User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
COVID-19 pulmonary severity ascribed to coagulation differences
Differences in COVID-19-related death rates between people of white and Asian ancestry may be partly explained by documented ethnic/racial differences in risk for blood clotting and pulmonary thrombotic events, investigators propose.
“Our novel findings demonstrate that COVID-19 is associated with a unique type of blood clotting disorder that is primarily focused within the lungs and which undoubtedly contributes to the high levels of mortality being seen in patients with COVID-19,” said James O’Donnell, MB, PhD, director of the Irish Centre for Vascular Biology at the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
Dr. O’Donnell and colleagues studied pulmonary effects and outcomes of 83 patients admitted to St. James Hospital in Dublin, and found evidence to suggest that the diffuse, bilateral pulmonary inflammation seen in many patients with severe COVID-19 infections may be caused by a pulmonary-specific vasculopathy they label “pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy” (PIC), an entity distinct from disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
“Given that thrombotic risk is significantly impacted by race, coupled with the accumulating evidence that coagulopathy is important in COVID-19 pathogenesis, our findings raise the intriguing possibility that pulmonary vasculopathy may contribute to the unexplained differences that are beginning to emerge highlighting racial susceptibility to COVID-19 mortality,” they wrote in a study published online in the British Journal of Haematology.
Study flaws harm conclusions
But critical care specialists who agreed to review and comment on the study for MDedge News said that it has significant flaws that affect the ability to interpret the findings and “undermine the conclusions reached by the authors.”
“The underlying premise of the study is that there are racial and ethnic differences in the development of venous thromboembolism that may explain the racial and ethnic differences in outcomes from COVID-19,” J. Daryl Thornton, MD, MPH, a fellow of the American Thoracic Society and associate professor of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. “This is an interesting hypothesis and one that could be easily tested in a well-designed study with sufficient representation from the relevant racial and ethnic groups. However, this study is neither well designed nor does it have sufficient racial and ethnic representation.”
Elliott R. Haut, MD, PhD, associate professor of surgery, anesthesiology and critical care medicine at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, said in an interview that the study is “mediocre” and has the feel of a paper rushed to press.
“It talks about their theory that race, ethnicity, have an effect on venous thromboembolism, and that’s a pretty well-known fact. No one’s a hundred percent sure why that is, but certainly there are tons and tons of papers that show that there are groups that are at higher risk than others,” he said. “Their idea that this is caused by this pulmonary inflammation, that is totally a guess; there is no data in this paper to support that.”
Dr. Thornton and Dr. Haut both noted that the authors don’t define how race and ethnicity were determined and whether patients were asked to provide it, and although they mention the racial/ethnic breakdown once, subsequent references are to entire cohort are as “Caucasian.”
They also called into question the value of comparing laboratory data across continents in centers with different testing methods and parameters, especially in a time when the clinical picture changes so rapidly.
Coagulation differences
Dr. O’Donnell and colleagues noted that most studies of COVID-19-associated coagulopathy published to date have been with Chinese patients.
“This is important because race and ethnicity have major effects upon thrombotic risk. In particular, epidemiological studies have shown that the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is approximately three to fourfold lower in Chinese compared to Caucasian individuals. Conversely, VTE risk is significantly higher in African-Americans compared to Caucasians,” they wrote.
Because of the lower risk of VTE in the Chinese population, thromboprophylaxis with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) or other agents is less frequently used in Chinese hospitals than in hospitals with predominantly non-Asian patients, they noted.
To see whether the were differences in coagulopathy between Chinese and white patients, the researchers enrolled 55 men and 28 women, median age 64, who were admitted to St. James Hospital with COVID-19 infections from March 13 through April 10, 2020. The cohort included 67 patients of white background, 10 of Asian ancestry, 5 of African ethnicity, and 1 of Latino/Hispanic ancestry.
Of the 83 patients, 67 had comorbidities at admission. At the time of the report, 50 patients had fully recovered and were discharged, 20 remained in the hospital, and 13 had died. In all, 50 patients were discharged without needing ICU care, 23 were admitted to the ICU, and 10 required ICU but were deemed “clinically unsuitable” for ICU admission.
Although the patients had normal prothrombin time (PT) and normal activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), plasma d-dimer levels were significantly elevated and were above the range of normal in two-thirds of patients on admission.
Despite the increased d-dimer levels, however, there was no evidence of DIC as defined by the International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis Scientific and Standardization committee (ISTH SSC) guidelines. Platelet counts were in the normal range in 83.1% of patients, and only five had counts less than 100 x 109/L at admission. Fibrinogen levels were also elevated, as were C-reactive protein levels, both likely indicating an acute phase response.
“Thus, despite the fact that thrombotic risk is much higher in Caucasian patients and the significant elevated levels of d-dimers observed, overt DIC as defined according to the ISTH SSC DIC score was present in none of our COVID-19 patients at time of admission. Nevertheless, our data confirm that severe COVID-19 infection is associated with a significant coagulopathy in Caucasian patients that appears to be similar in magnitude to that previously reported in the original Chinese cohorts,” they wrote.
When they compared patients who required ICU admission for ventilator support and those who died with patients who were discharged without needing ICU support, they found that survivors were younger (median age 60.2 vs. 75.2 years), and that more critically ill patients were more likely to have comorbidities.
They also found that patients with abnormal coagulation parameters on admission were significantly more likely to have poor prognosis (P = .018), and that patients in the adverse outcomes group had significantly higher fibrinogen and CRP levels (P = .045 and .0005, respectively).
There was no significant difference in PT between the prognosis groups at admission, but by day 4 and beyond PT was a median of 13.1 vs. 12.5 seconds in the favorable outcomes groups (P = .007), and patients with poor prognosis continued to have significantly higher d-dimer levels. (P = .003)
“Cumulatively, these data support the hypothesis that COVID-19–associated coagulopathy probably contributes to the underlying pulmonary pathogenesis,” the researchers wrote.
They noted that the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor that COVID-19 uses to enter cells is expressed on both type II pneumocytes and vascular endothelial cells within the lung, suggesting that the coagulopathy may be related to direct pulmonary endothelial cell infection , activation, and/or damage, and to the documented cytokine storm that can affect thrombin generation and fibrin deposition within the lungs.
“In the context of this lung-centric vasculopathy, we hypothesize that the refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome phenotype observed in severe COVID-19 is due to concurrent ‘double-hit’ pathologies targeting both ventilation (V) and perfusion (Q) within the lungs where alveoli and pulmonary microvasculature exist in close anatomical juxtaposition,” they wrote.
The investigators noted that larger randomized trials will be needed to determine whether more aggressive anti-coagulation and/or targeted anti-inflammatory therapies could effectively treated PIC in patients with severe COVID-19.
The study was supported by the Wellcome Trust and the Health Research Board Health Service and the Research and Development Division, Northern Ireland. Dr. O’Donnell disclosed speakers bureau activities, advisory board participation, and research grants from multiple companies. The other doctors had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Fogarty H et al. Br J Haematol. 2020 Apr 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16749.
Differences in COVID-19-related death rates between people of white and Asian ancestry may be partly explained by documented ethnic/racial differences in risk for blood clotting and pulmonary thrombotic events, investigators propose.
“Our novel findings demonstrate that COVID-19 is associated with a unique type of blood clotting disorder that is primarily focused within the lungs and which undoubtedly contributes to the high levels of mortality being seen in patients with COVID-19,” said James O’Donnell, MB, PhD, director of the Irish Centre for Vascular Biology at the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
Dr. O’Donnell and colleagues studied pulmonary effects and outcomes of 83 patients admitted to St. James Hospital in Dublin, and found evidence to suggest that the diffuse, bilateral pulmonary inflammation seen in many patients with severe COVID-19 infections may be caused by a pulmonary-specific vasculopathy they label “pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy” (PIC), an entity distinct from disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
“Given that thrombotic risk is significantly impacted by race, coupled with the accumulating evidence that coagulopathy is important in COVID-19 pathogenesis, our findings raise the intriguing possibility that pulmonary vasculopathy may contribute to the unexplained differences that are beginning to emerge highlighting racial susceptibility to COVID-19 mortality,” they wrote in a study published online in the British Journal of Haematology.
Study flaws harm conclusions
But critical care specialists who agreed to review and comment on the study for MDedge News said that it has significant flaws that affect the ability to interpret the findings and “undermine the conclusions reached by the authors.”
“The underlying premise of the study is that there are racial and ethnic differences in the development of venous thromboembolism that may explain the racial and ethnic differences in outcomes from COVID-19,” J. Daryl Thornton, MD, MPH, a fellow of the American Thoracic Society and associate professor of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. “This is an interesting hypothesis and one that could be easily tested in a well-designed study with sufficient representation from the relevant racial and ethnic groups. However, this study is neither well designed nor does it have sufficient racial and ethnic representation.”
Elliott R. Haut, MD, PhD, associate professor of surgery, anesthesiology and critical care medicine at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, said in an interview that the study is “mediocre” and has the feel of a paper rushed to press.
“It talks about their theory that race, ethnicity, have an effect on venous thromboembolism, and that’s a pretty well-known fact. No one’s a hundred percent sure why that is, but certainly there are tons and tons of papers that show that there are groups that are at higher risk than others,” he said. “Their idea that this is caused by this pulmonary inflammation, that is totally a guess; there is no data in this paper to support that.”
Dr. Thornton and Dr. Haut both noted that the authors don’t define how race and ethnicity were determined and whether patients were asked to provide it, and although they mention the racial/ethnic breakdown once, subsequent references are to entire cohort are as “Caucasian.”
They also called into question the value of comparing laboratory data across continents in centers with different testing methods and parameters, especially in a time when the clinical picture changes so rapidly.
Coagulation differences
Dr. O’Donnell and colleagues noted that most studies of COVID-19-associated coagulopathy published to date have been with Chinese patients.
“This is important because race and ethnicity have major effects upon thrombotic risk. In particular, epidemiological studies have shown that the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is approximately three to fourfold lower in Chinese compared to Caucasian individuals. Conversely, VTE risk is significantly higher in African-Americans compared to Caucasians,” they wrote.
Because of the lower risk of VTE in the Chinese population, thromboprophylaxis with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) or other agents is less frequently used in Chinese hospitals than in hospitals with predominantly non-Asian patients, they noted.
To see whether the were differences in coagulopathy between Chinese and white patients, the researchers enrolled 55 men and 28 women, median age 64, who were admitted to St. James Hospital with COVID-19 infections from March 13 through April 10, 2020. The cohort included 67 patients of white background, 10 of Asian ancestry, 5 of African ethnicity, and 1 of Latino/Hispanic ancestry.
Of the 83 patients, 67 had comorbidities at admission. At the time of the report, 50 patients had fully recovered and were discharged, 20 remained in the hospital, and 13 had died. In all, 50 patients were discharged without needing ICU care, 23 were admitted to the ICU, and 10 required ICU but were deemed “clinically unsuitable” for ICU admission.
Although the patients had normal prothrombin time (PT) and normal activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), plasma d-dimer levels were significantly elevated and were above the range of normal in two-thirds of patients on admission.
Despite the increased d-dimer levels, however, there was no evidence of DIC as defined by the International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis Scientific and Standardization committee (ISTH SSC) guidelines. Platelet counts were in the normal range in 83.1% of patients, and only five had counts less than 100 x 109/L at admission. Fibrinogen levels were also elevated, as were C-reactive protein levels, both likely indicating an acute phase response.
“Thus, despite the fact that thrombotic risk is much higher in Caucasian patients and the significant elevated levels of d-dimers observed, overt DIC as defined according to the ISTH SSC DIC score was present in none of our COVID-19 patients at time of admission. Nevertheless, our data confirm that severe COVID-19 infection is associated with a significant coagulopathy in Caucasian patients that appears to be similar in magnitude to that previously reported in the original Chinese cohorts,” they wrote.
When they compared patients who required ICU admission for ventilator support and those who died with patients who were discharged without needing ICU support, they found that survivors were younger (median age 60.2 vs. 75.2 years), and that more critically ill patients were more likely to have comorbidities.
They also found that patients with abnormal coagulation parameters on admission were significantly more likely to have poor prognosis (P = .018), and that patients in the adverse outcomes group had significantly higher fibrinogen and CRP levels (P = .045 and .0005, respectively).
There was no significant difference in PT between the prognosis groups at admission, but by day 4 and beyond PT was a median of 13.1 vs. 12.5 seconds in the favorable outcomes groups (P = .007), and patients with poor prognosis continued to have significantly higher d-dimer levels. (P = .003)
“Cumulatively, these data support the hypothesis that COVID-19–associated coagulopathy probably contributes to the underlying pulmonary pathogenesis,” the researchers wrote.
They noted that the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor that COVID-19 uses to enter cells is expressed on both type II pneumocytes and vascular endothelial cells within the lung, suggesting that the coagulopathy may be related to direct pulmonary endothelial cell infection , activation, and/or damage, and to the documented cytokine storm that can affect thrombin generation and fibrin deposition within the lungs.
“In the context of this lung-centric vasculopathy, we hypothesize that the refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome phenotype observed in severe COVID-19 is due to concurrent ‘double-hit’ pathologies targeting both ventilation (V) and perfusion (Q) within the lungs where alveoli and pulmonary microvasculature exist in close anatomical juxtaposition,” they wrote.
The investigators noted that larger randomized trials will be needed to determine whether more aggressive anti-coagulation and/or targeted anti-inflammatory therapies could effectively treated PIC in patients with severe COVID-19.
The study was supported by the Wellcome Trust and the Health Research Board Health Service and the Research and Development Division, Northern Ireland. Dr. O’Donnell disclosed speakers bureau activities, advisory board participation, and research grants from multiple companies. The other doctors had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Fogarty H et al. Br J Haematol. 2020 Apr 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16749.
Differences in COVID-19-related death rates between people of white and Asian ancestry may be partly explained by documented ethnic/racial differences in risk for blood clotting and pulmonary thrombotic events, investigators propose.
“Our novel findings demonstrate that COVID-19 is associated with a unique type of blood clotting disorder that is primarily focused within the lungs and which undoubtedly contributes to the high levels of mortality being seen in patients with COVID-19,” said James O’Donnell, MB, PhD, director of the Irish Centre for Vascular Biology at the Royal College of Surgeons in Ireland.
Dr. O’Donnell and colleagues studied pulmonary effects and outcomes of 83 patients admitted to St. James Hospital in Dublin, and found evidence to suggest that the diffuse, bilateral pulmonary inflammation seen in many patients with severe COVID-19 infections may be caused by a pulmonary-specific vasculopathy they label “pulmonary intravascular coagulopathy” (PIC), an entity distinct from disseminated intravascular coagulopathy (DIC).
“Given that thrombotic risk is significantly impacted by race, coupled with the accumulating evidence that coagulopathy is important in COVID-19 pathogenesis, our findings raise the intriguing possibility that pulmonary vasculopathy may contribute to the unexplained differences that are beginning to emerge highlighting racial susceptibility to COVID-19 mortality,” they wrote in a study published online in the British Journal of Haematology.
Study flaws harm conclusions
But critical care specialists who agreed to review and comment on the study for MDedge News said that it has significant flaws that affect the ability to interpret the findings and “undermine the conclusions reached by the authors.”
“The underlying premise of the study is that there are racial and ethnic differences in the development of venous thromboembolism that may explain the racial and ethnic differences in outcomes from COVID-19,” J. Daryl Thornton, MD, MPH, a fellow of the American Thoracic Society and associate professor of pulmonary, critical care, and sleep medicine at Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland, said in an interview. “This is an interesting hypothesis and one that could be easily tested in a well-designed study with sufficient representation from the relevant racial and ethnic groups. However, this study is neither well designed nor does it have sufficient racial and ethnic representation.”
Elliott R. Haut, MD, PhD, associate professor of surgery, anesthesiology and critical care medicine at Johns Hopkins Medicine, Baltimore, said in an interview that the study is “mediocre” and has the feel of a paper rushed to press.
“It talks about their theory that race, ethnicity, have an effect on venous thromboembolism, and that’s a pretty well-known fact. No one’s a hundred percent sure why that is, but certainly there are tons and tons of papers that show that there are groups that are at higher risk than others,” he said. “Their idea that this is caused by this pulmonary inflammation, that is totally a guess; there is no data in this paper to support that.”
Dr. Thornton and Dr. Haut both noted that the authors don’t define how race and ethnicity were determined and whether patients were asked to provide it, and although they mention the racial/ethnic breakdown once, subsequent references are to entire cohort are as “Caucasian.”
They also called into question the value of comparing laboratory data across continents in centers with different testing methods and parameters, especially in a time when the clinical picture changes so rapidly.
Coagulation differences
Dr. O’Donnell and colleagues noted that most studies of COVID-19-associated coagulopathy published to date have been with Chinese patients.
“This is important because race and ethnicity have major effects upon thrombotic risk. In particular, epidemiological studies have shown that the incidence of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is approximately three to fourfold lower in Chinese compared to Caucasian individuals. Conversely, VTE risk is significantly higher in African-Americans compared to Caucasians,” they wrote.
Because of the lower risk of VTE in the Chinese population, thromboprophylaxis with low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) or other agents is less frequently used in Chinese hospitals than in hospitals with predominantly non-Asian patients, they noted.
To see whether the were differences in coagulopathy between Chinese and white patients, the researchers enrolled 55 men and 28 women, median age 64, who were admitted to St. James Hospital with COVID-19 infections from March 13 through April 10, 2020. The cohort included 67 patients of white background, 10 of Asian ancestry, 5 of African ethnicity, and 1 of Latino/Hispanic ancestry.
Of the 83 patients, 67 had comorbidities at admission. At the time of the report, 50 patients had fully recovered and were discharged, 20 remained in the hospital, and 13 had died. In all, 50 patients were discharged without needing ICU care, 23 were admitted to the ICU, and 10 required ICU but were deemed “clinically unsuitable” for ICU admission.
Although the patients had normal prothrombin time (PT) and normal activated partial thromboplastin time (APTT), plasma d-dimer levels were significantly elevated and were above the range of normal in two-thirds of patients on admission.
Despite the increased d-dimer levels, however, there was no evidence of DIC as defined by the International Society of Thrombosis and Hemostasis Scientific and Standardization committee (ISTH SSC) guidelines. Platelet counts were in the normal range in 83.1% of patients, and only five had counts less than 100 x 109/L at admission. Fibrinogen levels were also elevated, as were C-reactive protein levels, both likely indicating an acute phase response.
“Thus, despite the fact that thrombotic risk is much higher in Caucasian patients and the significant elevated levels of d-dimers observed, overt DIC as defined according to the ISTH SSC DIC score was present in none of our COVID-19 patients at time of admission. Nevertheless, our data confirm that severe COVID-19 infection is associated with a significant coagulopathy in Caucasian patients that appears to be similar in magnitude to that previously reported in the original Chinese cohorts,” they wrote.
When they compared patients who required ICU admission for ventilator support and those who died with patients who were discharged without needing ICU support, they found that survivors were younger (median age 60.2 vs. 75.2 years), and that more critically ill patients were more likely to have comorbidities.
They also found that patients with abnormal coagulation parameters on admission were significantly more likely to have poor prognosis (P = .018), and that patients in the adverse outcomes group had significantly higher fibrinogen and CRP levels (P = .045 and .0005, respectively).
There was no significant difference in PT between the prognosis groups at admission, but by day 4 and beyond PT was a median of 13.1 vs. 12.5 seconds in the favorable outcomes groups (P = .007), and patients with poor prognosis continued to have significantly higher d-dimer levels. (P = .003)
“Cumulatively, these data support the hypothesis that COVID-19–associated coagulopathy probably contributes to the underlying pulmonary pathogenesis,” the researchers wrote.
They noted that the angiotensin converting enzyme 2 (ACE-2) receptor that COVID-19 uses to enter cells is expressed on both type II pneumocytes and vascular endothelial cells within the lung, suggesting that the coagulopathy may be related to direct pulmonary endothelial cell infection , activation, and/or damage, and to the documented cytokine storm that can affect thrombin generation and fibrin deposition within the lungs.
“In the context of this lung-centric vasculopathy, we hypothesize that the refractory acute respiratory distress syndrome phenotype observed in severe COVID-19 is due to concurrent ‘double-hit’ pathologies targeting both ventilation (V) and perfusion (Q) within the lungs where alveoli and pulmonary microvasculature exist in close anatomical juxtaposition,” they wrote.
The investigators noted that larger randomized trials will be needed to determine whether more aggressive anti-coagulation and/or targeted anti-inflammatory therapies could effectively treated PIC in patients with severe COVID-19.
The study was supported by the Wellcome Trust and the Health Research Board Health Service and the Research and Development Division, Northern Ireland. Dr. O’Donnell disclosed speakers bureau activities, advisory board participation, and research grants from multiple companies. The other doctors had no relevant conflicts of interest to disclose.
SOURCE: Fogarty H et al. Br J Haematol. 2020 Apr 24. doi: 10.1111/bjh.16749.
FROM THE BRITISH JOURNAL OF HEMATOLOGY
New angiotensin studies in COVID-19 give more reassurance
Four more studies of the relationship of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) with COVID-19 have been published in the past few days in top-tier peer-reviewed journals, and on the whole, the data are reassuring.
Three of the new studies were published in the New England Journal of Medicine on May 1, and one study was published in JAMA Cardiology on May 5.
Although all the studies are observational in design and have some confounding factors, overall, However, there are some contradictory findings in secondary analyses regarding possible differences in the effects of the two drug classes.
Providing commentary, John McMurray, MD, professor of medical cardiology at the University of Glasgow, said: “The overall picture seems to suggest no increase in risk of adverse outcomes in patients taking renin-angiotensin system [RAS] blockers ― but with lots of caveats: These are all observational rather than randomized studies, and there may be residual or unmeasured confounding.”
Was it ‘Much ado about nothing’?
Franz Messerli, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Bern (Switzerland), added: “Given this state of the art, I am inclined to consider RAS blockade and COVID-19 – despite all the hype in the news media – as much ado about nothing.”
But both Dr. McMurray and Dr. Messerli said they were intrigued about possible differences in the effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs that some of the new results suggest.
In one study, a team led by Mandeep Mehra, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart and Vascular Center, Boston, analyzed data from 8,910 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 169 hospitals in Asia, Europe, and North America who had either died in the hospital (5.8%) or survived to hospital discharge (94.2%).
In multivariate logistic-regression analysis, age greater than 65 years, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, history of cardiac arrhythmia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and current smoking were associated with an increased risk for in-hospital death. Female sex was associated with a decreased risk. Neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs were associated with an increased risk for in-hospital death.
In fact, ACE inhibitors were associated with a significant reduction in mortality (odds ratio, 0.33), as were statins (OR, 0.35).
The authors, however, stressed that these observations about reduced mortality with ACE inhibitors and statins “should be considered with extreme caution.”
“Because our study was not a randomized, controlled trial, we cannot exclude the possibility of confounding. In addition, we examined relationships between many variables and in-hospital death, and no primary hypothesis was prespecified; these factors increased the probability of chance associations being found. Therefore, a cause-and-effect relationship between drug therapy and survival should not be inferred,” they wrote.
A secondary analysis that was restricted to patients with hypertension (those for whom an ACE inhibitor or an ARB would be indicated) also did not show harm.
A second study published in the New England Journal of Medicine had a case-control design. The authors, led by Giuseppe Mancia, MD, of the University of Milano-Bicocca (Italy), compared 6,272 patients with confirmed COVID-19 (case patients) with 30,759 control persons who were matched according to age, sex, and municipality of residence.
In a conditional logistic-regression multivariate analysis, neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs were associated with the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“Thus, our results do not provide evidence of an independent relationship between renin angiotensin aldosterone blockers and the susceptibility to COVID-19 in humans,” the authors concluded.
In addition, a second analysis that compared patients who had severe or fatal infections with matched control persons did not show an association between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and severe disease.
In the third study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, a group led by Harmony R. Reynolds, MD, of New York University, analyzed data from the health records of 12,594 patients in the NYU Langone Health system who had been tested for COVID-19. They found 5,894 patients whose test results were positive. Of these patients, 1,002 had severe illness, which was defined as illness requiring admission to the ICU, need for mechanical ventilation, or death.
Using Bayesian analysis and propensity score matching, the researchers assessed the relation between previous treatment with five different classes of antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta blockers, calcium blockers, and thiazide diuretics) and the likelihood of a positive or negative result on COVID-19 testing, as well as the likelihood of severe illness among patients who tested positive.
Results showed no positive association between any of the analyzed drug classes and either a positive test result or severe illness.
In an accompanying editorial, a group led by John A. Jarcho, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine, wrote: “Taken together, these three studies do not provide evidence to support the hypothesis that ACE inhibitor or ARB use is associated with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the risk of severe COVID-19 among those infected, or the risk of in-hospital death among those with a positive test.
“Each of these studies has weaknesses inherent in observational data, but we find it reassuring that three studies in different populations and with different designs arrive at the consistent message that the continued use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs is unlikely to be harmful in patients with COVID-19. Several other smaller studies from China and the United Kingdom have come to the same conclusion,” the authors of the editorial stated.
In the study published in JAMA Cardiology, a group led by Neil Mehta, MBBS, of the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, analyzed data on 18,472 patients who had been tested for COVID-19 between March 8 and April 12 in the Cleveland Clinic Health System in Ohio and Florida. Of these patients, 9.4% tested positive.
After overlap propensity score weighting for both ACE inhibitors and ARBs to take into account relevant comorbidities, there was no difference in risk for testing positive among patients taking an ACE inhibitor or an ARB in comparison with those not taking such medication.
Are there different effects between ACE inhibitors and ARBs?
A secondary exploratory analysis showed a higher likelihood of hospital admission among patients who tested positive and who were taking either ACE inhibitors (OR, 1.84) or ARBs (OR, 1.61), and there was a higher likelihood of ICU admission among patients who tested positive and who were taking an ACE inhibitor (OR 1.77), but no such difference was observed among those taking ARBs.
Coauthor Ankur Kalra, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that results of the exploratory analysis fit with the hypothesis that the two drugs classes may have different effects in patients with COVID-19.
“Angiotensin II promotes vasoconstriction, inflammation, and fibrosis in the lungs, and ARBs block the effects of angiotensin II more effectively than ACE inhibitors. In addition, ACE inhibitors (but not ARBs) increase levels of bradykinin, which may be one factor leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome,” he noted.
“However, these results should only be considered exploratory, as there is inherent bias in observational data,” Dr. Kalra stressed.
In an accompanying editorial in JAMA Cardiology, a group led by Laine E. Thomas, PhD, of Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, North Carolina, said that the results of this secondary exploratory analysis are limited by a small number of patients and “are likely explained by confounding and should not be inferred as causal.”
The New England Journal of Medicine editorialists reached a similar conclusion regarding the lower mortality in COVID-19 patients who took ACE inhibitors in the study by Dr. Mehra and colleagues. They say this unexpected result “may be due to unmeasured confounding and, in the absence of a randomized trial, should not be regarded as evidence to prescribe these drugs in patients with COVID-19.”
Providing further comment, Dr. McMurray said: “Normally, I would not read too much into the different effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs suggested in the Cleveland study because of the small numbers (about 28 ACE inhibitor–treated patients admitted to ICU) and the limited information about matching and/or adjustment for potential differences between groups.
“I could also argue that the comparison that would best answer the question about risk related to type of RAS blocker would be the direct comparison of people taking an ACE inhibitor with those taking an ARB (and that doesn’t look very different). The only thing that makes me a little cautious about completely dismissing the possibility of a difference between ACE inhibitor and ARB here is the suggestion of a similar trend in another large study from the VA [Veterans Affairs] system,” he added.
He also noted that speculation about there being mechanisms that involve different effects of the two drug classes on bradykinin and angiotensin II was “plausible but unproven.”
Dr. Messerli added: “Before turning the page, I would like to see an analysis comparing ACE inhibitors and ARBs, since experimentally, their effect on ACE2 (the receptor to which the virus binds) seems to differ. The study of Mehta et al in JAMA Cardiology may be the first clinical hint indicating that ARBs are more protective than ACEIs. However even here, the looming possibility of confounding cannot be excluded.”
Dr. Messerli also pointed to a hypothesis that suggests that direct viral infection of endothelial cells expressing ACE2 receptors may explain worse outcomes in patients with cardiovascular comorbidities, which provides a rationale for therapies to stabilize the endothelium, particularly with anti-inflammatory anticytokine drugs, ACE inhibitors, and statins.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Four more studies of the relationship of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) with COVID-19 have been published in the past few days in top-tier peer-reviewed journals, and on the whole, the data are reassuring.
Three of the new studies were published in the New England Journal of Medicine on May 1, and one study was published in JAMA Cardiology on May 5.
Although all the studies are observational in design and have some confounding factors, overall, However, there are some contradictory findings in secondary analyses regarding possible differences in the effects of the two drug classes.
Providing commentary, John McMurray, MD, professor of medical cardiology at the University of Glasgow, said: “The overall picture seems to suggest no increase in risk of adverse outcomes in patients taking renin-angiotensin system [RAS] blockers ― but with lots of caveats: These are all observational rather than randomized studies, and there may be residual or unmeasured confounding.”
Was it ‘Much ado about nothing’?
Franz Messerli, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Bern (Switzerland), added: “Given this state of the art, I am inclined to consider RAS blockade and COVID-19 – despite all the hype in the news media – as much ado about nothing.”
But both Dr. McMurray and Dr. Messerli said they were intrigued about possible differences in the effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs that some of the new results suggest.
In one study, a team led by Mandeep Mehra, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart and Vascular Center, Boston, analyzed data from 8,910 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 169 hospitals in Asia, Europe, and North America who had either died in the hospital (5.8%) or survived to hospital discharge (94.2%).
In multivariate logistic-regression analysis, age greater than 65 years, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, history of cardiac arrhythmia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and current smoking were associated with an increased risk for in-hospital death. Female sex was associated with a decreased risk. Neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs were associated with an increased risk for in-hospital death.
In fact, ACE inhibitors were associated with a significant reduction in mortality (odds ratio, 0.33), as were statins (OR, 0.35).
The authors, however, stressed that these observations about reduced mortality with ACE inhibitors and statins “should be considered with extreme caution.”
“Because our study was not a randomized, controlled trial, we cannot exclude the possibility of confounding. In addition, we examined relationships between many variables and in-hospital death, and no primary hypothesis was prespecified; these factors increased the probability of chance associations being found. Therefore, a cause-and-effect relationship between drug therapy and survival should not be inferred,” they wrote.
A secondary analysis that was restricted to patients with hypertension (those for whom an ACE inhibitor or an ARB would be indicated) also did not show harm.
A second study published in the New England Journal of Medicine had a case-control design. The authors, led by Giuseppe Mancia, MD, of the University of Milano-Bicocca (Italy), compared 6,272 patients with confirmed COVID-19 (case patients) with 30,759 control persons who were matched according to age, sex, and municipality of residence.
In a conditional logistic-regression multivariate analysis, neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs were associated with the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“Thus, our results do not provide evidence of an independent relationship between renin angiotensin aldosterone blockers and the susceptibility to COVID-19 in humans,” the authors concluded.
In addition, a second analysis that compared patients who had severe or fatal infections with matched control persons did not show an association between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and severe disease.
In the third study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, a group led by Harmony R. Reynolds, MD, of New York University, analyzed data from the health records of 12,594 patients in the NYU Langone Health system who had been tested for COVID-19. They found 5,894 patients whose test results were positive. Of these patients, 1,002 had severe illness, which was defined as illness requiring admission to the ICU, need for mechanical ventilation, or death.
Using Bayesian analysis and propensity score matching, the researchers assessed the relation between previous treatment with five different classes of antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta blockers, calcium blockers, and thiazide diuretics) and the likelihood of a positive or negative result on COVID-19 testing, as well as the likelihood of severe illness among patients who tested positive.
Results showed no positive association between any of the analyzed drug classes and either a positive test result or severe illness.
In an accompanying editorial, a group led by John A. Jarcho, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine, wrote: “Taken together, these three studies do not provide evidence to support the hypothesis that ACE inhibitor or ARB use is associated with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the risk of severe COVID-19 among those infected, or the risk of in-hospital death among those with a positive test.
“Each of these studies has weaknesses inherent in observational data, but we find it reassuring that three studies in different populations and with different designs arrive at the consistent message that the continued use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs is unlikely to be harmful in patients with COVID-19. Several other smaller studies from China and the United Kingdom have come to the same conclusion,” the authors of the editorial stated.
In the study published in JAMA Cardiology, a group led by Neil Mehta, MBBS, of the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, analyzed data on 18,472 patients who had been tested for COVID-19 between March 8 and April 12 in the Cleveland Clinic Health System in Ohio and Florida. Of these patients, 9.4% tested positive.
After overlap propensity score weighting for both ACE inhibitors and ARBs to take into account relevant comorbidities, there was no difference in risk for testing positive among patients taking an ACE inhibitor or an ARB in comparison with those not taking such medication.
Are there different effects between ACE inhibitors and ARBs?
A secondary exploratory analysis showed a higher likelihood of hospital admission among patients who tested positive and who were taking either ACE inhibitors (OR, 1.84) or ARBs (OR, 1.61), and there was a higher likelihood of ICU admission among patients who tested positive and who were taking an ACE inhibitor (OR 1.77), but no such difference was observed among those taking ARBs.
Coauthor Ankur Kalra, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that results of the exploratory analysis fit with the hypothesis that the two drugs classes may have different effects in patients with COVID-19.
“Angiotensin II promotes vasoconstriction, inflammation, and fibrosis in the lungs, and ARBs block the effects of angiotensin II more effectively than ACE inhibitors. In addition, ACE inhibitors (but not ARBs) increase levels of bradykinin, which may be one factor leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome,” he noted.
“However, these results should only be considered exploratory, as there is inherent bias in observational data,” Dr. Kalra stressed.
In an accompanying editorial in JAMA Cardiology, a group led by Laine E. Thomas, PhD, of Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, North Carolina, said that the results of this secondary exploratory analysis are limited by a small number of patients and “are likely explained by confounding and should not be inferred as causal.”
The New England Journal of Medicine editorialists reached a similar conclusion regarding the lower mortality in COVID-19 patients who took ACE inhibitors in the study by Dr. Mehra and colleagues. They say this unexpected result “may be due to unmeasured confounding and, in the absence of a randomized trial, should not be regarded as evidence to prescribe these drugs in patients with COVID-19.”
Providing further comment, Dr. McMurray said: “Normally, I would not read too much into the different effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs suggested in the Cleveland study because of the small numbers (about 28 ACE inhibitor–treated patients admitted to ICU) and the limited information about matching and/or adjustment for potential differences between groups.
“I could also argue that the comparison that would best answer the question about risk related to type of RAS blocker would be the direct comparison of people taking an ACE inhibitor with those taking an ARB (and that doesn’t look very different). The only thing that makes me a little cautious about completely dismissing the possibility of a difference between ACE inhibitor and ARB here is the suggestion of a similar trend in another large study from the VA [Veterans Affairs] system,” he added.
He also noted that speculation about there being mechanisms that involve different effects of the two drug classes on bradykinin and angiotensin II was “plausible but unproven.”
Dr. Messerli added: “Before turning the page, I would like to see an analysis comparing ACE inhibitors and ARBs, since experimentally, their effect on ACE2 (the receptor to which the virus binds) seems to differ. The study of Mehta et al in JAMA Cardiology may be the first clinical hint indicating that ARBs are more protective than ACEIs. However even here, the looming possibility of confounding cannot be excluded.”
Dr. Messerli also pointed to a hypothesis that suggests that direct viral infection of endothelial cells expressing ACE2 receptors may explain worse outcomes in patients with cardiovascular comorbidities, which provides a rationale for therapies to stabilize the endothelium, particularly with anti-inflammatory anticytokine drugs, ACE inhibitors, and statins.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Four more studies of the relationship of angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors and angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) with COVID-19 have been published in the past few days in top-tier peer-reviewed journals, and on the whole, the data are reassuring.
Three of the new studies were published in the New England Journal of Medicine on May 1, and one study was published in JAMA Cardiology on May 5.
Although all the studies are observational in design and have some confounding factors, overall, However, there are some contradictory findings in secondary analyses regarding possible differences in the effects of the two drug classes.
Providing commentary, John McMurray, MD, professor of medical cardiology at the University of Glasgow, said: “The overall picture seems to suggest no increase in risk of adverse outcomes in patients taking renin-angiotensin system [RAS] blockers ― but with lots of caveats: These are all observational rather than randomized studies, and there may be residual or unmeasured confounding.”
Was it ‘Much ado about nothing’?
Franz Messerli, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Bern (Switzerland), added: “Given this state of the art, I am inclined to consider RAS blockade and COVID-19 – despite all the hype in the news media – as much ado about nothing.”
But both Dr. McMurray and Dr. Messerli said they were intrigued about possible differences in the effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs that some of the new results suggest.
In one study, a team led by Mandeep Mehra, MD, of Brigham and Women’s Hospital Heart and Vascular Center, Boston, analyzed data from 8,910 patients with COVID-19 admitted to 169 hospitals in Asia, Europe, and North America who had either died in the hospital (5.8%) or survived to hospital discharge (94.2%).
In multivariate logistic-regression analysis, age greater than 65 years, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, history of cardiac arrhythmia, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, and current smoking were associated with an increased risk for in-hospital death. Female sex was associated with a decreased risk. Neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs were associated with an increased risk for in-hospital death.
In fact, ACE inhibitors were associated with a significant reduction in mortality (odds ratio, 0.33), as were statins (OR, 0.35).
The authors, however, stressed that these observations about reduced mortality with ACE inhibitors and statins “should be considered with extreme caution.”
“Because our study was not a randomized, controlled trial, we cannot exclude the possibility of confounding. In addition, we examined relationships between many variables and in-hospital death, and no primary hypothesis was prespecified; these factors increased the probability of chance associations being found. Therefore, a cause-and-effect relationship between drug therapy and survival should not be inferred,” they wrote.
A secondary analysis that was restricted to patients with hypertension (those for whom an ACE inhibitor or an ARB would be indicated) also did not show harm.
A second study published in the New England Journal of Medicine had a case-control design. The authors, led by Giuseppe Mancia, MD, of the University of Milano-Bicocca (Italy), compared 6,272 patients with confirmed COVID-19 (case patients) with 30,759 control persons who were matched according to age, sex, and municipality of residence.
In a conditional logistic-regression multivariate analysis, neither ACE inhibitors nor ARBs were associated with the likelihood of SARS-CoV-2 infection.
“Thus, our results do not provide evidence of an independent relationship between renin angiotensin aldosterone blockers and the susceptibility to COVID-19 in humans,” the authors concluded.
In addition, a second analysis that compared patients who had severe or fatal infections with matched control persons did not show an association between ACE inhibitors or ARBs and severe disease.
In the third study published in the New England Journal of Medicine, a group led by Harmony R. Reynolds, MD, of New York University, analyzed data from the health records of 12,594 patients in the NYU Langone Health system who had been tested for COVID-19. They found 5,894 patients whose test results were positive. Of these patients, 1,002 had severe illness, which was defined as illness requiring admission to the ICU, need for mechanical ventilation, or death.
Using Bayesian analysis and propensity score matching, the researchers assessed the relation between previous treatment with five different classes of antihypertensive drugs (ACE inhibitors, ARBs, beta blockers, calcium blockers, and thiazide diuretics) and the likelihood of a positive or negative result on COVID-19 testing, as well as the likelihood of severe illness among patients who tested positive.
Results showed no positive association between any of the analyzed drug classes and either a positive test result or severe illness.
In an accompanying editorial, a group led by John A. Jarcho, MD, of Harvard Medical School, Boston, and deputy editor of the New England Journal of Medicine, wrote: “Taken together, these three studies do not provide evidence to support the hypothesis that ACE inhibitor or ARB use is associated with the risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, the risk of severe COVID-19 among those infected, or the risk of in-hospital death among those with a positive test.
“Each of these studies has weaknesses inherent in observational data, but we find it reassuring that three studies in different populations and with different designs arrive at the consistent message that the continued use of ACE inhibitors and ARBs is unlikely to be harmful in patients with COVID-19. Several other smaller studies from China and the United Kingdom have come to the same conclusion,” the authors of the editorial stated.
In the study published in JAMA Cardiology, a group led by Neil Mehta, MBBS, of the Cleveland Clinic, Ohio, analyzed data on 18,472 patients who had been tested for COVID-19 between March 8 and April 12 in the Cleveland Clinic Health System in Ohio and Florida. Of these patients, 9.4% tested positive.
After overlap propensity score weighting for both ACE inhibitors and ARBs to take into account relevant comorbidities, there was no difference in risk for testing positive among patients taking an ACE inhibitor or an ARB in comparison with those not taking such medication.
Are there different effects between ACE inhibitors and ARBs?
A secondary exploratory analysis showed a higher likelihood of hospital admission among patients who tested positive and who were taking either ACE inhibitors (OR, 1.84) or ARBs (OR, 1.61), and there was a higher likelihood of ICU admission among patients who tested positive and who were taking an ACE inhibitor (OR 1.77), but no such difference was observed among those taking ARBs.
Coauthor Ankur Kalra, MD, of the Cleveland Clinic, said in an interview that results of the exploratory analysis fit with the hypothesis that the two drugs classes may have different effects in patients with COVID-19.
“Angiotensin II promotes vasoconstriction, inflammation, and fibrosis in the lungs, and ARBs block the effects of angiotensin II more effectively than ACE inhibitors. In addition, ACE inhibitors (but not ARBs) increase levels of bradykinin, which may be one factor leading to acute respiratory distress syndrome,” he noted.
“However, these results should only be considered exploratory, as there is inherent bias in observational data,” Dr. Kalra stressed.
In an accompanying editorial in JAMA Cardiology, a group led by Laine E. Thomas, PhD, of Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, North Carolina, said that the results of this secondary exploratory analysis are limited by a small number of patients and “are likely explained by confounding and should not be inferred as causal.”
The New England Journal of Medicine editorialists reached a similar conclusion regarding the lower mortality in COVID-19 patients who took ACE inhibitors in the study by Dr. Mehra and colleagues. They say this unexpected result “may be due to unmeasured confounding and, in the absence of a randomized trial, should not be regarded as evidence to prescribe these drugs in patients with COVID-19.”
Providing further comment, Dr. McMurray said: “Normally, I would not read too much into the different effects of ACE inhibitors and ARBs suggested in the Cleveland study because of the small numbers (about 28 ACE inhibitor–treated patients admitted to ICU) and the limited information about matching and/or adjustment for potential differences between groups.
“I could also argue that the comparison that would best answer the question about risk related to type of RAS blocker would be the direct comparison of people taking an ACE inhibitor with those taking an ARB (and that doesn’t look very different). The only thing that makes me a little cautious about completely dismissing the possibility of a difference between ACE inhibitor and ARB here is the suggestion of a similar trend in another large study from the VA [Veterans Affairs] system,” he added.
He also noted that speculation about there being mechanisms that involve different effects of the two drug classes on bradykinin and angiotensin II was “plausible but unproven.”
Dr. Messerli added: “Before turning the page, I would like to see an analysis comparing ACE inhibitors and ARBs, since experimentally, their effect on ACE2 (the receptor to which the virus binds) seems to differ. The study of Mehta et al in JAMA Cardiology may be the first clinical hint indicating that ARBs are more protective than ACEIs. However even here, the looming possibility of confounding cannot be excluded.”
Dr. Messerli also pointed to a hypothesis that suggests that direct viral infection of endothelial cells expressing ACE2 receptors may explain worse outcomes in patients with cardiovascular comorbidities, which provides a rationale for therapies to stabilize the endothelium, particularly with anti-inflammatory anticytokine drugs, ACE inhibitors, and statins.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
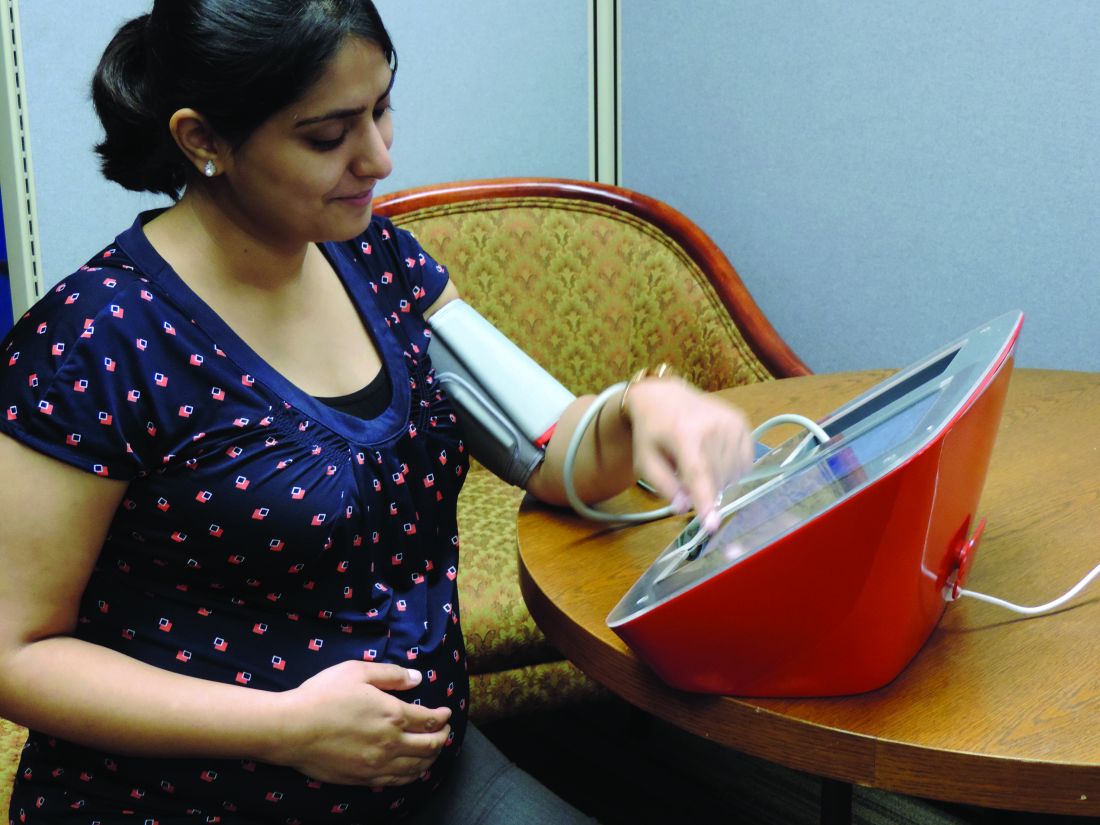
AHA emphasizes the need for cardio-obstetrics teams
according to a statement from the American Heart Association.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, and accounted for approximately 17 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2015, wrote Laxmi S. Mehta, MD, of The Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues.
Ideally, a woman with CVD at the time of pregnancy should be managed by a multidisciplinary cardio-obstetrics team that can assess cardiovascular risk, obstetric risk, and fetal risk throughout pregnancy, delivery, and up to a year post partum. The team should develop a shared strategy to promote best outcomes, according to the statement. The cardio-obstetrics team may include obstetricians, cardiologists, anesthesiologists, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, geneticists, neurologists, nurses, and pharmacists, according to the statement.
Women with preexisting CVD should receive counseling about maternal and fetal risks before conception, if possible, to involve the women in shared decision-making and to develop strategies for each stage of pregnancy and delivery, Dr. Mehta and associates said. Such counseling should include a review of all medications and assessment of risk factors.
However, some women present already in the early stages of pregnancy even with severe conditions such as pulmonary arterial hypertension, severe ventricular dysfunction, severe left-sided heart obstruction, and significant aortic dilatation with underlying connective tissue disease. Women with these conditions often are counseled to avoid pregnancy, but if they already are pregnant, a high-risk cardio-obstetrics team will need to work together to discover the best strategies going forward to mitigate risk, Dr. Mehta and associates said.
Common CVD conditions that affect pregnancy include hypertensive disorders, notably preeclampsia, defined as systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg in women after 20 weeks of gestation whose blood pressure was normal prior to pregnancy. A management strategy to reduce the risk of pregnancy-related complications from hypertension includes healthy lifestyle behaviors such as exercise, nutrition, and smoking cessation, according to the statement. However, patients with severe hypertension may require intravenous labetalol or hydralazine. The statement gives more information about handling preeclampsia with pulmonary edema, and prevention of eclampsia and treatment of seizures.
It is important to recognize that severe hypertension or superimposed preeclampsia may occur for the first time post partum. Early ambulatory visits in the first 1-2 weeks are sensible. Medications may be needed to keep a systolic blood pressure not higher than 150 mm Hg and a diastolic blood pressure not higher than 100 mm Hg, Dr. Mehta and associates said.
According to the statement, severe hypertriglyceridemia and familial hypercholesterolemia are the two most common conditions in which lipids should be addressed during pregnancy, with consideration of the fetal risks associated with certain medications.
“Statins are contraindicated during pregnancy, and all women who are on any lipid-lowering agents should review with their physician the safety of treatment during pregnancy and whether to discontinue treatment before pregnancy,” according to the statement. A heart-healthy lifestyle can help improve lipid profiles in all pregnant patients, Dr. Mehta and associates said. Patients with extremely high triglycerides above 500 mg/dL are at risk of pancreatitis and “may benefit from pharmacological agents (omega-3 fatty acids with or without fenofibrate or gemfibrozil) during the second trimester,” they noted. Pregnant women with familial hypercholesterolemia might take bile acid sequestrants, or as a last resort, low-density lipoprotein apheresis.
Other conditions calling for a multidisciplinary cardio-obstetric approach include preexisting coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, valvular heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and deep venous thrombosis, according to the statement, which provides information about the risks, diagnosis, and management.
When it is time for delivery, spontaneous labor and vaginal birth are preferable for most women with heart disease, as cesarean delivery is associated with increased risk of infection, thrombotic complications, and blood loss, according to the statement.
Women with CVD and associated complications will require “specialized long-term cardiovascular follow-up,” Dr. Mehta and associates said. “In women with a high-risk pregnancy, a cardio-obstetrics team is essential to prevent maternal morbidity and mortality during the length of the pregnancy and post partum.”
“The release of this document demonstrates the AHA’s recognition of the importance of CVD in pregnancy-related death and their commitment to education and ensuring best practices in this field,” said Lisa M. Hollier, MD, past president of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and chief medical officer at Texas Children’s Health Plan, Bellaire.
“I think one of the most important outcomes from the release of this scientific statement from AHA will be increased implementation of cardio-obstetrics teams,” she said in an interview.
“In the United States, cardiovascular disease and cardiomyopathy together are now the leading cause of death in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and constitute 26.5% of pregnancy-related deaths, with higher rates of mortality among women of color and women with lower incomes,” she said. “The rising trend in cardiovascular-related maternal deaths appears to be due to acquired, not congenital, heart disease.”
During her tenure as president of ACOG, Dr. Hollier convened a task force on cardiovascular disease in pregnancy that developed guidance that outlines screening, diagnosis, and management of CVD for women from prepregnancy through post partum.
Dr. Hollier noted that COVID-19 emphasizes racial disparities for maternal mortality.
“Pregnant patients with comorbidities, like heart conditions, may be at increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19 – consistent with the general population with similar comorbidities,” she said. “And as we know, black women’s risk of dying from CVD-related pregnancy complications is 3.4 times higher than that of white women. During the COVID-19 pandemic, we are seeing these racial health disparities exacerbated.”
However, any pregnant patients should not hesitate to communicate with their health care providers despite the pandemic situation, Dr. Hollier emphasized. “Communication between a patient and her ob.gyn., cardiologist, or other clinician is even more critical now during the COVID-19 pandemic. We’re hearing reports that patients who are experiencing symptoms or those with known cardiac conditions are avoiding the hospital and delaying or not seeking necessary treatment. This has the very real possibility of worsening the devastating maternal mortality crisis that we’re already experiencing in this country.”
To help overcome barriers to treatment, “collaboration between ob.gyns. and cardiologists, such as the cardio-obstetrics team or pregnancy heart team, is critical,” said Dr. Hollier. “These collaborative teams with a multidisciplinary approach can prospectively reduce the communication gaps across specialties when patients are seen separately. They can also improve the communication during care transitions such as between outpatient and inpatient care.
“In reviews of maternal deaths, we have found that there are often delays in diagnosis of heart conditions during and after pregnancy,” Dr. Hollier added. “Most maternal deaths from CVD are due to either undiagnosed cardiovascular disease or new-onset cardiomyopathy. ACOG recommends that all women be assessed for cardiovascular disease in the antepartum and postpartum periods using a recently developed algorithm,” she said. “Women who have known CVD and women who have concerning symptoms should have a consultation with this team. With increased awareness and screening, women can receive the additional care that they need.
“Because management of cardiac conditions in pregnancy is so complex, it is important to ensure that women receive care with teams and in facilities that have appropriate resources,” explained Dr. Hollier. “Women with known heart disease should see a cardiologist prior to pregnancy and receive prepregnancy counseling,” as noted in the AHA statement. “Patients determined to have moderate and high-risk CVD should be managed during pregnancy, delivery, and post partum in a medical center that is able to provide a higher level of care, including a cardio-obstetrics team.”
Early recognition of cardiovascular conditions is essential to help manage care and reduce risks to mother and baby, said Dr. Hollier. “Identification before a woman becomes pregnant means the patient’s care can be properly managed throughout the pregnancy and a detailed delivery plan can be developed through shared decision making between the patient and provider. We must think of heart disease as a possibility in every pregnant or postpartum patient we see to detect and treat at-risk mothers,” she said.
Additional research should focus on identifying risk factors prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Hollier. “There are often delays in recognizing symptoms during pregnancy and post partum, particularly for black women. We need data to understand which protocols are best to identify heart disease,”
Dr. Hollier had no financial conflicts to disclose. The authors of the AHA statement had no financial conflicts to disclose. The scientific statement was produced on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; and the Stroke Council.
SOURCE: Mehta LS et al. Circulation. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000772.
according to a statement from the American Heart Association.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, and accounted for approximately 17 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2015, wrote Laxmi S. Mehta, MD, of The Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues.
Ideally, a woman with CVD at the time of pregnancy should be managed by a multidisciplinary cardio-obstetrics team that can assess cardiovascular risk, obstetric risk, and fetal risk throughout pregnancy, delivery, and up to a year post partum. The team should develop a shared strategy to promote best outcomes, according to the statement. The cardio-obstetrics team may include obstetricians, cardiologists, anesthesiologists, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, geneticists, neurologists, nurses, and pharmacists, according to the statement.
Women with preexisting CVD should receive counseling about maternal and fetal risks before conception, if possible, to involve the women in shared decision-making and to develop strategies for each stage of pregnancy and delivery, Dr. Mehta and associates said. Such counseling should include a review of all medications and assessment of risk factors.
However, some women present already in the early stages of pregnancy even with severe conditions such as pulmonary arterial hypertension, severe ventricular dysfunction, severe left-sided heart obstruction, and significant aortic dilatation with underlying connective tissue disease. Women with these conditions often are counseled to avoid pregnancy, but if they already are pregnant, a high-risk cardio-obstetrics team will need to work together to discover the best strategies going forward to mitigate risk, Dr. Mehta and associates said.
Common CVD conditions that affect pregnancy include hypertensive disorders, notably preeclampsia, defined as systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg in women after 20 weeks of gestation whose blood pressure was normal prior to pregnancy. A management strategy to reduce the risk of pregnancy-related complications from hypertension includes healthy lifestyle behaviors such as exercise, nutrition, and smoking cessation, according to the statement. However, patients with severe hypertension may require intravenous labetalol or hydralazine. The statement gives more information about handling preeclampsia with pulmonary edema, and prevention of eclampsia and treatment of seizures.
It is important to recognize that severe hypertension or superimposed preeclampsia may occur for the first time post partum. Early ambulatory visits in the first 1-2 weeks are sensible. Medications may be needed to keep a systolic blood pressure not higher than 150 mm Hg and a diastolic blood pressure not higher than 100 mm Hg, Dr. Mehta and associates said.
According to the statement, severe hypertriglyceridemia and familial hypercholesterolemia are the two most common conditions in which lipids should be addressed during pregnancy, with consideration of the fetal risks associated with certain medications.
“Statins are contraindicated during pregnancy, and all women who are on any lipid-lowering agents should review with their physician the safety of treatment during pregnancy and whether to discontinue treatment before pregnancy,” according to the statement. A heart-healthy lifestyle can help improve lipid profiles in all pregnant patients, Dr. Mehta and associates said. Patients with extremely high triglycerides above 500 mg/dL are at risk of pancreatitis and “may benefit from pharmacological agents (omega-3 fatty acids with or without fenofibrate or gemfibrozil) during the second trimester,” they noted. Pregnant women with familial hypercholesterolemia might take bile acid sequestrants, or as a last resort, low-density lipoprotein apheresis.
Other conditions calling for a multidisciplinary cardio-obstetric approach include preexisting coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, valvular heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and deep venous thrombosis, according to the statement, which provides information about the risks, diagnosis, and management.
When it is time for delivery, spontaneous labor and vaginal birth are preferable for most women with heart disease, as cesarean delivery is associated with increased risk of infection, thrombotic complications, and blood loss, according to the statement.
Women with CVD and associated complications will require “specialized long-term cardiovascular follow-up,” Dr. Mehta and associates said. “In women with a high-risk pregnancy, a cardio-obstetrics team is essential to prevent maternal morbidity and mortality during the length of the pregnancy and post partum.”
“The release of this document demonstrates the AHA’s recognition of the importance of CVD in pregnancy-related death and their commitment to education and ensuring best practices in this field,” said Lisa M. Hollier, MD, past president of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and chief medical officer at Texas Children’s Health Plan, Bellaire.
“I think one of the most important outcomes from the release of this scientific statement from AHA will be increased implementation of cardio-obstetrics teams,” she said in an interview.
“In the United States, cardiovascular disease and cardiomyopathy together are now the leading cause of death in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and constitute 26.5% of pregnancy-related deaths, with higher rates of mortality among women of color and women with lower incomes,” she said. “The rising trend in cardiovascular-related maternal deaths appears to be due to acquired, not congenital, heart disease.”
During her tenure as president of ACOG, Dr. Hollier convened a task force on cardiovascular disease in pregnancy that developed guidance that outlines screening, diagnosis, and management of CVD for women from prepregnancy through post partum.
Dr. Hollier noted that COVID-19 emphasizes racial disparities for maternal mortality.
“Pregnant patients with comorbidities, like heart conditions, may be at increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19 – consistent with the general population with similar comorbidities,” she said. “And as we know, black women’s risk of dying from CVD-related pregnancy complications is 3.4 times higher than that of white women. During the COVID-19 pandemic, we are seeing these racial health disparities exacerbated.”
However, any pregnant patients should not hesitate to communicate with their health care providers despite the pandemic situation, Dr. Hollier emphasized. “Communication between a patient and her ob.gyn., cardiologist, or other clinician is even more critical now during the COVID-19 pandemic. We’re hearing reports that patients who are experiencing symptoms or those with known cardiac conditions are avoiding the hospital and delaying or not seeking necessary treatment. This has the very real possibility of worsening the devastating maternal mortality crisis that we’re already experiencing in this country.”
To help overcome barriers to treatment, “collaboration between ob.gyns. and cardiologists, such as the cardio-obstetrics team or pregnancy heart team, is critical,” said Dr. Hollier. “These collaborative teams with a multidisciplinary approach can prospectively reduce the communication gaps across specialties when patients are seen separately. They can also improve the communication during care transitions such as between outpatient and inpatient care.
“In reviews of maternal deaths, we have found that there are often delays in diagnosis of heart conditions during and after pregnancy,” Dr. Hollier added. “Most maternal deaths from CVD are due to either undiagnosed cardiovascular disease or new-onset cardiomyopathy. ACOG recommends that all women be assessed for cardiovascular disease in the antepartum and postpartum periods using a recently developed algorithm,” she said. “Women who have known CVD and women who have concerning symptoms should have a consultation with this team. With increased awareness and screening, women can receive the additional care that they need.
“Because management of cardiac conditions in pregnancy is so complex, it is important to ensure that women receive care with teams and in facilities that have appropriate resources,” explained Dr. Hollier. “Women with known heart disease should see a cardiologist prior to pregnancy and receive prepregnancy counseling,” as noted in the AHA statement. “Patients determined to have moderate and high-risk CVD should be managed during pregnancy, delivery, and post partum in a medical center that is able to provide a higher level of care, including a cardio-obstetrics team.”
Early recognition of cardiovascular conditions is essential to help manage care and reduce risks to mother and baby, said Dr. Hollier. “Identification before a woman becomes pregnant means the patient’s care can be properly managed throughout the pregnancy and a detailed delivery plan can be developed through shared decision making between the patient and provider. We must think of heart disease as a possibility in every pregnant or postpartum patient we see to detect and treat at-risk mothers,” she said.
Additional research should focus on identifying risk factors prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Hollier. “There are often delays in recognizing symptoms during pregnancy and post partum, particularly for black women. We need data to understand which protocols are best to identify heart disease,”
Dr. Hollier had no financial conflicts to disclose. The authors of the AHA statement had no financial conflicts to disclose. The scientific statement was produced on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; and the Stroke Council.
SOURCE: Mehta LS et al. Circulation. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000772.
according to a statement from the American Heart Association.
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) remains the leading cause of pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, and accounted for approximately 17 deaths per 100,000 live births in 2015, wrote Laxmi S. Mehta, MD, of The Ohio State University, Columbus, and colleagues.
Ideally, a woman with CVD at the time of pregnancy should be managed by a multidisciplinary cardio-obstetrics team that can assess cardiovascular risk, obstetric risk, and fetal risk throughout pregnancy, delivery, and up to a year post partum. The team should develop a shared strategy to promote best outcomes, according to the statement. The cardio-obstetrics team may include obstetricians, cardiologists, anesthesiologists, maternal-fetal medicine specialists, geneticists, neurologists, nurses, and pharmacists, according to the statement.
Women with preexisting CVD should receive counseling about maternal and fetal risks before conception, if possible, to involve the women in shared decision-making and to develop strategies for each stage of pregnancy and delivery, Dr. Mehta and associates said. Such counseling should include a review of all medications and assessment of risk factors.
However, some women present already in the early stages of pregnancy even with severe conditions such as pulmonary arterial hypertension, severe ventricular dysfunction, severe left-sided heart obstruction, and significant aortic dilatation with underlying connective tissue disease. Women with these conditions often are counseled to avoid pregnancy, but if they already are pregnant, a high-risk cardio-obstetrics team will need to work together to discover the best strategies going forward to mitigate risk, Dr. Mehta and associates said.
Common CVD conditions that affect pregnancy include hypertensive disorders, notably preeclampsia, defined as systolic blood pressure greater than 140 mm Hg or diastolic blood pressure greater than 90 mm Hg in women after 20 weeks of gestation whose blood pressure was normal prior to pregnancy. A management strategy to reduce the risk of pregnancy-related complications from hypertension includes healthy lifestyle behaviors such as exercise, nutrition, and smoking cessation, according to the statement. However, patients with severe hypertension may require intravenous labetalol or hydralazine. The statement gives more information about handling preeclampsia with pulmonary edema, and prevention of eclampsia and treatment of seizures.
It is important to recognize that severe hypertension or superimposed preeclampsia may occur for the first time post partum. Early ambulatory visits in the first 1-2 weeks are sensible. Medications may be needed to keep a systolic blood pressure not higher than 150 mm Hg and a diastolic blood pressure not higher than 100 mm Hg, Dr. Mehta and associates said.
According to the statement, severe hypertriglyceridemia and familial hypercholesterolemia are the two most common conditions in which lipids should be addressed during pregnancy, with consideration of the fetal risks associated with certain medications.
“Statins are contraindicated during pregnancy, and all women who are on any lipid-lowering agents should review with their physician the safety of treatment during pregnancy and whether to discontinue treatment before pregnancy,” according to the statement. A heart-healthy lifestyle can help improve lipid profiles in all pregnant patients, Dr. Mehta and associates said. Patients with extremely high triglycerides above 500 mg/dL are at risk of pancreatitis and “may benefit from pharmacological agents (omega-3 fatty acids with or without fenofibrate or gemfibrozil) during the second trimester,” they noted. Pregnant women with familial hypercholesterolemia might take bile acid sequestrants, or as a last resort, low-density lipoprotein apheresis.
Other conditions calling for a multidisciplinary cardio-obstetric approach include preexisting coronary artery disease, cardiomyopathies, arrhythmias, valvular heart disease, cerebrovascular disease, and deep venous thrombosis, according to the statement, which provides information about the risks, diagnosis, and management.
When it is time for delivery, spontaneous labor and vaginal birth are preferable for most women with heart disease, as cesarean delivery is associated with increased risk of infection, thrombotic complications, and blood loss, according to the statement.
Women with CVD and associated complications will require “specialized long-term cardiovascular follow-up,” Dr. Mehta and associates said. “In women with a high-risk pregnancy, a cardio-obstetrics team is essential to prevent maternal morbidity and mortality during the length of the pregnancy and post partum.”
“The release of this document demonstrates the AHA’s recognition of the importance of CVD in pregnancy-related death and their commitment to education and ensuring best practices in this field,” said Lisa M. Hollier, MD, past president of the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and chief medical officer at Texas Children’s Health Plan, Bellaire.
“I think one of the most important outcomes from the release of this scientific statement from AHA will be increased implementation of cardio-obstetrics teams,” she said in an interview.
“In the United States, cardiovascular disease and cardiomyopathy together are now the leading cause of death in pregnancy and the postpartum period, and constitute 26.5% of pregnancy-related deaths, with higher rates of mortality among women of color and women with lower incomes,” she said. “The rising trend in cardiovascular-related maternal deaths appears to be due to acquired, not congenital, heart disease.”
During her tenure as president of ACOG, Dr. Hollier convened a task force on cardiovascular disease in pregnancy that developed guidance that outlines screening, diagnosis, and management of CVD for women from prepregnancy through post partum.
Dr. Hollier noted that COVID-19 emphasizes racial disparities for maternal mortality.
“Pregnant patients with comorbidities, like heart conditions, may be at increased risk for severe illness from COVID-19 – consistent with the general population with similar comorbidities,” she said. “And as we know, black women’s risk of dying from CVD-related pregnancy complications is 3.4 times higher than that of white women. During the COVID-19 pandemic, we are seeing these racial health disparities exacerbated.”
However, any pregnant patients should not hesitate to communicate with their health care providers despite the pandemic situation, Dr. Hollier emphasized. “Communication between a patient and her ob.gyn., cardiologist, or other clinician is even more critical now during the COVID-19 pandemic. We’re hearing reports that patients who are experiencing symptoms or those with known cardiac conditions are avoiding the hospital and delaying or not seeking necessary treatment. This has the very real possibility of worsening the devastating maternal mortality crisis that we’re already experiencing in this country.”
To help overcome barriers to treatment, “collaboration between ob.gyns. and cardiologists, such as the cardio-obstetrics team or pregnancy heart team, is critical,” said Dr. Hollier. “These collaborative teams with a multidisciplinary approach can prospectively reduce the communication gaps across specialties when patients are seen separately. They can also improve the communication during care transitions such as between outpatient and inpatient care.
“In reviews of maternal deaths, we have found that there are often delays in diagnosis of heart conditions during and after pregnancy,” Dr. Hollier added. “Most maternal deaths from CVD are due to either undiagnosed cardiovascular disease or new-onset cardiomyopathy. ACOG recommends that all women be assessed for cardiovascular disease in the antepartum and postpartum periods using a recently developed algorithm,” she said. “Women who have known CVD and women who have concerning symptoms should have a consultation with this team. With increased awareness and screening, women can receive the additional care that they need.
“Because management of cardiac conditions in pregnancy is so complex, it is important to ensure that women receive care with teams and in facilities that have appropriate resources,” explained Dr. Hollier. “Women with known heart disease should see a cardiologist prior to pregnancy and receive prepregnancy counseling,” as noted in the AHA statement. “Patients determined to have moderate and high-risk CVD should be managed during pregnancy, delivery, and post partum in a medical center that is able to provide a higher level of care, including a cardio-obstetrics team.”
Early recognition of cardiovascular conditions is essential to help manage care and reduce risks to mother and baby, said Dr. Hollier. “Identification before a woman becomes pregnant means the patient’s care can be properly managed throughout the pregnancy and a detailed delivery plan can be developed through shared decision making between the patient and provider. We must think of heart disease as a possibility in every pregnant or postpartum patient we see to detect and treat at-risk mothers,” she said.
Additional research should focus on identifying risk factors prior to pregnancy, said Dr. Hollier. “There are often delays in recognizing symptoms during pregnancy and post partum, particularly for black women. We need data to understand which protocols are best to identify heart disease,”
Dr. Hollier had no financial conflicts to disclose. The authors of the AHA statement had no financial conflicts to disclose. The scientific statement was produced on behalf of the American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology; Council on Atherosclerosis, Thrombosis and Vascular Biology; Council on Cardiovascular and Stroke Nursing; and the Stroke Council.
SOURCE: Mehta LS et al. Circulation. 2020 May 4. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000772.
FROM CIRCULATION
Multisociety roadmap eyes restarting elective cardiac cases
As COVID-19 case levels plateau in some regions, 16 North American cardiovascular societies have released a framework for reintroducing cardiovascular services disrupted by the pandemic.
The consensus document outlines a phased approach to restarting invasive cardiovascular (CV) procedures and diagnostic tests that aims to reduce patient and health care provider exposure to the coronavirus and still provide essential care. It also emphasizes some of the ethical considerations in patient selection and the need for a collaborative approach.
“The key message in our document is we need a new unprecedented collaboration with public health officials so that we can carefully monitor the situation and we’re aware of what’s happening with the penetrance of the pandemic in the community, but they’re aware of the morbidity and mortality that’s occurring on our ever-growing waiting list,” lead author David A. Wood, MD, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
The recommendations were jointly published May 4 in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology , the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, and The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, and are endorsed by, among others, the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology (ACC), and Canadian Cardiovascular Society.
The guidance comes as hospitals are facing revenue shortfalls because of canceled elective procedures and resource-intensive COVID-19 cases, prompting some healthcare systems to furlough, lay off, or even fire staff.
“It’s obvious that volumes are down between 40% and 60%,” said Wood, director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at Vancouver General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of British Columbia, Canada. “Part of that is that some areas have restricted case volumes totally appropriately and it’s partly because patients are very afraid of coming to the hospital and, unfortunately, are having bad events at home. And some are dying.”
The new report features a detailed table outlining three different response levels: reintroduction of some services (level 2); reintroduction of most services (level 1); and regular services (level 0). It covers a range of services from transthoracic echocardiography and exercise testing with imaging to care for acute coronary syndrome and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
“We’ve learned that we can very quickly turn off the tap and go to doing only 10% of our normal volumes, whether that’s surgery, cath lab, EP, diagnostic tests,” Wood said. “It’s much more difficult to thoughtfully turn the tap part way back on or restart the engine … you don’t just go from 0 to 100 [mph]. You go from 0 to 30 to 60 then maybe to 80 [mph].”
The document also includes eight guiding principles such as:
- The expectation that response levels will be different between regions, and even within a given region.
- A “transparent collaborative plan” for COVID-19 testing and personal protective equipment (PPE) must be in place before restarting cases.
- A less invasive test or alternate imaging modality should be considered, if both tests have similar efficacy.
- In general, a minimally invasive procedure with a shorter length of stay is preferable, if both strategies have similar efficacy and safety.
Although previous reports on cath lab considerations during the pandemic or restarting elective surgeries peg various actions to specific thresholds or time intervals, the language here is noticeably and intentionally broad.
Instead of stating when cardiovascular services should resume, for example, the experts say it’s appropriate to put the guidance document into place if there’s a “sustained reduction” in the rate of new COVID-19 admissions and deaths in the relevant geographic region for a “prespecified time interval.”
As for when or how frequently patients and healthcare providers should be tested for COVID-19, the document encourages “routine screening of all patients prior to any cardiovascular procedure or test.”
Overly prescriptive language in previous documents wasn’t felt to be that helpful, whereas language like “selective” cases and “some” or “most” cardiovascular procedures gives clinicians, health systems, and policy makers flexibility when moving between response levels, Wood explained.
“Different regions might be at different levels based on principles of public health as far as the penetrance of the pandemic in that community, as well as how can you actually do the physical distancing in your hospital or ambulatory clinic. Because, I tell you, that is the Achilles heel,” he said. “Our run rates are going to be determined by testing, the availability of PPE, but also how we’re going to use our existing infrastructure and maintain physical distancing.”
That may mean using telehealth for initial visits, having clinics open earlier in the morning or on weekends, or doing partial volumes for surgery or in the cath lab so patients can be staggered and recover at different times and in different areas of the hospital. “These are very granular, specific infrastructure things that we’ve never really had to consider before,” Wood observed.
The document also had to be flexible and nimble enough to respond to a potential rebound of COVID-19 cases, which in newly released models are projected to rise sharply to 200,000 cases a day and be accompanied by some 3,000 deaths each day by June 1.
“This is my own personal opinion but I think it’s foolish to think that we are going to be able to come back to 100% of the cases we were doing before, even with testing, PPE, and all of that until we have a vaccine,” he said.
Similar to decisions made in preparation for the initial COVID-19 surge, the consensus document outlines the need for ethical considerations when turning the tap back on. This means prioritizing procedures and tests that are likely to benefit more people and to a greater degree, and ensuring that patients are treated fairly and consistently, regardless of their ethnicity, perceived social worth, or ability to pay, said coauthor and ACC President Athena Poppas, MD, Brown University School of Medicine, Providence, Rhode Island.
“It’s an ethical tenet that exists in a lot of places but it’s usually not overtly called out,” Poppas told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “It’s not rationing care; I think people jump to that but it’s actually the opposite of rationing care. It’s about being thoughtful about prioritizing patients.”
“There’s a variety of data that should help in the prioritization, not only how much hospital resources are utilized, that’s on one side, but there’s also the patient risk of delaying or doing a procedure, and then the societal risk,” she said.
Susheel Kodali, MD, of New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, who recently published recommendations on restructuring structural heart disease practice during the pandemic, said the document is timely as centers, including his own, are trying to restart some outpatient visits, as early as next week.
“They made a point about talking about cohesive partnerships with regional public health officials and I think that’s great. The question is how does that happen,” he told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “In New York, we’re not allowed to do elective cases but what’s considered elective is not so clearly defined. An AS [aortic stenosis] patient that had a syncopal episode 2 weeks ago, is that considered elective or is that semi-urgent? I think that’s one of the challenges and that’s where these partnerships would be useful.”
Other challenges include the need for regional partnerships to better align hospitals, which in the New York area means half a dozen large healthcare systems, and to coordinate care between hospital departments – all of which will be scheduling imaging and OR time for their own backlog of hernia, knee, or hip surgeries.
Finally, there’s the need for a lot of conversation with the patient and their family about returning to a hospital amid a deadly pandemic.
“I had a patient today and the daughter was very concerned about bringing her in,” Kodali said. “She’s in class IV heart failure but her [daughter’s] big concern was: who is she going to be exposed to when she gets the echo? What kind of protection is there for her? Is the tech wearing a mask?
“It’s not just the health care providers that have to have the comfort, but it’s the patients and their families who have to feel comfortable bringing their loved ones here for treatment,” he said. “Because everyone is concerned about the environment.”
Wood reports receiving unrestricted grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Abbott Vascular and serving as a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, and Boston Scientific. Poppas reports no relevant conflicts of interest. Kodali reports consultant (honoraria) from Admedus, Meril Life Sciences, JenaValve, and Abbott Vascular; SAB (equity) from Dura Biotech, MicroInterventional Devices, Thubrikar Aortic Valve, Supira, and Admedus; and institutional funding from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 case levels plateau in some regions, 16 North American cardiovascular societies have released a framework for reintroducing cardiovascular services disrupted by the pandemic.
The consensus document outlines a phased approach to restarting invasive cardiovascular (CV) procedures and diagnostic tests that aims to reduce patient and health care provider exposure to the coronavirus and still provide essential care. It also emphasizes some of the ethical considerations in patient selection and the need for a collaborative approach.
“The key message in our document is we need a new unprecedented collaboration with public health officials so that we can carefully monitor the situation and we’re aware of what’s happening with the penetrance of the pandemic in the community, but they’re aware of the morbidity and mortality that’s occurring on our ever-growing waiting list,” lead author David A. Wood, MD, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
The recommendations were jointly published May 4 in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology , the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, and The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, and are endorsed by, among others, the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology (ACC), and Canadian Cardiovascular Society.
The guidance comes as hospitals are facing revenue shortfalls because of canceled elective procedures and resource-intensive COVID-19 cases, prompting some healthcare systems to furlough, lay off, or even fire staff.
“It’s obvious that volumes are down between 40% and 60%,” said Wood, director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at Vancouver General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of British Columbia, Canada. “Part of that is that some areas have restricted case volumes totally appropriately and it’s partly because patients are very afraid of coming to the hospital and, unfortunately, are having bad events at home. And some are dying.”
The new report features a detailed table outlining three different response levels: reintroduction of some services (level 2); reintroduction of most services (level 1); and regular services (level 0). It covers a range of services from transthoracic echocardiography and exercise testing with imaging to care for acute coronary syndrome and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
“We’ve learned that we can very quickly turn off the tap and go to doing only 10% of our normal volumes, whether that’s surgery, cath lab, EP, diagnostic tests,” Wood said. “It’s much more difficult to thoughtfully turn the tap part way back on or restart the engine … you don’t just go from 0 to 100 [mph]. You go from 0 to 30 to 60 then maybe to 80 [mph].”
The document also includes eight guiding principles such as:
- The expectation that response levels will be different between regions, and even within a given region.
- A “transparent collaborative plan” for COVID-19 testing and personal protective equipment (PPE) must be in place before restarting cases.
- A less invasive test or alternate imaging modality should be considered, if both tests have similar efficacy.
- In general, a minimally invasive procedure with a shorter length of stay is preferable, if both strategies have similar efficacy and safety.
Although previous reports on cath lab considerations during the pandemic or restarting elective surgeries peg various actions to specific thresholds or time intervals, the language here is noticeably and intentionally broad.
Instead of stating when cardiovascular services should resume, for example, the experts say it’s appropriate to put the guidance document into place if there’s a “sustained reduction” in the rate of new COVID-19 admissions and deaths in the relevant geographic region for a “prespecified time interval.”
As for when or how frequently patients and healthcare providers should be tested for COVID-19, the document encourages “routine screening of all patients prior to any cardiovascular procedure or test.”
Overly prescriptive language in previous documents wasn’t felt to be that helpful, whereas language like “selective” cases and “some” or “most” cardiovascular procedures gives clinicians, health systems, and policy makers flexibility when moving between response levels, Wood explained.
“Different regions might be at different levels based on principles of public health as far as the penetrance of the pandemic in that community, as well as how can you actually do the physical distancing in your hospital or ambulatory clinic. Because, I tell you, that is the Achilles heel,” he said. “Our run rates are going to be determined by testing, the availability of PPE, but also how we’re going to use our existing infrastructure and maintain physical distancing.”
That may mean using telehealth for initial visits, having clinics open earlier in the morning or on weekends, or doing partial volumes for surgery or in the cath lab so patients can be staggered and recover at different times and in different areas of the hospital. “These are very granular, specific infrastructure things that we’ve never really had to consider before,” Wood observed.
The document also had to be flexible and nimble enough to respond to a potential rebound of COVID-19 cases, which in newly released models are projected to rise sharply to 200,000 cases a day and be accompanied by some 3,000 deaths each day by June 1.
“This is my own personal opinion but I think it’s foolish to think that we are going to be able to come back to 100% of the cases we were doing before, even with testing, PPE, and all of that until we have a vaccine,” he said.
Similar to decisions made in preparation for the initial COVID-19 surge, the consensus document outlines the need for ethical considerations when turning the tap back on. This means prioritizing procedures and tests that are likely to benefit more people and to a greater degree, and ensuring that patients are treated fairly and consistently, regardless of their ethnicity, perceived social worth, or ability to pay, said coauthor and ACC President Athena Poppas, MD, Brown University School of Medicine, Providence, Rhode Island.
“It’s an ethical tenet that exists in a lot of places but it’s usually not overtly called out,” Poppas told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “It’s not rationing care; I think people jump to that but it’s actually the opposite of rationing care. It’s about being thoughtful about prioritizing patients.”
“There’s a variety of data that should help in the prioritization, not only how much hospital resources are utilized, that’s on one side, but there’s also the patient risk of delaying or doing a procedure, and then the societal risk,” she said.
Susheel Kodali, MD, of New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, who recently published recommendations on restructuring structural heart disease practice during the pandemic, said the document is timely as centers, including his own, are trying to restart some outpatient visits, as early as next week.
“They made a point about talking about cohesive partnerships with regional public health officials and I think that’s great. The question is how does that happen,” he told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “In New York, we’re not allowed to do elective cases but what’s considered elective is not so clearly defined. An AS [aortic stenosis] patient that had a syncopal episode 2 weeks ago, is that considered elective or is that semi-urgent? I think that’s one of the challenges and that’s where these partnerships would be useful.”
Other challenges include the need for regional partnerships to better align hospitals, which in the New York area means half a dozen large healthcare systems, and to coordinate care between hospital departments – all of which will be scheduling imaging and OR time for their own backlog of hernia, knee, or hip surgeries.
Finally, there’s the need for a lot of conversation with the patient and their family about returning to a hospital amid a deadly pandemic.
“I had a patient today and the daughter was very concerned about bringing her in,” Kodali said. “She’s in class IV heart failure but her [daughter’s] big concern was: who is she going to be exposed to when she gets the echo? What kind of protection is there for her? Is the tech wearing a mask?
“It’s not just the health care providers that have to have the comfort, but it’s the patients and their families who have to feel comfortable bringing their loved ones here for treatment,” he said. “Because everyone is concerned about the environment.”
Wood reports receiving unrestricted grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Abbott Vascular and serving as a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, and Boston Scientific. Poppas reports no relevant conflicts of interest. Kodali reports consultant (honoraria) from Admedus, Meril Life Sciences, JenaValve, and Abbott Vascular; SAB (equity) from Dura Biotech, MicroInterventional Devices, Thubrikar Aortic Valve, Supira, and Admedus; and institutional funding from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 case levels plateau in some regions, 16 North American cardiovascular societies have released a framework for reintroducing cardiovascular services disrupted by the pandemic.
The consensus document outlines a phased approach to restarting invasive cardiovascular (CV) procedures and diagnostic tests that aims to reduce patient and health care provider exposure to the coronavirus and still provide essential care. It also emphasizes some of the ethical considerations in patient selection and the need for a collaborative approach.
“The key message in our document is we need a new unprecedented collaboration with public health officials so that we can carefully monitor the situation and we’re aware of what’s happening with the penetrance of the pandemic in the community, but they’re aware of the morbidity and mortality that’s occurring on our ever-growing waiting list,” lead author David A. Wood, MD, told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology.
The recommendations were jointly published May 4 in the Canadian Journal of Cardiology , the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, and The Annals of Thoracic Surgery, and are endorsed by, among others, the American Heart Association, American College of Cardiology (ACC), and Canadian Cardiovascular Society.
The guidance comes as hospitals are facing revenue shortfalls because of canceled elective procedures and resource-intensive COVID-19 cases, prompting some healthcare systems to furlough, lay off, or even fire staff.
“It’s obvious that volumes are down between 40% and 60%,” said Wood, director of the cardiac catheterization laboratory at Vancouver General Hospital and professor of medicine at the University of British Columbia, Canada. “Part of that is that some areas have restricted case volumes totally appropriately and it’s partly because patients are very afraid of coming to the hospital and, unfortunately, are having bad events at home. And some are dying.”
The new report features a detailed table outlining three different response levels: reintroduction of some services (level 2); reintroduction of most services (level 1); and regular services (level 0). It covers a range of services from transthoracic echocardiography and exercise testing with imaging to care for acute coronary syndrome and ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.
“We’ve learned that we can very quickly turn off the tap and go to doing only 10% of our normal volumes, whether that’s surgery, cath lab, EP, diagnostic tests,” Wood said. “It’s much more difficult to thoughtfully turn the tap part way back on or restart the engine … you don’t just go from 0 to 100 [mph]. You go from 0 to 30 to 60 then maybe to 80 [mph].”
The document also includes eight guiding principles such as:
- The expectation that response levels will be different between regions, and even within a given region.
- A “transparent collaborative plan” for COVID-19 testing and personal protective equipment (PPE) must be in place before restarting cases.
- A less invasive test or alternate imaging modality should be considered, if both tests have similar efficacy.
- In general, a minimally invasive procedure with a shorter length of stay is preferable, if both strategies have similar efficacy and safety.
Although previous reports on cath lab considerations during the pandemic or restarting elective surgeries peg various actions to specific thresholds or time intervals, the language here is noticeably and intentionally broad.
Instead of stating when cardiovascular services should resume, for example, the experts say it’s appropriate to put the guidance document into place if there’s a “sustained reduction” in the rate of new COVID-19 admissions and deaths in the relevant geographic region for a “prespecified time interval.”
As for when or how frequently patients and healthcare providers should be tested for COVID-19, the document encourages “routine screening of all patients prior to any cardiovascular procedure or test.”
Overly prescriptive language in previous documents wasn’t felt to be that helpful, whereas language like “selective” cases and “some” or “most” cardiovascular procedures gives clinicians, health systems, and policy makers flexibility when moving between response levels, Wood explained.
“Different regions might be at different levels based on principles of public health as far as the penetrance of the pandemic in that community, as well as how can you actually do the physical distancing in your hospital or ambulatory clinic. Because, I tell you, that is the Achilles heel,” he said. “Our run rates are going to be determined by testing, the availability of PPE, but also how we’re going to use our existing infrastructure and maintain physical distancing.”
That may mean using telehealth for initial visits, having clinics open earlier in the morning or on weekends, or doing partial volumes for surgery or in the cath lab so patients can be staggered and recover at different times and in different areas of the hospital. “These are very granular, specific infrastructure things that we’ve never really had to consider before,” Wood observed.
The document also had to be flexible and nimble enough to respond to a potential rebound of COVID-19 cases, which in newly released models are projected to rise sharply to 200,000 cases a day and be accompanied by some 3,000 deaths each day by June 1.
“This is my own personal opinion but I think it’s foolish to think that we are going to be able to come back to 100% of the cases we were doing before, even with testing, PPE, and all of that until we have a vaccine,” he said.
Similar to decisions made in preparation for the initial COVID-19 surge, the consensus document outlines the need for ethical considerations when turning the tap back on. This means prioritizing procedures and tests that are likely to benefit more people and to a greater degree, and ensuring that patients are treated fairly and consistently, regardless of their ethnicity, perceived social worth, or ability to pay, said coauthor and ACC President Athena Poppas, MD, Brown University School of Medicine, Providence, Rhode Island.
“It’s an ethical tenet that exists in a lot of places but it’s usually not overtly called out,” Poppas told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “It’s not rationing care; I think people jump to that but it’s actually the opposite of rationing care. It’s about being thoughtful about prioritizing patients.”
“There’s a variety of data that should help in the prioritization, not only how much hospital resources are utilized, that’s on one side, but there’s also the patient risk of delaying or doing a procedure, and then the societal risk,” she said.
Susheel Kodali, MD, of New York–Presbyterian Hospital/Columbia University Irving Medical Center, who recently published recommendations on restructuring structural heart disease practice during the pandemic, said the document is timely as centers, including his own, are trying to restart some outpatient visits, as early as next week.
“They made a point about talking about cohesive partnerships with regional public health officials and I think that’s great. The question is how does that happen,” he told theheart.org | Medscape Cardiology. “In New York, we’re not allowed to do elective cases but what’s considered elective is not so clearly defined. An AS [aortic stenosis] patient that had a syncopal episode 2 weeks ago, is that considered elective or is that semi-urgent? I think that’s one of the challenges and that’s where these partnerships would be useful.”
Other challenges include the need for regional partnerships to better align hospitals, which in the New York area means half a dozen large healthcare systems, and to coordinate care between hospital departments – all of which will be scheduling imaging and OR time for their own backlog of hernia, knee, or hip surgeries.
Finally, there’s the need for a lot of conversation with the patient and their family about returning to a hospital amid a deadly pandemic.
“I had a patient today and the daughter was very concerned about bringing her in,” Kodali said. “She’s in class IV heart failure but her [daughter’s] big concern was: who is she going to be exposed to when she gets the echo? What kind of protection is there for her? Is the tech wearing a mask?
“It’s not just the health care providers that have to have the comfort, but it’s the patients and their families who have to feel comfortable bringing their loved ones here for treatment,” he said. “Because everyone is concerned about the environment.”
Wood reports receiving unrestricted grant support from Edwards Lifesciences and Abbott Vascular and serving as a consultant for Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, and Boston Scientific. Poppas reports no relevant conflicts of interest. Kodali reports consultant (honoraria) from Admedus, Meril Life Sciences, JenaValve, and Abbott Vascular; SAB (equity) from Dura Biotech, MicroInterventional Devices, Thubrikar Aortic Valve, Supira, and Admedus; and institutional funding from Edwards Lifesciences, Medtronic, Abbott Vascular, Boston Scientific, and JenaValve.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Triage, L&D, postpartum care during the COVID-19 pandemic
The meteoric rise in the number of test-positive and clinical cases of COVID-19 because of infection with the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in states and cities across the United States has added urgency to the efforts to develop protocols for hospital triage, admission, labor and delivery management, and other aspects of obstetrical care.
Emerging data suggest that, while SARS-CoV-2 is less lethal overall than the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proved to be, it is significantly more contagious. Although a severe disease, the limited worldwide data so far available (as of early May) do not indicate that pregnant women are at greater risk of severe disease, compared with the general population. However, there remains a critical need for data on maternal and perinatal outcomes in women infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Multiple physiological changes in pregnancy, from reduced cell-based immune competence to changes in respiratory tract and pulmonary function – e.g., edema of the respiratory tract, increases in secretions and oxygen consumption, elevation of the diaphragm, and decrease in functional residual capacity – have historically contributed to worse obstetric outcomes in pregnant women who have had viral pneumonias. Furthermore, limited published experience with COVID-19 in China suggests worse perinatal outcomes in some affected pregnancies, including prematurity and perinatal death.
With evolution of the pandemic and accumulation of experience, it is expected that data-driven guidelines on assessment and management of infected pregnant women will contribute to improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. What is clear now, however, is that,
Here are my recommendations, based on a currently limited body of literature on COVID-19 and other communicable viral respiratory disorders, as well my experience in the greater Detroit area, a COVID-19 hot spot.
Preparing for hospital evaluation and admission
The obstetric triage or labor and delivery (L&D) unit should be notified prior to the arrival of a patient suspected of or known to be infected with the virus. This will minimize staff exposure and allow sufficient time to prepare appropriate accommodations, equipment, and supplies for the patient’s care. Hospital infection control should be promptly notified by L&D of the expected arrival of such a patient. Placement ideally should be in a negative-pressure room, which allows outside air to flow into the room but prevents contaminated air from escaping. In the absence of a negative-pressure room, an infection isolation area should be utilized.
The patient and one accompanying support individual should wear either medical-grade masks brought from home or supplied upon entry to the hospital or homemade masks or bandanas. This will reduce the risk of viral transmission to hospital workers and other individuals encountered in the hospital prior to arriving in L&D. An ideal setup is to have separate entry areas, access corridors, and elevators for patients known or suspected to have COVID-19 infection. The patient and visitor should be expeditiously escorted to the prepared area for evaluation. Patients who are not known or suspected to be infected ideally should be tested.
Screening of patients & support individuals
Proper screening of patients and support individuals is critical to protecting both patients and staff in the L&D unit. This should include an expanded questionnaire that asks about disturbances of smell and taste and GI symptoms like loss of appetite – not only the more commonly queried symptoms of fever, shortness of breath, coughing, and exposure to someone who may have been ill.
Recent studies regarding presenting symptoms cast significant doubt, in fact, on the validity of patients with “asymptomatic COVID-19.” Over 15% of patients with confirmed infection in one published case series had solely GI symptoms and almost all had some digestive symptoms, for example, and almost 90% in another study had absent or reduced sense of smell and/or taste.1,2 In fact, the use of the term “paucisymptomatic” rather than “asymptomatic” may be most appropriate.
Support individuals also should undergo temperature screening, ideally with laser noncontact thermometers on entry to the hospital or triage.
Visitor policy
The number of visitors/support individuals should be kept to a minimum to reduce transmission risk. The actual number will be determined by hospital or state policy, but up to one visitor in the labor room appears reasonable. Very strong individual justification should be required to exceed this threshold! The visitor should not only be screened for an expanded list of symptoms, but they also should be queried for underlying illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease, significant lung disease, undergoing cancer therapy) as well as for age over 65 years, each of which increase the chances of severe COVID-19 disease should infection occur. The visitor should be informed of such risks and, especially when accompanying a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, provided the option of voluntarily revoking their visitor status. A visitor with known or suspected COVID-19 infection based on testing or screening should not be allowed into the L&D unit.
In addition, institutions may be considered to have obligations to the visitor/support person beyond screening. These include instructions in proper mask usage, hand washing, and limiting the touching of surfaces to lower infection risk.
“Visitor relays” where one visitor replaces another should be strongly discouraged. Visitors should similarly not be allowed to wander around the hospital (to use phones, for instance); transiting back and forth to obtain food and coffee should be kept to a strict minimum. For visitors accompanying COVID-19–-infected women, “visitor’s plates” provided by the hospital at reasonable cost is a much-preferred arrangement for obtaining meals during the course of the hospital stay. In addition, visitors should be sent out of the room during the performance of aerosolizing procedures.
Labor and delivery management
The successful management of patients with COVID-19 requires a rigorous infection control protocol informed by guidelines from national entities, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and by state health departments when available.
Strict limits on the number of obstetricians and other health care workers (HCWs) entering the patient’s room should be enforced and documented to minimize risk to the HCWs attending to patients who have a positive diagnosis or who are under investigation. Only in cases of demonstrable clinical benefit should repeat visits by the same or additional HCWs be permitted. Conventional and electronic tablets present an excellent opportunity for patient follow-up visits without room entry. In our institution, this has been successfully piloted in nonpregnant patients. Obstetricians and others caring for obstetrical patients – especially those who are infected or under investigation for infection – should always wear a properly fitted N95 mask.
Because patients with COVID-19 may have or go on to develop a constellation of organ abnormalities (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary), it is vital that a standardized panel of baseline laboratory studies be developed for pregnant patients. This will minimize the need for repeated blood draws and other testing which may increase HCW exposure.
A negative screen based on nonreport of symptoms, lack of temperature elevation, and reported nonexposure to individuals with COVID-19 symptoms still has limitations in terms of disease detection. A recent report from a tertiary care hospital in New York City found that close to one-third of pregnant patients with confirmed COVID-19 admitted over a 2-week period had no viral symptoms or instructive history on initial admission.3 This is consistent with our clinical experience. Most importantly, therefore, routine quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction testing should be performed on all patients admitted to the L&D unit.
Given the reported variability in the accuracy of polymerase chain reaction testing induced by variable effectiveness of sampling techniques, stage of infection, and inherent test accuracy issues, symptomatic patients with a negative test should first obtain clearance from infectious disease specialists before isolation precautions are discontinued. Repeat testing in 24 hours, including testing of multiple sites, may subsequently yield a positive result in persistently symptomatic patients.
Intrapartum management
As much as possible, standard obstetric indications should guide the timing and route of delivery. In the case of a COVID-19–positive patient or a patient under investigation, nonobstetric factors may bear heavily on decision making, and management flexibility is of great value. For example, in cases of severe or critical disease status, evidence suggests that early delivery regardless of gestational age can improve maternal oxygenation; this supports the liberal use of C-sections in these circumstances. In addition, shortening labor length as well as duration of hospitalization may be expected to reduce the risk of transmission to HCWs, other staff, and other patients.
High rates of cesarean delivery unsurprisingly have been reported thus far: One review of 108 case reports and series of test-positive COVID-19 pregnancies found a 92% C-section rate, and another review and meta-analysis of studies of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 during pregnancy similarly found that the majority of patients – 84% across all coronavirus infections and 91% in COVID-19 pregnancies – were delivered by C-section.4,5 Given these high rates of cesarean deliveries, the early placement of neuraxial anesthesia while the patient is stable appears to be prudent and obviates the need for intubation, the latter of which is associated with increased aerosol generation and increased virus transmission risk.
Strict protocols for the optimal protection of staff should be observed, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) protection. Protocols have been detailed in various guidelines and publications; they include the wearing of shoe covers, gowns, N95 masks, goggles, face shields, and two layers of gloves.
For institutions that currently do not offer routine COVID-19 testing to pregnant patients – especially those in areas of outbreaks – N95 masks and eye protection should still be provided to all HCWs involved in the intrapartum management of untested asymptomatic patients, particularly those in the active phase of labor. This protection is justified given the limitations of symptom- and history-based screening and the not-uncommon experience of the patient with a negative screen who subsequently develops the clinical syndrome.
Obstetric management of labor requires close patient contact that potentially elevates the risk of contamination and infection. During the active stage of labor, patient shouting, rapid mouth breathing, and other behaviors inherent to labor all increase the risk of aerosolization of oronasal secretions. In addition, nasal-prong oxygen administration is believed to independently increase the risk of aerosolization of secretions. The casual practice of nasal oxygen application should thus be discontinued and, where felt to be absolutely necessary, a mask should be worn on top of the prongs.
Regarding operative delivery, each participating obstetric surgeon should observe guidelines and recommendations of governing national organizations and professional groups – including the American College of Surgeons – regarding the safe conduct of operations on patients with COVID-19. Written guidelines should be tailored as needed to the performance of C-sections and readily available in L&D. Drills and simulations are generally valuable, and expertise and support should always be available in the labor room to assist with donning and doffing of PPE.
Postpartum care
Expeditious separation of the COVID-19–positive mother from her infant is recommended, including avoidance of delayed cord clamping because of insufficient evidence of benefit to the infant. Insufficient evidence exists to support vertical transmission, but the possibility of maternal-infant transmission is clinically accepted based on small case reports of infection in a neonate at 30 hours of life and in infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.6,7 Accordingly, it is recommended that the benefit of early infant separation should be discussed with the mother. If approved, the infant should be kept in a separate isolation area and observed.
There is no evidence of breast milk transmission of the virus. For those electing to breastfeed, the patient should be provided with a breast pump to express and store the milk for subsequent bottle feeding. For mothers who elect to room in with the infant, a separation distance of 6 feet is recommended with an intervening barrier curtain. For COVID-19–positive mothers who elect breastfeeding, meticulous hand and face washing, continuous wearing of a mask, and cleansing of the breast prior to feeding needs to be maintained.
Restrictive visiting policies of no more than one visitor should be maintained. For severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19, it has been suggested that no visitors be allowed. As with other hospitalizations of COVID-19 patients, the HCW contact should be kept at a justifiable minimum to reduce the risk of transmission.
Protecting the obstetrician and other HCWs
Protecting the health of obstetricians and other HCWs is central to any successful strategy to fight the COVID-19 epidemic. For the individual obstetrician, careful attention to national and local hospital guidelines is required as these are rapidly evolving.
Physicians and their leadership must maintain an ongoing dialogue with hospital leadership to continually upgrade and optimize infection prevention and control measures, and to uphold best practices. The experience in Wuhan, China, illustrates the effectiveness of the proper use of PPE along with population control measures to reduce infections in HCWs. Prior to understanding the mechanism of virus transmission and using protective equipment, infection rates of 3%-29% were reported among HCWs. With the meticulous utilization of mitigation strategies and population control measures – including consistent use of PPE – the rate of infection of HCWs reportedly fell to zero.
In outpatient offices, all staff and HCWs should wear masks at all times and engage in social distancing and in frequent hand sanitization. Patients should be strongly encouraged to wear masks during office visits and on all other occasions when they will be in physical proximity to other individuals outside of the home.
Reports from epidemic areas describe transmission from household sources as a significant cause of HCW infection. The information emphasizes the need for ongoing vigilance and attention to sanitization measures even when at home with one’s family. An additional benefit is reduced risk of transmission from HCWs to family members.
Dr. Bahado-Singh is professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System.
References
1. Luo S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043.
2. Lechien JR et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1.
3. Breslin N et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100118.
4. Zaigham M, Andersson O. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13867.
5. Di Mascio D et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107.
6. Ital J. Pediatr 2020;46(1) doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0820-x.
7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;149(2):130-6.
*This article was updated 5/6/2020.
The meteoric rise in the number of test-positive and clinical cases of COVID-19 because of infection with the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in states and cities across the United States has added urgency to the efforts to develop protocols for hospital triage, admission, labor and delivery management, and other aspects of obstetrical care.
Emerging data suggest that, while SARS-CoV-2 is less lethal overall than the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proved to be, it is significantly more contagious. Although a severe disease, the limited worldwide data so far available (as of early May) do not indicate that pregnant women are at greater risk of severe disease, compared with the general population. However, there remains a critical need for data on maternal and perinatal outcomes in women infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Multiple physiological changes in pregnancy, from reduced cell-based immune competence to changes in respiratory tract and pulmonary function – e.g., edema of the respiratory tract, increases in secretions and oxygen consumption, elevation of the diaphragm, and decrease in functional residual capacity – have historically contributed to worse obstetric outcomes in pregnant women who have had viral pneumonias. Furthermore, limited published experience with COVID-19 in China suggests worse perinatal outcomes in some affected pregnancies, including prematurity and perinatal death.
With evolution of the pandemic and accumulation of experience, it is expected that data-driven guidelines on assessment and management of infected pregnant women will contribute to improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. What is clear now, however, is that,
Here are my recommendations, based on a currently limited body of literature on COVID-19 and other communicable viral respiratory disorders, as well my experience in the greater Detroit area, a COVID-19 hot spot.
Preparing for hospital evaluation and admission
The obstetric triage or labor and delivery (L&D) unit should be notified prior to the arrival of a patient suspected of or known to be infected with the virus. This will minimize staff exposure and allow sufficient time to prepare appropriate accommodations, equipment, and supplies for the patient’s care. Hospital infection control should be promptly notified by L&D of the expected arrival of such a patient. Placement ideally should be in a negative-pressure room, which allows outside air to flow into the room but prevents contaminated air from escaping. In the absence of a negative-pressure room, an infection isolation area should be utilized.
The patient and one accompanying support individual should wear either medical-grade masks brought from home or supplied upon entry to the hospital or homemade masks or bandanas. This will reduce the risk of viral transmission to hospital workers and other individuals encountered in the hospital prior to arriving in L&D. An ideal setup is to have separate entry areas, access corridors, and elevators for patients known or suspected to have COVID-19 infection. The patient and visitor should be expeditiously escorted to the prepared area for evaluation. Patients who are not known or suspected to be infected ideally should be tested.
Screening of patients & support individuals
Proper screening of patients and support individuals is critical to protecting both patients and staff in the L&D unit. This should include an expanded questionnaire that asks about disturbances of smell and taste and GI symptoms like loss of appetite – not only the more commonly queried symptoms of fever, shortness of breath, coughing, and exposure to someone who may have been ill.
Recent studies regarding presenting symptoms cast significant doubt, in fact, on the validity of patients with “asymptomatic COVID-19.” Over 15% of patients with confirmed infection in one published case series had solely GI symptoms and almost all had some digestive symptoms, for example, and almost 90% in another study had absent or reduced sense of smell and/or taste.1,2 In fact, the use of the term “paucisymptomatic” rather than “asymptomatic” may be most appropriate.
Support individuals also should undergo temperature screening, ideally with laser noncontact thermometers on entry to the hospital or triage.
Visitor policy
The number of visitors/support individuals should be kept to a minimum to reduce transmission risk. The actual number will be determined by hospital or state policy, but up to one visitor in the labor room appears reasonable. Very strong individual justification should be required to exceed this threshold! The visitor should not only be screened for an expanded list of symptoms, but they also should be queried for underlying illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease, significant lung disease, undergoing cancer therapy) as well as for age over 65 years, each of which increase the chances of severe COVID-19 disease should infection occur. The visitor should be informed of such risks and, especially when accompanying a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, provided the option of voluntarily revoking their visitor status. A visitor with known or suspected COVID-19 infection based on testing or screening should not be allowed into the L&D unit.
In addition, institutions may be considered to have obligations to the visitor/support person beyond screening. These include instructions in proper mask usage, hand washing, and limiting the touching of surfaces to lower infection risk.
“Visitor relays” where one visitor replaces another should be strongly discouraged. Visitors should similarly not be allowed to wander around the hospital (to use phones, for instance); transiting back and forth to obtain food and coffee should be kept to a strict minimum. For visitors accompanying COVID-19–-infected women, “visitor’s plates” provided by the hospital at reasonable cost is a much-preferred arrangement for obtaining meals during the course of the hospital stay. In addition, visitors should be sent out of the room during the performance of aerosolizing procedures.
Labor and delivery management
The successful management of patients with COVID-19 requires a rigorous infection control protocol informed by guidelines from national entities, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and by state health departments when available.
Strict limits on the number of obstetricians and other health care workers (HCWs) entering the patient’s room should be enforced and documented to minimize risk to the HCWs attending to patients who have a positive diagnosis or who are under investigation. Only in cases of demonstrable clinical benefit should repeat visits by the same or additional HCWs be permitted. Conventional and electronic tablets present an excellent opportunity for patient follow-up visits without room entry. In our institution, this has been successfully piloted in nonpregnant patients. Obstetricians and others caring for obstetrical patients – especially those who are infected or under investigation for infection – should always wear a properly fitted N95 mask.
Because patients with COVID-19 may have or go on to develop a constellation of organ abnormalities (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary), it is vital that a standardized panel of baseline laboratory studies be developed for pregnant patients. This will minimize the need for repeated blood draws and other testing which may increase HCW exposure.
A negative screen based on nonreport of symptoms, lack of temperature elevation, and reported nonexposure to individuals with COVID-19 symptoms still has limitations in terms of disease detection. A recent report from a tertiary care hospital in New York City found that close to one-third of pregnant patients with confirmed COVID-19 admitted over a 2-week period had no viral symptoms or instructive history on initial admission.3 This is consistent with our clinical experience. Most importantly, therefore, routine quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction testing should be performed on all patients admitted to the L&D unit.
Given the reported variability in the accuracy of polymerase chain reaction testing induced by variable effectiveness of sampling techniques, stage of infection, and inherent test accuracy issues, symptomatic patients with a negative test should first obtain clearance from infectious disease specialists before isolation precautions are discontinued. Repeat testing in 24 hours, including testing of multiple sites, may subsequently yield a positive result in persistently symptomatic patients.
Intrapartum management
As much as possible, standard obstetric indications should guide the timing and route of delivery. In the case of a COVID-19–positive patient or a patient under investigation, nonobstetric factors may bear heavily on decision making, and management flexibility is of great value. For example, in cases of severe or critical disease status, evidence suggests that early delivery regardless of gestational age can improve maternal oxygenation; this supports the liberal use of C-sections in these circumstances. In addition, shortening labor length as well as duration of hospitalization may be expected to reduce the risk of transmission to HCWs, other staff, and other patients.
High rates of cesarean delivery unsurprisingly have been reported thus far: One review of 108 case reports and series of test-positive COVID-19 pregnancies found a 92% C-section rate, and another review and meta-analysis of studies of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 during pregnancy similarly found that the majority of patients – 84% across all coronavirus infections and 91% in COVID-19 pregnancies – were delivered by C-section.4,5 Given these high rates of cesarean deliveries, the early placement of neuraxial anesthesia while the patient is stable appears to be prudent and obviates the need for intubation, the latter of which is associated with increased aerosol generation and increased virus transmission risk.
Strict protocols for the optimal protection of staff should be observed, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) protection. Protocols have been detailed in various guidelines and publications; they include the wearing of shoe covers, gowns, N95 masks, goggles, face shields, and two layers of gloves.
For institutions that currently do not offer routine COVID-19 testing to pregnant patients – especially those in areas of outbreaks – N95 masks and eye protection should still be provided to all HCWs involved in the intrapartum management of untested asymptomatic patients, particularly those in the active phase of labor. This protection is justified given the limitations of symptom- and history-based screening and the not-uncommon experience of the patient with a negative screen who subsequently develops the clinical syndrome.
Obstetric management of labor requires close patient contact that potentially elevates the risk of contamination and infection. During the active stage of labor, patient shouting, rapid mouth breathing, and other behaviors inherent to labor all increase the risk of aerosolization of oronasal secretions. In addition, nasal-prong oxygen administration is believed to independently increase the risk of aerosolization of secretions. The casual practice of nasal oxygen application should thus be discontinued and, where felt to be absolutely necessary, a mask should be worn on top of the prongs.
Regarding operative delivery, each participating obstetric surgeon should observe guidelines and recommendations of governing national organizations and professional groups – including the American College of Surgeons – regarding the safe conduct of operations on patients with COVID-19. Written guidelines should be tailored as needed to the performance of C-sections and readily available in L&D. Drills and simulations are generally valuable, and expertise and support should always be available in the labor room to assist with donning and doffing of PPE.
Postpartum care
Expeditious separation of the COVID-19–positive mother from her infant is recommended, including avoidance of delayed cord clamping because of insufficient evidence of benefit to the infant. Insufficient evidence exists to support vertical transmission, but the possibility of maternal-infant transmission is clinically accepted based on small case reports of infection in a neonate at 30 hours of life and in infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.6,7 Accordingly, it is recommended that the benefit of early infant separation should be discussed with the mother. If approved, the infant should be kept in a separate isolation area and observed.
There is no evidence of breast milk transmission of the virus. For those electing to breastfeed, the patient should be provided with a breast pump to express and store the milk for subsequent bottle feeding. For mothers who elect to room in with the infant, a separation distance of 6 feet is recommended with an intervening barrier curtain. For COVID-19–positive mothers who elect breastfeeding, meticulous hand and face washing, continuous wearing of a mask, and cleansing of the breast prior to feeding needs to be maintained.
Restrictive visiting policies of no more than one visitor should be maintained. For severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19, it has been suggested that no visitors be allowed. As with other hospitalizations of COVID-19 patients, the HCW contact should be kept at a justifiable minimum to reduce the risk of transmission.
Protecting the obstetrician and other HCWs
Protecting the health of obstetricians and other HCWs is central to any successful strategy to fight the COVID-19 epidemic. For the individual obstetrician, careful attention to national and local hospital guidelines is required as these are rapidly evolving.
Physicians and their leadership must maintain an ongoing dialogue with hospital leadership to continually upgrade and optimize infection prevention and control measures, and to uphold best practices. The experience in Wuhan, China, illustrates the effectiveness of the proper use of PPE along with population control measures to reduce infections in HCWs. Prior to understanding the mechanism of virus transmission and using protective equipment, infection rates of 3%-29% were reported among HCWs. With the meticulous utilization of mitigation strategies and population control measures – including consistent use of PPE – the rate of infection of HCWs reportedly fell to zero.
In outpatient offices, all staff and HCWs should wear masks at all times and engage in social distancing and in frequent hand sanitization. Patients should be strongly encouraged to wear masks during office visits and on all other occasions when they will be in physical proximity to other individuals outside of the home.
Reports from epidemic areas describe transmission from household sources as a significant cause of HCW infection. The information emphasizes the need for ongoing vigilance and attention to sanitization measures even when at home with one’s family. An additional benefit is reduced risk of transmission from HCWs to family members.
Dr. Bahado-Singh is professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System.
References
1. Luo S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043.
2. Lechien JR et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1.
3. Breslin N et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100118.
4. Zaigham M, Andersson O. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13867.
5. Di Mascio D et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107.
6. Ital J. Pediatr 2020;46(1) doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0820-x.
7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;149(2):130-6.
*This article was updated 5/6/2020.
The meteoric rise in the number of test-positive and clinical cases of COVID-19 because of infection with the SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2) in states and cities across the United States has added urgency to the efforts to develop protocols for hospital triage, admission, labor and delivery management, and other aspects of obstetrical care.
Emerging data suggest that, while SARS-CoV-2 is less lethal overall than the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV) and Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV) proved to be, it is significantly more contagious. Although a severe disease, the limited worldwide data so far available (as of early May) do not indicate that pregnant women are at greater risk of severe disease, compared with the general population. However, there remains a critical need for data on maternal and perinatal outcomes in women infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Multiple physiological changes in pregnancy, from reduced cell-based immune competence to changes in respiratory tract and pulmonary function – e.g., edema of the respiratory tract, increases in secretions and oxygen consumption, elevation of the diaphragm, and decrease in functional residual capacity – have historically contributed to worse obstetric outcomes in pregnant women who have had viral pneumonias. Furthermore, limited published experience with COVID-19 in China suggests worse perinatal outcomes in some affected pregnancies, including prematurity and perinatal death.
With evolution of the pandemic and accumulation of experience, it is expected that data-driven guidelines on assessment and management of infected pregnant women will contribute to improved maternal and perinatal outcomes. What is clear now, however, is that,
Here are my recommendations, based on a currently limited body of literature on COVID-19 and other communicable viral respiratory disorders, as well my experience in the greater Detroit area, a COVID-19 hot spot.
Preparing for hospital evaluation and admission
The obstetric triage or labor and delivery (L&D) unit should be notified prior to the arrival of a patient suspected of or known to be infected with the virus. This will minimize staff exposure and allow sufficient time to prepare appropriate accommodations, equipment, and supplies for the patient’s care. Hospital infection control should be promptly notified by L&D of the expected arrival of such a patient. Placement ideally should be in a negative-pressure room, which allows outside air to flow into the room but prevents contaminated air from escaping. In the absence of a negative-pressure room, an infection isolation area should be utilized.
The patient and one accompanying support individual should wear either medical-grade masks brought from home or supplied upon entry to the hospital or homemade masks or bandanas. This will reduce the risk of viral transmission to hospital workers and other individuals encountered in the hospital prior to arriving in L&D. An ideal setup is to have separate entry areas, access corridors, and elevators for patients known or suspected to have COVID-19 infection. The patient and visitor should be expeditiously escorted to the prepared area for evaluation. Patients who are not known or suspected to be infected ideally should be tested.
Screening of patients & support individuals
Proper screening of patients and support individuals is critical to protecting both patients and staff in the L&D unit. This should include an expanded questionnaire that asks about disturbances of smell and taste and GI symptoms like loss of appetite – not only the more commonly queried symptoms of fever, shortness of breath, coughing, and exposure to someone who may have been ill.
Recent studies regarding presenting symptoms cast significant doubt, in fact, on the validity of patients with “asymptomatic COVID-19.” Over 15% of patients with confirmed infection in one published case series had solely GI symptoms and almost all had some digestive symptoms, for example, and almost 90% in another study had absent or reduced sense of smell and/or taste.1,2 In fact, the use of the term “paucisymptomatic” rather than “asymptomatic” may be most appropriate.
Support individuals also should undergo temperature screening, ideally with laser noncontact thermometers on entry to the hospital or triage.
Visitor policy
The number of visitors/support individuals should be kept to a minimum to reduce transmission risk. The actual number will be determined by hospital or state policy, but up to one visitor in the labor room appears reasonable. Very strong individual justification should be required to exceed this threshold! The visitor should not only be screened for an expanded list of symptoms, but they also should be queried for underlying illnesses (e.g., diabetes, cardiovascular disease, significant lung disease, undergoing cancer therapy) as well as for age over 65 years, each of which increase the chances of severe COVID-19 disease should infection occur. The visitor should be informed of such risks and, especially when accompanying a patient with known or suspected COVID-19, provided the option of voluntarily revoking their visitor status. A visitor with known or suspected COVID-19 infection based on testing or screening should not be allowed into the L&D unit.
In addition, institutions may be considered to have obligations to the visitor/support person beyond screening. These include instructions in proper mask usage, hand washing, and limiting the touching of surfaces to lower infection risk.
“Visitor relays” where one visitor replaces another should be strongly discouraged. Visitors should similarly not be allowed to wander around the hospital (to use phones, for instance); transiting back and forth to obtain food and coffee should be kept to a strict minimum. For visitors accompanying COVID-19–-infected women, “visitor’s plates” provided by the hospital at reasonable cost is a much-preferred arrangement for obtaining meals during the course of the hospital stay. In addition, visitors should be sent out of the room during the performance of aerosolizing procedures.
Labor and delivery management
The successful management of patients with COVID-19 requires a rigorous infection control protocol informed by guidelines from national entities, such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, the Society for Maternal-Fetal Medicine, and the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists, and by state health departments when available.
Strict limits on the number of obstetricians and other health care workers (HCWs) entering the patient’s room should be enforced and documented to minimize risk to the HCWs attending to patients who have a positive diagnosis or who are under investigation. Only in cases of demonstrable clinical benefit should repeat visits by the same or additional HCWs be permitted. Conventional and electronic tablets present an excellent opportunity for patient follow-up visits without room entry. In our institution, this has been successfully piloted in nonpregnant patients. Obstetricians and others caring for obstetrical patients – especially those who are infected or under investigation for infection – should always wear a properly fitted N95 mask.
Because patients with COVID-19 may have or go on to develop a constellation of organ abnormalities (e.g., cardiovascular, renal, pulmonary), it is vital that a standardized panel of baseline laboratory studies be developed for pregnant patients. This will minimize the need for repeated blood draws and other testing which may increase HCW exposure.
A negative screen based on nonreport of symptoms, lack of temperature elevation, and reported nonexposure to individuals with COVID-19 symptoms still has limitations in terms of disease detection. A recent report from a tertiary care hospital in New York City found that close to one-third of pregnant patients with confirmed COVID-19 admitted over a 2-week period had no viral symptoms or instructive history on initial admission.3 This is consistent with our clinical experience. Most importantly, therefore, routine quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction testing should be performed on all patients admitted to the L&D unit.
Given the reported variability in the accuracy of polymerase chain reaction testing induced by variable effectiveness of sampling techniques, stage of infection, and inherent test accuracy issues, symptomatic patients with a negative test should first obtain clearance from infectious disease specialists before isolation precautions are discontinued. Repeat testing in 24 hours, including testing of multiple sites, may subsequently yield a positive result in persistently symptomatic patients.
Intrapartum management
As much as possible, standard obstetric indications should guide the timing and route of delivery. In the case of a COVID-19–positive patient or a patient under investigation, nonobstetric factors may bear heavily on decision making, and management flexibility is of great value. For example, in cases of severe or critical disease status, evidence suggests that early delivery regardless of gestational age can improve maternal oxygenation; this supports the liberal use of C-sections in these circumstances. In addition, shortening labor length as well as duration of hospitalization may be expected to reduce the risk of transmission to HCWs, other staff, and other patients.
High rates of cesarean delivery unsurprisingly have been reported thus far: One review of 108 case reports and series of test-positive COVID-19 pregnancies found a 92% C-section rate, and another review and meta-analysis of studies of SARS, MERS, and COVID-19 during pregnancy similarly found that the majority of patients – 84% across all coronavirus infections and 91% in COVID-19 pregnancies – were delivered by C-section.4,5 Given these high rates of cesarean deliveries, the early placement of neuraxial anesthesia while the patient is stable appears to be prudent and obviates the need for intubation, the latter of which is associated with increased aerosol generation and increased virus transmission risk.
Strict protocols for the optimal protection of staff should be observed, including proper personal protective equipment (PPE) protection. Protocols have been detailed in various guidelines and publications; they include the wearing of shoe covers, gowns, N95 masks, goggles, face shields, and two layers of gloves.
For institutions that currently do not offer routine COVID-19 testing to pregnant patients – especially those in areas of outbreaks – N95 masks and eye protection should still be provided to all HCWs involved in the intrapartum management of untested asymptomatic patients, particularly those in the active phase of labor. This protection is justified given the limitations of symptom- and history-based screening and the not-uncommon experience of the patient with a negative screen who subsequently develops the clinical syndrome.
Obstetric management of labor requires close patient contact that potentially elevates the risk of contamination and infection. During the active stage of labor, patient shouting, rapid mouth breathing, and other behaviors inherent to labor all increase the risk of aerosolization of oronasal secretions. In addition, nasal-prong oxygen administration is believed to independently increase the risk of aerosolization of secretions. The casual practice of nasal oxygen application should thus be discontinued and, where felt to be absolutely necessary, a mask should be worn on top of the prongs.
Regarding operative delivery, each participating obstetric surgeon should observe guidelines and recommendations of governing national organizations and professional groups – including the American College of Surgeons – regarding the safe conduct of operations on patients with COVID-19. Written guidelines should be tailored as needed to the performance of C-sections and readily available in L&D. Drills and simulations are generally valuable, and expertise and support should always be available in the labor room to assist with donning and doffing of PPE.
Postpartum care
Expeditious separation of the COVID-19–positive mother from her infant is recommended, including avoidance of delayed cord clamping because of insufficient evidence of benefit to the infant. Insufficient evidence exists to support vertical transmission, but the possibility of maternal-infant transmission is clinically accepted based on small case reports of infection in a neonate at 30 hours of life and in infants of mothers with suspected or confirmed COVID-19.6,7 Accordingly, it is recommended that the benefit of early infant separation should be discussed with the mother. If approved, the infant should be kept in a separate isolation area and observed.
There is no evidence of breast milk transmission of the virus. For those electing to breastfeed, the patient should be provided with a breast pump to express and store the milk for subsequent bottle feeding. For mothers who elect to room in with the infant, a separation distance of 6 feet is recommended with an intervening barrier curtain. For COVID-19–positive mothers who elect breastfeeding, meticulous hand and face washing, continuous wearing of a mask, and cleansing of the breast prior to feeding needs to be maintained.
Restrictive visiting policies of no more than one visitor should be maintained. For severely or critically ill patients with COVID-19, it has been suggested that no visitors be allowed. As with other hospitalizations of COVID-19 patients, the HCW contact should be kept at a justifiable minimum to reduce the risk of transmission.
Protecting the obstetrician and other HCWs
Protecting the health of obstetricians and other HCWs is central to any successful strategy to fight the COVID-19 epidemic. For the individual obstetrician, careful attention to national and local hospital guidelines is required as these are rapidly evolving.
Physicians and their leadership must maintain an ongoing dialogue with hospital leadership to continually upgrade and optimize infection prevention and control measures, and to uphold best practices. The experience in Wuhan, China, illustrates the effectiveness of the proper use of PPE along with population control measures to reduce infections in HCWs. Prior to understanding the mechanism of virus transmission and using protective equipment, infection rates of 3%-29% were reported among HCWs. With the meticulous utilization of mitigation strategies and population control measures – including consistent use of PPE – the rate of infection of HCWs reportedly fell to zero.
In outpatient offices, all staff and HCWs should wear masks at all times and engage in social distancing and in frequent hand sanitization. Patients should be strongly encouraged to wear masks during office visits and on all other occasions when they will be in physical proximity to other individuals outside of the home.
Reports from epidemic areas describe transmission from household sources as a significant cause of HCW infection. The information emphasizes the need for ongoing vigilance and attention to sanitization measures even when at home with one’s family. An additional benefit is reduced risk of transmission from HCWs to family members.
Dr. Bahado-Singh is professor and chair of obstetrics and gynecology at Oakland University, Rochester, Mich., and health system chair for obstetrics and gynecology at Beaumont Health System.
References
1. Luo S et al. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020 Mar 20. doi: 10.1016/j.cgh.2020.03.043.
2. Lechien JR et al. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2020 Apr 6. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05965-1.
3. Breslin N et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Apr 9. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100118.
4. Zaigham M, Andersson O. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand. 2020 Apr 7. doi: 10.1111/aogs.13867.
5. Di Mascio D et al. Am J Obstet Gynecol MFM. 2020 Mar 25. doi: 10.1016/j.ajogmf.2020.100107.
6. Ital J. Pediatr 2020;46(1) doi: 10.1186/s13052-020-0820-x.
7. Int J Gynaecol Obstet. 2020;149(2):130-6.
*This article was updated 5/6/2020.
Pandemic effect: All other health care visits can wait
according to survey conducted at the end of April.
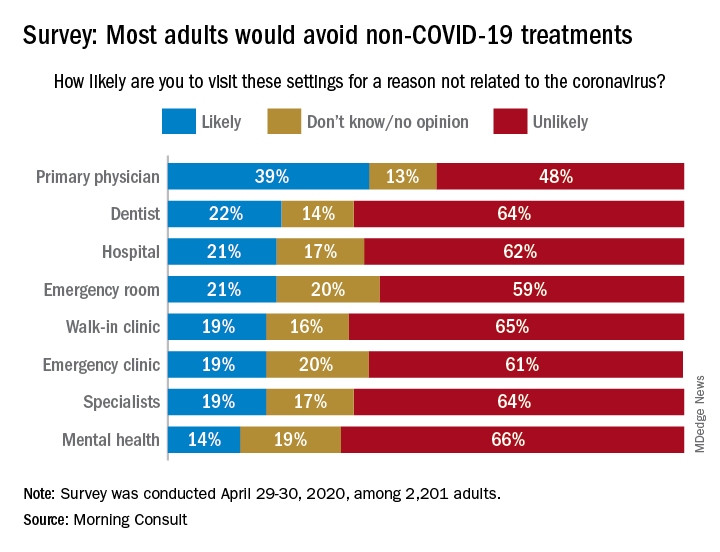
When asked how likely they were to visit a variety of health care settings for treatment not related to the coronavirus, 62% of respondents said it was unlikely that they would go to a hospital, 64% wouldn’t go to a specialist, and 65% would avoid walk-in clinics, digital media company Morning Consult reported May 4.
The only setting with less than a majority on the unlikely-to-visit side was primary physicians, who managed to combine a 39% likely vote with a 13% undecided/no-opinion tally, Morning Consult said after surveying 2,201 adults on April 29-30 (margin of error, ±2 percentage points).
As to when they might feel comfortable making such an in-person visit with their primary physician, 24% of respondents said they would willing to go in the next month, 14% said 2 months, 18% said 3 months, 13% said 6 months, and 10% said more than 6 months, the Morning Consult data show.
“Hospitals, despite being overburdened in recent weeks in coronavirus hot spots such as New York City, have reported dips in revenue as a result of potential patients opting against receiving elective surgeries out of fear of contracting COVID-19,” Morning Consult wrote, and these poll results suggest that “health care companies could continue to feel the pinch as long as the coronavirus lingers.”
according to survey conducted at the end of April.

When asked how likely they were to visit a variety of health care settings for treatment not related to the coronavirus, 62% of respondents said it was unlikely that they would go to a hospital, 64% wouldn’t go to a specialist, and 65% would avoid walk-in clinics, digital media company Morning Consult reported May 4.
The only setting with less than a majority on the unlikely-to-visit side was primary physicians, who managed to combine a 39% likely vote with a 13% undecided/no-opinion tally, Morning Consult said after surveying 2,201 adults on April 29-30 (margin of error, ±2 percentage points).
As to when they might feel comfortable making such an in-person visit with their primary physician, 24% of respondents said they would willing to go in the next month, 14% said 2 months, 18% said 3 months, 13% said 6 months, and 10% said more than 6 months, the Morning Consult data show.
“Hospitals, despite being overburdened in recent weeks in coronavirus hot spots such as New York City, have reported dips in revenue as a result of potential patients opting against receiving elective surgeries out of fear of contracting COVID-19,” Morning Consult wrote, and these poll results suggest that “health care companies could continue to feel the pinch as long as the coronavirus lingers.”
according to survey conducted at the end of April.

When asked how likely they were to visit a variety of health care settings for treatment not related to the coronavirus, 62% of respondents said it was unlikely that they would go to a hospital, 64% wouldn’t go to a specialist, and 65% would avoid walk-in clinics, digital media company Morning Consult reported May 4.
The only setting with less than a majority on the unlikely-to-visit side was primary physicians, who managed to combine a 39% likely vote with a 13% undecided/no-opinion tally, Morning Consult said after surveying 2,201 adults on April 29-30 (margin of error, ±2 percentage points).
As to when they might feel comfortable making such an in-person visit with their primary physician, 24% of respondents said they would willing to go in the next month, 14% said 2 months, 18% said 3 months, 13% said 6 months, and 10% said more than 6 months, the Morning Consult data show.
“Hospitals, despite being overburdened in recent weeks in coronavirus hot spots such as New York City, have reported dips in revenue as a result of potential patients opting against receiving elective surgeries out of fear of contracting COVID-19,” Morning Consult wrote, and these poll results suggest that “health care companies could continue to feel the pinch as long as the coronavirus lingers.”
FDA grants EUA to muscle stimulator to reduce mechanical ventilator usage
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator in order to potentially reduce the number of days adult patients, including those with COVID-19, require mechanical ventilation, according to a press release from Liberate Medical.
In comparison with mechanical ventilation, which is invasive and commonly weakens the breathing muscles, the VentFree system uses noninvasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation, according to the press release. This allows patients to begin treatment during the early stages of ventilation while they are sedated and to continue until they are weaned off of ventilation.
A pair of pilot randomized, controlled studies, completed in Europe and Australia, showed that VentFree helped to reduce ventilation duration and ICU length of stay, compared with placebo stimulation. The FDA granted VentFree Breakthrough Device status in 2019.
“We are grateful to the FDA for recognizing the potential of VentFree and feel privileged to have the opportunity to help patients on mechanical ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Angus McLachlan PhD, cofounder and CEO of Liberate Medical, said in the press release.
VentFree has been authorized for use only for the duration of the current COVID-19 emergency, as it has not yet been approved or cleared for usage by primary care providers.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator in order to potentially reduce the number of days adult patients, including those with COVID-19, require mechanical ventilation, according to a press release from Liberate Medical.
In comparison with mechanical ventilation, which is invasive and commonly weakens the breathing muscles, the VentFree system uses noninvasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation, according to the press release. This allows patients to begin treatment during the early stages of ventilation while they are sedated and to continue until they are weaned off of ventilation.
A pair of pilot randomized, controlled studies, completed in Europe and Australia, showed that VentFree helped to reduce ventilation duration and ICU length of stay, compared with placebo stimulation. The FDA granted VentFree Breakthrough Device status in 2019.
“We are grateful to the FDA for recognizing the potential of VentFree and feel privileged to have the opportunity to help patients on mechanical ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Angus McLachlan PhD, cofounder and CEO of Liberate Medical, said in the press release.
VentFree has been authorized for use only for the duration of the current COVID-19 emergency, as it has not yet been approved or cleared for usage by primary care providers.
The Food and Drug Administration has issued an Emergency Use Authorization (EUA) for the VentFree Respiratory Muscle Stimulator in order to potentially reduce the number of days adult patients, including those with COVID-19, require mechanical ventilation, according to a press release from Liberate Medical.
In comparison with mechanical ventilation, which is invasive and commonly weakens the breathing muscles, the VentFree system uses noninvasive neuromuscular electrical stimulation to contract the abdominal wall muscles in synchrony with exhalation during mechanical ventilation, according to the press release. This allows patients to begin treatment during the early stages of ventilation while they are sedated and to continue until they are weaned off of ventilation.
A pair of pilot randomized, controlled studies, completed in Europe and Australia, showed that VentFree helped to reduce ventilation duration and ICU length of stay, compared with placebo stimulation. The FDA granted VentFree Breakthrough Device status in 2019.
“We are grateful to the FDA for recognizing the potential of VentFree and feel privileged to have the opportunity to help patients on mechanical ventilation during the COVID-19 pandemic,” Angus McLachlan PhD, cofounder and CEO of Liberate Medical, said in the press release.
VentFree has been authorized for use only for the duration of the current COVID-19 emergency, as it has not yet been approved or cleared for usage by primary care providers.
Fountains of Wayne, and a hospitalist’s first day, remembered
Like many in the health care field, I have found it hard to watch the news over these past couple of months when it seems that almost every story is about COVID-19 or its repercussions. Luckily, I have two young daughters who “encourage” me to listen to the Frozen 2 soundtrack instead of putting on the evening news when I get home from work. Still, news manages to seep through my defenses. As I scrolled through some headlines recently, I learned of the death of musician Adam Schlesinger from COVID-19. He wasn’t a household name, but his death still hit me in unexpected ways.
I started internship in late June 2005, in a city (Portland, Ore.) about as different from my previous home (Dallas) as any two places can possibly be. I think the day before internship started still ranks as the most nervous of my life. I’m not sure how I slept at all that night, but somehow I did and arrived at the Portland Veterans Affairs Hospital the following morning to start my new career.
And then … nothing happened. Early on that first day, the electronic medical records crashed, and no patients were admitted during our time on “short call.” My upper level resident took care of the one or two established patients on the team (both discharged), so I ended the day with records that would not be broken during the remainder of my residency: 0 notes written, 0 patients seen. Perhaps the most successful first day that any intern, anywhere has ever had, although it prepared me quite poorly for all the subsequent days.
Since I had some time on my hands, I made the 20-minute walk to one of my new hometown’s record stores where Fountains of Wayne (FOW) was playing an acoustic in-store set. Their album from a few years prior, “Welcome Interstate Managers,” was in heavy rotation when I made the drive from Dallas to Portland. It was (and is) a great album for long drives – melodic, catchy, and (mostly) up-tempo. Adam and the band’s singer, Chris Collingwood, played several songs that night on the store’s stage. Then they headed out to the next city, and I headed back home and on to many far-busier days of residency.
We would cross paths again a decade later. I moved back to Texas and became a hospitalist. It turns out that, if you have enough hospitalists of a certain age and if enough of those hospitalists have unearned confidence in their musical ability, then a covers band will undoubtedly be formed. And so, it happened here in San Antonio. We were not selective in our song choices – we played songs from every decade of the last 50 years, bands as popular as the Beatles and as indie as the Rentals. And we played some FOW.
Our band (which will go nameless here so that our YouTube recordings are more difficult to find) played a grand total of one gig during our years of intermittent practicing. That one gig was my wedding rehearsal dinner and the penultimate song we played was “Stacy’s Mom,” which is notable for being both FOW’s biggest hit and a completely inappropriate song to play at a wedding rehearsal dinner. The crowd was probably around the same size as the one that had seen Adam and Chris play in Portland 10 years prior. I don’t think the applause we received was quite as genuine or deserved, though.
After Adam and Chris played their gig, there was an autograph session and I took home a signed poster. Last year, I decided to take it out of storage and hang it in my office. The date of the show and the first day of my physician career, a date now nearly 15 years ago, is written in psychedelic typography at the bottom. The store that I went to that day is no longer there, a victim of progress like so many other record stores across the country. Another location of the same store is still open in Portland. I hope that it and all the other small book and music stores across the country can survive this current crisis, but I know that many will not.
So, here’s to you Adam, and to all the others who have lost their lives to this terrible illness. As a small token of remembrance, I’ll be playing some Fountains of Wayne on the drive home tonight. It’s not quite the same as playing it on a cross-country drive, but hopefully, we will all be able to do that again soon.
Dr. Sehgal is a clinical associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System and UT-Health San Antonio. He is a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Like many in the health care field, I have found it hard to watch the news over these past couple of months when it seems that almost every story is about COVID-19 or its repercussions. Luckily, I have two young daughters who “encourage” me to listen to the Frozen 2 soundtrack instead of putting on the evening news when I get home from work. Still, news manages to seep through my defenses. As I scrolled through some headlines recently, I learned of the death of musician Adam Schlesinger from COVID-19. He wasn’t a household name, but his death still hit me in unexpected ways.
I started internship in late June 2005, in a city (Portland, Ore.) about as different from my previous home (Dallas) as any two places can possibly be. I think the day before internship started still ranks as the most nervous of my life. I’m not sure how I slept at all that night, but somehow I did and arrived at the Portland Veterans Affairs Hospital the following morning to start my new career.
And then … nothing happened. Early on that first day, the electronic medical records crashed, and no patients were admitted during our time on “short call.” My upper level resident took care of the one or two established patients on the team (both discharged), so I ended the day with records that would not be broken during the remainder of my residency: 0 notes written, 0 patients seen. Perhaps the most successful first day that any intern, anywhere has ever had, although it prepared me quite poorly for all the subsequent days.
Since I had some time on my hands, I made the 20-minute walk to one of my new hometown’s record stores where Fountains of Wayne (FOW) was playing an acoustic in-store set. Their album from a few years prior, “Welcome Interstate Managers,” was in heavy rotation when I made the drive from Dallas to Portland. It was (and is) a great album for long drives – melodic, catchy, and (mostly) up-tempo. Adam and the band’s singer, Chris Collingwood, played several songs that night on the store’s stage. Then they headed out to the next city, and I headed back home and on to many far-busier days of residency.
We would cross paths again a decade later. I moved back to Texas and became a hospitalist. It turns out that, if you have enough hospitalists of a certain age and if enough of those hospitalists have unearned confidence in their musical ability, then a covers band will undoubtedly be formed. And so, it happened here in San Antonio. We were not selective in our song choices – we played songs from every decade of the last 50 years, bands as popular as the Beatles and as indie as the Rentals. And we played some FOW.
Our band (which will go nameless here so that our YouTube recordings are more difficult to find) played a grand total of one gig during our years of intermittent practicing. That one gig was my wedding rehearsal dinner and the penultimate song we played was “Stacy’s Mom,” which is notable for being both FOW’s biggest hit and a completely inappropriate song to play at a wedding rehearsal dinner. The crowd was probably around the same size as the one that had seen Adam and Chris play in Portland 10 years prior. I don’t think the applause we received was quite as genuine or deserved, though.
After Adam and Chris played their gig, there was an autograph session and I took home a signed poster. Last year, I decided to take it out of storage and hang it in my office. The date of the show and the first day of my physician career, a date now nearly 15 years ago, is written in psychedelic typography at the bottom. The store that I went to that day is no longer there, a victim of progress like so many other record stores across the country. Another location of the same store is still open in Portland. I hope that it and all the other small book and music stores across the country can survive this current crisis, but I know that many will not.
So, here’s to you Adam, and to all the others who have lost their lives to this terrible illness. As a small token of remembrance, I’ll be playing some Fountains of Wayne on the drive home tonight. It’s not quite the same as playing it on a cross-country drive, but hopefully, we will all be able to do that again soon.
Dr. Sehgal is a clinical associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System and UT-Health San Antonio. He is a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Like many in the health care field, I have found it hard to watch the news over these past couple of months when it seems that almost every story is about COVID-19 or its repercussions. Luckily, I have two young daughters who “encourage” me to listen to the Frozen 2 soundtrack instead of putting on the evening news when I get home from work. Still, news manages to seep through my defenses. As I scrolled through some headlines recently, I learned of the death of musician Adam Schlesinger from COVID-19. He wasn’t a household name, but his death still hit me in unexpected ways.
I started internship in late June 2005, in a city (Portland, Ore.) about as different from my previous home (Dallas) as any two places can possibly be. I think the day before internship started still ranks as the most nervous of my life. I’m not sure how I slept at all that night, but somehow I did and arrived at the Portland Veterans Affairs Hospital the following morning to start my new career.
And then … nothing happened. Early on that first day, the electronic medical records crashed, and no patients were admitted during our time on “short call.” My upper level resident took care of the one or two established patients on the team (both discharged), so I ended the day with records that would not be broken during the remainder of my residency: 0 notes written, 0 patients seen. Perhaps the most successful first day that any intern, anywhere has ever had, although it prepared me quite poorly for all the subsequent days.
Since I had some time on my hands, I made the 20-minute walk to one of my new hometown’s record stores where Fountains of Wayne (FOW) was playing an acoustic in-store set. Their album from a few years prior, “Welcome Interstate Managers,” was in heavy rotation when I made the drive from Dallas to Portland. It was (and is) a great album for long drives – melodic, catchy, and (mostly) up-tempo. Adam and the band’s singer, Chris Collingwood, played several songs that night on the store’s stage. Then they headed out to the next city, and I headed back home and on to many far-busier days of residency.
We would cross paths again a decade later. I moved back to Texas and became a hospitalist. It turns out that, if you have enough hospitalists of a certain age and if enough of those hospitalists have unearned confidence in their musical ability, then a covers band will undoubtedly be formed. And so, it happened here in San Antonio. We were not selective in our song choices – we played songs from every decade of the last 50 years, bands as popular as the Beatles and as indie as the Rentals. And we played some FOW.
Our band (which will go nameless here so that our YouTube recordings are more difficult to find) played a grand total of one gig during our years of intermittent practicing. That one gig was my wedding rehearsal dinner and the penultimate song we played was “Stacy’s Mom,” which is notable for being both FOW’s biggest hit and a completely inappropriate song to play at a wedding rehearsal dinner. The crowd was probably around the same size as the one that had seen Adam and Chris play in Portland 10 years prior. I don’t think the applause we received was quite as genuine or deserved, though.
After Adam and Chris played their gig, there was an autograph session and I took home a signed poster. Last year, I decided to take it out of storage and hang it in my office. The date of the show and the first day of my physician career, a date now nearly 15 years ago, is written in psychedelic typography at the bottom. The store that I went to that day is no longer there, a victim of progress like so many other record stores across the country. Another location of the same store is still open in Portland. I hope that it and all the other small book and music stores across the country can survive this current crisis, but I know that many will not.
So, here’s to you Adam, and to all the others who have lost their lives to this terrible illness. As a small token of remembrance, I’ll be playing some Fountains of Wayne on the drive home tonight. It’s not quite the same as playing it on a cross-country drive, but hopefully, we will all be able to do that again soon.
Dr. Sehgal is a clinical associate professor of medicine in the division of general and hospital medicine at the South Texas Veterans Health Care System and UT-Health San Antonio. He is a member of the editorial advisory board for The Hospitalist.
Doctor with a mask: Enhancing communication and empathy
Delivering a goodbye monologue to an elderly patient, I said: “Tomorrow, my colleague Dr. XYZ, who is an excellent physician, will be here in my place, and I will leave a detailed sign out for them.” I was on the last day of a 7-day-long block on hospital medicine service. Typically, when I say goodbye, some patients respond “thank you, enjoy your time,” some don’t care, and some show disappointment at the transition. This patient became uneasy, choking back tears, and said: “But, I don’t want a new doctor. You know me well. ... They don’t even allow my family in the hospital.”
That expression of anxiety, of having to build rapport with a new provider, concerns about continuity of care, and missing support of family members were not alien to me. As I instinctively took a step toward him to offer a comforting hug, an unsolicited voice in my head said, “social distancing.” I steered back, handing him a box of tissues. I continued: “You have come a long way, and things are looking good from here,” providing more details before I left the room. There was a change in my practice that week. I didn’t shake hands with my patients; I didn’t sit on any unassigned chair; I had no family members in the room asking me questions or supporting my patients. I was trying to show empathy or a smile behind a mask and protective eyewear. The business card with photograph had become more critical than ever for patients to “see” their doctor.
Moving from room to room and examining patients, it felt like the coronavirus was changing the practice of medicine beyond concerns of virus transmission, losing a patient, or putting in extra hours. I realized I was missing so-called “nonverbal communication” amid social distancing: facial expressions, social touch, and the support of family or friends to motivate or destress patients. With no visitors and curbed health care staff entries into patient’s rooms, social distancing was amounting to social isolation. My protective gear and social distancing seemed to be reducing my perceived empathy with patients, and the ability to build a good patient-physician relationship.
Amid alarms, beeps, and buzzes, patients were not only missing their families but also the familiar faces of their physicians. I needed to raise my game while embracing the “new normal” of health care. Cut to the next 13 patients: I paid more attention to voice, tone, and posture. I called patient families from the bedside instead of the office. I translated my emotions with words, loud and clear, replacing “your renal function looks better” (said without a smile) with “I am happy to see your renal function better.”
Through years of practice, I felt prepared to deal with feelings of denial, grief, anxiety, and much more, but the emotions arising as a result of this pandemic were unique. “I knew my mother was old, and this day would come,” said one of the inconsolable family members of a critically ill patient. “However, I wished to be at her side that day, not like this.” I spend my days listening to patient and family concerns about unemployment with quarantine, fears of spreading the disease to loved ones, and the possibility of medications not working.
After a long day, I went back to that first elderly patient to see if he was comfortable with the transition of care. I did a video conference with his daughter, and repeated my goodbyes. The patient smiled and said: “Doc, you deserve a break.” That day I learned about the challenges of good clinical rounding in coronavirus times, and how to overcome them. For “millennial” physicians, it is our first pandemic, and we are learning from it every day.
Driving home through empty streets, I concluded that my answers to the clinical questions asked by patients and families lean heavily on ever-changing data, and the treatments offered have yet to prove their mettle. As a result, I will continue to focus as much on the time-tested fundamentals of clinical practice: communication and empathy. I cannot allow the social distancing and the mask to hide my compassion, or take away from patient satisfaction. Shifting gears, I turned on my car radio, using music to reset my mind before attending to my now-homeschooling kids.
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Wong CK et al. Effect of facemasks on empathy and relational continuity: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:200.
2. Little P et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly nonverbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65(635):e351-6.
3. Varghese A. A doctor’s touch. TEDGlobal 2011. 2011 Jul. https://www.ted.com/talks/abraham_verghese_a_doctor_s_touch?language=en
Delivering a goodbye monologue to an elderly patient, I said: “Tomorrow, my colleague Dr. XYZ, who is an excellent physician, will be here in my place, and I will leave a detailed sign out for them.” I was on the last day of a 7-day-long block on hospital medicine service. Typically, when I say goodbye, some patients respond “thank you, enjoy your time,” some don’t care, and some show disappointment at the transition. This patient became uneasy, choking back tears, and said: “But, I don’t want a new doctor. You know me well. ... They don’t even allow my family in the hospital.”
That expression of anxiety, of having to build rapport with a new provider, concerns about continuity of care, and missing support of family members were not alien to me. As I instinctively took a step toward him to offer a comforting hug, an unsolicited voice in my head said, “social distancing.” I steered back, handing him a box of tissues. I continued: “You have come a long way, and things are looking good from here,” providing more details before I left the room. There was a change in my practice that week. I didn’t shake hands with my patients; I didn’t sit on any unassigned chair; I had no family members in the room asking me questions or supporting my patients. I was trying to show empathy or a smile behind a mask and protective eyewear. The business card with photograph had become more critical than ever for patients to “see” their doctor.
Moving from room to room and examining patients, it felt like the coronavirus was changing the practice of medicine beyond concerns of virus transmission, losing a patient, or putting in extra hours. I realized I was missing so-called “nonverbal communication” amid social distancing: facial expressions, social touch, and the support of family or friends to motivate or destress patients. With no visitors and curbed health care staff entries into patient’s rooms, social distancing was amounting to social isolation. My protective gear and social distancing seemed to be reducing my perceived empathy with patients, and the ability to build a good patient-physician relationship.
Amid alarms, beeps, and buzzes, patients were not only missing their families but also the familiar faces of their physicians. I needed to raise my game while embracing the “new normal” of health care. Cut to the next 13 patients: I paid more attention to voice, tone, and posture. I called patient families from the bedside instead of the office. I translated my emotions with words, loud and clear, replacing “your renal function looks better” (said without a smile) with “I am happy to see your renal function better.”
Through years of practice, I felt prepared to deal with feelings of denial, grief, anxiety, and much more, but the emotions arising as a result of this pandemic were unique. “I knew my mother was old, and this day would come,” said one of the inconsolable family members of a critically ill patient. “However, I wished to be at her side that day, not like this.” I spend my days listening to patient and family concerns about unemployment with quarantine, fears of spreading the disease to loved ones, and the possibility of medications not working.
After a long day, I went back to that first elderly patient to see if he was comfortable with the transition of care. I did a video conference with his daughter, and repeated my goodbyes. The patient smiled and said: “Doc, you deserve a break.” That day I learned about the challenges of good clinical rounding in coronavirus times, and how to overcome them. For “millennial” physicians, it is our first pandemic, and we are learning from it every day.
Driving home through empty streets, I concluded that my answers to the clinical questions asked by patients and families lean heavily on ever-changing data, and the treatments offered have yet to prove their mettle. As a result, I will continue to focus as much on the time-tested fundamentals of clinical practice: communication and empathy. I cannot allow the social distancing and the mask to hide my compassion, or take away from patient satisfaction. Shifting gears, I turned on my car radio, using music to reset my mind before attending to my now-homeschooling kids.
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Wong CK et al. Effect of facemasks on empathy and relational continuity: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:200.
2. Little P et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly nonverbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65(635):e351-6.
3. Varghese A. A doctor’s touch. TEDGlobal 2011. 2011 Jul. https://www.ted.com/talks/abraham_verghese_a_doctor_s_touch?language=en
Delivering a goodbye monologue to an elderly patient, I said: “Tomorrow, my colleague Dr. XYZ, who is an excellent physician, will be here in my place, and I will leave a detailed sign out for them.” I was on the last day of a 7-day-long block on hospital medicine service. Typically, when I say goodbye, some patients respond “thank you, enjoy your time,” some don’t care, and some show disappointment at the transition. This patient became uneasy, choking back tears, and said: “But, I don’t want a new doctor. You know me well. ... They don’t even allow my family in the hospital.”
That expression of anxiety, of having to build rapport with a new provider, concerns about continuity of care, and missing support of family members were not alien to me. As I instinctively took a step toward him to offer a comforting hug, an unsolicited voice in my head said, “social distancing.” I steered back, handing him a box of tissues. I continued: “You have come a long way, and things are looking good from here,” providing more details before I left the room. There was a change in my practice that week. I didn’t shake hands with my patients; I didn’t sit on any unassigned chair; I had no family members in the room asking me questions or supporting my patients. I was trying to show empathy or a smile behind a mask and protective eyewear. The business card with photograph had become more critical than ever for patients to “see” their doctor.
Moving from room to room and examining patients, it felt like the coronavirus was changing the practice of medicine beyond concerns of virus transmission, losing a patient, or putting in extra hours. I realized I was missing so-called “nonverbal communication” amid social distancing: facial expressions, social touch, and the support of family or friends to motivate or destress patients. With no visitors and curbed health care staff entries into patient’s rooms, social distancing was amounting to social isolation. My protective gear and social distancing seemed to be reducing my perceived empathy with patients, and the ability to build a good patient-physician relationship.
Amid alarms, beeps, and buzzes, patients were not only missing their families but also the familiar faces of their physicians. I needed to raise my game while embracing the “new normal” of health care. Cut to the next 13 patients: I paid more attention to voice, tone, and posture. I called patient families from the bedside instead of the office. I translated my emotions with words, loud and clear, replacing “your renal function looks better” (said without a smile) with “I am happy to see your renal function better.”
Through years of practice, I felt prepared to deal with feelings of denial, grief, anxiety, and much more, but the emotions arising as a result of this pandemic were unique. “I knew my mother was old, and this day would come,” said one of the inconsolable family members of a critically ill patient. “However, I wished to be at her side that day, not like this.” I spend my days listening to patient and family concerns about unemployment with quarantine, fears of spreading the disease to loved ones, and the possibility of medications not working.
After a long day, I went back to that first elderly patient to see if he was comfortable with the transition of care. I did a video conference with his daughter, and repeated my goodbyes. The patient smiled and said: “Doc, you deserve a break.” That day I learned about the challenges of good clinical rounding in coronavirus times, and how to overcome them. For “millennial” physicians, it is our first pandemic, and we are learning from it every day.
Driving home through empty streets, I concluded that my answers to the clinical questions asked by patients and families lean heavily on ever-changing data, and the treatments offered have yet to prove their mettle. As a result, I will continue to focus as much on the time-tested fundamentals of clinical practice: communication and empathy. I cannot allow the social distancing and the mask to hide my compassion, or take away from patient satisfaction. Shifting gears, I turned on my car radio, using music to reset my mind before attending to my now-homeschooling kids.
Dr. Saigal is a hospitalist and clinical assistant professor of medicine in the division of hospital medicine at the Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center, Columbus.
References
1. Wong CK et al. Effect of facemasks on empathy and relational continuity: A randomised controlled trial in primary care. BMC Fam Pract. 2013;14:200.
2. Little P et al. Randomised controlled trial of a brief intervention targeting predominantly nonverbal communication in general practice consultations. Br J Gen Pract. 2015;65(635):e351-6.
3. Varghese A. A doctor’s touch. TEDGlobal 2011. 2011 Jul. https://www.ted.com/talks/abraham_verghese_a_doctor_s_touch?language=en
Case reports illustrate heterogeneity of skin manifestations in COVID patients
Two infection.
It is not yet clear from these or other case reports which, if any, skin eruptions accompanying COVID-19 infections are caused by the virus, but the authors of the editorial, led by Lauren M. Madigan, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, urged dermatologists to lead efforts to find out.
“To fully characterize skin manifestations, it may be necessary for dermatologists to evaluate these patients directly; comprehensive evaluation could reveal important morphologic clues, such as the subtle purpuric nature of skin lesions or the characteristic mucosal or ophthalmologic features of COVID-19,” the authors of the editorial stated.
So far, the patterns of skin symptoms, which have been identified in up to 20% of COVID-19–infected patients in some series, have been heterogeneous as demonstrated in the two published case reports.
In one case, a papulosquamous and erythematous periumbilical patch that appeared on the trunk in an elderly patient 1 day after hospital admission for acute respiratory distress rapidly evolved into a digitate papulosquamous eruption involving the upper arms, shoulder, and back. It was described as “clinically reminiscent” of pityriasis rosea by the authors, from the divisions of dermatology and venereology, pathology, intensive care, and the virology laboratory, of the Hôpital Cochin, Paris.
In the other, pruritic erythematous macules, papules, and petechiae affecting the buttocks, popliteal fossae, anterior thighs, and lower abdomen appeared 3 days after the onset of fever in a 48-year-old man hospitalized in Madrid. A biopsy demonstrated a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with red cell extravasation and focal papillary edema, “along with focal parakeratosis and isolated dyskeratotic cells,” according to the authors of this report, from the department of dermatology at Ramon y Cajal University, Madrid.
It was unclear whether COVID-19 directly caused either skin eruption. In the patient with the digitate papulosquamous eruption, no virus could be isolated from the skin. Based on high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that the rash might have been secondary to an immune response. The rash resolved within a week, but the patient subsequently died of the infection.
In the second case, the petechial lesions, which developed before any treatment was initiated, were said to resemble those associated with other viruses, such as parvovirus B19. This led the investigators to speculate that SARS-CoV-2 “could affect the skin in a similar way,” even though other potential etiologies could not be excluded. Treated with a topical steroid and an oral antihistamine, the skin lesions resolved after 5 days. This patient was discharged after recovering from the respiratory illness after 12 days.
Like previously reported cutaneous eruptions associated with COVID-19 infection, these cases “raise more questions than they provide answers,” wrote the authors of the editorial, but the limited information currently available was the basis for encouraging dermatologists to get involved.
To participate, dermatologists need not necessarily be affiliated with an academic center, according to one of the editorial coauthors, Kanade Shinkai, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She noted that any health professional is invited to submit cases of COVID-19–associated dermatoses to a registry set up by the American Academy of Dermatology.
It is hoped that cases captured in this registry will create sufficient data to allow clinically relevant patterns and etiologies to be characterized.
The need for data is clear to those on the front lines. Kirsten Lo Sicco, MD, associate director of the skin and cancer unit at New York University, reported that her center is already set up to collect data systematically. “At NYU, we are currently working on standardizing laboratory and histopathology work up for COVID-19 patients who present with various skin eruptions.”
The goal, she added, is “to better determine COVID-19 pathophysiology, systemic associations, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutics.”
“Presumably, many of the eruptions seen in the setting of COVID-19 infection are related,” Dr. Lo Sicco explained in an interview. However, skin complications of infection “may overlap with or be a result of other etiologies as well.”
While better testing for COVID-19 and more lesion biopsies will play a critical role in differentiating etiologies, “we must not overcall COVID-19–related skin eruptions and potentially overlook other diagnoses,” Dr. Lo Sicco said.
In recounting some challenges from the NYU experience so far, Dr. Lo Sicco described the difficulty of differentiating COVID-19–related skin eruptions from skin eruptions caused by treatments, such as antibiotics and antivirals, when the presentation is delayed.
“This is where collaboration with our dermatopathologists becomes important. Drug eruptions, viral exanthems, urticarial eruptions, vasculopathy, and vasculitis can all be differentiated on dermpath,” she said.
One early obstacle to the skin biopsies essential for these types of studies was the limited supply of personal protective equipment at many centers, including hospitals in New York. Biopsies could not be safely performed if supplies of masks and gowns were limited.
Recent evidence suggests that some of the more common morphologies, such as purpuric eruptions, livedo reticularis, and retiform purpura, are linked to the vasculopathy associated with COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Lo Sicco, but this invites a new set of questions.
One is whether vasculopathies can be prevented with prophylactic anticoagulation. Many hospitalized COVID-19 patients are already receiving therapeutic anticoagulation, but Dr. Lo Sicco questioned whether prophylactic anticoagulation might improve prognosis for outpatients, such as those discharged or those never hospitalized. This is a strategy now being investigated.
Ultimately, she agreed with the thrust of the JAMA Dermatology editorial.
“Dermatologists are vital to determine if various morphologies, such as urticarial, vesicular, purpuric, or papulosquamous lesions, have any specific systemic implications or relate to differences in patient outcomes,” she said.
These are exactly the types of issues being actively investigated at her center.
Neither the authors of the case reports nor of the editorial reported any conflicts of interest.
SOURCEs: Madigan LM et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1438; Diaz-Guimaraens B et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1741; Sanchez A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1704.
Two infection.
It is not yet clear from these or other case reports which, if any, skin eruptions accompanying COVID-19 infections are caused by the virus, but the authors of the editorial, led by Lauren M. Madigan, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, urged dermatologists to lead efforts to find out.
“To fully characterize skin manifestations, it may be necessary for dermatologists to evaluate these patients directly; comprehensive evaluation could reveal important morphologic clues, such as the subtle purpuric nature of skin lesions or the characteristic mucosal or ophthalmologic features of COVID-19,” the authors of the editorial stated.
So far, the patterns of skin symptoms, which have been identified in up to 20% of COVID-19–infected patients in some series, have been heterogeneous as demonstrated in the two published case reports.
In one case, a papulosquamous and erythematous periumbilical patch that appeared on the trunk in an elderly patient 1 day after hospital admission for acute respiratory distress rapidly evolved into a digitate papulosquamous eruption involving the upper arms, shoulder, and back. It was described as “clinically reminiscent” of pityriasis rosea by the authors, from the divisions of dermatology and venereology, pathology, intensive care, and the virology laboratory, of the Hôpital Cochin, Paris.
In the other, pruritic erythematous macules, papules, and petechiae affecting the buttocks, popliteal fossae, anterior thighs, and lower abdomen appeared 3 days after the onset of fever in a 48-year-old man hospitalized in Madrid. A biopsy demonstrated a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with red cell extravasation and focal papillary edema, “along with focal parakeratosis and isolated dyskeratotic cells,” according to the authors of this report, from the department of dermatology at Ramon y Cajal University, Madrid.
It was unclear whether COVID-19 directly caused either skin eruption. In the patient with the digitate papulosquamous eruption, no virus could be isolated from the skin. Based on high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that the rash might have been secondary to an immune response. The rash resolved within a week, but the patient subsequently died of the infection.
In the second case, the petechial lesions, which developed before any treatment was initiated, were said to resemble those associated with other viruses, such as parvovirus B19. This led the investigators to speculate that SARS-CoV-2 “could affect the skin in a similar way,” even though other potential etiologies could not be excluded. Treated with a topical steroid and an oral antihistamine, the skin lesions resolved after 5 days. This patient was discharged after recovering from the respiratory illness after 12 days.
Like previously reported cutaneous eruptions associated with COVID-19 infection, these cases “raise more questions than they provide answers,” wrote the authors of the editorial, but the limited information currently available was the basis for encouraging dermatologists to get involved.
To participate, dermatologists need not necessarily be affiliated with an academic center, according to one of the editorial coauthors, Kanade Shinkai, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She noted that any health professional is invited to submit cases of COVID-19–associated dermatoses to a registry set up by the American Academy of Dermatology.
It is hoped that cases captured in this registry will create sufficient data to allow clinically relevant patterns and etiologies to be characterized.
The need for data is clear to those on the front lines. Kirsten Lo Sicco, MD, associate director of the skin and cancer unit at New York University, reported that her center is already set up to collect data systematically. “At NYU, we are currently working on standardizing laboratory and histopathology work up for COVID-19 patients who present with various skin eruptions.”
The goal, she added, is “to better determine COVID-19 pathophysiology, systemic associations, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutics.”
“Presumably, many of the eruptions seen in the setting of COVID-19 infection are related,” Dr. Lo Sicco explained in an interview. However, skin complications of infection “may overlap with or be a result of other etiologies as well.”
While better testing for COVID-19 and more lesion biopsies will play a critical role in differentiating etiologies, “we must not overcall COVID-19–related skin eruptions and potentially overlook other diagnoses,” Dr. Lo Sicco said.
In recounting some challenges from the NYU experience so far, Dr. Lo Sicco described the difficulty of differentiating COVID-19–related skin eruptions from skin eruptions caused by treatments, such as antibiotics and antivirals, when the presentation is delayed.
“This is where collaboration with our dermatopathologists becomes important. Drug eruptions, viral exanthems, urticarial eruptions, vasculopathy, and vasculitis can all be differentiated on dermpath,” she said.
One early obstacle to the skin biopsies essential for these types of studies was the limited supply of personal protective equipment at many centers, including hospitals in New York. Biopsies could not be safely performed if supplies of masks and gowns were limited.
Recent evidence suggests that some of the more common morphologies, such as purpuric eruptions, livedo reticularis, and retiform purpura, are linked to the vasculopathy associated with COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Lo Sicco, but this invites a new set of questions.
One is whether vasculopathies can be prevented with prophylactic anticoagulation. Many hospitalized COVID-19 patients are already receiving therapeutic anticoagulation, but Dr. Lo Sicco questioned whether prophylactic anticoagulation might improve prognosis for outpatients, such as those discharged or those never hospitalized. This is a strategy now being investigated.
Ultimately, she agreed with the thrust of the JAMA Dermatology editorial.
“Dermatologists are vital to determine if various morphologies, such as urticarial, vesicular, purpuric, or papulosquamous lesions, have any specific systemic implications or relate to differences in patient outcomes,” she said.
These are exactly the types of issues being actively investigated at her center.
Neither the authors of the case reports nor of the editorial reported any conflicts of interest.
SOURCEs: Madigan LM et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1438; Diaz-Guimaraens B et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1741; Sanchez A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1704.
Two infection.
It is not yet clear from these or other case reports which, if any, skin eruptions accompanying COVID-19 infections are caused by the virus, but the authors of the editorial, led by Lauren M. Madigan, MD, of the department of dermatology at the University of Utah, Salt Lake City, urged dermatologists to lead efforts to find out.
“To fully characterize skin manifestations, it may be necessary for dermatologists to evaluate these patients directly; comprehensive evaluation could reveal important morphologic clues, such as the subtle purpuric nature of skin lesions or the characteristic mucosal or ophthalmologic features of COVID-19,” the authors of the editorial stated.
So far, the patterns of skin symptoms, which have been identified in up to 20% of COVID-19–infected patients in some series, have been heterogeneous as demonstrated in the two published case reports.
In one case, a papulosquamous and erythematous periumbilical patch that appeared on the trunk in an elderly patient 1 day after hospital admission for acute respiratory distress rapidly evolved into a digitate papulosquamous eruption involving the upper arms, shoulder, and back. It was described as “clinically reminiscent” of pityriasis rosea by the authors, from the divisions of dermatology and venereology, pathology, intensive care, and the virology laboratory, of the Hôpital Cochin, Paris.
In the other, pruritic erythematous macules, papules, and petechiae affecting the buttocks, popliteal fossae, anterior thighs, and lower abdomen appeared 3 days after the onset of fever in a 48-year-old man hospitalized in Madrid. A biopsy demonstrated a superficial perivascular lymphocytic infiltrate with red cell extravasation and focal papillary edema, “along with focal parakeratosis and isolated dyskeratotic cells,” according to the authors of this report, from the department of dermatology at Ramon y Cajal University, Madrid.
It was unclear whether COVID-19 directly caused either skin eruption. In the patient with the digitate papulosquamous eruption, no virus could be isolated from the skin. Based on high levels of proinflammatory cytokines, it was hypothesized that the rash might have been secondary to an immune response. The rash resolved within a week, but the patient subsequently died of the infection.
In the second case, the petechial lesions, which developed before any treatment was initiated, were said to resemble those associated with other viruses, such as parvovirus B19. This led the investigators to speculate that SARS-CoV-2 “could affect the skin in a similar way,” even though other potential etiologies could not be excluded. Treated with a topical steroid and an oral antihistamine, the skin lesions resolved after 5 days. This patient was discharged after recovering from the respiratory illness after 12 days.
Like previously reported cutaneous eruptions associated with COVID-19 infection, these cases “raise more questions than they provide answers,” wrote the authors of the editorial, but the limited information currently available was the basis for encouraging dermatologists to get involved.
To participate, dermatologists need not necessarily be affiliated with an academic center, according to one of the editorial coauthors, Kanade Shinkai, MD, PhD, professor of dermatology at the University of California, San Francisco. She noted that any health professional is invited to submit cases of COVID-19–associated dermatoses to a registry set up by the American Academy of Dermatology.
It is hoped that cases captured in this registry will create sufficient data to allow clinically relevant patterns and etiologies to be characterized.
The need for data is clear to those on the front lines. Kirsten Lo Sicco, MD, associate director of the skin and cancer unit at New York University, reported that her center is already set up to collect data systematically. “At NYU, we are currently working on standardizing laboratory and histopathology work up for COVID-19 patients who present with various skin eruptions.”
The goal, she added, is “to better determine COVID-19 pathophysiology, systemic associations, patient outcomes, and potential therapeutics.”
“Presumably, many of the eruptions seen in the setting of COVID-19 infection are related,” Dr. Lo Sicco explained in an interview. However, skin complications of infection “may overlap with or be a result of other etiologies as well.”
While better testing for COVID-19 and more lesion biopsies will play a critical role in differentiating etiologies, “we must not overcall COVID-19–related skin eruptions and potentially overlook other diagnoses,” Dr. Lo Sicco said.
In recounting some challenges from the NYU experience so far, Dr. Lo Sicco described the difficulty of differentiating COVID-19–related skin eruptions from skin eruptions caused by treatments, such as antibiotics and antivirals, when the presentation is delayed.
“This is where collaboration with our dermatopathologists becomes important. Drug eruptions, viral exanthems, urticarial eruptions, vasculopathy, and vasculitis can all be differentiated on dermpath,” she said.
One early obstacle to the skin biopsies essential for these types of studies was the limited supply of personal protective equipment at many centers, including hospitals in New York. Biopsies could not be safely performed if supplies of masks and gowns were limited.
Recent evidence suggests that some of the more common morphologies, such as purpuric eruptions, livedo reticularis, and retiform purpura, are linked to the vasculopathy associated with COVID-19 infection, according to Dr. Lo Sicco, but this invites a new set of questions.
One is whether vasculopathies can be prevented with prophylactic anticoagulation. Many hospitalized COVID-19 patients are already receiving therapeutic anticoagulation, but Dr. Lo Sicco questioned whether prophylactic anticoagulation might improve prognosis for outpatients, such as those discharged or those never hospitalized. This is a strategy now being investigated.
Ultimately, she agreed with the thrust of the JAMA Dermatology editorial.
“Dermatologists are vital to determine if various morphologies, such as urticarial, vesicular, purpuric, or papulosquamous lesions, have any specific systemic implications or relate to differences in patient outcomes,” she said.
These are exactly the types of issues being actively investigated at her center.
Neither the authors of the case reports nor of the editorial reported any conflicts of interest.
SOURCEs: Madigan LM et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1438; Diaz-Guimaraens B et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1741; Sanchez A et al. JAMA Dermatol. 2020 Apr 30. doi: 10.1001/jamadermatol.2020.1704.











