User login
In Case You Missed It: COVID
Is it flu, RSV, or COVID? Experts fear the ‘tripledemic’
Just when we thought this holiday season, finally, would be the back-to-normal one, some infectious disease experts are warning that a so-called “tripledemic” – influenza, COVID-19, and RSV – may be in the forecast.
The warning isn’t without basis.
The flu season has gotten an early start. As of Oct. 21, early increases in seasonal flu activity have been reported in most of the country, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, with the southeast and south-central areas having the highest activity levels.
Children’s hospitals and EDs are seeing a surge in children with RSV.
COVID-19 cases are trending down, according to the CDC, but epidemiologists – scientists who study disease outbreaks – always have their eyes on emerging variants.
said Justin Lessler, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Lessler is on the coordinating team for the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub, which aims to predict the course COVID-19, and the Flu Scenario Modeling Hub, which does the same for influenza.
For COVID-19, some models are predicting some spikes before Christmas, he said, and others see a new wave in 2023. For the flu, the model is predicting an earlier-than-usual start, as the CDC has reported.
While flu activity is relatively low, the CDC said, the season is off to an early start. For the week ending Oct. 21, 1,674 patients were hospitalized for flu, higher than in the summer months but fewer than the 2,675 hospitalizations for the week of May 15, 2022.
As of Oct. 20, COVID-19 cases have declined 12% over the last 2 weeks, nationwide. But hospitalizations are up 10% in much of the Northeast, The New York Times reports, and the improvement in cases and deaths has been slowing down.
As of Oct. 15, 15% of RSV tests reported nationwide were positive, compared with about 11% at that time in 2021, the CDC said. The surveillance collects information from 75 counties in 12 states.
Experts point out that the viruses – all three are respiratory viruses – are simply playing catchup.
“They spread the same way and along with lots of other viruses, and you tend to see an increase in them during the cold months,” said Timothy Brewer, MD, professor of medicine and epidemiology at UCLA.
The increase in all three viruses “is almost predictable at this point in the pandemic,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor and chief of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of California Davis Health. “All the respiratory viruses are out of whack.”
Last year, RSV cases were up, too, and began to appear very early, he said, in the summer instead of in the cooler months. Flu also appeared early in 2021, as it has in 2022.
That contrasts with the flu season of 2020-2021, when COVID precautions were nearly universal, and cases were down. At UC Davis, “we didn’t have one pediatric admission due to influenza in the 2020-2021 [flu] season,” Dr. Blumberg said.
The number of pediatric flu deaths usually range from 37 to 199 per year, according to CDC records. But in the 2020-2021 season, the CDC recorded one pediatric flu death in the U.S.
Both children and adults have had less contact with others the past two seasons, Dr. Blumberg said, “and they don’t get the immunity they got with those infections [previously]. That’s why we are seeing out-of-season, early season [viruses].”
Eventually, he said, the cases of flu and RSV will return to previous levels. “It could be as soon as next year,” Dr. Blumberg said. And COVID-19, hopefully, will become like influenza, he said.
“RSV has always come around in the fall and winter,” said Elizabeth Murray, DO, a pediatric emergency medicine doctor at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics. In 2022, children are back in school and for the most part not masking. “It’s a perfect storm for all the germs to spread now. They’ve just been waiting for their opportunity to come back.”
Self-care vs. not
RSV can pose a risk for anyone, but most at risk are children under age 5, especially infants under age 1, and adults over age 65. There is no vaccine for it. Symptoms include a runny nose, decreased appetite, coughing, sneezing, fever, and wheezing. But in young infants, there may only be decreased activity, crankiness, and breathing issues, the CDC said.
Keep an eye on the breathing if RSV is suspected, Dr. Murray tells parents. If your child can’t breathe easily, is unable to lie down comfortably, can’t speak clearly, or is sucking in the chest muscles to breathe, get medical help. Most kids with RSV can stay home and recover, she said, but often will need to be checked by a medical professional.
She advises against getting an oximeter to measure oxygen levels for home use. “They are often not accurate,” she said. If in doubt about how serious your child’s symptoms are, “don’t wait it out,” and don’t hesitate to call 911.
Symptoms of flu, COVID, and RSV can overlap. But each can involve breathing problems, which can be an emergency.
“It’s important to seek medical attention for any concerning symptoms, but especially severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, as these could signal the need for supplemental oxygen or other emergency interventions,” said Mandy De Vries, a respiratory therapist and director of education at the American Association for Respiratory Care. Inhalation treatment or mechanical ventilation may be needed for severe respiratory issues.
Precautions
To avoid the tripledemic – or any single infection – Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, suggests some familiar measures: “Stay home if you’re feeling sick. Make sure you are up to date on your vaccinations. Wear a mask indoors.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Just when we thought this holiday season, finally, would be the back-to-normal one, some infectious disease experts are warning that a so-called “tripledemic” – influenza, COVID-19, and RSV – may be in the forecast.
The warning isn’t without basis.
The flu season has gotten an early start. As of Oct. 21, early increases in seasonal flu activity have been reported in most of the country, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, with the southeast and south-central areas having the highest activity levels.
Children’s hospitals and EDs are seeing a surge in children with RSV.
COVID-19 cases are trending down, according to the CDC, but epidemiologists – scientists who study disease outbreaks – always have their eyes on emerging variants.
said Justin Lessler, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Lessler is on the coordinating team for the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub, which aims to predict the course COVID-19, and the Flu Scenario Modeling Hub, which does the same for influenza.
For COVID-19, some models are predicting some spikes before Christmas, he said, and others see a new wave in 2023. For the flu, the model is predicting an earlier-than-usual start, as the CDC has reported.
While flu activity is relatively low, the CDC said, the season is off to an early start. For the week ending Oct. 21, 1,674 patients were hospitalized for flu, higher than in the summer months but fewer than the 2,675 hospitalizations for the week of May 15, 2022.
As of Oct. 20, COVID-19 cases have declined 12% over the last 2 weeks, nationwide. But hospitalizations are up 10% in much of the Northeast, The New York Times reports, and the improvement in cases and deaths has been slowing down.
As of Oct. 15, 15% of RSV tests reported nationwide were positive, compared with about 11% at that time in 2021, the CDC said. The surveillance collects information from 75 counties in 12 states.
Experts point out that the viruses – all three are respiratory viruses – are simply playing catchup.
“They spread the same way and along with lots of other viruses, and you tend to see an increase in them during the cold months,” said Timothy Brewer, MD, professor of medicine and epidemiology at UCLA.
The increase in all three viruses “is almost predictable at this point in the pandemic,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor and chief of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of California Davis Health. “All the respiratory viruses are out of whack.”
Last year, RSV cases were up, too, and began to appear very early, he said, in the summer instead of in the cooler months. Flu also appeared early in 2021, as it has in 2022.
That contrasts with the flu season of 2020-2021, when COVID precautions were nearly universal, and cases were down. At UC Davis, “we didn’t have one pediatric admission due to influenza in the 2020-2021 [flu] season,” Dr. Blumberg said.
The number of pediatric flu deaths usually range from 37 to 199 per year, according to CDC records. But in the 2020-2021 season, the CDC recorded one pediatric flu death in the U.S.
Both children and adults have had less contact with others the past two seasons, Dr. Blumberg said, “and they don’t get the immunity they got with those infections [previously]. That’s why we are seeing out-of-season, early season [viruses].”
Eventually, he said, the cases of flu and RSV will return to previous levels. “It could be as soon as next year,” Dr. Blumberg said. And COVID-19, hopefully, will become like influenza, he said.
“RSV has always come around in the fall and winter,” said Elizabeth Murray, DO, a pediatric emergency medicine doctor at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics. In 2022, children are back in school and for the most part not masking. “It’s a perfect storm for all the germs to spread now. They’ve just been waiting for their opportunity to come back.”
Self-care vs. not
RSV can pose a risk for anyone, but most at risk are children under age 5, especially infants under age 1, and adults over age 65. There is no vaccine for it. Symptoms include a runny nose, decreased appetite, coughing, sneezing, fever, and wheezing. But in young infants, there may only be decreased activity, crankiness, and breathing issues, the CDC said.
Keep an eye on the breathing if RSV is suspected, Dr. Murray tells parents. If your child can’t breathe easily, is unable to lie down comfortably, can’t speak clearly, or is sucking in the chest muscles to breathe, get medical help. Most kids with RSV can stay home and recover, she said, but often will need to be checked by a medical professional.
She advises against getting an oximeter to measure oxygen levels for home use. “They are often not accurate,” she said. If in doubt about how serious your child’s symptoms are, “don’t wait it out,” and don’t hesitate to call 911.
Symptoms of flu, COVID, and RSV can overlap. But each can involve breathing problems, which can be an emergency.
“It’s important to seek medical attention for any concerning symptoms, but especially severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, as these could signal the need for supplemental oxygen or other emergency interventions,” said Mandy De Vries, a respiratory therapist and director of education at the American Association for Respiratory Care. Inhalation treatment or mechanical ventilation may be needed for severe respiratory issues.
Precautions
To avoid the tripledemic – or any single infection – Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, suggests some familiar measures: “Stay home if you’re feeling sick. Make sure you are up to date on your vaccinations. Wear a mask indoors.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Just when we thought this holiday season, finally, would be the back-to-normal one, some infectious disease experts are warning that a so-called “tripledemic” – influenza, COVID-19, and RSV – may be in the forecast.
The warning isn’t without basis.
The flu season has gotten an early start. As of Oct. 21, early increases in seasonal flu activity have been reported in most of the country, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said, with the southeast and south-central areas having the highest activity levels.
Children’s hospitals and EDs are seeing a surge in children with RSV.
COVID-19 cases are trending down, according to the CDC, but epidemiologists – scientists who study disease outbreaks – always have their eyes on emerging variants.
said Justin Lessler, PhD, a professor of epidemiology at the University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill. Dr. Lessler is on the coordinating team for the COVID-19 Scenario Modeling Hub, which aims to predict the course COVID-19, and the Flu Scenario Modeling Hub, which does the same for influenza.
For COVID-19, some models are predicting some spikes before Christmas, he said, and others see a new wave in 2023. For the flu, the model is predicting an earlier-than-usual start, as the CDC has reported.
While flu activity is relatively low, the CDC said, the season is off to an early start. For the week ending Oct. 21, 1,674 patients were hospitalized for flu, higher than in the summer months but fewer than the 2,675 hospitalizations for the week of May 15, 2022.
As of Oct. 20, COVID-19 cases have declined 12% over the last 2 weeks, nationwide. But hospitalizations are up 10% in much of the Northeast, The New York Times reports, and the improvement in cases and deaths has been slowing down.
As of Oct. 15, 15% of RSV tests reported nationwide were positive, compared with about 11% at that time in 2021, the CDC said. The surveillance collects information from 75 counties in 12 states.
Experts point out that the viruses – all three are respiratory viruses – are simply playing catchup.
“They spread the same way and along with lots of other viruses, and you tend to see an increase in them during the cold months,” said Timothy Brewer, MD, professor of medicine and epidemiology at UCLA.
The increase in all three viruses “is almost predictable at this point in the pandemic,” said Dean Blumberg, MD, a professor and chief of pediatric infectious diseases at the University of California Davis Health. “All the respiratory viruses are out of whack.”
Last year, RSV cases were up, too, and began to appear very early, he said, in the summer instead of in the cooler months. Flu also appeared early in 2021, as it has in 2022.
That contrasts with the flu season of 2020-2021, when COVID precautions were nearly universal, and cases were down. At UC Davis, “we didn’t have one pediatric admission due to influenza in the 2020-2021 [flu] season,” Dr. Blumberg said.
The number of pediatric flu deaths usually range from 37 to 199 per year, according to CDC records. But in the 2020-2021 season, the CDC recorded one pediatric flu death in the U.S.
Both children and adults have had less contact with others the past two seasons, Dr. Blumberg said, “and they don’t get the immunity they got with those infections [previously]. That’s why we are seeing out-of-season, early season [viruses].”
Eventually, he said, the cases of flu and RSV will return to previous levels. “It could be as soon as next year,” Dr. Blumberg said. And COVID-19, hopefully, will become like influenza, he said.
“RSV has always come around in the fall and winter,” said Elizabeth Murray, DO, a pediatric emergency medicine doctor at the University of Rochester (N.Y.) Medical Center and a spokesperson for the American Academy of Pediatrics. In 2022, children are back in school and for the most part not masking. “It’s a perfect storm for all the germs to spread now. They’ve just been waiting for their opportunity to come back.”
Self-care vs. not
RSV can pose a risk for anyone, but most at risk are children under age 5, especially infants under age 1, and adults over age 65. There is no vaccine for it. Symptoms include a runny nose, decreased appetite, coughing, sneezing, fever, and wheezing. But in young infants, there may only be decreased activity, crankiness, and breathing issues, the CDC said.
Keep an eye on the breathing if RSV is suspected, Dr. Murray tells parents. If your child can’t breathe easily, is unable to lie down comfortably, can’t speak clearly, or is sucking in the chest muscles to breathe, get medical help. Most kids with RSV can stay home and recover, she said, but often will need to be checked by a medical professional.
She advises against getting an oximeter to measure oxygen levels for home use. “They are often not accurate,” she said. If in doubt about how serious your child’s symptoms are, “don’t wait it out,” and don’t hesitate to call 911.
Symptoms of flu, COVID, and RSV can overlap. But each can involve breathing problems, which can be an emergency.
“It’s important to seek medical attention for any concerning symptoms, but especially severe shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, as these could signal the need for supplemental oxygen or other emergency interventions,” said Mandy De Vries, a respiratory therapist and director of education at the American Association for Respiratory Care. Inhalation treatment or mechanical ventilation may be needed for severe respiratory issues.
Precautions
To avoid the tripledemic – or any single infection – Timothy Brewer, MD, a professor of medicine and epidemiology at the University of California, Los Angeles, suggests some familiar measures: “Stay home if you’re feeling sick. Make sure you are up to date on your vaccinations. Wear a mask indoors.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ivermectin for COVID-19: Final nail in the coffin
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.
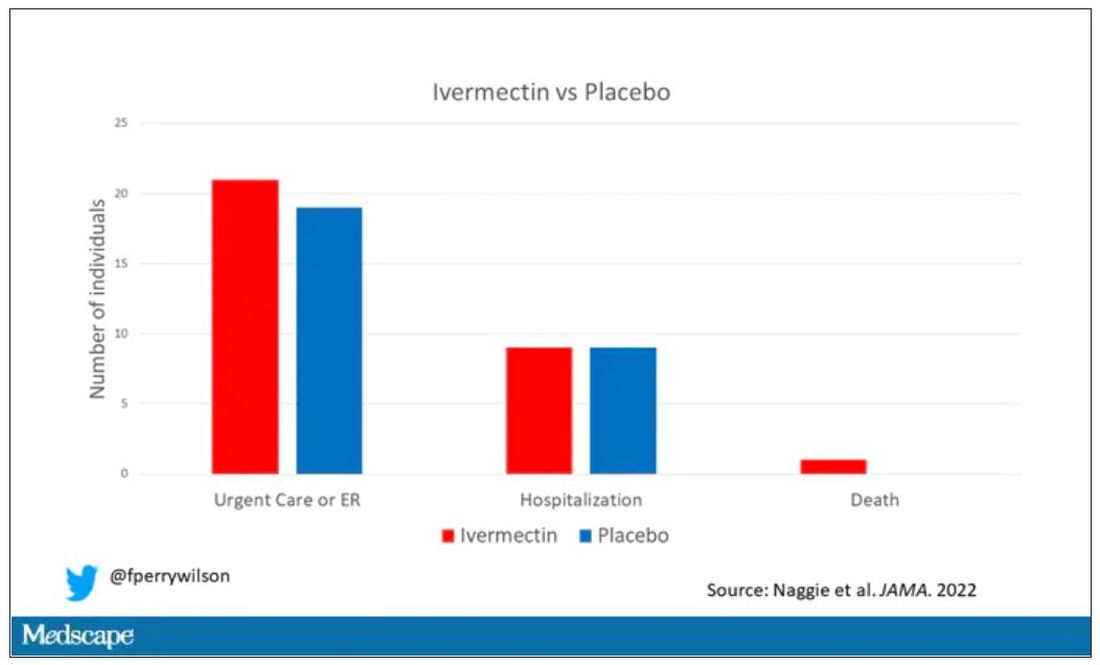
But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.

But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Welcome to Impact Factor, your weekly dose of commentary on a new medical study. I’m Dr F. Perry Wilson of the Yale School of Medicine.
It began in a petri dish.
Ivermectin, a widely available, cheap, and well-tolerated drug on the WHO’s list of essential medicines for its critical role in treating river blindness, was shown to dramatically reduce the proliferation of SARS-CoV-2 virus in cell culture.
You know the rest of the story. Despite the fact that the median inhibitory concentration in cell culture is about 100-fold higher than what one can achieve with oral dosing in humans, anecdotal reports of miraculous cures proliferated.
Cohort studies suggested that people who got ivermectin did very well in terms of COVID outcomes.
A narrative started to develop online – one that is still quite present today – that authorities were suppressing the good news about ivermectin in order to line their own pockets and those of the execs at Big Pharma. The official Twitter account of the Food and Drug Administration clapped back, reminding the populace that we are not horses or cows.
And every time a study came out that seemed like the nail in the coffin for the so-called horse paste, it rose again, vampire-like, feasting on the blood of social media outrage.
The truth is that, while excitement for ivermectin mounted online, it crashed quite quickly in scientific circles. Most randomized trials showed no effect of the drug. A couple of larger trials which seemed to show dramatic effects were subsequently shown to be fraudulent.
Then the TOGETHER trial was published. The 1,400-patient study from Brazil, which treated outpatients with COVID-19, found no significant difference in hospitalization or ER visits – the primary outcome – between those randomized to ivermectin vs. placebo or another therapy.
But still, Brazil. Different population than the United States. Different health systems. And very different rates of Strongyloides infections (this is a parasite that may be incidentally treated by ivermectin, leading to improvement independent of the drug’s effect on COVID). We all wanted a U.S. trial.
And now we have it. ACTIV-6 was published Oct. 21 in JAMA, a study randomizing outpatients with COVID-19 from 93 sites around the United States to ivermectin or placebo.
A total of 1,591 individuals – median age 47, 60% female – with confirmed symptomatic COVID-19 were randomized from June 2021 to February 2022. About half had been vaccinated.
The primary outcome was straightforward: time to clinical recovery. The time to recovery, defined as having three symptom-free days, was 12 days in the ivermectin group and 13 days in the placebo group – that’s within the margin of error.

But overall, everyone in the trial did fairly well. Serious outcomes, like death, hospitalization, urgent care, or ER visits, occurred in 32 people in the ivermectin group and 28 in the placebo group. Death itself was rare – just one occurred in the trial, in someone receiving ivermectin.OK, are we done with this drug yet? Is this nice U.S. randomized trial enough to convince people that results from a petri dish don’t always transfer to humans, regardless of the presence or absence of an evil pharmaceutical cabal?
No, of course not. At this point, I can predict the responses. The dose wasn’t high enough. It wasn’t given early enough. The patients weren’t sick enough, or they were too sick. This is motivated reasoning, plain and simple. It’s not to say that there isn’t a chance that this drug has some off-target effects on COVID that we haven’t adequately measured, but studies like ACTIV-6 effectively rule out the idea that it’s a miracle cure. And you know what? That’s OK. Miracle cures are vanishingly rare. Most things that work in medicine work OK; they make us a little better, and we learn why they do that and improve on them, and try again and again. It’s not flashy; it doesn’t have that allure of secret knowledge. But it’s what separates science from magic.
F. Perry Wilson, MD, MSCE, is an associate professor of medicine and director of Yale’s Clinical and Translational Research Accelerator; his science communication work can be found in the Huffington Post, on NPR, and on Medscape.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Side effects from COVID vaccine show its effectiveness
It means your body had a greater antibody response than people who had just a little pain or rash at the injection site, or no reaction at all.
That’s according to new research published in the journal JAMA Network Open .
“These findings support reframing postvaccination symptoms as signals of vaccine effectiveness and reinforce guidelines for vaccine boosters in older adults,” researchers from Columbia University in New York, the University of Vermont, and Boston University wrote.
The vaccines provided strong protection regardless of the level of reaction, researchers said. Almost all the study’s 928 adult participants had a positive antibody response after receiving two doses of vaccine.
“I don’t want a patient to tell me that, ‘Golly, I didn’t get any reaction, my arm wasn’t sore, I didn’t have fever. The vaccine didn’t work.’ I don’t want that conclusion to be out there,” William Schaffner, MD, a professor in the division of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told CNN.
“This is more to reassure people who have had a reaction that that’s their immune system responding, actually in a rather good way, to the vaccine, even though it has caused them some discomfort,” said Dr. Schaffner, who was not involved in the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It means your body had a greater antibody response than people who had just a little pain or rash at the injection site, or no reaction at all.
That’s according to new research published in the journal JAMA Network Open .
“These findings support reframing postvaccination symptoms as signals of vaccine effectiveness and reinforce guidelines for vaccine boosters in older adults,” researchers from Columbia University in New York, the University of Vermont, and Boston University wrote.
The vaccines provided strong protection regardless of the level of reaction, researchers said. Almost all the study’s 928 adult participants had a positive antibody response after receiving two doses of vaccine.
“I don’t want a patient to tell me that, ‘Golly, I didn’t get any reaction, my arm wasn’t sore, I didn’t have fever. The vaccine didn’t work.’ I don’t want that conclusion to be out there,” William Schaffner, MD, a professor in the division of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told CNN.
“This is more to reassure people who have had a reaction that that’s their immune system responding, actually in a rather good way, to the vaccine, even though it has caused them some discomfort,” said Dr. Schaffner, who was not involved in the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
It means your body had a greater antibody response than people who had just a little pain or rash at the injection site, or no reaction at all.
That’s according to new research published in the journal JAMA Network Open .
“These findings support reframing postvaccination symptoms as signals of vaccine effectiveness and reinforce guidelines for vaccine boosters in older adults,” researchers from Columbia University in New York, the University of Vermont, and Boston University wrote.
The vaccines provided strong protection regardless of the level of reaction, researchers said. Almost all the study’s 928 adult participants had a positive antibody response after receiving two doses of vaccine.
“I don’t want a patient to tell me that, ‘Golly, I didn’t get any reaction, my arm wasn’t sore, I didn’t have fever. The vaccine didn’t work.’ I don’t want that conclusion to be out there,” William Schaffner, MD, a professor in the division of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tenn., told CNN.
“This is more to reassure people who have had a reaction that that’s their immune system responding, actually in a rather good way, to the vaccine, even though it has caused them some discomfort,” said Dr. Schaffner, who was not involved in the study.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM JAMA NETWORK OPEN
Children and COVID: Weekly cases fall to lowest level in over a year
With the third autumn of the COVID era now upon us, the discussion has turned again to a possible influenza/COVID twindemic, as well as the new-for-2022 influenza/COVID/respiratory syncytial virus tripledemic. It appears, however, that COVID may have missed the memo.
For the sixth time in the last 7 weeks, the number of new COVID cases in children fell, with just under 23,000 reported during the week of Oct. 14-20, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. That is the lowest weekly count so far this year, and the lowest since early July of 2021, just as the Delta surge was starting. New pediatric cases had dipped to 8,500, the lowest for any week during the pandemic, a couple of weeks before that, the AAP/CHA data show.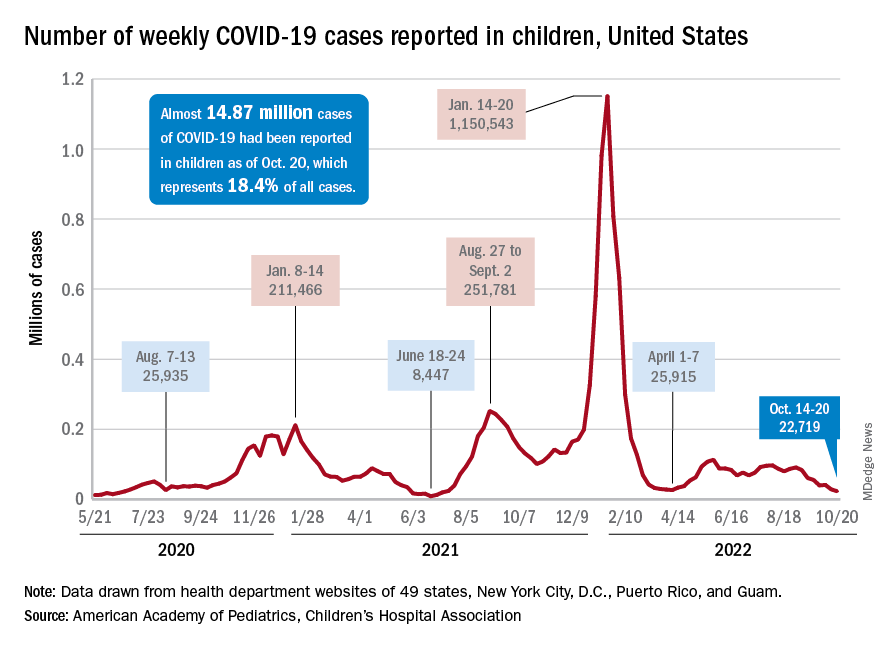
Weekly cases have fallen by almost 75% since over 90,000 were reported for the week of Aug. 26 to Sept. 1, even as children have returned to school and vaccine uptake remains slow in the youngest age groups. Rates of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID also have continued to drop, as have new admissions, and both are nearing their 2021 lows, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New vaccinations in children under age 5 years were up slightly for the most recent week (Oct. 13-19), but total uptake for that age group is only 7.1% for an initial dose and 2.9% for full vaccination. Among children aged 5-11 years, 38.7% have received at least one dose and 31.6% have completed the primary series, with corresponding figures of 71.2% and 60.9% for those aged 12-17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Despite the low overall numbers, though, the youngest children are, in one respect, punching above their weight when it comes to vaccinations. In the 2 weeks from Oct. 6 to Oct. 19, children under 5 years of age, who represent 5.9% of the U.S. population, received 9.2% of the initial vaccine doses administered. Children aged 5-11 years, who represent 8.7% of the total population, got just 4.2% of all first doses over those same 2 weeks, while 12- to 17-year-olds, who make up 7.6% of the population, got 3.4% of the vaccine doses, the CDC reported.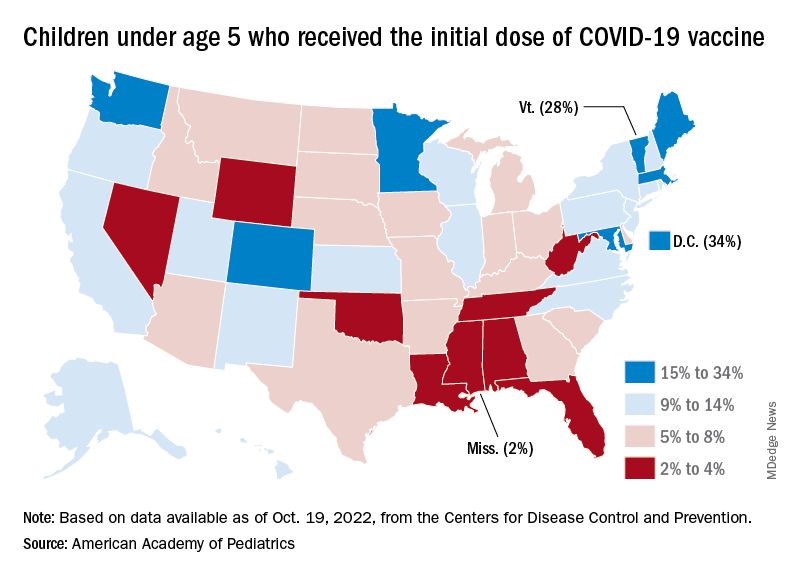
On the vaccine-approval front, the Food and Drug Administration recently announced that the new bivalent COVID-19 vaccines are now included in the emergency use authorizations for children who have completed primary or booster vaccination. The Moderna vaccine is authorized as a single-dose booster for children as young as 6 years and the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine can be given as a single booster dose in children as young as 5 years, the FDA said.
“These bivalent COVID-19 vaccines include an mRNA component of the original strain to provide an immune response that is broadly protective against COVID-19 and an mRNA component in common between the omicron variant BA.4 and BA.5 lineages,” the FDA said.
With the third autumn of the COVID era now upon us, the discussion has turned again to a possible influenza/COVID twindemic, as well as the new-for-2022 influenza/COVID/respiratory syncytial virus tripledemic. It appears, however, that COVID may have missed the memo.
For the sixth time in the last 7 weeks, the number of new COVID cases in children fell, with just under 23,000 reported during the week of Oct. 14-20, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. That is the lowest weekly count so far this year, and the lowest since early July of 2021, just as the Delta surge was starting. New pediatric cases had dipped to 8,500, the lowest for any week during the pandemic, a couple of weeks before that, the AAP/CHA data show.
Weekly cases have fallen by almost 75% since over 90,000 were reported for the week of Aug. 26 to Sept. 1, even as children have returned to school and vaccine uptake remains slow in the youngest age groups. Rates of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID also have continued to drop, as have new admissions, and both are nearing their 2021 lows, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New vaccinations in children under age 5 years were up slightly for the most recent week (Oct. 13-19), but total uptake for that age group is only 7.1% for an initial dose and 2.9% for full vaccination. Among children aged 5-11 years, 38.7% have received at least one dose and 31.6% have completed the primary series, with corresponding figures of 71.2% and 60.9% for those aged 12-17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Despite the low overall numbers, though, the youngest children are, in one respect, punching above their weight when it comes to vaccinations. In the 2 weeks from Oct. 6 to Oct. 19, children under 5 years of age, who represent 5.9% of the U.S. population, received 9.2% of the initial vaccine doses administered. Children aged 5-11 years, who represent 8.7% of the total population, got just 4.2% of all first doses over those same 2 weeks, while 12- to 17-year-olds, who make up 7.6% of the population, got 3.4% of the vaccine doses, the CDC reported.
On the vaccine-approval front, the Food and Drug Administration recently announced that the new bivalent COVID-19 vaccines are now included in the emergency use authorizations for children who have completed primary or booster vaccination. The Moderna vaccine is authorized as a single-dose booster for children as young as 6 years and the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine can be given as a single booster dose in children as young as 5 years, the FDA said.
“These bivalent COVID-19 vaccines include an mRNA component of the original strain to provide an immune response that is broadly protective against COVID-19 and an mRNA component in common between the omicron variant BA.4 and BA.5 lineages,” the FDA said.
With the third autumn of the COVID era now upon us, the discussion has turned again to a possible influenza/COVID twindemic, as well as the new-for-2022 influenza/COVID/respiratory syncytial virus tripledemic. It appears, however, that COVID may have missed the memo.
For the sixth time in the last 7 weeks, the number of new COVID cases in children fell, with just under 23,000 reported during the week of Oct. 14-20, according to the American Academy of Pediatrics and the Children’s Hospital Association. That is the lowest weekly count so far this year, and the lowest since early July of 2021, just as the Delta surge was starting. New pediatric cases had dipped to 8,500, the lowest for any week during the pandemic, a couple of weeks before that, the AAP/CHA data show.
Weekly cases have fallen by almost 75% since over 90,000 were reported for the week of Aug. 26 to Sept. 1, even as children have returned to school and vaccine uptake remains slow in the youngest age groups. Rates of emergency department visits with diagnosed COVID also have continued to drop, as have new admissions, and both are nearing their 2021 lows, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
New vaccinations in children under age 5 years were up slightly for the most recent week (Oct. 13-19), but total uptake for that age group is only 7.1% for an initial dose and 2.9% for full vaccination. Among children aged 5-11 years, 38.7% have received at least one dose and 31.6% have completed the primary series, with corresponding figures of 71.2% and 60.9% for those aged 12-17, the CDC said on its COVID Data Tracker.
Despite the low overall numbers, though, the youngest children are, in one respect, punching above their weight when it comes to vaccinations. In the 2 weeks from Oct. 6 to Oct. 19, children under 5 years of age, who represent 5.9% of the U.S. population, received 9.2% of the initial vaccine doses administered. Children aged 5-11 years, who represent 8.7% of the total population, got just 4.2% of all first doses over those same 2 weeks, while 12- to 17-year-olds, who make up 7.6% of the population, got 3.4% of the vaccine doses, the CDC reported.
On the vaccine-approval front, the Food and Drug Administration recently announced that the new bivalent COVID-19 vaccines are now included in the emergency use authorizations for children who have completed primary or booster vaccination. The Moderna vaccine is authorized as a single-dose booster for children as young as 6 years and the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine can be given as a single booster dose in children as young as 5 years, the FDA said.
“These bivalent COVID-19 vaccines include an mRNA component of the original strain to provide an immune response that is broadly protective against COVID-19 and an mRNA component in common between the omicron variant BA.4 and BA.5 lineages,” the FDA said.
Myocarditis after COVID vax rare and mild in teens
New data from Israel provide further evidence that myocarditis is a rare adverse event of vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents – one that predominantly occurs in males and typically after the second dose.
The new data also indicate a “mild and benign” clinical course of myocarditis after vaccination, with “favorable” long-term prognosis based on cardiac imaging findings.
Guy Witberg, MD, MPH, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues report their latest observations in correspondence in The New England Journal of Medicine, online.
The group previously reported in December 2021 that the incidence of myocarditis in Israel after receipt of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine was highest among males between the ages of 16 and 29 (10.7 cases per 100,000).
The vaccine has since been approved for adolescents aged 12-15. Initial evidence for this age group, reported by Dr. Witberg and colleagues in March 2022, suggests a similar low incidence and mild course of myocarditis, although follow-up was limited to 30 days.
In their latest report, with follow-up out to 6 months, Dr. Witberg and colleagues identified nine probable or definite cases of myocarditis among 182,605 Israeli adolescents aged 12-15 who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine – an incidence of 4.8 cases per 100,000.
Eight cases occurred after the second vaccine dose. All nine cases were mild.
Cardiac and inflammatory markers were elevated in all adolescent patients and electrocardiographic results were abnormal in two-thirds.
Eight patients had a normal ejection fraction, and four had a pericardial effusion. The patients spent 2-4 days hospitalized, and the in-hospital course was uneventful.
Echocardiographic findings were available a median of 10 days after discharge for eight patients. All echocardiograms showed a normal ejection fraction and resolution of pericardial effusion.
Five patients underwent cardiac MRI, including three scans performed at a median of 104 days after discharge. The scans showed “minimal evidence” of myocardial scarring or fibrosis, with evidence of late gadolinium enhancement ranging from 0% to 2%.
At a median of 206 days following discharge, all of the patients were alive, and none had been readmitted to the hospital, Dr. Witberg and colleagues report.
This research had no specific funding. Five authors have received research grants from Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from Israel provide further evidence that myocarditis is a rare adverse event of vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents – one that predominantly occurs in males and typically after the second dose.
The new data also indicate a “mild and benign” clinical course of myocarditis after vaccination, with “favorable” long-term prognosis based on cardiac imaging findings.
Guy Witberg, MD, MPH, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues report their latest observations in correspondence in The New England Journal of Medicine, online.
The group previously reported in December 2021 that the incidence of myocarditis in Israel after receipt of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine was highest among males between the ages of 16 and 29 (10.7 cases per 100,000).
The vaccine has since been approved for adolescents aged 12-15. Initial evidence for this age group, reported by Dr. Witberg and colleagues in March 2022, suggests a similar low incidence and mild course of myocarditis, although follow-up was limited to 30 days.
In their latest report, with follow-up out to 6 months, Dr. Witberg and colleagues identified nine probable or definite cases of myocarditis among 182,605 Israeli adolescents aged 12-15 who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine – an incidence of 4.8 cases per 100,000.
Eight cases occurred after the second vaccine dose. All nine cases were mild.
Cardiac and inflammatory markers were elevated in all adolescent patients and electrocardiographic results were abnormal in two-thirds.
Eight patients had a normal ejection fraction, and four had a pericardial effusion. The patients spent 2-4 days hospitalized, and the in-hospital course was uneventful.
Echocardiographic findings were available a median of 10 days after discharge for eight patients. All echocardiograms showed a normal ejection fraction and resolution of pericardial effusion.
Five patients underwent cardiac MRI, including three scans performed at a median of 104 days after discharge. The scans showed “minimal evidence” of myocardial scarring or fibrosis, with evidence of late gadolinium enhancement ranging from 0% to 2%.
At a median of 206 days following discharge, all of the patients were alive, and none had been readmitted to the hospital, Dr. Witberg and colleagues report.
This research had no specific funding. Five authors have received research grants from Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New data from Israel provide further evidence that myocarditis is a rare adverse event of vaccination with the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in adolescents – one that predominantly occurs in males and typically after the second dose.
The new data also indicate a “mild and benign” clinical course of myocarditis after vaccination, with “favorable” long-term prognosis based on cardiac imaging findings.
Guy Witberg, MD, MPH, Rabin Medical Center, Petah Tikva, Israel, and colleagues report their latest observations in correspondence in The New England Journal of Medicine, online.
The group previously reported in December 2021 that the incidence of myocarditis in Israel after receipt of the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine was highest among males between the ages of 16 and 29 (10.7 cases per 100,000).
The vaccine has since been approved for adolescents aged 12-15. Initial evidence for this age group, reported by Dr. Witberg and colleagues in March 2022, suggests a similar low incidence and mild course of myocarditis, although follow-up was limited to 30 days.
In their latest report, with follow-up out to 6 months, Dr. Witberg and colleagues identified nine probable or definite cases of myocarditis among 182,605 Israeli adolescents aged 12-15 who received the Pfizer/BioNTech mRNA vaccine – an incidence of 4.8 cases per 100,000.
Eight cases occurred after the second vaccine dose. All nine cases were mild.
Cardiac and inflammatory markers were elevated in all adolescent patients and electrocardiographic results were abnormal in two-thirds.
Eight patients had a normal ejection fraction, and four had a pericardial effusion. The patients spent 2-4 days hospitalized, and the in-hospital course was uneventful.
Echocardiographic findings were available a median of 10 days after discharge for eight patients. All echocardiograms showed a normal ejection fraction and resolution of pericardial effusion.
Five patients underwent cardiac MRI, including three scans performed at a median of 104 days after discharge. The scans showed “minimal evidence” of myocardial scarring or fibrosis, with evidence of late gadolinium enhancement ranging from 0% to 2%.
At a median of 206 days following discharge, all of the patients were alive, and none had been readmitted to the hospital, Dr. Witberg and colleagues report.
This research had no specific funding. Five authors have received research grants from Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Worse COVID outcomes seen with gout, particularly in women
People with gout, especially women, appear to be at higher risk for poor COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization and death, regardless of COVID-19 vaccination status, researchers suggest.
“We found that the risks of SARS-CoV-2 infection, 30-day hospitalization, and 30-day death among individuals with gout were higher than the general population irrespective of the vaccination status,” lead study author Dongxing Xie, MD, PhD, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and his colleagues write in their large population study. “This finding informs individuals with gout, especially women, that additional measures, even after vaccination, should be considered in order to mitigate the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its severe sequelae.”
People with gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, often have other conditions that are linked to higher risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor outcomes as well, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease, the authors write. And elevated serum urate may contribute to inflammation and possible COVID-19 complications. But unlike in the case of diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, little is known about SARS-CoV-2 infection risk among patients with gout.
As reported in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Xie and his research team used the Health Improvement Network ([THIN], now called IQVIA Medical Research Database) repository of medical conditions, demographics, and other details of around 17 million people in the United Kingdom to estimate the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization, and death in people with gout. They compared those outcomes with outcomes of people without gout and compared outcomes of vaccinated vs. nonvaccinated participants.
From December 2020 through October 2021, the researchers investigated the risk for SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection in vaccinated people between age 18 and 90 years who had gout and were hospitalized within 30 days after the infection diagnosis or who died within 30 days after the diagnosis. They compared these outcomes with the outcomes of people in the general population without gout after COVID-19 vaccination. They also compared the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and its severe outcomes between individuals with gout and the general population among unvaccinated people.
They weighted these comparisons on the basis of age, sex, body mass index, socioeconomic deprivation index score, region, and number of previous COVID-19 tests in one model. A more fully adjusted model also weighted the comparisons for lifestyle factors, comorbidities, medications, and healthcare utilization.
The vaccinated cohort consisted of 54,576 people with gout and 1,336,377 without gout from the general population. The unvaccinated cohort included 61,111 individuals with gout and 1,697,168 individuals without gout from the general population.
Women more likely to be hospitalized and die
The risk for breakthrough infection in the vaccinated cohort was significantly higher among people with gout than among those without gout in the general population, particularly for men, who had hazard ratios (HRs) ranging from 1.22 with a fully adjusted exposure score to 1.30 with a partially adjusted score, but this was not seen in women. The overall incidence of breakthrough infection per 1,000 person-months for these groups was 4.68 with gout vs. 3.76 without gout.
The researchers showed a similar pattern of a higher rate of hospitalizations for people with gout vs. without (0.42/1,000 person-months vs. 0.28); in this case, women had higher risks than did men, with HRs for women ranging from 1.55 with a fully adjusted exposure score to 1.91 with a partially adjusted score, compared with 1.22 and 1.43 for men, respectively.
People with gout had significantly higher mortality than did those without (0.06/1,000 person-months vs. 0.04), but the risk for death was only higher for women, with HRs calculated to be 2.23 in fully adjusted exposure scores and 3.01 in partially adjusted scores.
These same comparisons in the unvaccinated cohort all went in the same direction as did those in the vaccinated cohort but showed higher rates for infection (8.69/1,000 person-months vs. 6.89), hospitalization (2.57/1,000 person-months vs. 1.71), and death (0.65/1,000 person-months vs. 0.53). Similar sex-specific links between gout and risks for SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization, and death were seen in the unvaccinated cohort.
Patients with gout and COVID-19 need close monitoring
Four experts who were not involved in the study encourage greater attention to the needs of patients with gout.
Pamela B. Davis, MD, PhD, research professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, told this news organization, “This study brings to attention yet another potentially vulnerable group for physicians to monitor closely if they are infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“It is not clear why women with gout are more vulnerable, but fewer women than men were in the cohort with gout, and the confidence intervals for the results in women were, in general, larger,” she said.
“The authors suggest that women with gout tend to be older and have more comorbidities than men with gout,” Dr. Davis added. “The excess risk diminishes when the model is fully adjusted for comorbidities, such as obesity, hypertension, or heart disease, suggesting that already-known antecedents of infection severity account for a great deal of the excess risk.”
Kevin D. Deane, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and chair in rheumatology research at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, advises physicians to keep in mind other conditions linked with increased risk for severe COVID-19, including advanced age; heart, lung, or kidney problems; and autoimmune diseases.
“I would be very cautious about the finding that there was not a difference in outcomes in individuals with gout based on vaccination status,” he cautioned, urging clinicians to “still strongly recommend vaccines according to guidelines.”
Sarah E. Waldman, MD, associate clinical professor of infectious diseases at UC Davis Health in Sacramento, Calif., called the study interesting but not surprising.
“The reason for increased risk for COVID-19 infection among those with gout may have to do with their underlying inflammatory state. Additional research needs to be done on this topic.
“Retrospective population-based cohort studies can be difficult to interpret due to biases,” she added. Associations identified in this type of study do not determine causation.
“As the researchers noted, those with gout tend to have additional comorbidities as well as advanced age,” she said. “They may also seek medical care more often and be tested for SARS-CoV-2 more frequently.”
Dr. Waldman advises clinicians to counsel patients with gout about their potential increased infection risk and ways they can protect themselves, including COVID-19 vaccinations.
“The strong association between gout and COVID-19 infection could involve coexisting conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease,” Dr. Aung added.
Earlier studies show links between gout and severe COVID-19 outcomes
Lead author Kanon Jatuworapruk, MD, PhD, of Thammasat University in Pathumthani, Thailand, and his colleagues investigated characteristics and outcomes of people with gout who were hospitalized for COVID-19 between March 2020 and October 2021, using data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance registry.
“This cohort of people with gout and COVID-19 who were hospitalized had high frequencies of ventilatory support and death,” the authors write in ACR Open Rheumatology . “This suggests that patients with gout who were hospitalized for COVID-19 may be at risk of poor outcomes, perhaps related to known risk factors for poor outcomes, such as age and presence of comorbidity.”
In their study, the average age of the 163 patients was 63 years, and 85% were men. Most lived in the Western Pacific Region and North America, and 46% had two or more comorbidities, most commonly hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity. The researchers found that:
- Sixty-eight percent of the cohort required supplemental oxygen or ventilatory support during hospitalization.
- Sixteen percent of deaths were related to COVID-19, with 73% of deaths occurring in people with two or more comorbidities.
Ruth K. Topless, assistant research fellow in the department of biochemistry at the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is the lead author on a study she and her colleagues are conducting using the UK Biobank databases of 459,837 participants in the United Kingdom, including 15,871 people with gout, through April 6, 2021, to investigate whether gout is a risk factor for diagnosis of COVID-19 and COVID-19–related death.
“Gout is a risk factor for COVID-19-related death in the UK Biobank cohort, with an increased risk in women with gout, which was driven by risk factors independent of the metabolic comorbidities of gout,” the researchers conclude in The Lancet Rheumatology.
In their study, gout was linked with COVID-19 diagnosis (odds ratio, 1.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.29) but not with risk for COVID-19–related death in the group of patients with COVID-19 (OR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.96-1.51). In the entire cohort, gout was linked with COVID-19–related death (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.06-1.56); women with gout were at increased risk for COVID-19–related death (OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.34-2.94), but men with gout were not (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.93-1.45). The risk for COVID-19 diagnosis was significant in the nonvaccinated group (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.11-1.30) but not in the vaccinated group (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.65-1.85).
Editorial authors join in recommending further related research
In a commentary in The Lancet Rheumatology about the UK Biobank and other related research, Christoffer B. Nissen, MD, of University Hospital of Southern Denmark in Sonderborg, and his co-authors call the Topless and colleagues study “an elegantly conducted analysis of data from the UK Biobank supporting the hypothesis that gout needs attention in patients with COVID-19.”
Further studies are needed to investigate to what degree a diagnosis of gout is a risk factor for COVID-19 and whether treatment modifies the risk of a severe disease course,” they write. “However, in the interim, the results of this study could be considered when risk stratifying patients with gout in view of vaccination recommendations and early treatment interventions.”
Each of the three studies received grant funding. Several of the authors of the studies report financial involvements with pharmaceutical companies. All outside experts commented by email and report no relevant financial involvements.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with gout, especially women, appear to be at higher risk for poor COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization and death, regardless of COVID-19 vaccination status, researchers suggest.
“We found that the risks of SARS-CoV-2 infection, 30-day hospitalization, and 30-day death among individuals with gout were higher than the general population irrespective of the vaccination status,” lead study author Dongxing Xie, MD, PhD, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and his colleagues write in their large population study. “This finding informs individuals with gout, especially women, that additional measures, even after vaccination, should be considered in order to mitigate the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its severe sequelae.”
People with gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, often have other conditions that are linked to higher risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor outcomes as well, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease, the authors write. And elevated serum urate may contribute to inflammation and possible COVID-19 complications. But unlike in the case of diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, little is known about SARS-CoV-2 infection risk among patients with gout.
As reported in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Xie and his research team used the Health Improvement Network ([THIN], now called IQVIA Medical Research Database) repository of medical conditions, demographics, and other details of around 17 million people in the United Kingdom to estimate the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization, and death in people with gout. They compared those outcomes with outcomes of people without gout and compared outcomes of vaccinated vs. nonvaccinated participants.
From December 2020 through October 2021, the researchers investigated the risk for SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection in vaccinated people between age 18 and 90 years who had gout and were hospitalized within 30 days after the infection diagnosis or who died within 30 days after the diagnosis. They compared these outcomes with the outcomes of people in the general population without gout after COVID-19 vaccination. They also compared the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and its severe outcomes between individuals with gout and the general population among unvaccinated people.
They weighted these comparisons on the basis of age, sex, body mass index, socioeconomic deprivation index score, region, and number of previous COVID-19 tests in one model. A more fully adjusted model also weighted the comparisons for lifestyle factors, comorbidities, medications, and healthcare utilization.
The vaccinated cohort consisted of 54,576 people with gout and 1,336,377 without gout from the general population. The unvaccinated cohort included 61,111 individuals with gout and 1,697,168 individuals without gout from the general population.
Women more likely to be hospitalized and die
The risk for breakthrough infection in the vaccinated cohort was significantly higher among people with gout than among those without gout in the general population, particularly for men, who had hazard ratios (HRs) ranging from 1.22 with a fully adjusted exposure score to 1.30 with a partially adjusted score, but this was not seen in women. The overall incidence of breakthrough infection per 1,000 person-months for these groups was 4.68 with gout vs. 3.76 without gout.
The researchers showed a similar pattern of a higher rate of hospitalizations for people with gout vs. without (0.42/1,000 person-months vs. 0.28); in this case, women had higher risks than did men, with HRs for women ranging from 1.55 with a fully adjusted exposure score to 1.91 with a partially adjusted score, compared with 1.22 and 1.43 for men, respectively.
People with gout had significantly higher mortality than did those without (0.06/1,000 person-months vs. 0.04), but the risk for death was only higher for women, with HRs calculated to be 2.23 in fully adjusted exposure scores and 3.01 in partially adjusted scores.
These same comparisons in the unvaccinated cohort all went in the same direction as did those in the vaccinated cohort but showed higher rates for infection (8.69/1,000 person-months vs. 6.89), hospitalization (2.57/1,000 person-months vs. 1.71), and death (0.65/1,000 person-months vs. 0.53). Similar sex-specific links between gout and risks for SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization, and death were seen in the unvaccinated cohort.
Patients with gout and COVID-19 need close monitoring
Four experts who were not involved in the study encourage greater attention to the needs of patients with gout.
Pamela B. Davis, MD, PhD, research professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, told this news organization, “This study brings to attention yet another potentially vulnerable group for physicians to monitor closely if they are infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“It is not clear why women with gout are more vulnerable, but fewer women than men were in the cohort with gout, and the confidence intervals for the results in women were, in general, larger,” she said.
“The authors suggest that women with gout tend to be older and have more comorbidities than men with gout,” Dr. Davis added. “The excess risk diminishes when the model is fully adjusted for comorbidities, such as obesity, hypertension, or heart disease, suggesting that already-known antecedents of infection severity account for a great deal of the excess risk.”
Kevin D. Deane, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and chair in rheumatology research at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, advises physicians to keep in mind other conditions linked with increased risk for severe COVID-19, including advanced age; heart, lung, or kidney problems; and autoimmune diseases.
“I would be very cautious about the finding that there was not a difference in outcomes in individuals with gout based on vaccination status,” he cautioned, urging clinicians to “still strongly recommend vaccines according to guidelines.”
Sarah E. Waldman, MD, associate clinical professor of infectious diseases at UC Davis Health in Sacramento, Calif., called the study interesting but not surprising.
“The reason for increased risk for COVID-19 infection among those with gout may have to do with their underlying inflammatory state. Additional research needs to be done on this topic.
“Retrospective population-based cohort studies can be difficult to interpret due to biases,” she added. Associations identified in this type of study do not determine causation.
“As the researchers noted, those with gout tend to have additional comorbidities as well as advanced age,” she said. “They may also seek medical care more often and be tested for SARS-CoV-2 more frequently.”
Dr. Waldman advises clinicians to counsel patients with gout about their potential increased infection risk and ways they can protect themselves, including COVID-19 vaccinations.
“The strong association between gout and COVID-19 infection could involve coexisting conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease,” Dr. Aung added.
Earlier studies show links between gout and severe COVID-19 outcomes
Lead author Kanon Jatuworapruk, MD, PhD, of Thammasat University in Pathumthani, Thailand, and his colleagues investigated characteristics and outcomes of people with gout who were hospitalized for COVID-19 between March 2020 and October 2021, using data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance registry.
“This cohort of people with gout and COVID-19 who were hospitalized had high frequencies of ventilatory support and death,” the authors write in ACR Open Rheumatology . “This suggests that patients with gout who were hospitalized for COVID-19 may be at risk of poor outcomes, perhaps related to known risk factors for poor outcomes, such as age and presence of comorbidity.”
In their study, the average age of the 163 patients was 63 years, and 85% were men. Most lived in the Western Pacific Region and North America, and 46% had two or more comorbidities, most commonly hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity. The researchers found that:
- Sixty-eight percent of the cohort required supplemental oxygen or ventilatory support during hospitalization.
- Sixteen percent of deaths were related to COVID-19, with 73% of deaths occurring in people with two or more comorbidities.
Ruth K. Topless, assistant research fellow in the department of biochemistry at the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is the lead author on a study she and her colleagues are conducting using the UK Biobank databases of 459,837 participants in the United Kingdom, including 15,871 people with gout, through April 6, 2021, to investigate whether gout is a risk factor for diagnosis of COVID-19 and COVID-19–related death.
“Gout is a risk factor for COVID-19-related death in the UK Biobank cohort, with an increased risk in women with gout, which was driven by risk factors independent of the metabolic comorbidities of gout,” the researchers conclude in The Lancet Rheumatology.
In their study, gout was linked with COVID-19 diagnosis (odds ratio, 1.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.29) but not with risk for COVID-19–related death in the group of patients with COVID-19 (OR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.96-1.51). In the entire cohort, gout was linked with COVID-19–related death (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.06-1.56); women with gout were at increased risk for COVID-19–related death (OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.34-2.94), but men with gout were not (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.93-1.45). The risk for COVID-19 diagnosis was significant in the nonvaccinated group (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.11-1.30) but not in the vaccinated group (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.65-1.85).
Editorial authors join in recommending further related research
In a commentary in The Lancet Rheumatology about the UK Biobank and other related research, Christoffer B. Nissen, MD, of University Hospital of Southern Denmark in Sonderborg, and his co-authors call the Topless and colleagues study “an elegantly conducted analysis of data from the UK Biobank supporting the hypothesis that gout needs attention in patients with COVID-19.”
Further studies are needed to investigate to what degree a diagnosis of gout is a risk factor for COVID-19 and whether treatment modifies the risk of a severe disease course,” they write. “However, in the interim, the results of this study could be considered when risk stratifying patients with gout in view of vaccination recommendations and early treatment interventions.”
Each of the three studies received grant funding. Several of the authors of the studies report financial involvements with pharmaceutical companies. All outside experts commented by email and report no relevant financial involvements.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with gout, especially women, appear to be at higher risk for poor COVID-19 outcomes, including hospitalization and death, regardless of COVID-19 vaccination status, researchers suggest.
“We found that the risks of SARS-CoV-2 infection, 30-day hospitalization, and 30-day death among individuals with gout were higher than the general population irrespective of the vaccination status,” lead study author Dongxing Xie, MD, PhD, Xiangya Hospital, Central South University, Changsha, China, and his colleagues write in their large population study. “This finding informs individuals with gout, especially women, that additional measures, even after vaccination, should be considered in order to mitigate the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection and its severe sequelae.”
People with gout, the most common inflammatory arthritis, often have other conditions that are linked to higher risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and poor outcomes as well, including obesity, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease, the authors write. And elevated serum urate may contribute to inflammation and possible COVID-19 complications. But unlike in the case of diseases such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, little is known about SARS-CoV-2 infection risk among patients with gout.
As reported in Arthritis & Rheumatology, Dr. Xie and his research team used the Health Improvement Network ([THIN], now called IQVIA Medical Research Database) repository of medical conditions, demographics, and other details of around 17 million people in the United Kingdom to estimate the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization, and death in people with gout. They compared those outcomes with outcomes of people without gout and compared outcomes of vaccinated vs. nonvaccinated participants.
From December 2020 through October 2021, the researchers investigated the risk for SARS-CoV-2 breakthrough infection in vaccinated people between age 18 and 90 years who had gout and were hospitalized within 30 days after the infection diagnosis or who died within 30 days after the diagnosis. They compared these outcomes with the outcomes of people in the general population without gout after COVID-19 vaccination. They also compared the risk for SARS-CoV-2 infection and its severe outcomes between individuals with gout and the general population among unvaccinated people.
They weighted these comparisons on the basis of age, sex, body mass index, socioeconomic deprivation index score, region, and number of previous COVID-19 tests in one model. A more fully adjusted model also weighted the comparisons for lifestyle factors, comorbidities, medications, and healthcare utilization.
The vaccinated cohort consisted of 54,576 people with gout and 1,336,377 without gout from the general population. The unvaccinated cohort included 61,111 individuals with gout and 1,697,168 individuals without gout from the general population.
Women more likely to be hospitalized and die
The risk for breakthrough infection in the vaccinated cohort was significantly higher among people with gout than among those without gout in the general population, particularly for men, who had hazard ratios (HRs) ranging from 1.22 with a fully adjusted exposure score to 1.30 with a partially adjusted score, but this was not seen in women. The overall incidence of breakthrough infection per 1,000 person-months for these groups was 4.68 with gout vs. 3.76 without gout.
The researchers showed a similar pattern of a higher rate of hospitalizations for people with gout vs. without (0.42/1,000 person-months vs. 0.28); in this case, women had higher risks than did men, with HRs for women ranging from 1.55 with a fully adjusted exposure score to 1.91 with a partially adjusted score, compared with 1.22 and 1.43 for men, respectively.
People with gout had significantly higher mortality than did those without (0.06/1,000 person-months vs. 0.04), but the risk for death was only higher for women, with HRs calculated to be 2.23 in fully adjusted exposure scores and 3.01 in partially adjusted scores.
These same comparisons in the unvaccinated cohort all went in the same direction as did those in the vaccinated cohort but showed higher rates for infection (8.69/1,000 person-months vs. 6.89), hospitalization (2.57/1,000 person-months vs. 1.71), and death (0.65/1,000 person-months vs. 0.53). Similar sex-specific links between gout and risks for SARS-CoV-2 infection, hospitalization, and death were seen in the unvaccinated cohort.
Patients with gout and COVID-19 need close monitoring
Four experts who were not involved in the study encourage greater attention to the needs of patients with gout.
Pamela B. Davis, MD, PhD, research professor at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, told this news organization, “This study brings to attention yet another potentially vulnerable group for physicians to monitor closely if they are infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“It is not clear why women with gout are more vulnerable, but fewer women than men were in the cohort with gout, and the confidence intervals for the results in women were, in general, larger,” she said.
“The authors suggest that women with gout tend to be older and have more comorbidities than men with gout,” Dr. Davis added. “The excess risk diminishes when the model is fully adjusted for comorbidities, such as obesity, hypertension, or heart disease, suggesting that already-known antecedents of infection severity account for a great deal of the excess risk.”
Kevin D. Deane, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and chair in rheumatology research at the University of Colorado at Denver, Aurora, advises physicians to keep in mind other conditions linked with increased risk for severe COVID-19, including advanced age; heart, lung, or kidney problems; and autoimmune diseases.
“I would be very cautious about the finding that there was not a difference in outcomes in individuals with gout based on vaccination status,” he cautioned, urging clinicians to “still strongly recommend vaccines according to guidelines.”
Sarah E. Waldman, MD, associate clinical professor of infectious diseases at UC Davis Health in Sacramento, Calif., called the study interesting but not surprising.
“The reason for increased risk for COVID-19 infection among those with gout may have to do with their underlying inflammatory state. Additional research needs to be done on this topic.
“Retrospective population-based cohort studies can be difficult to interpret due to biases,” she added. Associations identified in this type of study do not determine causation.
“As the researchers noted, those with gout tend to have additional comorbidities as well as advanced age,” she said. “They may also seek medical care more often and be tested for SARS-CoV-2 more frequently.”
Dr. Waldman advises clinicians to counsel patients with gout about their potential increased infection risk and ways they can protect themselves, including COVID-19 vaccinations.
“The strong association between gout and COVID-19 infection could involve coexisting conditions such as diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and chronic kidney disease,” Dr. Aung added.
Earlier studies show links between gout and severe COVID-19 outcomes
Lead author Kanon Jatuworapruk, MD, PhD, of Thammasat University in Pathumthani, Thailand, and his colleagues investigated characteristics and outcomes of people with gout who were hospitalized for COVID-19 between March 2020 and October 2021, using data from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance registry.
“This cohort of people with gout and COVID-19 who were hospitalized had high frequencies of ventilatory support and death,” the authors write in ACR Open Rheumatology . “This suggests that patients with gout who were hospitalized for COVID-19 may be at risk of poor outcomes, perhaps related to known risk factors for poor outcomes, such as age and presence of comorbidity.”
In their study, the average age of the 163 patients was 63 years, and 85% were men. Most lived in the Western Pacific Region and North America, and 46% had two or more comorbidities, most commonly hypertension, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic kidney disease, and obesity. The researchers found that:
- Sixty-eight percent of the cohort required supplemental oxygen or ventilatory support during hospitalization.
- Sixteen percent of deaths were related to COVID-19, with 73% of deaths occurring in people with two or more comorbidities.
Ruth K. Topless, assistant research fellow in the department of biochemistry at the University of Otago in Dunedin, New Zealand, is the lead author on a study she and her colleagues are conducting using the UK Biobank databases of 459,837 participants in the United Kingdom, including 15,871 people with gout, through April 6, 2021, to investigate whether gout is a risk factor for diagnosis of COVID-19 and COVID-19–related death.
“Gout is a risk factor for COVID-19-related death in the UK Biobank cohort, with an increased risk in women with gout, which was driven by risk factors independent of the metabolic comorbidities of gout,” the researchers conclude in The Lancet Rheumatology.
In their study, gout was linked with COVID-19 diagnosis (odds ratio, 1.20; 95% confidence interval, 1.11-1.29) but not with risk for COVID-19–related death in the group of patients with COVID-19 (OR, 1.20; 95% CI, 0.96-1.51). In the entire cohort, gout was linked with COVID-19–related death (OR, 1.29; 95% CI, 1.06-1.56); women with gout were at increased risk for COVID-19–related death (OR, 1.98; 95% CI, 1.34-2.94), but men with gout were not (OR, 1.16; 95% CI, 0.93-1.45). The risk for COVID-19 diagnosis was significant in the nonvaccinated group (OR, 1.21; 95% CI, 1.11-1.30) but not in the vaccinated group (OR, 1.09; 95% CI, 0.65-1.85).
Editorial authors join in recommending further related research
In a commentary in The Lancet Rheumatology about the UK Biobank and other related research, Christoffer B. Nissen, MD, of University Hospital of Southern Denmark in Sonderborg, and his co-authors call the Topless and colleagues study “an elegantly conducted analysis of data from the UK Biobank supporting the hypothesis that gout needs attention in patients with COVID-19.”
Further studies are needed to investigate to what degree a diagnosis of gout is a risk factor for COVID-19 and whether treatment modifies the risk of a severe disease course,” they write. “However, in the interim, the results of this study could be considered when risk stratifying patients with gout in view of vaccination recommendations and early treatment interventions.”
Each of the three studies received grant funding. Several of the authors of the studies report financial involvements with pharmaceutical companies. All outside experts commented by email and report no relevant financial involvements.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated Moderna booster shows greater activity against COVID in adults
WASHINGTON –
The bivalent booster was superior regardless of age and whether a person had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Additionally, no new safety concerns emerged.
Spyros Chalkias, MD, senior medical director of clinical development at Moderna, presented the data during an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
In the phase 2/3 trial, participants received either 50 mcg of the bivalent vaccine mRNA-1273.214 (25 mcg each of the original Wuhan-Hu-1 and Omicron BA.1 spike mRNAs) or 50 mcg of the standard authorized mRNA-1273. The doses were given as second boosters in adults who had previously received a two-dose primary series and a first booster at least 3 months before.
The model-based geometric mean titers (GMTs) ratio of the enhanced booster compared with the standard booster was 1.74 (1.49-2.04), meeting the prespecified bar for superiority against Omicron BA.1.
In participants without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection who received updated booster doses and those who received standard boosters, the neutralizing antibody GMTs against Omicron BA.1 were 2372.4 and 1473.5, respectively.
Additionally, the updated booster elicited higher GMTs (727.4) than the standard booster (492.1) against Omicron subvariants BA.4/BA.5. Safety and reactogenicity were similar for both vaccine groups.
“By the end of this year, we expect to also have clinical trial data from our BA.4/BA.5 bivalent booster,” Dr. Chalkias said.
In the interim, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently granted emergency use authorization for Moderna’s BA.4/BA.5 Omicron-targeting bivalent COVID-19 booster vaccine in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years.
Pfizer/BioNTech also has recently issued an announcement that their COVID-19 booster, adapted for the BA.4 and the BA.5 Omicron subvariants, generated a strong immune response and was well tolerated in human tests.
Pfizer/BioNTech said data from roughly 80 adult patients showed that the booster led to a substantial increase in neutralizing antibody levels against the BA.4/BA.5 variants after 1 week.
Separate study of causes of severe breakthrough infections in early vaccine formulations
Though COVID vaccines reduce the incidence of severe outcomes, there are reports of breakthrough infections in persons who received the original vaccines, and some of these have been serious.
In a separate study, also presented at the meeting, researchers led by first author Austin D. Vo, BS, with the VA Boston Healthcare System, used data collected from Dec. 15, 2020, through Feb. 28, 2022, in a U.S. veteran population to assess those at highest risk for severe disease despite vaccination.
Results of the large, nationwide retrospective study were simultaneously published in JAMA Network Open.
The primary outcome was development of severe COVID, defined as a hospitalization within 14 days of a confirmed positive SARS-CoV-2 test, receipt of supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or death within 28 days.
Among 110,760 participants with severe disease after primary vaccination, 13% (14,690) were hospitalized with severe COVID-19 or died.
The strongest risk factor for severe disease despite vaccination was age, the researchers found.
Presenting author Westyn Branch-Elliman, MD, associate professor of medicine with VA Boston Healthcare System, said, “We found that age greater than 50 was associated with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.42 for every 5-year increase.”
To put that in perspective, she said, “compared to patients who are 45 to 50, those over 80 had an adjusted odds ratio of 16 for hospitalization or death following breakthrough infection.”
Priya Nori, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, said in an interview that the evidence that age is a strong risk factor for severe disease – even after vaccination – confirms that attention should be focused on those in the highest age groups, particularly those 80 years and older.
Other top risk factors included having immunocompromising conditions; having received cytotoxic chemotherapy within 6 months (adjusted odds ratio, 2.69; 95% confidence interval, 2.25-3.21); having leukemias/lymphomas (aOR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.59-2.14); and having chronic conditions associated with end-organ disease.
“We also found that receipt of an additional booster dose of vaccine was associated with a 50% reduction in adjusted odds of severe disease,” noted Dr. Branch-Elliman.
Dr. Nori emphasized that, given these data, emphatic messaging is needed to encourage uptake of the updated Omicron-targeted vaccines for these high-risk age groups.
The study by Dr. Chalkias and colleagues was funded by Moderna. Dr. Chalkias and several coauthors are employed by Moderna. One coauthor has relationships with DLA Piper/Medtronic, and Gilead Pharmaceuticals, and one has relationships with Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, ChemoCentryx, Gilead, and Kiniksa. Dr. Nori has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON –
The bivalent booster was superior regardless of age and whether a person had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Additionally, no new safety concerns emerged.
Spyros Chalkias, MD, senior medical director of clinical development at Moderna, presented the data during an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
In the phase 2/3 trial, participants received either 50 mcg of the bivalent vaccine mRNA-1273.214 (25 mcg each of the original Wuhan-Hu-1 and Omicron BA.1 spike mRNAs) or 50 mcg of the standard authorized mRNA-1273. The doses were given as second boosters in adults who had previously received a two-dose primary series and a first booster at least 3 months before.
The model-based geometric mean titers (GMTs) ratio of the enhanced booster compared with the standard booster was 1.74 (1.49-2.04), meeting the prespecified bar for superiority against Omicron BA.1.
In participants without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection who received updated booster doses and those who received standard boosters, the neutralizing antibody GMTs against Omicron BA.1 were 2372.4 and 1473.5, respectively.
Additionally, the updated booster elicited higher GMTs (727.4) than the standard booster (492.1) against Omicron subvariants BA.4/BA.5. Safety and reactogenicity were similar for both vaccine groups.
“By the end of this year, we expect to also have clinical trial data from our BA.4/BA.5 bivalent booster,” Dr. Chalkias said.
In the interim, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently granted emergency use authorization for Moderna’s BA.4/BA.5 Omicron-targeting bivalent COVID-19 booster vaccine in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years.
Pfizer/BioNTech also has recently issued an announcement that their COVID-19 booster, adapted for the BA.4 and the BA.5 Omicron subvariants, generated a strong immune response and was well tolerated in human tests.
Pfizer/BioNTech said data from roughly 80 adult patients showed that the booster led to a substantial increase in neutralizing antibody levels against the BA.4/BA.5 variants after 1 week.
Separate study of causes of severe breakthrough infections in early vaccine formulations
Though COVID vaccines reduce the incidence of severe outcomes, there are reports of breakthrough infections in persons who received the original vaccines, and some of these have been serious.
In a separate study, also presented at the meeting, researchers led by first author Austin D. Vo, BS, with the VA Boston Healthcare System, used data collected from Dec. 15, 2020, through Feb. 28, 2022, in a U.S. veteran population to assess those at highest risk for severe disease despite vaccination.
Results of the large, nationwide retrospective study were simultaneously published in JAMA Network Open.
The primary outcome was development of severe COVID, defined as a hospitalization within 14 days of a confirmed positive SARS-CoV-2 test, receipt of supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or death within 28 days.
Among 110,760 participants with severe disease after primary vaccination, 13% (14,690) were hospitalized with severe COVID-19 or died.
The strongest risk factor for severe disease despite vaccination was age, the researchers found.
Presenting author Westyn Branch-Elliman, MD, associate professor of medicine with VA Boston Healthcare System, said, “We found that age greater than 50 was associated with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.42 for every 5-year increase.”
To put that in perspective, she said, “compared to patients who are 45 to 50, those over 80 had an adjusted odds ratio of 16 for hospitalization or death following breakthrough infection.”
Priya Nori, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, said in an interview that the evidence that age is a strong risk factor for severe disease – even after vaccination – confirms that attention should be focused on those in the highest age groups, particularly those 80 years and older.
Other top risk factors included having immunocompromising conditions; having received cytotoxic chemotherapy within 6 months (adjusted odds ratio, 2.69; 95% confidence interval, 2.25-3.21); having leukemias/lymphomas (aOR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.59-2.14); and having chronic conditions associated with end-organ disease.
“We also found that receipt of an additional booster dose of vaccine was associated with a 50% reduction in adjusted odds of severe disease,” noted Dr. Branch-Elliman.
Dr. Nori emphasized that, given these data, emphatic messaging is needed to encourage uptake of the updated Omicron-targeted vaccines for these high-risk age groups.
The study by Dr. Chalkias and colleagues was funded by Moderna. Dr. Chalkias and several coauthors are employed by Moderna. One coauthor has relationships with DLA Piper/Medtronic, and Gilead Pharmaceuticals, and one has relationships with Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, ChemoCentryx, Gilead, and Kiniksa. Dr. Nori has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
WASHINGTON –
The bivalent booster was superior regardless of age and whether a person had previously been infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Additionally, no new safety concerns emerged.
Spyros Chalkias, MD, senior medical director of clinical development at Moderna, presented the data during an annual scientific meeting on infectious diseases.
In the phase 2/3 trial, participants received either 50 mcg of the bivalent vaccine mRNA-1273.214 (25 mcg each of the original Wuhan-Hu-1 and Omicron BA.1 spike mRNAs) or 50 mcg of the standard authorized mRNA-1273. The doses were given as second boosters in adults who had previously received a two-dose primary series and a first booster at least 3 months before.
The model-based geometric mean titers (GMTs) ratio of the enhanced booster compared with the standard booster was 1.74 (1.49-2.04), meeting the prespecified bar for superiority against Omicron BA.1.
In participants without prior SARS-CoV-2 infection who received updated booster doses and those who received standard boosters, the neutralizing antibody GMTs against Omicron BA.1 were 2372.4 and 1473.5, respectively.
Additionally, the updated booster elicited higher GMTs (727.4) than the standard booster (492.1) against Omicron subvariants BA.4/BA.5. Safety and reactogenicity were similar for both vaccine groups.
“By the end of this year, we expect to also have clinical trial data from our BA.4/BA.5 bivalent booster,” Dr. Chalkias said.
In the interim, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration recently granted emergency use authorization for Moderna’s BA.4/BA.5 Omicron-targeting bivalent COVID-19 booster vaccine in children and adolescents aged 6-17 years.
Pfizer/BioNTech also has recently issued an announcement that their COVID-19 booster, adapted for the BA.4 and the BA.5 Omicron subvariants, generated a strong immune response and was well tolerated in human tests.
Pfizer/BioNTech said data from roughly 80 adult patients showed that the booster led to a substantial increase in neutralizing antibody levels against the BA.4/BA.5 variants after 1 week.
Separate study of causes of severe breakthrough infections in early vaccine formulations
Though COVID vaccines reduce the incidence of severe outcomes, there are reports of breakthrough infections in persons who received the original vaccines, and some of these have been serious.
In a separate study, also presented at the meeting, researchers led by first author Austin D. Vo, BS, with the VA Boston Healthcare System, used data collected from Dec. 15, 2020, through Feb. 28, 2022, in a U.S. veteran population to assess those at highest risk for severe disease despite vaccination.
Results of the large, nationwide retrospective study were simultaneously published in JAMA Network Open.
The primary outcome was development of severe COVID, defined as a hospitalization within 14 days of a confirmed positive SARS-CoV-2 test, receipt of supplemental oxygen, mechanical ventilation, or death within 28 days.
Among 110,760 participants with severe disease after primary vaccination, 13% (14,690) were hospitalized with severe COVID-19 or died.
The strongest risk factor for severe disease despite vaccination was age, the researchers found.
Presenting author Westyn Branch-Elliman, MD, associate professor of medicine with VA Boston Healthcare System, said, “We found that age greater than 50 was associated with an adjusted odds ratio of 1.42 for every 5-year increase.”
To put that in perspective, she said, “compared to patients who are 45 to 50, those over 80 had an adjusted odds ratio of 16 for hospitalization or death following breakthrough infection.”
Priya Nori, MD, an infectious disease specialist at Montefiore Medical Center in New York, said in an interview that the evidence that age is a strong risk factor for severe disease – even after vaccination – confirms that attention should be focused on those in the highest age groups, particularly those 80 years and older.
Other top risk factors included having immunocompromising conditions; having received cytotoxic chemotherapy within 6 months (adjusted odds ratio, 2.69; 95% confidence interval, 2.25-3.21); having leukemias/lymphomas (aOR, 1.84; 95% CI, 1.59-2.14); and having chronic conditions associated with end-organ disease.
“We also found that receipt of an additional booster dose of vaccine was associated with a 50% reduction in adjusted odds of severe disease,” noted Dr. Branch-Elliman.
Dr. Nori emphasized that, given these data, emphatic messaging is needed to encourage uptake of the updated Omicron-targeted vaccines for these high-risk age groups.
The study by Dr. Chalkias and colleagues was funded by Moderna. Dr. Chalkias and several coauthors are employed by Moderna. One coauthor has relationships with DLA Piper/Medtronic, and Gilead Pharmaceuticals, and one has relationships with Celgene/Bristol-Myers Squibb, ChemoCentryx, Gilead, and Kiniksa. Dr. Nori has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
AT IDWEEK 2022
More data suggest preexisting statin use improves COVID outcomes
Compared with patients who didn’t take statins, statin users had better health outcomes. For those who used these medications, the researchers saw lower mortality, lower clinical severity, and shorter hospital stays, aligning with previous observational studies, said lead author Ettore Crimi, MD, of the University of Central Florida, Orlando, and colleagues in their abstract, which was part of the agenda for the Anesthesiology annual meeting.
They attributed these clinical improvements to the pleiotropic – non–cholesterol lowering – effects of statins.
“[These] benefits of statins have been reported since the 1990s,” Dr. Crimi said in an interview. “Statin treatment has been associated with a marked reduction of markers of inflammation, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), ferritin, and white blood cell count, among others.”
He noted that these effects have been studied in an array of conditions, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory disease, and in the perioperative setting, and with infectious diseases, including COVID-19.
In those previous studies, “preexisting statin use was protective among hospitalized COVID-19 patients, but a large, multicenter cohort study has not been reported in the United States,” Dr. Crimi and his colleagues wrote in their abstract.
To address this knowledge gap, they turned to electronic medical records from 38,875 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from January to September 2020. Almost one-third of the population (n = 11,533) were using statins prior to hospitalization, while the remainder (n = 27,342) were nonusers.
The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included death from COVID-19, along with a variety of severe complications. While the analysis did account for a range of potentially confounding variables, the effects of different SARS-CoV-2 variants and new therapeutics were not considered. Vaccines were not yet available at the time the data were collected.
Statin users had a 31% lower rate of all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.75; P = .001) and a 37% reduced rate of death from COVID-19 (OR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.58-0.69; P = .001).
A litany of other secondary variables also favored statin users, including reduced rates of discharge to hospice (OR, 0.79), ICU admission (OR, 0.69), severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDs; OR, 0.72), critical ARDs (OR, 0.57), mechanical ventilation (OR, 0.60), severe sepsis with septic shock (OR, 0.66), and thrombosis (OR, 0.46). Statin users also had, on average, shorter hospital stays and briefer mechanical ventilation.
“Our study showed a strong association between preexisting statin use and reduced mortality and morbidity rates in hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” the investigators concluded. “Pleiotropic benefits of statins could be repurposed for COVID-19 illness.”
Prospective studies needed before practice changes
How to best use statins against COVID-19, if at all, remains unclear, Dr. Crimi said, as initiation upon infection has generated mixed results in other studies, possibly because of statin pharmacodynamics. Cholesterol normalization can take about 6 weeks, so other benefits may track a similar timeline.
“The delayed onset of statins’ pleiotropic effects may likely fail to keep pace with the rapidly progressive, devastating COVID-19 disease,” Dr. Crimi said. “Therefore, initiating statins for an acute disease may not be an ideal first-line treatment.”
Stronger data are on the horizon, he added, noting that 19 federally funded prospective trials are underway to better understand the relationship between statins and COVID-19.
Daniel Rader, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the present findings are “not especially notable” because they “mostly confirm previous studies, but in a large U.S. cohort.”
Dr. Rader, who wrote about the potential repurposing of statins for COVID-19 back in the first year of the pandemic (Cell Metab. 2020 Aug 4;32[2]:145-7), agreed with the investigators that recommending changes to clinical practice would be imprudent until randomized controlled data confirm the benefits of initiating statins in patients with active COVID-19.
“More research on the impact of cellular cholesterol metabolism on SARS-CoV-2 infection of cells and generation of inflammation would also be of interest,” he added.
The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Rader disclosed relationships with Novartis, Pfizer, Verve, and others.
Compared with patients who didn’t take statins, statin users had better health outcomes. For those who used these medications, the researchers saw lower mortality, lower clinical severity, and shorter hospital stays, aligning with previous observational studies, said lead author Ettore Crimi, MD, of the University of Central Florida, Orlando, and colleagues in their abstract, which was part of the agenda for the Anesthesiology annual meeting.
They attributed these clinical improvements to the pleiotropic – non–cholesterol lowering – effects of statins.
“[These] benefits of statins have been reported since the 1990s,” Dr. Crimi said in an interview. “Statin treatment has been associated with a marked reduction of markers of inflammation, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), ferritin, and white blood cell count, among others.”
He noted that these effects have been studied in an array of conditions, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory disease, and in the perioperative setting, and with infectious diseases, including COVID-19.
In those previous studies, “preexisting statin use was protective among hospitalized COVID-19 patients, but a large, multicenter cohort study has not been reported in the United States,” Dr. Crimi and his colleagues wrote in their abstract.
To address this knowledge gap, they turned to electronic medical records from 38,875 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from January to September 2020. Almost one-third of the population (n = 11,533) were using statins prior to hospitalization, while the remainder (n = 27,342) were nonusers.
The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included death from COVID-19, along with a variety of severe complications. While the analysis did account for a range of potentially confounding variables, the effects of different SARS-CoV-2 variants and new therapeutics were not considered. Vaccines were not yet available at the time the data were collected.
Statin users had a 31% lower rate of all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.75; P = .001) and a 37% reduced rate of death from COVID-19 (OR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.58-0.69; P = .001).
A litany of other secondary variables also favored statin users, including reduced rates of discharge to hospice (OR, 0.79), ICU admission (OR, 0.69), severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDs; OR, 0.72), critical ARDs (OR, 0.57), mechanical ventilation (OR, 0.60), severe sepsis with septic shock (OR, 0.66), and thrombosis (OR, 0.46). Statin users also had, on average, shorter hospital stays and briefer mechanical ventilation.
“Our study showed a strong association between preexisting statin use and reduced mortality and morbidity rates in hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” the investigators concluded. “Pleiotropic benefits of statins could be repurposed for COVID-19 illness.”
Prospective studies needed before practice changes
How to best use statins against COVID-19, if at all, remains unclear, Dr. Crimi said, as initiation upon infection has generated mixed results in other studies, possibly because of statin pharmacodynamics. Cholesterol normalization can take about 6 weeks, so other benefits may track a similar timeline.
“The delayed onset of statins’ pleiotropic effects may likely fail to keep pace with the rapidly progressive, devastating COVID-19 disease,” Dr. Crimi said. “Therefore, initiating statins for an acute disease may not be an ideal first-line treatment.”
Stronger data are on the horizon, he added, noting that 19 federally funded prospective trials are underway to better understand the relationship between statins and COVID-19.
Daniel Rader, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the present findings are “not especially notable” because they “mostly confirm previous studies, but in a large U.S. cohort.”
Dr. Rader, who wrote about the potential repurposing of statins for COVID-19 back in the first year of the pandemic (Cell Metab. 2020 Aug 4;32[2]:145-7), agreed with the investigators that recommending changes to clinical practice would be imprudent until randomized controlled data confirm the benefits of initiating statins in patients with active COVID-19.
“More research on the impact of cellular cholesterol metabolism on SARS-CoV-2 infection of cells and generation of inflammation would also be of interest,” he added.
The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Rader disclosed relationships with Novartis, Pfizer, Verve, and others.
Compared with patients who didn’t take statins, statin users had better health outcomes. For those who used these medications, the researchers saw lower mortality, lower clinical severity, and shorter hospital stays, aligning with previous observational studies, said lead author Ettore Crimi, MD, of the University of Central Florida, Orlando, and colleagues in their abstract, which was part of the agenda for the Anesthesiology annual meeting.
They attributed these clinical improvements to the pleiotropic – non–cholesterol lowering – effects of statins.
“[These] benefits of statins have been reported since the 1990s,” Dr. Crimi said in an interview. “Statin treatment has been associated with a marked reduction of markers of inflammation, such as erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) and C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), ferritin, and white blood cell count, among others.”
He noted that these effects have been studied in an array of conditions, including cancer, autoimmune diseases, chronic inflammatory disease, and in the perioperative setting, and with infectious diseases, including COVID-19.
In those previous studies, “preexisting statin use was protective among hospitalized COVID-19 patients, but a large, multicenter cohort study has not been reported in the United States,” Dr. Crimi and his colleagues wrote in their abstract.
To address this knowledge gap, they turned to electronic medical records from 38,875 patients hospitalized with COVID-19 from January to September 2020. Almost one-third of the population (n = 11,533) were using statins prior to hospitalization, while the remainder (n = 27,342) were nonusers.
The primary outcome was all-cause mortality. Secondary outcomes included death from COVID-19, along with a variety of severe complications. While the analysis did account for a range of potentially confounding variables, the effects of different SARS-CoV-2 variants and new therapeutics were not considered. Vaccines were not yet available at the time the data were collected.
Statin users had a 31% lower rate of all-cause mortality (odds ratio, 0.69; 95% confidence interval, 0.64-0.75; P = .001) and a 37% reduced rate of death from COVID-19 (OR, 0.63; 95% CI, 0.58-0.69; P = .001).
A litany of other secondary variables also favored statin users, including reduced rates of discharge to hospice (OR, 0.79), ICU admission (OR, 0.69), severe acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDs; OR, 0.72), critical ARDs (OR, 0.57), mechanical ventilation (OR, 0.60), severe sepsis with septic shock (OR, 0.66), and thrombosis (OR, 0.46). Statin users also had, on average, shorter hospital stays and briefer mechanical ventilation.
“Our study showed a strong association between preexisting statin use and reduced mortality and morbidity rates in hospitalized COVID-19 patients,” the investigators concluded. “Pleiotropic benefits of statins could be repurposed for COVID-19 illness.”
Prospective studies needed before practice changes
How to best use statins against COVID-19, if at all, remains unclear, Dr. Crimi said, as initiation upon infection has generated mixed results in other studies, possibly because of statin pharmacodynamics. Cholesterol normalization can take about 6 weeks, so other benefits may track a similar timeline.
“The delayed onset of statins’ pleiotropic effects may likely fail to keep pace with the rapidly progressive, devastating COVID-19 disease,” Dr. Crimi said. “Therefore, initiating statins for an acute disease may not be an ideal first-line treatment.”
Stronger data are on the horizon, he added, noting that 19 federally funded prospective trials are underway to better understand the relationship between statins and COVID-19.
Daniel Rader, MD, of the University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, said the present findings are “not especially notable” because they “mostly confirm previous studies, but in a large U.S. cohort.”
Dr. Rader, who wrote about the potential repurposing of statins for COVID-19 back in the first year of the pandemic (Cell Metab. 2020 Aug 4;32[2]:145-7), agreed with the investigators that recommending changes to clinical practice would be imprudent until randomized controlled data confirm the benefits of initiating statins in patients with active COVID-19.
“More research on the impact of cellular cholesterol metabolism on SARS-CoV-2 infection of cells and generation of inflammation would also be of interest,” he added.
The investigators disclosed no competing interests. Dr. Rader disclosed relationships with Novartis, Pfizer, Verve, and others.
FROM ANESTHESIOLOGY 2022
COVID lawsuits have arrived: Which doctors are at risk?
A pregnant patient who had COVID-19 showed up at a hospital with respiratory difficulty caused by her illness. Physicians had to perform an emergency delivery of her near-term baby.
The infant survived, but the woman lost oxygen during the ordeal and suffered hypoxic brain damage. She is now suing an obstetrician, a pulmonologist, and an intensive care unit physician for medical malpractice.
The plaintiff contends there was a failure “to adequately recognize and treat her condition,” said Peter Kolbert, senior vice president for claim and litigation services for Healthcare Risk Advisors, part of TDC Group, which includes national medical liability insurer The Doctors Company.
“The physicians involved vehemently disagree and believe they treated her appropriately,” Mr. Kolbert said. “In fact, we believe their actions were heroic.”
In another case, a patient with COVID-19 and multiple comorbidities was admitted to a hospital. Physicians sedated and intubated the patient to maintain her airway. She recovered, but the patient now alleges doctors were negligent because she developed ulcers during her hospital stay. The case occurred during the height of the pandemic. In addition to the hospital, a pulmonologist, an ICU physician, and an acute care physician are named in the suit.
Both of these lawsuits are being defined as COVID claims because at the time, the plaintiffs either had COVID and needed care because of COVID, or because the care that physicians provided was affected by COVID in some way.
In the second case, the patient had COVID and needed treatment. During her recovery, ulcers developed. A significant aspect of this case is that it occurred during the height of the pandemic. Hospitals were overcrowded, the staff was swamped, and resources were limited. One factor may be that physicians were doing the best they could at the time but that the pandemic affected the extent of care they could provide.
Now, new data reflect the grim news: COVID claims have arrived. These cases from the claims database of The Doctors Company are just two examples of many COVID-related claims that have been levied since the pandemic started.
Currently, there are 162 open COVID-related claims in The Doctors Company database, according to Mr. Kolbert. A September 2022 benchmark report from Aon and the American Society for Health Care Risk Management indicates that 245 claims that pertain to patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 have been filed since the pandemic began. The findings in this report stem from an analysis of 95,600 hospital and physician liability claims that occurred between 2012 and 2021.
Of the 245 cases, 89 claims have been closed. The average cost was $43,000 per claim, said Kanika Vats, a director and actuary for Aon, a global firm that provides risk, reinsurance, and health solutions. Six of the claims cost $300,000 or more; the highest settlement was for $700,000.
“Most of the allegations in these claims revolve around delay in treatment or delay in diagnosis,” Ms. Vats said.
Which specialties are involved in legal actions?
Physicians working in acute care settings such as emergency departments and urgent care centers are the primary targets in COVID-related lawsuits involving doctors, say legal analysts. However, other specialties are also being affected. Physicians being sued include some who practiced telemedicine during the pandemic.
In one case, a primary care physician saw a patient via telemedicine because the physical medical office was closed. The patient was evaluated virtually and was sent for bloodwork and an x-ray.
The patient is now suing the primary care physician, alleging that failure to immediately send her to a hospital resulted in tuberculosis going untreated and that the failure led to a bad outcome. The allegation is that the physician underevaluated the case during the telemedicine visit, Mr. Kolbert said.
Drew Graham, an attorney at Hall Booth Smith PC, which is based in New York, said that most of the COVID-related liability claims he has seen involve facilities that provide postacute care, such as nursing homes and assisted living facilities. His firm has also seen a small number of COVID-related claims against physicians.
At least two of the claims involved allegations of improper treatment of COVID during hospitalizations, he said. Another involved a telehealth visit in which the patient claimed the virtual care that was provided was improper and that their condition required an in-person examination. Mr. Graham declined to specify the specialties of the physicians sued.
The Medical Professional Liability Association reports similar trends in COVID-related claims. Long-term facilities and hospitals are the most common focus of COVID-19 claims, followed by emergency medicine, primary care, and ob/gyn medical specialties, according to Kwon Miller, manager of data and analytics for MPL Association, a national trade association for medical liability insurers that operates a large claims database.
Between January 2020 and June 2022, the MPL Association Data Sharing Project recorded 280 COVID-19 events. “Events” refers to notifications, licensing board inquiries, and claims involving COVID. Of these events, 180 were closed with no indemnity payment, and 13 were closed with an average indemnity payment of $3,816, Mr. Miller said.
Complaints of delayed care associated with the pandemic are also on the rise. For example, one patient is suing a gastroenterologist for delaying his colonoscopy, alleging the postponement led to a delayed colon cancer diagnosis and worse prognosis, Mr. Kolbert said.
“It was delayed because all elective procedures at the time were being put off,” he said. “The patient claims that had they received the scheduled screening, the cancer would have been diagnosed at stage I as opposed to stage III.”
Why isn’t federal immunity shielding physicians?
A pressing question about the growing number of COVID claims is why state and federal immunity isn’t preventing such lawsuits.
In 2020, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services published a declaration under the Public Readiness and Emergency Preparedness Act (PREP Act) that provided liability immunity to health care professionals for any activity related to medical countermeasures against COVID-19. The act allows an exception for negligence claims associated with death or serious injury caused by willful misconduct.
At the same time, most states implemented laws or executive orders shielding physicians from liability claims related to the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, unless gross negligence or willful misconduct is proven.
Mr. Graham said some COVID-related claims against physicians have included allegations of gross negligence to avoid the application of state immunity, while others combine allegations of deviations from standard of care unrelated to the pandemic.
Some plaintiffs are attempting to skirt the protections by making complaints sound as if they’re not related to COVID-19, Mr. Kolbert said. That way, they don’t have to prove gross negligence or willful misconduct at all.
“The filings at first blush may not tell you it’s a COVID case, but it may be a COVID case,” he said. “Plaintiffs’ attorneys are trying to assert that COVID defenses do not apply and that these cases are ‘traditional physician negligence’ claims. They’re trying to plead around the protections.”
The federal and state immunities are likely keeping the volume of COVID claims down overall and are discouraging some complaints from moving forward, attorneys say.
But because some plaintiffs are downplaying or ignoring the COVID association, it’s likely that more COVID lawsuits exist than anyone realizes, according to Mr. Kolbert.
“I expect there’s an underestimation of how many COVID claims are really out there,” he said.
What does the future hold for COVID claims?
Currently, the frequency and the severity of COVID claims are low, Ms. Vats said. She believes the cost of such claims will continue to remain at low levels.
“But again, there is a lot of uncertainty,” she said. “This year, states have started to roll back their immunity protections, and in a lot of states, there is no cap in awarding [noneconomic] damages. There could well be a scenario where they allege wrongful death, and in a state with no cap on the pain and suffering component, if juries continue to behave the way they have been behaving, we could see aberration verdicts.”
Another lingering issue concerns which court systems have jurisdiction in cases involving COVID-related claims. Because of the nationwide response to the pandemic, Mr. Graham thinks it makes sense that federal courts handle the cases, but the plaintiffs’ bar has generally been opposed to federal jurisdiction.
“A second issue is the long-term impact of COVID litigation on our providers,” he said. “If the protections in place to limit liability are determined to be ineffective, our state and federal leaders must act aggressively and in a bipartisan way to make sure our health care providers are protected when we face the next crisis.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A pregnant patient who had COVID-19 showed up at a hospital with respiratory difficulty caused by her illness. Physicians had to perform an emergency delivery of her near-term baby.
The infant survived, but the woman lost oxygen during the ordeal and suffered hypoxic brain damage. She is now suing an obstetrician, a pulmonologist, and an intensive care unit physician for medical malpractice.
The plaintiff contends there was a failure “to adequately recognize and treat her condition,” said Peter Kolbert, senior vice president for claim and litigation services for Healthcare Risk Advisors, part of TDC Group, which includes national medical liability insurer The Doctors Company.
“The physicians involved vehemently disagree and believe they treated her appropriately,” Mr. Kolbert said. “In fact, we believe their actions were heroic.”
In another case, a patient with COVID-19 and multiple comorbidities was admitted to a hospital. Physicians sedated and intubated the patient to maintain her airway. She recovered, but the patient now alleges doctors were negligent because she developed ulcers during her hospital stay. The case occurred during the height of the pandemic. In addition to the hospital, a pulmonologist, an ICU physician, and an acute care physician are named in the suit.
Both of these lawsuits are being defined as COVID claims because at the time, the plaintiffs either had COVID and needed care because of COVID, or because the care that physicians provided was affected by COVID in some way.
In the second case, the patient had COVID and needed treatment. During her recovery, ulcers developed. A significant aspect of this case is that it occurred during the height of the pandemic. Hospitals were overcrowded, the staff was swamped, and resources were limited. One factor may be that physicians were doing the best they could at the time but that the pandemic affected the extent of care they could provide.
Now, new data reflect the grim news: COVID claims have arrived. These cases from the claims database of The Doctors Company are just two examples of many COVID-related claims that have been levied since the pandemic started.
Currently, there are 162 open COVID-related claims in The Doctors Company database, according to Mr. Kolbert. A September 2022 benchmark report from Aon and the American Society for Health Care Risk Management indicates that 245 claims that pertain to patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 have been filed since the pandemic began. The findings in this report stem from an analysis of 95,600 hospital and physician liability claims that occurred between 2012 and 2021.
Of the 245 cases, 89 claims have been closed. The average cost was $43,000 per claim, said Kanika Vats, a director and actuary for Aon, a global firm that provides risk, reinsurance, and health solutions. Six of the claims cost $300,000 or more; the highest settlement was for $700,000.
“Most of the allegations in these claims revolve around delay in treatment or delay in diagnosis,” Ms. Vats said.
Which specialties are involved in legal actions?
Physicians working in acute care settings such as emergency departments and urgent care centers are the primary targets in COVID-related lawsuits involving doctors, say legal analysts. However, other specialties are also being affected. Physicians being sued include some who practiced telemedicine during the pandemic.
In one case, a primary care physician saw a patient via telemedicine because the physical medical office was closed. The patient was evaluated virtually and was sent for bloodwork and an x-ray.
The patient is now suing the primary care physician, alleging that failure to immediately send her to a hospital resulted in tuberculosis going untreated and that the failure led to a bad outcome. The allegation is that the physician underevaluated the case during the telemedicine visit, Mr. Kolbert said.
Drew Graham, an attorney at Hall Booth Smith PC, which is based in New York, said that most of the COVID-related liability claims he has seen involve facilities that provide postacute care, such as nursing homes and assisted living facilities. His firm has also seen a small number of COVID-related claims against physicians.
At least two of the claims involved allegations of improper treatment of COVID during hospitalizations, he said. Another involved a telehealth visit in which the patient claimed the virtual care that was provided was improper and that their condition required an in-person examination. Mr. Graham declined to specify the specialties of the physicians sued.
The Medical Professional Liability Association reports similar trends in COVID-related claims. Long-term facilities and hospitals are the most common focus of COVID-19 claims, followed by emergency medicine, primary care, and ob/gyn medical specialties, according to Kwon Miller, manager of data and analytics for MPL Association, a national trade association for medical liability insurers that operates a large claims database.
Between January 2020 and June 2022, the MPL Association Data Sharing Project recorded 280 COVID-19 events. “Events” refers to notifications, licensing board inquiries, and claims involving COVID. Of these events, 180 were closed with no indemnity payment, and 13 were closed with an average indemnity payment of $3,816, Mr. Miller said.
Complaints of delayed care associated with the pandemic are also on the rise. For example, one patient is suing a gastroenterologist for delaying his colonoscopy, alleging the postponement led to a delayed colon cancer diagnosis and worse prognosis, Mr. Kolbert said.
“It was delayed because all elective procedures at the time were being put off,” he said. “The patient claims that had they received the scheduled screening, the cancer would have been diagnosed at stage I as opposed to stage III.”
Why isn’t federal immunity shielding physicians?
A pressing question about the growing number of COVID claims is why state and federal immunity isn’t preventing such lawsuits.
In 2020, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services published a declaration under the Public Readiness and Emergency Preparedness Act (PREP Act) that provided liability immunity to health care professionals for any activity related to medical countermeasures against COVID-19. The act allows an exception for negligence claims associated with death or serious injury caused by willful misconduct.
At the same time, most states implemented laws or executive orders shielding physicians from liability claims related to the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, unless gross negligence or willful misconduct is proven.
Mr. Graham said some COVID-related claims against physicians have included allegations of gross negligence to avoid the application of state immunity, while others combine allegations of deviations from standard of care unrelated to the pandemic.
Some plaintiffs are attempting to skirt the protections by making complaints sound as if they’re not related to COVID-19, Mr. Kolbert said. That way, they don’t have to prove gross negligence or willful misconduct at all.
“The filings at first blush may not tell you it’s a COVID case, but it may be a COVID case,” he said. “Plaintiffs’ attorneys are trying to assert that COVID defenses do not apply and that these cases are ‘traditional physician negligence’ claims. They’re trying to plead around the protections.”
The federal and state immunities are likely keeping the volume of COVID claims down overall and are discouraging some complaints from moving forward, attorneys say.
But because some plaintiffs are downplaying or ignoring the COVID association, it’s likely that more COVID lawsuits exist than anyone realizes, according to Mr. Kolbert.
“I expect there’s an underestimation of how many COVID claims are really out there,” he said.
What does the future hold for COVID claims?
Currently, the frequency and the severity of COVID claims are low, Ms. Vats said. She believes the cost of such claims will continue to remain at low levels.
“But again, there is a lot of uncertainty,” she said. “This year, states have started to roll back their immunity protections, and in a lot of states, there is no cap in awarding [noneconomic] damages. There could well be a scenario where they allege wrongful death, and in a state with no cap on the pain and suffering component, if juries continue to behave the way they have been behaving, we could see aberration verdicts.”
Another lingering issue concerns which court systems have jurisdiction in cases involving COVID-related claims. Because of the nationwide response to the pandemic, Mr. Graham thinks it makes sense that federal courts handle the cases, but the plaintiffs’ bar has generally been opposed to federal jurisdiction.
“A second issue is the long-term impact of COVID litigation on our providers,” he said. “If the protections in place to limit liability are determined to be ineffective, our state and federal leaders must act aggressively and in a bipartisan way to make sure our health care providers are protected when we face the next crisis.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A pregnant patient who had COVID-19 showed up at a hospital with respiratory difficulty caused by her illness. Physicians had to perform an emergency delivery of her near-term baby.
The infant survived, but the woman lost oxygen during the ordeal and suffered hypoxic brain damage. She is now suing an obstetrician, a pulmonologist, and an intensive care unit physician for medical malpractice.
The plaintiff contends there was a failure “to adequately recognize and treat her condition,” said Peter Kolbert, senior vice president for claim and litigation services for Healthcare Risk Advisors, part of TDC Group, which includes national medical liability insurer The Doctors Company.
“The physicians involved vehemently disagree and believe they treated her appropriately,” Mr. Kolbert said. “In fact, we believe their actions were heroic.”
In another case, a patient with COVID-19 and multiple comorbidities was admitted to a hospital. Physicians sedated and intubated the patient to maintain her airway. She recovered, but the patient now alleges doctors were negligent because she developed ulcers during her hospital stay. The case occurred during the height of the pandemic. In addition to the hospital, a pulmonologist, an ICU physician, and an acute care physician are named in the suit.
Both of these lawsuits are being defined as COVID claims because at the time, the plaintiffs either had COVID and needed care because of COVID, or because the care that physicians provided was affected by COVID in some way.
In the second case, the patient had COVID and needed treatment. During her recovery, ulcers developed. A significant aspect of this case is that it occurred during the height of the pandemic. Hospitals were overcrowded, the staff was swamped, and resources were limited. One factor may be that physicians were doing the best they could at the time but that the pandemic affected the extent of care they could provide.
Now, new data reflect the grim news: COVID claims have arrived. These cases from the claims database of The Doctors Company are just two examples of many COVID-related claims that have been levied since the pandemic started.
Currently, there are 162 open COVID-related claims in The Doctors Company database, according to Mr. Kolbert. A September 2022 benchmark report from Aon and the American Society for Health Care Risk Management indicates that 245 claims that pertain to patients with confirmed or suspected COVID-19 have been filed since the pandemic began. The findings in this report stem from an analysis of 95,600 hospital and physician liability claims that occurred between 2012 and 2021.
Of the 245 cases, 89 claims have been closed. The average cost was $43,000 per claim, said Kanika Vats, a director and actuary for Aon, a global firm that provides risk, reinsurance, and health solutions. Six of the claims cost $300,000 or more; the highest settlement was for $700,000.
“Most of the allegations in these claims revolve around delay in treatment or delay in diagnosis,” Ms. Vats said.
Which specialties are involved in legal actions?
Physicians working in acute care settings such as emergency departments and urgent care centers are the primary targets in COVID-related lawsuits involving doctors, say legal analysts. However, other specialties are also being affected. Physicians being sued include some who practiced telemedicine during the pandemic.
In one case, a primary care physician saw a patient via telemedicine because the physical medical office was closed. The patient was evaluated virtually and was sent for bloodwork and an x-ray.
The patient is now suing the primary care physician, alleging that failure to immediately send her to a hospital resulted in tuberculosis going untreated and that the failure led to a bad outcome. The allegation is that the physician underevaluated the case during the telemedicine visit, Mr. Kolbert said.
Drew Graham, an attorney at Hall Booth Smith PC, which is based in New York, said that most of the COVID-related liability claims he has seen involve facilities that provide postacute care, such as nursing homes and assisted living facilities. His firm has also seen a small number of COVID-related claims against physicians.
At least two of the claims involved allegations of improper treatment of COVID during hospitalizations, he said. Another involved a telehealth visit in which the patient claimed the virtual care that was provided was improper and that their condition required an in-person examination. Mr. Graham declined to specify the specialties of the physicians sued.
The Medical Professional Liability Association reports similar trends in COVID-related claims. Long-term facilities and hospitals are the most common focus of COVID-19 claims, followed by emergency medicine, primary care, and ob/gyn medical specialties, according to Kwon Miller, manager of data and analytics for MPL Association, a national trade association for medical liability insurers that operates a large claims database.
Between January 2020 and June 2022, the MPL Association Data Sharing Project recorded 280 COVID-19 events. “Events” refers to notifications, licensing board inquiries, and claims involving COVID. Of these events, 180 were closed with no indemnity payment, and 13 were closed with an average indemnity payment of $3,816, Mr. Miller said.
Complaints of delayed care associated with the pandemic are also on the rise. For example, one patient is suing a gastroenterologist for delaying his colonoscopy, alleging the postponement led to a delayed colon cancer diagnosis and worse prognosis, Mr. Kolbert said.
“It was delayed because all elective procedures at the time were being put off,” he said. “The patient claims that had they received the scheduled screening, the cancer would have been diagnosed at stage I as opposed to stage III.”
Why isn’t federal immunity shielding physicians?
A pressing question about the growing number of COVID claims is why state and federal immunity isn’t preventing such lawsuits.
In 2020, the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services published a declaration under the Public Readiness and Emergency Preparedness Act (PREP Act) that provided liability immunity to health care professionals for any activity related to medical countermeasures against COVID-19. The act allows an exception for negligence claims associated with death or serious injury caused by willful misconduct.
At the same time, most states implemented laws or executive orders shielding physicians from liability claims related to the prevention and treatment of COVID-19, unless gross negligence or willful misconduct is proven.
Mr. Graham said some COVID-related claims against physicians have included allegations of gross negligence to avoid the application of state immunity, while others combine allegations of deviations from standard of care unrelated to the pandemic.
Some plaintiffs are attempting to skirt the protections by making complaints sound as if they’re not related to COVID-19, Mr. Kolbert said. That way, they don’t have to prove gross negligence or willful misconduct at all.
“The filings at first blush may not tell you it’s a COVID case, but it may be a COVID case,” he said. “Plaintiffs’ attorneys are trying to assert that COVID defenses do not apply and that these cases are ‘traditional physician negligence’ claims. They’re trying to plead around the protections.”
The federal and state immunities are likely keeping the volume of COVID claims down overall and are discouraging some complaints from moving forward, attorneys say.
But because some plaintiffs are downplaying or ignoring the COVID association, it’s likely that more COVID lawsuits exist than anyone realizes, according to Mr. Kolbert.
“I expect there’s an underestimation of how many COVID claims are really out there,” he said.
What does the future hold for COVID claims?
Currently, the frequency and the severity of COVID claims are low, Ms. Vats said. She believes the cost of such claims will continue to remain at low levels.
“But again, there is a lot of uncertainty,” she said. “This year, states have started to roll back their immunity protections, and in a lot of states, there is no cap in awarding [noneconomic] damages. There could well be a scenario where they allege wrongful death, and in a state with no cap on the pain and suffering component, if juries continue to behave the way they have been behaving, we could see aberration verdicts.”
Another lingering issue concerns which court systems have jurisdiction in cases involving COVID-related claims. Because of the nationwide response to the pandemic, Mr. Graham thinks it makes sense that federal courts handle the cases, but the plaintiffs’ bar has generally been opposed to federal jurisdiction.
“A second issue is the long-term impact of COVID litigation on our providers,” he said. “If the protections in place to limit liability are determined to be ineffective, our state and federal leaders must act aggressively and in a bipartisan way to make sure our health care providers are protected when we face the next crisis.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ten-day methotrexate pause after COVID vaccine booster enhances immunity against Omicron variant
People taking methotrexate for immunomodulatory diseases can skip one or two scheduled doses after they get an mRNA-based vaccine booster for COVID-19 and achieve a level of immunity against Omicron variants that’s comparable to people who aren’t immunosuppressed, a small observational cohort study from Germany reported.
“In general, the data suggest that pausing methotrexate is feasible, and it’s sufficient if the last dose occurs 1-3 days before the vaccination,” study coauthor Gerd Burmester, MD, a senior professor of rheumatology and immunology at the University of Medicine Berlin, told this news organization. “In pragmatic terms: pausing the methotrexate injection just twice after the vaccine is finished and, interestingly, not prior to the vaccination.”
The study, published online in RMD Open, included a statistical analysis that determined that a 10-day pause after the vaccination would be optimal, Dr. Burmester said.
Dr. Burmester and coauthors claimed this is the first study to evaluate the antibody response in patients on methotrexate against Omicron variants – in this study, variants BA.1 and BA.2 – after getting a COVID-19 mRNA booster. The study compared neutralizing serum activity of 50 patients taking methotrexate – 24 of whom continued treatments uninterrupted and 26 of whom paused treatments after getting a second booster – with 25 nonimmunosuppressed patients who served as controls. A total of 24% of the patients taking methotrexate received the mRNA-1273 vaccine while the entire control group received the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine.
The researchers used SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate post-vaccination antibody levels.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other government health agencies have recommended that immunocompromised patients get a fourth COVID-19 vaccination. But these vaccines can be problematic in patients taking methotrexate, which was linked to a reduced response after the second and third doses of the COVID-19 vaccine.
Previous studies reported that pausing methotrexate for 10 or 14 days after the first two vaccinations improved the production of neutralizing antibodies. A 2022 study found that a 2-week pause after a booster increased antibody response against S1 RBD (receptor binding domain) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein about twofold. Another recently published study of mRNA vaccines found that taking methotrexate with either a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug reduces the efficacy of a third (booster) shot of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in older adults but not younger patients with RA.
“Our study and also the other studies suggested that you can pause methotrexate treatment safely from a point of view of disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Burmester said. “If you do the pause just twice or once only, it doesn’t lead to significant flares.”
Study results
The study found that serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron BA.1 variant, measured as geometric mean 50% inhibitory serum dilution (ID50s), wasn’t significantly different between the methotrexate and the nonimmunosuppressed groups before getting their mRNA booster (P = .657). However, 4 weeks after getting the booster, the nonimmunosuppressed group had a 68-fold increase in antibody activity versus a 20-fold increase in the methotrexate patients. After 12 weeks, ID50s in both groups decreased by about half (P = .001).
The methotrexate patients who continued therapy after the booster had significantly lower neutralization against Omicron BA.1 at both 4 weeks and 12 weeks than did their counterparts who paused therapy, as well as control patients.
The results were very similar in the same group comparisons of the serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron BA.2 variant at 4 and 12 weeks after booster vaccination.
Expert commentary
This study is noteworthy because it used SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate antibody levels, Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious disease and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who was not involved in the study, said. “A lot of studies don’t look at neutralizing antibody titers, and that’s really what we care about,” Dr. Winthrop said. “What we want are functional antibodies that are doing something, and the only way to do that is to test them.”
The study is “confirmatory” of other studies that call for pausing methotrexate after vaccination, Dr. Winthrop said, including a study he coauthored, and which the German researchers cited, that found pausing methotrexate for a week or so after the influenza vaccination in RA patients improved vaccine immunogenicity. He added that the findings with the early Omicron variants are important because the newest boosters target the later Omicron variants, BA.4 and BA.5.
“The bottom line is that when someone comes in for a COVID-19 vaccination, tell them to be off of methotrexate for 7-10 days,” Dr. Winthrop said. “This is for the booster, but it raises the question: If you go out to three, four, or five vaccinations, does this matter anymore? With the flu vaccine, most people are out to 10 or 15 boosters, and we haven’t seen any significant increase in disease flares.”
The study received funding from Medac, Gilead/Galapagos, and Friends and Sponsors of Berlin Charity. Dr. Burmester reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Winthrop is a research consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People taking methotrexate for immunomodulatory diseases can skip one or two scheduled doses after they get an mRNA-based vaccine booster for COVID-19 and achieve a level of immunity against Omicron variants that’s comparable to people who aren’t immunosuppressed, a small observational cohort study from Germany reported.
“In general, the data suggest that pausing methotrexate is feasible, and it’s sufficient if the last dose occurs 1-3 days before the vaccination,” study coauthor Gerd Burmester, MD, a senior professor of rheumatology and immunology at the University of Medicine Berlin, told this news organization. “In pragmatic terms: pausing the methotrexate injection just twice after the vaccine is finished and, interestingly, not prior to the vaccination.”
The study, published online in RMD Open, included a statistical analysis that determined that a 10-day pause after the vaccination would be optimal, Dr. Burmester said.
Dr. Burmester and coauthors claimed this is the first study to evaluate the antibody response in patients on methotrexate against Omicron variants – in this study, variants BA.1 and BA.2 – after getting a COVID-19 mRNA booster. The study compared neutralizing serum activity of 50 patients taking methotrexate – 24 of whom continued treatments uninterrupted and 26 of whom paused treatments after getting a second booster – with 25 nonimmunosuppressed patients who served as controls. A total of 24% of the patients taking methotrexate received the mRNA-1273 vaccine while the entire control group received the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine.
The researchers used SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate post-vaccination antibody levels.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other government health agencies have recommended that immunocompromised patients get a fourth COVID-19 vaccination. But these vaccines can be problematic in patients taking methotrexate, which was linked to a reduced response after the second and third doses of the COVID-19 vaccine.
Previous studies reported that pausing methotrexate for 10 or 14 days after the first two vaccinations improved the production of neutralizing antibodies. A 2022 study found that a 2-week pause after a booster increased antibody response against S1 RBD (receptor binding domain) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein about twofold. Another recently published study of mRNA vaccines found that taking methotrexate with either a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug reduces the efficacy of a third (booster) shot of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in older adults but not younger patients with RA.
“Our study and also the other studies suggested that you can pause methotrexate treatment safely from a point of view of disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Burmester said. “If you do the pause just twice or once only, it doesn’t lead to significant flares.”
Study results
The study found that serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron BA.1 variant, measured as geometric mean 50% inhibitory serum dilution (ID50s), wasn’t significantly different between the methotrexate and the nonimmunosuppressed groups before getting their mRNA booster (P = .657). However, 4 weeks after getting the booster, the nonimmunosuppressed group had a 68-fold increase in antibody activity versus a 20-fold increase in the methotrexate patients. After 12 weeks, ID50s in both groups decreased by about half (P = .001).
The methotrexate patients who continued therapy after the booster had significantly lower neutralization against Omicron BA.1 at both 4 weeks and 12 weeks than did their counterparts who paused therapy, as well as control patients.
The results were very similar in the same group comparisons of the serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron BA.2 variant at 4 and 12 weeks after booster vaccination.
Expert commentary
This study is noteworthy because it used SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate antibody levels, Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious disease and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who was not involved in the study, said. “A lot of studies don’t look at neutralizing antibody titers, and that’s really what we care about,” Dr. Winthrop said. “What we want are functional antibodies that are doing something, and the only way to do that is to test them.”
The study is “confirmatory” of other studies that call for pausing methotrexate after vaccination, Dr. Winthrop said, including a study he coauthored, and which the German researchers cited, that found pausing methotrexate for a week or so after the influenza vaccination in RA patients improved vaccine immunogenicity. He added that the findings with the early Omicron variants are important because the newest boosters target the later Omicron variants, BA.4 and BA.5.
“The bottom line is that when someone comes in for a COVID-19 vaccination, tell them to be off of methotrexate for 7-10 days,” Dr. Winthrop said. “This is for the booster, but it raises the question: If you go out to three, four, or five vaccinations, does this matter anymore? With the flu vaccine, most people are out to 10 or 15 boosters, and we haven’t seen any significant increase in disease flares.”
The study received funding from Medac, Gilead/Galapagos, and Friends and Sponsors of Berlin Charity. Dr. Burmester reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Winthrop is a research consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People taking methotrexate for immunomodulatory diseases can skip one or two scheduled doses after they get an mRNA-based vaccine booster for COVID-19 and achieve a level of immunity against Omicron variants that’s comparable to people who aren’t immunosuppressed, a small observational cohort study from Germany reported.
“In general, the data suggest that pausing methotrexate is feasible, and it’s sufficient if the last dose occurs 1-3 days before the vaccination,” study coauthor Gerd Burmester, MD, a senior professor of rheumatology and immunology at the University of Medicine Berlin, told this news organization. “In pragmatic terms: pausing the methotrexate injection just twice after the vaccine is finished and, interestingly, not prior to the vaccination.”
The study, published online in RMD Open, included a statistical analysis that determined that a 10-day pause after the vaccination would be optimal, Dr. Burmester said.
Dr. Burmester and coauthors claimed this is the first study to evaluate the antibody response in patients on methotrexate against Omicron variants – in this study, variants BA.1 and BA.2 – after getting a COVID-19 mRNA booster. The study compared neutralizing serum activity of 50 patients taking methotrexate – 24 of whom continued treatments uninterrupted and 26 of whom paused treatments after getting a second booster – with 25 nonimmunosuppressed patients who served as controls. A total of 24% of the patients taking methotrexate received the mRNA-1273 vaccine while the entire control group received the Pfizer/BioNTech BNT162b2 vaccine.
The researchers used SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate post-vaccination antibody levels.
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and other government health agencies have recommended that immunocompromised patients get a fourth COVID-19 vaccination. But these vaccines can be problematic in patients taking methotrexate, which was linked to a reduced response after the second and third doses of the COVID-19 vaccine.
Previous studies reported that pausing methotrexate for 10 or 14 days after the first two vaccinations improved the production of neutralizing antibodies. A 2022 study found that a 2-week pause after a booster increased antibody response against S1 RBD (receptor binding domain) of the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein about twofold. Another recently published study of mRNA vaccines found that taking methotrexate with either a biologic or targeted synthetic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug reduces the efficacy of a third (booster) shot of SARS-CoV-2 mRNA vaccine in older adults but not younger patients with RA.
“Our study and also the other studies suggested that you can pause methotrexate treatment safely from a point of view of disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis,” Dr. Burmester said. “If you do the pause just twice or once only, it doesn’t lead to significant flares.”
Study results
The study found that serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron BA.1 variant, measured as geometric mean 50% inhibitory serum dilution (ID50s), wasn’t significantly different between the methotrexate and the nonimmunosuppressed groups before getting their mRNA booster (P = .657). However, 4 weeks after getting the booster, the nonimmunosuppressed group had a 68-fold increase in antibody activity versus a 20-fold increase in the methotrexate patients. After 12 weeks, ID50s in both groups decreased by about half (P = .001).
The methotrexate patients who continued therapy after the booster had significantly lower neutralization against Omicron BA.1 at both 4 weeks and 12 weeks than did their counterparts who paused therapy, as well as control patients.
The results were very similar in the same group comparisons of the serum neutralizing activity against the Omicron BA.2 variant at 4 and 12 weeks after booster vaccination.
Expert commentary
This study is noteworthy because it used SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus neutralization assays to evaluate antibody levels, Kevin Winthrop, MD, MPH, professor of infectious disease and public health at Oregon Health & Science University, Portland, who was not involved in the study, said. “A lot of studies don’t look at neutralizing antibody titers, and that’s really what we care about,” Dr. Winthrop said. “What we want are functional antibodies that are doing something, and the only way to do that is to test them.”
The study is “confirmatory” of other studies that call for pausing methotrexate after vaccination, Dr. Winthrop said, including a study he coauthored, and which the German researchers cited, that found pausing methotrexate for a week or so after the influenza vaccination in RA patients improved vaccine immunogenicity. He added that the findings with the early Omicron variants are important because the newest boosters target the later Omicron variants, BA.4 and BA.5.
“The bottom line is that when someone comes in for a COVID-19 vaccination, tell them to be off of methotrexate for 7-10 days,” Dr. Winthrop said. “This is for the booster, but it raises the question: If you go out to three, four, or five vaccinations, does this matter anymore? With the flu vaccine, most people are out to 10 or 15 boosters, and we haven’t seen any significant increase in disease flares.”
The study received funding from Medac, Gilead/Galapagos, and Friends and Sponsors of Berlin Charity. Dr. Burmester reported no relevant disclosures. Dr. Winthrop is a research consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM RMD OPEN