User login
-
CMS suspends advance payment program to clinicians for COVID-19 relief
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will suspend its Medicare advance payment program for clinicians and is reevaluating how much to pay to hospitals going forward through particular COVID-19 relief initiatives. CMS announced the changes on April 26. Physicians and others who use the accelerated and advance Medicare payments program repay these advances, and they are typically given 1 year or less to repay the funding.
CMS said in a news release it will not accept new applications for the advanced Medicare payment, and it will be reevaluating all pending and new applications “in light of historical direct payments made available through the Department of Health & Human Services’ (HHS) Provider Relief Fund.”
The advance Medicare payment program predates COVID-19, although it previously was used on a much smaller scale. In the past 5 years, CMS approved about 100 total requests for advanced Medicare payment, with most being tied to natural disasters such as hurricanes.
CMS said it has approved, since March, more than 21,000 applications for advanced Medicare payment, totaling $59.6 billion, for hospitals and other organizations that bill its Part A program. In addition, CMS approved almost 24,000 applications for its Part B program, advancing $40.4 billion for physicians, other clinicians, and medical equipment suppliers.
CMS noted that Congress also has provided $175 billion in aid for the medical community that clinicians and medical organizations would not need to repay. The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act enacted in March included $100 billion, and the Paycheck Protection Program and Health Care Enhancement Act, enacted March 24, includes another $75 billion.
A version of this article was originally published on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will suspend its Medicare advance payment program for clinicians and is reevaluating how much to pay to hospitals going forward through particular COVID-19 relief initiatives. CMS announced the changes on April 26. Physicians and others who use the accelerated and advance Medicare payments program repay these advances, and they are typically given 1 year or less to repay the funding.
CMS said in a news release it will not accept new applications for the advanced Medicare payment, and it will be reevaluating all pending and new applications “in light of historical direct payments made available through the Department of Health & Human Services’ (HHS) Provider Relief Fund.”
The advance Medicare payment program predates COVID-19, although it previously was used on a much smaller scale. In the past 5 years, CMS approved about 100 total requests for advanced Medicare payment, with most being tied to natural disasters such as hurricanes.
CMS said it has approved, since March, more than 21,000 applications for advanced Medicare payment, totaling $59.6 billion, for hospitals and other organizations that bill its Part A program. In addition, CMS approved almost 24,000 applications for its Part B program, advancing $40.4 billion for physicians, other clinicians, and medical equipment suppliers.
CMS noted that Congress also has provided $175 billion in aid for the medical community that clinicians and medical organizations would not need to repay. The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act enacted in March included $100 billion, and the Paycheck Protection Program and Health Care Enhancement Act, enacted March 24, includes another $75 billion.
A version of this article was originally published on Medscape.com.
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services will suspend its Medicare advance payment program for clinicians and is reevaluating how much to pay to hospitals going forward through particular COVID-19 relief initiatives. CMS announced the changes on April 26. Physicians and others who use the accelerated and advance Medicare payments program repay these advances, and they are typically given 1 year or less to repay the funding.
CMS said in a news release it will not accept new applications for the advanced Medicare payment, and it will be reevaluating all pending and new applications “in light of historical direct payments made available through the Department of Health & Human Services’ (HHS) Provider Relief Fund.”
The advance Medicare payment program predates COVID-19, although it previously was used on a much smaller scale. In the past 5 years, CMS approved about 100 total requests for advanced Medicare payment, with most being tied to natural disasters such as hurricanes.
CMS said it has approved, since March, more than 21,000 applications for advanced Medicare payment, totaling $59.6 billion, for hospitals and other organizations that bill its Part A program. In addition, CMS approved almost 24,000 applications for its Part B program, advancing $40.4 billion for physicians, other clinicians, and medical equipment suppliers.
CMS noted that Congress also has provided $175 billion in aid for the medical community that clinicians and medical organizations would not need to repay. The Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act enacted in March included $100 billion, and the Paycheck Protection Program and Health Care Enhancement Act, enacted March 24, includes another $75 billion.
A version of this article was originally published on Medscape.com.
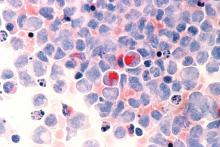
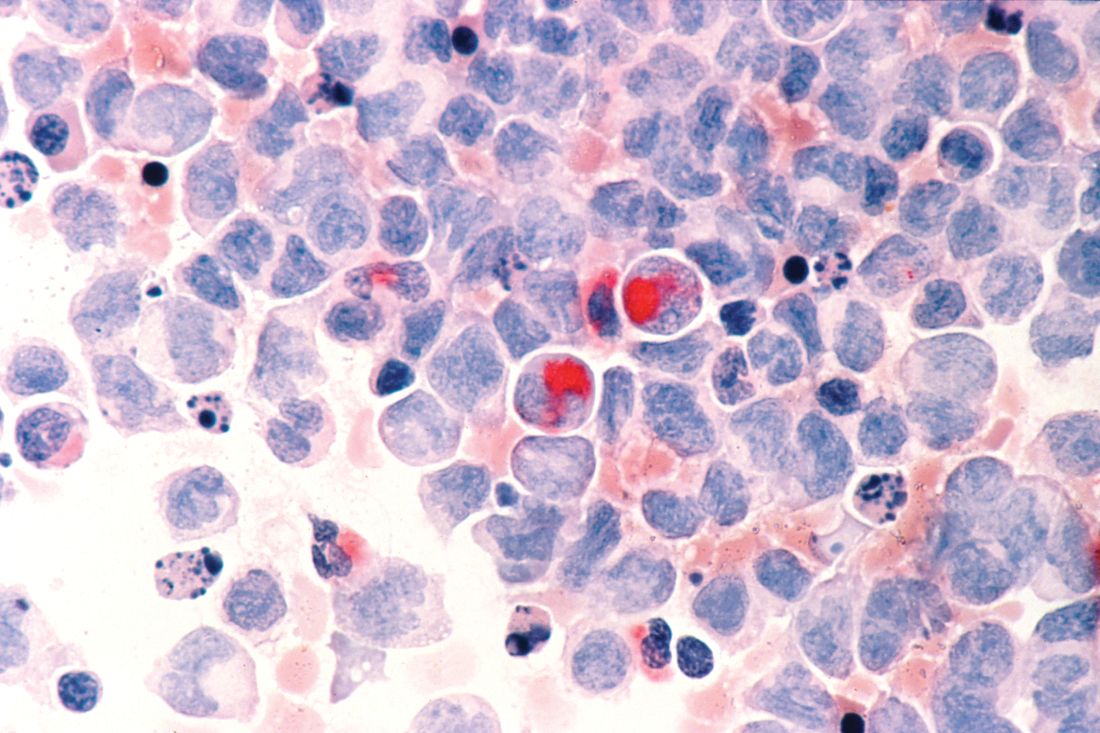
EHA webinar addresses treating AML patients with COVID-19
A hematologist in Italy shared his personal experience addressing the intersection of COVID-19 and the care of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients during a webinar hosted by the European Hematology Association (EHA).
Felicetto Ferrara, MD, of Cardarelli Hospital in Naples, Italy, discussed the main difficulties in administering optimal treatment for AML patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
The major problems include the need to isolate patients while simultaneously allowing for collaboration with pulmonologists and intensivists, the delays in AML treatment caused by COVID-19, and the risk of drug-drug interactions while treating AML patients with COVID-19.
The need to isolate AML patients with COVID-19 is paramount, according to Dr. Ferrara. Isolation can be accomplished, ideally, by the creation of a dedicated COVID-19 unit or, alternatively, with the use of single-patient negative pressure rooms. Dr. Ferrara stressed that all patients with AML should be tested for COVID-19 before admission.
Delaying or reducing AML treatment
Treatment delays are of particular concern, according to Dr. Ferrara, and some patients may require dose reductions, especially for AML treatments that might have a detrimental effect on the immune system.
Decisions must be made as to whether planned approaches to induction or consolidation therapy should be changed, and special concern has to be paid to elderly AML patients, who have the highest risks of bad COVID-19 outcomes.
Specific attention should be paid to patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia as well, according to Dr. Ferrara. These patients are of concern in the COVID-19 era because of their risk of differentiation syndrome, which can induce respiratory distress.
In all cases, autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplant should be deferred until confirmed COVID-19–negative test results are obtained.
Continuing AML treatment
Of particular concern is the fact that, without a standard therapy for COVID-19, many different drugs might be used in treatment efforts. This raises the potential for serious drug-drug interactions with the patient’s AML medications, so close attention should be paid to an individual patient’s medications.
In terms of continuing AML treatment for younger adults (less than 65 years) who are positive for COVID-19, symptomatic and asymptomatic patients should be treated differently, Dr. Ferarra said.
Symptomatic patients should be given hydroxyurea until symptom resolution, and unless urgent, any further AML treatments should be delayed. However, if treatment is needed immediately, it should be given in a COVID-19–dedicated unit.
The restrictions are much looser for young adult asymptomatic COVID-19 patients with AML. Standard induction therapy should be given, with intermediate-dose cytarabine used as consolidation therapy.
Therapy in elderly patients with AML and COVID-19 should be based on symptom status as well, said Dr. Ferrara.
Asymptomatic but otherwise fit elderly patients should have standard induction therapy if they are in the European Leukemia Network favorable genetic subgroup. Asymptomatic elderly patients with high-risk molecular disease can receive venetoclax with a hypomethylating agent.
Symptomatic elderly patients should continue with hydroxyurea until symptom resolution, and any other treatments should be delayed in nonemergency cases.
Relapsed AML patients with COVID-19 should have their treatments postponed until they obtain negative COVID-19 test results whenever possible, Dr. Ferarra said. However, if treatment is necessary, molecularly targeted therapies (gilteritinib, ivosidenib, and enasidenib) are preferable to high-dose chemotherapy.
In all cases, treatment decisions should be made in conjunction with pulmonologists and intensivists, Dr. Ferrera noted.
Webinar moderator Francesco Cerisoli, MD, head of research and mentoring at EHA, highlighted the fact that EHA has published specific recommendations for treating AML patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The majority of these were discussed by and are aligned with the recommendations presented by Dr. Ferrara.
The EHA webinar contains a disclaimer that the content discussed was based on the personal experiences and opinions of the speakers and that no general, evidence-based guidance could be derived from the discussion. There were no disclosures given.
A hematologist in Italy shared his personal experience addressing the intersection of COVID-19 and the care of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients during a webinar hosted by the European Hematology Association (EHA).
Felicetto Ferrara, MD, of Cardarelli Hospital in Naples, Italy, discussed the main difficulties in administering optimal treatment for AML patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
The major problems include the need to isolate patients while simultaneously allowing for collaboration with pulmonologists and intensivists, the delays in AML treatment caused by COVID-19, and the risk of drug-drug interactions while treating AML patients with COVID-19.
The need to isolate AML patients with COVID-19 is paramount, according to Dr. Ferrara. Isolation can be accomplished, ideally, by the creation of a dedicated COVID-19 unit or, alternatively, with the use of single-patient negative pressure rooms. Dr. Ferrara stressed that all patients with AML should be tested for COVID-19 before admission.
Delaying or reducing AML treatment
Treatment delays are of particular concern, according to Dr. Ferrara, and some patients may require dose reductions, especially for AML treatments that might have a detrimental effect on the immune system.
Decisions must be made as to whether planned approaches to induction or consolidation therapy should be changed, and special concern has to be paid to elderly AML patients, who have the highest risks of bad COVID-19 outcomes.
Specific attention should be paid to patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia as well, according to Dr. Ferrara. These patients are of concern in the COVID-19 era because of their risk of differentiation syndrome, which can induce respiratory distress.
In all cases, autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplant should be deferred until confirmed COVID-19–negative test results are obtained.
Continuing AML treatment
Of particular concern is the fact that, without a standard therapy for COVID-19, many different drugs might be used in treatment efforts. This raises the potential for serious drug-drug interactions with the patient’s AML medications, so close attention should be paid to an individual patient’s medications.
In terms of continuing AML treatment for younger adults (less than 65 years) who are positive for COVID-19, symptomatic and asymptomatic patients should be treated differently, Dr. Ferarra said.
Symptomatic patients should be given hydroxyurea until symptom resolution, and unless urgent, any further AML treatments should be delayed. However, if treatment is needed immediately, it should be given in a COVID-19–dedicated unit.
The restrictions are much looser for young adult asymptomatic COVID-19 patients with AML. Standard induction therapy should be given, with intermediate-dose cytarabine used as consolidation therapy.
Therapy in elderly patients with AML and COVID-19 should be based on symptom status as well, said Dr. Ferrara.
Asymptomatic but otherwise fit elderly patients should have standard induction therapy if they are in the European Leukemia Network favorable genetic subgroup. Asymptomatic elderly patients with high-risk molecular disease can receive venetoclax with a hypomethylating agent.
Symptomatic elderly patients should continue with hydroxyurea until symptom resolution, and any other treatments should be delayed in nonemergency cases.
Relapsed AML patients with COVID-19 should have their treatments postponed until they obtain negative COVID-19 test results whenever possible, Dr. Ferarra said. However, if treatment is necessary, molecularly targeted therapies (gilteritinib, ivosidenib, and enasidenib) are preferable to high-dose chemotherapy.
In all cases, treatment decisions should be made in conjunction with pulmonologists and intensivists, Dr. Ferrera noted.
Webinar moderator Francesco Cerisoli, MD, head of research and mentoring at EHA, highlighted the fact that EHA has published specific recommendations for treating AML patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The majority of these were discussed by and are aligned with the recommendations presented by Dr. Ferrara.
The EHA webinar contains a disclaimer that the content discussed was based on the personal experiences and opinions of the speakers and that no general, evidence-based guidance could be derived from the discussion. There were no disclosures given.
A hematologist in Italy shared his personal experience addressing the intersection of COVID-19 and the care of acute myeloid leukemia (AML) patients during a webinar hosted by the European Hematology Association (EHA).
Felicetto Ferrara, MD, of Cardarelli Hospital in Naples, Italy, discussed the main difficulties in administering optimal treatment for AML patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
The major problems include the need to isolate patients while simultaneously allowing for collaboration with pulmonologists and intensivists, the delays in AML treatment caused by COVID-19, and the risk of drug-drug interactions while treating AML patients with COVID-19.
The need to isolate AML patients with COVID-19 is paramount, according to Dr. Ferrara. Isolation can be accomplished, ideally, by the creation of a dedicated COVID-19 unit or, alternatively, with the use of single-patient negative pressure rooms. Dr. Ferrara stressed that all patients with AML should be tested for COVID-19 before admission.
Delaying or reducing AML treatment
Treatment delays are of particular concern, according to Dr. Ferrara, and some patients may require dose reductions, especially for AML treatments that might have a detrimental effect on the immune system.
Decisions must be made as to whether planned approaches to induction or consolidation therapy should be changed, and special concern has to be paid to elderly AML patients, who have the highest risks of bad COVID-19 outcomes.
Specific attention should be paid to patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia as well, according to Dr. Ferrara. These patients are of concern in the COVID-19 era because of their risk of differentiation syndrome, which can induce respiratory distress.
In all cases, autologous or allogeneic stem cell transplant should be deferred until confirmed COVID-19–negative test results are obtained.
Continuing AML treatment
Of particular concern is the fact that, without a standard therapy for COVID-19, many different drugs might be used in treatment efforts. This raises the potential for serious drug-drug interactions with the patient’s AML medications, so close attention should be paid to an individual patient’s medications.
In terms of continuing AML treatment for younger adults (less than 65 years) who are positive for COVID-19, symptomatic and asymptomatic patients should be treated differently, Dr. Ferarra said.
Symptomatic patients should be given hydroxyurea until symptom resolution, and unless urgent, any further AML treatments should be delayed. However, if treatment is needed immediately, it should be given in a COVID-19–dedicated unit.
The restrictions are much looser for young adult asymptomatic COVID-19 patients with AML. Standard induction therapy should be given, with intermediate-dose cytarabine used as consolidation therapy.
Therapy in elderly patients with AML and COVID-19 should be based on symptom status as well, said Dr. Ferrara.
Asymptomatic but otherwise fit elderly patients should have standard induction therapy if they are in the European Leukemia Network favorable genetic subgroup. Asymptomatic elderly patients with high-risk molecular disease can receive venetoclax with a hypomethylating agent.
Symptomatic elderly patients should continue with hydroxyurea until symptom resolution, and any other treatments should be delayed in nonemergency cases.
Relapsed AML patients with COVID-19 should have their treatments postponed until they obtain negative COVID-19 test results whenever possible, Dr. Ferarra said. However, if treatment is necessary, molecularly targeted therapies (gilteritinib, ivosidenib, and enasidenib) are preferable to high-dose chemotherapy.
In all cases, treatment decisions should be made in conjunction with pulmonologists and intensivists, Dr. Ferrera noted.
Webinar moderator Francesco Cerisoli, MD, head of research and mentoring at EHA, highlighted the fact that EHA has published specific recommendations for treating AML patients during the COVID-19 pandemic. The majority of these were discussed by and are aligned with the recommendations presented by Dr. Ferrara.
The EHA webinar contains a disclaimer that the content discussed was based on the personal experiences and opinions of the speakers and that no general, evidence-based guidance could be derived from the discussion. There were no disclosures given.
Changing habits, sleep patterns, and home duties during the pandemic
Like you, I’m not sure when this weird Twilight Zone world of coronavirus will end. Even when it does, its effects will be with us for a long time to come.
But in some ways, they may be for the better. Hopefully some of these changes will stick. Like every new situation, I try to take away something of value from it.
As pithy as it sounds, I used to obsess (sort of) over the daily mail delivery. My secretary would check it mid-afternoon, and if it wasn’t there either she or I would run down again before we left. If it still wasn’t there I’d swing by the box when I came in early the next morning. On Saturdays, I’d sometimes drive in just to get the mail.
There certainly are things that come in that are important: payments, bills, medical records, legal cases to review ... but realistically a lot of mail is junk. Office-supply catalogs, CME or pharmaceutical ads, credit card promotions, and so on.
Now? I just don’t care. If I go several days without seeing patients at the office, the mail is at the back of my mind. It’s in a locked box and isn’t going anywhere. Why worry about it? Next time I’m there I can deal with it. It’s not worth thinking about, it’s just the mail. It’s not worth a special trip.
Sleep is another thing. For years my internal alarm has had me up around 4:00 a.m. (I don’t even bother to set one on my phone), and I get up and go in to get started on the day.
Now? I don’t think I’ve ever slept this much. If I have to go to my office, I’m much less rushed. Many days I don’t even have to do that. I walk down to my home office, call up my charts and the day’s video appointment schedule, and we’re off. Granted, once things return to speed, this will probably be back to normal.
My kids are all home from college, so I have the extra time at home to enjoy them and our dogs. My wife, an oncology infusion nurse, doesn’t get home until 6:00 each night, so for now I’ve become a stay-at-home dad. This is actually something I’ve always liked (in high school, I was voted “most likely to to be a house husband”). So I do the laundry and am in charge of dinner each night. I’m enjoying the last, as I get to pick things out, go through recipes, and cook. I won’t say I’m a great cook, but I’m learning and having fun. As strange as it sounds, being a house husband has always been something I wanted to do, so I’m appreciating the opportunity while it lasts.
I think all of us have come to accept this strange pause button that’s been pushed, and I’ll try to learn what I can from it and take that with me as I move forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz. He has no relevant disclosures.
Like you, I’m not sure when this weird Twilight Zone world of coronavirus will end. Even when it does, its effects will be with us for a long time to come.
But in some ways, they may be for the better. Hopefully some of these changes will stick. Like every new situation, I try to take away something of value from it.
As pithy as it sounds, I used to obsess (sort of) over the daily mail delivery. My secretary would check it mid-afternoon, and if it wasn’t there either she or I would run down again before we left. If it still wasn’t there I’d swing by the box when I came in early the next morning. On Saturdays, I’d sometimes drive in just to get the mail.
There certainly are things that come in that are important: payments, bills, medical records, legal cases to review ... but realistically a lot of mail is junk. Office-supply catalogs, CME or pharmaceutical ads, credit card promotions, and so on.
Now? I just don’t care. If I go several days without seeing patients at the office, the mail is at the back of my mind. It’s in a locked box and isn’t going anywhere. Why worry about it? Next time I’m there I can deal with it. It’s not worth thinking about, it’s just the mail. It’s not worth a special trip.
Sleep is another thing. For years my internal alarm has had me up around 4:00 a.m. (I don’t even bother to set one on my phone), and I get up and go in to get started on the day.
Now? I don’t think I’ve ever slept this much. If I have to go to my office, I’m much less rushed. Many days I don’t even have to do that. I walk down to my home office, call up my charts and the day’s video appointment schedule, and we’re off. Granted, once things return to speed, this will probably be back to normal.
My kids are all home from college, so I have the extra time at home to enjoy them and our dogs. My wife, an oncology infusion nurse, doesn’t get home until 6:00 each night, so for now I’ve become a stay-at-home dad. This is actually something I’ve always liked (in high school, I was voted “most likely to to be a house husband”). So I do the laundry and am in charge of dinner each night. I’m enjoying the last, as I get to pick things out, go through recipes, and cook. I won’t say I’m a great cook, but I’m learning and having fun. As strange as it sounds, being a house husband has always been something I wanted to do, so I’m appreciating the opportunity while it lasts.
I think all of us have come to accept this strange pause button that’s been pushed, and I’ll try to learn what I can from it and take that with me as I move forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz. He has no relevant disclosures.
Like you, I’m not sure when this weird Twilight Zone world of coronavirus will end. Even when it does, its effects will be with us for a long time to come.
But in some ways, they may be for the better. Hopefully some of these changes will stick. Like every new situation, I try to take away something of value from it.
As pithy as it sounds, I used to obsess (sort of) over the daily mail delivery. My secretary would check it mid-afternoon, and if it wasn’t there either she or I would run down again before we left. If it still wasn’t there I’d swing by the box when I came in early the next morning. On Saturdays, I’d sometimes drive in just to get the mail.
There certainly are things that come in that are important: payments, bills, medical records, legal cases to review ... but realistically a lot of mail is junk. Office-supply catalogs, CME or pharmaceutical ads, credit card promotions, and so on.
Now? I just don’t care. If I go several days without seeing patients at the office, the mail is at the back of my mind. It’s in a locked box and isn’t going anywhere. Why worry about it? Next time I’m there I can deal with it. It’s not worth thinking about, it’s just the mail. It’s not worth a special trip.
Sleep is another thing. For years my internal alarm has had me up around 4:00 a.m. (I don’t even bother to set one on my phone), and I get up and go in to get started on the day.
Now? I don’t think I’ve ever slept this much. If I have to go to my office, I’m much less rushed. Many days I don’t even have to do that. I walk down to my home office, call up my charts and the day’s video appointment schedule, and we’re off. Granted, once things return to speed, this will probably be back to normal.
My kids are all home from college, so I have the extra time at home to enjoy them and our dogs. My wife, an oncology infusion nurse, doesn’t get home until 6:00 each night, so for now I’ve become a stay-at-home dad. This is actually something I’ve always liked (in high school, I was voted “most likely to to be a house husband”). So I do the laundry and am in charge of dinner each night. I’m enjoying the last, as I get to pick things out, go through recipes, and cook. I won’t say I’m a great cook, but I’m learning and having fun. As strange as it sounds, being a house husband has always been something I wanted to do, so I’m appreciating the opportunity while it lasts.
I think all of us have come to accept this strange pause button that’s been pushed, and I’ll try to learn what I can from it and take that with me as I move forward.
Dr. Block has a solo neurology practice in Scottsdale, Ariz. He has no relevant disclosures.
Rural ICU capacity could be strained by COVID-19
The nonmetropolitan, largely rural, areas of the United States have fewer ICU beds than do urban areas, but their populations may be at higher risk for COVID-19 complications, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.
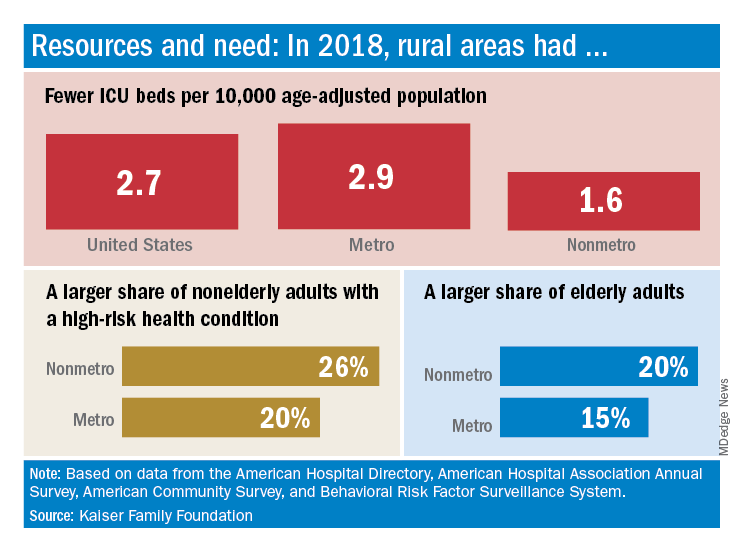
In 2018, the United States had 2.7 ICU beds per 10,000 age-adjusted population, but that number drops to 1.6 beds per 10,000 in nonmetro America and rises to 2.9 per 10,000 in metro areas. Counts for all hospital beds were much closer: 21.6 per 10,000 (rural) and 23.9 per 10,000 (urban), Kaiser investigators reported.
“The novel coronavirus was slower to spread to rural areas in the U.S., but that appears to be changing, with new outbreaks becoming evident in less densely populated parts of the country,” Kendal Orgera and associates said in a recent analysis.
Those rural areas have COVID-19 issues beyond ICU bed counts. Populations in nonmetro areas are less healthy – 26% of adults under age 65 years had a preexisting medical condition in 2018, compared with 20% in metro areas – and older – 20% of people are 65 and older, versus 15% in metro areas, they said.
“If coronavirus continues to spread in rural communities across the U.S., it is possible many [nonmetro] areas will face shortages of ICU beds with limited options to adapt. Patients in rural areas experiencing more severe illnesses may be transferred to hospitals with greater capacity, but if nearby urban areas are also overwhelmed, transfer may not be an option,” Ms. Orgera and associates wrote.
They defined nonmetro counties as those with rural towns of fewer than 2,500 people and/or “urban areas with populations ranging from 2,500 to 49,999 that are not part of larger labor market areas.” The Kaiser analysis involved 2018 data from the American Hospital Association, American Hospital Directory, American Community Survey, and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
The nonmetropolitan, largely rural, areas of the United States have fewer ICU beds than do urban areas, but their populations may be at higher risk for COVID-19 complications, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.

In 2018, the United States had 2.7 ICU beds per 10,000 age-adjusted population, but that number drops to 1.6 beds per 10,000 in nonmetro America and rises to 2.9 per 10,000 in metro areas. Counts for all hospital beds were much closer: 21.6 per 10,000 (rural) and 23.9 per 10,000 (urban), Kaiser investigators reported.
“The novel coronavirus was slower to spread to rural areas in the U.S., but that appears to be changing, with new outbreaks becoming evident in less densely populated parts of the country,” Kendal Orgera and associates said in a recent analysis.
Those rural areas have COVID-19 issues beyond ICU bed counts. Populations in nonmetro areas are less healthy – 26% of adults under age 65 years had a preexisting medical condition in 2018, compared with 20% in metro areas – and older – 20% of people are 65 and older, versus 15% in metro areas, they said.
“If coronavirus continues to spread in rural communities across the U.S., it is possible many [nonmetro] areas will face shortages of ICU beds with limited options to adapt. Patients in rural areas experiencing more severe illnesses may be transferred to hospitals with greater capacity, but if nearby urban areas are also overwhelmed, transfer may not be an option,” Ms. Orgera and associates wrote.
They defined nonmetro counties as those with rural towns of fewer than 2,500 people and/or “urban areas with populations ranging from 2,500 to 49,999 that are not part of larger labor market areas.” The Kaiser analysis involved 2018 data from the American Hospital Association, American Hospital Directory, American Community Survey, and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
The nonmetropolitan, largely rural, areas of the United States have fewer ICU beds than do urban areas, but their populations may be at higher risk for COVID-19 complications, according to the Kaiser Family Foundation.

In 2018, the United States had 2.7 ICU beds per 10,000 age-adjusted population, but that number drops to 1.6 beds per 10,000 in nonmetro America and rises to 2.9 per 10,000 in metro areas. Counts for all hospital beds were much closer: 21.6 per 10,000 (rural) and 23.9 per 10,000 (urban), Kaiser investigators reported.
“The novel coronavirus was slower to spread to rural areas in the U.S., but that appears to be changing, with new outbreaks becoming evident in less densely populated parts of the country,” Kendal Orgera and associates said in a recent analysis.
Those rural areas have COVID-19 issues beyond ICU bed counts. Populations in nonmetro areas are less healthy – 26% of adults under age 65 years had a preexisting medical condition in 2018, compared with 20% in metro areas – and older – 20% of people are 65 and older, versus 15% in metro areas, they said.
“If coronavirus continues to spread in rural communities across the U.S., it is possible many [nonmetro] areas will face shortages of ICU beds with limited options to adapt. Patients in rural areas experiencing more severe illnesses may be transferred to hospitals with greater capacity, but if nearby urban areas are also overwhelmed, transfer may not be an option,” Ms. Orgera and associates wrote.
They defined nonmetro counties as those with rural towns of fewer than 2,500 people and/or “urban areas with populations ranging from 2,500 to 49,999 that are not part of larger labor market areas.” The Kaiser analysis involved 2018 data from the American Hospital Association, American Hospital Directory, American Community Survey, and the Behavioral Risk Factor Surveillance System.
Seniors with COVID-19 show unusual symptoms, doctors say
complicating efforts to ensure they get timely and appropriate treatment, according to physicians.
COVID-19 is typically signaled by three symptoms: a fever, an insistent cough, and shortness of breath. But older adults – the age group most at risk of severe complications or death from this condition – may have none of these characteristics.
Instead, seniors may seem “off” – not acting like themselves – early on after being infected by the coronavirus. They may sleep more than usual or stop eating. They may seem unusually apathetic or confused, losing orientation to their surroundings. They may become dizzy and fall. Sometimes, seniors stop speaking or simply collapse.
“With a lot of conditions, older adults don’t present in a typical way, and we’re seeing that with COVID-19 as well,” said Camille Vaughan, MD, section chief of geriatrics and gerontology at Emory University, Atlanta.
The reason has to do with how older bodies respond to illness and infection.
At advanced ages, “someone’s immune response may be blunted and their ability to regulate temperature may be altered,” said Dr. Joseph Ouslander, a professor of geriatric medicine at Florida Atlantic University in Boca Raton.
“Underlying chronic illnesses can mask or interfere with signs of infection,” he said. “Some older people, whether from age-related changes or previous neurologic issues such as a stroke, may have altered cough reflexes. Others with cognitive impairment may not be able to communicate their symptoms.”
Recognizing danger signs is important: If early signs of COVID-19 are missed, seniors may deteriorate before getting needed care. And people may go in and out of their homes without adequate protective measures, risking the spread of infection.
Quratulain Syed, MD, an Atlanta geriatrician, describes a man in his 80s whom she treated in mid-March. Over a period of days, this patient, who had heart disease, diabetes and moderate cognitive impairment, stopped walking and became incontinent and profoundly lethargic. But he didn’t have a fever or a cough. His only respiratory symptom: sneezing off and on.
The man’s elderly spouse called 911 twice. Both times, paramedics checked his vital signs and declared he was OK. After another worried call from the overwhelmed spouse, Dr. Syed insisted the patient be taken to the hospital, where he tested positive for COVID-19.
“I was quite concerned about the paramedics and health aides who’d been in the house and who hadn’t used PPE [personal protective equipment],” Dr. Syed said.
Dr. Sam Torbati, medical director of the emergency department at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, describes treating seniors who initially appear to be trauma patients but are found to have COVID-19.
“They get weak and dehydrated,” he said, “and when they stand to walk, they collapse and injure themselves badly.”
Dr. Torbati has seen older adults who are profoundly disoriented and unable to speak and who appear at first to have suffered strokes.
“When we test them, we discover that what’s producing these changes is a central nervous system effect of coronavirus,” he said.
Laura Perry, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, saw a patient like this several weeks ago. The woman, in her 80s, had what seemed to be a cold before becoming very confused. In the hospital, she couldn’t identify where she was or stay awake during an examination. Dr. Perry diagnosed hypoactive delirium, an altered mental state in which people become inactive and drowsy. The patient tested positive for coronavirus and is still in the ICU.
Anthony Perry, MD, of the department of geriatric medicine at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, tells of an 81-year-old woman with nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea who tested positive for COVID-19 in the emergency room. After receiving intravenous fluids, oxygen, and medication for her intestinal upset, she returned home after 2 days and is doing well.
Another 80-year-old Rush patient with similar symptoms – nausea and vomiting, but no cough, fever, or shortness of breath – is in intensive care after getting a positive COVID-19 test and due to be put on a ventilator. The difference? This patient is frail with “a lot of cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Perry said. Other than that, it’s not yet clear why some older patients do well while others do not.
So far, reports of cases like these have been anecdotal. But a few physicians are trying to gather more systematic information.
In Switzerland, Sylvain Nguyen, MD, a geriatrician at the University of Lausanne Hospital Center, put together a list of typical and atypical symptoms in older COVID-19 patients for a paper to be published in the Revue Médicale Suisse. Included on the atypical list are changes in a patient’s usual status, delirium, falls, fatigue, lethargy, low blood pressure, painful swallowing, fainting, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and the loss of smell and taste.
Data come from hospitals and nursing homes in Switzerland, Italy, and France, Dr. Nguyen said in an email.
On the front lines, physicians need to make sure they carefully assess an older patient’s symptoms.
“While we have to have a high suspicion of COVID-19 because it’s so dangerous in the older population, there are many other things to consider,” said Kathleen Unroe, MD, a geriatrician at Indiana University, Indianapolis.
Seniors may also do poorly because their routines have changed. In nursing homes and most assisted living centers, activities have stopped and “residents are going to get weaker and more deconditioned because they’re not walking to and from the dining hall,” she said.
At home, isolated seniors may not be getting as much help with medication management or other essential needs from family members who are keeping their distance, other experts suggested. Or they may have become apathetic or depressed.
“I’d want to know ‘What’s the potential this person has had an exposure [to the coronavirus], especially in the last 2 weeks?’ ” said Dr. Vaughan of Emory. “Do they have home health personnel coming in? Have they gotten together with other family members? Are chronic conditions being controlled? Is there another diagnosis that seems more likely?”
“Someone may be just having a bad day. But if they’re not themselves for a couple of days, absolutely reach out to a primary care doctor or a local health system hotline to see if they meet the threshold for [coronavirus] testing,” Dr. Vaughan advised. “Be persistent. If you get a ‘no’ the first time and things aren’t improving, call back and ask again.”
Kaiser Health News (khn.org) is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of the Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
complicating efforts to ensure they get timely and appropriate treatment, according to physicians.
COVID-19 is typically signaled by three symptoms: a fever, an insistent cough, and shortness of breath. But older adults – the age group most at risk of severe complications or death from this condition – may have none of these characteristics.
Instead, seniors may seem “off” – not acting like themselves – early on after being infected by the coronavirus. They may sleep more than usual or stop eating. They may seem unusually apathetic or confused, losing orientation to their surroundings. They may become dizzy and fall. Sometimes, seniors stop speaking or simply collapse.
“With a lot of conditions, older adults don’t present in a typical way, and we’re seeing that with COVID-19 as well,” said Camille Vaughan, MD, section chief of geriatrics and gerontology at Emory University, Atlanta.
The reason has to do with how older bodies respond to illness and infection.
At advanced ages, “someone’s immune response may be blunted and their ability to regulate temperature may be altered,” said Dr. Joseph Ouslander, a professor of geriatric medicine at Florida Atlantic University in Boca Raton.
“Underlying chronic illnesses can mask or interfere with signs of infection,” he said. “Some older people, whether from age-related changes or previous neurologic issues such as a stroke, may have altered cough reflexes. Others with cognitive impairment may not be able to communicate their symptoms.”
Recognizing danger signs is important: If early signs of COVID-19 are missed, seniors may deteriorate before getting needed care. And people may go in and out of their homes without adequate protective measures, risking the spread of infection.
Quratulain Syed, MD, an Atlanta geriatrician, describes a man in his 80s whom she treated in mid-March. Over a period of days, this patient, who had heart disease, diabetes and moderate cognitive impairment, stopped walking and became incontinent and profoundly lethargic. But he didn’t have a fever or a cough. His only respiratory symptom: sneezing off and on.
The man’s elderly spouse called 911 twice. Both times, paramedics checked his vital signs and declared he was OK. After another worried call from the overwhelmed spouse, Dr. Syed insisted the patient be taken to the hospital, where he tested positive for COVID-19.
“I was quite concerned about the paramedics and health aides who’d been in the house and who hadn’t used PPE [personal protective equipment],” Dr. Syed said.
Dr. Sam Torbati, medical director of the emergency department at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, describes treating seniors who initially appear to be trauma patients but are found to have COVID-19.
“They get weak and dehydrated,” he said, “and when they stand to walk, they collapse and injure themselves badly.”
Dr. Torbati has seen older adults who are profoundly disoriented and unable to speak and who appear at first to have suffered strokes.
“When we test them, we discover that what’s producing these changes is a central nervous system effect of coronavirus,” he said.
Laura Perry, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, saw a patient like this several weeks ago. The woman, in her 80s, had what seemed to be a cold before becoming very confused. In the hospital, she couldn’t identify where she was or stay awake during an examination. Dr. Perry diagnosed hypoactive delirium, an altered mental state in which people become inactive and drowsy. The patient tested positive for coronavirus and is still in the ICU.
Anthony Perry, MD, of the department of geriatric medicine at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, tells of an 81-year-old woman with nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea who tested positive for COVID-19 in the emergency room. After receiving intravenous fluids, oxygen, and medication for her intestinal upset, she returned home after 2 days and is doing well.
Another 80-year-old Rush patient with similar symptoms – nausea and vomiting, but no cough, fever, or shortness of breath – is in intensive care after getting a positive COVID-19 test and due to be put on a ventilator. The difference? This patient is frail with “a lot of cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Perry said. Other than that, it’s not yet clear why some older patients do well while others do not.
So far, reports of cases like these have been anecdotal. But a few physicians are trying to gather more systematic information.
In Switzerland, Sylvain Nguyen, MD, a geriatrician at the University of Lausanne Hospital Center, put together a list of typical and atypical symptoms in older COVID-19 patients for a paper to be published in the Revue Médicale Suisse. Included on the atypical list are changes in a patient’s usual status, delirium, falls, fatigue, lethargy, low blood pressure, painful swallowing, fainting, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and the loss of smell and taste.
Data come from hospitals and nursing homes in Switzerland, Italy, and France, Dr. Nguyen said in an email.
On the front lines, physicians need to make sure they carefully assess an older patient’s symptoms.
“While we have to have a high suspicion of COVID-19 because it’s so dangerous in the older population, there are many other things to consider,” said Kathleen Unroe, MD, a geriatrician at Indiana University, Indianapolis.
Seniors may also do poorly because their routines have changed. In nursing homes and most assisted living centers, activities have stopped and “residents are going to get weaker and more deconditioned because they’re not walking to and from the dining hall,” she said.
At home, isolated seniors may not be getting as much help with medication management or other essential needs from family members who are keeping their distance, other experts suggested. Or they may have become apathetic or depressed.
“I’d want to know ‘What’s the potential this person has had an exposure [to the coronavirus], especially in the last 2 weeks?’ ” said Dr. Vaughan of Emory. “Do they have home health personnel coming in? Have they gotten together with other family members? Are chronic conditions being controlled? Is there another diagnosis that seems more likely?”
“Someone may be just having a bad day. But if they’re not themselves for a couple of days, absolutely reach out to a primary care doctor or a local health system hotline to see if they meet the threshold for [coronavirus] testing,” Dr. Vaughan advised. “Be persistent. If you get a ‘no’ the first time and things aren’t improving, call back and ask again.”
Kaiser Health News (khn.org) is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of the Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
complicating efforts to ensure they get timely and appropriate treatment, according to physicians.
COVID-19 is typically signaled by three symptoms: a fever, an insistent cough, and shortness of breath. But older adults – the age group most at risk of severe complications or death from this condition – may have none of these characteristics.
Instead, seniors may seem “off” – not acting like themselves – early on after being infected by the coronavirus. They may sleep more than usual or stop eating. They may seem unusually apathetic or confused, losing orientation to their surroundings. They may become dizzy and fall. Sometimes, seniors stop speaking or simply collapse.
“With a lot of conditions, older adults don’t present in a typical way, and we’re seeing that with COVID-19 as well,” said Camille Vaughan, MD, section chief of geriatrics and gerontology at Emory University, Atlanta.
The reason has to do with how older bodies respond to illness and infection.
At advanced ages, “someone’s immune response may be blunted and their ability to regulate temperature may be altered,” said Dr. Joseph Ouslander, a professor of geriatric medicine at Florida Atlantic University in Boca Raton.
“Underlying chronic illnesses can mask or interfere with signs of infection,” he said. “Some older people, whether from age-related changes or previous neurologic issues such as a stroke, may have altered cough reflexes. Others with cognitive impairment may not be able to communicate their symptoms.”
Recognizing danger signs is important: If early signs of COVID-19 are missed, seniors may deteriorate before getting needed care. And people may go in and out of their homes without adequate protective measures, risking the spread of infection.
Quratulain Syed, MD, an Atlanta geriatrician, describes a man in his 80s whom she treated in mid-March. Over a period of days, this patient, who had heart disease, diabetes and moderate cognitive impairment, stopped walking and became incontinent and profoundly lethargic. But he didn’t have a fever or a cough. His only respiratory symptom: sneezing off and on.
The man’s elderly spouse called 911 twice. Both times, paramedics checked his vital signs and declared he was OK. After another worried call from the overwhelmed spouse, Dr. Syed insisted the patient be taken to the hospital, where he tested positive for COVID-19.
“I was quite concerned about the paramedics and health aides who’d been in the house and who hadn’t used PPE [personal protective equipment],” Dr. Syed said.
Dr. Sam Torbati, medical director of the emergency department at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, describes treating seniors who initially appear to be trauma patients but are found to have COVID-19.
“They get weak and dehydrated,” he said, “and when they stand to walk, they collapse and injure themselves badly.”
Dr. Torbati has seen older adults who are profoundly disoriented and unable to speak and who appear at first to have suffered strokes.
“When we test them, we discover that what’s producing these changes is a central nervous system effect of coronavirus,” he said.
Laura Perry, MD, of the University of California, San Francisco, saw a patient like this several weeks ago. The woman, in her 80s, had what seemed to be a cold before becoming very confused. In the hospital, she couldn’t identify where she was or stay awake during an examination. Dr. Perry diagnosed hypoactive delirium, an altered mental state in which people become inactive and drowsy. The patient tested positive for coronavirus and is still in the ICU.
Anthony Perry, MD, of the department of geriatric medicine at Rush University Medical Center in Chicago, tells of an 81-year-old woman with nausea, vomiting, and diarrhea who tested positive for COVID-19 in the emergency room. After receiving intravenous fluids, oxygen, and medication for her intestinal upset, she returned home after 2 days and is doing well.
Another 80-year-old Rush patient with similar symptoms – nausea and vomiting, but no cough, fever, or shortness of breath – is in intensive care after getting a positive COVID-19 test and due to be put on a ventilator. The difference? This patient is frail with “a lot of cardiovascular disease,” Dr. Perry said. Other than that, it’s not yet clear why some older patients do well while others do not.
So far, reports of cases like these have been anecdotal. But a few physicians are trying to gather more systematic information.
In Switzerland, Sylvain Nguyen, MD, a geriatrician at the University of Lausanne Hospital Center, put together a list of typical and atypical symptoms in older COVID-19 patients for a paper to be published in the Revue Médicale Suisse. Included on the atypical list are changes in a patient’s usual status, delirium, falls, fatigue, lethargy, low blood pressure, painful swallowing, fainting, diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, and the loss of smell and taste.
Data come from hospitals and nursing homes in Switzerland, Italy, and France, Dr. Nguyen said in an email.
On the front lines, physicians need to make sure they carefully assess an older patient’s symptoms.
“While we have to have a high suspicion of COVID-19 because it’s so dangerous in the older population, there are many other things to consider,” said Kathleen Unroe, MD, a geriatrician at Indiana University, Indianapolis.
Seniors may also do poorly because their routines have changed. In nursing homes and most assisted living centers, activities have stopped and “residents are going to get weaker and more deconditioned because they’re not walking to and from the dining hall,” she said.
At home, isolated seniors may not be getting as much help with medication management or other essential needs from family members who are keeping their distance, other experts suggested. Or they may have become apathetic or depressed.
“I’d want to know ‘What’s the potential this person has had an exposure [to the coronavirus], especially in the last 2 weeks?’ ” said Dr. Vaughan of Emory. “Do they have home health personnel coming in? Have they gotten together with other family members? Are chronic conditions being controlled? Is there another diagnosis that seems more likely?”
“Someone may be just having a bad day. But if they’re not themselves for a couple of days, absolutely reach out to a primary care doctor or a local health system hotline to see if they meet the threshold for [coronavirus] testing,” Dr. Vaughan advised. “Be persistent. If you get a ‘no’ the first time and things aren’t improving, call back and ask again.”
Kaiser Health News (khn.org) is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of the Kaiser Family Foundation that is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
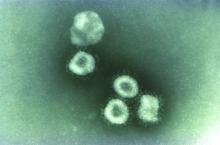
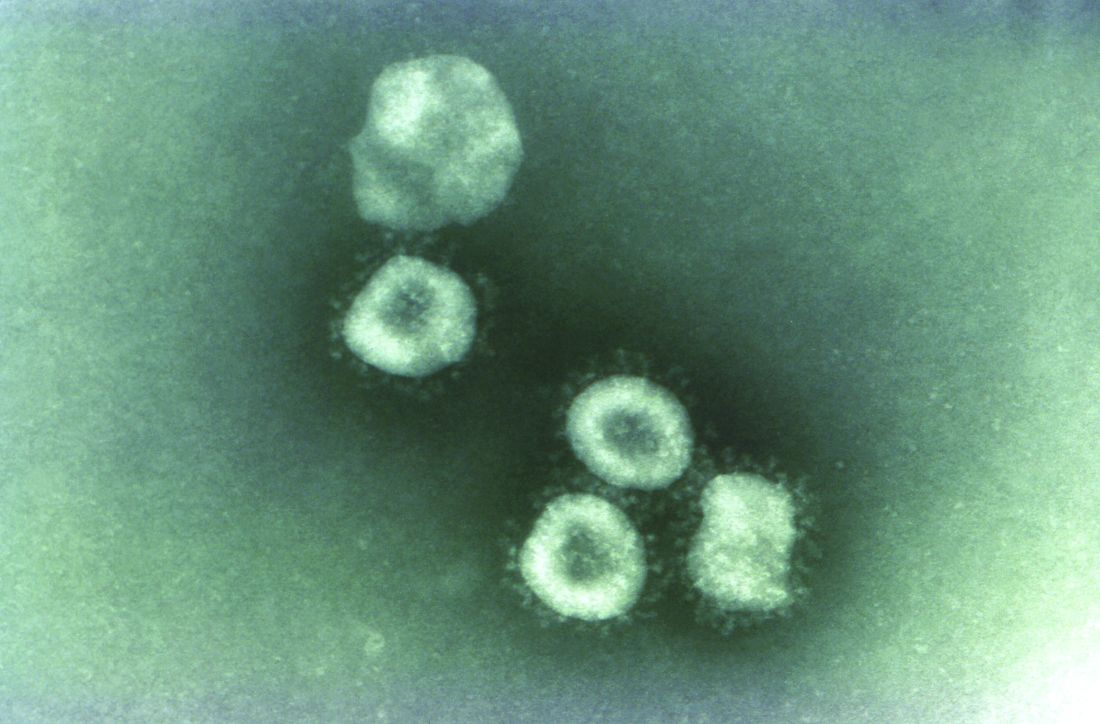
SARS-CoV-2 present significantly longer in stool than in respiratory, serum samples
A study from China showed that the presence of SARS-CoV-2 lasts significantly longer in stool samples from COVID-19 patients than in respiratory and serum samples.
However, the virus also persists longer with higher loads and later peaks in the respiratory tissue of patients with severe disease than in those with mild disease, according to an analysis of 96 consecutively admitted patients with laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The retrospective study cohort data were collected from Jan. 19 to March 20 at a designated hospital for patients with COVID-19 in Zhejiang province. Among the patients, 22 had mild disease, and 74 had severe disease, according to the researchers.
Infection was confirmed in all patients by testing sputum and saliva samples. Viral RNA was detected in the stool of 59% of the patients and in the serum of 41% of patients. Only one of the patients had a positive urine sample. The median duration of virus in stool (22 days) was significantly longer than in respiratory (18 days; P = .002) and serum samples (16 days; P < .001).
In addition, the median duration of virus in the respiratory samples of patients with severe disease (21 days) was significantly longer than in patients with mild disease (14 days; P = .04).
“In the mild group, the viral loads peaked in respiratory samples in the second week from disease onset, whereas viral load continued to be high during the third week in the severe group,” the authors stated.
Virus duration was also longer in patients older than 60 years and in men.
The longer duration of SARS-CoV-2 in stool samples highlights the need to strengthen the management of stool samples in the prevention and control of the epidemic, especially for patients in the later stages of the disease, the authors advised.
“Compared with patients with mild disease, those with severe disease showed longer duration of SARS-CoV-2 in respiratory samples, higher viral load, and a later shedding peak. These findings suggest that reducing viral loads through clinical means and strengthening management during each stage of severe disease should help to prevent the spread of the virus,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by the China National Mega-Projects for Infectious Diseases and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors reported they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zheng S et al. BMJ. 2020;369:m1443.
A study from China showed that the presence of SARS-CoV-2 lasts significantly longer in stool samples from COVID-19 patients than in respiratory and serum samples.
However, the virus also persists longer with higher loads and later peaks in the respiratory tissue of patients with severe disease than in those with mild disease, according to an analysis of 96 consecutively admitted patients with laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The retrospective study cohort data were collected from Jan. 19 to March 20 at a designated hospital for patients with COVID-19 in Zhejiang province. Among the patients, 22 had mild disease, and 74 had severe disease, according to the researchers.
Infection was confirmed in all patients by testing sputum and saliva samples. Viral RNA was detected in the stool of 59% of the patients and in the serum of 41% of patients. Only one of the patients had a positive urine sample. The median duration of virus in stool (22 days) was significantly longer than in respiratory (18 days; P = .002) and serum samples (16 days; P < .001).
In addition, the median duration of virus in the respiratory samples of patients with severe disease (21 days) was significantly longer than in patients with mild disease (14 days; P = .04).
“In the mild group, the viral loads peaked in respiratory samples in the second week from disease onset, whereas viral load continued to be high during the third week in the severe group,” the authors stated.
Virus duration was also longer in patients older than 60 years and in men.
The longer duration of SARS-CoV-2 in stool samples highlights the need to strengthen the management of stool samples in the prevention and control of the epidemic, especially for patients in the later stages of the disease, the authors advised.
“Compared with patients with mild disease, those with severe disease showed longer duration of SARS-CoV-2 in respiratory samples, higher viral load, and a later shedding peak. These findings suggest that reducing viral loads through clinical means and strengthening management during each stage of severe disease should help to prevent the spread of the virus,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by the China National Mega-Projects for Infectious Diseases and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors reported they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zheng S et al. BMJ. 2020;369:m1443.
A study from China showed that the presence of SARS-CoV-2 lasts significantly longer in stool samples from COVID-19 patients than in respiratory and serum samples.
However, the virus also persists longer with higher loads and later peaks in the respiratory tissue of patients with severe disease than in those with mild disease, according to an analysis of 96 consecutively admitted patients with laboratory confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The retrospective study cohort data were collected from Jan. 19 to March 20 at a designated hospital for patients with COVID-19 in Zhejiang province. Among the patients, 22 had mild disease, and 74 had severe disease, according to the researchers.
Infection was confirmed in all patients by testing sputum and saliva samples. Viral RNA was detected in the stool of 59% of the patients and in the serum of 41% of patients. Only one of the patients had a positive urine sample. The median duration of virus in stool (22 days) was significantly longer than in respiratory (18 days; P = .002) and serum samples (16 days; P < .001).
In addition, the median duration of virus in the respiratory samples of patients with severe disease (21 days) was significantly longer than in patients with mild disease (14 days; P = .04).
“In the mild group, the viral loads peaked in respiratory samples in the second week from disease onset, whereas viral load continued to be high during the third week in the severe group,” the authors stated.
Virus duration was also longer in patients older than 60 years and in men.
The longer duration of SARS-CoV-2 in stool samples highlights the need to strengthen the management of stool samples in the prevention and control of the epidemic, especially for patients in the later stages of the disease, the authors advised.
“Compared with patients with mild disease, those with severe disease showed longer duration of SARS-CoV-2 in respiratory samples, higher viral load, and a later shedding peak. These findings suggest that reducing viral loads through clinical means and strengthening management during each stage of severe disease should help to prevent the spread of the virus,” the researchers concluded.
The study was funded by the China National Mega-Projects for Infectious Diseases and the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The authors reported they had no disclosures.
SOURCE: Zheng S et al. BMJ. 2020;369:m1443.
FROM THE BRITISH MEDICAL JOURNAL
Undeterred during COVID-19, hospital chaplains transform delivery of spiritual care
The first time that the Rev. Michael Mercier, BCC (a board-certified chaplain), provided spiritual care for a patient hospitalized with COVID-19 in March, he found himself engaged in a bit of soul-searching. Even though he donned a mask, gloves, and gown, he could get no closer than the hospital room doorway to interact with the patient because of infection-control measures.
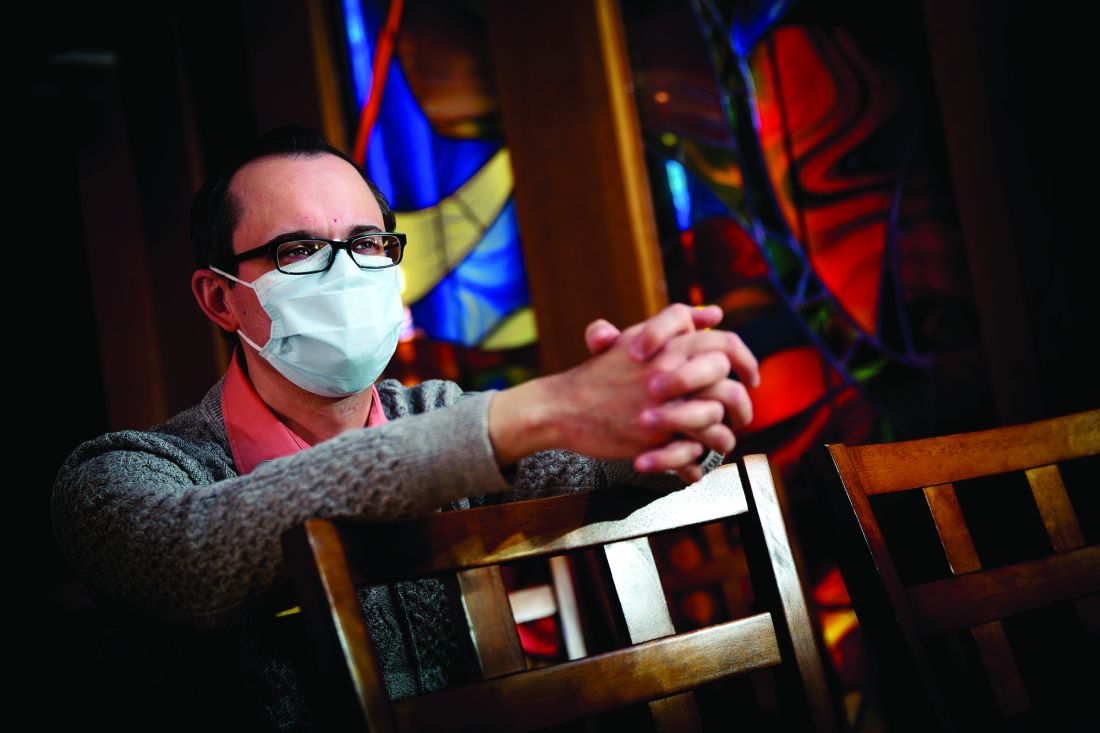
“It went against all my natural instincts and my experience as a chaplain,” said Rev. Mercier, who serves as director of spiritual care for Rhode Island Hospital, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Newport Hospital, which are operated by Lifespan, Rhode Island’s largest health system. “The first instinct is to be physically present in the room with the person who’s dying, to have the family gathered around the bedside.”
Prior to standing in the doorway that day, he’d been on the phone with family members, “just listening to their fear and their anxiety that they could not be with their loved one when their loved one was dying,” he said. “I validated their feelings. I also urged them to work with me and the nurse to bring a phone into the room, hold it to the patient’s ear, and they were able to say their goodbyes and how much they loved the person.”
The patient was a devout Roman Catholic, he added, and the family requested that the Prayer of Commendation and the Apostolic Pardon be performed. Rev. Mercier arranged for a Catholic priest to carry out this request. “The nurse told the patient what was going on, and the priest offered the prayers and the rituals from the doorway,” Rev. Mercier said. “It was a surreal experience. For me, it was almost entirely phone based, and it was mostly with the family because the patient couldn’t talk too much.”
To add to the sense of detachment in a situation like that, doctors, nurses, and chaplains caring for COVID-19 patients are wearing masks and face shields, and sometimes the sickest patients are intubated, which can complicate efforts to communicate. “I’m surprised at how we find the mask as somewhat of a barrier,” said Carolanne B. Hauck, BCC, director of chaplaincy care & education and volunteer services at Lancaster (Pa.) General Hospital, which is part of the Penn Medicine system. “By that I mean, often for us, sitting at the bedside and really being able to see someone’s face and have them see our face – with our masks, that’s just not happening. We’re also having briefer visits when we’re visiting with COVID patients.”
COVID-19 may have quarantined some traditional ways of providing spiritual care, but hospital chaplains are relying on technology more than ever in their efforts to meet the needs of patients and their families, including the use of iPads, FaceTime, and video conferencing programs like Zoom and BlueJeans.
“We’ve used Zoom to talk with family members that live out of state,” Rev. Mercier said. “Most of the time, I get an invitation to join a Zoom meeting, but now I need to become proficient in utilizing Zoom to set up those end-of-life family meetings. There’s a lot of learning on the fly, how to use these technologies in a way that’s helpful for everybody. That’s the biggest thing I’m learning: Connection is connection during this time of high stress and anxiety, and we just have to get creative.”
Despite the “disembodied” nature of technology, patients and their families have expressed gratitude to chaplains for their efforts to facilitate connections between loved ones and to be “a guide on the side,” as Mary Wetsch-Johnson, BCC, put it. She recalled one phone conversation with the daughter of a man with COVID-19 who was placed on comfort measures. “She said her dad was like the dad on the TV series Father Knows Best, just a kind-hearted, loving, wonderful man,” said Ms. Wetsch-Johnson, a chaplain at CHI Franciscan Health, which operates 10 acute-care hospitals in the Puget Sound region of Washington state. “She was able to describe him in a way that I felt like I knew him. She talked about the discord they had in their family and how they’re processing through that, and about her own personal journey with grief and loss. She then asked me for information about funeral homes, and I provided her with information. At the end of it, she said, ‘I did not know that I needed you today, but you are exactly what I needed.’ ”
Hospital chaplains may be using smartphones and other gadgets to communicate with patients and their families more than they did in the pre-COVID-19 world, but their basic job has not changed, said Rabbi Neal J. Loevinger, BCC, director of spiritual care services at Vassar Brothers Medical Center in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., part of a seven-hospital system operated by Nuvance Health. “We offer the hope of a caring presence,” said Rabbi Loevinger, who is also a member of the board of directors for Neshama: Association of Jewish Chaplains. “If someone is in a hole, our job is to climb down into the hole with them and say, ‘We’re going to get out of this hole together.’ We can’t promise that someone’s going to get better. We can’t promise that everything’s going to be all right. What we can promise is that we will not abandon you. We can promise that there will be someone accompanying you in any way we can through this crisis.”
Ms. Hauck remembered a phone conversation with the granddaughter of a patient hospitalized with COVID-19 who was nearing the end of her life. The granddaughter told her a story about how her grandmother and her best friend made a pact with each other that, when one was dying, the other would come to her side and pray the Rosary with her. “The granddaughter got tearful and said, ‘That can’t happen now,’ ” said Ms. Hauck, who oversees a staff of 9 chaplains and 10 per diem chaplains. “I made a promise that I would do my best to be at the bedside and pray the Rosary with her grandmother.”
The nurses were aware of the request, and about a day later, Ms. Hauck received a call at 1 a.m., indicating that the patient was close to dying. She drove to Lancaster General, put on her personal protective equipment, made it to the patient’s bedside, and began to pray the Rosary with her, with a nurse in the room. “The nurse said to me, ‘Carolanne, all of her stats are going up,’ and the patient actually became a little more alert,” she recalled. “We talked a little bit, and I asked, ‘Would you like to pray the Rosary now?’ She shook her head yes, and said, ‘Hail Mary, full of grace ...’ and those were the last words that she spoke. I finished the prayers for her, and then she died. It was very meaningful knowing that I could honor that wish for her, but more importantly, that I could do that for the family, who otherwise would have been at her side saying the Rosary with her. We have a recognition of how hard it is to leave someone at the hospital and not be at their bedside.”

Hospital chaplains are also supporting interdisciplinary teams of physicians, nurses, and other staff, as they navigate the provision of care in the wake of a pandemic. “They are under a great deal of stress – not only from being at work but with all the role changes that have happened in their home life,” Ms. Wetsch-Johnson said. “Some of them now are being the teacher at home and having to care for children. They have a lot that they come in with. My job is to help them so that they can go do their job. Regularly what I do is check in with the units and ask, ‘How are you doing today? What’s going on for you?’ Because people need to know that someone’s there to be with them and walk with them and listen to them.”
In the spirit of being present for their staff, she and her colleagues established “respite rooms” at CHI Franciscan hospitals, where workers can decompress and get recentered before returning to work. “We usually have water and snacks in there for them, and some type of soothing music,” Ms. Wetsch-Johnson said. “There is also literature on breathing exercises and stretching exercises. We’re also inviting people to write little notes of hope and gratitude, and they’re putting those up for each other. It’s important that we keep supporting them as they support the patients. Personally, I also round with our physicians, because they carry a lot with them, just as much as any other staff. I check in with dietary and environmental services. Everybody’s giving in their own unique way; that helps this whole health care system keep going.”
On any given day, it’s not uncommon for hospital staff members to spontaneously pull aside chaplains to vent, pray, or just to talk. “They process their own fears and anxieties about working in this kind of environment,” Rev. Mercier said. “They’re scared for themselves. They think, ‘Could I get the virus? Could I spread the virus to my family?’ Or, they may express the care and concern they have for their patients. Oftentimes, it’s a mixture of both. Those spontaneous conversations are often the most powerful.”
Ms. Hauck noted that some nurses and clinicians at Lancaster General Hospital “are doing work they may have not done before,” she said. “Some of them are experiencing death for the first time, so we help them to navigate that. One of the best things we can do is hear the anxiety they have or the sadness they have when a patient dies. Also, maybe the frustration that they couldn’t do more in some cases and helping them to see that sometimes their best is good enough.”
She recalled one younger patient with COVID-19 who fell seriously ill. “It was really affecting a lot of people on the unit because of the patient’s age,” she said. “When we saw that the patient was getting better and would be discharged, there was such a sense of relief. I’m not sure that patient will ever understand how that helped us. It was comforting to us to know that people are getting better. It is something we celebrate.”
As chaplains adjust to their “new normal,” carving out time for self-care is key. Ms. Hauck and her staff periodically meet on Zoom with a psychotherapist “who understands what we do, asks us really good questions, and reminds us to take care of ourselves,” she said. “Personally, I’m making sure I get my exercise in, I pack a healthy lunch. We do check in with each other. Part of our handoff at every shift provides for an opportunity to debrief about how your day was.”
Rev. Mercier’s self check-in includes deep-breathing meditation and reciting certain prayers throughout the day. “The deep breathing helps me center and refocus with my body, while the prayers remind me of my connection to the Divine,” he said. “It also reminds me that in the midst of the fear and the anxiety, I fear for myself. It’s hard not to be concerned that I could be infected. I have a family at home and could spread this to them. The prayer practices are a reminder to me that it’s okay to feel those fears and anxieties. Sometimes the spiritual practice helps me find that place of acceptance. That enables me to keep moving forward.”
Ms. Wetsch-Johnson described the sense of upendedness caused by the COVID-19 pandemic as a “ripple in the water that’s going to have long-lasting effects on the delivery of health care. People are taking the time to listen to one another. I’ve seen people in all departments be more compassionate with one another. I’ve seen managers go out of their way to make sure their staff are deeply cared for. I think that will have a ripple effect. That’s my hope, that we will continue to be more compassionate, more loving, and more understanding.”
Rabbi Loevinger hopes that even the most reticent physicians remember that chaplains serve as their advocate, too, especially during times of crisis. “This has been a time of unprecedented ethical wrestling in our hospitals, where there’s been a real concern that doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists are going to be faced with morally distressing situations regarding insufficient PPE, or insufficient ventilator or dialysis machine supply to support everybody that needs to be supported,” he said. “Chaplains are a key part of the process of making ethical decisions, but also supporting physicians who are in distress over [being in] situations they never had imagined. Physicians don’t like to talk about the fact that a lot of the decisions they make are really heartbreaking. But if chaplains understand anything, it’s that being brokenhearted is part of the human condition, and that we can be part of the answer for keeping physicians morally and spiritually grounded in their work. We always invite that conversation.”
For Rev. Mercier, serving in a time of crisis reminds him of the importance of providing care as a team, “not just for patients and families, but for one another,” he said. “One of the lessons we can learn is, how can we build that connection with one another, to support and care for one another? How can we make sure that no one feels alone while working in the hospital?”
He draws inspiration from a saying credited to St. John of the Cross, which reads, “I saw the river through which every soul must pass, and the name of that river is suffering. I saw the boat that carries each soul across that river, and the name of that boat is love.”
“It’s that image that’s sticking with me, not just for myself as a chaplain but for all of my colleagues in the hospital,” said Rev. Mercier, who also pastors Tabernacle Baptist Church in Hope, R.I. “We’re in that river with the patients right now, suffering, and we’re doing our best to help them get to the other side – whatever the other side may look like.”
Correction, 4/30/20: An earlier version of the caption for the photo with Mary Wetsch-Johnson misstated the location. The photo was taken outside St. Elizabeth Hospital in Enumclaw, Wash.
The first time that the Rev. Michael Mercier, BCC (a board-certified chaplain), provided spiritual care for a patient hospitalized with COVID-19 in March, he found himself engaged in a bit of soul-searching. Even though he donned a mask, gloves, and gown, he could get no closer than the hospital room doorway to interact with the patient because of infection-control measures.

“It went against all my natural instincts and my experience as a chaplain,” said Rev. Mercier, who serves as director of spiritual care for Rhode Island Hospital, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Newport Hospital, which are operated by Lifespan, Rhode Island’s largest health system. “The first instinct is to be physically present in the room with the person who’s dying, to have the family gathered around the bedside.”
Prior to standing in the doorway that day, he’d been on the phone with family members, “just listening to their fear and their anxiety that they could not be with their loved one when their loved one was dying,” he said. “I validated their feelings. I also urged them to work with me and the nurse to bring a phone into the room, hold it to the patient’s ear, and they were able to say their goodbyes and how much they loved the person.”
The patient was a devout Roman Catholic, he added, and the family requested that the Prayer of Commendation and the Apostolic Pardon be performed. Rev. Mercier arranged for a Catholic priest to carry out this request. “The nurse told the patient what was going on, and the priest offered the prayers and the rituals from the doorway,” Rev. Mercier said. “It was a surreal experience. For me, it was almost entirely phone based, and it was mostly with the family because the patient couldn’t talk too much.”
To add to the sense of detachment in a situation like that, doctors, nurses, and chaplains caring for COVID-19 patients are wearing masks and face shields, and sometimes the sickest patients are intubated, which can complicate efforts to communicate. “I’m surprised at how we find the mask as somewhat of a barrier,” said Carolanne B. Hauck, BCC, director of chaplaincy care & education and volunteer services at Lancaster (Pa.) General Hospital, which is part of the Penn Medicine system. “By that I mean, often for us, sitting at the bedside and really being able to see someone’s face and have them see our face – with our masks, that’s just not happening. We’re also having briefer visits when we’re visiting with COVID patients.”
COVID-19 may have quarantined some traditional ways of providing spiritual care, but hospital chaplains are relying on technology more than ever in their efforts to meet the needs of patients and their families, including the use of iPads, FaceTime, and video conferencing programs like Zoom and BlueJeans.
“We’ve used Zoom to talk with family members that live out of state,” Rev. Mercier said. “Most of the time, I get an invitation to join a Zoom meeting, but now I need to become proficient in utilizing Zoom to set up those end-of-life family meetings. There’s a lot of learning on the fly, how to use these technologies in a way that’s helpful for everybody. That’s the biggest thing I’m learning: Connection is connection during this time of high stress and anxiety, and we just have to get creative.”
Despite the “disembodied” nature of technology, patients and their families have expressed gratitude to chaplains for their efforts to facilitate connections between loved ones and to be “a guide on the side,” as Mary Wetsch-Johnson, BCC, put it. She recalled one phone conversation with the daughter of a man with COVID-19 who was placed on comfort measures. “She said her dad was like the dad on the TV series Father Knows Best, just a kind-hearted, loving, wonderful man,” said Ms. Wetsch-Johnson, a chaplain at CHI Franciscan Health, which operates 10 acute-care hospitals in the Puget Sound region of Washington state. “She was able to describe him in a way that I felt like I knew him. She talked about the discord they had in their family and how they’re processing through that, and about her own personal journey with grief and loss. She then asked me for information about funeral homes, and I provided her with information. At the end of it, she said, ‘I did not know that I needed you today, but you are exactly what I needed.’ ”
Hospital chaplains may be using smartphones and other gadgets to communicate with patients and their families more than they did in the pre-COVID-19 world, but their basic job has not changed, said Rabbi Neal J. Loevinger, BCC, director of spiritual care services at Vassar Brothers Medical Center in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., part of a seven-hospital system operated by Nuvance Health. “We offer the hope of a caring presence,” said Rabbi Loevinger, who is also a member of the board of directors for Neshama: Association of Jewish Chaplains. “If someone is in a hole, our job is to climb down into the hole with them and say, ‘We’re going to get out of this hole together.’ We can’t promise that someone’s going to get better. We can’t promise that everything’s going to be all right. What we can promise is that we will not abandon you. We can promise that there will be someone accompanying you in any way we can through this crisis.”
Ms. Hauck remembered a phone conversation with the granddaughter of a patient hospitalized with COVID-19 who was nearing the end of her life. The granddaughter told her a story about how her grandmother and her best friend made a pact with each other that, when one was dying, the other would come to her side and pray the Rosary with her. “The granddaughter got tearful and said, ‘That can’t happen now,’ ” said Ms. Hauck, who oversees a staff of 9 chaplains and 10 per diem chaplains. “I made a promise that I would do my best to be at the bedside and pray the Rosary with her grandmother.”
The nurses were aware of the request, and about a day later, Ms. Hauck received a call at 1 a.m., indicating that the patient was close to dying. She drove to Lancaster General, put on her personal protective equipment, made it to the patient’s bedside, and began to pray the Rosary with her, with a nurse in the room. “The nurse said to me, ‘Carolanne, all of her stats are going up,’ and the patient actually became a little more alert,” she recalled. “We talked a little bit, and I asked, ‘Would you like to pray the Rosary now?’ She shook her head yes, and said, ‘Hail Mary, full of grace ...’ and those were the last words that she spoke. I finished the prayers for her, and then she died. It was very meaningful knowing that I could honor that wish for her, but more importantly, that I could do that for the family, who otherwise would have been at her side saying the Rosary with her. We have a recognition of how hard it is to leave someone at the hospital and not be at their bedside.”

Hospital chaplains are also supporting interdisciplinary teams of physicians, nurses, and other staff, as they navigate the provision of care in the wake of a pandemic. “They are under a great deal of stress – not only from being at work but with all the role changes that have happened in their home life,” Ms. Wetsch-Johnson said. “Some of them now are being the teacher at home and having to care for children. They have a lot that they come in with. My job is to help them so that they can go do their job. Regularly what I do is check in with the units and ask, ‘How are you doing today? What’s going on for you?’ Because people need to know that someone’s there to be with them and walk with them and listen to them.”
In the spirit of being present for their staff, she and her colleagues established “respite rooms” at CHI Franciscan hospitals, where workers can decompress and get recentered before returning to work. “We usually have water and snacks in there for them, and some type of soothing music,” Ms. Wetsch-Johnson said. “There is also literature on breathing exercises and stretching exercises. We’re also inviting people to write little notes of hope and gratitude, and they’re putting those up for each other. It’s important that we keep supporting them as they support the patients. Personally, I also round with our physicians, because they carry a lot with them, just as much as any other staff. I check in with dietary and environmental services. Everybody’s giving in their own unique way; that helps this whole health care system keep going.”
On any given day, it’s not uncommon for hospital staff members to spontaneously pull aside chaplains to vent, pray, or just to talk. “They process their own fears and anxieties about working in this kind of environment,” Rev. Mercier said. “They’re scared for themselves. They think, ‘Could I get the virus? Could I spread the virus to my family?’ Or, they may express the care and concern they have for their patients. Oftentimes, it’s a mixture of both. Those spontaneous conversations are often the most powerful.”
Ms. Hauck noted that some nurses and clinicians at Lancaster General Hospital “are doing work they may have not done before,” she said. “Some of them are experiencing death for the first time, so we help them to navigate that. One of the best things we can do is hear the anxiety they have or the sadness they have when a patient dies. Also, maybe the frustration that they couldn’t do more in some cases and helping them to see that sometimes their best is good enough.”
She recalled one younger patient with COVID-19 who fell seriously ill. “It was really affecting a lot of people on the unit because of the patient’s age,” she said. “When we saw that the patient was getting better and would be discharged, there was such a sense of relief. I’m not sure that patient will ever understand how that helped us. It was comforting to us to know that people are getting better. It is something we celebrate.”
As chaplains adjust to their “new normal,” carving out time for self-care is key. Ms. Hauck and her staff periodically meet on Zoom with a psychotherapist “who understands what we do, asks us really good questions, and reminds us to take care of ourselves,” she said. “Personally, I’m making sure I get my exercise in, I pack a healthy lunch. We do check in with each other. Part of our handoff at every shift provides for an opportunity to debrief about how your day was.”
Rev. Mercier’s self check-in includes deep-breathing meditation and reciting certain prayers throughout the day. “The deep breathing helps me center and refocus with my body, while the prayers remind me of my connection to the Divine,” he said. “It also reminds me that in the midst of the fear and the anxiety, I fear for myself. It’s hard not to be concerned that I could be infected. I have a family at home and could spread this to them. The prayer practices are a reminder to me that it’s okay to feel those fears and anxieties. Sometimes the spiritual practice helps me find that place of acceptance. That enables me to keep moving forward.”
Ms. Wetsch-Johnson described the sense of upendedness caused by the COVID-19 pandemic as a “ripple in the water that’s going to have long-lasting effects on the delivery of health care. People are taking the time to listen to one another. I’ve seen people in all departments be more compassionate with one another. I’ve seen managers go out of their way to make sure their staff are deeply cared for. I think that will have a ripple effect. That’s my hope, that we will continue to be more compassionate, more loving, and more understanding.”
Rabbi Loevinger hopes that even the most reticent physicians remember that chaplains serve as their advocate, too, especially during times of crisis. “This has been a time of unprecedented ethical wrestling in our hospitals, where there’s been a real concern that doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists are going to be faced with morally distressing situations regarding insufficient PPE, or insufficient ventilator or dialysis machine supply to support everybody that needs to be supported,” he said. “Chaplains are a key part of the process of making ethical decisions, but also supporting physicians who are in distress over [being in] situations they never had imagined. Physicians don’t like to talk about the fact that a lot of the decisions they make are really heartbreaking. But if chaplains understand anything, it’s that being brokenhearted is part of the human condition, and that we can be part of the answer for keeping physicians morally and spiritually grounded in their work. We always invite that conversation.”
For Rev. Mercier, serving in a time of crisis reminds him of the importance of providing care as a team, “not just for patients and families, but for one another,” he said. “One of the lessons we can learn is, how can we build that connection with one another, to support and care for one another? How can we make sure that no one feels alone while working in the hospital?”
He draws inspiration from a saying credited to St. John of the Cross, which reads, “I saw the river through which every soul must pass, and the name of that river is suffering. I saw the boat that carries each soul across that river, and the name of that boat is love.”
“It’s that image that’s sticking with me, not just for myself as a chaplain but for all of my colleagues in the hospital,” said Rev. Mercier, who also pastors Tabernacle Baptist Church in Hope, R.I. “We’re in that river with the patients right now, suffering, and we’re doing our best to help them get to the other side – whatever the other side may look like.”
Correction, 4/30/20: An earlier version of the caption for the photo with Mary Wetsch-Johnson misstated the location. The photo was taken outside St. Elizabeth Hospital in Enumclaw, Wash.
The first time that the Rev. Michael Mercier, BCC (a board-certified chaplain), provided spiritual care for a patient hospitalized with COVID-19 in March, he found himself engaged in a bit of soul-searching. Even though he donned a mask, gloves, and gown, he could get no closer than the hospital room doorway to interact with the patient because of infection-control measures.

“It went against all my natural instincts and my experience as a chaplain,” said Rev. Mercier, who serves as director of spiritual care for Rhode Island Hospital, Hasbro Children’s Hospital, Miriam Hospital, and Newport Hospital, which are operated by Lifespan, Rhode Island’s largest health system. “The first instinct is to be physically present in the room with the person who’s dying, to have the family gathered around the bedside.”
Prior to standing in the doorway that day, he’d been on the phone with family members, “just listening to their fear and their anxiety that they could not be with their loved one when their loved one was dying,” he said. “I validated their feelings. I also urged them to work with me and the nurse to bring a phone into the room, hold it to the patient’s ear, and they were able to say their goodbyes and how much they loved the person.”
The patient was a devout Roman Catholic, he added, and the family requested that the Prayer of Commendation and the Apostolic Pardon be performed. Rev. Mercier arranged for a Catholic priest to carry out this request. “The nurse told the patient what was going on, and the priest offered the prayers and the rituals from the doorway,” Rev. Mercier said. “It was a surreal experience. For me, it was almost entirely phone based, and it was mostly with the family because the patient couldn’t talk too much.”
To add to the sense of detachment in a situation like that, doctors, nurses, and chaplains caring for COVID-19 patients are wearing masks and face shields, and sometimes the sickest patients are intubated, which can complicate efforts to communicate. “I’m surprised at how we find the mask as somewhat of a barrier,” said Carolanne B. Hauck, BCC, director of chaplaincy care & education and volunteer services at Lancaster (Pa.) General Hospital, which is part of the Penn Medicine system. “By that I mean, often for us, sitting at the bedside and really being able to see someone’s face and have them see our face – with our masks, that’s just not happening. We’re also having briefer visits when we’re visiting with COVID patients.”
COVID-19 may have quarantined some traditional ways of providing spiritual care, but hospital chaplains are relying on technology more than ever in their efforts to meet the needs of patients and their families, including the use of iPads, FaceTime, and video conferencing programs like Zoom and BlueJeans.
“We’ve used Zoom to talk with family members that live out of state,” Rev. Mercier said. “Most of the time, I get an invitation to join a Zoom meeting, but now I need to become proficient in utilizing Zoom to set up those end-of-life family meetings. There’s a lot of learning on the fly, how to use these technologies in a way that’s helpful for everybody. That’s the biggest thing I’m learning: Connection is connection during this time of high stress and anxiety, and we just have to get creative.”
Despite the “disembodied” nature of technology, patients and their families have expressed gratitude to chaplains for their efforts to facilitate connections between loved ones and to be “a guide on the side,” as Mary Wetsch-Johnson, BCC, put it. She recalled one phone conversation with the daughter of a man with COVID-19 who was placed on comfort measures. “She said her dad was like the dad on the TV series Father Knows Best, just a kind-hearted, loving, wonderful man,” said Ms. Wetsch-Johnson, a chaplain at CHI Franciscan Health, which operates 10 acute-care hospitals in the Puget Sound region of Washington state. “She was able to describe him in a way that I felt like I knew him. She talked about the discord they had in their family and how they’re processing through that, and about her own personal journey with grief and loss. She then asked me for information about funeral homes, and I provided her with information. At the end of it, she said, ‘I did not know that I needed you today, but you are exactly what I needed.’ ”
Hospital chaplains may be using smartphones and other gadgets to communicate with patients and their families more than they did in the pre-COVID-19 world, but their basic job has not changed, said Rabbi Neal J. Loevinger, BCC, director of spiritual care services at Vassar Brothers Medical Center in Poughkeepsie, N.Y., part of a seven-hospital system operated by Nuvance Health. “We offer the hope of a caring presence,” said Rabbi Loevinger, who is also a member of the board of directors for Neshama: Association of Jewish Chaplains. “If someone is in a hole, our job is to climb down into the hole with them and say, ‘We’re going to get out of this hole together.’ We can’t promise that someone’s going to get better. We can’t promise that everything’s going to be all right. What we can promise is that we will not abandon you. We can promise that there will be someone accompanying you in any way we can through this crisis.”
Ms. Hauck remembered a phone conversation with the granddaughter of a patient hospitalized with COVID-19 who was nearing the end of her life. The granddaughter told her a story about how her grandmother and her best friend made a pact with each other that, when one was dying, the other would come to her side and pray the Rosary with her. “The granddaughter got tearful and said, ‘That can’t happen now,’ ” said Ms. Hauck, who oversees a staff of 9 chaplains and 10 per diem chaplains. “I made a promise that I would do my best to be at the bedside and pray the Rosary with her grandmother.”
The nurses were aware of the request, and about a day later, Ms. Hauck received a call at 1 a.m., indicating that the patient was close to dying. She drove to Lancaster General, put on her personal protective equipment, made it to the patient’s bedside, and began to pray the Rosary with her, with a nurse in the room. “The nurse said to me, ‘Carolanne, all of her stats are going up,’ and the patient actually became a little more alert,” she recalled. “We talked a little bit, and I asked, ‘Would you like to pray the Rosary now?’ She shook her head yes, and said, ‘Hail Mary, full of grace ...’ and those were the last words that she spoke. I finished the prayers for her, and then she died. It was very meaningful knowing that I could honor that wish for her, but more importantly, that I could do that for the family, who otherwise would have been at her side saying the Rosary with her. We have a recognition of how hard it is to leave someone at the hospital and not be at their bedside.”

Hospital chaplains are also supporting interdisciplinary teams of physicians, nurses, and other staff, as they navigate the provision of care in the wake of a pandemic. “They are under a great deal of stress – not only from being at work but with all the role changes that have happened in their home life,” Ms. Wetsch-Johnson said. “Some of them now are being the teacher at home and having to care for children. They have a lot that they come in with. My job is to help them so that they can go do their job. Regularly what I do is check in with the units and ask, ‘How are you doing today? What’s going on for you?’ Because people need to know that someone’s there to be with them and walk with them and listen to them.”
In the spirit of being present for their staff, she and her colleagues established “respite rooms” at CHI Franciscan hospitals, where workers can decompress and get recentered before returning to work. “We usually have water and snacks in there for them, and some type of soothing music,” Ms. Wetsch-Johnson said. “There is also literature on breathing exercises and stretching exercises. We’re also inviting people to write little notes of hope and gratitude, and they’re putting those up for each other. It’s important that we keep supporting them as they support the patients. Personally, I also round with our physicians, because they carry a lot with them, just as much as any other staff. I check in with dietary and environmental services. Everybody’s giving in their own unique way; that helps this whole health care system keep going.”
On any given day, it’s not uncommon for hospital staff members to spontaneously pull aside chaplains to vent, pray, or just to talk. “They process their own fears and anxieties about working in this kind of environment,” Rev. Mercier said. “They’re scared for themselves. They think, ‘Could I get the virus? Could I spread the virus to my family?’ Or, they may express the care and concern they have for their patients. Oftentimes, it’s a mixture of both. Those spontaneous conversations are often the most powerful.”
Ms. Hauck noted that some nurses and clinicians at Lancaster General Hospital “are doing work they may have not done before,” she said. “Some of them are experiencing death for the first time, so we help them to navigate that. One of the best things we can do is hear the anxiety they have or the sadness they have when a patient dies. Also, maybe the frustration that they couldn’t do more in some cases and helping them to see that sometimes their best is good enough.”
She recalled one younger patient with COVID-19 who fell seriously ill. “It was really affecting a lot of people on the unit because of the patient’s age,” she said. “When we saw that the patient was getting better and would be discharged, there was such a sense of relief. I’m not sure that patient will ever understand how that helped us. It was comforting to us to know that people are getting better. It is something we celebrate.”
As chaplains adjust to their “new normal,” carving out time for self-care is key. Ms. Hauck and her staff periodically meet on Zoom with a psychotherapist “who understands what we do, asks us really good questions, and reminds us to take care of ourselves,” she said. “Personally, I’m making sure I get my exercise in, I pack a healthy lunch. We do check in with each other. Part of our handoff at every shift provides for an opportunity to debrief about how your day was.”
Rev. Mercier’s self check-in includes deep-breathing meditation and reciting certain prayers throughout the day. “The deep breathing helps me center and refocus with my body, while the prayers remind me of my connection to the Divine,” he said. “It also reminds me that in the midst of the fear and the anxiety, I fear for myself. It’s hard not to be concerned that I could be infected. I have a family at home and could spread this to them. The prayer practices are a reminder to me that it’s okay to feel those fears and anxieties. Sometimes the spiritual practice helps me find that place of acceptance. That enables me to keep moving forward.”
Ms. Wetsch-Johnson described the sense of upendedness caused by the COVID-19 pandemic as a “ripple in the water that’s going to have long-lasting effects on the delivery of health care. People are taking the time to listen to one another. I’ve seen people in all departments be more compassionate with one another. I’ve seen managers go out of their way to make sure their staff are deeply cared for. I think that will have a ripple effect. That’s my hope, that we will continue to be more compassionate, more loving, and more understanding.”
Rabbi Loevinger hopes that even the most reticent physicians remember that chaplains serve as their advocate, too, especially during times of crisis. “This has been a time of unprecedented ethical wrestling in our hospitals, where there’s been a real concern that doctors, nurses, and respiratory therapists are going to be faced with morally distressing situations regarding insufficient PPE, or insufficient ventilator or dialysis machine supply to support everybody that needs to be supported,” he said. “Chaplains are a key part of the process of making ethical decisions, but also supporting physicians who are in distress over [being in] situations they never had imagined. Physicians don’t like to talk about the fact that a lot of the decisions they make are really heartbreaking. But if chaplains understand anything, it’s that being brokenhearted is part of the human condition, and that we can be part of the answer for keeping physicians morally and spiritually grounded in their work. We always invite that conversation.”
For Rev. Mercier, serving in a time of crisis reminds him of the importance of providing care as a team, “not just for patients and families, but for one another,” he said. “One of the lessons we can learn is, how can we build that connection with one another, to support and care for one another? How can we make sure that no one feels alone while working in the hospital?”
He draws inspiration from a saying credited to St. John of the Cross, which reads, “I saw the river through which every soul must pass, and the name of that river is suffering. I saw the boat that carries each soul across that river, and the name of that boat is love.”
“It’s that image that’s sticking with me, not just for myself as a chaplain but for all of my colleagues in the hospital,” said Rev. Mercier, who also pastors Tabernacle Baptist Church in Hope, R.I. “We’re in that river with the patients right now, suffering, and we’re doing our best to help them get to the other side – whatever the other side may look like.”
Correction, 4/30/20: An earlier version of the caption for the photo with Mary Wetsch-Johnson misstated the location. The photo was taken outside St. Elizabeth Hospital in Enumclaw, Wash.
Visa worries besiege immigrant physicians fighting COVID-19
Physicians and their sponsoring health care facilities shouldn’t have to worry about visa technicalities as they work on the front lines during the COVID-19 pandemic, said health care leaders and immigration reform advocates.
In a press call hosted by the National Immigration Forum, speakers highlighted the need for fast and flexible solutions to enable health care workers, including physicians, to contribute to efforts to combat the pandemic.
Nationwide, over one in five physicians are immigrants, according to data from the Forum. That figure is over one in three in New York, New Jersey, and California, three states hard-hit by COVID-19 cases.
Many physicians stand willing and able to serve where they’re needed, but visa restrictions often block the ability of immigrant physicians to meet COVID-19 surges across the country, said Amit Vashist, MD, senior vice president and chief clinical officer for Ballad Health, Johnson City, Tenn., and a member of the public policy committee of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Ballad Health is an integrated health care system that serves 29 counties in the rural Southeast.
“This pandemic is a war with an invisible enemy, and immigrant physicians have been absolutely critical to providing quality care, especially on the front lines – but current visa restrictions have limited the ability to deploy these physicians in communities with the greatest need,” said Dr. Vashist during the press conference.
Visa requirements currently tie a non-US citizen resident physician to a particular institution and facility, limiting the ability to meet demand flexibly. “Federal agencies and Congress should provide additional flexibility in visa processing to allow for automatic renewals and expediting processing so immigrant medical workers can focus on treating the sick and not on their visa requirements,” said Dr. Vashist.
Dr. Vashist noted that, when he speaks with the many Ballad Health hospitalists who are waiting on permanent residency or citizenship, many of them also cite worries about the fate of their families should they themselves fall ill. Depending on the physician’s visa status, the family may face deportation without recourse if the physician should die.
“Tens of thousands of our physicians continue to endure years, even decades of waiting to obtain a permanent residency in the United States and at the same time, relentlessly and fearlessly serve their communities including in this COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Vashist. “It’s time we take care of them and their long-term immigration needs, and give them the peace of mind that they so desperately deserve,” he added.
Frank Trinity, chief legal officer for the Association of American Medical Colleges, also participated in the call. “For decades,” he said, the United States “has relied on physicians from other countries, especially in rural and underserved areas.”
One of these physicians, Mihir Patel, MD, FHM, a hospitalist at Ballad Health, came to the United States in 2005, but 15 years later is still waiting for the green card that signifies U.S. permanent residency status. He is the corporate director of Ballad’s telemedicine program and is now also the medical director of the health system’s COVID-10 Strike Team.
“During the COVID crisis, these restrictions can cause significant negative impact for small rural hospitals,” Dr. Patel said. “There are physicians on a visa who cannot legally work outside their primary facilities – even though they are willing to do so.”
Regarding the pandemic, Mr. Trinity expressed concerns about whether the surge of patients would “outstrip our workforce.” He noted that, with an unprecedented number of desperately ill patients needing emergency care all across the country, “now is the time for our government to take every possible action to ensure that these highly qualified and courageous health professionals are available in the fight against the coronavirus.”
Mr. Trinity outlined five governmental actions AAMC is proposing to allow immigrant physicians to participate fully in the battle against COVID-19. The first would be to approve a blanket extension of visa deadlines. The second would be to expedite processing of visa extension applications, including reinstating expedited processing of physicians currently holding H-1B visa status.
The third action proposed by AAMC is to provide flexibility to visa sponsors during the emergency so that an individual whose visa is currently limited to a particular program can provide care at another location or by means of telehealth.
Fourth, AAMC proposes streamlined entry for the 4,200 physicians who are matched into residency programs so that they may begin their residencies on time or early.
Finally, Mr. Trinity said that AAMC is proposing that work authorizations be maintained for the 29,000 physicians who are currently not U.S. citizens and actively participating in the health care workforce.
Jacinta Ma, the Forum’s vice president of policy and advocacy, said immigrants are a critical component of the U.S. health care workforce as a whole.
“With immigrants accounting for 17% of health care workers amid the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s clear that they are vital to our communities,” she said. “Congress and the Trump administration both have an opportunity to advance solutions that protect immigrants, and remove immigration-related barriers for immigrant medical professionals by ensuring that immigrant doctors, nurses, home health care workers, researchers, and others can continue their vital work during this pandemic while being afforded adequate protection from COVID-19.”
Physicians and their sponsoring health care facilities shouldn’t have to worry about visa technicalities as they work on the front lines during the COVID-19 pandemic, said health care leaders and immigration reform advocates.
In a press call hosted by the National Immigration Forum, speakers highlighted the need for fast and flexible solutions to enable health care workers, including physicians, to contribute to efforts to combat the pandemic.
Nationwide, over one in five physicians are immigrants, according to data from the Forum. That figure is over one in three in New York, New Jersey, and California, three states hard-hit by COVID-19 cases.
Many physicians stand willing and able to serve where they’re needed, but visa restrictions often block the ability of immigrant physicians to meet COVID-19 surges across the country, said Amit Vashist, MD, senior vice president and chief clinical officer for Ballad Health, Johnson City, Tenn., and a member of the public policy committee of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Ballad Health is an integrated health care system that serves 29 counties in the rural Southeast.
“This pandemic is a war with an invisible enemy, and immigrant physicians have been absolutely critical to providing quality care, especially on the front lines – but current visa restrictions have limited the ability to deploy these physicians in communities with the greatest need,” said Dr. Vashist during the press conference.
Visa requirements currently tie a non-US citizen resident physician to a particular institution and facility, limiting the ability to meet demand flexibly. “Federal agencies and Congress should provide additional flexibility in visa processing to allow for automatic renewals and expediting processing so immigrant medical workers can focus on treating the sick and not on their visa requirements,” said Dr. Vashist.
Dr. Vashist noted that, when he speaks with the many Ballad Health hospitalists who are waiting on permanent residency or citizenship, many of them also cite worries about the fate of their families should they themselves fall ill. Depending on the physician’s visa status, the family may face deportation without recourse if the physician should die.
“Tens of thousands of our physicians continue to endure years, even decades of waiting to obtain a permanent residency in the United States and at the same time, relentlessly and fearlessly serve their communities including in this COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Vashist. “It’s time we take care of them and their long-term immigration needs, and give them the peace of mind that they so desperately deserve,” he added.
Frank Trinity, chief legal officer for the Association of American Medical Colleges, also participated in the call. “For decades,” he said, the United States “has relied on physicians from other countries, especially in rural and underserved areas.”
One of these physicians, Mihir Patel, MD, FHM, a hospitalist at Ballad Health, came to the United States in 2005, but 15 years later is still waiting for the green card that signifies U.S. permanent residency status. He is the corporate director of Ballad’s telemedicine program and is now also the medical director of the health system’s COVID-10 Strike Team.
“During the COVID crisis, these restrictions can cause significant negative impact for small rural hospitals,” Dr. Patel said. “There are physicians on a visa who cannot legally work outside their primary facilities – even though they are willing to do so.”
Regarding the pandemic, Mr. Trinity expressed concerns about whether the surge of patients would “outstrip our workforce.” He noted that, with an unprecedented number of desperately ill patients needing emergency care all across the country, “now is the time for our government to take every possible action to ensure that these highly qualified and courageous health professionals are available in the fight against the coronavirus.”
Mr. Trinity outlined five governmental actions AAMC is proposing to allow immigrant physicians to participate fully in the battle against COVID-19. The first would be to approve a blanket extension of visa deadlines. The second would be to expedite processing of visa extension applications, including reinstating expedited processing of physicians currently holding H-1B visa status.
The third action proposed by AAMC is to provide flexibility to visa sponsors during the emergency so that an individual whose visa is currently limited to a particular program can provide care at another location or by means of telehealth.
Fourth, AAMC proposes streamlined entry for the 4,200 physicians who are matched into residency programs so that they may begin their residencies on time or early.
Finally, Mr. Trinity said that AAMC is proposing that work authorizations be maintained for the 29,000 physicians who are currently not U.S. citizens and actively participating in the health care workforce.
Jacinta Ma, the Forum’s vice president of policy and advocacy, said immigrants are a critical component of the U.S. health care workforce as a whole.
“With immigrants accounting for 17% of health care workers amid the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s clear that they are vital to our communities,” she said. “Congress and the Trump administration both have an opportunity to advance solutions that protect immigrants, and remove immigration-related barriers for immigrant medical professionals by ensuring that immigrant doctors, nurses, home health care workers, researchers, and others can continue their vital work during this pandemic while being afforded adequate protection from COVID-19.”
Physicians and their sponsoring health care facilities shouldn’t have to worry about visa technicalities as they work on the front lines during the COVID-19 pandemic, said health care leaders and immigration reform advocates.
In a press call hosted by the National Immigration Forum, speakers highlighted the need for fast and flexible solutions to enable health care workers, including physicians, to contribute to efforts to combat the pandemic.
Nationwide, over one in five physicians are immigrants, according to data from the Forum. That figure is over one in three in New York, New Jersey, and California, three states hard-hit by COVID-19 cases.
Many physicians stand willing and able to serve where they’re needed, but visa restrictions often block the ability of immigrant physicians to meet COVID-19 surges across the country, said Amit Vashist, MD, senior vice president and chief clinical officer for Ballad Health, Johnson City, Tenn., and a member of the public policy committee of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Ballad Health is an integrated health care system that serves 29 counties in the rural Southeast.
“This pandemic is a war with an invisible enemy, and immigrant physicians have been absolutely critical to providing quality care, especially on the front lines – but current visa restrictions have limited the ability to deploy these physicians in communities with the greatest need,” said Dr. Vashist during the press conference.
Visa requirements currently tie a non-US citizen resident physician to a particular institution and facility, limiting the ability to meet demand flexibly. “Federal agencies and Congress should provide additional flexibility in visa processing to allow for automatic renewals and expediting processing so immigrant medical workers can focus on treating the sick and not on their visa requirements,” said Dr. Vashist.
Dr. Vashist noted that, when he speaks with the many Ballad Health hospitalists who are waiting on permanent residency or citizenship, many of them also cite worries about the fate of their families should they themselves fall ill. Depending on the physician’s visa status, the family may face deportation without recourse if the physician should die.
“Tens of thousands of our physicians continue to endure years, even decades of waiting to obtain a permanent residency in the United States and at the same time, relentlessly and fearlessly serve their communities including in this COVID-19 pandemic,” said Dr. Vashist. “It’s time we take care of them and their long-term immigration needs, and give them the peace of mind that they so desperately deserve,” he added.
Frank Trinity, chief legal officer for the Association of American Medical Colleges, also participated in the call. “For decades,” he said, the United States “has relied on physicians from other countries, especially in rural and underserved areas.”
One of these physicians, Mihir Patel, MD, FHM, a hospitalist at Ballad Health, came to the United States in 2005, but 15 years later is still waiting for the green card that signifies U.S. permanent residency status. He is the corporate director of Ballad’s telemedicine program and is now also the medical director of the health system’s COVID-10 Strike Team.
“During the COVID crisis, these restrictions can cause significant negative impact for small rural hospitals,” Dr. Patel said. “There are physicians on a visa who cannot legally work outside their primary facilities – even though they are willing to do so.”
Regarding the pandemic, Mr. Trinity expressed concerns about whether the surge of patients would “outstrip our workforce.” He noted that, with an unprecedented number of desperately ill patients needing emergency care all across the country, “now is the time for our government to take every possible action to ensure that these highly qualified and courageous health professionals are available in the fight against the coronavirus.”
Mr. Trinity outlined five governmental actions AAMC is proposing to allow immigrant physicians to participate fully in the battle against COVID-19. The first would be to approve a blanket extension of visa deadlines. The second would be to expedite processing of visa extension applications, including reinstating expedited processing of physicians currently holding H-1B visa status.
The third action proposed by AAMC is to provide flexibility to visa sponsors during the emergency so that an individual whose visa is currently limited to a particular program can provide care at another location or by means of telehealth.
Fourth, AAMC proposes streamlined entry for the 4,200 physicians who are matched into residency programs so that they may begin their residencies on time or early.
Finally, Mr. Trinity said that AAMC is proposing that work authorizations be maintained for the 29,000 physicians who are currently not U.S. citizens and actively participating in the health care workforce.
Jacinta Ma, the Forum’s vice president of policy and advocacy, said immigrants are a critical component of the U.S. health care workforce as a whole.
“With immigrants accounting for 17% of health care workers amid the COVID-19 pandemic, it’s clear that they are vital to our communities,” she said. “Congress and the Trump administration both have an opportunity to advance solutions that protect immigrants, and remove immigration-related barriers for immigrant medical professionals by ensuring that immigrant doctors, nurses, home health care workers, researchers, and others can continue their vital work during this pandemic while being afforded adequate protection from COVID-19.”
COVID-19 registry tracks pregnant women, newborns
A multidisciplinary team of researchers has created a national registry to study how COVID-19 affects pregnant women and their newborns.
“Pregnant women are generally considered healthy, but they are also a vulnerable group, and we currently have no data on COVID-19 in pregnancy,” coprincipal investigator Yalda Afshar, MD, PhD, an ob.gyn. at UCLA Health in Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“We expect this registry to provide data that will be critical in helping to improve care for pregnant women during this global pandemic,” Dr. Afshar, a fellow with UCLA Biodesign, stated in a news release.
The Pregnancy Coronavirus Outcomes Registry is enrolling pregnant women and those who have been pregnant or post partum within the past 6 weeks and who have either received a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or are being evaluated for COVID-19.
Women are being recruited through their health care provider. A study coordinator contacts the participants by telephone. Women can also join the registry on their own without a referral by visiting the registry website.
The registry collects data on COVID-19 symptoms, clinical course, pregnancy, and neonatal outcomes and follows women from enrollment through the second and third trimesters and the postpartum period. The goal is to follow the mothers and babies for up to 1 year.
Hundreds of women already enrolled
Dr. Afshar noted that these kinds of registries often take months to design and to receive funding, but with COVID-19, “there was no time for that. We had to get it up and running ASAP.”
She said the team has been “blown away” by how quickly people have come forward to join the registry. Within 2 weeks of going live, the registry had enrolled more than 400 participants from across the United States. “At this rate, I think we will easily get 1,000 participants in a month or so,” Dr. Afshar said.
“With the global reach of this disease, the findings resulting from this work have the potential to impact millions of lives in an entire generation,” Johnese Spisso, CEO of UCLA Health, said in the news release.
Dr. Afshar noted that, although the impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy remains unknown, history suggests the disease will make some pregnancies and deliveries more challenging. “We know that in previous outbreaks of the regular flu, for example, there have been more deaths and poorer outcomes among pregnant women compared with nonpregnant women.”
Dr. Afshar is overseeing the study with colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the University of California, San Francisco, where the registry data will be coordinated.
“In addition to gaining a better understanding of the course of the disease, we will investigate disease transmission to determine if it can be passed from a mother to her baby in utero and during the postpartum period, such as in breast milk,” UCSF’s Stephanie Gaw, MD, PhD, who is leading the biospecimen core of the study, said in the release.
Health care providers interested in more information about the registry may send an email to [email protected]. A YouTube video on the registry is also available.
Dr. Afshar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers has created a national registry to study how COVID-19 affects pregnant women and their newborns.
“Pregnant women are generally considered healthy, but they are also a vulnerable group, and we currently have no data on COVID-19 in pregnancy,” coprincipal investigator Yalda Afshar, MD, PhD, an ob.gyn. at UCLA Health in Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“We expect this registry to provide data that will be critical in helping to improve care for pregnant women during this global pandemic,” Dr. Afshar, a fellow with UCLA Biodesign, stated in a news release.
The Pregnancy Coronavirus Outcomes Registry is enrolling pregnant women and those who have been pregnant or post partum within the past 6 weeks and who have either received a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or are being evaluated for COVID-19.
Women are being recruited through their health care provider. A study coordinator contacts the participants by telephone. Women can also join the registry on their own without a referral by visiting the registry website.
The registry collects data on COVID-19 symptoms, clinical course, pregnancy, and neonatal outcomes and follows women from enrollment through the second and third trimesters and the postpartum period. The goal is to follow the mothers and babies for up to 1 year.
Hundreds of women already enrolled
Dr. Afshar noted that these kinds of registries often take months to design and to receive funding, but with COVID-19, “there was no time for that. We had to get it up and running ASAP.”
She said the team has been “blown away” by how quickly people have come forward to join the registry. Within 2 weeks of going live, the registry had enrolled more than 400 participants from across the United States. “At this rate, I think we will easily get 1,000 participants in a month or so,” Dr. Afshar said.
“With the global reach of this disease, the findings resulting from this work have the potential to impact millions of lives in an entire generation,” Johnese Spisso, CEO of UCLA Health, said in the news release.
Dr. Afshar noted that, although the impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy remains unknown, history suggests the disease will make some pregnancies and deliveries more challenging. “We know that in previous outbreaks of the regular flu, for example, there have been more deaths and poorer outcomes among pregnant women compared with nonpregnant women.”
Dr. Afshar is overseeing the study with colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the University of California, San Francisco, where the registry data will be coordinated.
“In addition to gaining a better understanding of the course of the disease, we will investigate disease transmission to determine if it can be passed from a mother to her baby in utero and during the postpartum period, such as in breast milk,” UCSF’s Stephanie Gaw, MD, PhD, who is leading the biospecimen core of the study, said in the release.
Health care providers interested in more information about the registry may send an email to [email protected]. A YouTube video on the registry is also available.
Dr. Afshar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
A multidisciplinary team of researchers has created a national registry to study how COVID-19 affects pregnant women and their newborns.
“Pregnant women are generally considered healthy, but they are also a vulnerable group, and we currently have no data on COVID-19 in pregnancy,” coprincipal investigator Yalda Afshar, MD, PhD, an ob.gyn. at UCLA Health in Los Angeles, said in an interview.
“We expect this registry to provide data that will be critical in helping to improve care for pregnant women during this global pandemic,” Dr. Afshar, a fellow with UCLA Biodesign, stated in a news release.
The Pregnancy Coronavirus Outcomes Registry is enrolling pregnant women and those who have been pregnant or post partum within the past 6 weeks and who have either received a confirmed diagnosis of COVID-19 or are being evaluated for COVID-19.
Women are being recruited through their health care provider. A study coordinator contacts the participants by telephone. Women can also join the registry on their own without a referral by visiting the registry website.
The registry collects data on COVID-19 symptoms, clinical course, pregnancy, and neonatal outcomes and follows women from enrollment through the second and third trimesters and the postpartum period. The goal is to follow the mothers and babies for up to 1 year.
Hundreds of women already enrolled
Dr. Afshar noted that these kinds of registries often take months to design and to receive funding, but with COVID-19, “there was no time for that. We had to get it up and running ASAP.”
She said the team has been “blown away” by how quickly people have come forward to join the registry. Within 2 weeks of going live, the registry had enrolled more than 400 participants from across the United States. “At this rate, I think we will easily get 1,000 participants in a month or so,” Dr. Afshar said.
“With the global reach of this disease, the findings resulting from this work have the potential to impact millions of lives in an entire generation,” Johnese Spisso, CEO of UCLA Health, said in the news release.
Dr. Afshar noted that, although the impact of COVID-19 on pregnancy remains unknown, history suggests the disease will make some pregnancies and deliveries more challenging. “We know that in previous outbreaks of the regular flu, for example, there have been more deaths and poorer outcomes among pregnant women compared with nonpregnant women.”
Dr. Afshar is overseeing the study with colleagues at the University of California, Los Angeles, and the University of California, San Francisco, where the registry data will be coordinated.
“In addition to gaining a better understanding of the course of the disease, we will investigate disease transmission to determine if it can be passed from a mother to her baby in utero and during the postpartum period, such as in breast milk,” UCSF’s Stephanie Gaw, MD, PhD, who is leading the biospecimen core of the study, said in the release.
Health care providers interested in more information about the registry may send an email to [email protected]. A YouTube video on the registry is also available.
Dr. Afshar disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 decimates outpatient visits
There has been a massive decline in outpatient office visits as patients have stayed home – likely deferring needed care – because of COVID-19, new research shows.
The number of visits to ambulatory practices dropped by a whopping 60% in mid-March, and continues to be down by at least 50% since early February, according to new data compiled and analyzed by Harvard University and Phreesia, a health care technology company.
Phreesia – which helps medical practices with patient registration, insurance verification, and payments – has data on 50,000 providers in all 50 states; in a typical year, Phreesia tracks 50 million outpatient visits.
The report was published online April 23 by the Commonwealth Fund.
The company captured data on visits from February 1 through April 16. The decline was greatest in New England and the Mid-Atlantic states, where, at the steepest end of the decline in late March, visits were down 66%.
They have rebounded slightly since then but are still down 64%. Practices in the mountain states had the smallest decline, but visits were down by 45% as of April 16.
Many practices have attempted to reach out to patients through telemedicine. As of April 16, about 30% of all visits tracked by Phreesia were provided via telemedicine – by phone or through video. That’s a monumental increase from mid-February, when zero visits were conducted virtually.
However, the Harvard researchers found that telemedicine visits barely made up for the huge decline in office visits.
Decline by specialty
Not surprisingly, declining visits have been steeper in procedure-oriented specialties.
Overall visits – including telemedicine – to ophthalmologists and otolaryngologists had declined by 79% and 75%, respectively, as of the week of April 5. Dermatology saw a 73% decline. Surgery, pulmonology, urology, orthopedics, cardiology, and gastroenterology all experienced declines ranging from 61% to 66%.
Primary care offices, oncology, endocrinology, and obstetrics/gynecology all fared slightly better, with visits down by half. Behavioral health experienced the lowest rate of decline (30%).
School-aged children were skipping care most often. The study showed a 71% drop in visits in 7- to 17-year-olds, and a 59% decline in visits by neonates, infants, and toddlers (up to age 6). Overall, pediatric practices experienced a 62% drop-off in visits.
Nearly two-thirds of Americans over age 65 also stayed away from their doctors. Only half of those aged 18 to 64 reduced their physician visits.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There has been a massive decline in outpatient office visits as patients have stayed home – likely deferring needed care – because of COVID-19, new research shows.
The number of visits to ambulatory practices dropped by a whopping 60% in mid-March, and continues to be down by at least 50% since early February, according to new data compiled and analyzed by Harvard University and Phreesia, a health care technology company.
Phreesia – which helps medical practices with patient registration, insurance verification, and payments – has data on 50,000 providers in all 50 states; in a typical year, Phreesia tracks 50 million outpatient visits.
The report was published online April 23 by the Commonwealth Fund.
The company captured data on visits from February 1 through April 16. The decline was greatest in New England and the Mid-Atlantic states, where, at the steepest end of the decline in late March, visits were down 66%.
They have rebounded slightly since then but are still down 64%. Practices in the mountain states had the smallest decline, but visits were down by 45% as of April 16.
Many practices have attempted to reach out to patients through telemedicine. As of April 16, about 30% of all visits tracked by Phreesia were provided via telemedicine – by phone or through video. That’s a monumental increase from mid-February, when zero visits were conducted virtually.
However, the Harvard researchers found that telemedicine visits barely made up for the huge decline in office visits.
Decline by specialty
Not surprisingly, declining visits have been steeper in procedure-oriented specialties.
Overall visits – including telemedicine – to ophthalmologists and otolaryngologists had declined by 79% and 75%, respectively, as of the week of April 5. Dermatology saw a 73% decline. Surgery, pulmonology, urology, orthopedics, cardiology, and gastroenterology all experienced declines ranging from 61% to 66%.
Primary care offices, oncology, endocrinology, and obstetrics/gynecology all fared slightly better, with visits down by half. Behavioral health experienced the lowest rate of decline (30%).
School-aged children were skipping care most often. The study showed a 71% drop in visits in 7- to 17-year-olds, and a 59% decline in visits by neonates, infants, and toddlers (up to age 6). Overall, pediatric practices experienced a 62% drop-off in visits.
Nearly two-thirds of Americans over age 65 also stayed away from their doctors. Only half of those aged 18 to 64 reduced their physician visits.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
There has been a massive decline in outpatient office visits as patients have stayed home – likely deferring needed care – because of COVID-19, new research shows.
The number of visits to ambulatory practices dropped by a whopping 60% in mid-March, and continues to be down by at least 50% since early February, according to new data compiled and analyzed by Harvard University and Phreesia, a health care technology company.
Phreesia – which helps medical practices with patient registration, insurance verification, and payments – has data on 50,000 providers in all 50 states; in a typical year, Phreesia tracks 50 million outpatient visits.
The report was published online April 23 by the Commonwealth Fund.
The company captured data on visits from February 1 through April 16. The decline was greatest in New England and the Mid-Atlantic states, where, at the steepest end of the decline in late March, visits were down 66%.
They have rebounded slightly since then but are still down 64%. Practices in the mountain states had the smallest decline, but visits were down by 45% as of April 16.
Many practices have attempted to reach out to patients through telemedicine. As of April 16, about 30% of all visits tracked by Phreesia were provided via telemedicine – by phone or through video. That’s a monumental increase from mid-February, when zero visits were conducted virtually.
However, the Harvard researchers found that telemedicine visits barely made up for the huge decline in office visits.
Decline by specialty
Not surprisingly, declining visits have been steeper in procedure-oriented specialties.
Overall visits – including telemedicine – to ophthalmologists and otolaryngologists had declined by 79% and 75%, respectively, as of the week of April 5. Dermatology saw a 73% decline. Surgery, pulmonology, urology, orthopedics, cardiology, and gastroenterology all experienced declines ranging from 61% to 66%.
Primary care offices, oncology, endocrinology, and obstetrics/gynecology all fared slightly better, with visits down by half. Behavioral health experienced the lowest rate of decline (30%).
School-aged children were skipping care most often. The study showed a 71% drop in visits in 7- to 17-year-olds, and a 59% decline in visits by neonates, infants, and toddlers (up to age 6). Overall, pediatric practices experienced a 62% drop-off in visits.
Nearly two-thirds of Americans over age 65 also stayed away from their doctors. Only half of those aged 18 to 64 reduced their physician visits.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.