User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
‘We just have to keep them alive’: Transitioning youth with type 1 diabetes
“No one has asked young people what they want,” said Tabitha Randell, MBChB, an endocrinologist with Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, who specializes in treating teenagers with type 1 diabetes as they transition to adult care.
Dr. Randell, who has set up a very successful specialist service in her hospital for such patients, said: “We consistently have the best, or the second best, outcomes in this country for our diabetes patients.” She believes this is one of the most important issues in modern endocrinology today.
Speaking at the Diabetes Professional Care conference in London at the end of 2021, and sharing her thoughts afterward with this news organization, she noted that in general there are “virtually no published outcomes” on how best to transition a patient with type 1 diabetes from pediatric to adult care.
“If you actually get them to transition – because some just drop out and disengage and there’s nothing you can do – none of them get lost. Some of them disengage in the adult clinic, but if you’re in the young diabetes service [in England] the rules are that if you miss a diabetes appointment you do not get discharged, as compared with the adult clinic, where if you miss an appointment, you are discharged.”
In the young diabetes clinic, doctors will “carry on trying to contact you, and get you back,” she explained. “And the patients do eventually come back in – it might be a year or 2, but they do come back. We’ve just got to keep them alive in the meantime!”
This issue needs tackling all over the world. Dr. Randell said she’s not aware of any one country – although there may be “pockets” of good care within a given country – that is doing this perfectly.
Across the pond, Grazia Aleppo, MD, division of endocrinology at Northwestern University, Chicago, agreed that transitioning pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes to adult care presents “unique challenges.”
Challenges when transitioning from pediatric to adult care
During childhood, type 1 diabetes management is largely supervised by patients’ parents and members of the pediatric diabetes care team, which may include diabetes educators, psychologists, or social workers, as well as pediatric endocrinologists.
When the patient with type 1 diabetes becomes a young adult and takes over management of their own health, Dr. Aleppo said, the care team may diminish along with the time spent in provider visits.
The adult endocrinology setting focuses more on self-management and autonomous functioning of the individual with diabetes.
Adult appointments are typically shorter, and the patient is usually expected to follow doctors’ suggestions independently, she noted. They are also expected to manage the practical aspects of their diabetes care, including prescriptions, diabetes supplies, laboratory tests, scheduling, and keeping appointments.
At the same time that the emerging adult needs to start asserting independence over their health care, they will also be going through a myriad of other important lifestyle changes, such as attending college, living on their own for the first time, and starting a career.
“With these fundamental differences and challenges, competing priorities, such as college, work and relationships, medical care may become of secondary importance and patients may become disengaged,” Dr. Aleppo explained.
As Dr. Randell has said, loss to follow-up is a big problem with this patient population, with disengagement from specialist services and worsening A1c across the transition, Dr. Aleppo noted. This makes addressing these patients’ specific needs extremely important.
Engage with kid, not disease; don’t palm them off on new recruits
“The really key thing these kids say is, ‘I do not want to be a disease,’” Dr. Randell said. “They want you to know that they are a person. Engage these kids!” she suggested. “Ask them: ‘How is your exam revision going?’ Find something positive to say, even if it’s just: ‘I’m glad you came today.’ ”
“If the first thing that you do is tell them off [for poor diabetes care], you are never going to see them again,” she cautioned.
Dr. Randell also said that role models with type 1 diabetes, such as Lila Moss – daughter of British supermodel Kate Moss – who was recently pictured wearing an insulin pump on her leg on the catwalk, are helping youngsters not feel so self-conscious about their diabetes.
“Let them know it’s not the end of the world, having [type 1] diabetes,” she emphasized.
And Partha Kar, MBBS, OBE, national specialty advisor, diabetes with NHS England, agreed wholeheartedly with Dr. Randall.
Reminiscing about his early days as a newly qualified endocrinologist, Dr. Kar, who works at Portsmouth (England) Hospital NHS Trust, noted that as a new member of staff he was given the youth with type 1 diabetes – those getting ready to transition to adult care – to look after.
But this is the exact opposite of what should be happening, he emphasized. “If you don’t think transition care is important, you shouldn’t be treating type 1 diabetes.”
He believes that every diabetes center “must have a young-adult team lead” and this job must not be given to the least experienced member of staff.
This lead “doesn’t need to be a doctor,” Dr. Kar stressed. “It can be a psychologist, or a diabetes nurse, or a pharmacist, or a dietician.”
In short, it must be someone experienced who loves working with this age group.
Dr. Randell agreed: “Make sure the team is interested in young people. It shouldn’t be the last person in who gets the job no one else wants.” Teens “are my favorite group to work with. They don’t take any nonsense.”
And she explained: “Young people like to get to know the person who’s going to take care of them. So, stay with them for their young adult years.” This can be “quite a fluid period,” with it normally extending to age 25, but in some cases, “it can be up to 32 years old.”
Preparing for the transition
To ease pediatric patients into the transition to adult care, Dr. Aleppo recommended that the pediatric diabetes team provide enough time so that any concerns the patient and their family may have can be addressed.
This should also include transferring management responsibilities to the young adult rather than their parent.
The pediatric provider should discuss with the patient available potential adult colleagues, personalizing these options to their needs, she said.
And the adult and pediatric clinicians should collaborate and provide important information beyond medical records or health summaries.
Adult providers should guide young adults on how to navigate the new practices, from scheduling follow-up appointments to policies regarding medication refills or supplies, to providing information about urgent numbers or email addresses for after-hours communications.
Dr. Kar reiterated that there are too few published outcomes in this patient group to guide the establishment of good transition services.
“Without data, we are dead on the ground. Without data, it’s all conjecture, anecdotes,” he said.
What he does know is that, in the latest national type 1 diabetes audit for England, “Diabetic ketoacidosis admissions ... are up in this age group,” which suggests these patients are not receiving adequate care.
Be a guide, not a gatekeeper
Dr. Kar stressed that, of the 8,760 hours in a year, the average patient with type 1 diabetes in the United Kingdom gets just “1-2 hours with you as a clinician, based on four appointments per year of 30 minutes each.”
“So you spend 0.02% of their time with individuals with type 1 diabetes. So, what’s the one thing you can do with that minimal contact? Be nice!”
Dr. Kar said he always has his email open to his adult patients and they are very respectful of his time. “They don’t email you at 1 a.m. That means every one of my patients has got support [from me]. Don’t be a barrier.”
“We have to fundamentally change the narrative. Doctors must have more empathy,” he said, stating that the one thing adolescents have constantly given feedback on has been, “Why don’t appointments start with: ‘How are you?’
“For a teenager, if you throw type 1 diabetes into the loop, it’s not easy,” he stressed. “Talk to them about something else. As a clinician, be a guide, not a gatekeeper. Give people the tools to self-manage better.”
Adult providers can meet these young adult patients “at their level,” Dr. Aleppo agreed.
“Pay attention to their immediate needs and focus on their present circumstances – whether how to get through their next semester in college, navigating job interviews, or handling having diabetes in the workplace.”
Paying attention to the mental health needs of these young patients is equally “paramount,” Dr. Aleppo said.
While access to mental health professionals may be challenging in the adult setting, providers should bring it up with their patients and offer counseling referrals.
“Diabetes impacts everything, and office appointments and conversations carry weight on these patients’ lives as a whole, not just on their diabetes,” she stressed. “A patient told me recently: ‘We’re learning to be adults,’ which can be hard enough, and with diabetes it can be even more challenging. Adult providers need to be aware of the patient’s ‘diabetes language’ in that often it is not what a patient is saying, rather how they are saying it that gives us information on what they truly need.
“As adult providers, we need to also train and teach our young patients to advocate for themselves on where to find resources that can help them navigate adulthood with diabetes,” she added.
One particularly helpful resource in the United States is the College Diabetes Network, a not-for-profit organization whose mission is to equip young adults with type 1 diabetes to successfully manage the challenging transition to independence at college and beyond.
“The sweetest thing that can happen to us as adult diabetes providers is when a patient – seen as an emerging adult during college – returns to your practice 10 years later after moving back and seeks you out for their diabetes care because of the relationship and trust you developed in those transitioning years,” Dr. Aleppo said.
Another resource is a freely available comic book series cocreated by Dr. Kar and colleague Mayank Patel, MBBS, an endocrinologist from University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust.
As detailed by this news organization in 2021, the series consists of three volumes: the first, Type 1: Origins, focuses on actual experiences of patients who have type 1 diabetes; the second, Type 1: Attack of the Ketones, is aimed at professionals who may provide care but have limited understanding of type 1 diabetes; and the third, Type 1 Mission 3: S.T.I.G.M.A., addresses the stigmas and misconceptions that patients with type 1 diabetes may face.
The idea for the first comic was inspired by a patient who compared having diabetes to being like the Marvel character The Hulk, said Dr. Kar, and has been expanded to include the additional volumes.
Dr. Kar and Dr. Patel have also just launched the fourth comic in the series, Type 1: Generations, to mark the 100-year anniversary since insulin was first given to a human.
“This is high priority”
Dr. Kar said the NHS in England has just appointed a national lead for type 1 diabetes in youth, Fulya Mehta, MD, of Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool, England.
“If you have a plan, bring it to us,” he told the audience at the DPC conference, and “tell us, what is the one thing you would change? This is not a session we are doing just to tick a box. This is high priority.
“Encourage your colleagues to think about transition services. This is an absolute priority. We will be asking every center [in England] who is your transitioning lead?”
And he once again stressed that “a lead of transition service does not have to be a medic. This should be a multidisciplinary team. But they do need to be comfortable in that space. To that teenager, your job title means nothing. Give them time and space.”
Dr. Randell summed it up: “If we can work together, it’s only going to result in better outcomes. We need to blaze the trail for young people.”
Dr. Aleppo has reported serving as a consultant to Dexcom and Insulet and receiving support to Northwestern University from AstraZeneca, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Fractyl Health, Insulet, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Randell and Dr. Kar have no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“No one has asked young people what they want,” said Tabitha Randell, MBChB, an endocrinologist with Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, who specializes in treating teenagers with type 1 diabetes as they transition to adult care.
Dr. Randell, who has set up a very successful specialist service in her hospital for such patients, said: “We consistently have the best, or the second best, outcomes in this country for our diabetes patients.” She believes this is one of the most important issues in modern endocrinology today.
Speaking at the Diabetes Professional Care conference in London at the end of 2021, and sharing her thoughts afterward with this news organization, she noted that in general there are “virtually no published outcomes” on how best to transition a patient with type 1 diabetes from pediatric to adult care.
“If you actually get them to transition – because some just drop out and disengage and there’s nothing you can do – none of them get lost. Some of them disengage in the adult clinic, but if you’re in the young diabetes service [in England] the rules are that if you miss a diabetes appointment you do not get discharged, as compared with the adult clinic, where if you miss an appointment, you are discharged.”
In the young diabetes clinic, doctors will “carry on trying to contact you, and get you back,” she explained. “And the patients do eventually come back in – it might be a year or 2, but they do come back. We’ve just got to keep them alive in the meantime!”
This issue needs tackling all over the world. Dr. Randell said she’s not aware of any one country – although there may be “pockets” of good care within a given country – that is doing this perfectly.
Across the pond, Grazia Aleppo, MD, division of endocrinology at Northwestern University, Chicago, agreed that transitioning pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes to adult care presents “unique challenges.”
Challenges when transitioning from pediatric to adult care
During childhood, type 1 diabetes management is largely supervised by patients’ parents and members of the pediatric diabetes care team, which may include diabetes educators, psychologists, or social workers, as well as pediatric endocrinologists.
When the patient with type 1 diabetes becomes a young adult and takes over management of their own health, Dr. Aleppo said, the care team may diminish along with the time spent in provider visits.
The adult endocrinology setting focuses more on self-management and autonomous functioning of the individual with diabetes.
Adult appointments are typically shorter, and the patient is usually expected to follow doctors’ suggestions independently, she noted. They are also expected to manage the practical aspects of their diabetes care, including prescriptions, diabetes supplies, laboratory tests, scheduling, and keeping appointments.
At the same time that the emerging adult needs to start asserting independence over their health care, they will also be going through a myriad of other important lifestyle changes, such as attending college, living on their own for the first time, and starting a career.
“With these fundamental differences and challenges, competing priorities, such as college, work and relationships, medical care may become of secondary importance and patients may become disengaged,” Dr. Aleppo explained.
As Dr. Randell has said, loss to follow-up is a big problem with this patient population, with disengagement from specialist services and worsening A1c across the transition, Dr. Aleppo noted. This makes addressing these patients’ specific needs extremely important.
Engage with kid, not disease; don’t palm them off on new recruits
“The really key thing these kids say is, ‘I do not want to be a disease,’” Dr. Randell said. “They want you to know that they are a person. Engage these kids!” she suggested. “Ask them: ‘How is your exam revision going?’ Find something positive to say, even if it’s just: ‘I’m glad you came today.’ ”
“If the first thing that you do is tell them off [for poor diabetes care], you are never going to see them again,” she cautioned.
Dr. Randell also said that role models with type 1 diabetes, such as Lila Moss – daughter of British supermodel Kate Moss – who was recently pictured wearing an insulin pump on her leg on the catwalk, are helping youngsters not feel so self-conscious about their diabetes.
“Let them know it’s not the end of the world, having [type 1] diabetes,” she emphasized.
And Partha Kar, MBBS, OBE, national specialty advisor, diabetes with NHS England, agreed wholeheartedly with Dr. Randall.
Reminiscing about his early days as a newly qualified endocrinologist, Dr. Kar, who works at Portsmouth (England) Hospital NHS Trust, noted that as a new member of staff he was given the youth with type 1 diabetes – those getting ready to transition to adult care – to look after.
But this is the exact opposite of what should be happening, he emphasized. “If you don’t think transition care is important, you shouldn’t be treating type 1 diabetes.”
He believes that every diabetes center “must have a young-adult team lead” and this job must not be given to the least experienced member of staff.
This lead “doesn’t need to be a doctor,” Dr. Kar stressed. “It can be a psychologist, or a diabetes nurse, or a pharmacist, or a dietician.”
In short, it must be someone experienced who loves working with this age group.
Dr. Randell agreed: “Make sure the team is interested in young people. It shouldn’t be the last person in who gets the job no one else wants.” Teens “are my favorite group to work with. They don’t take any nonsense.”
And she explained: “Young people like to get to know the person who’s going to take care of them. So, stay with them for their young adult years.” This can be “quite a fluid period,” with it normally extending to age 25, but in some cases, “it can be up to 32 years old.”
Preparing for the transition
To ease pediatric patients into the transition to adult care, Dr. Aleppo recommended that the pediatric diabetes team provide enough time so that any concerns the patient and their family may have can be addressed.
This should also include transferring management responsibilities to the young adult rather than their parent.
The pediatric provider should discuss with the patient available potential adult colleagues, personalizing these options to their needs, she said.
And the adult and pediatric clinicians should collaborate and provide important information beyond medical records or health summaries.
Adult providers should guide young adults on how to navigate the new practices, from scheduling follow-up appointments to policies regarding medication refills or supplies, to providing information about urgent numbers or email addresses for after-hours communications.
Dr. Kar reiterated that there are too few published outcomes in this patient group to guide the establishment of good transition services.
“Without data, we are dead on the ground. Without data, it’s all conjecture, anecdotes,” he said.
What he does know is that, in the latest national type 1 diabetes audit for England, “Diabetic ketoacidosis admissions ... are up in this age group,” which suggests these patients are not receiving adequate care.
Be a guide, not a gatekeeper
Dr. Kar stressed that, of the 8,760 hours in a year, the average patient with type 1 diabetes in the United Kingdom gets just “1-2 hours with you as a clinician, based on four appointments per year of 30 minutes each.”
“So you spend 0.02% of their time with individuals with type 1 diabetes. So, what’s the one thing you can do with that minimal contact? Be nice!”
Dr. Kar said he always has his email open to his adult patients and they are very respectful of his time. “They don’t email you at 1 a.m. That means every one of my patients has got support [from me]. Don’t be a barrier.”
“We have to fundamentally change the narrative. Doctors must have more empathy,” he said, stating that the one thing adolescents have constantly given feedback on has been, “Why don’t appointments start with: ‘How are you?’
“For a teenager, if you throw type 1 diabetes into the loop, it’s not easy,” he stressed. “Talk to them about something else. As a clinician, be a guide, not a gatekeeper. Give people the tools to self-manage better.”
Adult providers can meet these young adult patients “at their level,” Dr. Aleppo agreed.
“Pay attention to their immediate needs and focus on their present circumstances – whether how to get through their next semester in college, navigating job interviews, or handling having diabetes in the workplace.”
Paying attention to the mental health needs of these young patients is equally “paramount,” Dr. Aleppo said.
While access to mental health professionals may be challenging in the adult setting, providers should bring it up with their patients and offer counseling referrals.
“Diabetes impacts everything, and office appointments and conversations carry weight on these patients’ lives as a whole, not just on their diabetes,” she stressed. “A patient told me recently: ‘We’re learning to be adults,’ which can be hard enough, and with diabetes it can be even more challenging. Adult providers need to be aware of the patient’s ‘diabetes language’ in that often it is not what a patient is saying, rather how they are saying it that gives us information on what they truly need.
“As adult providers, we need to also train and teach our young patients to advocate for themselves on where to find resources that can help them navigate adulthood with diabetes,” she added.
One particularly helpful resource in the United States is the College Diabetes Network, a not-for-profit organization whose mission is to equip young adults with type 1 diabetes to successfully manage the challenging transition to independence at college and beyond.
“The sweetest thing that can happen to us as adult diabetes providers is when a patient – seen as an emerging adult during college – returns to your practice 10 years later after moving back and seeks you out for their diabetes care because of the relationship and trust you developed in those transitioning years,” Dr. Aleppo said.
Another resource is a freely available comic book series cocreated by Dr. Kar and colleague Mayank Patel, MBBS, an endocrinologist from University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust.
As detailed by this news organization in 2021, the series consists of three volumes: the first, Type 1: Origins, focuses on actual experiences of patients who have type 1 diabetes; the second, Type 1: Attack of the Ketones, is aimed at professionals who may provide care but have limited understanding of type 1 diabetes; and the third, Type 1 Mission 3: S.T.I.G.M.A., addresses the stigmas and misconceptions that patients with type 1 diabetes may face.
The idea for the first comic was inspired by a patient who compared having diabetes to being like the Marvel character The Hulk, said Dr. Kar, and has been expanded to include the additional volumes.
Dr. Kar and Dr. Patel have also just launched the fourth comic in the series, Type 1: Generations, to mark the 100-year anniversary since insulin was first given to a human.
“This is high priority”
Dr. Kar said the NHS in England has just appointed a national lead for type 1 diabetes in youth, Fulya Mehta, MD, of Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool, England.
“If you have a plan, bring it to us,” he told the audience at the DPC conference, and “tell us, what is the one thing you would change? This is not a session we are doing just to tick a box. This is high priority.
“Encourage your colleagues to think about transition services. This is an absolute priority. We will be asking every center [in England] who is your transitioning lead?”
And he once again stressed that “a lead of transition service does not have to be a medic. This should be a multidisciplinary team. But they do need to be comfortable in that space. To that teenager, your job title means nothing. Give them time and space.”
Dr. Randell summed it up: “If we can work together, it’s only going to result in better outcomes. We need to blaze the trail for young people.”
Dr. Aleppo has reported serving as a consultant to Dexcom and Insulet and receiving support to Northwestern University from AstraZeneca, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Fractyl Health, Insulet, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Randell and Dr. Kar have no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
“No one has asked young people what they want,” said Tabitha Randell, MBChB, an endocrinologist with Nottingham (England) University Hospitals NHS Trust, who specializes in treating teenagers with type 1 diabetes as they transition to adult care.
Dr. Randell, who has set up a very successful specialist service in her hospital for such patients, said: “We consistently have the best, or the second best, outcomes in this country for our diabetes patients.” She believes this is one of the most important issues in modern endocrinology today.
Speaking at the Diabetes Professional Care conference in London at the end of 2021, and sharing her thoughts afterward with this news organization, she noted that in general there are “virtually no published outcomes” on how best to transition a patient with type 1 diabetes from pediatric to adult care.
“If you actually get them to transition – because some just drop out and disengage and there’s nothing you can do – none of them get lost. Some of them disengage in the adult clinic, but if you’re in the young diabetes service [in England] the rules are that if you miss a diabetes appointment you do not get discharged, as compared with the adult clinic, where if you miss an appointment, you are discharged.”
In the young diabetes clinic, doctors will “carry on trying to contact you, and get you back,” she explained. “And the patients do eventually come back in – it might be a year or 2, but they do come back. We’ve just got to keep them alive in the meantime!”
This issue needs tackling all over the world. Dr. Randell said she’s not aware of any one country – although there may be “pockets” of good care within a given country – that is doing this perfectly.
Across the pond, Grazia Aleppo, MD, division of endocrinology at Northwestern University, Chicago, agreed that transitioning pediatric patients with type 1 diabetes to adult care presents “unique challenges.”
Challenges when transitioning from pediatric to adult care
During childhood, type 1 diabetes management is largely supervised by patients’ parents and members of the pediatric diabetes care team, which may include diabetes educators, psychologists, or social workers, as well as pediatric endocrinologists.
When the patient with type 1 diabetes becomes a young adult and takes over management of their own health, Dr. Aleppo said, the care team may diminish along with the time spent in provider visits.
The adult endocrinology setting focuses more on self-management and autonomous functioning of the individual with diabetes.
Adult appointments are typically shorter, and the patient is usually expected to follow doctors’ suggestions independently, she noted. They are also expected to manage the practical aspects of their diabetes care, including prescriptions, diabetes supplies, laboratory tests, scheduling, and keeping appointments.
At the same time that the emerging adult needs to start asserting independence over their health care, they will also be going through a myriad of other important lifestyle changes, such as attending college, living on their own for the first time, and starting a career.
“With these fundamental differences and challenges, competing priorities, such as college, work and relationships, medical care may become of secondary importance and patients may become disengaged,” Dr. Aleppo explained.
As Dr. Randell has said, loss to follow-up is a big problem with this patient population, with disengagement from specialist services and worsening A1c across the transition, Dr. Aleppo noted. This makes addressing these patients’ specific needs extremely important.
Engage with kid, not disease; don’t palm them off on new recruits
“The really key thing these kids say is, ‘I do not want to be a disease,’” Dr. Randell said. “They want you to know that they are a person. Engage these kids!” she suggested. “Ask them: ‘How is your exam revision going?’ Find something positive to say, even if it’s just: ‘I’m glad you came today.’ ”
“If the first thing that you do is tell them off [for poor diabetes care], you are never going to see them again,” she cautioned.
Dr. Randell also said that role models with type 1 diabetes, such as Lila Moss – daughter of British supermodel Kate Moss – who was recently pictured wearing an insulin pump on her leg on the catwalk, are helping youngsters not feel so self-conscious about their diabetes.
“Let them know it’s not the end of the world, having [type 1] diabetes,” she emphasized.
And Partha Kar, MBBS, OBE, national specialty advisor, diabetes with NHS England, agreed wholeheartedly with Dr. Randall.
Reminiscing about his early days as a newly qualified endocrinologist, Dr. Kar, who works at Portsmouth (England) Hospital NHS Trust, noted that as a new member of staff he was given the youth with type 1 diabetes – those getting ready to transition to adult care – to look after.
But this is the exact opposite of what should be happening, he emphasized. “If you don’t think transition care is important, you shouldn’t be treating type 1 diabetes.”
He believes that every diabetes center “must have a young-adult team lead” and this job must not be given to the least experienced member of staff.
This lead “doesn’t need to be a doctor,” Dr. Kar stressed. “It can be a psychologist, or a diabetes nurse, or a pharmacist, or a dietician.”
In short, it must be someone experienced who loves working with this age group.
Dr. Randell agreed: “Make sure the team is interested in young people. It shouldn’t be the last person in who gets the job no one else wants.” Teens “are my favorite group to work with. They don’t take any nonsense.”
And she explained: “Young people like to get to know the person who’s going to take care of them. So, stay with them for their young adult years.” This can be “quite a fluid period,” with it normally extending to age 25, but in some cases, “it can be up to 32 years old.”
Preparing for the transition
To ease pediatric patients into the transition to adult care, Dr. Aleppo recommended that the pediatric diabetes team provide enough time so that any concerns the patient and their family may have can be addressed.
This should also include transferring management responsibilities to the young adult rather than their parent.
The pediatric provider should discuss with the patient available potential adult colleagues, personalizing these options to their needs, she said.
And the adult and pediatric clinicians should collaborate and provide important information beyond medical records or health summaries.
Adult providers should guide young adults on how to navigate the new practices, from scheduling follow-up appointments to policies regarding medication refills or supplies, to providing information about urgent numbers or email addresses for after-hours communications.
Dr. Kar reiterated that there are too few published outcomes in this patient group to guide the establishment of good transition services.
“Without data, we are dead on the ground. Without data, it’s all conjecture, anecdotes,” he said.
What he does know is that, in the latest national type 1 diabetes audit for England, “Diabetic ketoacidosis admissions ... are up in this age group,” which suggests these patients are not receiving adequate care.
Be a guide, not a gatekeeper
Dr. Kar stressed that, of the 8,760 hours in a year, the average patient with type 1 diabetes in the United Kingdom gets just “1-2 hours with you as a clinician, based on four appointments per year of 30 minutes each.”
“So you spend 0.02% of their time with individuals with type 1 diabetes. So, what’s the one thing you can do with that minimal contact? Be nice!”
Dr. Kar said he always has his email open to his adult patients and they are very respectful of his time. “They don’t email you at 1 a.m. That means every one of my patients has got support [from me]. Don’t be a barrier.”
“We have to fundamentally change the narrative. Doctors must have more empathy,” he said, stating that the one thing adolescents have constantly given feedback on has been, “Why don’t appointments start with: ‘How are you?’
“For a teenager, if you throw type 1 diabetes into the loop, it’s not easy,” he stressed. “Talk to them about something else. As a clinician, be a guide, not a gatekeeper. Give people the tools to self-manage better.”
Adult providers can meet these young adult patients “at their level,” Dr. Aleppo agreed.
“Pay attention to their immediate needs and focus on their present circumstances – whether how to get through their next semester in college, navigating job interviews, or handling having diabetes in the workplace.”
Paying attention to the mental health needs of these young patients is equally “paramount,” Dr. Aleppo said.
While access to mental health professionals may be challenging in the adult setting, providers should bring it up with their patients and offer counseling referrals.
“Diabetes impacts everything, and office appointments and conversations carry weight on these patients’ lives as a whole, not just on their diabetes,” she stressed. “A patient told me recently: ‘We’re learning to be adults,’ which can be hard enough, and with diabetes it can be even more challenging. Adult providers need to be aware of the patient’s ‘diabetes language’ in that often it is not what a patient is saying, rather how they are saying it that gives us information on what they truly need.
“As adult providers, we need to also train and teach our young patients to advocate for themselves on where to find resources that can help them navigate adulthood with diabetes,” she added.
One particularly helpful resource in the United States is the College Diabetes Network, a not-for-profit organization whose mission is to equip young adults with type 1 diabetes to successfully manage the challenging transition to independence at college and beyond.
“The sweetest thing that can happen to us as adult diabetes providers is when a patient – seen as an emerging adult during college – returns to your practice 10 years later after moving back and seeks you out for their diabetes care because of the relationship and trust you developed in those transitioning years,” Dr. Aleppo said.
Another resource is a freely available comic book series cocreated by Dr. Kar and colleague Mayank Patel, MBBS, an endocrinologist from University Hospital Southampton NHS Foundation Trust.
As detailed by this news organization in 2021, the series consists of three volumes: the first, Type 1: Origins, focuses on actual experiences of patients who have type 1 diabetes; the second, Type 1: Attack of the Ketones, is aimed at professionals who may provide care but have limited understanding of type 1 diabetes; and the third, Type 1 Mission 3: S.T.I.G.M.A., addresses the stigmas and misconceptions that patients with type 1 diabetes may face.
The idea for the first comic was inspired by a patient who compared having diabetes to being like the Marvel character The Hulk, said Dr. Kar, and has been expanded to include the additional volumes.
Dr. Kar and Dr. Patel have also just launched the fourth comic in the series, Type 1: Generations, to mark the 100-year anniversary since insulin was first given to a human.
“This is high priority”
Dr. Kar said the NHS in England has just appointed a national lead for type 1 diabetes in youth, Fulya Mehta, MD, of Alder Hey Children’s NHS Foundation Trust, Liverpool, England.
“If you have a plan, bring it to us,” he told the audience at the DPC conference, and “tell us, what is the one thing you would change? This is not a session we are doing just to tick a box. This is high priority.
“Encourage your colleagues to think about transition services. This is an absolute priority. We will be asking every center [in England] who is your transitioning lead?”
And he once again stressed that “a lead of transition service does not have to be a medic. This should be a multidisciplinary team. But they do need to be comfortable in that space. To that teenager, your job title means nothing. Give them time and space.”
Dr. Randell summed it up: “If we can work together, it’s only going to result in better outcomes. We need to blaze the trail for young people.”
Dr. Aleppo has reported serving as a consultant to Dexcom and Insulet and receiving support to Northwestern University from AstraZeneca, Dexcom, Eli Lilly, Fractyl Health, Insulet, and Novo Nordisk. Dr. Randell and Dr. Kar have no conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
‘Incomprehensible’ CABG recommendation raises concerns
BUENOS AIRES – The Latin American Association of Cardiac and Endovascular Surgery (LACES) has demanded “urgent reconsideration” of the decision to downgrade the strength of the recommendation for revascularization or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery for multivessel disease in the new guideline on coronary artery revascularization, putting it in the same class as the recommendation for percutaneous coronary intervention, which has no apparent advantage over optimal medical therapy.
With the prevalence of stable ischemic heart disease in patients with multivessel disease, the contradiction between the evidence and the new recommendation “may affect the lives and survival of millions of patients worldwide and have a major socio-economic impact,” the association warned in a public letter.
In the 2011 guideline, CABG for patients with multivessel coronary artery disease was given a class I recommendation, which means that it is considered useful and effective and should be performed in the majority of patients in most circumstances. But the new, much weaker class IIb recommendation suggests that the benefit only marginally exceeds the risk and that it should be used selectively and only after careful consideration.
“It is an incomprehensible rollercoaster drop in the recommendation level. We totally disagree. In the absence of evidence, a IIb level provides equal freedom to send a patient to surgery or not. And in patients who are not being sent to surgery, it could take years of survival before we can be sure that we are doing the right thing,” said LACES president Víctor Dayan, MD, PhD, from the cardiovascular center at the Hospital de Clínicas “Dr. Manuel Quintela”, which is part of the School of Medicine at the University of the Republic, Montevideo, Uruguay.
The change in the recommendation for this indication “reflects new evidence showing no advantage of coronary artery bypass grafting over medical therapy alone to improve survival in patients with three-vessel coronary disease with preserved left ventricular function and no left main disease,” according to the authors of the guideline, issued jointly by the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association, and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI). In particular, they cite the 2019 ISCHEMIA clinical study that failed to show that an early invasive strategy reduces major adverse cardiovascular events, compared with optimal medical therapy and a handful of meta-analyses.
However, ISCHEMIA did not discriminate between the two types of invasive strategy – CABG and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) – so cannot be considered as a basis to downgrade the CABG recommendation, Dr. Dayan explained.
“Furthermore, the authors neglected previous RCTs that have shown the survival benefit of CABG in these patients and decided to put PCI in the same [class of recommendation], although no RCT has been able to show any survival advantage of PCI compared to optimal medical treatment,” the LACES letter states.
Basis should be evidence, ‘not inferences’
Three large randomized clinical trials and a 1994 meta-analysis with individual patient data from seven studies firmly established that survival is better with CABG than with medical treatment, the letter continues. However, the guideline authors did not provide any additional randomized clinical trials that refute this evidence.
“Furthermore, the committee disregarded data from the Ten-Year Follow-up Survival of the Medicine, Angioplasty, or Surgery Study (MASS II) randomized control[led] trial, which showed a lower incidence of cardiac mortality (as part of its secondary outcomes) following CABG compared to optimal medical therapy and PCI,” the letter explains.
The guideline authors might have judged current optimal medical therapy to be better than what existed 10, 15, or 30 years ago, diluting the relative benefits of surgery, but the “recommendation in a guideline must act on evidence, not inferences. And there is no evidence to support this drop in recommendation class,” Dr. Dayan said.
Other experts have drawn attention to the fact that two surgical societies – the American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AAST) and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) – did not endorse the final document, despite having participated in its review, reported this news organization.
“This is a very disappointing update that will negatively affect the lives of many people,” tweeted Marc Pelletier, MD, head of cardiac surgery at University Hospitals, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Contradictions in the text that examines the evidence and the final recommendations, are “unclear” and “open to various interpretations, when they should be a pillar for decisionmaking,” said Javier Ferrari Ayarragaray, MD, president of the Argentine College of Cardiovascular Surgeons (CACCV) and vice president of LACES.
The new guidelines “show no additional randomized controlled trial to support this downgrade in the level of evidence,” according to a recent CACCV statement. “The inclusion, approval and endorsement of this type of [recommendation,] including [other] international surgical scientific societies, such as STS, AATS, EACTS, LACES[,] is necessary to obtain a better understanding and agreement on the current evidence.”
In a Dec. 17, 2021 response to LACES, Patrick O’Gara, MD, who was chair of the ACC/AHA Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines at the time, and his successor, Joshua Beckman, MD, explained that both organizations approved the guideline for publication and support its authors “in their interpretation of the published evidence and findings.”
The pair pointed out that the drafting committee members, who have extensive clinical judgment and experience, deliberated extensively on the issue and that the change from a class I to a class IIb recommendation was “carefully considered after a review of the entire available and relevant evidence.”
“When we bring together multiple organizations to review and summarize the evidence, we work collaboratively to interpret the extensive catalog of published and peer-reviewed literature and create clinical practice recommendations,” said Thomas Getchius, director of guideline strategy and operations at the AHA.
“The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for coronary artery revascularization, as agreed upon by the ACC, AHA, SCAI, and the full drafting committee,” Mr. Getchius said.
Dr. Dayan and Dr. Ferrari Ayarragaray have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Getchius is an employee of the American Heart Association.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BUENOS AIRES – The Latin American Association of Cardiac and Endovascular Surgery (LACES) has demanded “urgent reconsideration” of the decision to downgrade the strength of the recommendation for revascularization or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery for multivessel disease in the new guideline on coronary artery revascularization, putting it in the same class as the recommendation for percutaneous coronary intervention, which has no apparent advantage over optimal medical therapy.
With the prevalence of stable ischemic heart disease in patients with multivessel disease, the contradiction between the evidence and the new recommendation “may affect the lives and survival of millions of patients worldwide and have a major socio-economic impact,” the association warned in a public letter.
In the 2011 guideline, CABG for patients with multivessel coronary artery disease was given a class I recommendation, which means that it is considered useful and effective and should be performed in the majority of patients in most circumstances. But the new, much weaker class IIb recommendation suggests that the benefit only marginally exceeds the risk and that it should be used selectively and only after careful consideration.
“It is an incomprehensible rollercoaster drop in the recommendation level. We totally disagree. In the absence of evidence, a IIb level provides equal freedom to send a patient to surgery or not. And in patients who are not being sent to surgery, it could take years of survival before we can be sure that we are doing the right thing,” said LACES president Víctor Dayan, MD, PhD, from the cardiovascular center at the Hospital de Clínicas “Dr. Manuel Quintela”, which is part of the School of Medicine at the University of the Republic, Montevideo, Uruguay.
The change in the recommendation for this indication “reflects new evidence showing no advantage of coronary artery bypass grafting over medical therapy alone to improve survival in patients with three-vessel coronary disease with preserved left ventricular function and no left main disease,” according to the authors of the guideline, issued jointly by the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association, and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI). In particular, they cite the 2019 ISCHEMIA clinical study that failed to show that an early invasive strategy reduces major adverse cardiovascular events, compared with optimal medical therapy and a handful of meta-analyses.
However, ISCHEMIA did not discriminate between the two types of invasive strategy – CABG and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) – so cannot be considered as a basis to downgrade the CABG recommendation, Dr. Dayan explained.
“Furthermore, the authors neglected previous RCTs that have shown the survival benefit of CABG in these patients and decided to put PCI in the same [class of recommendation], although no RCT has been able to show any survival advantage of PCI compared to optimal medical treatment,” the LACES letter states.
Basis should be evidence, ‘not inferences’
Three large randomized clinical trials and a 1994 meta-analysis with individual patient data from seven studies firmly established that survival is better with CABG than with medical treatment, the letter continues. However, the guideline authors did not provide any additional randomized clinical trials that refute this evidence.
“Furthermore, the committee disregarded data from the Ten-Year Follow-up Survival of the Medicine, Angioplasty, or Surgery Study (MASS II) randomized control[led] trial, which showed a lower incidence of cardiac mortality (as part of its secondary outcomes) following CABG compared to optimal medical therapy and PCI,” the letter explains.
The guideline authors might have judged current optimal medical therapy to be better than what existed 10, 15, or 30 years ago, diluting the relative benefits of surgery, but the “recommendation in a guideline must act on evidence, not inferences. And there is no evidence to support this drop in recommendation class,” Dr. Dayan said.
Other experts have drawn attention to the fact that two surgical societies – the American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AAST) and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) – did not endorse the final document, despite having participated in its review, reported this news organization.
“This is a very disappointing update that will negatively affect the lives of many people,” tweeted Marc Pelletier, MD, head of cardiac surgery at University Hospitals, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Contradictions in the text that examines the evidence and the final recommendations, are “unclear” and “open to various interpretations, when they should be a pillar for decisionmaking,” said Javier Ferrari Ayarragaray, MD, president of the Argentine College of Cardiovascular Surgeons (CACCV) and vice president of LACES.
The new guidelines “show no additional randomized controlled trial to support this downgrade in the level of evidence,” according to a recent CACCV statement. “The inclusion, approval and endorsement of this type of [recommendation,] including [other] international surgical scientific societies, such as STS, AATS, EACTS, LACES[,] is necessary to obtain a better understanding and agreement on the current evidence.”
In a Dec. 17, 2021 response to LACES, Patrick O’Gara, MD, who was chair of the ACC/AHA Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines at the time, and his successor, Joshua Beckman, MD, explained that both organizations approved the guideline for publication and support its authors “in their interpretation of the published evidence and findings.”
The pair pointed out that the drafting committee members, who have extensive clinical judgment and experience, deliberated extensively on the issue and that the change from a class I to a class IIb recommendation was “carefully considered after a review of the entire available and relevant evidence.”
“When we bring together multiple organizations to review and summarize the evidence, we work collaboratively to interpret the extensive catalog of published and peer-reviewed literature and create clinical practice recommendations,” said Thomas Getchius, director of guideline strategy and operations at the AHA.
“The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for coronary artery revascularization, as agreed upon by the ACC, AHA, SCAI, and the full drafting committee,” Mr. Getchius said.
Dr. Dayan and Dr. Ferrari Ayarragaray have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Getchius is an employee of the American Heart Association.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
BUENOS AIRES – The Latin American Association of Cardiac and Endovascular Surgery (LACES) has demanded “urgent reconsideration” of the decision to downgrade the strength of the recommendation for revascularization or coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery for multivessel disease in the new guideline on coronary artery revascularization, putting it in the same class as the recommendation for percutaneous coronary intervention, which has no apparent advantage over optimal medical therapy.
With the prevalence of stable ischemic heart disease in patients with multivessel disease, the contradiction between the evidence and the new recommendation “may affect the lives and survival of millions of patients worldwide and have a major socio-economic impact,” the association warned in a public letter.
In the 2011 guideline, CABG for patients with multivessel coronary artery disease was given a class I recommendation, which means that it is considered useful and effective and should be performed in the majority of patients in most circumstances. But the new, much weaker class IIb recommendation suggests that the benefit only marginally exceeds the risk and that it should be used selectively and only after careful consideration.
“It is an incomprehensible rollercoaster drop in the recommendation level. We totally disagree. In the absence of evidence, a IIb level provides equal freedom to send a patient to surgery or not. And in patients who are not being sent to surgery, it could take years of survival before we can be sure that we are doing the right thing,” said LACES president Víctor Dayan, MD, PhD, from the cardiovascular center at the Hospital de Clínicas “Dr. Manuel Quintela”, which is part of the School of Medicine at the University of the Republic, Montevideo, Uruguay.
The change in the recommendation for this indication “reflects new evidence showing no advantage of coronary artery bypass grafting over medical therapy alone to improve survival in patients with three-vessel coronary disease with preserved left ventricular function and no left main disease,” according to the authors of the guideline, issued jointly by the American College of Cardiology (ACC), the American Heart Association, and the Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions (SCAI). In particular, they cite the 2019 ISCHEMIA clinical study that failed to show that an early invasive strategy reduces major adverse cardiovascular events, compared with optimal medical therapy and a handful of meta-analyses.
However, ISCHEMIA did not discriminate between the two types of invasive strategy – CABG and percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) – so cannot be considered as a basis to downgrade the CABG recommendation, Dr. Dayan explained.
“Furthermore, the authors neglected previous RCTs that have shown the survival benefit of CABG in these patients and decided to put PCI in the same [class of recommendation], although no RCT has been able to show any survival advantage of PCI compared to optimal medical treatment,” the LACES letter states.
Basis should be evidence, ‘not inferences’
Three large randomized clinical trials and a 1994 meta-analysis with individual patient data from seven studies firmly established that survival is better with CABG than with medical treatment, the letter continues. However, the guideline authors did not provide any additional randomized clinical trials that refute this evidence.
“Furthermore, the committee disregarded data from the Ten-Year Follow-up Survival of the Medicine, Angioplasty, or Surgery Study (MASS II) randomized control[led] trial, which showed a lower incidence of cardiac mortality (as part of its secondary outcomes) following CABG compared to optimal medical therapy and PCI,” the letter explains.
The guideline authors might have judged current optimal medical therapy to be better than what existed 10, 15, or 30 years ago, diluting the relative benefits of surgery, but the “recommendation in a guideline must act on evidence, not inferences. And there is no evidence to support this drop in recommendation class,” Dr. Dayan said.
Other experts have drawn attention to the fact that two surgical societies – the American Association for Thoracic Surgery (AAST) and the Society of Thoracic Surgeons (STS) – did not endorse the final document, despite having participated in its review, reported this news organization.
“This is a very disappointing update that will negatively affect the lives of many people,” tweeted Marc Pelletier, MD, head of cardiac surgery at University Hospitals, Case Western Reserve University, Cleveland.
Contradictions in the text that examines the evidence and the final recommendations, are “unclear” and “open to various interpretations, when they should be a pillar for decisionmaking,” said Javier Ferrari Ayarragaray, MD, president of the Argentine College of Cardiovascular Surgeons (CACCV) and vice president of LACES.
The new guidelines “show no additional randomized controlled trial to support this downgrade in the level of evidence,” according to a recent CACCV statement. “The inclusion, approval and endorsement of this type of [recommendation,] including [other] international surgical scientific societies, such as STS, AATS, EACTS, LACES[,] is necessary to obtain a better understanding and agreement on the current evidence.”
In a Dec. 17, 2021 response to LACES, Patrick O’Gara, MD, who was chair of the ACC/AHA Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines at the time, and his successor, Joshua Beckman, MD, explained that both organizations approved the guideline for publication and support its authors “in their interpretation of the published evidence and findings.”
The pair pointed out that the drafting committee members, who have extensive clinical judgment and experience, deliberated extensively on the issue and that the change from a class I to a class IIb recommendation was “carefully considered after a review of the entire available and relevant evidence.”
“When we bring together multiple organizations to review and summarize the evidence, we work collaboratively to interpret the extensive catalog of published and peer-reviewed literature and create clinical practice recommendations,” said Thomas Getchius, director of guideline strategy and operations at the AHA.
“The final guideline reflects the latest evidence-based recommendations for coronary artery revascularization, as agreed upon by the ACC, AHA, SCAI, and the full drafting committee,” Mr. Getchius said.
Dr. Dayan and Dr. Ferrari Ayarragaray have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Mr. Getchius is an employee of the American Heart Association.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Unraveling plaque changes in CAD With elevated Lp(a)
New research suggests serial coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can provide novel insights into the association between lipoprotein(a) and plaque progression over time in patients with advanced coronary artery disease.
Researchers examined data from 191 individuals with multivessel coronary disease receiving preventive statin (95%) and antiplatelet (100%) therapy in the single-center Scottish DIAMOND trial and compared CCTA at baseline and 12 months available for 160 patients.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, patients with high Lp(a), defined as at least 70 mg/dL, had higher baseline high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASSIGN scores than those with low Lp(a) but had comparable coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores and total, calcific, noncalcific, and low-attenuation plaque (LAP) volumes.
At 1 year, however, LAP volume – a marker for necrotic core – increased by 26.2 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group and decreased by –0.7 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
There was no significant difference in change in total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes between groups.
In multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for body mass index, ASSIGN score, and segment involvement score, LAP volume increased by 10.5% for each 50 mg/dL increment in Lp(a) (P = .034).
“It’s an exciting observation, because we’ve done previous studies where we’ve demonstrated the association of that particular plaque type with future myocardial infarction,” senior author Marc R. Dweck, MD, PhD, University of Amsterdam, told this news organization. “So, you’ve potentially got an explanation for the adverse prognosis associated with high lipoprotein(a) and its link to cardiovascular events and, in particular, myocardial infarction.”
The team’s recent SCOT-HEART analysis found that LAP burden was a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction (MI) than cardiovascular risk scores, stenosis severity, and CAC scoring, with MI risk nearly five-fold higher if LAP was above 4%.
As to why total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes didn’t change significantly on repeat CCTA in the present study, Dr. Dweck said it’s possible that the sample was too small and follow-up too short but also that “total plaque volume is really dominated by the fibrous plaque, which doesn’t appear affected by Lp(a).” Nevertheless, Lp(a)’s effect on low-attenuation plaque was clearly present and supported by the change in fibro-fatty plaque, the next-most unstable plaque type.
At 1 year, fibro-fatty plaque volume was 55.0 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group versus –25.0 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
Lp(a) was associated with fibro-fatty plaque progression in univariate analysis (β = 6.7%; P = .034) and showed a trend in multivariable analysis (β = 6.0%; P = .062).
“This study shows you can track changes in plaque over time and highlight important disease mechanisms and use them to understand the pathology of the disease,” Dr. Dweck said. “I’m very encouraged by this.”
What’s novel in the present study is that “it represents the beginning of our understanding of the role of Lp(a) in plaque progression,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, University of California, San Diego, and Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, say in an accompanying commentary.
They note that prior studies, including the Dallas Heart Study, have struggled to find a strong association between Lp(a) with the extent or progression of CAC, despite elevated Lp(a) and CAC identifying higher-risk patients.
Similarly, a meta-analysis of intravascular ultrasound trials turned up only a 1.2% absolute difference in atheroma volume in patients with elevated Lp(a), and a recent optical coherence tomography study found an association of Lp(a) with thin-cap fibroatheromas but not lipid core.
With just 36 patients with elevated Lp(a), however, the current findings need validation in a larger data set, Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula say.
Although Lp(a) is genetically elevated in about one in five individuals and measurement is recommended in European dyslipidemia guidelines, testing rates are low, in part because the argument has been that there are no Lp(a)-lowering therapies available, Dr. Dweck observed. That may change with the phase 3 cardiovascular outcomes Lp(a)HORIZON trial, which follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and is enrolling patients similar to the current cohort.
“Ultimately it comes down to that fundamental thing, that you need an action once you’ve done the test and then insurers will be happy to pay for it and clinicians will ask for it. That’s why that trial is so important,” Dr. Dweck said.
Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula also point to the eagerly awaited results of that trial, expected in 2025. “A positive trial is likely to lead to additional trials and new drugs that may reinvigorate the use of imaging modalities that could go beyond plaque volume and atherosclerosis to also predict clinically relevant inflammation and atherothrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Dweck is supported by the British Heart Foundation and is the recipient of the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research 2015; has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Novartis; and has received consultancy fees from Novartis, Jupiter Bioventures, and Silence Therapeutics. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tsimikas has a dual appointment at the University of California, San Diego, (UCSD) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals; is a coinventor and receives royalties from patents owned by UCSD; and is a cofounder and has an equity interest in Oxitope and its affiliates, Kleanthi Diagnostics, and Covicept Therapeutics. Dr. Narula reports having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests serial coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can provide novel insights into the association between lipoprotein(a) and plaque progression over time in patients with advanced coronary artery disease.
Researchers examined data from 191 individuals with multivessel coronary disease receiving preventive statin (95%) and antiplatelet (100%) therapy in the single-center Scottish DIAMOND trial and compared CCTA at baseline and 12 months available for 160 patients.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, patients with high Lp(a), defined as at least 70 mg/dL, had higher baseline high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASSIGN scores than those with low Lp(a) but had comparable coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores and total, calcific, noncalcific, and low-attenuation plaque (LAP) volumes.
At 1 year, however, LAP volume – a marker for necrotic core – increased by 26.2 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group and decreased by –0.7 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
There was no significant difference in change in total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes between groups.
In multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for body mass index, ASSIGN score, and segment involvement score, LAP volume increased by 10.5% for each 50 mg/dL increment in Lp(a) (P = .034).
“It’s an exciting observation, because we’ve done previous studies where we’ve demonstrated the association of that particular plaque type with future myocardial infarction,” senior author Marc R. Dweck, MD, PhD, University of Amsterdam, told this news organization. “So, you’ve potentially got an explanation for the adverse prognosis associated with high lipoprotein(a) and its link to cardiovascular events and, in particular, myocardial infarction.”
The team’s recent SCOT-HEART analysis found that LAP burden was a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction (MI) than cardiovascular risk scores, stenosis severity, and CAC scoring, with MI risk nearly five-fold higher if LAP was above 4%.
As to why total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes didn’t change significantly on repeat CCTA in the present study, Dr. Dweck said it’s possible that the sample was too small and follow-up too short but also that “total plaque volume is really dominated by the fibrous plaque, which doesn’t appear affected by Lp(a).” Nevertheless, Lp(a)’s effect on low-attenuation plaque was clearly present and supported by the change in fibro-fatty plaque, the next-most unstable plaque type.
At 1 year, fibro-fatty plaque volume was 55.0 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group versus –25.0 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
Lp(a) was associated with fibro-fatty plaque progression in univariate analysis (β = 6.7%; P = .034) and showed a trend in multivariable analysis (β = 6.0%; P = .062).
“This study shows you can track changes in plaque over time and highlight important disease mechanisms and use them to understand the pathology of the disease,” Dr. Dweck said. “I’m very encouraged by this.”
What’s novel in the present study is that “it represents the beginning of our understanding of the role of Lp(a) in plaque progression,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, University of California, San Diego, and Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, say in an accompanying commentary.
They note that prior studies, including the Dallas Heart Study, have struggled to find a strong association between Lp(a) with the extent or progression of CAC, despite elevated Lp(a) and CAC identifying higher-risk patients.
Similarly, a meta-analysis of intravascular ultrasound trials turned up only a 1.2% absolute difference in atheroma volume in patients with elevated Lp(a), and a recent optical coherence tomography study found an association of Lp(a) with thin-cap fibroatheromas but not lipid core.
With just 36 patients with elevated Lp(a), however, the current findings need validation in a larger data set, Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula say.
Although Lp(a) is genetically elevated in about one in five individuals and measurement is recommended in European dyslipidemia guidelines, testing rates are low, in part because the argument has been that there are no Lp(a)-lowering therapies available, Dr. Dweck observed. That may change with the phase 3 cardiovascular outcomes Lp(a)HORIZON trial, which follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and is enrolling patients similar to the current cohort.
“Ultimately it comes down to that fundamental thing, that you need an action once you’ve done the test and then insurers will be happy to pay for it and clinicians will ask for it. That’s why that trial is so important,” Dr. Dweck said.
Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula also point to the eagerly awaited results of that trial, expected in 2025. “A positive trial is likely to lead to additional trials and new drugs that may reinvigorate the use of imaging modalities that could go beyond plaque volume and atherosclerosis to also predict clinically relevant inflammation and atherothrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Dweck is supported by the British Heart Foundation and is the recipient of the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research 2015; has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Novartis; and has received consultancy fees from Novartis, Jupiter Bioventures, and Silence Therapeutics. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tsimikas has a dual appointment at the University of California, San Diego, (UCSD) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals; is a coinventor and receives royalties from patents owned by UCSD; and is a cofounder and has an equity interest in Oxitope and its affiliates, Kleanthi Diagnostics, and Covicept Therapeutics. Dr. Narula reports having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research suggests serial coronary CT angiography (CCTA) can provide novel insights into the association between lipoprotein(a) and plaque progression over time in patients with advanced coronary artery disease.
Researchers examined data from 191 individuals with multivessel coronary disease receiving preventive statin (95%) and antiplatelet (100%) therapy in the single-center Scottish DIAMOND trial and compared CCTA at baseline and 12 months available for 160 patients.
As reported in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology, patients with high Lp(a), defined as at least 70 mg/dL, had higher baseline high-density lipoprotein cholesterol and ASSIGN scores than those with low Lp(a) but had comparable coronary artery calcium (CAC) scores and total, calcific, noncalcific, and low-attenuation plaque (LAP) volumes.
At 1 year, however, LAP volume – a marker for necrotic core – increased by 26.2 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group and decreased by –0.7 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
There was no significant difference in change in total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes between groups.
In multivariate linear regression analysis adjusting for body mass index, ASSIGN score, and segment involvement score, LAP volume increased by 10.5% for each 50 mg/dL increment in Lp(a) (P = .034).
“It’s an exciting observation, because we’ve done previous studies where we’ve demonstrated the association of that particular plaque type with future myocardial infarction,” senior author Marc R. Dweck, MD, PhD, University of Amsterdam, told this news organization. “So, you’ve potentially got an explanation for the adverse prognosis associated with high lipoprotein(a) and its link to cardiovascular events and, in particular, myocardial infarction.”
The team’s recent SCOT-HEART analysis found that LAP burden was a stronger predictor of myocardial infarction (MI) than cardiovascular risk scores, stenosis severity, and CAC scoring, with MI risk nearly five-fold higher if LAP was above 4%.
As to why total, calcific, and noncalcific plaque volumes didn’t change significantly on repeat CCTA in the present study, Dr. Dweck said it’s possible that the sample was too small and follow-up too short but also that “total plaque volume is really dominated by the fibrous plaque, which doesn’t appear affected by Lp(a).” Nevertheless, Lp(a)’s effect on low-attenuation plaque was clearly present and supported by the change in fibro-fatty plaque, the next-most unstable plaque type.
At 1 year, fibro-fatty plaque volume was 55.0 mm3 in the high-Lp(a) group versus –25.0 mm3 in the low-Lp(a) group (P = .020).
Lp(a) was associated with fibro-fatty plaque progression in univariate analysis (β = 6.7%; P = .034) and showed a trend in multivariable analysis (β = 6.0%; P = .062).
“This study shows you can track changes in plaque over time and highlight important disease mechanisms and use them to understand the pathology of the disease,” Dr. Dweck said. “I’m very encouraged by this.”
What’s novel in the present study is that “it represents the beginning of our understanding of the role of Lp(a) in plaque progression,” Sotirios Tsimikas, MD, University of California, San Diego, and Jagat Narula, MD, PhD, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York, say in an accompanying commentary.
They note that prior studies, including the Dallas Heart Study, have struggled to find a strong association between Lp(a) with the extent or progression of CAC, despite elevated Lp(a) and CAC identifying higher-risk patients.
Similarly, a meta-analysis of intravascular ultrasound trials turned up only a 1.2% absolute difference in atheroma volume in patients with elevated Lp(a), and a recent optical coherence tomography study found an association of Lp(a) with thin-cap fibroatheromas but not lipid core.
With just 36 patients with elevated Lp(a), however, the current findings need validation in a larger data set, Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula say.
Although Lp(a) is genetically elevated in about one in five individuals and measurement is recommended in European dyslipidemia guidelines, testing rates are low, in part because the argument has been that there are no Lp(a)-lowering therapies available, Dr. Dweck observed. That may change with the phase 3 cardiovascular outcomes Lp(a)HORIZON trial, which follows strong phase 2 results with the antisense agent AKCEA-APO(a)-LRx and is enrolling patients similar to the current cohort.
“Ultimately it comes down to that fundamental thing, that you need an action once you’ve done the test and then insurers will be happy to pay for it and clinicians will ask for it. That’s why that trial is so important,” Dr. Dweck said.
Dr. Tsimikas and Dr. Narula also point to the eagerly awaited results of that trial, expected in 2025. “A positive trial is likely to lead to additional trials and new drugs that may reinvigorate the use of imaging modalities that could go beyond plaque volume and atherosclerosis to also predict clinically relevant inflammation and atherothrombosis,” they conclude.
Dr. Dweck is supported by the British Heart Foundation and is the recipient of the Sir Jules Thorn Award for Biomedical Research 2015; has received speaker fees from Pfizer and Novartis; and has received consultancy fees from Novartis, Jupiter Bioventures, and Silence Therapeutics. Coauthor disclosures are listed in the paper. Dr. Tsimikas has a dual appointment at the University of California, San Diego, (UCSD) and Ionis Pharmaceuticals; is a coinventor and receives royalties from patents owned by UCSD; and is a cofounder and has an equity interest in Oxitope and its affiliates, Kleanthi Diagnostics, and Covicept Therapeutics. Dr. Narula reports having no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Five things you should know about ‘free’ at-home COVID tests
Americans keep hearing that it is important to test frequently for COVID-19 at home. But just try to find an “at-home” rapid COVID test in a store and at a price that makes frequent tests affordable.
Testing, as well as mask-wearing, is an important measure if the country ever hopes to beat COVID, restore normal routines and get the economy running efficiently. To get Americans cheaper tests, the federal government now plans to have insurance companies pay for them.
You can either get one without any out-of-pocket expense from retail pharmacies that are part of an insurance company’s network or buy it at any store and get reimbursed by the insurer.
Congress said private insurers must cover all COVID testing and any associated medical services when it passed the Families First Coronavirus Response Act and the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security, or CARES, Act. The have-insurance-pay-for-it solution has been used frequently through the pandemic. Insurance companies have been told to pay for polymerase chain reaction tests, COVID treatments and the administration of vaccines. (Taxpayers are paying for the cost of the vaccines themselves.) It appears to be an elegant solution for a politician because it looks free and isn’t using taxpayer money.
1. Are the tests really free?
Well, no. As many an economist will tell you, there ain’t no such thing as a free lunch. Someone has to pick up the tab. Initially, the insurance companies bear the cost. Cynthia Cox, a vice president at KFF who studies the Affordable Care Act and private insurers, said the total bill could amount to billions of dollars. Exactly how much depends on “how easy it is to get them, and how many will be reimbursed,” she said.
2. Will the insurance company just swallow those imposed costs?
If companies draw from the time-tested insurance giants’ playbook, they’ll pass along those costs to customers. “This will put upward pressure on premiums,” said Emily Gee, vice president and coordinator for health policy at the Center for American Progress.
Major insurance companies like Cigna, Anthem, UnitedHealthcare, and Aetna did not respond to requests to discuss this issue.
3. If that’s the case, why haven’t I been hit with higher premiums already?
Insurance companies had the chance last year to raise premiums but, mostly, they did not.
Why? Perhaps because insurers have so far made so much money during the pandemic they didn’t need to. For example, the industry’s profits in 2020 increased 41% to $31 billion from $22 billion, according to the National Association of Insurance Commissioners. The NAIC said the industry has continued its “tremendous growth trend” that started before COVID emerged. Companies will be reporting 2021 results soon.
The reason behind these profits is clear. You were paying premiums based on projections your insurance company made about how much health care consumers would use that year. Because people stayed home, had fewer accidents, postponed surgeries and often avoided going to visit the doctor or the hospital, insurers paid out less. They rebated some of their earnings back to customers, but they pocketed a lot more.
As the companies’ actuaries work on predicting 2023 expenditures, premiums could go up if they foresee more claims and expenses. Paying for millions of rapid tests is something they would include in their calculations.
4. Regardless of my premiums, will the tests cost me money directly?
It’s quite possible. If your insurance company doesn’t have an arrangement with a retailer where you can simply pick up your allotted tests, you’ll have to pay for them – at whatever price the store sets. If that’s the case, you’ll need to fill out a form to request a reimbursement from the insurance company. How many times have you lost receipts or just plain neglected to mail in for rebates on something you bought? A lot, right?
Here’s another thing: The reimbursement is set at $12 per test. If you pay $30 for a test – and that is not unheard of – your insurer is only on the hook for $12. You eat the $18.
And by the way, people on Medicare will have to pay for their tests themselves. People who get their health care covered by Medicaid can obtain free test kits at community centers.
A few free tests are supposed to arrive at every American home via the U.S. Postal Service. And the Biden administration has activated a website where Americans can order free tests from a cache of a billion the federal government ordered.
5. Will this help bring down the costs of at-home tests and make them easier to find?
The free COVID tests are unlikely to have much immediate impact on general cost and availability. You will still need to search for them. The federal measures likely will stimulate the demand for tests, which in the short term may make them harder to find.
But the demand, and some government guarantees to manufacturers, may induce test makers to make more of them faster. The increased competition and supply theoretically could bring down the price. There is certainly room for prices to decline since the wholesale cost of the test is between $5 and $7, analysts estimate. “It’s a big step in the right direction,” Ms. Gee said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Americans keep hearing that it is important to test frequently for COVID-19 at home. But just try to find an “at-home” rapid COVID test in a store and at a price that makes frequent tests affordable.
Testing, as well as mask-wearing, is an important measure if the country ever hopes to beat COVID, restore normal routines and get the economy running efficiently. To get Americans cheaper tests, the federal government now plans to have insurance companies pay for them.
You can either get one without any out-of-pocket expense from retail pharmacies that are part of an insurance company’s network or buy it at any store and get reimbursed by the insurer.
Congress said private insurers must cover all COVID testing and any associated medical services when it passed the Families First Coronavirus Response Act and the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security, or CARES, Act. The have-insurance-pay-for-it solution has been used frequently through the pandemic. Insurance companies have been told to pay for polymerase chain reaction tests, COVID treatments and the administration of vaccines. (Taxpayers are paying for the cost of the vaccines themselves.) It appears to be an elegant solution for a politician because it looks free and isn’t using taxpayer money.
1. Are the tests really free?
Well, no. As many an economist will tell you, there ain’t no such thing as a free lunch. Someone has to pick up the tab. Initially, the insurance companies bear the cost. Cynthia Cox, a vice president at KFF who studies the Affordable Care Act and private insurers, said the total bill could amount to billions of dollars. Exactly how much depends on “how easy it is to get them, and how many will be reimbursed,” she said.
2. Will the insurance company just swallow those imposed costs?
If companies draw from the time-tested insurance giants’ playbook, they’ll pass along those costs to customers. “This will put upward pressure on premiums,” said Emily Gee, vice president and coordinator for health policy at the Center for American Progress.
Major insurance companies like Cigna, Anthem, UnitedHealthcare, and Aetna did not respond to requests to discuss this issue.
3. If that’s the case, why haven’t I been hit with higher premiums already?
Insurance companies had the chance last year to raise premiums but, mostly, they did not.
Why? Perhaps because insurers have so far made so much money during the pandemic they didn’t need to. For example, the industry’s profits in 2020 increased 41% to $31 billion from $22 billion, according to the National Association of Insurance Commissioners. The NAIC said the industry has continued its “tremendous growth trend” that started before COVID emerged. Companies will be reporting 2021 results soon.
The reason behind these profits is clear. You were paying premiums based on projections your insurance company made about how much health care consumers would use that year. Because people stayed home, had fewer accidents, postponed surgeries and often avoided going to visit the doctor or the hospital, insurers paid out less. They rebated some of their earnings back to customers, but they pocketed a lot more.
As the companies’ actuaries work on predicting 2023 expenditures, premiums could go up if they foresee more claims and expenses. Paying for millions of rapid tests is something they would include in their calculations.
4. Regardless of my premiums, will the tests cost me money directly?
It’s quite possible. If your insurance company doesn’t have an arrangement with a retailer where you can simply pick up your allotted tests, you’ll have to pay for them – at whatever price the store sets. If that’s the case, you’ll need to fill out a form to request a reimbursement from the insurance company. How many times have you lost receipts or just plain neglected to mail in for rebates on something you bought? A lot, right?
Here’s another thing: The reimbursement is set at $12 per test. If you pay $30 for a test – and that is not unheard of – your insurer is only on the hook for $12. You eat the $18.
And by the way, people on Medicare will have to pay for their tests themselves. People who get their health care covered by Medicaid can obtain free test kits at community centers.
A few free tests are supposed to arrive at every American home via the U.S. Postal Service. And the Biden administration has activated a website where Americans can order free tests from a cache of a billion the federal government ordered.
5. Will this help bring down the costs of at-home tests and make them easier to find?
The free COVID tests are unlikely to have much immediate impact on general cost and availability. You will still need to search for them. The federal measures likely will stimulate the demand for tests, which in the short term may make them harder to find.
But the demand, and some government guarantees to manufacturers, may induce test makers to make more of them faster. The increased competition and supply theoretically could bring down the price. There is certainly room for prices to decline since the wholesale cost of the test is between $5 and $7, analysts estimate. “It’s a big step in the right direction,” Ms. Gee said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
Americans keep hearing that it is important to test frequently for COVID-19 at home. But just try to find an “at-home” rapid COVID test in a store and at a price that makes frequent tests affordable.
Testing, as well as mask-wearing, is an important measure if the country ever hopes to beat COVID, restore normal routines and get the economy running efficiently. To get Americans cheaper tests, the federal government now plans to have insurance companies pay for them.
You can either get one without any out-of-pocket expense from retail pharmacies that are part of an insurance company’s network or buy it at any store and get reimbursed by the insurer.
Congress said private insurers must cover all COVID testing and any associated medical services when it passed the Families First Coronavirus Response Act and the Coronavirus Aid, Relief and Economic Security, or CARES, Act. The have-insurance-pay-for-it solution has been used frequently through the pandemic. Insurance companies have been told to pay for polymerase chain reaction tests, COVID treatments and the administration of vaccines. (Taxpayers are paying for the cost of the vaccines themselves.) It appears to be an elegant solution for a politician because it looks free and isn’t using taxpayer money.
1. Are the tests really free?
Well, no. As many an economist will tell you, there ain’t no such thing as a free lunch. Someone has to pick up the tab. Initially, the insurance companies bear the cost. Cynthia Cox, a vice president at KFF who studies the Affordable Care Act and private insurers, said the total bill could amount to billions of dollars. Exactly how much depends on “how easy it is to get them, and how many will be reimbursed,” she said.
2. Will the insurance company just swallow those imposed costs?
If companies draw from the time-tested insurance giants’ playbook, they’ll pass along those costs to customers. “This will put upward pressure on premiums,” said Emily Gee, vice president and coordinator for health policy at the Center for American Progress.
Major insurance companies like Cigna, Anthem, UnitedHealthcare, and Aetna did not respond to requests to discuss this issue.
3. If that’s the case, why haven’t I been hit with higher premiums already?
Insurance companies had the chance last year to raise premiums but, mostly, they did not.
Why? Perhaps because insurers have so far made so much money during the pandemic they didn’t need to. For example, the industry’s profits in 2020 increased 41% to $31 billion from $22 billion, according to the National Association of Insurance Commissioners. The NAIC said the industry has continued its “tremendous growth trend” that started before COVID emerged. Companies will be reporting 2021 results soon.
The reason behind these profits is clear. You were paying premiums based on projections your insurance company made about how much health care consumers would use that year. Because people stayed home, had fewer accidents, postponed surgeries and often avoided going to visit the doctor or the hospital, insurers paid out less. They rebated some of their earnings back to customers, but they pocketed a lot more.
As the companies’ actuaries work on predicting 2023 expenditures, premiums could go up if they foresee more claims and expenses. Paying for millions of rapid tests is something they would include in their calculations.
4. Regardless of my premiums, will the tests cost me money directly?
It’s quite possible. If your insurance company doesn’t have an arrangement with a retailer where you can simply pick up your allotted tests, you’ll have to pay for them – at whatever price the store sets. If that’s the case, you’ll need to fill out a form to request a reimbursement from the insurance company. How many times have you lost receipts or just plain neglected to mail in for rebates on something you bought? A lot, right?
Here’s another thing: The reimbursement is set at $12 per test. If you pay $30 for a test – and that is not unheard of – your insurer is only on the hook for $12. You eat the $18.
And by the way, people on Medicare will have to pay for their tests themselves. People who get their health care covered by Medicaid can obtain free test kits at community centers.
A few free tests are supposed to arrive at every American home via the U.S. Postal Service. And the Biden administration has activated a website where Americans can order free tests from a cache of a billion the federal government ordered.
5. Will this help bring down the costs of at-home tests and make them easier to find?
The free COVID tests are unlikely to have much immediate impact on general cost and availability. You will still need to search for them. The federal measures likely will stimulate the demand for tests, which in the short term may make them harder to find.
But the demand, and some government guarantees to manufacturers, may induce test makers to make more of them faster. The increased competition and supply theoretically could bring down the price. There is certainly room for prices to decline since the wholesale cost of the test is between $5 and $7, analysts estimate. “It’s a big step in the right direction,” Ms. Gee said.
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
‘Artificial pancreas’ life-changing in kids with type 1 diabetes
A semiautomated insulin delivery system improved glycemic control in young children with type 1 diabetes aged 1-7 years without increasing hypoglycemia.
“Hybrid closed-loop” systems – comprising an insulin pump, a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), and software enabling communication that semiautomates insulin delivery based on glucose levels – have been shown to improve glucose control in older children and adults.
The technology, also known as an artificial pancreas, has been less studied in very young children even though it may uniquely benefit them, said the authors of the new study, led by Julia Ware, MD, of the Wellcome Trust–Medical Research Council Institute of Metabolic Science and the University of Cambridge (England). The findings were published online Jan. 19, 2022, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Very young children are extremely vulnerable to changes in their blood sugar levels. High levels in particular can have potentially lasting consequences to their brain development. On top of that, diabetes is very challenging to manage in this age group, creating a huge burden for families,” she said in a University of Cambridge statement.
There is “high variability of insulin requirements, marked insulin sensitivity, and unpredictable eating and activity patterns,” Dr. Ware and colleagues noted.
“Caregiver fear of hypoglycemia, particularly overnight, is common and, coupled with young children’s unawareness that hypoglycemia is occurring, contributes to children not meeting the recommended glycemic targets or having difficulty maintaining recommended glycemic control unless caregivers can provide constant monitoring. These issues often lead to ... reduced quality of life for the whole family,” they added.
Except for mealtimes, device is fully automated
The new multicenter, randomized, crossover trial was conducted at seven centers across Austria, Germany, Luxembourg, and the United Kingdom in 2019-2020.
The trial compared the safety and efficacy of hybrid closed-loop therapy with sensor-augmented pump therapy (that is, without the device communication, as a control). All 74 children used the CamAPS FX hybrid closed-loop system for 16 weeks, and then used the control treatment for 16 weeks. The children were a mean age of 5.6 years and had a baseline hemoglobin A1c of 7.3% (56.6 mmol/mol).
The hybrid closed-loop system consisted of components that are commercially available in Europe: the Sooil insulin pump (Dana Diabecare RS) and the Dexcom G6 CGM, along with an unlocked Samsung Galaxy 8 smartphone housing an app (CamAPS FX, CamDiab) that runs the Cambridge proprietary model predictive control algorithm.
The smartphone communicates wirelessly with both the pump and the CGM transmitter and automatically adjusts the pump’s insulin delivery based on real-time sensor glucose readings. It also issues alarms if glucose levels fall below or rise above user-specified thresholds. This functionality was disabled during the study control periods.
Senior investigator Roman Hovorka, PhD, who developed the CamAPS FX app, explained in the University of Cambridge statement that the app “makes predictions about what it thinks is likely to happen next based on past experience. It learns how much insulin the child needs per day and how this changes at different times of the day.
“It then uses this [information] to adjust insulin levels to help achieve ideal blood sugar levels. Other than at mealtimes, it is fully automated, so parents do not need to continually monitor their child’s blood sugar levels.”
Indeed, the time spent in target glucose range (70-180 mg/dL) during the 16-week closed-loop period was 8.7 percentage points higher than during the control period (P < .001).
That difference translates to “a clinically meaningful 125 minutes per day,” and represented around three-quarters of their day (71.6%) in the target range, the investigators wrote.
The mean adjusted difference in time spent above 180 mg/dL was 8.5 percentage points lower with the closed-loop, also a significant difference (P < .001). Time spent below 70 mg/dL did not differ significantly between the two interventions (P = .74).
At the end of the study periods, the mean adjusted between-treatment difference in A1c was –0.4 percentage points, significantly lower following the closed-loop, compared with the control period (P < .001).
That percentage point difference (equivalent to 3.9 mmol/mol) “is important in a population of patients who had tight glycemic control at baseline. This result was observed without an increase in the time spent in a hypoglycemic state,” Dr. Ware and colleagues noted.
Median glucose sensor use was 99% during the closed-loop period and 96% during the control periods. During the closed-loop periods, the system was in closed-loop mode 95% of the time.
This finding supports longer-term usability in this age group and compares well with use in older children, they said.
One serious hypoglycemic episode, attributed to parental error rather than system malfunction, occurred during the closed-loop period. There were no episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis. Rates of other adverse events didn’t differ between the two periods.
“CamAPS FX led to improvements in several measures, including hyperglycemia and average blood sugar levels, without increasing the risk of hypos. This is likely to have important benefits for those children who use it,” Dr. Ware summarized.
Sleep quality could improve for children and caregivers
Reductions in time spent in hyperglycemia without increasing hypoglycemia could minimize the risk for neurocognitive deficits that have been reported among young children with type 1 diabetes, the authors speculated.
In addition, they noted that because 80% of overnight sensor readings were within target range and less than 3% were below 70 mg/dL, sleep quality could improve for both the children and their parents. This, in turn, “would confer associated quality of life benefits.”
“Parents have described our artificial pancreas as ‘life changing’ as it meant they were able to relax and spend less time worrying about their child’s blood sugar levels, particularly at nighttime. They tell us it gives them more time to do what any ‘normal’ family can do, to play and do fun things with their children,” observed Dr. Ware.
The CamAPS FX has been commercialized by CamDiab, a spin-out company set up by Dr. Hovorka. It is currently available through several NHS trusts across the United Kingdom, including Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and is expected to be more widely available soon.
The study was supported by the European Commission within the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, the NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, and JDRF. Dr. Ware had no further disclosures. Dr. Hovorka has reported acting as consultant for Abbott Diabetes Care, BD, Dexcom, being a speaker for Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, and receiving royalty payments from B. Braun for software. He is director of CamDiab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A semiautomated insulin delivery system improved glycemic control in young children with type 1 diabetes aged 1-7 years without increasing hypoglycemia.
“Hybrid closed-loop” systems – comprising an insulin pump, a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), and software enabling communication that semiautomates insulin delivery based on glucose levels – have been shown to improve glucose control in older children and adults.
The technology, also known as an artificial pancreas, has been less studied in very young children even though it may uniquely benefit them, said the authors of the new study, led by Julia Ware, MD, of the Wellcome Trust–Medical Research Council Institute of Metabolic Science and the University of Cambridge (England). The findings were published online Jan. 19, 2022, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Very young children are extremely vulnerable to changes in their blood sugar levels. High levels in particular can have potentially lasting consequences to their brain development. On top of that, diabetes is very challenging to manage in this age group, creating a huge burden for families,” she said in a University of Cambridge statement.
There is “high variability of insulin requirements, marked insulin sensitivity, and unpredictable eating and activity patterns,” Dr. Ware and colleagues noted.
“Caregiver fear of hypoglycemia, particularly overnight, is common and, coupled with young children’s unawareness that hypoglycemia is occurring, contributes to children not meeting the recommended glycemic targets or having difficulty maintaining recommended glycemic control unless caregivers can provide constant monitoring. These issues often lead to ... reduced quality of life for the whole family,” they added.
Except for mealtimes, device is fully automated
The new multicenter, randomized, crossover trial was conducted at seven centers across Austria, Germany, Luxembourg, and the United Kingdom in 2019-2020.
The trial compared the safety and efficacy of hybrid closed-loop therapy with sensor-augmented pump therapy (that is, without the device communication, as a control). All 74 children used the CamAPS FX hybrid closed-loop system for 16 weeks, and then used the control treatment for 16 weeks. The children were a mean age of 5.6 years and had a baseline hemoglobin A1c of 7.3% (56.6 mmol/mol).
The hybrid closed-loop system consisted of components that are commercially available in Europe: the Sooil insulin pump (Dana Diabecare RS) and the Dexcom G6 CGM, along with an unlocked Samsung Galaxy 8 smartphone housing an app (CamAPS FX, CamDiab) that runs the Cambridge proprietary model predictive control algorithm.
The smartphone communicates wirelessly with both the pump and the CGM transmitter and automatically adjusts the pump’s insulin delivery based on real-time sensor glucose readings. It also issues alarms if glucose levels fall below or rise above user-specified thresholds. This functionality was disabled during the study control periods.
Senior investigator Roman Hovorka, PhD, who developed the CamAPS FX app, explained in the University of Cambridge statement that the app “makes predictions about what it thinks is likely to happen next based on past experience. It learns how much insulin the child needs per day and how this changes at different times of the day.
“It then uses this [information] to adjust insulin levels to help achieve ideal blood sugar levels. Other than at mealtimes, it is fully automated, so parents do not need to continually monitor their child’s blood sugar levels.”
Indeed, the time spent in target glucose range (70-180 mg/dL) during the 16-week closed-loop period was 8.7 percentage points higher than during the control period (P < .001).
That difference translates to “a clinically meaningful 125 minutes per day,” and represented around three-quarters of their day (71.6%) in the target range, the investigators wrote.
The mean adjusted difference in time spent above 180 mg/dL was 8.5 percentage points lower with the closed-loop, also a significant difference (P < .001). Time spent below 70 mg/dL did not differ significantly between the two interventions (P = .74).
At the end of the study periods, the mean adjusted between-treatment difference in A1c was –0.4 percentage points, significantly lower following the closed-loop, compared with the control period (P < .001).
That percentage point difference (equivalent to 3.9 mmol/mol) “is important in a population of patients who had tight glycemic control at baseline. This result was observed without an increase in the time spent in a hypoglycemic state,” Dr. Ware and colleagues noted.
Median glucose sensor use was 99% during the closed-loop period and 96% during the control periods. During the closed-loop periods, the system was in closed-loop mode 95% of the time.
This finding supports longer-term usability in this age group and compares well with use in older children, they said.
One serious hypoglycemic episode, attributed to parental error rather than system malfunction, occurred during the closed-loop period. There were no episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis. Rates of other adverse events didn’t differ between the two periods.
“CamAPS FX led to improvements in several measures, including hyperglycemia and average blood sugar levels, without increasing the risk of hypos. This is likely to have important benefits for those children who use it,” Dr. Ware summarized.
Sleep quality could improve for children and caregivers
Reductions in time spent in hyperglycemia without increasing hypoglycemia could minimize the risk for neurocognitive deficits that have been reported among young children with type 1 diabetes, the authors speculated.
In addition, they noted that because 80% of overnight sensor readings were within target range and less than 3% were below 70 mg/dL, sleep quality could improve for both the children and their parents. This, in turn, “would confer associated quality of life benefits.”
“Parents have described our artificial pancreas as ‘life changing’ as it meant they were able to relax and spend less time worrying about their child’s blood sugar levels, particularly at nighttime. They tell us it gives them more time to do what any ‘normal’ family can do, to play and do fun things with their children,” observed Dr. Ware.
The CamAPS FX has been commercialized by CamDiab, a spin-out company set up by Dr. Hovorka. It is currently available through several NHS trusts across the United Kingdom, including Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and is expected to be more widely available soon.
The study was supported by the European Commission within the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, the NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, and JDRF. Dr. Ware had no further disclosures. Dr. Hovorka has reported acting as consultant for Abbott Diabetes Care, BD, Dexcom, being a speaker for Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, and receiving royalty payments from B. Braun for software. He is director of CamDiab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A semiautomated insulin delivery system improved glycemic control in young children with type 1 diabetes aged 1-7 years without increasing hypoglycemia.
“Hybrid closed-loop” systems – comprising an insulin pump, a continuous glucose monitor (CGM), and software enabling communication that semiautomates insulin delivery based on glucose levels – have been shown to improve glucose control in older children and adults.
The technology, also known as an artificial pancreas, has been less studied in very young children even though it may uniquely benefit them, said the authors of the new study, led by Julia Ware, MD, of the Wellcome Trust–Medical Research Council Institute of Metabolic Science and the University of Cambridge (England). The findings were published online Jan. 19, 2022, in the New England Journal of Medicine.
“Very young children are extremely vulnerable to changes in their blood sugar levels. High levels in particular can have potentially lasting consequences to their brain development. On top of that, diabetes is very challenging to manage in this age group, creating a huge burden for families,” she said in a University of Cambridge statement.
There is “high variability of insulin requirements, marked insulin sensitivity, and unpredictable eating and activity patterns,” Dr. Ware and colleagues noted.
“Caregiver fear of hypoglycemia, particularly overnight, is common and, coupled with young children’s unawareness that hypoglycemia is occurring, contributes to children not meeting the recommended glycemic targets or having difficulty maintaining recommended glycemic control unless caregivers can provide constant monitoring. These issues often lead to ... reduced quality of life for the whole family,” they added.
Except for mealtimes, device is fully automated
The new multicenter, randomized, crossover trial was conducted at seven centers across Austria, Germany, Luxembourg, and the United Kingdom in 2019-2020.
The trial compared the safety and efficacy of hybrid closed-loop therapy with sensor-augmented pump therapy (that is, without the device communication, as a control). All 74 children used the CamAPS FX hybrid closed-loop system for 16 weeks, and then used the control treatment for 16 weeks. The children were a mean age of 5.6 years and had a baseline hemoglobin A1c of 7.3% (56.6 mmol/mol).
The hybrid closed-loop system consisted of components that are commercially available in Europe: the Sooil insulin pump (Dana Diabecare RS) and the Dexcom G6 CGM, along with an unlocked Samsung Galaxy 8 smartphone housing an app (CamAPS FX, CamDiab) that runs the Cambridge proprietary model predictive control algorithm.
The smartphone communicates wirelessly with both the pump and the CGM transmitter and automatically adjusts the pump’s insulin delivery based on real-time sensor glucose readings. It also issues alarms if glucose levels fall below or rise above user-specified thresholds. This functionality was disabled during the study control periods.
Senior investigator Roman Hovorka, PhD, who developed the CamAPS FX app, explained in the University of Cambridge statement that the app “makes predictions about what it thinks is likely to happen next based on past experience. It learns how much insulin the child needs per day and how this changes at different times of the day.
“It then uses this [information] to adjust insulin levels to help achieve ideal blood sugar levels. Other than at mealtimes, it is fully automated, so parents do not need to continually monitor their child’s blood sugar levels.”
Indeed, the time spent in target glucose range (70-180 mg/dL) during the 16-week closed-loop period was 8.7 percentage points higher than during the control period (P < .001).
That difference translates to “a clinically meaningful 125 minutes per day,” and represented around three-quarters of their day (71.6%) in the target range, the investigators wrote.
The mean adjusted difference in time spent above 180 mg/dL was 8.5 percentage points lower with the closed-loop, also a significant difference (P < .001). Time spent below 70 mg/dL did not differ significantly between the two interventions (P = .74).
At the end of the study periods, the mean adjusted between-treatment difference in A1c was –0.4 percentage points, significantly lower following the closed-loop, compared with the control period (P < .001).
That percentage point difference (equivalent to 3.9 mmol/mol) “is important in a population of patients who had tight glycemic control at baseline. This result was observed without an increase in the time spent in a hypoglycemic state,” Dr. Ware and colleagues noted.
Median glucose sensor use was 99% during the closed-loop period and 96% during the control periods. During the closed-loop periods, the system was in closed-loop mode 95% of the time.
This finding supports longer-term usability in this age group and compares well with use in older children, they said.
One serious hypoglycemic episode, attributed to parental error rather than system malfunction, occurred during the closed-loop period. There were no episodes of diabetic ketoacidosis. Rates of other adverse events didn’t differ between the two periods.
“CamAPS FX led to improvements in several measures, including hyperglycemia and average blood sugar levels, without increasing the risk of hypos. This is likely to have important benefits for those children who use it,” Dr. Ware summarized.
Sleep quality could improve for children and caregivers
Reductions in time spent in hyperglycemia without increasing hypoglycemia could minimize the risk for neurocognitive deficits that have been reported among young children with type 1 diabetes, the authors speculated.
In addition, they noted that because 80% of overnight sensor readings were within target range and less than 3% were below 70 mg/dL, sleep quality could improve for both the children and their parents. This, in turn, “would confer associated quality of life benefits.”
“Parents have described our artificial pancreas as ‘life changing’ as it meant they were able to relax and spend less time worrying about their child’s blood sugar levels, particularly at nighttime. They tell us it gives them more time to do what any ‘normal’ family can do, to play and do fun things with their children,” observed Dr. Ware.
The CamAPS FX has been commercialized by CamDiab, a spin-out company set up by Dr. Hovorka. It is currently available through several NHS trusts across the United Kingdom, including Cambridge University Hospitals NHS Foundation Trust, and is expected to be more widely available soon.
The study was supported by the European Commission within the Horizon 2020 Framework Program, the NIHR Cambridge Biomedical Research Centre, and JDRF. Dr. Ware had no further disclosures. Dr. Hovorka has reported acting as consultant for Abbott Diabetes Care, BD, Dexcom, being a speaker for Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly, and receiving royalty payments from B. Braun for software. He is director of CamDiab.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Breastfeeding linked to lower CVD risk in later life
In a meta-analysis of more than 1 million mothers, those who breastfed their children had an 11% to 17% lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD), coronary heart disease (CHD), or stroke, and of dying from CVD, in later life than mothers who did not.
On average, the women had two children and had breastfed for 15.9 months in total. Longer breastfeeding was associated with greater CV health benefit.
This meta-analysis of eight studies from different countries was published online Jan. 11 in an issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association devoted to the impact of pregnancy on CV health in the mother and child.
Breastfeeding is known to be associated with a lower risk for death from infectious disease and with fewer respiratory infections in babies, the researchers write, but what is less well known is that it is also associated with a reduced risk for breast and ovarian cancer and type 2 diabetes in mothers.
The current study showed a clear association between breastfeeding and reduced risk for CVD in later life, lead author Lena Tschiderer, Dipl.-Ing., PhD, and senior author Peter Willeit, MD, MPhil, PhD, summarized in a joint email to this news organization.
Specifically, mothers who had breastfed their children at any time had an 11% lower risk for CVD, a 14% lower risk for CHD, a 12% lower risk for stroke, and a 17% lower risk of dying from CVD in later life, compared with other mothers.
On the basis of existing evidence, the researchers write, the World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding until a baby is 6 months old, followed by breastfeeding plus complementary feeding until the baby is 2 years or older.
“We believe that [breastfeeding] benefits for the mother are communicated poorly,” said Dr. Tschiderer and Dr. Willeit, from the University of Innsbruck, Austria.
“Positive effects of breastfeeding on mothers need to be communicated effectively, awareness for breastfeeding recommendations needs to be raised, and interventions to promote and facilitate breastfeeding need to be implemented and reinforced,” the researchers conclude.
‘Should not be ignored’
Two cardiologists invited to comment, who were not involved with the research, noted that this study provides insight into an important topic.
“This is yet another body of evidence [and the largest population to date] to show that breastfeeding is protective for women and may show important beneficial effects in terms of CV risk,” Roxana Mehran, MD, said in an email.
“The risk reductions were 11% for CVD events and 14% for CHD events; these are impressive numbers,” said Dr. Mehran, from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The caveat,” she said, “is that these are data from several trials, but nonetheless, this is a very important observation that should not be ignored.”
The study did not address the definitive amount of time of breastfeeding and its correlation to the improvement of CVD risk, but it did show that for the lifetime duration, the longer the better.
“The beneficial effects,” she noted, “can be linked to hormones during breastfeeding, as well as weight loss associated with breastfeeding, and resetting the maternal metabolism, as the authors suggest.”
Clinicians and employers “must provide ways to educate women about breastfeeding and make it easy for women who are in the workplace to pump, and to provide them with resources” where possible, Dr. Mehran said.
Michelle O’Donoghue, MD, MPH, noted that over the past several years, there has been intense interest in the possible health benefits of breastfeeding for both mother and child.
There is biologic plausibility for some of the possible maternal benefits because the favorable CV effects of both prolactin and oxytocin are only now being better understood, said Dr. O’Donoghue, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“The current meta-analysis provides a large dataset that helps support the concept that breastfeeding may offer some cardiovascular benefit for the mother,” she agreed.
“However, ultimately more research will be necessary since this method of combining data across trials relies upon the robustness of the statistical method in each study,” Dr. O’Donoghue said. “I applaud the authors for shining a spotlight on this important topic.”
Although the benefits of breastfeeding appear to continue over time, “it is incredibly difficult for women to continue breastfeeding once they return to work,” she added. “Women in some countries outside the U.S. have an advantage due to longer durations of maternity leave.
“If we want to encourage breastfeeding,” Dr. O’Donoghue stressed, “we need to make sure that we put the right supports in place. Women need protected places to breastfeed in the workplace and places to store their milk. Most importantly, women need to be allowed dedicated time to make it happen.”
First large study of CVD in mothers
Emerging individual studies suggest that mothers who breastfeed may have a lower risk for CVD in later life, but studies have been inconsistent, and it is not clear if longer breastfeeding would strengthen this benefit, the authors note.
To examine this, they pooled data from the following eight studies (with study acronym, country, and baseline enrolment dates in brackets): 45&Up (Australia, 2006-2009), China Kadoorie Biobank (CKB, China, 2004-2008), European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC, multinational, 1992-2000), Gallagher et al. (China, 1989-1991), Nord-Trøndelag Health Survey 2 (HUNT2, Norway, 1995-1997), Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study (JPHC, Japan, 1990-1994), Nurses’ Health Study (NHS, U.S., 1986), and the Woman’s Health Initiative (WHI, U.S., 1993-1998).
On average, the women were 51.3 years old (range, 40-65 years) when they enrolled in the study, and they were followed for a median of 10.3 years (range, 7.9-20.9 years, in the individual studies).
On average, they had their first child at age 25 and had two to three children (mean, 2.3); 82% had breastfed at some point (ranging from 58% of women in the two U.S. studies to 97% in CKB and HUNT2).
The women had breastfed for a mean of 7.4 to 18.9 months during their lifetimes (except women in the CKB study, who had breastfed for a median of 24 months).
Among the 1,192,700 women, there were 54,226 incident CVD events, 26,913 incident CHD events, 30,843 incident strokes, and 10,766 deaths from CVD during follow-up.
The researchers acknowledge that study limitations include the fact that there could have been publication bias, since fewer than 10 studies were available for pooling. There was significant between-study heterogeneity for CVD, CHD, and stroke outcomes.
Participant-level data were also lacking, and breastfeeding was self-reported. There may have been unaccounted residual confounding, and the benefits of lifetime breastfeeding that is longer than 2 years are not clear, because few women in this population breastfed that long.
The research was funded by the Austrian Science Fund. The researchers and Dr. Mehran and Dr. O’Donoghue have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a meta-analysis of more than 1 million mothers, those who breastfed their children had an 11% to 17% lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD), coronary heart disease (CHD), or stroke, and of dying from CVD, in later life than mothers who did not.
On average, the women had two children and had breastfed for 15.9 months in total. Longer breastfeeding was associated with greater CV health benefit.
This meta-analysis of eight studies from different countries was published online Jan. 11 in an issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association devoted to the impact of pregnancy on CV health in the mother and child.
Breastfeeding is known to be associated with a lower risk for death from infectious disease and with fewer respiratory infections in babies, the researchers write, but what is less well known is that it is also associated with a reduced risk for breast and ovarian cancer and type 2 diabetes in mothers.
The current study showed a clear association between breastfeeding and reduced risk for CVD in later life, lead author Lena Tschiderer, Dipl.-Ing., PhD, and senior author Peter Willeit, MD, MPhil, PhD, summarized in a joint email to this news organization.
Specifically, mothers who had breastfed their children at any time had an 11% lower risk for CVD, a 14% lower risk for CHD, a 12% lower risk for stroke, and a 17% lower risk of dying from CVD in later life, compared with other mothers.
On the basis of existing evidence, the researchers write, the World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding until a baby is 6 months old, followed by breastfeeding plus complementary feeding until the baby is 2 years or older.
“We believe that [breastfeeding] benefits for the mother are communicated poorly,” said Dr. Tschiderer and Dr. Willeit, from the University of Innsbruck, Austria.
“Positive effects of breastfeeding on mothers need to be communicated effectively, awareness for breastfeeding recommendations needs to be raised, and interventions to promote and facilitate breastfeeding need to be implemented and reinforced,” the researchers conclude.
‘Should not be ignored’
Two cardiologists invited to comment, who were not involved with the research, noted that this study provides insight into an important topic.
“This is yet another body of evidence [and the largest population to date] to show that breastfeeding is protective for women and may show important beneficial effects in terms of CV risk,” Roxana Mehran, MD, said in an email.
“The risk reductions were 11% for CVD events and 14% for CHD events; these are impressive numbers,” said Dr. Mehran, from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The caveat,” she said, “is that these are data from several trials, but nonetheless, this is a very important observation that should not be ignored.”
The study did not address the definitive amount of time of breastfeeding and its correlation to the improvement of CVD risk, but it did show that for the lifetime duration, the longer the better.
“The beneficial effects,” she noted, “can be linked to hormones during breastfeeding, as well as weight loss associated with breastfeeding, and resetting the maternal metabolism, as the authors suggest.”
Clinicians and employers “must provide ways to educate women about breastfeeding and make it easy for women who are in the workplace to pump, and to provide them with resources” where possible, Dr. Mehran said.
Michelle O’Donoghue, MD, MPH, noted that over the past several years, there has been intense interest in the possible health benefits of breastfeeding for both mother and child.
There is biologic plausibility for some of the possible maternal benefits because the favorable CV effects of both prolactin and oxytocin are only now being better understood, said Dr. O’Donoghue, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“The current meta-analysis provides a large dataset that helps support the concept that breastfeeding may offer some cardiovascular benefit for the mother,” she agreed.
“However, ultimately more research will be necessary since this method of combining data across trials relies upon the robustness of the statistical method in each study,” Dr. O’Donoghue said. “I applaud the authors for shining a spotlight on this important topic.”
Although the benefits of breastfeeding appear to continue over time, “it is incredibly difficult for women to continue breastfeeding once they return to work,” she added. “Women in some countries outside the U.S. have an advantage due to longer durations of maternity leave.
“If we want to encourage breastfeeding,” Dr. O’Donoghue stressed, “we need to make sure that we put the right supports in place. Women need protected places to breastfeed in the workplace and places to store their milk. Most importantly, women need to be allowed dedicated time to make it happen.”
First large study of CVD in mothers
Emerging individual studies suggest that mothers who breastfeed may have a lower risk for CVD in later life, but studies have been inconsistent, and it is not clear if longer breastfeeding would strengthen this benefit, the authors note.
To examine this, they pooled data from the following eight studies (with study acronym, country, and baseline enrolment dates in brackets): 45&Up (Australia, 2006-2009), China Kadoorie Biobank (CKB, China, 2004-2008), European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC, multinational, 1992-2000), Gallagher et al. (China, 1989-1991), Nord-Trøndelag Health Survey 2 (HUNT2, Norway, 1995-1997), Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study (JPHC, Japan, 1990-1994), Nurses’ Health Study (NHS, U.S., 1986), and the Woman’s Health Initiative (WHI, U.S., 1993-1998).
On average, the women were 51.3 years old (range, 40-65 years) when they enrolled in the study, and they were followed for a median of 10.3 years (range, 7.9-20.9 years, in the individual studies).
On average, they had their first child at age 25 and had two to three children (mean, 2.3); 82% had breastfed at some point (ranging from 58% of women in the two U.S. studies to 97% in CKB and HUNT2).
The women had breastfed for a mean of 7.4 to 18.9 months during their lifetimes (except women in the CKB study, who had breastfed for a median of 24 months).
Among the 1,192,700 women, there were 54,226 incident CVD events, 26,913 incident CHD events, 30,843 incident strokes, and 10,766 deaths from CVD during follow-up.
The researchers acknowledge that study limitations include the fact that there could have been publication bias, since fewer than 10 studies were available for pooling. There was significant between-study heterogeneity for CVD, CHD, and stroke outcomes.
Participant-level data were also lacking, and breastfeeding was self-reported. There may have been unaccounted residual confounding, and the benefits of lifetime breastfeeding that is longer than 2 years are not clear, because few women in this population breastfed that long.
The research was funded by the Austrian Science Fund. The researchers and Dr. Mehran and Dr. O’Donoghue have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a meta-analysis of more than 1 million mothers, those who breastfed their children had an 11% to 17% lower risk of developing cardiovascular disease (CVD), coronary heart disease (CHD), or stroke, and of dying from CVD, in later life than mothers who did not.
On average, the women had two children and had breastfed for 15.9 months in total. Longer breastfeeding was associated with greater CV health benefit.
This meta-analysis of eight studies from different countries was published online Jan. 11 in an issue of the Journal of the American Heart Association devoted to the impact of pregnancy on CV health in the mother and child.
Breastfeeding is known to be associated with a lower risk for death from infectious disease and with fewer respiratory infections in babies, the researchers write, but what is less well known is that it is also associated with a reduced risk for breast and ovarian cancer and type 2 diabetes in mothers.
The current study showed a clear association between breastfeeding and reduced risk for CVD in later life, lead author Lena Tschiderer, Dipl.-Ing., PhD, and senior author Peter Willeit, MD, MPhil, PhD, summarized in a joint email to this news organization.
Specifically, mothers who had breastfed their children at any time had an 11% lower risk for CVD, a 14% lower risk for CHD, a 12% lower risk for stroke, and a 17% lower risk of dying from CVD in later life, compared with other mothers.
On the basis of existing evidence, the researchers write, the World Health Organization recommends exclusive breastfeeding until a baby is 6 months old, followed by breastfeeding plus complementary feeding until the baby is 2 years or older.
“We believe that [breastfeeding] benefits for the mother are communicated poorly,” said Dr. Tschiderer and Dr. Willeit, from the University of Innsbruck, Austria.
“Positive effects of breastfeeding on mothers need to be communicated effectively, awareness for breastfeeding recommendations needs to be raised, and interventions to promote and facilitate breastfeeding need to be implemented and reinforced,” the researchers conclude.
‘Should not be ignored’
Two cardiologists invited to comment, who were not involved with the research, noted that this study provides insight into an important topic.
“This is yet another body of evidence [and the largest population to date] to show that breastfeeding is protective for women and may show important beneficial effects in terms of CV risk,” Roxana Mehran, MD, said in an email.
“The risk reductions were 11% for CVD events and 14% for CHD events; these are impressive numbers,” said Dr. Mehran, from Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York.
“The caveat,” she said, “is that these are data from several trials, but nonetheless, this is a very important observation that should not be ignored.”
The study did not address the definitive amount of time of breastfeeding and its correlation to the improvement of CVD risk, but it did show that for the lifetime duration, the longer the better.
“The beneficial effects,” she noted, “can be linked to hormones during breastfeeding, as well as weight loss associated with breastfeeding, and resetting the maternal metabolism, as the authors suggest.”
Clinicians and employers “must provide ways to educate women about breastfeeding and make it easy for women who are in the workplace to pump, and to provide them with resources” where possible, Dr. Mehran said.
Michelle O’Donoghue, MD, MPH, noted that over the past several years, there has been intense interest in the possible health benefits of breastfeeding for both mother and child.
There is biologic plausibility for some of the possible maternal benefits because the favorable CV effects of both prolactin and oxytocin are only now being better understood, said Dr. O’Donoghue, from Brigham and Women’s Hospital and Harvard Medical School, Boston.
“The current meta-analysis provides a large dataset that helps support the concept that breastfeeding may offer some cardiovascular benefit for the mother,” she agreed.
“However, ultimately more research will be necessary since this method of combining data across trials relies upon the robustness of the statistical method in each study,” Dr. O’Donoghue said. “I applaud the authors for shining a spotlight on this important topic.”
Although the benefits of breastfeeding appear to continue over time, “it is incredibly difficult for women to continue breastfeeding once they return to work,” she added. “Women in some countries outside the U.S. have an advantage due to longer durations of maternity leave.
“If we want to encourage breastfeeding,” Dr. O’Donoghue stressed, “we need to make sure that we put the right supports in place. Women need protected places to breastfeed in the workplace and places to store their milk. Most importantly, women need to be allowed dedicated time to make it happen.”
First large study of CVD in mothers
Emerging individual studies suggest that mothers who breastfeed may have a lower risk for CVD in later life, but studies have been inconsistent, and it is not clear if longer breastfeeding would strengthen this benefit, the authors note.
To examine this, they pooled data from the following eight studies (with study acronym, country, and baseline enrolment dates in brackets): 45&Up (Australia, 2006-2009), China Kadoorie Biobank (CKB, China, 2004-2008), European Prospective Investigation into Cancer and Nutrition (EPIC, multinational, 1992-2000), Gallagher et al. (China, 1989-1991), Nord-Trøndelag Health Survey 2 (HUNT2, Norway, 1995-1997), Japan Public Health Center-based Prospective Study (JPHC, Japan, 1990-1994), Nurses’ Health Study (NHS, U.S., 1986), and the Woman’s Health Initiative (WHI, U.S., 1993-1998).
On average, the women were 51.3 years old (range, 40-65 years) when they enrolled in the study, and they were followed for a median of 10.3 years (range, 7.9-20.9 years, in the individual studies).
On average, they had their first child at age 25 and had two to three children (mean, 2.3); 82% had breastfed at some point (ranging from 58% of women in the two U.S. studies to 97% in CKB and HUNT2).
The women had breastfed for a mean of 7.4 to 18.9 months during their lifetimes (except women in the CKB study, who had breastfed for a median of 24 months).
Among the 1,192,700 women, there were 54,226 incident CVD events, 26,913 incident CHD events, 30,843 incident strokes, and 10,766 deaths from CVD during follow-up.
The researchers acknowledge that study limitations include the fact that there could have been publication bias, since fewer than 10 studies were available for pooling. There was significant between-study heterogeneity for CVD, CHD, and stroke outcomes.
Participant-level data were also lacking, and breastfeeding was self-reported. There may have been unaccounted residual confounding, and the benefits of lifetime breastfeeding that is longer than 2 years are not clear, because few women in this population breastfed that long.
The research was funded by the Austrian Science Fund. The researchers and Dr. Mehran and Dr. O’Donoghue have no relevant financial disclosures.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID at 2 years: Preparing for a different ‘normal’
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.
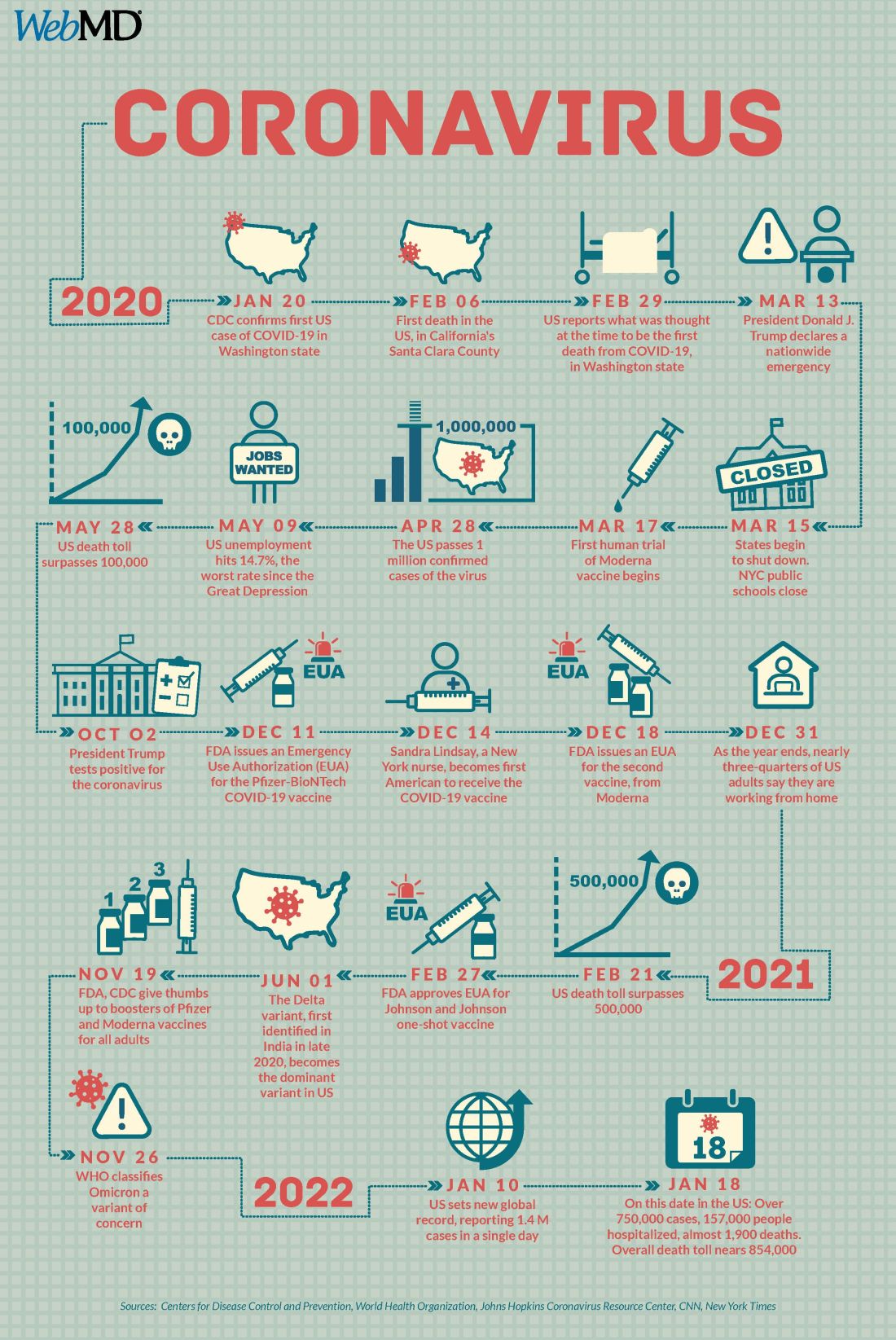
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.

A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Two years into the COVID-19 pandemic, the United States is still breaking records in hospital overcrowding and new cases.
The United States is logging nearly 800,000 cases a day, hospitals are starting to fray, and deaths have topped 850,000. Schools oscillate from remote to in-person learning, polarizing communities.
The vaccines are lifesaving for many, yet frustration mounts as the numbers of unvaccinated people in this country stays relatively stagnant (63% in the United States are fully vaccinated) and other parts of the world have seen hardly a single dose. Africa has the slowest vaccination rate among continents, with only 14% of the population receiving one shot, according to the New York Times tracker.
Yet
Effective vaccines and treatments that can keep people out of the hospital were developed at an astounding pace, and advances in tracking and testing – in both access and effectiveness – are starting to pay off.
Some experts say it’s possible that the raging Omicron surge will slow by late spring, providing some relief and maybe shifting the pandemic to a slower-burning endemic.
But other experts caution to keep our guard up, saying it’s time to settle into a “new normal” and upend the strategy for fighting COVID-19.
Time to change COVID thinking
Three former members of the Biden-Harris Transition COVID-19 Advisory Board wrote recently in JAMA that COVID-19 has now become one of the many viral respiratory diseases that health care providers and patients will manage each year.
The group of experts from the University of Pennsylvania, University of Minnesota, and New York University write that “many of the measures to reduce transmission of SARS-CoV-2 (for example, ventilation) will also reduce transmission of other respiratory viruses. Thus, policy makers should retire previous public health categorizations, including deaths from pneumonia and influenza or pneumonia, influenza, and COVID-19, and focus on a new category: the aggregate risk of all respiratory virus infections.”
Other experts, including Amesh Adalja, MD, a senior scholar at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security, Baltimore, have said it’s been clear since the early days of SARS-CoV-2 that we must learn to live with the virus because it “will be ever present for the remaining history of our species.”
But that doesn’t mean the virus will always have the upper hand. Although the United States has been reaching record numbers of hospitalizations in January, these hospitalizations differ from those of last year – marked by fewer extreme lifesaving measures, fewer deaths, and shorter hospital stays – caused in part by medical and therapeutic advances and in part to the nature of the Omicron variant itself.
One sign of progress, Dr. Adalja said, will be the widespread decoupling of cases from hospitalizations, something that has already happened in countries such as the United Kingdom.
“That’s a reflection of how well they have vaccinated their high-risk population and how poorly we have vaccinated our high-risk population,” he said.
Omicron will bump up natural immunity
Dr. Adalja said though the numbers of unvaccinated in the United States appear to be stuck, Omicron’s sweep will make the difference, leaving behind more natural immunity in the population.
Currently, hospitals are struggling with staffing concerns as a “direct result” of too many unvaccinated people, he said.
Andrew Badley, MD, an infectious diseases specialist at Mayo Clinic in Rochester, Minn., and director of the clinic’s COVID-19 Task Force, said the good news with Omicron is that nearly all people it infects will recover.
Over time, when the body sees foreign antigens repeatedly, the quantity and quality of the antibodies the immune system produces increase and the body becomes better at fighting disease.
So “a large amount of the population will have recovered and have a degree of immunity,” Dr. Badley said.
His optimism is tempered by his belief that “it’s going to get worse before it gets better.”
But Dr. Badley still predicts a turnaround. “We’ll see a downturn in COVID in late spring or early summer,” and well into the second quarter of 2022, “we’ll see a reemergence of control.”
Right now, with Omicron, one infected person is infecting three to five others, he said. The hope is that it will eventually reach one-to-one endemic levels.
As for the threat of new variants, Badley said, “it’s not predictable whether they will be stronger or weaker.”
Masks may be around for years
Many experts predict that masks will continue to be part of the national wardrobe for the foreseeable future.
“We will continue to see new cases for years and years to come. Some will respond to that with masks in public places for a very long time. I personally will do so,” Dr. Badley said.
Two mindsets: Inside/outside the hospital
Emily Landon, MD, an infectious disease doctor and the executive medical director of infection prevention and control at University of Chicago Medicine, told this news organization she views the pandemic from two different vantage points.
As a health care provider, she sees her hospital, like others worldwide, overwhelmed. Supplies of a major weapon to help prevent hospitalization, the monoclonal antibody sotrovimab, are running out. Dr. Landon said she has been calling other hospitals to see if they have supplies and, if so, whether Omicron patients can transfer there.
Bottom line: The things they relied on a month ago to keep people out of the hospital are no longer there, she said.
Meanwhile, “We have more COVID patients than we have ever had,” Dr. Landon said.
Last year, UChicago hit a high of 170 people hospitalized with COVID. This year, so far, the peak was 270.
Dr. Landon said she is frustrated when she leaves that overburdened world inside the hospital for the outside world, where people wear no masks or ineffective face coverings and gather unsafely. Although some of that behavior reflects an intention to flout the advice of medical experts, some is caused in part, she said, by the lack of a clear national health strategy and garbled communication from those in charge of public safety.
Americans are deciding for themselves, on an a la carte basis, whether to wear a mask or get tested or travel, and school districts decide individually when it’s time to go virtual.
“People are exhausted from having to do a risk-benefit analysis for every single activity they, their friends, their kids want to participate in,” she said.
U.S. behind in several areas
Despite our self-image as the global leader in science and medicine, the United States stumbled badly in its response to the pandemic, with grave consequences both at home and abroad, experts say.
In a recent commentary in JAMA, Lawrence Gostin, JD, from Georgetown University, Washington, and Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, pointed to several critical shortfalls in the nation’s efforts to control the disease.
One such shortfall is public trust.
This news organization reported in June 2021 that a poll of its readers found that 44% said their trust in the CDC had waned during the pandemic, and 33% said their trust in the FDA had eroded as well.
Health care providers who responded to the poll lost trust as well. About half of the doctors and nurses who responded said they disagreed with the FDA’s decision-making during the pandemic. Nearly 60% of doctors and 65% of nurses said they disagreed with the CDC’s overall pandemic guidance.
Lack of trust can make people resist vaccines and efforts to fight the virus, the authors wrote.
“This will become really relevant when we have ample supply of Pfizer’s antiviral medication,” Mr. Gostin, who directs the O’Neill Institute for National and Global Health Law at Georgetown, told this news organization. “The next phase of the pandemic is not to link testing to contact tracing, because we’re way past that, but to link testing to treatment.”
Lack of regional manufacturing of products is also thwarting global progress.
“It is extraordinarily important that our pharmaceutical industry transfer technology in a pandemic,” Mr. Gostin said. “The most glaring failure to do that is the mRNA vaccines. We’ve got this enormously effective vaccine and the two manufacturers – Pfizer and Moderna – are refusing to share the technology with producers in other countries. That keeps coming back to haunt us.”
Another problem: When the vaccines are shared with other countries, they are being delivered close to the date they expire or arriving at a shipyards without warning, so even some of the doses that get delivered are going to waste, Mr. Gostin said.
“It’s one of the greatest moral failures of my lifetime,” he said.
Also a failure is the “jaw-dropping” state of testing 2 years into the pandemic, he said, as people continue to pay high prices for tests or endure long lines.
The U.S. government updated its calculations and ordered 1 billion tests for the general public. The COVIDtests.gov website to order the free tests is now live.
It’s a step in the right direction. Mr. Gostin and Dr. Nuzzo wrote that there is every reason to expect future epidemics that are as serious or more serious than COVID.
“Failure to address clearly observed weaknesses in the COVID-19 response will have preventable adverse health, social, and economic consequences when the next novel outbreak occurs,” they wrote.

A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Make America beautiful: Support mask mandates
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
In space, no one can hear your red blood cells scream
There are many reasons why space is the final frontier, not least of which are the major health issues space travel places on the human body. So until a shady billionaire finds an alien protomolecule on a Saturnian moon and starts splicing it with human DNA so we can hang out in space all day without a spacesuit, we’re stuck with things like space anemia, a condition many astronauts develop after extended time in space.
Space anemia has been known for many years, but it was assumed that it developed as a reaction to microgravity and was a short-term phenomenon only – a temporary compensation as fluids and blood volume adjusted themselves. But as new research shows, that assumption seems to be wrong.
For the study, published in Nature Medicine, 13 astronauts who were in space for at least 120 days – long enough for all their red blood cells to have been produced in space – had their blood tested consistently. Before their flights, the astronauts created and destroyed 2 million red blood cells per second, but while they were in space, they destroyed 3 million cells per second. Notably, this process continued for the entire duration of the space flight. So, not a temporary reaction.
Consequently, 5 of the 13 astronauts developed anemia when they returned to Earth. (Interesting space fact: Having fewer blood cells isn’t a problem while you’re in space; the effects of anemia only manifest when the body returns to full gravity.) The anemia disappeared after a few months, but the astronauts were still destroying 30% more red blood cells a year after their spaceflight than they were before leaving Earth.
You may be thinking: Well, if they were destroying 50% more red blood cells while in space, how come they didn’t all develop severe anemia? The researchers theorized that production was boosted as well, which sounds like a good thing. The body is compensating, as it should. Unfortunately, that increased production stresses bone marrow function and the demand for energy spikes. That’s not such a good thing. And of course, many of the astronauts got anemia anyway.
To tackle the issue, the researchers emphasized the importance of feeding astronauts a proper diet, plus potential supplements before spaceflight. So don’t worry, Captain Kirk will be able to arm wrestle Klingons and romance suspiciously human-looking aliens without fear of keeling over from anemia-induced fatigue. Earth will stay safe.
Tell me with your eyes
Communication can be hard, even under the best of circumstances, but for many nonverbal patients in the intensive care unit who can’t move, getting a point across to the health care team can be a huge struggle in itself.
Health care professionals have been making do with eye-blinking or head-nodding, but what if that’s just not enough? New research shows that it’s not, and there’s a more effective way for patients to say what they mean just by looking.
In a study published in the Journal of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery, researchers looked into using eye-tracking systems for nonverbal ICU patients to communicate. Eye-tracking isn’t anything new, but using it as a form of communication among nonverbal patients with critical illness hasn’t been looked at before.
How does it work? The eye-tracking system is set up in the patient’s line of sight and its various algorithms and software collect data to calculate where exactly the patient is looking. Established scores and scales assess the patient’s mood, quality of life, pain, and self-esteem.
The researchers found that participating patients were actually experiencing more negative moods, pain, and feelings of frustration than was once believed. Making this tool even more valuable for treatment adjustment and meeting patients’ needs.
In this case, it means that health care providers are getting an eyeful … of communication.
Make America grave again
Here we go again. Somebody just found something else that the United States is not the best at. To go along with math and science education, infrastructure investment, quality of life …
That’s going to go on for a while, so let’s get to the new stuff. An international group of researchers surveyed end-of-life care in 81 countries and ranked them based on the assessment of 181 experts in those countries. They looked at 13 different factors, including proper management of pain and comfort, having a clean and safe space, being treated kindly, lack of cost barriers to appropriate care, and treatments that address quality of life and don’t just extend life.
… press freedom, industrial production, racial equality, Internet connectivity …
Their report card, published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, gave six countries an A, with Great Britain at the top. The other five were Ireland, Taiwan, Australia, South Korea, and Costa Rica. The lowest grade went to Paraguay in 81st place, with Lebanon, Brazil, Senegal, and Haiti just ahead.
… environmental stewardship, body-mass index, social mobility, COVID safeness …
The United States, getting a firm grasp on mediocrity, ranked 43rd. Here are some countries that did better: North Macedonia (7th), Sri Lanka (16th), Uganda (31st), and Uruguay 33rd). In the United States, “we spend so much money trying to get people to live longer, but we don’t spend enough money in helping people die better,” lead author Eric A. Finkelstein, PhD, said in a written statement.
… economic stability, and soccer; we’re also not the best at dying. Wait, did we already say that?
The face mask that launched a thousand ships
Face masks, clearly, have been a source of social strife during the pandemic. People may not agree on mandates, but a mask can be a pretty-low-maintenance face shield if you don’t feel like putting on make-up or want to cover up some blemishes.
Before the pandemic, people thought that those wearing face masks were less attractive because the masks represented illness or disease, according to Dr. Michael Lewis of Cardiff (Wales) University. Back then, no one really wore masks besides doctors and nurses, so if you saw someone wearing one on the street, you probably wondered what they were trying to hide.
Now, though, the subject of face mask attractiveness has been revisited by Dr. Lewis and his associate, Oliver Hies, who found that face masks now make people more attractive.
“Our study suggests faces are considered most attractive when covered by medical face masks. … At a time when we feel vulnerable, we may find the wearing of medical masks reassuring and so feel more positive towards the wearer,” Dr. Lewis told the Guardian.
He suggested that we’re no longer looking at people wearing a mask as disease riddled, but rather doing their part to protect society. Or maybe we focus more on someone’s eyes when that’s all there is to look at. Or, maybe we wind up making up what the rest of someone’s face looks like to meet our attractiveness criteria.
However you feel about masks, they’re cheaper than plastic surgery. And you can go out wearing a new face every day.
Pandemic weighing on physicians’ happiness outside of work: survey
One of the unexpected consequences of the pandemic is that many people are rethinking their priorities and lifestyles, and physicians are no exception.
Pets, prayer, and partners
The pandemic has taken a toll on physicians outside of work as well as on the job. Eight in 10 physicians (82% of men and 80% of women) said they were “somewhat” or “very” happy outside of work before the pandemic. This is almost exactly the same result as in last year’s survey.
However, when asked how happy they are outside of work currently, only 6 in 10 (59%) reported being “somewhat” or “very” happy. While the pandemic has made life difficult for everyone, health care professionals face particular stresses even outside of work. Wayne M. Sotile, PhD, founder of the Center for Physician Resilience, says he has counseled doctors who witnessed COVID-related suffering and death at work, then came home to a partner who didn’t believe that the pandemic was real.
Still, physicians reported that spending time with people they love and engaging in favorite activities helps them stay happy. “Spending time with pets” and “religious practice/prayer” were frequent “other” responses to the question, “What do you do to maintain happiness and mental health?” Seven in 10 physicians reported having some kind of religious or spiritual beliefs.
The majority of physicians (83%) are either married or living with a partner, with male physicians edging out their female peers (89% vs. 75%). Among married physicians, 8 in 10 physicians reported that their union is “good” or “very good.” The pandemic may have helped in this respect. Dr. Sotile says he’s heard physicians say that they’ve connected more with their families in the past 18 months. Specialists with the highest rates of happy marriages were otolaryngologists and immunologists (both 91%), followed closely by dermatologists, rheumatologists, and nephrologists (all 90%).
Among physicians balancing a medical career and parenthood, female physicians reported feeling conflicted more often than males (48% vs. 29%). Nicole A. Sparks, MD, an ob.gyn. and a health and lifestyle blogger, cites not being there for her kids as a source of stress. She notes that her two young children notice when she’s not there to help with homework, read bedtime stories, or make their dinner. “Mom guilt can definitely set in if I have to miss important events,” she says.
Work-life balance is an important, if elusive, goal for physicians, and not just females. Sixty percent of female doctors and 53% of male doctors said they would be willing to take a cut in pay if it meant more free time and a better work-life balance. Many doctors do manage to get away from work occasionally, with one-fifth of all physicians taking 5 or more weeks of vacation each year.
Seeking a ‘balanced life’
Alexis Polles, MD, medical director for the Professionals Resource Network, points out the importance of taking time for personal health and wellness. “When we work with professionals who have problems with mental health or substance abuse, they often don’t have a balanced life,” she says. “They are usually in a workaholic mindset and disregard their own needs.”
Few physicians seem to prioritize self-care, with a third indicating they “always” or “most of the time” spend enough time on their own health and wellness. But of those who do, males (38%) are more likely than females (27%) to spend enough time on their own health and wellness. Dr. Polles adds that exercising after a shift can help physicians better make the transition from professional to personal life. Though they did not report when they exercised, about a third of physicians reported doing so four or more times per week. Controlling weight is an issue as well, with 49% of male and 55% of female physicians saying they are currently trying to lose weight.
Of physicians who drink alcohol, about a third have three or more drinks per week. (The CDC defines “heavy drinking” as consuming 15 drinks or more per week for men and eight drinks or more per week for women.)
Of those surveyed, 92% say they do not regularly use cannabidiol or cannabis, and a mere 4% of respondents said they would use at least one of these substances if they were to become legal in their state.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One of the unexpected consequences of the pandemic is that many people are rethinking their priorities and lifestyles, and physicians are no exception.
Pets, prayer, and partners
The pandemic has taken a toll on physicians outside of work as well as on the job. Eight in 10 physicians (82% of men and 80% of women) said they were “somewhat” or “very” happy outside of work before the pandemic. This is almost exactly the same result as in last year’s survey.
However, when asked how happy they are outside of work currently, only 6 in 10 (59%) reported being “somewhat” or “very” happy. While the pandemic has made life difficult for everyone, health care professionals face particular stresses even outside of work. Wayne M. Sotile, PhD, founder of the Center for Physician Resilience, says he has counseled doctors who witnessed COVID-related suffering and death at work, then came home to a partner who didn’t believe that the pandemic was real.
Still, physicians reported that spending time with people they love and engaging in favorite activities helps them stay happy. “Spending time with pets” and “religious practice/prayer” were frequent “other” responses to the question, “What do you do to maintain happiness and mental health?” Seven in 10 physicians reported having some kind of religious or spiritual beliefs.
The majority of physicians (83%) are either married or living with a partner, with male physicians edging out their female peers (89% vs. 75%). Among married physicians, 8 in 10 physicians reported that their union is “good” or “very good.” The pandemic may have helped in this respect. Dr. Sotile says he’s heard physicians say that they’ve connected more with their families in the past 18 months. Specialists with the highest rates of happy marriages were otolaryngologists and immunologists (both 91%), followed closely by dermatologists, rheumatologists, and nephrologists (all 90%).
Among physicians balancing a medical career and parenthood, female physicians reported feeling conflicted more often than males (48% vs. 29%). Nicole A. Sparks, MD, an ob.gyn. and a health and lifestyle blogger, cites not being there for her kids as a source of stress. She notes that her two young children notice when she’s not there to help with homework, read bedtime stories, or make their dinner. “Mom guilt can definitely set in if I have to miss important events,” she says.
Work-life balance is an important, if elusive, goal for physicians, and not just females. Sixty percent of female doctors and 53% of male doctors said they would be willing to take a cut in pay if it meant more free time and a better work-life balance. Many doctors do manage to get away from work occasionally, with one-fifth of all physicians taking 5 or more weeks of vacation each year.
Seeking a ‘balanced life’
Alexis Polles, MD, medical director for the Professionals Resource Network, points out the importance of taking time for personal health and wellness. “When we work with professionals who have problems with mental health or substance abuse, they often don’t have a balanced life,” she says. “They are usually in a workaholic mindset and disregard their own needs.”
Few physicians seem to prioritize self-care, with a third indicating they “always” or “most of the time” spend enough time on their own health and wellness. But of those who do, males (38%) are more likely than females (27%) to spend enough time on their own health and wellness. Dr. Polles adds that exercising after a shift can help physicians better make the transition from professional to personal life. Though they did not report when they exercised, about a third of physicians reported doing so four or more times per week. Controlling weight is an issue as well, with 49% of male and 55% of female physicians saying they are currently trying to lose weight.
Of physicians who drink alcohol, about a third have three or more drinks per week. (The CDC defines “heavy drinking” as consuming 15 drinks or more per week for men and eight drinks or more per week for women.)
Of those surveyed, 92% say they do not regularly use cannabidiol or cannabis, and a mere 4% of respondents said they would use at least one of these substances if they were to become legal in their state.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
One of the unexpected consequences of the pandemic is that many people are rethinking their priorities and lifestyles, and physicians are no exception.
Pets, prayer, and partners
The pandemic has taken a toll on physicians outside of work as well as on the job. Eight in 10 physicians (82% of men and 80% of women) said they were “somewhat” or “very” happy outside of work before the pandemic. This is almost exactly the same result as in last year’s survey.
However, when asked how happy they are outside of work currently, only 6 in 10 (59%) reported being “somewhat” or “very” happy. While the pandemic has made life difficult for everyone, health care professionals face particular stresses even outside of work. Wayne M. Sotile, PhD, founder of the Center for Physician Resilience, says he has counseled doctors who witnessed COVID-related suffering and death at work, then came home to a partner who didn’t believe that the pandemic was real.
Still, physicians reported that spending time with people they love and engaging in favorite activities helps them stay happy. “Spending time with pets” and “religious practice/prayer” were frequent “other” responses to the question, “What do you do to maintain happiness and mental health?” Seven in 10 physicians reported having some kind of religious or spiritual beliefs.
The majority of physicians (83%) are either married or living with a partner, with male physicians edging out their female peers (89% vs. 75%). Among married physicians, 8 in 10 physicians reported that their union is “good” or “very good.” The pandemic may have helped in this respect. Dr. Sotile says he’s heard physicians say that they’ve connected more with their families in the past 18 months. Specialists with the highest rates of happy marriages were otolaryngologists and immunologists (both 91%), followed closely by dermatologists, rheumatologists, and nephrologists (all 90%).
Among physicians balancing a medical career and parenthood, female physicians reported feeling conflicted more often than males (48% vs. 29%). Nicole A. Sparks, MD, an ob.gyn. and a health and lifestyle blogger, cites not being there for her kids as a source of stress. She notes that her two young children notice when she’s not there to help with homework, read bedtime stories, or make their dinner. “Mom guilt can definitely set in if I have to miss important events,” she says.
Work-life balance is an important, if elusive, goal for physicians, and not just females. Sixty percent of female doctors and 53% of male doctors said they would be willing to take a cut in pay if it meant more free time and a better work-life balance. Many doctors do manage to get away from work occasionally, with one-fifth of all physicians taking 5 or more weeks of vacation each year.
Seeking a ‘balanced life’
Alexis Polles, MD, medical director for the Professionals Resource Network, points out the importance of taking time for personal health and wellness. “When we work with professionals who have problems with mental health or substance abuse, they often don’t have a balanced life,” she says. “They are usually in a workaholic mindset and disregard their own needs.”
Few physicians seem to prioritize self-care, with a third indicating they “always” or “most of the time” spend enough time on their own health and wellness. But of those who do, males (38%) are more likely than females (27%) to spend enough time on their own health and wellness. Dr. Polles adds that exercising after a shift can help physicians better make the transition from professional to personal life. Though they did not report when they exercised, about a third of physicians reported doing so four or more times per week. Controlling weight is an issue as well, with 49% of male and 55% of female physicians saying they are currently trying to lose weight.
Of physicians who drink alcohol, about a third have three or more drinks per week. (The CDC defines “heavy drinking” as consuming 15 drinks or more per week for men and eight drinks or more per week for women.)
Of those surveyed, 92% say they do not regularly use cannabidiol or cannabis, and a mere 4% of respondents said they would use at least one of these substances if they were to become legal in their state.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
CVS Caremark formulary change freezes out apixaban
Patients looking to refill a prescription for apixaban (Eliquis) through CVS Caremark may be in for a surprise following its decision to exclude the direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) from its formulary starting Jan. 1.
The move leaves just one DOAC, rivaroxaban (Xarelto), on CVS’ commercial formulary and is being assailed as the latest example of “nonmedical switching” used by health insurers to control costs.
In a letter to CVS Caremark backed by 14 provider and patient organizations, the nonprofit Partnership to Advance Cardiovascular Health (PACH) calls on the pharmacy chain to reverse its “dangerously disruptive” decision to force stable patients at high risk of cardiovascular events to switch anticoagulation, without an apparent option to be grandfathered into the new plan.
PACH president Dharmesh Patel, MD, Stern Cardiovascular Center, Memphis, called the formulary change “reckless and irresponsible, especially because the decision is not based in science and evidence, but on budgets. Patients and their health care providers, not insurance companies, need to be trusted to determine what medication is best,” he said in a statement.
Craig Beavers, PharmD, vice president of Baptist Health Paducah, Kentucky, said that, as chair of the American College of Cardiology’s Cardiovascular Team Section, he and other organizations have met with CVS Caremark medical leadership to advocate for patients and to understand the company’s perspective.
“The underlying driver is cost,” he told this news organization.
Current guidelines recommend DOACs in general for a variety of indications, including to reduce the risk of stroke and embolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and to prevent deep vein thrombosis, but there are select instances where a particular DOAC might be more appropriate, he observed.
“Apixaban may be better for a patient with a history of GI bleeding because there’s less GI bleeding, but the guidelines don’t necessarily spell those things out,” Dr. Beavers said. “That’s where the clinician should advocate for their patient and, unfortunately, they are making their decision strictly based off the guidelines.”
Requests to speak with medical officers at CVS Caremark went unanswered, but its executive director of communications, Christina Peaslee, told this news organization that the formulary decision “maintains clinically appropriate, cost-effective prescription coverage” for its clients and members.
“Both the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Rhythm Society and 2021 CHEST guidelines recommend DOACs over warfarin for treatment of various cardiology conditions such as atrial fibrillation, but neither list a specific agent as preferred – showing that consensus clinical guidelines do not favor one over the other,” she said in an email. “Further, Xarelto has more FDA-approved indications than Eliquis (e.g., Xarelto is approved for a reduction in risk of major CV events in patients with CAD or PAD) in addition to all the same FDA indications as Eliquis.”
Ms. Peaslee pointed out that all formulary changes are evaluated by an external medical expert specializing in the disease state, followed by review and approval by an independent national Pharmacy & Therapeutics Committee.
The decision to exclude apixaban is also limited to a “subset of commercial drug lists,” she said, although specifics on which plans and the number of affected patients were not forthcoming.
The choice of DOAC is a timely question in cardiology, with recent studies suggesting an advantage for apixaban over rivaroxaban in reducing the risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism, as well as reducing the risk of major ischemic or hemorrhagic events in atrial fibrillation.
Ms. Peaslee said CVS Caremark closely monitors medical literature for relevant clinical trial data and that most clients allow reasonable formulary exceptions when justified. “This formulary exceptions process has been successfully used for changes of this type and allows patients to get a medication that is safe and effective, as determined by their prescriber.”
The company will also continue to provide “robust, personalized outreach to the small number of members who will need to switch to an alternative medication,” she added.
Dr. Beavers said negotiations with CVS are still in the early stages, but, in the meantime, the ACC is providing health care providers with tools, such as drug copay cards and electronic prior authorizations, to help ensure patients don’t have gaps in coverage.
In a Jan. 14 news release addressing the formulary change, ACC notes that a patient’s pharmacy can also request a one-time override when trying to fill a nonpreferred DOAC in January to buy time if switching medications with their clinician or requesting a formulary exception.
During discussions with CVS Caremark, it says the ACC and the American Society of Hematology “underscored the negative impacts of this decision on patients currently taking one of the nonpreferred DOACs and on those who have previously tried rivaroxaban and changed medications.”
The groups also highlighted difficulties with other prior authorization programs in terms of the need for dedicated staff and time away from direct patient care.
“The ACC and ASH will continue discussions with CVS Caremark regarding the burden on clinicians and the effect of the formulary decision on patient access,” the release says.
In its letter to CVS, PACH argues that the apixaban exclusion will disproportionately affect historically disadvantaged patients, leaving those who can least afford the change with limited options. Notably, no generic is available for either apixaban or rivaroxaban.
The group also highlights a 2019 national poll, in which nearly 40% of patients who had their medication switched were so frustrated that they stopped their medication altogether.
PACH has an online petition against nonmedical switching, which at press time had garnered 2,126 signatures.
One signee, Jan Griffin, who survived bilateral pulmonary embolisms, writes that she has been on Eliquis [apixaban] successfully since her hospital discharge. “Now, as of midnight, Caremark apparently knows better than my hematologist as to what blood thinner is better for me and will no longer cover my Eliquis prescription. This is criminal, immoral, and unethical. #StopTheSwitch.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients looking to refill a prescription for apixaban (Eliquis) through CVS Caremark may be in for a surprise following its decision to exclude the direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) from its formulary starting Jan. 1.
The move leaves just one DOAC, rivaroxaban (Xarelto), on CVS’ commercial formulary and is being assailed as the latest example of “nonmedical switching” used by health insurers to control costs.
In a letter to CVS Caremark backed by 14 provider and patient organizations, the nonprofit Partnership to Advance Cardiovascular Health (PACH) calls on the pharmacy chain to reverse its “dangerously disruptive” decision to force stable patients at high risk of cardiovascular events to switch anticoagulation, without an apparent option to be grandfathered into the new plan.
PACH president Dharmesh Patel, MD, Stern Cardiovascular Center, Memphis, called the formulary change “reckless and irresponsible, especially because the decision is not based in science and evidence, but on budgets. Patients and their health care providers, not insurance companies, need to be trusted to determine what medication is best,” he said in a statement.
Craig Beavers, PharmD, vice president of Baptist Health Paducah, Kentucky, said that, as chair of the American College of Cardiology’s Cardiovascular Team Section, he and other organizations have met with CVS Caremark medical leadership to advocate for patients and to understand the company’s perspective.
“The underlying driver is cost,” he told this news organization.
Current guidelines recommend DOACs in general for a variety of indications, including to reduce the risk of stroke and embolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and to prevent deep vein thrombosis, but there are select instances where a particular DOAC might be more appropriate, he observed.
“Apixaban may be better for a patient with a history of GI bleeding because there’s less GI bleeding, but the guidelines don’t necessarily spell those things out,” Dr. Beavers said. “That’s where the clinician should advocate for their patient and, unfortunately, they are making their decision strictly based off the guidelines.”
Requests to speak with medical officers at CVS Caremark went unanswered, but its executive director of communications, Christina Peaslee, told this news organization that the formulary decision “maintains clinically appropriate, cost-effective prescription coverage” for its clients and members.
“Both the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Rhythm Society and 2021 CHEST guidelines recommend DOACs over warfarin for treatment of various cardiology conditions such as atrial fibrillation, but neither list a specific agent as preferred – showing that consensus clinical guidelines do not favor one over the other,” she said in an email. “Further, Xarelto has more FDA-approved indications than Eliquis (e.g., Xarelto is approved for a reduction in risk of major CV events in patients with CAD or PAD) in addition to all the same FDA indications as Eliquis.”
Ms. Peaslee pointed out that all formulary changes are evaluated by an external medical expert specializing in the disease state, followed by review and approval by an independent national Pharmacy & Therapeutics Committee.
The decision to exclude apixaban is also limited to a “subset of commercial drug lists,” she said, although specifics on which plans and the number of affected patients were not forthcoming.
The choice of DOAC is a timely question in cardiology, with recent studies suggesting an advantage for apixaban over rivaroxaban in reducing the risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism, as well as reducing the risk of major ischemic or hemorrhagic events in atrial fibrillation.
Ms. Peaslee said CVS Caremark closely monitors medical literature for relevant clinical trial data and that most clients allow reasonable formulary exceptions when justified. “This formulary exceptions process has been successfully used for changes of this type and allows patients to get a medication that is safe and effective, as determined by their prescriber.”
The company will also continue to provide “robust, personalized outreach to the small number of members who will need to switch to an alternative medication,” she added.
Dr. Beavers said negotiations with CVS are still in the early stages, but, in the meantime, the ACC is providing health care providers with tools, such as drug copay cards and electronic prior authorizations, to help ensure patients don’t have gaps in coverage.
In a Jan. 14 news release addressing the formulary change, ACC notes that a patient’s pharmacy can also request a one-time override when trying to fill a nonpreferred DOAC in January to buy time if switching medications with their clinician or requesting a formulary exception.
During discussions with CVS Caremark, it says the ACC and the American Society of Hematology “underscored the negative impacts of this decision on patients currently taking one of the nonpreferred DOACs and on those who have previously tried rivaroxaban and changed medications.”
The groups also highlighted difficulties with other prior authorization programs in terms of the need for dedicated staff and time away from direct patient care.
“The ACC and ASH will continue discussions with CVS Caremark regarding the burden on clinicians and the effect of the formulary decision on patient access,” the release says.
In its letter to CVS, PACH argues that the apixaban exclusion will disproportionately affect historically disadvantaged patients, leaving those who can least afford the change with limited options. Notably, no generic is available for either apixaban or rivaroxaban.
The group also highlights a 2019 national poll, in which nearly 40% of patients who had their medication switched were so frustrated that they stopped their medication altogether.
PACH has an online petition against nonmedical switching, which at press time had garnered 2,126 signatures.
One signee, Jan Griffin, who survived bilateral pulmonary embolisms, writes that she has been on Eliquis [apixaban] successfully since her hospital discharge. “Now, as of midnight, Caremark apparently knows better than my hematologist as to what blood thinner is better for me and will no longer cover my Eliquis prescription. This is criminal, immoral, and unethical. #StopTheSwitch.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients looking to refill a prescription for apixaban (Eliquis) through CVS Caremark may be in for a surprise following its decision to exclude the direct oral anticoagulant (DOAC) from its formulary starting Jan. 1.
The move leaves just one DOAC, rivaroxaban (Xarelto), on CVS’ commercial formulary and is being assailed as the latest example of “nonmedical switching” used by health insurers to control costs.
In a letter to CVS Caremark backed by 14 provider and patient organizations, the nonprofit Partnership to Advance Cardiovascular Health (PACH) calls on the pharmacy chain to reverse its “dangerously disruptive” decision to force stable patients at high risk of cardiovascular events to switch anticoagulation, without an apparent option to be grandfathered into the new plan.
PACH president Dharmesh Patel, MD, Stern Cardiovascular Center, Memphis, called the formulary change “reckless and irresponsible, especially because the decision is not based in science and evidence, but on budgets. Patients and their health care providers, not insurance companies, need to be trusted to determine what medication is best,” he said in a statement.
Craig Beavers, PharmD, vice president of Baptist Health Paducah, Kentucky, said that, as chair of the American College of Cardiology’s Cardiovascular Team Section, he and other organizations have met with CVS Caremark medical leadership to advocate for patients and to understand the company’s perspective.
“The underlying driver is cost,” he told this news organization.
Current guidelines recommend DOACs in general for a variety of indications, including to reduce the risk of stroke and embolism in nonvalvular atrial fibrillation and to prevent deep vein thrombosis, but there are select instances where a particular DOAC might be more appropriate, he observed.
“Apixaban may be better for a patient with a history of GI bleeding because there’s less GI bleeding, but the guidelines don’t necessarily spell those things out,” Dr. Beavers said. “That’s where the clinician should advocate for their patient and, unfortunately, they are making their decision strictly based off the guidelines.”
Requests to speak with medical officers at CVS Caremark went unanswered, but its executive director of communications, Christina Peaslee, told this news organization that the formulary decision “maintains clinically appropriate, cost-effective prescription coverage” for its clients and members.
“Both the American Heart Association/American College of Cardiology/Heart Rhythm Society and 2021 CHEST guidelines recommend DOACs over warfarin for treatment of various cardiology conditions such as atrial fibrillation, but neither list a specific agent as preferred – showing that consensus clinical guidelines do not favor one over the other,” she said in an email. “Further, Xarelto has more FDA-approved indications than Eliquis (e.g., Xarelto is approved for a reduction in risk of major CV events in patients with CAD or PAD) in addition to all the same FDA indications as Eliquis.”
Ms. Peaslee pointed out that all formulary changes are evaluated by an external medical expert specializing in the disease state, followed by review and approval by an independent national Pharmacy & Therapeutics Committee.
The decision to exclude apixaban is also limited to a “subset of commercial drug lists,” she said, although specifics on which plans and the number of affected patients were not forthcoming.
The choice of DOAC is a timely question in cardiology, with recent studies suggesting an advantage for apixaban over rivaroxaban in reducing the risk of recurrent venous thromboembolism, as well as reducing the risk of major ischemic or hemorrhagic events in atrial fibrillation.
Ms. Peaslee said CVS Caremark closely monitors medical literature for relevant clinical trial data and that most clients allow reasonable formulary exceptions when justified. “This formulary exceptions process has been successfully used for changes of this type and allows patients to get a medication that is safe and effective, as determined by their prescriber.”
The company will also continue to provide “robust, personalized outreach to the small number of members who will need to switch to an alternative medication,” she added.
Dr. Beavers said negotiations with CVS are still in the early stages, but, in the meantime, the ACC is providing health care providers with tools, such as drug copay cards and electronic prior authorizations, to help ensure patients don’t have gaps in coverage.
In a Jan. 14 news release addressing the formulary change, ACC notes that a patient’s pharmacy can also request a one-time override when trying to fill a nonpreferred DOAC in January to buy time if switching medications with their clinician or requesting a formulary exception.
During discussions with CVS Caremark, it says the ACC and the American Society of Hematology “underscored the negative impacts of this decision on patients currently taking one of the nonpreferred DOACs and on those who have previously tried rivaroxaban and changed medications.”
The groups also highlighted difficulties with other prior authorization programs in terms of the need for dedicated staff and time away from direct patient care.
“The ACC and ASH will continue discussions with CVS Caremark regarding the burden on clinicians and the effect of the formulary decision on patient access,” the release says.
In its letter to CVS, PACH argues that the apixaban exclusion will disproportionately affect historically disadvantaged patients, leaving those who can least afford the change with limited options. Notably, no generic is available for either apixaban or rivaroxaban.
The group also highlights a 2019 national poll, in which nearly 40% of patients who had their medication switched were so frustrated that they stopped their medication altogether.
PACH has an online petition against nonmedical switching, which at press time had garnered 2,126 signatures.
One signee, Jan Griffin, who survived bilateral pulmonary embolisms, writes that she has been on Eliquis [apixaban] successfully since her hospital discharge. “Now, as of midnight, Caremark apparently knows better than my hematologist as to what blood thinner is better for me and will no longer cover my Eliquis prescription. This is criminal, immoral, and unethical. #StopTheSwitch.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.







