User login
-
Ischemic stroke rates higher in young women than young men
Young women appear to be at a higher risk of ischemic stroke than young men, according to a new systematic review of studies on this topic.
The review included 19 studies that reported on sex-specific stroke incidence among young adults and found that overall, in young adults aged 18-35 years, there were 44% more women with ischemic strokes than men.
This gap narrowed in the age group 35-45 years, for which there was conflicting evidence whether more men or women have ischemic strokes.
“An assertion that young women may be disproportionately at risk of ischemic stroke represents a significant departure from our current scientific understanding and may have important implications about the etiology of ischemic strokes in young adults,” the authors note.
“One of the take-home messages from this study is that stroke happens across the entire age spectrum, including young adults, even if they do not have traditional risk factors,” study coauthor Sharon N. Poisson, MD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, told this news organization.
“If a young person presents with focal neurological symptoms, the possibility of a stroke should not be discounted just because they may not fit the typical profile of a stroke patient. We need more education of the population that young people – including young women – can have a stroke and that fast action to call emergency services is critical,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 24 in the journal Stroke as part of a special “Go Red for Women” spotlight issue.
The researchers note that historically it has been believed that men have a higher incidence of stroke in every age group until very old age. However, recent evidence focused on the young adult age group has reported that there are more young women (ages 18-45) with ischemic strokes compared with young men, suggesting that young women may be disproportionately at risk compared with their male counterparts.
Pointing out that a better understanding of these sex differences is important in implementing strategies that can more effectively prevent and treat strokes in this age group, the researchers conducted the current review to synthesize the updated evidence.
They searched PubMed from January 2008 to July 2021 for relevant studies that were population-based and reported stroke incidence by sex or sex-specific incidence rate ratios of young adults age 45 and younger. Statistical synthesis was performed to estimate sex difference by age group (less than or equal to 35, 35-45 and less than or equal to 45 years) and stroke type.
They found 19 relevant studies, including three that reported on overlapping data, with a total of 69,793 young adults (33,775 women and 36,018 men).
Nine studies did not show a statistically significant sex difference among young adults less than or equal to 45 years. Three studies found higher rates of ischemic stroke among men among young adults less than or equal to 30 to 35 years. Four studies showed more women with ischemic strokes among young adults less than or equal to 35 years.
Overall, there was an effect of a significantly higher incidence of ischemic stroke in women younger than age 35 years, with an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 1.44. In the 35- to 45-year age group, there was a nonsignificant sex difference in the rate of ischemic stroke, with a slight trend toward a higher incidence in women (IRR, 1.08).
“In this study the sex difference was not clear in the 35-45 age group. But in the age group of over 45 years we know that men have a higher risk of stroke than women, which is probably related to a higher level of atherosclerotic risk factors,” Dr. Poisson commented.
“Interpreting data on stroke in young people is challenging, as stroke is not so common in this population,” she said. “Combining multiple studies helps, but this also introduces a lot of variability, so we need to interpret these results with some caution. However, this is certainly intriguing data and suggests that something interesting may be going on in young adults,” she added. “These observations give us an initial clue that we need to look further into this issue.”
The study did not look at the possible mechanisms behind the results, as the current data came from administrative datasets that are limited in terms of the information collected.
But Dr. Poisson noted that the traditional risk factors for stroke are high blood pressure and the usual atherosclerotic factors such as high cholesterol.
“These are normally more common in men than in women, and myocardial infarction is more common in younger men than in younger women. But the observation that young women may have a higher risk of stroke than young men suggests that something different may be going on in the mechanism for stroke.”
She pointed out that women have some unique risk factors for stroke, including oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and the postpartum period, particularly pre-eclampsia during pregnancy. In addition, migraine, especially migraine with aura, is associated with an increased stroke risk, and migraine is more common in young women than in young men.
“We don’t completely understand the role of these risk factors, but they may contribute to the results that we found,” Dr. Poisson commented. “The role of estrogen in stroke is complicated. While estrogen is generally thought to be protective against atherosclerotic risk factors, it also increases risk of clotting, so high estrogen states like pregnancy increase risk of stroke,” she added.
To better understand what is happening, prospectively collected clinical data on younger patients who have had a stroke are needed. Some such studies are underway, but a concerted effort to do this in a large, multicenter registry would be desirable, Dr. Poisson said.
She noted that the presentation of a stroke in young people would be similar to that in the older population, with the most recent acronym to help recognize stroke symptoms being “BE FAST” – balance, eyes (vision), face (drooping), arm, speech (slurred), time (call emergency services quickly).
Call for more women in clinical trials
In an accompanying commentary, Cheryl Bushnell, MD, professor of neurology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and Moira Kapral, MD, professor in medicine and health policy at the University of Toronto, say these findings support the need for further study to understand and address the causes and risk factors of stroke in young women.
However, they point out that representation and reporting of women in clinical trials of acute stroke continues to be suboptimal, and they call for improved incorporation of sex and gender into study design, analysis, and interpretation, which they say is critical for producing research that is broadly generalizable and applicable to different populations.
Coauthor Stacey L. Daugherty, MD, is funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Poisson and Dr. Kapral have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bushnell reports ownership interest in Care Directions.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women appear to be at a higher risk of ischemic stroke than young men, according to a new systematic review of studies on this topic.
The review included 19 studies that reported on sex-specific stroke incidence among young adults and found that overall, in young adults aged 18-35 years, there were 44% more women with ischemic strokes than men.
This gap narrowed in the age group 35-45 years, for which there was conflicting evidence whether more men or women have ischemic strokes.
“An assertion that young women may be disproportionately at risk of ischemic stroke represents a significant departure from our current scientific understanding and may have important implications about the etiology of ischemic strokes in young adults,” the authors note.
“One of the take-home messages from this study is that stroke happens across the entire age spectrum, including young adults, even if they do not have traditional risk factors,” study coauthor Sharon N. Poisson, MD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, told this news organization.
“If a young person presents with focal neurological symptoms, the possibility of a stroke should not be discounted just because they may not fit the typical profile of a stroke patient. We need more education of the population that young people – including young women – can have a stroke and that fast action to call emergency services is critical,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 24 in the journal Stroke as part of a special “Go Red for Women” spotlight issue.
The researchers note that historically it has been believed that men have a higher incidence of stroke in every age group until very old age. However, recent evidence focused on the young adult age group has reported that there are more young women (ages 18-45) with ischemic strokes compared with young men, suggesting that young women may be disproportionately at risk compared with their male counterparts.
Pointing out that a better understanding of these sex differences is important in implementing strategies that can more effectively prevent and treat strokes in this age group, the researchers conducted the current review to synthesize the updated evidence.
They searched PubMed from January 2008 to July 2021 for relevant studies that were population-based and reported stroke incidence by sex or sex-specific incidence rate ratios of young adults age 45 and younger. Statistical synthesis was performed to estimate sex difference by age group (less than or equal to 35, 35-45 and less than or equal to 45 years) and stroke type.
They found 19 relevant studies, including three that reported on overlapping data, with a total of 69,793 young adults (33,775 women and 36,018 men).
Nine studies did not show a statistically significant sex difference among young adults less than or equal to 45 years. Three studies found higher rates of ischemic stroke among men among young adults less than or equal to 30 to 35 years. Four studies showed more women with ischemic strokes among young adults less than or equal to 35 years.
Overall, there was an effect of a significantly higher incidence of ischemic stroke in women younger than age 35 years, with an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 1.44. In the 35- to 45-year age group, there was a nonsignificant sex difference in the rate of ischemic stroke, with a slight trend toward a higher incidence in women (IRR, 1.08).
“In this study the sex difference was not clear in the 35-45 age group. But in the age group of over 45 years we know that men have a higher risk of stroke than women, which is probably related to a higher level of atherosclerotic risk factors,” Dr. Poisson commented.
“Interpreting data on stroke in young people is challenging, as stroke is not so common in this population,” she said. “Combining multiple studies helps, but this also introduces a lot of variability, so we need to interpret these results with some caution. However, this is certainly intriguing data and suggests that something interesting may be going on in young adults,” she added. “These observations give us an initial clue that we need to look further into this issue.”
The study did not look at the possible mechanisms behind the results, as the current data came from administrative datasets that are limited in terms of the information collected.
But Dr. Poisson noted that the traditional risk factors for stroke are high blood pressure and the usual atherosclerotic factors such as high cholesterol.
“These are normally more common in men than in women, and myocardial infarction is more common in younger men than in younger women. But the observation that young women may have a higher risk of stroke than young men suggests that something different may be going on in the mechanism for stroke.”
She pointed out that women have some unique risk factors for stroke, including oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and the postpartum period, particularly pre-eclampsia during pregnancy. In addition, migraine, especially migraine with aura, is associated with an increased stroke risk, and migraine is more common in young women than in young men.
“We don’t completely understand the role of these risk factors, but they may contribute to the results that we found,” Dr. Poisson commented. “The role of estrogen in stroke is complicated. While estrogen is generally thought to be protective against atherosclerotic risk factors, it also increases risk of clotting, so high estrogen states like pregnancy increase risk of stroke,” she added.
To better understand what is happening, prospectively collected clinical data on younger patients who have had a stroke are needed. Some such studies are underway, but a concerted effort to do this in a large, multicenter registry would be desirable, Dr. Poisson said.
She noted that the presentation of a stroke in young people would be similar to that in the older population, with the most recent acronym to help recognize stroke symptoms being “BE FAST” – balance, eyes (vision), face (drooping), arm, speech (slurred), time (call emergency services quickly).
Call for more women in clinical trials
In an accompanying commentary, Cheryl Bushnell, MD, professor of neurology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and Moira Kapral, MD, professor in medicine and health policy at the University of Toronto, say these findings support the need for further study to understand and address the causes and risk factors of stroke in young women.
However, they point out that representation and reporting of women in clinical trials of acute stroke continues to be suboptimal, and they call for improved incorporation of sex and gender into study design, analysis, and interpretation, which they say is critical for producing research that is broadly generalizable and applicable to different populations.
Coauthor Stacey L. Daugherty, MD, is funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Poisson and Dr. Kapral have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bushnell reports ownership interest in Care Directions.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Young women appear to be at a higher risk of ischemic stroke than young men, according to a new systematic review of studies on this topic.
The review included 19 studies that reported on sex-specific stroke incidence among young adults and found that overall, in young adults aged 18-35 years, there were 44% more women with ischemic strokes than men.
This gap narrowed in the age group 35-45 years, for which there was conflicting evidence whether more men or women have ischemic strokes.
“An assertion that young women may be disproportionately at risk of ischemic stroke represents a significant departure from our current scientific understanding and may have important implications about the etiology of ischemic strokes in young adults,” the authors note.
“One of the take-home messages from this study is that stroke happens across the entire age spectrum, including young adults, even if they do not have traditional risk factors,” study coauthor Sharon N. Poisson, MD, associate professor of neurology at the University of Colorado Anschutz Medical Campus, Denver, told this news organization.
“If a young person presents with focal neurological symptoms, the possibility of a stroke should not be discounted just because they may not fit the typical profile of a stroke patient. We need more education of the population that young people – including young women – can have a stroke and that fast action to call emergency services is critical,” she said.
The study was published online Jan. 24 in the journal Stroke as part of a special “Go Red for Women” spotlight issue.
The researchers note that historically it has been believed that men have a higher incidence of stroke in every age group until very old age. However, recent evidence focused on the young adult age group has reported that there are more young women (ages 18-45) with ischemic strokes compared with young men, suggesting that young women may be disproportionately at risk compared with their male counterparts.
Pointing out that a better understanding of these sex differences is important in implementing strategies that can more effectively prevent and treat strokes in this age group, the researchers conducted the current review to synthesize the updated evidence.
They searched PubMed from January 2008 to July 2021 for relevant studies that were population-based and reported stroke incidence by sex or sex-specific incidence rate ratios of young adults age 45 and younger. Statistical synthesis was performed to estimate sex difference by age group (less than or equal to 35, 35-45 and less than or equal to 45 years) and stroke type.
They found 19 relevant studies, including three that reported on overlapping data, with a total of 69,793 young adults (33,775 women and 36,018 men).
Nine studies did not show a statistically significant sex difference among young adults less than or equal to 45 years. Three studies found higher rates of ischemic stroke among men among young adults less than or equal to 30 to 35 years. Four studies showed more women with ischemic strokes among young adults less than or equal to 35 years.
Overall, there was an effect of a significantly higher incidence of ischemic stroke in women younger than age 35 years, with an incidence rate ratio (IRR) of 1.44. In the 35- to 45-year age group, there was a nonsignificant sex difference in the rate of ischemic stroke, with a slight trend toward a higher incidence in women (IRR, 1.08).
“In this study the sex difference was not clear in the 35-45 age group. But in the age group of over 45 years we know that men have a higher risk of stroke than women, which is probably related to a higher level of atherosclerotic risk factors,” Dr. Poisson commented.
“Interpreting data on stroke in young people is challenging, as stroke is not so common in this population,” she said. “Combining multiple studies helps, but this also introduces a lot of variability, so we need to interpret these results with some caution. However, this is certainly intriguing data and suggests that something interesting may be going on in young adults,” she added. “These observations give us an initial clue that we need to look further into this issue.”
The study did not look at the possible mechanisms behind the results, as the current data came from administrative datasets that are limited in terms of the information collected.
But Dr. Poisson noted that the traditional risk factors for stroke are high blood pressure and the usual atherosclerotic factors such as high cholesterol.
“These are normally more common in men than in women, and myocardial infarction is more common in younger men than in younger women. But the observation that young women may have a higher risk of stroke than young men suggests that something different may be going on in the mechanism for stroke.”
She pointed out that women have some unique risk factors for stroke, including oral contraceptive use, pregnancy, and the postpartum period, particularly pre-eclampsia during pregnancy. In addition, migraine, especially migraine with aura, is associated with an increased stroke risk, and migraine is more common in young women than in young men.
“We don’t completely understand the role of these risk factors, but they may contribute to the results that we found,” Dr. Poisson commented. “The role of estrogen in stroke is complicated. While estrogen is generally thought to be protective against atherosclerotic risk factors, it also increases risk of clotting, so high estrogen states like pregnancy increase risk of stroke,” she added.
To better understand what is happening, prospectively collected clinical data on younger patients who have had a stroke are needed. Some such studies are underway, but a concerted effort to do this in a large, multicenter registry would be desirable, Dr. Poisson said.
She noted that the presentation of a stroke in young people would be similar to that in the older population, with the most recent acronym to help recognize stroke symptoms being “BE FAST” – balance, eyes (vision), face (drooping), arm, speech (slurred), time (call emergency services quickly).
Call for more women in clinical trials
In an accompanying commentary, Cheryl Bushnell, MD, professor of neurology at Wake Forest School of Medicine, Winston-Salem, N.C., and Moira Kapral, MD, professor in medicine and health policy at the University of Toronto, say these findings support the need for further study to understand and address the causes and risk factors of stroke in young women.
However, they point out that representation and reporting of women in clinical trials of acute stroke continues to be suboptimal, and they call for improved incorporation of sex and gender into study design, analysis, and interpretation, which they say is critical for producing research that is broadly generalizable and applicable to different populations.
Coauthor Stacey L. Daugherty, MD, is funded by the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Poisson and Dr. Kapral have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Bushnell reports ownership interest in Care Directions.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FDA grants full approval to Moderna COVID-19 vaccine
Moderna announced today that its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine has received full Food and Drug Administration approval for adults 18 years and older.
The move lifts an FDA emergency use authorization for the vaccine, which started Dec. 18, 2020.
The Moderna vaccine also now has a new trade name: Spikevax.
The FDA approval comes a little more than 5 months after the agency granted full approval to the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine on Aug. 23. At the time, the Pfizer vaccine received the trade name Comirnaty.
The FDA approved the Moderna vaccine based on how well it works and its safety for 6 months after a second dose, including follow-up data from a phase 3 study, Moderna announced this morning through a news release. The FDA also announced the news.
Spikevax is the first Moderna product to be fully licensed in the United States.
The United States joins more than 70 other countries where regulators have approved the vaccine. A total of 807 million doses of Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine were shipped worldwide in 2021, the company reported.
“The full licensure of Spikevax in the U.S. now joins that in Canada, Japan, the European Union, the U.K., Israel, and other countries, where the adolescent indication is also approved,” Stéphane Bancel, Moderna chief executive officer, said in the release.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Moderna announced today that its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine has received full Food and Drug Administration approval for adults 18 years and older.
The move lifts an FDA emergency use authorization for the vaccine, which started Dec. 18, 2020.
The Moderna vaccine also now has a new trade name: Spikevax.
The FDA approval comes a little more than 5 months after the agency granted full approval to the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine on Aug. 23. At the time, the Pfizer vaccine received the trade name Comirnaty.
The FDA approved the Moderna vaccine based on how well it works and its safety for 6 months after a second dose, including follow-up data from a phase 3 study, Moderna announced this morning through a news release. The FDA also announced the news.
Spikevax is the first Moderna product to be fully licensed in the United States.
The United States joins more than 70 other countries where regulators have approved the vaccine. A total of 807 million doses of Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine were shipped worldwide in 2021, the company reported.
“The full licensure of Spikevax in the U.S. now joins that in Canada, Japan, the European Union, the U.K., Israel, and other countries, where the adolescent indication is also approved,” Stéphane Bancel, Moderna chief executive officer, said in the release.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Moderna announced today that its mRNA COVID-19 vaccine has received full Food and Drug Administration approval for adults 18 years and older.
The move lifts an FDA emergency use authorization for the vaccine, which started Dec. 18, 2020.
The Moderna vaccine also now has a new trade name: Spikevax.
The FDA approval comes a little more than 5 months after the agency granted full approval to the Pfizer/BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine on Aug. 23. At the time, the Pfizer vaccine received the trade name Comirnaty.
The FDA approved the Moderna vaccine based on how well it works and its safety for 6 months after a second dose, including follow-up data from a phase 3 study, Moderna announced this morning through a news release. The FDA also announced the news.
Spikevax is the first Moderna product to be fully licensed in the United States.
The United States joins more than 70 other countries where regulators have approved the vaccine. A total of 807 million doses of Moderna’s COVID-19 vaccine were shipped worldwide in 2021, the company reported.
“The full licensure of Spikevax in the U.S. now joins that in Canada, Japan, the European Union, the U.K., Israel, and other countries, where the adolescent indication is also approved,” Stéphane Bancel, Moderna chief executive officer, said in the release.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Billionaire Mark Cuban launches online pharmacy for generics
The Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drugs Company (MCCPDC) plans to offer the leukemia therapy imatinib for $47 per month, for example, compared with $120 or more with a common voucher and a retail price of $9,657 per month.
Other examples of lower-priced generics include the ulcerative colitis treatment mesalamine, which goes for $32.40 per month on the new online pharmacy versus $940 per month retail. In addition, the MCCPDC will offer the gout treatment colchicine at a lower price, charging $8.70, compared with $182 per month retail.
Likely in part because of claims of significant cost savings and in part because of Mr. Cuban’s celebrity status, the new venture is getting widespread media attention. Forbes, NPR, and TMZ have shared the news since the new digital pharmacy was announced earlier this month.
The new venture plans to charge consumers 15% above the manufacturing cost for the generic medications, plus a $3 fee for pharmacists and $5 for shipping. People will still require a prescription from their doctor to get the medications.
Generic pricing and social benefit
The top 100 generic products account for about half of generic sales, and there is enough competition for these high-demand medications that “the prices have come down close to zero,” said William Comanor, PhD, a health economist and professor of health policy and management at the University of California, Los Angeles. The remaining generic agents have lower-volume demand.
One prominent example is Daraprim, a decades-old treatment for the life-threatening parasitic infection toxoplasmosis. The drug jumped into the spotlight in 2015 when Martin Shkreli and his company Vyera Pharmaceuticals bought the rights to make the generic drug and raised the price overnight from $13.50 to $750. In January 2022, a U.S. judge banned Mr. Shkreli from the pharmaceutical industry and ordered him to pay an almost $65 million fine.
Dr. Comanor agreed the price should have been raised – $13.50 “was not economically viable” – but not as steep as $750.
“Say Mark Cuban says he will cut the price from $750 to $300. He will still make money. There is a market for these low-volume products,” he said. “There would also be a social benefit.”
A direct-to-consumer digital pharmacy
MCCPDC is “cutting out the middleman” in two ways. The business model calls for charging consumers out of pocket, so insurance companies are not involved. Also, the company created its own pharmacy business manager firm in October 2021, allowing it to negotiate prices with drugmakers in house.
The company also announced plans to complete construction of a 22,000-square-foot pharmaceutical factory in Dallas by the end of 2022.
Reactions on social media ranged from celebratory to people disappointed their generic medication would not cost significantly less or is not provided by the digital pharmacy.
When weighted by the number of prescriptions, prices for generics have declined in the United States.
“Overall, U.S. generic prices are the lowest in the world,” Dr. Comanor said. “People say U.S. drug prices are the highest in the world. That’s true for branded, but it’s not true for generics.
“So if someone asks if U.S. drug prices are the highest or lowest in the world, the answer is both,” he said.
“Maybe there is a role to play for this new pharmacy,” Dr. Comanor said when asked if the initiative seems like a positive development.
The state of California also announced plans to provide its own generic drugs, he said.
“But you won’t see a lot of entrepreneurs getting into this because the volumes are so low. If Cuban called me, I would tell him to provide Daraprim and similar, low-volume products,” Dr. Comanor said of the billionaire. “He’s a rich guy; maybe he can do it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drugs Company (MCCPDC) plans to offer the leukemia therapy imatinib for $47 per month, for example, compared with $120 or more with a common voucher and a retail price of $9,657 per month.
Other examples of lower-priced generics include the ulcerative colitis treatment mesalamine, which goes for $32.40 per month on the new online pharmacy versus $940 per month retail. In addition, the MCCPDC will offer the gout treatment colchicine at a lower price, charging $8.70, compared with $182 per month retail.
Likely in part because of claims of significant cost savings and in part because of Mr. Cuban’s celebrity status, the new venture is getting widespread media attention. Forbes, NPR, and TMZ have shared the news since the new digital pharmacy was announced earlier this month.
The new venture plans to charge consumers 15% above the manufacturing cost for the generic medications, plus a $3 fee for pharmacists and $5 for shipping. People will still require a prescription from their doctor to get the medications.
Generic pricing and social benefit
The top 100 generic products account for about half of generic sales, and there is enough competition for these high-demand medications that “the prices have come down close to zero,” said William Comanor, PhD, a health economist and professor of health policy and management at the University of California, Los Angeles. The remaining generic agents have lower-volume demand.
One prominent example is Daraprim, a decades-old treatment for the life-threatening parasitic infection toxoplasmosis. The drug jumped into the spotlight in 2015 when Martin Shkreli and his company Vyera Pharmaceuticals bought the rights to make the generic drug and raised the price overnight from $13.50 to $750. In January 2022, a U.S. judge banned Mr. Shkreli from the pharmaceutical industry and ordered him to pay an almost $65 million fine.
Dr. Comanor agreed the price should have been raised – $13.50 “was not economically viable” – but not as steep as $750.
“Say Mark Cuban says he will cut the price from $750 to $300. He will still make money. There is a market for these low-volume products,” he said. “There would also be a social benefit.”
A direct-to-consumer digital pharmacy
MCCPDC is “cutting out the middleman” in two ways. The business model calls for charging consumers out of pocket, so insurance companies are not involved. Also, the company created its own pharmacy business manager firm in October 2021, allowing it to negotiate prices with drugmakers in house.
The company also announced plans to complete construction of a 22,000-square-foot pharmaceutical factory in Dallas by the end of 2022.
Reactions on social media ranged from celebratory to people disappointed their generic medication would not cost significantly less or is not provided by the digital pharmacy.
When weighted by the number of prescriptions, prices for generics have declined in the United States.
“Overall, U.S. generic prices are the lowest in the world,” Dr. Comanor said. “People say U.S. drug prices are the highest in the world. That’s true for branded, but it’s not true for generics.
“So if someone asks if U.S. drug prices are the highest or lowest in the world, the answer is both,” he said.
“Maybe there is a role to play for this new pharmacy,” Dr. Comanor said when asked if the initiative seems like a positive development.
The state of California also announced plans to provide its own generic drugs, he said.
“But you won’t see a lot of entrepreneurs getting into this because the volumes are so low. If Cuban called me, I would tell him to provide Daraprim and similar, low-volume products,” Dr. Comanor said of the billionaire. “He’s a rich guy; maybe he can do it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Mark Cuban Cost Plus Drugs Company (MCCPDC) plans to offer the leukemia therapy imatinib for $47 per month, for example, compared with $120 or more with a common voucher and a retail price of $9,657 per month.
Other examples of lower-priced generics include the ulcerative colitis treatment mesalamine, which goes for $32.40 per month on the new online pharmacy versus $940 per month retail. In addition, the MCCPDC will offer the gout treatment colchicine at a lower price, charging $8.70, compared with $182 per month retail.
Likely in part because of claims of significant cost savings and in part because of Mr. Cuban’s celebrity status, the new venture is getting widespread media attention. Forbes, NPR, and TMZ have shared the news since the new digital pharmacy was announced earlier this month.
The new venture plans to charge consumers 15% above the manufacturing cost for the generic medications, plus a $3 fee for pharmacists and $5 for shipping. People will still require a prescription from their doctor to get the medications.
Generic pricing and social benefit
The top 100 generic products account for about half of generic sales, and there is enough competition for these high-demand medications that “the prices have come down close to zero,” said William Comanor, PhD, a health economist and professor of health policy and management at the University of California, Los Angeles. The remaining generic agents have lower-volume demand.
One prominent example is Daraprim, a decades-old treatment for the life-threatening parasitic infection toxoplasmosis. The drug jumped into the spotlight in 2015 when Martin Shkreli and his company Vyera Pharmaceuticals bought the rights to make the generic drug and raised the price overnight from $13.50 to $750. In January 2022, a U.S. judge banned Mr. Shkreli from the pharmaceutical industry and ordered him to pay an almost $65 million fine.
Dr. Comanor agreed the price should have been raised – $13.50 “was not economically viable” – but not as steep as $750.
“Say Mark Cuban says he will cut the price from $750 to $300. He will still make money. There is a market for these low-volume products,” he said. “There would also be a social benefit.”
A direct-to-consumer digital pharmacy
MCCPDC is “cutting out the middleman” in two ways. The business model calls for charging consumers out of pocket, so insurance companies are not involved. Also, the company created its own pharmacy business manager firm in October 2021, allowing it to negotiate prices with drugmakers in house.
The company also announced plans to complete construction of a 22,000-square-foot pharmaceutical factory in Dallas by the end of 2022.
Reactions on social media ranged from celebratory to people disappointed their generic medication would not cost significantly less or is not provided by the digital pharmacy.
When weighted by the number of prescriptions, prices for generics have declined in the United States.
“Overall, U.S. generic prices are the lowest in the world,” Dr. Comanor said. “People say U.S. drug prices are the highest in the world. That’s true for branded, but it’s not true for generics.
“So if someone asks if U.S. drug prices are the highest or lowest in the world, the answer is both,” he said.
“Maybe there is a role to play for this new pharmacy,” Dr. Comanor said when asked if the initiative seems like a positive development.
The state of California also announced plans to provide its own generic drugs, he said.
“But you won’t see a lot of entrepreneurs getting into this because the volumes are so low. If Cuban called me, I would tell him to provide Daraprim and similar, low-volume products,” Dr. Comanor said of the billionaire. “He’s a rich guy; maybe he can do it.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Long COVID is real, and many real questions remain
Long story short, we still have a lot to learn about long COVID-19.
But it is a real phenomenon with real long-term health effects for people recovering from coronavirus infections. And diagnosing and managing it can get tricky, as some symptoms of long COVID-19 overlap with those of other conditions – and what many people have as they recover from any challenging stay in the ICU.
Risk factors remain largely unknown as well: What makes one person more likely to have symptoms like fatigue, “brain fog,” or headaches versus someone else? Researchers are just starting to offer some intriguing answers, but the evidence is preliminary at this point, experts said at a media briefing sponsored by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Unanswered questions include: Does an autoimmune reaction drive long COVID? Does the coronavirus linger in reservoirs within the body and reactivate later? What protection against long COVID do vaccines and treatments offer, if any?
To get a handle on these and other questions, nailing down a standard definition of long COVID would be a good start.
“Studies so far have used different definitions of long COVID,” Nahid Bhadelia, MD, founding director of the Boston University Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases Policy and Research, said during the briefing.
Fatigue is the most commonly symptom of long COVID in research so far, said Dr. Bhadelia, who is also an associate professor of medicine at Boston University.
“What’s difficult in this situation is it’s been 2 years in a global pandemic. We’re all fatigued. How do you tease this apart?” she asked.
Other common symptoms are a hard time thinking quickly – also known as “brain fog” – and the feeling that, despite normal oxygen levels, breathing is difficult, said Kathleen Bell, MD.
Headache, joint and muscle pain, and persistent loss of smell and taste are also widely reported, said Dr. Bell, a professor and chair of the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Not all the symptoms are physical either.
“Pretty prominent things that we’re seeing are very high levels of anxiety, depression, and insomnia,” Dr. Bell said. These “actually seem to be associated independently with the virus as opposed to just being a completely reactive component.”
More research will be needed to distinguish the causes of these conditions.
A difficult diagnosis
the experts said.
“We are starting to see some interesting features of inaccurate attributions to COVID, both on the part of perhaps the person with long COVID symptoms and health care providers,” Dr. Bell said.“It’s sometimes a little difficult to sort it out.”
Dr. Bell said she was not suggesting misdiagnoses are common, “but it is difficult for physicians that don’t see a lot of people with long COVID.”
The advice is to consider other conditions. “You can have both a long COVID syndrome and other syndromes as well,” she said. “As one of my teachers used to say: ‘You can have both ticks and fleas.’ ”
Predicting long COVID
In a study getting attention, researchers identified four early things linked to greater chances that someone with COVID-19 will have long-term effects: type 2 diabetes at the time of diagnosis, the presence of specific autoantibodies, unusual levels of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the blood, and signs of the Epstein-Barr virus in the blood.
The study, published in Cell, followed 309 people 2-3 months after COVID-19.
“That’s important work, but it’s early work,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “I think we still have a while to go in terms of understanding the mechanism of long COVID.”
Unexpected patients getting long COVID care
“We are seeing different populations than we all expected to see when this pandemic first started,” Dr. Bell said.
Instead of seeing primarily patients who had severe COVID-19, “the preponderance of people that we’re seeing in long COVID clinics are people who are enabled, were never hospitalized, and have what people might call mild to moderate cases of coronavirus infection,” she said.
Also, instead of just older patients, people of all ages are seeking long COVID care.
One thing that appears more certain is a lack of diversity in people seeking care at long COVID clinics nationwide.
“Many of us who have long COVID specialty clinics will tell you that we are tending to see fairly educated, socioeconomically stable population in these clinics,” Dr. Bell said. “We know that based on the early statistics of who’s getting COVID and having significant COVID that we may not be seeing those populations for follow-up.”
Is an autoinflammatory process to blame?
It remains unclear if a hyperinflammatory response is driving persistent post–COVID-19 symptoms. Children and some adults have developed multisystem inflammatory conditions associated with COVID-19, for example.
There is a signal, and “I think there is enough data now to show something does happen,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “The question is, how often does it happen?”
Spending time in critical care, even without COVID-19, can result in persistent symptoms after a hospital stay, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. Recovery can take time because being in an ICU is “basically the physiologically equivalent of a car crash,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “So you’re recovering from that, too.”
Dr. Bell agreed. “You’re not only recovering from the virus itself, you’re recovering from intubation, secondary infections, secondary lung conditions, perhaps other organ failure, and prolonged bed rest. There are so many things that go into that, that it’s a little bit hard to sort that out from what long COVID is and what the direct effects of the virus are.”
Also a research opportunity
“I hate to call it this, but we’ve never had an opportunity [where] we have so many people in such a short amount of time with the same viral disorder,” Dr. Bell said. “We also have the technology to investigate it. This has never happened.
“SARS-CoV-2 is not the only virus. This is just the only one we’ve gotten whacked with in such a huge quantity at one time,” she said.
What researchers learn now about COVID-19 and long COVID “is a model that’s going to be able to be applied in the future to infectious diseases in general,” Dr. Bell predicted.
How long will long COVID last?
The vast majority of people with long COVID will get better over time, given enough support and relief of their symptoms, Dr. Bell said.
Type 2 diabetes, preexisting pulmonary disease, and other things could affect how long it takes to recover from long COVID, she said, although more evidence is needed.
“I don’t think at this point that anyone can say how long this long COVID will last because there are a variety of factors,” Dr. Bell said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Long story short, we still have a lot to learn about long COVID-19.
But it is a real phenomenon with real long-term health effects for people recovering from coronavirus infections. And diagnosing and managing it can get tricky, as some symptoms of long COVID-19 overlap with those of other conditions – and what many people have as they recover from any challenging stay in the ICU.
Risk factors remain largely unknown as well: What makes one person more likely to have symptoms like fatigue, “brain fog,” or headaches versus someone else? Researchers are just starting to offer some intriguing answers, but the evidence is preliminary at this point, experts said at a media briefing sponsored by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Unanswered questions include: Does an autoimmune reaction drive long COVID? Does the coronavirus linger in reservoirs within the body and reactivate later? What protection against long COVID do vaccines and treatments offer, if any?
To get a handle on these and other questions, nailing down a standard definition of long COVID would be a good start.
“Studies so far have used different definitions of long COVID,” Nahid Bhadelia, MD, founding director of the Boston University Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases Policy and Research, said during the briefing.
Fatigue is the most commonly symptom of long COVID in research so far, said Dr. Bhadelia, who is also an associate professor of medicine at Boston University.
“What’s difficult in this situation is it’s been 2 years in a global pandemic. We’re all fatigued. How do you tease this apart?” she asked.
Other common symptoms are a hard time thinking quickly – also known as “brain fog” – and the feeling that, despite normal oxygen levels, breathing is difficult, said Kathleen Bell, MD.
Headache, joint and muscle pain, and persistent loss of smell and taste are also widely reported, said Dr. Bell, a professor and chair of the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Not all the symptoms are physical either.
“Pretty prominent things that we’re seeing are very high levels of anxiety, depression, and insomnia,” Dr. Bell said. These “actually seem to be associated independently with the virus as opposed to just being a completely reactive component.”
More research will be needed to distinguish the causes of these conditions.
A difficult diagnosis
the experts said.
“We are starting to see some interesting features of inaccurate attributions to COVID, both on the part of perhaps the person with long COVID symptoms and health care providers,” Dr. Bell said.“It’s sometimes a little difficult to sort it out.”
Dr. Bell said she was not suggesting misdiagnoses are common, “but it is difficult for physicians that don’t see a lot of people with long COVID.”
The advice is to consider other conditions. “You can have both a long COVID syndrome and other syndromes as well,” she said. “As one of my teachers used to say: ‘You can have both ticks and fleas.’ ”
Predicting long COVID
In a study getting attention, researchers identified four early things linked to greater chances that someone with COVID-19 will have long-term effects: type 2 diabetes at the time of diagnosis, the presence of specific autoantibodies, unusual levels of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the blood, and signs of the Epstein-Barr virus in the blood.
The study, published in Cell, followed 309 people 2-3 months after COVID-19.
“That’s important work, but it’s early work,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “I think we still have a while to go in terms of understanding the mechanism of long COVID.”
Unexpected patients getting long COVID care
“We are seeing different populations than we all expected to see when this pandemic first started,” Dr. Bell said.
Instead of seeing primarily patients who had severe COVID-19, “the preponderance of people that we’re seeing in long COVID clinics are people who are enabled, were never hospitalized, and have what people might call mild to moderate cases of coronavirus infection,” she said.
Also, instead of just older patients, people of all ages are seeking long COVID care.
One thing that appears more certain is a lack of diversity in people seeking care at long COVID clinics nationwide.
“Many of us who have long COVID specialty clinics will tell you that we are tending to see fairly educated, socioeconomically stable population in these clinics,” Dr. Bell said. “We know that based on the early statistics of who’s getting COVID and having significant COVID that we may not be seeing those populations for follow-up.”
Is an autoinflammatory process to blame?
It remains unclear if a hyperinflammatory response is driving persistent post–COVID-19 symptoms. Children and some adults have developed multisystem inflammatory conditions associated with COVID-19, for example.
There is a signal, and “I think there is enough data now to show something does happen,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “The question is, how often does it happen?”
Spending time in critical care, even without COVID-19, can result in persistent symptoms after a hospital stay, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. Recovery can take time because being in an ICU is “basically the physiologically equivalent of a car crash,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “So you’re recovering from that, too.”
Dr. Bell agreed. “You’re not only recovering from the virus itself, you’re recovering from intubation, secondary infections, secondary lung conditions, perhaps other organ failure, and prolonged bed rest. There are so many things that go into that, that it’s a little bit hard to sort that out from what long COVID is and what the direct effects of the virus are.”
Also a research opportunity
“I hate to call it this, but we’ve never had an opportunity [where] we have so many people in such a short amount of time with the same viral disorder,” Dr. Bell said. “We also have the technology to investigate it. This has never happened.
“SARS-CoV-2 is not the only virus. This is just the only one we’ve gotten whacked with in such a huge quantity at one time,” she said.
What researchers learn now about COVID-19 and long COVID “is a model that’s going to be able to be applied in the future to infectious diseases in general,” Dr. Bell predicted.
How long will long COVID last?
The vast majority of people with long COVID will get better over time, given enough support and relief of their symptoms, Dr. Bell said.
Type 2 diabetes, preexisting pulmonary disease, and other things could affect how long it takes to recover from long COVID, she said, although more evidence is needed.
“I don’t think at this point that anyone can say how long this long COVID will last because there are a variety of factors,” Dr. Bell said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Long story short, we still have a lot to learn about long COVID-19.
But it is a real phenomenon with real long-term health effects for people recovering from coronavirus infections. And diagnosing and managing it can get tricky, as some symptoms of long COVID-19 overlap with those of other conditions – and what many people have as they recover from any challenging stay in the ICU.
Risk factors remain largely unknown as well: What makes one person more likely to have symptoms like fatigue, “brain fog,” or headaches versus someone else? Researchers are just starting to offer some intriguing answers, but the evidence is preliminary at this point, experts said at a media briefing sponsored by the Infectious Diseases Society of America.
Unanswered questions include: Does an autoimmune reaction drive long COVID? Does the coronavirus linger in reservoirs within the body and reactivate later? What protection against long COVID do vaccines and treatments offer, if any?
To get a handle on these and other questions, nailing down a standard definition of long COVID would be a good start.
“Studies so far have used different definitions of long COVID,” Nahid Bhadelia, MD, founding director of the Boston University Center for Emerging Infectious Diseases Policy and Research, said during the briefing.
Fatigue is the most commonly symptom of long COVID in research so far, said Dr. Bhadelia, who is also an associate professor of medicine at Boston University.
“What’s difficult in this situation is it’s been 2 years in a global pandemic. We’re all fatigued. How do you tease this apart?” she asked.
Other common symptoms are a hard time thinking quickly – also known as “brain fog” – and the feeling that, despite normal oxygen levels, breathing is difficult, said Kathleen Bell, MD.
Headache, joint and muscle pain, and persistent loss of smell and taste are also widely reported, said Dr. Bell, a professor and chair of the department of physical medicine and rehabilitation at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center in Dallas.
Not all the symptoms are physical either.
“Pretty prominent things that we’re seeing are very high levels of anxiety, depression, and insomnia,” Dr. Bell said. These “actually seem to be associated independently with the virus as opposed to just being a completely reactive component.”
More research will be needed to distinguish the causes of these conditions.
A difficult diagnosis
the experts said.
“We are starting to see some interesting features of inaccurate attributions to COVID, both on the part of perhaps the person with long COVID symptoms and health care providers,” Dr. Bell said.“It’s sometimes a little difficult to sort it out.”
Dr. Bell said she was not suggesting misdiagnoses are common, “but it is difficult for physicians that don’t see a lot of people with long COVID.”
The advice is to consider other conditions. “You can have both a long COVID syndrome and other syndromes as well,” she said. “As one of my teachers used to say: ‘You can have both ticks and fleas.’ ”
Predicting long COVID
In a study getting attention, researchers identified four early things linked to greater chances that someone with COVID-19 will have long-term effects: type 2 diabetes at the time of diagnosis, the presence of specific autoantibodies, unusual levels of SARS-CoV-2 RNA in the blood, and signs of the Epstein-Barr virus in the blood.
The study, published in Cell, followed 309 people 2-3 months after COVID-19.
“That’s important work, but it’s early work,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “I think we still have a while to go in terms of understanding the mechanism of long COVID.”
Unexpected patients getting long COVID care
“We are seeing different populations than we all expected to see when this pandemic first started,” Dr. Bell said.
Instead of seeing primarily patients who had severe COVID-19, “the preponderance of people that we’re seeing in long COVID clinics are people who are enabled, were never hospitalized, and have what people might call mild to moderate cases of coronavirus infection,” she said.
Also, instead of just older patients, people of all ages are seeking long COVID care.
One thing that appears more certain is a lack of diversity in people seeking care at long COVID clinics nationwide.
“Many of us who have long COVID specialty clinics will tell you that we are tending to see fairly educated, socioeconomically stable population in these clinics,” Dr. Bell said. “We know that based on the early statistics of who’s getting COVID and having significant COVID that we may not be seeing those populations for follow-up.”
Is an autoinflammatory process to blame?
It remains unclear if a hyperinflammatory response is driving persistent post–COVID-19 symptoms. Children and some adults have developed multisystem inflammatory conditions associated with COVID-19, for example.
There is a signal, and “I think there is enough data now to show something does happen,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “The question is, how often does it happen?”
Spending time in critical care, even without COVID-19, can result in persistent symptoms after a hospital stay, such as acute respiratory distress syndrome. Recovery can take time because being in an ICU is “basically the physiologically equivalent of a car crash,” Dr. Bhadelia said. “So you’re recovering from that, too.”
Dr. Bell agreed. “You’re not only recovering from the virus itself, you’re recovering from intubation, secondary infections, secondary lung conditions, perhaps other organ failure, and prolonged bed rest. There are so many things that go into that, that it’s a little bit hard to sort that out from what long COVID is and what the direct effects of the virus are.”
Also a research opportunity
“I hate to call it this, but we’ve never had an opportunity [where] we have so many people in such a short amount of time with the same viral disorder,” Dr. Bell said. “We also have the technology to investigate it. This has never happened.
“SARS-CoV-2 is not the only virus. This is just the only one we’ve gotten whacked with in such a huge quantity at one time,” she said.
What researchers learn now about COVID-19 and long COVID “is a model that’s going to be able to be applied in the future to infectious diseases in general,” Dr. Bell predicted.
How long will long COVID last?
The vast majority of people with long COVID will get better over time, given enough support and relief of their symptoms, Dr. Bell said.
Type 2 diabetes, preexisting pulmonary disease, and other things could affect how long it takes to recover from long COVID, she said, although more evidence is needed.
“I don’t think at this point that anyone can say how long this long COVID will last because there are a variety of factors,” Dr. Bell said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Immunocompromised patients should receive fourth COVID shot: CDC
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention contacted pharmacies on Jan. 26 to reinforce the message that people with moderate to severe immune suppression should receive a fourth COVID-19 vaccine, according to Kaiser Health News.
The conference call came a day after the news outlet reported that immunocompromised people were being turned away by pharmacies. White House officials also emphasized on Jan. 26 that immunocompromised people should receive an additional shot.
During the call, the CDC “reiterated the recommendations, running through case examples,” Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates for the American Pharmacists Association, told KHN.
While on the call, Mr. Rothholz asked for a “prepared document” with the CDC’s recommendations “so we can clearly and consistently communicate the message.” The CDC officials on the call said they would create a document but “don’t know how long that will take,” Mr. Rothholz told KHN.
The CDC recommends an additional shot -– or a fourth shot – for those who have weak immune systems, which makes them more at risk for severe COVID-19 and death. About 7 million American adults are considered immunocompromised, KHN reported, which includes people who have certain medical conditions that impair their immune response or who take immune-suppressing drugs because of organ transplants, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
The CDC first recommended fourth shots for immunocompromised people in October. This month, the CDC shortened the time for booster shots from 6 months to 5 months, and some immunocompromised people who are due for another shot have begun to seek them. The agency has been educating pharmacists and other health providers since then, a CDC spokesperson told KHN.
While patients don’t need to provide proof that they are immunocompromised, according to the CDC, some have been turned away, KHN reported.
To improve communication with the public, large pharmacies could issue news releases and update their websites “explicitly stating that they are offering fourth doses” to immunocompromised people, Ameet Kini, MD, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago, told KHN.
Pharmacies should also update their patient portals and provide “clear guidance for their pharmacists,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention contacted pharmacies on Jan. 26 to reinforce the message that people with moderate to severe immune suppression should receive a fourth COVID-19 vaccine, according to Kaiser Health News.
The conference call came a day after the news outlet reported that immunocompromised people were being turned away by pharmacies. White House officials also emphasized on Jan. 26 that immunocompromised people should receive an additional shot.
During the call, the CDC “reiterated the recommendations, running through case examples,” Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates for the American Pharmacists Association, told KHN.
While on the call, Mr. Rothholz asked for a “prepared document” with the CDC’s recommendations “so we can clearly and consistently communicate the message.” The CDC officials on the call said they would create a document but “don’t know how long that will take,” Mr. Rothholz told KHN.
The CDC recommends an additional shot -– or a fourth shot – for those who have weak immune systems, which makes them more at risk for severe COVID-19 and death. About 7 million American adults are considered immunocompromised, KHN reported, which includes people who have certain medical conditions that impair their immune response or who take immune-suppressing drugs because of organ transplants, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
The CDC first recommended fourth shots for immunocompromised people in October. This month, the CDC shortened the time for booster shots from 6 months to 5 months, and some immunocompromised people who are due for another shot have begun to seek them. The agency has been educating pharmacists and other health providers since then, a CDC spokesperson told KHN.
While patients don’t need to provide proof that they are immunocompromised, according to the CDC, some have been turned away, KHN reported.
To improve communication with the public, large pharmacies could issue news releases and update their websites “explicitly stating that they are offering fourth doses” to immunocompromised people, Ameet Kini, MD, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago, told KHN.
Pharmacies should also update their patient portals and provide “clear guidance for their pharmacists,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention contacted pharmacies on Jan. 26 to reinforce the message that people with moderate to severe immune suppression should receive a fourth COVID-19 vaccine, according to Kaiser Health News.
The conference call came a day after the news outlet reported that immunocompromised people were being turned away by pharmacies. White House officials also emphasized on Jan. 26 that immunocompromised people should receive an additional shot.
During the call, the CDC “reiterated the recommendations, running through case examples,” Mitchel Rothholz, RPh, MBA, chief of governance and state affiliates for the American Pharmacists Association, told KHN.
While on the call, Mr. Rothholz asked for a “prepared document” with the CDC’s recommendations “so we can clearly and consistently communicate the message.” The CDC officials on the call said they would create a document but “don’t know how long that will take,” Mr. Rothholz told KHN.
The CDC recommends an additional shot -– or a fourth shot – for those who have weak immune systems, which makes them more at risk for severe COVID-19 and death. About 7 million American adults are considered immunocompromised, KHN reported, which includes people who have certain medical conditions that impair their immune response or who take immune-suppressing drugs because of organ transplants, cancer, or autoimmune diseases.
The CDC first recommended fourth shots for immunocompromised people in October. This month, the CDC shortened the time for booster shots from 6 months to 5 months, and some immunocompromised people who are due for another shot have begun to seek them. The agency has been educating pharmacists and other health providers since then, a CDC spokesperson told KHN.
While patients don’t need to provide proof that they are immunocompromised, according to the CDC, some have been turned away, KHN reported.
To improve communication with the public, large pharmacies could issue news releases and update their websites “explicitly stating that they are offering fourth doses” to immunocompromised people, Ameet Kini, MD, a professor of pathology and laboratory medicine at Loyola University Medical Center in Chicago, told KHN.
Pharmacies should also update their patient portals and provide “clear guidance for their pharmacists,” he said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Hong Kong, U.S., Israeli data illuminate COVID vaccine myocarditis
Why some COVID-19 vaccines seem occasionally to cause a distinctive form of myocarditis, and why adolescent boys and young men appear most vulnerable, remain a mystery. But the entity’s prevalence, nuances of presentation, and likely clinical course have come into sharper view after recent additions to the literature.
Two new publications all but confirm that the rare cases of myocarditis closely following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, primarily with one of the mRNA-based vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, is a clinically different creature from myocarditis physicians were likely to see before the pandemic.
A third report unveils rates of hospitalization for myocarditis linked to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in the 12- to 15-year age group, based on active surveillance across Israel. Of note, the rates were lower than corresponding numbers among the country’s 16- to 19-year-olds published in late 2021 by the same authors.
No link with CoronaVac
A case-control study covering almost the entire population of Hong Kong from February to August 2021 confirms a slight but significant excess risk for myocarditis and, to a lesser degree, pericarditis, after injections of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. As consistently reported from other studies, the risks were highest in adolescent and young adult males and after a second dose.
The study estimated an overall carditis incidence of 5.7 cases per million doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, for a risk 3.5 times that in the unvaccinated Hong Kong population. Carditis rates after a first dose were about 2.5 per million and 10 per million after a second dose.
Hong Kong launched its public SARS-CoV-2 immunization program in late February 2021 with the Chinese-made CoronaVac (Sinovac) inactivated-virus vaccine, and introduced the mRNA-based alternative several weeks later. By August 2021, the vaccines had reached about 3.3 million people in the region – 49% of the Hong Kong population at least 12 years of age.
In a novel finding, there were no excesses in carditis cases after CoronaVac vaccination. The difference between vaccines likely isn’t caused by chance, because three-fourths of the carditis-associated Pfizer-BioNTech injections arose within a week, whereas “71% of cases following the use of CoronaVac occurred more than 30 days after vaccination,” senior author Ian Chi Kei Wong, PhD, University of Hong Kong, said in an interview.
“This onset distribution for cases having received CoronaVac demonstrates that it is highly unlikely the carditis cases are related to the vaccine,” he said. And that “plausibly implies a specific underlying mechanism between vaccination and carditis that may only be applicable to mRNA vaccines.”
That inference is in line with case reports and other research, including large population-based studies from Israel and Denmark, although a recent study from the United Kingdom hinted at a potential excess myocarditis risk associated with the adenovirus-based AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
The Hong Kong study identified 160 patients age 12 or older with a first diagnosis of carditis during February to August 2021, in electronic health records covering nearly the entire region.
“We used laboratory test results of troponin levels to further eliminate unlikely cases of carditis,” Dr. Wong said. The health records were linked to a “population-based vaccination record” maintained by the government’s department of health.
About 10 control patients from among all hospitalized patients without carditis were matched by age, sex, and admission date to each of the 160 carditis cases. About 83% of cases and 92% of the controls were unvaccinated.
Among those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, representing 12.5% of cases and 4.2% of controls, the estimated carditis incidence was 0.57 per 100,000 doses. For those who received CoronaVac, representing 4.4% of cases and 3.9% of controls, it was 0.31 per 100,000 doses.
In adjusted analysis, the odds ratios for carditis among Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients, compared with unvaccinated controls, were 3.57 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-6.60) overall, 4.68 (95% CI, 2.25-9.71) for males, 2.22 (95% CI, 0.57-8.69) for females, 2.41 (95% CI, 1.18-4.90) for ages 18 and older, and 13.8 (95% CI, 2.86-110.4) for ages 12-17
Myocarditis accounted for most of the excess cases, with an overall OR of 9.29 (95% CI, 3.94-21.9). The OR reached only 1.06 (95% CI, 0.35-3.22) for pericarditis alone.
The case-control study is noteworthy for its design, which contrasts with the many recent case series and passive or active surveillance studies, and even the more robust population-based studies of vaccine-related myocarditis, observed Dongngan Truong, MD, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, both in Salt Lake City, who wasn’t part of the study.
Among its strengths, she said in an interview, are its linkage of comprehensive hospital and vaccination data sets for two different vaccines; and that it corroborates other research suggesting there is “something in particular about mRNA vaccination that seems to be associated with the development of myocarditis.”
Active surveillance in Israel
In an October 2021 report based on an Israeli Ministry of Health database covering up to May 2021, rates of myocarditis arising within 21 days of a second Pfizer-BioNTech dose in 16- to 19-year-olds reached about 1 per 6,637 males and 1 per 99,853 females. Those numbers compared with 1 per 26,000 males and 1 per 218,000 females across all age groups.
Now authors led by Dror Mevorach, MD, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, have published corresponding numbers from the same data base for myocarditis associated with the same vaccine in males and females aged 12-15.
Their research covers 404,407 people in that age group who received a first dose of the mRNA-based vaccine and 326,463 who received the second dose from June to October, 2021. Only 18 cases of myocarditis were observed within 21 days of either dose.
The estimated rates for males were 0.56 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 8.09 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
For females, the estimates were 0 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 0.69 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
“The pattern observed, mainly following the second vaccination in males, suggests causality,” the group wrote.
Leveraging passive surveillance reports
Another new report adds a twist to updated numbers from the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Prevalences derived from the passive-surveillance data base, known for including case records of inconsistent quality or completeness, are considered especially prone to reporting bias, the authors acknowledged.
The current analysis, however, plunges deep into VAERS-reported cases of presumed SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated myocarditis to help clarify “more of the characteristics of the patients and some of the treatments and short-term outcomes,” Matthew E. Oster, MD, MPH, said in an interview.
Dr. Oster, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Emory University, Atlanta, is lead author on the study’s Jan. 25, 2022, publication in JAMA.
The group reviewed charts and interviewed involved clinicians to adjudicate and document presentations, therapies, and the clinical course of cases reported as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–associated myocarditis from December 2020 to August 2021. Out of the nearly 2000 reports, which were limited to patients younger than 30, the group identified 1,626 likely cases of such myocarditis arising within 7 days of a second mRNA vaccine dose.
The confirmed cases consistently represented higher prevalences than expected compared with prepandemic myocarditis claims data for both sexes and across age groups spanning 12-29 years.
For example, rates were highest for adolescent males – about 106 and 71 cases per million second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in those aged 16-17 and 12-16, respectively, for example. They were lowest for women aged 25-29, at 2.23 cases per million second Pfizer-BioNTech doses; the highest rate among females was about 11 per million for the 16-17 age group.
The observed rates, Dr. Oster said, represent an update to VAERS numbers published June 2021 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report covering cases through June 2021.
“Overall, the general risk of having myocarditis from the vaccines is still extremely low. Even in the highest risk groups, it is still extremely low, and still lower than the risk of having cardiac complications from COVID,” he noted.
How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.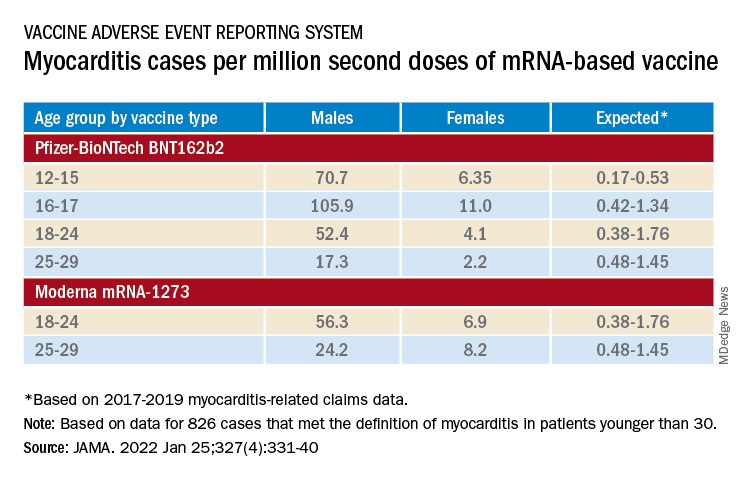
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why some COVID-19 vaccines seem occasionally to cause a distinctive form of myocarditis, and why adolescent boys and young men appear most vulnerable, remain a mystery. But the entity’s prevalence, nuances of presentation, and likely clinical course have come into sharper view after recent additions to the literature.
Two new publications all but confirm that the rare cases of myocarditis closely following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, primarily with one of the mRNA-based vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, is a clinically different creature from myocarditis physicians were likely to see before the pandemic.
A third report unveils rates of hospitalization for myocarditis linked to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in the 12- to 15-year age group, based on active surveillance across Israel. Of note, the rates were lower than corresponding numbers among the country’s 16- to 19-year-olds published in late 2021 by the same authors.
No link with CoronaVac
A case-control study covering almost the entire population of Hong Kong from February to August 2021 confirms a slight but significant excess risk for myocarditis and, to a lesser degree, pericarditis, after injections of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. As consistently reported from other studies, the risks were highest in adolescent and young adult males and after a second dose.
The study estimated an overall carditis incidence of 5.7 cases per million doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, for a risk 3.5 times that in the unvaccinated Hong Kong population. Carditis rates after a first dose were about 2.5 per million and 10 per million after a second dose.
Hong Kong launched its public SARS-CoV-2 immunization program in late February 2021 with the Chinese-made CoronaVac (Sinovac) inactivated-virus vaccine, and introduced the mRNA-based alternative several weeks later. By August 2021, the vaccines had reached about 3.3 million people in the region – 49% of the Hong Kong population at least 12 years of age.
In a novel finding, there were no excesses in carditis cases after CoronaVac vaccination. The difference between vaccines likely isn’t caused by chance, because three-fourths of the carditis-associated Pfizer-BioNTech injections arose within a week, whereas “71% of cases following the use of CoronaVac occurred more than 30 days after vaccination,” senior author Ian Chi Kei Wong, PhD, University of Hong Kong, said in an interview.
“This onset distribution for cases having received CoronaVac demonstrates that it is highly unlikely the carditis cases are related to the vaccine,” he said. And that “plausibly implies a specific underlying mechanism between vaccination and carditis that may only be applicable to mRNA vaccines.”
That inference is in line with case reports and other research, including large population-based studies from Israel and Denmark, although a recent study from the United Kingdom hinted at a potential excess myocarditis risk associated with the adenovirus-based AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
The Hong Kong study identified 160 patients age 12 or older with a first diagnosis of carditis during February to August 2021, in electronic health records covering nearly the entire region.
“We used laboratory test results of troponin levels to further eliminate unlikely cases of carditis,” Dr. Wong said. The health records were linked to a “population-based vaccination record” maintained by the government’s department of health.
About 10 control patients from among all hospitalized patients without carditis were matched by age, sex, and admission date to each of the 160 carditis cases. About 83% of cases and 92% of the controls were unvaccinated.
Among those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, representing 12.5% of cases and 4.2% of controls, the estimated carditis incidence was 0.57 per 100,000 doses. For those who received CoronaVac, representing 4.4% of cases and 3.9% of controls, it was 0.31 per 100,000 doses.
In adjusted analysis, the odds ratios for carditis among Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients, compared with unvaccinated controls, were 3.57 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-6.60) overall, 4.68 (95% CI, 2.25-9.71) for males, 2.22 (95% CI, 0.57-8.69) for females, 2.41 (95% CI, 1.18-4.90) for ages 18 and older, and 13.8 (95% CI, 2.86-110.4) for ages 12-17
Myocarditis accounted for most of the excess cases, with an overall OR of 9.29 (95% CI, 3.94-21.9). The OR reached only 1.06 (95% CI, 0.35-3.22) for pericarditis alone.
The case-control study is noteworthy for its design, which contrasts with the many recent case series and passive or active surveillance studies, and even the more robust population-based studies of vaccine-related myocarditis, observed Dongngan Truong, MD, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, both in Salt Lake City, who wasn’t part of the study.
Among its strengths, she said in an interview, are its linkage of comprehensive hospital and vaccination data sets for two different vaccines; and that it corroborates other research suggesting there is “something in particular about mRNA vaccination that seems to be associated with the development of myocarditis.”
Active surveillance in Israel
In an October 2021 report based on an Israeli Ministry of Health database covering up to May 2021, rates of myocarditis arising within 21 days of a second Pfizer-BioNTech dose in 16- to 19-year-olds reached about 1 per 6,637 males and 1 per 99,853 females. Those numbers compared with 1 per 26,000 males and 1 per 218,000 females across all age groups.
Now authors led by Dror Mevorach, MD, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, have published corresponding numbers from the same data base for myocarditis associated with the same vaccine in males and females aged 12-15.
Their research covers 404,407 people in that age group who received a first dose of the mRNA-based vaccine and 326,463 who received the second dose from June to October, 2021. Only 18 cases of myocarditis were observed within 21 days of either dose.
The estimated rates for males were 0.56 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 8.09 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
For females, the estimates were 0 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 0.69 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
“The pattern observed, mainly following the second vaccination in males, suggests causality,” the group wrote.
Leveraging passive surveillance reports
Another new report adds a twist to updated numbers from the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Prevalences derived from the passive-surveillance data base, known for including case records of inconsistent quality or completeness, are considered especially prone to reporting bias, the authors acknowledged.
The current analysis, however, plunges deep into VAERS-reported cases of presumed SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated myocarditis to help clarify “more of the characteristics of the patients and some of the treatments and short-term outcomes,” Matthew E. Oster, MD, MPH, said in an interview.
Dr. Oster, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Emory University, Atlanta, is lead author on the study’s Jan. 25, 2022, publication in JAMA.
The group reviewed charts and interviewed involved clinicians to adjudicate and document presentations, therapies, and the clinical course of cases reported as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–associated myocarditis from December 2020 to August 2021. Out of the nearly 2000 reports, which were limited to patients younger than 30, the group identified 1,626 likely cases of such myocarditis arising within 7 days of a second mRNA vaccine dose.
The confirmed cases consistently represented higher prevalences than expected compared with prepandemic myocarditis claims data for both sexes and across age groups spanning 12-29 years.
For example, rates were highest for adolescent males – about 106 and 71 cases per million second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in those aged 16-17 and 12-16, respectively, for example. They were lowest for women aged 25-29, at 2.23 cases per million second Pfizer-BioNTech doses; the highest rate among females was about 11 per million for the 16-17 age group.
The observed rates, Dr. Oster said, represent an update to VAERS numbers published June 2021 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report covering cases through June 2021.
“Overall, the general risk of having myocarditis from the vaccines is still extremely low. Even in the highest risk groups, it is still extremely low, and still lower than the risk of having cardiac complications from COVID,” he noted.
How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Why some COVID-19 vaccines seem occasionally to cause a distinctive form of myocarditis, and why adolescent boys and young men appear most vulnerable, remain a mystery. But the entity’s prevalence, nuances of presentation, and likely clinical course have come into sharper view after recent additions to the literature.
Two new publications all but confirm that the rare cases of myocarditis closely following vaccination against SARS-CoV-2, primarily with one of the mRNA-based vaccines from Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna, is a clinically different creature from myocarditis physicians were likely to see before the pandemic.
A third report unveils rates of hospitalization for myocarditis linked to Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in the 12- to 15-year age group, based on active surveillance across Israel. Of note, the rates were lower than corresponding numbers among the country’s 16- to 19-year-olds published in late 2021 by the same authors.
No link with CoronaVac
A case-control study covering almost the entire population of Hong Kong from February to August 2021 confirms a slight but significant excess risk for myocarditis and, to a lesser degree, pericarditis, after injections of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine. As consistently reported from other studies, the risks were highest in adolescent and young adult males and after a second dose.
The study estimated an overall carditis incidence of 5.7 cases per million doses of Pfizer-BioNTech, for a risk 3.5 times that in the unvaccinated Hong Kong population. Carditis rates after a first dose were about 2.5 per million and 10 per million after a second dose.
Hong Kong launched its public SARS-CoV-2 immunization program in late February 2021 with the Chinese-made CoronaVac (Sinovac) inactivated-virus vaccine, and introduced the mRNA-based alternative several weeks later. By August 2021, the vaccines had reached about 3.3 million people in the region – 49% of the Hong Kong population at least 12 years of age.
In a novel finding, there were no excesses in carditis cases after CoronaVac vaccination. The difference between vaccines likely isn’t caused by chance, because three-fourths of the carditis-associated Pfizer-BioNTech injections arose within a week, whereas “71% of cases following the use of CoronaVac occurred more than 30 days after vaccination,” senior author Ian Chi Kei Wong, PhD, University of Hong Kong, said in an interview.
“This onset distribution for cases having received CoronaVac demonstrates that it is highly unlikely the carditis cases are related to the vaccine,” he said. And that “plausibly implies a specific underlying mechanism between vaccination and carditis that may only be applicable to mRNA vaccines.”
That inference is in line with case reports and other research, including large population-based studies from Israel and Denmark, although a recent study from the United Kingdom hinted at a potential excess myocarditis risk associated with the adenovirus-based AstraZeneca-Oxford vaccine.
The Hong Kong study identified 160 patients age 12 or older with a first diagnosis of carditis during February to August 2021, in electronic health records covering nearly the entire region.
“We used laboratory test results of troponin levels to further eliminate unlikely cases of carditis,” Dr. Wong said. The health records were linked to a “population-based vaccination record” maintained by the government’s department of health.
About 10 control patients from among all hospitalized patients without carditis were matched by age, sex, and admission date to each of the 160 carditis cases. About 83% of cases and 92% of the controls were unvaccinated.
Among those who received the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, representing 12.5% of cases and 4.2% of controls, the estimated carditis incidence was 0.57 per 100,000 doses. For those who received CoronaVac, representing 4.4% of cases and 3.9% of controls, it was 0.31 per 100,000 doses.
In adjusted analysis, the odds ratios for carditis among Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine recipients, compared with unvaccinated controls, were 3.57 (95% confidence interval, 1.93-6.60) overall, 4.68 (95% CI, 2.25-9.71) for males, 2.22 (95% CI, 0.57-8.69) for females, 2.41 (95% CI, 1.18-4.90) for ages 18 and older, and 13.8 (95% CI, 2.86-110.4) for ages 12-17
Myocarditis accounted for most of the excess cases, with an overall OR of 9.29 (95% CI, 3.94-21.9). The OR reached only 1.06 (95% CI, 0.35-3.22) for pericarditis alone.
The case-control study is noteworthy for its design, which contrasts with the many recent case series and passive or active surveillance studies, and even the more robust population-based studies of vaccine-related myocarditis, observed Dongngan Truong, MD, University of Utah and Primary Children’s Hospital, both in Salt Lake City, who wasn’t part of the study.
Among its strengths, she said in an interview, are its linkage of comprehensive hospital and vaccination data sets for two different vaccines; and that it corroborates other research suggesting there is “something in particular about mRNA vaccination that seems to be associated with the development of myocarditis.”
Active surveillance in Israel
In an October 2021 report based on an Israeli Ministry of Health database covering up to May 2021, rates of myocarditis arising within 21 days of a second Pfizer-BioNTech dose in 16- to 19-year-olds reached about 1 per 6,637 males and 1 per 99,853 females. Those numbers compared with 1 per 26,000 males and 1 per 218,000 females across all age groups.
Now authors led by Dror Mevorach, MD, Hadassah Medical Center, Jerusalem, have published corresponding numbers from the same data base for myocarditis associated with the same vaccine in males and females aged 12-15.
Their research covers 404,407 people in that age group who received a first dose of the mRNA-based vaccine and 326,463 who received the second dose from June to October, 2021. Only 18 cases of myocarditis were observed within 21 days of either dose.
The estimated rates for males were 0.56 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 8.09 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
For females, the estimates were 0 cases per 100,000 after a first dose and 0.69 cases per 100,000 after a second dose.
“The pattern observed, mainly following the second vaccination in males, suggests causality,” the group wrote.
Leveraging passive surveillance reports
Another new report adds a twist to updated numbers from the U.S. Vaccine Adverse Event Reporting System (VAERS).
Prevalences derived from the passive-surveillance data base, known for including case records of inconsistent quality or completeness, are considered especially prone to reporting bias, the authors acknowledged.
The current analysis, however, plunges deep into VAERS-reported cases of presumed SARS-CoV-2 vaccine-associated myocarditis to help clarify “more of the characteristics of the patients and some of the treatments and short-term outcomes,” Matthew E. Oster, MD, MPH, said in an interview.
Dr. Oster, from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention and Emory University, Atlanta, is lead author on the study’s Jan. 25, 2022, publication in JAMA.
The group reviewed charts and interviewed involved clinicians to adjudicate and document presentations, therapies, and the clinical course of cases reported as SARS-CoV-2 vaccine–associated myocarditis from December 2020 to August 2021. Out of the nearly 2000 reports, which were limited to patients younger than 30, the group identified 1,626 likely cases of such myocarditis arising within 7 days of a second mRNA vaccine dose.
The confirmed cases consistently represented higher prevalences than expected compared with prepandemic myocarditis claims data for both sexes and across age groups spanning 12-29 years.
For example, rates were highest for adolescent males – about 106 and 71 cases per million second doses of the Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine in those aged 16-17 and 12-16, respectively, for example. They were lowest for women aged 25-29, at 2.23 cases per million second Pfizer-BioNTech doses; the highest rate among females was about 11 per million for the 16-17 age group.
The observed rates, Dr. Oster said, represent an update to VAERS numbers published June 2021 in Morbidity and Mortality Weekly Report covering cases through June 2021.
“Overall, the general risk of having myocarditis from the vaccines is still extremely low. Even in the highest risk groups, it is still extremely low, and still lower than the risk of having cardiac complications from COVID,” he noted.
How do patients fare clinically?
From their chart reviews and interviews with case clinicians, Dr. Oster said, “we started to learn quickly that this is really a different type of myocarditis.”
For example, its onset, typically within a few days of the potential immunologic cause, was more rapid than in viral myocarditis, and its symptoms resolved faster, the report notes. Clinical presentations tended to be less severe, treatments not as intensive, and outcomes not as serious, compared with “the kind of typical viral myocarditis that most of the providers were used to taking care of in the past,” he said. “The pattern for these cases was very consistent.”
The study covered VAERS reports of suspected myocarditis arising within a week of first dose of a mRNA-based vaccine from the United States launch of public vaccination in December 2020 to August 2021, the CDC-based group reported. By then, more than 192 million people in the country had received either the Pfizer-BioNTech (age 12 or older) or Moderna (age 18 or older) vaccines.
Of the 1,991 reports of myocarditis, including 391 also involving pericarditis, 1,626 met the study’s definition for myocarditis on adjudication; about 82% of the latter cases were in males.
Based on the investigators’ review of charts and clinician interviews connected with 826 cases that met their definition of myocarditis in patients younger than 30, 89% reported “chest pain, pressure, or discomfort” and 30% reported dyspnea or shortness of breath. Troponin levels were elevated in 98%, 72% of patients who underwent electrocardiography showed abnormalities, and 12% of those with echocardiography had left ventricular ejection fractions less than 50%.
About 96% were hospitalized, and presenting symptoms resolved by discharge in 87% of those with available data, the group noted. Among patients with data on in-hospital therapy, they wrote, NSAIDs were the most common therapy, in 87%.
‘Mild and self-limiting’
The case-control study from Hong Kong didn’t specifically examine patients’ treatment and clinical course, but it does portray their vaccine-associated myocarditis as contrasting with more familiar viral myocarditis.
Patients with “typical” myocarditis tend to be “overall much sicker than what we’re seeing with myocarditis following vaccination,” Dr. Truong agreed. None of the 20 patients with myocarditis after Pfizer-BioNTech vaccination in Hong Kong were admitted to the intensive care unit. That, she added, suggests none required extracorporeal membrane oxygenation or vasoactive support, often necessary in viral myocarditis. “And they had shorter hospital stays.”
In contrast, Dr. Wong noted, 14 of the study’s unvaccinated patients required ICU admission; 12 of them died during the follow-up period. None with vaccine-related carditis died during the study’s follow-up. “We also showed that cases following [Pfizer-BioNTech] vaccination were all mild and self-limiting.”
Dr. Truong largely agreed that SARS-CoV-2 vaccine myocarditis and most myocarditis seen before the pandemic can be viewed as distinct clinical entities, “at least in the short term. I think we do need to follow these patients to look at more long-term outcomes, because at this point I don’t think we know the long-term implications. But at least in the short term, it seems like these patients are different, are much less sick, and recover pretty quickly overall.”
Dr. Oster emphasized that the many and varied acute and long-term hazards from contracting COVID-19 far outweigh any risk for myocarditis from vaccination. But for individuals who were hit with myocarditis soon after their first mRNA vaccine dose, who have already established their susceptibility, he and his colleagues would recommend that they “consider alternatives and not get the vaccine again.”
Dr. Oster reported no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Wong and colleagues did not report any relevant disclosures. Dr. Truong has previously disclosed serving as a consultant to Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Get free masks at grocery stores and pharmacies starting Jan. 28
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The first batches are expected to arrive in some stores on Jan. 27, and many locations will begin offering them to customers on Jan. 28, according to NPR.
Meijer, which operates more than 250 groceries and pharmacies throughout the Midwest, has received about 3 million masks. Customers can pick up masks from the greeter stand at the store entrance.
More than 2,200 Kroger stores with pharmacies will give out free masks, with the first shipment expected to arrive on Jan. 27, a spokeswoman told NPR.
Walgreens will likely begin offering masks in some stores on Jan. 28, which will continue “on a rolling basis in the days and weeks following,” a spokesman told NPR.
Masks should arrive by Jan. 28 at Southeastern Grocers locations with in-store pharmacies, including Fresco y Mas, Harveys, and Winn-Dixie, according to CNN.
Hy-Vee received and began giving out masks on Jan. 21, and most stores with pharmacies were giving them out Jan. 26, according to Today.
CVS Pharmacy locations will offer free masks as early as Jan. 27, a spokesman told Today. That will include CVS Pharmacy locations inside Target and Schnucks.
Albertsons is “currently working to finalize details regarding inventory and distribution,” the chain told Today.
Rite Aid will have free masks in some stores at the end of the week, with all stores receiving them by early February, Today reported.
Walmart and Sam’s Club will offer free masks late next week at the earliest, according to NBC Chicago.
The Biden administration is sending out 400 million N95 masks from the Strategic National Stockpile. Each person can take up to three free masks, if they’re available, the Department of Health and Human Services has said.
The distribution of masks is meant to align with the CDC’s latest recommendation to wear an N95 or KN95 mask to prevent the spread of the highly transmissible Omicron variant. When worn correctly over the mouth and nose, the high-filtration masks are made to filter out 95% or more of airborne particles.
The Biden administration is also sending masks to community health centers and COVID-19 test kits directly to Americans. The programs are ramping up now and should be fully running by early February, NPR reported.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Another winter for our discontent
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
Here we are. Again. It’s cold and it’s gray. The sun rises late and sets early, so that it feels like midnight by 8 p.m. Indoor venues are risky with the highly contagious Omicron variant, and I feel like we are all pushing the replay button on 2021’s miserable winter.
In some ways, it’s worse: In 2021 we had the hope that vaccines would pull us out of the pandemic and we had guidance on all that we should not be doing. In January, we were gaming the various Internet sites to get a coveted vaccine for ourselves or our family and friends, then lining up to get jabbed. We did not yet know that it wouldn’t be enough – that we’d need boosters, that Delta and Omicron would defy the vaccines. Yes, the vaccines work miracles to prevent severe disease and death, but the worry of passing the virus to someone who is vulnerable or unvaccinated(!), or both, remains – and now we can wonder how we’ll ever get out of this mess with hopeful talk of an endemic, while we wait on the next variant. I like certainty, and this pandemic is one big screaming reminder that certainty about anything is just a pleasant notion, death and taxes excluded, of course.
Kris Lukish, vice president of human resources at Johns Hopkins Hospital in Baltimore, started an update to the hospital employees with: “As we begin 2022, it feels like we are experiencing dejà vu, or ‘Groundhog Day,’ or ‘50 First Dates.’ In ‘50 First Dates,’ Drew Barrymore wakes up each day reliving one specific day. It never changes. I realize our world may seem a little like that right now. We thought we’d turned a corner with COVID, and instead we saw a rapid rise in cases and hospitalizations due to the Omicron variant, higher than in previous surges.”
In 2021, many of us skipped holiday travel and ate outdoors. My morning coffee group moved to Zoom and it wasn’t until late spring, when community rates of COVID nose-dived, that I began seeing patients in my office for the first time in over a year. Since many of my patients are over 60, I tested myself with a home antigen test before going into the office. I changed my schedule so sessions began on the half-hour to be sure the suite’s waiting room would be empty, and I purchased an air purifier, cracked the window open, and figured everyone was as safe as we could reasonably be.
By the first Monday in January 2022, the positivity rate in Maryland was just shy of 30%. Twitter circulated anecdotes about false negatives with the home antigen test kits, and I decided it was safest to return to all-virtual appointments.
Mona Masood, DO, is cofounder of the Physician Support Line, a call-in service for doctors that started in March 2020. She has noted a change in the problems physicians face.
“We’re seeing a lot of empathy fatigue,” Dr. Masood said. “It’s not unexpected with a prolonged situation like this – the trauma has doctors in survival mode and they need to be present for themselves, their families, and their patients. People are emotionally drained, and we’re stretching them to the limit. Now at the front lines, doctors are getting a lot of backlash. There are the conspiracy theories, and people who challenge their knowledge and training and it leads them to ask if they should be doing this work. and these are large decisions that are being made in a specific context.
“The other thing we’re hearing is from trainees – residents and fellows – who are expected to carry a lot of work on the COVID units. Some are being told that they can’t graduate because they haven’t finished their other training requirements. This type of systemic issue produces moral injury.”
Dr. Masood talked about what running the support line has been like for her. “I know people want to give more in a catastrophe, and I was realistic that the enthusiasm might die off. I would go as long as psychiatrists volunteer, and the most incredible thing is that it hasn’t stopped. Some of the original people are no longer with us, but others have come aboard, and it’s been incredible to be a part of this.”
In her Jan. 26, 2022, newsletter, epidemiologist Katelyn Jetelina, PhD, MPH, tried to be reassuring about the future. “In order to know how this will end, we need to look at how other pandemics ended,” Dr. Jetelina wrote. “First, recognize the last part of that sentence ... pandemics end. Every epi curve comes down. This pandemic will end, too. Hold that fact close to you.”
She wrote about the three ways that pandemics end. The SARS pandemic of 2002 lasted 1.5 years as public health measures were effective, in large part because the disease was spread only by symptomatic patients. Vaccines offer a second way to end pandemics, as they have for polio and smallpox. “If the globe works together, we could possibly eradicate SARS-CoV-2 with vaccines. [Now that we have numerous animal reservoirs, though, this is close to impossible.]”
Finally, Dr. Jetelina noted that the 1918 flu changed from a pandemic situation to being endemic. “Over time, the virus attenuated, it became less severe.” Society acclimates to a virus with a low mortality rate. “The vast majority of scientists think an endemic state is the future of SARS-CoV-2. I agree.” And she goes on to define endemic as a steady state, but not the absence of suffering. She likens it to malaria and tuberculosis, illnesses with high global mortality.
“An endemic will come without an announcement or headlines, we won’t know we’re there until well after we’ve arrived.” She wrote of the uncertainty that faces us moving forward: We don’t know how much, or how long, immunity from Omicron infections will last, or if future variants will cause more or less severe disease. She casted her vote for global vaccinations, boosters, masks, better ventilation, communication, empathy, and tolerance to end the pandemic.
In Maryland, hospitalizations and positivity are starting to decline from the postholiday surge. I have figured out that I am not good at predicting what will happen next, and the experts don’t seem to be much better. I’d like a headline ending, the kind we looked to be heading toward last June.
I’ve told my patients who want to come in person that I will reassess in March. We have written our own rules, and mine are somewhere in the middle – I don’t go to public indoor spaces unmasked, but I do see vaccinated family and friends in our homes without masks. I don’t want to be responsible for transmitting a potentially fatal illness to a vulnerable patient. Honestly, this makes no sense, but since there is a video option, I feel I should not risk passing a potentially lethal virus to my patients. I just hope I’m not writing this same article again in January 2023.
Dr. Miller is a coauthor of “Committed: The Battle Over Involuntary Psychiatric Care” (Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press, 2016). She has a private practice and is assistant professor of psychiatry and behavioral sciences at Johns Hopkins. Dr. Miller has no conflicts of interest.
We’re dying to tell you about fatigability
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
Are you tired? Or are you death tired?
When we’re feeling that burnout monster creep in we sometimes say that we’re being worked to death or that we’re dead tired, but what if that feeling could predict when it’s your actual time to go?
In a recent study published in the Journals of Gerontology: Series A, epidemiologists from the University of Pittsburgh were able to associate a level of “physical fatigability” with mortality.
The researchers administered the Pittsburgh Fatigability Scale to almost 3,000 participants aged ≥ 60 years, who ranked from 0 to 5 on how tired they thought they would be after doing activities like light housework or a leisurely 30-minute walk. After accounting for factors such as preexisting conditions and mental health, the researchers found that people who scored 25 or more points were 2.3 times more likely to die in the next 2.7 years, compared with those who scored under 25.
So what does that tell us about the importance of being continuously active? It’s pretty important.
“Previous research indicates that getting more physical activity can reduce a person’s fatigability. Our study is the first to link more severe physical fatigability to an earlier death,” lead author Nancy W. Glynn, PhD, said in a separate statement. The best way to keep physically active, she suggested, is to set manageable goals and a routine.
A nice walk around the neighborhood during golden hour or a little bit of yoga before breakfast could be a great way to keep the body moving, because you know what they say: Use it or lose it.
This work is NFT protected: Do not screenshot
If you’ve been following the nonmedical news, you’ve likely heard the term “NFT” explode in the past few months. Standing for nonfungible token, NFTs are, at least theoretically, a proof of ownership for digital creations that prevents anyone other than the buyer from reselling the artwork. Sounds like a great idea: It protects artists and buyers alike.
Much like its cousin cryptocurrency, however, the NFT world is rife with speculation, scams, misunderstanding, and drawings of bored monkeys. It’s the Wild West out there in the digital art universe: One poor unfortunate accidentally sold a $300k NFT image for $3,000, a group of investors spent $3 million buying an NFT for a rare version of Dune believing it gave them the copyright (it did not), and an Indonesian engineering student’s 5-year series of expressionless selfies is now worth a million dollars.
This is a column detailing weird medical news, however, so with our setup complete (though our understanding of NFTs is very much not), we move to France and meet our hero (?), Emmanuel Masmejean, an orthopedic surgeon who apparently wasn’t making enough money in his lucrative medical career.
In a move of apocalyptic madness, he threw ethics out the window, delved into his archive, and found an x-ray of a young woman with a bullet lodged in her arm. The woman was a survivor of the Bataclan mass shooting and bombing in 2015, and don’t you worry, our intrepid entrepreneur made sure to identify her as such when he tried selling the x-ray as an NFT on an online art website for $2,776. Yes, this is very much a violation of doctor-patient confidentiality, and no, that’s not a lot of money to risk your medical career on.
Naturally, the woman was horrified and shocked to learn that the image was being sold, her lawyer told the Guardian. When the doctor called her, he merely attempted to justify his action, rather than apologizing or showing any remorse. Dr. Masmejean is now facing legal action and a disciplinary charge for his attempted entry into the NFT world for publishing the image without permission, and the NFT has been removed from the website. Should have stuck with the bored monkeys.
Avatars could be the future
Zoom, FaceTime, and Skype are great when people can’t be together in the same room, state, or country. Not the same as being somewhere in person, but a pretty good replacement during a global pandemic. But what if you had a robot that could be present for you?
Seven-year-old Joshua Martinangeli of Berlin has a severe lung disease and needs to wear a tube in his neck, so he cannot attend school. A robot avatar, donated to Joshua through a private initiative, sits in his seat in the classroom and is able to interact with the students and teacher, according to Reuters. A light on the avatar blinks when Joshua wants to speak and the children can talk with him too. Joshua and his classmates agree that it’s not the same as him really being there to talk and learn, but it’s a great way to keep him included.
“We are the only district in Berlin that has bought four avatars for its schools. The impetus was COVID-19, but I think this will be the future well beyond the pandemic,” Torsten Kuehne, district education councilor, told Reuters.
So where do we get an avatar to go out and run errands? Can we send it to the office instead of Zooming the next meeting? Or maybe our avatar could go to the gym for us. But how do we get the results to show up on our bodies? C’mon science, figure this out.
Futility, thy name is Kiribati
Before we get to the rest of our regularly scheduled hilarity, a brief geography lesson is in order: Kiribati is an island nation – actually 32 atolls and one coral island – in the central Pacific Ocean. Those atolls are spread out across 1.4 million square miles around the intersection of the equator and the International Date Line, so Kiribati is the only country in the world located in all four hemispheres.
Now, back to the news.
Kiribati closed its borders early in the COVID-19 pandemic and recorded only two cases in almost 2 years. Things were going so well that the authorities recently decided to reopen the country to international travelers. Silly authorities.
The first plane was set to arrive on Jan. 14 from Fiji. This being the age of COVID, plans were made and precautions were taken. All 54 passengers quarantined for 2 weeks before the flight and underwent regular testing, the Guardian noted, and “they were only allowed on the flight after returning negative tests.”
You guessed it. Two-thirds of those 54 people tested positive for COVID-19 after landing in Kiribati.
All of the passengers were quarantined, but since then a security guard at the quarantine center has tested positive, as has someone who was not involved in the quarantine. According to NPR, the government said that “there is now an assumption that COVID-19 is now spreading in the community on South Tarawa and Betio.”
Moral of the story? You can’t beat COVID, so never try.
[EDITOR: Is that really the message we want to send to our readers?]
If you can’t beat them, join them.
[EDITOR: Nope. Try again.]
Resistance is futile?
[EDITOR: Sigh. Close enough.]
35% of employers to proceed with vaccine mandate, poll shows
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
despite a recent U.S. Supreme Court ruling that blocked the Biden administration’s vaccine-or-test rule for big businesses.
But the poll by Gartner Inc. showed no consensus among employers. About 4% of polled executives said they’re dropping their vaccine mandate, 29% are in a wait-and-see position, and 12% are less likely to impose a mandate now, Bloomberg reported.
Executives were divided on how a vaccine mandate would affect absenteeism and employee morale. Almost 40% of polled employers said they thought a mandate would attract workers, but about 25% said it would do the opposite, Bloomberg said.
“What is more attractive -- to have a mandate or not?” Brian Kropp, PhD, Gartner’s chief of human resources research, said in an interview with Bloomberg. “Most are not exactly sure what to do.”
Big companies have reacted differently since the court’s ruling.
Starbucks announced it was dropping its vaccine-or-test rule for the company’s approximately 228,000 employees. General Electric dropped its mandate after the ruling, but Honeywell International Inc. announced it was staying with its vaccination policy, Bloomberg said.
The Supreme Court ruled Jan. 13 against the Biden administration’s mandate for businesses. The Occupational Safety and Health Administration had proposed that every company with more than 100 employees would be required to ensure workers were either vaccinated or tested weekly for COVID-19.
State governments and business groups immediately appealed, and the court ruled 6-3 against the mandate. The Biden administration officially dropped its rule on Wednesday.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.