User login
Even small changes can make endoscopy more sustainable: Study
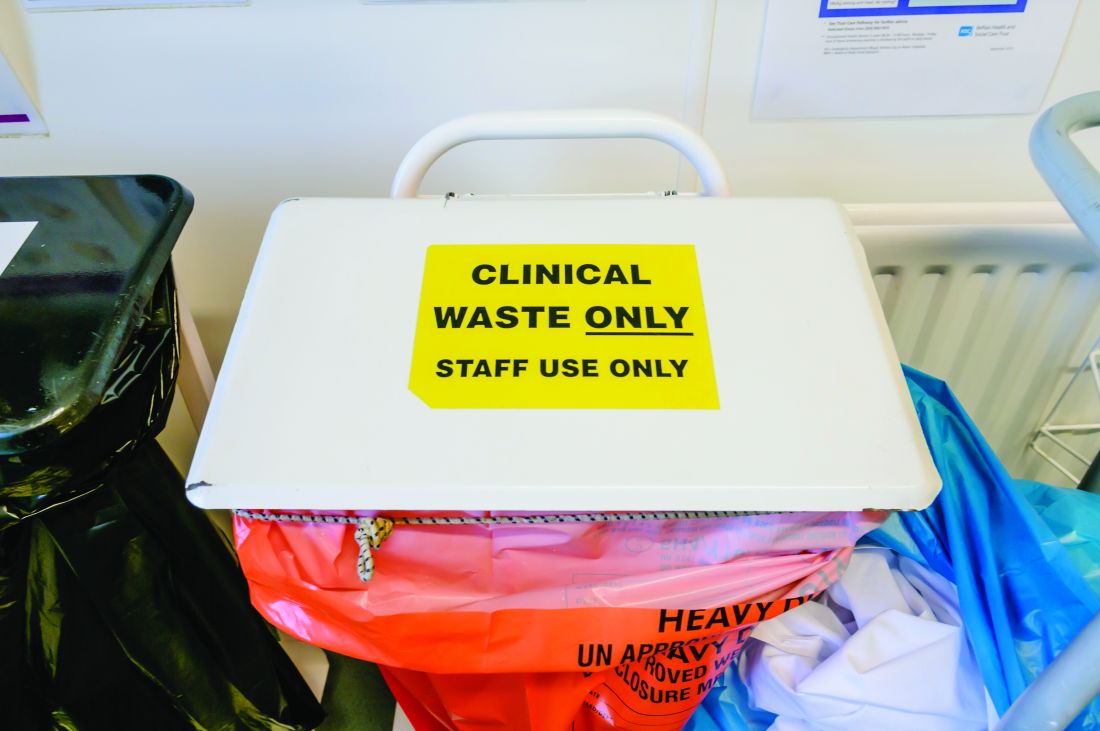
Moving recycling bins and providing education to staff led to a reduction in the carbon footprint at a Portuguese hospital’s endoscopy unit, according to a study published in Gut.
“Sustainable endoscopy regarding waste handling was achievable and sustained over time, did not compromise productivity, and may be cost-effective for stakeholders,” wrote João A Cunha Neves, MD, MMSc, of Algarve University Hospital Centre in Portimão, Portugal, and his colleagues.
Although other work has shown that several of the strategies for reducing endoscopic waste are ‘easy wins,’ the authors noted that “lack of awareness by most endoscopy staff regarding the expenses and correct categorisation of endoscopic waste is the primary barrier to recycling in many endoscopy units.”
The four-stage prospective study took place at the Portimão endoscopy unit of Algarve University Hospital Centre in Portugal. It began with a 4-week audit that involved weighing regulated medical waste (“material fully contaminated with blood or body fluids or containing infectious agents”) and landfill waste (nonrecyclable material that isn’t fully contaminated). The researchers excluded from the analysis all waste from sharps containers, pre- and postprocedure activities, and endoscope reprocessing.
The second stage was one week of medical, nursing, and auxiliary team education about handling waste, in part based on observations collected during the first stage. Each endoscopy generates an estimated 1.5 kg of plastic waste, but recycling bins often are not available for the 0.3 kg of waste that’s recyclable. During the second stage, recycling bins were placed in endoscopy rooms while regulated medical waste and landfill bins were moved elsewhere.
The final two stages involved weighing both types of waste 1 month after the training and then 4 months after the training. For their calculations, the researchers assumed that 1 kg of landfill waste equated to 1 kg of carbon dioxide and 1 kg of regulated medical waste equated to 3 kg of carbon dioxide.
At the third stage, mean total waste fell by 12.9%, albeit not statistically significantly (P = .16), while the 41.4% regulated medical waste reduction was significant (P = .01). Landfill waste had increased 12.3% and both paper (0 to 1.2 kg) and plastic (0 to 2.1 kg) recycling waste increased. Mean endoscopy load had not significantly changed (46.2 vs. 44.5). Overall carbon dioxide was reduced by 31.6%, from 109.7 kg of carbon dioxide to 74.9 kg (P = .018), equating to an annual decrease of 1,665.6 kg. At four months postintervention, these effects remained.
“In both assessment periods, total waste produced by diagnostic standard endoscopic procedures was similar, but both regulated medical waste and overall carbon footprint were reduced,” the authors reported.
In a four-question assessment of the intervention with staff, “the entire team agreed that the study did not interfere with the daily work routine and was helpful in raising awareness about waste sorting within the unit,” the authors reported. The staff “also acknowledged that recycling waste allowed for more sustainable activity within the endoscopy unit, and that the achievements of the study were to be maintained in the future.”
How feasible is change?
The authors noted that health care accounts for 4.4% of the world’s carbon footprint and that endoscopy is the third largest generator of hospital medical waste, primarily because of single-use consumables. However, 71% of that health care carbon footprint comes from supply chain issues, particularly transportation, John I. Allen, MD, MBA, a retired clinical professor of medicine at the University Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “Facility emissions add 17% and heating/cooling add 12%,” he said. “So, the actual footprint of endoscopy is quite small.”
Reducing single-use equipment and disposables by a third is a small overall impact considering the “labor-intensive education and monitoring system,” said Dr. Allen, who was not involved in the study. “That said, this paper and numerous others remind us of small steps that we can take – mostly to raise awareness about new technologies and more sustainable processes that are available or should be studied – to help transition us from the current [terrible] state to a more climate-friendly style of practice and life.”
One of the study’s limitations was the lack of a cost-benefit or impact analysis, according to Dr. Allen. Climate policies claiming to have local impact can be problematic when they “ignore both externalities and the actual wider impact on gas or temperature mitigation,” he added.
But he noted that “many health care systems are already implementing new ways of working with temperature- and carbon-mitigation in mind,” such as his own institution’s pledge to become carbon-neutral within a year. One step on that path has included transitioning more than 30% of their clinic visits to virtual visits, “thus saving [literally] millions of miles in travel and altering our parking construction plans,” Dr. Allen said.
“Reduction in climate impact will come from new ways to manufacture endoscopes, less reliance on single-use equipment, and increasing use of materials that encourage recycling,” Dr. Allen said. “In order to achieve meaningful climate impact, we need research into what current regulations and processes are necessary to protect patients and staff from infection transmission while creating an environmentally favorable workflow.”
Where does making a difference begin?
Another limitation was simply the small size of the department itself, which limits how much impact the intervention can have, but the study also showed the feasibility of getting buy-in from a department to make meaningful changes, according to Bishr Omary, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Rutgers University’s Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, N.J. He was not involved in the study.
“Culture is an important aspect of this, but that’s where education comes in,” Dr. Omary said in an interview. “Leadership has to try to encourage and incentivize different units, not just endoscopy, but other surgery, too. I think the most effective approach is going to be top-down, where hospitals and health systems buy into this.”
One challenge to that buy-in is that climate change has become political, said Linda Anh B. Nguyen, MD, clinical professor of medicine and vice chief of clinical operations in Stanford (Calif.) University’s division of gastroenterology and hepatology.
“There may be resistance to implementation by those who do not see the value of reducing waste,” Dr. Nguyen, who was not involved in this study, said in an interview. “Successful implementation requires a culture change and reducing the physical barriers to make waste reduction easier. Having an advocate for the program embedded within the endoscopy unit will help with implementation.”
One of the advantages of the intervention in this study, Dr. Nguyen said, was its relative ease of implementation.
“The next step would be identifying which of the items that go into landfill can be replaced with reusable products,” Dr. Nguyen added.
Dr. Omary pointed to Practice Greenhealth as an example of an organization working toward the goal of climate change mitigation through a wide range of initiatives, including ones he has written about. The responsibility for reducing carbon footprints should be shared among individuals, institutions, and systems, Dr. Omary said, adding that individuals’ travel, such as to medical meetings, is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
A forthcoming publication from the four major gastroenterology medical organizations will outline additional ways gastroenterology can address climate change mitigation, Dr. Omary noted.
Dr. Nguyen said that gastroenterologists, as well as the entire health care industry, have a responsibility to combat climate change through waste reduction and that it can be done without sacrificing individual patient safety.
“Climate change must be at the forefront of our priorities for present and future generations,” Dr. Nguyen said. “We need to leave this world better than when we entered.”
But much of that change must especially occur at levels far higher than individual physicians or institutions, Dr. Allen said.
“Major responsibility for altering gastroenterology practices in order to mitigate climate change must originate in regulatory agencies and the manufacturers of our equipment,” Dr. Allen said. “Regulations must be based on demonstrated positive impact that is cost-effective for practices and health care systems.”
The research did not use external funding, and the authors reported no financial disclosures or conflicts of interests. Dr. Allen has consulted for Topography Health, OSHI Health, and Lynxmd. Dr. Nguyen has consulted for Alnylam, Ardelyx, Eli Lilly, Evoke Pharma, Ironwood, Pendulum, Phathom, Neurogastx, Sanofi, and Takeda; has served on the advisory board of Gemelli Biotech; and has received grants from Bold Health and Vanda. Dr. Omary had no disclosures.
Moving recycling bins and providing education to staff led to a reduction in the carbon footprint at a Portuguese hospital’s endoscopy unit, according to a study published in Gut.
“Sustainable endoscopy regarding waste handling was achievable and sustained over time, did not compromise productivity, and may be cost-effective for stakeholders,” wrote João A Cunha Neves, MD, MMSc, of Algarve University Hospital Centre in Portimão, Portugal, and his colleagues.
Although other work has shown that several of the strategies for reducing endoscopic waste are ‘easy wins,’ the authors noted that “lack of awareness by most endoscopy staff regarding the expenses and correct categorisation of endoscopic waste is the primary barrier to recycling in many endoscopy units.”
The four-stage prospective study took place at the Portimão endoscopy unit of Algarve University Hospital Centre in Portugal. It began with a 4-week audit that involved weighing regulated medical waste (“material fully contaminated with blood or body fluids or containing infectious agents”) and landfill waste (nonrecyclable material that isn’t fully contaminated). The researchers excluded from the analysis all waste from sharps containers, pre- and postprocedure activities, and endoscope reprocessing.
The second stage was one week of medical, nursing, and auxiliary team education about handling waste, in part based on observations collected during the first stage. Each endoscopy generates an estimated 1.5 kg of plastic waste, but recycling bins often are not available for the 0.3 kg of waste that’s recyclable. During the second stage, recycling bins were placed in endoscopy rooms while regulated medical waste and landfill bins were moved elsewhere.
The final two stages involved weighing both types of waste 1 month after the training and then 4 months after the training. For their calculations, the researchers assumed that 1 kg of landfill waste equated to 1 kg of carbon dioxide and 1 kg of regulated medical waste equated to 3 kg of carbon dioxide.
At the third stage, mean total waste fell by 12.9%, albeit not statistically significantly (P = .16), while the 41.4% regulated medical waste reduction was significant (P = .01). Landfill waste had increased 12.3% and both paper (0 to 1.2 kg) and plastic (0 to 2.1 kg) recycling waste increased. Mean endoscopy load had not significantly changed (46.2 vs. 44.5). Overall carbon dioxide was reduced by 31.6%, from 109.7 kg of carbon dioxide to 74.9 kg (P = .018), equating to an annual decrease of 1,665.6 kg. At four months postintervention, these effects remained.
“In both assessment periods, total waste produced by diagnostic standard endoscopic procedures was similar, but both regulated medical waste and overall carbon footprint were reduced,” the authors reported.
In a four-question assessment of the intervention with staff, “the entire team agreed that the study did not interfere with the daily work routine and was helpful in raising awareness about waste sorting within the unit,” the authors reported. The staff “also acknowledged that recycling waste allowed for more sustainable activity within the endoscopy unit, and that the achievements of the study were to be maintained in the future.”
How feasible is change?
The authors noted that health care accounts for 4.4% of the world’s carbon footprint and that endoscopy is the third largest generator of hospital medical waste, primarily because of single-use consumables. However, 71% of that health care carbon footprint comes from supply chain issues, particularly transportation, John I. Allen, MD, MBA, a retired clinical professor of medicine at the University Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “Facility emissions add 17% and heating/cooling add 12%,” he said. “So, the actual footprint of endoscopy is quite small.”
Reducing single-use equipment and disposables by a third is a small overall impact considering the “labor-intensive education and monitoring system,” said Dr. Allen, who was not involved in the study. “That said, this paper and numerous others remind us of small steps that we can take – mostly to raise awareness about new technologies and more sustainable processes that are available or should be studied – to help transition us from the current [terrible] state to a more climate-friendly style of practice and life.”
One of the study’s limitations was the lack of a cost-benefit or impact analysis, according to Dr. Allen. Climate policies claiming to have local impact can be problematic when they “ignore both externalities and the actual wider impact on gas or temperature mitigation,” he added.
But he noted that “many health care systems are already implementing new ways of working with temperature- and carbon-mitigation in mind,” such as his own institution’s pledge to become carbon-neutral within a year. One step on that path has included transitioning more than 30% of their clinic visits to virtual visits, “thus saving [literally] millions of miles in travel and altering our parking construction plans,” Dr. Allen said.
“Reduction in climate impact will come from new ways to manufacture endoscopes, less reliance on single-use equipment, and increasing use of materials that encourage recycling,” Dr. Allen said. “In order to achieve meaningful climate impact, we need research into what current regulations and processes are necessary to protect patients and staff from infection transmission while creating an environmentally favorable workflow.”
Where does making a difference begin?
Another limitation was simply the small size of the department itself, which limits how much impact the intervention can have, but the study also showed the feasibility of getting buy-in from a department to make meaningful changes, according to Bishr Omary, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Rutgers University’s Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, N.J. He was not involved in the study.
“Culture is an important aspect of this, but that’s where education comes in,” Dr. Omary said in an interview. “Leadership has to try to encourage and incentivize different units, not just endoscopy, but other surgery, too. I think the most effective approach is going to be top-down, where hospitals and health systems buy into this.”
One challenge to that buy-in is that climate change has become political, said Linda Anh B. Nguyen, MD, clinical professor of medicine and vice chief of clinical operations in Stanford (Calif.) University’s division of gastroenterology and hepatology.
“There may be resistance to implementation by those who do not see the value of reducing waste,” Dr. Nguyen, who was not involved in this study, said in an interview. “Successful implementation requires a culture change and reducing the physical barriers to make waste reduction easier. Having an advocate for the program embedded within the endoscopy unit will help with implementation.”
One of the advantages of the intervention in this study, Dr. Nguyen said, was its relative ease of implementation.
“The next step would be identifying which of the items that go into landfill can be replaced with reusable products,” Dr. Nguyen added.
Dr. Omary pointed to Practice Greenhealth as an example of an organization working toward the goal of climate change mitigation through a wide range of initiatives, including ones he has written about. The responsibility for reducing carbon footprints should be shared among individuals, institutions, and systems, Dr. Omary said, adding that individuals’ travel, such as to medical meetings, is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
A forthcoming publication from the four major gastroenterology medical organizations will outline additional ways gastroenterology can address climate change mitigation, Dr. Omary noted.
Dr. Nguyen said that gastroenterologists, as well as the entire health care industry, have a responsibility to combat climate change through waste reduction and that it can be done without sacrificing individual patient safety.
“Climate change must be at the forefront of our priorities for present and future generations,” Dr. Nguyen said. “We need to leave this world better than when we entered.”
But much of that change must especially occur at levels far higher than individual physicians or institutions, Dr. Allen said.
“Major responsibility for altering gastroenterology practices in order to mitigate climate change must originate in regulatory agencies and the manufacturers of our equipment,” Dr. Allen said. “Regulations must be based on demonstrated positive impact that is cost-effective for practices and health care systems.”
The research did not use external funding, and the authors reported no financial disclosures or conflicts of interests. Dr. Allen has consulted for Topography Health, OSHI Health, and Lynxmd. Dr. Nguyen has consulted for Alnylam, Ardelyx, Eli Lilly, Evoke Pharma, Ironwood, Pendulum, Phathom, Neurogastx, Sanofi, and Takeda; has served on the advisory board of Gemelli Biotech; and has received grants from Bold Health and Vanda. Dr. Omary had no disclosures.
Moving recycling bins and providing education to staff led to a reduction in the carbon footprint at a Portuguese hospital’s endoscopy unit, according to a study published in Gut.
“Sustainable endoscopy regarding waste handling was achievable and sustained over time, did not compromise productivity, and may be cost-effective for stakeholders,” wrote João A Cunha Neves, MD, MMSc, of Algarve University Hospital Centre in Portimão, Portugal, and his colleagues.
Although other work has shown that several of the strategies for reducing endoscopic waste are ‘easy wins,’ the authors noted that “lack of awareness by most endoscopy staff regarding the expenses and correct categorisation of endoscopic waste is the primary barrier to recycling in many endoscopy units.”
The four-stage prospective study took place at the Portimão endoscopy unit of Algarve University Hospital Centre in Portugal. It began with a 4-week audit that involved weighing regulated medical waste (“material fully contaminated with blood or body fluids or containing infectious agents”) and landfill waste (nonrecyclable material that isn’t fully contaminated). The researchers excluded from the analysis all waste from sharps containers, pre- and postprocedure activities, and endoscope reprocessing.
The second stage was one week of medical, nursing, and auxiliary team education about handling waste, in part based on observations collected during the first stage. Each endoscopy generates an estimated 1.5 kg of plastic waste, but recycling bins often are not available for the 0.3 kg of waste that’s recyclable. During the second stage, recycling bins were placed in endoscopy rooms while regulated medical waste and landfill bins were moved elsewhere.
The final two stages involved weighing both types of waste 1 month after the training and then 4 months after the training. For their calculations, the researchers assumed that 1 kg of landfill waste equated to 1 kg of carbon dioxide and 1 kg of regulated medical waste equated to 3 kg of carbon dioxide.
At the third stage, mean total waste fell by 12.9%, albeit not statistically significantly (P = .16), while the 41.4% regulated medical waste reduction was significant (P = .01). Landfill waste had increased 12.3% and both paper (0 to 1.2 kg) and plastic (0 to 2.1 kg) recycling waste increased. Mean endoscopy load had not significantly changed (46.2 vs. 44.5). Overall carbon dioxide was reduced by 31.6%, from 109.7 kg of carbon dioxide to 74.9 kg (P = .018), equating to an annual decrease of 1,665.6 kg. At four months postintervention, these effects remained.
“In both assessment periods, total waste produced by diagnostic standard endoscopic procedures was similar, but both regulated medical waste and overall carbon footprint were reduced,” the authors reported.
In a four-question assessment of the intervention with staff, “the entire team agreed that the study did not interfere with the daily work routine and was helpful in raising awareness about waste sorting within the unit,” the authors reported. The staff “also acknowledged that recycling waste allowed for more sustainable activity within the endoscopy unit, and that the achievements of the study were to be maintained in the future.”
How feasible is change?
The authors noted that health care accounts for 4.4% of the world’s carbon footprint and that endoscopy is the third largest generator of hospital medical waste, primarily because of single-use consumables. However, 71% of that health care carbon footprint comes from supply chain issues, particularly transportation, John I. Allen, MD, MBA, a retired clinical professor of medicine at the University Michigan, Ann Arbor, said in an interview. “Facility emissions add 17% and heating/cooling add 12%,” he said. “So, the actual footprint of endoscopy is quite small.”
Reducing single-use equipment and disposables by a third is a small overall impact considering the “labor-intensive education and monitoring system,” said Dr. Allen, who was not involved in the study. “That said, this paper and numerous others remind us of small steps that we can take – mostly to raise awareness about new technologies and more sustainable processes that are available or should be studied – to help transition us from the current [terrible] state to a more climate-friendly style of practice and life.”
One of the study’s limitations was the lack of a cost-benefit or impact analysis, according to Dr. Allen. Climate policies claiming to have local impact can be problematic when they “ignore both externalities and the actual wider impact on gas or temperature mitigation,” he added.
But he noted that “many health care systems are already implementing new ways of working with temperature- and carbon-mitigation in mind,” such as his own institution’s pledge to become carbon-neutral within a year. One step on that path has included transitioning more than 30% of their clinic visits to virtual visits, “thus saving [literally] millions of miles in travel and altering our parking construction plans,” Dr. Allen said.
“Reduction in climate impact will come from new ways to manufacture endoscopes, less reliance on single-use equipment, and increasing use of materials that encourage recycling,” Dr. Allen said. “In order to achieve meaningful climate impact, we need research into what current regulations and processes are necessary to protect patients and staff from infection transmission while creating an environmentally favorable workflow.”
Where does making a difference begin?
Another limitation was simply the small size of the department itself, which limits how much impact the intervention can have, but the study also showed the feasibility of getting buy-in from a department to make meaningful changes, according to Bishr Omary, MD, PhD, professor of medicine at Rutgers University’s Robert Wood Johnson Medical School, Piscataway, N.J. He was not involved in the study.
“Culture is an important aspect of this, but that’s where education comes in,” Dr. Omary said in an interview. “Leadership has to try to encourage and incentivize different units, not just endoscopy, but other surgery, too. I think the most effective approach is going to be top-down, where hospitals and health systems buy into this.”
One challenge to that buy-in is that climate change has become political, said Linda Anh B. Nguyen, MD, clinical professor of medicine and vice chief of clinical operations in Stanford (Calif.) University’s division of gastroenterology and hepatology.
“There may be resistance to implementation by those who do not see the value of reducing waste,” Dr. Nguyen, who was not involved in this study, said in an interview. “Successful implementation requires a culture change and reducing the physical barriers to make waste reduction easier. Having an advocate for the program embedded within the endoscopy unit will help with implementation.”
One of the advantages of the intervention in this study, Dr. Nguyen said, was its relative ease of implementation.
“The next step would be identifying which of the items that go into landfill can be replaced with reusable products,” Dr. Nguyen added.
Dr. Omary pointed to Practice Greenhealth as an example of an organization working toward the goal of climate change mitigation through a wide range of initiatives, including ones he has written about. The responsibility for reducing carbon footprints should be shared among individuals, institutions, and systems, Dr. Omary said, adding that individuals’ travel, such as to medical meetings, is a major contributor to greenhouse gas emissions.
A forthcoming publication from the four major gastroenterology medical organizations will outline additional ways gastroenterology can address climate change mitigation, Dr. Omary noted.
Dr. Nguyen said that gastroenterologists, as well as the entire health care industry, have a responsibility to combat climate change through waste reduction and that it can be done without sacrificing individual patient safety.
“Climate change must be at the forefront of our priorities for present and future generations,” Dr. Nguyen said. “We need to leave this world better than when we entered.”
But much of that change must especially occur at levels far higher than individual physicians or institutions, Dr. Allen said.
“Major responsibility for altering gastroenterology practices in order to mitigate climate change must originate in regulatory agencies and the manufacturers of our equipment,” Dr. Allen said. “Regulations must be based on demonstrated positive impact that is cost-effective for practices and health care systems.”
The research did not use external funding, and the authors reported no financial disclosures or conflicts of interests. Dr. Allen has consulted for Topography Health, OSHI Health, and Lynxmd. Dr. Nguyen has consulted for Alnylam, Ardelyx, Eli Lilly, Evoke Pharma, Ironwood, Pendulum, Phathom, Neurogastx, Sanofi, and Takeda; has served on the advisory board of Gemelli Biotech; and has received grants from Bold Health and Vanda. Dr. Omary had no disclosures.
FROM GUT
EHR: A progress report
I wrote my first column on electronic health records in the mid-1990s. At the time, it seemed like an idea whose time had come. After all, in an era when just about every essential process in medicine had already been computerized, we physicians continued to process clinical data – our key asset – with pen and paper. Most of us were reluctant to make the switch, and for good reason:
Then, the government stepped in. Shortly after his inauguration in 2000, President George W. Bush outlined a plan to ensure that most Americans had electronic health records within 10 years. “By computerizing health records,” the president said, “we can avoid dangerous medical mistakes, reduce costs, and improve care.” The goal was to eliminate missing charts, duplication of lab testing, ineffective documentation, and inordinate amounts of time spent on paperwork, not to mention illegible handwriting, poor coordination of care between physicians, and many other problems. Studies were quoted, suggesting that EHR shortened inpatient stays, decreased risk of adverse drug interactions, improved the consistency and content of records, and improved continuity of care and follow-up.
The EHR Incentive Program (later renamed the Promoting Interoperability Program) was introduced to encourage physicians and hospitals “to adopt, implement, upgrade, and demonstrate meaningful use of certified electronic health record technology.”
Nearly a quarter-century later, implementation is well behind schedule. According to a 2019 federal study, while nearly all hospitals (96%) have adopted a certified EHR, only 72% of office-based physicians have done so.
There are multiple reasons for this. For one thing, EHR is still by and large slower than pen and paper, because direct data entry is still primarily done by keyboard. Voice recognition, hand-held and wireless devices have been developed, but most work only on specialized tasks. Even the best systems take more clinician time per encounter than the manual processes they replace.
Physicians have been slow to warm to a system that slows them down and forces them to change the way they think and work. In addition, paper systems never crash; the prospect of a server malfunction or Internet failure bringing an entire clinic to a grinding halt is not particularly inviting.
The special needs of dermatology – high patient volumes, multiple diagnoses and prescriptions per patient, the wide variety of procedures we perform, and digital image storage – present further hurdles.
Nevertheless, the march toward electronic record keeping continues, and I continue to receive many questions about choosing a good EHR system. As always, I cannot recommend any specific products since every office has unique needs and requirements.
The key phrase to keep in mind is caveat emptor. Several regulatory bodies exist to test vendor claims and certify system behaviors, but different agencies use different criteria that may or may not be relevant to your requirements. Vaporware is still as common as real software; beware the “feature in the next release” that might never appear, particularly if you need it right now.
Avoid the temptation to buy a flashy new system and then try to adapt it to your office; figure out your needs first, then find a system that meets them.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way around doing the work of comparing one system with another. The most important information a vendor can give you is the names and addresses of two or more offices where you can go watch their system in action. Site visits are time-consuming, but they are only way to pick the best EHR the first time around.
Don’t be the first office using a new system. Let the vendor work out the bugs somewhere else.
Above all, if you have disorganized paper records, don’t count on EHR to automatically solve your problems. Well-designed paper systems usually lend themselves to effective automation, but automating a poorly designed system just increases the chaos. If your paper system is in disarray, solve that problem before considering EHR.
With all of its problems and hurdles, EHRs will inevitably be a part of most of our lives. And for those who take the time to do it right, it will ultimately be an improvement.
Think of information technologies as power tools: They can help you to do things better, but they can also amplify your errors. So choose carefully.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
I wrote my first column on electronic health records in the mid-1990s. At the time, it seemed like an idea whose time had come. After all, in an era when just about every essential process in medicine had already been computerized, we physicians continued to process clinical data – our key asset – with pen and paper. Most of us were reluctant to make the switch, and for good reason:
Then, the government stepped in. Shortly after his inauguration in 2000, President George W. Bush outlined a plan to ensure that most Americans had electronic health records within 10 years. “By computerizing health records,” the president said, “we can avoid dangerous medical mistakes, reduce costs, and improve care.” The goal was to eliminate missing charts, duplication of lab testing, ineffective documentation, and inordinate amounts of time spent on paperwork, not to mention illegible handwriting, poor coordination of care between physicians, and many other problems. Studies were quoted, suggesting that EHR shortened inpatient stays, decreased risk of adverse drug interactions, improved the consistency and content of records, and improved continuity of care and follow-up.
The EHR Incentive Program (later renamed the Promoting Interoperability Program) was introduced to encourage physicians and hospitals “to adopt, implement, upgrade, and demonstrate meaningful use of certified electronic health record technology.”
Nearly a quarter-century later, implementation is well behind schedule. According to a 2019 federal study, while nearly all hospitals (96%) have adopted a certified EHR, only 72% of office-based physicians have done so.
There are multiple reasons for this. For one thing, EHR is still by and large slower than pen and paper, because direct data entry is still primarily done by keyboard. Voice recognition, hand-held and wireless devices have been developed, but most work only on specialized tasks. Even the best systems take more clinician time per encounter than the manual processes they replace.
Physicians have been slow to warm to a system that slows them down and forces them to change the way they think and work. In addition, paper systems never crash; the prospect of a server malfunction or Internet failure bringing an entire clinic to a grinding halt is not particularly inviting.
The special needs of dermatology – high patient volumes, multiple diagnoses and prescriptions per patient, the wide variety of procedures we perform, and digital image storage – present further hurdles.
Nevertheless, the march toward electronic record keeping continues, and I continue to receive many questions about choosing a good EHR system. As always, I cannot recommend any specific products since every office has unique needs and requirements.
The key phrase to keep in mind is caveat emptor. Several regulatory bodies exist to test vendor claims and certify system behaviors, but different agencies use different criteria that may or may not be relevant to your requirements. Vaporware is still as common as real software; beware the “feature in the next release” that might never appear, particularly if you need it right now.
Avoid the temptation to buy a flashy new system and then try to adapt it to your office; figure out your needs first, then find a system that meets them.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way around doing the work of comparing one system with another. The most important information a vendor can give you is the names and addresses of two or more offices where you can go watch their system in action. Site visits are time-consuming, but they are only way to pick the best EHR the first time around.
Don’t be the first office using a new system. Let the vendor work out the bugs somewhere else.
Above all, if you have disorganized paper records, don’t count on EHR to automatically solve your problems. Well-designed paper systems usually lend themselves to effective automation, but automating a poorly designed system just increases the chaos. If your paper system is in disarray, solve that problem before considering EHR.
With all of its problems and hurdles, EHRs will inevitably be a part of most of our lives. And for those who take the time to do it right, it will ultimately be an improvement.
Think of information technologies as power tools: They can help you to do things better, but they can also amplify your errors. So choose carefully.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
I wrote my first column on electronic health records in the mid-1990s. At the time, it seemed like an idea whose time had come. After all, in an era when just about every essential process in medicine had already been computerized, we physicians continued to process clinical data – our key asset – with pen and paper. Most of us were reluctant to make the switch, and for good reason:
Then, the government stepped in. Shortly after his inauguration in 2000, President George W. Bush outlined a plan to ensure that most Americans had electronic health records within 10 years. “By computerizing health records,” the president said, “we can avoid dangerous medical mistakes, reduce costs, and improve care.” The goal was to eliminate missing charts, duplication of lab testing, ineffective documentation, and inordinate amounts of time spent on paperwork, not to mention illegible handwriting, poor coordination of care between physicians, and many other problems. Studies were quoted, suggesting that EHR shortened inpatient stays, decreased risk of adverse drug interactions, improved the consistency and content of records, and improved continuity of care and follow-up.
The EHR Incentive Program (later renamed the Promoting Interoperability Program) was introduced to encourage physicians and hospitals “to adopt, implement, upgrade, and demonstrate meaningful use of certified electronic health record technology.”
Nearly a quarter-century later, implementation is well behind schedule. According to a 2019 federal study, while nearly all hospitals (96%) have adopted a certified EHR, only 72% of office-based physicians have done so.
There are multiple reasons for this. For one thing, EHR is still by and large slower than pen and paper, because direct data entry is still primarily done by keyboard. Voice recognition, hand-held and wireless devices have been developed, but most work only on specialized tasks. Even the best systems take more clinician time per encounter than the manual processes they replace.
Physicians have been slow to warm to a system that slows them down and forces them to change the way they think and work. In addition, paper systems never crash; the prospect of a server malfunction or Internet failure bringing an entire clinic to a grinding halt is not particularly inviting.
The special needs of dermatology – high patient volumes, multiple diagnoses and prescriptions per patient, the wide variety of procedures we perform, and digital image storage – present further hurdles.
Nevertheless, the march toward electronic record keeping continues, and I continue to receive many questions about choosing a good EHR system. As always, I cannot recommend any specific products since every office has unique needs and requirements.
The key phrase to keep in mind is caveat emptor. Several regulatory bodies exist to test vendor claims and certify system behaviors, but different agencies use different criteria that may or may not be relevant to your requirements. Vaporware is still as common as real software; beware the “feature in the next release” that might never appear, particularly if you need it right now.
Avoid the temptation to buy a flashy new system and then try to adapt it to your office; figure out your needs first, then find a system that meets them.
Unfortunately, there is no easy way around doing the work of comparing one system with another. The most important information a vendor can give you is the names and addresses of two or more offices where you can go watch their system in action. Site visits are time-consuming, but they are only way to pick the best EHR the first time around.
Don’t be the first office using a new system. Let the vendor work out the bugs somewhere else.
Above all, if you have disorganized paper records, don’t count on EHR to automatically solve your problems. Well-designed paper systems usually lend themselves to effective automation, but automating a poorly designed system just increases the chaos. If your paper system is in disarray, solve that problem before considering EHR.
With all of its problems and hurdles, EHRs will inevitably be a part of most of our lives. And for those who take the time to do it right, it will ultimately be an improvement.
Think of information technologies as power tools: They can help you to do things better, but they can also amplify your errors. So choose carefully.
Dr. Eastern practices dermatology and dermatologic surgery in Belleville, N.J. He is the author of numerous articles and textbook chapters, and is a longtime monthly columnist for Dermatology News. Write to him at [email protected].
At EASD, docs to eye new tactics for type 2 diabetes
Highlights of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes 2022 annual meeting include new data on weight loss with the blockbuster twincretin tirzepatide and on the effects of dapagliflozin on heart failure in people with diabetes, as well as updated guidelines for type 2 diabetes management.
The EASD meeting will take place Sept. 19-23 in Stockholm. It will be the first in-person meeting since 2019 but will also feature live-streamed content for participants around the world.
“The EASD congress will cover all the different areas and aspects of diabetes research – clinical, basic, epidemiologic, and psychological,” EASD President Stefano Del Prato, MD, told this news organization.
What attendees should expect, said Del Prato of the University of Pisa (Italy), “is the pleasure to be able to participate in person at a meeting and get useful information, not only in terms of the knowledge and intellectual aspects of diabetes, but also something that can be implemented the following day in their daily clinical activities.”
EASD Honorary Secretary Mikael Rydén, MD, added: “I think meeting attendees will really be able to get the absolutely latest developments in all the areas that are relevant to diabetes treatments. It’s the best way to keep yourself up to date.”
This year, in particular, there’s a focus on past, present, and future trends in type 2 diabetes management, along with the co-occurring conditions of obesity, heart failure, and metabolic fatty liver disease.
DELIVER: The diabetes side
On Sept. 22, new data will be presented from the DELIVER trial on the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, comparing data for participants with diabetes, prediabetes, and normoglycemia.
Primary results from DELIVER were presented Aug. 26 at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2022 in Barcelona and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The results showed that dapagliflozin benefits patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, as previously demonstrated in those with reduced ejection fraction in the DAPA-HF trial.
“This information is quite important and is becoming of major interest in the field of diabetes,” Dr. Del Prato said, adding that a related joint EASD/ESC symposium will take place the next morning, on Sept. 23, entitled, “New perspectives on heart function and failure in diabetes.”
“So, within the congress, you get the background, pathophysiology, the diagnostic aspects, and the results of the effect of dapagliflozin on those individuals.”
Dr. Rydén commented, “I think this underlines how important it is for diabetologists to screen our patients better for heart failure because we can actually treat them now.”
However, Dr. Rydén of the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also cautioned about use of SGLT2 inhibitors in people with diabetes who use insulin, given the risk of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. “These drugs have side effects and you have to be wary who you prescribe them to. For those on multiple daily [insulin] injections, the side effects probably outweigh the benefits.”
Tirzepatide, weight loss, and type 2 diabetes remission
On Sept. 21, a symposium will provide new data for the dual glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist tirzepatide, approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the United States in May with the brand name Mounjaro. The agent is now being studied as an obesity treatment.
Data from the SURMOUNT-1 trial presented at the ADA meeting in June showed the drug produced “unprecedented” weight loss of up to 22.5%.
At EASD, those findings will be reviewed and new data presented on morbidity and mortality, along with a new commentary. The degree of weight loss seen with this new twincretin has furthered discussion about the concept of remission in type 2 diabetes, Dr. Rydén noted. That will also be the subject of the Diabetologia symposium on Sept. 21, entitled, “Remission of type 2 diabetes – fact or fiction?”
Regarding tirzepatide, Dr. Rydén said: “It’s amazing, the most powerful antiobesity drug we have at our disposal. These drugs slow gastric emptying and have other beneficial effects. … We’re now closing in on drugs that produce more than 15% weight loss. That appears to be the ‘magic bullet’ where you can achieve type 2 diabetes remission.” He pointed to a symposium sponsored by The Lancet on this topic at last year’s EASD meeting.
“I think what we want with our drugs is not to treat but actually to combat type 2 diabetes and really to achieve remission. Of course, if you’ve had it for many decades that might be impossible, but we know that particularly in the first 5-10 years it’s very important to have good glucose control and we know we can also achieve remission.”
Dr. Del Prato noted the importance of weight reduction at the time of type 2 diabetes diagnosis will be emphasized in the ADA/EASD consensus document on the management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, to be presented in its final form on Sept. 23.
“I think we’ll be learning more about potential remission in the future, both because of metabolic surgery and agents like tirzepatide. The reduction in body weight that can be achieved [with these newer drugs], or that has been reported so far, is the closest to what can be obtained with metabolic surgery. I think there will be more and more information and a lot of discussion about this, and of course about the definition of remission and what to do after remission has occurred,” Dr. Del Prato said.
The revised ADA/EASD consensus document is expected to endorse weight loss as a “co-primary goal” of care for those without cardiorenal disease, along with early initiation of combination therapies – for example, taking two drugs immediately upon diagnosis, rather than just metformin – as opposed to the prior stepwise approach. The document will also cover use of newer glucose-lowering therapies, surgery, and behavioral interventions.
The key is a holistic approach, Dr. Del Prato said. “Of course, glucose control is important, but it’s not the only thing. The heterogeneity of the population with diabetes is also important. Some may already have microvascular complications, kidney dysfunction, are more or less obese, and older or younger. We need to keep these differences in mind to provide more and more individualized treatment.”
Related to that, he noted, will be a joint EASD/ADA symposium on Sept. 19, entitled, “Precision medicine in type 2 diabetes: How far can we get?”
COVID-19 and diabetes, UKPDS, type 1 diabetes, and much more
As always, there’s a whole lot more. On Sept. 21, there will be a symposium on COVID-19 and diabetes.
Another, on diabetes technology, has a somewhat cautionary theme: “A new hope (Star Wars) or strange new worlds (Star Trek): Submerging diabetes into emerging technologies.” One of the speakers will address the question: “Are we becoming robots? Automated insulin delivery (AID) systems for everyone with type 1 diabetes: Strengths and limitations.” And this year’s EASD/JDRF symposium topic will be prevention of type 1 diabetes.
Yet another symposium on Sept. 21 will present 44-year follow-up data from the landmark United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), including an economic analysis and a look at dementia outcomes. “It’s a historical thing. This big trial represents a gold mine of information,” Dr. Del Prato commented.
On Sept. 22, new data will be presented for the investigational once-weekly insulins during a symposium entitled, “Re-inventing the insulin experience: Exploring the prospects of once-weekly insulins.”
And lest anyone was thinking of leaving the conference early, there’s a full agenda on Sept. 23, including symposia on diabetic nephropathy, type 1 diabetes, diabetes in old age, dietary management, and the role of primary care, among others. There will also be 12 separate oral presentation sessions that day.
Overall, the meeting will reflect the multidisciplinary direction the field is headed, Dr. Rydén said.
“We’re still in an era of medicine where a lot of things happen every year. Now we have the next generation of drugs that are coming that combine many areas of treatment – obesity, cardiology, and nephrology. So, we’re integrating. The future is integrating the diabetes world with our friends in other areas of clinical medicine.”
Dr. Del Prato has reported being a consultant, advisory board member, and/or lecturer for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Abbott, and Applied Therapeutics. Dr. Rydén has reported receiving lecture fees from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and serving on advisory boards for MSD, Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Highlights of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes 2022 annual meeting include new data on weight loss with the blockbuster twincretin tirzepatide and on the effects of dapagliflozin on heart failure in people with diabetes, as well as updated guidelines for type 2 diabetes management.
The EASD meeting will take place Sept. 19-23 in Stockholm. It will be the first in-person meeting since 2019 but will also feature live-streamed content for participants around the world.
“The EASD congress will cover all the different areas and aspects of diabetes research – clinical, basic, epidemiologic, and psychological,” EASD President Stefano Del Prato, MD, told this news organization.
What attendees should expect, said Del Prato of the University of Pisa (Italy), “is the pleasure to be able to participate in person at a meeting and get useful information, not only in terms of the knowledge and intellectual aspects of diabetes, but also something that can be implemented the following day in their daily clinical activities.”
EASD Honorary Secretary Mikael Rydén, MD, added: “I think meeting attendees will really be able to get the absolutely latest developments in all the areas that are relevant to diabetes treatments. It’s the best way to keep yourself up to date.”
This year, in particular, there’s a focus on past, present, and future trends in type 2 diabetes management, along with the co-occurring conditions of obesity, heart failure, and metabolic fatty liver disease.
DELIVER: The diabetes side
On Sept. 22, new data will be presented from the DELIVER trial on the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, comparing data for participants with diabetes, prediabetes, and normoglycemia.
Primary results from DELIVER were presented Aug. 26 at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2022 in Barcelona and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The results showed that dapagliflozin benefits patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, as previously demonstrated in those with reduced ejection fraction in the DAPA-HF trial.
“This information is quite important and is becoming of major interest in the field of diabetes,” Dr. Del Prato said, adding that a related joint EASD/ESC symposium will take place the next morning, on Sept. 23, entitled, “New perspectives on heart function and failure in diabetes.”
“So, within the congress, you get the background, pathophysiology, the diagnostic aspects, and the results of the effect of dapagliflozin on those individuals.”
Dr. Rydén commented, “I think this underlines how important it is for diabetologists to screen our patients better for heart failure because we can actually treat them now.”
However, Dr. Rydén of the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also cautioned about use of SGLT2 inhibitors in people with diabetes who use insulin, given the risk of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. “These drugs have side effects and you have to be wary who you prescribe them to. For those on multiple daily [insulin] injections, the side effects probably outweigh the benefits.”
Tirzepatide, weight loss, and type 2 diabetes remission
On Sept. 21, a symposium will provide new data for the dual glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist tirzepatide, approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the United States in May with the brand name Mounjaro. The agent is now being studied as an obesity treatment.
Data from the SURMOUNT-1 trial presented at the ADA meeting in June showed the drug produced “unprecedented” weight loss of up to 22.5%.
At EASD, those findings will be reviewed and new data presented on morbidity and mortality, along with a new commentary. The degree of weight loss seen with this new twincretin has furthered discussion about the concept of remission in type 2 diabetes, Dr. Rydén noted. That will also be the subject of the Diabetologia symposium on Sept. 21, entitled, “Remission of type 2 diabetes – fact or fiction?”
Regarding tirzepatide, Dr. Rydén said: “It’s amazing, the most powerful antiobesity drug we have at our disposal. These drugs slow gastric emptying and have other beneficial effects. … We’re now closing in on drugs that produce more than 15% weight loss. That appears to be the ‘magic bullet’ where you can achieve type 2 diabetes remission.” He pointed to a symposium sponsored by The Lancet on this topic at last year’s EASD meeting.
“I think what we want with our drugs is not to treat but actually to combat type 2 diabetes and really to achieve remission. Of course, if you’ve had it for many decades that might be impossible, but we know that particularly in the first 5-10 years it’s very important to have good glucose control and we know we can also achieve remission.”
Dr. Del Prato noted the importance of weight reduction at the time of type 2 diabetes diagnosis will be emphasized in the ADA/EASD consensus document on the management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, to be presented in its final form on Sept. 23.
“I think we’ll be learning more about potential remission in the future, both because of metabolic surgery and agents like tirzepatide. The reduction in body weight that can be achieved [with these newer drugs], or that has been reported so far, is the closest to what can be obtained with metabolic surgery. I think there will be more and more information and a lot of discussion about this, and of course about the definition of remission and what to do after remission has occurred,” Dr. Del Prato said.
The revised ADA/EASD consensus document is expected to endorse weight loss as a “co-primary goal” of care for those without cardiorenal disease, along with early initiation of combination therapies – for example, taking two drugs immediately upon diagnosis, rather than just metformin – as opposed to the prior stepwise approach. The document will also cover use of newer glucose-lowering therapies, surgery, and behavioral interventions.
The key is a holistic approach, Dr. Del Prato said. “Of course, glucose control is important, but it’s not the only thing. The heterogeneity of the population with diabetes is also important. Some may already have microvascular complications, kidney dysfunction, are more or less obese, and older or younger. We need to keep these differences in mind to provide more and more individualized treatment.”
Related to that, he noted, will be a joint EASD/ADA symposium on Sept. 19, entitled, “Precision medicine in type 2 diabetes: How far can we get?”
COVID-19 and diabetes, UKPDS, type 1 diabetes, and much more
As always, there’s a whole lot more. On Sept. 21, there will be a symposium on COVID-19 and diabetes.
Another, on diabetes technology, has a somewhat cautionary theme: “A new hope (Star Wars) or strange new worlds (Star Trek): Submerging diabetes into emerging technologies.” One of the speakers will address the question: “Are we becoming robots? Automated insulin delivery (AID) systems for everyone with type 1 diabetes: Strengths and limitations.” And this year’s EASD/JDRF symposium topic will be prevention of type 1 diabetes.
Yet another symposium on Sept. 21 will present 44-year follow-up data from the landmark United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), including an economic analysis and a look at dementia outcomes. “It’s a historical thing. This big trial represents a gold mine of information,” Dr. Del Prato commented.
On Sept. 22, new data will be presented for the investigational once-weekly insulins during a symposium entitled, “Re-inventing the insulin experience: Exploring the prospects of once-weekly insulins.”
And lest anyone was thinking of leaving the conference early, there’s a full agenda on Sept. 23, including symposia on diabetic nephropathy, type 1 diabetes, diabetes in old age, dietary management, and the role of primary care, among others. There will also be 12 separate oral presentation sessions that day.
Overall, the meeting will reflect the multidisciplinary direction the field is headed, Dr. Rydén said.
“We’re still in an era of medicine where a lot of things happen every year. Now we have the next generation of drugs that are coming that combine many areas of treatment – obesity, cardiology, and nephrology. So, we’re integrating. The future is integrating the diabetes world with our friends in other areas of clinical medicine.”
Dr. Del Prato has reported being a consultant, advisory board member, and/or lecturer for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Abbott, and Applied Therapeutics. Dr. Rydén has reported receiving lecture fees from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and serving on advisory boards for MSD, Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Highlights of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes 2022 annual meeting include new data on weight loss with the blockbuster twincretin tirzepatide and on the effects of dapagliflozin on heart failure in people with diabetes, as well as updated guidelines for type 2 diabetes management.
The EASD meeting will take place Sept. 19-23 in Stockholm. It will be the first in-person meeting since 2019 but will also feature live-streamed content for participants around the world.
“The EASD congress will cover all the different areas and aspects of diabetes research – clinical, basic, epidemiologic, and psychological,” EASD President Stefano Del Prato, MD, told this news organization.
What attendees should expect, said Del Prato of the University of Pisa (Italy), “is the pleasure to be able to participate in person at a meeting and get useful information, not only in terms of the knowledge and intellectual aspects of diabetes, but also something that can be implemented the following day in their daily clinical activities.”
EASD Honorary Secretary Mikael Rydén, MD, added: “I think meeting attendees will really be able to get the absolutely latest developments in all the areas that are relevant to diabetes treatments. It’s the best way to keep yourself up to date.”
This year, in particular, there’s a focus on past, present, and future trends in type 2 diabetes management, along with the co-occurring conditions of obesity, heart failure, and metabolic fatty liver disease.
DELIVER: The diabetes side
On Sept. 22, new data will be presented from the DELIVER trial on the sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, comparing data for participants with diabetes, prediabetes, and normoglycemia.
Primary results from DELIVER were presented Aug. 26 at the European Society of Cardiology Congress 2022 in Barcelona and simultaneously published in the New England Journal of Medicine. The results showed that dapagliflozin benefits patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction, as previously demonstrated in those with reduced ejection fraction in the DAPA-HF trial.
“This information is quite important and is becoming of major interest in the field of diabetes,” Dr. Del Prato said, adding that a related joint EASD/ESC symposium will take place the next morning, on Sept. 23, entitled, “New perspectives on heart function and failure in diabetes.”
“So, within the congress, you get the background, pathophysiology, the diagnostic aspects, and the results of the effect of dapagliflozin on those individuals.”
Dr. Rydén commented, “I think this underlines how important it is for diabetologists to screen our patients better for heart failure because we can actually treat them now.”
However, Dr. Rydén of the Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, also cautioned about use of SGLT2 inhibitors in people with diabetes who use insulin, given the risk of euglycemic diabetic ketoacidosis. “These drugs have side effects and you have to be wary who you prescribe them to. For those on multiple daily [insulin] injections, the side effects probably outweigh the benefits.”
Tirzepatide, weight loss, and type 2 diabetes remission
On Sept. 21, a symposium will provide new data for the dual glucagonlike peptide-1 (GLP-1) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) agonist tirzepatide, approved for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in the United States in May with the brand name Mounjaro. The agent is now being studied as an obesity treatment.
Data from the SURMOUNT-1 trial presented at the ADA meeting in June showed the drug produced “unprecedented” weight loss of up to 22.5%.
At EASD, those findings will be reviewed and new data presented on morbidity and mortality, along with a new commentary. The degree of weight loss seen with this new twincretin has furthered discussion about the concept of remission in type 2 diabetes, Dr. Rydén noted. That will also be the subject of the Diabetologia symposium on Sept. 21, entitled, “Remission of type 2 diabetes – fact or fiction?”
Regarding tirzepatide, Dr. Rydén said: “It’s amazing, the most powerful antiobesity drug we have at our disposal. These drugs slow gastric emptying and have other beneficial effects. … We’re now closing in on drugs that produce more than 15% weight loss. That appears to be the ‘magic bullet’ where you can achieve type 2 diabetes remission.” He pointed to a symposium sponsored by The Lancet on this topic at last year’s EASD meeting.
“I think what we want with our drugs is not to treat but actually to combat type 2 diabetes and really to achieve remission. Of course, if you’ve had it for many decades that might be impossible, but we know that particularly in the first 5-10 years it’s very important to have good glucose control and we know we can also achieve remission.”
Dr. Del Prato noted the importance of weight reduction at the time of type 2 diabetes diagnosis will be emphasized in the ADA/EASD consensus document on the management of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes, to be presented in its final form on Sept. 23.
“I think we’ll be learning more about potential remission in the future, both because of metabolic surgery and agents like tirzepatide. The reduction in body weight that can be achieved [with these newer drugs], or that has been reported so far, is the closest to what can be obtained with metabolic surgery. I think there will be more and more information and a lot of discussion about this, and of course about the definition of remission and what to do after remission has occurred,” Dr. Del Prato said.
The revised ADA/EASD consensus document is expected to endorse weight loss as a “co-primary goal” of care for those without cardiorenal disease, along with early initiation of combination therapies – for example, taking two drugs immediately upon diagnosis, rather than just metformin – as opposed to the prior stepwise approach. The document will also cover use of newer glucose-lowering therapies, surgery, and behavioral interventions.
The key is a holistic approach, Dr. Del Prato said. “Of course, glucose control is important, but it’s not the only thing. The heterogeneity of the population with diabetes is also important. Some may already have microvascular complications, kidney dysfunction, are more or less obese, and older or younger. We need to keep these differences in mind to provide more and more individualized treatment.”
Related to that, he noted, will be a joint EASD/ADA symposium on Sept. 19, entitled, “Precision medicine in type 2 diabetes: How far can we get?”
COVID-19 and diabetes, UKPDS, type 1 diabetes, and much more
As always, there’s a whole lot more. On Sept. 21, there will be a symposium on COVID-19 and diabetes.
Another, on diabetes technology, has a somewhat cautionary theme: “A new hope (Star Wars) or strange new worlds (Star Trek): Submerging diabetes into emerging technologies.” One of the speakers will address the question: “Are we becoming robots? Automated insulin delivery (AID) systems for everyone with type 1 diabetes: Strengths and limitations.” And this year’s EASD/JDRF symposium topic will be prevention of type 1 diabetes.
Yet another symposium on Sept. 21 will present 44-year follow-up data from the landmark United Kingdom Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS), including an economic analysis and a look at dementia outcomes. “It’s a historical thing. This big trial represents a gold mine of information,” Dr. Del Prato commented.
On Sept. 22, new data will be presented for the investigational once-weekly insulins during a symposium entitled, “Re-inventing the insulin experience: Exploring the prospects of once-weekly insulins.”
And lest anyone was thinking of leaving the conference early, there’s a full agenda on Sept. 23, including symposia on diabetic nephropathy, type 1 diabetes, diabetes in old age, dietary management, and the role of primary care, among others. There will also be 12 separate oral presentation sessions that day.
Overall, the meeting will reflect the multidisciplinary direction the field is headed, Dr. Rydén said.
“We’re still in an era of medicine where a lot of things happen every year. Now we have the next generation of drugs that are coming that combine many areas of treatment – obesity, cardiology, and nephrology. So, we’re integrating. The future is integrating the diabetes world with our friends in other areas of clinical medicine.”
Dr. Del Prato has reported being a consultant, advisory board member, and/or lecturer for AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Takeda, Eli Lilly, Abbott, and Applied Therapeutics. Dr. Rydén has reported receiving lecture fees from the Novo Nordisk Foundation and serving on advisory boards for MSD, Lilly, Boehringer Ingelheim, and AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 linked to increased Alzheimer’s risk
The study of more than 6 million people aged 65 years or older found a 50%-80% increased risk for AD in the year after COVID-19; the risk was especially high for women older than 85 years.
However, the investigators were quick to point out that the observational retrospective study offers no evidence that COVID-19 causes AD. There could be a viral etiology at play, or the connection could be related to inflammation in neural tissue from the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Or it could simply be that exposure to the health care system for COVID-19 increased the odds of detection of existing undiagnosed AD cases.
Whatever the case, these findings point to a potential spike in AD cases, which is a cause for concern, study investigator Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, a professor in the Center for Community Health Integration at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“COVID may be giving us a legacy of ongoing medical difficulties,” Dr. Davis said. “We were already concerned about having a very large care burden and cost burden from Alzheimer’s disease. If this is another burden that’s increased by COVID, this is something we’re really going to have to prepare for.”
The findings were published online in Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Increased risk
Earlier research points to a potential link between COVID-19 and increased risk for AD and Parkinson’s disease.
For the current study, researchers analyzed anonymous electronic health records of 6.2 million adults aged 65 years or older who received medical treatment between February 2020 and May 2021 and had no prior diagnosis of AD. The database includes information on almost 30% of the entire U.S. population.
Overall, there were 410,748 cases of COVID-19 during the study period.
The overall risk for new diagnosis of AD in the COVID-19 cohort was close to double that of those who did not have COVID-19 (0.68% vs. 0.35%, respectively).
After propensity-score matching, those who have had COVID-19 had a significantly higher risk for an AD diagnosis compared with those who were not infected (hazard ratio [HR], 1.69; 95% confidence interval [CI],1.53-1.72).
Risk for AD was elevated in all age groups, regardless of gender or ethnicity. Researchers did not collect data on COVID-19 severity, and the medical codes for long COVID were not published until after the study had ended.
Those with the highest risk were individuals older than 85 years (HR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.73-2.07) and women (HR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.69-1.97).
“We expected to see some impact, but I was surprised that it was as potent as it was,” Dr. Davis said.
Association, not causation
Heather Snyder, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and scientific relations, who commented on the findings for this article, called the study interesting but emphasized caution in interpreting the results.
“Because this study only showed an association through medical records, we cannot know what the underlying mechanisms driving this association are without more research,” Dr. Snyder said. “If you have had COVID-19, it doesn’t mean you’re going to get dementia. But if you have had COVID-19 and are experiencing long-term symptoms including cognitive difficulties, talk to your doctor.”
Dr. Davis agreed, noting that this type of study offers information on association, but not causation. “I do think that this makes it imperative that we continue to follow the population for what’s going on in various neurodegenerative diseases,” Dr. Davis said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Synder reports no relevant financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study of more than 6 million people aged 65 years or older found a 50%-80% increased risk for AD in the year after COVID-19; the risk was especially high for women older than 85 years.
However, the investigators were quick to point out that the observational retrospective study offers no evidence that COVID-19 causes AD. There could be a viral etiology at play, or the connection could be related to inflammation in neural tissue from the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Or it could simply be that exposure to the health care system for COVID-19 increased the odds of detection of existing undiagnosed AD cases.
Whatever the case, these findings point to a potential spike in AD cases, which is a cause for concern, study investigator Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, a professor in the Center for Community Health Integration at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“COVID may be giving us a legacy of ongoing medical difficulties,” Dr. Davis said. “We were already concerned about having a very large care burden and cost burden from Alzheimer’s disease. If this is another burden that’s increased by COVID, this is something we’re really going to have to prepare for.”
The findings were published online in Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Increased risk
Earlier research points to a potential link between COVID-19 and increased risk for AD and Parkinson’s disease.
For the current study, researchers analyzed anonymous electronic health records of 6.2 million adults aged 65 years or older who received medical treatment between February 2020 and May 2021 and had no prior diagnosis of AD. The database includes information on almost 30% of the entire U.S. population.
Overall, there were 410,748 cases of COVID-19 during the study period.
The overall risk for new diagnosis of AD in the COVID-19 cohort was close to double that of those who did not have COVID-19 (0.68% vs. 0.35%, respectively).
After propensity-score matching, those who have had COVID-19 had a significantly higher risk for an AD diagnosis compared with those who were not infected (hazard ratio [HR], 1.69; 95% confidence interval [CI],1.53-1.72).
Risk for AD was elevated in all age groups, regardless of gender or ethnicity. Researchers did not collect data on COVID-19 severity, and the medical codes for long COVID were not published until after the study had ended.
Those with the highest risk were individuals older than 85 years (HR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.73-2.07) and women (HR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.69-1.97).
“We expected to see some impact, but I was surprised that it was as potent as it was,” Dr. Davis said.
Association, not causation
Heather Snyder, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and scientific relations, who commented on the findings for this article, called the study interesting but emphasized caution in interpreting the results.
“Because this study only showed an association through medical records, we cannot know what the underlying mechanisms driving this association are without more research,” Dr. Snyder said. “If you have had COVID-19, it doesn’t mean you’re going to get dementia. But if you have had COVID-19 and are experiencing long-term symptoms including cognitive difficulties, talk to your doctor.”
Dr. Davis agreed, noting that this type of study offers information on association, but not causation. “I do think that this makes it imperative that we continue to follow the population for what’s going on in various neurodegenerative diseases,” Dr. Davis said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Synder reports no relevant financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The study of more than 6 million people aged 65 years or older found a 50%-80% increased risk for AD in the year after COVID-19; the risk was especially high for women older than 85 years.
However, the investigators were quick to point out that the observational retrospective study offers no evidence that COVID-19 causes AD. There could be a viral etiology at play, or the connection could be related to inflammation in neural tissue from the SARS-CoV-2 infection. Or it could simply be that exposure to the health care system for COVID-19 increased the odds of detection of existing undiagnosed AD cases.
Whatever the case, these findings point to a potential spike in AD cases, which is a cause for concern, study investigator Pamela Davis, MD, PhD, a professor in the Center for Community Health Integration at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview.
“COVID may be giving us a legacy of ongoing medical difficulties,” Dr. Davis said. “We were already concerned about having a very large care burden and cost burden from Alzheimer’s disease. If this is another burden that’s increased by COVID, this is something we’re really going to have to prepare for.”
The findings were published online in Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease.
Increased risk
Earlier research points to a potential link between COVID-19 and increased risk for AD and Parkinson’s disease.
For the current study, researchers analyzed anonymous electronic health records of 6.2 million adults aged 65 years or older who received medical treatment between February 2020 and May 2021 and had no prior diagnosis of AD. The database includes information on almost 30% of the entire U.S. population.
Overall, there were 410,748 cases of COVID-19 during the study period.
The overall risk for new diagnosis of AD in the COVID-19 cohort was close to double that of those who did not have COVID-19 (0.68% vs. 0.35%, respectively).
After propensity-score matching, those who have had COVID-19 had a significantly higher risk for an AD diagnosis compared with those who were not infected (hazard ratio [HR], 1.69; 95% confidence interval [CI],1.53-1.72).
Risk for AD was elevated in all age groups, regardless of gender or ethnicity. Researchers did not collect data on COVID-19 severity, and the medical codes for long COVID were not published until after the study had ended.
Those with the highest risk were individuals older than 85 years (HR, 1.89; 95% CI, 1.73-2.07) and women (HR, 1.82; 95% CI, 1.69-1.97).
“We expected to see some impact, but I was surprised that it was as potent as it was,” Dr. Davis said.
Association, not causation
Heather Snyder, PhD, Alzheimer’s Association vice president of medical and scientific relations, who commented on the findings for this article, called the study interesting but emphasized caution in interpreting the results.
“Because this study only showed an association through medical records, we cannot know what the underlying mechanisms driving this association are without more research,” Dr. Snyder said. “If you have had COVID-19, it doesn’t mean you’re going to get dementia. But if you have had COVID-19 and are experiencing long-term symptoms including cognitive difficulties, talk to your doctor.”
Dr. Davis agreed, noting that this type of study offers information on association, but not causation. “I do think that this makes it imperative that we continue to follow the population for what’s going on in various neurodegenerative diseases,” Dr. Davis said.
The study was funded by the National Institute of Aging, National Institute on Alcohol Abuse and Alcoholism, the Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, and the National Cancer Institute. Dr. Synder reports no relevant financial conflicts.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF ALZHEIMER’S DISEASE
Anesthesiologist arrested, implicated in death of colleague
at Baylor Scott & White Surgicare, a North Dallas surgical center. Raynaldo Rivera Ortiz Jr., MD, 59, is accused of injecting nerve-blocking and bronchodilating drugs into patient IV bags, resulting in at least one death and multiple cardiac emergencies.
In June, an anesthesiologist identified by Dallas ABC affiliate WFAA as Melanie Kaspar, MD, a colleague of Dr. Ortiz’s at the outpatient center, was ill and treated herself for dehydration using an IV bag of saline she had taken home from work. She died immediately after injecting the contents of the bag. According to the autopsy report, she died from a lethal dose of bupivacaine, a nerve-blocking agent often used during the administration of anesthesia. According to WFAA, Dr. Kaspar’s death was initially ruled accidental, but the Dallas County Medical Examiner has since reopened the case.
Then in August, an 18-year-old male patient, identified in court documents as J.A., experienced a cardiac emergency during a scheduled surgery at the clinic. The teen, who according to local press coverage was undergoing nose surgery after a dirt bike accident, was transferred to a local ICU. A chemical analysis of the fluid from the saline bag that was used during his surgery found epinephrine (a stimulant that could have caused his symptoms), bupivacaine, and lidocaine.
According to court documents, an investigation by the surgical center identified about 10 additional unexpected cardiac emergencies that occurred during what should have been unremarkable surgeries, an exceptionally high rate of complications, suggesting a pattern of intentional adulteration of IV bags. These surgeries were performed between May and August.
In addition, the complaint alleges that none of the cardiac incidents occurred during Dr. Ortiz’s surgeries; however, all of the incidents occurred around the time Dr. Ortiz performed services at the facility, and no incidents occurred while he was on vacation. The incidents began 2 days after Dr. Ortiz had been notified that he was the subject of a disciplinary inquiry stemming from an incident in which he allegedly “deviated from the standard of care” during an anesthesia procedure when a patient experienced a medical emergency, according to federal officials.
The complaint also alleges that Dr. Ortiz had a history of disciplinary actions against him, including at the facility, and he complained that the center was trying to “crucify” him.
Surveillance video from the hallway of the center’s operating room shows Dr. Ortiz placing IV bags in the stainless-steel bag warmer shortly before other doctors’ patients experienced cardiac emergencies, according to the complaint. In the description of one instance captured on video, Dr. Ortiz was observed walking quickly from an operating room to the bag warmer, placing a single IV bag inside, visually scanning the empty hallway, and quickly walking away. Just over an hour later, according to the complaint, a 56-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
The complaint alleges that in another instance, Dr. Ortiz was observed exiting his operating room carrying an IV bag concealed in what appeared to be a paper folder, swapping the bag with another bag from the warmer, and walking away. Roughly 30 minutes later, a 54-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
“Our complaint alleges this defendant surreptitiously injected heart-stopping drugs into patient IV bags, decimating the Hippocratic Oath,” said Chad E. Meacham, U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Texas. “A single incident of seemingly intentional patient harm would be disconcerting; multiple incidents are truly disturbing. At this point, however, we believe that the problem is limited to one individual, who is currently behind bars. We will work tirelessly to hold him accountable.”
Dr. Ortiz is charged with tampering with a consumer product and with intentionally adulterating drugs. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of life in prison. Dr. Ortiz will make his initial appearance before U.S. Magistrate Judge Renee Toliver in Dallas Sept. 16.
On Sept. 9, the Texas Medical Board suspended Dr. Ortiz’s license in connection with this investigation, noting that the panel found “an imminent peril to the public health, safety, or welfare” and that Dr. Ortiz’s “continuation in the practice of medicine poses a continuing threat to public welfare.”
“It is astounding, stunning [for the victims] to think that anyone did this intentionally,” said Bruce W. Steckler, an attorney for some of the victims, in an interview with WFAA.
Baylor Scott & White Health, which operates the surgical center, said in a statement that the North Dallas facility will remain closed as the investigation continues.
“We actively assisted authorities in their investigation and will continue to do so. We also remain focused on communicating with patients,” the health system said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
at Baylor Scott & White Surgicare, a North Dallas surgical center. Raynaldo Rivera Ortiz Jr., MD, 59, is accused of injecting nerve-blocking and bronchodilating drugs into patient IV bags, resulting in at least one death and multiple cardiac emergencies.
In June, an anesthesiologist identified by Dallas ABC affiliate WFAA as Melanie Kaspar, MD, a colleague of Dr. Ortiz’s at the outpatient center, was ill and treated herself for dehydration using an IV bag of saline she had taken home from work. She died immediately after injecting the contents of the bag. According to the autopsy report, she died from a lethal dose of bupivacaine, a nerve-blocking agent often used during the administration of anesthesia. According to WFAA, Dr. Kaspar’s death was initially ruled accidental, but the Dallas County Medical Examiner has since reopened the case.
Then in August, an 18-year-old male patient, identified in court documents as J.A., experienced a cardiac emergency during a scheduled surgery at the clinic. The teen, who according to local press coverage was undergoing nose surgery after a dirt bike accident, was transferred to a local ICU. A chemical analysis of the fluid from the saline bag that was used during his surgery found epinephrine (a stimulant that could have caused his symptoms), bupivacaine, and lidocaine.
According to court documents, an investigation by the surgical center identified about 10 additional unexpected cardiac emergencies that occurred during what should have been unremarkable surgeries, an exceptionally high rate of complications, suggesting a pattern of intentional adulteration of IV bags. These surgeries were performed between May and August.
In addition, the complaint alleges that none of the cardiac incidents occurred during Dr. Ortiz’s surgeries; however, all of the incidents occurred around the time Dr. Ortiz performed services at the facility, and no incidents occurred while he was on vacation. The incidents began 2 days after Dr. Ortiz had been notified that he was the subject of a disciplinary inquiry stemming from an incident in which he allegedly “deviated from the standard of care” during an anesthesia procedure when a patient experienced a medical emergency, according to federal officials.
The complaint also alleges that Dr. Ortiz had a history of disciplinary actions against him, including at the facility, and he complained that the center was trying to “crucify” him.
Surveillance video from the hallway of the center’s operating room shows Dr. Ortiz placing IV bags in the stainless-steel bag warmer shortly before other doctors’ patients experienced cardiac emergencies, according to the complaint. In the description of one instance captured on video, Dr. Ortiz was observed walking quickly from an operating room to the bag warmer, placing a single IV bag inside, visually scanning the empty hallway, and quickly walking away. Just over an hour later, according to the complaint, a 56-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
The complaint alleges that in another instance, Dr. Ortiz was observed exiting his operating room carrying an IV bag concealed in what appeared to be a paper folder, swapping the bag with another bag from the warmer, and walking away. Roughly 30 minutes later, a 54-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
“Our complaint alleges this defendant surreptitiously injected heart-stopping drugs into patient IV bags, decimating the Hippocratic Oath,” said Chad E. Meacham, U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Texas. “A single incident of seemingly intentional patient harm would be disconcerting; multiple incidents are truly disturbing. At this point, however, we believe that the problem is limited to one individual, who is currently behind bars. We will work tirelessly to hold him accountable.”
Dr. Ortiz is charged with tampering with a consumer product and with intentionally adulterating drugs. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of life in prison. Dr. Ortiz will make his initial appearance before U.S. Magistrate Judge Renee Toliver in Dallas Sept. 16.
On Sept. 9, the Texas Medical Board suspended Dr. Ortiz’s license in connection with this investigation, noting that the panel found “an imminent peril to the public health, safety, or welfare” and that Dr. Ortiz’s “continuation in the practice of medicine poses a continuing threat to public welfare.”
“It is astounding, stunning [for the victims] to think that anyone did this intentionally,” said Bruce W. Steckler, an attorney for some of the victims, in an interview with WFAA.
Baylor Scott & White Health, which operates the surgical center, said in a statement that the North Dallas facility will remain closed as the investigation continues.
“We actively assisted authorities in their investigation and will continue to do so. We also remain focused on communicating with patients,” the health system said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
at Baylor Scott & White Surgicare, a North Dallas surgical center. Raynaldo Rivera Ortiz Jr., MD, 59, is accused of injecting nerve-blocking and bronchodilating drugs into patient IV bags, resulting in at least one death and multiple cardiac emergencies.
In June, an anesthesiologist identified by Dallas ABC affiliate WFAA as Melanie Kaspar, MD, a colleague of Dr. Ortiz’s at the outpatient center, was ill and treated herself for dehydration using an IV bag of saline she had taken home from work. She died immediately after injecting the contents of the bag. According to the autopsy report, she died from a lethal dose of bupivacaine, a nerve-blocking agent often used during the administration of anesthesia. According to WFAA, Dr. Kaspar’s death was initially ruled accidental, but the Dallas County Medical Examiner has since reopened the case.
Then in August, an 18-year-old male patient, identified in court documents as J.A., experienced a cardiac emergency during a scheduled surgery at the clinic. The teen, who according to local press coverage was undergoing nose surgery after a dirt bike accident, was transferred to a local ICU. A chemical analysis of the fluid from the saline bag that was used during his surgery found epinephrine (a stimulant that could have caused his symptoms), bupivacaine, and lidocaine.
According to court documents, an investigation by the surgical center identified about 10 additional unexpected cardiac emergencies that occurred during what should have been unremarkable surgeries, an exceptionally high rate of complications, suggesting a pattern of intentional adulteration of IV bags. These surgeries were performed between May and August.
In addition, the complaint alleges that none of the cardiac incidents occurred during Dr. Ortiz’s surgeries; however, all of the incidents occurred around the time Dr. Ortiz performed services at the facility, and no incidents occurred while he was on vacation. The incidents began 2 days after Dr. Ortiz had been notified that he was the subject of a disciplinary inquiry stemming from an incident in which he allegedly “deviated from the standard of care” during an anesthesia procedure when a patient experienced a medical emergency, according to federal officials.
The complaint also alleges that Dr. Ortiz had a history of disciplinary actions against him, including at the facility, and he complained that the center was trying to “crucify” him.
Surveillance video from the hallway of the center’s operating room shows Dr. Ortiz placing IV bags in the stainless-steel bag warmer shortly before other doctors’ patients experienced cardiac emergencies, according to the complaint. In the description of one instance captured on video, Dr. Ortiz was observed walking quickly from an operating room to the bag warmer, placing a single IV bag inside, visually scanning the empty hallway, and quickly walking away. Just over an hour later, according to the complaint, a 56-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
The complaint alleges that in another instance, Dr. Ortiz was observed exiting his operating room carrying an IV bag concealed in what appeared to be a paper folder, swapping the bag with another bag from the warmer, and walking away. Roughly 30 minutes later, a 54-year-old woman suffered a cardiac emergency during a scheduled cosmetic surgery after a bag from the warmer was used during her procedure.
“Our complaint alleges this defendant surreptitiously injected heart-stopping drugs into patient IV bags, decimating the Hippocratic Oath,” said Chad E. Meacham, U.S. Attorney for the Northern District of Texas. “A single incident of seemingly intentional patient harm would be disconcerting; multiple incidents are truly disturbing. At this point, however, we believe that the problem is limited to one individual, who is currently behind bars. We will work tirelessly to hold him accountable.”
Dr. Ortiz is charged with tampering with a consumer product and with intentionally adulterating drugs. If convicted, he faces a maximum penalty of life in prison. Dr. Ortiz will make his initial appearance before U.S. Magistrate Judge Renee Toliver in Dallas Sept. 16.
On Sept. 9, the Texas Medical Board suspended Dr. Ortiz’s license in connection with this investigation, noting that the panel found “an imminent peril to the public health, safety, or welfare” and that Dr. Ortiz’s “continuation in the practice of medicine poses a continuing threat to public welfare.”
“It is astounding, stunning [for the victims] to think that anyone did this intentionally,” said Bruce W. Steckler, an attorney for some of the victims, in an interview with WFAA.
Baylor Scott & White Health, which operates the surgical center, said in a statement that the North Dallas facility will remain closed as the investigation continues.
“We actively assisted authorities in their investigation and will continue to do so. We also remain focused on communicating with patients,” the health system said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Quiet quitting: Are physicians dying inside bit by bit? Or setting healthy boundaries?
In the past few months, “quiet quitting” has garnered increasing traction across social media platforms. My morning review of social media revealed thousands of posts ranging from “Why doing less at work could be good for you – and your employer” to “After ‘quiet quitting’ here comes ‘quiet firing.’ ”
But quiet quitting is neither quiet nor quitting.
Quiet quitting is a misnomer. In addition, quiet quitters are firmer with their boundaries, do not take on work above and beyond clearly stated expectations, do not respond after hours, and do not feel like they are “not doing their job” when they are not immediately available.
Individuals who “quiet quit” continue to meet the demands of their job but reject the hustle-culture mentality that you must always be available for more work and, most importantly, that your value as person and self-worth are defined and determined by your work. Quiet quitters believe that it is possible to have good boundaries and yet remain productive, engaged, and active within the workplace.
Earlier this month, NPR’s posted tutorial on how to set better boundaries at work garnered 491,000 views, reflecting employees’ difficulties in communicating their needs, thoughts, and availability to their employers. Quiet quitting refers to not only rejecting the idea of going above and beyond in the workplace but also feeling confident that there will not be negative ramifications for not consistently working beyond the expected requirements.
A focus on balance, life, loves, and family is rarely addressed or emphasized by traditional employers; employees have little skill in addressing boundaries and clarifying their value and availability. For decades, “needing” flexibility of any kind or valuing activities as much as your job were viewed as negative attributes, making those individuals less-desired employees.
Data support the quiet quitting trend. Gallup data reveal that employee engagement has fallen for 2 consecutive years in the U.S. workforce. Across the first quarter of 2022, Generation Z and younger Millennials report the lowest engagement across populations at 31%. More than half of this cohort, 54%, classified as “not engaged” in their workplace.
Why is quiet quitting gaining prominence now? COVID may play a role.
Many suggest that self-evaluation and establishing firmer boundaries is a logical response to emotional sequelae caused by COVID. Quiet quitting appears to have been fueled by the pandemic. Employees were forced into crisis mode by COVID; the lines between work, life, and home evaporated, allowing or forcing workers to evaluate their efficacy and satisfaction. With the structural impact of COVID reducing and a return to more standard work practices, it is expected that the job “rules” once held as truths come under evaluation and scrutiny.
Perhaps COVID has forced, and provided, another opportunity for us to closely examine our routines and habits and take stock of what really matters. Generations expectedly differ in their values and definitions of success. COVID has set prior established rules on fire, by forcing patterns and expectations that were neither expected nor wanted, within the context of a global health crisis. Within this backdrop, should we really believe our worth is determined by our job?
The truth is, we are still grieving what we lost during COVID and we have expectedly not assimilated to “the new normal.” Psychology has long recognized that losing structures and supports, routines and habits, causes symptoms of significant discomfort.
The idea that we would return to prior workplace expectations is naive. The idea we would “return to life as it was” is naive. It seems expected, then, that both employers and employees should evaluate their goals and communicate more openly about how each can be met.
It is incumbent upon the employers to set up clear guidelines regarding expectations, including rewards for performance and expectations for time, both within and outside of the work schedule. Employers must recognize symptoms of detachment in their employees and engage in the process of continuing clarifying roles and expectations while providing necessities for employees to succeed at their highest level. Employees, in turn, must self-examine their goals, communicate their needs, meet their responsibilities fully, and take on the challenge of determining their own definition of balance.
Maybe instead of quiet quitting, we should call it this new movement “self-awareness, growth, and evolution.” Hmmm, there’s an intriguing thought.
Dr. Calvery is professor of pediatrics at the University of Louisville (Ky.) She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the past few months, “quiet quitting” has garnered increasing traction across social media platforms. My morning review of social media revealed thousands of posts ranging from “Why doing less at work could be good for you – and your employer” to “After ‘quiet quitting’ here comes ‘quiet firing.’ ”
But quiet quitting is neither quiet nor quitting.
Quiet quitting is a misnomer. In addition, quiet quitters are firmer with their boundaries, do not take on work above and beyond clearly stated expectations, do not respond after hours, and do not feel like they are “not doing their job” when they are not immediately available.
Individuals who “quiet quit” continue to meet the demands of their job but reject the hustle-culture mentality that you must always be available for more work and, most importantly, that your value as person and self-worth are defined and determined by your work. Quiet quitters believe that it is possible to have good boundaries and yet remain productive, engaged, and active within the workplace.
Earlier this month, NPR’s posted tutorial on how to set better boundaries at work garnered 491,000 views, reflecting employees’ difficulties in communicating their needs, thoughts, and availability to their employers. Quiet quitting refers to not only rejecting the idea of going above and beyond in the workplace but also feeling confident that there will not be negative ramifications for not consistently working beyond the expected requirements.
A focus on balance, life, loves, and family is rarely addressed or emphasized by traditional employers; employees have little skill in addressing boundaries and clarifying their value and availability. For decades, “needing” flexibility of any kind or valuing activities as much as your job were viewed as negative attributes, making those individuals less-desired employees.
Data support the quiet quitting trend. Gallup data reveal that employee engagement has fallen for 2 consecutive years in the U.S. workforce. Across the first quarter of 2022, Generation Z and younger Millennials report the lowest engagement across populations at 31%. More than half of this cohort, 54%, classified as “not engaged” in their workplace.
Why is quiet quitting gaining prominence now? COVID may play a role.
Many suggest that self-evaluation and establishing firmer boundaries is a logical response to emotional sequelae caused by COVID. Quiet quitting appears to have been fueled by the pandemic. Employees were forced into crisis mode by COVID; the lines between work, life, and home evaporated, allowing or forcing workers to evaluate their efficacy and satisfaction. With the structural impact of COVID reducing and a return to more standard work practices, it is expected that the job “rules” once held as truths come under evaluation and scrutiny.
Perhaps COVID has forced, and provided, another opportunity for us to closely examine our routines and habits and take stock of what really matters. Generations expectedly differ in their values and definitions of success. COVID has set prior established rules on fire, by forcing patterns and expectations that were neither expected nor wanted, within the context of a global health crisis. Within this backdrop, should we really believe our worth is determined by our job?
The truth is, we are still grieving what we lost during COVID and we have expectedly not assimilated to “the new normal.” Psychology has long recognized that losing structures and supports, routines and habits, causes symptoms of significant discomfort.
The idea that we would return to prior workplace expectations is naive. The idea we would “return to life as it was” is naive. It seems expected, then, that both employers and employees should evaluate their goals and communicate more openly about how each can be met.
It is incumbent upon the employers to set up clear guidelines regarding expectations, including rewards for performance and expectations for time, both within and outside of the work schedule. Employers must recognize symptoms of detachment in their employees and engage in the process of continuing clarifying roles and expectations while providing necessities for employees to succeed at their highest level. Employees, in turn, must self-examine their goals, communicate their needs, meet their responsibilities fully, and take on the challenge of determining their own definition of balance.
Maybe instead of quiet quitting, we should call it this new movement “self-awareness, growth, and evolution.” Hmmm, there’s an intriguing thought.
Dr. Calvery is professor of pediatrics at the University of Louisville (Ky.) She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In the past few months, “quiet quitting” has garnered increasing traction across social media platforms. My morning review of social media revealed thousands of posts ranging from “Why doing less at work could be good for you – and your employer” to “After ‘quiet quitting’ here comes ‘quiet firing.’ ”
But quiet quitting is neither quiet nor quitting.
Quiet quitting is a misnomer. In addition, quiet quitters are firmer with their boundaries, do not take on work above and beyond clearly stated expectations, do not respond after hours, and do not feel like they are “not doing their job” when they are not immediately available.
Individuals who “quiet quit” continue to meet the demands of their job but reject the hustle-culture mentality that you must always be available for more work and, most importantly, that your value as person and self-worth are defined and determined by your work. Quiet quitters believe that it is possible to have good boundaries and yet remain productive, engaged, and active within the workplace.
Earlier this month, NPR’s posted tutorial on how to set better boundaries at work garnered 491,000 views, reflecting employees’ difficulties in communicating their needs, thoughts, and availability to their employers. Quiet quitting refers to not only rejecting the idea of going above and beyond in the workplace but also feeling confident that there will not be negative ramifications for not consistently working beyond the expected requirements.
A focus on balance, life, loves, and family is rarely addressed or emphasized by traditional employers; employees have little skill in addressing boundaries and clarifying their value and availability. For decades, “needing” flexibility of any kind or valuing activities as much as your job were viewed as negative attributes, making those individuals less-desired employees.
Data support the quiet quitting trend. Gallup data reveal that employee engagement has fallen for 2 consecutive years in the U.S. workforce. Across the first quarter of 2022, Generation Z and younger Millennials report the lowest engagement across populations at 31%. More than half of this cohort, 54%, classified as “not engaged” in their workplace.
Why is quiet quitting gaining prominence now? COVID may play a role.
Many suggest that self-evaluation and establishing firmer boundaries is a logical response to emotional sequelae caused by COVID. Quiet quitting appears to have been fueled by the pandemic. Employees were forced into crisis mode by COVID; the lines between work, life, and home evaporated, allowing or forcing workers to evaluate their efficacy and satisfaction. With the structural impact of COVID reducing and a return to more standard work practices, it is expected that the job “rules” once held as truths come under evaluation and scrutiny.
Perhaps COVID has forced, and provided, another opportunity for us to closely examine our routines and habits and take stock of what really matters. Generations expectedly differ in their values and definitions of success. COVID has set prior established rules on fire, by forcing patterns and expectations that were neither expected nor wanted, within the context of a global health crisis. Within this backdrop, should we really believe our worth is determined by our job?
The truth is, we are still grieving what we lost during COVID and we have expectedly not assimilated to “the new normal.” Psychology has long recognized that losing structures and supports, routines and habits, causes symptoms of significant discomfort.
The idea that we would return to prior workplace expectations is naive. The idea we would “return to life as it was” is naive. It seems expected, then, that both employers and employees should evaluate their goals and communicate more openly about how each can be met.
It is incumbent upon the employers to set up clear guidelines regarding expectations, including rewards for performance and expectations for time, both within and outside of the work schedule. Employers must recognize symptoms of detachment in their employees and engage in the process of continuing clarifying roles and expectations while providing necessities for employees to succeed at their highest level. Employees, in turn, must self-examine their goals, communicate their needs, meet their responsibilities fully, and take on the challenge of determining their own definition of balance.
Maybe instead of quiet quitting, we should call it this new movement “self-awareness, growth, and evolution.” Hmmm, there’s an intriguing thought.
Dr. Calvery is professor of pediatrics at the University of Louisville (Ky.) She disclosed no relevant conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Statin exposure potentially beneficial against gastric cancer
Key clinical point: Statin exposure reduces the risk for and improves the prognosis of gastric cancer.
Major finding: The statin-exposed vs -nonexposed population showed a significantly reduced incidence (odds ratio [OR] 0.78; P < .001) and improved prognosis (OR 0.78; P = .002) of gastric cancer.
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of 19 studies that analyzed the correlation between statin exposure and the occurrence and progression of gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lou D et al. Association between statins' exposure with incidence and prognosis of gastric cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022; 1-12 (Aug 15). Doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2112178
Key clinical point: Statin exposure reduces the risk for and improves the prognosis of gastric cancer.
Major finding: The statin-exposed vs -nonexposed population showed a significantly reduced incidence (odds ratio [OR] 0.78; P < .001) and improved prognosis (OR 0.78; P = .002) of gastric cancer.
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of 19 studies that analyzed the correlation between statin exposure and the occurrence and progression of gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lou D et al. Association between statins' exposure with incidence and prognosis of gastric cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022; 1-12 (Aug 15). Doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2112178
Key clinical point: Statin exposure reduces the risk for and improves the prognosis of gastric cancer.
Major finding: The statin-exposed vs -nonexposed population showed a significantly reduced incidence (odds ratio [OR] 0.78; P < .001) and improved prognosis (OR 0.78; P = .002) of gastric cancer.
Study details: This was a meta-analysis of 19 studies that analyzed the correlation between statin exposure and the occurrence and progression of gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study did not receive any funding. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lou D et al. Association between statins' exposure with incidence and prognosis of gastric cancer: An updated meta-analysis. Expert Rev Clin Pharmacol. 2022; 1-12 (Aug 15). Doi: 10.1080/17512433.2022.2112178
Myosteatosis and systemic inflammation hold prognostic value in resectable gastric cancer
Key clinical point: The presence of myosteatosis along with increased systemic inflammatory response markers, such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), serves as an independent prognostic indicator in patients with resectable gastric cancer.
Major finding: Co-occurrence of myosteatosis and an NLR of > 2.3 was significantly associated with worse disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 2.77; P = .001) and overall survival (HR 3.31; P < .001).
Study details: This single-center retrospective observational study included 280 patients with gastric cancer who underwent total or partial gastrectomy with curative intent.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lascala F et al. Prognostic value of myosteatosis and systemic inflammation in patients with resectable gastric cancer: A retrospective study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022 (Sep 8). Doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01201-7
Key clinical point: The presence of myosteatosis along with increased systemic inflammatory response markers, such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), serves as an independent prognostic indicator in patients with resectable gastric cancer.
Major finding: Co-occurrence of myosteatosis and an NLR of > 2.3 was significantly associated with worse disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 2.77; P = .001) and overall survival (HR 3.31; P < .001).
Study details: This single-center retrospective observational study included 280 patients with gastric cancer who underwent total or partial gastrectomy with curative intent.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lascala F et al. Prognostic value of myosteatosis and systemic inflammation in patients with resectable gastric cancer: A retrospective study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022 (Sep 8). Doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01201-7
Key clinical point: The presence of myosteatosis along with increased systemic inflammatory response markers, such as neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), serves as an independent prognostic indicator in patients with resectable gastric cancer.
Major finding: Co-occurrence of myosteatosis and an NLR of > 2.3 was significantly associated with worse disease-free survival (hazard ratio [HR] 2.77; P = .001) and overall survival (HR 3.31; P < .001).
Study details: This single-center retrospective observational study included 280 patients with gastric cancer who underwent total or partial gastrectomy with curative intent.
Disclosures: This study was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico, Brazil. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Lascala F et al. Prognostic value of myosteatosis and systemic inflammation in patients with resectable gastric cancer: A retrospective study. Eur J Clin Nutr. 2022 (Sep 8). Doi: 10.1038/s41430-022-01201-7
Gastric cancer: Diagnostic accuracy of esophagogastroduodenoscopy depends on gastric observation time
Key clinical point: A shorter gastric observation time during index esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD; preceding gastric cancer diagnosis) serves as an important predictor of the occurrence of interval advanced gastric cancer.
Major finding: A shorter observation time (<3 min; adjusted odds ratio 2.27; 95% CI 1.20-4.30) at preceding endoscopy was independently associated with an increased risk for interval advanced gastric cancer.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective nested case-control study that included 1257 patients diagnosed with gastric cancer within 6-36 months of “cancer-negative” index EGD, of which 102 patients had advanced gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Research Fund of the Korean Society of Gastroenterology and a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim TJ et al. Interval advanced gastric cancer after negative endoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 (Sep 5). Doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.08.027
Key clinical point: A shorter gastric observation time during index esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD; preceding gastric cancer diagnosis) serves as an important predictor of the occurrence of interval advanced gastric cancer.
Major finding: A shorter observation time (<3 min; adjusted odds ratio 2.27; 95% CI 1.20-4.30) at preceding endoscopy was independently associated with an increased risk for interval advanced gastric cancer.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective nested case-control study that included 1257 patients diagnosed with gastric cancer within 6-36 months of “cancer-negative” index EGD, of which 102 patients had advanced gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Research Fund of the Korean Society of Gastroenterology and a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim TJ et al. Interval advanced gastric cancer after negative endoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 (Sep 5). Doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.08.027
Key clinical point: A shorter gastric observation time during index esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD; preceding gastric cancer diagnosis) serves as an important predictor of the occurrence of interval advanced gastric cancer.
Major finding: A shorter observation time (<3 min; adjusted odds ratio 2.27; 95% CI 1.20-4.30) at preceding endoscopy was independently associated with an increased risk for interval advanced gastric cancer.
Study details: Findings are from a retrospective nested case-control study that included 1257 patients diagnosed with gastric cancer within 6-36 months of “cancer-negative” index EGD, of which 102 patients had advanced gastric cancer.
Disclosures: This study was supported by the Research Fund of the Korean Society of Gastroenterology and a National Research Foundation of Korea grant funded by the Korea government. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Kim TJ et al. Interval advanced gastric cancer after negative endoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2022 (Sep 5). Doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2022.08.027
Proximal and total gastrectomy with laparoscopy have similar outcomes in stage I gastric cancer
Key clinical point: Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy (LPG) and laparoscopic total gastrectomy (LTG) lead to similar long-term outcomes and postoperative complications in patients with upper third clinical stage I gastric cancer.
Major finding: Patients who underwent LPG and LTG showed no significant difference in the 3-year overall survival (92.6% and 92.3%, respectively; P = .74), recurrence-free survival (both 85.3%; P = .72), early complication (eg, surgical site infection; P = .31), and late complication (eg, anastomotic stenosis; P = .31) rates.
Study details: This retrospective study propensity score-matched patients with upper third clinical stage I gastric cancer who underwent LTG (n = 28) and those who underwent LPG (n = 28).
Disclosures: No source of funding was reported. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yamamoto M et al. Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy with novel valvuloplastic esophagogastrostomy vs laparoscopic total gastrectomy for stage I gastric cancer: A propensity score matching analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2022 (Aug 29). Doi: 10.1007/s11605-022-05404-y
Key clinical point: Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy (LPG) and laparoscopic total gastrectomy (LTG) lead to similar long-term outcomes and postoperative complications in patients with upper third clinical stage I gastric cancer.
Major finding: Patients who underwent LPG and LTG showed no significant difference in the 3-year overall survival (92.6% and 92.3%, respectively; P = .74), recurrence-free survival (both 85.3%; P = .72), early complication (eg, surgical site infection; P = .31), and late complication (eg, anastomotic stenosis; P = .31) rates.
Study details: This retrospective study propensity score-matched patients with upper third clinical stage I gastric cancer who underwent LTG (n = 28) and those who underwent LPG (n = 28).
Disclosures: No source of funding was reported. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yamamoto M et al. Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy with novel valvuloplastic esophagogastrostomy vs laparoscopic total gastrectomy for stage I gastric cancer: A propensity score matching analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2022 (Aug 29). Doi: 10.1007/s11605-022-05404-y
Key clinical point: Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy (LPG) and laparoscopic total gastrectomy (LTG) lead to similar long-term outcomes and postoperative complications in patients with upper third clinical stage I gastric cancer.
Major finding: Patients who underwent LPG and LTG showed no significant difference in the 3-year overall survival (92.6% and 92.3%, respectively; P = .74), recurrence-free survival (both 85.3%; P = .72), early complication (eg, surgical site infection; P = .31), and late complication (eg, anastomotic stenosis; P = .31) rates.
Study details: This retrospective study propensity score-matched patients with upper third clinical stage I gastric cancer who underwent LTG (n = 28) and those who underwent LPG (n = 28).
Disclosures: No source of funding was reported. The authors declared no conflicts of interest.
Source: Yamamoto M et al. Laparoscopic proximal gastrectomy with novel valvuloplastic esophagogastrostomy vs laparoscopic total gastrectomy for stage I gastric cancer: A propensity score matching analysis. J Gastrointest Surg. 2022 (Aug 29). Doi: 10.1007/s11605-022-05404-y