User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
ACEIs, ARBs safe to continue in COVID-19: Trial published
The BRACE-CORONA trial, the first randomized trial to address the question of whether patients with COVID-19 should continue to take ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) – has now been published.
The study, which was conducted in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who were taking ACEIs or ARBs before hospitalization, showed no significant difference in the mean number of days alive and out of the hospital for those assigned to discontinue versus those assigned to continue these medications.
There were, however, hints that continuing to take ACEIs or ARBs may be beneficial for patients with more severe COVID-19.
The study was first presented at last year’s European Society of Cardiology Congress and was reported by this news organization at that time. The study was published online in JAMA on Jan. 19, 2021.
“These findings do not support routinely discontinuing ACEIs or ARBs among patients hospitalized with mild to moderate COVID-19 if there is an indication for treatment,” the authors concluded.
Led by Renato D. Lopes, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., the researchers explained that there has been conflicting speculation about the effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors on the course of COVID-19.
On the one hand, observations from animal models suggest that ACEIs and ARBs up-regulate the expression of ACE2, a receptor involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection of host target cells. This led to suggestions that these medications may enhance viral binding and cell entry. Conversely, RAAS inhibitors could benefit patients with COVID-19 through effects on angiotensin II expression and subsequent increases in angiotensin 1-7 and 1-9, which have vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory effects that might attenuate lung injury.
The BRACE-CORONA trial included 659 patients hospitalized in Brazil with mild to moderate COVID-19 who were taking ACEIs or ARBs prior to hospitalization. The median age of the patients was 55 years. Of these patients, 57.1% were considered to have mild cases at hospital admission, and 42.9% were considered to have moderate cases.
Results showed no significant difference in the number of days alive and out of the hospital for patients in the discontinuation group (mean, 21.9 days) in comparison with patients in the continuation group (mean, 22.9 days). The mean ratio was 0.95 (95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.01).
There also was no statistically significant difference in deaths (2.7% of the discontinuation group vs. 2.8% for the continuation group); cardiovascular death (0.6% vs. 0.3%), or COVID-19 progression (38.3% vs. 32.3%).
The most common adverse events were respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation (9.6% in the discontinuation group vs. 7.7% in the continuation group), shock requiring vasopressors (8.4% vs. 7.1%), acute MI (7.5% vs. 4.6%), new or worsening heart failure (4.2% vs. 4.9%), and acute kidney failure requiring hemodialysis (3.3% vs. 2.8%).
The authors note that hypertension is an important comorbidity in patients with COVID-19. Recent data suggest that immune dysfunction may contribute to poor outcomes among patients who have COVID-19 and hypertension.
It has been shown that, when use of long-term medications is discontinued during hospitalization, the use of those medications is often not resumed, owing to clinical inertia. Long-term outcomes worsen as a result, the authors reported. In the current study, all patients had hypertension, and more than 50% were obese; both of these comorbidities increase the risk for poor outcomes with COVID-19.
The investigators pointed out that a sensitivity analysis in which site was regarded as a random effect showed a statistically significant finding in favor of the group that continued ACEIs or ARBs. This finding was similar to that of the on-treatment analysis. There were also statistically significant interactions between treatment effect and some subgroups, such as patients with lower oxygen saturation and greater disease severity at hospital admission. For these patients, continuing ACEIs or ARBs may be beneficial.
“The primary analyses with the null results but wide 95% confidence intervals suggest that the study might have been underpowered to detect a statistically significant benefit of continuing ACEIs or ARBs,” they said.
Dr. Lopes has received grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Sanofi and consulting fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Merck, Pfizer, Portola, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The BRACE-CORONA trial, the first randomized trial to address the question of whether patients with COVID-19 should continue to take ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) – has now been published.
The study, which was conducted in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who were taking ACEIs or ARBs before hospitalization, showed no significant difference in the mean number of days alive and out of the hospital for those assigned to discontinue versus those assigned to continue these medications.
There were, however, hints that continuing to take ACEIs or ARBs may be beneficial for patients with more severe COVID-19.
The study was first presented at last year’s European Society of Cardiology Congress and was reported by this news organization at that time. The study was published online in JAMA on Jan. 19, 2021.
“These findings do not support routinely discontinuing ACEIs or ARBs among patients hospitalized with mild to moderate COVID-19 if there is an indication for treatment,” the authors concluded.
Led by Renato D. Lopes, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., the researchers explained that there has been conflicting speculation about the effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors on the course of COVID-19.
On the one hand, observations from animal models suggest that ACEIs and ARBs up-regulate the expression of ACE2, a receptor involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection of host target cells. This led to suggestions that these medications may enhance viral binding and cell entry. Conversely, RAAS inhibitors could benefit patients with COVID-19 through effects on angiotensin II expression and subsequent increases in angiotensin 1-7 and 1-9, which have vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory effects that might attenuate lung injury.
The BRACE-CORONA trial included 659 patients hospitalized in Brazil with mild to moderate COVID-19 who were taking ACEIs or ARBs prior to hospitalization. The median age of the patients was 55 years. Of these patients, 57.1% were considered to have mild cases at hospital admission, and 42.9% were considered to have moderate cases.
Results showed no significant difference in the number of days alive and out of the hospital for patients in the discontinuation group (mean, 21.9 days) in comparison with patients in the continuation group (mean, 22.9 days). The mean ratio was 0.95 (95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.01).
There also was no statistically significant difference in deaths (2.7% of the discontinuation group vs. 2.8% for the continuation group); cardiovascular death (0.6% vs. 0.3%), or COVID-19 progression (38.3% vs. 32.3%).
The most common adverse events were respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation (9.6% in the discontinuation group vs. 7.7% in the continuation group), shock requiring vasopressors (8.4% vs. 7.1%), acute MI (7.5% vs. 4.6%), new or worsening heart failure (4.2% vs. 4.9%), and acute kidney failure requiring hemodialysis (3.3% vs. 2.8%).
The authors note that hypertension is an important comorbidity in patients with COVID-19. Recent data suggest that immune dysfunction may contribute to poor outcomes among patients who have COVID-19 and hypertension.
It has been shown that, when use of long-term medications is discontinued during hospitalization, the use of those medications is often not resumed, owing to clinical inertia. Long-term outcomes worsen as a result, the authors reported. In the current study, all patients had hypertension, and more than 50% were obese; both of these comorbidities increase the risk for poor outcomes with COVID-19.
The investigators pointed out that a sensitivity analysis in which site was regarded as a random effect showed a statistically significant finding in favor of the group that continued ACEIs or ARBs. This finding was similar to that of the on-treatment analysis. There were also statistically significant interactions between treatment effect and some subgroups, such as patients with lower oxygen saturation and greater disease severity at hospital admission. For these patients, continuing ACEIs or ARBs may be beneficial.
“The primary analyses with the null results but wide 95% confidence intervals suggest that the study might have been underpowered to detect a statistically significant benefit of continuing ACEIs or ARBs,” they said.
Dr. Lopes has received grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Sanofi and consulting fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Merck, Pfizer, Portola, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The BRACE-CORONA trial, the first randomized trial to address the question of whether patients with COVID-19 should continue to take ACE inhibitors (ACEIs) or angiotensin-receptor blockers (ARBs) – has now been published.
The study, which was conducted in patients hospitalized with COVID-19 who were taking ACEIs or ARBs before hospitalization, showed no significant difference in the mean number of days alive and out of the hospital for those assigned to discontinue versus those assigned to continue these medications.
There were, however, hints that continuing to take ACEIs or ARBs may be beneficial for patients with more severe COVID-19.
The study was first presented at last year’s European Society of Cardiology Congress and was reported by this news organization at that time. The study was published online in JAMA on Jan. 19, 2021.
“These findings do not support routinely discontinuing ACEIs or ARBs among patients hospitalized with mild to moderate COVID-19 if there is an indication for treatment,” the authors concluded.
Led by Renato D. Lopes, MD, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., the researchers explained that there has been conflicting speculation about the effect of renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) inhibitors on the course of COVID-19.
On the one hand, observations from animal models suggest that ACEIs and ARBs up-regulate the expression of ACE2, a receptor involved in SARS-CoV-2 infection of host target cells. This led to suggestions that these medications may enhance viral binding and cell entry. Conversely, RAAS inhibitors could benefit patients with COVID-19 through effects on angiotensin II expression and subsequent increases in angiotensin 1-7 and 1-9, which have vasodilatory and anti-inflammatory effects that might attenuate lung injury.
The BRACE-CORONA trial included 659 patients hospitalized in Brazil with mild to moderate COVID-19 who were taking ACEIs or ARBs prior to hospitalization. The median age of the patients was 55 years. Of these patients, 57.1% were considered to have mild cases at hospital admission, and 42.9% were considered to have moderate cases.
Results showed no significant difference in the number of days alive and out of the hospital for patients in the discontinuation group (mean, 21.9 days) in comparison with patients in the continuation group (mean, 22.9 days). The mean ratio was 0.95 (95% confidence interval, 0.90-1.01).
There also was no statistically significant difference in deaths (2.7% of the discontinuation group vs. 2.8% for the continuation group); cardiovascular death (0.6% vs. 0.3%), or COVID-19 progression (38.3% vs. 32.3%).
The most common adverse events were respiratory failure requiring invasive mechanical ventilation (9.6% in the discontinuation group vs. 7.7% in the continuation group), shock requiring vasopressors (8.4% vs. 7.1%), acute MI (7.5% vs. 4.6%), new or worsening heart failure (4.2% vs. 4.9%), and acute kidney failure requiring hemodialysis (3.3% vs. 2.8%).
The authors note that hypertension is an important comorbidity in patients with COVID-19. Recent data suggest that immune dysfunction may contribute to poor outcomes among patients who have COVID-19 and hypertension.
It has been shown that, when use of long-term medications is discontinued during hospitalization, the use of those medications is often not resumed, owing to clinical inertia. Long-term outcomes worsen as a result, the authors reported. In the current study, all patients had hypertension, and more than 50% were obese; both of these comorbidities increase the risk for poor outcomes with COVID-19.
The investigators pointed out that a sensitivity analysis in which site was regarded as a random effect showed a statistically significant finding in favor of the group that continued ACEIs or ARBs. This finding was similar to that of the on-treatment analysis. There were also statistically significant interactions between treatment effect and some subgroups, such as patients with lower oxygen saturation and greater disease severity at hospital admission. For these patients, continuing ACEIs or ARBs may be beneficial.
“The primary analyses with the null results but wide 95% confidence intervals suggest that the study might have been underpowered to detect a statistically significant benefit of continuing ACEIs or ARBs,” they said.
Dr. Lopes has received grant support from Bristol-Myers Squibb, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Pfizer, and Sanofi and consulting fees from Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Daiichi Sankyo, GlaxoSmithKline, Medtronic, Merck, Pfizer, Portola, and Sanofi.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Widespread liver disease missed in patients with T2D
Among these calls is a pending statement from the Endocrine Society, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American Gastroenterology Association, and other groups on what the growing appreciation of highly prevalent liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) means for assessing and managing patients. Publication of the statement is expected by spring 2021, said Christos S. Mantzoros, MD, DSc, PhD, chief of endocrinology for the Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System and a representative from the Endocrine Society to the statement-writing panel.
This upcoming “Call to Action” from these groups argues for a “need to collaborate across disciplines, and work together on establishing clinical guidelines, and creating new diagnostics and therapeutics,” said Dr. Mantzoros in an interview.
“Over time, it is becoming clearer that management of NAFLD [nonalcoholic fatty liver disease]/NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] requires a multidisciplinary panel of doctors ranging from primary care practitioners, to endocrinologists, and hepatologists. Given that the nature of the disease crosses scientific discipline boundaries, and that the number of patients is so large (it is estimated that about one in four U.S. adults have NAFLD), not all patients can be treated at the limited number of hepatology centers.
“However, not all stakeholders have fully realized this fact, and no effort had been undertaken so far by any professional society to develop a coordinated approach and clinical care pathway for NAFLD/NASH. The ‘Call to Action’ meeting can be considered as a starting point for such an important effort,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is also a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the human nutrition unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
Dramatic prevalence rates in patients with T2D
Results from two independent epidemiology reports, published in December 2020, documented steatosis (the fatty liver of NAFLD) in 70%-74% of unselected U.S. patients with T2D, advanced liver fibrosis accompanying this disease in 6%-15%, and previously unrecognized cirrhosis in 3%-8%.
One of these reports analyzed 825 patients with T2D included in the National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey of 2017-2018 run by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All these patients, selected to be representative of the overall U.S. adult population with T2D, underwent transient elastography to identify steatosis and fibrosis, the first U.S. National Health Survey to run this type of population-based survey. The results showed an overall steatosis prevalence of 74% with grade 3 steatosis in 58%, advanced liver fibrosis in 15%, and cirrhosis in 8%, reported the team of Italian researchers who analyzed the data .
The second study focused on a single-center series of 561 patients with T2D who also underwent screening by transient elastography during 2018-2020 and had no history of NAFLD or other liver disease, or alcohol abuse. The imaging results showed a NAFLD prevalence of 70%, with 54% of the entire group diagnosed with severe steatosis, severe fibrosis in 6%, and cirrhosis in 3%. Among the 54% of patients with severe steatosis, 30% also had severe liver fibrosis. About 70% of the 561 patients assessed came from either the family medicine or general internal medicine clinics of the University of Florida, Gainesville, with the remaining 30% enrolled from the center’s endocrinology/diabetes outpatient clinic.
Neither report documented a NASH prevalence, which cannot receive definitive diagnosis by imaging alone. “This is the first study of its kind in the U.S. to establish the magnitude of [liver] disease burden in random patients with T2D seeking regular outpatient care,” wrote the University of Florida research team, led by Kenneth Cusi, MD, professor and chief of the university’s division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. Their finding that patients with T2D and previously unknown to have NAFLD had a 15% prevalence of moderate or advanced liver fibrosis “should trigger a call to action by all clinicians taking care of patients with T2D. Patient and physician awareness of the hepatic and extrahepatic complications of NASH, and reversing current diagnosis and treatment inertia will be the only way to avert the looming epidemic of cirrhosis in patients with diabetes.”
“Endocrinologists don’t ‘see’ NAFLD and NASH” in their patients with T2D “ because they don’t think about it,” Dr. Mantzoros declared.
“Why is NASH underdiagnosed and undertreated? Because many physicians aren’t aware of it,” agreed Dr. Cusi during a talk in December 2020 at the 18th World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease (WCIRDC). “You never find what you don’t look for.”
“Endocrinologists should do the tests for NASH [in patients with T2D], but we’re all guilty of not doing it enough,” Tracey McLaughlin, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, commented during the WCIRDC.
These prevalence numbers demand that clinicians suspect liver disease “in any patient with diabetes, especially patients with obesity who are older and have components of metabolic syndrome,” said Dr. Mantzoros. “We need to screen, refer the most advanced cases, and treat the early- and mid-stage cases.”
How to find NASH
Both the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes call for routine screening of patients with T2D, starting with a check of liver enzymes, such as ALT, but no clear consensus exists for the specifics of screening beyond that. Dr. Mantzoros, Dr. Cusi, and other experts agree that the scheme for assessing liver disease in patients with T2D starts with regular monitoring of elevations in liver enzymes including ALT. Next is noninvasive ultrasound assessment of the extent of liver fibrosis inferred from the organ’s stiffness using transient elastography. Another frequently cited initial screening tool is the Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score, which incorporates a patient’s age, platelet count, and levels of ALT and a second liver enzyme, AST.
“There is more consensus about FIB-4 and then elastography, but some people use tests other than FIB-4. Unfortunately there is no perfect diagnostic test today. A top priority is to define the best diagnostic test,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is leading an effort to try to refine screening using artificial intelligence.
“FIB-4 is simple, easy, and well validated,” commented Dr. Cusi during the WCIRDC last December. “FIB-4 and elastography should get you pretty close” to identifying patients with T2D and significant liver disease.
But in a recent editorial, Dr. Cusi agreed on the need for “more reliable tests for the diagnosis of NASH and advanced fibrosis in patients with T2D. Significant work is being done in the field to validate novel and more sophisticated fibrosis biomarkers. Future studies will help us enter a new era of precision medicine where biomarkers will identify and target therapy to those with more active disease at risk for cirrhosis,” he wrote.
“The ultimate goal is to diagnose fibrosis at an early stage to prevent people from developing cirrhosis,” Dr. Cusi said in a recent written statement. “We’re trying to identify these problems before they’re unfixable. Once someone has cirrhosis, there isn’t a whole lot you can do.”
Pioglitazone remains the best-documented treatment
Perhaps some of the inertia in diagnosing NAFLD, NASH, and liver fibrosis in patients with T2D is dissatisfaction with current treatment options, although several proven options exist, notably weight loss and diet, and thiazolidinedione (TZD) pioglitazone. But weight loss and diet pose issues for patient compliance and durability of the intervention, and many clinicians consider pioglitazone flawed by its potential adverse effects.
“When we don’t have an established treatment for something, we tend to not measure it or go after it. That’s been true of liver disease” in patients with T2D, said Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and diabetes specialist who is medical director of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., during the WCIRDC.
Treatment with pioglitazone has resolved NASH in about a third of patients compared with placebo, prevented fibrosis progression, and cut cardiovascular disease events, noted Dr. Cusi during the WCIRDC.
“Pioglitazone is used in only 8% of patients with T2D, or less, but we need to use it more often because of its proven efficacy in patients with T2D and NASH” said Dr. Mantzoros. “The problem is that pioglitazone has side effects, including weight gain and fluid retention, that makes it less attractive unless one thinks about the diagnosis of NASH.”
Others highlight that the adverse effects of pioglitazone have been either misunderstood, or can be effectively minimized with careful dosing.
“The data with the TZDs are much stronger than the data from anything else. TZDs have gotten a bad name because they also work in the kidney and enhance fluid reabsorption. We use modest dosages of pioglitazone, 15 mg or 30 mg a day, to avoid excess fluid retention,” Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, chief of the diabetes division and professor of medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, said during the WCIRDC. “The best drug for NASH is pioglitazone. No other drug beats it” based on current data, Dr. DeFronzo asserted.
Other strategies include the potential to pair pioglitazone with other interventions that can blunt a weight-gain effect. One intriguing combination would combine pioglitazone with a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a drug class that can produce significant weight loss. Results from a phase 2 study showed promise for semaglutide (Rybelsus) in treating patients with NASH.
Getting the name right
Another factor that may be keeping NAFLD and NASH from achieving a higher profile for patients with T2D are those names, which focus on what the diseases are not – nonalcoholic – rather than what they are.
A series of recent publications in both the endocrinology and hepatology literature have called for renaming these disorders either “metabolic (dysfunction)–associated fatty liver disease (MALFD)”, or “dysmetabolism-associated fatty liver disease (DALFD)”.
“The names NAFLD and NASH indicate absence of alcohol as a cause, but the disease is also characterized by the absence of other causes, such as autoimmune disorders or hepatitis. The names were coined when we did not know much about these diseases. We now know that it is dysmetabolism that causes these conditions, and so we need to adopt a new, more accurate name,” explained Dr. Mantzoros, who has published support for a name change.
While many agree, some have raised concerns as to whether a name change now is premature. A group of hepatologists recently published a rebuttal to an immediate name change , saying that, “although we are in agreement that metabolic fatty liver disease may more accurately and positively reflect the relevant risk factors better than the age-old term nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the term still leaves a great deal of ambiguity. A name change will be appropriate when informed by a new understanding of the molecular basis of the disease entity, insights that fundamentally change risk stratification, or other important aspects of the disease. We may be on the cusp of this, but we are not there yet.”
Dr. Mantzoros agreed, but for somewhat different reasons.
“We need to be careful and deliberate, because there is a significant body of knowledge and a lot of data from clinical trials collected using the old definitions. We need to find an appropriate time frame for a [name] transition. We need to find a nice and robust way to productively bridge the old to the new,” he said. “We also need new diagnostic criteria, and new therapies. A new name and definition will facilitate progress.”
Dr. Mantzoros been a shareholder of and consultant to Coherus and Pangea, he has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Eisai, Genfit, Intercept, Novo Nordisk, P.E.S., and Regeneron, and has received travel support from the Metabolic Institute of America and the California Walnut Commission. Dr. Cusi has been a consultant to and has received research funding from numerous drug companies. Dr. McLaughlin is a consultant to January AI. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to numerous drug companies. Dr. DeFronzo received research grants from AstraZeneca, Janssen, and Merck; he has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, Janssen, and Novo Nordisk; and he has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk.
Among these calls is a pending statement from the Endocrine Society, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American Gastroenterology Association, and other groups on what the growing appreciation of highly prevalent liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) means for assessing and managing patients. Publication of the statement is expected by spring 2021, said Christos S. Mantzoros, MD, DSc, PhD, chief of endocrinology for the Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System and a representative from the Endocrine Society to the statement-writing panel.
This upcoming “Call to Action” from these groups argues for a “need to collaborate across disciplines, and work together on establishing clinical guidelines, and creating new diagnostics and therapeutics,” said Dr. Mantzoros in an interview.
“Over time, it is becoming clearer that management of NAFLD [nonalcoholic fatty liver disease]/NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] requires a multidisciplinary panel of doctors ranging from primary care practitioners, to endocrinologists, and hepatologists. Given that the nature of the disease crosses scientific discipline boundaries, and that the number of patients is so large (it is estimated that about one in four U.S. adults have NAFLD), not all patients can be treated at the limited number of hepatology centers.
“However, not all stakeholders have fully realized this fact, and no effort had been undertaken so far by any professional society to develop a coordinated approach and clinical care pathway for NAFLD/NASH. The ‘Call to Action’ meeting can be considered as a starting point for such an important effort,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is also a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the human nutrition unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
Dramatic prevalence rates in patients with T2D
Results from two independent epidemiology reports, published in December 2020, documented steatosis (the fatty liver of NAFLD) in 70%-74% of unselected U.S. patients with T2D, advanced liver fibrosis accompanying this disease in 6%-15%, and previously unrecognized cirrhosis in 3%-8%.
One of these reports analyzed 825 patients with T2D included in the National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey of 2017-2018 run by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All these patients, selected to be representative of the overall U.S. adult population with T2D, underwent transient elastography to identify steatosis and fibrosis, the first U.S. National Health Survey to run this type of population-based survey. The results showed an overall steatosis prevalence of 74% with grade 3 steatosis in 58%, advanced liver fibrosis in 15%, and cirrhosis in 8%, reported the team of Italian researchers who analyzed the data .
The second study focused on a single-center series of 561 patients with T2D who also underwent screening by transient elastography during 2018-2020 and had no history of NAFLD or other liver disease, or alcohol abuse. The imaging results showed a NAFLD prevalence of 70%, with 54% of the entire group diagnosed with severe steatosis, severe fibrosis in 6%, and cirrhosis in 3%. Among the 54% of patients with severe steatosis, 30% also had severe liver fibrosis. About 70% of the 561 patients assessed came from either the family medicine or general internal medicine clinics of the University of Florida, Gainesville, with the remaining 30% enrolled from the center’s endocrinology/diabetes outpatient clinic.
Neither report documented a NASH prevalence, which cannot receive definitive diagnosis by imaging alone. “This is the first study of its kind in the U.S. to establish the magnitude of [liver] disease burden in random patients with T2D seeking regular outpatient care,” wrote the University of Florida research team, led by Kenneth Cusi, MD, professor and chief of the university’s division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. Their finding that patients with T2D and previously unknown to have NAFLD had a 15% prevalence of moderate or advanced liver fibrosis “should trigger a call to action by all clinicians taking care of patients with T2D. Patient and physician awareness of the hepatic and extrahepatic complications of NASH, and reversing current diagnosis and treatment inertia will be the only way to avert the looming epidemic of cirrhosis in patients with diabetes.”
“Endocrinologists don’t ‘see’ NAFLD and NASH” in their patients with T2D “ because they don’t think about it,” Dr. Mantzoros declared.
“Why is NASH underdiagnosed and undertreated? Because many physicians aren’t aware of it,” agreed Dr. Cusi during a talk in December 2020 at the 18th World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease (WCIRDC). “You never find what you don’t look for.”
“Endocrinologists should do the tests for NASH [in patients with T2D], but we’re all guilty of not doing it enough,” Tracey McLaughlin, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, commented during the WCIRDC.
These prevalence numbers demand that clinicians suspect liver disease “in any patient with diabetes, especially patients with obesity who are older and have components of metabolic syndrome,” said Dr. Mantzoros. “We need to screen, refer the most advanced cases, and treat the early- and mid-stage cases.”
How to find NASH
Both the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes call for routine screening of patients with T2D, starting with a check of liver enzymes, such as ALT, but no clear consensus exists for the specifics of screening beyond that. Dr. Mantzoros, Dr. Cusi, and other experts agree that the scheme for assessing liver disease in patients with T2D starts with regular monitoring of elevations in liver enzymes including ALT. Next is noninvasive ultrasound assessment of the extent of liver fibrosis inferred from the organ’s stiffness using transient elastography. Another frequently cited initial screening tool is the Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score, which incorporates a patient’s age, platelet count, and levels of ALT and a second liver enzyme, AST.
“There is more consensus about FIB-4 and then elastography, but some people use tests other than FIB-4. Unfortunately there is no perfect diagnostic test today. A top priority is to define the best diagnostic test,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is leading an effort to try to refine screening using artificial intelligence.
“FIB-4 is simple, easy, and well validated,” commented Dr. Cusi during the WCIRDC last December. “FIB-4 and elastography should get you pretty close” to identifying patients with T2D and significant liver disease.
But in a recent editorial, Dr. Cusi agreed on the need for “more reliable tests for the diagnosis of NASH and advanced fibrosis in patients with T2D. Significant work is being done in the field to validate novel and more sophisticated fibrosis biomarkers. Future studies will help us enter a new era of precision medicine where biomarkers will identify and target therapy to those with more active disease at risk for cirrhosis,” he wrote.
“The ultimate goal is to diagnose fibrosis at an early stage to prevent people from developing cirrhosis,” Dr. Cusi said in a recent written statement. “We’re trying to identify these problems before they’re unfixable. Once someone has cirrhosis, there isn’t a whole lot you can do.”
Pioglitazone remains the best-documented treatment
Perhaps some of the inertia in diagnosing NAFLD, NASH, and liver fibrosis in patients with T2D is dissatisfaction with current treatment options, although several proven options exist, notably weight loss and diet, and thiazolidinedione (TZD) pioglitazone. But weight loss and diet pose issues for patient compliance and durability of the intervention, and many clinicians consider pioglitazone flawed by its potential adverse effects.
“When we don’t have an established treatment for something, we tend to not measure it or go after it. That’s been true of liver disease” in patients with T2D, said Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and diabetes specialist who is medical director of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., during the WCIRDC.
Treatment with pioglitazone has resolved NASH in about a third of patients compared with placebo, prevented fibrosis progression, and cut cardiovascular disease events, noted Dr. Cusi during the WCIRDC.
“Pioglitazone is used in only 8% of patients with T2D, or less, but we need to use it more often because of its proven efficacy in patients with T2D and NASH” said Dr. Mantzoros. “The problem is that pioglitazone has side effects, including weight gain and fluid retention, that makes it less attractive unless one thinks about the diagnosis of NASH.”
Others highlight that the adverse effects of pioglitazone have been either misunderstood, or can be effectively minimized with careful dosing.
“The data with the TZDs are much stronger than the data from anything else. TZDs have gotten a bad name because they also work in the kidney and enhance fluid reabsorption. We use modest dosages of pioglitazone, 15 mg or 30 mg a day, to avoid excess fluid retention,” Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, chief of the diabetes division and professor of medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, said during the WCIRDC. “The best drug for NASH is pioglitazone. No other drug beats it” based on current data, Dr. DeFronzo asserted.
Other strategies include the potential to pair pioglitazone with other interventions that can blunt a weight-gain effect. One intriguing combination would combine pioglitazone with a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a drug class that can produce significant weight loss. Results from a phase 2 study showed promise for semaglutide (Rybelsus) in treating patients with NASH.
Getting the name right
Another factor that may be keeping NAFLD and NASH from achieving a higher profile for patients with T2D are those names, which focus on what the diseases are not – nonalcoholic – rather than what they are.
A series of recent publications in both the endocrinology and hepatology literature have called for renaming these disorders either “metabolic (dysfunction)–associated fatty liver disease (MALFD)”, or “dysmetabolism-associated fatty liver disease (DALFD)”.
“The names NAFLD and NASH indicate absence of alcohol as a cause, but the disease is also characterized by the absence of other causes, such as autoimmune disorders or hepatitis. The names were coined when we did not know much about these diseases. We now know that it is dysmetabolism that causes these conditions, and so we need to adopt a new, more accurate name,” explained Dr. Mantzoros, who has published support for a name change.
While many agree, some have raised concerns as to whether a name change now is premature. A group of hepatologists recently published a rebuttal to an immediate name change , saying that, “although we are in agreement that metabolic fatty liver disease may more accurately and positively reflect the relevant risk factors better than the age-old term nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the term still leaves a great deal of ambiguity. A name change will be appropriate when informed by a new understanding of the molecular basis of the disease entity, insights that fundamentally change risk stratification, or other important aspects of the disease. We may be on the cusp of this, but we are not there yet.”
Dr. Mantzoros agreed, but for somewhat different reasons.
“We need to be careful and deliberate, because there is a significant body of knowledge and a lot of data from clinical trials collected using the old definitions. We need to find an appropriate time frame for a [name] transition. We need to find a nice and robust way to productively bridge the old to the new,” he said. “We also need new diagnostic criteria, and new therapies. A new name and definition will facilitate progress.”
Dr. Mantzoros been a shareholder of and consultant to Coherus and Pangea, he has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Eisai, Genfit, Intercept, Novo Nordisk, P.E.S., and Regeneron, and has received travel support from the Metabolic Institute of America and the California Walnut Commission. Dr. Cusi has been a consultant to and has received research funding from numerous drug companies. Dr. McLaughlin is a consultant to January AI. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to numerous drug companies. Dr. DeFronzo received research grants from AstraZeneca, Janssen, and Merck; he has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, Janssen, and Novo Nordisk; and he has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk.
Among these calls is a pending statement from the Endocrine Society, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists, the American Gastroenterology Association, and other groups on what the growing appreciation of highly prevalent liver disease in patients with type 2 diabetes (T2D) means for assessing and managing patients. Publication of the statement is expected by spring 2021, said Christos S. Mantzoros, MD, DSc, PhD, chief of endocrinology for the Veterans Affairs Boston Healthcare System and a representative from the Endocrine Society to the statement-writing panel.
This upcoming “Call to Action” from these groups argues for a “need to collaborate across disciplines, and work together on establishing clinical guidelines, and creating new diagnostics and therapeutics,” said Dr. Mantzoros in an interview.
“Over time, it is becoming clearer that management of NAFLD [nonalcoholic fatty liver disease]/NASH [nonalcoholic steatohepatitis] requires a multidisciplinary panel of doctors ranging from primary care practitioners, to endocrinologists, and hepatologists. Given that the nature of the disease crosses scientific discipline boundaries, and that the number of patients is so large (it is estimated that about one in four U.S. adults have NAFLD), not all patients can be treated at the limited number of hepatology centers.
“However, not all stakeholders have fully realized this fact, and no effort had been undertaken so far by any professional society to develop a coordinated approach and clinical care pathway for NAFLD/NASH. The ‘Call to Action’ meeting can be considered as a starting point for such an important effort,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is also a professor of medicine at Harvard Medical School and director of the human nutrition unit at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, both in Boston.
Dramatic prevalence rates in patients with T2D
Results from two independent epidemiology reports, published in December 2020, documented steatosis (the fatty liver of NAFLD) in 70%-74% of unselected U.S. patients with T2D, advanced liver fibrosis accompanying this disease in 6%-15%, and previously unrecognized cirrhosis in 3%-8%.
One of these reports analyzed 825 patients with T2D included in the National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey of 2017-2018 run by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. All these patients, selected to be representative of the overall U.S. adult population with T2D, underwent transient elastography to identify steatosis and fibrosis, the first U.S. National Health Survey to run this type of population-based survey. The results showed an overall steatosis prevalence of 74% with grade 3 steatosis in 58%, advanced liver fibrosis in 15%, and cirrhosis in 8%, reported the team of Italian researchers who analyzed the data .
The second study focused on a single-center series of 561 patients with T2D who also underwent screening by transient elastography during 2018-2020 and had no history of NAFLD or other liver disease, or alcohol abuse. The imaging results showed a NAFLD prevalence of 70%, with 54% of the entire group diagnosed with severe steatosis, severe fibrosis in 6%, and cirrhosis in 3%. Among the 54% of patients with severe steatosis, 30% also had severe liver fibrosis. About 70% of the 561 patients assessed came from either the family medicine or general internal medicine clinics of the University of Florida, Gainesville, with the remaining 30% enrolled from the center’s endocrinology/diabetes outpatient clinic.
Neither report documented a NASH prevalence, which cannot receive definitive diagnosis by imaging alone. “This is the first study of its kind in the U.S. to establish the magnitude of [liver] disease burden in random patients with T2D seeking regular outpatient care,” wrote the University of Florida research team, led by Kenneth Cusi, MD, professor and chief of the university’s division of endocrinology, diabetes, and metabolism. Their finding that patients with T2D and previously unknown to have NAFLD had a 15% prevalence of moderate or advanced liver fibrosis “should trigger a call to action by all clinicians taking care of patients with T2D. Patient and physician awareness of the hepatic and extrahepatic complications of NASH, and reversing current diagnosis and treatment inertia will be the only way to avert the looming epidemic of cirrhosis in patients with diabetes.”
“Endocrinologists don’t ‘see’ NAFLD and NASH” in their patients with T2D “ because they don’t think about it,” Dr. Mantzoros declared.
“Why is NASH underdiagnosed and undertreated? Because many physicians aren’t aware of it,” agreed Dr. Cusi during a talk in December 2020 at the 18th World Congress on Insulin Resistance, Diabetes, and Cardiovascular Disease (WCIRDC). “You never find what you don’t look for.”
“Endocrinologists should do the tests for NASH [in patients with T2D], but we’re all guilty of not doing it enough,” Tracey McLaughlin, MD, an endocrinologist and professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, commented during the WCIRDC.
These prevalence numbers demand that clinicians suspect liver disease “in any patient with diabetes, especially patients with obesity who are older and have components of metabolic syndrome,” said Dr. Mantzoros. “We need to screen, refer the most advanced cases, and treat the early- and mid-stage cases.”
How to find NASH
Both the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes call for routine screening of patients with T2D, starting with a check of liver enzymes, such as ALT, but no clear consensus exists for the specifics of screening beyond that. Dr. Mantzoros, Dr. Cusi, and other experts agree that the scheme for assessing liver disease in patients with T2D starts with regular monitoring of elevations in liver enzymes including ALT. Next is noninvasive ultrasound assessment of the extent of liver fibrosis inferred from the organ’s stiffness using transient elastography. Another frequently cited initial screening tool is the Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) score, which incorporates a patient’s age, platelet count, and levels of ALT and a second liver enzyme, AST.
“There is more consensus about FIB-4 and then elastography, but some people use tests other than FIB-4. Unfortunately there is no perfect diagnostic test today. A top priority is to define the best diagnostic test,” said Dr. Mantzoros, who is leading an effort to try to refine screening using artificial intelligence.
“FIB-4 is simple, easy, and well validated,” commented Dr. Cusi during the WCIRDC last December. “FIB-4 and elastography should get you pretty close” to identifying patients with T2D and significant liver disease.
But in a recent editorial, Dr. Cusi agreed on the need for “more reliable tests for the diagnosis of NASH and advanced fibrosis in patients with T2D. Significant work is being done in the field to validate novel and more sophisticated fibrosis biomarkers. Future studies will help us enter a new era of precision medicine where biomarkers will identify and target therapy to those with more active disease at risk for cirrhosis,” he wrote.
“The ultimate goal is to diagnose fibrosis at an early stage to prevent people from developing cirrhosis,” Dr. Cusi said in a recent written statement. “We’re trying to identify these problems before they’re unfixable. Once someone has cirrhosis, there isn’t a whole lot you can do.”
Pioglitazone remains the best-documented treatment
Perhaps some of the inertia in diagnosing NAFLD, NASH, and liver fibrosis in patients with T2D is dissatisfaction with current treatment options, although several proven options exist, notably weight loss and diet, and thiazolidinedione (TZD) pioglitazone. But weight loss and diet pose issues for patient compliance and durability of the intervention, and many clinicians consider pioglitazone flawed by its potential adverse effects.
“When we don’t have an established treatment for something, we tend to not measure it or go after it. That’s been true of liver disease” in patients with T2D, said Yehuda Handelsman, MD, an endocrinologist and diabetes specialist who is medical director of the Metabolic Institute of America in Tarzana, Calif., during the WCIRDC.
Treatment with pioglitazone has resolved NASH in about a third of patients compared with placebo, prevented fibrosis progression, and cut cardiovascular disease events, noted Dr. Cusi during the WCIRDC.
“Pioglitazone is used in only 8% of patients with T2D, or less, but we need to use it more often because of its proven efficacy in patients with T2D and NASH” said Dr. Mantzoros. “The problem is that pioglitazone has side effects, including weight gain and fluid retention, that makes it less attractive unless one thinks about the diagnosis of NASH.”
Others highlight that the adverse effects of pioglitazone have been either misunderstood, or can be effectively minimized with careful dosing.
“The data with the TZDs are much stronger than the data from anything else. TZDs have gotten a bad name because they also work in the kidney and enhance fluid reabsorption. We use modest dosages of pioglitazone, 15 mg or 30 mg a day, to avoid excess fluid retention,” Ralph A. DeFronzo, MD, chief of the diabetes division and professor of medicine at the University of Texas Health Science Center, San Antonio, said during the WCIRDC. “The best drug for NASH is pioglitazone. No other drug beats it” based on current data, Dr. DeFronzo asserted.
Other strategies include the potential to pair pioglitazone with other interventions that can blunt a weight-gain effect. One intriguing combination would combine pioglitazone with a GLP-1 receptor agonist, a drug class that can produce significant weight loss. Results from a phase 2 study showed promise for semaglutide (Rybelsus) in treating patients with NASH.
Getting the name right
Another factor that may be keeping NAFLD and NASH from achieving a higher profile for patients with T2D are those names, which focus on what the diseases are not – nonalcoholic – rather than what they are.
A series of recent publications in both the endocrinology and hepatology literature have called for renaming these disorders either “metabolic (dysfunction)–associated fatty liver disease (MALFD)”, or “dysmetabolism-associated fatty liver disease (DALFD)”.
“The names NAFLD and NASH indicate absence of alcohol as a cause, but the disease is also characterized by the absence of other causes, such as autoimmune disorders or hepatitis. The names were coined when we did not know much about these diseases. We now know that it is dysmetabolism that causes these conditions, and so we need to adopt a new, more accurate name,” explained Dr. Mantzoros, who has published support for a name change.
While many agree, some have raised concerns as to whether a name change now is premature. A group of hepatologists recently published a rebuttal to an immediate name change , saying that, “although we are in agreement that metabolic fatty liver disease may more accurately and positively reflect the relevant risk factors better than the age-old term nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, the term still leaves a great deal of ambiguity. A name change will be appropriate when informed by a new understanding of the molecular basis of the disease entity, insights that fundamentally change risk stratification, or other important aspects of the disease. We may be on the cusp of this, but we are not there yet.”
Dr. Mantzoros agreed, but for somewhat different reasons.
“We need to be careful and deliberate, because there is a significant body of knowledge and a lot of data from clinical trials collected using the old definitions. We need to find an appropriate time frame for a [name] transition. We need to find a nice and robust way to productively bridge the old to the new,” he said. “We also need new diagnostic criteria, and new therapies. A new name and definition will facilitate progress.”
Dr. Mantzoros been a shareholder of and consultant to Coherus and Pangea, he has been a consultant to AstraZeneca, Eisai, Genfit, Intercept, Novo Nordisk, P.E.S., and Regeneron, and has received travel support from the Metabolic Institute of America and the California Walnut Commission. Dr. Cusi has been a consultant to and has received research funding from numerous drug companies. Dr. McLaughlin is a consultant to January AI. Dr. Handelsman has been a consultant to numerous drug companies. Dr. DeFronzo received research grants from AstraZeneca, Janssen, and Merck; he has been an adviser to AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Intarcia, Janssen, and Novo Nordisk; and he has been a speaker on behalf of AstraZeneca and Novo Nordisk.
President Biden signs 10 new orders to help fight COVID-19

“For the past year, we couldn’t rely on the federal government to act with the urgency and focus and coordination we needed, and we have seen the tragic cost of that failure,” Mr. Biden said in remarks from the White House, unveiling his 198-page National Strategy for the COVID-19 Response and Pandemic Preparedness.
He said as many as 500,000 Americans will have died by February. “It’s going to take months for us to turn things around,” he said.
“Our national strategy is comprehensive – it’s based on science, not politics; it’s based on truth, not denial,” Mr. Biden said. He also promised to restore public trust, in part by having scientists and public health experts speak to the public. “That’s why you’ll be hearing a lot more from Dr. Fauci again, not from the president,” he said, adding that the experts will be “free from political interference.”
While the president’s executive orders can help accomplish some of the plan’s proposals, the majority will require new funding from Congress and will be included in the $1.9 trillion American Rescue package that Mr. Biden hopes legislators will approve.
Ten new orders
The 10 new pandemic-related orders Biden signed on Jan. 21 follow two he signed on his first day in office.
One establishes a COVID-19 Response Office responsible for coordinating the pandemic response across all federal departments and agencies and also reestablishes the White House Directorate on Global Health Security and Biodefense, which was disabled by the Trump administration.
The other order requires masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
Among the new orders will be directives that:
- Require individuals to also wear masks in airports and planes, and when using other modes of public transportation including trains, boats, and intercity buses, and also require international travelers to produce proof of a recent negative COVID-19 test prior to entry and to quarantine after entry.
- Federal agencies use all powers, including the Defense Production Act, to accelerate manufacturing and delivery of supplies such as N95 masks, gowns, gloves, swabs, reagents, pipette tips, rapid test kits, and nitrocellulose material for rapid antigen tests, and all equipment and material needed to accelerate manufacture, delivery, and administration of COVID-19 vaccine.
- Create a Pandemic Testing Board to expand supply and access, to promote more surge capacity, and to ensure equitable access to tests.
- Facilitate discovery, development, and trials of potential COVID-19 treatments, as well as expand access to programs that can meet the long-term health needs of those recovering from the disease.
- Facilitate more and better data sharing that will allow businesses, schools, hospitals, and individuals to make real-time decisions based on spread in their community.
- Direct the Education and Health & Human Services departments to provide schools and child-care operations guidance on how to reopen and operate safely.
- Direct the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to immediately release clear guidance for employers to help keep workers safe and to enforce health and safety requirements.
The plan also sets goals for vaccination – including 100 million shots in the administration’s first 100 days. President Biden had already previewed his goals for vaccination, including setting up mass vaccination sites and mobile vaccination sites. During his remarks, Mr. Biden said that he had already directed the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to begin setting up the vaccination centers.
The administration is also going to look into improving reimbursement for giving vaccines. As a start, the HHS will ask the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to consider if a higher rate “may more accurately compensate providers,” according to the Biden plan.
“But the brutal truth is it will take months before we can get the majority of Americans vaccinated,” said Mr. Biden.
As part of the goal of ensuring an equitable pandemic response, the president will sign an order that establishes a COVID-19 Health Equity Task Force. The task force is charged with providing recommendations for allocating resources and funding in communities with inequities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, geography, disability, and other considerations.
Finally, the administration has committed to being more transparent and sharing more information. The national plan calls for the federal government to conduct regular, expert-led, science-based public briefings and to release regular reports on the pandemic. The administration said it will launch massive science-based public information campaigns – in multiple languages – to educate Americans on masks, testing, and vaccines, and also work to counter misinformation and disinformation.
The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) applauded Mr. Biden’s initiative. “If enacted, this bold legislative agenda will provide much-needed support to American families struggling during the pandemic – especially communities of color and those hardest hit by the virus,” Ada D. Stewart, MD, AAFP president, said in a statement.
Dr. Stewart also noted that family physicians “are uniquely positioned in their communities to educate patients, prioritize access, and coordinate administration of the COVID-19 vaccines,” and urged the administration to ensure that family physicians and staff be vaccinated as soon as possible, to help them “more safely provide care to their communities.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

“For the past year, we couldn’t rely on the federal government to act with the urgency and focus and coordination we needed, and we have seen the tragic cost of that failure,” Mr. Biden said in remarks from the White House, unveiling his 198-page National Strategy for the COVID-19 Response and Pandemic Preparedness.
He said as many as 500,000 Americans will have died by February. “It’s going to take months for us to turn things around,” he said.
“Our national strategy is comprehensive – it’s based on science, not politics; it’s based on truth, not denial,” Mr. Biden said. He also promised to restore public trust, in part by having scientists and public health experts speak to the public. “That’s why you’ll be hearing a lot more from Dr. Fauci again, not from the president,” he said, adding that the experts will be “free from political interference.”
While the president’s executive orders can help accomplish some of the plan’s proposals, the majority will require new funding from Congress and will be included in the $1.9 trillion American Rescue package that Mr. Biden hopes legislators will approve.
Ten new orders
The 10 new pandemic-related orders Biden signed on Jan. 21 follow two he signed on his first day in office.
One establishes a COVID-19 Response Office responsible for coordinating the pandemic response across all federal departments and agencies and also reestablishes the White House Directorate on Global Health Security and Biodefense, which was disabled by the Trump administration.
The other order requires masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
Among the new orders will be directives that:
- Require individuals to also wear masks in airports and planes, and when using other modes of public transportation including trains, boats, and intercity buses, and also require international travelers to produce proof of a recent negative COVID-19 test prior to entry and to quarantine after entry.
- Federal agencies use all powers, including the Defense Production Act, to accelerate manufacturing and delivery of supplies such as N95 masks, gowns, gloves, swabs, reagents, pipette tips, rapid test kits, and nitrocellulose material for rapid antigen tests, and all equipment and material needed to accelerate manufacture, delivery, and administration of COVID-19 vaccine.
- Create a Pandemic Testing Board to expand supply and access, to promote more surge capacity, and to ensure equitable access to tests.
- Facilitate discovery, development, and trials of potential COVID-19 treatments, as well as expand access to programs that can meet the long-term health needs of those recovering from the disease.
- Facilitate more and better data sharing that will allow businesses, schools, hospitals, and individuals to make real-time decisions based on spread in their community.
- Direct the Education and Health & Human Services departments to provide schools and child-care operations guidance on how to reopen and operate safely.
- Direct the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to immediately release clear guidance for employers to help keep workers safe and to enforce health and safety requirements.
The plan also sets goals for vaccination – including 100 million shots in the administration’s first 100 days. President Biden had already previewed his goals for vaccination, including setting up mass vaccination sites and mobile vaccination sites. During his remarks, Mr. Biden said that he had already directed the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to begin setting up the vaccination centers.
The administration is also going to look into improving reimbursement for giving vaccines. As a start, the HHS will ask the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to consider if a higher rate “may more accurately compensate providers,” according to the Biden plan.
“But the brutal truth is it will take months before we can get the majority of Americans vaccinated,” said Mr. Biden.
As part of the goal of ensuring an equitable pandemic response, the president will sign an order that establishes a COVID-19 Health Equity Task Force. The task force is charged with providing recommendations for allocating resources and funding in communities with inequities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, geography, disability, and other considerations.
Finally, the administration has committed to being more transparent and sharing more information. The national plan calls for the federal government to conduct regular, expert-led, science-based public briefings and to release regular reports on the pandemic. The administration said it will launch massive science-based public information campaigns – in multiple languages – to educate Americans on masks, testing, and vaccines, and also work to counter misinformation and disinformation.
The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) applauded Mr. Biden’s initiative. “If enacted, this bold legislative agenda will provide much-needed support to American families struggling during the pandemic – especially communities of color and those hardest hit by the virus,” Ada D. Stewart, MD, AAFP president, said in a statement.
Dr. Stewart also noted that family physicians “are uniquely positioned in their communities to educate patients, prioritize access, and coordinate administration of the COVID-19 vaccines,” and urged the administration to ensure that family physicians and staff be vaccinated as soon as possible, to help them “more safely provide care to their communities.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.

“For the past year, we couldn’t rely on the federal government to act with the urgency and focus and coordination we needed, and we have seen the tragic cost of that failure,” Mr. Biden said in remarks from the White House, unveiling his 198-page National Strategy for the COVID-19 Response and Pandemic Preparedness.
He said as many as 500,000 Americans will have died by February. “It’s going to take months for us to turn things around,” he said.
“Our national strategy is comprehensive – it’s based on science, not politics; it’s based on truth, not denial,” Mr. Biden said. He also promised to restore public trust, in part by having scientists and public health experts speak to the public. “That’s why you’ll be hearing a lot more from Dr. Fauci again, not from the president,” he said, adding that the experts will be “free from political interference.”
While the president’s executive orders can help accomplish some of the plan’s proposals, the majority will require new funding from Congress and will be included in the $1.9 trillion American Rescue package that Mr. Biden hopes legislators will approve.
Ten new orders
The 10 new pandemic-related orders Biden signed on Jan. 21 follow two he signed on his first day in office.
One establishes a COVID-19 Response Office responsible for coordinating the pandemic response across all federal departments and agencies and also reestablishes the White House Directorate on Global Health Security and Biodefense, which was disabled by the Trump administration.
The other order requires masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
Among the new orders will be directives that:
- Require individuals to also wear masks in airports and planes, and when using other modes of public transportation including trains, boats, and intercity buses, and also require international travelers to produce proof of a recent negative COVID-19 test prior to entry and to quarantine after entry.
- Federal agencies use all powers, including the Defense Production Act, to accelerate manufacturing and delivery of supplies such as N95 masks, gowns, gloves, swabs, reagents, pipette tips, rapid test kits, and nitrocellulose material for rapid antigen tests, and all equipment and material needed to accelerate manufacture, delivery, and administration of COVID-19 vaccine.
- Create a Pandemic Testing Board to expand supply and access, to promote more surge capacity, and to ensure equitable access to tests.
- Facilitate discovery, development, and trials of potential COVID-19 treatments, as well as expand access to programs that can meet the long-term health needs of those recovering from the disease.
- Facilitate more and better data sharing that will allow businesses, schools, hospitals, and individuals to make real-time decisions based on spread in their community.
- Direct the Education and Health & Human Services departments to provide schools and child-care operations guidance on how to reopen and operate safely.
- Direct the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) to immediately release clear guidance for employers to help keep workers safe and to enforce health and safety requirements.
The plan also sets goals for vaccination – including 100 million shots in the administration’s first 100 days. President Biden had already previewed his goals for vaccination, including setting up mass vaccination sites and mobile vaccination sites. During his remarks, Mr. Biden said that he had already directed the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) to begin setting up the vaccination centers.
The administration is also going to look into improving reimbursement for giving vaccines. As a start, the HHS will ask the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to consider if a higher rate “may more accurately compensate providers,” according to the Biden plan.
“But the brutal truth is it will take months before we can get the majority of Americans vaccinated,” said Mr. Biden.
As part of the goal of ensuring an equitable pandemic response, the president will sign an order that establishes a COVID-19 Health Equity Task Force. The task force is charged with providing recommendations for allocating resources and funding in communities with inequities in COVID-19 outcomes by race, ethnicity, geography, disability, and other considerations.
Finally, the administration has committed to being more transparent and sharing more information. The national plan calls for the federal government to conduct regular, expert-led, science-based public briefings and to release regular reports on the pandemic. The administration said it will launch massive science-based public information campaigns – in multiple languages – to educate Americans on masks, testing, and vaccines, and also work to counter misinformation and disinformation.
The American Academy of Family Physicians (AAFP) applauded Mr. Biden’s initiative. “If enacted, this bold legislative agenda will provide much-needed support to American families struggling during the pandemic – especially communities of color and those hardest hit by the virus,” Ada D. Stewart, MD, AAFP president, said in a statement.
Dr. Stewart also noted that family physicians “are uniquely positioned in their communities to educate patients, prioritize access, and coordinate administration of the COVID-19 vaccines,” and urged the administration to ensure that family physicians and staff be vaccinated as soon as possible, to help them “more safely provide care to their communities.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Metformin treatment again linked to fewer deaths from COVID-19
People with type 2 diabetes who develop COVID-19 show a substantially reduced risk of dying if they are taking metformin, shows a study that adds to prior research indicating the drug might somehow play a role in reducing the severity of infection.
“Unlike several previous analyses, this was a study in a racially diverse population with a high proportion of Blacks/African Americans and [it] revealed that metformin treatment of diabetes prior to diagnosis with COVID-19 was associated with a dramatic threefold reduced mortality in subjects with type 2 diabetes, even after correcting for multiple covariates,” first author Anath Shalev, MD, of the Comprehensive Diabetes Center at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview.
But Anne Peters, MD, a professor of clinical medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said caution is needed when interpreting these findings.
“It’s hard to tease out the true effects because, for instance, those treated with insulin may be a sicker subset of patients with diabetes than those on metformin, or those with comorbidities such as renal insufficiency may not be treated with metformin” she said in an interview.
“In general, though, treatment obviously matters and people who are better treated tend to do better, so while I think this study raises the question of what role metformin plays in the risk of mortality and COVID-19, I don’t think it necessarily proves the association,” Dr. Peters asserted.
Diverse population
The new study, published this month in Frontiers of Endocrinology, included 25,326 individuals who were tested for COVID-19 at the University of Alabama at Birmingham Hospital between February and June 2020.
Overall, 2.4% tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 604), which the authors note is likely a low figure because screening included asymptomatic hospital staff and patients having elective procedures.
Black/African American patients had a significantly higher risk of COVID-19 positivity, compared with White patients (odds ratio, 2.6; P < .0001). Rates were also higher among those with hypertension (OR, 2.46), diabetes (OR, 2.11), and obesity (OR, 1.93), compared with those without each condition (all P < .0001).
The overall mortality rate in COVID-19-positive patients was 11%. Diabetes was associated with a dramatically increased risk of death (OR, 3.62; P < .0001), and remained an independent risk factor even after adjusting for age, race, sex, obesity, and hypertension.
Notably, the reduction in mortality among those with diabetes taking metformin prior to COVID-19 diagnosis was significant: 11% of those patients died, compared with 23% of those with diabetes not taking metformin (OR, 0.33; P = .021).
Similar findings reported across varied populations
The study adds to mounting research suggesting metformin could have a protective effect on COVID-19 mortality, including an early report from Wuhan, China, findings from the French CORONADO study, and a U.S. study linking treatment with decreased mortality among women with COVID-19.
Of note, the effects of metformin on mortality in the current study were observed in men and women alike, as well as in high-risk subgroups including African Americans.
“The fact that such similar results were obtained in different populations from around the world suggests that the observed reduction in mortality risk, associated with metformin use in subjects with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19, might be generalizable,” the authors wrote.
“Furthermore, these findings underline the importance of following general diabetes treatment and prevention guidelines and not delaying or discontinuing any metformin treatment,” they add.
Speculation of mechanisms includes anti-inflammatory effects
While the mechanisms behind metformin’s potential role in reducing mortality risk in COVID-19 are unknown, the authors note that the most obvious assumption – that improved glycemic control may be a key factor – is disputed by the study’s finding that blood glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c were not significantly different among COVID-19 survivors taking versus not taking metformin.
They point instead to metformin’s known anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic properties.
“We therefore hypothesize that, by exerting some of these effects, metformin might improve outcomes and we are now in the process of investigating this possibility further,” Dr. Shalev said.
Dr. Peters noted that anti-inflammatory properties, themselves, are not necessarily unique to metformin in the treatment of diabetes.
“Many other agents, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors can reduce inflammation, so I don’t know if that would explain it, but it certainly could help,” she said. “[Reducing inflammation] is a hypothesis you see commonly with diabetes drugs, but I think there are also a lot of metabolic benefits from metformin.”
“It was fascinating that they had the A1c data and that survival with metformin didn’t appear to be as related to A1c levels as one might think,” she added.
Notably, a key advantage, should the effects and mechanisms be validated, is metformin’s high accessibility, Dr. Peters added.
“This doesn’t necessarily tell us what we can do to reduce the health care disparities surrounding COVID-19, but the fact that metformin is low cost and easily available is very important, so maybe it will help as we try to grapple with other risk factors.”
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with type 2 diabetes who develop COVID-19 show a substantially reduced risk of dying if they are taking metformin, shows a study that adds to prior research indicating the drug might somehow play a role in reducing the severity of infection.
“Unlike several previous analyses, this was a study in a racially diverse population with a high proportion of Blacks/African Americans and [it] revealed that metformin treatment of diabetes prior to diagnosis with COVID-19 was associated with a dramatic threefold reduced mortality in subjects with type 2 diabetes, even after correcting for multiple covariates,” first author Anath Shalev, MD, of the Comprehensive Diabetes Center at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview.
But Anne Peters, MD, a professor of clinical medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said caution is needed when interpreting these findings.
“It’s hard to tease out the true effects because, for instance, those treated with insulin may be a sicker subset of patients with diabetes than those on metformin, or those with comorbidities such as renal insufficiency may not be treated with metformin” she said in an interview.
“In general, though, treatment obviously matters and people who are better treated tend to do better, so while I think this study raises the question of what role metformin plays in the risk of mortality and COVID-19, I don’t think it necessarily proves the association,” Dr. Peters asserted.
Diverse population
The new study, published this month in Frontiers of Endocrinology, included 25,326 individuals who were tested for COVID-19 at the University of Alabama at Birmingham Hospital between February and June 2020.
Overall, 2.4% tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 604), which the authors note is likely a low figure because screening included asymptomatic hospital staff and patients having elective procedures.
Black/African American patients had a significantly higher risk of COVID-19 positivity, compared with White patients (odds ratio, 2.6; P < .0001). Rates were also higher among those with hypertension (OR, 2.46), diabetes (OR, 2.11), and obesity (OR, 1.93), compared with those without each condition (all P < .0001).
The overall mortality rate in COVID-19-positive patients was 11%. Diabetes was associated with a dramatically increased risk of death (OR, 3.62; P < .0001), and remained an independent risk factor even after adjusting for age, race, sex, obesity, and hypertension.
Notably, the reduction in mortality among those with diabetes taking metformin prior to COVID-19 diagnosis was significant: 11% of those patients died, compared with 23% of those with diabetes not taking metformin (OR, 0.33; P = .021).
Similar findings reported across varied populations
The study adds to mounting research suggesting metformin could have a protective effect on COVID-19 mortality, including an early report from Wuhan, China, findings from the French CORONADO study, and a U.S. study linking treatment with decreased mortality among women with COVID-19.
Of note, the effects of metformin on mortality in the current study were observed in men and women alike, as well as in high-risk subgroups including African Americans.
“The fact that such similar results were obtained in different populations from around the world suggests that the observed reduction in mortality risk, associated with metformin use in subjects with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19, might be generalizable,” the authors wrote.
“Furthermore, these findings underline the importance of following general diabetes treatment and prevention guidelines and not delaying or discontinuing any metformin treatment,” they add.
Speculation of mechanisms includes anti-inflammatory effects
While the mechanisms behind metformin’s potential role in reducing mortality risk in COVID-19 are unknown, the authors note that the most obvious assumption – that improved glycemic control may be a key factor – is disputed by the study’s finding that blood glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c were not significantly different among COVID-19 survivors taking versus not taking metformin.
They point instead to metformin’s known anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic properties.
“We therefore hypothesize that, by exerting some of these effects, metformin might improve outcomes and we are now in the process of investigating this possibility further,” Dr. Shalev said.
Dr. Peters noted that anti-inflammatory properties, themselves, are not necessarily unique to metformin in the treatment of diabetes.
“Many other agents, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors can reduce inflammation, so I don’t know if that would explain it, but it certainly could help,” she said. “[Reducing inflammation] is a hypothesis you see commonly with diabetes drugs, but I think there are also a lot of metabolic benefits from metformin.”
“It was fascinating that they had the A1c data and that survival with metformin didn’t appear to be as related to A1c levels as one might think,” she added.
Notably, a key advantage, should the effects and mechanisms be validated, is metformin’s high accessibility, Dr. Peters added.
“This doesn’t necessarily tell us what we can do to reduce the health care disparities surrounding COVID-19, but the fact that metformin is low cost and easily available is very important, so maybe it will help as we try to grapple with other risk factors.”
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People with type 2 diabetes who develop COVID-19 show a substantially reduced risk of dying if they are taking metformin, shows a study that adds to prior research indicating the drug might somehow play a role in reducing the severity of infection.
“Unlike several previous analyses, this was a study in a racially diverse population with a high proportion of Blacks/African Americans and [it] revealed that metformin treatment of diabetes prior to diagnosis with COVID-19 was associated with a dramatic threefold reduced mortality in subjects with type 2 diabetes, even after correcting for multiple covariates,” first author Anath Shalev, MD, of the Comprehensive Diabetes Center at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, said in an interview.
But Anne Peters, MD, a professor of clinical medicine at the University of Southern California, Los Angeles, said caution is needed when interpreting these findings.
“It’s hard to tease out the true effects because, for instance, those treated with insulin may be a sicker subset of patients with diabetes than those on metformin, or those with comorbidities such as renal insufficiency may not be treated with metformin” she said in an interview.
“In general, though, treatment obviously matters and people who are better treated tend to do better, so while I think this study raises the question of what role metformin plays in the risk of mortality and COVID-19, I don’t think it necessarily proves the association,” Dr. Peters asserted.
Diverse population
The new study, published this month in Frontiers of Endocrinology, included 25,326 individuals who were tested for COVID-19 at the University of Alabama at Birmingham Hospital between February and June 2020.
Overall, 2.4% tested positive for COVID-19 (n = 604), which the authors note is likely a low figure because screening included asymptomatic hospital staff and patients having elective procedures.
Black/African American patients had a significantly higher risk of COVID-19 positivity, compared with White patients (odds ratio, 2.6; P < .0001). Rates were also higher among those with hypertension (OR, 2.46), diabetes (OR, 2.11), and obesity (OR, 1.93), compared with those without each condition (all P < .0001).
The overall mortality rate in COVID-19-positive patients was 11%. Diabetes was associated with a dramatically increased risk of death (OR, 3.62; P < .0001), and remained an independent risk factor even after adjusting for age, race, sex, obesity, and hypertension.
Notably, the reduction in mortality among those with diabetes taking metformin prior to COVID-19 diagnosis was significant: 11% of those patients died, compared with 23% of those with diabetes not taking metformin (OR, 0.33; P = .021).
Similar findings reported across varied populations
The study adds to mounting research suggesting metformin could have a protective effect on COVID-19 mortality, including an early report from Wuhan, China, findings from the French CORONADO study, and a U.S. study linking treatment with decreased mortality among women with COVID-19.
Of note, the effects of metformin on mortality in the current study were observed in men and women alike, as well as in high-risk subgroups including African Americans.
“The fact that such similar results were obtained in different populations from around the world suggests that the observed reduction in mortality risk, associated with metformin use in subjects with type 2 diabetes and COVID-19, might be generalizable,” the authors wrote.
“Furthermore, these findings underline the importance of following general diabetes treatment and prevention guidelines and not delaying or discontinuing any metformin treatment,” they add.
Speculation of mechanisms includes anti-inflammatory effects
While the mechanisms behind metformin’s potential role in reducing mortality risk in COVID-19 are unknown, the authors note that the most obvious assumption – that improved glycemic control may be a key factor – is disputed by the study’s finding that blood glucose levels and hemoglobin A1c were not significantly different among COVID-19 survivors taking versus not taking metformin.
They point instead to metformin’s known anti-inflammatory and antithrombotic properties.
“We therefore hypothesize that, by exerting some of these effects, metformin might improve outcomes and we are now in the process of investigating this possibility further,” Dr. Shalev said.
Dr. Peters noted that anti-inflammatory properties, themselves, are not necessarily unique to metformin in the treatment of diabetes.
“Many other agents, such as sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors can reduce inflammation, so I don’t know if that would explain it, but it certainly could help,” she said. “[Reducing inflammation] is a hypothesis you see commonly with diabetes drugs, but I think there are also a lot of metabolic benefits from metformin.”
“It was fascinating that they had the A1c data and that survival with metformin didn’t appear to be as related to A1c levels as one might think,” she added.
Notably, a key advantage, should the effects and mechanisms be validated, is metformin’s high accessibility, Dr. Peters added.
“This doesn’t necessarily tell us what we can do to reduce the health care disparities surrounding COVID-19, but the fact that metformin is low cost and easily available is very important, so maybe it will help as we try to grapple with other risk factors.”
The authors have reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Seven ways President Biden could now change health care
President Joe Biden has come into office after an unexpected shift in Congress. On Jan. 5, Democrats scored an upset by winning two U.S. Senate seats in runoff elections in Georgia, giving them control of the Senate.
Now the Democrats have control of all three levers of power – the Senate, the House, and the presidency – for the first time since the early years of the Obama administration.
How will President Biden use this new concentration of power to shape health care policy?
Democrats’ small majorities in both houses of Congress suggest that moderation and bipartisanship will be necessary to get things done. Moreover, Mr. Biden himself is calling for bipartisanship. “On this January day,” he said in his inauguration speech, “my whole soul is in this: Bringing America together, uniting our people, uniting our nation.”
Key health care actions that Mr. Biden could pursue include the following.
1. Passing a new COVID-19 relief bill
Above all, Mr. Biden is focused on overcoming the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been registering record deaths recently, and getting newly released vaccines to Americans.
“Dealing with the coronavirus pandemic is one of the most important battles our administration will face, and I will be informed by science and by experts,” the president said.
“There is no question that the pandemic is the highest priority for the Biden administration,” said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. “COVID will dominate the early weeks and months of this administration. His success rests, in particular, on improving the rollout of vaccines.”
Five days before his inauguration, the president-elect unveiled the American Rescue Plan, a massive, $1.9 trillion legislative package intended to hasten rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, improve COVID-19 testing, and provide financial help to businesses and individuals, among many other things.
The bill would add $1,400 to the recently passed $600 government relief payments for each American, amounting to a $2,000 check. It would also enact many non-COVID-19 measures, such as a $15-an-hour minimum wage and measures to bolster the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
If Democrats cannot reach a deal with the Republicans, they might turn the proposal into a reconciliation bill, which could then be passed with a simple majority. However, drafting a reconciliation bill is a long, complicated process that would require removing provisions that don’t meet the requirements of reconciliation, said Hazen Marshall, a Washington lobbyist and former staffer for Sen. Mitch McConnell.
Most importantly, Mr. Marshall said, reconciliation bills bring out diehard partisanship. “They involve a sledgehammer mentality,” he says. “You’re telling the other side that their views aren’t going to matter.” The final version of the ACA, for example, was passed as a reconciliation bill, with not one Republican vote.
In the Trump years, “the last four reconciliation bills did not get any votes from the minority,” added Rodney Whitlock, PhD, a political consultant at McDermott+Consulting, who worked 21 years for Republicans in the House. “When the majority chooses to use reconciliation, it is an admission that it has no interest in working with the minority.”
Hammering out a compromise will be tough, but Robert Pearl MD, former CEO of the Permanente Medical Group and a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that if anyone can do it, it would be President Biden. Having served in the Senate for 36 years, “Biden knows Congress better than any president since Lyndon Johnson,” he said. “He can reach across the aisle and get legislation passed as much as anyone could these days.”
2. Restoring Obamacare
Mr. Biden has vowed to undo a gradual dismantling of the ACA that went on during the Trump administration through executive orders, rule-making, and new laws. “Reinvigorating the ACA was a central part of Biden’s platform as a candidate,” Mr. Levitt said.
Each Trump action against the ACA must be undone in the same way. Presidential orders must be met with presidential orders, regulations with regulations, and legislation with legislation.
The ACA is also being challenged in the Supreme Court. Republicans under Trump passed a law that reduced the penalty for not buying health insurance under the ACA to zero. Then a group of 20 states, led by Texas, filed a lawsuit asserting that this change makes the ACA unconstitutional.
The lawsuit was heard by the Supreme Court in November. From remarks made by the justices then, it appears that the court might well uphold the law when a verdict comes down in June.
But just in case, Mr. Biden wants Congress to enact a small penalty for not buying health insurance, which would remove the basis of the lawsuit.
Mr. Biden’s choice for secretary of Health and Human Services shows his level of commitment to protecting the ACA. His HHS nominee is California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who led a group of 17 states defending the ACA in the current lawsuit.
In addition to undoing Trump’s changes, Mr. Biden plans to expand the ACA beyond the original legislation. The new COVID-19 bill contains provisions that would expand subsidies to buy insurance on the exchanges and would lower the maximum percentage of income that anyone has to pay for health insurance to 8.5%.
Dealing with Medicaid is also related to the ACA. In 2012, the Supreme Court struck down a mandate that states expand their Medicaid programs, with substantial funding from the federal government.
To date, 12 states still do not participate in the Medicaid expansion. To lure them into the expansion, the Democrat-controlled House last session passed a bill that would offer to pay the entire bill for the first 3 years of Medicaid expansion if they chose to enact an expansion.
3. Undoing other Trump actions in health care
In addition to changes in the ACA, Trump also enacted a number of other changes in health care that President Biden could undo. For example, Mr. Biden says he will reenter the World Health Organization (WHO) so that the United States could better coordinate a COVID-19 response with other nations. Trump exited the WHO with the stroke of a pen, and Mr. Biden can do the same in reverse.
Under Trump, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services used waivers to weaken the ACA and allow states to alter their Medicaid programs. One waiver allows Georgia to leave the ACA exchanges and put brokers in charge of buying coverage. Other waivers allow states to transform federal Medicaid payments into block grants, which several states are planning to do.
The Trump CMS has allowed several states to use Medicaid waivers to add work requirements for Medicaid recipients. The courts have blocked the work rules so far, and the Biden CMS may decide to reverse these waivers or modify them.
“Undoing waivers is normally a fairly simple thing,” Mr. Levitt said. In January, however, the Trump CMS asked some waiver states to sign new contracts in which the CMS pledges not to end a waiver without 9 months’ notice. It’s unclear how many states signed such contracts and what obligation the Biden CMS has to enforce them.
The Trump CMS also stopped reimbursing insurers for waiving deductibles and copayments for low-income customers, as directed by the ACA. Without federal reimbursement, some insurers raised premiums by as much as 20% to cover the costs. It is unclear how the Biden CMS would tackle this change.
4. Negotiating lower drug prices
Allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices, a major plank in Mr. Biden’s campaign, would seem like a slam dunk for the Democrats. This approach is backed by 89% of Americans, including 84% of Republicans, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation survey in December.
“With that level of support, it’s hard to go wrong politically on this issue,” Mr. Levitt said.
Many Republicans, however, do not favor negotiating drug prices, and the two parties continue to be far apart on how to control drug prices. Trump signed an action that allows Americans to buy cheaper drugs abroad, an approach that Mr. Biden also supports, but it is now tied up in the courts.
“A drug pricing bill has always been difficult to pass,” Dr. Whitlock said. “The issue is popular with the public, but change does not come easily. The drug lobby is one the strongest in Washington, and now it may be even stronger, since it was the drug companies that gave us the COVID vaccines.”
Dr. Whitlock said Republicans will want Democrats to compromise on drug pricing, but he doubts they will do so. The House passed a bill to negotiate drug prices last year, which never was voted on in the Senate. “It is difficult to imagine that the Democrats will be able to move rightward from that House bill,” Dr. Whitlock said. “Democrats are likely to stand pat on drug pricing.”
5. Introducing a public option
President Biden’s campaign proposal for a public option – health insurance offered by the federal government – and to lower the age for Medicare eligibility from 65 years to 60 years, resulted from a compromise between two factions of the Democratic party on how to expand coverage.
Although Mr. Biden and other moderates wanted to focus on fixing the ACA, Democrats led by Sen. Bernie Sanders of Vermont called for a single-payer system, dubbed “Medicare for all.” A public option was seen as the middle ground between the two camps.
“A public option would be a very controversial,” Dr. Whitlock said. Critics say it would pay at Medicare rates, which would reduce doctors’ reimbursements, and save very little money compared with a single-payer system.
Dr. Pearl sees similar problems with lowering the Medicare age. “This would be an expensive change that the federal government could not afford, particularly with all the spending on the pandemic,” he said. “And it would be tough on doctors and hospitals, because Medicare pays less than the private insurance payment they are now getting.”
“The public option is likely to get serious discussion within the Democratic caucus and get onto the Senate floor,” Mr. Levitt said. “The party won’t ignore it.” He notes that in the new Senate, Sen. Sanders chairs the budget committee, and from that position he is likely to push for expanding access to care.
Mr. Levitt says the Biden CMS might allow states to experiment with a statewide public option or even a single-payer model, but he concedes that states, with their budgets ravaged by COVID-19, do not currently have the money to launch such programs.
6. Reviving the CMS
Under President Obama, the CMS was the engine that implemented the ACA and shepherded wider use of value-based reimbursements, which reward providers for quality and outcomes rather than volume.
Under the Trump administration, CMS leadership continued to uphold value-based reimbursement, Dr. Pearl observed. “CMS leadership championed value-based payments, but they encountered a lot of pushback from doctors and hospitals and had to scale back their goals,” he said.
On the other hand, the Trump CMS took a 180-degree turn on the ACA and worked to take it apart. This took a toll on staff morale, according to Donald M. Berwick, MD, who ran the CMS under President Obama. “Many people in CMS did not feel supported during the Trump administration, and some of them left,” Dr. Berwick said.
The CMS needs experienced staff on board to write comprehensible rules and regulations that can overcome court challenges.
Having a fully functioning CMS also requires consistent leadership, which was a problem for Obama. When Mr. Obama nominated Dr. Berwick, 60 Senate votes were needed to confirm him, and Republicans would not vote for him. Mr. Obama eventually brought Dr. Berwick in as a recess appointment, but it meant he could serve for only 17 months.
Since then, Senate confirmation rules have changed so that only a simple majority is needed to confirm appointments. This is important for Biden’s nominees, Dr. Berwick said. “For a president, having your team in place means you are able to execute the policies you want,” he said. “You need to have consistent leadership.”
7. Potentially changing health care without Congress
Even with their newly won control of the Senate, the Democrats’ thin majorities in both houses of Congress may not be enough to pass much legislation if Republicans are solidly opposed.
Democrats in the House also have a narrow path this session in which to pass legislation. The Democratic leadership has an 11-vote majority, but it must contend with 15 moderate representatives in purple districts (where Democrats and Republicans have about equal support).
A bigger problem looms before the Democrats. In 2022, the party may well lose its majorities in both houses. Mr. Whitlock notes that the party of an incoming president normally loses seats in the first midterm election. “The last incoming president to keep both houses of Congress in his first midterm was Jimmy Carter,” he said.
If this happens, President Biden would have to govern without the support of Congress, which is what Barack Obama had to do through most of his presidency. As Mr. Obama’s vice president, Mr. Biden is well aware how that goes. Governing without Congress means relying on presidential orders and decrees.
In health care, Mr. Biden has a powerful policy-making tool, the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation (CMMI). The CMMI was empowered by the ACA to initiate pilot programs for new payment models.
So far, the CMMI’s work has been mainly limited to accountable care organizations, bundled payments, and patient-centered medical homes, but it could also be used to enact new federal policies that would normally require Congressional action, Mr. Levitt said.
Conclusion
Expectations have been very high for what President Joe Biden can do in health care. He needs to unite a very divided political system to defeat a deadly pandemic, restore Obamacare, and sign landmark legislation, such as a drug-pricing bill.
But shepherding bills through Congress will be a challenge. “You need to have accountability, unity, and civility, which is a Herculean task,” Mr. Whitlock said. “You have to keep policies off the table that could blow up the bipartisanship.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Joe Biden has come into office after an unexpected shift in Congress. On Jan. 5, Democrats scored an upset by winning two U.S. Senate seats in runoff elections in Georgia, giving them control of the Senate.
Now the Democrats have control of all three levers of power – the Senate, the House, and the presidency – for the first time since the early years of the Obama administration.
How will President Biden use this new concentration of power to shape health care policy?
Democrats’ small majorities in both houses of Congress suggest that moderation and bipartisanship will be necessary to get things done. Moreover, Mr. Biden himself is calling for bipartisanship. “On this January day,” he said in his inauguration speech, “my whole soul is in this: Bringing America together, uniting our people, uniting our nation.”
Key health care actions that Mr. Biden could pursue include the following.
1. Passing a new COVID-19 relief bill
Above all, Mr. Biden is focused on overcoming the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been registering record deaths recently, and getting newly released vaccines to Americans.
“Dealing with the coronavirus pandemic is one of the most important battles our administration will face, and I will be informed by science and by experts,” the president said.
“There is no question that the pandemic is the highest priority for the Biden administration,” said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. “COVID will dominate the early weeks and months of this administration. His success rests, in particular, on improving the rollout of vaccines.”
Five days before his inauguration, the president-elect unveiled the American Rescue Plan, a massive, $1.9 trillion legislative package intended to hasten rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, improve COVID-19 testing, and provide financial help to businesses and individuals, among many other things.
The bill would add $1,400 to the recently passed $600 government relief payments for each American, amounting to a $2,000 check. It would also enact many non-COVID-19 measures, such as a $15-an-hour minimum wage and measures to bolster the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
If Democrats cannot reach a deal with the Republicans, they might turn the proposal into a reconciliation bill, which could then be passed with a simple majority. However, drafting a reconciliation bill is a long, complicated process that would require removing provisions that don’t meet the requirements of reconciliation, said Hazen Marshall, a Washington lobbyist and former staffer for Sen. Mitch McConnell.
Most importantly, Mr. Marshall said, reconciliation bills bring out diehard partisanship. “They involve a sledgehammer mentality,” he says. “You’re telling the other side that their views aren’t going to matter.” The final version of the ACA, for example, was passed as a reconciliation bill, with not one Republican vote.
In the Trump years, “the last four reconciliation bills did not get any votes from the minority,” added Rodney Whitlock, PhD, a political consultant at McDermott+Consulting, who worked 21 years for Republicans in the House. “When the majority chooses to use reconciliation, it is an admission that it has no interest in working with the minority.”
Hammering out a compromise will be tough, but Robert Pearl MD, former CEO of the Permanente Medical Group and a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that if anyone can do it, it would be President Biden. Having served in the Senate for 36 years, “Biden knows Congress better than any president since Lyndon Johnson,” he said. “He can reach across the aisle and get legislation passed as much as anyone could these days.”
2. Restoring Obamacare
Mr. Biden has vowed to undo a gradual dismantling of the ACA that went on during the Trump administration through executive orders, rule-making, and new laws. “Reinvigorating the ACA was a central part of Biden’s platform as a candidate,” Mr. Levitt said.
Each Trump action against the ACA must be undone in the same way. Presidential orders must be met with presidential orders, regulations with regulations, and legislation with legislation.
The ACA is also being challenged in the Supreme Court. Republicans under Trump passed a law that reduced the penalty for not buying health insurance under the ACA to zero. Then a group of 20 states, led by Texas, filed a lawsuit asserting that this change makes the ACA unconstitutional.
The lawsuit was heard by the Supreme Court in November. From remarks made by the justices then, it appears that the court might well uphold the law when a verdict comes down in June.
But just in case, Mr. Biden wants Congress to enact a small penalty for not buying health insurance, which would remove the basis of the lawsuit.
Mr. Biden’s choice for secretary of Health and Human Services shows his level of commitment to protecting the ACA. His HHS nominee is California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who led a group of 17 states defending the ACA in the current lawsuit.
In addition to undoing Trump’s changes, Mr. Biden plans to expand the ACA beyond the original legislation. The new COVID-19 bill contains provisions that would expand subsidies to buy insurance on the exchanges and would lower the maximum percentage of income that anyone has to pay for health insurance to 8.5%.
Dealing with Medicaid is also related to the ACA. In 2012, the Supreme Court struck down a mandate that states expand their Medicaid programs, with substantial funding from the federal government.
To date, 12 states still do not participate in the Medicaid expansion. To lure them into the expansion, the Democrat-controlled House last session passed a bill that would offer to pay the entire bill for the first 3 years of Medicaid expansion if they chose to enact an expansion.
3. Undoing other Trump actions in health care
In addition to changes in the ACA, Trump also enacted a number of other changes in health care that President Biden could undo. For example, Mr. Biden says he will reenter the World Health Organization (WHO) so that the United States could better coordinate a COVID-19 response with other nations. Trump exited the WHO with the stroke of a pen, and Mr. Biden can do the same in reverse.
Under Trump, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services used waivers to weaken the ACA and allow states to alter their Medicaid programs. One waiver allows Georgia to leave the ACA exchanges and put brokers in charge of buying coverage. Other waivers allow states to transform federal Medicaid payments into block grants, which several states are planning to do.
The Trump CMS has allowed several states to use Medicaid waivers to add work requirements for Medicaid recipients. The courts have blocked the work rules so far, and the Biden CMS may decide to reverse these waivers or modify them.
“Undoing waivers is normally a fairly simple thing,” Mr. Levitt said. In January, however, the Trump CMS asked some waiver states to sign new contracts in which the CMS pledges not to end a waiver without 9 months’ notice. It’s unclear how many states signed such contracts and what obligation the Biden CMS has to enforce them.
The Trump CMS also stopped reimbursing insurers for waiving deductibles and copayments for low-income customers, as directed by the ACA. Without federal reimbursement, some insurers raised premiums by as much as 20% to cover the costs. It is unclear how the Biden CMS would tackle this change.
4. Negotiating lower drug prices
Allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices, a major plank in Mr. Biden’s campaign, would seem like a slam dunk for the Democrats. This approach is backed by 89% of Americans, including 84% of Republicans, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation survey in December.
“With that level of support, it’s hard to go wrong politically on this issue,” Mr. Levitt said.
Many Republicans, however, do not favor negotiating drug prices, and the two parties continue to be far apart on how to control drug prices. Trump signed an action that allows Americans to buy cheaper drugs abroad, an approach that Mr. Biden also supports, but it is now tied up in the courts.
“A drug pricing bill has always been difficult to pass,” Dr. Whitlock said. “The issue is popular with the public, but change does not come easily. The drug lobby is one the strongest in Washington, and now it may be even stronger, since it was the drug companies that gave us the COVID vaccines.”
Dr. Whitlock said Republicans will want Democrats to compromise on drug pricing, but he doubts they will do so. The House passed a bill to negotiate drug prices last year, which never was voted on in the Senate. “It is difficult to imagine that the Democrats will be able to move rightward from that House bill,” Dr. Whitlock said. “Democrats are likely to stand pat on drug pricing.”
5. Introducing a public option
President Biden’s campaign proposal for a public option – health insurance offered by the federal government – and to lower the age for Medicare eligibility from 65 years to 60 years, resulted from a compromise between two factions of the Democratic party on how to expand coverage.
Although Mr. Biden and other moderates wanted to focus on fixing the ACA, Democrats led by Sen. Bernie Sanders of Vermont called for a single-payer system, dubbed “Medicare for all.” A public option was seen as the middle ground between the two camps.
“A public option would be a very controversial,” Dr. Whitlock said. Critics say it would pay at Medicare rates, which would reduce doctors’ reimbursements, and save very little money compared with a single-payer system.
Dr. Pearl sees similar problems with lowering the Medicare age. “This would be an expensive change that the federal government could not afford, particularly with all the spending on the pandemic,” he said. “And it would be tough on doctors and hospitals, because Medicare pays less than the private insurance payment they are now getting.”
“The public option is likely to get serious discussion within the Democratic caucus and get onto the Senate floor,” Mr. Levitt said. “The party won’t ignore it.” He notes that in the new Senate, Sen. Sanders chairs the budget committee, and from that position he is likely to push for expanding access to care.
Mr. Levitt says the Biden CMS might allow states to experiment with a statewide public option or even a single-payer model, but he concedes that states, with their budgets ravaged by COVID-19, do not currently have the money to launch such programs.
6. Reviving the CMS
Under President Obama, the CMS was the engine that implemented the ACA and shepherded wider use of value-based reimbursements, which reward providers for quality and outcomes rather than volume.
Under the Trump administration, CMS leadership continued to uphold value-based reimbursement, Dr. Pearl observed. “CMS leadership championed value-based payments, but they encountered a lot of pushback from doctors and hospitals and had to scale back their goals,” he said.
On the other hand, the Trump CMS took a 180-degree turn on the ACA and worked to take it apart. This took a toll on staff morale, according to Donald M. Berwick, MD, who ran the CMS under President Obama. “Many people in CMS did not feel supported during the Trump administration, and some of them left,” Dr. Berwick said.
The CMS needs experienced staff on board to write comprehensible rules and regulations that can overcome court challenges.
Having a fully functioning CMS also requires consistent leadership, which was a problem for Obama. When Mr. Obama nominated Dr. Berwick, 60 Senate votes were needed to confirm him, and Republicans would not vote for him. Mr. Obama eventually brought Dr. Berwick in as a recess appointment, but it meant he could serve for only 17 months.
Since then, Senate confirmation rules have changed so that only a simple majority is needed to confirm appointments. This is important for Biden’s nominees, Dr. Berwick said. “For a president, having your team in place means you are able to execute the policies you want,” he said. “You need to have consistent leadership.”
7. Potentially changing health care without Congress
Even with their newly won control of the Senate, the Democrats’ thin majorities in both houses of Congress may not be enough to pass much legislation if Republicans are solidly opposed.
Democrats in the House also have a narrow path this session in which to pass legislation. The Democratic leadership has an 11-vote majority, but it must contend with 15 moderate representatives in purple districts (where Democrats and Republicans have about equal support).
A bigger problem looms before the Democrats. In 2022, the party may well lose its majorities in both houses. Mr. Whitlock notes that the party of an incoming president normally loses seats in the first midterm election. “The last incoming president to keep both houses of Congress in his first midterm was Jimmy Carter,” he said.
If this happens, President Biden would have to govern without the support of Congress, which is what Barack Obama had to do through most of his presidency. As Mr. Obama’s vice president, Mr. Biden is well aware how that goes. Governing without Congress means relying on presidential orders and decrees.
In health care, Mr. Biden has a powerful policy-making tool, the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation (CMMI). The CMMI was empowered by the ACA to initiate pilot programs for new payment models.
So far, the CMMI’s work has been mainly limited to accountable care organizations, bundled payments, and patient-centered medical homes, but it could also be used to enact new federal policies that would normally require Congressional action, Mr. Levitt said.
Conclusion
Expectations have been very high for what President Joe Biden can do in health care. He needs to unite a very divided political system to defeat a deadly pandemic, restore Obamacare, and sign landmark legislation, such as a drug-pricing bill.
But shepherding bills through Congress will be a challenge. “You need to have accountability, unity, and civility, which is a Herculean task,” Mr. Whitlock said. “You have to keep policies off the table that could blow up the bipartisanship.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Joe Biden has come into office after an unexpected shift in Congress. On Jan. 5, Democrats scored an upset by winning two U.S. Senate seats in runoff elections in Georgia, giving them control of the Senate.
Now the Democrats have control of all three levers of power – the Senate, the House, and the presidency – for the first time since the early years of the Obama administration.
How will President Biden use this new concentration of power to shape health care policy?
Democrats’ small majorities in both houses of Congress suggest that moderation and bipartisanship will be necessary to get things done. Moreover, Mr. Biden himself is calling for bipartisanship. “On this January day,” he said in his inauguration speech, “my whole soul is in this: Bringing America together, uniting our people, uniting our nation.”
Key health care actions that Mr. Biden could pursue include the following.
1. Passing a new COVID-19 relief bill
Above all, Mr. Biden is focused on overcoming the COVID-19 pandemic, which has been registering record deaths recently, and getting newly released vaccines to Americans.
“Dealing with the coronavirus pandemic is one of the most important battles our administration will face, and I will be informed by science and by experts,” the president said.
“There is no question that the pandemic is the highest priority for the Biden administration,” said Larry Levitt, executive vice president for health policy at the Henry J. Kaiser Family Foundation. “COVID will dominate the early weeks and months of this administration. His success rests, in particular, on improving the rollout of vaccines.”
Five days before his inauguration, the president-elect unveiled the American Rescue Plan, a massive, $1.9 trillion legislative package intended to hasten rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, improve COVID-19 testing, and provide financial help to businesses and individuals, among many other things.
The bill would add $1,400 to the recently passed $600 government relief payments for each American, amounting to a $2,000 check. It would also enact many non-COVID-19 measures, such as a $15-an-hour minimum wage and measures to bolster the Affordable Care Act (ACA).
If Democrats cannot reach a deal with the Republicans, they might turn the proposal into a reconciliation bill, which could then be passed with a simple majority. However, drafting a reconciliation bill is a long, complicated process that would require removing provisions that don’t meet the requirements of reconciliation, said Hazen Marshall, a Washington lobbyist and former staffer for Sen. Mitch McConnell.
Most importantly, Mr. Marshall said, reconciliation bills bring out diehard partisanship. “They involve a sledgehammer mentality,” he says. “You’re telling the other side that their views aren’t going to matter.” The final version of the ACA, for example, was passed as a reconciliation bill, with not one Republican vote.
In the Trump years, “the last four reconciliation bills did not get any votes from the minority,” added Rodney Whitlock, PhD, a political consultant at McDermott+Consulting, who worked 21 years for Republicans in the House. “When the majority chooses to use reconciliation, it is an admission that it has no interest in working with the minority.”
Hammering out a compromise will be tough, but Robert Pearl MD, former CEO of the Permanente Medical Group and a professor at Stanford (Calif.) University, said that if anyone can do it, it would be President Biden. Having served in the Senate for 36 years, “Biden knows Congress better than any president since Lyndon Johnson,” he said. “He can reach across the aisle and get legislation passed as much as anyone could these days.”
2. Restoring Obamacare
Mr. Biden has vowed to undo a gradual dismantling of the ACA that went on during the Trump administration through executive orders, rule-making, and new laws. “Reinvigorating the ACA was a central part of Biden’s platform as a candidate,” Mr. Levitt said.
Each Trump action against the ACA must be undone in the same way. Presidential orders must be met with presidential orders, regulations with regulations, and legislation with legislation.
The ACA is also being challenged in the Supreme Court. Republicans under Trump passed a law that reduced the penalty for not buying health insurance under the ACA to zero. Then a group of 20 states, led by Texas, filed a lawsuit asserting that this change makes the ACA unconstitutional.
The lawsuit was heard by the Supreme Court in November. From remarks made by the justices then, it appears that the court might well uphold the law when a verdict comes down in June.
But just in case, Mr. Biden wants Congress to enact a small penalty for not buying health insurance, which would remove the basis of the lawsuit.
Mr. Biden’s choice for secretary of Health and Human Services shows his level of commitment to protecting the ACA. His HHS nominee is California Attorney General Xavier Becerra, who led a group of 17 states defending the ACA in the current lawsuit.
In addition to undoing Trump’s changes, Mr. Biden plans to expand the ACA beyond the original legislation. The new COVID-19 bill contains provisions that would expand subsidies to buy insurance on the exchanges and would lower the maximum percentage of income that anyone has to pay for health insurance to 8.5%.
Dealing with Medicaid is also related to the ACA. In 2012, the Supreme Court struck down a mandate that states expand their Medicaid programs, with substantial funding from the federal government.
To date, 12 states still do not participate in the Medicaid expansion. To lure them into the expansion, the Democrat-controlled House last session passed a bill that would offer to pay the entire bill for the first 3 years of Medicaid expansion if they chose to enact an expansion.
3. Undoing other Trump actions in health care
In addition to changes in the ACA, Trump also enacted a number of other changes in health care that President Biden could undo. For example, Mr. Biden says he will reenter the World Health Organization (WHO) so that the United States could better coordinate a COVID-19 response with other nations. Trump exited the WHO with the stroke of a pen, and Mr. Biden can do the same in reverse.
Under Trump, the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services used waivers to weaken the ACA and allow states to alter their Medicaid programs. One waiver allows Georgia to leave the ACA exchanges and put brokers in charge of buying coverage. Other waivers allow states to transform federal Medicaid payments into block grants, which several states are planning to do.
The Trump CMS has allowed several states to use Medicaid waivers to add work requirements for Medicaid recipients. The courts have blocked the work rules so far, and the Biden CMS may decide to reverse these waivers or modify them.
“Undoing waivers is normally a fairly simple thing,” Mr. Levitt said. In January, however, the Trump CMS asked some waiver states to sign new contracts in which the CMS pledges not to end a waiver without 9 months’ notice. It’s unclear how many states signed such contracts and what obligation the Biden CMS has to enforce them.
The Trump CMS also stopped reimbursing insurers for waiving deductibles and copayments for low-income customers, as directed by the ACA. Without federal reimbursement, some insurers raised premiums by as much as 20% to cover the costs. It is unclear how the Biden CMS would tackle this change.
4. Negotiating lower drug prices
Allowing Medicare to negotiate drug prices, a major plank in Mr. Biden’s campaign, would seem like a slam dunk for the Democrats. This approach is backed by 89% of Americans, including 84% of Republicans, according to a Kaiser Family Foundation survey in December.
“With that level of support, it’s hard to go wrong politically on this issue,” Mr. Levitt said.
Many Republicans, however, do not favor negotiating drug prices, and the two parties continue to be far apart on how to control drug prices. Trump signed an action that allows Americans to buy cheaper drugs abroad, an approach that Mr. Biden also supports, but it is now tied up in the courts.
“A drug pricing bill has always been difficult to pass,” Dr. Whitlock said. “The issue is popular with the public, but change does not come easily. The drug lobby is one the strongest in Washington, and now it may be even stronger, since it was the drug companies that gave us the COVID vaccines.”
Dr. Whitlock said Republicans will want Democrats to compromise on drug pricing, but he doubts they will do so. The House passed a bill to negotiate drug prices last year, which never was voted on in the Senate. “It is difficult to imagine that the Democrats will be able to move rightward from that House bill,” Dr. Whitlock said. “Democrats are likely to stand pat on drug pricing.”
5. Introducing a public option
President Biden’s campaign proposal for a public option – health insurance offered by the federal government – and to lower the age for Medicare eligibility from 65 years to 60 years, resulted from a compromise between two factions of the Democratic party on how to expand coverage.
Although Mr. Biden and other moderates wanted to focus on fixing the ACA, Democrats led by Sen. Bernie Sanders of Vermont called for a single-payer system, dubbed “Medicare for all.” A public option was seen as the middle ground between the two camps.
“A public option would be a very controversial,” Dr. Whitlock said. Critics say it would pay at Medicare rates, which would reduce doctors’ reimbursements, and save very little money compared with a single-payer system.
Dr. Pearl sees similar problems with lowering the Medicare age. “This would be an expensive change that the federal government could not afford, particularly with all the spending on the pandemic,” he said. “And it would be tough on doctors and hospitals, because Medicare pays less than the private insurance payment they are now getting.”
“The public option is likely to get serious discussion within the Democratic caucus and get onto the Senate floor,” Mr. Levitt said. “The party won’t ignore it.” He notes that in the new Senate, Sen. Sanders chairs the budget committee, and from that position he is likely to push for expanding access to care.
Mr. Levitt says the Biden CMS might allow states to experiment with a statewide public option or even a single-payer model, but he concedes that states, with their budgets ravaged by COVID-19, do not currently have the money to launch such programs.
6. Reviving the CMS
Under President Obama, the CMS was the engine that implemented the ACA and shepherded wider use of value-based reimbursements, which reward providers for quality and outcomes rather than volume.
Under the Trump administration, CMS leadership continued to uphold value-based reimbursement, Dr. Pearl observed. “CMS leadership championed value-based payments, but they encountered a lot of pushback from doctors and hospitals and had to scale back their goals,” he said.
On the other hand, the Trump CMS took a 180-degree turn on the ACA and worked to take it apart. This took a toll on staff morale, according to Donald M. Berwick, MD, who ran the CMS under President Obama. “Many people in CMS did not feel supported during the Trump administration, and some of them left,” Dr. Berwick said.
The CMS needs experienced staff on board to write comprehensible rules and regulations that can overcome court challenges.
Having a fully functioning CMS also requires consistent leadership, which was a problem for Obama. When Mr. Obama nominated Dr. Berwick, 60 Senate votes were needed to confirm him, and Republicans would not vote for him. Mr. Obama eventually brought Dr. Berwick in as a recess appointment, but it meant he could serve for only 17 months.
Since then, Senate confirmation rules have changed so that only a simple majority is needed to confirm appointments. This is important for Biden’s nominees, Dr. Berwick said. “For a president, having your team in place means you are able to execute the policies you want,” he said. “You need to have consistent leadership.”
7. Potentially changing health care without Congress
Even with their newly won control of the Senate, the Democrats’ thin majorities in both houses of Congress may not be enough to pass much legislation if Republicans are solidly opposed.
Democrats in the House also have a narrow path this session in which to pass legislation. The Democratic leadership has an 11-vote majority, but it must contend with 15 moderate representatives in purple districts (where Democrats and Republicans have about equal support).
A bigger problem looms before the Democrats. In 2022, the party may well lose its majorities in both houses. Mr. Whitlock notes that the party of an incoming president normally loses seats in the first midterm election. “The last incoming president to keep both houses of Congress in his first midterm was Jimmy Carter,” he said.
If this happens, President Biden would have to govern without the support of Congress, which is what Barack Obama had to do through most of his presidency. As Mr. Obama’s vice president, Mr. Biden is well aware how that goes. Governing without Congress means relying on presidential orders and decrees.
In health care, Mr. Biden has a powerful policy-making tool, the Center for Medicare & Medicaid Innovation (CMMI). The CMMI was empowered by the ACA to initiate pilot programs for new payment models.
So far, the CMMI’s work has been mainly limited to accountable care organizations, bundled payments, and patient-centered medical homes, but it could also be used to enact new federal policies that would normally require Congressional action, Mr. Levitt said.
Conclusion
Expectations have been very high for what President Joe Biden can do in health care. He needs to unite a very divided political system to defeat a deadly pandemic, restore Obamacare, and sign landmark legislation, such as a drug-pricing bill.
But shepherding bills through Congress will be a challenge. “You need to have accountability, unity, and civility, which is a Herculean task,” Mr. Whitlock said. “You have to keep policies off the table that could blow up the bipartisanship.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
PCPs play a small part in low-value care spending
according to a brief report published online Jan. 18 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
However, one expert said there are better ways to curb low-value care than focusing on which specialties are guilty of the practice.
Analyzing a 20% random sample of Medicare Part B claims, Aaron Baum, PhD, with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues found that the services primary care physicians performed or ordered made up on average 8.3% of the low-value care their patients received (interquartile range, 3.9%-15.1%; 95th percentile, 35.6%) and their referrals made up 15.4% (IQR, 6.3%-26.4%; 95th percentile, 44.6%).
By specialty, cardiology had the worst record with 27% of all spending on low-value services ($1.8 billion) attributed to that specialty. Yet, of the 25 highest-spending specialties in the report, 12 of them were associated with 1% or less than 1% each of all low-value spending, indicating the waste was widely distributed.
Dr. Baum said in an interview that though there are some PCPs guilty of high spending on low-value services, overall, most primary care physicians’ low-value services add up to only 0.3% of Part B spending. He noted that Part B spending is about one-third of all Medicare spending.
Primary care is often thought to be at the core of care management and spending and PCPs are often seen as the gatekeepers, but this analysis suggests that efforts to make big differences in curtailing low-value spending might be more effective elsewhere.
“There’s only so much spending you can reduce by changing primary care physicians’ services that they directly perform,” Dr. Baum said.
Low-value care is costly, can be harmful
Mark Fendrick, MD, director of the University of Michigan’s Center for Value-Based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that the report adds confirmation to previous research that has consistently shown low-value care is “extremely common, very costly, and provided by primary care providers and specialists alike.” He noted that it can also be harmful.
“The math is simple,” he said. “If we want to improve coverage and lower patient costs for essential services like visits, diagnostic tests, and drugs, we have to reduce spending on those services that do not make Americans any healthier.”
The study ranked 31 clinical services judged to be low value by physician societies, Medicare and clinical guidelines, and their use among beneficiaries enrolled between 2007 and 2014. Here’s how the top six low-value services compare.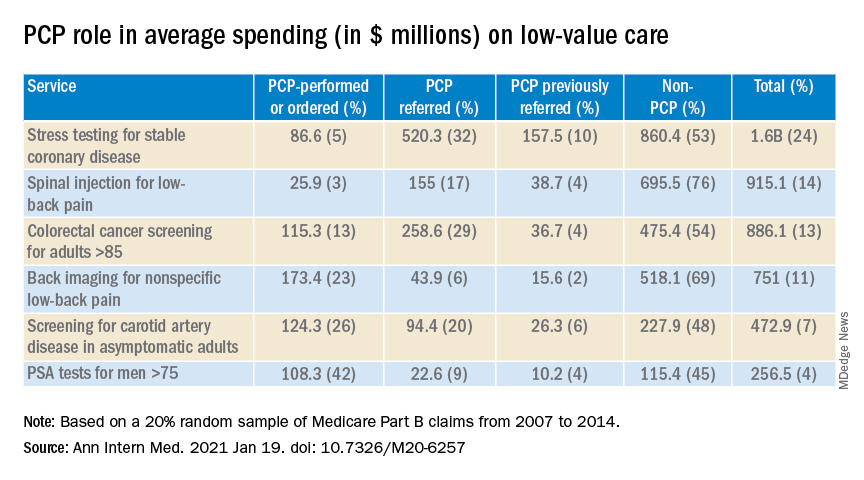
Dr. Fendrick said a weakness of the paper is the years of the data (2007-2014). Some of the criteria around low-value care have changed since then. The age that a prostate-specific antigen test becomes low-value is now 70 years, for instance, instead of 75. He added that some of the figures attributed to non-PCP providers appear out of date.
Dr. Fendrick said, “I understand that there are Medicare patients who end up at a gastroenterologist or surgeon’s office to get colorectal cancer screening, but it would be very hard for me to believe that half of stress tests and over half of colon cancer screening over [age] 85 [years] and half of PSA for people over 75 did not have some type of referring clinicians involved. I certainly don’t think that would be the case in 2020-2021.”
Dr. Baum said those years were the latest years available for the data points needed for this analysis, but he and his colleagues were working to update the data for future publication.
Dr. Fendrick said not much has changed in recent years in terms of waste on low-value care, even with campaigns such as Choosing Wisely dedicated to identifying low-value services or procedures in each specialty.
“I believe there’s not a particular group of clinicians one way or the other who are actually doing any better now than they were 7 years ago,” he said. He would rather focus less on which specialties are associated with the most low-value care and more on the underlying policies that encourage low-value care.
“If you’re going to get paid for doing a stress test and get paid nothing or significantly less if you don’t, the incentives are in the wrong direction,” he said.
Dr. Fendrick said the pandemic era provides an opportunity to eliminate low-value care because use of those services has dropped drastically as resources have been diverted to COVID-19 patients and many services have been delayed or canceled.
He said he has been pushing an approach that providers should be paid more after the pandemic “to do the things we want them to do.”
As an example, he said, instead of paying $886 million on colonoscopies for people over the age of 85, “why don’t we put a policy in place that would make it better for patients by lowering cost sharing and better for providers by paying them more to do the service on the people who need it as opposed to the people who don’t?”
The research was funded by the American Board of Family Medicine Foundation. Dr. Baum and a coauthor reported receiving personal fees from American Board of Family Medicine Foundation during the conduct of the study. Another coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Collective Health, HealthRight 360, PLOS Medicine, and the New England Journal of Medicine, outside the submitted work. Dr. Fendrick disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a brief report published online Jan. 18 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
However, one expert said there are better ways to curb low-value care than focusing on which specialties are guilty of the practice.
Analyzing a 20% random sample of Medicare Part B claims, Aaron Baum, PhD, with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues found that the services primary care physicians performed or ordered made up on average 8.3% of the low-value care their patients received (interquartile range, 3.9%-15.1%; 95th percentile, 35.6%) and their referrals made up 15.4% (IQR, 6.3%-26.4%; 95th percentile, 44.6%).
By specialty, cardiology had the worst record with 27% of all spending on low-value services ($1.8 billion) attributed to that specialty. Yet, of the 25 highest-spending specialties in the report, 12 of them were associated with 1% or less than 1% each of all low-value spending, indicating the waste was widely distributed.
Dr. Baum said in an interview that though there are some PCPs guilty of high spending on low-value services, overall, most primary care physicians’ low-value services add up to only 0.3% of Part B spending. He noted that Part B spending is about one-third of all Medicare spending.
Primary care is often thought to be at the core of care management and spending and PCPs are often seen as the gatekeepers, but this analysis suggests that efforts to make big differences in curtailing low-value spending might be more effective elsewhere.
“There’s only so much spending you can reduce by changing primary care physicians’ services that they directly perform,” Dr. Baum said.
Low-value care is costly, can be harmful
Mark Fendrick, MD, director of the University of Michigan’s Center for Value-Based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that the report adds confirmation to previous research that has consistently shown low-value care is “extremely common, very costly, and provided by primary care providers and specialists alike.” He noted that it can also be harmful.
“The math is simple,” he said. “If we want to improve coverage and lower patient costs for essential services like visits, diagnostic tests, and drugs, we have to reduce spending on those services that do not make Americans any healthier.”
The study ranked 31 clinical services judged to be low value by physician societies, Medicare and clinical guidelines, and their use among beneficiaries enrolled between 2007 and 2014. Here’s how the top six low-value services compare.
Dr. Fendrick said a weakness of the paper is the years of the data (2007-2014). Some of the criteria around low-value care have changed since then. The age that a prostate-specific antigen test becomes low-value is now 70 years, for instance, instead of 75. He added that some of the figures attributed to non-PCP providers appear out of date.
Dr. Fendrick said, “I understand that there are Medicare patients who end up at a gastroenterologist or surgeon’s office to get colorectal cancer screening, but it would be very hard for me to believe that half of stress tests and over half of colon cancer screening over [age] 85 [years] and half of PSA for people over 75 did not have some type of referring clinicians involved. I certainly don’t think that would be the case in 2020-2021.”
Dr. Baum said those years were the latest years available for the data points needed for this analysis, but he and his colleagues were working to update the data for future publication.
Dr. Fendrick said not much has changed in recent years in terms of waste on low-value care, even with campaigns such as Choosing Wisely dedicated to identifying low-value services or procedures in each specialty.
“I believe there’s not a particular group of clinicians one way or the other who are actually doing any better now than they were 7 years ago,” he said. He would rather focus less on which specialties are associated with the most low-value care and more on the underlying policies that encourage low-value care.
“If you’re going to get paid for doing a stress test and get paid nothing or significantly less if you don’t, the incentives are in the wrong direction,” he said.
Dr. Fendrick said the pandemic era provides an opportunity to eliminate low-value care because use of those services has dropped drastically as resources have been diverted to COVID-19 patients and many services have been delayed or canceled.
He said he has been pushing an approach that providers should be paid more after the pandemic “to do the things we want them to do.”
As an example, he said, instead of paying $886 million on colonoscopies for people over the age of 85, “why don’t we put a policy in place that would make it better for patients by lowering cost sharing and better for providers by paying them more to do the service on the people who need it as opposed to the people who don’t?”
The research was funded by the American Board of Family Medicine Foundation. Dr. Baum and a coauthor reported receiving personal fees from American Board of Family Medicine Foundation during the conduct of the study. Another coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Collective Health, HealthRight 360, PLOS Medicine, and the New England Journal of Medicine, outside the submitted work. Dr. Fendrick disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
according to a brief report published online Jan. 18 in Annals of Internal Medicine.
However, one expert said there are better ways to curb low-value care than focusing on which specialties are guilty of the practice.
Analyzing a 20% random sample of Medicare Part B claims, Aaron Baum, PhD, with the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, and colleagues found that the services primary care physicians performed or ordered made up on average 8.3% of the low-value care their patients received (interquartile range, 3.9%-15.1%; 95th percentile, 35.6%) and their referrals made up 15.4% (IQR, 6.3%-26.4%; 95th percentile, 44.6%).
By specialty, cardiology had the worst record with 27% of all spending on low-value services ($1.8 billion) attributed to that specialty. Yet, of the 25 highest-spending specialties in the report, 12 of them were associated with 1% or less than 1% each of all low-value spending, indicating the waste was widely distributed.
Dr. Baum said in an interview that though there are some PCPs guilty of high spending on low-value services, overall, most primary care physicians’ low-value services add up to only 0.3% of Part B spending. He noted that Part B spending is about one-third of all Medicare spending.
Primary care is often thought to be at the core of care management and spending and PCPs are often seen as the gatekeepers, but this analysis suggests that efforts to make big differences in curtailing low-value spending might be more effective elsewhere.
“There’s only so much spending you can reduce by changing primary care physicians’ services that they directly perform,” Dr. Baum said.
Low-value care is costly, can be harmful
Mark Fendrick, MD, director of the University of Michigan’s Center for Value-Based Insurance Design in Ann Arbor, said in an interview that the report adds confirmation to previous research that has consistently shown low-value care is “extremely common, very costly, and provided by primary care providers and specialists alike.” He noted that it can also be harmful.
“The math is simple,” he said. “If we want to improve coverage and lower patient costs for essential services like visits, diagnostic tests, and drugs, we have to reduce spending on those services that do not make Americans any healthier.”
The study ranked 31 clinical services judged to be low value by physician societies, Medicare and clinical guidelines, and their use among beneficiaries enrolled between 2007 and 2014. Here’s how the top six low-value services compare.
Dr. Fendrick said a weakness of the paper is the years of the data (2007-2014). Some of the criteria around low-value care have changed since then. The age that a prostate-specific antigen test becomes low-value is now 70 years, for instance, instead of 75. He added that some of the figures attributed to non-PCP providers appear out of date.
Dr. Fendrick said, “I understand that there are Medicare patients who end up at a gastroenterologist or surgeon’s office to get colorectal cancer screening, but it would be very hard for me to believe that half of stress tests and over half of colon cancer screening over [age] 85 [years] and half of PSA for people over 75 did not have some type of referring clinicians involved. I certainly don’t think that would be the case in 2020-2021.”
Dr. Baum said those years were the latest years available for the data points needed for this analysis, but he and his colleagues were working to update the data for future publication.
Dr. Fendrick said not much has changed in recent years in terms of waste on low-value care, even with campaigns such as Choosing Wisely dedicated to identifying low-value services or procedures in each specialty.
“I believe there’s not a particular group of clinicians one way or the other who are actually doing any better now than they were 7 years ago,” he said. He would rather focus less on which specialties are associated with the most low-value care and more on the underlying policies that encourage low-value care.
“If you’re going to get paid for doing a stress test and get paid nothing or significantly less if you don’t, the incentives are in the wrong direction,” he said.
Dr. Fendrick said the pandemic era provides an opportunity to eliminate low-value care because use of those services has dropped drastically as resources have been diverted to COVID-19 patients and many services have been delayed or canceled.
He said he has been pushing an approach that providers should be paid more after the pandemic “to do the things we want them to do.”
As an example, he said, instead of paying $886 million on colonoscopies for people over the age of 85, “why don’t we put a policy in place that would make it better for patients by lowering cost sharing and better for providers by paying them more to do the service on the people who need it as opposed to the people who don’t?”
The research was funded by the American Board of Family Medicine Foundation. Dr. Baum and a coauthor reported receiving personal fees from American Board of Family Medicine Foundation during the conduct of the study. Another coauthor reported receiving personal fees from Collective Health, HealthRight 360, PLOS Medicine, and the New England Journal of Medicine, outside the submitted work. Dr. Fendrick disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Low-carb diets boost diabetes remission rates, at least short term
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) for at least 6 months appear to have significantly higher remission rates than those following other diets, although the benefits diminish by 12 months, suggests a new analysis of trial data from over 1,300 individuals.
“Based on other evidence, it is likely the degree of weight loss would have been a contributing factor, combined with the lower intake of dietary carbohydrates,” study coauthor Grant D. Brinkworth, PhD, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Sydney, , said in an interview.
He acknowledged, however, that “diets in general can be difficult to sustain over the long term. ... We need to provide patients with easy-to-use support tools and convenient solutions to help them adhere to a low-carb diet long term to gain these greater health improvements.
“In addition, more long-term, well-controlled, randomized trials are needed to determine the effects of low-carb diets on sustained weight loss, diabetes remission, and health outcomes,” Dr. Brinkworth added.
The research was published on Janu. 13 in the BMJ by a consortium of international scientists, led by Joshua Z. Goldenberg, PhD, department of nutrition, Texas A&M University, College Station.
Confusion as to best diet for those with diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a “significant and worsening” worldwide health problem, wrote Dr. Goldenberg and coauthors, in spite of “many pharmaceutical developments and a global emphasis on glycemic control.”
Although structured diets are “recognized as an essential component of treating diabetes, confusion remains about which diet to choose,” with multiple systemic reviews and meta-analyses of carbohydrate-restricted diets “reporting mixed results,” they noted.
They therefore undertook a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of LCDs and very-low-carbohydrate diets (VLCDs) using the CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, and CAB databases, as well as other literature sources.
Researchers defined LCDs as less than 130 g/day of carbohydrates or less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates as part of a 2,000 kcal/day diet and VLCDs as less than 50 g/day or less than 10% of daily calories. They focused on interventions that lasted at least 12 weeks in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 23 trials involving 1,357 participants met the inclusion criteria; 52% used VLCDs and the control comparator was a low-fat diet in 78% of the studies. The mean age range of patients was 47-67 years, and treatment duration spanned from 3 months to 2 years.
LCDs were associated with a higher rate of diabetes remission when defined as a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5%, compared with control diets at 6 months, at 57% versus 31% – an increase in remission of 32% associated with LCDs (P < .001 for overall effect).
But when defined more tightly as an A1c level of less than 6.5% in the absence of diabetes medications, remission with LCDs was reduced to a nonsignificant 5% versus control diets at 6 months.
At 12 months, data on remission were sparse, ranging from a small effect to a trivial increased risk of diabetes.
Subgroup analysis demonstrated that patients on an LCD achieved greater weight loss at 6 months than those on a control diet, at a mean reduction of 3.46 kg (approximately 7.6 lb). However, the researchers noted that, at 12 months, any weight-loss benefit was “trivial and nonsignificant.”
A similar pattern was seen for reductions in A1c and fasting glucose levels with LCDs: Notable reductions at 6 months largely disappeared by 12 months.
LCDs were also associated with “greater reductions in diabetes medication and clinically important benefits” in triglycerides and insulin resistance at 6 and 12 months, the team wrote.
VLCDs: Adherence Is key
Finally, the team looked at weight loss achieved with VLCDs.
VLCDs were less effective for weight loss at 6 months than less restrictive LCDs. However, this effect was explained by diet adherence, the researchers noted.
Restricting the analysis to “credible” studies, VLCDs were associated with a larger “clinically important” weight-loss versus control diets when patients were highly adherent to the diet, at a mean reduction of 4.47 kg (9.9 lb) versus a mean increase of 0.55 kg (1.2 lb) among patients who were less adherent.
The team noted that their review has a number of limitations, not least of which is the definition of diabetes remission used, which “is the subject of considerable debate,” as well as the safety concerns raised over LCDs.
Given the latter concerns, “clinicians might consider short-term LCDs for management of type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed,” they concluded.
This study was funded in part by Texas A&M University. One coauthor reported receiving funding from Texas A&M AgriLife Research for a separate research project. Dr. Brinkworth is author of the book “The CSIRO Low Carb Diet,” but does not receive financial royalties or funds either directly or indirectly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) for at least 6 months appear to have significantly higher remission rates than those following other diets, although the benefits diminish by 12 months, suggests a new analysis of trial data from over 1,300 individuals.
“Based on other evidence, it is likely the degree of weight loss would have been a contributing factor, combined with the lower intake of dietary carbohydrates,” study coauthor Grant D. Brinkworth, PhD, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Sydney, , said in an interview.
He acknowledged, however, that “diets in general can be difficult to sustain over the long term. ... We need to provide patients with easy-to-use support tools and convenient solutions to help them adhere to a low-carb diet long term to gain these greater health improvements.
“In addition, more long-term, well-controlled, randomized trials are needed to determine the effects of low-carb diets on sustained weight loss, diabetes remission, and health outcomes,” Dr. Brinkworth added.
The research was published on Janu. 13 in the BMJ by a consortium of international scientists, led by Joshua Z. Goldenberg, PhD, department of nutrition, Texas A&M University, College Station.
Confusion as to best diet for those with diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a “significant and worsening” worldwide health problem, wrote Dr. Goldenberg and coauthors, in spite of “many pharmaceutical developments and a global emphasis on glycemic control.”
Although structured diets are “recognized as an essential component of treating diabetes, confusion remains about which diet to choose,” with multiple systemic reviews and meta-analyses of carbohydrate-restricted diets “reporting mixed results,” they noted.
They therefore undertook a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of LCDs and very-low-carbohydrate diets (VLCDs) using the CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, and CAB databases, as well as other literature sources.
Researchers defined LCDs as less than 130 g/day of carbohydrates or less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates as part of a 2,000 kcal/day diet and VLCDs as less than 50 g/day or less than 10% of daily calories. They focused on interventions that lasted at least 12 weeks in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 23 trials involving 1,357 participants met the inclusion criteria; 52% used VLCDs and the control comparator was a low-fat diet in 78% of the studies. The mean age range of patients was 47-67 years, and treatment duration spanned from 3 months to 2 years.
LCDs were associated with a higher rate of diabetes remission when defined as a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5%, compared with control diets at 6 months, at 57% versus 31% – an increase in remission of 32% associated with LCDs (P < .001 for overall effect).
But when defined more tightly as an A1c level of less than 6.5% in the absence of diabetes medications, remission with LCDs was reduced to a nonsignificant 5% versus control diets at 6 months.
At 12 months, data on remission were sparse, ranging from a small effect to a trivial increased risk of diabetes.
Subgroup analysis demonstrated that patients on an LCD achieved greater weight loss at 6 months than those on a control diet, at a mean reduction of 3.46 kg (approximately 7.6 lb). However, the researchers noted that, at 12 months, any weight-loss benefit was “trivial and nonsignificant.”
A similar pattern was seen for reductions in A1c and fasting glucose levels with LCDs: Notable reductions at 6 months largely disappeared by 12 months.
LCDs were also associated with “greater reductions in diabetes medication and clinically important benefits” in triglycerides and insulin resistance at 6 and 12 months, the team wrote.
VLCDs: Adherence Is key
Finally, the team looked at weight loss achieved with VLCDs.
VLCDs were less effective for weight loss at 6 months than less restrictive LCDs. However, this effect was explained by diet adherence, the researchers noted.
Restricting the analysis to “credible” studies, VLCDs were associated with a larger “clinically important” weight-loss versus control diets when patients were highly adherent to the diet, at a mean reduction of 4.47 kg (9.9 lb) versus a mean increase of 0.55 kg (1.2 lb) among patients who were less adherent.
The team noted that their review has a number of limitations, not least of which is the definition of diabetes remission used, which “is the subject of considerable debate,” as well as the safety concerns raised over LCDs.
Given the latter concerns, “clinicians might consider short-term LCDs for management of type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed,” they concluded.
This study was funded in part by Texas A&M University. One coauthor reported receiving funding from Texas A&M AgriLife Research for a separate research project. Dr. Brinkworth is author of the book “The CSIRO Low Carb Diet,” but does not receive financial royalties or funds either directly or indirectly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with type 2 diabetes who follow a low-carbohydrate diet (LCD) for at least 6 months appear to have significantly higher remission rates than those following other diets, although the benefits diminish by 12 months, suggests a new analysis of trial data from over 1,300 individuals.
“Based on other evidence, it is likely the degree of weight loss would have been a contributing factor, combined with the lower intake of dietary carbohydrates,” study coauthor Grant D. Brinkworth, PhD, Commonwealth Scientific and Industrial Research Organisation, Sydney, , said in an interview.
He acknowledged, however, that “diets in general can be difficult to sustain over the long term. ... We need to provide patients with easy-to-use support tools and convenient solutions to help them adhere to a low-carb diet long term to gain these greater health improvements.
“In addition, more long-term, well-controlled, randomized trials are needed to determine the effects of low-carb diets on sustained weight loss, diabetes remission, and health outcomes,” Dr. Brinkworth added.
The research was published on Janu. 13 in the BMJ by a consortium of international scientists, led by Joshua Z. Goldenberg, PhD, department of nutrition, Texas A&M University, College Station.
Confusion as to best diet for those with diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is a “significant and worsening” worldwide health problem, wrote Dr. Goldenberg and coauthors, in spite of “many pharmaceutical developments and a global emphasis on glycemic control.”
Although structured diets are “recognized as an essential component of treating diabetes, confusion remains about which diet to choose,” with multiple systemic reviews and meta-analyses of carbohydrate-restricted diets “reporting mixed results,” they noted.
They therefore undertook a systematic review of randomized, controlled trials on the efficacy and safety of LCDs and very-low-carbohydrate diets (VLCDs) using the CENTRAL, Medline, CINAHL, and CAB databases, as well as other literature sources.
Researchers defined LCDs as less than 130 g/day of carbohydrates or less than 26% of calories from carbohydrates as part of a 2,000 kcal/day diet and VLCDs as less than 50 g/day or less than 10% of daily calories. They focused on interventions that lasted at least 12 weeks in adults with type 2 diabetes.
Overall, 23 trials involving 1,357 participants met the inclusion criteria; 52% used VLCDs and the control comparator was a low-fat diet in 78% of the studies. The mean age range of patients was 47-67 years, and treatment duration spanned from 3 months to 2 years.
LCDs were associated with a higher rate of diabetes remission when defined as a hemoglobin A1c level of less than 6.5%, compared with control diets at 6 months, at 57% versus 31% – an increase in remission of 32% associated with LCDs (P < .001 for overall effect).
But when defined more tightly as an A1c level of less than 6.5% in the absence of diabetes medications, remission with LCDs was reduced to a nonsignificant 5% versus control diets at 6 months.
At 12 months, data on remission were sparse, ranging from a small effect to a trivial increased risk of diabetes.
Subgroup analysis demonstrated that patients on an LCD achieved greater weight loss at 6 months than those on a control diet, at a mean reduction of 3.46 kg (approximately 7.6 lb). However, the researchers noted that, at 12 months, any weight-loss benefit was “trivial and nonsignificant.”
A similar pattern was seen for reductions in A1c and fasting glucose levels with LCDs: Notable reductions at 6 months largely disappeared by 12 months.
LCDs were also associated with “greater reductions in diabetes medication and clinically important benefits” in triglycerides and insulin resistance at 6 and 12 months, the team wrote.
VLCDs: Adherence Is key
Finally, the team looked at weight loss achieved with VLCDs.
VLCDs were less effective for weight loss at 6 months than less restrictive LCDs. However, this effect was explained by diet adherence, the researchers noted.
Restricting the analysis to “credible” studies, VLCDs were associated with a larger “clinically important” weight-loss versus control diets when patients were highly adherent to the diet, at a mean reduction of 4.47 kg (9.9 lb) versus a mean increase of 0.55 kg (1.2 lb) among patients who were less adherent.
The team noted that their review has a number of limitations, not least of which is the definition of diabetes remission used, which “is the subject of considerable debate,” as well as the safety concerns raised over LCDs.
Given the latter concerns, “clinicians might consider short-term LCDs for management of type 2 diabetes, while actively monitoring and adjusting diabetes medication as needed,” they concluded.
This study was funded in part by Texas A&M University. One coauthor reported receiving funding from Texas A&M AgriLife Research for a separate research project. Dr. Brinkworth is author of the book “The CSIRO Low Carb Diet,” but does not receive financial royalties or funds either directly or indirectly.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Biden kicks off health agenda with COVID actions, WHO outreach
President Joe Biden kicked off his new administration Jan. 20 with an immediate focus on attempts to stop the spread of COVID-19, including closer coordination with other nations.
Mr. Biden signed 17 executive orders, memoranda, and directives addressing not only the pandemic but also economic concerns, climate change, and racial inequity.
At the top of the list of actions was what his transition team called a “100 Days Masking Challenge.” Mr. Biden issued an executive order requiring masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
The president also halted the Trump administration’s process of withdrawing from the World Health Organization. Instead, Mr. Biden named Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, as the head of a delegation to participate in the WHO executive board meeting that is being held this week.
Mr. Biden also signed an executive order creating the position of COVID-19 response coordinator, which will report directly to the president and be responsible for coordinating all elements of the COVID-19 response across government, including the production and distribution of vaccines and medical supplies.
The newly inaugurated president also intends to restore the National Security Council’s Directorate for Global Health Security and Biodefense, which will aid in the response to the pandemic, his transition team said.
The American Medical Association was among the first to commend the first-day actions.
“Defeating COVID-19 requires bold, coordinated federal leadership and strong adherence to the public health steps we know stop the spread of this virus – wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and washing hands,” said AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD in a news release. “We are pleased by the Biden administration’s steps today, including universal mask wearing within federal jurisdictions, providing federal leadership for COVID-19 response, and reengaging with the World Health Organization. Taking these actions on day 1 of the administration sends the right message – that our nation is laser focused on stopping the ravages of COVID-19.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Joe Biden kicked off his new administration Jan. 20 with an immediate focus on attempts to stop the spread of COVID-19, including closer coordination with other nations.
Mr. Biden signed 17 executive orders, memoranda, and directives addressing not only the pandemic but also economic concerns, climate change, and racial inequity.
At the top of the list of actions was what his transition team called a “100 Days Masking Challenge.” Mr. Biden issued an executive order requiring masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
The president also halted the Trump administration’s process of withdrawing from the World Health Organization. Instead, Mr. Biden named Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, as the head of a delegation to participate in the WHO executive board meeting that is being held this week.
Mr. Biden also signed an executive order creating the position of COVID-19 response coordinator, which will report directly to the president and be responsible for coordinating all elements of the COVID-19 response across government, including the production and distribution of vaccines and medical supplies.
The newly inaugurated president also intends to restore the National Security Council’s Directorate for Global Health Security and Biodefense, which will aid in the response to the pandemic, his transition team said.
The American Medical Association was among the first to commend the first-day actions.
“Defeating COVID-19 requires bold, coordinated federal leadership and strong adherence to the public health steps we know stop the spread of this virus – wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and washing hands,” said AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD in a news release. “We are pleased by the Biden administration’s steps today, including universal mask wearing within federal jurisdictions, providing federal leadership for COVID-19 response, and reengaging with the World Health Organization. Taking these actions on day 1 of the administration sends the right message – that our nation is laser focused on stopping the ravages of COVID-19.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
President Joe Biden kicked off his new administration Jan. 20 with an immediate focus on attempts to stop the spread of COVID-19, including closer coordination with other nations.
Mr. Biden signed 17 executive orders, memoranda, and directives addressing not only the pandemic but also economic concerns, climate change, and racial inequity.
At the top of the list of actions was what his transition team called a “100 Days Masking Challenge.” Mr. Biden issued an executive order requiring masks and physical distancing in all federal buildings, on all federal lands, and by federal employees and contractors.
The president also halted the Trump administration’s process of withdrawing from the World Health Organization. Instead, Mr. Biden named Anthony Fauci, MD, the director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, as the head of a delegation to participate in the WHO executive board meeting that is being held this week.
Mr. Biden also signed an executive order creating the position of COVID-19 response coordinator, which will report directly to the president and be responsible for coordinating all elements of the COVID-19 response across government, including the production and distribution of vaccines and medical supplies.
The newly inaugurated president also intends to restore the National Security Council’s Directorate for Global Health Security and Biodefense, which will aid in the response to the pandemic, his transition team said.
The American Medical Association was among the first to commend the first-day actions.
“Defeating COVID-19 requires bold, coordinated federal leadership and strong adherence to the public health steps we know stop the spread of this virus – wearing masks, practicing physical distancing, and washing hands,” said AMA President Susan R. Bailey, MD in a news release. “We are pleased by the Biden administration’s steps today, including universal mask wearing within federal jurisdictions, providing federal leadership for COVID-19 response, and reengaging with the World Health Organization. Taking these actions on day 1 of the administration sends the right message – that our nation is laser focused on stopping the ravages of COVID-19.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 may damage blood vessels in the brain
Until now, the neurological manifestations of COVID-19 have been believed to be a result of direct damage to nerve cells. However, a new study suggests that the virus might actually damage the brain’s small blood vessels rather than nerve cells themselves.
The findings add further weight to previous research into neurological complications from COVID-19, according to Anna Cervantes, MD. Dr. Cervantes is assistant professor of neurology at the Boston University and has been studying the neurological effects of COVID-19, though she was not involved in this study. “I can tell from my personal experience, and things we’ve published on and the literature that’s out there – there are patients that are having complications like stroke that aren’t even critically ill from COVID. We’re seeing that not in just the acute setting, but also in a delayed fashion. Even though most of the coagulopathy is largely venous and probably microvascular, this does affect the brain through a myriad of ways,” Dr. Cervantes said.
The research was published online Jan. 12 in the New England Journal of Medicine. Myoung‑Hwa Lee, PhD, was the lead author.
The study included high resolution magnetic resonance imaging and histopathological examination of 13 individuals with a median age of 50 years. Among 10 patients with brain alterations, the researchers conducted further studies in 5 individuals using multiplex fluorescence imaging and chromogenic immunostaining in all 10.
The team conducted conventional histopathology on the brains of 18 individuals. Fourteen had a history of chronic illness, including diabetes, and hypertension, and 11 had died unexpectedly or been found dead. Magnetic resonance microscopy revealed punctuate hypo-intensities in nine subjects, indicating microvascular injury and fibrinogen leakage. Histopathology using fluorescence imaging showed the same features. Collagen IV immunostaining showed thinning of the basal lamina of the endothelial cells in five patients. Ten patients had congested blood vessels and surrounding fibrinogen leakage, but comparatively intact vasculature. The researchers interpreted linear hypo-intensities as micro-hemorrhages.
The researchers found little perivascular inflammation, and no vascular occlusion. Thirteen subjects had perivascular-activated microglia, macrophage infiltrates, and hypertrophic astrocytes. Eight had CD3+ and CD8+ T cells in the perivascular spaces and in lumens next to endothelial cells, which could help explain vascular injury.
The researchers found no evidence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself, despite efforts using polymerase chain reaction with multiple primer sets, RNA sequencing within the brain, or RNA in situ hybridization and immunostaining. Subjects may have cleared the virus by the time they died, or viral copy numbers could have been below the detection limit of the assays.
The researchers also obtained a convenience sample of subjects who had died from COVID-19. Magnetic resonance microscopy, histopathology, and immunohistochemical analysis of sections revealed microvascular injury in the brain and olfactory bulb, despite no evidence of viral infection. The authors stressed that they could not draw conclusions about the neurological features of COVID-19 because of a lack of clinical information.
Dr. Cervantes noted that limitation: “We’re seeing a lot of patients with encephalopathy or alterations in their mental status. A lot of things can cause that, and some are common in patients who are critically ill, like medications and metabolic derangement.”
Still, the findings could help to inform future medical management. “There’s going to be a large number of patients who don’t have really bad pulmonary disease but still may have encephalopathy. So if there is small vessel involvement because of inflammation that we might not necessarily catch in a lumbar puncture or routine imaging, there’s still somebody we can make better (using) steroids. Having more information on what’s happening on a pathophysiologic level and on pathology is really helpful.”
The study was supported by internal funds from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Cervantes has no relevant financial disclosures.
Until now, the neurological manifestations of COVID-19 have been believed to be a result of direct damage to nerve cells. However, a new study suggests that the virus might actually damage the brain’s small blood vessels rather than nerve cells themselves.
The findings add further weight to previous research into neurological complications from COVID-19, according to Anna Cervantes, MD. Dr. Cervantes is assistant professor of neurology at the Boston University and has been studying the neurological effects of COVID-19, though she was not involved in this study. “I can tell from my personal experience, and things we’ve published on and the literature that’s out there – there are patients that are having complications like stroke that aren’t even critically ill from COVID. We’re seeing that not in just the acute setting, but also in a delayed fashion. Even though most of the coagulopathy is largely venous and probably microvascular, this does affect the brain through a myriad of ways,” Dr. Cervantes said.
The research was published online Jan. 12 in the New England Journal of Medicine. Myoung‑Hwa Lee, PhD, was the lead author.
The study included high resolution magnetic resonance imaging and histopathological examination of 13 individuals with a median age of 50 years. Among 10 patients with brain alterations, the researchers conducted further studies in 5 individuals using multiplex fluorescence imaging and chromogenic immunostaining in all 10.
The team conducted conventional histopathology on the brains of 18 individuals. Fourteen had a history of chronic illness, including diabetes, and hypertension, and 11 had died unexpectedly or been found dead. Magnetic resonance microscopy revealed punctuate hypo-intensities in nine subjects, indicating microvascular injury and fibrinogen leakage. Histopathology using fluorescence imaging showed the same features. Collagen IV immunostaining showed thinning of the basal lamina of the endothelial cells in five patients. Ten patients had congested blood vessels and surrounding fibrinogen leakage, but comparatively intact vasculature. The researchers interpreted linear hypo-intensities as micro-hemorrhages.
The researchers found little perivascular inflammation, and no vascular occlusion. Thirteen subjects had perivascular-activated microglia, macrophage infiltrates, and hypertrophic astrocytes. Eight had CD3+ and CD8+ T cells in the perivascular spaces and in lumens next to endothelial cells, which could help explain vascular injury.
The researchers found no evidence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself, despite efforts using polymerase chain reaction with multiple primer sets, RNA sequencing within the brain, or RNA in situ hybridization and immunostaining. Subjects may have cleared the virus by the time they died, or viral copy numbers could have been below the detection limit of the assays.
The researchers also obtained a convenience sample of subjects who had died from COVID-19. Magnetic resonance microscopy, histopathology, and immunohistochemical analysis of sections revealed microvascular injury in the brain and olfactory bulb, despite no evidence of viral infection. The authors stressed that they could not draw conclusions about the neurological features of COVID-19 because of a lack of clinical information.
Dr. Cervantes noted that limitation: “We’re seeing a lot of patients with encephalopathy or alterations in their mental status. A lot of things can cause that, and some are common in patients who are critically ill, like medications and metabolic derangement.”
Still, the findings could help to inform future medical management. “There’s going to be a large number of patients who don’t have really bad pulmonary disease but still may have encephalopathy. So if there is small vessel involvement because of inflammation that we might not necessarily catch in a lumbar puncture or routine imaging, there’s still somebody we can make better (using) steroids. Having more information on what’s happening on a pathophysiologic level and on pathology is really helpful.”
The study was supported by internal funds from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Cervantes has no relevant financial disclosures.
Until now, the neurological manifestations of COVID-19 have been believed to be a result of direct damage to nerve cells. However, a new study suggests that the virus might actually damage the brain’s small blood vessels rather than nerve cells themselves.
The findings add further weight to previous research into neurological complications from COVID-19, according to Anna Cervantes, MD. Dr. Cervantes is assistant professor of neurology at the Boston University and has been studying the neurological effects of COVID-19, though she was not involved in this study. “I can tell from my personal experience, and things we’ve published on and the literature that’s out there – there are patients that are having complications like stroke that aren’t even critically ill from COVID. We’re seeing that not in just the acute setting, but also in a delayed fashion. Even though most of the coagulopathy is largely venous and probably microvascular, this does affect the brain through a myriad of ways,” Dr. Cervantes said.
The research was published online Jan. 12 in the New England Journal of Medicine. Myoung‑Hwa Lee, PhD, was the lead author.
The study included high resolution magnetic resonance imaging and histopathological examination of 13 individuals with a median age of 50 years. Among 10 patients with brain alterations, the researchers conducted further studies in 5 individuals using multiplex fluorescence imaging and chromogenic immunostaining in all 10.
The team conducted conventional histopathology on the brains of 18 individuals. Fourteen had a history of chronic illness, including diabetes, and hypertension, and 11 had died unexpectedly or been found dead. Magnetic resonance microscopy revealed punctuate hypo-intensities in nine subjects, indicating microvascular injury and fibrinogen leakage. Histopathology using fluorescence imaging showed the same features. Collagen IV immunostaining showed thinning of the basal lamina of the endothelial cells in five patients. Ten patients had congested blood vessels and surrounding fibrinogen leakage, but comparatively intact vasculature. The researchers interpreted linear hypo-intensities as micro-hemorrhages.
The researchers found little perivascular inflammation, and no vascular occlusion. Thirteen subjects had perivascular-activated microglia, macrophage infiltrates, and hypertrophic astrocytes. Eight had CD3+ and CD8+ T cells in the perivascular spaces and in lumens next to endothelial cells, which could help explain vascular injury.
The researchers found no evidence of the SARS-CoV-2 virus itself, despite efforts using polymerase chain reaction with multiple primer sets, RNA sequencing within the brain, or RNA in situ hybridization and immunostaining. Subjects may have cleared the virus by the time they died, or viral copy numbers could have been below the detection limit of the assays.
The researchers also obtained a convenience sample of subjects who had died from COVID-19. Magnetic resonance microscopy, histopathology, and immunohistochemical analysis of sections revealed microvascular injury in the brain and olfactory bulb, despite no evidence of viral infection. The authors stressed that they could not draw conclusions about the neurological features of COVID-19 because of a lack of clinical information.
Dr. Cervantes noted that limitation: “We’re seeing a lot of patients with encephalopathy or alterations in their mental status. A lot of things can cause that, and some are common in patients who are critically ill, like medications and metabolic derangement.”
Still, the findings could help to inform future medical management. “There’s going to be a large number of patients who don’t have really bad pulmonary disease but still may have encephalopathy. So if there is small vessel involvement because of inflammation that we might not necessarily catch in a lumbar puncture or routine imaging, there’s still somebody we can make better (using) steroids. Having more information on what’s happening on a pathophysiologic level and on pathology is really helpful.”
The study was supported by internal funds from the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Cervantes has no relevant financial disclosures.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Patients fend for themselves to access highly touted COVID antibody treatments
By the time he tested positive for COVID-19 on Jan. 12, Gary Herritz was feeling pretty sick. He suspects he was infected a week earlier, during a medical appointment in which he saw health workers who were wearing masks beneath their noses or who had removed them entirely.
His scratchy throat had turned to a dry cough, headache, joint pain, and fever – all warning signs to Mr. Herritz, who underwent liver transplant surgery in 2012, followed by a rejection scare in 2018. He knew his compromised immune system left him especially vulnerable to a potentially deadly case of COVID.
“The thing with transplant patients is we can crash in a heartbeat,” said Mr. Herritz, 39. “The outcome for transplant patients [with COVID] is not good.”
On Twitter, Mr. Herritz had read about monoclonal antibody therapy, the treatment famously given to President Donald Trump and other high-profile politicians and authorized by the Food and Drug Administration for emergency use in high-risk COVID patients. But as his symptoms worsened, Mr. Herritz found himself very much on his own as he scrambled for access.
His primary care doctor wasn’t sure he qualified for treatment. His transplant team in Wisconsin, where he’d had the liver surgery, wasn’t calling back. No one was sure exactly where he should go to get it. From bed in Pascagoula, Miss., he spent 2 days punching in phone numbers, reaching out to health officials in four states, before he finally landed an appointment to receive a treatment aimed at keeping patients like him out of the hospital – and, perhaps, the morgue.
“I am not rich, I am not special, I am not a political figure,” Mr. Herritz, a former community service officer, wrote on Twitter. “I just called until someone would listen.”
Months after Mr. Trump emphatically credited an experimental antibody therapy for his quick recovery from covid and even as drugmakers ramp up supplies, only a trickle of the product has found its way into regular people. While hundreds of thousands of vials sit unused, sick patients who, research indicates, could benefit from early treatment – available for free – have largely been fending for themselves.
Federal officials have allocated more than 785,000 doses of two antibody treatments authorized for emergency use during the pandemic, and more than 550,000 doses have been delivered to sites across the nation. The federal government has contracted for nearly 2.5 million doses of the products from drugmakers Eli Lilly and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals at a cost of more than $4.4 billion.
So far, however, only about 30% of the available doses have been administered to patients, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services officials said.
Scores of high-risk COVID patients who are eligible remain unaware or have not been offered the option. Research has shown the therapy is most effective if given early in the illness, within 10 days of a positive COVID test. But many would-be recipients have missed this crucial window because of a patchwork system in the United States that can delay testing and diagnosis.
“The bottleneck here in the funnel is administration, not availability of the product,” said Dr. Janet Woodcock, a veteran FDA official in charge of therapeutics for the federal Operation Warp Speed effort.
Among the daunting hurdles: Until this week, there has been no nationwide system to tell people where they could obtain the drugs, which are delivered through IV infusions that require hours to administer and monitor. Finding space to keep COVID-infected patients separate from others has been difficult in some health centers slammed by the pandemic.
“The health care system is crashing,” Dr. Woodcock told reporters. “What we’ve heard around the country is the No. 1 barrier is staffing.”
At the same time, many hospitals have refused to offer the therapy because doctors were unimpressed with the research federal officials used to justify its use.
Monoclonal antibodies are lab-produced molecules that act as substitutes for the body’s own antibodies that fight infection. The COVID treatments are designed to block the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes infection from attaching to and entering human cells. Such treatments are usually prohibitively expensive, but for the time being the federal government is footing the bulk of the bill, though patients likely will be charged administrative fees.
Nationwide, nearly 4,000 sites offer the infusion therapies. But for patients and families of people most at risk – those 65 and older or with underlying health conditions – finding the sites and gaining access has been almost impossible, said Brian Nyquist, chief executive officer of the National Infusion Center Association, which is tracking supplies of the antibody products. Like Mr. Herritz, many seeking information about monoclonals find themselves on a lone crusade.
“If they’re not hammering the phones and advocating for access for their loved ones, others often won’t,” he said. “Tenacity is critical.”
Regeneron officials said they’re fielding calls about COVID treatments daily to the company’s medical information line. More than 3,500 people have flooded Eli Lilly’s COVID hotline with questions about access.
As of this week, all states are required to list on a federal locator map sites that have received the monoclonal antibody products, HHS officials said. The updated map shows wide distribution, but a listing doesn’t guarantee availability or access; patients still need to check. It’s best to confer with a primary care provider before reaching out to the centers. For best results, treatment should occur as soon as possible after a positive COVID test.
Some health systems have refused to offer the monoclonal antibody therapies because of doubts about the data used to authorize them. Early studies suggested that Lilly’s therapy, bamlanivimab, reduced the need for hospitalization or emergency treatment in outpatient COVID cases by about 70%, while Regeneron’s antibody cocktail of casirivimab plus imdevimab reduced the need by about 50%.
But those studies were small, just a few hundred subjects, and the results were limited. “A lot of doctors, actually, they’re not impressed with the data,” said Dr. Daniel Griffin, an infectious disease expert at Columbia University who cohosts the podcast “This Week in Virology.” “There really is still that question of, ‘Does this stuff really work?’ ”
As more patients are treated, however, there’s growing evidence that the therapies can keep high-risk patients out of the hospital, not only easing their recovery but also decreasing the burden on health systems struggling with record numbers of patients.
Dr. Raymund Razonable, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, said he has treated more than 2,500 COVID patients with monoclonal antibody therapy with promising results. “It’s looking good,” he said, declining to provide details because they’re embargoed for publication. “We are seeing reductions in hospitalizations; we’re seeing reductions in ICU care; we’re also seeing reductions in mortality.”
Banking on observations from Mayo experts and others, federal officials have been pushing for wider use of antibody therapies. HHS officials have partnered with hospitals in three hard-hit states – California, Arizona, and Nevada – to set up infusion centers that are treating dozens of COVID patients each day.
One of those sites went up in late December at El Centro Regional Medical Center in California’s Imperial County, an impoverished farming region on the state’s southern border that has recorded among the highest COVID infection rates in the state. For months, the medical center strained to absorb the overwhelming influx of patients, but chief executive Dr. Adolphe Edward said a new walk-up infusion site has already put a dent in the COVID load.
More than 130 people have been treated, all patients who were able to get the 2-hour infusions and then recuperate at home. “If those folks would not have had the treatment, they would have come through the emergency department and we would have had to admit the lion’s share of them,” he said.
It’s important to make sure people in high-risk groups know to seek out the therapy and to get it early, Dr. Edward said. He and his staff have been working with area doctors’ offices and nonprofit groups and relying on word of mouth.
“On multiple levels, we’re saying, ‘If you’ve tested positive for the virus, come and let us see if you are eligible,’ ” Dr. Edward said.
Greater awareness is a goal of the HHS effort, said Dr. John Redd, chief medical officer for the assistant secretary for preparedness and response. “These antibodies are meant for everyone,” he said. “Everyone across the country should have equal access to these products.”
For now, patients like Mr. Herritz, the Mississippi liver transplant recipient, say reality is falling well short of that goal. If he hadn’t continued to call in search of a referral, he wouldn’t have been treated. And without the therapy, Mr. Herritz believes, he was just days away from hospitalization.
“I think it’s horrible that if I didn’t have Twitter, I wouldn’t know anything about this,” he said. “I think about all the people who have died not knowing this was an option for high-risk individuals.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
By the time he tested positive for COVID-19 on Jan. 12, Gary Herritz was feeling pretty sick. He suspects he was infected a week earlier, during a medical appointment in which he saw health workers who were wearing masks beneath their noses or who had removed them entirely.
His scratchy throat had turned to a dry cough, headache, joint pain, and fever – all warning signs to Mr. Herritz, who underwent liver transplant surgery in 2012, followed by a rejection scare in 2018. He knew his compromised immune system left him especially vulnerable to a potentially deadly case of COVID.
“The thing with transplant patients is we can crash in a heartbeat,” said Mr. Herritz, 39. “The outcome for transplant patients [with COVID] is not good.”
On Twitter, Mr. Herritz had read about monoclonal antibody therapy, the treatment famously given to President Donald Trump and other high-profile politicians and authorized by the Food and Drug Administration for emergency use in high-risk COVID patients. But as his symptoms worsened, Mr. Herritz found himself very much on his own as he scrambled for access.
His primary care doctor wasn’t sure he qualified for treatment. His transplant team in Wisconsin, where he’d had the liver surgery, wasn’t calling back. No one was sure exactly where he should go to get it. From bed in Pascagoula, Miss., he spent 2 days punching in phone numbers, reaching out to health officials in four states, before he finally landed an appointment to receive a treatment aimed at keeping patients like him out of the hospital – and, perhaps, the morgue.
“I am not rich, I am not special, I am not a political figure,” Mr. Herritz, a former community service officer, wrote on Twitter. “I just called until someone would listen.”
Months after Mr. Trump emphatically credited an experimental antibody therapy for his quick recovery from covid and even as drugmakers ramp up supplies, only a trickle of the product has found its way into regular people. While hundreds of thousands of vials sit unused, sick patients who, research indicates, could benefit from early treatment – available for free – have largely been fending for themselves.
Federal officials have allocated more than 785,000 doses of two antibody treatments authorized for emergency use during the pandemic, and more than 550,000 doses have been delivered to sites across the nation. The federal government has contracted for nearly 2.5 million doses of the products from drugmakers Eli Lilly and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals at a cost of more than $4.4 billion.
So far, however, only about 30% of the available doses have been administered to patients, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services officials said.
Scores of high-risk COVID patients who are eligible remain unaware or have not been offered the option. Research has shown the therapy is most effective if given early in the illness, within 10 days of a positive COVID test. But many would-be recipients have missed this crucial window because of a patchwork system in the United States that can delay testing and diagnosis.
“The bottleneck here in the funnel is administration, not availability of the product,” said Dr. Janet Woodcock, a veteran FDA official in charge of therapeutics for the federal Operation Warp Speed effort.
Among the daunting hurdles: Until this week, there has been no nationwide system to tell people where they could obtain the drugs, which are delivered through IV infusions that require hours to administer and monitor. Finding space to keep COVID-infected patients separate from others has been difficult in some health centers slammed by the pandemic.
“The health care system is crashing,” Dr. Woodcock told reporters. “What we’ve heard around the country is the No. 1 barrier is staffing.”
At the same time, many hospitals have refused to offer the therapy because doctors were unimpressed with the research federal officials used to justify its use.
Monoclonal antibodies are lab-produced molecules that act as substitutes for the body’s own antibodies that fight infection. The COVID treatments are designed to block the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes infection from attaching to and entering human cells. Such treatments are usually prohibitively expensive, but for the time being the federal government is footing the bulk of the bill, though patients likely will be charged administrative fees.
Nationwide, nearly 4,000 sites offer the infusion therapies. But for patients and families of people most at risk – those 65 and older or with underlying health conditions – finding the sites and gaining access has been almost impossible, said Brian Nyquist, chief executive officer of the National Infusion Center Association, which is tracking supplies of the antibody products. Like Mr. Herritz, many seeking information about monoclonals find themselves on a lone crusade.
“If they’re not hammering the phones and advocating for access for their loved ones, others often won’t,” he said. “Tenacity is critical.”
Regeneron officials said they’re fielding calls about COVID treatments daily to the company’s medical information line. More than 3,500 people have flooded Eli Lilly’s COVID hotline with questions about access.
As of this week, all states are required to list on a federal locator map sites that have received the monoclonal antibody products, HHS officials said. The updated map shows wide distribution, but a listing doesn’t guarantee availability or access; patients still need to check. It’s best to confer with a primary care provider before reaching out to the centers. For best results, treatment should occur as soon as possible after a positive COVID test.
Some health systems have refused to offer the monoclonal antibody therapies because of doubts about the data used to authorize them. Early studies suggested that Lilly’s therapy, bamlanivimab, reduced the need for hospitalization or emergency treatment in outpatient COVID cases by about 70%, while Regeneron’s antibody cocktail of casirivimab plus imdevimab reduced the need by about 50%.
But those studies were small, just a few hundred subjects, and the results were limited. “A lot of doctors, actually, they’re not impressed with the data,” said Dr. Daniel Griffin, an infectious disease expert at Columbia University who cohosts the podcast “This Week in Virology.” “There really is still that question of, ‘Does this stuff really work?’ ”
As more patients are treated, however, there’s growing evidence that the therapies can keep high-risk patients out of the hospital, not only easing their recovery but also decreasing the burden on health systems struggling with record numbers of patients.
Dr. Raymund Razonable, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, said he has treated more than 2,500 COVID patients with monoclonal antibody therapy with promising results. “It’s looking good,” he said, declining to provide details because they’re embargoed for publication. “We are seeing reductions in hospitalizations; we’re seeing reductions in ICU care; we’re also seeing reductions in mortality.”
Banking on observations from Mayo experts and others, federal officials have been pushing for wider use of antibody therapies. HHS officials have partnered with hospitals in three hard-hit states – California, Arizona, and Nevada – to set up infusion centers that are treating dozens of COVID patients each day.
One of those sites went up in late December at El Centro Regional Medical Center in California’s Imperial County, an impoverished farming region on the state’s southern border that has recorded among the highest COVID infection rates in the state. For months, the medical center strained to absorb the overwhelming influx of patients, but chief executive Dr. Adolphe Edward said a new walk-up infusion site has already put a dent in the COVID load.
More than 130 people have been treated, all patients who were able to get the 2-hour infusions and then recuperate at home. “If those folks would not have had the treatment, they would have come through the emergency department and we would have had to admit the lion’s share of them,” he said.
It’s important to make sure people in high-risk groups know to seek out the therapy and to get it early, Dr. Edward said. He and his staff have been working with area doctors’ offices and nonprofit groups and relying on word of mouth.
“On multiple levels, we’re saying, ‘If you’ve tested positive for the virus, come and let us see if you are eligible,’ ” Dr. Edward said.
Greater awareness is a goal of the HHS effort, said Dr. John Redd, chief medical officer for the assistant secretary for preparedness and response. “These antibodies are meant for everyone,” he said. “Everyone across the country should have equal access to these products.”
For now, patients like Mr. Herritz, the Mississippi liver transplant recipient, say reality is falling well short of that goal. If he hadn’t continued to call in search of a referral, he wouldn’t have been treated. And without the therapy, Mr. Herritz believes, he was just days away from hospitalization.
“I think it’s horrible that if I didn’t have Twitter, I wouldn’t know anything about this,” he said. “I think about all the people who have died not knowing this was an option for high-risk individuals.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.
By the time he tested positive for COVID-19 on Jan. 12, Gary Herritz was feeling pretty sick. He suspects he was infected a week earlier, during a medical appointment in which he saw health workers who were wearing masks beneath their noses or who had removed them entirely.
His scratchy throat had turned to a dry cough, headache, joint pain, and fever – all warning signs to Mr. Herritz, who underwent liver transplant surgery in 2012, followed by a rejection scare in 2018. He knew his compromised immune system left him especially vulnerable to a potentially deadly case of COVID.
“The thing with transplant patients is we can crash in a heartbeat,” said Mr. Herritz, 39. “The outcome for transplant patients [with COVID] is not good.”
On Twitter, Mr. Herritz had read about monoclonal antibody therapy, the treatment famously given to President Donald Trump and other high-profile politicians and authorized by the Food and Drug Administration for emergency use in high-risk COVID patients. But as his symptoms worsened, Mr. Herritz found himself very much on his own as he scrambled for access.
His primary care doctor wasn’t sure he qualified for treatment. His transplant team in Wisconsin, where he’d had the liver surgery, wasn’t calling back. No one was sure exactly where he should go to get it. From bed in Pascagoula, Miss., he spent 2 days punching in phone numbers, reaching out to health officials in four states, before he finally landed an appointment to receive a treatment aimed at keeping patients like him out of the hospital – and, perhaps, the morgue.
“I am not rich, I am not special, I am not a political figure,” Mr. Herritz, a former community service officer, wrote on Twitter. “I just called until someone would listen.”
Months after Mr. Trump emphatically credited an experimental antibody therapy for his quick recovery from covid and even as drugmakers ramp up supplies, only a trickle of the product has found its way into regular people. While hundreds of thousands of vials sit unused, sick patients who, research indicates, could benefit from early treatment – available for free – have largely been fending for themselves.
Federal officials have allocated more than 785,000 doses of two antibody treatments authorized for emergency use during the pandemic, and more than 550,000 doses have been delivered to sites across the nation. The federal government has contracted for nearly 2.5 million doses of the products from drugmakers Eli Lilly and Regeneron Pharmaceuticals at a cost of more than $4.4 billion.
So far, however, only about 30% of the available doses have been administered to patients, U.S. Department of Health & Human Services officials said.
Scores of high-risk COVID patients who are eligible remain unaware or have not been offered the option. Research has shown the therapy is most effective if given early in the illness, within 10 days of a positive COVID test. But many would-be recipients have missed this crucial window because of a patchwork system in the United States that can delay testing and diagnosis.
“The bottleneck here in the funnel is administration, not availability of the product,” said Dr. Janet Woodcock, a veteran FDA official in charge of therapeutics for the federal Operation Warp Speed effort.
Among the daunting hurdles: Until this week, there has been no nationwide system to tell people where they could obtain the drugs, which are delivered through IV infusions that require hours to administer and monitor. Finding space to keep COVID-infected patients separate from others has been difficult in some health centers slammed by the pandemic.
“The health care system is crashing,” Dr. Woodcock told reporters. “What we’ve heard around the country is the No. 1 barrier is staffing.”
At the same time, many hospitals have refused to offer the therapy because doctors were unimpressed with the research federal officials used to justify its use.
Monoclonal antibodies are lab-produced molecules that act as substitutes for the body’s own antibodies that fight infection. The COVID treatments are designed to block the SARS-CoV-2 virus that causes infection from attaching to and entering human cells. Such treatments are usually prohibitively expensive, but for the time being the federal government is footing the bulk of the bill, though patients likely will be charged administrative fees.
Nationwide, nearly 4,000 sites offer the infusion therapies. But for patients and families of people most at risk – those 65 and older or with underlying health conditions – finding the sites and gaining access has been almost impossible, said Brian Nyquist, chief executive officer of the National Infusion Center Association, which is tracking supplies of the antibody products. Like Mr. Herritz, many seeking information about monoclonals find themselves on a lone crusade.
“If they’re not hammering the phones and advocating for access for their loved ones, others often won’t,” he said. “Tenacity is critical.”
Regeneron officials said they’re fielding calls about COVID treatments daily to the company’s medical information line. More than 3,500 people have flooded Eli Lilly’s COVID hotline with questions about access.
As of this week, all states are required to list on a federal locator map sites that have received the monoclonal antibody products, HHS officials said. The updated map shows wide distribution, but a listing doesn’t guarantee availability or access; patients still need to check. It’s best to confer with a primary care provider before reaching out to the centers. For best results, treatment should occur as soon as possible after a positive COVID test.
Some health systems have refused to offer the monoclonal antibody therapies because of doubts about the data used to authorize them. Early studies suggested that Lilly’s therapy, bamlanivimab, reduced the need for hospitalization or emergency treatment in outpatient COVID cases by about 70%, while Regeneron’s antibody cocktail of casirivimab plus imdevimab reduced the need by about 50%.
But those studies were small, just a few hundred subjects, and the results were limited. “A lot of doctors, actually, they’re not impressed with the data,” said Dr. Daniel Griffin, an infectious disease expert at Columbia University who cohosts the podcast “This Week in Virology.” “There really is still that question of, ‘Does this stuff really work?’ ”
As more patients are treated, however, there’s growing evidence that the therapies can keep high-risk patients out of the hospital, not only easing their recovery but also decreasing the burden on health systems struggling with record numbers of patients.
Dr. Raymund Razonable, an infectious disease expert at the Mayo Clinic in Minnesota, said he has treated more than 2,500 COVID patients with monoclonal antibody therapy with promising results. “It’s looking good,” he said, declining to provide details because they’re embargoed for publication. “We are seeing reductions in hospitalizations; we’re seeing reductions in ICU care; we’re also seeing reductions in mortality.”
Banking on observations from Mayo experts and others, federal officials have been pushing for wider use of antibody therapies. HHS officials have partnered with hospitals in three hard-hit states – California, Arizona, and Nevada – to set up infusion centers that are treating dozens of COVID patients each day.
One of those sites went up in late December at El Centro Regional Medical Center in California’s Imperial County, an impoverished farming region on the state’s southern border that has recorded among the highest COVID infection rates in the state. For months, the medical center strained to absorb the overwhelming influx of patients, but chief executive Dr. Adolphe Edward said a new walk-up infusion site has already put a dent in the COVID load.
More than 130 people have been treated, all patients who were able to get the 2-hour infusions and then recuperate at home. “If those folks would not have had the treatment, they would have come through the emergency department and we would have had to admit the lion’s share of them,” he said.
It’s important to make sure people in high-risk groups know to seek out the therapy and to get it early, Dr. Edward said. He and his staff have been working with area doctors’ offices and nonprofit groups and relying on word of mouth.
“On multiple levels, we’re saying, ‘If you’ve tested positive for the virus, come and let us see if you are eligible,’ ” Dr. Edward said.
Greater awareness is a goal of the HHS effort, said Dr. John Redd, chief medical officer for the assistant secretary for preparedness and response. “These antibodies are meant for everyone,” he said. “Everyone across the country should have equal access to these products.”
For now, patients like Mr. Herritz, the Mississippi liver transplant recipient, say reality is falling well short of that goal. If he hadn’t continued to call in search of a referral, he wouldn’t have been treated. And without the therapy, Mr. Herritz believes, he was just days away from hospitalization.
“I think it’s horrible that if I didn’t have Twitter, I wouldn’t know anything about this,” he said. “I think about all the people who have died not knowing this was an option for high-risk individuals.”
Kaiser Health News is a nonprofit news service covering health issues. It is an editorially independent program of KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation), which is not affiliated with Kaiser Permanente.



