that “we need to educate oncologists and primary care providers on the risks our survivors face long after completion of therapy,” said Dr. Phillips, of the epidemiology and cancer control department at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Cancer survivors face an elevated risk for severe neurocognitive effects that can emerge 5-10 years following their diagnosis and treatment. However, it’s unclear whether new-onset neurocognitive problems can still develop a decade or more following diagnosis.
Over a long-term follow-up, Dr. Phillips and colleagues explored this question in 2,375 adult survivors of childhood cancer from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and 232 of their siblings.
Among the cancer cohort, 1,316 patients were survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), 488 were survivors of central nervous system (CNS) tumors, and 571 had survived Hodgkin lymphoma.
The researchers determined the prevalence of new-onset neurocognitive impairment between baseline (23 years after diagnosis) and follow-up (35 years after diagnosis). New-onset neurocognitive impairment – present at follow-up but not at baseline – was defined as having a score in the worst 10% of the sibling cohort.
A higher proportion of survivors had new-onset memory impairment at follow-up compared with siblings. Specifically, about 8% of siblings had new-onset memory trouble, compared with 14% of ALL survivors treated with chemotherapy only, 26% of ALL survivors treated with cranial radiation, 35% of CNS tumor survivors, and 17% of Hodgkin lymphoma survivors.
New-onset memory impairment was associated with cranial radiation among CNS tumor survivors (relative risk [RR], 1.97) and alkylator chemotherapy at or above 8,000 mg/m2 among survivors of ALL who were treated without cranial radiation (RR, 2.80). The authors also found that smoking, low educational attainment, and low physical activity were associated with an elevated risk for new-onset memory impairment.
Dr. Phillips noted that current guidelines emphasize the importance of short-term monitoring of a survivor’s neurocognitive status on the basis of that person’s chemotherapy and radiation exposures.
However, “our study suggests that all survivors, regardless of their therapy, should be screened regularly for new-onset neurocognitive problems. And this screening should be done regularly for decades after diagnosis,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Phillips also noted the importance of communicating lifestyle modifications, such as not smoking and maintaining an active lifestyle.
“We need to start early and use the power of repetition when communicating with our survivors and their families,” Dr. Phillips said. “When our families and survivors hear the word ‘exercise,’ they think of gym memberships, lifting weights, and running on treadmills. But what we really want our survivors to do is stay active.”
What this means is engaging for about 2.5 hours a week in a range of activities, such as ballet, basketball, volleyball, bicycling, or swimming.
“And if our kids want to quit after 3 months, let them know that this is okay. They just need to replace that activity with another activity,” said Dr. Phillips. “We want them to find a fun hobby that they will enjoy that will keep them active.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Phillips has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among more than 2,300 adult survivors of childhood cancer and their siblings, who served as controls, new-onset memory impairment emerged more often in survivors decades later.
The increased risk was associated with the cancer treatment that was provided as well as modifiable health behaviors and chronic health conditions.
Even 35 years after being diagnosed, cancer survivors who never received chemotherapies or radiation therapies known to damage the brain reported far greater memory impairment than did their siblings, first author Nicholas Phillips, MD, told this news organization.
What the findings suggest is that “we need to educate oncologists and primary care providers on the risks our survivors face long after completion of therapy,” said Dr. Phillips, of the epidemiology and cancer control department at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Cancer survivors face an elevated risk for severe neurocognitive effects that can emerge 5-10 years following their diagnosis and treatment. However, it’s unclear whether new-onset neurocognitive problems can still develop a decade or more following diagnosis.
Over a long-term follow-up, Dr. Phillips and colleagues explored this question in 2,375 adult survivors of childhood cancer from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and 232 of their siblings.
Among the cancer cohort, 1,316 patients were survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), 488 were survivors of central nervous system (CNS) tumors, and 571 had survived Hodgkin lymphoma.
The researchers determined the prevalence of new-onset neurocognitive impairment between baseline (23 years after diagnosis) and follow-up (35 years after diagnosis). New-onset neurocognitive impairment – present at follow-up but not at baseline – was defined as having a score in the worst 10% of the sibling cohort.
A higher proportion of survivors had new-onset memory impairment at follow-up compared with siblings. Specifically, about 8% of siblings had new-onset memory trouble, compared with 14% of ALL survivors treated with chemotherapy only, 26% of ALL survivors treated with cranial radiation, 35% of CNS tumor survivors, and 17% of Hodgkin lymphoma survivors.
New-onset memory impairment was associated with cranial radiation among CNS tumor survivors (relative risk [RR], 1.97) and alkylator chemotherapy at or above 8,000 mg/m2 among survivors of ALL who were treated without cranial radiation (RR, 2.80). The authors also found that smoking, low educational attainment, and low physical activity were associated with an elevated risk for new-onset memory impairment.
Dr. Phillips noted that current guidelines emphasize the importance of short-term monitoring of a survivor’s neurocognitive status on the basis of that person’s chemotherapy and radiation exposures.
However, “our study suggests that all survivors, regardless of their therapy, should be screened regularly for new-onset neurocognitive problems. And this screening should be done regularly for decades after diagnosis,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Phillips also noted the importance of communicating lifestyle modifications, such as not smoking and maintaining an active lifestyle.
“We need to start early and use the power of repetition when communicating with our survivors and their families,” Dr. Phillips said. “When our families and survivors hear the word ‘exercise,’ they think of gym memberships, lifting weights, and running on treadmills. But what we really want our survivors to do is stay active.”
What this means is engaging for about 2.5 hours a week in a range of activities, such as ballet, basketball, volleyball, bicycling, or swimming.
“And if our kids want to quit after 3 months, let them know that this is okay. They just need to replace that activity with another activity,” said Dr. Phillips. “We want them to find a fun hobby that they will enjoy that will keep them active.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Phillips has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Among more than 2,300 adult survivors of childhood cancer and their siblings, who served as controls, new-onset memory impairment emerged more often in survivors decades later.
The increased risk was associated with the cancer treatment that was provided as well as modifiable health behaviors and chronic health conditions.
Even 35 years after being diagnosed, cancer survivors who never received chemotherapies or radiation therapies known to damage the brain reported far greater memory impairment than did their siblings, first author Nicholas Phillips, MD, told this news organization.
What the findings suggest is that “we need to educate oncologists and primary care providers on the risks our survivors face long after completion of therapy,” said Dr. Phillips, of the epidemiology and cancer control department at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital, Memphis, Tenn.
The study was published online in JAMA Network Open.
Cancer survivors face an elevated risk for severe neurocognitive effects that can emerge 5-10 years following their diagnosis and treatment. However, it’s unclear whether new-onset neurocognitive problems can still develop a decade or more following diagnosis.
Over a long-term follow-up, Dr. Phillips and colleagues explored this question in 2,375 adult survivors of childhood cancer from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study and 232 of their siblings.
Among the cancer cohort, 1,316 patients were survivors of acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL), 488 were survivors of central nervous system (CNS) tumors, and 571 had survived Hodgkin lymphoma.
The researchers determined the prevalence of new-onset neurocognitive impairment between baseline (23 years after diagnosis) and follow-up (35 years after diagnosis). New-onset neurocognitive impairment – present at follow-up but not at baseline – was defined as having a score in the worst 10% of the sibling cohort.
A higher proportion of survivors had new-onset memory impairment at follow-up compared with siblings. Specifically, about 8% of siblings had new-onset memory trouble, compared with 14% of ALL survivors treated with chemotherapy only, 26% of ALL survivors treated with cranial radiation, 35% of CNS tumor survivors, and 17% of Hodgkin lymphoma survivors.
New-onset memory impairment was associated with cranial radiation among CNS tumor survivors (relative risk [RR], 1.97) and alkylator chemotherapy at or above 8,000 mg/m2 among survivors of ALL who were treated without cranial radiation (RR, 2.80). The authors also found that smoking, low educational attainment, and low physical activity were associated with an elevated risk for new-onset memory impairment.
Dr. Phillips noted that current guidelines emphasize the importance of short-term monitoring of a survivor’s neurocognitive status on the basis of that person’s chemotherapy and radiation exposures.
However, “our study suggests that all survivors, regardless of their therapy, should be screened regularly for new-onset neurocognitive problems. And this screening should be done regularly for decades after diagnosis,” he said in an interview.
Dr. Phillips also noted the importance of communicating lifestyle modifications, such as not smoking and maintaining an active lifestyle.
“We need to start early and use the power of repetition when communicating with our survivors and their families,” Dr. Phillips said. “When our families and survivors hear the word ‘exercise,’ they think of gym memberships, lifting weights, and running on treadmills. But what we really want our survivors to do is stay active.”
What this means is engaging for about 2.5 hours a week in a range of activities, such as ballet, basketball, volleyball, bicycling, or swimming.
“And if our kids want to quit after 3 months, let them know that this is okay. They just need to replace that activity with another activity,” said Dr. Phillips. “We want them to find a fun hobby that they will enjoy that will keep them active.”
The study was supported by the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Phillips has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN