User login
ACTRIMS 2022: Updates in Multiple Sclerosis Symptom Management
Dr Enrique Alvarez, Associate Professor at the University of Colorado, reviews updates in symptom management that were presented at the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS) 2022 meeting.
First, Dr Alvarez highlights two studies of nabiximols — a complex botanical mixture of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol — in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). In both the GWSP0604 and SAVANT studies, patients taking nabiximols demonstrated significant spasticity improvement and reductions in spasm frequency.
Next, Dr Alvarez shares study results that compared patient responses to the responses of healthcare practitioners (HCPs) treating these patients for their MS. This analysis, which focused on cases of fatigue, mood, and cognition, found that patients reported significantly higher rates of these symptoms compared with HCP responses.
Another study assessed the importance of shared decision-making between HCPs and patients with MS, drawing from MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CINAHL databases. The researchers identified apparent challenges in patient education and access to information and recommended that shared decision-making be integrated into routine practice.
Dr Alvarez concludes with a review of new resources launched by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the goal of which is to inform and empower patients about dietary approaches for self-management and to support clinicians who are facilitating related discussions with their patients.
--
Enrique Alvarez, MD, PhD, Vice Chair of Clinical Research, Associate Professor, Department of Neurology, Division Neuroimmunology, University of Colorado, Rocky Mountain MS Center Anschutz Medical Center, Aurora, Colorado
Enrique Alvarez, MD, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Genentech/Roche; Novartis; TG Therapeutics; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Initiative; National Multiple Sclerosis Society; National Institutes of Health; Rocky Mountain MS Center
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Actelion
Dr Enrique Alvarez, Associate Professor at the University of Colorado, reviews updates in symptom management that were presented at the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS) 2022 meeting.
First, Dr Alvarez highlights two studies of nabiximols — a complex botanical mixture of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol — in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). In both the GWSP0604 and SAVANT studies, patients taking nabiximols demonstrated significant spasticity improvement and reductions in spasm frequency.
Next, Dr Alvarez shares study results that compared patient responses to the responses of healthcare practitioners (HCPs) treating these patients for their MS. This analysis, which focused on cases of fatigue, mood, and cognition, found that patients reported significantly higher rates of these symptoms compared with HCP responses.
Another study assessed the importance of shared decision-making between HCPs and patients with MS, drawing from MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CINAHL databases. The researchers identified apparent challenges in patient education and access to information and recommended that shared decision-making be integrated into routine practice.
Dr Alvarez concludes with a review of new resources launched by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the goal of which is to inform and empower patients about dietary approaches for self-management and to support clinicians who are facilitating related discussions with their patients.
--
Enrique Alvarez, MD, PhD, Vice Chair of Clinical Research, Associate Professor, Department of Neurology, Division Neuroimmunology, University of Colorado, Rocky Mountain MS Center Anschutz Medical Center, Aurora, Colorado
Enrique Alvarez, MD, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Genentech/Roche; Novartis; TG Therapeutics; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Initiative; National Multiple Sclerosis Society; National Institutes of Health; Rocky Mountain MS Center
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Actelion
Dr Enrique Alvarez, Associate Professor at the University of Colorado, reviews updates in symptom management that were presented at the Americas Committee for Treatment and Research in Multiple Sclerosis (ACTRIMS) 2022 meeting.
First, Dr Alvarez highlights two studies of nabiximols — a complex botanical mixture of tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol — in patients with multiple sclerosis (MS). In both the GWSP0604 and SAVANT studies, patients taking nabiximols demonstrated significant spasticity improvement and reductions in spasm frequency.
Next, Dr Alvarez shares study results that compared patient responses to the responses of healthcare practitioners (HCPs) treating these patients for their MS. This analysis, which focused on cases of fatigue, mood, and cognition, found that patients reported significantly higher rates of these symptoms compared with HCP responses.
Another study assessed the importance of shared decision-making between HCPs and patients with MS, drawing from MEDLINE, EMBASE, and CINAHL databases. The researchers identified apparent challenges in patient education and access to information and recommended that shared decision-making be integrated into routine practice.
Dr Alvarez concludes with a review of new resources launched by the National Multiple Sclerosis Society, the goal of which is to inform and empower patients about dietary approaches for self-management and to support clinicians who are facilitating related discussions with their patients.
--
Enrique Alvarez, MD, PhD, Vice Chair of Clinical Research, Associate Professor, Department of Neurology, Division Neuroimmunology, University of Colorado, Rocky Mountain MS Center Anschutz Medical Center, Aurora, Colorado
Enrique Alvarez, MD, PhD, has disclosed the following relevant financial relationships:
Received research grant from: Biogen; Genentech/Roche; Novartis; TG Therapeutics; Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Initiative; National Multiple Sclerosis Society; National Institutes of Health; Rocky Mountain MS Center
Received income in an amount equal to or greater than $250 from: Actelion

Aerosolized hydrogen peroxide can significantly reduce C. difficile infections
Aerosolized hydrogen peroxide (aHP) can significantly reduce Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) and is an effective disinfection system, suggests a study published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
C. difficile is the most common cause of health care–associated infection and increasingly occurs outside acute care hospitals. CDI symptoms can range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis and sepsis, sometimes requiring urgent colon removal.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has reported that, in the United States, 223,900 people required hospitalization for CDI and at least 12,800 died in 2017. Because of its large toll, CDI is grouped with antimicrobial-resistant “threat” organisms that often accompany it. People older than age 65 are at particular risk for disease, and at least 20% of patients experience recurrence.
In health care facilities, C. difficile is transmitted by bacterial spores that readily contaminate surfaces in patients’ rooms, from handrails to bedside tables to light switches and knobs. The spores are resistant to disinfectants, and rooms are often cleaned with bleach solutions. But those bleach fumes are irritating and may cause bronchospasm for patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so alternative cleaning agents are needed.
In a retrospective study of an acute-care facility in Philadelphia, researchers compared the incidence of health care–associated CDI (HA-CDI) at the facility before and after adding aHP to other infection control practices. The aHP process produces an aerosolized dry-mist fog that contains a specified percentage of hydrogen peroxide. The fog is used after the room has been physically cleaned, settling on exposed surfaces and killing any remaining C. difficile spores.
The aHP mixture also contains 0.01% ionic silver. The study lead was Christopher L. Truitt, PhD, of Wayland Baptist University. Dr. Truitt told this news organization that hydrogen peroxide affects the endospore layer of the C. difficile organism and allows the “ionic silver to get into the cell and is shown to bind to enzymes and inactivate those inside the cell and actually improve the efficacy.”
Asked whether it’s the silver or the peroxide that disinfects, Dr. Truitt replied: “I can’t answer that. We don’t know if it’s the silver or the hydrogen peroxide. The commercially available chemical that’s used in that machine is a proprietary set-up ... with EPA approval as a sporicidal.”
In the baseline 27-month period, the hospital tallied 120 HA-CDI cases. After aHP was introduced, they counted just 72 cases over 33 months, a 41% decrease in the facility’s HA-CDI rate, from 4.6 per 10,000 patient-days to 2.7 per 10,000 patient-days (P < .001).
There was also a progressive decrease in hospital-onset CDI even after aHP was introduced, from 5.4 per 10,000 patient-days in 2015 to 1.4 per 10,000 patient-days in 2019.
Yoav Golan, MD, of Tufts University, Boston, told this news organization there were two major study limitations. “One is the fact that they did not control for other interventions that may have an effect on C. difficile: antibiotic stewardship and infection control,” he explained. This limitation was noted by the study authors and may explain the continued decline in infections after the introduction of aHP. The other limitation was not using a crossover study design.
“I would argue that they should have provided a little more information about their own practices in their own hospital when it comes to intensification of infection control [and] when it comes to a stewardship and changes that they’ve made to antibiotic usage,” Dr. Golan continued. “The description of changes over time and those practices would have allowed us to better understand the impact of the hydrogen peroxide intervention.”
Despite his criticisms, Dr. Golan concluded: “I think that the study is important. I think their intervention is unique in a way that they’ve been using an aerosolizing system that’s using a relatively high concentration of hydrogen peroxide. I think that there’s enough in this paper to suggest that using such a system may have an impact on the environment, and through that, on dissemination.”
Dr. Truitt added that a next step would be to compare aHP with ultraviolet light, which is commonly used to disinfect hospital rooms.
Dr. Truitt is chief science officer at Infection Controls, dba Germblast, a proprietary service that uses cold-mist hydrogen peroxide and other modalities to disinfect surfaces. Dr. Golan has reported being a consultant for Merck, Seres Therapeutics, Vedanta Biosciences, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerosolized hydrogen peroxide (aHP) can significantly reduce Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) and is an effective disinfection system, suggests a study published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
C. difficile is the most common cause of health care–associated infection and increasingly occurs outside acute care hospitals. CDI symptoms can range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis and sepsis, sometimes requiring urgent colon removal.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has reported that, in the United States, 223,900 people required hospitalization for CDI and at least 12,800 died in 2017. Because of its large toll, CDI is grouped with antimicrobial-resistant “threat” organisms that often accompany it. People older than age 65 are at particular risk for disease, and at least 20% of patients experience recurrence.
In health care facilities, C. difficile is transmitted by bacterial spores that readily contaminate surfaces in patients’ rooms, from handrails to bedside tables to light switches and knobs. The spores are resistant to disinfectants, and rooms are often cleaned with bleach solutions. But those bleach fumes are irritating and may cause bronchospasm for patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so alternative cleaning agents are needed.
In a retrospective study of an acute-care facility in Philadelphia, researchers compared the incidence of health care–associated CDI (HA-CDI) at the facility before and after adding aHP to other infection control practices. The aHP process produces an aerosolized dry-mist fog that contains a specified percentage of hydrogen peroxide. The fog is used after the room has been physically cleaned, settling on exposed surfaces and killing any remaining C. difficile spores.
The aHP mixture also contains 0.01% ionic silver. The study lead was Christopher L. Truitt, PhD, of Wayland Baptist University. Dr. Truitt told this news organization that hydrogen peroxide affects the endospore layer of the C. difficile organism and allows the “ionic silver to get into the cell and is shown to bind to enzymes and inactivate those inside the cell and actually improve the efficacy.”
Asked whether it’s the silver or the peroxide that disinfects, Dr. Truitt replied: “I can’t answer that. We don’t know if it’s the silver or the hydrogen peroxide. The commercially available chemical that’s used in that machine is a proprietary set-up ... with EPA approval as a sporicidal.”
In the baseline 27-month period, the hospital tallied 120 HA-CDI cases. After aHP was introduced, they counted just 72 cases over 33 months, a 41% decrease in the facility’s HA-CDI rate, from 4.6 per 10,000 patient-days to 2.7 per 10,000 patient-days (P < .001).
There was also a progressive decrease in hospital-onset CDI even after aHP was introduced, from 5.4 per 10,000 patient-days in 2015 to 1.4 per 10,000 patient-days in 2019.
Yoav Golan, MD, of Tufts University, Boston, told this news organization there were two major study limitations. “One is the fact that they did not control for other interventions that may have an effect on C. difficile: antibiotic stewardship and infection control,” he explained. This limitation was noted by the study authors and may explain the continued decline in infections after the introduction of aHP. The other limitation was not using a crossover study design.
“I would argue that they should have provided a little more information about their own practices in their own hospital when it comes to intensification of infection control [and] when it comes to a stewardship and changes that they’ve made to antibiotic usage,” Dr. Golan continued. “The description of changes over time and those practices would have allowed us to better understand the impact of the hydrogen peroxide intervention.”
Despite his criticisms, Dr. Golan concluded: “I think that the study is important. I think their intervention is unique in a way that they’ve been using an aerosolizing system that’s using a relatively high concentration of hydrogen peroxide. I think that there’s enough in this paper to suggest that using such a system may have an impact on the environment, and through that, on dissemination.”
Dr. Truitt added that a next step would be to compare aHP with ultraviolet light, which is commonly used to disinfect hospital rooms.
Dr. Truitt is chief science officer at Infection Controls, dba Germblast, a proprietary service that uses cold-mist hydrogen peroxide and other modalities to disinfect surfaces. Dr. Golan has reported being a consultant for Merck, Seres Therapeutics, Vedanta Biosciences, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Aerosolized hydrogen peroxide (aHP) can significantly reduce Clostridioides difficile infection (CDI) and is an effective disinfection system, suggests a study published in the American Journal of Infection Control.
C. difficile is the most common cause of health care–associated infection and increasingly occurs outside acute care hospitals. CDI symptoms can range from mild diarrhea to life-threatening colitis and sepsis, sometimes requiring urgent colon removal.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has reported that, in the United States, 223,900 people required hospitalization for CDI and at least 12,800 died in 2017. Because of its large toll, CDI is grouped with antimicrobial-resistant “threat” organisms that often accompany it. People older than age 65 are at particular risk for disease, and at least 20% of patients experience recurrence.
In health care facilities, C. difficile is transmitted by bacterial spores that readily contaminate surfaces in patients’ rooms, from handrails to bedside tables to light switches and knobs. The spores are resistant to disinfectants, and rooms are often cleaned with bleach solutions. But those bleach fumes are irritating and may cause bronchospasm for patients with asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and so alternative cleaning agents are needed.
In a retrospective study of an acute-care facility in Philadelphia, researchers compared the incidence of health care–associated CDI (HA-CDI) at the facility before and after adding aHP to other infection control practices. The aHP process produces an aerosolized dry-mist fog that contains a specified percentage of hydrogen peroxide. The fog is used after the room has been physically cleaned, settling on exposed surfaces and killing any remaining C. difficile spores.
The aHP mixture also contains 0.01% ionic silver. The study lead was Christopher L. Truitt, PhD, of Wayland Baptist University. Dr. Truitt told this news organization that hydrogen peroxide affects the endospore layer of the C. difficile organism and allows the “ionic silver to get into the cell and is shown to bind to enzymes and inactivate those inside the cell and actually improve the efficacy.”
Asked whether it’s the silver or the peroxide that disinfects, Dr. Truitt replied: “I can’t answer that. We don’t know if it’s the silver or the hydrogen peroxide. The commercially available chemical that’s used in that machine is a proprietary set-up ... with EPA approval as a sporicidal.”
In the baseline 27-month period, the hospital tallied 120 HA-CDI cases. After aHP was introduced, they counted just 72 cases over 33 months, a 41% decrease in the facility’s HA-CDI rate, from 4.6 per 10,000 patient-days to 2.7 per 10,000 patient-days (P < .001).
There was also a progressive decrease in hospital-onset CDI even after aHP was introduced, from 5.4 per 10,000 patient-days in 2015 to 1.4 per 10,000 patient-days in 2019.
Yoav Golan, MD, of Tufts University, Boston, told this news organization there were two major study limitations. “One is the fact that they did not control for other interventions that may have an effect on C. difficile: antibiotic stewardship and infection control,” he explained. This limitation was noted by the study authors and may explain the continued decline in infections after the introduction of aHP. The other limitation was not using a crossover study design.
“I would argue that they should have provided a little more information about their own practices in their own hospital when it comes to intensification of infection control [and] when it comes to a stewardship and changes that they’ve made to antibiotic usage,” Dr. Golan continued. “The description of changes over time and those practices would have allowed us to better understand the impact of the hydrogen peroxide intervention.”
Despite his criticisms, Dr. Golan concluded: “I think that the study is important. I think their intervention is unique in a way that they’ve been using an aerosolizing system that’s using a relatively high concentration of hydrogen peroxide. I think that there’s enough in this paper to suggest that using such a system may have an impact on the environment, and through that, on dissemination.”
Dr. Truitt added that a next step would be to compare aHP with ultraviolet light, which is commonly used to disinfect hospital rooms.
Dr. Truitt is chief science officer at Infection Controls, dba Germblast, a proprietary service that uses cold-mist hydrogen peroxide and other modalities to disinfect surfaces. Dr. Golan has reported being a consultant for Merck, Seres Therapeutics, Vedanta Biosciences, and Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AMERICAN JOURNAL OF INFECTION CONTROL
‘Vast majority’ of COVID patients wake up after mechanical ventilation
COVID-19 patients who are successfully weaned off a ventilator may take days, or even weeks, to regain consciousness, especially those who experienced episodes of hypoxemia while intubated, a new study shows.
“As we started to see the first patients waking up after successful COVID-19 ICU treatments, we also encountered many patients who remained comatose for days and weeks and then regained consciousness to become fully oriented,” co-senior investigator Nicholas Schiff, MD, with NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, says in a news release.
The findings have immediate implications regarding life-sustaining therapies for unresponsive COVID-19 patients, the investigators note.
“In critical care medicine, one of our main tasks is to advise families about planning in the event a patient does not regain consciousness,” said co-senior author Jan Claassen, MD, with New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
“Our findings suggest that for patients with severe COVID, the decision to withdraw life support shouldn’t be based solely on prolonged periods of unconsciousness, as these patients may eventually recover,” Dr. Claassen adds.
The study was published online March 7 in Annals of Neurology.
Slow road back
The researchers examined 795 intubated patients with severe COVID-19 at three medical centers in New York during the first wave of the pandemic (March-July 2020). All patients had impaired consciousness (Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] motor score less than 6) on day 7 of intubation.
A total of 571 patients (72%) survived and regained consciousness.
The median time to recovery of consciousness was 30 days. One-quarter of the patients recovered consciousness 10 days or longer after they stopped receiving ventilator support and 10% took 23 days or longer to recover.
Time to recovery of consciousness was associated with hypoxemia. The hazard ratio was 0.56 (95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.68) with arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) less than or equal to 55 mm Hg and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.85-0.91) with a PaO2 less than or equal to 70 mm Hg.
Each additional day of hypoxemia decreased the odds of recovery of consciousness after accounting for confounding factors including sedation.
These findings were confirmed among patients without any imaging evidence of structural brain injury and in a non-overlapping cohort of 427 patients from the second wave of the pandemic (October-April 2021).
“These findings provide us with more accurate information to guide families who are deciding whether to continue life-sustaining therapy in unconscious COVID-19 patients,” co-senior author Brian Edlow, MD, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, says in the news release.
“Encouragingly,” adds Dr. Claassen, “our study shows that the vast majority of unconscious COVID patients recover consciousness, but it is important to consider that we did not look at the quality of recovery. That’s something that should be the focus of long-term follow-up studies.”
The study was supported by the James S. McDonnell Foundation (JSMF). Dr. Schiff, Dr. Claassen, and Dr. Edlow have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 patients who are successfully weaned off a ventilator may take days, or even weeks, to regain consciousness, especially those who experienced episodes of hypoxemia while intubated, a new study shows.
“As we started to see the first patients waking up after successful COVID-19 ICU treatments, we also encountered many patients who remained comatose for days and weeks and then regained consciousness to become fully oriented,” co-senior investigator Nicholas Schiff, MD, with NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, says in a news release.
The findings have immediate implications regarding life-sustaining therapies for unresponsive COVID-19 patients, the investigators note.
“In critical care medicine, one of our main tasks is to advise families about planning in the event a patient does not regain consciousness,” said co-senior author Jan Claassen, MD, with New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
“Our findings suggest that for patients with severe COVID, the decision to withdraw life support shouldn’t be based solely on prolonged periods of unconsciousness, as these patients may eventually recover,” Dr. Claassen adds.
The study was published online March 7 in Annals of Neurology.
Slow road back
The researchers examined 795 intubated patients with severe COVID-19 at three medical centers in New York during the first wave of the pandemic (March-July 2020). All patients had impaired consciousness (Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] motor score less than 6) on day 7 of intubation.
A total of 571 patients (72%) survived and regained consciousness.
The median time to recovery of consciousness was 30 days. One-quarter of the patients recovered consciousness 10 days or longer after they stopped receiving ventilator support and 10% took 23 days or longer to recover.
Time to recovery of consciousness was associated with hypoxemia. The hazard ratio was 0.56 (95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.68) with arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) less than or equal to 55 mm Hg and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.85-0.91) with a PaO2 less than or equal to 70 mm Hg.
Each additional day of hypoxemia decreased the odds of recovery of consciousness after accounting for confounding factors including sedation.
These findings were confirmed among patients without any imaging evidence of structural brain injury and in a non-overlapping cohort of 427 patients from the second wave of the pandemic (October-April 2021).
“These findings provide us with more accurate information to guide families who are deciding whether to continue life-sustaining therapy in unconscious COVID-19 patients,” co-senior author Brian Edlow, MD, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, says in the news release.
“Encouragingly,” adds Dr. Claassen, “our study shows that the vast majority of unconscious COVID patients recover consciousness, but it is important to consider that we did not look at the quality of recovery. That’s something that should be the focus of long-term follow-up studies.”
The study was supported by the James S. McDonnell Foundation (JSMF). Dr. Schiff, Dr. Claassen, and Dr. Edlow have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 patients who are successfully weaned off a ventilator may take days, or even weeks, to regain consciousness, especially those who experienced episodes of hypoxemia while intubated, a new study shows.
“As we started to see the first patients waking up after successful COVID-19 ICU treatments, we also encountered many patients who remained comatose for days and weeks and then regained consciousness to become fully oriented,” co-senior investigator Nicholas Schiff, MD, with NewYork-Presbyterian/Weill Cornell Medical Center, says in a news release.
The findings have immediate implications regarding life-sustaining therapies for unresponsive COVID-19 patients, the investigators note.
“In critical care medicine, one of our main tasks is to advise families about planning in the event a patient does not regain consciousness,” said co-senior author Jan Claassen, MD, with New York-Presbyterian/Columbia University Irving Medical Center.
“Our findings suggest that for patients with severe COVID, the decision to withdraw life support shouldn’t be based solely on prolonged periods of unconsciousness, as these patients may eventually recover,” Dr. Claassen adds.
The study was published online March 7 in Annals of Neurology.
Slow road back
The researchers examined 795 intubated patients with severe COVID-19 at three medical centers in New York during the first wave of the pandemic (March-July 2020). All patients had impaired consciousness (Glasgow Coma Scale [GCS] motor score less than 6) on day 7 of intubation.
A total of 571 patients (72%) survived and regained consciousness.
The median time to recovery of consciousness was 30 days. One-quarter of the patients recovered consciousness 10 days or longer after they stopped receiving ventilator support and 10% took 23 days or longer to recover.
Time to recovery of consciousness was associated with hypoxemia. The hazard ratio was 0.56 (95% confidence interval, 0.46-0.68) with arterial partial pressure of oxygen (PaO2) less than or equal to 55 mm Hg and 0.88 (95% CI, 0.85-0.91) with a PaO2 less than or equal to 70 mm Hg.
Each additional day of hypoxemia decreased the odds of recovery of consciousness after accounting for confounding factors including sedation.
These findings were confirmed among patients without any imaging evidence of structural brain injury and in a non-overlapping cohort of 427 patients from the second wave of the pandemic (October-April 2021).
“These findings provide us with more accurate information to guide families who are deciding whether to continue life-sustaining therapy in unconscious COVID-19 patients,” co-senior author Brian Edlow, MD, with Massachusetts General Hospital and Harvard Medical School in Boston, says in the news release.
“Encouragingly,” adds Dr. Claassen, “our study shows that the vast majority of unconscious COVID patients recover consciousness, but it is important to consider that we did not look at the quality of recovery. That’s something that should be the focus of long-term follow-up studies.”
The study was supported by the James S. McDonnell Foundation (JSMF). Dr. Schiff, Dr. Claassen, and Dr. Edlow have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF NEUROLOGY
Antiretroviral therapy associated with less risk of preterm birth
Over the past decade, data have suggested that antiretroviral therapy (ART) may be associated with an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, namely, preterm birth (PTB). But a combination of methodologic challenges, demographic gaps, and spotty clinical data has left the question unresolved, especially for pregnant women with HIV who reside in developed countries.
“Given that a lot of the emerging data has come out of resource-limited settings where patient and clinical characteristics are different from developed world settings like the United States, we felt that this was an important question to address,” Kartik Venkatesh, MD, PhD, a high-risk obstetrician and perinatal epidemiologist at the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, told this news organization.
In a prospective cohort study of U.S. women with or at risk for HIV, Dr. Venkatesh and his colleagues found that ART exposure (including highly active antiretroviral therapy [HAART]) was associated with as much as an 80% decline in the likelihood of PTB (defined as birth less than 34 weeks). The study was published in HIV Medicine.
24 years of data analyzed
Dr. Venkatesh and his team analyzed self-reported birth data of women with singleton live-born pregnancies enrolled in the ongoing, multicenter, prospective observational Women’s Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) from Oct. 1, 1995, to March 31, 2019.
“We first looked at women with HIV versus without HIV, [who were] matched on many clinical and sociodemographic characteristics and at similarly high risk of some of these obstetrical outcomes like PTB,” explained Dr. Venkatesh. “We then looked at the relative impact of antiretroviral therapy amongst women living with HIV compared to no antiretroviral therapy.”
ART regimens were classified as none, monotherapy, dual therapy, or HAART. (HAART was defined as more than three antiretrovirals, including at least one protease inhibitor [PI], nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, integrase inhibitor, or entry inhibitor.) In this cohort, for 63.5% of women receiving ART, therapy was initiated before pregnancy (mean duration of HAART, 6 years), and most were virally suppressed.
Among the 4,944 women assessed in the WIHS trial, 74% (3,646) had HIV. In total, 383 women had 488 singleton deliveries, including 218 women with HIV (272 deliveries) and 165 without HIV (216 deliveries). Sociodemographics in both cohorts were well matched. For most participants, the mean age was 40-41 years at delivery, most were non-Hispanic Black persons, and the mean pregnancy body mass index was greater than or equal to 29 kg/m2. Of the women with HIV, 33% had chronic hypertension; of those without HIV, 42.1% had chronic hypertension; 4.7% and 5.0%, respectively, had pregestational diabetes.
The findings showed that PTB risk less than 34 weeks was similar between women with (10%) and without (8%) HIV (adjusted risk ratio, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-2.31). Among deliveries to women with HIV who were receiving ART, PTB risk less than 34 weeks was lower with HAART (7%), compared with not receiving ART (26%) (aRR, 0.19), as well as with monotherapy or dual therapy (3% vs. no ART) (aRR, 0.12). Notably, 67% of deliveries to women receiving HAART included a PI-containing regimen, but these women were not significantly more likely to have a PTB less than 34 weeks, compared with women taking non-PI HAART regimens (aRR, 2.61; 95% CI, 0.65-10.59). Results were similar for secondary outcomes (PTB less than 28 weeks, less than 37 weeks).
Filling in the gaps toward the safest regimen
“This study spans 25 years, so it covers a lot of the history of HIV in pregnancy and is reassuring around using ART in pregnancy,” Shahin Lockman, MD, told this news organization. Dr. Lockman is an associate professor of infectious diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a co-PI of the Botswana Clinical Trials Unit at the Botswana Harvard AIDS Institute Partnership. She was not involved in the study. “One of the worst things for a mother and for pregnancy outcomes, for the fetus and baby’s health and development, is uncontrolled maternal HIV,’’ she said.
Dr. Lockman also noted potential confounders that drive poor birth outcomes in Southern African women, compared with U.S. women, making comparisons between this and other observational studies difficult. Still, she said that the question is not whether women should be receiving treatment but whether or not there are differences between antiretroviral regimens.
“One of the areas that we did not go deeper into was the subtype of antiretroviral therapy, given the relatively small study numbers [did not] allow us to do a robust analysis,” Dr. Venkatesh said.
Rather, he emphasized that the findings might lend more weight to speculation that immunologic characteristics associated with HIV status and immunotherapy – such as low CD4 cell counts prior to delivery, or duration of HIV infection – may be important drivers of adverse birth outcomes among women with HIV taking ART.
And at least in this cohort, many of these characteristics were similar between the treatment groups.
Both researchers agree that the findings – while reassuring – highlight the importance of collecting robust obstetric and safety data as part of prospective databases of individuals living with HIV, not only in resource-limited settings but also among the domestic U.S. population.
“We’ve learned a lot over the last 10 years,” Dr. Lockman said. “Some regimens (like lopinavir/ritonavir or nevirapine) are associated with significantly worse birth outcomes, whereas efavirenz doesn’t seem to be, or less so, and dolutegravir seems to be associated with even better outcomes. So, I think that where we are moving is to regimens that are the safest.”
Moving forward, Dr. Venkatesh explained, not only should researchers focus on exploring which antiretrovirals are safest in this context but also if the use of preexposure prophylaxis during conception periods affects birth outcomes.
Dr. Venkatesh and Dr. Lockman report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past decade, data have suggested that antiretroviral therapy (ART) may be associated with an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, namely, preterm birth (PTB). But a combination of methodologic challenges, demographic gaps, and spotty clinical data has left the question unresolved, especially for pregnant women with HIV who reside in developed countries.
“Given that a lot of the emerging data has come out of resource-limited settings where patient and clinical characteristics are different from developed world settings like the United States, we felt that this was an important question to address,” Kartik Venkatesh, MD, PhD, a high-risk obstetrician and perinatal epidemiologist at the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, told this news organization.
In a prospective cohort study of U.S. women with or at risk for HIV, Dr. Venkatesh and his colleagues found that ART exposure (including highly active antiretroviral therapy [HAART]) was associated with as much as an 80% decline in the likelihood of PTB (defined as birth less than 34 weeks). The study was published in HIV Medicine.
24 years of data analyzed
Dr. Venkatesh and his team analyzed self-reported birth data of women with singleton live-born pregnancies enrolled in the ongoing, multicenter, prospective observational Women’s Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) from Oct. 1, 1995, to March 31, 2019.
“We first looked at women with HIV versus without HIV, [who were] matched on many clinical and sociodemographic characteristics and at similarly high risk of some of these obstetrical outcomes like PTB,” explained Dr. Venkatesh. “We then looked at the relative impact of antiretroviral therapy amongst women living with HIV compared to no antiretroviral therapy.”
ART regimens were classified as none, monotherapy, dual therapy, or HAART. (HAART was defined as more than three antiretrovirals, including at least one protease inhibitor [PI], nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, integrase inhibitor, or entry inhibitor.) In this cohort, for 63.5% of women receiving ART, therapy was initiated before pregnancy (mean duration of HAART, 6 years), and most were virally suppressed.
Among the 4,944 women assessed in the WIHS trial, 74% (3,646) had HIV. In total, 383 women had 488 singleton deliveries, including 218 women with HIV (272 deliveries) and 165 without HIV (216 deliveries). Sociodemographics in both cohorts were well matched. For most participants, the mean age was 40-41 years at delivery, most were non-Hispanic Black persons, and the mean pregnancy body mass index was greater than or equal to 29 kg/m2. Of the women with HIV, 33% had chronic hypertension; of those without HIV, 42.1% had chronic hypertension; 4.7% and 5.0%, respectively, had pregestational diabetes.
The findings showed that PTB risk less than 34 weeks was similar between women with (10%) and without (8%) HIV (adjusted risk ratio, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-2.31). Among deliveries to women with HIV who were receiving ART, PTB risk less than 34 weeks was lower with HAART (7%), compared with not receiving ART (26%) (aRR, 0.19), as well as with monotherapy or dual therapy (3% vs. no ART) (aRR, 0.12). Notably, 67% of deliveries to women receiving HAART included a PI-containing regimen, but these women were not significantly more likely to have a PTB less than 34 weeks, compared with women taking non-PI HAART regimens (aRR, 2.61; 95% CI, 0.65-10.59). Results were similar for secondary outcomes (PTB less than 28 weeks, less than 37 weeks).
Filling in the gaps toward the safest regimen
“This study spans 25 years, so it covers a lot of the history of HIV in pregnancy and is reassuring around using ART in pregnancy,” Shahin Lockman, MD, told this news organization. Dr. Lockman is an associate professor of infectious diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a co-PI of the Botswana Clinical Trials Unit at the Botswana Harvard AIDS Institute Partnership. She was not involved in the study. “One of the worst things for a mother and for pregnancy outcomes, for the fetus and baby’s health and development, is uncontrolled maternal HIV,’’ she said.
Dr. Lockman also noted potential confounders that drive poor birth outcomes in Southern African women, compared with U.S. women, making comparisons between this and other observational studies difficult. Still, she said that the question is not whether women should be receiving treatment but whether or not there are differences between antiretroviral regimens.
“One of the areas that we did not go deeper into was the subtype of antiretroviral therapy, given the relatively small study numbers [did not] allow us to do a robust analysis,” Dr. Venkatesh said.
Rather, he emphasized that the findings might lend more weight to speculation that immunologic characteristics associated with HIV status and immunotherapy – such as low CD4 cell counts prior to delivery, or duration of HIV infection – may be important drivers of adverse birth outcomes among women with HIV taking ART.
And at least in this cohort, many of these characteristics were similar between the treatment groups.
Both researchers agree that the findings – while reassuring – highlight the importance of collecting robust obstetric and safety data as part of prospective databases of individuals living with HIV, not only in resource-limited settings but also among the domestic U.S. population.
“We’ve learned a lot over the last 10 years,” Dr. Lockman said. “Some regimens (like lopinavir/ritonavir or nevirapine) are associated with significantly worse birth outcomes, whereas efavirenz doesn’t seem to be, or less so, and dolutegravir seems to be associated with even better outcomes. So, I think that where we are moving is to regimens that are the safest.”
Moving forward, Dr. Venkatesh explained, not only should researchers focus on exploring which antiretrovirals are safest in this context but also if the use of preexposure prophylaxis during conception periods affects birth outcomes.
Dr. Venkatesh and Dr. Lockman report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Over the past decade, data have suggested that antiretroviral therapy (ART) may be associated with an increased risk for adverse pregnancy outcomes, namely, preterm birth (PTB). But a combination of methodologic challenges, demographic gaps, and spotty clinical data has left the question unresolved, especially for pregnant women with HIV who reside in developed countries.
“Given that a lot of the emerging data has come out of resource-limited settings where patient and clinical characteristics are different from developed world settings like the United States, we felt that this was an important question to address,” Kartik Venkatesh, MD, PhD, a high-risk obstetrician and perinatal epidemiologist at the Ohio State Wexner Medical Center, Columbus, told this news organization.
In a prospective cohort study of U.S. women with or at risk for HIV, Dr. Venkatesh and his colleagues found that ART exposure (including highly active antiretroviral therapy [HAART]) was associated with as much as an 80% decline in the likelihood of PTB (defined as birth less than 34 weeks). The study was published in HIV Medicine.
24 years of data analyzed
Dr. Venkatesh and his team analyzed self-reported birth data of women with singleton live-born pregnancies enrolled in the ongoing, multicenter, prospective observational Women’s Interagency HIV Study (WIHS) from Oct. 1, 1995, to March 31, 2019.
“We first looked at women with HIV versus without HIV, [who were] matched on many clinical and sociodemographic characteristics and at similarly high risk of some of these obstetrical outcomes like PTB,” explained Dr. Venkatesh. “We then looked at the relative impact of antiretroviral therapy amongst women living with HIV compared to no antiretroviral therapy.”
ART regimens were classified as none, monotherapy, dual therapy, or HAART. (HAART was defined as more than three antiretrovirals, including at least one protease inhibitor [PI], nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, integrase inhibitor, or entry inhibitor.) In this cohort, for 63.5% of women receiving ART, therapy was initiated before pregnancy (mean duration of HAART, 6 years), and most were virally suppressed.
Among the 4,944 women assessed in the WIHS trial, 74% (3,646) had HIV. In total, 383 women had 488 singleton deliveries, including 218 women with HIV (272 deliveries) and 165 without HIV (216 deliveries). Sociodemographics in both cohorts were well matched. For most participants, the mean age was 40-41 years at delivery, most were non-Hispanic Black persons, and the mean pregnancy body mass index was greater than or equal to 29 kg/m2. Of the women with HIV, 33% had chronic hypertension; of those without HIV, 42.1% had chronic hypertension; 4.7% and 5.0%, respectively, had pregestational diabetes.
The findings showed that PTB risk less than 34 weeks was similar between women with (10%) and without (8%) HIV (adjusted risk ratio, 1.30; 95% confidence interval, 0.74-2.31). Among deliveries to women with HIV who were receiving ART, PTB risk less than 34 weeks was lower with HAART (7%), compared with not receiving ART (26%) (aRR, 0.19), as well as with monotherapy or dual therapy (3% vs. no ART) (aRR, 0.12). Notably, 67% of deliveries to women receiving HAART included a PI-containing regimen, but these women were not significantly more likely to have a PTB less than 34 weeks, compared with women taking non-PI HAART regimens (aRR, 2.61; 95% CI, 0.65-10.59). Results were similar for secondary outcomes (PTB less than 28 weeks, less than 37 weeks).
Filling in the gaps toward the safest regimen
“This study spans 25 years, so it covers a lot of the history of HIV in pregnancy and is reassuring around using ART in pregnancy,” Shahin Lockman, MD, told this news organization. Dr. Lockman is an associate professor of infectious diseases at Brigham and Women’s Hospital and a co-PI of the Botswana Clinical Trials Unit at the Botswana Harvard AIDS Institute Partnership. She was not involved in the study. “One of the worst things for a mother and for pregnancy outcomes, for the fetus and baby’s health and development, is uncontrolled maternal HIV,’’ she said.
Dr. Lockman also noted potential confounders that drive poor birth outcomes in Southern African women, compared with U.S. women, making comparisons between this and other observational studies difficult. Still, she said that the question is not whether women should be receiving treatment but whether or not there are differences between antiretroviral regimens.
“One of the areas that we did not go deeper into was the subtype of antiretroviral therapy, given the relatively small study numbers [did not] allow us to do a robust analysis,” Dr. Venkatesh said.
Rather, he emphasized that the findings might lend more weight to speculation that immunologic characteristics associated with HIV status and immunotherapy – such as low CD4 cell counts prior to delivery, or duration of HIV infection – may be important drivers of adverse birth outcomes among women with HIV taking ART.
And at least in this cohort, many of these characteristics were similar between the treatment groups.
Both researchers agree that the findings – while reassuring – highlight the importance of collecting robust obstetric and safety data as part of prospective databases of individuals living with HIV, not only in resource-limited settings but also among the domestic U.S. population.
“We’ve learned a lot over the last 10 years,” Dr. Lockman said. “Some regimens (like lopinavir/ritonavir or nevirapine) are associated with significantly worse birth outcomes, whereas efavirenz doesn’t seem to be, or less so, and dolutegravir seems to be associated with even better outcomes. So, I think that where we are moving is to regimens that are the safest.”
Moving forward, Dr. Venkatesh explained, not only should researchers focus on exploring which antiretrovirals are safest in this context but also if the use of preexposure prophylaxis during conception periods affects birth outcomes.
Dr. Venkatesh and Dr. Lockman report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Integrating psychogastroenterology into GI care
Psychogastroenterology, or gastrointestinal psychology, refers to psychosocial research and clinical practice related to GI conditions. This field is situated within a biopsychosocial model of illness and grounded in an understanding of the gut-brain axis. A key feature of GI psychology intervention is behavioral symptom management. Commonly referred to as “brain-gut psychotherapies,” the primary goal of these interventions is to reduce GI symptoms and their impact on those experiencing them. Additionally, GI-focused psychotherapies can help patients with GI disorders cope with their symptoms, diagnosis, or treatment.
GI psychology providers
GI-focused psychotherapies are typically provided by clinical health psychologists (PhDs or PsyDs) with specialized training in GI disorders, although sometimes they are provided by a clinical social worker or advanced-practice nursing provider. Psychologists that identify GI as their primary specialty area often refer to themselves as “GI psychologists.” Psychologists that treat patients with a variety of medical concerns, which may include GI disorders, typically refer to themselves with the broader term, “health psychologists.”
Interventions
A variety of psychological treatments have been applied to GI populations, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH), psychodynamic interpersonal therapy, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Psychological therapies have been shown to be useful in a variety of GI disorders, with a number needed to treat of four in IBS.1 Common ingredients of GI-focused psychotherapy interventions include psychoeducation regarding the gut-brain relationship and relaxation strategies to provide in-the-moment tools to deescalate the body’s stress response.
CBT and GDH are the most commonly used interventions across a range of GI conditions, with the bulk of empirical evidence in IBS.2-5 CBT is a theoretical orientation in which thoughts and behaviors are understood to be modifiable factors that impact emotions and physical sensations. When utilized in a GI setting (i.e., GI-CBT), treatment aims to address GI-specific outcomes such as reducing GI symptoms, optimizing health care utilization, and improving quality of life. These interventions target cognitive and behavioral factors common among GI patient populations, such as GI-specific anxiety, symptom hypervigilance, and rigid coping strategies. See Figure 1 for a GI-CBT model.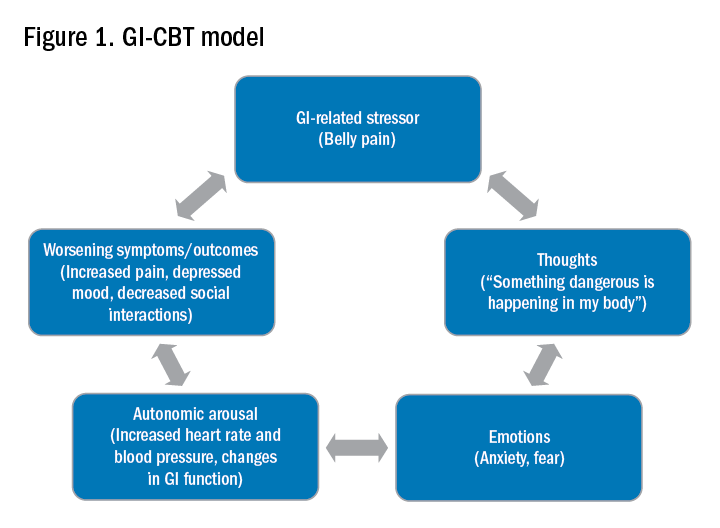
While research studies often implement manualized protocols, in clinical practice many GI psychologists use cognitive-behavioral interventions flexibly to tailor them to each patient’s presentation, while also integrating theory and practice from other types of therapies such as acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT; pronounced as one word). ACT, a “new wave” therapy derived from traditional CBT, emphasizes acceptance of distress (including GI symptoms), with a focus on engaging in values-based activities rather than symptom reduction.
Clinical hypnotherapy is utilized in a variety of medical specialties and has been studied in GI disorders for over 30 years. There are two evidence-based gut-directed hypnotherapy protocols, the Manchester6 and the North Carolina,7 that are widely used by GI psychologists. Though the exact mechanisms of hypnotherapy are unknown, it is thought to improve GI symptoms by modulating autonomic arousal and nerve sensitivity in the GI tract.
Evaluation
GI psychologists typically meet with patients for a 1-hour evaluation to determine appropriateness for psychogastroenterology intervention and develop a treatment plan. If GI-focused psychotherapy is indicated, patients are typically offered a course of treatment ranging from four to eight sessions. Depending on the nature of the patient’s concerns, longer courses of treatment may be offered, such as for with patients with active inflammatory bowel disease undergoing changes in medical treatment.
Appropriateness for psychogastroenterology treatment
Ideal patients are those who are psychologically stable and whose distress is primarily related to GI concerns, as opposed to family, work, or other situational stressors. While these other stressors can certainly impact GI symptoms, general mental health professionals are best suited to assist patients with these concerns. Patients experiencing more severe mental health concerns may be recommended to pursue a different treatment, such as mental health treatment for depression or anxiety or specialized treatments for trauma, eating disorders, or substance use. In both cases, once these general, non-GI, stressors or significant mental health concerns are more optimally managed, patients are likely to benefit from a GI-focused psychological treatment. Note, however, that because a GI psychologist’s particular practice can vary because of interest, experience, and institutional factors, it is best to connect directly with the GI psychologist you work with to clarify the types of referrals they are comfortable seeing and any specific characteristics of their practice.
Best practice recommendations for gastroenterologists
Developing a collaborative relationship with the GI psychologist, as well as any therapists to whom you regularly refer patients, is key to the success of integrated care. When talking to patients about the referral, refer to the GI psychologist as your colleague and a member of the treatment team. Maintain communication with the GI psychologist, and let the patient know that you are doing so.
When referring a patient, do so after you have completed your work-up and have optimized basic medical management for their condition but suspect that psychosocial factors may be negatively impacting their symptoms or ability to cope. Present the referral as an evaluation rather than implying a guarantee of treatment. This is particularly helpful in those cases where the patient is recommended to pursue a different treatment prior to GI-focused psychotherapy. Additionally, avoid telling patients that they are being referred for a specific intervention such as “a referral for CBT” or “a referral for hypnotherapy,” as the GI psychologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the patient upon evaluation. See Figure 2 for example scripts to use when referring.
Expect to maintain communication with the GI psychologist after making the referral. GI psychologists typically send the referring provider a written summary following the initial evaluation and conclusion of treatment and, in some cases, provide updates throughout. Be prepared to answer questions or provide input as requested. Not only may the psychologist have questions about the medical diagnosis or treatment, but they may enlist your help for medical expert opinion during treatment to address misinformation, which can often fuel concerns like treatment nonadherence or anxiety.
Identifying a psychogastroenterology provider
In recent years there has been significant growth in the training and hiring of GI psychologists, and it is increasingly common for GI psychologists to be employed at academic medical centers. However, the majority of gastroenterologists do not have access to a fully integrated or co-located GI psychologist. In these cases, gastroenterologists should search for other health psychology options in their area, such as psychologists or clinical social workers with experience with patients with chronic medical conditions and CBT. One positive product of the COVID-19 pandemic is that telemedicine has become increasingly utilized, and in some cases GI psychologists are able to provide virtual therapy to patients across state lines. However, this should be confirmed with the therapy practice as there are numerous factors to consider regarding virtual practice.
Dr. Bedell is assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Resources available
To locate a GI psychology provider in your area: Search the Rome Psychogastroenterology directory (https://romegipsych.org/).
To locate general mental health providers: Search the Psychology Today website using the therapist finder function, which allows patients or providers to search by insurance, location, and specialty area (www.psychologytoday.com/us). The patient can also request a list of in-network psychotherapy providers from their insurance company and may find it helpful to cross-check these providers for potential fit by searching them online.
References
1. Ford AC et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;114(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5.
2. Laird KT et al. Short-term and long-term efficacy of psychological therapies for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;14(7):937-47.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.020.
3. Lackner JM et al. Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after cognitive behavior therapy for refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jul;155(1):47-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.063.
4. Lövdahl J et al. Nurse-administered, gut-directed hypnotherapy in IBS: Efficacy and factors predicting a positive response. Am J Clin Hypn. 2015 Jul;58(1):100-14. doi: 10.1080/00029157.2015.1030492.
5. Smith GD. Effect of nurse-led gut-directed hypnotherapy upon health-related quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Nurs. 2006 Jun;15(6):678-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01356.x.
6. Gonsalkorale WM. Gut-directed hypnotherapy: the Manchester approach for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/00207140500323030.
7. Palsson OS. Standardized hypnosis treatment for irritable bowel syndrome: The North Carolina protocol. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):51-64. doi: 10.1080/00207140500322933.
Psychogastroenterology, or gastrointestinal psychology, refers to psychosocial research and clinical practice related to GI conditions. This field is situated within a biopsychosocial model of illness and grounded in an understanding of the gut-brain axis. A key feature of GI psychology intervention is behavioral symptom management. Commonly referred to as “brain-gut psychotherapies,” the primary goal of these interventions is to reduce GI symptoms and their impact on those experiencing them. Additionally, GI-focused psychotherapies can help patients with GI disorders cope with their symptoms, diagnosis, or treatment.
GI psychology providers
GI-focused psychotherapies are typically provided by clinical health psychologists (PhDs or PsyDs) with specialized training in GI disorders, although sometimes they are provided by a clinical social worker or advanced-practice nursing provider. Psychologists that identify GI as their primary specialty area often refer to themselves as “GI psychologists.” Psychologists that treat patients with a variety of medical concerns, which may include GI disorders, typically refer to themselves with the broader term, “health psychologists.”
Interventions
A variety of psychological treatments have been applied to GI populations, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH), psychodynamic interpersonal therapy, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Psychological therapies have been shown to be useful in a variety of GI disorders, with a number needed to treat of four in IBS.1 Common ingredients of GI-focused psychotherapy interventions include psychoeducation regarding the gut-brain relationship and relaxation strategies to provide in-the-moment tools to deescalate the body’s stress response.
CBT and GDH are the most commonly used interventions across a range of GI conditions, with the bulk of empirical evidence in IBS.2-5 CBT is a theoretical orientation in which thoughts and behaviors are understood to be modifiable factors that impact emotions and physical sensations. When utilized in a GI setting (i.e., GI-CBT), treatment aims to address GI-specific outcomes such as reducing GI symptoms, optimizing health care utilization, and improving quality of life. These interventions target cognitive and behavioral factors common among GI patient populations, such as GI-specific anxiety, symptom hypervigilance, and rigid coping strategies. See Figure 1 for a GI-CBT model.
While research studies often implement manualized protocols, in clinical practice many GI psychologists use cognitive-behavioral interventions flexibly to tailor them to each patient’s presentation, while also integrating theory and practice from other types of therapies such as acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT; pronounced as one word). ACT, a “new wave” therapy derived from traditional CBT, emphasizes acceptance of distress (including GI symptoms), with a focus on engaging in values-based activities rather than symptom reduction.
Clinical hypnotherapy is utilized in a variety of medical specialties and has been studied in GI disorders for over 30 years. There are two evidence-based gut-directed hypnotherapy protocols, the Manchester6 and the North Carolina,7 that are widely used by GI psychologists. Though the exact mechanisms of hypnotherapy are unknown, it is thought to improve GI symptoms by modulating autonomic arousal and nerve sensitivity in the GI tract.
Evaluation
GI psychologists typically meet with patients for a 1-hour evaluation to determine appropriateness for psychogastroenterology intervention and develop a treatment plan. If GI-focused psychotherapy is indicated, patients are typically offered a course of treatment ranging from four to eight sessions. Depending on the nature of the patient’s concerns, longer courses of treatment may be offered, such as for with patients with active inflammatory bowel disease undergoing changes in medical treatment.
Appropriateness for psychogastroenterology treatment
Ideal patients are those who are psychologically stable and whose distress is primarily related to GI concerns, as opposed to family, work, or other situational stressors. While these other stressors can certainly impact GI symptoms, general mental health professionals are best suited to assist patients with these concerns. Patients experiencing more severe mental health concerns may be recommended to pursue a different treatment, such as mental health treatment for depression or anxiety or specialized treatments for trauma, eating disorders, or substance use. In both cases, once these general, non-GI, stressors or significant mental health concerns are more optimally managed, patients are likely to benefit from a GI-focused psychological treatment. Note, however, that because a GI psychologist’s particular practice can vary because of interest, experience, and institutional factors, it is best to connect directly with the GI psychologist you work with to clarify the types of referrals they are comfortable seeing and any specific characteristics of their practice.
Best practice recommendations for gastroenterologists
Developing a collaborative relationship with the GI psychologist, as well as any therapists to whom you regularly refer patients, is key to the success of integrated care. When talking to patients about the referral, refer to the GI psychologist as your colleague and a member of the treatment team. Maintain communication with the GI psychologist, and let the patient know that you are doing so.
When referring a patient, do so after you have completed your work-up and have optimized basic medical management for their condition but suspect that psychosocial factors may be negatively impacting their symptoms or ability to cope. Present the referral as an evaluation rather than implying a guarantee of treatment. This is particularly helpful in those cases where the patient is recommended to pursue a different treatment prior to GI-focused psychotherapy. Additionally, avoid telling patients that they are being referred for a specific intervention such as “a referral for CBT” or “a referral for hypnotherapy,” as the GI psychologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the patient upon evaluation. See Figure 2 for example scripts to use when referring.
Expect to maintain communication with the GI psychologist after making the referral. GI psychologists typically send the referring provider a written summary following the initial evaluation and conclusion of treatment and, in some cases, provide updates throughout. Be prepared to answer questions or provide input as requested. Not only may the psychologist have questions about the medical diagnosis or treatment, but they may enlist your help for medical expert opinion during treatment to address misinformation, which can often fuel concerns like treatment nonadherence or anxiety.
Identifying a psychogastroenterology provider
In recent years there has been significant growth in the training and hiring of GI psychologists, and it is increasingly common for GI psychologists to be employed at academic medical centers. However, the majority of gastroenterologists do not have access to a fully integrated or co-located GI psychologist. In these cases, gastroenterologists should search for other health psychology options in their area, such as psychologists or clinical social workers with experience with patients with chronic medical conditions and CBT. One positive product of the COVID-19 pandemic is that telemedicine has become increasingly utilized, and in some cases GI psychologists are able to provide virtual therapy to patients across state lines. However, this should be confirmed with the therapy practice as there are numerous factors to consider regarding virtual practice.
Dr. Bedell is assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Resources available
To locate a GI psychology provider in your area: Search the Rome Psychogastroenterology directory (https://romegipsych.org/).
To locate general mental health providers: Search the Psychology Today website using the therapist finder function, which allows patients or providers to search by insurance, location, and specialty area (www.psychologytoday.com/us). The patient can also request a list of in-network psychotherapy providers from their insurance company and may find it helpful to cross-check these providers for potential fit by searching them online.
References
1. Ford AC et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;114(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5.
2. Laird KT et al. Short-term and long-term efficacy of psychological therapies for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;14(7):937-47.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.020.
3. Lackner JM et al. Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after cognitive behavior therapy for refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jul;155(1):47-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.063.
4. Lövdahl J et al. Nurse-administered, gut-directed hypnotherapy in IBS: Efficacy and factors predicting a positive response. Am J Clin Hypn. 2015 Jul;58(1):100-14. doi: 10.1080/00029157.2015.1030492.
5. Smith GD. Effect of nurse-led gut-directed hypnotherapy upon health-related quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Nurs. 2006 Jun;15(6):678-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01356.x.
6. Gonsalkorale WM. Gut-directed hypnotherapy: the Manchester approach for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/00207140500323030.
7. Palsson OS. Standardized hypnosis treatment for irritable bowel syndrome: The North Carolina protocol. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):51-64. doi: 10.1080/00207140500322933.
Psychogastroenterology, or gastrointestinal psychology, refers to psychosocial research and clinical practice related to GI conditions. This field is situated within a biopsychosocial model of illness and grounded in an understanding of the gut-brain axis. A key feature of GI psychology intervention is behavioral symptom management. Commonly referred to as “brain-gut psychotherapies,” the primary goal of these interventions is to reduce GI symptoms and their impact on those experiencing them. Additionally, GI-focused psychotherapies can help patients with GI disorders cope with their symptoms, diagnosis, or treatment.
GI psychology providers
GI-focused psychotherapies are typically provided by clinical health psychologists (PhDs or PsyDs) with specialized training in GI disorders, although sometimes they are provided by a clinical social worker or advanced-practice nursing provider. Psychologists that identify GI as their primary specialty area often refer to themselves as “GI psychologists.” Psychologists that treat patients with a variety of medical concerns, which may include GI disorders, typically refer to themselves with the broader term, “health psychologists.”
Interventions
A variety of psychological treatments have been applied to GI populations, including cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT), gut-directed hypnotherapy (GDH), psychodynamic interpersonal therapy, relaxation training, and mindfulness-based stress reduction. Psychological therapies have been shown to be useful in a variety of GI disorders, with a number needed to treat of four in IBS.1 Common ingredients of GI-focused psychotherapy interventions include psychoeducation regarding the gut-brain relationship and relaxation strategies to provide in-the-moment tools to deescalate the body’s stress response.
CBT and GDH are the most commonly used interventions across a range of GI conditions, with the bulk of empirical evidence in IBS.2-5 CBT is a theoretical orientation in which thoughts and behaviors are understood to be modifiable factors that impact emotions and physical sensations. When utilized in a GI setting (i.e., GI-CBT), treatment aims to address GI-specific outcomes such as reducing GI symptoms, optimizing health care utilization, and improving quality of life. These interventions target cognitive and behavioral factors common among GI patient populations, such as GI-specific anxiety, symptom hypervigilance, and rigid coping strategies. See Figure 1 for a GI-CBT model.
While research studies often implement manualized protocols, in clinical practice many GI psychologists use cognitive-behavioral interventions flexibly to tailor them to each patient’s presentation, while also integrating theory and practice from other types of therapies such as acceptance and commitment therapy (ACT; pronounced as one word). ACT, a “new wave” therapy derived from traditional CBT, emphasizes acceptance of distress (including GI symptoms), with a focus on engaging in values-based activities rather than symptom reduction.
Clinical hypnotherapy is utilized in a variety of medical specialties and has been studied in GI disorders for over 30 years. There are two evidence-based gut-directed hypnotherapy protocols, the Manchester6 and the North Carolina,7 that are widely used by GI psychologists. Though the exact mechanisms of hypnotherapy are unknown, it is thought to improve GI symptoms by modulating autonomic arousal and nerve sensitivity in the GI tract.
Evaluation
GI psychologists typically meet with patients for a 1-hour evaluation to determine appropriateness for psychogastroenterology intervention and develop a treatment plan. If GI-focused psychotherapy is indicated, patients are typically offered a course of treatment ranging from four to eight sessions. Depending on the nature of the patient’s concerns, longer courses of treatment may be offered, such as for with patients with active inflammatory bowel disease undergoing changes in medical treatment.
Appropriateness for psychogastroenterology treatment
Ideal patients are those who are psychologically stable and whose distress is primarily related to GI concerns, as opposed to family, work, or other situational stressors. While these other stressors can certainly impact GI symptoms, general mental health professionals are best suited to assist patients with these concerns. Patients experiencing more severe mental health concerns may be recommended to pursue a different treatment, such as mental health treatment for depression or anxiety or specialized treatments for trauma, eating disorders, or substance use. In both cases, once these general, non-GI, stressors or significant mental health concerns are more optimally managed, patients are likely to benefit from a GI-focused psychological treatment. Note, however, that because a GI psychologist’s particular practice can vary because of interest, experience, and institutional factors, it is best to connect directly with the GI psychologist you work with to clarify the types of referrals they are comfortable seeing and any specific characteristics of their practice.
Best practice recommendations for gastroenterologists
Developing a collaborative relationship with the GI psychologist, as well as any therapists to whom you regularly refer patients, is key to the success of integrated care. When talking to patients about the referral, refer to the GI psychologist as your colleague and a member of the treatment team. Maintain communication with the GI psychologist, and let the patient know that you are doing so.
When referring a patient, do so after you have completed your work-up and have optimized basic medical management for their condition but suspect that psychosocial factors may be negatively impacting their symptoms or ability to cope. Present the referral as an evaluation rather than implying a guarantee of treatment. This is particularly helpful in those cases where the patient is recommended to pursue a different treatment prior to GI-focused psychotherapy. Additionally, avoid telling patients that they are being referred for a specific intervention such as “a referral for CBT” or “a referral for hypnotherapy,” as the GI psychologist will recommend the most appropriate treatment for the patient upon evaluation. See Figure 2 for example scripts to use when referring.
Expect to maintain communication with the GI psychologist after making the referral. GI psychologists typically send the referring provider a written summary following the initial evaluation and conclusion of treatment and, in some cases, provide updates throughout. Be prepared to answer questions or provide input as requested. Not only may the psychologist have questions about the medical diagnosis or treatment, but they may enlist your help for medical expert opinion during treatment to address misinformation, which can often fuel concerns like treatment nonadherence or anxiety.
Identifying a psychogastroenterology provider
In recent years there has been significant growth in the training and hiring of GI psychologists, and it is increasingly common for GI psychologists to be employed at academic medical centers. However, the majority of gastroenterologists do not have access to a fully integrated or co-located GI psychologist. In these cases, gastroenterologists should search for other health psychology options in their area, such as psychologists or clinical social workers with experience with patients with chronic medical conditions and CBT. One positive product of the COVID-19 pandemic is that telemedicine has become increasingly utilized, and in some cases GI psychologists are able to provide virtual therapy to patients across state lines. However, this should be confirmed with the therapy practice as there are numerous factors to consider regarding virtual practice.
Dr. Bedell is assistant professor in the department of psychiatry and behavioral neuroscience at the University of Chicago. She has no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Resources available
To locate a GI psychology provider in your area: Search the Rome Psychogastroenterology directory (https://romegipsych.org/).
To locate general mental health providers: Search the Psychology Today website using the therapist finder function, which allows patients or providers to search by insurance, location, and specialty area (www.psychologytoday.com/us). The patient can also request a list of in-network psychotherapy providers from their insurance company and may find it helpful to cross-check these providers for potential fit by searching them online.
References
1. Ford AC et al. Effect of antidepressants and psychological therapies in irritable bowel syndrome: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2019 Jan;114(1):21-39. doi: 10.1038/s41395-018-0222-5.
2. Laird KT et al. Short-term and long-term efficacy of psychological therapies for irritable bowel syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2016 Jul;14(7):937-47.e4. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2015.11.020.
3. Lackner JM et al. Improvement in gastrointestinal symptoms after cognitive behavior therapy for refractory irritable bowel syndrome. Gastroenterology. 2018 Jul;155(1):47-57. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2018.03.063.
4. Lövdahl J et al. Nurse-administered, gut-directed hypnotherapy in IBS: Efficacy and factors predicting a positive response. Am J Clin Hypn. 2015 Jul;58(1):100-14. doi: 10.1080/00029157.2015.1030492.
5. Smith GD. Effect of nurse-led gut-directed hypnotherapy upon health-related quality of life in patients with irritable bowel syndrome. J Clin Nurs. 2006 Jun;15(6):678-84. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2702.2006.01356.x.
6. Gonsalkorale WM. Gut-directed hypnotherapy: the Manchester approach for treatment of irritable bowel syndrome. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):27-50. doi: 10.1080/00207140500323030.
7. Palsson OS. Standardized hypnosis treatment for irritable bowel syndrome: The North Carolina protocol. Int J Clin Exp Hypn. 2006 Jan;54(1):51-64. doi: 10.1080/00207140500322933.
Adverse skin effects of cancer immunotherapy reviewed
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have unquestionably revolutionized the care of patients with malignant melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other types of cancer.
, according to members of a European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) task force.
“The desirable, immune-mediated oncologic response is often achieved at the cost of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may potentially affect any organ system,” they write in a position statement on the management of ICI-derived dermatologic adverse events.
Recommendations from the EADV “Dermatology for Cancer Patients” task force have been published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Task force members developed the recommendations based on clinical experience from published data and came up with specific recommendations for treating cutaneous toxicities associated with dermatologic immune-related adverse events (dirAEs) that occur in patients receiving immunotherapy with an ICI.
ICIs include the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol Myers Squibb), and inhibitors of programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1), including nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol Myers Squibb), pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck), and other agents.
“The basic principle of management is that the interventions should be tailored to serve the equilibrium between patients’ relief from the symptoms and signs of skin toxicity and the preservation of an unimpeded oncologic treatment,” they write.
The recommendations are in line with those included in a 2021 update of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines on the management of irAEs in patients treated with ICIs across the whole range of organ systems, said Milan J. Anadkat, MD, professor of dermatology and director of dermatology clinical trials at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis. Dr. Anadkat was a coauthor of the ASCO guideline update.
Although the European recommendations focus only on dermatologic side effects of ICIs in patients with cancer, “that doesn’t diminish their importance. They do a good job of summarizing how to approach and how to manage it depending on the severity of the toxicities and the various types of toxicities,” he told this news organization.
Having a paper focused exclusively on the dermatologic side effects of ICIs allows the inclusion of photographs that can help clinicians identify specific conditions that may require referral to a dermatologist, he said.
Both Dr. Anadkat and the authors of the European recommendations noted that dermatologic irAEs are more common with CTLA-4 inhibition than with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition.
“It has to do with where the target is,” Dr. Anadkat said. “CTLA-4 inhibition works on a central aspect of the immune system, so it’s a much less specific site, whereas PD-1 affects an interaction at the site of the tumor cell itself, so it’s a little more specific.”
Pruritus
ICI-induced pruritus can occur without apparent skin changes, they write, noting that in a recent study of patients with dirAEs, about one-third had isolated pruritus.
The task force members cite a meta-analysis indicating a pruritus incidence of 13.2% for patients treated with nivolumab and 20.2% for patients treated with pembrolizumab but respective grade 3 pruritus rates of only 0.5% and 2.3%. The reported incidence of pruritus with ipilimumab was 47% in a different study.
Recommended treatments include topical moisturizers with or without medium-to-high potency corticosteroids for grade 1 reactions, non-sedating histamines and/or GABA agonists such as pregabalin, or gabapentin for grade 2 pruritus, and suspension of ICIs until pruritus improves in patients with grade 3 pruritus.
Maculopapular rash
Maculopapular or eczema-like rashes may occur in up to 68% of patients who receive a CTLA-4 inhibitor and up to 20% of those who receive a PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor, the authors note. Rashes commonly appear within 3-6 weeks of initiating therapy.
“The clinical presentation is nonspecific and consists of a rapid onset of multiple minimally scaly, erythematous macules and papules, congregating into plaques. Lesions are mostly located on trunk and extensor surfaces of the extremities and the face is generally spared,” they write.
Maculopapular rashes are typically accompanied by itching but could be asymptomatic, they noted.
Mild (grade 1) rashes may respond to moisturizers and topical potent or super-potent corticosteroids. Patients with grade 2 rash should also receive oral antihistamines. Systemic corticosteroids may be considered for patients with grade 3 rashes but only after other dirAEs that may require specific management, such as psoriasis, are ruled out.
Psoriasis-like rash
The most common form of psoriasis seen in patients treated with ICIs is psoriasis vulgaris with plaques, but other clinical variants are also seen, the authors note.
“Topical agents (corticosteroids, Vitamin D analogues) are prescribed in Grades 1/2 and supplementary” to systemic treatment for patients with grade 3 or recalcitrant lesions, they write. “If skin-directed therapies fail to provide symptomatic control,” systemic treatment and narrow band UVB phototherapy “should be considered,” they add.
Evidence regarding the use of systemic therapies to treat psoriasis-like rash associated with ICIs is sparse. Acitretin can be safely used in patients with cancer. Low-dose methotrexate is also safe to use except in patients with non-melanoma skin cancers. Cyclosporine, however, should be avoided because of the potential for tumor-promoting effects, they emphasized.
The recommendations also cover treatment of lichen planus-like and vitiligo-like rashes, as well as hair and nail changes, autoimmune bullous disorders, and oral mucosal dirAEs.
In addition, the recommendations cover severe cutaneous adverse reactions as well as serious, potentially life-threatening dirAEs, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms/drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS/DIHS).
“The dose of corticosteroids may be adapted to the severity of DRESS. The therapeutic benefit of systemic corticosteroids in the management of SJS/TEN remains controversial, and some authors favor treatment with cyclosporine. However, the use of corticosteroids in this context of ICI treatment appears reasonable and should be proposed. Short courses of steroids seem also effective in AGEP,” the task force members write.
The recommendations did not have outside funding. Of the 19 authors, 6 disclosed relationships with various pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Leo Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, and/or Janssen. Dr. Anadkat disclosed previous relationships with Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, and current relationships with others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have unquestionably revolutionized the care of patients with malignant melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other types of cancer.
, according to members of a European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) task force.
“The desirable, immune-mediated oncologic response is often achieved at the cost of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may potentially affect any organ system,” they write in a position statement on the management of ICI-derived dermatologic adverse events.
Recommendations from the EADV “Dermatology for Cancer Patients” task force have been published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Task force members developed the recommendations based on clinical experience from published data and came up with specific recommendations for treating cutaneous toxicities associated with dermatologic immune-related adverse events (dirAEs) that occur in patients receiving immunotherapy with an ICI.
ICIs include the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol Myers Squibb), and inhibitors of programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1), including nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol Myers Squibb), pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck), and other agents.
“The basic principle of management is that the interventions should be tailored to serve the equilibrium between patients’ relief from the symptoms and signs of skin toxicity and the preservation of an unimpeded oncologic treatment,” they write.
The recommendations are in line with those included in a 2021 update of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines on the management of irAEs in patients treated with ICIs across the whole range of organ systems, said Milan J. Anadkat, MD, professor of dermatology and director of dermatology clinical trials at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis. Dr. Anadkat was a coauthor of the ASCO guideline update.
Although the European recommendations focus only on dermatologic side effects of ICIs in patients with cancer, “that doesn’t diminish their importance. They do a good job of summarizing how to approach and how to manage it depending on the severity of the toxicities and the various types of toxicities,” he told this news organization.
Having a paper focused exclusively on the dermatologic side effects of ICIs allows the inclusion of photographs that can help clinicians identify specific conditions that may require referral to a dermatologist, he said.
Both Dr. Anadkat and the authors of the European recommendations noted that dermatologic irAEs are more common with CTLA-4 inhibition than with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition.
“It has to do with where the target is,” Dr. Anadkat said. “CTLA-4 inhibition works on a central aspect of the immune system, so it’s a much less specific site, whereas PD-1 affects an interaction at the site of the tumor cell itself, so it’s a little more specific.”
Pruritus
ICI-induced pruritus can occur without apparent skin changes, they write, noting that in a recent study of patients with dirAEs, about one-third had isolated pruritus.
The task force members cite a meta-analysis indicating a pruritus incidence of 13.2% for patients treated with nivolumab and 20.2% for patients treated with pembrolizumab but respective grade 3 pruritus rates of only 0.5% and 2.3%. The reported incidence of pruritus with ipilimumab was 47% in a different study.
Recommended treatments include topical moisturizers with or without medium-to-high potency corticosteroids for grade 1 reactions, non-sedating histamines and/or GABA agonists such as pregabalin, or gabapentin for grade 2 pruritus, and suspension of ICIs until pruritus improves in patients with grade 3 pruritus.
Maculopapular rash
Maculopapular or eczema-like rashes may occur in up to 68% of patients who receive a CTLA-4 inhibitor and up to 20% of those who receive a PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor, the authors note. Rashes commonly appear within 3-6 weeks of initiating therapy.
“The clinical presentation is nonspecific and consists of a rapid onset of multiple minimally scaly, erythematous macules and papules, congregating into plaques. Lesions are mostly located on trunk and extensor surfaces of the extremities and the face is generally spared,” they write.
Maculopapular rashes are typically accompanied by itching but could be asymptomatic, they noted.
Mild (grade 1) rashes may respond to moisturizers and topical potent or super-potent corticosteroids. Patients with grade 2 rash should also receive oral antihistamines. Systemic corticosteroids may be considered for patients with grade 3 rashes but only after other dirAEs that may require specific management, such as psoriasis, are ruled out.
Psoriasis-like rash
The most common form of psoriasis seen in patients treated with ICIs is psoriasis vulgaris with plaques, but other clinical variants are also seen, the authors note.
“Topical agents (corticosteroids, Vitamin D analogues) are prescribed in Grades 1/2 and supplementary” to systemic treatment for patients with grade 3 or recalcitrant lesions, they write. “If skin-directed therapies fail to provide symptomatic control,” systemic treatment and narrow band UVB phototherapy “should be considered,” they add.
Evidence regarding the use of systemic therapies to treat psoriasis-like rash associated with ICIs is sparse. Acitretin can be safely used in patients with cancer. Low-dose methotrexate is also safe to use except in patients with non-melanoma skin cancers. Cyclosporine, however, should be avoided because of the potential for tumor-promoting effects, they emphasized.
The recommendations also cover treatment of lichen planus-like and vitiligo-like rashes, as well as hair and nail changes, autoimmune bullous disorders, and oral mucosal dirAEs.
In addition, the recommendations cover severe cutaneous adverse reactions as well as serious, potentially life-threatening dirAEs, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms/drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS/DIHS).
“The dose of corticosteroids may be adapted to the severity of DRESS. The therapeutic benefit of systemic corticosteroids in the management of SJS/TEN remains controversial, and some authors favor treatment with cyclosporine. However, the use of corticosteroids in this context of ICI treatment appears reasonable and should be proposed. Short courses of steroids seem also effective in AGEP,” the task force members write.
The recommendations did not have outside funding. Of the 19 authors, 6 disclosed relationships with various pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Leo Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, and/or Janssen. Dr. Anadkat disclosed previous relationships with Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, and current relationships with others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) have unquestionably revolutionized the care of patients with malignant melanoma, non-small cell lung cancer, and other types of cancer.
, according to members of a European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology (EADV) task force.
“The desirable, immune-mediated oncologic response is often achieved at the cost of immune-related adverse events (irAEs) that may potentially affect any organ system,” they write in a position statement on the management of ICI-derived dermatologic adverse events.
Recommendations from the EADV “Dermatology for Cancer Patients” task force have been published in the Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology.
Task force members developed the recommendations based on clinical experience from published data and came up with specific recommendations for treating cutaneous toxicities associated with dermatologic immune-related adverse events (dirAEs) that occur in patients receiving immunotherapy with an ICI.
ICIs include the cytotoxic T-lymphocyte–associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) inhibitor ipilimumab (Yervoy, Bristol Myers Squibb), and inhibitors of programmed death protein 1 (PD-1) and its ligand (PD-L1), including nivolumab (Opdivo, Bristol Myers Squibb), pembrolizumab (Keytruda, Merck), and other agents.
“The basic principle of management is that the interventions should be tailored to serve the equilibrium between patients’ relief from the symptoms and signs of skin toxicity and the preservation of an unimpeded oncologic treatment,” they write.
The recommendations are in line with those included in a 2021 update of the American Society of Clinical Oncology (ASCO) guidelines on the management of irAEs in patients treated with ICIs across the whole range of organ systems, said Milan J. Anadkat, MD, professor of dermatology and director of dermatology clinical trials at Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis. Dr. Anadkat was a coauthor of the ASCO guideline update.
Although the European recommendations focus only on dermatologic side effects of ICIs in patients with cancer, “that doesn’t diminish their importance. They do a good job of summarizing how to approach and how to manage it depending on the severity of the toxicities and the various types of toxicities,” he told this news organization.
Having a paper focused exclusively on the dermatologic side effects of ICIs allows the inclusion of photographs that can help clinicians identify specific conditions that may require referral to a dermatologist, he said.
Both Dr. Anadkat and the authors of the European recommendations noted that dermatologic irAEs are more common with CTLA-4 inhibition than with PD-1/PD-L1 inhibition.
“It has to do with where the target is,” Dr. Anadkat said. “CTLA-4 inhibition works on a central aspect of the immune system, so it’s a much less specific site, whereas PD-1 affects an interaction at the site of the tumor cell itself, so it’s a little more specific.”
Pruritus
ICI-induced pruritus can occur without apparent skin changes, they write, noting that in a recent study of patients with dirAEs, about one-third had isolated pruritus.
The task force members cite a meta-analysis indicating a pruritus incidence of 13.2% for patients treated with nivolumab and 20.2% for patients treated with pembrolizumab but respective grade 3 pruritus rates of only 0.5% and 2.3%. The reported incidence of pruritus with ipilimumab was 47% in a different study.
Recommended treatments include topical moisturizers with or without medium-to-high potency corticosteroids for grade 1 reactions, non-sedating histamines and/or GABA agonists such as pregabalin, or gabapentin for grade 2 pruritus, and suspension of ICIs until pruritus improves in patients with grade 3 pruritus.
Maculopapular rash
Maculopapular or eczema-like rashes may occur in up to 68% of patients who receive a CTLA-4 inhibitor and up to 20% of those who receive a PD1/PD-L1 inhibitor, the authors note. Rashes commonly appear within 3-6 weeks of initiating therapy.
“The clinical presentation is nonspecific and consists of a rapid onset of multiple minimally scaly, erythematous macules and papules, congregating into plaques. Lesions are mostly located on trunk and extensor surfaces of the extremities and the face is generally spared,” they write.
Maculopapular rashes are typically accompanied by itching but could be asymptomatic, they noted.
Mild (grade 1) rashes may respond to moisturizers and topical potent or super-potent corticosteroids. Patients with grade 2 rash should also receive oral antihistamines. Systemic corticosteroids may be considered for patients with grade 3 rashes but only after other dirAEs that may require specific management, such as psoriasis, are ruled out.
Psoriasis-like rash
The most common form of psoriasis seen in patients treated with ICIs is psoriasis vulgaris with plaques, but other clinical variants are also seen, the authors note.
“Topical agents (corticosteroids, Vitamin D analogues) are prescribed in Grades 1/2 and supplementary” to systemic treatment for patients with grade 3 or recalcitrant lesions, they write. “If skin-directed therapies fail to provide symptomatic control,” systemic treatment and narrow band UVB phototherapy “should be considered,” they add.
Evidence regarding the use of systemic therapies to treat psoriasis-like rash associated with ICIs is sparse. Acitretin can be safely used in patients with cancer. Low-dose methotrexate is also safe to use except in patients with non-melanoma skin cancers. Cyclosporine, however, should be avoided because of the potential for tumor-promoting effects, they emphasized.
The recommendations also cover treatment of lichen planus-like and vitiligo-like rashes, as well as hair and nail changes, autoimmune bullous disorders, and oral mucosal dirAEs.
In addition, the recommendations cover severe cutaneous adverse reactions as well as serious, potentially life-threatening dirAEs, including Stevens-Johnson syndrome/TEN, acute generalized exanthematous pustulosis (AGEP), and drug reaction with eosinophilia and systemic symptoms/drug-induced hypersensitivity syndrome (DRESS/DIHS).
“The dose of corticosteroids may be adapted to the severity of DRESS. The therapeutic benefit of systemic corticosteroids in the management of SJS/TEN remains controversial, and some authors favor treatment with cyclosporine. However, the use of corticosteroids in this context of ICI treatment appears reasonable and should be proposed. Short courses of steroids seem also effective in AGEP,” the task force members write.
The recommendations did not have outside funding. Of the 19 authors, 6 disclosed relationships with various pharmaceutical companies, including AbbVie, Leo Pharma, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol Myers Squibb, and/or Janssen. Dr. Anadkat disclosed previous relationships with Merck, Bristol Myers Squibb, and current relationships with others.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
HCC risk differs among various liver cirrhosis etiologies
Key clinical point: The risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) varies with underlying etiologies, with active hepatitis C virus (HCV) cirrhosis posing the highest and alcoholic or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) cirrhosis posing the lowest risk of developing HCC.
Major finding: Patients with active HCV (3.36%) showed the highest annual HCC incidence rate, followed by those with cured HCV (1.71%), alcoholic liver disease (1.32%), and NAFLD cirrhosis (1.24%). Patients with active HCV vs. NAFLD were at a 2.1-fold higher risk for HCC (adjusted hazard ratio 2.16; 95% CI, 1.16-4.04).
Study details: This multicenter, prospective cohort study analyzed data from two multiethnic cohorts enrolling a total of 2,733 patients with cirrhosis.
Disclosures: The study received financial support from the National Cancer Institute; Cancer Prevention & Research Institute of Texas grant; and Center for Gastrointestinal Development, Infection, and Injury. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Kanwal F et al. Risk factors for hepatocellular cancer in contemporary cohorts of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2022 (Mar 1). Doi: 10.1002/hep.32434
Key clinical point: The risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) varies with underlying etiologies, with active hepatitis C virus (HCV) cirrhosis posing the highest and alcoholic or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) cirrhosis posing the lowest risk of developing HCC.
Major finding: Patients with active HCV (3.36%) showed the highest annual HCC incidence rate, followed by those with cured HCV (1.71%), alcoholic liver disease (1.32%), and NAFLD cirrhosis (1.24%). Patients with active HCV vs. NAFLD were at a 2.1-fold higher risk for HCC (adjusted hazard ratio 2.16; 95% CI, 1.16-4.04).
Study details: This multicenter, prospective cohort study analyzed data from two multiethnic cohorts enrolling a total of 2,733 patients with cirrhosis.
Disclosures: The study received financial support from the National Cancer Institute; Cancer Prevention & Research Institute of Texas grant; and Center for Gastrointestinal Development, Infection, and Injury. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Kanwal F et al. Risk factors for hepatocellular cancer in contemporary cohorts of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2022 (Mar 1). Doi: 10.1002/hep.32434
Key clinical point: The risk for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) varies with underlying etiologies, with active hepatitis C virus (HCV) cirrhosis posing the highest and alcoholic or nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) cirrhosis posing the lowest risk of developing HCC.
Major finding: Patients with active HCV (3.36%) showed the highest annual HCC incidence rate, followed by those with cured HCV (1.71%), alcoholic liver disease (1.32%), and NAFLD cirrhosis (1.24%). Patients with active HCV vs. NAFLD were at a 2.1-fold higher risk for HCC (adjusted hazard ratio 2.16; 95% CI, 1.16-4.04).
Study details: This multicenter, prospective cohort study analyzed data from two multiethnic cohorts enrolling a total of 2,733 patients with cirrhosis.
Disclosures: The study received financial support from the National Cancer Institute; Cancer Prevention & Research Institute of Texas grant; and Center for Gastrointestinal Development, Infection, and Injury. No conflicts of interest were reported.
Source: Kanwal F et al. Risk factors for hepatocellular cancer in contemporary cohorts of patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2022 (Mar 1). Doi: 10.1002/hep.32434
Active HCV infection worsens the prognosis of very early-stage HCC after ablation therapy
Key clinical point: Active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection negatively affects overall and recurrence-free survival in patients with very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after curative radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Major finding: Active HCV infection was a significant risk factor for shorter overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 2.17; P = .003) and early recurrence of HCC (aHR 1.47; P = .022). Patients with vs. without active HCV infection had a shorter median overall (66 months vs. 145 months) and recurrence-free (20 months vs. 31 months) survival (both P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a single-center retrospective study including 302 patients with very early-stage HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0) who underwent RFA and had follow-up of >6 months, of which 195 had HCV infection, including 132 active infection cases.
Disclosures: M Kurosaki and N Izumi declared funding support from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development and Japanese Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Labor, respectively, and along with K Tsuchiya, receiving lecture fees from several sources.
Source: Takaura K et al. The impact of background liver disease on the long-term prognosis of very-early-stage HCC after ablation therapy. PLoS One. 2022;17(2):e0264075 (Feb 23). Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264075
Key clinical point: Active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection negatively affects overall and recurrence-free survival in patients with very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after curative radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Major finding: Active HCV infection was a significant risk factor for shorter overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 2.17; P = .003) and early recurrence of HCC (aHR 1.47; P = .022). Patients with vs. without active HCV infection had a shorter median overall (66 months vs. 145 months) and recurrence-free (20 months vs. 31 months) survival (both P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a single-center retrospective study including 302 patients with very early-stage HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0) who underwent RFA and had follow-up of >6 months, of which 195 had HCV infection, including 132 active infection cases.
Disclosures: M Kurosaki and N Izumi declared funding support from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development and Japanese Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Labor, respectively, and along with K Tsuchiya, receiving lecture fees from several sources.
Source: Takaura K et al. The impact of background liver disease on the long-term prognosis of very-early-stage HCC after ablation therapy. PLoS One. 2022;17(2):e0264075 (Feb 23). Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264075
Key clinical point: Active hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection negatively affects overall and recurrence-free survival in patients with very early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) after curative radiofrequency ablation (RFA).
Major finding: Active HCV infection was a significant risk factor for shorter overall survival (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 2.17; P = .003) and early recurrence of HCC (aHR 1.47; P = .022). Patients with vs. without active HCV infection had a shorter median overall (66 months vs. 145 months) and recurrence-free (20 months vs. 31 months) survival (both P < .001).
Study details: Findings are from a single-center retrospective study including 302 patients with very early-stage HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0) who underwent RFA and had follow-up of >6 months, of which 195 had HCV infection, including 132 active infection cases.
Disclosures: M Kurosaki and N Izumi declared funding support from the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development and Japanese Ministry of Health, Welfare, and Labor, respectively, and along with K Tsuchiya, receiving lecture fees from several sources.
Source: Takaura K et al. The impact of background liver disease on the long-term prognosis of very-early-stage HCC after ablation therapy. PLoS One. 2022;17(2):e0264075 (Feb 23). Doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0264075
Risk factors for recurrence after hepatic resection for early-stage HCC
Key clinical point: Independent risk factors for postoperative recurrence among patients undergoing curative hepatic resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) include preoperative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level >400 µg/L, tumor size >5 cm, satellite nodules, multiple tumors, and microvascular invasion.
Major finding: Cirrhosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.49; P < .001), preoperative AFP level >400 µg/L (aHR 1.28; P = .004), tumor size >5 cm (aHR 1.74; P < .001), satellite nodules (aHR 1.35; P = .040), multiple tumors (aHR 1.63; P = .015), microvascular invasion (aHR 1.51; P < .001), and intraoperative blood transfusion (aHR 1.50; P = .013) were identified as independent risk factors associated with postoperative recurrence.
Study details: The data come from a large-scale, multicenter retrospective study including 1,424 adult patients who underwent curative hepatic resection for early-stage HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A).
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Source: Yao L-Q et al. Clinical features of recurrence after hepatic resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma and long-term survival outcomes of patients with recurrence: A multi-institutional analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Feb 22. Doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11454-y
Key clinical point: Independent risk factors for postoperative recurrence among patients undergoing curative hepatic resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) include preoperative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level >400 µg/L, tumor size >5 cm, satellite nodules, multiple tumors, and microvascular invasion.
Major finding: Cirrhosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.49; P < .001), preoperative AFP level >400 µg/L (aHR 1.28; P = .004), tumor size >5 cm (aHR 1.74; P < .001), satellite nodules (aHR 1.35; P = .040), multiple tumors (aHR 1.63; P = .015), microvascular invasion (aHR 1.51; P < .001), and intraoperative blood transfusion (aHR 1.50; P = .013) were identified as independent risk factors associated with postoperative recurrence.
Study details: The data come from a large-scale, multicenter retrospective study including 1,424 adult patients who underwent curative hepatic resection for early-stage HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A).
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Source: Yao L-Q et al. Clinical features of recurrence after hepatic resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma and long-term survival outcomes of patients with recurrence: A multi-institutional analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Feb 22. Doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11454-y
Key clinical point: Independent risk factors for postoperative recurrence among patients undergoing curative hepatic resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) include preoperative alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level >400 µg/L, tumor size >5 cm, satellite nodules, multiple tumors, and microvascular invasion.
Major finding: Cirrhosis (adjusted hazard ratio [aHR] 1.49; P < .001), preoperative AFP level >400 µg/L (aHR 1.28; P = .004), tumor size >5 cm (aHR 1.74; P < .001), satellite nodules (aHR 1.35; P = .040), multiple tumors (aHR 1.63; P = .015), microvascular invasion (aHR 1.51; P < .001), and intraoperative blood transfusion (aHR 1.50; P = .013) were identified as independent risk factors associated with postoperative recurrence.
Study details: The data come from a large-scale, multicenter retrospective study including 1,424 adult patients who underwent curative hepatic resection for early-stage HCC (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage 0/A).
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors reported no conflict of interests.
Source: Yao L-Q et al. Clinical features of recurrence after hepatic resection for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma and long-term survival outcomes of patients with recurrence: A multi-institutional analysis. Ann Surg Oncol. 2022 Feb 22. Doi: 10.1245/s10434-022-11454-y
Inadequate ultrasound quality negatively influences HCC surveillance test performance
Key clinical point: Hampered ultrasound visualization in patients with cirrhosis receiving hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance is associated with worse test performance, negatively affecting both sensitivity and specificity of surveillance.
Major finding: Patients with cirrhosis and HCC having severely impaired ultrasound visualization before HCC diagnosis showed increased odds of false-negative results (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 7.94; 95% CI 1.23-51.16), whereas those with only cirrhosis having moderately impaired visualization showed increased odds of false-positive results (aOR 1.60; 95% CI 1.13-2.27).
Study details: This was a retrospective cohort study involving 2,238 patients with cirrhosis, with (n = 186) or without (n = 2,052) HCC, who underwent at least one abdominal ultrasound examination.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the United States National Institute of Health. A Singal and D Fetzer declared serving as consultants or advisory board members of or having research agreements with various organizations.
Source: Chong N et al. Association between ultrasound quality and test performance for HCC surveillance in patients with cirrhosis: a retrospective cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(6):683-690 (Feb 15). Doi: 10.1111/apt.16779
Key clinical point: Hampered ultrasound visualization in patients with cirrhosis receiving hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance is associated with worse test performance, negatively affecting both sensitivity and specificity of surveillance.
Major finding: Patients with cirrhosis and HCC having severely impaired ultrasound visualization before HCC diagnosis showed increased odds of false-negative results (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 7.94; 95% CI 1.23-51.16), whereas those with only cirrhosis having moderately impaired visualization showed increased odds of false-positive results (aOR 1.60; 95% CI 1.13-2.27).
Study details: This was a retrospective cohort study involving 2,238 patients with cirrhosis, with (n = 186) or without (n = 2,052) HCC, who underwent at least one abdominal ultrasound examination.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the United States National Institute of Health. A Singal and D Fetzer declared serving as consultants or advisory board members of or having research agreements with various organizations.
Source: Chong N et al. Association between ultrasound quality and test performance for HCC surveillance in patients with cirrhosis: a retrospective cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(6):683-690 (Feb 15). Doi: 10.1111/apt.16779
Key clinical point: Hampered ultrasound visualization in patients with cirrhosis receiving hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) surveillance is associated with worse test performance, negatively affecting both sensitivity and specificity of surveillance.
Major finding: Patients with cirrhosis and HCC having severely impaired ultrasound visualization before HCC diagnosis showed increased odds of false-negative results (adjusted odds ratio [aOR] 7.94; 95% CI 1.23-51.16), whereas those with only cirrhosis having moderately impaired visualization showed increased odds of false-positive results (aOR 1.60; 95% CI 1.13-2.27).
Study details: This was a retrospective cohort study involving 2,238 patients with cirrhosis, with (n = 186) or without (n = 2,052) HCC, who underwent at least one abdominal ultrasound examination.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the United States National Institute of Health. A Singal and D Fetzer declared serving as consultants or advisory board members of or having research agreements with various organizations.
Source: Chong N et al. Association between ultrasound quality and test performance for HCC surveillance in patients with cirrhosis: a retrospective cohort study. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2022;55(6):683-690 (Feb 15). Doi: 10.1111/apt.16779

