User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
Severe COVID-19 linked to new diabetes diagnoses
COVID can more than triple the chance of being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes within a year of being infected, according to a new Canadian study.
Men who had even a mild case of COVID were significantly more likely than were noninfected men to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Women didn’t have an increased risk unless they were severely ill.
Both men and women who had severe cases were at the highest risk. , and those who were admitted to intensive care units had more than a tripled risk.
“This is definitely a concern in terms of long-term outcomes,” researcher and University of British Columbia professor Naveed Z. Janjua, PhD, told The New York Times. “With a respiratory infection, you usually think, ‘Seven or eight days and I’m done with it, that’s it.’ [But] here we’re seeing lingering effects that are lifelong.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open. Researchers analyzed health data from 2020 and 2021 for 629,935 people, 20% of whom were diagnosed with COVID during that time. Most people in the study had not been vaccinated because vaccines were not widely available then. The health information came from a registry maintained by public health officials in British Columbia. The follow-up period was 257 days.
The authors cautioned that their findings could not say that COVID causes type 2 diabetes; rather, in a commentary published along with the study, Pamela B. Davis, MD, PhD, said the link makes sense because COVID is known to impact the pancreas.
“Such a stress may move a patient from a prediabetic state into diabetes,” wrote Dr. Davis, former dean of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, where she is now a professor.
The researchers estimated that the increased pattern of diagnoses of diabetes following COVID infection could increase the rate of the disease occurring in the general population by 3%-5% overall.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID can more than triple the chance of being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes within a year of being infected, according to a new Canadian study.
Men who had even a mild case of COVID were significantly more likely than were noninfected men to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Women didn’t have an increased risk unless they were severely ill.
Both men and women who had severe cases were at the highest risk. , and those who were admitted to intensive care units had more than a tripled risk.
“This is definitely a concern in terms of long-term outcomes,” researcher and University of British Columbia professor Naveed Z. Janjua, PhD, told The New York Times. “With a respiratory infection, you usually think, ‘Seven or eight days and I’m done with it, that’s it.’ [But] here we’re seeing lingering effects that are lifelong.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open. Researchers analyzed health data from 2020 and 2021 for 629,935 people, 20% of whom were diagnosed with COVID during that time. Most people in the study had not been vaccinated because vaccines were not widely available then. The health information came from a registry maintained by public health officials in British Columbia. The follow-up period was 257 days.
The authors cautioned that their findings could not say that COVID causes type 2 diabetes; rather, in a commentary published along with the study, Pamela B. Davis, MD, PhD, said the link makes sense because COVID is known to impact the pancreas.
“Such a stress may move a patient from a prediabetic state into diabetes,” wrote Dr. Davis, former dean of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, where she is now a professor.
The researchers estimated that the increased pattern of diagnoses of diabetes following COVID infection could increase the rate of the disease occurring in the general population by 3%-5% overall.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID can more than triple the chance of being diagnosed with type 2 diabetes within a year of being infected, according to a new Canadian study.
Men who had even a mild case of COVID were significantly more likely than were noninfected men to be diagnosed with type 2 diabetes. Women didn’t have an increased risk unless they were severely ill.
Both men and women who had severe cases were at the highest risk. , and those who were admitted to intensive care units had more than a tripled risk.
“This is definitely a concern in terms of long-term outcomes,” researcher and University of British Columbia professor Naveed Z. Janjua, PhD, told The New York Times. “With a respiratory infection, you usually think, ‘Seven or eight days and I’m done with it, that’s it.’ [But] here we’re seeing lingering effects that are lifelong.”
The study was published in JAMA Network Open. Researchers analyzed health data from 2020 and 2021 for 629,935 people, 20% of whom were diagnosed with COVID during that time. Most people in the study had not been vaccinated because vaccines were not widely available then. The health information came from a registry maintained by public health officials in British Columbia. The follow-up period was 257 days.
The authors cautioned that their findings could not say that COVID causes type 2 diabetes; rather, in a commentary published along with the study, Pamela B. Davis, MD, PhD, said the link makes sense because COVID is known to impact the pancreas.
“Such a stress may move a patient from a prediabetic state into diabetes,” wrote Dr. Davis, former dean of Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, where she is now a professor.
The researchers estimated that the increased pattern of diagnoses of diabetes following COVID infection could increase the rate of the disease occurring in the general population by 3%-5% overall.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Dried blood spot test validated for HIV, hep B, and hep C
A test that uses a single drop of dried blood to detect HIV, hepatitis B virus, and HCV has been validated and is now in use in some high-risk settings in Denmark, according to research presented at the annual European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
Molecular biologist Stephen Nilsson-Møller, MSc, and colleagues at the department of clinical microbiology, Copenhagen University Hospital, developed and validated the test, known as the Dried Blood Spot (DBS), for HIV, HBV, and HCV.
The “test that can detect low viral loads for all three viruses from a single drop of blood, and can be done using existing hospital equipment,” Mr. Nilsson-Møller said in an interview. “Importantly, it does not require venipuncture, but can be done from a drop of dried blood from the finger.”
He highlighted the utility of the new test in more challenging settings. “This method is particularly useful in high-risk settings such as homeless shelters, drug rehabilitation centers, and prisons, where needles might be misused, and it can be difficult to convince people to have the more invasive test.”
“Also, in some places – such as in low- and middle-income settings – there is a distinct risk of ruining blood samples before analysis due to limited refrigeration for transit and storage,” he added. “[Standard] blood samples need to be analyzed within 6 hours when kept at room temperature, while dried blood spots can last for 9 months at room temperature and can be mailed to a laboratory with the right equipment to analyze it.”
Tiny amounts of virus detected
Mr. Nilsson-Møller was tasked with developing a test for use by the university’s department of infectious diseases to screen people in high-risk settings in the capital region of Copenhagen. The work forms part of a PhD project by Jonas Demant at the University of Copenhagen, for which he is screening for HIV, HBV, and HCV in drug rehabilitation centers, prisons, and homeless shelters.
The study is the first to use the Hologic Panther system (a nucleic acid amplification test) combining all three viruses, Mr. Nilsson-Møller pointed out. “A tiny amount of virus can be detected because it is a very sensitive platform using transcription-mediated amplification.”
“If it detects low amounts of virus, it will create many copies very quickly, creating a signal that tells us that the sample is positive,” he explained.
The researchers collected whole blood from a finger prick, dried it out on a protein saver card (filter paper), and cut out a 1.2-cm diameter dry blood spot which was then prepared for analysis.
Twenty blood samples with known amounts of HIV, HBV, and HCV were analyzed via the DBS method (60 in total) and the viruses were detected in all of the samples.
To validate the method, the researchers used plasma with a known viral load, and a series of dilutions were performed to determine the lower limit for positive detection of all three viruses.
“Untreated patients typically have above 1 million IU/mL of viral loads in their plasma, and we found that we can detect much lower levels,” said Mr. Nilsson-Møller. “Ideally, 40 mcL of blood is good, but less should be sufficient if the test is on untreated patients.”
Early testing and treatment reduces morbidity and mortality
Elimination of HBV, HCV, and HIV by 2030 is a global health strategy set by the World Health Organization, but to meet this goal, new approaches for diagnostic testing are required. The DBS test for HIV, HBV, and HCV promises to make a significant contribution toward this goal.
“One in two people currently living with HIV is diagnosed late in the course of their infection, and an even larger proportion of the estimated 6 million Europeans living with chronic hepatitis B or C are not aware that they are infected,” said Anastasia Pharris, PhD, from the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control Principal Expert Infectious Diseases.
“Increasing testing coverage and uptake, especially for those most at risk, is an essential element of any strategy to eliminate HBV, HCV, and HIV in the European Union and European Economic Area,” she pointed out.
Dr. Pharris also highlighted that, while HIV, and often HBV infection, require lifelong treatment, HCV infection is now curable within a few weeks. “To maximize the benefits of individual treatment for all three infections, it is critical to test and diagnose people as soon as possible – in itself a challenge given that these infections can typically be asymptomatic for years.
“Early diagnosis of HBV, HCV, or HIV is vital as it allows people to access treatment, which significantly reduces associated long-term morbidity and mortality.
“In many cases, those most at risk of one of these infections are also more vulnerable to infection with one or both of the other viruses, making the argument for integrated testing even stronger,” she said in an interview.
Mr. Nilsson-Møller and Dr. Pharris reported no relevant financial relationships. Aptima kits for validation were provided by Hologic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A test that uses a single drop of dried blood to detect HIV, hepatitis B virus, and HCV has been validated and is now in use in some high-risk settings in Denmark, according to research presented at the annual European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
Molecular biologist Stephen Nilsson-Møller, MSc, and colleagues at the department of clinical microbiology, Copenhagen University Hospital, developed and validated the test, known as the Dried Blood Spot (DBS), for HIV, HBV, and HCV.
The “test that can detect low viral loads for all three viruses from a single drop of blood, and can be done using existing hospital equipment,” Mr. Nilsson-Møller said in an interview. “Importantly, it does not require venipuncture, but can be done from a drop of dried blood from the finger.”
He highlighted the utility of the new test in more challenging settings. “This method is particularly useful in high-risk settings such as homeless shelters, drug rehabilitation centers, and prisons, where needles might be misused, and it can be difficult to convince people to have the more invasive test.”
“Also, in some places – such as in low- and middle-income settings – there is a distinct risk of ruining blood samples before analysis due to limited refrigeration for transit and storage,” he added. “[Standard] blood samples need to be analyzed within 6 hours when kept at room temperature, while dried blood spots can last for 9 months at room temperature and can be mailed to a laboratory with the right equipment to analyze it.”
Tiny amounts of virus detected
Mr. Nilsson-Møller was tasked with developing a test for use by the university’s department of infectious diseases to screen people in high-risk settings in the capital region of Copenhagen. The work forms part of a PhD project by Jonas Demant at the University of Copenhagen, for which he is screening for HIV, HBV, and HCV in drug rehabilitation centers, prisons, and homeless shelters.
The study is the first to use the Hologic Panther system (a nucleic acid amplification test) combining all three viruses, Mr. Nilsson-Møller pointed out. “A tiny amount of virus can be detected because it is a very sensitive platform using transcription-mediated amplification.”
“If it detects low amounts of virus, it will create many copies very quickly, creating a signal that tells us that the sample is positive,” he explained.
The researchers collected whole blood from a finger prick, dried it out on a protein saver card (filter paper), and cut out a 1.2-cm diameter dry blood spot which was then prepared for analysis.
Twenty blood samples with known amounts of HIV, HBV, and HCV were analyzed via the DBS method (60 in total) and the viruses were detected in all of the samples.
To validate the method, the researchers used plasma with a known viral load, and a series of dilutions were performed to determine the lower limit for positive detection of all three viruses.
“Untreated patients typically have above 1 million IU/mL of viral loads in their plasma, and we found that we can detect much lower levels,” said Mr. Nilsson-Møller. “Ideally, 40 mcL of blood is good, but less should be sufficient if the test is on untreated patients.”
Early testing and treatment reduces morbidity and mortality
Elimination of HBV, HCV, and HIV by 2030 is a global health strategy set by the World Health Organization, but to meet this goal, new approaches for diagnostic testing are required. The DBS test for HIV, HBV, and HCV promises to make a significant contribution toward this goal.
“One in two people currently living with HIV is diagnosed late in the course of their infection, and an even larger proportion of the estimated 6 million Europeans living with chronic hepatitis B or C are not aware that they are infected,” said Anastasia Pharris, PhD, from the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control Principal Expert Infectious Diseases.
“Increasing testing coverage and uptake, especially for those most at risk, is an essential element of any strategy to eliminate HBV, HCV, and HIV in the European Union and European Economic Area,” she pointed out.
Dr. Pharris also highlighted that, while HIV, and often HBV infection, require lifelong treatment, HCV infection is now curable within a few weeks. “To maximize the benefits of individual treatment for all three infections, it is critical to test and diagnose people as soon as possible – in itself a challenge given that these infections can typically be asymptomatic for years.
“Early diagnosis of HBV, HCV, or HIV is vital as it allows people to access treatment, which significantly reduces associated long-term morbidity and mortality.
“In many cases, those most at risk of one of these infections are also more vulnerable to infection with one or both of the other viruses, making the argument for integrated testing even stronger,” she said in an interview.
Mr. Nilsson-Møller and Dr. Pharris reported no relevant financial relationships. Aptima kits for validation were provided by Hologic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A test that uses a single drop of dried blood to detect HIV, hepatitis B virus, and HCV has been validated and is now in use in some high-risk settings in Denmark, according to research presented at the annual European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases.
Molecular biologist Stephen Nilsson-Møller, MSc, and colleagues at the department of clinical microbiology, Copenhagen University Hospital, developed and validated the test, known as the Dried Blood Spot (DBS), for HIV, HBV, and HCV.
The “test that can detect low viral loads for all three viruses from a single drop of blood, and can be done using existing hospital equipment,” Mr. Nilsson-Møller said in an interview. “Importantly, it does not require venipuncture, but can be done from a drop of dried blood from the finger.”
He highlighted the utility of the new test in more challenging settings. “This method is particularly useful in high-risk settings such as homeless shelters, drug rehabilitation centers, and prisons, where needles might be misused, and it can be difficult to convince people to have the more invasive test.”
“Also, in some places – such as in low- and middle-income settings – there is a distinct risk of ruining blood samples before analysis due to limited refrigeration for transit and storage,” he added. “[Standard] blood samples need to be analyzed within 6 hours when kept at room temperature, while dried blood spots can last for 9 months at room temperature and can be mailed to a laboratory with the right equipment to analyze it.”
Tiny amounts of virus detected
Mr. Nilsson-Møller was tasked with developing a test for use by the university’s department of infectious diseases to screen people in high-risk settings in the capital region of Copenhagen. The work forms part of a PhD project by Jonas Demant at the University of Copenhagen, for which he is screening for HIV, HBV, and HCV in drug rehabilitation centers, prisons, and homeless shelters.
The study is the first to use the Hologic Panther system (a nucleic acid amplification test) combining all three viruses, Mr. Nilsson-Møller pointed out. “A tiny amount of virus can be detected because it is a very sensitive platform using transcription-mediated amplification.”
“If it detects low amounts of virus, it will create many copies very quickly, creating a signal that tells us that the sample is positive,” he explained.
The researchers collected whole blood from a finger prick, dried it out on a protein saver card (filter paper), and cut out a 1.2-cm diameter dry blood spot which was then prepared for analysis.
Twenty blood samples with known amounts of HIV, HBV, and HCV were analyzed via the DBS method (60 in total) and the viruses were detected in all of the samples.
To validate the method, the researchers used plasma with a known viral load, and a series of dilutions were performed to determine the lower limit for positive detection of all three viruses.
“Untreated patients typically have above 1 million IU/mL of viral loads in their plasma, and we found that we can detect much lower levels,” said Mr. Nilsson-Møller. “Ideally, 40 mcL of blood is good, but less should be sufficient if the test is on untreated patients.”
Early testing and treatment reduces morbidity and mortality
Elimination of HBV, HCV, and HIV by 2030 is a global health strategy set by the World Health Organization, but to meet this goal, new approaches for diagnostic testing are required. The DBS test for HIV, HBV, and HCV promises to make a significant contribution toward this goal.
“One in two people currently living with HIV is diagnosed late in the course of their infection, and an even larger proportion of the estimated 6 million Europeans living with chronic hepatitis B or C are not aware that they are infected,” said Anastasia Pharris, PhD, from the European Center for Disease Prevention and Control Principal Expert Infectious Diseases.
“Increasing testing coverage and uptake, especially for those most at risk, is an essential element of any strategy to eliminate HBV, HCV, and HIV in the European Union and European Economic Area,” she pointed out.
Dr. Pharris also highlighted that, while HIV, and often HBV infection, require lifelong treatment, HCV infection is now curable within a few weeks. “To maximize the benefits of individual treatment for all three infections, it is critical to test and diagnose people as soon as possible – in itself a challenge given that these infections can typically be asymptomatic for years.
“Early diagnosis of HBV, HCV, or HIV is vital as it allows people to access treatment, which significantly reduces associated long-term morbidity and mortality.
“In many cases, those most at risk of one of these infections are also more vulnerable to infection with one or both of the other viruses, making the argument for integrated testing even stronger,” she said in an interview.
Mr. Nilsson-Møller and Dr. Pharris reported no relevant financial relationships. Aptima kits for validation were provided by Hologic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECCMID 2023
Are delayed antibiotic prescriptions futile?
I recently posted a case about a smoker who became angry when I hesitated to prescribe antibiotics for his self-diagnosed bronchitis. He even threatened to retaliate by posting negative online reviews of my practice. In the end, I decided to use the strategy of a delayed prescription for antibiotics, instructing him to fill the prescription only if his symptoms worsened. I asked whether readers agreed with this approach. Thank you for the thoughtful comments regarding a case that certainly seemed familiar to many of you. I very much appreciate the chance to interact and share perspectives in a challenging clinical dilemma.
One theme that emerged through several comments was the perceived futility of the delayed prescriptions for antibiotics. To summarize, the collective logic stated that there is no point in delaying a prescription, because the patient will be very likely to fill that prescription right away despite counseling from the health care provider (HCP).
However, studies of delayed antibiotic prescriptions show that patients generally honor the advice to only fill the prescription if they are not improving clinically. In a study comparing immediate, delayed, or no antibiotic prescriptions among a cohort of children with uncomplicated respiratory infections, the overall rates of use of antibiotics in the three respective groups were 96%, 25.3%, and 12.0%. In another randomized trial exploring different strategies for delayed prescriptions among adults with upper respiratory infections, the rate of antibiotic use was 37% with delayed prescription strategies vs. 97% of patients prescribed antibiotics immediately. Neither of these prospective studies found a significant difference in clinical symptoms or complications in comparing the delayed and immediate antibiotic prescription groups.
Another common theme in the comments on this case focused on the challenge of online reviews of HCPs by patients. Multiple popular websites are devoted to patients’ unedited comments on HCPs and their practices, but there are still certain patterns to the comments. Some reviews describe the professionalism or empathy of the HCP, but others might focus more attention on the overall practice or office. These latter comments might emphasize issues such as timeliness of appointments, interactions with staff, or even parking and traffic. These are issues over which the HCP usually has little control.
HCPs are quite human, and therefore we might feel great about positive comments and dispirited or even angry with negative comments. So what is the best practice for HCPs in managing these online comments? A review by Dr Rebekah Bernard, which was published in the Sept. 25, 2018, issue of Medical Economics, offered some pragmatic advice:
Do not perseverate on one or two negative reviews. In fact, they might help! Dr. Bernard describes the psychological theory of the “pratfall effect,” in which people are more likely to prefer someone who is generally very good but not perfect to someone with nothing but exceptional reviews. HCPs with perfect reviews every time may be seen as intimidating or unapproachable.
Satisfied patients will frequently rally to support an HCP with an unfavorable review. This group may not be very motivated to complete online reviews until they see a comment which does at all match their own experience with the HCP.
Most importantly, HCPs can take an active role in minimizing the impact of negative online reviews while also enhancing their business model. Increasing your presence on the Internet and social media can help dilute negative reviews and push them down the list when someone performs a search on your name or practice. Creating a website for your practice is an effective means to be first on search engine lists, and HCPs should seek search-engine optimization features that promote this outcome. Adding social media contacts for yourself and/or your practice, as many as you can tolerate and maintain, allows HCPs to further control the narrative regarding their practice and central messaging to patients and the community.
In conclusion, delayed antibiotic prescriptions can reduce the use of unnecessary antibiotics for upper respiratory infections among children and adults, and they are not associated with worse clinical outcomes vs. immediate antibiotic prescriptions. They can also improve patient satisfaction for these visits, which can minimize the challenging issue of negative reviews of HCPs. HCPs should therefore consider delayed prescriptions as a strong option among patients without an indication for an antibiotic prescription.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I recently posted a case about a smoker who became angry when I hesitated to prescribe antibiotics for his self-diagnosed bronchitis. He even threatened to retaliate by posting negative online reviews of my practice. In the end, I decided to use the strategy of a delayed prescription for antibiotics, instructing him to fill the prescription only if his symptoms worsened. I asked whether readers agreed with this approach. Thank you for the thoughtful comments regarding a case that certainly seemed familiar to many of you. I very much appreciate the chance to interact and share perspectives in a challenging clinical dilemma.
One theme that emerged through several comments was the perceived futility of the delayed prescriptions for antibiotics. To summarize, the collective logic stated that there is no point in delaying a prescription, because the patient will be very likely to fill that prescription right away despite counseling from the health care provider (HCP).
However, studies of delayed antibiotic prescriptions show that patients generally honor the advice to only fill the prescription if they are not improving clinically. In a study comparing immediate, delayed, or no antibiotic prescriptions among a cohort of children with uncomplicated respiratory infections, the overall rates of use of antibiotics in the three respective groups were 96%, 25.3%, and 12.0%. In another randomized trial exploring different strategies for delayed prescriptions among adults with upper respiratory infections, the rate of antibiotic use was 37% with delayed prescription strategies vs. 97% of patients prescribed antibiotics immediately. Neither of these prospective studies found a significant difference in clinical symptoms or complications in comparing the delayed and immediate antibiotic prescription groups.
Another common theme in the comments on this case focused on the challenge of online reviews of HCPs by patients. Multiple popular websites are devoted to patients’ unedited comments on HCPs and their practices, but there are still certain patterns to the comments. Some reviews describe the professionalism or empathy of the HCP, but others might focus more attention on the overall practice or office. These latter comments might emphasize issues such as timeliness of appointments, interactions with staff, or even parking and traffic. These are issues over which the HCP usually has little control.
HCPs are quite human, and therefore we might feel great about positive comments and dispirited or even angry with negative comments. So what is the best practice for HCPs in managing these online comments? A review by Dr Rebekah Bernard, which was published in the Sept. 25, 2018, issue of Medical Economics, offered some pragmatic advice:
Do not perseverate on one or two negative reviews. In fact, they might help! Dr. Bernard describes the psychological theory of the “pratfall effect,” in which people are more likely to prefer someone who is generally very good but not perfect to someone with nothing but exceptional reviews. HCPs with perfect reviews every time may be seen as intimidating or unapproachable.
Satisfied patients will frequently rally to support an HCP with an unfavorable review. This group may not be very motivated to complete online reviews until they see a comment which does at all match their own experience with the HCP.
Most importantly, HCPs can take an active role in minimizing the impact of negative online reviews while also enhancing their business model. Increasing your presence on the Internet and social media can help dilute negative reviews and push them down the list when someone performs a search on your name or practice. Creating a website for your practice is an effective means to be first on search engine lists, and HCPs should seek search-engine optimization features that promote this outcome. Adding social media contacts for yourself and/or your practice, as many as you can tolerate and maintain, allows HCPs to further control the narrative regarding their practice and central messaging to patients and the community.
In conclusion, delayed antibiotic prescriptions can reduce the use of unnecessary antibiotics for upper respiratory infections among children and adults, and they are not associated with worse clinical outcomes vs. immediate antibiotic prescriptions. They can also improve patient satisfaction for these visits, which can minimize the challenging issue of negative reviews of HCPs. HCPs should therefore consider delayed prescriptions as a strong option among patients without an indication for an antibiotic prescription.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
I recently posted a case about a smoker who became angry when I hesitated to prescribe antibiotics for his self-diagnosed bronchitis. He even threatened to retaliate by posting negative online reviews of my practice. In the end, I decided to use the strategy of a delayed prescription for antibiotics, instructing him to fill the prescription only if his symptoms worsened. I asked whether readers agreed with this approach. Thank you for the thoughtful comments regarding a case that certainly seemed familiar to many of you. I very much appreciate the chance to interact and share perspectives in a challenging clinical dilemma.
One theme that emerged through several comments was the perceived futility of the delayed prescriptions for antibiotics. To summarize, the collective logic stated that there is no point in delaying a prescription, because the patient will be very likely to fill that prescription right away despite counseling from the health care provider (HCP).
However, studies of delayed antibiotic prescriptions show that patients generally honor the advice to only fill the prescription if they are not improving clinically. In a study comparing immediate, delayed, or no antibiotic prescriptions among a cohort of children with uncomplicated respiratory infections, the overall rates of use of antibiotics in the three respective groups were 96%, 25.3%, and 12.0%. In another randomized trial exploring different strategies for delayed prescriptions among adults with upper respiratory infections, the rate of antibiotic use was 37% with delayed prescription strategies vs. 97% of patients prescribed antibiotics immediately. Neither of these prospective studies found a significant difference in clinical symptoms or complications in comparing the delayed and immediate antibiotic prescription groups.
Another common theme in the comments on this case focused on the challenge of online reviews of HCPs by patients. Multiple popular websites are devoted to patients’ unedited comments on HCPs and their practices, but there are still certain patterns to the comments. Some reviews describe the professionalism or empathy of the HCP, but others might focus more attention on the overall practice or office. These latter comments might emphasize issues such as timeliness of appointments, interactions with staff, or even parking and traffic. These are issues over which the HCP usually has little control.
HCPs are quite human, and therefore we might feel great about positive comments and dispirited or even angry with negative comments. So what is the best practice for HCPs in managing these online comments? A review by Dr Rebekah Bernard, which was published in the Sept. 25, 2018, issue of Medical Economics, offered some pragmatic advice:
Do not perseverate on one or two negative reviews. In fact, they might help! Dr. Bernard describes the psychological theory of the “pratfall effect,” in which people are more likely to prefer someone who is generally very good but not perfect to someone with nothing but exceptional reviews. HCPs with perfect reviews every time may be seen as intimidating or unapproachable.
Satisfied patients will frequently rally to support an HCP with an unfavorable review. This group may not be very motivated to complete online reviews until they see a comment which does at all match their own experience with the HCP.
Most importantly, HCPs can take an active role in minimizing the impact of negative online reviews while also enhancing their business model. Increasing your presence on the Internet and social media can help dilute negative reviews and push them down the list when someone performs a search on your name or practice. Creating a website for your practice is an effective means to be first on search engine lists, and HCPs should seek search-engine optimization features that promote this outcome. Adding social media contacts for yourself and/or your practice, as many as you can tolerate and maintain, allows HCPs to further control the narrative regarding their practice and central messaging to patients and the community.
In conclusion, delayed antibiotic prescriptions can reduce the use of unnecessary antibiotics for upper respiratory infections among children and adults, and they are not associated with worse clinical outcomes vs. immediate antibiotic prescriptions. They can also improve patient satisfaction for these visits, which can minimize the challenging issue of negative reviews of HCPs. HCPs should therefore consider delayed prescriptions as a strong option among patients without an indication for an antibiotic prescription.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CMS inpatient payment rule for 2024: Key takeaways
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released its annual update to the inpatient prospective payment system (IPPS) and long-term care hospital (LTCH) PPS on April 10, with many changes centered around improving health equity and quality as well as alleviating rural clinician shortages.
“This proposed rule reflects our person-centric approach to better measure health care quality and safety in hospitals to reduce preventable harm and our commitment to ensure that people with Medicare in rural and underserved areas have improved access to high-quality health care,” said CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure said in a statement.
Here are 14 things to know about the fiscal year (FY) 2024 proposal:
1. New payment rate: Acute-care hospitals that report inpatient quality data and participate in the EHR Meaningful Use program will receive a 2.8% net increase in payment rates. The rate adjustment will send approximately $3.3 billion more funding to hospitals compared with 2023.
2. LTCH payments: CMS projects that the LTCH standard payment rate will increase by 2.9%, whereas discharge payments will decrease by 2.5% or $59 million.
3. Disproportionate share hospital payments: Medicare disproportionate share hospital payments and Medicare uncompensated care payments will decrease by about $115 million for FY 2024.
4. Health equity categories: CMS proposes adding 15 new health equity hospital categorizations for IPPS payments to advance the goals of its Framework for Health Equity initiative.
5. Social determinants of health codes: To reflect increased resource utilization, the severity designation for the three International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnosis codes describing homelessness will change from noncomplication or comorbidity to complication or comorbidity.
6. Rural emergency hospitals: The proposed rule will allow designated rural emergency hospitals to serve as training sites and receive Medicare graduate medical education payments to address concerns over rural hospital closures.
7. COVID treatment add-on payments: If the public health emergency ends in May, add-on payments for discharges involving eligible products like convalescent plasma and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir will expire on Sept. 30.
8. Technology add-on payments: Requests for new technology add-on payments must include a complete, active Food and Drug Administration market authorization application. Beginning with FY 2025 applications, the FDA approval deadline will move from July 1 to May 1.
9. Physician-owned hospitals: To receive Medicare payment for services referred by a physician owner or investor, the hospital must satisfy all requirements of the whole hospital exception or the rural provider exception to the Stark Law. In either case, a hospital may not increase the aggregate number of operating rooms, procedure rooms, or beds above the level it was licensed for on March 23, 2010, unless CMS grants an exception.
10. Electronic clinical quality measures: The new rule will remove and modify several existing electronic clinical quality measures and add three new ones: hospital harm, pressure injury; hospital harm, acute kidney injury; and excessive radiation dose or inadequate image quality for diagnostic CT in adult inpatients.
11. HCAHPS survey: Beginning Jan. 1, 2025, modifications to the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey will extend the data collection period from 42 to 49 days, limit supplemental survey items to 12, and require an official Spanish translation for patients.
12. Safety-net hospitals request for information: CMS seeks public input about the unique challenges faced by safety-net hospitals and potential solutions to ensure that uninsured, underinsured, and other vulnerable populations have access to essential services.
13. LTCH quality reporting: CMS proposes several quality-measure updates, including a functional discharge score measure beginning in FY 2025 and reporting the percentage of patients current with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recommended COVID vaccinations starting in FY 2026.
14. Commenting period: CMS will accept comments on the proposed rule through June 9.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released its annual update to the inpatient prospective payment system (IPPS) and long-term care hospital (LTCH) PPS on April 10, with many changes centered around improving health equity and quality as well as alleviating rural clinician shortages.
“This proposed rule reflects our person-centric approach to better measure health care quality and safety in hospitals to reduce preventable harm and our commitment to ensure that people with Medicare in rural and underserved areas have improved access to high-quality health care,” said CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure said in a statement.
Here are 14 things to know about the fiscal year (FY) 2024 proposal:
1. New payment rate: Acute-care hospitals that report inpatient quality data and participate in the EHR Meaningful Use program will receive a 2.8% net increase in payment rates. The rate adjustment will send approximately $3.3 billion more funding to hospitals compared with 2023.
2. LTCH payments: CMS projects that the LTCH standard payment rate will increase by 2.9%, whereas discharge payments will decrease by 2.5% or $59 million.
3. Disproportionate share hospital payments: Medicare disproportionate share hospital payments and Medicare uncompensated care payments will decrease by about $115 million for FY 2024.
4. Health equity categories: CMS proposes adding 15 new health equity hospital categorizations for IPPS payments to advance the goals of its Framework for Health Equity initiative.
5. Social determinants of health codes: To reflect increased resource utilization, the severity designation for the three International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnosis codes describing homelessness will change from noncomplication or comorbidity to complication or comorbidity.
6. Rural emergency hospitals: The proposed rule will allow designated rural emergency hospitals to serve as training sites and receive Medicare graduate medical education payments to address concerns over rural hospital closures.
7. COVID treatment add-on payments: If the public health emergency ends in May, add-on payments for discharges involving eligible products like convalescent plasma and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir will expire on Sept. 30.
8. Technology add-on payments: Requests for new technology add-on payments must include a complete, active Food and Drug Administration market authorization application. Beginning with FY 2025 applications, the FDA approval deadline will move from July 1 to May 1.
9. Physician-owned hospitals: To receive Medicare payment for services referred by a physician owner or investor, the hospital must satisfy all requirements of the whole hospital exception or the rural provider exception to the Stark Law. In either case, a hospital may not increase the aggregate number of operating rooms, procedure rooms, or beds above the level it was licensed for on March 23, 2010, unless CMS grants an exception.
10. Electronic clinical quality measures: The new rule will remove and modify several existing electronic clinical quality measures and add three new ones: hospital harm, pressure injury; hospital harm, acute kidney injury; and excessive radiation dose or inadequate image quality for diagnostic CT in adult inpatients.
11. HCAHPS survey: Beginning Jan. 1, 2025, modifications to the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey will extend the data collection period from 42 to 49 days, limit supplemental survey items to 12, and require an official Spanish translation for patients.
12. Safety-net hospitals request for information: CMS seeks public input about the unique challenges faced by safety-net hospitals and potential solutions to ensure that uninsured, underinsured, and other vulnerable populations have access to essential services.
13. LTCH quality reporting: CMS proposes several quality-measure updates, including a functional discharge score measure beginning in FY 2025 and reporting the percentage of patients current with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recommended COVID vaccinations starting in FY 2026.
14. Commenting period: CMS will accept comments on the proposed rule through June 9.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) released its annual update to the inpatient prospective payment system (IPPS) and long-term care hospital (LTCH) PPS on April 10, with many changes centered around improving health equity and quality as well as alleviating rural clinician shortages.
“This proposed rule reflects our person-centric approach to better measure health care quality and safety in hospitals to reduce preventable harm and our commitment to ensure that people with Medicare in rural and underserved areas have improved access to high-quality health care,” said CMS Administrator Chiquita Brooks-LaSure said in a statement.
Here are 14 things to know about the fiscal year (FY) 2024 proposal:
1. New payment rate: Acute-care hospitals that report inpatient quality data and participate in the EHR Meaningful Use program will receive a 2.8% net increase in payment rates. The rate adjustment will send approximately $3.3 billion more funding to hospitals compared with 2023.
2. LTCH payments: CMS projects that the LTCH standard payment rate will increase by 2.9%, whereas discharge payments will decrease by 2.5% or $59 million.
3. Disproportionate share hospital payments: Medicare disproportionate share hospital payments and Medicare uncompensated care payments will decrease by about $115 million for FY 2024.
4. Health equity categories: CMS proposes adding 15 new health equity hospital categorizations for IPPS payments to advance the goals of its Framework for Health Equity initiative.
5. Social determinants of health codes: To reflect increased resource utilization, the severity designation for the three International Classification of Diseases, Tenth Revision, Clinical Modification (ICD-10-CM) diagnosis codes describing homelessness will change from noncomplication or comorbidity to complication or comorbidity.
6. Rural emergency hospitals: The proposed rule will allow designated rural emergency hospitals to serve as training sites and receive Medicare graduate medical education payments to address concerns over rural hospital closures.
7. COVID treatment add-on payments: If the public health emergency ends in May, add-on payments for discharges involving eligible products like convalescent plasma and nirmatrelvir-ritonavir will expire on Sept. 30.
8. Technology add-on payments: Requests for new technology add-on payments must include a complete, active Food and Drug Administration market authorization application. Beginning with FY 2025 applications, the FDA approval deadline will move from July 1 to May 1.
9. Physician-owned hospitals: To receive Medicare payment for services referred by a physician owner or investor, the hospital must satisfy all requirements of the whole hospital exception or the rural provider exception to the Stark Law. In either case, a hospital may not increase the aggregate number of operating rooms, procedure rooms, or beds above the level it was licensed for on March 23, 2010, unless CMS grants an exception.
10. Electronic clinical quality measures: The new rule will remove and modify several existing electronic clinical quality measures and add three new ones: hospital harm, pressure injury; hospital harm, acute kidney injury; and excessive radiation dose or inadequate image quality for diagnostic CT in adult inpatients.
11. HCAHPS survey: Beginning Jan. 1, 2025, modifications to the Hospital Consumer Assessment of Healthcare Providers and Systems (HCAHPS) survey will extend the data collection period from 42 to 49 days, limit supplemental survey items to 12, and require an official Spanish translation for patients.
12. Safety-net hospitals request for information: CMS seeks public input about the unique challenges faced by safety-net hospitals and potential solutions to ensure that uninsured, underinsured, and other vulnerable populations have access to essential services.
13. LTCH quality reporting: CMS proposes several quality-measure updates, including a functional discharge score measure beginning in FY 2025 and reporting the percentage of patients current with Centers for Disease Control and Prevention–recommended COVID vaccinations starting in FY 2026.
14. Commenting period: CMS will accept comments on the proposed rule through June 9.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
CDC backs FDA’s call for second COVID booster for those at high risk
This backs the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization April 18 of the additional shot.
“Following FDA regulatory action, CDC has taken steps to simplify COVID-19 vaccine recommendations and allow more flexibility for people at higher risk who want the option of added protection from additional COVID-19 vaccine doses,” the CDC said in a statement.
The agency is following the recommendations made by its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). While there was no vote, the group reaffirmed its commitment to boosters overall, proposing that all Americans over age 6 who have not had a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 booster vaccine go ahead and get one.
But most others who’ve already had the bivalent shot – which targets the original COVID strain and the two Omicron variants BA.4 and BA.5 – should wait until the fall to get whatever updated vaccine is available.
The panel did carve out exceptions for people over age 65 and those who are immunocompromised because they are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 complications, Evelyn Twentyman, MD, MPH, the lead official in the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Policy Unit, said during the meeting.
People over 65 can now choose to get a second bivalent mRNA booster shot as long as it has been at least 4 months since the last one, she said, and people who are immunocompromised also should have the flexibility to receive one or more additional bivalent boosters at least 2 months after an initial dose.
Regardless of whether someone is unvaccinated, and regardless of how many single-strain COVID vaccines an individual has previously received, they should get a mRNA bivalent shot, Dr. Twentyman said.
If an individual has already received a bivalent mRNA booster – made by either Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna – “your vaccination is complete,” she said. “No doses indicated at this time, come back and see us in autumn of 2023.”
The CDC is trying to encourage more people to get the updated COVID shot, as just 17% of Americans of any age have received a bivalent booster and only 43% of those age 65 and over.
The CDC followed the FDA’s lead in its statement, phasing out the original single-strain COVID vaccine, saying it will no longer be recommended for use in the United States.
‘Unnecessary drama’ over children’s recs
The CDC panel mostly followed the FDA’s guidance on who should get a booster, but many ACIP members expressed consternation and confusion about what was being recommended for children.
For children aged 6 months to 4 years, the CDC will offer tables to help physicians determine how many bivalent doses to give, depending on the child’s vaccination history.
All children those ages should get at least two vaccine doses, one of which is bivalent, Dr. Twentyman said. For children in that age group who have already received a monovalent series and a bivalent dose, “their vaccination is complete,” she said.
For 5-year-olds, the recommendations will be similar if they received a Pfizer monovalent series, but the shot regimen will have to be customized if they had previously received a Moderna shot, because of differences in the dosages.
ACIP member Sarah S. Long, MD, professor of pediatrics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, said that it was unclear why a set age couldn’t be established for COVID-19 vaccination as it had been for other immunizations.
“We picked 60 months for most immunizations in children,” Dr. Long said. “Immunologically there is not a difference between a 4-, a 5- and a 6-year-old.
“There isn’t a reason to have all this unnecessary drama around those ages,” she said, adding that having the different ages would make it harder for pediatricians to appropriately stock vaccines.
Dr. Twentyman said that the CDC would be providing more detailed guidance on its COVID-19 website soon and would be holding a call with health care professionals to discuss the updated recommendations on May 11.
New vaccine by fall
CDC and ACIP members both said they hoped to have an even simpler vaccine schedule by the fall, when it is anticipated that the FDA may have authorized a new, updated bivalent vaccine that targets other COVID variants.
“We all recognize this is a work in progress,” said ACIP Chair Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, acknowledging that there is continued confusion over COVID-19 vaccination.
“The goal really is to try to simplify things over time to be able to help communicate with our provider community, and our patients and families what vaccine is right for them, when do they need it, and how often should they get it,” said Dr. Lee, professor of pediatrics, Stanford (Calif.) University.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com .
This backs the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization April 18 of the additional shot.
“Following FDA regulatory action, CDC has taken steps to simplify COVID-19 vaccine recommendations and allow more flexibility for people at higher risk who want the option of added protection from additional COVID-19 vaccine doses,” the CDC said in a statement.
The agency is following the recommendations made by its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). While there was no vote, the group reaffirmed its commitment to boosters overall, proposing that all Americans over age 6 who have not had a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 booster vaccine go ahead and get one.
But most others who’ve already had the bivalent shot – which targets the original COVID strain and the two Omicron variants BA.4 and BA.5 – should wait until the fall to get whatever updated vaccine is available.
The panel did carve out exceptions for people over age 65 and those who are immunocompromised because they are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 complications, Evelyn Twentyman, MD, MPH, the lead official in the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Policy Unit, said during the meeting.
People over 65 can now choose to get a second bivalent mRNA booster shot as long as it has been at least 4 months since the last one, she said, and people who are immunocompromised also should have the flexibility to receive one or more additional bivalent boosters at least 2 months after an initial dose.
Regardless of whether someone is unvaccinated, and regardless of how many single-strain COVID vaccines an individual has previously received, they should get a mRNA bivalent shot, Dr. Twentyman said.
If an individual has already received a bivalent mRNA booster – made by either Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna – “your vaccination is complete,” she said. “No doses indicated at this time, come back and see us in autumn of 2023.”
The CDC is trying to encourage more people to get the updated COVID shot, as just 17% of Americans of any age have received a bivalent booster and only 43% of those age 65 and over.
The CDC followed the FDA’s lead in its statement, phasing out the original single-strain COVID vaccine, saying it will no longer be recommended for use in the United States.
‘Unnecessary drama’ over children’s recs
The CDC panel mostly followed the FDA’s guidance on who should get a booster, but many ACIP members expressed consternation and confusion about what was being recommended for children.
For children aged 6 months to 4 years, the CDC will offer tables to help physicians determine how many bivalent doses to give, depending on the child’s vaccination history.
All children those ages should get at least two vaccine doses, one of which is bivalent, Dr. Twentyman said. For children in that age group who have already received a monovalent series and a bivalent dose, “their vaccination is complete,” she said.
For 5-year-olds, the recommendations will be similar if they received a Pfizer monovalent series, but the shot regimen will have to be customized if they had previously received a Moderna shot, because of differences in the dosages.
ACIP member Sarah S. Long, MD, professor of pediatrics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, said that it was unclear why a set age couldn’t be established for COVID-19 vaccination as it had been for other immunizations.
“We picked 60 months for most immunizations in children,” Dr. Long said. “Immunologically there is not a difference between a 4-, a 5- and a 6-year-old.
“There isn’t a reason to have all this unnecessary drama around those ages,” she said, adding that having the different ages would make it harder for pediatricians to appropriately stock vaccines.
Dr. Twentyman said that the CDC would be providing more detailed guidance on its COVID-19 website soon and would be holding a call with health care professionals to discuss the updated recommendations on May 11.
New vaccine by fall
CDC and ACIP members both said they hoped to have an even simpler vaccine schedule by the fall, when it is anticipated that the FDA may have authorized a new, updated bivalent vaccine that targets other COVID variants.
“We all recognize this is a work in progress,” said ACIP Chair Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, acknowledging that there is continued confusion over COVID-19 vaccination.
“The goal really is to try to simplify things over time to be able to help communicate with our provider community, and our patients and families what vaccine is right for them, when do they need it, and how often should they get it,” said Dr. Lee, professor of pediatrics, Stanford (Calif.) University.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com .
This backs the Food and Drug Administration’s authorization April 18 of the additional shot.
“Following FDA regulatory action, CDC has taken steps to simplify COVID-19 vaccine recommendations and allow more flexibility for people at higher risk who want the option of added protection from additional COVID-19 vaccine doses,” the CDC said in a statement.
The agency is following the recommendations made by its Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). While there was no vote, the group reaffirmed its commitment to boosters overall, proposing that all Americans over age 6 who have not had a bivalent mRNA COVID-19 booster vaccine go ahead and get one.
But most others who’ve already had the bivalent shot – which targets the original COVID strain and the two Omicron variants BA.4 and BA.5 – should wait until the fall to get whatever updated vaccine is available.
The panel did carve out exceptions for people over age 65 and those who are immunocompromised because they are at higher risk for severe COVID-19 complications, Evelyn Twentyman, MD, MPH, the lead official in the CDC’s COVID-19 Vaccine Policy Unit, said during the meeting.
People over 65 can now choose to get a second bivalent mRNA booster shot as long as it has been at least 4 months since the last one, she said, and people who are immunocompromised also should have the flexibility to receive one or more additional bivalent boosters at least 2 months after an initial dose.
Regardless of whether someone is unvaccinated, and regardless of how many single-strain COVID vaccines an individual has previously received, they should get a mRNA bivalent shot, Dr. Twentyman said.
If an individual has already received a bivalent mRNA booster – made by either Pfizer/BioNTech or Moderna – “your vaccination is complete,” she said. “No doses indicated at this time, come back and see us in autumn of 2023.”
The CDC is trying to encourage more people to get the updated COVID shot, as just 17% of Americans of any age have received a bivalent booster and only 43% of those age 65 and over.
The CDC followed the FDA’s lead in its statement, phasing out the original single-strain COVID vaccine, saying it will no longer be recommended for use in the United States.
‘Unnecessary drama’ over children’s recs
The CDC panel mostly followed the FDA’s guidance on who should get a booster, but many ACIP members expressed consternation and confusion about what was being recommended for children.
For children aged 6 months to 4 years, the CDC will offer tables to help physicians determine how many bivalent doses to give, depending on the child’s vaccination history.
All children those ages should get at least two vaccine doses, one of which is bivalent, Dr. Twentyman said. For children in that age group who have already received a monovalent series and a bivalent dose, “their vaccination is complete,” she said.
For 5-year-olds, the recommendations will be similar if they received a Pfizer monovalent series, but the shot regimen will have to be customized if they had previously received a Moderna shot, because of differences in the dosages.
ACIP member Sarah S. Long, MD, professor of pediatrics, Drexel University, Philadelphia, said that it was unclear why a set age couldn’t be established for COVID-19 vaccination as it had been for other immunizations.
“We picked 60 months for most immunizations in children,” Dr. Long said. “Immunologically there is not a difference between a 4-, a 5- and a 6-year-old.
“There isn’t a reason to have all this unnecessary drama around those ages,” she said, adding that having the different ages would make it harder for pediatricians to appropriately stock vaccines.
Dr. Twentyman said that the CDC would be providing more detailed guidance on its COVID-19 website soon and would be holding a call with health care professionals to discuss the updated recommendations on May 11.
New vaccine by fall
CDC and ACIP members both said they hoped to have an even simpler vaccine schedule by the fall, when it is anticipated that the FDA may have authorized a new, updated bivalent vaccine that targets other COVID variants.
“We all recognize this is a work in progress,” said ACIP Chair Grace M. Lee, MD, MPH, acknowledging that there is continued confusion over COVID-19 vaccination.
“The goal really is to try to simplify things over time to be able to help communicate with our provider community, and our patients and families what vaccine is right for them, when do they need it, and how often should they get it,” said Dr. Lee, professor of pediatrics, Stanford (Calif.) University.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com .
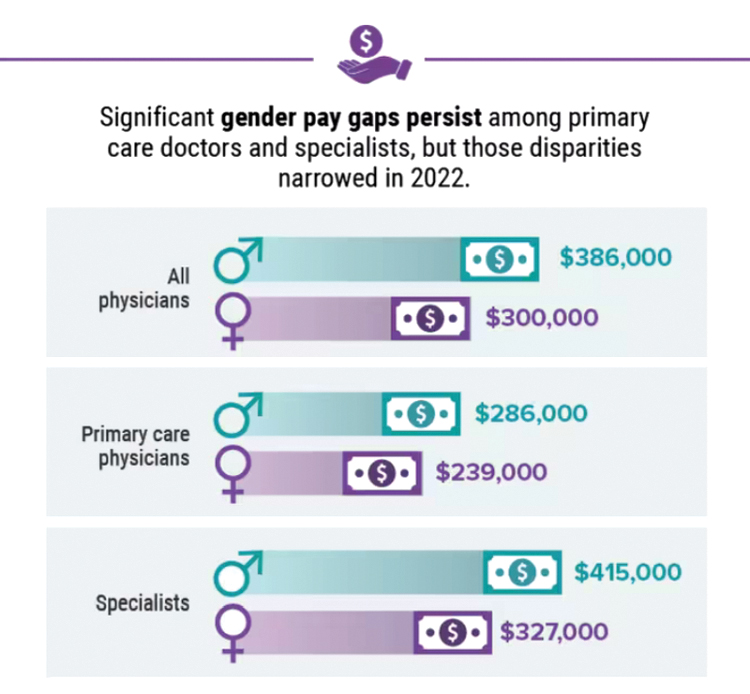
Infographic: Is your compensation rising as fast as your peers?
Did doctors’ salaries continue their zesty postpandemic rise in 2022? Are female physicians making pay gains versus their male counterparts that spark optimism for the future?
reveals which medical specialties pay better than others, and evaluates the current gender pay gap in medicine. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out Your Income vs. Your Peers’: Physician Compensation Report 2023.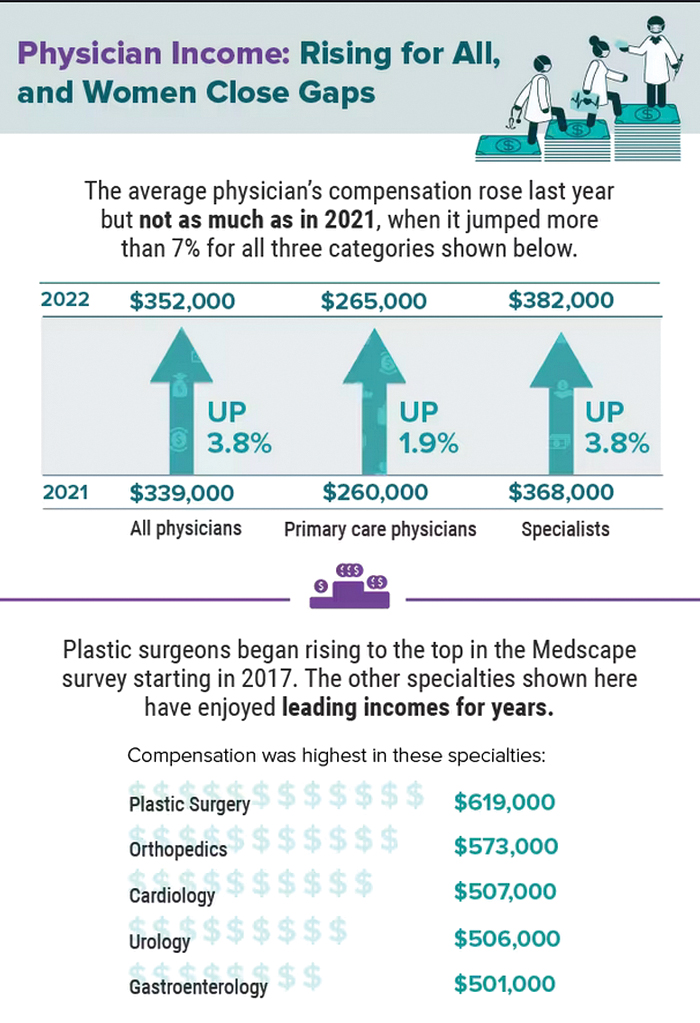
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Did doctors’ salaries continue their zesty postpandemic rise in 2022? Are female physicians making pay gains versus their male counterparts that spark optimism for the future?
reveals which medical specialties pay better than others, and evaluates the current gender pay gap in medicine. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out Your Income vs. Your Peers’: Physician Compensation Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Did doctors’ salaries continue their zesty postpandemic rise in 2022? Are female physicians making pay gains versus their male counterparts that spark optimism for the future?
reveals which medical specialties pay better than others, and evaluates the current gender pay gap in medicine. If you’re interested in delving deeper into the data, check out Your Income vs. Your Peers’: Physician Compensation Report 2023.

A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
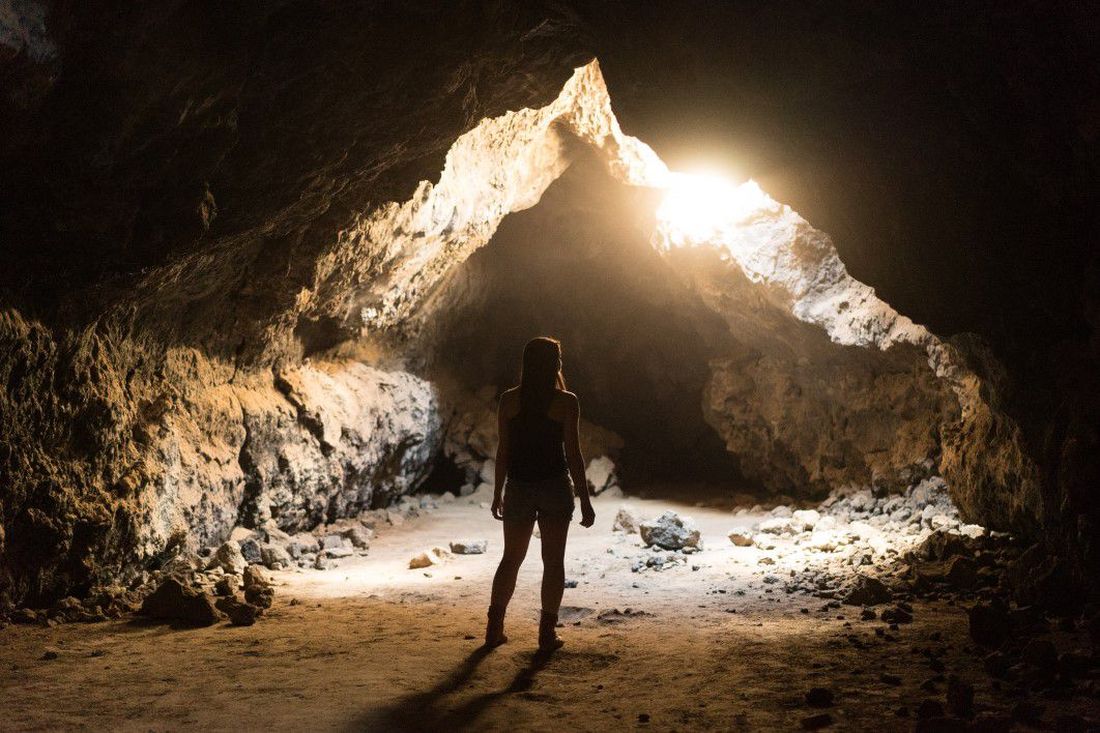
Living the introvert’s dream: Alone for 500 days, but never lonely
Beating the allegory of the cave
When Beatriz Flamini spoke with reporters on April 14, she knew nothing of the previous 18 months. The Russian invasion of Ukraine? Nope. The death of Queen Elizabeth? Also no. But before you make fun of her, she has an excuse. She’s been living under a rock.
As part of an experiment to test how social isolation and disorientation affect a person’s mind, sense of time, and sleeping patterns, Ms. Flamini lived in a 70-meter-deep cave in southern Spain for 500 days, starting in November 2021. Alone. No outside communication with the outside world in any way, though she was constantly monitored by a team of researchers. She also had multiple cameras filming her for an upcoming documentary.
This is a massive step up from the previous record for time spent underground for science: A team of 15 spent 50 days underground in 2021 to similar study of isolation and how it affected circadian rhythms. It’s also almost certainly a world record for time spent underground.
All that time alone certainly sounds like some sort of medieval torture, but Ms. Flamini had access to food, water, and a library of books. Which she made liberal use of, reading at least 60 books during her stay. She also had a panic button in case the isolation became too much or an emergency developed, but she never considered using it.
She lost track of time after 2 months, flies invaded the cave on occasion, and maintaining coherence was occasionally a struggle, but she kept things together very well. In fact, she didn’t even want to leave when her team came for her. She wasn’t even finished with her 61st book.
When she spoke with gathered reporters after the ordeal, words were obviously difficult to come by for her, having not spoken in nearly 18 months, but her mind was clearly still sharp and she had a very important question for everyone gathered around her.
Who’s buying the beer?
We approve of this request.
Staphylococcus and the speed of evolution
Bacteria, we know, are tough little buggers that are hard to see and even harder to get rid of. So hard, actually, that human bodies eventually gave up on the task and decided to just incorporate them into our organ systems. But why are bacteria so hard to eliminate?
Two words: rapid evolution. How rapid? For the first time, scientists have directly observed adaptive evolution by Staphylococcus aureus in a single person’s skin microbiome. That’s how rapid.
For their study, the researchers collected samples from the nostrils, backs of knees, insides of elbows, and forearms of 23 children with eczema. They eventually cultured almost 1,500 unique colonies of S. aureus cells from those samples and sequenced the cells’ genomes.
All that sampling and culturing and sequencing showed that it was rare for a new S. aureus strain to come in and replace the existing strain. “Despite the stability at the lineage level, we see a lot of dynamics at the whole genome level, where new mutations are constantly arising in these bacteria and then spreading throughout the entire body,” Tami D. Lieberman, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, said in a written statement from MIT.
One frequent mutation involved a gene called capD, which encodes an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the capsular polysaccharide – a coating that protects S. aureus from recognition by immune cells. In one patient, four different mutations of capD arose independently in different samples before one variant became dominant and spread over the entire microbiome, MIT reported.
The mutation, which actually results in the loss of the polysaccharide capsule, may allow cells to grow faster than those without the mutation because they have more fuel to power their own growth, the researchers suggested. It’s also possible that loss of the capsule allows S. aureus cells to stick to the skin better because proteins that allow them to adhere to the skin are more exposed.
Dr. Lieberman and her associates hope that these variant-containing cells could be a new target for eczema treatments, but we’re never optimistic when it comes to bacteria. That’s because some of us are old enough to remember evolutionary biologist Stephen Jay Gould, who wrote in his book “Full House”: “Our planet has always been in the ‘Age of Bacteria,’ ever since the first fossils – bacteria, of course – were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are – and always have been – the dominant forms of life on Earth.”
In the distant future, long after humans have left the scene, the bacteria will be laughing at the last rats and cockroaches scurrying across the landscape. Wanna bet?
The height of genetic prediction
Genetics are practically a DNA Scrabble bag. Traits like eye color and hair texture are chosen in the same fashion, based on what gets pulled from our own genetic bag of letters, but what about height? Researchers may now have a way to predict adult height and make it more than just an educated guess.
How? By looking at the genes in our growth plates. The cartilage on the ends of our bones hardens as we age, eventually deciding an individual’s stature. In a recently published study, a research team looked at 600 million cartilage cells linked to maturation and cell growth in mice. Because everything starts with rodents.
After that search identified 145 genes linked to growth plate maturation and formation of the bones, they compared the mouse genes with data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of human height to look for hotspots where the height genes exist in human DNA.
The results showed which genes play a role in deciding height, and the GWAS data also suggested that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height, said the investigators, who hope that earlier interventions can improve outcomes in patients with conditions such as skeletal dysplasia.
So, yeah, you may want to be a little taller or shorter, but the outcome of that particular Scrabble game was determined when your parents, you know, dropped the letters in the bag.
Beating the allegory of the cave
When Beatriz Flamini spoke with reporters on April 14, she knew nothing of the previous 18 months. The Russian invasion of Ukraine? Nope. The death of Queen Elizabeth? Also no. But before you make fun of her, she has an excuse. She’s been living under a rock.
As part of an experiment to test how social isolation and disorientation affect a person’s mind, sense of time, and sleeping patterns, Ms. Flamini lived in a 70-meter-deep cave in southern Spain for 500 days, starting in November 2021. Alone. No outside communication with the outside world in any way, though she was constantly monitored by a team of researchers. She also had multiple cameras filming her for an upcoming documentary.
This is a massive step up from the previous record for time spent underground for science: A team of 15 spent 50 days underground in 2021 to similar study of isolation and how it affected circadian rhythms. It’s also almost certainly a world record for time spent underground.
All that time alone certainly sounds like some sort of medieval torture, but Ms. Flamini had access to food, water, and a library of books. Which she made liberal use of, reading at least 60 books during her stay. She also had a panic button in case the isolation became too much or an emergency developed, but she never considered using it.
She lost track of time after 2 months, flies invaded the cave on occasion, and maintaining coherence was occasionally a struggle, but she kept things together very well. In fact, she didn’t even want to leave when her team came for her. She wasn’t even finished with her 61st book.
When she spoke with gathered reporters after the ordeal, words were obviously difficult to come by for her, having not spoken in nearly 18 months, but her mind was clearly still sharp and she had a very important question for everyone gathered around her.
Who’s buying the beer?
We approve of this request.
Staphylococcus and the speed of evolution
Bacteria, we know, are tough little buggers that are hard to see and even harder to get rid of. So hard, actually, that human bodies eventually gave up on the task and decided to just incorporate them into our organ systems. But why are bacteria so hard to eliminate?
Two words: rapid evolution. How rapid? For the first time, scientists have directly observed adaptive evolution by Staphylococcus aureus in a single person’s skin microbiome. That’s how rapid.
For their study, the researchers collected samples from the nostrils, backs of knees, insides of elbows, and forearms of 23 children with eczema. They eventually cultured almost 1,500 unique colonies of S. aureus cells from those samples and sequenced the cells’ genomes.
All that sampling and culturing and sequencing showed that it was rare for a new S. aureus strain to come in and replace the existing strain. “Despite the stability at the lineage level, we see a lot of dynamics at the whole genome level, where new mutations are constantly arising in these bacteria and then spreading throughout the entire body,” Tami D. Lieberman, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, said in a written statement from MIT.
One frequent mutation involved a gene called capD, which encodes an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the capsular polysaccharide – a coating that protects S. aureus from recognition by immune cells. In one patient, four different mutations of capD arose independently in different samples before one variant became dominant and spread over the entire microbiome, MIT reported.
The mutation, which actually results in the loss of the polysaccharide capsule, may allow cells to grow faster than those without the mutation because they have more fuel to power their own growth, the researchers suggested. It’s also possible that loss of the capsule allows S. aureus cells to stick to the skin better because proteins that allow them to adhere to the skin are more exposed.
Dr. Lieberman and her associates hope that these variant-containing cells could be a new target for eczema treatments, but we’re never optimistic when it comes to bacteria. That’s because some of us are old enough to remember evolutionary biologist Stephen Jay Gould, who wrote in his book “Full House”: “Our planet has always been in the ‘Age of Bacteria,’ ever since the first fossils – bacteria, of course – were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are – and always have been – the dominant forms of life on Earth.”
In the distant future, long after humans have left the scene, the bacteria will be laughing at the last rats and cockroaches scurrying across the landscape. Wanna bet?
The height of genetic prediction
Genetics are practically a DNA Scrabble bag. Traits like eye color and hair texture are chosen in the same fashion, based on what gets pulled from our own genetic bag of letters, but what about height? Researchers may now have a way to predict adult height and make it more than just an educated guess.
How? By looking at the genes in our growth plates. The cartilage on the ends of our bones hardens as we age, eventually deciding an individual’s stature. In a recently published study, a research team looked at 600 million cartilage cells linked to maturation and cell growth in mice. Because everything starts with rodents.
After that search identified 145 genes linked to growth plate maturation and formation of the bones, they compared the mouse genes with data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of human height to look for hotspots where the height genes exist in human DNA.
The results showed which genes play a role in deciding height, and the GWAS data also suggested that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height, said the investigators, who hope that earlier interventions can improve outcomes in patients with conditions such as skeletal dysplasia.
So, yeah, you may want to be a little taller or shorter, but the outcome of that particular Scrabble game was determined when your parents, you know, dropped the letters in the bag.
Beating the allegory of the cave
When Beatriz Flamini spoke with reporters on April 14, she knew nothing of the previous 18 months. The Russian invasion of Ukraine? Nope. The death of Queen Elizabeth? Also no. But before you make fun of her, she has an excuse. She’s been living under a rock.
As part of an experiment to test how social isolation and disorientation affect a person’s mind, sense of time, and sleeping patterns, Ms. Flamini lived in a 70-meter-deep cave in southern Spain for 500 days, starting in November 2021. Alone. No outside communication with the outside world in any way, though she was constantly monitored by a team of researchers. She also had multiple cameras filming her for an upcoming documentary.
This is a massive step up from the previous record for time spent underground for science: A team of 15 spent 50 days underground in 2021 to similar study of isolation and how it affected circadian rhythms. It’s also almost certainly a world record for time spent underground.
All that time alone certainly sounds like some sort of medieval torture, but Ms. Flamini had access to food, water, and a library of books. Which she made liberal use of, reading at least 60 books during her stay. She also had a panic button in case the isolation became too much or an emergency developed, but she never considered using it.
She lost track of time after 2 months, flies invaded the cave on occasion, and maintaining coherence was occasionally a struggle, but she kept things together very well. In fact, she didn’t even want to leave when her team came for her. She wasn’t even finished with her 61st book.
When she spoke with gathered reporters after the ordeal, words were obviously difficult to come by for her, having not spoken in nearly 18 months, but her mind was clearly still sharp and she had a very important question for everyone gathered around her.
Who’s buying the beer?
We approve of this request.
Staphylococcus and the speed of evolution
Bacteria, we know, are tough little buggers that are hard to see and even harder to get rid of. So hard, actually, that human bodies eventually gave up on the task and decided to just incorporate them into our organ systems. But why are bacteria so hard to eliminate?
Two words: rapid evolution. How rapid? For the first time, scientists have directly observed adaptive evolution by Staphylococcus aureus in a single person’s skin microbiome. That’s how rapid.
For their study, the researchers collected samples from the nostrils, backs of knees, insides of elbows, and forearms of 23 children with eczema. They eventually cultured almost 1,500 unique colonies of S. aureus cells from those samples and sequenced the cells’ genomes.
All that sampling and culturing and sequencing showed that it was rare for a new S. aureus strain to come in and replace the existing strain. “Despite the stability at the lineage level, we see a lot of dynamics at the whole genome level, where new mutations are constantly arising in these bacteria and then spreading throughout the entire body,” Tami D. Lieberman, PhD, of the Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, said in a written statement from MIT.
One frequent mutation involved a gene called capD, which encodes an enzyme necessary for synthesizing the capsular polysaccharide – a coating that protects S. aureus from recognition by immune cells. In one patient, four different mutations of capD arose independently in different samples before one variant became dominant and spread over the entire microbiome, MIT reported.
The mutation, which actually results in the loss of the polysaccharide capsule, may allow cells to grow faster than those without the mutation because they have more fuel to power their own growth, the researchers suggested. It’s also possible that loss of the capsule allows S. aureus cells to stick to the skin better because proteins that allow them to adhere to the skin are more exposed.
Dr. Lieberman and her associates hope that these variant-containing cells could be a new target for eczema treatments, but we’re never optimistic when it comes to bacteria. That’s because some of us are old enough to remember evolutionary biologist Stephen Jay Gould, who wrote in his book “Full House”: “Our planet has always been in the ‘Age of Bacteria,’ ever since the first fossils – bacteria, of course – were entombed in rocks more than 3 billion years ago. On any possible, reasonable or fair criterion, bacteria are – and always have been – the dominant forms of life on Earth.”
In the distant future, long after humans have left the scene, the bacteria will be laughing at the last rats and cockroaches scurrying across the landscape. Wanna bet?
The height of genetic prediction
Genetics are practically a DNA Scrabble bag. Traits like eye color and hair texture are chosen in the same fashion, based on what gets pulled from our own genetic bag of letters, but what about height? Researchers may now have a way to predict adult height and make it more than just an educated guess.
How? By looking at the genes in our growth plates. The cartilage on the ends of our bones hardens as we age, eventually deciding an individual’s stature. In a recently published study, a research team looked at 600 million cartilage cells linked to maturation and cell growth in mice. Because everything starts with rodents.
After that search identified 145 genes linked to growth plate maturation and formation of the bones, they compared the mouse genes with data from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) of human height to look for hotspots where the height genes exist in human DNA.
The results showed which genes play a role in deciding height, and the GWAS data also suggested that genetic changes affecting cartilage cell maturation may strongly influence adult height, said the investigators, who hope that earlier interventions can improve outcomes in patients with conditions such as skeletal dysplasia.
So, yeah, you may want to be a little taller or shorter, but the outcome of that particular Scrabble game was determined when your parents, you know, dropped the letters in the bag.
Rabies: How to respond to parents’ questions
When most families hear the word rabies, they envision a dog foaming at the mouth and think about receiving multiple painful, often intra-abdominal injections. However, the epidemiology of rabies has changed in the United States. Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) may not always be indicated and for certain persons preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is available and recommended.
Rabies is a Lyssavirus that is transmitted through saliva most often from the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Sometimes it’s via direct contact with mucous membranes. Although rare, cases have been described in which an undiagnosed donor passed the virus via transplant to recipients and four cases of aerosolized transmission were documented in two spelunkers and two laboratory technicians working with the virus. Worldwide it’s estimated that rabies causes 59,000 deaths annually.
Most cases (98%) are secondary to canine rabies. Prior to 1960, dogs were the major reservoir in the United States; however, after introduction of leash laws and animal vaccination in 1947, there was a drastic decline in cases caused by the canine rabies virus variant (CRVV). By 2004, CRVV was eliminated in the United States.
However, the proportion of strains associated with wildlife including raccoons, skunks, foxes, bats, coyotes, and mongoose now account for most of the cases in humans. Wildlife rabies is found in all states except Hawaii. Between 1960 and 2018, 89 cases were acquired in the United States and 62 (70%) were from bat exposure. Dog bites acquired during international travel were the cause of 36 cases.
Once signs and symptoms of disease develop there is no treatment. Regardless of the species variant, rabies virus infection is fatal in over 99% of cases. However, disease can be prevented with prompt initiation of PEP, which includes administration of rabies immune globulin (RIG) and rabies vaccine. Let’s look at a few different scenarios.
1. A delivery person is bitten by your neighbor’s dog while making a delivery. He was told to get rabies vaccine. What should we advise?
Canine rabies has been eliminated in the United States. However, unvaccinated canines can acquire rabies from wildlife. In this situation, you can determine the immunization status of the dog. Contact your local/state health department to assist with enforcement and management. Bites by cats and ferrets should be managed similarly.
Healthy dog:
1. Observe for 10 days.
2. PEP is not indicated unless the animal develops signs/symptoms of rabies. Then euthanize and begin PEP.
Dog appears rabid or suspected to be rabid:
1. Begin PEP.
2. Animal should be euthanized. If immunofluorescent test is negative discontinue PEP.
Dog unavailable:
Contact local/state health department. They are more familiar with rabies surveillance data.
2. Patient relocating to Malaysia for 3-4 years. Rabies PrEP was recommended but the family wants your opinion before receiving the vaccine. What would you advise?
Canine rabies is felt to be the primary cause of rabies outside of the United States. Canines are not routinely vaccinated in many foreign destinations, and the availability of RIG and rabies vaccine is not guaranteed in developing countries. As noted above, dog bites during international travel accounted for 28% of U.S. cases between 1960 and 2018.
In May 2022 recommendations for a modified two-dose PrEP schedule was published that identifies five risk groups and includes specific timing for checking rabies titers. The third rabies dose can now be administered up until year 3 (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 May 6;71[18]:619-27). For individuals relocating to countries where CRVV is present, I prefer the traditional three-dose PrEP schedule administered between 21 and 28 days. However, we now have options. If exposure occurs any time after completion of a three-dose PrEP series or within 3 years after completion of a two-dose PrEP series, RIG would not be required. All patients would receive two doses of rabies vaccine (days 0, 3). If exposure occurs after 3 years in a person who received two doses of PrEP who did not have documentation of a protective rabies titer (> 5 IU/mL), treatment will include RIG plus four doses of vaccine (days 0, 3, 7, 14).
For this relocating patient, supporting PrEP would be strongly recommended.
3. A mother tells you she sees bats flying around her home at night and a few have even gotten into the home. This morning she saw one in her child’s room. He was still sleeping. Is there anything she needs to do?
Bats have become the predominant source of rabies in the United States. In addition to the cases noted above, three fatal cases occurred between Sept. 28 and Nov. 10, 2021, after bat exposures in August 2021 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 7;71:31-2). All had recognized contact with a bat 3-7 weeks prior to onset of symptoms and died 2-3 weeks after symptom onset. One declined PEP and the other two did not realize the risk for rabies from their exposure or did not notice a scratch or bite. Bites from bats may be small and unnoticed. Exposure to a bat in a closed room while sleeping is considered an exposure. Hawaii is the only state not reporting rabid bats.
PEP is recommended for her child. She should identify potential areas bats may enter the home and seal them in addition to removal of any bat roosts.
4. A parent realizes a house guest has been feeding raccoons in the backyard. What’s your response?
While bat rabies is the predominant variant associated with disease in the United States, as illustrated in Figure 1, other species of wildlife including raccoons are a major source of rabies. The geographic spread of the raccoon variant of rabies has been limited by oral vaccination via bait. In the situation noted here, the raccoons have returned because food was being offered thus increasing the families chance of a potential rabies exposure. Wildlife including skunks, raccoons, coyotes, foxes, and mongooses are always considered rabid until proven negative by laboratory testing.
You recommend to stop feeding wildlife and never to approach them. Have them contact the local rabies control unit and/or state wildlife services to assist with removal of the raccoons. Depending on the locale, pest control may be required at the owners expense. Inform the family to seek PEP if anyone is bitten or scratched by the raccoons.
As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 55,000 residents receive PEP annually with health-associated expenditures including diagnostics, prevention, and control estimated between $245 and $510 million annually. Rabies is one of the most fatal diseases that can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals, maintenance of high immunization rates in pets, and keeping people informed of potential sources including bats. One can’t determine if an animal has rabies by looking at it. Rabies remains an urgent disease that we have to remember to address with our patients and their families. For additional information go to www.CDC.gov/rabies.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
When most families hear the word rabies, they envision a dog foaming at the mouth and think about receiving multiple painful, often intra-abdominal injections. However, the epidemiology of rabies has changed in the United States. Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) may not always be indicated and for certain persons preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is available and recommended.
Rabies is a Lyssavirus that is transmitted through saliva most often from the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Sometimes it’s via direct contact with mucous membranes. Although rare, cases have been described in which an undiagnosed donor passed the virus via transplant to recipients and four cases of aerosolized transmission were documented in two spelunkers and two laboratory technicians working with the virus. Worldwide it’s estimated that rabies causes 59,000 deaths annually.

Most cases (98%) are secondary to canine rabies. Prior to 1960, dogs were the major reservoir in the United States; however, after introduction of leash laws and animal vaccination in 1947, there was a drastic decline in cases caused by the canine rabies virus variant (CRVV). By 2004, CRVV was eliminated in the United States.
However, the proportion of strains associated with wildlife including raccoons, skunks, foxes, bats, coyotes, and mongoose now account for most of the cases in humans. Wildlife rabies is found in all states except Hawaii. Between 1960 and 2018, 89 cases were acquired in the United States and 62 (70%) were from bat exposure. Dog bites acquired during international travel were the cause of 36 cases.
Once signs and symptoms of disease develop there is no treatment. Regardless of the species variant, rabies virus infection is fatal in over 99% of cases. However, disease can be prevented with prompt initiation of PEP, which includes administration of rabies immune globulin (RIG) and rabies vaccine. Let’s look at a few different scenarios.
1. A delivery person is bitten by your neighbor’s dog while making a delivery. He was told to get rabies vaccine. What should we advise?
Canine rabies has been eliminated in the United States. However, unvaccinated canines can acquire rabies from wildlife. In this situation, you can determine the immunization status of the dog. Contact your local/state health department to assist with enforcement and management. Bites by cats and ferrets should be managed similarly.
Healthy dog:
1. Observe for 10 days.
2. PEP is not indicated unless the animal develops signs/symptoms of rabies. Then euthanize and begin PEP.
Dog appears rabid or suspected to be rabid:
1. Begin PEP.
2. Animal should be euthanized. If immunofluorescent test is negative discontinue PEP.
Dog unavailable:
Contact local/state health department. They are more familiar with rabies surveillance data.
2. Patient relocating to Malaysia for 3-4 years. Rabies PrEP was recommended but the family wants your opinion before receiving the vaccine. What would you advise?
Canine rabies is felt to be the primary cause of rabies outside of the United States. Canines are not routinely vaccinated in many foreign destinations, and the availability of RIG and rabies vaccine is not guaranteed in developing countries. As noted above, dog bites during international travel accounted for 28% of U.S. cases between 1960 and 2018.
In May 2022 recommendations for a modified two-dose PrEP schedule was published that identifies five risk groups and includes specific timing for checking rabies titers. The third rabies dose can now be administered up until year 3 (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 May 6;71[18]:619-27). For individuals relocating to countries where CRVV is present, I prefer the traditional three-dose PrEP schedule administered between 21 and 28 days. However, we now have options. If exposure occurs any time after completion of a three-dose PrEP series or within 3 years after completion of a two-dose PrEP series, RIG would not be required. All patients would receive two doses of rabies vaccine (days 0, 3). If exposure occurs after 3 years in a person who received two doses of PrEP who did not have documentation of a protective rabies titer (> 5 IU/mL), treatment will include RIG plus four doses of vaccine (days 0, 3, 7, 14).
For this relocating patient, supporting PrEP would be strongly recommended.
3. A mother tells you she sees bats flying around her home at night and a few have even gotten into the home. This morning she saw one in her child’s room. He was still sleeping. Is there anything she needs to do?
Bats have become the predominant source of rabies in the United States. In addition to the cases noted above, three fatal cases occurred between Sept. 28 and Nov. 10, 2021, after bat exposures in August 2021 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 7;71:31-2). All had recognized contact with a bat 3-7 weeks prior to onset of symptoms and died 2-3 weeks after symptom onset. One declined PEP and the other two did not realize the risk for rabies from their exposure or did not notice a scratch or bite. Bites from bats may be small and unnoticed. Exposure to a bat in a closed room while sleeping is considered an exposure. Hawaii is the only state not reporting rabid bats.
PEP is recommended for her child. She should identify potential areas bats may enter the home and seal them in addition to removal of any bat roosts.
4. A parent realizes a house guest has been feeding raccoons in the backyard. What’s your response?
While bat rabies is the predominant variant associated with disease in the United States, as illustrated in Figure 1, other species of wildlife including raccoons are a major source of rabies. The geographic spread of the raccoon variant of rabies has been limited by oral vaccination via bait. In the situation noted here, the raccoons have returned because food was being offered thus increasing the families chance of a potential rabies exposure. Wildlife including skunks, raccoons, coyotes, foxes, and mongooses are always considered rabid until proven negative by laboratory testing.

You recommend to stop feeding wildlife and never to approach them. Have them contact the local rabies control unit and/or state wildlife services to assist with removal of the raccoons. Depending on the locale, pest control may be required at the owners expense. Inform the family to seek PEP if anyone is bitten or scratched by the raccoons.
As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 55,000 residents receive PEP annually with health-associated expenditures including diagnostics, prevention, and control estimated between $245 and $510 million annually. Rabies is one of the most fatal diseases that can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals, maintenance of high immunization rates in pets, and keeping people informed of potential sources including bats. One can’t determine if an animal has rabies by looking at it. Rabies remains an urgent disease that we have to remember to address with our patients and their families. For additional information go to www.CDC.gov/rabies.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
When most families hear the word rabies, they envision a dog foaming at the mouth and think about receiving multiple painful, often intra-abdominal injections. However, the epidemiology of rabies has changed in the United States. Postexposure prophylaxis (PEP) may not always be indicated and for certain persons preexposure prophylaxis (PrEP) is available and recommended.
Rabies is a Lyssavirus that is transmitted through saliva most often from the bite or scratch of an infected animal. Sometimes it’s via direct contact with mucous membranes. Although rare, cases have been described in which an undiagnosed donor passed the virus via transplant to recipients and four cases of aerosolized transmission were documented in two spelunkers and two laboratory technicians working with the virus. Worldwide it’s estimated that rabies causes 59,000 deaths annually.

Most cases (98%) are secondary to canine rabies. Prior to 1960, dogs were the major reservoir in the United States; however, after introduction of leash laws and animal vaccination in 1947, there was a drastic decline in cases caused by the canine rabies virus variant (CRVV). By 2004, CRVV was eliminated in the United States.
However, the proportion of strains associated with wildlife including raccoons, skunks, foxes, bats, coyotes, and mongoose now account for most of the cases in humans. Wildlife rabies is found in all states except Hawaii. Between 1960 and 2018, 89 cases were acquired in the United States and 62 (70%) were from bat exposure. Dog bites acquired during international travel were the cause of 36 cases.
Once signs and symptoms of disease develop there is no treatment. Regardless of the species variant, rabies virus infection is fatal in over 99% of cases. However, disease can be prevented with prompt initiation of PEP, which includes administration of rabies immune globulin (RIG) and rabies vaccine. Let’s look at a few different scenarios.
1. A delivery person is bitten by your neighbor’s dog while making a delivery. He was told to get rabies vaccine. What should we advise?
Canine rabies has been eliminated in the United States. However, unvaccinated canines can acquire rabies from wildlife. In this situation, you can determine the immunization status of the dog. Contact your local/state health department to assist with enforcement and management. Bites by cats and ferrets should be managed similarly.
Healthy dog:
1. Observe for 10 days.
2. PEP is not indicated unless the animal develops signs/symptoms of rabies. Then euthanize and begin PEP.
Dog appears rabid or suspected to be rabid:
1. Begin PEP.
2. Animal should be euthanized. If immunofluorescent test is negative discontinue PEP.
Dog unavailable:
Contact local/state health department. They are more familiar with rabies surveillance data.
2. Patient relocating to Malaysia for 3-4 years. Rabies PrEP was recommended but the family wants your opinion before receiving the vaccine. What would you advise?
Canine rabies is felt to be the primary cause of rabies outside of the United States. Canines are not routinely vaccinated in many foreign destinations, and the availability of RIG and rabies vaccine is not guaranteed in developing countries. As noted above, dog bites during international travel accounted for 28% of U.S. cases between 1960 and 2018.
In May 2022 recommendations for a modified two-dose PrEP schedule was published that identifies five risk groups and includes specific timing for checking rabies titers. The third rabies dose can now be administered up until year 3 (Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 May 6;71[18]:619-27). For individuals relocating to countries where CRVV is present, I prefer the traditional three-dose PrEP schedule administered between 21 and 28 days. However, we now have options. If exposure occurs any time after completion of a three-dose PrEP series or within 3 years after completion of a two-dose PrEP series, RIG would not be required. All patients would receive two doses of rabies vaccine (days 0, 3). If exposure occurs after 3 years in a person who received two doses of PrEP who did not have documentation of a protective rabies titer (> 5 IU/mL), treatment will include RIG plus four doses of vaccine (days 0, 3, 7, 14).
For this relocating patient, supporting PrEP would be strongly recommended.
3. A mother tells you she sees bats flying around her home at night and a few have even gotten into the home. This morning she saw one in her child’s room. He was still sleeping. Is there anything she needs to do?
Bats have become the predominant source of rabies in the United States. In addition to the cases noted above, three fatal cases occurred between Sept. 28 and Nov. 10, 2021, after bat exposures in August 2021 (MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2022 Jan 7;71:31-2). All had recognized contact with a bat 3-7 weeks prior to onset of symptoms and died 2-3 weeks after symptom onset. One declined PEP and the other two did not realize the risk for rabies from their exposure or did not notice a scratch or bite. Bites from bats may be small and unnoticed. Exposure to a bat in a closed room while sleeping is considered an exposure. Hawaii is the only state not reporting rabid bats.
PEP is recommended for her child. She should identify potential areas bats may enter the home and seal them in addition to removal of any bat roosts.
4. A parent realizes a house guest has been feeding raccoons in the backyard. What’s your response?
While bat rabies is the predominant variant associated with disease in the United States, as illustrated in Figure 1, other species of wildlife including raccoons are a major source of rabies. The geographic spread of the raccoon variant of rabies has been limited by oral vaccination via bait. In the situation noted here, the raccoons have returned because food was being offered thus increasing the families chance of a potential rabies exposure. Wildlife including skunks, raccoons, coyotes, foxes, and mongooses are always considered rabid until proven negative by laboratory testing.

You recommend to stop feeding wildlife and never to approach them. Have them contact the local rabies control unit and/or state wildlife services to assist with removal of the raccoons. Depending on the locale, pest control may be required at the owners expense. Inform the family to seek PEP if anyone is bitten or scratched by the raccoons.
As per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, about 55,000 residents receive PEP annually with health-associated expenditures including diagnostics, prevention, and control estimated between $245 and $510 million annually. Rabies is one of the most fatal diseases that can be prevented by avoiding contact with wild animals, maintenance of high immunization rates in pets, and keeping people informed of potential sources including bats. One can’t determine if an animal has rabies by looking at it. Rabies remains an urgent disease that we have to remember to address with our patients and their families. For additional information go to www.CDC.gov/rabies.
Dr. Word is a pediatric infectious disease specialist and director of the Houston Travel Medicine Clinic. She has no relevant financial disclosures.
Physicians may retire en masse soon. What does that mean for medicine?
The double whammy of pandemic burnout and the aging of baby boomer physicians has, indeed, the makings of some scary headlines. A recent survey by Elsevier Health predicts that up to 75% of health care workers will leave the profession by 2025. And a 2020 study conducted by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) projected a shortfall of up to 139,000 physicians by 2033.
“We’ve paid a lot of attention to physician retirement,” says Michael Dill, AAMC’s director of workforce studies. “It’s a significant concern in terms of whether we have an adequate supply of physicians in the U.S. to meet our nation’s medical care needs. Anyone who thinks otherwise is incorrect.”
To Mr. Dill,
“The physician workforce as a whole is aging,” he said. “Close to a quarter of the physicians in the U.S. are 65 and over. So, you don’t need any extraordinary events driving retirement in order for retirement to be a real phenomenon of which we should all be concerned.”
And, although Mr. Dill said there aren’t any data to suggest that doctors in rural or urban areas are retiring faster than in the suburbs, that doesn’t mean retirement will have the same impact depending on where patients live.
“If you live in a rural area with one small practice in town and that physician retires, there goes the entirety of the physician supply,” he said. “In a major metro area, that’s not as big a deal.”
Why younger doctors are fast-tracking retirement
Fernando Mendoza, MD, 54, a pediatric emergency department physician in Miami, worries that physicians are getting so bogged down by paperwork that this may lead to even more doctors, at younger ages, leaving the profession.
“I love taking care of kids, but there’s going to be a cost to doing your work when you’re spending as much time as we need to spend on charts, pharmacy requests, and making sure all of the Medicare and Medicaid compliance issues are worked out.”
These stressors may compel some younger doctors to consider carving out a second career or fast-track younger physicians toward retirement.
“A medical degree carries a lot of weight, which helps when pivoting,” said Dr. Mendoza, who launched Scrivas, a Miami-based medical scribe agency, to help reduce the paperwork workload for physicians. “It might be that a doctor wants to get involved in the acquisition of medical equipment, or maybe they can focus on their investments. Either way, by leaving medicine, they’re not dealing with the hassle and churn-and-burn of seeing patients.”
What this means for patients
The time is now to stem the upcoming tide of retirement, said Mr. Dill. But the challenges remain daunting. For starters, the country needs more physicians trained now – but it will take years to replace those baby boomer doctors ready to hang up their white coats.
The medical profession also needs to find ways to support physicians who spend their days juggling an endless array of responsibilities, he said.
The AAMC study found that patients already feel the physician shortfall. Their public opinion research in 2019 said 35% of patients had trouble finding a physician over the past 2 or 3 years, up 10 percentage points since they asked the question in 2015.
Moreover, according to the report, the over-65 population is expected to grow by 45.1%, leaving a specialty care gap because older people generally have more complicated health cases that require specialists. In addition, physician burnout may lead more physicians under 65 to retire much earlier than expected.
Changes in how medicine is practiced, telemedicine care, and medical education – such as disruption of classes or clinical rotations, regulatory changes, and a lack of interest in certain specialties – could also be affected by a mass physician retirement.
What can we do about mass retirement?
The AAMC reports in “The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections From 2019 to 2034” that federally funded GME support is in the works to train 15,000 physicians per year, with 3,000 new residency slots added per year over 5 years. The proposed model will add 3,750 new physicians each year beginning in 2026.
Other efforts include increasing use of APRNs and PAs, whose population is estimated to more than double by 2034, improve population health through preventive care, increase equity in health outcomes, and improve access and affordable care.
Removing licensing barriers for immigrant doctors can also help alleviate the shortage.
“We need to find better ways to leverage the entirety of the health care team so that not as much falls on physicians,” Mr. Dill said. “It’s also imperative that we focus on ways to support physician wellness and allow physicians to remain active in the field, but at a reduced rate.”
That’s precisely what Marie Brown, MD, director of practice redesign at the American Medical Association, is seeing nationwide. Cutting back their hours is not only trending, but it’s also helping doctors cope with burnout.
“We’re seeing physicians take a 20% or more cut in salary in order to decrease their burden,” she said. “They’ll spend 4 days on clinical time with patients so that on that fifth ‘day off,’ they’re doing the paperwork and documentation they need to do so they don’t compromise care on the other 4 days of the week.”
And this may only be a Band-Aid solution, she fears.
“If a physician is spending 3 hours a day doing unnecessary work that could be done by another team member, that’s contributing to burnout,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s no surprise that they’ll want to escape and retire if they’re in a financial situation to do so.”
“I advocate negotiating within your organization so you’re doing more of what you like, such as mentoring or running a residency, and less of what you don’t, while cutting back from full-time to something less than full-time while maintaining benefits,” said Joel Greenwald, MD, a certified financial planner in Minneapolis, who specializes in helping physicians manage their financial affairs.
“Falling into the ‘like less’ bucket are usually things like working weekends and taking calls,” he said.
“This benefits everyone on a large scale because those doctors who find things they enjoy are generally working to a later age but working less hard,” he said. “Remaining comfortably and happily gainfully employed for a longer period, even if you’re not working full-time, has a very powerful effect on your financial planning, and you’ll avoid the risk of running out of money.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The double whammy of pandemic burnout and the aging of baby boomer physicians has, indeed, the makings of some scary headlines. A recent survey by Elsevier Health predicts that up to 75% of health care workers will leave the profession by 2025. And a 2020 study conducted by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) projected a shortfall of up to 139,000 physicians by 2033.
“We’ve paid a lot of attention to physician retirement,” says Michael Dill, AAMC’s director of workforce studies. “It’s a significant concern in terms of whether we have an adequate supply of physicians in the U.S. to meet our nation’s medical care needs. Anyone who thinks otherwise is incorrect.”
To Mr. Dill,
“The physician workforce as a whole is aging,” he said. “Close to a quarter of the physicians in the U.S. are 65 and over. So, you don’t need any extraordinary events driving retirement in order for retirement to be a real phenomenon of which we should all be concerned.”
And, although Mr. Dill said there aren’t any data to suggest that doctors in rural or urban areas are retiring faster than in the suburbs, that doesn’t mean retirement will have the same impact depending on where patients live.
“If you live in a rural area with one small practice in town and that physician retires, there goes the entirety of the physician supply,” he said. “In a major metro area, that’s not as big a deal.”
Why younger doctors are fast-tracking retirement
Fernando Mendoza, MD, 54, a pediatric emergency department physician in Miami, worries that physicians are getting so bogged down by paperwork that this may lead to even more doctors, at younger ages, leaving the profession.
“I love taking care of kids, but there’s going to be a cost to doing your work when you’re spending as much time as we need to spend on charts, pharmacy requests, and making sure all of the Medicare and Medicaid compliance issues are worked out.”
These stressors may compel some younger doctors to consider carving out a second career or fast-track younger physicians toward retirement.
“A medical degree carries a lot of weight, which helps when pivoting,” said Dr. Mendoza, who launched Scrivas, a Miami-based medical scribe agency, to help reduce the paperwork workload for physicians. “It might be that a doctor wants to get involved in the acquisition of medical equipment, or maybe they can focus on their investments. Either way, by leaving medicine, they’re not dealing with the hassle and churn-and-burn of seeing patients.”
What this means for patients
The time is now to stem the upcoming tide of retirement, said Mr. Dill. But the challenges remain daunting. For starters, the country needs more physicians trained now – but it will take years to replace those baby boomer doctors ready to hang up their white coats.
The medical profession also needs to find ways to support physicians who spend their days juggling an endless array of responsibilities, he said.
The AAMC study found that patients already feel the physician shortfall. Their public opinion research in 2019 said 35% of patients had trouble finding a physician over the past 2 or 3 years, up 10 percentage points since they asked the question in 2015.
Moreover, according to the report, the over-65 population is expected to grow by 45.1%, leaving a specialty care gap because older people generally have more complicated health cases that require specialists. In addition, physician burnout may lead more physicians under 65 to retire much earlier than expected.
Changes in how medicine is practiced, telemedicine care, and medical education – such as disruption of classes or clinical rotations, regulatory changes, and a lack of interest in certain specialties – could also be affected by a mass physician retirement.
What can we do about mass retirement?
The AAMC reports in “The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections From 2019 to 2034” that federally funded GME support is in the works to train 15,000 physicians per year, with 3,000 new residency slots added per year over 5 years. The proposed model will add 3,750 new physicians each year beginning in 2026.
Other efforts include increasing use of APRNs and PAs, whose population is estimated to more than double by 2034, improve population health through preventive care, increase equity in health outcomes, and improve access and affordable care.
Removing licensing barriers for immigrant doctors can also help alleviate the shortage.
“We need to find better ways to leverage the entirety of the health care team so that not as much falls on physicians,” Mr. Dill said. “It’s also imperative that we focus on ways to support physician wellness and allow physicians to remain active in the field, but at a reduced rate.”
That’s precisely what Marie Brown, MD, director of practice redesign at the American Medical Association, is seeing nationwide. Cutting back their hours is not only trending, but it’s also helping doctors cope with burnout.
“We’re seeing physicians take a 20% or more cut in salary in order to decrease their burden,” she said. “They’ll spend 4 days on clinical time with patients so that on that fifth ‘day off,’ they’re doing the paperwork and documentation they need to do so they don’t compromise care on the other 4 days of the week.”
And this may only be a Band-Aid solution, she fears.
“If a physician is spending 3 hours a day doing unnecessary work that could be done by another team member, that’s contributing to burnout,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s no surprise that they’ll want to escape and retire if they’re in a financial situation to do so.”
“I advocate negotiating within your organization so you’re doing more of what you like, such as mentoring or running a residency, and less of what you don’t, while cutting back from full-time to something less than full-time while maintaining benefits,” said Joel Greenwald, MD, a certified financial planner in Minneapolis, who specializes in helping physicians manage their financial affairs.
“Falling into the ‘like less’ bucket are usually things like working weekends and taking calls,” he said.
“This benefits everyone on a large scale because those doctors who find things they enjoy are generally working to a later age but working less hard,” he said. “Remaining comfortably and happily gainfully employed for a longer period, even if you’re not working full-time, has a very powerful effect on your financial planning, and you’ll avoid the risk of running out of money.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The double whammy of pandemic burnout and the aging of baby boomer physicians has, indeed, the makings of some scary headlines. A recent survey by Elsevier Health predicts that up to 75% of health care workers will leave the profession by 2025. And a 2020 study conducted by the Association of American Medical Colleges (AAMC) projected a shortfall of up to 139,000 physicians by 2033.
“We’ve paid a lot of attention to physician retirement,” says Michael Dill, AAMC’s director of workforce studies. “It’s a significant concern in terms of whether we have an adequate supply of physicians in the U.S. to meet our nation’s medical care needs. Anyone who thinks otherwise is incorrect.”
To Mr. Dill,
“The physician workforce as a whole is aging,” he said. “Close to a quarter of the physicians in the U.S. are 65 and over. So, you don’t need any extraordinary events driving retirement in order for retirement to be a real phenomenon of which we should all be concerned.”
And, although Mr. Dill said there aren’t any data to suggest that doctors in rural or urban areas are retiring faster than in the suburbs, that doesn’t mean retirement will have the same impact depending on where patients live.
“If you live in a rural area with one small practice in town and that physician retires, there goes the entirety of the physician supply,” he said. “In a major metro area, that’s not as big a deal.”
Why younger doctors are fast-tracking retirement
Fernando Mendoza, MD, 54, a pediatric emergency department physician in Miami, worries that physicians are getting so bogged down by paperwork that this may lead to even more doctors, at younger ages, leaving the profession.
“I love taking care of kids, but there’s going to be a cost to doing your work when you’re spending as much time as we need to spend on charts, pharmacy requests, and making sure all of the Medicare and Medicaid compliance issues are worked out.”
These stressors may compel some younger doctors to consider carving out a second career or fast-track younger physicians toward retirement.
“A medical degree carries a lot of weight, which helps when pivoting,” said Dr. Mendoza, who launched Scrivas, a Miami-based medical scribe agency, to help reduce the paperwork workload for physicians. “It might be that a doctor wants to get involved in the acquisition of medical equipment, or maybe they can focus on their investments. Either way, by leaving medicine, they’re not dealing with the hassle and churn-and-burn of seeing patients.”
What this means for patients
The time is now to stem the upcoming tide of retirement, said Mr. Dill. But the challenges remain daunting. For starters, the country needs more physicians trained now – but it will take years to replace those baby boomer doctors ready to hang up their white coats.
The medical profession also needs to find ways to support physicians who spend their days juggling an endless array of responsibilities, he said.
The AAMC study found that patients already feel the physician shortfall. Their public opinion research in 2019 said 35% of patients had trouble finding a physician over the past 2 or 3 years, up 10 percentage points since they asked the question in 2015.
Moreover, according to the report, the over-65 population is expected to grow by 45.1%, leaving a specialty care gap because older people generally have more complicated health cases that require specialists. In addition, physician burnout may lead more physicians under 65 to retire much earlier than expected.
Changes in how medicine is practiced, telemedicine care, and medical education – such as disruption of classes or clinical rotations, regulatory changes, and a lack of interest in certain specialties – could also be affected by a mass physician retirement.
What can we do about mass retirement?
The AAMC reports in “The Complexities of Physician Supply and Demand: Projections From 2019 to 2034” that federally funded GME support is in the works to train 15,000 physicians per year, with 3,000 new residency slots added per year over 5 years. The proposed model will add 3,750 new physicians each year beginning in 2026.
Other efforts include increasing use of APRNs and PAs, whose population is estimated to more than double by 2034, improve population health through preventive care, increase equity in health outcomes, and improve access and affordable care.
Removing licensing barriers for immigrant doctors can also help alleviate the shortage.
“We need to find better ways to leverage the entirety of the health care team so that not as much falls on physicians,” Mr. Dill said. “It’s also imperative that we focus on ways to support physician wellness and allow physicians to remain active in the field, but at a reduced rate.”
That’s precisely what Marie Brown, MD, director of practice redesign at the American Medical Association, is seeing nationwide. Cutting back their hours is not only trending, but it’s also helping doctors cope with burnout.
“We’re seeing physicians take a 20% or more cut in salary in order to decrease their burden,” she said. “They’ll spend 4 days on clinical time with patients so that on that fifth ‘day off,’ they’re doing the paperwork and documentation they need to do so they don’t compromise care on the other 4 days of the week.”
And this may only be a Band-Aid solution, she fears.
“If a physician is spending 3 hours a day doing unnecessary work that could be done by another team member, that’s contributing to burnout,” Dr. Brown said. “It’s no surprise that they’ll want to escape and retire if they’re in a financial situation to do so.”
“I advocate negotiating within your organization so you’re doing more of what you like, such as mentoring or running a residency, and less of what you don’t, while cutting back from full-time to something less than full-time while maintaining benefits,” said Joel Greenwald, MD, a certified financial planner in Minneapolis, who specializes in helping physicians manage their financial affairs.
“Falling into the ‘like less’ bucket are usually things like working weekends and taking calls,” he said.
“This benefits everyone on a large scale because those doctors who find things they enjoy are generally working to a later age but working less hard,” he said. “Remaining comfortably and happily gainfully employed for a longer period, even if you’re not working full-time, has a very powerful effect on your financial planning, and you’ll avoid the risk of running out of money.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Sleep disturbances linked to post-COVID dyspnea
according to data from the U.K.’s CircCOVID study.
The researchers, led by John Blaikley, MRCP, PhD, respiratory physician and clinical scientist from the University of Manchester (England), found that sleep disturbance is a common problem after hospital admission for COVID-19 and may last for at least 1 year.
The study also showed that sleep disturbance after COVID hospitalization was associated with dyspnea and lower lung function. Further in-depth analysis revealed that the effects of sleep disturbance on dyspnea were partially mediated through both anxiety and muscle weakness; however, “this does not fully explain the association, suggesting other pathways are involved,” said Dr. Blaikley.
The study was jointly conducted by researchers from the University of Leicester (England), as well as 20 other U.K. institutes and the University of Helsinki. It was presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases and was simultaneously published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
“Sleep disturbance is a common problem after hospitalization for COVID-19 and is associated with several symptoms in the post-COVID syndrome,” said Dr. Blaikley. “Clinicians should be aware of this association in their post-COVID syndrome clinics.”
He added that further work needs to be done to define the mechanism and to see whether the links are causal. “However, if they are, then treating sleep disturbance could have beneficial effects beyond improving sleep quality,” he said in an interview.
A large study recently showed that 4 in 10 people with post-COVID syndrome had moderate to severe sleep problems. Black people were at least three times more likely than White people to experience sleep problems. A total of 59% of all participants with long COVID reported having normal sleep or mild sleep disturbances, and 41% reported having moderate to severe sleep disturbances.
Unlike prior studies that evaluated sleep quality after COVID-19, which used either objective or subjective measures of sleep disturbance, the current study used both. “Using both measures revealed previously poorly described associations between sleep disturbance, breathlessness, reduced lung function, anxiety, and muscle weakness,” Dr. Blaikley pointed out.
Subjective and objective measures of sleep
The multicenter CircCOVID cohort study aimed to shed light on the prevalence and nature of sleep disturbance after patients are discharged from hospital for COVID-19 and to assess whether this was associated with dyspnea.
The study recruited a total of 2,320 participants who were part of a larger parent PHOSP-COVID study. After attending an early follow-up visit (at a median of 5 months after discharge from 83 U.K. hospitals for COVID-19), 638 participants provided data for analysis as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (a subjective measure of sleep quality); 729 participants provided data for analysis as measured by actigraphy (an objective, wrist-worn, device-based measure of sleep quality) at a median of 7 months.
Breathlessness, the primary outcome, was assessed using the Dyspnea-12 validated questionnaire.
Actigraphy measurements were compared with an age-matched, sex-matched, body mass index (BMI)–matched, and time from discharge–matched cohort from the UK Biobank (a prepandemic comparator longitudinal cohort of 502,540 individuals, one-fifth of whom wore actigraphy devices). Sleep regularity was found to be 19% less in previously hospitalized patients with post-COVID syndrome, compared with matched controls who had been hospitalized for other reasons.
This “revealed that the actigraphy changes may be, in part, due to COVID-19 rather than hospitalization alone,” said Dr. Blaikley.
Data were collected at two time points after hospital discharge: 2-7 months (early), and 10-14 months (late). At the early time point, participants were clinically assessed with respect to anxiety, muscle function, and dyspnea, and lung function.
After discharge from hospital, the majority (62%) of post–COVID-19 participants reported poor sleep quality on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire. A “comparable” proportion (53%) felt that their quality of sleep had deteriorated following hospital discharge according to the numerical rating scale (subjective measure).
Also, sleep disturbance was found likely to persist for at least 12 months, since subjective sleep quality hardly changed between the early and late time points after hospital discharge.
Both subjective metrics (sleep quality and sleep quality deterioration after hospital discharge) and objective, device-based metrics (sleep regularity) were found to be associated with dyspnea and reduced lung function in patients with post-COVID syndrome.
“One of the striking findings in our study is the consistency with breathlessness and reduced lung function across different methods used to evaluate sleep,” highlighted Dr. Blaikley.
“The other striking finding was that participants following COVID-19 hospitalization actually slept longer [65 min; 95% confidence interval, 59-71 min] than participants hospitalized for non-COVID; however, their bedtimes were irregular, and it was this irregularity that was associated with breathlessness,” he added.
In comparison with nonhospitalized controls, also from the UK Biobank, study participants with lower sleep regularity had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 4.38; 95%: CI, 2.10-6.65). Those with poor sleep quality overall also had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 3.94; 95% CI, 2.78-5.10), and those who reported sleep quality deterioration had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 3,00; 95% CI, 1.82-4.28).
In comparison with hospitalized controls, CircCOVID participants had lower sleep regularity index (–19%; 95% CI, –20 to –16) and lower sleep efficiency (3.83 percentage points; 95% CI, 3.40-4.26).
Sleep disturbance after COVID hospitalization was also associated with lower lung function, from a 7% to a 14% reduction in predicted forced vital capacity, depending on which sleep measure used.
In an analysis of mediating factors active in the relationship between sleep disturbance and dyspnea/decreased lung function, the researchers found that reduced muscle function and anxiety, which are both recognized causes of dyspnea, could partially contribute to the association.
Regarding anxiety, and depending on the sleep metric, anxiety mediated 18%-39% of the effect of sleep disturbance on dyspnea, while muscle weakness mediated 27%-41% of this effect, reported Dr. Blaikley. Those with poor sleep quality were more likely to have mild, moderate, or severe anxiety, compared with participants who reported good-quality sleep.
A similar association was observed between anxiety and sleep quality deterioration.
“Two key questions are raised by our study: Do sleep interventions have a beneficial effect in post–COVID-19 syndrome, and are the associations causal?” asked Dr. Blaikley. “We hope to do a sleep intervention trial to answer these questions to explore if this is an effective treatment for post–COVID-19 syndrome.”
‘Underlying mechanisms remain unclear’
Amitava Banerjee, MD, professor of clinical data science and honorary consultant cardiologist, Institute of Health Informatics, UCL, London, welcomed the study but noted that it did not include nonhospitalized post-COVID patients.
“The majority of people with long COVID were not hospitalized for COVID, so the results may not be generalizable to this larger group,” she said in an interview. “Good-quality sleep is important for health and reduces risk of chronic diseases; quality of sleep is therefore likely to be important for those with long COVID in reducing their risk of chronic disease, but the role of sleep in the mechanism of long COVID needs further research.”
In a commentary also published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, W. Cameron McGuire, MD, pulmonary and critical care specialist from San Diego, California, and colleagues wrote: “These findings suggest that sleep disturbance, dyspnea, and anxiety are common after COVID-19 and are associated with one another, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.”
The commentators “applauded” the work overall but noted that the findings represent correlation rather than causation. “It is unclear whether sleep disturbance is causing anxiety or whether anxiety is contributing to poor sleep. ... For the sleep disturbances, increased BMI in the cohort reporting poor sleep, compared with those reporting good sleep might suggest underlying obstructive sleep apnea,” they wrote.
Dr. McGuire and colleagues added that many questions remain for researchers and clinicians, including “whether anxiety and dyspnoea are contributing to a low arousal threshold [disrupting sleep] ... whether the observed abnormalities (e.g., in dyspnea score) are clinically significant,” and “whether therapies such as glucocorticoids, anticoagulants, or previous vaccinations mitigate the observed abnormalities during COVID-19 recovery.”
Dr. Blaikley has received support to his institute from an MRC Transition Fellowship, Asthma + Lung UK, NIHR Manchester BRC, and UKRI; grants to his institution from the Small Business Research Initiative Home Spirometer and the National Institute of Academic Anaesthesia; and support from TEVA and Therakos for attending meetings. He is a committee member of the Royal Society of Medicine. A coauthor received funding from the National Institutes of Health and income for medical education from Zoll, Livanova, Jazz, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Banerjee is the chief investigator of STIMULATE-ICP (an NIHR-funded study) and has received research funding from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to data from the U.K.’s CircCOVID study.
The researchers, led by John Blaikley, MRCP, PhD, respiratory physician and clinical scientist from the University of Manchester (England), found that sleep disturbance is a common problem after hospital admission for COVID-19 and may last for at least 1 year.
The study also showed that sleep disturbance after COVID hospitalization was associated with dyspnea and lower lung function. Further in-depth analysis revealed that the effects of sleep disturbance on dyspnea were partially mediated through both anxiety and muscle weakness; however, “this does not fully explain the association, suggesting other pathways are involved,” said Dr. Blaikley.
The study was jointly conducted by researchers from the University of Leicester (England), as well as 20 other U.K. institutes and the University of Helsinki. It was presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases and was simultaneously published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
“Sleep disturbance is a common problem after hospitalization for COVID-19 and is associated with several symptoms in the post-COVID syndrome,” said Dr. Blaikley. “Clinicians should be aware of this association in their post-COVID syndrome clinics.”
He added that further work needs to be done to define the mechanism and to see whether the links are causal. “However, if they are, then treating sleep disturbance could have beneficial effects beyond improving sleep quality,” he said in an interview.
A large study recently showed that 4 in 10 people with post-COVID syndrome had moderate to severe sleep problems. Black people were at least three times more likely than White people to experience sleep problems. A total of 59% of all participants with long COVID reported having normal sleep or mild sleep disturbances, and 41% reported having moderate to severe sleep disturbances.
Unlike prior studies that evaluated sleep quality after COVID-19, which used either objective or subjective measures of sleep disturbance, the current study used both. “Using both measures revealed previously poorly described associations between sleep disturbance, breathlessness, reduced lung function, anxiety, and muscle weakness,” Dr. Blaikley pointed out.
Subjective and objective measures of sleep
The multicenter CircCOVID cohort study aimed to shed light on the prevalence and nature of sleep disturbance after patients are discharged from hospital for COVID-19 and to assess whether this was associated with dyspnea.
The study recruited a total of 2,320 participants who were part of a larger parent PHOSP-COVID study. After attending an early follow-up visit (at a median of 5 months after discharge from 83 U.K. hospitals for COVID-19), 638 participants provided data for analysis as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (a subjective measure of sleep quality); 729 participants provided data for analysis as measured by actigraphy (an objective, wrist-worn, device-based measure of sleep quality) at a median of 7 months.
Breathlessness, the primary outcome, was assessed using the Dyspnea-12 validated questionnaire.
Actigraphy measurements were compared with an age-matched, sex-matched, body mass index (BMI)–matched, and time from discharge–matched cohort from the UK Biobank (a prepandemic comparator longitudinal cohort of 502,540 individuals, one-fifth of whom wore actigraphy devices). Sleep regularity was found to be 19% less in previously hospitalized patients with post-COVID syndrome, compared with matched controls who had been hospitalized for other reasons.
This “revealed that the actigraphy changes may be, in part, due to COVID-19 rather than hospitalization alone,” said Dr. Blaikley.
Data were collected at two time points after hospital discharge: 2-7 months (early), and 10-14 months (late). At the early time point, participants were clinically assessed with respect to anxiety, muscle function, and dyspnea, and lung function.
After discharge from hospital, the majority (62%) of post–COVID-19 participants reported poor sleep quality on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire. A “comparable” proportion (53%) felt that their quality of sleep had deteriorated following hospital discharge according to the numerical rating scale (subjective measure).
Also, sleep disturbance was found likely to persist for at least 12 months, since subjective sleep quality hardly changed between the early and late time points after hospital discharge.
Both subjective metrics (sleep quality and sleep quality deterioration after hospital discharge) and objective, device-based metrics (sleep regularity) were found to be associated with dyspnea and reduced lung function in patients with post-COVID syndrome.
“One of the striking findings in our study is the consistency with breathlessness and reduced lung function across different methods used to evaluate sleep,” highlighted Dr. Blaikley.
“The other striking finding was that participants following COVID-19 hospitalization actually slept longer [65 min; 95% confidence interval, 59-71 min] than participants hospitalized for non-COVID; however, their bedtimes were irregular, and it was this irregularity that was associated with breathlessness,” he added.
In comparison with nonhospitalized controls, also from the UK Biobank, study participants with lower sleep regularity had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 4.38; 95%: CI, 2.10-6.65). Those with poor sleep quality overall also had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 3.94; 95% CI, 2.78-5.10), and those who reported sleep quality deterioration had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 3,00; 95% CI, 1.82-4.28).
In comparison with hospitalized controls, CircCOVID participants had lower sleep regularity index (–19%; 95% CI, –20 to –16) and lower sleep efficiency (3.83 percentage points; 95% CI, 3.40-4.26).
Sleep disturbance after COVID hospitalization was also associated with lower lung function, from a 7% to a 14% reduction in predicted forced vital capacity, depending on which sleep measure used.
In an analysis of mediating factors active in the relationship between sleep disturbance and dyspnea/decreased lung function, the researchers found that reduced muscle function and anxiety, which are both recognized causes of dyspnea, could partially contribute to the association.
Regarding anxiety, and depending on the sleep metric, anxiety mediated 18%-39% of the effect of sleep disturbance on dyspnea, while muscle weakness mediated 27%-41% of this effect, reported Dr. Blaikley. Those with poor sleep quality were more likely to have mild, moderate, or severe anxiety, compared with participants who reported good-quality sleep.
A similar association was observed between anxiety and sleep quality deterioration.
“Two key questions are raised by our study: Do sleep interventions have a beneficial effect in post–COVID-19 syndrome, and are the associations causal?” asked Dr. Blaikley. “We hope to do a sleep intervention trial to answer these questions to explore if this is an effective treatment for post–COVID-19 syndrome.”
‘Underlying mechanisms remain unclear’
Amitava Banerjee, MD, professor of clinical data science and honorary consultant cardiologist, Institute of Health Informatics, UCL, London, welcomed the study but noted that it did not include nonhospitalized post-COVID patients.
“The majority of people with long COVID were not hospitalized for COVID, so the results may not be generalizable to this larger group,” she said in an interview. “Good-quality sleep is important for health and reduces risk of chronic diseases; quality of sleep is therefore likely to be important for those with long COVID in reducing their risk of chronic disease, but the role of sleep in the mechanism of long COVID needs further research.”
In a commentary also published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, W. Cameron McGuire, MD, pulmonary and critical care specialist from San Diego, California, and colleagues wrote: “These findings suggest that sleep disturbance, dyspnea, and anxiety are common after COVID-19 and are associated with one another, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.”
The commentators “applauded” the work overall but noted that the findings represent correlation rather than causation. “It is unclear whether sleep disturbance is causing anxiety or whether anxiety is contributing to poor sleep. ... For the sleep disturbances, increased BMI in the cohort reporting poor sleep, compared with those reporting good sleep might suggest underlying obstructive sleep apnea,” they wrote.
Dr. McGuire and colleagues added that many questions remain for researchers and clinicians, including “whether anxiety and dyspnoea are contributing to a low arousal threshold [disrupting sleep] ... whether the observed abnormalities (e.g., in dyspnea score) are clinically significant,” and “whether therapies such as glucocorticoids, anticoagulants, or previous vaccinations mitigate the observed abnormalities during COVID-19 recovery.”
Dr. Blaikley has received support to his institute from an MRC Transition Fellowship, Asthma + Lung UK, NIHR Manchester BRC, and UKRI; grants to his institution from the Small Business Research Initiative Home Spirometer and the National Institute of Academic Anaesthesia; and support from TEVA and Therakos for attending meetings. He is a committee member of the Royal Society of Medicine. A coauthor received funding from the National Institutes of Health and income for medical education from Zoll, Livanova, Jazz, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Banerjee is the chief investigator of STIMULATE-ICP (an NIHR-funded study) and has received research funding from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to data from the U.K.’s CircCOVID study.
The researchers, led by John Blaikley, MRCP, PhD, respiratory physician and clinical scientist from the University of Manchester (England), found that sleep disturbance is a common problem after hospital admission for COVID-19 and may last for at least 1 year.
The study also showed that sleep disturbance after COVID hospitalization was associated with dyspnea and lower lung function. Further in-depth analysis revealed that the effects of sleep disturbance on dyspnea were partially mediated through both anxiety and muscle weakness; however, “this does not fully explain the association, suggesting other pathways are involved,” said Dr. Blaikley.
The study was jointly conducted by researchers from the University of Leicester (England), as well as 20 other U.K. institutes and the University of Helsinki. It was presented at the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases and was simultaneously published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine.
“Sleep disturbance is a common problem after hospitalization for COVID-19 and is associated with several symptoms in the post-COVID syndrome,” said Dr. Blaikley. “Clinicians should be aware of this association in their post-COVID syndrome clinics.”
He added that further work needs to be done to define the mechanism and to see whether the links are causal. “However, if they are, then treating sleep disturbance could have beneficial effects beyond improving sleep quality,” he said in an interview.
A large study recently showed that 4 in 10 people with post-COVID syndrome had moderate to severe sleep problems. Black people were at least three times more likely than White people to experience sleep problems. A total of 59% of all participants with long COVID reported having normal sleep or mild sleep disturbances, and 41% reported having moderate to severe sleep disturbances.
Unlike prior studies that evaluated sleep quality after COVID-19, which used either objective or subjective measures of sleep disturbance, the current study used both. “Using both measures revealed previously poorly described associations between sleep disturbance, breathlessness, reduced lung function, anxiety, and muscle weakness,” Dr. Blaikley pointed out.
Subjective and objective measures of sleep
The multicenter CircCOVID cohort study aimed to shed light on the prevalence and nature of sleep disturbance after patients are discharged from hospital for COVID-19 and to assess whether this was associated with dyspnea.
The study recruited a total of 2,320 participants who were part of a larger parent PHOSP-COVID study. After attending an early follow-up visit (at a median of 5 months after discharge from 83 U.K. hospitals for COVID-19), 638 participants provided data for analysis as measured by the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (a subjective measure of sleep quality); 729 participants provided data for analysis as measured by actigraphy (an objective, wrist-worn, device-based measure of sleep quality) at a median of 7 months.
Breathlessness, the primary outcome, was assessed using the Dyspnea-12 validated questionnaire.
Actigraphy measurements were compared with an age-matched, sex-matched, body mass index (BMI)–matched, and time from discharge–matched cohort from the UK Biobank (a prepandemic comparator longitudinal cohort of 502,540 individuals, one-fifth of whom wore actigraphy devices). Sleep regularity was found to be 19% less in previously hospitalized patients with post-COVID syndrome, compared with matched controls who had been hospitalized for other reasons.
This “revealed that the actigraphy changes may be, in part, due to COVID-19 rather than hospitalization alone,” said Dr. Blaikley.
Data were collected at two time points after hospital discharge: 2-7 months (early), and 10-14 months (late). At the early time point, participants were clinically assessed with respect to anxiety, muscle function, and dyspnea, and lung function.
After discharge from hospital, the majority (62%) of post–COVID-19 participants reported poor sleep quality on the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index questionnaire. A “comparable” proportion (53%) felt that their quality of sleep had deteriorated following hospital discharge according to the numerical rating scale (subjective measure).
Also, sleep disturbance was found likely to persist for at least 12 months, since subjective sleep quality hardly changed between the early and late time points after hospital discharge.
Both subjective metrics (sleep quality and sleep quality deterioration after hospital discharge) and objective, device-based metrics (sleep regularity) were found to be associated with dyspnea and reduced lung function in patients with post-COVID syndrome.
“One of the striking findings in our study is the consistency with breathlessness and reduced lung function across different methods used to evaluate sleep,” highlighted Dr. Blaikley.
“The other striking finding was that participants following COVID-19 hospitalization actually slept longer [65 min; 95% confidence interval, 59-71 min] than participants hospitalized for non-COVID; however, their bedtimes were irregular, and it was this irregularity that was associated with breathlessness,” he added.
In comparison with nonhospitalized controls, also from the UK Biobank, study participants with lower sleep regularity had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 4.38; 95%: CI, 2.10-6.65). Those with poor sleep quality overall also had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 3.94; 95% CI, 2.78-5.10), and those who reported sleep quality deterioration had higher Dyspnea-12 scores (unadjusted effect estimate, 3,00; 95% CI, 1.82-4.28).
In comparison with hospitalized controls, CircCOVID participants had lower sleep regularity index (–19%; 95% CI, –20 to –16) and lower sleep efficiency (3.83 percentage points; 95% CI, 3.40-4.26).
Sleep disturbance after COVID hospitalization was also associated with lower lung function, from a 7% to a 14% reduction in predicted forced vital capacity, depending on which sleep measure used.
In an analysis of mediating factors active in the relationship between sleep disturbance and dyspnea/decreased lung function, the researchers found that reduced muscle function and anxiety, which are both recognized causes of dyspnea, could partially contribute to the association.
Regarding anxiety, and depending on the sleep metric, anxiety mediated 18%-39% of the effect of sleep disturbance on dyspnea, while muscle weakness mediated 27%-41% of this effect, reported Dr. Blaikley. Those with poor sleep quality were more likely to have mild, moderate, or severe anxiety, compared with participants who reported good-quality sleep.
A similar association was observed between anxiety and sleep quality deterioration.
“Two key questions are raised by our study: Do sleep interventions have a beneficial effect in post–COVID-19 syndrome, and are the associations causal?” asked Dr. Blaikley. “We hope to do a sleep intervention trial to answer these questions to explore if this is an effective treatment for post–COVID-19 syndrome.”
‘Underlying mechanisms remain unclear’
Amitava Banerjee, MD, professor of clinical data science and honorary consultant cardiologist, Institute of Health Informatics, UCL, London, welcomed the study but noted that it did not include nonhospitalized post-COVID patients.
“The majority of people with long COVID were not hospitalized for COVID, so the results may not be generalizable to this larger group,” she said in an interview. “Good-quality sleep is important for health and reduces risk of chronic diseases; quality of sleep is therefore likely to be important for those with long COVID in reducing their risk of chronic disease, but the role of sleep in the mechanism of long COVID needs further research.”
In a commentary also published in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, W. Cameron McGuire, MD, pulmonary and critical care specialist from San Diego, California, and colleagues wrote: “These findings suggest that sleep disturbance, dyspnea, and anxiety are common after COVID-19 and are associated with one another, although the underlying mechanisms remain unclear.”
The commentators “applauded” the work overall but noted that the findings represent correlation rather than causation. “It is unclear whether sleep disturbance is causing anxiety or whether anxiety is contributing to poor sleep. ... For the sleep disturbances, increased BMI in the cohort reporting poor sleep, compared with those reporting good sleep might suggest underlying obstructive sleep apnea,” they wrote.
Dr. McGuire and colleagues added that many questions remain for researchers and clinicians, including “whether anxiety and dyspnoea are contributing to a low arousal threshold [disrupting sleep] ... whether the observed abnormalities (e.g., in dyspnea score) are clinically significant,” and “whether therapies such as glucocorticoids, anticoagulants, or previous vaccinations mitigate the observed abnormalities during COVID-19 recovery.”
Dr. Blaikley has received support to his institute from an MRC Transition Fellowship, Asthma + Lung UK, NIHR Manchester BRC, and UKRI; grants to his institution from the Small Business Research Initiative Home Spirometer and the National Institute of Academic Anaesthesia; and support from TEVA and Therakos for attending meetings. He is a committee member of the Royal Society of Medicine. A coauthor received funding from the National Institutes of Health and income for medical education from Zoll, Livanova, Jazz, and Eli Lilly. Dr. Banerjee is the chief investigator of STIMULATE-ICP (an NIHR-funded study) and has received research funding from AstraZeneca.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ECCMID 2023