User login
Bringing you the latest news, research and reviews, exclusive interviews, podcasts, quizzes, and more.
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
California will make low-cost insulin, Gov. Newsom says
On July 7, he said he had just signed a state budget that includes $50 million for development of the insulin and another $50 million for a place to make it.
“Nothing, nothing epitomizes market failures more than the cost of insulin,” Gov. Newsom said in a video posted on the governor’s Twitter page. He noted that many Americans have out-of-pocket costs ranging from $300 to $500 per month for insulin, which is used to treat diabetes.
“In California, we know people should not go into debt to receive lifesaving medication,” he said.
Gov. Newsom said that when he first took office, he signed an executive order to launch California’s own prescription drug system and that the insulin initiative is the first step toward making that happen.
People who take insulin have long complained about its high price. A November 2021 report from The Lancet said 25% of the insulin patients in the United States struggle to pay for it.
The cost of insulin for patients with insurance ranges from $334 to $1,000 a month, ABC News said, citing the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Legislation in Congress would bring down the cost of insulin if passed, with one bill capping costs at $35 per month for patients with health insurance. But The Hill reported that some Republicans oppose the legislation because it would interfere with free markets and raise costs for drug companies.
The CDC says 37.3 million people in the United States – about 11.3% of the population – have diabetes, with 8.5 million of them undiagnosed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
On July 7, he said he had just signed a state budget that includes $50 million for development of the insulin and another $50 million for a place to make it.
“Nothing, nothing epitomizes market failures more than the cost of insulin,” Gov. Newsom said in a video posted on the governor’s Twitter page. He noted that many Americans have out-of-pocket costs ranging from $300 to $500 per month for insulin, which is used to treat diabetes.
“In California, we know people should not go into debt to receive lifesaving medication,” he said.
Gov. Newsom said that when he first took office, he signed an executive order to launch California’s own prescription drug system and that the insulin initiative is the first step toward making that happen.
People who take insulin have long complained about its high price. A November 2021 report from The Lancet said 25% of the insulin patients in the United States struggle to pay for it.
The cost of insulin for patients with insurance ranges from $334 to $1,000 a month, ABC News said, citing the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Legislation in Congress would bring down the cost of insulin if passed, with one bill capping costs at $35 per month for patients with health insurance. But The Hill reported that some Republicans oppose the legislation because it would interfere with free markets and raise costs for drug companies.
The CDC says 37.3 million people in the United States – about 11.3% of the population – have diabetes, with 8.5 million of them undiagnosed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
On July 7, he said he had just signed a state budget that includes $50 million for development of the insulin and another $50 million for a place to make it.
“Nothing, nothing epitomizes market failures more than the cost of insulin,” Gov. Newsom said in a video posted on the governor’s Twitter page. He noted that many Americans have out-of-pocket costs ranging from $300 to $500 per month for insulin, which is used to treat diabetes.
“In California, we know people should not go into debt to receive lifesaving medication,” he said.
Gov. Newsom said that when he first took office, he signed an executive order to launch California’s own prescription drug system and that the insulin initiative is the first step toward making that happen.
People who take insulin have long complained about its high price. A November 2021 report from The Lancet said 25% of the insulin patients in the United States struggle to pay for it.
The cost of insulin for patients with insurance ranges from $334 to $1,000 a month, ABC News said, citing the Kaiser Family Foundation.
Legislation in Congress would bring down the cost of insulin if passed, with one bill capping costs at $35 per month for patients with health insurance. But The Hill reported that some Republicans oppose the legislation because it would interfere with free markets and raise costs for drug companies.
The CDC says 37.3 million people in the United States – about 11.3% of the population – have diabetes, with 8.5 million of them undiagnosed.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Docs reveal perils of giving medical advice to friends and family
Stephen Pribut, DPM, a sports medicine podiatrist based in Washington, has had many friends or family members ask him for medical advice. It’s a scenario every doctor will face at one point or another in their careers, and it’s never an easy one.
Dr. Pribut received a call from a friend about a sore shoulder from swimming, saying that his doctor had dismissed the potential for a rotator cuff injury. “Months later, images revealed it was a rotator cuff tear and he wanted my advice,” says Dr. Pribut.
Not being a shoulder specialist, Dr. Pribut limited his input. “I told him to consider a good physical therapist or a shoulder specialist and gave him some alternative strokes for swimming that hopefully wouldn’t aggravate the injury,” he explains.
But he admits some situations are challenging. “I had a relative asking about a third party with an ankle injury. I advised he hold off on using a balance board until things healed, and to make sure he went to see a specialist. Unfortunately, he went to his general practitioner who likely knows nothing about ankle anatomy,” says Dr. Pribut.
“I finally saw a photo, which revealed swelling higher up on the ankle and no evidence of a hematoma – much lower than we would see in an ankle ligament injury. I would like him to see a sports podiatrist or foot and ankle orthopedist, but now I have to stay calm when the advice isn’t followed,” he says.
When asked, “Do you give medical advice to your friends?” 96% of respondents answered yes.
Yazan Abou-Ismail, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of hematology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, has often faced questions from friends and family, particularly throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. “How you respond is something all physicians need to analyze carefully,” he says. “I get questions on a regular basis, but this greatly increased with COVID.”
“Sharing general information is okay, and it’s even a requirement that we educate on such topics,” says Dr. Abou-Ismail. “But if someone knows they have COVID, for instance, and wants advice on how to proceed, it’s important to send them to their primary care physician for an evaluation rather than give them instructions on care.”
Dr. Abou-Ismail says that most “curbside consulting” equates to lack of an ethical follow-up. “If you gave medical advice without having assessed them, you’re lacking the medical history, a physical exam, and you should not be giving advice,” he says. “This applies to follow-ups, too.”
Throughout the pandemic, Dr. Abou-Ismail’s requests for advice on COVID even extended to online inquiries, often from strangers. “This is not a place to do a formal assessment,” he reminds. “But there are certain types of advice you can offer appropriately.”
Dr. Abou-Ismail considers safe advice to be simple public health messages that stay far out of specifics. Things like “don’t smoke,” or “eat a healthy diet,” and “get enough sleep,” fall into this safety zone. Even, “What is XYZ disease?” or “How do COVID vaccines work?” are topics he says he answers comfortably.
“But telling someone you need a specific treatment for a condition is inappropriate,” he explains. “This is a general way of practicing medicine – your advice should never venture into the potential of doing harm.”
This approach is exactly in line with legal advice, according to Jeff Caesar Chukwuma, founder and senior partner at Chukwuma Law Group, Miami. “It doesn’t mean that doctors should never give medical advice to friends or family, but if they do, they should make sure to take several precautions to protect both themselves and their family and friends,” he says.
When the request for medical advice from an acquaintance migrates into areas in which a physician is not a specialist, sharing recommendations gets even trickier – and more ethically questionable.
Says Mr. Chukwuma, “Doctors should avoid giving advice in areas outside their area of expertise to lower the possibility of providing erroneous or harmful information,” he says.
How to stay safe when asked for advice
The American Medical Association has weighed in on the topic. In the Code of Medical Ethics Opinion 1.2.1, the AMA states that, “Treating oneself or a member of one’s own family poses several challenges for physicians, including concerns about professional objectivity, patient autonomy, and informed consent.”
What about friends or acquaintances, however?
Even so, some respondents voiced their concerns with the scenario. Responses like, “Due to ethics, I would prefer they go and get first, second, and third opinions,” and “Usually the medical advice is very basic first aid (often mental health first aid), and if it’s anything remotely more complicated, I direct them to the appropriate provider.”
The AMA places advising friends in the same basket as advising and treating family members or oneself. In an article appearing in the AMA Journal of Ethics, Horacio Hojman, MD, of Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, weighed in: “First and foremost, patients deserve objectivity from their doctors. When a physician is emotionally involved with a patient, that physician’s objectivity can be called into question.”
Why is medical advice so thorny when dealing with friends or relatives?
In some cases, a physician might not ask a friend relevant personal questions about his or her medical history, for instance. Or the friend might not want to share details with the doctor. In either case, the lack of information exchange can lead to improper advice.
The issue of giving medical advice to friends, family, and acquaintances can also wade into legal territory. “Personally or professionally, trust is the decisive factor that puts us at ease with the people we surround ourselves with,” says Mr. Chukwuma. “Nowhere is this truer than in medicine, where we approach doctors with some of the most sensitive matters in our lives and entrust our care to them, especially when the physician in question is a close friend or family member.”
Mr. Chukwuma points out that, while there are few strict legal prohibitions against doctors providing care or advice to family and friends, the AMA’s code of ethics states that such action should be reserved for rare situations, such as emergency settings or isolated settings where there is no other qualified physician available, or for minor, not long-term problems.
This was part of the equation for Dr. Pribut when helping his mother navigate her treatment for breast cancer. “With close relatives, offering advice and help can be very hard,” he says.
“This is to protect both patients and doctors,” says Mr. Chukwuma. “Although seeking advice from a family member or friend who is a doctor may be more convenient for a patient, they run the risk of receiving inadequate care by not going in for a formal medical visit complete with tests, medical examination, and follow-up care.”
Mr. Chukwuma offers guidance on how to share medical advice ethically and legally with family, friends, and acquaintances. “First, as much as possible, speak to general medical facts and knowledge rather than comment directly on the patient’s particular situation,” he says. “In the absence of thorough examination and tests, the doctor’s knowledge of a patient’s condition is limited, therefore, you should take care not to provide seemingly definitive answers on that patient’s unique condition in situations where they can’t rely on data to back up their advice and recommendations.”
The AMA’s Journal of Ethics article shares these tips for staying on the right side of the ethical line when dealing with friends and family members:
- Politely decline.
- Offer other forms of assistance – this might help a friend find the right qualified physician – as Dr. Pribut tends to do. Maybe help in navigating the sometimes-confusing health care system.
- Don’t hesitate in an emergency – the old “is there a doctor on board,” scenario on a plane when someone is in distress is a perfectly acceptable, and recommended, time to step in, even if it is a friend or family member.
Dr. Pribut, a long-time veteran of the tricky medical waters involving friends and family, has this to offer: “Be cautious and always stay in the realm of what you know,” he says. “Always encourage people to seek an opinion from a qualified doctor. Help them find a reputable doctor if that’s useful.”
Mr. Chukwuma adds also that doctors should stand firm when pushed by a friend or family member, especially when offering advice, even if it’s in the form of general education. “The doctor should make it clear to the family member or friend that their advice in no way takes the place of actual treatment or examination by a medical professional and that, if need be, the patient should seek formal medical help from another doctor, ideally one not related to or friends with the patient,” he says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stephen Pribut, DPM, a sports medicine podiatrist based in Washington, has had many friends or family members ask him for medical advice. It’s a scenario every doctor will face at one point or another in their careers, and it’s never an easy one.
Dr. Pribut received a call from a friend about a sore shoulder from swimming, saying that his doctor had dismissed the potential for a rotator cuff injury. “Months later, images revealed it was a rotator cuff tear and he wanted my advice,” says Dr. Pribut.
Not being a shoulder specialist, Dr. Pribut limited his input. “I told him to consider a good physical therapist or a shoulder specialist and gave him some alternative strokes for swimming that hopefully wouldn’t aggravate the injury,” he explains.
But he admits some situations are challenging. “I had a relative asking about a third party with an ankle injury. I advised he hold off on using a balance board until things healed, and to make sure he went to see a specialist. Unfortunately, he went to his general practitioner who likely knows nothing about ankle anatomy,” says Dr. Pribut.
“I finally saw a photo, which revealed swelling higher up on the ankle and no evidence of a hematoma – much lower than we would see in an ankle ligament injury. I would like him to see a sports podiatrist or foot and ankle orthopedist, but now I have to stay calm when the advice isn’t followed,” he says.
When asked, “Do you give medical advice to your friends?” 96% of respondents answered yes.
Yazan Abou-Ismail, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of hematology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, has often faced questions from friends and family, particularly throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. “How you respond is something all physicians need to analyze carefully,” he says. “I get questions on a regular basis, but this greatly increased with COVID.”
“Sharing general information is okay, and it’s even a requirement that we educate on such topics,” says Dr. Abou-Ismail. “But if someone knows they have COVID, for instance, and wants advice on how to proceed, it’s important to send them to their primary care physician for an evaluation rather than give them instructions on care.”
Dr. Abou-Ismail says that most “curbside consulting” equates to lack of an ethical follow-up. “If you gave medical advice without having assessed them, you’re lacking the medical history, a physical exam, and you should not be giving advice,” he says. “This applies to follow-ups, too.”
Throughout the pandemic, Dr. Abou-Ismail’s requests for advice on COVID even extended to online inquiries, often from strangers. “This is not a place to do a formal assessment,” he reminds. “But there are certain types of advice you can offer appropriately.”
Dr. Abou-Ismail considers safe advice to be simple public health messages that stay far out of specifics. Things like “don’t smoke,” or “eat a healthy diet,” and “get enough sleep,” fall into this safety zone. Even, “What is XYZ disease?” or “How do COVID vaccines work?” are topics he says he answers comfortably.
“But telling someone you need a specific treatment for a condition is inappropriate,” he explains. “This is a general way of practicing medicine – your advice should never venture into the potential of doing harm.”
This approach is exactly in line with legal advice, according to Jeff Caesar Chukwuma, founder and senior partner at Chukwuma Law Group, Miami. “It doesn’t mean that doctors should never give medical advice to friends or family, but if they do, they should make sure to take several precautions to protect both themselves and their family and friends,” he says.
When the request for medical advice from an acquaintance migrates into areas in which a physician is not a specialist, sharing recommendations gets even trickier – and more ethically questionable.
Says Mr. Chukwuma, “Doctors should avoid giving advice in areas outside their area of expertise to lower the possibility of providing erroneous or harmful information,” he says.
How to stay safe when asked for advice
The American Medical Association has weighed in on the topic. In the Code of Medical Ethics Opinion 1.2.1, the AMA states that, “Treating oneself or a member of one’s own family poses several challenges for physicians, including concerns about professional objectivity, patient autonomy, and informed consent.”
What about friends or acquaintances, however?
Even so, some respondents voiced their concerns with the scenario. Responses like, “Due to ethics, I would prefer they go and get first, second, and third opinions,” and “Usually the medical advice is very basic first aid (often mental health first aid), and if it’s anything remotely more complicated, I direct them to the appropriate provider.”
The AMA places advising friends in the same basket as advising and treating family members or oneself. In an article appearing in the AMA Journal of Ethics, Horacio Hojman, MD, of Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, weighed in: “First and foremost, patients deserve objectivity from their doctors. When a physician is emotionally involved with a patient, that physician’s objectivity can be called into question.”
Why is medical advice so thorny when dealing with friends or relatives?
In some cases, a physician might not ask a friend relevant personal questions about his or her medical history, for instance. Or the friend might not want to share details with the doctor. In either case, the lack of information exchange can lead to improper advice.
The issue of giving medical advice to friends, family, and acquaintances can also wade into legal territory. “Personally or professionally, trust is the decisive factor that puts us at ease with the people we surround ourselves with,” says Mr. Chukwuma. “Nowhere is this truer than in medicine, where we approach doctors with some of the most sensitive matters in our lives and entrust our care to them, especially when the physician in question is a close friend or family member.”
Mr. Chukwuma points out that, while there are few strict legal prohibitions against doctors providing care or advice to family and friends, the AMA’s code of ethics states that such action should be reserved for rare situations, such as emergency settings or isolated settings where there is no other qualified physician available, or for minor, not long-term problems.
This was part of the equation for Dr. Pribut when helping his mother navigate her treatment for breast cancer. “With close relatives, offering advice and help can be very hard,” he says.
“This is to protect both patients and doctors,” says Mr. Chukwuma. “Although seeking advice from a family member or friend who is a doctor may be more convenient for a patient, they run the risk of receiving inadequate care by not going in for a formal medical visit complete with tests, medical examination, and follow-up care.”
Mr. Chukwuma offers guidance on how to share medical advice ethically and legally with family, friends, and acquaintances. “First, as much as possible, speak to general medical facts and knowledge rather than comment directly on the patient’s particular situation,” he says. “In the absence of thorough examination and tests, the doctor’s knowledge of a patient’s condition is limited, therefore, you should take care not to provide seemingly definitive answers on that patient’s unique condition in situations where they can’t rely on data to back up their advice and recommendations.”
The AMA’s Journal of Ethics article shares these tips for staying on the right side of the ethical line when dealing with friends and family members:
- Politely decline.
- Offer other forms of assistance – this might help a friend find the right qualified physician – as Dr. Pribut tends to do. Maybe help in navigating the sometimes-confusing health care system.
- Don’t hesitate in an emergency – the old “is there a doctor on board,” scenario on a plane when someone is in distress is a perfectly acceptable, and recommended, time to step in, even if it is a friend or family member.
Dr. Pribut, a long-time veteran of the tricky medical waters involving friends and family, has this to offer: “Be cautious and always stay in the realm of what you know,” he says. “Always encourage people to seek an opinion from a qualified doctor. Help them find a reputable doctor if that’s useful.”
Mr. Chukwuma adds also that doctors should stand firm when pushed by a friend or family member, especially when offering advice, even if it’s in the form of general education. “The doctor should make it clear to the family member or friend that their advice in no way takes the place of actual treatment or examination by a medical professional and that, if need be, the patient should seek formal medical help from another doctor, ideally one not related to or friends with the patient,” he says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Stephen Pribut, DPM, a sports medicine podiatrist based in Washington, has had many friends or family members ask him for medical advice. It’s a scenario every doctor will face at one point or another in their careers, and it’s never an easy one.
Dr. Pribut received a call from a friend about a sore shoulder from swimming, saying that his doctor had dismissed the potential for a rotator cuff injury. “Months later, images revealed it was a rotator cuff tear and he wanted my advice,” says Dr. Pribut.
Not being a shoulder specialist, Dr. Pribut limited his input. “I told him to consider a good physical therapist or a shoulder specialist and gave him some alternative strokes for swimming that hopefully wouldn’t aggravate the injury,” he explains.
But he admits some situations are challenging. “I had a relative asking about a third party with an ankle injury. I advised he hold off on using a balance board until things healed, and to make sure he went to see a specialist. Unfortunately, he went to his general practitioner who likely knows nothing about ankle anatomy,” says Dr. Pribut.
“I finally saw a photo, which revealed swelling higher up on the ankle and no evidence of a hematoma – much lower than we would see in an ankle ligament injury. I would like him to see a sports podiatrist or foot and ankle orthopedist, but now I have to stay calm when the advice isn’t followed,” he says.
When asked, “Do you give medical advice to your friends?” 96% of respondents answered yes.
Yazan Abou-Ismail, MD, assistant professor of medicine in the division of hematology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, has often faced questions from friends and family, particularly throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. “How you respond is something all physicians need to analyze carefully,” he says. “I get questions on a regular basis, but this greatly increased with COVID.”
“Sharing general information is okay, and it’s even a requirement that we educate on such topics,” says Dr. Abou-Ismail. “But if someone knows they have COVID, for instance, and wants advice on how to proceed, it’s important to send them to their primary care physician for an evaluation rather than give them instructions on care.”
Dr. Abou-Ismail says that most “curbside consulting” equates to lack of an ethical follow-up. “If you gave medical advice without having assessed them, you’re lacking the medical history, a physical exam, and you should not be giving advice,” he says. “This applies to follow-ups, too.”
Throughout the pandemic, Dr. Abou-Ismail’s requests for advice on COVID even extended to online inquiries, often from strangers. “This is not a place to do a formal assessment,” he reminds. “But there are certain types of advice you can offer appropriately.”
Dr. Abou-Ismail considers safe advice to be simple public health messages that stay far out of specifics. Things like “don’t smoke,” or “eat a healthy diet,” and “get enough sleep,” fall into this safety zone. Even, “What is XYZ disease?” or “How do COVID vaccines work?” are topics he says he answers comfortably.
“But telling someone you need a specific treatment for a condition is inappropriate,” he explains. “This is a general way of practicing medicine – your advice should never venture into the potential of doing harm.”
This approach is exactly in line with legal advice, according to Jeff Caesar Chukwuma, founder and senior partner at Chukwuma Law Group, Miami. “It doesn’t mean that doctors should never give medical advice to friends or family, but if they do, they should make sure to take several precautions to protect both themselves and their family and friends,” he says.
When the request for medical advice from an acquaintance migrates into areas in which a physician is not a specialist, sharing recommendations gets even trickier – and more ethically questionable.
Says Mr. Chukwuma, “Doctors should avoid giving advice in areas outside their area of expertise to lower the possibility of providing erroneous or harmful information,” he says.
How to stay safe when asked for advice
The American Medical Association has weighed in on the topic. In the Code of Medical Ethics Opinion 1.2.1, the AMA states that, “Treating oneself or a member of one’s own family poses several challenges for physicians, including concerns about professional objectivity, patient autonomy, and informed consent.”
What about friends or acquaintances, however?
Even so, some respondents voiced their concerns with the scenario. Responses like, “Due to ethics, I would prefer they go and get first, second, and third opinions,” and “Usually the medical advice is very basic first aid (often mental health first aid), and if it’s anything remotely more complicated, I direct them to the appropriate provider.”
The AMA places advising friends in the same basket as advising and treating family members or oneself. In an article appearing in the AMA Journal of Ethics, Horacio Hojman, MD, of Tufts University School of Medicine, Boston, weighed in: “First and foremost, patients deserve objectivity from their doctors. When a physician is emotionally involved with a patient, that physician’s objectivity can be called into question.”
Why is medical advice so thorny when dealing with friends or relatives?
In some cases, a physician might not ask a friend relevant personal questions about his or her medical history, for instance. Or the friend might not want to share details with the doctor. In either case, the lack of information exchange can lead to improper advice.
The issue of giving medical advice to friends, family, and acquaintances can also wade into legal territory. “Personally or professionally, trust is the decisive factor that puts us at ease with the people we surround ourselves with,” says Mr. Chukwuma. “Nowhere is this truer than in medicine, where we approach doctors with some of the most sensitive matters in our lives and entrust our care to them, especially when the physician in question is a close friend or family member.”
Mr. Chukwuma points out that, while there are few strict legal prohibitions against doctors providing care or advice to family and friends, the AMA’s code of ethics states that such action should be reserved for rare situations, such as emergency settings or isolated settings where there is no other qualified physician available, or for minor, not long-term problems.
This was part of the equation for Dr. Pribut when helping his mother navigate her treatment for breast cancer. “With close relatives, offering advice and help can be very hard,” he says.
“This is to protect both patients and doctors,” says Mr. Chukwuma. “Although seeking advice from a family member or friend who is a doctor may be more convenient for a patient, they run the risk of receiving inadequate care by not going in for a formal medical visit complete with tests, medical examination, and follow-up care.”
Mr. Chukwuma offers guidance on how to share medical advice ethically and legally with family, friends, and acquaintances. “First, as much as possible, speak to general medical facts and knowledge rather than comment directly on the patient’s particular situation,” he says. “In the absence of thorough examination and tests, the doctor’s knowledge of a patient’s condition is limited, therefore, you should take care not to provide seemingly definitive answers on that patient’s unique condition in situations where they can’t rely on data to back up their advice and recommendations.”
The AMA’s Journal of Ethics article shares these tips for staying on the right side of the ethical line when dealing with friends and family members:
- Politely decline.
- Offer other forms of assistance – this might help a friend find the right qualified physician – as Dr. Pribut tends to do. Maybe help in navigating the sometimes-confusing health care system.
- Don’t hesitate in an emergency – the old “is there a doctor on board,” scenario on a plane when someone is in distress is a perfectly acceptable, and recommended, time to step in, even if it is a friend or family member.
Dr. Pribut, a long-time veteran of the tricky medical waters involving friends and family, has this to offer: “Be cautious and always stay in the realm of what you know,” he says. “Always encourage people to seek an opinion from a qualified doctor. Help them find a reputable doctor if that’s useful.”
Mr. Chukwuma adds also that doctors should stand firm when pushed by a friend or family member, especially when offering advice, even if it’s in the form of general education. “The doctor should make it clear to the family member or friend that their advice in no way takes the place of actual treatment or examination by a medical professional and that, if need be, the patient should seek formal medical help from another doctor, ideally one not related to or friends with the patient,” he says.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Transgender youth on hormone therapy risk substantial bone loss
, and this is true regardless of gender assignment at birth.
The problem worsens as the time during which these patients receive sex steroid hormones increases. So far, the “bone mineral density effects of these therapies are understudied,” warned Natalie Nokoff, MD, who presented a cross-sectional study at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The study of bone density is part of a larger body of research being conducted by Dr. Nokoff and her co-investigators on the long-term health effects of gender-affirming therapy in children and adolescents. In one of several recent studies, transgender youths taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which effectively block puberty, were shown to be at greater risk of adverse changes in body composition and markers of cardiometabolic health than youths who were not taking them.
“We need more information on the optimal length of treatment with puberty-delaying medications before either discontinuation or introduction of gender-affirming hormones,” said Dr. Nokoff, an assistant professor of pediatrics and endocrinology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
In this study, 56 transgender youth underwent total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The patients ranged in age from 10 years to almost 20 years. Just over half (53%) were assigned female sex at birth.
The mean Z scores, signifying deviation from age-matched norms, were lower regardless of current use or past use of GnRH agonists in both transgender males or transgender females, relative to age-matched norms.
Asked to comment, Michele A. O’Connell, MBBCh, department of endocrinology and diabetes, Royal Children’s Hospital, Victoria, Australia, said the risk of bone loss is real.
“Monitoring of bone health is recommended for all transgender-diverse adolescents treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists,” said Dr. O’Connell. He referred to multiple guidelines, including those issued by the World Professional Association of Transgender Health in 2012 and those from the Endocrine Society that were issued in 2017.
Inverse correlation between duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores
In Dr. Nokoff’s study, for transgender males, the BMD Z score was reduced 0.2 relative to male norms and by 0.4 relative to female norms. For transgender females, the scores were reduced by 0.4 relative to male norms and by 0.2 relative to female norms.
Among transgender males who were taking testosterone and who had previously been exposed to GnRH agonists, the Z score was significantly lower than those taking testosterone alone (P = .004). There were no differences in Z score for transgender females taking estradiol alone relative to estradiol with current or past use of GnRH agonists.
There was a significant inverse correlation for duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores for transgender females relative to male norms (P = .005) or female norms (P = .029). However, Z scores were unrelated to length of time receiving testosterone or estradiol therapy or to sex steroid concentrations.
The number of children and adolescents taking puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies is increasing. Although reliable data are limited, the exploration of gender identify appears to have become more common with the growing social acceptance of gender dysphoria. That term refers to a sense of unease among individuals who feel that their biological sex does not match their gender identity, according to Dr. Nokoff.
“It is now estimated that 2% of youths identify as transgender,” she said.
Findings from studies investigating the relationship between gender-affirming therapy and bone loss among adults have not been consistent. In a single-center study that followed 543 transgender men and 711 transgender women who had undergone DEXA scanning at baseline prior to starting hormone therapy, there did not appear to be any substantial negative effects on lumbar bone density over time (J Bone Min Res. 2018 Dec;34:447-54).
For adolescents, there is growing evidence of the risk of bone loss in relation to gender-affirming therapy, but there is limited agreement on clinical risks and how they can be avoided. Relevant variables include genetics and diet, as well as the types, doses, and length of time receiving gender-affirming therapy.
Monitor bone in transgender youth; Use vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise
Dr. O’Connell is the first author of a recent summary of the pharmacologic management of trans and gender-diverse adolescents. That summary covered multiple topics in addition to risk of bone loss, including the impact on growth, cognition, and mental health (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;107:241-257).
Overall, she believes that bone health should be monitored for children receiving puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies but agrees with Dr. Nokoff that the clinical impact remains poorly defined.
“Long-term follow-up studies will be required to assess the impact, if any, on functional outcomes such as fracture risk,” she reported. Still, she encouraged use of standard ways of improving bone health, including adequate vitamin D intake and weight-bearing exercise.
Dr. Nokoff and Dr. O’Connell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, and this is true regardless of gender assignment at birth.
The problem worsens as the time during which these patients receive sex steroid hormones increases. So far, the “bone mineral density effects of these therapies are understudied,” warned Natalie Nokoff, MD, who presented a cross-sectional study at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The study of bone density is part of a larger body of research being conducted by Dr. Nokoff and her co-investigators on the long-term health effects of gender-affirming therapy in children and adolescents. In one of several recent studies, transgender youths taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which effectively block puberty, were shown to be at greater risk of adverse changes in body composition and markers of cardiometabolic health than youths who were not taking them.
“We need more information on the optimal length of treatment with puberty-delaying medications before either discontinuation or introduction of gender-affirming hormones,” said Dr. Nokoff, an assistant professor of pediatrics and endocrinology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
In this study, 56 transgender youth underwent total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The patients ranged in age from 10 years to almost 20 years. Just over half (53%) were assigned female sex at birth.
The mean Z scores, signifying deviation from age-matched norms, were lower regardless of current use or past use of GnRH agonists in both transgender males or transgender females, relative to age-matched norms.
Asked to comment, Michele A. O’Connell, MBBCh, department of endocrinology and diabetes, Royal Children’s Hospital, Victoria, Australia, said the risk of bone loss is real.
“Monitoring of bone health is recommended for all transgender-diverse adolescents treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists,” said Dr. O’Connell. He referred to multiple guidelines, including those issued by the World Professional Association of Transgender Health in 2012 and those from the Endocrine Society that were issued in 2017.
Inverse correlation between duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores
In Dr. Nokoff’s study, for transgender males, the BMD Z score was reduced 0.2 relative to male norms and by 0.4 relative to female norms. For transgender females, the scores were reduced by 0.4 relative to male norms and by 0.2 relative to female norms.
Among transgender males who were taking testosterone and who had previously been exposed to GnRH agonists, the Z score was significantly lower than those taking testosterone alone (P = .004). There were no differences in Z score for transgender females taking estradiol alone relative to estradiol with current or past use of GnRH agonists.
There was a significant inverse correlation for duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores for transgender females relative to male norms (P = .005) or female norms (P = .029). However, Z scores were unrelated to length of time receiving testosterone or estradiol therapy or to sex steroid concentrations.
The number of children and adolescents taking puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies is increasing. Although reliable data are limited, the exploration of gender identify appears to have become more common with the growing social acceptance of gender dysphoria. That term refers to a sense of unease among individuals who feel that their biological sex does not match their gender identity, according to Dr. Nokoff.
“It is now estimated that 2% of youths identify as transgender,” she said.
Findings from studies investigating the relationship between gender-affirming therapy and bone loss among adults have not been consistent. In a single-center study that followed 543 transgender men and 711 transgender women who had undergone DEXA scanning at baseline prior to starting hormone therapy, there did not appear to be any substantial negative effects on lumbar bone density over time (J Bone Min Res. 2018 Dec;34:447-54).
For adolescents, there is growing evidence of the risk of bone loss in relation to gender-affirming therapy, but there is limited agreement on clinical risks and how they can be avoided. Relevant variables include genetics and diet, as well as the types, doses, and length of time receiving gender-affirming therapy.
Monitor bone in transgender youth; Use vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise
Dr. O’Connell is the first author of a recent summary of the pharmacologic management of trans and gender-diverse adolescents. That summary covered multiple topics in addition to risk of bone loss, including the impact on growth, cognition, and mental health (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;107:241-257).
Overall, she believes that bone health should be monitored for children receiving puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies but agrees with Dr. Nokoff that the clinical impact remains poorly defined.
“Long-term follow-up studies will be required to assess the impact, if any, on functional outcomes such as fracture risk,” she reported. Still, she encouraged use of standard ways of improving bone health, including adequate vitamin D intake and weight-bearing exercise.
Dr. Nokoff and Dr. O’Connell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, and this is true regardless of gender assignment at birth.
The problem worsens as the time during which these patients receive sex steroid hormones increases. So far, the “bone mineral density effects of these therapies are understudied,” warned Natalie Nokoff, MD, who presented a cross-sectional study at the annual meeting of the Endocrine Society.
The study of bone density is part of a larger body of research being conducted by Dr. Nokoff and her co-investigators on the long-term health effects of gender-affirming therapy in children and adolescents. In one of several recent studies, transgender youths taking gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) agonists, which effectively block puberty, were shown to be at greater risk of adverse changes in body composition and markers of cardiometabolic health than youths who were not taking them.
“We need more information on the optimal length of treatment with puberty-delaying medications before either discontinuation or introduction of gender-affirming hormones,” said Dr. Nokoff, an assistant professor of pediatrics and endocrinology at the University of Colorado School of Medicine, Aurora.
In this study, 56 transgender youth underwent total body dual-energy x-ray absorptiometry (DEXA). The patients ranged in age from 10 years to almost 20 years. Just over half (53%) were assigned female sex at birth.
The mean Z scores, signifying deviation from age-matched norms, were lower regardless of current use or past use of GnRH agonists in both transgender males or transgender females, relative to age-matched norms.
Asked to comment, Michele A. O’Connell, MBBCh, department of endocrinology and diabetes, Royal Children’s Hospital, Victoria, Australia, said the risk of bone loss is real.
“Monitoring of bone health is recommended for all transgender-diverse adolescents treated with gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists,” said Dr. O’Connell. He referred to multiple guidelines, including those issued by the World Professional Association of Transgender Health in 2012 and those from the Endocrine Society that were issued in 2017.
Inverse correlation between duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores
In Dr. Nokoff’s study, for transgender males, the BMD Z score was reduced 0.2 relative to male norms and by 0.4 relative to female norms. For transgender females, the scores were reduced by 0.4 relative to male norms and by 0.2 relative to female norms.
Among transgender males who were taking testosterone and who had previously been exposed to GnRH agonists, the Z score was significantly lower than those taking testosterone alone (P = .004). There were no differences in Z score for transgender females taking estradiol alone relative to estradiol with current or past use of GnRH agonists.
There was a significant inverse correlation for duration of GnRH agonist therapy and Z scores for transgender females relative to male norms (P = .005) or female norms (P = .029). However, Z scores were unrelated to length of time receiving testosterone or estradiol therapy or to sex steroid concentrations.
The number of children and adolescents taking puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies is increasing. Although reliable data are limited, the exploration of gender identify appears to have become more common with the growing social acceptance of gender dysphoria. That term refers to a sense of unease among individuals who feel that their biological sex does not match their gender identity, according to Dr. Nokoff.
“It is now estimated that 2% of youths identify as transgender,” she said.
Findings from studies investigating the relationship between gender-affirming therapy and bone loss among adults have not been consistent. In a single-center study that followed 543 transgender men and 711 transgender women who had undergone DEXA scanning at baseline prior to starting hormone therapy, there did not appear to be any substantial negative effects on lumbar bone density over time (J Bone Min Res. 2018 Dec;34:447-54).
For adolescents, there is growing evidence of the risk of bone loss in relation to gender-affirming therapy, but there is limited agreement on clinical risks and how they can be avoided. Relevant variables include genetics and diet, as well as the types, doses, and length of time receiving gender-affirming therapy.
Monitor bone in transgender youth; Use vitamin D and weight-bearing exercise
Dr. O’Connell is the first author of a recent summary of the pharmacologic management of trans and gender-diverse adolescents. That summary covered multiple topics in addition to risk of bone loss, including the impact on growth, cognition, and mental health (J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2022 Jan;107:241-257).
Overall, she believes that bone health should be monitored for children receiving puberty-delaying or gender-affirming therapies but agrees with Dr. Nokoff that the clinical impact remains poorly defined.
“Long-term follow-up studies will be required to assess the impact, if any, on functional outcomes such as fracture risk,” she reported. Still, she encouraged use of standard ways of improving bone health, including adequate vitamin D intake and weight-bearing exercise.
Dr. Nokoff and Dr. O’Connell have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ENDO 2022
WHO tracking new Omicron subvariant in India
The subvariant, a sublineage of BA.2 being called BA.2.75, has been reported in eight countries and hasn’t yet been declared a variant of concern.
“There’s been an emergence of a ‘could be’ subvariant. It’s been not yet officially called, but some people are referring to it as BA.2.75,” Soumya Swaminathan, MD, the WHO’s chief scientist, said in a video posted on Twitter.
The subvariant appears to have mutations similar to other contagious strains, she said, though there are a limited number of sequences available to analyze. How transmissible and severe it is, and how well it can evade our immunity, aren’t yet known.
“We have to wait and see, and of course, we are tracking it,” Dr. Swaminathan said.
The WHO committee responsible for analyzing global coronavirus data will label the subvariant officially and release more information as the situation warrants it, she said.
Public health experts around the world are also talking about the subvariant, which has been nicknamed Centaurus. BA.2.75 was first found in India in May and is now competing with BA.5, which has become dominant in the United States.
BA.2.75 has eight mutations beyond those seen in BA.5, which “could make immune escape worse than what we’re seeing now,” Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief at Medscape, wrote in a Twitter post.
Individually, the extra mutations aren’t too concerning, “but all appearing together at once is another matter,” Tom Peacock, PhD, a virologist at Imperial College London, wrote in a Twitter post.
The “apparent rapid growth and wide geographical spread” are “worth keeping a close eye on,” he said.
BA.2.75 has been found in a handful of cases in the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. In India, the sequence accounts for about 23% of recent samples.
“It is really too early to know if BA.2.75 will take over relative to BA.2 or even relative to BA.5,” Ulrich Elling, PhD, a researcher at Australia’s Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, wrote in a Twitter post.
“Just to emphasize it again: While the distribution across Indian regions as well as internationally and the very rapid appearance makes it likely we are dealing with a variant spreading fast and spread widely already, the absolute data points are few,” he said.
Globally, coronavirus cases have increased nearly 30% during the past 2 weeks, the WHO said July 6. Four out of six of the WHO subregions reported an increase in the last week, with BA.4 and BA.5 driving waves in the United States and Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The subvariant, a sublineage of BA.2 being called BA.2.75, has been reported in eight countries and hasn’t yet been declared a variant of concern.
“There’s been an emergence of a ‘could be’ subvariant. It’s been not yet officially called, but some people are referring to it as BA.2.75,” Soumya Swaminathan, MD, the WHO’s chief scientist, said in a video posted on Twitter.
The subvariant appears to have mutations similar to other contagious strains, she said, though there are a limited number of sequences available to analyze. How transmissible and severe it is, and how well it can evade our immunity, aren’t yet known.
“We have to wait and see, and of course, we are tracking it,” Dr. Swaminathan said.
The WHO committee responsible for analyzing global coronavirus data will label the subvariant officially and release more information as the situation warrants it, she said.
Public health experts around the world are also talking about the subvariant, which has been nicknamed Centaurus. BA.2.75 was first found in India in May and is now competing with BA.5, which has become dominant in the United States.
BA.2.75 has eight mutations beyond those seen in BA.5, which “could make immune escape worse than what we’re seeing now,” Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief at Medscape, wrote in a Twitter post.
Individually, the extra mutations aren’t too concerning, “but all appearing together at once is another matter,” Tom Peacock, PhD, a virologist at Imperial College London, wrote in a Twitter post.
The “apparent rapid growth and wide geographical spread” are “worth keeping a close eye on,” he said.
BA.2.75 has been found in a handful of cases in the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. In India, the sequence accounts for about 23% of recent samples.
“It is really too early to know if BA.2.75 will take over relative to BA.2 or even relative to BA.5,” Ulrich Elling, PhD, a researcher at Australia’s Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, wrote in a Twitter post.
“Just to emphasize it again: While the distribution across Indian regions as well as internationally and the very rapid appearance makes it likely we are dealing with a variant spreading fast and spread widely already, the absolute data points are few,” he said.
Globally, coronavirus cases have increased nearly 30% during the past 2 weeks, the WHO said July 6. Four out of six of the WHO subregions reported an increase in the last week, with BA.4 and BA.5 driving waves in the United States and Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The subvariant, a sublineage of BA.2 being called BA.2.75, has been reported in eight countries and hasn’t yet been declared a variant of concern.
“There’s been an emergence of a ‘could be’ subvariant. It’s been not yet officially called, but some people are referring to it as BA.2.75,” Soumya Swaminathan, MD, the WHO’s chief scientist, said in a video posted on Twitter.
The subvariant appears to have mutations similar to other contagious strains, she said, though there are a limited number of sequences available to analyze. How transmissible and severe it is, and how well it can evade our immunity, aren’t yet known.
“We have to wait and see, and of course, we are tracking it,” Dr. Swaminathan said.
The WHO committee responsible for analyzing global coronavirus data will label the subvariant officially and release more information as the situation warrants it, she said.
Public health experts around the world are also talking about the subvariant, which has been nicknamed Centaurus. BA.2.75 was first found in India in May and is now competing with BA.5, which has become dominant in the United States.
BA.2.75 has eight mutations beyond those seen in BA.5, which “could make immune escape worse than what we’re seeing now,” Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief at Medscape, wrote in a Twitter post.
Individually, the extra mutations aren’t too concerning, “but all appearing together at once is another matter,” Tom Peacock, PhD, a virologist at Imperial College London, wrote in a Twitter post.
The “apparent rapid growth and wide geographical spread” are “worth keeping a close eye on,” he said.
BA.2.75 has been found in a handful of cases in the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. In India, the sequence accounts for about 23% of recent samples.
“It is really too early to know if BA.2.75 will take over relative to BA.2 or even relative to BA.5,” Ulrich Elling, PhD, a researcher at Australia’s Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, wrote in a Twitter post.
“Just to emphasize it again: While the distribution across Indian regions as well as internationally and the very rapid appearance makes it likely we are dealing with a variant spreading fast and spread widely already, the absolute data points are few,” he said.
Globally, coronavirus cases have increased nearly 30% during the past 2 weeks, the WHO said July 6. Four out of six of the WHO subregions reported an increase in the last week, with BA.4 and BA.5 driving waves in the United States and Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Doc releases song after racist massacre in Buffalo
Physician-musician Cleveland Francis, MD, responded to the recent mass shooting in Buffalo, New York, which left 10 dead, in the only way he knew how. He wrote and recorded a song to honor the victims as “a plea to the other side to recognize us as people,” the Black cardiologist told this news organization.
He couldn’t sleep after the shooting, and “this song was just in my head.” In the 1990s, Dr. Francis took a 3-year sabbatical from medicine to perform and tour as a country singer. He leveraged his Nashville connections to get “Buffalo” produced and recorded.
Acclaimed artist James Threalkill created the accompanying art, titled “The Heavenly Escort of the Buffalo 10,” after listening to a scratch demo.
Dr. Francis doesn’t want people to overlook the massacre as just another gun violence incident because this was “overt hate-crime racism,” he said.
According to the affidavit submitted by FBI agent Christopher J. Dlugokinski, the suspect’s “motive for the mass shooting was to prevent Black people from replacing White people and eliminating the White race, and to inspire others to commit similar attacks.”
Dr. Francis views the Buffalo shooting as distinct from cases like the murder of George Floyd that involved crime or police. It immediately made him think of the Mother Emanuel Church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina. “Having a black skin is now a death warrant,” he said.
The song is also an appeal for White people to fight racism. Dr. Francis is concerned about young men caught up in white supremacy and suggests that we be more alert to children or grandchildren who disconnect from their families, spend time on the dark web, and access guns. The lyrics deliberately don’t mention guns because Dr. Francis wanted to stay out of that debate. “I just sang: ‘What else do I have to do to prove to you that I’m human too?’ ”
Despite his country credentials, Dr. Francis wrote “Buffalo” as a Gospel song because that genre “connects with Black people more and because that civil rights movement was through the church with Dr. Martin Luther King,” he explained. Although he sings all styles of music, the song is performed by Nashville-based singer Michael Lusk so that it’s not a “Cleve Francis thing,” he said, referring to his stage name.
Songwriter Norman Kerner collaborated on the song. The music was produced and recorded by David Thein and mixed by Bob Bullock of Nashville, who Dr. Francis had worked with when he was an artist on Capitol Records.
They sent the video and artwork to the Mayor of Buffalo, Byron Brown, but have yet to hear back. Dr. Francis hopes it could be part of their healing, noting that some people used the song in their Juneteenth celebrations.
The Louisiana native grew up during segregation and was one of two Black students in the Medical College of Virginia class of 1973. After completing his cardiology fellowship, no one would hire him, so Dr. Francis set up his own practice in Northern Virginia. He now works at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Alexandria, Va. He remains optimistic about race relations in America and would love a Black pop or Gospel star to record “Buffalo” and bring it to a wider audience.
Dr. Francis is a regular blogger for Medscape. His contribution to country music is recognized in the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. You can find more of his music on YouTube.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician-musician Cleveland Francis, MD, responded to the recent mass shooting in Buffalo, New York, which left 10 dead, in the only way he knew how. He wrote and recorded a song to honor the victims as “a plea to the other side to recognize us as people,” the Black cardiologist told this news organization.
He couldn’t sleep after the shooting, and “this song was just in my head.” In the 1990s, Dr. Francis took a 3-year sabbatical from medicine to perform and tour as a country singer. He leveraged his Nashville connections to get “Buffalo” produced and recorded.
Acclaimed artist James Threalkill created the accompanying art, titled “The Heavenly Escort of the Buffalo 10,” after listening to a scratch demo.
Dr. Francis doesn’t want people to overlook the massacre as just another gun violence incident because this was “overt hate-crime racism,” he said.
According to the affidavit submitted by FBI agent Christopher J. Dlugokinski, the suspect’s “motive for the mass shooting was to prevent Black people from replacing White people and eliminating the White race, and to inspire others to commit similar attacks.”
Dr. Francis views the Buffalo shooting as distinct from cases like the murder of George Floyd that involved crime or police. It immediately made him think of the Mother Emanuel Church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina. “Having a black skin is now a death warrant,” he said.
The song is also an appeal for White people to fight racism. Dr. Francis is concerned about young men caught up in white supremacy and suggests that we be more alert to children or grandchildren who disconnect from their families, spend time on the dark web, and access guns. The lyrics deliberately don’t mention guns because Dr. Francis wanted to stay out of that debate. “I just sang: ‘What else do I have to do to prove to you that I’m human too?’ ”
Despite his country credentials, Dr. Francis wrote “Buffalo” as a Gospel song because that genre “connects with Black people more and because that civil rights movement was through the church with Dr. Martin Luther King,” he explained. Although he sings all styles of music, the song is performed by Nashville-based singer Michael Lusk so that it’s not a “Cleve Francis thing,” he said, referring to his stage name.
Songwriter Norman Kerner collaborated on the song. The music was produced and recorded by David Thein and mixed by Bob Bullock of Nashville, who Dr. Francis had worked with when he was an artist on Capitol Records.
They sent the video and artwork to the Mayor of Buffalo, Byron Brown, but have yet to hear back. Dr. Francis hopes it could be part of their healing, noting that some people used the song in their Juneteenth celebrations.
The Louisiana native grew up during segregation and was one of two Black students in the Medical College of Virginia class of 1973. After completing his cardiology fellowship, no one would hire him, so Dr. Francis set up his own practice in Northern Virginia. He now works at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Alexandria, Va. He remains optimistic about race relations in America and would love a Black pop or Gospel star to record “Buffalo” and bring it to a wider audience.
Dr. Francis is a regular blogger for Medscape. His contribution to country music is recognized in the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. You can find more of his music on YouTube.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician-musician Cleveland Francis, MD, responded to the recent mass shooting in Buffalo, New York, which left 10 dead, in the only way he knew how. He wrote and recorded a song to honor the victims as “a plea to the other side to recognize us as people,” the Black cardiologist told this news organization.
He couldn’t sleep after the shooting, and “this song was just in my head.” In the 1990s, Dr. Francis took a 3-year sabbatical from medicine to perform and tour as a country singer. He leveraged his Nashville connections to get “Buffalo” produced and recorded.
Acclaimed artist James Threalkill created the accompanying art, titled “The Heavenly Escort of the Buffalo 10,” after listening to a scratch demo.
Dr. Francis doesn’t want people to overlook the massacre as just another gun violence incident because this was “overt hate-crime racism,” he said.
According to the affidavit submitted by FBI agent Christopher J. Dlugokinski, the suspect’s “motive for the mass shooting was to prevent Black people from replacing White people and eliminating the White race, and to inspire others to commit similar attacks.”
Dr. Francis views the Buffalo shooting as distinct from cases like the murder of George Floyd that involved crime or police. It immediately made him think of the Mother Emanuel Church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina. “Having a black skin is now a death warrant,” he said.
The song is also an appeal for White people to fight racism. Dr. Francis is concerned about young men caught up in white supremacy and suggests that we be more alert to children or grandchildren who disconnect from their families, spend time on the dark web, and access guns. The lyrics deliberately don’t mention guns because Dr. Francis wanted to stay out of that debate. “I just sang: ‘What else do I have to do to prove to you that I’m human too?’ ”
Despite his country credentials, Dr. Francis wrote “Buffalo” as a Gospel song because that genre “connects with Black people more and because that civil rights movement was through the church with Dr. Martin Luther King,” he explained. Although he sings all styles of music, the song is performed by Nashville-based singer Michael Lusk so that it’s not a “Cleve Francis thing,” he said, referring to his stage name.
Songwriter Norman Kerner collaborated on the song. The music was produced and recorded by David Thein and mixed by Bob Bullock of Nashville, who Dr. Francis had worked with when he was an artist on Capitol Records.
They sent the video and artwork to the Mayor of Buffalo, Byron Brown, but have yet to hear back. Dr. Francis hopes it could be part of their healing, noting that some people used the song in their Juneteenth celebrations.
The Louisiana native grew up during segregation and was one of two Black students in the Medical College of Virginia class of 1973. After completing his cardiology fellowship, no one would hire him, so Dr. Francis set up his own practice in Northern Virginia. He now works at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Alexandria, Va. He remains optimistic about race relations in America and would love a Black pop or Gospel star to record “Buffalo” and bring it to a wider audience.
Dr. Francis is a regular blogger for Medscape. His contribution to country music is recognized in the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. You can find more of his music on YouTube.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
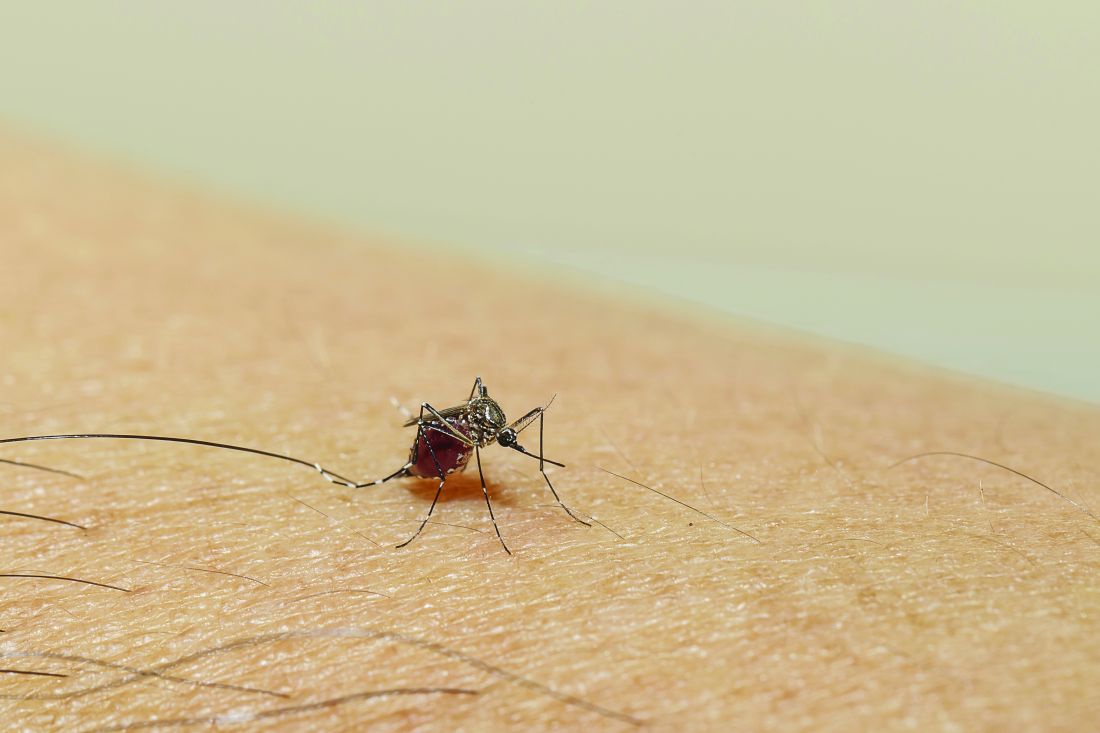
Mosquitoes and the vicious circle that’s gone viral
These viruses want mosquitoes with good taste
Taste can be a pretty subjective sense. Not everyone agrees on what tastes good and what tastes bad. Most people would agree that freshly baked cookies taste good, but what about lima beans? And what about mosquitoes? What tastes good to a mosquito?
The answer? Blood. Blood tastes good to a mosquito. That really wasn’t a very hard question, was it? You did know the answer, didn’t you? They don’t care about cookies, and they certainly don’t care about lima beans. It’s blood that they love.
That brings us back to subjectivity, because it is possible for blood to taste even better. The secret ingredient is dengue … and Zika.
A study just published in Cell demonstrates that mice infected with dengue and Zika viruses release a volatile compound called acetophenone. “We found that flavivirus [like dengue and Zika] can utilize the increased release of acetophenone to help itself achieve its lifecycles more effectively by making their hosts more attractive to mosquito vectors,” senior author Gong Cheng of Tsinghua University, Beijing, said in a written statement.
How do they do it? The viruses, he explained, promote the proliferation of acetophenone-producing skin bacteria. “As a result, some bacteria overreplicate and produce more acetophenone. Suddenly, these sick individuals smell as delicious to mosquitoes as a tray of freshly baked cookies to a group of five-year-old children,” the statement said.
And how do you stop a group of tiny, flying 5-year-olds? That’s right, with acne medication. Really? You knew that one but not the blood one before? The investigators fed isotretinoin to the infected mice, which led to reduced acetophenone release from skin bacteria and made the animals no more attractive to the mosquitoes than their uninfected counterparts.
The investigators are planning to take the next step – feeding isotretinoin to people with dengue and Zika – having gotten the official fictional taste-test approval of celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay, who said, “You’re going to feed this #$^% to sick people? ARE YOU &%*$@#& KIDDING ME?”
Okay, so maybe approval isn’t quite the right word.
Welcome to bladders of the rich and famous!
Don’t you hate it when you’re driving out to your multimillion-dollar second home in the Hamptons and traffic is so bad you absolutely have to find a place to “rest” along the way? But wouldn’t you know it, there just isn’t anywhere to stop! Geez, how do we live?
That’s where David Shusterman, MD, a urologist in New York City and a true American hero, comes in. He’s identified a market and positioned himself as the king of both bladder surgery and “bladder Botox” for the wealthy New Yorkers who regularly make long journeys from the city out to their second homes in the Hamptons. Traffic has increased dramatically on Long Island roads in recent years, and the journey can now taking upward of 4 hours. Some people just can’t make it that long without a bathroom break, and there are very few places to stop along the way.
Dr. Shusterman understands the plight of the Hamptons vacationer, as he told Insider.com: “I can’t tell you how many arguments I personally get into – I’ve lost three friends because I’m the driver and refuse to stop for them.” A tragedy worthy of Shakespeare himself.
During the summer season, Dr. Shusterman performs about 10 prostate artery embolizations a week, an hour-long procedure that shrinks the prostate, which is great for 50- to 60-year-old men with enlarged prostates that cause more frequent bathroom trips. He also performs Botox injections into the bladder once or twice a week for women, which reduces the need to urinate for roughly 6 months. The perfect amount of time to get them through the summer season.
These procedures are sometimes covered by insurance but can cost as much as $20,000 if paid out of pocket. That’s a lot of money to us, but if you’re the sort of person who has a second home in the Hamptons, $20,000 is chump change, especially if it means you won’t have to go 2 entire minutes out of your way to use a gas-station bathroom. Then again, having seen a more than a few gas-station bathrooms in our time, maybe they have a point.
Ditch the apples. Go for the avocados
We’ve all heard about “an apple a day,” but instead of apples you might want to go with avocados.
Avocados are generally thought to be a healthy fat. A study just published in the Journal of the American Heart Association proves that they actually don’t do anything for your waistline but will work wonders on your cholesterol level. The study involved 923 participants who were considered overweight/obese split into two groups: One was asked to consume an avocado a day, and the other continued their usual diets and were asked to consume fewer than two avocados a month.
At the end of the 6 months, the researchers found total cholesterol decreased by an additional 2.9 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by 2.5 mg/dL in those who ate one avocado every day, compared with the usual-diet group. And even though avocados have a lot of calories, there was no clinical evidence that it impacted weight gain or any cardiometabolic risk factors, according to a statement from Penn State University.
Avocados, then, can be considered a guilt-free food. The findings from this study suggest it can give a substantial boost to your overall quality of diet, in turn lessening your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and some cancers, Kristina Peterson, PhD, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, said in the statement.
So get creative with your avocado recipes. You can only eat so much guacamole.
Your nose knows a good friend for you
You’ve probably noticed how dogs sniff other dogs and people before becoming friends. It would be pretty comical if people did the same thing, right? Just walked up to strangers and started sniffing them like dogs?
Well, apparently humans do go by smell when it comes to making friends, and they prefer people who smell like them. Maybe you’ve noticed that your friends look like you, share your values, and think the same way as you. You’re probably right, seeing as previous research has pointed to this.
For the current study, done to show how smell affects human behavior, researchers recruited people who befriended each other quickly, before knowing much about each other. They assumed that the relationships between these same-sex, nonromantic “click friends” relied more on physiological traits, including smell. After collecting samples from the click friends, researchers used an eNose to scan chemical signatures. In another experiment, human volunteers sniffed samples to determine if any were similar. Both experiments showed that click friends had more similar smells than pairs of random people.
“This is not to say that we act like goats or shrews – humans likely rely on other, far more dominant cues in their social decision-making. Nevertheless, our study’s results do suggest that our nose plays a bigger role than previously thought in our choice of friends,” said senior author Noam Sobel, PhD, of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Lead author Inbal Ravreby, a graduate student at the institute, put it this way: “These results imply that, as the saying goes, there is chemistry in social chemistry.”
These viruses want mosquitoes with good taste
Taste can be a pretty subjective sense. Not everyone agrees on what tastes good and what tastes bad. Most people would agree that freshly baked cookies taste good, but what about lima beans? And what about mosquitoes? What tastes good to a mosquito?
The answer? Blood. Blood tastes good to a mosquito. That really wasn’t a very hard question, was it? You did know the answer, didn’t you? They don’t care about cookies, and they certainly don’t care about lima beans. It’s blood that they love.
That brings us back to subjectivity, because it is possible for blood to taste even better. The secret ingredient is dengue … and Zika.
A study just published in Cell demonstrates that mice infected with dengue and Zika viruses release a volatile compound called acetophenone. “We found that flavivirus [like dengue and Zika] can utilize the increased release of acetophenone to help itself achieve its lifecycles more effectively by making their hosts more attractive to mosquito vectors,” senior author Gong Cheng of Tsinghua University, Beijing, said in a written statement.
How do they do it? The viruses, he explained, promote the proliferation of acetophenone-producing skin bacteria. “As a result, some bacteria overreplicate and produce more acetophenone. Suddenly, these sick individuals smell as delicious to mosquitoes as a tray of freshly baked cookies to a group of five-year-old children,” the statement said.
And how do you stop a group of tiny, flying 5-year-olds? That’s right, with acne medication. Really? You knew that one but not the blood one before? The investigators fed isotretinoin to the infected mice, which led to reduced acetophenone release from skin bacteria and made the animals no more attractive to the mosquitoes than their uninfected counterparts.
The investigators are planning to take the next step – feeding isotretinoin to people with dengue and Zika – having gotten the official fictional taste-test approval of celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay, who said, “You’re going to feed this #$^% to sick people? ARE YOU &%*$@#& KIDDING ME?”
Okay, so maybe approval isn’t quite the right word.
Welcome to bladders of the rich and famous!
Don’t you hate it when you’re driving out to your multimillion-dollar second home in the Hamptons and traffic is so bad you absolutely have to find a place to “rest” along the way? But wouldn’t you know it, there just isn’t anywhere to stop! Geez, how do we live?
That’s where David Shusterman, MD, a urologist in New York City and a true American hero, comes in. He’s identified a market and positioned himself as the king of both bladder surgery and “bladder Botox” for the wealthy New Yorkers who regularly make long journeys from the city out to their second homes in the Hamptons. Traffic has increased dramatically on Long Island roads in recent years, and the journey can now taking upward of 4 hours. Some people just can’t make it that long without a bathroom break, and there are very few places to stop along the way.
Dr. Shusterman understands the plight of the Hamptons vacationer, as he told Insider.com: “I can’t tell you how many arguments I personally get into – I’ve lost three friends because I’m the driver and refuse to stop for them.” A tragedy worthy of Shakespeare himself.
During the summer season, Dr. Shusterman performs about 10 prostate artery embolizations a week, an hour-long procedure that shrinks the prostate, which is great for 50- to 60-year-old men with enlarged prostates that cause more frequent bathroom trips. He also performs Botox injections into the bladder once or twice a week for women, which reduces the need to urinate for roughly 6 months. The perfect amount of time to get them through the summer season.
These procedures are sometimes covered by insurance but can cost as much as $20,000 if paid out of pocket. That’s a lot of money to us, but if you’re the sort of person who has a second home in the Hamptons, $20,000 is chump change, especially if it means you won’t have to go 2 entire minutes out of your way to use a gas-station bathroom. Then again, having seen a more than a few gas-station bathrooms in our time, maybe they have a point.
Ditch the apples. Go for the avocados
We’ve all heard about “an apple a day,” but instead of apples you might want to go with avocados.
Avocados are generally thought to be a healthy fat. A study just published in the Journal of the American Heart Association proves that they actually don’t do anything for your waistline but will work wonders on your cholesterol level. The study involved 923 participants who were considered overweight/obese split into two groups: One was asked to consume an avocado a day, and the other continued their usual diets and were asked to consume fewer than two avocados a month.
At the end of the 6 months, the researchers found total cholesterol decreased by an additional 2.9 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by 2.5 mg/dL in those who ate one avocado every day, compared with the usual-diet group. And even though avocados have a lot of calories, there was no clinical evidence that it impacted weight gain or any cardiometabolic risk factors, according to a statement from Penn State University.
Avocados, then, can be considered a guilt-free food. The findings from this study suggest it can give a substantial boost to your overall quality of diet, in turn lessening your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and some cancers, Kristina Peterson, PhD, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, said in the statement.
So get creative with your avocado recipes. You can only eat so much guacamole.
Your nose knows a good friend for you
You’ve probably noticed how dogs sniff other dogs and people before becoming friends. It would be pretty comical if people did the same thing, right? Just walked up to strangers and started sniffing them like dogs?
Well, apparently humans do go by smell when it comes to making friends, and they prefer people who smell like them. Maybe you’ve noticed that your friends look like you, share your values, and think the same way as you. You’re probably right, seeing as previous research has pointed to this.
For the current study, done to show how smell affects human behavior, researchers recruited people who befriended each other quickly, before knowing much about each other. They assumed that the relationships between these same-sex, nonromantic “click friends” relied more on physiological traits, including smell. After collecting samples from the click friends, researchers used an eNose to scan chemical signatures. In another experiment, human volunteers sniffed samples to determine if any were similar. Both experiments showed that click friends had more similar smells than pairs of random people.
“This is not to say that we act like goats or shrews – humans likely rely on other, far more dominant cues in their social decision-making. Nevertheless, our study’s results do suggest that our nose plays a bigger role than previously thought in our choice of friends,” said senior author Noam Sobel, PhD, of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Lead author Inbal Ravreby, a graduate student at the institute, put it this way: “These results imply that, as the saying goes, there is chemistry in social chemistry.”
These viruses want mosquitoes with good taste
Taste can be a pretty subjective sense. Not everyone agrees on what tastes good and what tastes bad. Most people would agree that freshly baked cookies taste good, but what about lima beans? And what about mosquitoes? What tastes good to a mosquito?
The answer? Blood. Blood tastes good to a mosquito. That really wasn’t a very hard question, was it? You did know the answer, didn’t you? They don’t care about cookies, and they certainly don’t care about lima beans. It’s blood that they love.
That brings us back to subjectivity, because it is possible for blood to taste even better. The secret ingredient is dengue … and Zika.
A study just published in Cell demonstrates that mice infected with dengue and Zika viruses release a volatile compound called acetophenone. “We found that flavivirus [like dengue and Zika] can utilize the increased release of acetophenone to help itself achieve its lifecycles more effectively by making their hosts more attractive to mosquito vectors,” senior author Gong Cheng of Tsinghua University, Beijing, said in a written statement.
How do they do it? The viruses, he explained, promote the proliferation of acetophenone-producing skin bacteria. “As a result, some bacteria overreplicate and produce more acetophenone. Suddenly, these sick individuals smell as delicious to mosquitoes as a tray of freshly baked cookies to a group of five-year-old children,” the statement said.
And how do you stop a group of tiny, flying 5-year-olds? That’s right, with acne medication. Really? You knew that one but not the blood one before? The investigators fed isotretinoin to the infected mice, which led to reduced acetophenone release from skin bacteria and made the animals no more attractive to the mosquitoes than their uninfected counterparts.
The investigators are planning to take the next step – feeding isotretinoin to people with dengue and Zika – having gotten the official fictional taste-test approval of celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay, who said, “You’re going to feed this #$^% to sick people? ARE YOU &%*$@#& KIDDING ME?”
Okay, so maybe approval isn’t quite the right word.
Welcome to bladders of the rich and famous!
Don’t you hate it when you’re driving out to your multimillion-dollar second home in the Hamptons and traffic is so bad you absolutely have to find a place to “rest” along the way? But wouldn’t you know it, there just isn’t anywhere to stop! Geez, how do we live?
That’s where David Shusterman, MD, a urologist in New York City and a true American hero, comes in. He’s identified a market and positioned himself as the king of both bladder surgery and “bladder Botox” for the wealthy New Yorkers who regularly make long journeys from the city out to their second homes in the Hamptons. Traffic has increased dramatically on Long Island roads in recent years, and the journey can now taking upward of 4 hours. Some people just can’t make it that long without a bathroom break, and there are very few places to stop along the way.
Dr. Shusterman understands the plight of the Hamptons vacationer, as he told Insider.com: “I can’t tell you how many arguments I personally get into – I’ve lost three friends because I’m the driver and refuse to stop for them.” A tragedy worthy of Shakespeare himself.
During the summer season, Dr. Shusterman performs about 10 prostate artery embolizations a week, an hour-long procedure that shrinks the prostate, which is great for 50- to 60-year-old men with enlarged prostates that cause more frequent bathroom trips. He also performs Botox injections into the bladder once or twice a week for women, which reduces the need to urinate for roughly 6 months. The perfect amount of time to get them through the summer season.
These procedures are sometimes covered by insurance but can cost as much as $20,000 if paid out of pocket. That’s a lot of money to us, but if you’re the sort of person who has a second home in the Hamptons, $20,000 is chump change, especially if it means you won’t have to go 2 entire minutes out of your way to use a gas-station bathroom. Then again, having seen a more than a few gas-station bathrooms in our time, maybe they have a point.
Ditch the apples. Go for the avocados
We’ve all heard about “an apple a day,” but instead of apples you might want to go with avocados.
Avocados are generally thought to be a healthy fat. A study just published in the Journal of the American Heart Association proves that they actually don’t do anything for your waistline but will work wonders on your cholesterol level. The study involved 923 participants who were considered overweight/obese split into two groups: One was asked to consume an avocado a day, and the other continued their usual diets and were asked to consume fewer than two avocados a month.
At the end of the 6 months, the researchers found total cholesterol decreased by an additional 2.9 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by 2.5 mg/dL in those who ate one avocado every day, compared with the usual-diet group. And even though avocados have a lot of calories, there was no clinical evidence that it impacted weight gain or any cardiometabolic risk factors, according to a statement from Penn State University.
Avocados, then, can be considered a guilt-free food. The findings from this study suggest it can give a substantial boost to your overall quality of diet, in turn lessening your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and some cancers, Kristina Peterson, PhD, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, said in the statement.
So get creative with your avocado recipes. You can only eat so much guacamole.
Your nose knows a good friend for you
You’ve probably noticed how dogs sniff other dogs and people before becoming friends. It would be pretty comical if people did the same thing, right? Just walked up to strangers and started sniffing them like dogs?
Well, apparently humans do go by smell when it comes to making friends, and they prefer people who smell like them. Maybe you’ve noticed that your friends look like you, share your values, and think the same way as you. You’re probably right, seeing as previous research has pointed to this.
For the current study, done to show how smell affects human behavior, researchers recruited people who befriended each other quickly, before knowing much about each other. They assumed that the relationships between these same-sex, nonromantic “click friends” relied more on physiological traits, including smell. After collecting samples from the click friends, researchers used an eNose to scan chemical signatures. In another experiment, human volunteers sniffed samples to determine if any were similar. Both experiments showed that click friends had more similar smells than pairs of random people.
“This is not to say that we act like goats or shrews – humans likely rely on other, far more dominant cues in their social decision-making. Nevertheless, our study’s results do suggest that our nose plays a bigger role than previously thought in our choice of friends,” said senior author Noam Sobel, PhD, of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Lead author Inbal Ravreby, a graduate student at the institute, put it this way: “These results imply that, as the saying goes, there is chemistry in social chemistry.”
‘Not their fault:’ Obesity warrants long-term management
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s important to remember and to think about the first time when patients with obesity come to see us: What have they faced? What have been their struggles? What shame and blame and bias have they faced?
One of the first things that I do when a patient comes to see me is invite them to share their weight journey with me. I ask them to tell me about their struggles, about what’s worked and what hasn’t worked, what they would like, and what their health goals are.
As they share their stories, I look for the opportunity to share with them that obesity is not their fault, but that it’s biology driving their body to carry extra weight and their body is super smart. Neither their body nor their brain want them to starve.
Our bodies evolved during a time where there was food scarcity and the potential of famine. We have a complex system that was designed to make sure that we always held on to extra weight, specifically extra fat, because that’s how we store energy. In the current obesogenic environment, what happens is our bodies carry extra weight, or specifically, extra fat.
Again, I say to them, this is biology. Your body’s doing exactly what it was designed to do. Your body’s very smart, but now we have to figure out how to help your body want to carry less fat because it is impacting your health. This is not your fault. Having obesity is not your fault any more than having diabetes or hypertension is anyone’s fault. Now it’s time for all of us to use highly effective tools that target the pathophysiology of obesity.
When a patient comes to me for weight management or to help them treat their obesity, I listen to them, and I look for clues as to what might help that specific patient. Every patient deserves to have individualized treatment. One medicine may be right for one person, another medicine may be right for another, and surgery may be right for another patient. I really try to listen and hear what that patient is telling me.
What we as providers really need is tools – different options – to be able to provide for our patients and basically present them with different options, and then guide them toward the best therapy for them. Whether it’s semaglutide or tirzepatide potentially in the future, these types of medications are excellent options for our patients. They’re highly effective tools with safe profiles.
A question that I often get from providers or patients is, “Well, Doctor, I’ve lost the weight now. How long should I take this medicine? Can I stop it now?”
Then, we have a conversation, and we actually usually have this conversation even before we start the medicine. Basically, we talk about the fact that obesity is a chronic disease. There’s no cure for obesity. Because it’s a chronic disease, we need to treat it like we would treat any other chronic disease.
The example that I often use is, if you have a patient who has hypertension and you start them on an antihypertensive medication, what happens? Their blood pressure goes down. It improves. Now, if their blood pressure is improved with a specific antihypertensive, would you stop that medicine? What would happen if you stopped that antihypertensive? Well, their blood pressure would go up, and we wouldn’t be surprised.
In the same way, if you have a patient who has obesity and you start that patient on an antiobesity medication, and their weight decreases, and their body fat mass at that point decreases, what would happen if you stop that medicine? They lost the weight, but you stop the medicine. Well, their weight gain comes back. They regain the weight.
We should not be surprised that weight gain occurs when we stop the treatment. That really underscores the fact that treatment needs to be continued. If a patient is started on an antiobesity medication and they lose weight, that medication needs to be continued to maintain that weight loss.
Basically, we eat food and our body responds by releasing these hormones. The hormones are made in our gut and in our pancreas and these hormones inform our brain. Are we hungry? Are we full? Where are we with our homeostatic set point of fat mass? Based on that, our brain is like the sensor or the thermostat.
Obesity is a chronic, treatable disease. We should treat obesity as we treat any other chronic disease, with effective and safe approaches that target underlying disease mechanisms. These results in the SURMOUNT-1 trial underscore that tirzepatide may be doing just that. Remarkably, 9 in 10 individuals with obesity lost weight while taking tirzepatide. These results are impressive. They’re an important step forward in potentially expanding effective therapeutic options for people with obesity.
Dr. Jastreboff is an associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of weight management and obesity prevention at Yale Stress Center. She reported conducting trials with Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals; serving on scientific advisory boards for Ely Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and WW; and consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim and Scholar Rock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s important to remember and to think about the first time when patients with obesity come to see us: What have they faced? What have been their struggles? What shame and blame and bias have they faced?
One of the first things that I do when a patient comes to see me is invite them to share their weight journey with me. I ask them to tell me about their struggles, about what’s worked and what hasn’t worked, what they would like, and what their health goals are.
As they share their stories, I look for the opportunity to share with them that obesity is not their fault, but that it’s biology driving their body to carry extra weight and their body is super smart. Neither their body nor their brain want them to starve.
Our bodies evolved during a time where there was food scarcity and the potential of famine. We have a complex system that was designed to make sure that we always held on to extra weight, specifically extra fat, because that’s how we store energy. In the current obesogenic environment, what happens is our bodies carry extra weight, or specifically, extra fat.
Again, I say to them, this is biology. Your body’s doing exactly what it was designed to do. Your body’s very smart, but now we have to figure out how to help your body want to carry less fat because it is impacting your health. This is not your fault. Having obesity is not your fault any more than having diabetes or hypertension is anyone’s fault. Now it’s time for all of us to use highly effective tools that target the pathophysiology of obesity.
When a patient comes to me for weight management or to help them treat their obesity, I listen to them, and I look for clues as to what might help that specific patient. Every patient deserves to have individualized treatment. One medicine may be right for one person, another medicine may be right for another, and surgery may be right for another patient. I really try to listen and hear what that patient is telling me.
What we as providers really need is tools – different options – to be able to provide for our patients and basically present them with different options, and then guide them toward the best therapy for them. Whether it’s semaglutide or tirzepatide potentially in the future, these types of medications are excellent options for our patients. They’re highly effective tools with safe profiles.
A question that I often get from providers or patients is, “Well, Doctor, I’ve lost the weight now. How long should I take this medicine? Can I stop it now?”
Then, we have a conversation, and we actually usually have this conversation even before we start the medicine. Basically, we talk about the fact that obesity is a chronic disease. There’s no cure for obesity. Because it’s a chronic disease, we need to treat it like we would treat any other chronic disease.
The example that I often use is, if you have a patient who has hypertension and you start them on an antihypertensive medication, what happens? Their blood pressure goes down. It improves. Now, if their blood pressure is improved with a specific antihypertensive, would you stop that medicine? What would happen if you stopped that antihypertensive? Well, their blood pressure would go up, and we wouldn’t be surprised.
In the same way, if you have a patient who has obesity and you start that patient on an antiobesity medication, and their weight decreases, and their body fat mass at that point decreases, what would happen if you stop that medicine? They lost the weight, but you stop the medicine. Well, their weight gain comes back. They regain the weight.
We should not be surprised that weight gain occurs when we stop the treatment. That really underscores the fact that treatment needs to be continued. If a patient is started on an antiobesity medication and they lose weight, that medication needs to be continued to maintain that weight loss.
Basically, we eat food and our body responds by releasing these hormones. The hormones are made in our gut and in our pancreas and these hormones inform our brain. Are we hungry? Are we full? Where are we with our homeostatic set point of fat mass? Based on that, our brain is like the sensor or the thermostat.
Obesity is a chronic, treatable disease. We should treat obesity as we treat any other chronic disease, with effective and safe approaches that target underlying disease mechanisms. These results in the SURMOUNT-1 trial underscore that tirzepatide may be doing just that. Remarkably, 9 in 10 individuals with obesity lost weight while taking tirzepatide. These results are impressive. They’re an important step forward in potentially expanding effective therapeutic options for people with obesity.
Dr. Jastreboff is an associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of weight management and obesity prevention at Yale Stress Center. She reported conducting trials with Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals; serving on scientific advisory boards for Ely Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and WW; and consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim and Scholar Rock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s important to remember and to think about the first time when patients with obesity come to see us: What have they faced? What have been their struggles? What shame and blame and bias have they faced?
One of the first things that I do when a patient comes to see me is invite them to share their weight journey with me. I ask them to tell me about their struggles, about what’s worked and what hasn’t worked, what they would like, and what their health goals are.
As they share their stories, I look for the opportunity to share with them that obesity is not their fault, but that it’s biology driving their body to carry extra weight and their body is super smart. Neither their body nor their brain want them to starve.
Our bodies evolved during a time where there was food scarcity and the potential of famine. We have a complex system that was designed to make sure that we always held on to extra weight, specifically extra fat, because that’s how we store energy. In the current obesogenic environment, what happens is our bodies carry extra weight, or specifically, extra fat.
Again, I say to them, this is biology. Your body’s doing exactly what it was designed to do. Your body’s very smart, but now we have to figure out how to help your body want to carry less fat because it is impacting your health. This is not your fault. Having obesity is not your fault any more than having diabetes or hypertension is anyone’s fault. Now it’s time for all of us to use highly effective tools that target the pathophysiology of obesity.
When a patient comes to me for weight management or to help them treat their obesity, I listen to them, and I look for clues as to what might help that specific patient. Every patient deserves to have individualized treatment. One medicine may be right for one person, another medicine may be right for another, and surgery may be right for another patient. I really try to listen and hear what that patient is telling me.
What we as providers really need is tools – different options – to be able to provide for our patients and basically present them with different options, and then guide them toward the best therapy for them. Whether it’s semaglutide or tirzepatide potentially in the future, these types of medications are excellent options for our patients. They’re highly effective tools with safe profiles.
A question that I often get from providers or patients is, “Well, Doctor, I’ve lost the weight now. How long should I take this medicine? Can I stop it now?”
Then, we have a conversation, and we actually usually have this conversation even before we start the medicine. Basically, we talk about the fact that obesity is a chronic disease. There’s no cure for obesity. Because it’s a chronic disease, we need to treat it like we would treat any other chronic disease.
The example that I often use is, if you have a patient who has hypertension and you start them on an antihypertensive medication, what happens? Their blood pressure goes down. It improves. Now, if their blood pressure is improved with a specific antihypertensive, would you stop that medicine? What would happen if you stopped that antihypertensive? Well, their blood pressure would go up, and we wouldn’t be surprised.
In the same way, if you have a patient who has obesity and you start that patient on an antiobesity medication, and their weight decreases, and their body fat mass at that point decreases, what would happen if you stop that medicine? They lost the weight, but you stop the medicine. Well, their weight gain comes back. They regain the weight.
We should not be surprised that weight gain occurs when we stop the treatment. That really underscores the fact that treatment needs to be continued. If a patient is started on an antiobesity medication and they lose weight, that medication needs to be continued to maintain that weight loss.
Basically, we eat food and our body responds by releasing these hormones. The hormones are made in our gut and in our pancreas and these hormones inform our brain. Are we hungry? Are we full? Where are we with our homeostatic set point of fat mass? Based on that, our brain is like the sensor or the thermostat.
Obesity is a chronic, treatable disease. We should treat obesity as we treat any other chronic disease, with effective and safe approaches that target underlying disease mechanisms. These results in the SURMOUNT-1 trial underscore that tirzepatide may be doing just that. Remarkably, 9 in 10 individuals with obesity lost weight while taking tirzepatide. These results are impressive. They’re an important step forward in potentially expanding effective therapeutic options for people with obesity.
Dr. Jastreboff is an associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of weight management and obesity prevention at Yale Stress Center. She reported conducting trials with Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals; serving on scientific advisory boards for Ely Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and WW; and consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim and Scholar Rock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
No adverse impact of obesity in biologic-treated IBD
Patients with both inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and obesity starting on new biologic therapies do not face an increased risk for hospitalization, IBD-related surgery, or serious infection, reveals a multicenter U.S. study published online in American Journal of Gastroenterology.
“Our findings were a bit surprising, since prior studies had suggested higher clinical disease activity and risk of flare and lower rates of endoscopic remission in obese patients treated with biologics,” Siddharth Singh, MD, MS, director of the IBD Center at the University of California, San Diego, told this news organization.
“However, in this study we focused on harder outcomes, including risk of hospitalization and surgery, and did not observe any detrimental effect,” he said.
Based on the findings, Dr. Singh believes that biologics are “completely safe and effective to use in obese patients.”
He clarified, however, that “examining the overall body of evidence, I still think obesity results in more rapid clearance of biologics, which negatively impacts the likelihood of achieving symptomatic and endoscopic remission.”
“Hence, there should be a low threshold to monitor and optimize biologic drug concentrations in obese patients. I preferentially use biologics that are dosed based on body weight in patients with class II or III obesity,” he said.
Research findings
Dr. Singh and colleagues write that, given that between 15% and 45% of patients with IBD are obese and a further 20%-40% are overweight, obesity is an “increasingly important consideration” in its management.
It is believed that obesity, largely via visceral adiposity, has a negative impact on IBD via increased production of adipokines, chemokines, and cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and interleukin-6, thus affecting treatment response as well as increasing the risk for complications and infections.
However, studies of the association between obesity and poorer treatment response, both large and small, have yielded conflicting results, potentially owing to methodological limitations.
To investigate further, Dr. Singh and colleagues gathered electronic health record data from five health systems in California on adults with IBD who were new users of TNF-alpha antagonists, or the monoclonal antibodies vedolizumab or ustekinumab, between Jan. 1, 2010, and June 30, 2017.
World Health Organization definitions were used to classify the patients as having normal BMI, overweight, or obesity, and the risk for all-cause hospitalization, IBD-related surgery, or serious infection was compared between the groups.
The team reviewed the cases of 3,038 patients with IBD, of whom 31.1% had ulcerative colitis. Among the participants, 28.2% were classified as overweight and 13.7% as obese. TNF-alpha antagonists were used by 76.3% of patients.
Patients with obesity were significantly older, were more likely to be of Hispanic ethnicity, had a higher burden of comorbidities, and were more likely to have elevated C-reactive protein levels at baseline.
However, there were no significant differences between obese and nonobese patients in terms of IBD type, class of biologic prescribed, prior surgery, or prior biologic exposure.
Within 1 year of starting a new biologic therapy, 22.9% of patients required hospitalization, whereas 3.3% required surgery and 5.8% were hospitalized with a serious infection.
Cox proportional hazard analyses showed that obesity was not associated with an increased risk for hospitalization versus normal body mass index (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-1.13), nor was it associated with IBD-related surgery (aHR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.31-1.22) or serious infection (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.73-1.71).
The results were similar when the patients were stratified by IBD type and index biologic therapy, the researchers write.
When analyzed as a continuous variable, BMI was associated with a lower risk for hospitalization (aHR, 0.98 per 1 kg/m2; P = .044) but not with IBD-related surgery or serious infection.
Reassuring results for the standard of care
Discussing their findings, the authors note that “the discrepancy among studies potentially reflects the shortcomings of overall obesity measured using BMI to capture clinically meaningful adiposity.”
“A small but growing body of literature suggests visceral adipose tissue is a potentially superior prognostic measure of adiposity and better predicts adverse outcomes in IBD.”
Dr. Singh said that it would be “very interesting” to examine the relationship between visceral adiposity, as inferred from waist circumference, and IBD outcomes.
Approached for comment, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, Clifford Joseph Barborka Professor, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said, “At the present time, there are no new clinical implications based on this study.”
He said in an interview that it “does not require any change in the current standard of care but rather attempts to reassure that the standard of care does not change for obese patients.”
“With that being said, the standard of care may require dosing adjustments for patients based on weight, as is already the case for infliximab/ustekinumab, and monitoring to treat to target in obese patients as well as in normal or underweight patients,” Dr. Hanauer concluded.
The study was supported by the ACG Junior Faculty Development Award and the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Career Development Award to Dr. Singh. Dr. Singh is supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and reports relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, and Pfizer. The other authors report numerous financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with both inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and obesity starting on new biologic therapies do not face an increased risk for hospitalization, IBD-related surgery, or serious infection, reveals a multicenter U.S. study published online in American Journal of Gastroenterology.
“Our findings were a bit surprising, since prior studies had suggested higher clinical disease activity and risk of flare and lower rates of endoscopic remission in obese patients treated with biologics,” Siddharth Singh, MD, MS, director of the IBD Center at the University of California, San Diego, told this news organization.
“However, in this study we focused on harder outcomes, including risk of hospitalization and surgery, and did not observe any detrimental effect,” he said.
Based on the findings, Dr. Singh believes that biologics are “completely safe and effective to use in obese patients.”
He clarified, however, that “examining the overall body of evidence, I still think obesity results in more rapid clearance of biologics, which negatively impacts the likelihood of achieving symptomatic and endoscopic remission.”
“Hence, there should be a low threshold to monitor and optimize biologic drug concentrations in obese patients. I preferentially use biologics that are dosed based on body weight in patients with class II or III obesity,” he said.
Research findings
Dr. Singh and colleagues write that, given that between 15% and 45% of patients with IBD are obese and a further 20%-40% are overweight, obesity is an “increasingly important consideration” in its management.
It is believed that obesity, largely via visceral adiposity, has a negative impact on IBD via increased production of adipokines, chemokines, and cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and interleukin-6, thus affecting treatment response as well as increasing the risk for complications and infections.
However, studies of the association between obesity and poorer treatment response, both large and small, have yielded conflicting results, potentially owing to methodological limitations.
To investigate further, Dr. Singh and colleagues gathered electronic health record data from five health systems in California on adults with IBD who were new users of TNF-alpha antagonists, or the monoclonal antibodies vedolizumab or ustekinumab, between Jan. 1, 2010, and June 30, 2017.
World Health Organization definitions were used to classify the patients as having normal BMI, overweight, or obesity, and the risk for all-cause hospitalization, IBD-related surgery, or serious infection was compared between the groups.
The team reviewed the cases of 3,038 patients with IBD, of whom 31.1% had ulcerative colitis. Among the participants, 28.2% were classified as overweight and 13.7% as obese. TNF-alpha antagonists were used by 76.3% of patients.
Patients with obesity were significantly older, were more likely to be of Hispanic ethnicity, had a higher burden of comorbidities, and were more likely to have elevated C-reactive protein levels at baseline.
However, there were no significant differences between obese and nonobese patients in terms of IBD type, class of biologic prescribed, prior surgery, or prior biologic exposure.
Within 1 year of starting a new biologic therapy, 22.9% of patients required hospitalization, whereas 3.3% required surgery and 5.8% were hospitalized with a serious infection.
Cox proportional hazard analyses showed that obesity was not associated with an increased risk for hospitalization versus normal body mass index (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-1.13), nor was it associated with IBD-related surgery (aHR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.31-1.22) or serious infection (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.73-1.71).
The results were similar when the patients were stratified by IBD type and index biologic therapy, the researchers write.
When analyzed as a continuous variable, BMI was associated with a lower risk for hospitalization (aHR, 0.98 per 1 kg/m2; P = .044) but not with IBD-related surgery or serious infection.
Reassuring results for the standard of care
Discussing their findings, the authors note that “the discrepancy among studies potentially reflects the shortcomings of overall obesity measured using BMI to capture clinically meaningful adiposity.”
“A small but growing body of literature suggests visceral adipose tissue is a potentially superior prognostic measure of adiposity and better predicts adverse outcomes in IBD.”
Dr. Singh said that it would be “very interesting” to examine the relationship between visceral adiposity, as inferred from waist circumference, and IBD outcomes.
Approached for comment, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, Clifford Joseph Barborka Professor, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said, “At the present time, there are no new clinical implications based on this study.”
He said in an interview that it “does not require any change in the current standard of care but rather attempts to reassure that the standard of care does not change for obese patients.”
“With that being said, the standard of care may require dosing adjustments for patients based on weight, as is already the case for infliximab/ustekinumab, and monitoring to treat to target in obese patients as well as in normal or underweight patients,” Dr. Hanauer concluded.
The study was supported by the ACG Junior Faculty Development Award and the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Career Development Award to Dr. Singh. Dr. Singh is supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and reports relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, and Pfizer. The other authors report numerous financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with both inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) and obesity starting on new biologic therapies do not face an increased risk for hospitalization, IBD-related surgery, or serious infection, reveals a multicenter U.S. study published online in American Journal of Gastroenterology.
“Our findings were a bit surprising, since prior studies had suggested higher clinical disease activity and risk of flare and lower rates of endoscopic remission in obese patients treated with biologics,” Siddharth Singh, MD, MS, director of the IBD Center at the University of California, San Diego, told this news organization.
“However, in this study we focused on harder outcomes, including risk of hospitalization and surgery, and did not observe any detrimental effect,” he said.
Based on the findings, Dr. Singh believes that biologics are “completely safe and effective to use in obese patients.”
He clarified, however, that “examining the overall body of evidence, I still think obesity results in more rapid clearance of biologics, which negatively impacts the likelihood of achieving symptomatic and endoscopic remission.”
“Hence, there should be a low threshold to monitor and optimize biologic drug concentrations in obese patients. I preferentially use biologics that are dosed based on body weight in patients with class II or III obesity,” he said.
Research findings
Dr. Singh and colleagues write that, given that between 15% and 45% of patients with IBD are obese and a further 20%-40% are overweight, obesity is an “increasingly important consideration” in its management.
It is believed that obesity, largely via visceral adiposity, has a negative impact on IBD via increased production of adipokines, chemokines, and cytokines, such as tumor necrosis factor (TNF) alpha and interleukin-6, thus affecting treatment response as well as increasing the risk for complications and infections.
However, studies of the association between obesity and poorer treatment response, both large and small, have yielded conflicting results, potentially owing to methodological limitations.
To investigate further, Dr. Singh and colleagues gathered electronic health record data from five health systems in California on adults with IBD who were new users of TNF-alpha antagonists, or the monoclonal antibodies vedolizumab or ustekinumab, between Jan. 1, 2010, and June 30, 2017.
World Health Organization definitions were used to classify the patients as having normal BMI, overweight, or obesity, and the risk for all-cause hospitalization, IBD-related surgery, or serious infection was compared between the groups.
The team reviewed the cases of 3,038 patients with IBD, of whom 31.1% had ulcerative colitis. Among the participants, 28.2% were classified as overweight and 13.7% as obese. TNF-alpha antagonists were used by 76.3% of patients.
Patients with obesity were significantly older, were more likely to be of Hispanic ethnicity, had a higher burden of comorbidities, and were more likely to have elevated C-reactive protein levels at baseline.
However, there were no significant differences between obese and nonobese patients in terms of IBD type, class of biologic prescribed, prior surgery, or prior biologic exposure.
Within 1 year of starting a new biologic therapy, 22.9% of patients required hospitalization, whereas 3.3% required surgery and 5.8% were hospitalized with a serious infection.
Cox proportional hazard analyses showed that obesity was not associated with an increased risk for hospitalization versus normal body mass index (adjusted hazard ratio, 0.90; 95% confidence interval, 0.72-1.13), nor was it associated with IBD-related surgery (aHR, 0.62; 95% CI, 0.31-1.22) or serious infection (aHR, 1.11; 95% CI, 0.73-1.71).
The results were similar when the patients were stratified by IBD type and index biologic therapy, the researchers write.
When analyzed as a continuous variable, BMI was associated with a lower risk for hospitalization (aHR, 0.98 per 1 kg/m2; P = .044) but not with IBD-related surgery or serious infection.
Reassuring results for the standard of care
Discussing their findings, the authors note that “the discrepancy among studies potentially reflects the shortcomings of overall obesity measured using BMI to capture clinically meaningful adiposity.”
“A small but growing body of literature suggests visceral adipose tissue is a potentially superior prognostic measure of adiposity and better predicts adverse outcomes in IBD.”
Dr. Singh said that it would be “very interesting” to examine the relationship between visceral adiposity, as inferred from waist circumference, and IBD outcomes.
Approached for comment, Stephen B. Hanauer, MD, Clifford Joseph Barborka Professor, Northwestern University Feinberg School of Medicine, Chicago, said, “At the present time, there are no new clinical implications based on this study.”
He said in an interview that it “does not require any change in the current standard of care but rather attempts to reassure that the standard of care does not change for obese patients.”
“With that being said, the standard of care may require dosing adjustments for patients based on weight, as is already the case for infliximab/ustekinumab, and monitoring to treat to target in obese patients as well as in normal or underweight patients,” Dr. Hanauer concluded.
The study was supported by the ACG Junior Faculty Development Award and the Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation Career Development Award to Dr. Singh. Dr. Singh is supported by the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases and reports relationships with AbbVie, Janssen, and Pfizer. The other authors report numerous financial relationships. Dr. Hanauer reports no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New AHA checklist: Only one in five adults has optimal heart health
About 80% of American adults have low to moderate cardiovascular (CV) health based on the American Heart Association checklist for optimal heart health, which now includes healthy sleep as an essential component for heart health.
With the addition of sleep, “Life’s Essential 8” replaces the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” checklist.
“The new metric of sleep duration reflects the latest research findings: Sleep impacts overall health, and people who have healthier sleep patterns manage health factors such as weight, blood pressure, or risk for type 2 diabetes more effectively,” AHA President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a news release.
“In addition, advances in ways to measure sleep, such as with wearable devices, now offer people the ability to reliably and routinely monitor their sleep habits at home,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The AHA Presidential Advisory – Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct on Cardiovascular Health – was published online in the journal Circulation.
A companion paper published simultaneously in Circulation reports the first study using Life’s Essential 8.
Overall, the results show that CV health of the U.S. population is “suboptimal, and we see important differences across age and sociodemographic groups,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Refining Life’s Simple 7
The AHA first defined the seven metrics for optimal CV health in 2010. After 12 years and more than 2,400 scientific papers on the topic, new discoveries in CV health and ways to measure it provided an opportunity to revisit each health component in more detail and provide updates as needed, the AHA explains.
“We felt it was the right time to conduct a comprehensive review of the latest research to refine the existing metrics and consider any new metrics that add value to assessing cardiovascular health for all people,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Four of the original metrics have been redefined for consistency with newer clinical guidelines or compatibility with new measurement tools, and the scoring system can now also be applied to anyone ages 2 and older. Here is a snapshot of Life’s Essential 8 metrics, including updates.
1. Diet (updated)
The tool includes a new guide to assess diet quality for adults and children at the individual and population level. At the population level, dietary assessment is based on daily intake of elements in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating pattern. For individuals, the Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans (MEPA) is used to assess and monitor cardiovascular health.
2. Physical activity (no changes)
Physical activity continues to be measured by the total number of minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week, as defined by the U.S. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (2nd edition). The optimal level is 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate physical activity or more per week or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity for adults; 420 minutes (7 hours) or more per week for children ages 6 and older; and age-specific modifications for younger children.
3. Nicotine exposure (updated)
Use of inhaled nicotine-delivery systems, which includes e-cigarettes or vaping devices, has been added since the previous metric monitored only traditional, combustible cigarettes. This reflects use by adults and youth and their implications on long-term health. Second-hand smoke exposure for children and adults has also been added.
4. Sleep duration (new)
Sleep duration is associated with CV health. Measured by average hours of sleep per night, the ideal level is 7-9 hours daily for adults. Ideal daily sleep ranges for children are 10-16 hours per 24 hours for ages 5 and younger; 9-12 hours for ages 6-12 years; and 8-10 hours for ages 13-18 years.
5. Body mass index (no changes)
The AHA acknowledges that body mass index (BMI) is an imperfect metric. Yet, because it’s easily calculated and widely available, BMI continues as a “reasonable” gauge to assess weight categories that may lead to health problems. BMI of 18.5-24.9 is associated with the highest levels of CV health. The AHA notes that BMI ranges and the subsequent health risks associated with them may differ among people from diverse racial or ethnic backgrounds or ancestry. This aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations to adjust BMI ranges for people of Asian or Pacific Islander ancestry because recent evidence indicates their risk of conditions such as CVD or type 2 diabetes is higher at a lower BMI.
6. Blood lipids (updated)
The metric for blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) is updated to use non-HDL cholesterol as the preferred number to monitor, rather than total cholesterol. This shift is made because non-HDL cholesterol can be measured without fasting beforehand (thereby increasing its availability at any time of day and implementation at more appointments) and reliably calculated among all people.
7. Blood glucose (updated)
This metric is expanded to include the option of hemoglobin A1c readings or blood glucose levels for people with or without type 1 or 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
8. Blood pressure (no changes)
Blood pressure criteria remain unchanged from 2017 guidance that established levels less than 120/80 mm Hg as optimal, and defined hypertension as 130-139 mm Hg systolic pressure or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic pressure.
‘Concerning’ new data
Results of the first study using Life’s Essential 8 show that the overall CV health of the U.S. population is “well below ideal,” with 80% of adults scoring at a low or moderate level, the researchers report.
Data for the analysis came from 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys (NHANES) of more than 13,500 adults aged 20-79 years and nearly 9,900 children aged 2-19 years. Among the key findings:
- The average CV health score based on Life’s Essential 8 was 64.7 for adults and 65.5 for children – in the moderate range on the 0-100 scale.
- Only 0.45% of adults had a perfect score of 100; 20% had high CV health (score of 80 or higher), 63% moderate (score of 50-79), and 18% had low CV health (score of less than 50).
- Adult women had higher average CV health scores (67) compared with men (62.5).
- In general, adults scored lowest in the areas of diet, physical activity, and BMI.
- CV health scores were generally lower at older ages.
- Non-Hispanic Asian Americans had a higher average CV health score than other racial/ethnic groups. Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest average CV health score, followed, in order, by Hispanic (other than Mexican), Mexican, and non-Hispanic Blacks.
- Children’s diet scores were low, at an average of 40.6.
- Adult sociodemographic groups varied notably in CV health scores for diet, nicotine exposure, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
“These data represent the first look at the cardiovascular health of the U.S. population using the AHA’s new Life’s Essential 8 scoring algorithm,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
“Life’s Essential 8 is a major step forward in our ability to identify when cardiovascular health can be preserved and when it is suboptimal. It should energize efforts to improve cardiovascular health for all people and at every life stage,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
“Analyses like this can help policymakers, communities, clinicians, and the public to understand the opportunities to intervene to improve and maintain optimal cardiovascular health across the life course,” he said.
This research had no commercial funding. The authors have no reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About 80% of American adults have low to moderate cardiovascular (CV) health based on the American Heart Association checklist for optimal heart health, which now includes healthy sleep as an essential component for heart health.
With the addition of sleep, “Life’s Essential 8” replaces the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” checklist.
“The new metric of sleep duration reflects the latest research findings: Sleep impacts overall health, and people who have healthier sleep patterns manage health factors such as weight, blood pressure, or risk for type 2 diabetes more effectively,” AHA President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a news release.
“In addition, advances in ways to measure sleep, such as with wearable devices, now offer people the ability to reliably and routinely monitor their sleep habits at home,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The AHA Presidential Advisory – Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct on Cardiovascular Health – was published online in the journal Circulation.
A companion paper published simultaneously in Circulation reports the first study using Life’s Essential 8.
Overall, the results show that CV health of the U.S. population is “suboptimal, and we see important differences across age and sociodemographic groups,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Refining Life’s Simple 7
The AHA first defined the seven metrics for optimal CV health in 2010. After 12 years and more than 2,400 scientific papers on the topic, new discoveries in CV health and ways to measure it provided an opportunity to revisit each health component in more detail and provide updates as needed, the AHA explains.
“We felt it was the right time to conduct a comprehensive review of the latest research to refine the existing metrics and consider any new metrics that add value to assessing cardiovascular health for all people,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Four of the original metrics have been redefined for consistency with newer clinical guidelines or compatibility with new measurement tools, and the scoring system can now also be applied to anyone ages 2 and older. Here is a snapshot of Life’s Essential 8 metrics, including updates.
1. Diet (updated)
The tool includes a new guide to assess diet quality for adults and children at the individual and population level. At the population level, dietary assessment is based on daily intake of elements in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating pattern. For individuals, the Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans (MEPA) is used to assess and monitor cardiovascular health.
2. Physical activity (no changes)
Physical activity continues to be measured by the total number of minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week, as defined by the U.S. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (2nd edition). The optimal level is 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate physical activity or more per week or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity for adults; 420 minutes (7 hours) or more per week for children ages 6 and older; and age-specific modifications for younger children.
3. Nicotine exposure (updated)
Use of inhaled nicotine-delivery systems, which includes e-cigarettes or vaping devices, has been added since the previous metric monitored only traditional, combustible cigarettes. This reflects use by adults and youth and their implications on long-term health. Second-hand smoke exposure for children and adults has also been added.
4. Sleep duration (new)
Sleep duration is associated with CV health. Measured by average hours of sleep per night, the ideal level is 7-9 hours daily for adults. Ideal daily sleep ranges for children are 10-16 hours per 24 hours for ages 5 and younger; 9-12 hours for ages 6-12 years; and 8-10 hours for ages 13-18 years.
5. Body mass index (no changes)
The AHA acknowledges that body mass index (BMI) is an imperfect metric. Yet, because it’s easily calculated and widely available, BMI continues as a “reasonable” gauge to assess weight categories that may lead to health problems. BMI of 18.5-24.9 is associated with the highest levels of CV health. The AHA notes that BMI ranges and the subsequent health risks associated with them may differ among people from diverse racial or ethnic backgrounds or ancestry. This aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations to adjust BMI ranges for people of Asian or Pacific Islander ancestry because recent evidence indicates their risk of conditions such as CVD or type 2 diabetes is higher at a lower BMI.
6. Blood lipids (updated)
The metric for blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) is updated to use non-HDL cholesterol as the preferred number to monitor, rather than total cholesterol. This shift is made because non-HDL cholesterol can be measured without fasting beforehand (thereby increasing its availability at any time of day and implementation at more appointments) and reliably calculated among all people.
7. Blood glucose (updated)
This metric is expanded to include the option of hemoglobin A1c readings or blood glucose levels for people with or without type 1 or 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
8. Blood pressure (no changes)
Blood pressure criteria remain unchanged from 2017 guidance that established levels less than 120/80 mm Hg as optimal, and defined hypertension as 130-139 mm Hg systolic pressure or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic pressure.
‘Concerning’ new data
Results of the first study using Life’s Essential 8 show that the overall CV health of the U.S. population is “well below ideal,” with 80% of adults scoring at a low or moderate level, the researchers report.
Data for the analysis came from 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys (NHANES) of more than 13,500 adults aged 20-79 years and nearly 9,900 children aged 2-19 years. Among the key findings:
- The average CV health score based on Life’s Essential 8 was 64.7 for adults and 65.5 for children – in the moderate range on the 0-100 scale.
- Only 0.45% of adults had a perfect score of 100; 20% had high CV health (score of 80 or higher), 63% moderate (score of 50-79), and 18% had low CV health (score of less than 50).
- Adult women had higher average CV health scores (67) compared with men (62.5).
- In general, adults scored lowest in the areas of diet, physical activity, and BMI.
- CV health scores were generally lower at older ages.
- Non-Hispanic Asian Americans had a higher average CV health score than other racial/ethnic groups. Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest average CV health score, followed, in order, by Hispanic (other than Mexican), Mexican, and non-Hispanic Blacks.
- Children’s diet scores were low, at an average of 40.6.
- Adult sociodemographic groups varied notably in CV health scores for diet, nicotine exposure, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
“These data represent the first look at the cardiovascular health of the U.S. population using the AHA’s new Life’s Essential 8 scoring algorithm,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
“Life’s Essential 8 is a major step forward in our ability to identify when cardiovascular health can be preserved and when it is suboptimal. It should energize efforts to improve cardiovascular health for all people and at every life stage,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
“Analyses like this can help policymakers, communities, clinicians, and the public to understand the opportunities to intervene to improve and maintain optimal cardiovascular health across the life course,” he said.
This research had no commercial funding. The authors have no reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About 80% of American adults have low to moderate cardiovascular (CV) health based on the American Heart Association checklist for optimal heart health, which now includes healthy sleep as an essential component for heart health.
With the addition of sleep, “Life’s Essential 8” replaces the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” checklist.
“The new metric of sleep duration reflects the latest research findings: Sleep impacts overall health, and people who have healthier sleep patterns manage health factors such as weight, blood pressure, or risk for type 2 diabetes more effectively,” AHA President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a news release.
“In addition, advances in ways to measure sleep, such as with wearable devices, now offer people the ability to reliably and routinely monitor their sleep habits at home,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The AHA Presidential Advisory – Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct on Cardiovascular Health – was published online in the journal Circulation.
A companion paper published simultaneously in Circulation reports the first study using Life’s Essential 8.
Overall, the results show that CV health of the U.S. population is “suboptimal, and we see important differences across age and sociodemographic groups,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Refining Life’s Simple 7
The AHA first defined the seven metrics for optimal CV health in 2010. After 12 years and more than 2,400 scientific papers on the topic, new discoveries in CV health and ways to measure it provided an opportunity to revisit each health component in more detail and provide updates as needed, the AHA explains.
“We felt it was the right time to conduct a comprehensive review of the latest research to refine the existing metrics and consider any new metrics that add value to assessing cardiovascular health for all people,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Four of the original metrics have been redefined for consistency with newer clinical guidelines or compatibility with new measurement tools, and the scoring system can now also be applied to anyone ages 2 and older. Here is a snapshot of Life’s Essential 8 metrics, including updates.
1. Diet (updated)
The tool includes a new guide to assess diet quality for adults and children at the individual and population level. At the population level, dietary assessment is based on daily intake of elements in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating pattern. For individuals, the Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans (MEPA) is used to assess and monitor cardiovascular health.
2. Physical activity (no changes)
Physical activity continues to be measured by the total number of minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week, as defined by the U.S. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (2nd edition). The optimal level is 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate physical activity or more per week or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity for adults; 420 minutes (7 hours) or more per week for children ages 6 and older; and age-specific modifications for younger children.
3. Nicotine exposure (updated)
Use of inhaled nicotine-delivery systems, which includes e-cigarettes or vaping devices, has been added since the previous metric monitored only traditional, combustible cigarettes. This reflects use by adults and youth and their implications on long-term health. Second-hand smoke exposure for children and adults has also been added.
4. Sleep duration (new)
Sleep duration is associated with CV health. Measured by average hours of sleep per night, the ideal level is 7-9 hours daily for adults. Ideal daily sleep ranges for children are 10-16 hours per 24 hours for ages 5 and younger; 9-12 hours for ages 6-12 years; and 8-10 hours for ages 13-18 years.
5. Body mass index (no changes)
The AHA acknowledges that body mass index (BMI) is an imperfect metric. Yet, because it’s easily calculated and widely available, BMI continues as a “reasonable” gauge to assess weight categories that may lead to health problems. BMI of 18.5-24.9 is associated with the highest levels of CV health. The AHA notes that BMI ranges and the subsequent health risks associated with them may differ among people from diverse racial or ethnic backgrounds or ancestry. This aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations to adjust BMI ranges for people of Asian or Pacific Islander ancestry because recent evidence indicates their risk of conditions such as CVD or type 2 diabetes is higher at a lower BMI.
6. Blood lipids (updated)
The metric for blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) is updated to use non-HDL cholesterol as the preferred number to monitor, rather than total cholesterol. This shift is made because non-HDL cholesterol can be measured without fasting beforehand (thereby increasing its availability at any time of day and implementation at more appointments) and reliably calculated among all people.
7. Blood glucose (updated)
This metric is expanded to include the option of hemoglobin A1c readings or blood glucose levels for people with or without type 1 or 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
8. Blood pressure (no changes)
Blood pressure criteria remain unchanged from 2017 guidance that established levels less than 120/80 mm Hg as optimal, and defined hypertension as 130-139 mm Hg systolic pressure or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic pressure.
‘Concerning’ new data
Results of the first study using Life’s Essential 8 show that the overall CV health of the U.S. population is “well below ideal,” with 80% of adults scoring at a low or moderate level, the researchers report.
Data for the analysis came from 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys (NHANES) of more than 13,500 adults aged 20-79 years and nearly 9,900 children aged 2-19 years. Among the key findings:
- The average CV health score based on Life’s Essential 8 was 64.7 for adults and 65.5 for children – in the moderate range on the 0-100 scale.
- Only 0.45% of adults had a perfect score of 100; 20% had high CV health (score of 80 or higher), 63% moderate (score of 50-79), and 18% had low CV health (score of less than 50).
- Adult women had higher average CV health scores (67) compared with men (62.5).
- In general, adults scored lowest in the areas of diet, physical activity, and BMI.
- CV health scores were generally lower at older ages.
- Non-Hispanic Asian Americans had a higher average CV health score than other racial/ethnic groups. Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest average CV health score, followed, in order, by Hispanic (other than Mexican), Mexican, and non-Hispanic Blacks.
- Children’s diet scores were low, at an average of 40.6.
- Adult sociodemographic groups varied notably in CV health scores for diet, nicotine exposure, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
“These data represent the first look at the cardiovascular health of the U.S. population using the AHA’s new Life’s Essential 8 scoring algorithm,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
“Life’s Essential 8 is a major step forward in our ability to identify when cardiovascular health can be preserved and when it is suboptimal. It should energize efforts to improve cardiovascular health for all people and at every life stage,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
“Analyses like this can help policymakers, communities, clinicians, and the public to understand the opportunities to intervene to improve and maintain optimal cardiovascular health across the life course,” he said.
This research had no commercial funding. The authors have no reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Physicians react: Compensation isn’t worth the hassles. What’s the solution?
How satisfied are physicians that they are fairly compensated for their dedication, skills, and time? That’s a subject that seems to steer many physicians to heated emotions and to a variety of issues with today’s medical field – not all of which directly affect their pay.
Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2022: “Incomes Gain, Pay Gaps Remain” generally shows encouraging trends. Physician income rose from a year earlier, when it stagnated as COVID-19 restrictions led patients to stay home and medical practices to cut hours or close. And for the first time in Medscape’s 11 years of reporting on physician compensation, average income rose for every medical specialty surveyed.
Heartening findings, right? Yet the tone of comments to the report was anything but peppy. One physician even complained his plumber earns more than he does.
A family physician lamented that he has “made less in the past 3 years, with more hassles and work” and he “can’t wait to retire next year.” Meanwhile, he complained, the U.S. health system is “the costliest, yet wasteful, with worse outcomes; reactive, not preventative; and has the costliest drugs and social issues.”
Do NPs and PAs encroach on your income?
The conversation about fair compensation launched some commenters into a discussion about competition from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Some physicians expressed wariness at best, and anger at worst, about NPs and PAs evolving beyond traditional doctor support roles into certain direct patient support.
One-fourth of respondents in the compensation report said their income was negatively affected by competition from NPs, PAs, and other nonphysician providers. For example, with states like Arkansas expanding independent practice for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), one commenter complained, “we are no longer needed.”
Added another physician, “primary care, especially internal medicine, is just going away for doctors. We wasted, by all accounts, 4 full years of our working lives because NPs are ‘just as good.’ ”
Greater independence for NPs and PAs strengthens the hands of health insurers and “will end up hastening the demise of primary care as we have known it,” another reader predicted. Other physicians’ takes: “For the institution, it’s much cheaper to hire NPs than to hire doctors” and “overall, physician negotiating power will decrease in the future.”
Medicare reimbursement rates grate
Although 7 in 10 respondents in the compensation report said they would continue to accept new Medicare or Medicaid patients, comments reveal resentment about the practical need to work with Medicare and its resentment rates.
“An open question to Medicare: Are you doing the dumbest thing possible by paying low wages and giving huge administrative burdens for internal medicine on purpose?” one physician wrote. “Or are you really that short-sighted?”
Another reader cited an analysis from the American College of Surgeons of Medicare’s 1998 surgical CPT codes. If Medicare had left those codes alone beyond annual inflation adjustments, the study found, reimbursement rates by 2019 would be half of what they became.
Another way of looking at the code reimbursement increases is a 50% pay cut over 20 years for doctors and medical practices, that reader insisted. “The rising cost of employee wages, particularly of the last two-and-a-half years of COVID-19, combined with the effective pay cuts over the last 20 years, equals time to quit!”
Another commenter concurred. “In the 1990s, most full-time docs were making almost double what you see [in the report], and everything cost almost half of what it does now. So, MD purchasing power is between half and one-quarter of what it was in the early 1990s.”
Are self-pay models better?
Do physicians have a better chance at consistently fair income under a self-pay practice that avoids dealing with insurance companies?
One commenter hypothesized that psychiatrists once trailed internists in income but today earn more because many “quit working for insurance and went to a cash business 15 years ago.” Many family physicians did something similar by switching to a direct primary care model, he said.
This physician said he has done the same “with great results” for patients as well: shorter office visits, faster booking of appointments, no deductibles owed. Best of all, “I love practicing medicine again, and my patients love the great health care they receive.”
Another commenter agreed. “Two words: cash practice.” But another objected, “I guess only the very rich can afford to cover your business costs.”
Regardless of the payment model, another physician argued for private practice over employed positions. “Save on the bureaucratic expenses. Go back to private practice and get rid of electronic records.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How satisfied are physicians that they are fairly compensated for their dedication, skills, and time? That’s a subject that seems to steer many physicians to heated emotions and to a variety of issues with today’s medical field – not all of which directly affect their pay.
Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2022: “Incomes Gain, Pay Gaps Remain” generally shows encouraging trends. Physician income rose from a year earlier, when it stagnated as COVID-19 restrictions led patients to stay home and medical practices to cut hours or close. And for the first time in Medscape’s 11 years of reporting on physician compensation, average income rose for every medical specialty surveyed.
Heartening findings, right? Yet the tone of comments to the report was anything but peppy. One physician even complained his plumber earns more than he does.
A family physician lamented that he has “made less in the past 3 years, with more hassles and work” and he “can’t wait to retire next year.” Meanwhile, he complained, the U.S. health system is “the costliest, yet wasteful, with worse outcomes; reactive, not preventative; and has the costliest drugs and social issues.”
Do NPs and PAs encroach on your income?
The conversation about fair compensation launched some commenters into a discussion about competition from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Some physicians expressed wariness at best, and anger at worst, about NPs and PAs evolving beyond traditional doctor support roles into certain direct patient support.
One-fourth of respondents in the compensation report said their income was negatively affected by competition from NPs, PAs, and other nonphysician providers. For example, with states like Arkansas expanding independent practice for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), one commenter complained, “we are no longer needed.”
Added another physician, “primary care, especially internal medicine, is just going away for doctors. We wasted, by all accounts, 4 full years of our working lives because NPs are ‘just as good.’ ”
Greater independence for NPs and PAs strengthens the hands of health insurers and “will end up hastening the demise of primary care as we have known it,” another reader predicted. Other physicians’ takes: “For the institution, it’s much cheaper to hire NPs than to hire doctors” and “overall, physician negotiating power will decrease in the future.”
Medicare reimbursement rates grate
Although 7 in 10 respondents in the compensation report said they would continue to accept new Medicare or Medicaid patients, comments reveal resentment about the practical need to work with Medicare and its resentment rates.
“An open question to Medicare: Are you doing the dumbest thing possible by paying low wages and giving huge administrative burdens for internal medicine on purpose?” one physician wrote. “Or are you really that short-sighted?”
Another reader cited an analysis from the American College of Surgeons of Medicare’s 1998 surgical CPT codes. If Medicare had left those codes alone beyond annual inflation adjustments, the study found, reimbursement rates by 2019 would be half of what they became.
Another way of looking at the code reimbursement increases is a 50% pay cut over 20 years for doctors and medical practices, that reader insisted. “The rising cost of employee wages, particularly of the last two-and-a-half years of COVID-19, combined with the effective pay cuts over the last 20 years, equals time to quit!”
Another commenter concurred. “In the 1990s, most full-time docs were making almost double what you see [in the report], and everything cost almost half of what it does now. So, MD purchasing power is between half and one-quarter of what it was in the early 1990s.”
Are self-pay models better?
Do physicians have a better chance at consistently fair income under a self-pay practice that avoids dealing with insurance companies?
One commenter hypothesized that psychiatrists once trailed internists in income but today earn more because many “quit working for insurance and went to a cash business 15 years ago.” Many family physicians did something similar by switching to a direct primary care model, he said.
This physician said he has done the same “with great results” for patients as well: shorter office visits, faster booking of appointments, no deductibles owed. Best of all, “I love practicing medicine again, and my patients love the great health care they receive.”
Another commenter agreed. “Two words: cash practice.” But another objected, “I guess only the very rich can afford to cover your business costs.”
Regardless of the payment model, another physician argued for private practice over employed positions. “Save on the bureaucratic expenses. Go back to private practice and get rid of electronic records.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How satisfied are physicians that they are fairly compensated for their dedication, skills, and time? That’s a subject that seems to steer many physicians to heated emotions and to a variety of issues with today’s medical field – not all of which directly affect their pay.
Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2022: “Incomes Gain, Pay Gaps Remain” generally shows encouraging trends. Physician income rose from a year earlier, when it stagnated as COVID-19 restrictions led patients to stay home and medical practices to cut hours or close. And for the first time in Medscape’s 11 years of reporting on physician compensation, average income rose for every medical specialty surveyed.
Heartening findings, right? Yet the tone of comments to the report was anything but peppy. One physician even complained his plumber earns more than he does.
A family physician lamented that he has “made less in the past 3 years, with more hassles and work” and he “can’t wait to retire next year.” Meanwhile, he complained, the U.S. health system is “the costliest, yet wasteful, with worse outcomes; reactive, not preventative; and has the costliest drugs and social issues.”
Do NPs and PAs encroach on your income?
The conversation about fair compensation launched some commenters into a discussion about competition from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Some physicians expressed wariness at best, and anger at worst, about NPs and PAs evolving beyond traditional doctor support roles into certain direct patient support.
One-fourth of respondents in the compensation report said their income was negatively affected by competition from NPs, PAs, and other nonphysician providers. For example, with states like Arkansas expanding independent practice for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), one commenter complained, “we are no longer needed.”
Added another physician, “primary care, especially internal medicine, is just going away for doctors. We wasted, by all accounts, 4 full years of our working lives because NPs are ‘just as good.’ ”
Greater independence for NPs and PAs strengthens the hands of health insurers and “will end up hastening the demise of primary care as we have known it,” another reader predicted. Other physicians’ takes: “For the institution, it’s much cheaper to hire NPs than to hire doctors” and “overall, physician negotiating power will decrease in the future.”
Medicare reimbursement rates grate
Although 7 in 10 respondents in the compensation report said they would continue to accept new Medicare or Medicaid patients, comments reveal resentment about the practical need to work with Medicare and its resentment rates.
“An open question to Medicare: Are you doing the dumbest thing possible by paying low wages and giving huge administrative burdens for internal medicine on purpose?” one physician wrote. “Or are you really that short-sighted?”
Another reader cited an analysis from the American College of Surgeons of Medicare’s 1998 surgical CPT codes. If Medicare had left those codes alone beyond annual inflation adjustments, the study found, reimbursement rates by 2019 would be half of what they became.
Another way of looking at the code reimbursement increases is a 50% pay cut over 20 years for doctors and medical practices, that reader insisted. “The rising cost of employee wages, particularly of the last two-and-a-half years of COVID-19, combined with the effective pay cuts over the last 20 years, equals time to quit!”
Another commenter concurred. “In the 1990s, most full-time docs were making almost double what you see [in the report], and everything cost almost half of what it does now. So, MD purchasing power is between half and one-quarter of what it was in the early 1990s.”
Are self-pay models better?
Do physicians have a better chance at consistently fair income under a self-pay practice that avoids dealing with insurance companies?
One commenter hypothesized that psychiatrists once trailed internists in income but today earn more because many “quit working for insurance and went to a cash business 15 years ago.” Many family physicians did something similar by switching to a direct primary care model, he said.
This physician said he has done the same “with great results” for patients as well: shorter office visits, faster booking of appointments, no deductibles owed. Best of all, “I love practicing medicine again, and my patients love the great health care they receive.”
Another commenter agreed. “Two words: cash practice.” But another objected, “I guess only the very rich can afford to cover your business costs.”
Regardless of the payment model, another physician argued for private practice over employed positions. “Save on the bureaucratic expenses. Go back to private practice and get rid of electronic records.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.