User login
-
Universal CAR-T therapy produces CRs in relapsed/refractory T-ALL
according to initial findings from an ongoing study.
The first five patients enrolled in this first-in-human study received conditioning and an infusion of the premanufactured CD7-targeted CAR T-cell therapy, TruUCAR GC027.
All five patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi), although one patient had a morphological relapse at 1 month.
Xinxin Wang, PhD, reported these results at the AACR Virtual Meeting I. Dr. Wang is employed by Gracell Biotechnologies in Shanghai, China, which is the company developing TruUCAR GC027.
The CAR T-cell therapy is manufactured using lentivirus and leukopaks from HLA-mismatched healthy donors, according to Dr. Wang. TruUCAR GC027 contains second-generation CAR T cells with genomic disruption of TCR-alpha and CD7 to help prevent graft-versus-host disease and fratricide.
TruUCAR GC027 was previously shown to expand and have antileukemic activity in a murine model, Dr. Wang noted.
Patients and treatment
The five patients in the phase 1 study had a median age of 24 years (range, 19 to 38 years). They had heavily pretreated T-ALL, with a median of 5 prior lines of therapy (range, 1-9). Baseline bone marrow tumor burden ranged from 4% to 80.2% (median, 38.2%).
None of the patients received prior allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
All patients received a preconditioning chemotherapy regimen. One patient received TruUCAR GC027 at dose level 1 (6 x 106 cells/kg), three patients received dose level 2 (1 x 107 cells/kg), and one patient received dose level 3 (1.5 x 107 cells/kg) – each as a single infusion.
Expansion, response, and safety
“GC027 expansion, analyzed by flow [cytometry] was observed in most of the patients treated,” Dr. Wang said. “We started to see GC027 in the peripheral blood as early as day 5, with peaks around day 7-14.”
All five patients had a CR or CRi at the first postinfusion evaluation, which occurred at day 14 in four of the five patients. Four patients also achieved minimum residual disease (MRD) negativity by 1 month of follow-up and remained in MRD-negative CR at the February 6, 2020, data cutoff.
One patient achieved MRD-positive CR at day 14 but experienced morphological relapse at 1 month.
In the four patients with MRD-negative CR at 1 month, cellular expansion was observed as early as day 5 and continued for 2 weeks, but the patient who relapsed at day 29 showed no cellular expansion on flow cytometry, Dr. Wang said.
However, by a more sensitive quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis, cellular expansion was observed in all five patients starting as early as day 1 after infusion, although the patient who relapsed had the shortest duration of expansion.
All patients developed cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Four patients experienced grade 3 CRS, and one experienced grade 4 CRS.
“The CRS was manageable and reversible,” Dr. Wang said, adding that none of the patients experienced neurotoxicity or graft-versus-host disease.
Prolonged cytopenia occurred in four patients, including one grade 1 case, two grade 3 cases, and one grade 4 case. Grade 3 pulmonary infections occurred in three patients, and grade 3 neutropenia occurred in all five patients.
‘Very impressive’ early results
Dr. Wang said the responses observed in this trial are notable because T-ALL constitutes 20%-25% of all adult ALL and 12%-15% of all pediatric ALL. T-ALL is highly aggressive, with event-free and overall survival of less than 25% in the relapsed setting. Dr. Wang noted that, despite the high unmet medical need and lack of treatment options for T-ALL, the development of novel immunotherapies has lagged.
One challenge is that T-ALL and normal T cells share common surface antigens, so targeted therapies for T-ALL will also target normal T cells. Another challenge is the potential contamination by malignant cells in autologous T-cell products, Dr. Wang said, noting that this can be avoided with universal CAR T cells.
Further, CD7 is a good target for T-ALL because it is expressed in more than 95% of T-ALL patients, she added.
“[TruUCAR GC027] demonstrated a very promising early response rate ... and showed a manageable toxicity profile at all three dose levels,” Dr. Wang said in closing, noting that further evaluation is warranted.
Indeed, the results of this next-generation CAR T-cell trial are “very impressive,” said invited discussant Yvonne Y. Chen, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
There have been concerns that “off-the-shelf” CAR T-cell products like TruUCAR GC027 might be limited by factors such as a reduced level of CAR T-cell persistence and therefore reduced efficacy leading to a need for repeat dosing, Dr. Chen noted. However, Dr. Wang and her colleagues showed a 100% CR/CRi rate with a single dose of CAR T cells and without graft-versus-host disease or neurotoxicity, Dr. Chen emphasized.
“I think it’s also important to note, however, that there’s quite a high incidence rate of grade 3 or higher toxicities, including CRS,” Dr. Chen said. “I suspect this may have something to do with the fairly high dosing levels used in this trial.”
The “big question,” however, is durability of the response, Dr. Chen said. “And this is something that the field will really watch as this trial progresses beyond the 7-month monitoring period ... reported today.”
Dr. Wang is an employee of Gracell Biotechnologies. Dr. Chen is cofounder of Kalthera Therapeutics and a scientific adviser for Gritstone Oncology and Notch Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Wang X et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT052.
according to initial findings from an ongoing study.
The first five patients enrolled in this first-in-human study received conditioning and an infusion of the premanufactured CD7-targeted CAR T-cell therapy, TruUCAR GC027.
All five patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi), although one patient had a morphological relapse at 1 month.
Xinxin Wang, PhD, reported these results at the AACR Virtual Meeting I. Dr. Wang is employed by Gracell Biotechnologies in Shanghai, China, which is the company developing TruUCAR GC027.
The CAR T-cell therapy is manufactured using lentivirus and leukopaks from HLA-mismatched healthy donors, according to Dr. Wang. TruUCAR GC027 contains second-generation CAR T cells with genomic disruption of TCR-alpha and CD7 to help prevent graft-versus-host disease and fratricide.
TruUCAR GC027 was previously shown to expand and have antileukemic activity in a murine model, Dr. Wang noted.
Patients and treatment
The five patients in the phase 1 study had a median age of 24 years (range, 19 to 38 years). They had heavily pretreated T-ALL, with a median of 5 prior lines of therapy (range, 1-9). Baseline bone marrow tumor burden ranged from 4% to 80.2% (median, 38.2%).
None of the patients received prior allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
All patients received a preconditioning chemotherapy regimen. One patient received TruUCAR GC027 at dose level 1 (6 x 106 cells/kg), three patients received dose level 2 (1 x 107 cells/kg), and one patient received dose level 3 (1.5 x 107 cells/kg) – each as a single infusion.
Expansion, response, and safety
“GC027 expansion, analyzed by flow [cytometry] was observed in most of the patients treated,” Dr. Wang said. “We started to see GC027 in the peripheral blood as early as day 5, with peaks around day 7-14.”
All five patients had a CR or CRi at the first postinfusion evaluation, which occurred at day 14 in four of the five patients. Four patients also achieved minimum residual disease (MRD) negativity by 1 month of follow-up and remained in MRD-negative CR at the February 6, 2020, data cutoff.
One patient achieved MRD-positive CR at day 14 but experienced morphological relapse at 1 month.
In the four patients with MRD-negative CR at 1 month, cellular expansion was observed as early as day 5 and continued for 2 weeks, but the patient who relapsed at day 29 showed no cellular expansion on flow cytometry, Dr. Wang said.
However, by a more sensitive quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis, cellular expansion was observed in all five patients starting as early as day 1 after infusion, although the patient who relapsed had the shortest duration of expansion.
All patients developed cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Four patients experienced grade 3 CRS, and one experienced grade 4 CRS.
“The CRS was manageable and reversible,” Dr. Wang said, adding that none of the patients experienced neurotoxicity or graft-versus-host disease.
Prolonged cytopenia occurred in four patients, including one grade 1 case, two grade 3 cases, and one grade 4 case. Grade 3 pulmonary infections occurred in three patients, and grade 3 neutropenia occurred in all five patients.
‘Very impressive’ early results
Dr. Wang said the responses observed in this trial are notable because T-ALL constitutes 20%-25% of all adult ALL and 12%-15% of all pediatric ALL. T-ALL is highly aggressive, with event-free and overall survival of less than 25% in the relapsed setting. Dr. Wang noted that, despite the high unmet medical need and lack of treatment options for T-ALL, the development of novel immunotherapies has lagged.
One challenge is that T-ALL and normal T cells share common surface antigens, so targeted therapies for T-ALL will also target normal T cells. Another challenge is the potential contamination by malignant cells in autologous T-cell products, Dr. Wang said, noting that this can be avoided with universal CAR T cells.
Further, CD7 is a good target for T-ALL because it is expressed in more than 95% of T-ALL patients, she added.
“[TruUCAR GC027] demonstrated a very promising early response rate ... and showed a manageable toxicity profile at all three dose levels,” Dr. Wang said in closing, noting that further evaluation is warranted.
Indeed, the results of this next-generation CAR T-cell trial are “very impressive,” said invited discussant Yvonne Y. Chen, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
There have been concerns that “off-the-shelf” CAR T-cell products like TruUCAR GC027 might be limited by factors such as a reduced level of CAR T-cell persistence and therefore reduced efficacy leading to a need for repeat dosing, Dr. Chen noted. However, Dr. Wang and her colleagues showed a 100% CR/CRi rate with a single dose of CAR T cells and without graft-versus-host disease or neurotoxicity, Dr. Chen emphasized.
“I think it’s also important to note, however, that there’s quite a high incidence rate of grade 3 or higher toxicities, including CRS,” Dr. Chen said. “I suspect this may have something to do with the fairly high dosing levels used in this trial.”
The “big question,” however, is durability of the response, Dr. Chen said. “And this is something that the field will really watch as this trial progresses beyond the 7-month monitoring period ... reported today.”
Dr. Wang is an employee of Gracell Biotechnologies. Dr. Chen is cofounder of Kalthera Therapeutics and a scientific adviser for Gritstone Oncology and Notch Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Wang X et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT052.
according to initial findings from an ongoing study.
The first five patients enrolled in this first-in-human study received conditioning and an infusion of the premanufactured CD7-targeted CAR T-cell therapy, TruUCAR GC027.
All five patients achieved a complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete count recovery (CRi), although one patient had a morphological relapse at 1 month.
Xinxin Wang, PhD, reported these results at the AACR Virtual Meeting I. Dr. Wang is employed by Gracell Biotechnologies in Shanghai, China, which is the company developing TruUCAR GC027.
The CAR T-cell therapy is manufactured using lentivirus and leukopaks from HLA-mismatched healthy donors, according to Dr. Wang. TruUCAR GC027 contains second-generation CAR T cells with genomic disruption of TCR-alpha and CD7 to help prevent graft-versus-host disease and fratricide.
TruUCAR GC027 was previously shown to expand and have antileukemic activity in a murine model, Dr. Wang noted.
Patients and treatment
The five patients in the phase 1 study had a median age of 24 years (range, 19 to 38 years). They had heavily pretreated T-ALL, with a median of 5 prior lines of therapy (range, 1-9). Baseline bone marrow tumor burden ranged from 4% to 80.2% (median, 38.2%).
None of the patients received prior allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant.
All patients received a preconditioning chemotherapy regimen. One patient received TruUCAR GC027 at dose level 1 (6 x 106 cells/kg), three patients received dose level 2 (1 x 107 cells/kg), and one patient received dose level 3 (1.5 x 107 cells/kg) – each as a single infusion.
Expansion, response, and safety
“GC027 expansion, analyzed by flow [cytometry] was observed in most of the patients treated,” Dr. Wang said. “We started to see GC027 in the peripheral blood as early as day 5, with peaks around day 7-14.”
All five patients had a CR or CRi at the first postinfusion evaluation, which occurred at day 14 in four of the five patients. Four patients also achieved minimum residual disease (MRD) negativity by 1 month of follow-up and remained in MRD-negative CR at the February 6, 2020, data cutoff.
One patient achieved MRD-positive CR at day 14 but experienced morphological relapse at 1 month.
In the four patients with MRD-negative CR at 1 month, cellular expansion was observed as early as day 5 and continued for 2 weeks, but the patient who relapsed at day 29 showed no cellular expansion on flow cytometry, Dr. Wang said.
However, by a more sensitive quantitative polymerase chain reaction analysis, cellular expansion was observed in all five patients starting as early as day 1 after infusion, although the patient who relapsed had the shortest duration of expansion.
All patients developed cytokine release syndrome (CRS). Four patients experienced grade 3 CRS, and one experienced grade 4 CRS.
“The CRS was manageable and reversible,” Dr. Wang said, adding that none of the patients experienced neurotoxicity or graft-versus-host disease.
Prolonged cytopenia occurred in four patients, including one grade 1 case, two grade 3 cases, and one grade 4 case. Grade 3 pulmonary infections occurred in three patients, and grade 3 neutropenia occurred in all five patients.
‘Very impressive’ early results
Dr. Wang said the responses observed in this trial are notable because T-ALL constitutes 20%-25% of all adult ALL and 12%-15% of all pediatric ALL. T-ALL is highly aggressive, with event-free and overall survival of less than 25% in the relapsed setting. Dr. Wang noted that, despite the high unmet medical need and lack of treatment options for T-ALL, the development of novel immunotherapies has lagged.
One challenge is that T-ALL and normal T cells share common surface antigens, so targeted therapies for T-ALL will also target normal T cells. Another challenge is the potential contamination by malignant cells in autologous T-cell products, Dr. Wang said, noting that this can be avoided with universal CAR T cells.
Further, CD7 is a good target for T-ALL because it is expressed in more than 95% of T-ALL patients, she added.
“[TruUCAR GC027] demonstrated a very promising early response rate ... and showed a manageable toxicity profile at all three dose levels,” Dr. Wang said in closing, noting that further evaluation is warranted.
Indeed, the results of this next-generation CAR T-cell trial are “very impressive,” said invited discussant Yvonne Y. Chen, PhD, of the University of California, Los Angeles.
There have been concerns that “off-the-shelf” CAR T-cell products like TruUCAR GC027 might be limited by factors such as a reduced level of CAR T-cell persistence and therefore reduced efficacy leading to a need for repeat dosing, Dr. Chen noted. However, Dr. Wang and her colleagues showed a 100% CR/CRi rate with a single dose of CAR T cells and without graft-versus-host disease or neurotoxicity, Dr. Chen emphasized.
“I think it’s also important to note, however, that there’s quite a high incidence rate of grade 3 or higher toxicities, including CRS,” Dr. Chen said. “I suspect this may have something to do with the fairly high dosing levels used in this trial.”
The “big question,” however, is durability of the response, Dr. Chen said. “And this is something that the field will really watch as this trial progresses beyond the 7-month monitoring period ... reported today.”
Dr. Wang is an employee of Gracell Biotechnologies. Dr. Chen is cofounder of Kalthera Therapeutics and a scientific adviser for Gritstone Oncology and Notch Therapeutics.
SOURCE: Wang X et al. AACR 2020, Abstract CT052.
FROM AACR 2020
AGS issues pandemic resource allocation recommendations amid ageism concerns
The American Geriatrics Society has issued policy recommendations aimed at protecting seniors from ageism when it comes to resource allocation in the current context of treating patients infected with COVID-19.
“The AGS is deeply concerned about Timothy W. Farrell, MD, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues wrote in an AGS position statement published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
“In particular, rationing strategies that are solely, or predominantly, based on age cutoffs could lead to persistent beliefs that older adults’ lives are less valuable than others or are even expendable, and contribute to already rampant ageism,” the authors continued. “Unless the injustice in these strategies is corrected, this will be a persistent issue if there is a resurgence of COVID-19 cases, a pandemic caused by a different virus in the future, or a different type of disaster where resources are scarce.”
To counter a potential bias against the elderly population should scarce resources force rationing decisions, AGS has made recommendations and strategies that health care systems should incorporate into a policy framework.
One principle in the AGS statement is clear: “Age per se should never be used as a means for a categorical exclusion from therapeutic interventions that represent the standard of care. ... Likewise, specific age-based cutoffs should not be used in resource allocation strategies.”
Peter Angelos, MD, chief of endocrine surgery at the University of Chicago, applauded the position statement.
“It is a well-written statement and I do think that it appropriately suggests that age in and of itself is not a good predictor of who is at greatest risk if infected with coronavirus,” Dr. Angelos, who also serves as the associate director of the MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics, said in an interview.
He suggested a scenario in which a younger person could have multiple comorbidities that could put that individual at a higher risk of death because of complications from COVID-19 (or another pandemic in the future), compared with an older patient who is otherwise a healthy individual with a lower risk of death.
“For that reason, I agree with the authors that there should not be an arbitrary cutoff of age for which we don’t treat people or we limit treatment.”
Rather, the authors state that the primary allocation method in emergency circumstances that require rationing because of lack of resources should “equally weigh in-hospital survival and severe comorbidities contributing to short-term (<6 months) mortality.”
When assessing comorbidities, “the disparate impact of social determinants of health including culture, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and other factors should be considered.”
AGS’s position statement adds that criteria such as “life-years saved” and “long-term predicted life expectancy” should not be used as they tend to disadvantage older adults.
The organization noted that institutions “should develop resource allocation strategies that are transparent, applied uniformly, and developed with forethought and input from multiple disciplines including ethics, medicine, law, and nursing. These strategies should be used consistently when making emergency decisions.” The AGS called for institutions to frequently review these strategies to ensure they are updated with the most recent evidence and to identify any issues of bias that may emerge.
Dr. Angelos stressed that these guidelines should be developed in a transparent and open fashion. He also highlighted the AGS recommendation of the use of triage officers or triage committees to make the determination about resource allocation should those decisions need to be made.
“We don’t want caregivers who are at the bedside taking care of patients to have the responsibility to say ‘We are going to treat one person as opposed to another person,’ ” he said. “You want to have those decisions made by a team that is separate from the bedside caregivers.”
He agreed with the statement authors that the goal of the triage committee decisions should be to maximize lives saved as opposed to life-years saved. Dr. Angelos noted that his institution’s plan focuses on lives saved should the need for resource rationing come to pass.
In addition to institutional strategies, AGS also emphasized in the position statement that older adults should develop individual care plans that include lists of medical conditions, medications, health care providers, and advance directives. The statement also noted that about only 50% of adults over age 60 years have complete advance directives, a rate Dr. Farrell and colleagues state is “unacceptably low.”
“Advance care planning should not be limited to the purview of only the primary care, geriatrics, or palliative care health professional, and urgent efforts should be made to discuss patient preferences before an emergent need arises,” the paper states, noting that specialists need to be a part of the conversation.
However, the position statement is clear that, while AGS is encouraging providers to talk about advance care planning with their patients, “providers should not pressure, even subtly, patients to engage in advance care planning or change to Do Not Resuscitate/Do Not Intubate (DNR/DNI) status with the intent to conserve health resources.”
Dr. Angelos reiterated this point and suggested that advance directive conversations need to be happening and happening more often.
“This current pandemic has forced us all to realize that, even in well-resourced societies like the United States, we may be faced with situations of absolute scarcity, so we ought to have these conversations up front so that we are not put in a position where we have to make decisions, and those decisions may not be well thought out and may not be ethically justifiable,” he said.
SOURCE: Farrell TW et al. J Am Geriat Soc. 2020 May 6; doi: 10.1111/jgs.16537.
The American Geriatrics Society has issued policy recommendations aimed at protecting seniors from ageism when it comes to resource allocation in the current context of treating patients infected with COVID-19.
“The AGS is deeply concerned about Timothy W. Farrell, MD, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues wrote in an AGS position statement published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
“In particular, rationing strategies that are solely, or predominantly, based on age cutoffs could lead to persistent beliefs that older adults’ lives are less valuable than others or are even expendable, and contribute to already rampant ageism,” the authors continued. “Unless the injustice in these strategies is corrected, this will be a persistent issue if there is a resurgence of COVID-19 cases, a pandemic caused by a different virus in the future, or a different type of disaster where resources are scarce.”
To counter a potential bias against the elderly population should scarce resources force rationing decisions, AGS has made recommendations and strategies that health care systems should incorporate into a policy framework.
One principle in the AGS statement is clear: “Age per se should never be used as a means for a categorical exclusion from therapeutic interventions that represent the standard of care. ... Likewise, specific age-based cutoffs should not be used in resource allocation strategies.”
Peter Angelos, MD, chief of endocrine surgery at the University of Chicago, applauded the position statement.
“It is a well-written statement and I do think that it appropriately suggests that age in and of itself is not a good predictor of who is at greatest risk if infected with coronavirus,” Dr. Angelos, who also serves as the associate director of the MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics, said in an interview.
He suggested a scenario in which a younger person could have multiple comorbidities that could put that individual at a higher risk of death because of complications from COVID-19 (or another pandemic in the future), compared with an older patient who is otherwise a healthy individual with a lower risk of death.
“For that reason, I agree with the authors that there should not be an arbitrary cutoff of age for which we don’t treat people or we limit treatment.”
Rather, the authors state that the primary allocation method in emergency circumstances that require rationing because of lack of resources should “equally weigh in-hospital survival and severe comorbidities contributing to short-term (<6 months) mortality.”
When assessing comorbidities, “the disparate impact of social determinants of health including culture, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and other factors should be considered.”
AGS’s position statement adds that criteria such as “life-years saved” and “long-term predicted life expectancy” should not be used as they tend to disadvantage older adults.
The organization noted that institutions “should develop resource allocation strategies that are transparent, applied uniformly, and developed with forethought and input from multiple disciplines including ethics, medicine, law, and nursing. These strategies should be used consistently when making emergency decisions.” The AGS called for institutions to frequently review these strategies to ensure they are updated with the most recent evidence and to identify any issues of bias that may emerge.
Dr. Angelos stressed that these guidelines should be developed in a transparent and open fashion. He also highlighted the AGS recommendation of the use of triage officers or triage committees to make the determination about resource allocation should those decisions need to be made.
“We don’t want caregivers who are at the bedside taking care of patients to have the responsibility to say ‘We are going to treat one person as opposed to another person,’ ” he said. “You want to have those decisions made by a team that is separate from the bedside caregivers.”
He agreed with the statement authors that the goal of the triage committee decisions should be to maximize lives saved as opposed to life-years saved. Dr. Angelos noted that his institution’s plan focuses on lives saved should the need for resource rationing come to pass.
In addition to institutional strategies, AGS also emphasized in the position statement that older adults should develop individual care plans that include lists of medical conditions, medications, health care providers, and advance directives. The statement also noted that about only 50% of adults over age 60 years have complete advance directives, a rate Dr. Farrell and colleagues state is “unacceptably low.”
“Advance care planning should not be limited to the purview of only the primary care, geriatrics, or palliative care health professional, and urgent efforts should be made to discuss patient preferences before an emergent need arises,” the paper states, noting that specialists need to be a part of the conversation.
However, the position statement is clear that, while AGS is encouraging providers to talk about advance care planning with their patients, “providers should not pressure, even subtly, patients to engage in advance care planning or change to Do Not Resuscitate/Do Not Intubate (DNR/DNI) status with the intent to conserve health resources.”
Dr. Angelos reiterated this point and suggested that advance directive conversations need to be happening and happening more often.
“This current pandemic has forced us all to realize that, even in well-resourced societies like the United States, we may be faced with situations of absolute scarcity, so we ought to have these conversations up front so that we are not put in a position where we have to make decisions, and those decisions may not be well thought out and may not be ethically justifiable,” he said.
SOURCE: Farrell TW et al. J Am Geriat Soc. 2020 May 6; doi: 10.1111/jgs.16537.
The American Geriatrics Society has issued policy recommendations aimed at protecting seniors from ageism when it comes to resource allocation in the current context of treating patients infected with COVID-19.
“The AGS is deeply concerned about Timothy W. Farrell, MD, University of Utah, Salt Lake City, and colleagues wrote in an AGS position statement published online in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
“In particular, rationing strategies that are solely, or predominantly, based on age cutoffs could lead to persistent beliefs that older adults’ lives are less valuable than others or are even expendable, and contribute to already rampant ageism,” the authors continued. “Unless the injustice in these strategies is corrected, this will be a persistent issue if there is a resurgence of COVID-19 cases, a pandemic caused by a different virus in the future, or a different type of disaster where resources are scarce.”
To counter a potential bias against the elderly population should scarce resources force rationing decisions, AGS has made recommendations and strategies that health care systems should incorporate into a policy framework.
One principle in the AGS statement is clear: “Age per se should never be used as a means for a categorical exclusion from therapeutic interventions that represent the standard of care. ... Likewise, specific age-based cutoffs should not be used in resource allocation strategies.”
Peter Angelos, MD, chief of endocrine surgery at the University of Chicago, applauded the position statement.
“It is a well-written statement and I do think that it appropriately suggests that age in and of itself is not a good predictor of who is at greatest risk if infected with coronavirus,” Dr. Angelos, who also serves as the associate director of the MacLean Center for Clinical Medical Ethics, said in an interview.
He suggested a scenario in which a younger person could have multiple comorbidities that could put that individual at a higher risk of death because of complications from COVID-19 (or another pandemic in the future), compared with an older patient who is otherwise a healthy individual with a lower risk of death.
“For that reason, I agree with the authors that there should not be an arbitrary cutoff of age for which we don’t treat people or we limit treatment.”
Rather, the authors state that the primary allocation method in emergency circumstances that require rationing because of lack of resources should “equally weigh in-hospital survival and severe comorbidities contributing to short-term (<6 months) mortality.”
When assessing comorbidities, “the disparate impact of social determinants of health including culture, ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and other factors should be considered.”
AGS’s position statement adds that criteria such as “life-years saved” and “long-term predicted life expectancy” should not be used as they tend to disadvantage older adults.
The organization noted that institutions “should develop resource allocation strategies that are transparent, applied uniformly, and developed with forethought and input from multiple disciplines including ethics, medicine, law, and nursing. These strategies should be used consistently when making emergency decisions.” The AGS called for institutions to frequently review these strategies to ensure they are updated with the most recent evidence and to identify any issues of bias that may emerge.
Dr. Angelos stressed that these guidelines should be developed in a transparent and open fashion. He also highlighted the AGS recommendation of the use of triage officers or triage committees to make the determination about resource allocation should those decisions need to be made.
“We don’t want caregivers who are at the bedside taking care of patients to have the responsibility to say ‘We are going to treat one person as opposed to another person,’ ” he said. “You want to have those decisions made by a team that is separate from the bedside caregivers.”
He agreed with the statement authors that the goal of the triage committee decisions should be to maximize lives saved as opposed to life-years saved. Dr. Angelos noted that his institution’s plan focuses on lives saved should the need for resource rationing come to pass.
In addition to institutional strategies, AGS also emphasized in the position statement that older adults should develop individual care plans that include lists of medical conditions, medications, health care providers, and advance directives. The statement also noted that about only 50% of adults over age 60 years have complete advance directives, a rate Dr. Farrell and colleagues state is “unacceptably low.”
“Advance care planning should not be limited to the purview of only the primary care, geriatrics, or palliative care health professional, and urgent efforts should be made to discuss patient preferences before an emergent need arises,” the paper states, noting that specialists need to be a part of the conversation.
However, the position statement is clear that, while AGS is encouraging providers to talk about advance care planning with their patients, “providers should not pressure, even subtly, patients to engage in advance care planning or change to Do Not Resuscitate/Do Not Intubate (DNR/DNI) status with the intent to conserve health resources.”
Dr. Angelos reiterated this point and suggested that advance directive conversations need to be happening and happening more often.
“This current pandemic has forced us all to realize that, even in well-resourced societies like the United States, we may be faced with situations of absolute scarcity, so we ought to have these conversations up front so that we are not put in a position where we have to make decisions, and those decisions may not be well thought out and may not be ethically justifiable,” he said.
SOURCE: Farrell TW et al. J Am Geriat Soc. 2020 May 6; doi: 10.1111/jgs.16537.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN GERIATRIC SOCIETY
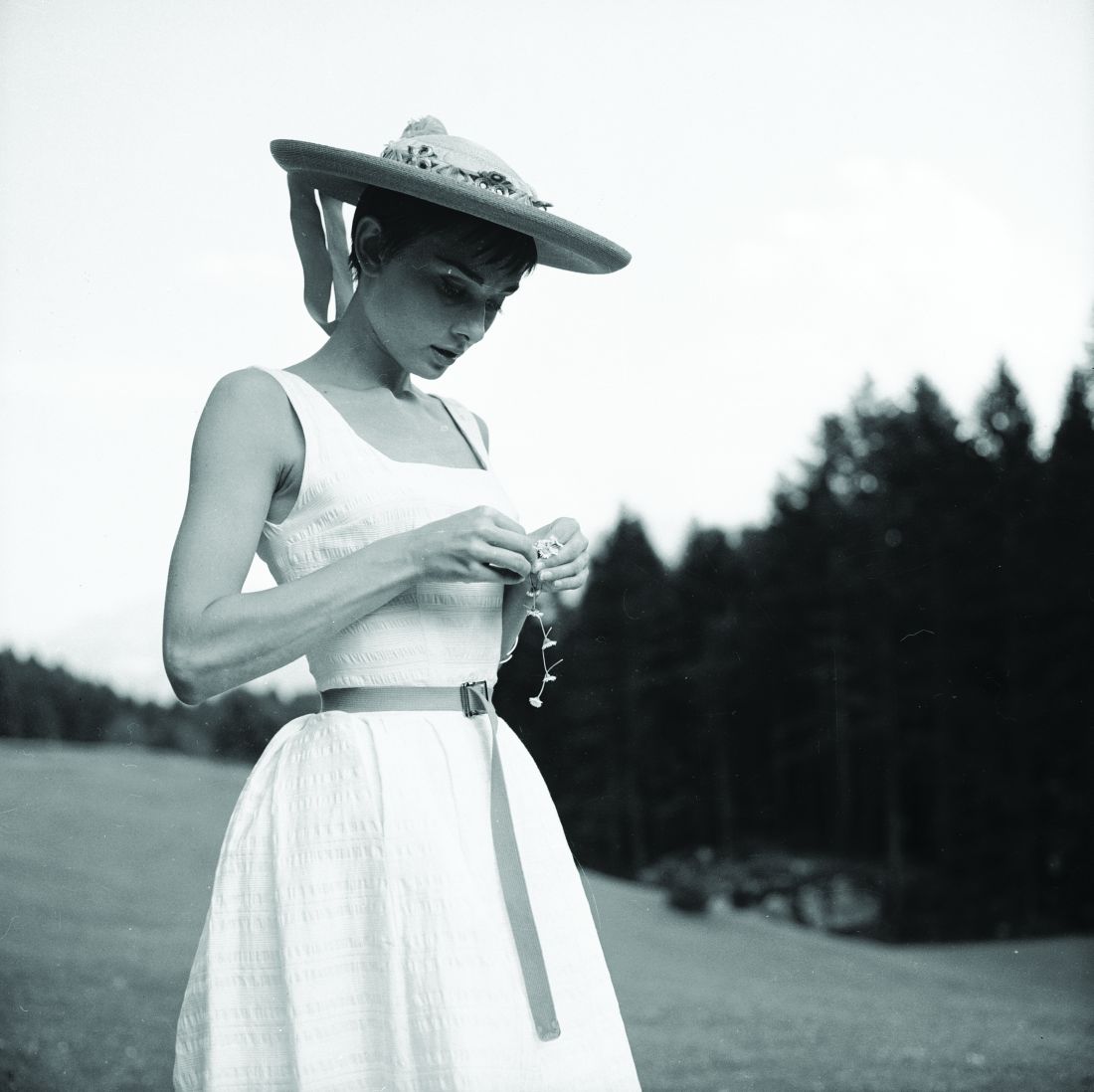
Audrey Hepburn’s lessons for a COVID clinic
Queues of patients wait to clear security and enter the sterile area at every medical office. Water bottles are allowed, fevers and visitors are not. Those who fail clearance or who are afraid to be seen in person must be treated virtually. In this context, virtually means by telephone or video, yet, aptly, it also means “nearly or almost,” as in we can nearly or almost treat them these ways. We’ve emerged safely, but we’ve lost sensibility. Because of this, what’s important in the doctor-patient relationships will drift a bit. Clinical acumen and technical skill won’t be enough. Successful practices will also have grace.
If your image of grace is Audrey Hepburn gliding along Fifth Avenue in a long black dress and elbow-length gloves, you’re in the right place. Ms. Hepburn embodied elegance and decorum and there are lessons to be drawn from her. Piling your hair high and donning oversized sunglasses along with your face mask would be to miss the point here though. Ms. Hepburn dressed exquisitely, yes, but her grace came from what wearing a difficult-to-walk-in dress meant to us, not to her. Appearance, self-control, and warmth are what made her charismatic.
To appear urbane requires effort; it’s the effort that we appreciate in someone who is graceful. When you’re thoughtful about how you look, you plan ahead, you work to look polished. In effect, you’re saying: “As my patient, you’re important enough for me to be well dressed.” It is a visible signal of all the unobservable work you’ve done to care for them. This is more critical now that our faces are covered and concern for infection means wearing shabby hospital scrubs rather than shirt and tie.
Effort is also required for telephone and video visits. In them, our doctor-patient connection is diminished – no matter how high definition, it’s a virtual affair. Ms. Hepburn would no doubt take the time to ensure she appeared professional, well lit, with a pleasing background. She’d plan for the call to be done in a quiet location and without distraction.
Whether in person or by phone, grace, as Ms. Hepburn demonstrated, is physical awareness and body control. She would often be completely still when someone is speaking, showing a countenance of warmth. She’d pause after the other person completed a thought and before replying. In doing so, she conveyed that she was present and engaged in what was being said. It is that confidence and ease of manner we perceived as grace.
I thought about this the other day during a mixed clinic of telephone and face-to-face visits. I had on my wrinkle-free scrubs (I could do better). I was listening to a patient describe all possible triggers for her hand dermatitis. My urge to interrupt grew with each paragraph of her storytelling. “Be patient,” I thought, “be at ease with her rambling. ... When she stops, thank her as if you were looking her in the eye acknowledging how interesting her observations were.” This is not just good manners, it’s the essence of grace: The art of showing how important others are to you.
Our world needs grace more than ever and what better place to start but with us. In pleasing, assisting, and honoring them, our patients can be reassured that we can and will care for them. Make Ms. Hepburn proud.
“For beautiful eyes, look for the good in others; for beautiful lips, speak only words of kindness; and for poise, walk with the knowledge that you are never alone.” – Audrey Hepburn
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. He has no disclosures related to this column. Write to him at [email protected] .
Queues of patients wait to clear security and enter the sterile area at every medical office. Water bottles are allowed, fevers and visitors are not. Those who fail clearance or who are afraid to be seen in person must be treated virtually. In this context, virtually means by telephone or video, yet, aptly, it also means “nearly or almost,” as in we can nearly or almost treat them these ways. We’ve emerged safely, but we’ve lost sensibility. Because of this, what’s important in the doctor-patient relationships will drift a bit. Clinical acumen and technical skill won’t be enough. Successful practices will also have grace.
If your image of grace is Audrey Hepburn gliding along Fifth Avenue in a long black dress and elbow-length gloves, you’re in the right place. Ms. Hepburn embodied elegance and decorum and there are lessons to be drawn from her. Piling your hair high and donning oversized sunglasses along with your face mask would be to miss the point here though. Ms. Hepburn dressed exquisitely, yes, but her grace came from what wearing a difficult-to-walk-in dress meant to us, not to her. Appearance, self-control, and warmth are what made her charismatic.
To appear urbane requires effort; it’s the effort that we appreciate in someone who is graceful. When you’re thoughtful about how you look, you plan ahead, you work to look polished. In effect, you’re saying: “As my patient, you’re important enough for me to be well dressed.” It is a visible signal of all the unobservable work you’ve done to care for them. This is more critical now that our faces are covered and concern for infection means wearing shabby hospital scrubs rather than shirt and tie.
Effort is also required for telephone and video visits. In them, our doctor-patient connection is diminished – no matter how high definition, it’s a virtual affair. Ms. Hepburn would no doubt take the time to ensure she appeared professional, well lit, with a pleasing background. She’d plan for the call to be done in a quiet location and without distraction.
Whether in person or by phone, grace, as Ms. Hepburn demonstrated, is physical awareness and body control. She would often be completely still when someone is speaking, showing a countenance of warmth. She’d pause after the other person completed a thought and before replying. In doing so, she conveyed that she was present and engaged in what was being said. It is that confidence and ease of manner we perceived as grace.
I thought about this the other day during a mixed clinic of telephone and face-to-face visits. I had on my wrinkle-free scrubs (I could do better). I was listening to a patient describe all possible triggers for her hand dermatitis. My urge to interrupt grew with each paragraph of her storytelling. “Be patient,” I thought, “be at ease with her rambling. ... When she stops, thank her as if you were looking her in the eye acknowledging how interesting her observations were.” This is not just good manners, it’s the essence of grace: The art of showing how important others are to you.
Our world needs grace more than ever and what better place to start but with us. In pleasing, assisting, and honoring them, our patients can be reassured that we can and will care for them. Make Ms. Hepburn proud.
“For beautiful eyes, look for the good in others; for beautiful lips, speak only words of kindness; and for poise, walk with the knowledge that you are never alone.” – Audrey Hepburn
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. He has no disclosures related to this column. Write to him at [email protected] .
Queues of patients wait to clear security and enter the sterile area at every medical office. Water bottles are allowed, fevers and visitors are not. Those who fail clearance or who are afraid to be seen in person must be treated virtually. In this context, virtually means by telephone or video, yet, aptly, it also means “nearly or almost,” as in we can nearly or almost treat them these ways. We’ve emerged safely, but we’ve lost sensibility. Because of this, what’s important in the doctor-patient relationships will drift a bit. Clinical acumen and technical skill won’t be enough. Successful practices will also have grace.
If your image of grace is Audrey Hepburn gliding along Fifth Avenue in a long black dress and elbow-length gloves, you’re in the right place. Ms. Hepburn embodied elegance and decorum and there are lessons to be drawn from her. Piling your hair high and donning oversized sunglasses along with your face mask would be to miss the point here though. Ms. Hepburn dressed exquisitely, yes, but her grace came from what wearing a difficult-to-walk-in dress meant to us, not to her. Appearance, self-control, and warmth are what made her charismatic.
To appear urbane requires effort; it’s the effort that we appreciate in someone who is graceful. When you’re thoughtful about how you look, you plan ahead, you work to look polished. In effect, you’re saying: “As my patient, you’re important enough for me to be well dressed.” It is a visible signal of all the unobservable work you’ve done to care for them. This is more critical now that our faces are covered and concern for infection means wearing shabby hospital scrubs rather than shirt and tie.
Effort is also required for telephone and video visits. In them, our doctor-patient connection is diminished – no matter how high definition, it’s a virtual affair. Ms. Hepburn would no doubt take the time to ensure she appeared professional, well lit, with a pleasing background. She’d plan for the call to be done in a quiet location and without distraction.
Whether in person or by phone, grace, as Ms. Hepburn demonstrated, is physical awareness and body control. She would often be completely still when someone is speaking, showing a countenance of warmth. She’d pause after the other person completed a thought and before replying. In doing so, she conveyed that she was present and engaged in what was being said. It is that confidence and ease of manner we perceived as grace.
I thought about this the other day during a mixed clinic of telephone and face-to-face visits. I had on my wrinkle-free scrubs (I could do better). I was listening to a patient describe all possible triggers for her hand dermatitis. My urge to interrupt grew with each paragraph of her storytelling. “Be patient,” I thought, “be at ease with her rambling. ... When she stops, thank her as if you were looking her in the eye acknowledging how interesting her observations were.” This is not just good manners, it’s the essence of grace: The art of showing how important others are to you.
Our world needs grace more than ever and what better place to start but with us. In pleasing, assisting, and honoring them, our patients can be reassured that we can and will care for them. Make Ms. Hepburn proud.
“For beautiful eyes, look for the good in others; for beautiful lips, speak only words of kindness; and for poise, walk with the knowledge that you are never alone.” – Audrey Hepburn
Dr. Benabio is director of Healthcare Transformation and chief of dermatology at Kaiser Permanente San Diego. The opinions expressed in this column are his own and do not represent those of Kaiser Permanente. Dr. Benabio is @Dermdoc on Twitter. He has no disclosures related to this column. Write to him at [email protected] .
Vitamin D: A low-hanging fruit in COVID-19?
Mainstream media outlets have been flooded recently with reports speculating on what role, if any, vitamin D may play in reducing the severity of COVID-19 infection.
as well as mortality, with the further suggestion of an effect of vitamin D on the immune response to infection.
But other studies question such a link, including any association between vitamin D concentration and differences in COVID-19 severity by ethnic group.
And while some researchers and clinicians believe people should get tested to see if they have adequate vitamin D levels during this pandemic – in particular frontline health care workers – most doctors say the best way to ensure that people have adequate levels of vitamin D during COVID-19 is to simply take supplements at currently recommended levels.
This is especially important given the fact that, during “lockdown” scenarios, many people are spending more time than usual indoors.
Clifford Rosen, MD, senior scientist at Maine Medical Center’s Research Institute in Scarborough, has been researching vitamin D for 25 years.
“There’s no randomized, controlled trial for sure, and that’s the gold standard,” he said in an interview, and “the observational data are so confounded, it’s difficult to know.”
Whether from diet or supplementation, having adequate vitamin D is important, especially for those at the highest risk of COVID-19, he said. Still, robust data supporting a role of vitamin D in prevention of COVID-19, or as any kind of “therapy” for the infection, are currently lacking.
Rose Anne Kenny, MD, professor of medical gerontology at Trinity College Dublin, recently coauthored an article detailing an inverse association between vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19 across countries in Europe.
“At no stage are any of us saying this is a given, but there’s a probability that [vitamin D] – a low-hanging fruit – is a contributory factor and we can do something about it now,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Kenny is calling for the Irish government to formally change their recommendations. “We call on the Irish government to update guidelines as a matter of urgency and encourage all adults to take [vitamin D] supplements during the COVID-19 crisis.” Northern Ireland, part of the United Kingdom, also has not yet made this recommendation, she said.
Meanwhile, Harpreet S. Bajaj, MD, MPH, a practicing endocrinologist from Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, said: “Vitamin D could have any of three potential roles in risk for COVID-19 and/or its severity: no role, simply a marker, or a causal factor.”
Dr. Bajaj said – as did Dr. Rosen and Dr. Kenny – that randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) are sorely needed to help ascertain whether there is a specific role of vitamin D.
“Until then, we should continue to follow established public health recommendations for vitamin D supplementation, in addition to following COVID-19 prevention guidance and evolving guidelines for COVID-19 treatment.”
What is the role of vitamin D fortification?
In their study in the Irish Medical Journal, Dr. Kenny and colleagues noted that, in Europe, despite being sunny, Spain and Northern Italy had high rates of vitamin D deficiency and have experienced some of the highest COVID-19 infection and mortality rates in the world.
But these countries do not formally fortify foods or recommend supplementation with vitamin D.
Conversely, the northern countries of Norway, Finland, and Sweden had higher vitamin D levels despite less UVB sunlight exposure, as a result of common supplementation and formal fortification of foods. These Nordic countries also had lower levels of COVID-19 infection and mortality.
Overall, the correlation between low vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19 was statistically significant (P = .046), the investigators reported.
“Optimizing vitamin D status to recommendations by national and international public health agencies will certainly have ... potential benefits for COVID-19,” they concluded.
“We’re not saying there aren’t any confounders. This can absolutely be the case, but this [finding] needs to be in the mix of evidence,” Dr. Kenny said.
Dr. Kenny also noted that countries in the Southern Hemisphere have been seeing a relatively low mortality from COVID-19, although she acknowledged the explanation could be that the virus spread later to those countries.
Dr. Rosen has doubts on this issue, too.
“Sure, vitamin D supplementation may have worked for [Nordic countries], their COVID-19 has been better controlled, but there’s no causality here; there’s another step to actually prove this. Other factors might be at play,” he said.
“Look at Brazil, it’s at the equator but the disease is devastating the country. Right now, I just don’t believe it.”
Does vitamin D have a role to play in immune modulation?
One theory currently circulating is that, if vitamin D does have any role to play in modulating response to COVID-19, this may be via a blunting of the immune system reaction to the virus.
In a recent preprint study, Ali Daneshkhah, PhD, and colleagues from Northwestern University, Chicago, interrogated hospital data from China, France, Germany, Italy, Iran, South Korea, Spain, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Specifically, the risk of severe COVID-19 cases among patients with severe vitamin D deficiency was 17.3%, whereas the equivalent figure for patients with normal vitamin D levels was 14.6% (a reduction of 15.6%).
“This potential effect may be attributed to vitamin D’s ability to suppress the adaptive immune system, regulating cytokine levels and thereby reducing the risk of developing severe COVID-19,” said the researchers.
Likewise, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, in a recent commentary, noted evidence from an observational study from three South Asian hospitals, in which the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was much higher among those with severe COVID-19 illness compared with those with mild illness.
“We also know that vitamin D has an immune-modulating effect and can lower inflammation, and this may be relevant to the respiratory response during COVID-19 and the cytokine storm that’s been demonstrated,” she noted.
Dr. Rosen said he is willing to listen on the issue of a potential role of vitamin D in immune modulation.
“I’ve been a huge skeptic from the get-go, and loudly criticized the data for doing nothing. I am surprised at myself for saying there might be some effect,” he said.
“Clearly most people don’t get this [cytokine storm] but of those that do, it’s unclear why they do. Maybe if you are vitamin D sufficient, it might have some impact down the road on your response to an infection,” Dr. Rosen said. “Vitamin D may induce proteins important in modulating the function of macrophages of the immune system.”
Ethnic minorities disproportionately affected
It is also well recognized that COVID-19 disproportionately affects black and Asian minority ethnic individuals.
But on the issue of vitamin D in this context, one recent peer-reviewed study using UK Biobank data found no evidence to support a potential role for vitamin D concentration to explain susceptibility to COVID-19 infection either overall or in explaining differences between ethnic groups.
“Vitamin D is unlikely to be the underlying mechanism for the higher risk observed in black and minority ethnic individuals, and vitamin D supplements are unlikely to provide an effective intervention,” Claire Hastie, PhD, of the University of Glasgow and colleagues concluded.
But this hasn’t stopped two endocrinologists from appealing to members of the British Association of Physicians of Indian Origin (BAPIO) to get their vitamin D levels tested.
The black and Asian minority ethnic population, “especially frontline staff, should get their Vitamin D3 levels checked and get appropriate replacement as required,” said Parag Singhal, MD, of Weston General Hospital, Weston-Super-Mare, England, and David C. Anderson, a retired endocrinologist, said in a letter to BAPIO members.
Indeed, they suggested a booster dose of 100,000 IU as a one-off for black and Asian minority ethnic health care staff that should raise vitamin D levels for 2-3 months. They referred to a systematic review that concludes that “single vitamin D3 doses ≥300,000 IU are most effective at improving vitamin D status ... for up to 3 months”.
Commenting on the idea, Dr. Rosen remarked that, in general, the high-dose 50,000-500,000 IU given as a one-off does not confer any greater benefit than a single dose of 1,000 IU per day, except that the blood levels go up quicker and higher.
“Really there is no evidence that getting to super-high levels of vitamin D confer a greater benefit than normal levels,” he said. “So if health care workers suspect vitamin D deficiency, daily doses of 1,000 IU seem reasonable; even if they miss doses, the blood levels are relatively stable.”
On the specific question of vitamin D needs in ethnic minorities, Dr. Rosen said while such individuals do have lower serum levels of vitamin D, the issue is whether there are meaningful clinical implications related to this.
“The real question is whether [ethnic minority individuals] have physiologically adapted for this in other ways because these low levels have been so for thousands of years. In fact, African Americans have lower vitamin D levels but they absolutely have better bones than [whites],” he pointed out.
Testing and governmental recommendations during COVID-19
The U.S. National Institutes of Health in general advises 400 IU to 800 IU per day intake of vitamin D, depending on age, with those over 70 years requiring the highest daily dose. This will result in blood levels that are sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. There are no additional recommendations specific to vitamin D intake during the COVID-19 pandemic, however.
And Dr. Rosen pointed out that there is no evidence for mass screening of vitamin D levels among the U.S. population.
“U.S. public health guidance was pre-COVID, and I think high-risk individuals might want to think about their levels; for example, someone with inflammatory bowel disease or liver or pancreatic disease. These people are at higher risk anyway, and it could be because their vitamin D is low,” he said.
“Skip the test and ensure you are getting adequate levels of vitamin D whether via diet or supplement [400-800 IU per day],” he suggested. “It won’t harm.”
The U.K.’s Public Health England (PHE) clarified its advice on vitamin D supplementation during COVID-19. Alison Tedstone, PhD, chief nutritionist at PHE, said: “Many people are spending more time indoors and may not get all the vitamin D they need from sunlight. To protect their bone and muscle health, they should consider taking a daily supplement containing 10 micrograms [400 IU] of vitamin D.”
However, “there is no sufficient evidence to support recommending Vitamin D for reducing the risk of COVID-19,” she stressed.
Dr. Bajaj is on the advisory board of Medscape Diabetes & Endocrinology. He has ties with Amgen, AstraZeneca Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Eli Lilly,Valeant, Canadian Collaborative Research Network, CMS Knowledge Translation, Diabetes Canada Scientific Group, LMC Healthcare,mdBriefCase,Medscape, andMeducom. Dr. Kenny, Dr. Rosen, and Dr. Singhal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mainstream media outlets have been flooded recently with reports speculating on what role, if any, vitamin D may play in reducing the severity of COVID-19 infection.
as well as mortality, with the further suggestion of an effect of vitamin D on the immune response to infection.
But other studies question such a link, including any association between vitamin D concentration and differences in COVID-19 severity by ethnic group.
And while some researchers and clinicians believe people should get tested to see if they have adequate vitamin D levels during this pandemic – in particular frontline health care workers – most doctors say the best way to ensure that people have adequate levels of vitamin D during COVID-19 is to simply take supplements at currently recommended levels.
This is especially important given the fact that, during “lockdown” scenarios, many people are spending more time than usual indoors.
Clifford Rosen, MD, senior scientist at Maine Medical Center’s Research Institute in Scarborough, has been researching vitamin D for 25 years.
“There’s no randomized, controlled trial for sure, and that’s the gold standard,” he said in an interview, and “the observational data are so confounded, it’s difficult to know.”
Whether from diet or supplementation, having adequate vitamin D is important, especially for those at the highest risk of COVID-19, he said. Still, robust data supporting a role of vitamin D in prevention of COVID-19, or as any kind of “therapy” for the infection, are currently lacking.
Rose Anne Kenny, MD, professor of medical gerontology at Trinity College Dublin, recently coauthored an article detailing an inverse association between vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19 across countries in Europe.
“At no stage are any of us saying this is a given, but there’s a probability that [vitamin D] – a low-hanging fruit – is a contributory factor and we can do something about it now,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Kenny is calling for the Irish government to formally change their recommendations. “We call on the Irish government to update guidelines as a matter of urgency and encourage all adults to take [vitamin D] supplements during the COVID-19 crisis.” Northern Ireland, part of the United Kingdom, also has not yet made this recommendation, she said.
Meanwhile, Harpreet S. Bajaj, MD, MPH, a practicing endocrinologist from Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, said: “Vitamin D could have any of three potential roles in risk for COVID-19 and/or its severity: no role, simply a marker, or a causal factor.”
Dr. Bajaj said – as did Dr. Rosen and Dr. Kenny – that randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) are sorely needed to help ascertain whether there is a specific role of vitamin D.
“Until then, we should continue to follow established public health recommendations for vitamin D supplementation, in addition to following COVID-19 prevention guidance and evolving guidelines for COVID-19 treatment.”
What is the role of vitamin D fortification?
In their study in the Irish Medical Journal, Dr. Kenny and colleagues noted that, in Europe, despite being sunny, Spain and Northern Italy had high rates of vitamin D deficiency and have experienced some of the highest COVID-19 infection and mortality rates in the world.
But these countries do not formally fortify foods or recommend supplementation with vitamin D.
Conversely, the northern countries of Norway, Finland, and Sweden had higher vitamin D levels despite less UVB sunlight exposure, as a result of common supplementation and formal fortification of foods. These Nordic countries also had lower levels of COVID-19 infection and mortality.
Overall, the correlation between low vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19 was statistically significant (P = .046), the investigators reported.
“Optimizing vitamin D status to recommendations by national and international public health agencies will certainly have ... potential benefits for COVID-19,” they concluded.
“We’re not saying there aren’t any confounders. This can absolutely be the case, but this [finding] needs to be in the mix of evidence,” Dr. Kenny said.
Dr. Kenny also noted that countries in the Southern Hemisphere have been seeing a relatively low mortality from COVID-19, although she acknowledged the explanation could be that the virus spread later to those countries.
Dr. Rosen has doubts on this issue, too.
“Sure, vitamin D supplementation may have worked for [Nordic countries], their COVID-19 has been better controlled, but there’s no causality here; there’s another step to actually prove this. Other factors might be at play,” he said.
“Look at Brazil, it’s at the equator but the disease is devastating the country. Right now, I just don’t believe it.”
Does vitamin D have a role to play in immune modulation?
One theory currently circulating is that, if vitamin D does have any role to play in modulating response to COVID-19, this may be via a blunting of the immune system reaction to the virus.
In a recent preprint study, Ali Daneshkhah, PhD, and colleagues from Northwestern University, Chicago, interrogated hospital data from China, France, Germany, Italy, Iran, South Korea, Spain, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Specifically, the risk of severe COVID-19 cases among patients with severe vitamin D deficiency was 17.3%, whereas the equivalent figure for patients with normal vitamin D levels was 14.6% (a reduction of 15.6%).
“This potential effect may be attributed to vitamin D’s ability to suppress the adaptive immune system, regulating cytokine levels and thereby reducing the risk of developing severe COVID-19,” said the researchers.
Likewise, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, in a recent commentary, noted evidence from an observational study from three South Asian hospitals, in which the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was much higher among those with severe COVID-19 illness compared with those with mild illness.
“We also know that vitamin D has an immune-modulating effect and can lower inflammation, and this may be relevant to the respiratory response during COVID-19 and the cytokine storm that’s been demonstrated,” she noted.
Dr. Rosen said he is willing to listen on the issue of a potential role of vitamin D in immune modulation.
“I’ve been a huge skeptic from the get-go, and loudly criticized the data for doing nothing. I am surprised at myself for saying there might be some effect,” he said.
“Clearly most people don’t get this [cytokine storm] but of those that do, it’s unclear why they do. Maybe if you are vitamin D sufficient, it might have some impact down the road on your response to an infection,” Dr. Rosen said. “Vitamin D may induce proteins important in modulating the function of macrophages of the immune system.”
Ethnic minorities disproportionately affected
It is also well recognized that COVID-19 disproportionately affects black and Asian minority ethnic individuals.
But on the issue of vitamin D in this context, one recent peer-reviewed study using UK Biobank data found no evidence to support a potential role for vitamin D concentration to explain susceptibility to COVID-19 infection either overall or in explaining differences between ethnic groups.
“Vitamin D is unlikely to be the underlying mechanism for the higher risk observed in black and minority ethnic individuals, and vitamin D supplements are unlikely to provide an effective intervention,” Claire Hastie, PhD, of the University of Glasgow and colleagues concluded.
But this hasn’t stopped two endocrinologists from appealing to members of the British Association of Physicians of Indian Origin (BAPIO) to get their vitamin D levels tested.
The black and Asian minority ethnic population, “especially frontline staff, should get their Vitamin D3 levels checked and get appropriate replacement as required,” said Parag Singhal, MD, of Weston General Hospital, Weston-Super-Mare, England, and David C. Anderson, a retired endocrinologist, said in a letter to BAPIO members.
Indeed, they suggested a booster dose of 100,000 IU as a one-off for black and Asian minority ethnic health care staff that should raise vitamin D levels for 2-3 months. They referred to a systematic review that concludes that “single vitamin D3 doses ≥300,000 IU are most effective at improving vitamin D status ... for up to 3 months”.
Commenting on the idea, Dr. Rosen remarked that, in general, the high-dose 50,000-500,000 IU given as a one-off does not confer any greater benefit than a single dose of 1,000 IU per day, except that the blood levels go up quicker and higher.
“Really there is no evidence that getting to super-high levels of vitamin D confer a greater benefit than normal levels,” he said. “So if health care workers suspect vitamin D deficiency, daily doses of 1,000 IU seem reasonable; even if they miss doses, the blood levels are relatively stable.”
On the specific question of vitamin D needs in ethnic minorities, Dr. Rosen said while such individuals do have lower serum levels of vitamin D, the issue is whether there are meaningful clinical implications related to this.
“The real question is whether [ethnic minority individuals] have physiologically adapted for this in other ways because these low levels have been so for thousands of years. In fact, African Americans have lower vitamin D levels but they absolutely have better bones than [whites],” he pointed out.
Testing and governmental recommendations during COVID-19
The U.S. National Institutes of Health in general advises 400 IU to 800 IU per day intake of vitamin D, depending on age, with those over 70 years requiring the highest daily dose. This will result in blood levels that are sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. There are no additional recommendations specific to vitamin D intake during the COVID-19 pandemic, however.
And Dr. Rosen pointed out that there is no evidence for mass screening of vitamin D levels among the U.S. population.
“U.S. public health guidance was pre-COVID, and I think high-risk individuals might want to think about their levels; for example, someone with inflammatory bowel disease or liver or pancreatic disease. These people are at higher risk anyway, and it could be because their vitamin D is low,” he said.
“Skip the test and ensure you are getting adequate levels of vitamin D whether via diet or supplement [400-800 IU per day],” he suggested. “It won’t harm.”
The U.K.’s Public Health England (PHE) clarified its advice on vitamin D supplementation during COVID-19. Alison Tedstone, PhD, chief nutritionist at PHE, said: “Many people are spending more time indoors and may not get all the vitamin D they need from sunlight. To protect their bone and muscle health, they should consider taking a daily supplement containing 10 micrograms [400 IU] of vitamin D.”
However, “there is no sufficient evidence to support recommending Vitamin D for reducing the risk of COVID-19,” she stressed.
Dr. Bajaj is on the advisory board of Medscape Diabetes & Endocrinology. He has ties with Amgen, AstraZeneca Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Eli Lilly,Valeant, Canadian Collaborative Research Network, CMS Knowledge Translation, Diabetes Canada Scientific Group, LMC Healthcare,mdBriefCase,Medscape, andMeducom. Dr. Kenny, Dr. Rosen, and Dr. Singhal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Mainstream media outlets have been flooded recently with reports speculating on what role, if any, vitamin D may play in reducing the severity of COVID-19 infection.
as well as mortality, with the further suggestion of an effect of vitamin D on the immune response to infection.
But other studies question such a link, including any association between vitamin D concentration and differences in COVID-19 severity by ethnic group.
And while some researchers and clinicians believe people should get tested to see if they have adequate vitamin D levels during this pandemic – in particular frontline health care workers – most doctors say the best way to ensure that people have adequate levels of vitamin D during COVID-19 is to simply take supplements at currently recommended levels.
This is especially important given the fact that, during “lockdown” scenarios, many people are spending more time than usual indoors.
Clifford Rosen, MD, senior scientist at Maine Medical Center’s Research Institute in Scarborough, has been researching vitamin D for 25 years.
“There’s no randomized, controlled trial for sure, and that’s the gold standard,” he said in an interview, and “the observational data are so confounded, it’s difficult to know.”
Whether from diet or supplementation, having adequate vitamin D is important, especially for those at the highest risk of COVID-19, he said. Still, robust data supporting a role of vitamin D in prevention of COVID-19, or as any kind of “therapy” for the infection, are currently lacking.
Rose Anne Kenny, MD, professor of medical gerontology at Trinity College Dublin, recently coauthored an article detailing an inverse association between vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19 across countries in Europe.
“At no stage are any of us saying this is a given, but there’s a probability that [vitamin D] – a low-hanging fruit – is a contributory factor and we can do something about it now,” she said in an interview.
Dr. Kenny is calling for the Irish government to formally change their recommendations. “We call on the Irish government to update guidelines as a matter of urgency and encourage all adults to take [vitamin D] supplements during the COVID-19 crisis.” Northern Ireland, part of the United Kingdom, also has not yet made this recommendation, she said.
Meanwhile, Harpreet S. Bajaj, MD, MPH, a practicing endocrinologist from Mount Sinai Hospital, Toronto, said: “Vitamin D could have any of three potential roles in risk for COVID-19 and/or its severity: no role, simply a marker, or a causal factor.”
Dr. Bajaj said – as did Dr. Rosen and Dr. Kenny – that randomized, controlled trials (RCTs) are sorely needed to help ascertain whether there is a specific role of vitamin D.
“Until then, we should continue to follow established public health recommendations for vitamin D supplementation, in addition to following COVID-19 prevention guidance and evolving guidelines for COVID-19 treatment.”
What is the role of vitamin D fortification?
In their study in the Irish Medical Journal, Dr. Kenny and colleagues noted that, in Europe, despite being sunny, Spain and Northern Italy had high rates of vitamin D deficiency and have experienced some of the highest COVID-19 infection and mortality rates in the world.
But these countries do not formally fortify foods or recommend supplementation with vitamin D.
Conversely, the northern countries of Norway, Finland, and Sweden had higher vitamin D levels despite less UVB sunlight exposure, as a result of common supplementation and formal fortification of foods. These Nordic countries also had lower levels of COVID-19 infection and mortality.
Overall, the correlation between low vitamin D levels and mortality from COVID-19 was statistically significant (P = .046), the investigators reported.
“Optimizing vitamin D status to recommendations by national and international public health agencies will certainly have ... potential benefits for COVID-19,” they concluded.
“We’re not saying there aren’t any confounders. This can absolutely be the case, but this [finding] needs to be in the mix of evidence,” Dr. Kenny said.
Dr. Kenny also noted that countries in the Southern Hemisphere have been seeing a relatively low mortality from COVID-19, although she acknowledged the explanation could be that the virus spread later to those countries.
Dr. Rosen has doubts on this issue, too.
“Sure, vitamin D supplementation may have worked for [Nordic countries], their COVID-19 has been better controlled, but there’s no causality here; there’s another step to actually prove this. Other factors might be at play,” he said.
“Look at Brazil, it’s at the equator but the disease is devastating the country. Right now, I just don’t believe it.”
Does vitamin D have a role to play in immune modulation?
One theory currently circulating is that, if vitamin D does have any role to play in modulating response to COVID-19, this may be via a blunting of the immune system reaction to the virus.
In a recent preprint study, Ali Daneshkhah, PhD, and colleagues from Northwestern University, Chicago, interrogated hospital data from China, France, Germany, Italy, Iran, South Korea, Spain, Switzerland, the United Kingdom, and the United States.
Specifically, the risk of severe COVID-19 cases among patients with severe vitamin D deficiency was 17.3%, whereas the equivalent figure for patients with normal vitamin D levels was 14.6% (a reduction of 15.6%).
“This potential effect may be attributed to vitamin D’s ability to suppress the adaptive immune system, regulating cytokine levels and thereby reducing the risk of developing severe COVID-19,” said the researchers.
Likewise, JoAnn E. Manson, MD, chief of the division of preventive medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, in a recent commentary, noted evidence from an observational study from three South Asian hospitals, in which the prevalence of vitamin D deficiency was much higher among those with severe COVID-19 illness compared with those with mild illness.
“We also know that vitamin D has an immune-modulating effect and can lower inflammation, and this may be relevant to the respiratory response during COVID-19 and the cytokine storm that’s been demonstrated,” she noted.
Dr. Rosen said he is willing to listen on the issue of a potential role of vitamin D in immune modulation.
“I’ve been a huge skeptic from the get-go, and loudly criticized the data for doing nothing. I am surprised at myself for saying there might be some effect,” he said.
“Clearly most people don’t get this [cytokine storm] but of those that do, it’s unclear why they do. Maybe if you are vitamin D sufficient, it might have some impact down the road on your response to an infection,” Dr. Rosen said. “Vitamin D may induce proteins important in modulating the function of macrophages of the immune system.”
Ethnic minorities disproportionately affected
It is also well recognized that COVID-19 disproportionately affects black and Asian minority ethnic individuals.
But on the issue of vitamin D in this context, one recent peer-reviewed study using UK Biobank data found no evidence to support a potential role for vitamin D concentration to explain susceptibility to COVID-19 infection either overall or in explaining differences between ethnic groups.
“Vitamin D is unlikely to be the underlying mechanism for the higher risk observed in black and minority ethnic individuals, and vitamin D supplements are unlikely to provide an effective intervention,” Claire Hastie, PhD, of the University of Glasgow and colleagues concluded.
But this hasn’t stopped two endocrinologists from appealing to members of the British Association of Physicians of Indian Origin (BAPIO) to get their vitamin D levels tested.
The black and Asian minority ethnic population, “especially frontline staff, should get their Vitamin D3 levels checked and get appropriate replacement as required,” said Parag Singhal, MD, of Weston General Hospital, Weston-Super-Mare, England, and David C. Anderson, a retired endocrinologist, said in a letter to BAPIO members.
Indeed, they suggested a booster dose of 100,000 IU as a one-off for black and Asian minority ethnic health care staff that should raise vitamin D levels for 2-3 months. They referred to a systematic review that concludes that “single vitamin D3 doses ≥300,000 IU are most effective at improving vitamin D status ... for up to 3 months”.
Commenting on the idea, Dr. Rosen remarked that, in general, the high-dose 50,000-500,000 IU given as a one-off does not confer any greater benefit than a single dose of 1,000 IU per day, except that the blood levels go up quicker and higher.
“Really there is no evidence that getting to super-high levels of vitamin D confer a greater benefit than normal levels,” he said. “So if health care workers suspect vitamin D deficiency, daily doses of 1,000 IU seem reasonable; even if they miss doses, the blood levels are relatively stable.”
On the specific question of vitamin D needs in ethnic minorities, Dr. Rosen said while such individuals do have lower serum levels of vitamin D, the issue is whether there are meaningful clinical implications related to this.
“The real question is whether [ethnic minority individuals] have physiologically adapted for this in other ways because these low levels have been so for thousands of years. In fact, African Americans have lower vitamin D levels but they absolutely have better bones than [whites],” he pointed out.
Testing and governmental recommendations during COVID-19
The U.S. National Institutes of Health in general advises 400 IU to 800 IU per day intake of vitamin D, depending on age, with those over 70 years requiring the highest daily dose. This will result in blood levels that are sufficient to maintain bone health and normal calcium metabolism in healthy people. There are no additional recommendations specific to vitamin D intake during the COVID-19 pandemic, however.
And Dr. Rosen pointed out that there is no evidence for mass screening of vitamin D levels among the U.S. population.
“U.S. public health guidance was pre-COVID, and I think high-risk individuals might want to think about their levels; for example, someone with inflammatory bowel disease or liver or pancreatic disease. These people are at higher risk anyway, and it could be because their vitamin D is low,” he said.
“Skip the test and ensure you are getting adequate levels of vitamin D whether via diet or supplement [400-800 IU per day],” he suggested. “It won’t harm.”
The U.K.’s Public Health England (PHE) clarified its advice on vitamin D supplementation during COVID-19. Alison Tedstone, PhD, chief nutritionist at PHE, said: “Many people are spending more time indoors and may not get all the vitamin D they need from sunlight. To protect their bone and muscle health, they should consider taking a daily supplement containing 10 micrograms [400 IU] of vitamin D.”
However, “there is no sufficient evidence to support recommending Vitamin D for reducing the risk of COVID-19,” she stressed.
Dr. Bajaj is on the advisory board of Medscape Diabetes & Endocrinology. He has ties with Amgen, AstraZeneca Boehringer Ingelheim, Janssen, Merck, Novo Nordisk, Sanofi, Eli Lilly,Valeant, Canadian Collaborative Research Network, CMS Knowledge Translation, Diabetes Canada Scientific Group, LMC Healthcare,mdBriefCase,Medscape, andMeducom. Dr. Kenny, Dr. Rosen, and Dr. Singhal have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
TNF inhibitors may dampen COVID-19 severity
Patients on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for their rheumatic disease when they became infected with COVID-19 were markedly less likely to subsequently require hospitalization, according to intriguing early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry.
On the other hand, those registry patients who were on 10 mg of prednisone or more daily when they got infected were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than were those who were not on corticosteroids, even after controlling for the severity of their rheumatic disease and other potential confounders, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, reported at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
“We saw a signal with moderate to high-dose steroids. I think it’s something we’re going to have to keep an eye out on as more data come in,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
The global registry launched on March 24, 2020, and was quickly embraced by rheumatologists from around the world. By May 12, the registry included more than 1,300 patients with a range of rheumatic diseases, all with confirmed COVID-19 infection as a requisite for enrollment; the cases were submitted by more than 300 rheumatologists in 40 countries. The registry is supported by the ACR and European League Against Rheumatism.
Dr. Yazdany, a member of the registry steering committee, described the project’s two main goals: To learn the outcomes of COVID-19–infected patients with various rheumatic diseases and to make inferences regarding the impact of the immunosuppressive and antimalarial medications widely prescribed by rheumatologists.
She presented soon-to-be-published data on the characteristics and disposition of the first 600 patients, 46% of whom were hospitalized and 9% died. A caveat regarding the registry, she noted, is that these are observational data and thus potentially subject to unrecognized confounders. Also, the registry population is skewed toward the sicker end of the COVID-19 disease spectrum because while all participants have confirmed infection, testing for the infection has been notoriously uneven. Many people are infected asymptomatically and thus may not undergo testing even where readily available.
Early key findings from registry
The risk factors for more severe infection resulting in hospitalization in patients with rheumatic diseases are by and large the same drivers described in the general population: older age and comorbid conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and lung disease. Notably, however, patients on the equivalent of 10 mg/day of prednisone or more were at a 105% increased risk for hospitalization, compared with those not on corticosteroids after adjustment for age, comorbid conditions, and rheumatic disease severity.
Patients on a background tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor had an adjusted 60% reduction in risk of hospitalization. This apparent protective effect against more severe COVID-19 disease is mechanistically plausible: In animal studies, being on a TNF inhibitor has been associated with less severe infection following exposure to influenza virus, Dr. Yazdany observed.
COVID-infected patients on any biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug had a 54% decreased risk of hospitalization. However, in this early analysis, the study was sufficiently powered only to specifically assess the impact of TNF inhibitors, since those agents were by far the most commonly used biologics. As the registry grows, it will be possible to analyze the impact of other antirheumatic medications.
Being on hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization.
The only rheumatic disease diagnosis with an odds of hospitalization significantly different from that of RA patients was systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus patients were at 80% increased risk of hospitalization. Although this was a statistically significant difference, Dr. Yazdany cautioned against making too much of it because of the strong potential for unmeasured confounding. In particular, lupus patients as a group are known to rate on the lower end of measures of social determinants of health, a status that is an established major risk factor for COVID-19 disease.
“A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” she said.
Being on background NSAIDs at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with increased risk of hospitalization; in fact, NSAID users were 36% less likely to be hospitalized for their COVID-19 disease, although this difference didn’t reach statistical significance.
Dr. Yazdany urged her fellow rheumatologists to enter their cases on the registry website: rheum-covid.org. There they can also join the registry mailing list and receive weekly updates.
Other recent insights on COVID-19 in rheumatology
An as-yet unpublished U.K. observational study involving electronic health record data on 17 million people included 885,000 individuals with RA, SLE, or psoriasis. After extensive statistical controlling for the known risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including a measure of socioeconomic deprivation, the group with one of these autoimmune diseases had an adjusted, statistically significant 23% increased risk of hospital death because of COVID-19 infection.
“This is the largest study of its kind to date. There’s potential for unmeasured confounding and selection bias here due to who gets tested. We’ll have to see where this study lands, but I think it does suggest there’s a slightly higher mortality risk in COVID-infected patients with rheumatic disease,” according to Dr. Yazdany.
On the other hand, there have been at least eight recently published patient surveys and case series of patients with rheumatic diseases in areas of the world hardest hit by the pandemic, and they paint a consistent picture.
“What we’ve learned from these studies was the infection rate was generally in the ballpark of people in the region. It doesn’t seem like there’s a dramatically higher infection rate in people with rheumatic disease in these surveys. The hospitalized rheumatology patients had many of the familiar comorbidities. This is the first glance at how likely people are to become infected and how they fared, and I think overall the data have been quite reassuring,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly and receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Patients on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for their rheumatic disease when they became infected with COVID-19 were markedly less likely to subsequently require hospitalization, according to intriguing early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry.
On the other hand, those registry patients who were on 10 mg of prednisone or more daily when they got infected were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than were those who were not on corticosteroids, even after controlling for the severity of their rheumatic disease and other potential confounders, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, reported at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
“We saw a signal with moderate to high-dose steroids. I think it’s something we’re going to have to keep an eye out on as more data come in,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
The global registry launched on March 24, 2020, and was quickly embraced by rheumatologists from around the world. By May 12, the registry included more than 1,300 patients with a range of rheumatic diseases, all with confirmed COVID-19 infection as a requisite for enrollment; the cases were submitted by more than 300 rheumatologists in 40 countries. The registry is supported by the ACR and European League Against Rheumatism.
Dr. Yazdany, a member of the registry steering committee, described the project’s two main goals: To learn the outcomes of COVID-19–infected patients with various rheumatic diseases and to make inferences regarding the impact of the immunosuppressive and antimalarial medications widely prescribed by rheumatologists.
She presented soon-to-be-published data on the characteristics and disposition of the first 600 patients, 46% of whom were hospitalized and 9% died. A caveat regarding the registry, she noted, is that these are observational data and thus potentially subject to unrecognized confounders. Also, the registry population is skewed toward the sicker end of the COVID-19 disease spectrum because while all participants have confirmed infection, testing for the infection has been notoriously uneven. Many people are infected asymptomatically and thus may not undergo testing even where readily available.
Early key findings from registry
The risk factors for more severe infection resulting in hospitalization in patients with rheumatic diseases are by and large the same drivers described in the general population: older age and comorbid conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and lung disease. Notably, however, patients on the equivalent of 10 mg/day of prednisone or more were at a 105% increased risk for hospitalization, compared with those not on corticosteroids after adjustment for age, comorbid conditions, and rheumatic disease severity.
Patients on a background tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor had an adjusted 60% reduction in risk of hospitalization. This apparent protective effect against more severe COVID-19 disease is mechanistically plausible: In animal studies, being on a TNF inhibitor has been associated with less severe infection following exposure to influenza virus, Dr. Yazdany observed.
COVID-infected patients on any biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug had a 54% decreased risk of hospitalization. However, in this early analysis, the study was sufficiently powered only to specifically assess the impact of TNF inhibitors, since those agents were by far the most commonly used biologics. As the registry grows, it will be possible to analyze the impact of other antirheumatic medications.
Being on hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization.
The only rheumatic disease diagnosis with an odds of hospitalization significantly different from that of RA patients was systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus patients were at 80% increased risk of hospitalization. Although this was a statistically significant difference, Dr. Yazdany cautioned against making too much of it because of the strong potential for unmeasured confounding. In particular, lupus patients as a group are known to rate on the lower end of measures of social determinants of health, a status that is an established major risk factor for COVID-19 disease.
“A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” she said.
Being on background NSAIDs at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with increased risk of hospitalization; in fact, NSAID users were 36% less likely to be hospitalized for their COVID-19 disease, although this difference didn’t reach statistical significance.
Dr. Yazdany urged her fellow rheumatologists to enter their cases on the registry website: rheum-covid.org. There they can also join the registry mailing list and receive weekly updates.
Other recent insights on COVID-19 in rheumatology
An as-yet unpublished U.K. observational study involving electronic health record data on 17 million people included 885,000 individuals with RA, SLE, or psoriasis. After extensive statistical controlling for the known risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including a measure of socioeconomic deprivation, the group with one of these autoimmune diseases had an adjusted, statistically significant 23% increased risk of hospital death because of COVID-19 infection.
“This is the largest study of its kind to date. There’s potential for unmeasured confounding and selection bias here due to who gets tested. We’ll have to see where this study lands, but I think it does suggest there’s a slightly higher mortality risk in COVID-infected patients with rheumatic disease,” according to Dr. Yazdany.
On the other hand, there have been at least eight recently published patient surveys and case series of patients with rheumatic diseases in areas of the world hardest hit by the pandemic, and they paint a consistent picture.
“What we’ve learned from these studies was the infection rate was generally in the ballpark of people in the region. It doesn’t seem like there’s a dramatically higher infection rate in people with rheumatic disease in these surveys. The hospitalized rheumatology patients had many of the familiar comorbidities. This is the first glance at how likely people are to become infected and how they fared, and I think overall the data have been quite reassuring,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly and receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Patients on a tumor necrosis factor inhibitor for their rheumatic disease when they became infected with COVID-19 were markedly less likely to subsequently require hospitalization, according to intriguing early evidence from the COVID-19 Global Rheumatology Alliance Registry.
On the other hand, those registry patients who were on 10 mg of prednisone or more daily when they got infected were more than twice as likely to be hospitalized than were those who were not on corticosteroids, even after controlling for the severity of their rheumatic disease and other potential confounders, Jinoos Yazdany, MD, reported at the virtual edition of the American College of Rheumatology’s 2020 State-of-the-Art Clinical Symposium.
“We saw a signal with moderate to high-dose steroids. I think it’s something we’re going to have to keep an eye out on as more data come in,” said Dr. Yazdany, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Francisco, and chief of rheumatology at San Francisco General Hospital.
The global registry launched on March 24, 2020, and was quickly embraced by rheumatologists from around the world. By May 12, the registry included more than 1,300 patients with a range of rheumatic diseases, all with confirmed COVID-19 infection as a requisite for enrollment; the cases were submitted by more than 300 rheumatologists in 40 countries. The registry is supported by the ACR and European League Against Rheumatism.
Dr. Yazdany, a member of the registry steering committee, described the project’s two main goals: To learn the outcomes of COVID-19–infected patients with various rheumatic diseases and to make inferences regarding the impact of the immunosuppressive and antimalarial medications widely prescribed by rheumatologists.
She presented soon-to-be-published data on the characteristics and disposition of the first 600 patients, 46% of whom were hospitalized and 9% died. A caveat regarding the registry, she noted, is that these are observational data and thus potentially subject to unrecognized confounders. Also, the registry population is skewed toward the sicker end of the COVID-19 disease spectrum because while all participants have confirmed infection, testing for the infection has been notoriously uneven. Many people are infected asymptomatically and thus may not undergo testing even where readily available.
Early key findings from registry
The risk factors for more severe infection resulting in hospitalization in patients with rheumatic diseases are by and large the same drivers described in the general population: older age and comorbid conditions including diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular disease, obesity, chronic kidney disease, and lung disease. Notably, however, patients on the equivalent of 10 mg/day of prednisone or more were at a 105% increased risk for hospitalization, compared with those not on corticosteroids after adjustment for age, comorbid conditions, and rheumatic disease severity.
Patients on a background tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor had an adjusted 60% reduction in risk of hospitalization. This apparent protective effect against more severe COVID-19 disease is mechanistically plausible: In animal studies, being on a TNF inhibitor has been associated with less severe infection following exposure to influenza virus, Dr. Yazdany observed.
COVID-infected patients on any biologic disease-modifying antirheumatic drug had a 54% decreased risk of hospitalization. However, in this early analysis, the study was sufficiently powered only to specifically assess the impact of TNF inhibitors, since those agents were by far the most commonly used biologics. As the registry grows, it will be possible to analyze the impact of other antirheumatic medications.
Being on hydroxychloroquine or other antimalarials at the time of COVID-19 infection had no impact on hospitalization.
The only rheumatic disease diagnosis with an odds of hospitalization significantly different from that of RA patients was systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Lupus patients were at 80% increased risk of hospitalization. Although this was a statistically significant difference, Dr. Yazdany cautioned against making too much of it because of the strong potential for unmeasured confounding. In particular, lupus patients as a group are known to rate on the lower end of measures of social determinants of health, a status that is an established major risk factor for COVID-19 disease.
“A strength of the global registry has been that it provides timely data that’s been very helpful for rheumatologists to rapidly dispel misinformation that has been spread about hydroxychloroquine, especially statements about lupus patients not getting COVID-19. We know from these data that’s not true,” she said.
Being on background NSAIDs at the time of SARS-CoV-2 infection was not associated with increased risk of hospitalization; in fact, NSAID users were 36% less likely to be hospitalized for their COVID-19 disease, although this difference didn’t reach statistical significance.
Dr. Yazdany urged her fellow rheumatologists to enter their cases on the registry website: rheum-covid.org. There they can also join the registry mailing list and receive weekly updates.
Other recent insights on COVID-19 in rheumatology
An as-yet unpublished U.K. observational study involving electronic health record data on 17 million people included 885,000 individuals with RA, SLE, or psoriasis. After extensive statistical controlling for the known risk factors for severe COVID-19 infection, including a measure of socioeconomic deprivation, the group with one of these autoimmune diseases had an adjusted, statistically significant 23% increased risk of hospital death because of COVID-19 infection.
“This is the largest study of its kind to date. There’s potential for unmeasured confounding and selection bias here due to who gets tested. We’ll have to see where this study lands, but I think it does suggest there’s a slightly higher mortality risk in COVID-infected patients with rheumatic disease,” according to Dr. Yazdany.
On the other hand, there have been at least eight recently published patient surveys and case series of patients with rheumatic diseases in areas of the world hardest hit by the pandemic, and they paint a consistent picture.
“What we’ve learned from these studies was the infection rate was generally in the ballpark of people in the region. It doesn’t seem like there’s a dramatically higher infection rate in people with rheumatic disease in these surveys. The hospitalized rheumatology patients had many of the familiar comorbidities. This is the first glance at how likely people are to become infected and how they fared, and I think overall the data have been quite reassuring,” she said.
Dr. Yazdany reported serving as a consultant to AstraZeneca and Eli Lilly and receiving research funding from the National Institutes of Health, the Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality, and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
REPORTING FROM SOTA 2020
Antibody testing suggests COVID-19 cases are being missed
The number of COVID-19 infections in the community may be “substantially greater” than totals confirmed by authorities, based on SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing among a random sample of adults in Los Angeles County, Calif.
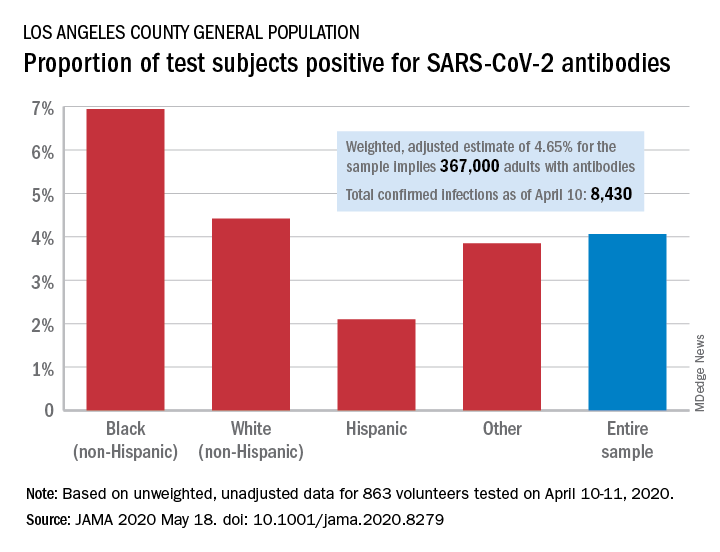
Testing of 863 people on April 10-11 revealed that 35 (4.06%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies (IgM or IgG), and after adjustment for test sensitivity and specificity, the weighted prevalence for the entire sample was 4.65%, Neeraj Sood, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and associates wrote in JAMA.
The estimate of 4.65% “implies that approximately 367,000 adults [in Los Angeles County] had SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, which is substantially greater than the 8,430 cumulative number of confirmed infections in the county on April 10,” they wrote.
It also suggests that fatality rates based on the larger number of infections may be lower than rates based on confirmed cases. “In addition, contact tracing methods to limit the spread of infection will face considerable challenges,” Dr. Sood and associates said.
Test positivity varied by race/ethnicity, sex, and income. The proportion of non-Hispanic blacks with a positive result was 6.94%, compared with 4.42% for non-Hispanic whites, 2.10% for Hispanics, and 3.85% for others. Men were much more likely than women to be positive for SARS-CoV-2: 5.18% vs. 3.31%, the investigators said.
Household income favored the middle ground. Those individuals making less than $50,000 a year had a positivity rate of 5.14% and those with an income of $100,000 or more had a rate of 4.90%, but only 1.58% of those making $50,000-$99,999 tested positive, they reported.
The authors reported numerous sources of nonprofit organization support.
SOURCE: Sood N et al. JAMA 2020 May 18. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.8279.
The number of COVID-19 infections in the community may be “substantially greater” than totals confirmed by authorities, based on SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing among a random sample of adults in Los Angeles County, Calif.

Testing of 863 people on April 10-11 revealed that 35 (4.06%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies (IgM or IgG), and after adjustment for test sensitivity and specificity, the weighted prevalence for the entire sample was 4.65%, Neeraj Sood, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and associates wrote in JAMA.
The estimate of 4.65% “implies that approximately 367,000 adults [in Los Angeles County] had SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, which is substantially greater than the 8,430 cumulative number of confirmed infections in the county on April 10,” they wrote.
It also suggests that fatality rates based on the larger number of infections may be lower than rates based on confirmed cases. “In addition, contact tracing methods to limit the spread of infection will face considerable challenges,” Dr. Sood and associates said.
Test positivity varied by race/ethnicity, sex, and income. The proportion of non-Hispanic blacks with a positive result was 6.94%, compared with 4.42% for non-Hispanic whites, 2.10% for Hispanics, and 3.85% for others. Men were much more likely than women to be positive for SARS-CoV-2: 5.18% vs. 3.31%, the investigators said.
Household income favored the middle ground. Those individuals making less than $50,000 a year had a positivity rate of 5.14% and those with an income of $100,000 or more had a rate of 4.90%, but only 1.58% of those making $50,000-$99,999 tested positive, they reported.
The authors reported numerous sources of nonprofit organization support.
SOURCE: Sood N et al. JAMA 2020 May 18. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.8279.
The number of COVID-19 infections in the community may be “substantially greater” than totals confirmed by authorities, based on SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing among a random sample of adults in Los Angeles County, Calif.

Testing of 863 people on April 10-11 revealed that 35 (4.06%) were positive for SARS-CoV-2–specific antibodies (IgM or IgG), and after adjustment for test sensitivity and specificity, the weighted prevalence for the entire sample was 4.65%, Neeraj Sood, PhD, of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, and associates wrote in JAMA.
The estimate of 4.65% “implies that approximately 367,000 adults [in Los Angeles County] had SARS-CoV-2 antibodies, which is substantially greater than the 8,430 cumulative number of confirmed infections in the county on April 10,” they wrote.
It also suggests that fatality rates based on the larger number of infections may be lower than rates based on confirmed cases. “In addition, contact tracing methods to limit the spread of infection will face considerable challenges,” Dr. Sood and associates said.
Test positivity varied by race/ethnicity, sex, and income. The proportion of non-Hispanic blacks with a positive result was 6.94%, compared with 4.42% for non-Hispanic whites, 2.10% for Hispanics, and 3.85% for others. Men were much more likely than women to be positive for SARS-CoV-2: 5.18% vs. 3.31%, the investigators said.
Household income favored the middle ground. Those individuals making less than $50,000 a year had a positivity rate of 5.14% and those with an income of $100,000 or more had a rate of 4.90%, but only 1.58% of those making $50,000-$99,999 tested positive, they reported.
The authors reported numerous sources of nonprofit organization support.
SOURCE: Sood N et al. JAMA 2020 May 18. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.8279.
FROM JAMA
Radiation-associated childhood cancer quantified in congenital heart disease
Children with congenital heart disease exposed to low-dose ionizing radiation from cardiac procedures had a cancer risk more than triple that of pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) patients without such exposures, according to a large Canadian nested case-control study presented at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This cancer risk was dose dependent. It rose stepwise with the number of cardiac procedures involving exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation (LDIR) and the total radiation dose. Moreover, roughly 80% of the cancers were of types known to be associated with radiation exposure in children, reported Elie Ganni, a medical student at McGill University, Montreal, working with MAUDE, the McGill Adult Unit for Congenital Heart Disease.
The MAUDE group previously published the first large, population-based study analyzing the association between LDIR from cardiac procedures and incident cancer in adults with CHD. The study, which included nearly 25,000 adult CHD patients aged 18-64 years with more than 250,000 person-years of follow-up, concluded that individuals with LDIR exposure from six or more cardiac procedures had a 140% greater cancer incidence than those with no or one exposure (Circulation. 2018 Mar 27;137[13]:1334-45).
Because children are considered to be more sensitive to the carcinogenic effects of LDIR than adults, the MAUDE group next did a similar study in a pediatric CHD population included in the Quebec Congenital Heart Disease Database. This nested case-control study included 232 children with CHD who were first diagnosed with cancer at a median age of 3.9 years and 8,160 pediatric CHD controls matched for gender and birth year. About 76% of cancers were diagnosed before age 7, 20% at ages 7-12 years, and the remaining 4% at ages 13-18. Hematologic malignancies accounted for 61% of the pediatric cancers, CNS cancers for another 12.5%, and thyroid cancers 6.6%; all three types of cancer are associated with radiation exposure.
After excluding all cardiac procedures involving LDIR performed within 6 months prior to cancer diagnosis, the risk of developing a pediatric cancer was 230% greater in children with LDIR exposure from cardiac procedures than in CHD patients without such exposure. For every 4 mSv in estimated LDIR exposure from cardiac procedures, the risk of cancer rose by 15.5%. In contrast, in the earlier study in adults with CHD, cancer risk climbed by 10% per 10 mSv. Patients with six or more LDIR cardiac procedures – not at all unusual in contemporary practice – were 2.4 times more likely to have cancer than those with no or one such radiation exposure.
Current ACC guidelines on radiation exposure from cardiac procedures recommend calculating an individual’s lifetime attributable cancer incidence and mortality risks, as well as adhering to the time-honored principle of ensuring that radiation exposure is as low as reasonably achievable without sacrificing quality of care.
“Our findings strongly support these ACC recommendations and moreover suggest that radiation surveillance for patients with congenital heart disease should be considered using radiation badges. Also, cancer surveillance guidelines should be considered for CHD patients exposed to LDIR,” Mr. Ganni said.
These suggestions for creation of patient radiation passports and cancer surveillance guidelines take on greater weight in light of two trends: the increasing life expectancy of children with CHD during the past 3 decades as a result of procedural advances that entail LDIR exposure, mostly for imaging, and the growing number of such procedures performed per patient earlier and earlier in life.
He and the MAUDE group plan to confirm their latest findings in other, larger data sets and hope to identify threshold effects for LDIR for specific cancers, with hematologic malignancies as the top priority.
Mr. Ganni reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Quebec Foundation for Health Research, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research.
Children with congenital heart disease exposed to low-dose ionizing radiation from cardiac procedures had a cancer risk more than triple that of pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) patients without such exposures, according to a large Canadian nested case-control study presented at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This cancer risk was dose dependent. It rose stepwise with the number of cardiac procedures involving exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation (LDIR) and the total radiation dose. Moreover, roughly 80% of the cancers were of types known to be associated with radiation exposure in children, reported Elie Ganni, a medical student at McGill University, Montreal, working with MAUDE, the McGill Adult Unit for Congenital Heart Disease.
The MAUDE group previously published the first large, population-based study analyzing the association between LDIR from cardiac procedures and incident cancer in adults with CHD. The study, which included nearly 25,000 adult CHD patients aged 18-64 years with more than 250,000 person-years of follow-up, concluded that individuals with LDIR exposure from six or more cardiac procedures had a 140% greater cancer incidence than those with no or one exposure (Circulation. 2018 Mar 27;137[13]:1334-45).
Because children are considered to be more sensitive to the carcinogenic effects of LDIR than adults, the MAUDE group next did a similar study in a pediatric CHD population included in the Quebec Congenital Heart Disease Database. This nested case-control study included 232 children with CHD who were first diagnosed with cancer at a median age of 3.9 years and 8,160 pediatric CHD controls matched for gender and birth year. About 76% of cancers were diagnosed before age 7, 20% at ages 7-12 years, and the remaining 4% at ages 13-18. Hematologic malignancies accounted for 61% of the pediatric cancers, CNS cancers for another 12.5%, and thyroid cancers 6.6%; all three types of cancer are associated with radiation exposure.
After excluding all cardiac procedures involving LDIR performed within 6 months prior to cancer diagnosis, the risk of developing a pediatric cancer was 230% greater in children with LDIR exposure from cardiac procedures than in CHD patients without such exposure. For every 4 mSv in estimated LDIR exposure from cardiac procedures, the risk of cancer rose by 15.5%. In contrast, in the earlier study in adults with CHD, cancer risk climbed by 10% per 10 mSv. Patients with six or more LDIR cardiac procedures – not at all unusual in contemporary practice – were 2.4 times more likely to have cancer than those with no or one such radiation exposure.
Current ACC guidelines on radiation exposure from cardiac procedures recommend calculating an individual’s lifetime attributable cancer incidence and mortality risks, as well as adhering to the time-honored principle of ensuring that radiation exposure is as low as reasonably achievable without sacrificing quality of care.
“Our findings strongly support these ACC recommendations and moreover suggest that radiation surveillance for patients with congenital heart disease should be considered using radiation badges. Also, cancer surveillance guidelines should be considered for CHD patients exposed to LDIR,” Mr. Ganni said.
These suggestions for creation of patient radiation passports and cancer surveillance guidelines take on greater weight in light of two trends: the increasing life expectancy of children with CHD during the past 3 decades as a result of procedural advances that entail LDIR exposure, mostly for imaging, and the growing number of such procedures performed per patient earlier and earlier in life.
He and the MAUDE group plan to confirm their latest findings in other, larger data sets and hope to identify threshold effects for LDIR for specific cancers, with hematologic malignancies as the top priority.
Mr. Ganni reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Quebec Foundation for Health Research, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research.
Children with congenital heart disease exposed to low-dose ionizing radiation from cardiac procedures had a cancer risk more than triple that of pediatric congenital heart disease (CHD) patients without such exposures, according to a large Canadian nested case-control study presented at the joint scientific sessions of the American College of Cardiology and the World Heart Federation. The meeting was conducted online after its cancellation because of the COVID-19 pandemic.
This cancer risk was dose dependent. It rose stepwise with the number of cardiac procedures involving exposure to low-dose ionizing radiation (LDIR) and the total radiation dose. Moreover, roughly 80% of the cancers were of types known to be associated with radiation exposure in children, reported Elie Ganni, a medical student at McGill University, Montreal, working with MAUDE, the McGill Adult Unit for Congenital Heart Disease.
The MAUDE group previously published the first large, population-based study analyzing the association between LDIR from cardiac procedures and incident cancer in adults with CHD. The study, which included nearly 25,000 adult CHD patients aged 18-64 years with more than 250,000 person-years of follow-up, concluded that individuals with LDIR exposure from six or more cardiac procedures had a 140% greater cancer incidence than those with no or one exposure (Circulation. 2018 Mar 27;137[13]:1334-45).
Because children are considered to be more sensitive to the carcinogenic effects of LDIR than adults, the MAUDE group next did a similar study in a pediatric CHD population included in the Quebec Congenital Heart Disease Database. This nested case-control study included 232 children with CHD who were first diagnosed with cancer at a median age of 3.9 years and 8,160 pediatric CHD controls matched for gender and birth year. About 76% of cancers were diagnosed before age 7, 20% at ages 7-12 years, and the remaining 4% at ages 13-18. Hematologic malignancies accounted for 61% of the pediatric cancers, CNS cancers for another 12.5%, and thyroid cancers 6.6%; all three types of cancer are associated with radiation exposure.
After excluding all cardiac procedures involving LDIR performed within 6 months prior to cancer diagnosis, the risk of developing a pediatric cancer was 230% greater in children with LDIR exposure from cardiac procedures than in CHD patients without such exposure. For every 4 mSv in estimated LDIR exposure from cardiac procedures, the risk of cancer rose by 15.5%. In contrast, in the earlier study in adults with CHD, cancer risk climbed by 10% per 10 mSv. Patients with six or more LDIR cardiac procedures – not at all unusual in contemporary practice – were 2.4 times more likely to have cancer than those with no or one such radiation exposure.
Current ACC guidelines on radiation exposure from cardiac procedures recommend calculating an individual’s lifetime attributable cancer incidence and mortality risks, as well as adhering to the time-honored principle of ensuring that radiation exposure is as low as reasonably achievable without sacrificing quality of care.
“Our findings strongly support these ACC recommendations and moreover suggest that radiation surveillance for patients with congenital heart disease should be considered using radiation badges. Also, cancer surveillance guidelines should be considered for CHD patients exposed to LDIR,” Mr. Ganni said.
These suggestions for creation of patient radiation passports and cancer surveillance guidelines take on greater weight in light of two trends: the increasing life expectancy of children with CHD during the past 3 decades as a result of procedural advances that entail LDIR exposure, mostly for imaging, and the growing number of such procedures performed per patient earlier and earlier in life.
He and the MAUDE group plan to confirm their latest findings in other, larger data sets and hope to identify threshold effects for LDIR for specific cancers, with hematologic malignancies as the top priority.
Mr. Ganni reported having no financial conflicts regarding his study, funded by the Heart and Stroke Foundation of Canada, the Quebec Foundation for Health Research, and the Canadian Institutes for Health Research.
FROM ACC 2020
COVID-19 in kids: Severe illness most common in infants, teens
Children and young adults in all age groups can develop severe illness after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but the oldest and youngest appear most likely to be hospitalized and possibly critically ill, based on data from a retrospective cohort study of 177 pediatric patients seen at a single center.
“Although children and young adults clearly are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, attention has focused primarily on their potential role in influencing spread and community transmission rather than the potential severity of infection in children and young adults themselves,” wrote Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 44 hospitalized and 133 non-hospitalized children and young adults infected with SARS-CoV-2. Of the 44 hospitalized patients, 35 were noncritically ill and 9 were critically ill. The study population ranged from 0.1-34 years of age, with a median of 10 years, which was similar between hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients. However, the median age of critically ill patients was significantly higher, compared with noncritically ill patients (17 years vs. 4 years). All age groups were represented in all cohorts. “However, we noted a bimodal distribution of patients less than 1 year of age and patients greater than 15 years of age representing the largest proportion of patients within the SARS-CoV-2–infected hospitalized and critically ill cohorts,” the researchers noted. Children less than 1 year and adolescents/young adults over 15 years each represented 32% of the 44 hospitalized patients.
Overall, 39% of the 177 patients had underlying medical conditions, the most frequent of which was asthma (20%), which was not significantly more common between hospitalized/nonhospitalized patients or critically ill/noncritically ill patients. Patients also presented with neurologic conditions (6%), diabetes (3%), obesity (2%), cardiac conditions (3%), hematologic conditions (3%) and oncologic conditions (1%). Underlying conditions occurred more commonly in the hospitalized cohort (63%) than in the nonhospitalized cohort (32%).
Neurologic disorders, cardiac conditions, hematologic conditions, and oncologic conditions were significantly more common in hospitalized patients, but not significantly more common among those critically ill versus noncritically ill.
About 76% of the patients presented with respiratory symptoms including rhinorrhea, congestion, sore throat, cough, or shortness of breath – with or without fever; 66% had fevers; and 48% had both respiratory symptoms and fever. Shortness of breath was significantly more common among hospitalized patients versus nonhospitalized patients (26% vs. 12%), but less severe respiratory symptoms were significantly more common among nonhospitalized patients, the researchers noted.
Other symptoms – such as diarrhea, vomiting, chest pain, and loss of sense or smell occurred in a small percentage of patients – but were not more likely to occur in any of the cohorts.
Among the critically ill patients, eight of nine needed some level of respiratory support, and four were on ventilators.
“One patient had features consistent with the recently emerged Kawasaki disease–like presentation with hyperinflammatory state, hypotension, and profound myocardial depression,” Dr. DiBiasi and associates noted.
The researchers found coinfection with routine coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, or rhinovirus/enterovirus in 4 of 63 (6%) patients, but the clinical impact of these coinfections are unclear.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and the ongoing transmission of COVID-19 in the Washington area, the researchers noted. “One potential bias of this study is our regional role in providing critical care for young adults age 21-35 years with COVID-19.” In addition, “we plan to address the role of race and ethnicity after validation of current administrative data and have elected to defer this analysis until completed.”
“Our findings highlight the potential for severe disease in this age group and inform other regions to anticipate and prepare their COVID-19 response to include a significant burden of hospitalized and critically ill children and young adults. As SARS-CoV-2 spreads within the United States, regional differences may be apparent based on virus and host factors that are yet to be identified,” Dr. DeBiasi and colleagues concluded.
Robin Steinhorn, MD, serves as an associate editor for the Journal of Pediatrics. The other researchers declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: DeBiasi RL et al. J Pediatr. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007.
This article was updated 5/19/20.
Children and young adults in all age groups can develop severe illness after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but the oldest and youngest appear most likely to be hospitalized and possibly critically ill, based on data from a retrospective cohort study of 177 pediatric patients seen at a single center.
“Although children and young adults clearly are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, attention has focused primarily on their potential role in influencing spread and community transmission rather than the potential severity of infection in children and young adults themselves,” wrote Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 44 hospitalized and 133 non-hospitalized children and young adults infected with SARS-CoV-2. Of the 44 hospitalized patients, 35 were noncritically ill and 9 were critically ill. The study population ranged from 0.1-34 years of age, with a median of 10 years, which was similar between hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients. However, the median age of critically ill patients was significantly higher, compared with noncritically ill patients (17 years vs. 4 years). All age groups were represented in all cohorts. “However, we noted a bimodal distribution of patients less than 1 year of age and patients greater than 15 years of age representing the largest proportion of patients within the SARS-CoV-2–infected hospitalized and critically ill cohorts,” the researchers noted. Children less than 1 year and adolescents/young adults over 15 years each represented 32% of the 44 hospitalized patients.
Overall, 39% of the 177 patients had underlying medical conditions, the most frequent of which was asthma (20%), which was not significantly more common between hospitalized/nonhospitalized patients or critically ill/noncritically ill patients. Patients also presented with neurologic conditions (6%), diabetes (3%), obesity (2%), cardiac conditions (3%), hematologic conditions (3%) and oncologic conditions (1%). Underlying conditions occurred more commonly in the hospitalized cohort (63%) than in the nonhospitalized cohort (32%).
Neurologic disorders, cardiac conditions, hematologic conditions, and oncologic conditions were significantly more common in hospitalized patients, but not significantly more common among those critically ill versus noncritically ill.
About 76% of the patients presented with respiratory symptoms including rhinorrhea, congestion, sore throat, cough, or shortness of breath – with or without fever; 66% had fevers; and 48% had both respiratory symptoms and fever. Shortness of breath was significantly more common among hospitalized patients versus nonhospitalized patients (26% vs. 12%), but less severe respiratory symptoms were significantly more common among nonhospitalized patients, the researchers noted.
Other symptoms – such as diarrhea, vomiting, chest pain, and loss of sense or smell occurred in a small percentage of patients – but were not more likely to occur in any of the cohorts.
Among the critically ill patients, eight of nine needed some level of respiratory support, and four were on ventilators.
“One patient had features consistent with the recently emerged Kawasaki disease–like presentation with hyperinflammatory state, hypotension, and profound myocardial depression,” Dr. DiBiasi and associates noted.
The researchers found coinfection with routine coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, or rhinovirus/enterovirus in 4 of 63 (6%) patients, but the clinical impact of these coinfections are unclear.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and the ongoing transmission of COVID-19 in the Washington area, the researchers noted. “One potential bias of this study is our regional role in providing critical care for young adults age 21-35 years with COVID-19.” In addition, “we plan to address the role of race and ethnicity after validation of current administrative data and have elected to defer this analysis until completed.”
“Our findings highlight the potential for severe disease in this age group and inform other regions to anticipate and prepare their COVID-19 response to include a significant burden of hospitalized and critically ill children and young adults. As SARS-CoV-2 spreads within the United States, regional differences may be apparent based on virus and host factors that are yet to be identified,” Dr. DeBiasi and colleagues concluded.
Robin Steinhorn, MD, serves as an associate editor for the Journal of Pediatrics. The other researchers declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: DeBiasi RL et al. J Pediatr. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007.
This article was updated 5/19/20.
Children and young adults in all age groups can develop severe illness after SARS-CoV-2 infection, but the oldest and youngest appear most likely to be hospitalized and possibly critically ill, based on data from a retrospective cohort study of 177 pediatric patients seen at a single center.
“Although children and young adults clearly are susceptible to SARS-CoV-2 infection, attention has focused primarily on their potential role in influencing spread and community transmission rather than the potential severity of infection in children and young adults themselves,” wrote Roberta L. DeBiasi, MD, chief of the division of pediatric infectious diseases at Children’s National Hospital, Washington, and colleagues.
In a study published in the Journal of Pediatrics, the researchers reviewed data from 44 hospitalized and 133 non-hospitalized children and young adults infected with SARS-CoV-2. Of the 44 hospitalized patients, 35 were noncritically ill and 9 were critically ill. The study population ranged from 0.1-34 years of age, with a median of 10 years, which was similar between hospitalized and nonhospitalized patients. However, the median age of critically ill patients was significantly higher, compared with noncritically ill patients (17 years vs. 4 years). All age groups were represented in all cohorts. “However, we noted a bimodal distribution of patients less than 1 year of age and patients greater than 15 years of age representing the largest proportion of patients within the SARS-CoV-2–infected hospitalized and critically ill cohorts,” the researchers noted. Children less than 1 year and adolescents/young adults over 15 years each represented 32% of the 44 hospitalized patients.
Overall, 39% of the 177 patients had underlying medical conditions, the most frequent of which was asthma (20%), which was not significantly more common between hospitalized/nonhospitalized patients or critically ill/noncritically ill patients. Patients also presented with neurologic conditions (6%), diabetes (3%), obesity (2%), cardiac conditions (3%), hematologic conditions (3%) and oncologic conditions (1%). Underlying conditions occurred more commonly in the hospitalized cohort (63%) than in the nonhospitalized cohort (32%).
Neurologic disorders, cardiac conditions, hematologic conditions, and oncologic conditions were significantly more common in hospitalized patients, but not significantly more common among those critically ill versus noncritically ill.
About 76% of the patients presented with respiratory symptoms including rhinorrhea, congestion, sore throat, cough, or shortness of breath – with or without fever; 66% had fevers; and 48% had both respiratory symptoms and fever. Shortness of breath was significantly more common among hospitalized patients versus nonhospitalized patients (26% vs. 12%), but less severe respiratory symptoms were significantly more common among nonhospitalized patients, the researchers noted.
Other symptoms – such as diarrhea, vomiting, chest pain, and loss of sense or smell occurred in a small percentage of patients – but were not more likely to occur in any of the cohorts.
Among the critically ill patients, eight of nine needed some level of respiratory support, and four were on ventilators.
“One patient had features consistent with the recently emerged Kawasaki disease–like presentation with hyperinflammatory state, hypotension, and profound myocardial depression,” Dr. DiBiasi and associates noted.
The researchers found coinfection with routine coronavirus, respiratory syncytial virus, or rhinovirus/enterovirus in 4 of 63 (6%) patients, but the clinical impact of these coinfections are unclear.
The study findings were limited by several factors including the retrospective design and the ongoing transmission of COVID-19 in the Washington area, the researchers noted. “One potential bias of this study is our regional role in providing critical care for young adults age 21-35 years with COVID-19.” In addition, “we plan to address the role of race and ethnicity after validation of current administrative data and have elected to defer this analysis until completed.”
“Our findings highlight the potential for severe disease in this age group and inform other regions to anticipate and prepare their COVID-19 response to include a significant burden of hospitalized and critically ill children and young adults. As SARS-CoV-2 spreads within the United States, regional differences may be apparent based on virus and host factors that are yet to be identified,” Dr. DeBiasi and colleagues concluded.
Robin Steinhorn, MD, serves as an associate editor for the Journal of Pediatrics. The other researchers declared no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: DeBiasi RL et al. J Pediatr. 2020 May 6. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2020.05.007.
This article was updated 5/19/20.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF PEDIATRICS
Dermatologic changes with COVID-19: What we know and don’t know
The dermatologic manifestations associated with SARS-CoV-2 are many and varied, with new information virtually daily. Graeme Lipper, MD, a member of the Medscape Dermatology advisory board, discussed what we know and what is still to be learned with Lindy Fox, MD, a professor of dermatology at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s COVID-19 Registry task force.
Graeme M. Lipper, MD
Earlier this spring, before there was any real talk about skin manifestations of COVID, my partner called me in to see an unusual case. His patient was a healthy 20-year-old who had just come back from college and had tender, purple discoloration and swelling on his toes. I shrugged and said “looks like chilblains,” but there was something weird about the case. It seemed more severe, with areas of blistering and erosions, and the discomfort was unusual for run-of-the-mill pernio. This young man had experienced a cough and shortness of breath a few weeks earlier but those symptoms had resolved when we saw him.
That evening, I was on a derm social media site and saw a series of pictures from Italy that blew me away. All of these pictures looked just like this kid’s toes. That’s the first I heard of “COVID toes,” but now they seem to be everywhere. How would you describe this presentation, and how does it differ from typical chilblains?
Lindy P. Fox, MD
I am so proud of dermatologists around the world who have really jumped into action to examine the pathophysiology and immunology behind these findings.
Your experience matches mine. Like you, I first heard about these pernio- or chilblains-like lesions when Europe was experiencing its surge in cases. And while it does indeed look like chilblains, I think the reality is that it is more severe and symptomatic than we would expect. I think your observation is exactly right. There are certainly clinicians who do not believe that this is an association with COVID-19 because the testing is often negative. But to my mind, there are just too many cases at the wrong time of year, all happening concomitantly, and simultaneous with a new virus for me to accept that they are not somehow related.
Dr. Lipper: Some have referred to this as “quarantine toes,” the result of more people at home and walking around barefoot. That doesn’t seem to make a whole lot of sense because it’s happening in both warm and cold climates.
Others have speculated that there is another, unrelated circulating virus causing these pernio cases, but that seems far-fetched.
But the idea of a reporting bias – more patients paying attention to these lesions because they’ve read something in the mass media or seen a report on television and are concerned, and thus present with mild lesions they might otherwise have ignored – may be contributing somewhat. But even that cannot be the sole reason behind the increase.
Dr. Fox: Agree.
Evaluation of the patient with chilblains – then and now
Dr. Lipper: In the past, how did you perform a workup for someone with chilblains?
Dr. Fox: Pre-COVID – and I think we all have divided our world into pre- and post-COVID – the most common thing that I’d be looking for would be a clotting disorder or an autoimmune disease, typically lupus. So I take a good history, review of systems, and look at the skin for signs of lupus or other autoimmune connective tissue diseases. My lab workup is probably limited to an antinuclear antibody (ANA). If the findings are severe and recurrent, I might check for hypercoagulability with an antiphospholipid antibody panel. But that was usually it unless there was something in the history or physical exam that would lead me to look for something less common – for example, cryoglobulins or an underlying hematologic disease that would lead to a predominance of lesions in acral sites.
My approach was the same. In New England, where I practice, I also always look at environmental factors. We would sometimes see chilblains in someone from a warmer climate who came home to the Northeast to ski.
Dr. Lipper: Now, in the post-COVID world, how do you assess these patients? What has changed?
Dr. Fox: That’s a great question. To be frank, our focus now is on not missing a secondary consequence of COVID infection that we might not have picked up before. I’m the first to admit that the workup that we have been doing at UCSF is extremely comprehensive. We may be ordering tests that don’t need to be done. But until we know better what might and might not be affected by COVID, we don’t actually have a sense of whether they’re worth looking for or not.
Right now, my workup includes nasal swab polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for COVID, as well as IgG and IgM serology if available. We have IgG easily available to us. IgM needs approval; at UCSF, it is primarily done in neonates as of now. I also do a workup for autoimmunity and cold-associated disease, which includes an ANA, rheumatoid factor, cryoglobulin, and cold agglutinins.
Because of reported concerns about hypercoagulability in COVID patients, particularly in those who are doing poorly in the hospital, we look for elevations in d-dimers and fibrinogen. We check antiphospholipid antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein. That is probably too much of a workup for the healthy young person, but as of yet, we are just unable to say that those things are universally normal.
There has also been concern that complement may be involved in patients who do poorly and tend to clot a lot. So we are also checking C3, C4, and CH50.
To date, in my patients who have had this workup, I have found one with a positive ANA that was significant (1:320) who also had low complements.
There have been a couple of patients at my institution, not my own patients, who are otherwise fine but have some slight elevation in d-dimers.
Dr. Lipper: Is COVID toes more than one condition?
Some of the initial reports of finger/toe cyanosis out of China were very alarming, with many patients developing skin necrosis or even gangrene. These were critically ill adults with pneumonia and blood markers of disseminated intravascular coagulation, and five out of seven died. In contrast, the cases of pseudo-pernio reported in Europe, and now the United States, seem to be much milder, usually occurring late in the illness or in asymptomatic young people. Do you think these are two different conditions?
Dr. Fox: I believe you have hit the nail on the head. I think it is really important that we don’t confuse those two things. In the inpatient setting, we are clearly seeing patients with a prothrombotic state with associated retiform purpura. For nondermatologists, that usually means star-like, stellate-like, or even lacy purpuric changes with potential for necrosis of the skin. In hospitalized patients, the fingers and toes are usually affected but, interestingly, also the buttocks. When these lesions are biopsied, as has been done by our colleague at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, Joanna Harp, MD, we tend to find thrombosis.
A study of endothelial cell function in patients with COVID-19, published in the Lancet tried to determine whether viral particles could be found in endothelial cells. And the investigators did indeed find these particles. So it appears that the virus is endothelially active, and this might provide some insight into the thromboses seen in hospitalized patients. These patients can develop purple necrotic toes that may progress to gangrene. But that is completely different from what we’re seeing when we say pernio-like or chilblains-like lesions.
The chilblains-like lesions come in several forms. They may be purple, red bumps, often involving the tops of the toes and sometimes the bottom of the feet. Some have been described as target-like or erythema multiforme–like. In others, there may not be individual discrete lesions but rather a redness or bluish, purplish discoloration accompanied by edema of the entire toe or several toes.
Biopsies that I am aware of have identified features consistent with an inflammatory process, all of which can be seen in a typical biopsy of pernio. You can sometimes see lymphocytes surrounding a vessel (called lymphocytic vasculitis) that may damage a vessel and cause a small clot, but the primary process is an inflammatory rather than thrombotic one. You may get a clot in a little tiny vessel secondary to inflammation, and that may lead to some blisters or little areas of necrosis. But you’re not going to see digital necrosis and gangrene. I think that’s an important distinction.
The patients who get the pernio-like lesions are typically children or young adults and are otherwise healthy. Half of them didn’t even have COVID symptoms. If they did have COVID symptoms they were typically mild. So we think the pernio-like lesions are most often occurring in the late stage of the disease and now represent a secondary inflammatory response.
Managing COVID toes
Dr. Lipper: One question I’ve been struggling with is, what do we tell these otherwise healthy patients with purple toes, especially those with no other symptoms? Many of them are testing SARS-CoV-2 negative, both with viral swabs and serologies. Some have suggestive histories like known COVID exposure, recent cough, or travel to high-risk areas. Do we tell them they’re at risk of transmitting the virus? Should they self-quarantine, and for how long? Is there any consensus emerging?
Dr. Fox: This is a good opportunity to plug the American Academy of Dermatology’s COVID-19 Registry, which is run by Esther Freeman, MD, at Massachusetts General Hospital. She has done a phenomenal job in helping us figure out the answers to these exact questions.
I’d encourage any clinicians who have a suspected COVID patient with a skin finding, whether or not infection is confirmed with testing, to enter information about that patient into the registry. That is the only way we will figure out evidence-based answers to a lot of the questions that we’re talking about today.
Based on working with the registry, we know that, rarely, patients who develop pernio-like changes will do so before they get COVID symptoms or at the same time as more typical symptoms. Some patients with these findings are PCR positive, and it is therefore theoretically possible that you could be shedding virus while you’re having the pernio toes. However, more commonly – and this is the experience of most of my colleagues and what we’re seeing at UCSF – pernio is a later finding and most patients are no longer shedding the virus. It appears that pseudo-pernio is an immune reaction and most people are not actively infectious at that point.
The only way to know for sure is to send patients for both PCR testing and antibody testing. If the PCR is negative, the most likely interpretation is that the person is no longer shedding virus, though there can be some false negatives. Therefore, these patients do not need to isolate outside of what I call their COVID pod – family or roommates who have probably been with them the whole time. Any transmission likely would have already occurred.
I tell people who call me concerned about their toes that I do think they should be given a workup for COVID. However, I reassure them that it is usually a good prognostic sign.
What is puzzling is that even in patients with pseudo-chilblains who have a clinical history consistent with COVID or exposure to a COVID-positive family member, antibody testing is often – in fact, most often – negative. There are many hypotheses as to why this is. Maybe the tests just aren’t good. Maybe people with mild disease don’t generate enough antibodies to be detected, Maybe we’re testing at the wrong time. Those are all things that we’re trying to figure out.
But currently, I tell patients that they do not need to strictly isolate. They should still practice social distancing, wear a mask, practice good hand hygiene, and do all of the careful things that we should all be doing. However, they can live within their home environment and be reassured that most likely they are in the convalescent stage.
Dr. Lipper: I find the antibody issue both fascinating and confusing.
In my practice, we’ve noticed a range of symptoms associated with pseudo-pernio. Some people barely realize it’s there and only called because they saw a headline in the news. Others complain of severe burning, throbbing, or itching that keeps them up at night and can sometimes last for weeks. Are there any treatments that seem to help?
Dr. Fox: We can start by saying, as you note, that a lot of patients don’t need interventions. They want reassurance that their toes aren’t going to fall off, that nothing terrible is going to happen to them, and often that’s enough. So far, many patients have contacted us just because they heard about the link between what they were seeing on their feet and COVID. They were likely toward the end of any other symptoms they may have had. But moving forward, I think we’re going to be seeing patients at the more active stage as the public is more aware of this finding.
Most of the time we can manage with clobetasol ointment and low-dose aspirin. I wouldn’t give aspirin to a young child with a high fever, but otherwise I think aspirin is not harmful. A paper published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings in 2014, before COVID, by Jonathan Cappel, MD, and David Wetter, MD, provides a nice therapeutic algorithm. Assuming that the findings we are seeing now are inflammatory, then I think that algorithm should apply. Nifedipine 20-60 mg/day is an option. Hydroxychloroquine, a maximum of 5 mg/kg per day, is an option. I have used hydroxychloroquine most commonly, pre-COVID, in patients who have symptomatic pernio.
I also use pentoxifylline 400 mg three times a day, which has a slight anti-inflammatory effect, when I think a blood vessel is incidentally involved or the patient has a predisposition to clotting. Nicotinamide 500 mg three times a day can be used, though I have not used it.
Some topical options are nitroglycerin, tacrolimus, and minoxidil.
However, during this post-COVID period, I have not come across many with pseudo-pernio who needed anything more than a topical steroid and some aspirin. But I do know of other physicians who have been taking care of patients with much more symptomatic disease.
Dr. Lipper: That is a comprehensive list. You’ve mentioned some options that I’ve wondered about, especially pentoxifylline, which I have found to be very helpful for livedoid vasculopathy. I should note that these are all off-label uses.
Let’s talk about some other suspected skin manifestations of COVID. A prospective nationwide study in Spain of 375 patients reported on a number of different skin manifestations of COVID.
You’re part of a team doing critically important work with the American Academy of Dermatology COVID-19 Dermatology Registry. I know it’s early going, but what are some of the other common skin presentations you’re finding?
Dr. Fox: I’m glad you brought up that paper out of Spain. I think it is really good and does highlight the difference in acute versus convalescent cutaneous manifestations and prognosis. It confirms what we’re seeing. Retiform purpura is an early finding associated with ill patients in the hospital. Pseudo pernio-like lesions tend to be later-stage and in younger, healthier patients.
Interestingly, the vesicular eruption that those investigators describe – monomorphic vesicles on the trunk and extremity – can occur in the more acute phase. That’s fascinating to me because widespread vesicular eruptions are not a thing that we commonly see. If it is not an autoimmune blistering disease, and not a drug-induced blistering process, then you’re really left with viral. Rickettsialpox can do that, as can primary varicella, disseminated herpes, disseminated zoster, and now COVID. So that’s intriguing.
I got called to see a patient yesterday who had symptoms of COVID about a month ago. She was not PCR tested at the time but she is now negative. She has a widespread eruption of tiny vesicles on an erythematous base. An IgG for COVID is positive. How do we decide whether her skin lesions have active virus in them?
The many dermatologic manifestations of COVID-19
Dr. Lipper: In the series in Spain, almost 1 out of 10 patients were found to have a widespread vesicular rash. And just under half had maculopapular exanthems. The information arising from the AAD registry will be of great interest and build on this paper.
In England, the National Health Service and the Paediatric Intensive Care Society recently put out a warning about an alarming number of children with COVID-19 who developed symptoms mimicking Kawasaki disease (high fever, abdominal pain, rash, swollen lymph nodes, mucositis, and conjunctivitis). These kids have systemic inflammation and vasculitis and are critically ill. That was followed by an alert from the New York City Health Department about cases there, which as of May 6 numbered 64. Another 25 children with similar findings have been identified in France.
This is such a scary development, especially because children were supposed to be relatively “safe” from this virus. Any thoughts on who is at risk or why?
Dr. Fox: It’s very alarming. It appears that these cases look just like Kawasaki disease.
It was once hypothesized that Coronaviridae was the cause of Kawasaki disease. Then that got debunked. But these cases now raise the question of whether Kawasaki disease may be virally mediated. Is it an immune reaction to an infectious trigger? Is it actually Coronaviridae that triggers it?
As with these pernio cases, I think we’re going to learn about the pathophysiology of these diseases that we currently look at as secondary responses or immune reactions to unknown triggers. We’re going to learn a lot about them and about the immune system because of how this virus is acting on the immune system.
Dr. Lipper: As is the case with patients with pernio-like lesions, some of these children with Kawasaki-like disease are PCR negative for SARS-CoV-2. It will be interesting to see what happens with antibody testing in this population.
Dr. Fox: Agree. While some of the manufacturers of serology tests have claimed that they have very high sensitivity and specificity, that has not been my experience.
Dr. Lipper: I’ve had a number of patients with a clinical picture that strongly suggests COVID whose serology tests have been negative.
Dr. Fox: As have I. While this could be the result of faulty tests, my biggest worry is that it means that people with mild disease do not mount an antibody response. And if people who have disease can’t make antibodies, then there’s no herd immunity. If there’s no herd immunity, we’re stuck in lockdown until there’s a vaccine.
Dr. Lipper: That is a scary but real possibility. We need evidence – evidence like that provided by the AAD registry.
Dr. Fox: Agree. I look forward to sharing those results with you when we have them.
Dr. Lipper is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and a partner at Advanced DermCare in Danbury, Conn.
Dr. Fox is a professor in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She is a hospital-based dermatologist who specializes in the care of patients with complex skin conditions. She is immediate past president of the Medical Dermatology Society and current president of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists.
This article was first published on Medscape.com.
The dermatologic manifestations associated with SARS-CoV-2 are many and varied, with new information virtually daily. Graeme Lipper, MD, a member of the Medscape Dermatology advisory board, discussed what we know and what is still to be learned with Lindy Fox, MD, a professor of dermatology at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s COVID-19 Registry task force.
Graeme M. Lipper, MD
Earlier this spring, before there was any real talk about skin manifestations of COVID, my partner called me in to see an unusual case. His patient was a healthy 20-year-old who had just come back from college and had tender, purple discoloration and swelling on his toes. I shrugged and said “looks like chilblains,” but there was something weird about the case. It seemed more severe, with areas of blistering and erosions, and the discomfort was unusual for run-of-the-mill pernio. This young man had experienced a cough and shortness of breath a few weeks earlier but those symptoms had resolved when we saw him.
That evening, I was on a derm social media site and saw a series of pictures from Italy that blew me away. All of these pictures looked just like this kid’s toes. That’s the first I heard of “COVID toes,” but now they seem to be everywhere. How would you describe this presentation, and how does it differ from typical chilblains?
Lindy P. Fox, MD
I am so proud of dermatologists around the world who have really jumped into action to examine the pathophysiology and immunology behind these findings.
Your experience matches mine. Like you, I first heard about these pernio- or chilblains-like lesions when Europe was experiencing its surge in cases. And while it does indeed look like chilblains, I think the reality is that it is more severe and symptomatic than we would expect. I think your observation is exactly right. There are certainly clinicians who do not believe that this is an association with COVID-19 because the testing is often negative. But to my mind, there are just too many cases at the wrong time of year, all happening concomitantly, and simultaneous with a new virus for me to accept that they are not somehow related.
Dr. Lipper: Some have referred to this as “quarantine toes,” the result of more people at home and walking around barefoot. That doesn’t seem to make a whole lot of sense because it’s happening in both warm and cold climates.
Others have speculated that there is another, unrelated circulating virus causing these pernio cases, but that seems far-fetched.
But the idea of a reporting bias – more patients paying attention to these lesions because they’ve read something in the mass media or seen a report on television and are concerned, and thus present with mild lesions they might otherwise have ignored – may be contributing somewhat. But even that cannot be the sole reason behind the increase.
Dr. Fox: Agree.
Evaluation of the patient with chilblains – then and now
Dr. Lipper: In the past, how did you perform a workup for someone with chilblains?
Dr. Fox: Pre-COVID – and I think we all have divided our world into pre- and post-COVID – the most common thing that I’d be looking for would be a clotting disorder or an autoimmune disease, typically lupus. So I take a good history, review of systems, and look at the skin for signs of lupus or other autoimmune connective tissue diseases. My lab workup is probably limited to an antinuclear antibody (ANA). If the findings are severe and recurrent, I might check for hypercoagulability with an antiphospholipid antibody panel. But that was usually it unless there was something in the history or physical exam that would lead me to look for something less common – for example, cryoglobulins or an underlying hematologic disease that would lead to a predominance of lesions in acral sites.
My approach was the same. In New England, where I practice, I also always look at environmental factors. We would sometimes see chilblains in someone from a warmer climate who came home to the Northeast to ski.
Dr. Lipper: Now, in the post-COVID world, how do you assess these patients? What has changed?
Dr. Fox: That’s a great question. To be frank, our focus now is on not missing a secondary consequence of COVID infection that we might not have picked up before. I’m the first to admit that the workup that we have been doing at UCSF is extremely comprehensive. We may be ordering tests that don’t need to be done. But until we know better what might and might not be affected by COVID, we don’t actually have a sense of whether they’re worth looking for or not.
Right now, my workup includes nasal swab polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for COVID, as well as IgG and IgM serology if available. We have IgG easily available to us. IgM needs approval; at UCSF, it is primarily done in neonates as of now. I also do a workup for autoimmunity and cold-associated disease, which includes an ANA, rheumatoid factor, cryoglobulin, and cold agglutinins.
Because of reported concerns about hypercoagulability in COVID patients, particularly in those who are doing poorly in the hospital, we look for elevations in d-dimers and fibrinogen. We check antiphospholipid antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein. That is probably too much of a workup for the healthy young person, but as of yet, we are just unable to say that those things are universally normal.
There has also been concern that complement may be involved in patients who do poorly and tend to clot a lot. So we are also checking C3, C4, and CH50.
To date, in my patients who have had this workup, I have found one with a positive ANA that was significant (1:320) who also had low complements.
There have been a couple of patients at my institution, not my own patients, who are otherwise fine but have some slight elevation in d-dimers.
Dr. Lipper: Is COVID toes more than one condition?
Some of the initial reports of finger/toe cyanosis out of China were very alarming, with many patients developing skin necrosis or even gangrene. These were critically ill adults with pneumonia and blood markers of disseminated intravascular coagulation, and five out of seven died. In contrast, the cases of pseudo-pernio reported in Europe, and now the United States, seem to be much milder, usually occurring late in the illness or in asymptomatic young people. Do you think these are two different conditions?
Dr. Fox: I believe you have hit the nail on the head. I think it is really important that we don’t confuse those two things. In the inpatient setting, we are clearly seeing patients with a prothrombotic state with associated retiform purpura. For nondermatologists, that usually means star-like, stellate-like, or even lacy purpuric changes with potential for necrosis of the skin. In hospitalized patients, the fingers and toes are usually affected but, interestingly, also the buttocks. When these lesions are biopsied, as has been done by our colleague at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, Joanna Harp, MD, we tend to find thrombosis.
A study of endothelial cell function in patients with COVID-19, published in the Lancet tried to determine whether viral particles could be found in endothelial cells. And the investigators did indeed find these particles. So it appears that the virus is endothelially active, and this might provide some insight into the thromboses seen in hospitalized patients. These patients can develop purple necrotic toes that may progress to gangrene. But that is completely different from what we’re seeing when we say pernio-like or chilblains-like lesions.
The chilblains-like lesions come in several forms. They may be purple, red bumps, often involving the tops of the toes and sometimes the bottom of the feet. Some have been described as target-like or erythema multiforme–like. In others, there may not be individual discrete lesions but rather a redness or bluish, purplish discoloration accompanied by edema of the entire toe or several toes.
Biopsies that I am aware of have identified features consistent with an inflammatory process, all of which can be seen in a typical biopsy of pernio. You can sometimes see lymphocytes surrounding a vessel (called lymphocytic vasculitis) that may damage a vessel and cause a small clot, but the primary process is an inflammatory rather than thrombotic one. You may get a clot in a little tiny vessel secondary to inflammation, and that may lead to some blisters or little areas of necrosis. But you’re not going to see digital necrosis and gangrene. I think that’s an important distinction.
The patients who get the pernio-like lesions are typically children or young adults and are otherwise healthy. Half of them didn’t even have COVID symptoms. If they did have COVID symptoms they were typically mild. So we think the pernio-like lesions are most often occurring in the late stage of the disease and now represent a secondary inflammatory response.
Managing COVID toes
Dr. Lipper: One question I’ve been struggling with is, what do we tell these otherwise healthy patients with purple toes, especially those with no other symptoms? Many of them are testing SARS-CoV-2 negative, both with viral swabs and serologies. Some have suggestive histories like known COVID exposure, recent cough, or travel to high-risk areas. Do we tell them they’re at risk of transmitting the virus? Should they self-quarantine, and for how long? Is there any consensus emerging?
Dr. Fox: This is a good opportunity to plug the American Academy of Dermatology’s COVID-19 Registry, which is run by Esther Freeman, MD, at Massachusetts General Hospital. She has done a phenomenal job in helping us figure out the answers to these exact questions.
I’d encourage any clinicians who have a suspected COVID patient with a skin finding, whether or not infection is confirmed with testing, to enter information about that patient into the registry. That is the only way we will figure out evidence-based answers to a lot of the questions that we’re talking about today.
Based on working with the registry, we know that, rarely, patients who develop pernio-like changes will do so before they get COVID symptoms or at the same time as more typical symptoms. Some patients with these findings are PCR positive, and it is therefore theoretically possible that you could be shedding virus while you’re having the pernio toes. However, more commonly – and this is the experience of most of my colleagues and what we’re seeing at UCSF – pernio is a later finding and most patients are no longer shedding the virus. It appears that pseudo-pernio is an immune reaction and most people are not actively infectious at that point.
The only way to know for sure is to send patients for both PCR testing and antibody testing. If the PCR is negative, the most likely interpretation is that the person is no longer shedding virus, though there can be some false negatives. Therefore, these patients do not need to isolate outside of what I call their COVID pod – family or roommates who have probably been with them the whole time. Any transmission likely would have already occurred.
I tell people who call me concerned about their toes that I do think they should be given a workup for COVID. However, I reassure them that it is usually a good prognostic sign.
What is puzzling is that even in patients with pseudo-chilblains who have a clinical history consistent with COVID or exposure to a COVID-positive family member, antibody testing is often – in fact, most often – negative. There are many hypotheses as to why this is. Maybe the tests just aren’t good. Maybe people with mild disease don’t generate enough antibodies to be detected, Maybe we’re testing at the wrong time. Those are all things that we’re trying to figure out.
But currently, I tell patients that they do not need to strictly isolate. They should still practice social distancing, wear a mask, practice good hand hygiene, and do all of the careful things that we should all be doing. However, they can live within their home environment and be reassured that most likely they are in the convalescent stage.
Dr. Lipper: I find the antibody issue both fascinating and confusing.
In my practice, we’ve noticed a range of symptoms associated with pseudo-pernio. Some people barely realize it’s there and only called because they saw a headline in the news. Others complain of severe burning, throbbing, or itching that keeps them up at night and can sometimes last for weeks. Are there any treatments that seem to help?
Dr. Fox: We can start by saying, as you note, that a lot of patients don’t need interventions. They want reassurance that their toes aren’t going to fall off, that nothing terrible is going to happen to them, and often that’s enough. So far, many patients have contacted us just because they heard about the link between what they were seeing on their feet and COVID. They were likely toward the end of any other symptoms they may have had. But moving forward, I think we’re going to be seeing patients at the more active stage as the public is more aware of this finding.
Most of the time we can manage with clobetasol ointment and low-dose aspirin. I wouldn’t give aspirin to a young child with a high fever, but otherwise I think aspirin is not harmful. A paper published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings in 2014, before COVID, by Jonathan Cappel, MD, and David Wetter, MD, provides a nice therapeutic algorithm. Assuming that the findings we are seeing now are inflammatory, then I think that algorithm should apply. Nifedipine 20-60 mg/day is an option. Hydroxychloroquine, a maximum of 5 mg/kg per day, is an option. I have used hydroxychloroquine most commonly, pre-COVID, in patients who have symptomatic pernio.
I also use pentoxifylline 400 mg three times a day, which has a slight anti-inflammatory effect, when I think a blood vessel is incidentally involved or the patient has a predisposition to clotting. Nicotinamide 500 mg three times a day can be used, though I have not used it.
Some topical options are nitroglycerin, tacrolimus, and minoxidil.
However, during this post-COVID period, I have not come across many with pseudo-pernio who needed anything more than a topical steroid and some aspirin. But I do know of other physicians who have been taking care of patients with much more symptomatic disease.
Dr. Lipper: That is a comprehensive list. You’ve mentioned some options that I’ve wondered about, especially pentoxifylline, which I have found to be very helpful for livedoid vasculopathy. I should note that these are all off-label uses.
Let’s talk about some other suspected skin manifestations of COVID. A prospective nationwide study in Spain of 375 patients reported on a number of different skin manifestations of COVID.
You’re part of a team doing critically important work with the American Academy of Dermatology COVID-19 Dermatology Registry. I know it’s early going, but what are some of the other common skin presentations you’re finding?
Dr. Fox: I’m glad you brought up that paper out of Spain. I think it is really good and does highlight the difference in acute versus convalescent cutaneous manifestations and prognosis. It confirms what we’re seeing. Retiform purpura is an early finding associated with ill patients in the hospital. Pseudo pernio-like lesions tend to be later-stage and in younger, healthier patients.
Interestingly, the vesicular eruption that those investigators describe – monomorphic vesicles on the trunk and extremity – can occur in the more acute phase. That’s fascinating to me because widespread vesicular eruptions are not a thing that we commonly see. If it is not an autoimmune blistering disease, and not a drug-induced blistering process, then you’re really left with viral. Rickettsialpox can do that, as can primary varicella, disseminated herpes, disseminated zoster, and now COVID. So that’s intriguing.
I got called to see a patient yesterday who had symptoms of COVID about a month ago. She was not PCR tested at the time but she is now negative. She has a widespread eruption of tiny vesicles on an erythematous base. An IgG for COVID is positive. How do we decide whether her skin lesions have active virus in them?
The many dermatologic manifestations of COVID-19
Dr. Lipper: In the series in Spain, almost 1 out of 10 patients were found to have a widespread vesicular rash. And just under half had maculopapular exanthems. The information arising from the AAD registry will be of great interest and build on this paper.
In England, the National Health Service and the Paediatric Intensive Care Society recently put out a warning about an alarming number of children with COVID-19 who developed symptoms mimicking Kawasaki disease (high fever, abdominal pain, rash, swollen lymph nodes, mucositis, and conjunctivitis). These kids have systemic inflammation and vasculitis and are critically ill. That was followed by an alert from the New York City Health Department about cases there, which as of May 6 numbered 64. Another 25 children with similar findings have been identified in France.
This is such a scary development, especially because children were supposed to be relatively “safe” from this virus. Any thoughts on who is at risk or why?
Dr. Fox: It’s very alarming. It appears that these cases look just like Kawasaki disease.
It was once hypothesized that Coronaviridae was the cause of Kawasaki disease. Then that got debunked. But these cases now raise the question of whether Kawasaki disease may be virally mediated. Is it an immune reaction to an infectious trigger? Is it actually Coronaviridae that triggers it?
As with these pernio cases, I think we’re going to learn about the pathophysiology of these diseases that we currently look at as secondary responses or immune reactions to unknown triggers. We’re going to learn a lot about them and about the immune system because of how this virus is acting on the immune system.
Dr. Lipper: As is the case with patients with pernio-like lesions, some of these children with Kawasaki-like disease are PCR negative for SARS-CoV-2. It will be interesting to see what happens with antibody testing in this population.
Dr. Fox: Agree. While some of the manufacturers of serology tests have claimed that they have very high sensitivity and specificity, that has not been my experience.
Dr. Lipper: I’ve had a number of patients with a clinical picture that strongly suggests COVID whose serology tests have been negative.
Dr. Fox: As have I. While this could be the result of faulty tests, my biggest worry is that it means that people with mild disease do not mount an antibody response. And if people who have disease can’t make antibodies, then there’s no herd immunity. If there’s no herd immunity, we’re stuck in lockdown until there’s a vaccine.
Dr. Lipper: That is a scary but real possibility. We need evidence – evidence like that provided by the AAD registry.
Dr. Fox: Agree. I look forward to sharing those results with you when we have them.
Dr. Lipper is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and a partner at Advanced DermCare in Danbury, Conn.
Dr. Fox is a professor in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She is a hospital-based dermatologist who specializes in the care of patients with complex skin conditions. She is immediate past president of the Medical Dermatology Society and current president of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists.
This article was first published on Medscape.com.
The dermatologic manifestations associated with SARS-CoV-2 are many and varied, with new information virtually daily. Graeme Lipper, MD, a member of the Medscape Dermatology advisory board, discussed what we know and what is still to be learned with Lindy Fox, MD, a professor of dermatology at University of California, San Francisco (UCSF) and a member of the American Academy of Dermatology’s COVID-19 Registry task force.
Graeme M. Lipper, MD
Earlier this spring, before there was any real talk about skin manifestations of COVID, my partner called me in to see an unusual case. His patient was a healthy 20-year-old who had just come back from college and had tender, purple discoloration and swelling on his toes. I shrugged and said “looks like chilblains,” but there was something weird about the case. It seemed more severe, with areas of blistering and erosions, and the discomfort was unusual for run-of-the-mill pernio. This young man had experienced a cough and shortness of breath a few weeks earlier but those symptoms had resolved when we saw him.
That evening, I was on a derm social media site and saw a series of pictures from Italy that blew me away. All of these pictures looked just like this kid’s toes. That’s the first I heard of “COVID toes,” but now they seem to be everywhere. How would you describe this presentation, and how does it differ from typical chilblains?
Lindy P. Fox, MD
I am so proud of dermatologists around the world who have really jumped into action to examine the pathophysiology and immunology behind these findings.
Your experience matches mine. Like you, I first heard about these pernio- or chilblains-like lesions when Europe was experiencing its surge in cases. And while it does indeed look like chilblains, I think the reality is that it is more severe and symptomatic than we would expect. I think your observation is exactly right. There are certainly clinicians who do not believe that this is an association with COVID-19 because the testing is often negative. But to my mind, there are just too many cases at the wrong time of year, all happening concomitantly, and simultaneous with a new virus for me to accept that they are not somehow related.
Dr. Lipper: Some have referred to this as “quarantine toes,” the result of more people at home and walking around barefoot. That doesn’t seem to make a whole lot of sense because it’s happening in both warm and cold climates.
Others have speculated that there is another, unrelated circulating virus causing these pernio cases, but that seems far-fetched.
But the idea of a reporting bias – more patients paying attention to these lesions because they’ve read something in the mass media or seen a report on television and are concerned, and thus present with mild lesions they might otherwise have ignored – may be contributing somewhat. But even that cannot be the sole reason behind the increase.
Dr. Fox: Agree.
Evaluation of the patient with chilblains – then and now
Dr. Lipper: In the past, how did you perform a workup for someone with chilblains?
Dr. Fox: Pre-COVID – and I think we all have divided our world into pre- and post-COVID – the most common thing that I’d be looking for would be a clotting disorder or an autoimmune disease, typically lupus. So I take a good history, review of systems, and look at the skin for signs of lupus or other autoimmune connective tissue diseases. My lab workup is probably limited to an antinuclear antibody (ANA). If the findings are severe and recurrent, I might check for hypercoagulability with an antiphospholipid antibody panel. But that was usually it unless there was something in the history or physical exam that would lead me to look for something less common – for example, cryoglobulins or an underlying hematologic disease that would lead to a predominance of lesions in acral sites.
My approach was the same. In New England, where I practice, I also always look at environmental factors. We would sometimes see chilblains in someone from a warmer climate who came home to the Northeast to ski.
Dr. Lipper: Now, in the post-COVID world, how do you assess these patients? What has changed?
Dr. Fox: That’s a great question. To be frank, our focus now is on not missing a secondary consequence of COVID infection that we might not have picked up before. I’m the first to admit that the workup that we have been doing at UCSF is extremely comprehensive. We may be ordering tests that don’t need to be done. But until we know better what might and might not be affected by COVID, we don’t actually have a sense of whether they’re worth looking for or not.
Right now, my workup includes nasal swab polymerase chain reaction (PCR) for COVID, as well as IgG and IgM serology if available. We have IgG easily available to us. IgM needs approval; at UCSF, it is primarily done in neonates as of now. I also do a workup for autoimmunity and cold-associated disease, which includes an ANA, rheumatoid factor, cryoglobulin, and cold agglutinins.
Because of reported concerns about hypercoagulability in COVID patients, particularly in those who are doing poorly in the hospital, we look for elevations in d-dimers and fibrinogen. We check antiphospholipid antibodies, anticardiolipin antibodies, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein. That is probably too much of a workup for the healthy young person, but as of yet, we are just unable to say that those things are universally normal.
There has also been concern that complement may be involved in patients who do poorly and tend to clot a lot. So we are also checking C3, C4, and CH50.
To date, in my patients who have had this workup, I have found one with a positive ANA that was significant (1:320) who also had low complements.
There have been a couple of patients at my institution, not my own patients, who are otherwise fine but have some slight elevation in d-dimers.
Dr. Lipper: Is COVID toes more than one condition?
Some of the initial reports of finger/toe cyanosis out of China were very alarming, with many patients developing skin necrosis or even gangrene. These were critically ill adults with pneumonia and blood markers of disseminated intravascular coagulation, and five out of seven died. In contrast, the cases of pseudo-pernio reported in Europe, and now the United States, seem to be much milder, usually occurring late in the illness or in asymptomatic young people. Do you think these are two different conditions?
Dr. Fox: I believe you have hit the nail on the head. I think it is really important that we don’t confuse those two things. In the inpatient setting, we are clearly seeing patients with a prothrombotic state with associated retiform purpura. For nondermatologists, that usually means star-like, stellate-like, or even lacy purpuric changes with potential for necrosis of the skin. In hospitalized patients, the fingers and toes are usually affected but, interestingly, also the buttocks. When these lesions are biopsied, as has been done by our colleague at Weill Cornell Medicine, New York, Joanna Harp, MD, we tend to find thrombosis.
A study of endothelial cell function in patients with COVID-19, published in the Lancet tried to determine whether viral particles could be found in endothelial cells. And the investigators did indeed find these particles. So it appears that the virus is endothelially active, and this might provide some insight into the thromboses seen in hospitalized patients. These patients can develop purple necrotic toes that may progress to gangrene. But that is completely different from what we’re seeing when we say pernio-like or chilblains-like lesions.
The chilblains-like lesions come in several forms. They may be purple, red bumps, often involving the tops of the toes and sometimes the bottom of the feet. Some have been described as target-like or erythema multiforme–like. In others, there may not be individual discrete lesions but rather a redness or bluish, purplish discoloration accompanied by edema of the entire toe or several toes.
Biopsies that I am aware of have identified features consistent with an inflammatory process, all of which can be seen in a typical biopsy of pernio. You can sometimes see lymphocytes surrounding a vessel (called lymphocytic vasculitis) that may damage a vessel and cause a small clot, but the primary process is an inflammatory rather than thrombotic one. You may get a clot in a little tiny vessel secondary to inflammation, and that may lead to some blisters or little areas of necrosis. But you’re not going to see digital necrosis and gangrene. I think that’s an important distinction.
The patients who get the pernio-like lesions are typically children or young adults and are otherwise healthy. Half of them didn’t even have COVID symptoms. If they did have COVID symptoms they were typically mild. So we think the pernio-like lesions are most often occurring in the late stage of the disease and now represent a secondary inflammatory response.
Managing COVID toes
Dr. Lipper: One question I’ve been struggling with is, what do we tell these otherwise healthy patients with purple toes, especially those with no other symptoms? Many of them are testing SARS-CoV-2 negative, both with viral swabs and serologies. Some have suggestive histories like known COVID exposure, recent cough, or travel to high-risk areas. Do we tell them they’re at risk of transmitting the virus? Should they self-quarantine, and for how long? Is there any consensus emerging?
Dr. Fox: This is a good opportunity to plug the American Academy of Dermatology’s COVID-19 Registry, which is run by Esther Freeman, MD, at Massachusetts General Hospital. She has done a phenomenal job in helping us figure out the answers to these exact questions.
I’d encourage any clinicians who have a suspected COVID patient with a skin finding, whether or not infection is confirmed with testing, to enter information about that patient into the registry. That is the only way we will figure out evidence-based answers to a lot of the questions that we’re talking about today.
Based on working with the registry, we know that, rarely, patients who develop pernio-like changes will do so before they get COVID symptoms or at the same time as more typical symptoms. Some patients with these findings are PCR positive, and it is therefore theoretically possible that you could be shedding virus while you’re having the pernio toes. However, more commonly – and this is the experience of most of my colleagues and what we’re seeing at UCSF – pernio is a later finding and most patients are no longer shedding the virus. It appears that pseudo-pernio is an immune reaction and most people are not actively infectious at that point.
The only way to know for sure is to send patients for both PCR testing and antibody testing. If the PCR is negative, the most likely interpretation is that the person is no longer shedding virus, though there can be some false negatives. Therefore, these patients do not need to isolate outside of what I call their COVID pod – family or roommates who have probably been with them the whole time. Any transmission likely would have already occurred.
I tell people who call me concerned about their toes that I do think they should be given a workup for COVID. However, I reassure them that it is usually a good prognostic sign.
What is puzzling is that even in patients with pseudo-chilblains who have a clinical history consistent with COVID or exposure to a COVID-positive family member, antibody testing is often – in fact, most often – negative. There are many hypotheses as to why this is. Maybe the tests just aren’t good. Maybe people with mild disease don’t generate enough antibodies to be detected, Maybe we’re testing at the wrong time. Those are all things that we’re trying to figure out.
But currently, I tell patients that they do not need to strictly isolate. They should still practice social distancing, wear a mask, practice good hand hygiene, and do all of the careful things that we should all be doing. However, they can live within their home environment and be reassured that most likely they are in the convalescent stage.
Dr. Lipper: I find the antibody issue both fascinating and confusing.
In my practice, we’ve noticed a range of symptoms associated with pseudo-pernio. Some people barely realize it’s there and only called because they saw a headline in the news. Others complain of severe burning, throbbing, or itching that keeps them up at night and can sometimes last for weeks. Are there any treatments that seem to help?
Dr. Fox: We can start by saying, as you note, that a lot of patients don’t need interventions. They want reassurance that their toes aren’t going to fall off, that nothing terrible is going to happen to them, and often that’s enough. So far, many patients have contacted us just because they heard about the link between what they were seeing on their feet and COVID. They were likely toward the end of any other symptoms they may have had. But moving forward, I think we’re going to be seeing patients at the more active stage as the public is more aware of this finding.
Most of the time we can manage with clobetasol ointment and low-dose aspirin. I wouldn’t give aspirin to a young child with a high fever, but otherwise I think aspirin is not harmful. A paper published in Mayo Clinic Proceedings in 2014, before COVID, by Jonathan Cappel, MD, and David Wetter, MD, provides a nice therapeutic algorithm. Assuming that the findings we are seeing now are inflammatory, then I think that algorithm should apply. Nifedipine 20-60 mg/day is an option. Hydroxychloroquine, a maximum of 5 mg/kg per day, is an option. I have used hydroxychloroquine most commonly, pre-COVID, in patients who have symptomatic pernio.
I also use pentoxifylline 400 mg three times a day, which has a slight anti-inflammatory effect, when I think a blood vessel is incidentally involved or the patient has a predisposition to clotting. Nicotinamide 500 mg three times a day can be used, though I have not used it.
Some topical options are nitroglycerin, tacrolimus, and minoxidil.
However, during this post-COVID period, I have not come across many with pseudo-pernio who needed anything more than a topical steroid and some aspirin. But I do know of other physicians who have been taking care of patients with much more symptomatic disease.
Dr. Lipper: That is a comprehensive list. You’ve mentioned some options that I’ve wondered about, especially pentoxifylline, which I have found to be very helpful for livedoid vasculopathy. I should note that these are all off-label uses.
Let’s talk about some other suspected skin manifestations of COVID. A prospective nationwide study in Spain of 375 patients reported on a number of different skin manifestations of COVID.
You’re part of a team doing critically important work with the American Academy of Dermatology COVID-19 Dermatology Registry. I know it’s early going, but what are some of the other common skin presentations you’re finding?
Dr. Fox: I’m glad you brought up that paper out of Spain. I think it is really good and does highlight the difference in acute versus convalescent cutaneous manifestations and prognosis. It confirms what we’re seeing. Retiform purpura is an early finding associated with ill patients in the hospital. Pseudo pernio-like lesions tend to be later-stage and in younger, healthier patients.
Interestingly, the vesicular eruption that those investigators describe – monomorphic vesicles on the trunk and extremity – can occur in the more acute phase. That’s fascinating to me because widespread vesicular eruptions are not a thing that we commonly see. If it is not an autoimmune blistering disease, and not a drug-induced blistering process, then you’re really left with viral. Rickettsialpox can do that, as can primary varicella, disseminated herpes, disseminated zoster, and now COVID. So that’s intriguing.
I got called to see a patient yesterday who had symptoms of COVID about a month ago. She was not PCR tested at the time but she is now negative. She has a widespread eruption of tiny vesicles on an erythematous base. An IgG for COVID is positive. How do we decide whether her skin lesions have active virus in them?
The many dermatologic manifestations of COVID-19
Dr. Lipper: In the series in Spain, almost 1 out of 10 patients were found to have a widespread vesicular rash. And just under half had maculopapular exanthems. The information arising from the AAD registry will be of great interest and build on this paper.
In England, the National Health Service and the Paediatric Intensive Care Society recently put out a warning about an alarming number of children with COVID-19 who developed symptoms mimicking Kawasaki disease (high fever, abdominal pain, rash, swollen lymph nodes, mucositis, and conjunctivitis). These kids have systemic inflammation and vasculitis and are critically ill. That was followed by an alert from the New York City Health Department about cases there, which as of May 6 numbered 64. Another 25 children with similar findings have been identified in France.
This is such a scary development, especially because children were supposed to be relatively “safe” from this virus. Any thoughts on who is at risk or why?
Dr. Fox: It’s very alarming. It appears that these cases look just like Kawasaki disease.
It was once hypothesized that Coronaviridae was the cause of Kawasaki disease. Then that got debunked. But these cases now raise the question of whether Kawasaki disease may be virally mediated. Is it an immune reaction to an infectious trigger? Is it actually Coronaviridae that triggers it?
As with these pernio cases, I think we’re going to learn about the pathophysiology of these diseases that we currently look at as secondary responses or immune reactions to unknown triggers. We’re going to learn a lot about them and about the immune system because of how this virus is acting on the immune system.
Dr. Lipper: As is the case with patients with pernio-like lesions, some of these children with Kawasaki-like disease are PCR negative for SARS-CoV-2. It will be interesting to see what happens with antibody testing in this population.
Dr. Fox: Agree. While some of the manufacturers of serology tests have claimed that they have very high sensitivity and specificity, that has not been my experience.
Dr. Lipper: I’ve had a number of patients with a clinical picture that strongly suggests COVID whose serology tests have been negative.
Dr. Fox: As have I. While this could be the result of faulty tests, my biggest worry is that it means that people with mild disease do not mount an antibody response. And if people who have disease can’t make antibodies, then there’s no herd immunity. If there’s no herd immunity, we’re stuck in lockdown until there’s a vaccine.
Dr. Lipper: That is a scary but real possibility. We need evidence – evidence like that provided by the AAD registry.
Dr. Fox: Agree. I look forward to sharing those results with you when we have them.
Dr. Lipper is a clinical assistant professor at the University of Vermont, Burlington, and a partner at Advanced DermCare in Danbury, Conn.
Dr. Fox is a professor in the department of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She is a hospital-based dermatologist who specializes in the care of patients with complex skin conditions. She is immediate past president of the Medical Dermatology Society and current president of the Society of Dermatology Hospitalists.
This article was first published on Medscape.com.
Planning for a psychiatric COVID-19–positive unit
Identifying key decision points is critical
Reports have emerged about the unique vulnerability of psychiatric hospitals to the ravages of COVID-19.
In a South Korea psychiatric hospital, 101 of 103 patients contracted SARS-CoV-2 during an outbreak; 7 eventually died.1,2 This report, among a few others, have led to the development of psychiatric COVID-19–positive units (PCU). However, it remains highly unclear how many are currently open, where they are located, or what their operations are like.
We knew that we could not allow a medically asymptomatic “covertly” COVID-19–positive patient to be introduced to the social community of our inpatient units because of the risks of transmission to other patients and staff.
In coordination with our health system infection prevention experts, we have therefore required a confirmed negative COVID-19 polymerase chain reaction nasal swab performed no more than 48 hours prior to the time/date of acute psychiatric inpatient admission. Furthermore, as part of the broad health system response and surge planning, we were asked by our respective incident command centers to begin planning for a Psychiatric COVID-19–positive Unit (PCU) that might allow us to safely care for a cohort of patients needing such hospitalization.
It is worth emphasizing that the typical patient who is a candidate for a PCU is so acutely psychiatrically ill that they cannot be managed in a less restrictive environment than an inpatient psychiatric unit and, at the same time, is likely to not be medically ill enough to warrant admission to an internal medicine service in a general acute care hospital.
We have identified eight principles and critical decision points that can help inpatient units plan for the safe care of COVID-19–positive patients on a PCU.
1. Triage: Patients admitted to a PCU should be medically stable, particularly with regard to COVID-19 and respiratory symptomatology. PCUs should establish clear criteria for admission and discharge (or medical transfer). Examples of potential exclusionary criteria to a PCU include:
- Respiratory distress, shortness of breath, hypoxia, requirement for supplemental oxygen, or requirement for respiratory therapy breathing treatments.
- Fever, or signs of sepsis, or systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
- Medical frailty, significant medical comorbidities, delirium, or altered mental status;
- Requirements for continuous vital sign monitoring or of a monitoring frequency beyond the capacity of the PCU.
Discharge criteria may also include a symptom-based strategy because emerging evidence suggests that patients may be less infectious by day 10-14 of the disease course,3 and viral lab testing is very sensitive and will be positive for periods of time after individuals are no longer infectious. The symptom-based strategy allows for patients to not require retesting prior to discharge. However, some receiving facilities (for example residential or skilled nursing facilities) may necessitate testing, in which case a testing-based strategy can be used. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides guidelines for both types of strategies.4
2. Infection control and personal protective equipment: PCUs require modifications or departures from the typical inpatient free-ranging environment in which common areas are provided for patients to engage in a community of care, including group therapy (such as occupational, recreational, Alcoholics Anonymous, and social work groups).
- Isolation: PCUs must consider whether they will require patients to isolate to their rooms or to allow modified or limited access to “public” or “community” areas. While there do not appear to be standard recommendations from the CDC or other public health entities regarding negative pressure or any specific room ventilation requirements, it is prudent to work with local infectious disease experts on protocols. Important considerations include spatial planning for infection control areas to don and doff appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and appropriate workspace to prevent contamination of non–COVID-19 work areas. Approaches can include establishing clearly identified and visually demarcated infection control “zones” (often referred to as “hot, warm, and cold zones”) that correspond to specific PPE requirements for staff. In addition, individuals should eat in their own rooms or designated areas because use of common areas for meals can potentially lead to aerosolized spread of the virus.
- Cohorting: Generally, PCUs should consider admitting only COVID-19–positive patients to a PCU to avoid exposure to other patients. Hospitals and health systems should determine protocols and locations for testing and managing “patients under investigation” for COVID-19, which should precede admission to the PCU.
- PPE: It is important to clearly establish and communicate PPE requirements and procedures for direct physical contact versus no physical contact (for example, visual safety checks). Identify clear supply chains for PPE and hand sanitizer.
3. Medical management and consultation: PCUs should establish clear pathways for accessing consultation from medical consultants. It may be ideal, in addition to standard daily psychiatric physician rounding, to have daily internal medicine rounding and/or medical nursing staff working on the unit. Given the potential of COVID-19–positive patients to rapidly devolve from asymptomatic to acutely ill, it is necessary to establish protocols for the provision of urgent medical care 24/7 and streamlined processes for transfer to a medical unit.
Clear protocols should be established to address any potential signs of decompensation in the respiratory status of a PCU unit, including administration of oxygen and restrictions (or appropriate precautions) related to aerosolizing treatment such as nebulizers or positive airway pressure.
4. Code blue protocol: Any emergent medical issues, including acute respiratory decompensation, should trigger a Code Blue response that has been specifically designed for COVID-19–positive patients, including considerations for proper PPE during resuscitation efforts.
5. Psychiatric staffing and workflows: When possible, it may be preferable to engage volunteer medical and nursing staff for the PCU, as opposed to mandating participation. Take into consideration support needs, including education and training about safe PPE practices, processes for testing health care workers, return-to-work guidance, and potential alternate housing.
- Telehealth: Clinicians (such as physicians, social workers, occupational therapists) should leverage and maximize the use of telemedicine to minimize direct or prolonged exposure to infectious disease risks.
- Nursing: It is important to establish appropriate ratios of nursing and support staff for a COVID-19–positive psychiatry unit given the unique work flows related to isolation precautions and to ensure patient and staff safety. These ratios may take into account patient-specific needs, including the need for additional staff to perform constant observation for high-risk patients, management of agitated patients, and sufficient staff to allow for relief and break-time from PPE. Admission and routine care processes should be adapted in order to limit equipment entering the room, such as computer workstations on wheels.
- Medication administration procedures: Develop work flows related to PPE and infection control when retrieving and administering medications.
- Workspace: Designate appropriate workspace for PCU clinicians to access computers and documents and to minimize use of non–COVID-19 unit work areas.
6. Restraints and management of agitated patients: PCUs should develop plans for addressing agitated patients, including contingency plans for whether seclusion or restraints should be administered in the patient’s individual room or in a dedicated restraint room in the PCU. Staff training should include protocols specifically designed for managing agitated patients in the PCU.
7. Discharge processes: If patients remain medically well and clear their COVID-19 PCR tests, it is conceivable that they might be transferred to a non–COVID-19 psychiatric unit if sufficient isolation time has passed and the infectious disease consultants deem it appropriate. It is also possible that patients would be discharged from a PCU to home or other residential setting. Such patients should be assessed for ability to comply with continued self-quarantine if necessary. Discharge planning must take into consideration follow-up plans for COVID-19 illness and primary care appointments, as well as needed psychiatric follow-up.
8. Patients’ rights: The apparently highly infectious and transmissible nature of SARS-CoV-2 creates novel tensions between a wide range of individual rights and the rights of others. In addition to manifesting in our general society, there are potentially unique tensions in acute inpatient psychiatric settings. Certain patients’ rights may require modification in a PCU (for example, access to outdoor space, personal belongings, visitors, and possibly civil commitment judicial hearings). These discussions may require input from hospital compliance officers, ethics committees, risk managers, and the local department of mental health and also may be partly solved by using video communication platforms.
A few other “pearls” may be of value: Psychiatric hospitals that are colocated with a general acute care hospital or ED might be better situated to develop protocols to safely care for COVID-19–positive psychiatric patients, by virtue of the close proximity of full-spectrum acute general hospital services. Direct engagement by a command center and hospital or health system senior leadership also seems crucial as a means for assuring authorization to proceed with planning what may be a frightening or controversial (but necessary) adaptation of inpatient psychiatric unit(s) to the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The resources of a robust community hospital or academic health system (including infection prevention leaders who engage in continuous liaison with local, county, state, and federal public health expertise) are crucial to the “learning health system” model, which requires flexibility, rapid adaptation to new knowledge, and accessibility to infectious disease and other consultation for special situations. Frequent and open communication with all professional stakeholders (through town halls, Q&A sessions, group discussions, and so on) is important in the planning process to socialize the principles and concepts that are critical for providing care in a PCU, reducing anxiety, and bolstering collegiality and staff morale.
References
1. Kim MJ. “ ‘It was a medical disaster’: The psychiatric ward that saw 100 patients with new coronavirus.” Independent. 2020 Mar 1.
2. Korean Society of Infectious Diseases et al. J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Mar 16;35(10):e112.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptom-based strategy to discontinue isolation for persons with COVID-19. Decision Memo. 2020 May 3.
4. He X et al. Nature Medicine. 2020. 26:672-5.
Dr. Cheung is associate medical director and chief quality officer at the Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Strouse is medical director, UCLA Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital and Maddie Katz Professor at the UCLA department of psychiatry/Semel Institute. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Li is associate medical director of quality improvement at Yale-New Haven Psychiatric Hospital in Connecticut. She also serves as medical director of clinical operations at the Yale-New Haven Health System. Dr. Li is a 2019-2020 Health and Aging Policy Fellow and receives funding support from the program.
Identifying key decision points is critical
Identifying key decision points is critical
Reports have emerged about the unique vulnerability of psychiatric hospitals to the ravages of COVID-19.
In a South Korea psychiatric hospital, 101 of 103 patients contracted SARS-CoV-2 during an outbreak; 7 eventually died.1,2 This report, among a few others, have led to the development of psychiatric COVID-19–positive units (PCU). However, it remains highly unclear how many are currently open, where they are located, or what their operations are like.
We knew that we could not allow a medically asymptomatic “covertly” COVID-19–positive patient to be introduced to the social community of our inpatient units because of the risks of transmission to other patients and staff.
In coordination with our health system infection prevention experts, we have therefore required a confirmed negative COVID-19 polymerase chain reaction nasal swab performed no more than 48 hours prior to the time/date of acute psychiatric inpatient admission. Furthermore, as part of the broad health system response and surge planning, we were asked by our respective incident command centers to begin planning for a Psychiatric COVID-19–positive Unit (PCU) that might allow us to safely care for a cohort of patients needing such hospitalization.
It is worth emphasizing that the typical patient who is a candidate for a PCU is so acutely psychiatrically ill that they cannot be managed in a less restrictive environment than an inpatient psychiatric unit and, at the same time, is likely to not be medically ill enough to warrant admission to an internal medicine service in a general acute care hospital.
We have identified eight principles and critical decision points that can help inpatient units plan for the safe care of COVID-19–positive patients on a PCU.
1. Triage: Patients admitted to a PCU should be medically stable, particularly with regard to COVID-19 and respiratory symptomatology. PCUs should establish clear criteria for admission and discharge (or medical transfer). Examples of potential exclusionary criteria to a PCU include:
- Respiratory distress, shortness of breath, hypoxia, requirement for supplemental oxygen, or requirement for respiratory therapy breathing treatments.
- Fever, or signs of sepsis, or systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
- Medical frailty, significant medical comorbidities, delirium, or altered mental status;
- Requirements for continuous vital sign monitoring or of a monitoring frequency beyond the capacity of the PCU.
Discharge criteria may also include a symptom-based strategy because emerging evidence suggests that patients may be less infectious by day 10-14 of the disease course,3 and viral lab testing is very sensitive and will be positive for periods of time after individuals are no longer infectious. The symptom-based strategy allows for patients to not require retesting prior to discharge. However, some receiving facilities (for example residential or skilled nursing facilities) may necessitate testing, in which case a testing-based strategy can be used. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides guidelines for both types of strategies.4
2. Infection control and personal protective equipment: PCUs require modifications or departures from the typical inpatient free-ranging environment in which common areas are provided for patients to engage in a community of care, including group therapy (such as occupational, recreational, Alcoholics Anonymous, and social work groups).
- Isolation: PCUs must consider whether they will require patients to isolate to their rooms or to allow modified or limited access to “public” or “community” areas. While there do not appear to be standard recommendations from the CDC or other public health entities regarding negative pressure or any specific room ventilation requirements, it is prudent to work with local infectious disease experts on protocols. Important considerations include spatial planning for infection control areas to don and doff appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and appropriate workspace to prevent contamination of non–COVID-19 work areas. Approaches can include establishing clearly identified and visually demarcated infection control “zones” (often referred to as “hot, warm, and cold zones”) that correspond to specific PPE requirements for staff. In addition, individuals should eat in their own rooms or designated areas because use of common areas for meals can potentially lead to aerosolized spread of the virus.
- Cohorting: Generally, PCUs should consider admitting only COVID-19–positive patients to a PCU to avoid exposure to other patients. Hospitals and health systems should determine protocols and locations for testing and managing “patients under investigation” for COVID-19, which should precede admission to the PCU.
- PPE: It is important to clearly establish and communicate PPE requirements and procedures for direct physical contact versus no physical contact (for example, visual safety checks). Identify clear supply chains for PPE and hand sanitizer.
3. Medical management and consultation: PCUs should establish clear pathways for accessing consultation from medical consultants. It may be ideal, in addition to standard daily psychiatric physician rounding, to have daily internal medicine rounding and/or medical nursing staff working on the unit. Given the potential of COVID-19–positive patients to rapidly devolve from asymptomatic to acutely ill, it is necessary to establish protocols for the provision of urgent medical care 24/7 and streamlined processes for transfer to a medical unit.
Clear protocols should be established to address any potential signs of decompensation in the respiratory status of a PCU unit, including administration of oxygen and restrictions (or appropriate precautions) related to aerosolizing treatment such as nebulizers or positive airway pressure.
4. Code blue protocol: Any emergent medical issues, including acute respiratory decompensation, should trigger a Code Blue response that has been specifically designed for COVID-19–positive patients, including considerations for proper PPE during resuscitation efforts.
5. Psychiatric staffing and workflows: When possible, it may be preferable to engage volunteer medical and nursing staff for the PCU, as opposed to mandating participation. Take into consideration support needs, including education and training about safe PPE practices, processes for testing health care workers, return-to-work guidance, and potential alternate housing.
- Telehealth: Clinicians (such as physicians, social workers, occupational therapists) should leverage and maximize the use of telemedicine to minimize direct or prolonged exposure to infectious disease risks.
- Nursing: It is important to establish appropriate ratios of nursing and support staff for a COVID-19–positive psychiatry unit given the unique work flows related to isolation precautions and to ensure patient and staff safety. These ratios may take into account patient-specific needs, including the need for additional staff to perform constant observation for high-risk patients, management of agitated patients, and sufficient staff to allow for relief and break-time from PPE. Admission and routine care processes should be adapted in order to limit equipment entering the room, such as computer workstations on wheels.
- Medication administration procedures: Develop work flows related to PPE and infection control when retrieving and administering medications.
- Workspace: Designate appropriate workspace for PCU clinicians to access computers and documents and to minimize use of non–COVID-19 unit work areas.
6. Restraints and management of agitated patients: PCUs should develop plans for addressing agitated patients, including contingency plans for whether seclusion or restraints should be administered in the patient’s individual room or in a dedicated restraint room in the PCU. Staff training should include protocols specifically designed for managing agitated patients in the PCU.
7. Discharge processes: If patients remain medically well and clear their COVID-19 PCR tests, it is conceivable that they might be transferred to a non–COVID-19 psychiatric unit if sufficient isolation time has passed and the infectious disease consultants deem it appropriate. It is also possible that patients would be discharged from a PCU to home or other residential setting. Such patients should be assessed for ability to comply with continued self-quarantine if necessary. Discharge planning must take into consideration follow-up plans for COVID-19 illness and primary care appointments, as well as needed psychiatric follow-up.
8. Patients’ rights: The apparently highly infectious and transmissible nature of SARS-CoV-2 creates novel tensions between a wide range of individual rights and the rights of others. In addition to manifesting in our general society, there are potentially unique tensions in acute inpatient psychiatric settings. Certain patients’ rights may require modification in a PCU (for example, access to outdoor space, personal belongings, visitors, and possibly civil commitment judicial hearings). These discussions may require input from hospital compliance officers, ethics committees, risk managers, and the local department of mental health and also may be partly solved by using video communication platforms.
A few other “pearls” may be of value: Psychiatric hospitals that are colocated with a general acute care hospital or ED might be better situated to develop protocols to safely care for COVID-19–positive psychiatric patients, by virtue of the close proximity of full-spectrum acute general hospital services. Direct engagement by a command center and hospital or health system senior leadership also seems crucial as a means for assuring authorization to proceed with planning what may be a frightening or controversial (but necessary) adaptation of inpatient psychiatric unit(s) to the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The resources of a robust community hospital or academic health system (including infection prevention leaders who engage in continuous liaison with local, county, state, and federal public health expertise) are crucial to the “learning health system” model, which requires flexibility, rapid adaptation to new knowledge, and accessibility to infectious disease and other consultation for special situations. Frequent and open communication with all professional stakeholders (through town halls, Q&A sessions, group discussions, and so on) is important in the planning process to socialize the principles and concepts that are critical for providing care in a PCU, reducing anxiety, and bolstering collegiality and staff morale.
References
1. Kim MJ. “ ‘It was a medical disaster’: The psychiatric ward that saw 100 patients with new coronavirus.” Independent. 2020 Mar 1.
2. Korean Society of Infectious Diseases et al. J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Mar 16;35(10):e112.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptom-based strategy to discontinue isolation for persons with COVID-19. Decision Memo. 2020 May 3.
4. He X et al. Nature Medicine. 2020. 26:672-5.
Dr. Cheung is associate medical director and chief quality officer at the Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Strouse is medical director, UCLA Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital and Maddie Katz Professor at the UCLA department of psychiatry/Semel Institute. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Li is associate medical director of quality improvement at Yale-New Haven Psychiatric Hospital in Connecticut. She also serves as medical director of clinical operations at the Yale-New Haven Health System. Dr. Li is a 2019-2020 Health and Aging Policy Fellow and receives funding support from the program.
Reports have emerged about the unique vulnerability of psychiatric hospitals to the ravages of COVID-19.
In a South Korea psychiatric hospital, 101 of 103 patients contracted SARS-CoV-2 during an outbreak; 7 eventually died.1,2 This report, among a few others, have led to the development of psychiatric COVID-19–positive units (PCU). However, it remains highly unclear how many are currently open, where they are located, or what their operations are like.
We knew that we could not allow a medically asymptomatic “covertly” COVID-19–positive patient to be introduced to the social community of our inpatient units because of the risks of transmission to other patients and staff.
In coordination with our health system infection prevention experts, we have therefore required a confirmed negative COVID-19 polymerase chain reaction nasal swab performed no more than 48 hours prior to the time/date of acute psychiatric inpatient admission. Furthermore, as part of the broad health system response and surge planning, we were asked by our respective incident command centers to begin planning for a Psychiatric COVID-19–positive Unit (PCU) that might allow us to safely care for a cohort of patients needing such hospitalization.
It is worth emphasizing that the typical patient who is a candidate for a PCU is so acutely psychiatrically ill that they cannot be managed in a less restrictive environment than an inpatient psychiatric unit and, at the same time, is likely to not be medically ill enough to warrant admission to an internal medicine service in a general acute care hospital.
We have identified eight principles and critical decision points that can help inpatient units plan for the safe care of COVID-19–positive patients on a PCU.
1. Triage: Patients admitted to a PCU should be medically stable, particularly with regard to COVID-19 and respiratory symptomatology. PCUs should establish clear criteria for admission and discharge (or medical transfer). Examples of potential exclusionary criteria to a PCU include:
- Respiratory distress, shortness of breath, hypoxia, requirement for supplemental oxygen, or requirement for respiratory therapy breathing treatments.
- Fever, or signs of sepsis, or systemic inflammatory response syndrome.
- Medical frailty, significant medical comorbidities, delirium, or altered mental status;
- Requirements for continuous vital sign monitoring or of a monitoring frequency beyond the capacity of the PCU.
Discharge criteria may also include a symptom-based strategy because emerging evidence suggests that patients may be less infectious by day 10-14 of the disease course,3 and viral lab testing is very sensitive and will be positive for periods of time after individuals are no longer infectious. The symptom-based strategy allows for patients to not require retesting prior to discharge. However, some receiving facilities (for example residential or skilled nursing facilities) may necessitate testing, in which case a testing-based strategy can be used. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention provides guidelines for both types of strategies.4
2. Infection control and personal protective equipment: PCUs require modifications or departures from the typical inpatient free-ranging environment in which common areas are provided for patients to engage in a community of care, including group therapy (such as occupational, recreational, Alcoholics Anonymous, and social work groups).
- Isolation: PCUs must consider whether they will require patients to isolate to their rooms or to allow modified or limited access to “public” or “community” areas. While there do not appear to be standard recommendations from the CDC or other public health entities regarding negative pressure or any specific room ventilation requirements, it is prudent to work with local infectious disease experts on protocols. Important considerations include spatial planning for infection control areas to don and doff appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) and appropriate workspace to prevent contamination of non–COVID-19 work areas. Approaches can include establishing clearly identified and visually demarcated infection control “zones” (often referred to as “hot, warm, and cold zones”) that correspond to specific PPE requirements for staff. In addition, individuals should eat in their own rooms or designated areas because use of common areas for meals can potentially lead to aerosolized spread of the virus.
- Cohorting: Generally, PCUs should consider admitting only COVID-19–positive patients to a PCU to avoid exposure to other patients. Hospitals and health systems should determine protocols and locations for testing and managing “patients under investigation” for COVID-19, which should precede admission to the PCU.
- PPE: It is important to clearly establish and communicate PPE requirements and procedures for direct physical contact versus no physical contact (for example, visual safety checks). Identify clear supply chains for PPE and hand sanitizer.
3. Medical management and consultation: PCUs should establish clear pathways for accessing consultation from medical consultants. It may be ideal, in addition to standard daily psychiatric physician rounding, to have daily internal medicine rounding and/or medical nursing staff working on the unit. Given the potential of COVID-19–positive patients to rapidly devolve from asymptomatic to acutely ill, it is necessary to establish protocols for the provision of urgent medical care 24/7 and streamlined processes for transfer to a medical unit.
Clear protocols should be established to address any potential signs of decompensation in the respiratory status of a PCU unit, including administration of oxygen and restrictions (or appropriate precautions) related to aerosolizing treatment such as nebulizers or positive airway pressure.
4. Code blue protocol: Any emergent medical issues, including acute respiratory decompensation, should trigger a Code Blue response that has been specifically designed for COVID-19–positive patients, including considerations for proper PPE during resuscitation efforts.
5. Psychiatric staffing and workflows: When possible, it may be preferable to engage volunteer medical and nursing staff for the PCU, as opposed to mandating participation. Take into consideration support needs, including education and training about safe PPE practices, processes for testing health care workers, return-to-work guidance, and potential alternate housing.
- Telehealth: Clinicians (such as physicians, social workers, occupational therapists) should leverage and maximize the use of telemedicine to minimize direct or prolonged exposure to infectious disease risks.
- Nursing: It is important to establish appropriate ratios of nursing and support staff for a COVID-19–positive psychiatry unit given the unique work flows related to isolation precautions and to ensure patient and staff safety. These ratios may take into account patient-specific needs, including the need for additional staff to perform constant observation for high-risk patients, management of agitated patients, and sufficient staff to allow for relief and break-time from PPE. Admission and routine care processes should be adapted in order to limit equipment entering the room, such as computer workstations on wheels.
- Medication administration procedures: Develop work flows related to PPE and infection control when retrieving and administering medications.
- Workspace: Designate appropriate workspace for PCU clinicians to access computers and documents and to minimize use of non–COVID-19 unit work areas.
6. Restraints and management of agitated patients: PCUs should develop plans for addressing agitated patients, including contingency plans for whether seclusion or restraints should be administered in the patient’s individual room or in a dedicated restraint room in the PCU. Staff training should include protocols specifically designed for managing agitated patients in the PCU.
7. Discharge processes: If patients remain medically well and clear their COVID-19 PCR tests, it is conceivable that they might be transferred to a non–COVID-19 psychiatric unit if sufficient isolation time has passed and the infectious disease consultants deem it appropriate. It is also possible that patients would be discharged from a PCU to home or other residential setting. Such patients should be assessed for ability to comply with continued self-quarantine if necessary. Discharge planning must take into consideration follow-up plans for COVID-19 illness and primary care appointments, as well as needed psychiatric follow-up.
8. Patients’ rights: The apparently highly infectious and transmissible nature of SARS-CoV-2 creates novel tensions between a wide range of individual rights and the rights of others. In addition to manifesting in our general society, there are potentially unique tensions in acute inpatient psychiatric settings. Certain patients’ rights may require modification in a PCU (for example, access to outdoor space, personal belongings, visitors, and possibly civil commitment judicial hearings). These discussions may require input from hospital compliance officers, ethics committees, risk managers, and the local department of mental health and also may be partly solved by using video communication platforms.
A few other “pearls” may be of value: Psychiatric hospitals that are colocated with a general acute care hospital or ED might be better situated to develop protocols to safely care for COVID-19–positive psychiatric patients, by virtue of the close proximity of full-spectrum acute general hospital services. Direct engagement by a command center and hospital or health system senior leadership also seems crucial as a means for assuring authorization to proceed with planning what may be a frightening or controversial (but necessary) adaptation of inpatient psychiatric unit(s) to the exigencies of the COVID-19 pandemic.
The resources of a robust community hospital or academic health system (including infection prevention leaders who engage in continuous liaison with local, county, state, and federal public health expertise) are crucial to the “learning health system” model, which requires flexibility, rapid adaptation to new knowledge, and accessibility to infectious disease and other consultation for special situations. Frequent and open communication with all professional stakeholders (through town halls, Q&A sessions, group discussions, and so on) is important in the planning process to socialize the principles and concepts that are critical for providing care in a PCU, reducing anxiety, and bolstering collegiality and staff morale.
References
1. Kim MJ. “ ‘It was a medical disaster’: The psychiatric ward that saw 100 patients with new coronavirus.” Independent. 2020 Mar 1.
2. Korean Society of Infectious Diseases et al. J Korean Med Sci. 2020 Mar 16;35(10):e112.
3. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Symptom-based strategy to discontinue isolation for persons with COVID-19. Decision Memo. 2020 May 3.
4. He X et al. Nature Medicine. 2020. 26:672-5.
Dr. Cheung is associate medical director and chief quality officer at the Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital at the University of California, Los Angeles. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Strouse is medical director, UCLA Stewart and Lynda Resnick Neuropsychiatric Hospital and Maddie Katz Professor at the UCLA department of psychiatry/Semel Institute. He has no conflicts of interest. Dr. Li is associate medical director of quality improvement at Yale-New Haven Psychiatric Hospital in Connecticut. She also serves as medical director of clinical operations at the Yale-New Haven Health System. Dr. Li is a 2019-2020 Health and Aging Policy Fellow and receives funding support from the program.