User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
WHO tracking new Omicron subvariant in India
The subvariant, a sublineage of BA.2 being called BA.2.75, has been reported in eight countries and hasn’t yet been declared a variant of concern.
“There’s been an emergence of a ‘could be’ subvariant. It’s been not yet officially called, but some people are referring to it as BA.2.75,” Soumya Swaminathan, MD, the WHO’s chief scientist, said in a video posted on Twitter.
The subvariant appears to have mutations similar to other contagious strains, she said, though there are a limited number of sequences available to analyze. How transmissible and severe it is, and how well it can evade our immunity, aren’t yet known.
“We have to wait and see, and of course, we are tracking it,” Dr. Swaminathan said.
The WHO committee responsible for analyzing global coronavirus data will label the subvariant officially and release more information as the situation warrants it, she said.
Public health experts around the world are also talking about the subvariant, which has been nicknamed Centaurus. BA.2.75 was first found in India in May and is now competing with BA.5, which has become dominant in the United States.
BA.2.75 has eight mutations beyond those seen in BA.5, which “could make immune escape worse than what we’re seeing now,” Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief at Medscape, wrote in a Twitter post.
Individually, the extra mutations aren’t too concerning, “but all appearing together at once is another matter,” Tom Peacock, PhD, a virologist at Imperial College London, wrote in a Twitter post.
The “apparent rapid growth and wide geographical spread” are “worth keeping a close eye on,” he said.
BA.2.75 has been found in a handful of cases in the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. In India, the sequence accounts for about 23% of recent samples.
“It is really too early to know if BA.2.75 will take over relative to BA.2 or even relative to BA.5,” Ulrich Elling, PhD, a researcher at Australia’s Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, wrote in a Twitter post.
“Just to emphasize it again: While the distribution across Indian regions as well as internationally and the very rapid appearance makes it likely we are dealing with a variant spreading fast and spread widely already, the absolute data points are few,” he said.
Globally, coronavirus cases have increased nearly 30% during the past 2 weeks, the WHO said July 6. Four out of six of the WHO subregions reported an increase in the last week, with BA.4 and BA.5 driving waves in the United States and Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The subvariant, a sublineage of BA.2 being called BA.2.75, has been reported in eight countries and hasn’t yet been declared a variant of concern.
“There’s been an emergence of a ‘could be’ subvariant. It’s been not yet officially called, but some people are referring to it as BA.2.75,” Soumya Swaminathan, MD, the WHO’s chief scientist, said in a video posted on Twitter.
The subvariant appears to have mutations similar to other contagious strains, she said, though there are a limited number of sequences available to analyze. How transmissible and severe it is, and how well it can evade our immunity, aren’t yet known.
“We have to wait and see, and of course, we are tracking it,” Dr. Swaminathan said.
The WHO committee responsible for analyzing global coronavirus data will label the subvariant officially and release more information as the situation warrants it, she said.
Public health experts around the world are also talking about the subvariant, which has been nicknamed Centaurus. BA.2.75 was first found in India in May and is now competing with BA.5, which has become dominant in the United States.
BA.2.75 has eight mutations beyond those seen in BA.5, which “could make immune escape worse than what we’re seeing now,” Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief at Medscape, wrote in a Twitter post.
Individually, the extra mutations aren’t too concerning, “but all appearing together at once is another matter,” Tom Peacock, PhD, a virologist at Imperial College London, wrote in a Twitter post.
The “apparent rapid growth and wide geographical spread” are “worth keeping a close eye on,” he said.
BA.2.75 has been found in a handful of cases in the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. In India, the sequence accounts for about 23% of recent samples.
“It is really too early to know if BA.2.75 will take over relative to BA.2 or even relative to BA.5,” Ulrich Elling, PhD, a researcher at Australia’s Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, wrote in a Twitter post.
“Just to emphasize it again: While the distribution across Indian regions as well as internationally and the very rapid appearance makes it likely we are dealing with a variant spreading fast and spread widely already, the absolute data points are few,” he said.
Globally, coronavirus cases have increased nearly 30% during the past 2 weeks, the WHO said July 6. Four out of six of the WHO subregions reported an increase in the last week, with BA.4 and BA.5 driving waves in the United States and Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
The subvariant, a sublineage of BA.2 being called BA.2.75, has been reported in eight countries and hasn’t yet been declared a variant of concern.
“There’s been an emergence of a ‘could be’ subvariant. It’s been not yet officially called, but some people are referring to it as BA.2.75,” Soumya Swaminathan, MD, the WHO’s chief scientist, said in a video posted on Twitter.
The subvariant appears to have mutations similar to other contagious strains, she said, though there are a limited number of sequences available to analyze. How transmissible and severe it is, and how well it can evade our immunity, aren’t yet known.
“We have to wait and see, and of course, we are tracking it,” Dr. Swaminathan said.
The WHO committee responsible for analyzing global coronavirus data will label the subvariant officially and release more information as the situation warrants it, she said.
Public health experts around the world are also talking about the subvariant, which has been nicknamed Centaurus. BA.2.75 was first found in India in May and is now competing with BA.5, which has become dominant in the United States.
BA.2.75 has eight mutations beyond those seen in BA.5, which “could make immune escape worse than what we’re seeing now,” Eric Topol, MD, founder and director of the Scripps Research Translational Institute and editor-in-chief at Medscape, wrote in a Twitter post.
Individually, the extra mutations aren’t too concerning, “but all appearing together at once is another matter,” Tom Peacock, PhD, a virologist at Imperial College London, wrote in a Twitter post.
The “apparent rapid growth and wide geographical spread” are “worth keeping a close eye on,” he said.
BA.2.75 has been found in a handful of cases in the United States, Australia, Canada, Germany, Japan, New Zealand, and the United Kingdom. In India, the sequence accounts for about 23% of recent samples.
“It is really too early to know if BA.2.75 will take over relative to BA.2 or even relative to BA.5,” Ulrich Elling, PhD, a researcher at Australia’s Institute of Molecular Biotechnology, wrote in a Twitter post.
“Just to emphasize it again: While the distribution across Indian regions as well as internationally and the very rapid appearance makes it likely we are dealing with a variant spreading fast and spread widely already, the absolute data points are few,” he said.
Globally, coronavirus cases have increased nearly 30% during the past 2 weeks, the WHO said July 6. Four out of six of the WHO subregions reported an increase in the last week, with BA.4 and BA.5 driving waves in the United States and Europe.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Doc releases song after racist massacre in Buffalo
Physician-musician Cleveland Francis, MD, responded to the recent mass shooting in Buffalo, New York, which left 10 dead, in the only way he knew how. He wrote and recorded a song to honor the victims as “a plea to the other side to recognize us as people,” the Black cardiologist told this news organization.
He couldn’t sleep after the shooting, and “this song was just in my head.” In the 1990s, Dr. Francis took a 3-year sabbatical from medicine to perform and tour as a country singer. He leveraged his Nashville connections to get “Buffalo” produced and recorded.
Acclaimed artist James Threalkill created the accompanying art, titled “The Heavenly Escort of the Buffalo 10,” after listening to a scratch demo.
Dr. Francis doesn’t want people to overlook the massacre as just another gun violence incident because this was “overt hate-crime racism,” he said.
According to the affidavit submitted by FBI agent Christopher J. Dlugokinski, the suspect’s “motive for the mass shooting was to prevent Black people from replacing White people and eliminating the White race, and to inspire others to commit similar attacks.”
Dr. Francis views the Buffalo shooting as distinct from cases like the murder of George Floyd that involved crime or police. It immediately made him think of the Mother Emanuel Church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina. “Having a black skin is now a death warrant,” he said.
The song is also an appeal for White people to fight racism. Dr. Francis is concerned about young men caught up in white supremacy and suggests that we be more alert to children or grandchildren who disconnect from their families, spend time on the dark web, and access guns. The lyrics deliberately don’t mention guns because Dr. Francis wanted to stay out of that debate. “I just sang: ‘What else do I have to do to prove to you that I’m human too?’ ”
Despite his country credentials, Dr. Francis wrote “Buffalo” as a Gospel song because that genre “connects with Black people more and because that civil rights movement was through the church with Dr. Martin Luther King,” he explained. Although he sings all styles of music, the song is performed by Nashville-based singer Michael Lusk so that it’s not a “Cleve Francis thing,” he said, referring to his stage name.
Songwriter Norman Kerner collaborated on the song. The music was produced and recorded by David Thein and mixed by Bob Bullock of Nashville, who Dr. Francis had worked with when he was an artist on Capitol Records.
They sent the video and artwork to the Mayor of Buffalo, Byron Brown, but have yet to hear back. Dr. Francis hopes it could be part of their healing, noting that some people used the song in their Juneteenth celebrations.
The Louisiana native grew up during segregation and was one of two Black students in the Medical College of Virginia class of 1973. After completing his cardiology fellowship, no one would hire him, so Dr. Francis set up his own practice in Northern Virginia. He now works at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Alexandria, Va. He remains optimistic about race relations in America and would love a Black pop or Gospel star to record “Buffalo” and bring it to a wider audience.
Dr. Francis is a regular blogger for Medscape. His contribution to country music is recognized in the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. You can find more of his music on YouTube.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician-musician Cleveland Francis, MD, responded to the recent mass shooting in Buffalo, New York, which left 10 dead, in the only way he knew how. He wrote and recorded a song to honor the victims as “a plea to the other side to recognize us as people,” the Black cardiologist told this news organization.
He couldn’t sleep after the shooting, and “this song was just in my head.” In the 1990s, Dr. Francis took a 3-year sabbatical from medicine to perform and tour as a country singer. He leveraged his Nashville connections to get “Buffalo” produced and recorded.
Acclaimed artist James Threalkill created the accompanying art, titled “The Heavenly Escort of the Buffalo 10,” after listening to a scratch demo.
Dr. Francis doesn’t want people to overlook the massacre as just another gun violence incident because this was “overt hate-crime racism,” he said.
According to the affidavit submitted by FBI agent Christopher J. Dlugokinski, the suspect’s “motive for the mass shooting was to prevent Black people from replacing White people and eliminating the White race, and to inspire others to commit similar attacks.”
Dr. Francis views the Buffalo shooting as distinct from cases like the murder of George Floyd that involved crime or police. It immediately made him think of the Mother Emanuel Church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina. “Having a black skin is now a death warrant,” he said.
The song is also an appeal for White people to fight racism. Dr. Francis is concerned about young men caught up in white supremacy and suggests that we be more alert to children or grandchildren who disconnect from their families, spend time on the dark web, and access guns. The lyrics deliberately don’t mention guns because Dr. Francis wanted to stay out of that debate. “I just sang: ‘What else do I have to do to prove to you that I’m human too?’ ”
Despite his country credentials, Dr. Francis wrote “Buffalo” as a Gospel song because that genre “connects with Black people more and because that civil rights movement was through the church with Dr. Martin Luther King,” he explained. Although he sings all styles of music, the song is performed by Nashville-based singer Michael Lusk so that it’s not a “Cleve Francis thing,” he said, referring to his stage name.
Songwriter Norman Kerner collaborated on the song. The music was produced and recorded by David Thein and mixed by Bob Bullock of Nashville, who Dr. Francis had worked with when he was an artist on Capitol Records.
They sent the video and artwork to the Mayor of Buffalo, Byron Brown, but have yet to hear back. Dr. Francis hopes it could be part of their healing, noting that some people used the song in their Juneteenth celebrations.
The Louisiana native grew up during segregation and was one of two Black students in the Medical College of Virginia class of 1973. After completing his cardiology fellowship, no one would hire him, so Dr. Francis set up his own practice in Northern Virginia. He now works at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Alexandria, Va. He remains optimistic about race relations in America and would love a Black pop or Gospel star to record “Buffalo” and bring it to a wider audience.
Dr. Francis is a regular blogger for Medscape. His contribution to country music is recognized in the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. You can find more of his music on YouTube.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Physician-musician Cleveland Francis, MD, responded to the recent mass shooting in Buffalo, New York, which left 10 dead, in the only way he knew how. He wrote and recorded a song to honor the victims as “a plea to the other side to recognize us as people,” the Black cardiologist told this news organization.
He couldn’t sleep after the shooting, and “this song was just in my head.” In the 1990s, Dr. Francis took a 3-year sabbatical from medicine to perform and tour as a country singer. He leveraged his Nashville connections to get “Buffalo” produced and recorded.
Acclaimed artist James Threalkill created the accompanying art, titled “The Heavenly Escort of the Buffalo 10,” after listening to a scratch demo.
Dr. Francis doesn’t want people to overlook the massacre as just another gun violence incident because this was “overt hate-crime racism,” he said.
According to the affidavit submitted by FBI agent Christopher J. Dlugokinski, the suspect’s “motive for the mass shooting was to prevent Black people from replacing White people and eliminating the White race, and to inspire others to commit similar attacks.”
Dr. Francis views the Buffalo shooting as distinct from cases like the murder of George Floyd that involved crime or police. It immediately made him think of the Mother Emanuel Church shooting in Charleston, South Carolina. “Having a black skin is now a death warrant,” he said.
The song is also an appeal for White people to fight racism. Dr. Francis is concerned about young men caught up in white supremacy and suggests that we be more alert to children or grandchildren who disconnect from their families, spend time on the dark web, and access guns. The lyrics deliberately don’t mention guns because Dr. Francis wanted to stay out of that debate. “I just sang: ‘What else do I have to do to prove to you that I’m human too?’ ”
Despite his country credentials, Dr. Francis wrote “Buffalo” as a Gospel song because that genre “connects with Black people more and because that civil rights movement was through the church with Dr. Martin Luther King,” he explained. Although he sings all styles of music, the song is performed by Nashville-based singer Michael Lusk so that it’s not a “Cleve Francis thing,” he said, referring to his stage name.
Songwriter Norman Kerner collaborated on the song. The music was produced and recorded by David Thein and mixed by Bob Bullock of Nashville, who Dr. Francis had worked with when he was an artist on Capitol Records.
They sent the video and artwork to the Mayor of Buffalo, Byron Brown, but have yet to hear back. Dr. Francis hopes it could be part of their healing, noting that some people used the song in their Juneteenth celebrations.
The Louisiana native grew up during segregation and was one of two Black students in the Medical College of Virginia class of 1973. After completing his cardiology fellowship, no one would hire him, so Dr. Francis set up his own practice in Northern Virginia. He now works at Inova Heart and Vascular Institute in Alexandria, Va. He remains optimistic about race relations in America and would love a Black pop or Gospel star to record “Buffalo” and bring it to a wider audience.
Dr. Francis is a regular blogger for Medscape. His contribution to country music is recognized in the National Museum of African American History and Culture in Washington, DC. You can find more of his music on YouTube.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
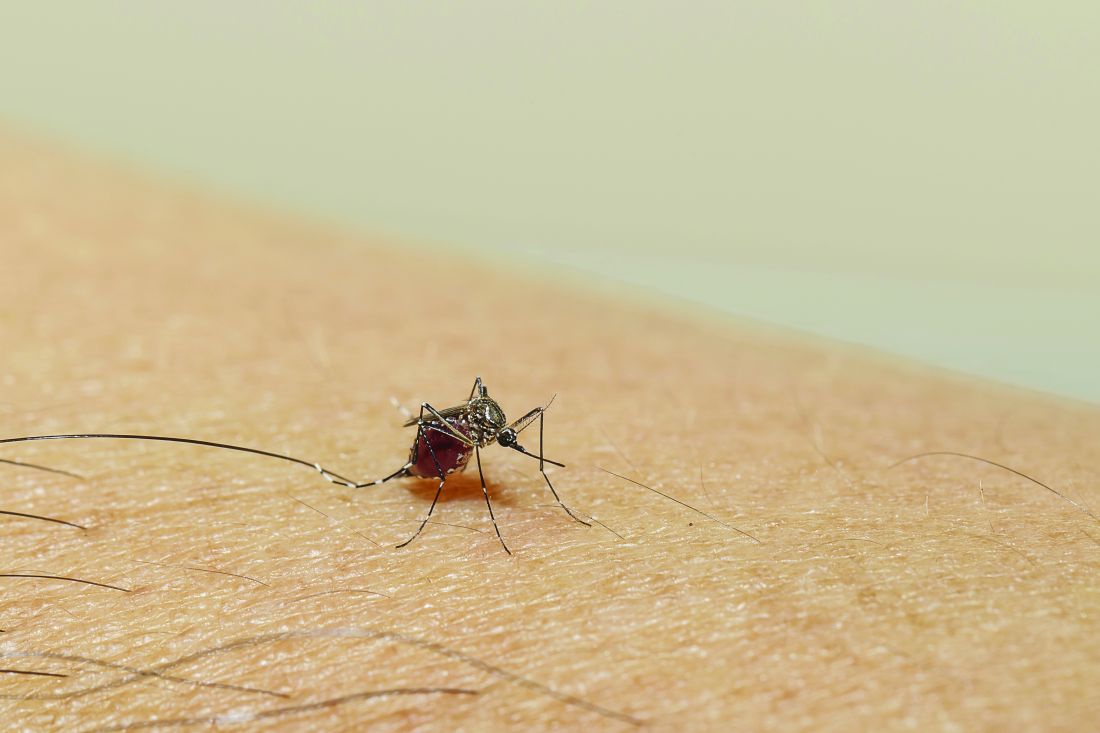
Mosquitoes and the vicious circle that’s gone viral
These viruses want mosquitoes with good taste
Taste can be a pretty subjective sense. Not everyone agrees on what tastes good and what tastes bad. Most people would agree that freshly baked cookies taste good, but what about lima beans? And what about mosquitoes? What tastes good to a mosquito?
The answer? Blood. Blood tastes good to a mosquito. That really wasn’t a very hard question, was it? You did know the answer, didn’t you? They don’t care about cookies, and they certainly don’t care about lima beans. It’s blood that they love.
That brings us back to subjectivity, because it is possible for blood to taste even better. The secret ingredient is dengue … and Zika.
A study just published in Cell demonstrates that mice infected with dengue and Zika viruses release a volatile compound called acetophenone. “We found that flavivirus [like dengue and Zika] can utilize the increased release of acetophenone to help itself achieve its lifecycles more effectively by making their hosts more attractive to mosquito vectors,” senior author Gong Cheng of Tsinghua University, Beijing, said in a written statement.
How do they do it? The viruses, he explained, promote the proliferation of acetophenone-producing skin bacteria. “As a result, some bacteria overreplicate and produce more acetophenone. Suddenly, these sick individuals smell as delicious to mosquitoes as a tray of freshly baked cookies to a group of five-year-old children,” the statement said.
And how do you stop a group of tiny, flying 5-year-olds? That’s right, with acne medication. Really? You knew that one but not the blood one before? The investigators fed isotretinoin to the infected mice, which led to reduced acetophenone release from skin bacteria and made the animals no more attractive to the mosquitoes than their uninfected counterparts.
The investigators are planning to take the next step – feeding isotretinoin to people with dengue and Zika – having gotten the official fictional taste-test approval of celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay, who said, “You’re going to feed this #$^% to sick people? ARE YOU &%*$@#& KIDDING ME?”
Okay, so maybe approval isn’t quite the right word.
Welcome to bladders of the rich and famous!
Don’t you hate it when you’re driving out to your multimillion-dollar second home in the Hamptons and traffic is so bad you absolutely have to find a place to “rest” along the way? But wouldn’t you know it, there just isn’t anywhere to stop! Geez, how do we live?
That’s where David Shusterman, MD, a urologist in New York City and a true American hero, comes in. He’s identified a market and positioned himself as the king of both bladder surgery and “bladder Botox” for the wealthy New Yorkers who regularly make long journeys from the city out to their second homes in the Hamptons. Traffic has increased dramatically on Long Island roads in recent years, and the journey can now taking upward of 4 hours. Some people just can’t make it that long without a bathroom break, and there are very few places to stop along the way.
Dr. Shusterman understands the plight of the Hamptons vacationer, as he told Insider.com: “I can’t tell you how many arguments I personally get into – I’ve lost three friends because I’m the driver and refuse to stop for them.” A tragedy worthy of Shakespeare himself.
During the summer season, Dr. Shusterman performs about 10 prostate artery embolizations a week, an hour-long procedure that shrinks the prostate, which is great for 50- to 60-year-old men with enlarged prostates that cause more frequent bathroom trips. He also performs Botox injections into the bladder once or twice a week for women, which reduces the need to urinate for roughly 6 months. The perfect amount of time to get them through the summer season.
These procedures are sometimes covered by insurance but can cost as much as $20,000 if paid out of pocket. That’s a lot of money to us, but if you’re the sort of person who has a second home in the Hamptons, $20,000 is chump change, especially if it means you won’t have to go 2 entire minutes out of your way to use a gas-station bathroom. Then again, having seen a more than a few gas-station bathrooms in our time, maybe they have a point.
Ditch the apples. Go for the avocados
We’ve all heard about “an apple a day,” but instead of apples you might want to go with avocados.
Avocados are generally thought to be a healthy fat. A study just published in the Journal of the American Heart Association proves that they actually don’t do anything for your waistline but will work wonders on your cholesterol level. The study involved 923 participants who were considered overweight/obese split into two groups: One was asked to consume an avocado a day, and the other continued their usual diets and were asked to consume fewer than two avocados a month.
At the end of the 6 months, the researchers found total cholesterol decreased by an additional 2.9 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by 2.5 mg/dL in those who ate one avocado every day, compared with the usual-diet group. And even though avocados have a lot of calories, there was no clinical evidence that it impacted weight gain or any cardiometabolic risk factors, according to a statement from Penn State University.
Avocados, then, can be considered a guilt-free food. The findings from this study suggest it can give a substantial boost to your overall quality of diet, in turn lessening your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and some cancers, Kristina Peterson, PhD, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, said in the statement.
So get creative with your avocado recipes. You can only eat so much guacamole.
Your nose knows a good friend for you
You’ve probably noticed how dogs sniff other dogs and people before becoming friends. It would be pretty comical if people did the same thing, right? Just walked up to strangers and started sniffing them like dogs?
Well, apparently humans do go by smell when it comes to making friends, and they prefer people who smell like them. Maybe you’ve noticed that your friends look like you, share your values, and think the same way as you. You’re probably right, seeing as previous research has pointed to this.
For the current study, done to show how smell affects human behavior, researchers recruited people who befriended each other quickly, before knowing much about each other. They assumed that the relationships between these same-sex, nonromantic “click friends” relied more on physiological traits, including smell. After collecting samples from the click friends, researchers used an eNose to scan chemical signatures. In another experiment, human volunteers sniffed samples to determine if any were similar. Both experiments showed that click friends had more similar smells than pairs of random people.
“This is not to say that we act like goats or shrews – humans likely rely on other, far more dominant cues in their social decision-making. Nevertheless, our study’s results do suggest that our nose plays a bigger role than previously thought in our choice of friends,” said senior author Noam Sobel, PhD, of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Lead author Inbal Ravreby, a graduate student at the institute, put it this way: “These results imply that, as the saying goes, there is chemistry in social chemistry.”
These viruses want mosquitoes with good taste
Taste can be a pretty subjective sense. Not everyone agrees on what tastes good and what tastes bad. Most people would agree that freshly baked cookies taste good, but what about lima beans? And what about mosquitoes? What tastes good to a mosquito?
The answer? Blood. Blood tastes good to a mosquito. That really wasn’t a very hard question, was it? You did know the answer, didn’t you? They don’t care about cookies, and they certainly don’t care about lima beans. It’s blood that they love.
That brings us back to subjectivity, because it is possible for blood to taste even better. The secret ingredient is dengue … and Zika.
A study just published in Cell demonstrates that mice infected with dengue and Zika viruses release a volatile compound called acetophenone. “We found that flavivirus [like dengue and Zika] can utilize the increased release of acetophenone to help itself achieve its lifecycles more effectively by making their hosts more attractive to mosquito vectors,” senior author Gong Cheng of Tsinghua University, Beijing, said in a written statement.
How do they do it? The viruses, he explained, promote the proliferation of acetophenone-producing skin bacteria. “As a result, some bacteria overreplicate and produce more acetophenone. Suddenly, these sick individuals smell as delicious to mosquitoes as a tray of freshly baked cookies to a group of five-year-old children,” the statement said.
And how do you stop a group of tiny, flying 5-year-olds? That’s right, with acne medication. Really? You knew that one but not the blood one before? The investigators fed isotretinoin to the infected mice, which led to reduced acetophenone release from skin bacteria and made the animals no more attractive to the mosquitoes than their uninfected counterparts.
The investigators are planning to take the next step – feeding isotretinoin to people with dengue and Zika – having gotten the official fictional taste-test approval of celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay, who said, “You’re going to feed this #$^% to sick people? ARE YOU &%*$@#& KIDDING ME?”
Okay, so maybe approval isn’t quite the right word.
Welcome to bladders of the rich and famous!
Don’t you hate it when you’re driving out to your multimillion-dollar second home in the Hamptons and traffic is so bad you absolutely have to find a place to “rest” along the way? But wouldn’t you know it, there just isn’t anywhere to stop! Geez, how do we live?
That’s where David Shusterman, MD, a urologist in New York City and a true American hero, comes in. He’s identified a market and positioned himself as the king of both bladder surgery and “bladder Botox” for the wealthy New Yorkers who regularly make long journeys from the city out to their second homes in the Hamptons. Traffic has increased dramatically on Long Island roads in recent years, and the journey can now taking upward of 4 hours. Some people just can’t make it that long without a bathroom break, and there are very few places to stop along the way.
Dr. Shusterman understands the plight of the Hamptons vacationer, as he told Insider.com: “I can’t tell you how many arguments I personally get into – I’ve lost three friends because I’m the driver and refuse to stop for them.” A tragedy worthy of Shakespeare himself.
During the summer season, Dr. Shusterman performs about 10 prostate artery embolizations a week, an hour-long procedure that shrinks the prostate, which is great for 50- to 60-year-old men with enlarged prostates that cause more frequent bathroom trips. He also performs Botox injections into the bladder once or twice a week for women, which reduces the need to urinate for roughly 6 months. The perfect amount of time to get them through the summer season.
These procedures are sometimes covered by insurance but can cost as much as $20,000 if paid out of pocket. That’s a lot of money to us, but if you’re the sort of person who has a second home in the Hamptons, $20,000 is chump change, especially if it means you won’t have to go 2 entire minutes out of your way to use a gas-station bathroom. Then again, having seen a more than a few gas-station bathrooms in our time, maybe they have a point.
Ditch the apples. Go for the avocados
We’ve all heard about “an apple a day,” but instead of apples you might want to go with avocados.
Avocados are generally thought to be a healthy fat. A study just published in the Journal of the American Heart Association proves that they actually don’t do anything for your waistline but will work wonders on your cholesterol level. The study involved 923 participants who were considered overweight/obese split into two groups: One was asked to consume an avocado a day, and the other continued their usual diets and were asked to consume fewer than two avocados a month.
At the end of the 6 months, the researchers found total cholesterol decreased by an additional 2.9 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by 2.5 mg/dL in those who ate one avocado every day, compared with the usual-diet group. And even though avocados have a lot of calories, there was no clinical evidence that it impacted weight gain or any cardiometabolic risk factors, according to a statement from Penn State University.
Avocados, then, can be considered a guilt-free food. The findings from this study suggest it can give a substantial boost to your overall quality of diet, in turn lessening your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and some cancers, Kristina Peterson, PhD, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, said in the statement.
So get creative with your avocado recipes. You can only eat so much guacamole.
Your nose knows a good friend for you
You’ve probably noticed how dogs sniff other dogs and people before becoming friends. It would be pretty comical if people did the same thing, right? Just walked up to strangers and started sniffing them like dogs?
Well, apparently humans do go by smell when it comes to making friends, and they prefer people who smell like them. Maybe you’ve noticed that your friends look like you, share your values, and think the same way as you. You’re probably right, seeing as previous research has pointed to this.
For the current study, done to show how smell affects human behavior, researchers recruited people who befriended each other quickly, before knowing much about each other. They assumed that the relationships between these same-sex, nonromantic “click friends” relied more on physiological traits, including smell. After collecting samples from the click friends, researchers used an eNose to scan chemical signatures. In another experiment, human volunteers sniffed samples to determine if any were similar. Both experiments showed that click friends had more similar smells than pairs of random people.
“This is not to say that we act like goats or shrews – humans likely rely on other, far more dominant cues in their social decision-making. Nevertheless, our study’s results do suggest that our nose plays a bigger role than previously thought in our choice of friends,” said senior author Noam Sobel, PhD, of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Lead author Inbal Ravreby, a graduate student at the institute, put it this way: “These results imply that, as the saying goes, there is chemistry in social chemistry.”
These viruses want mosquitoes with good taste
Taste can be a pretty subjective sense. Not everyone agrees on what tastes good and what tastes bad. Most people would agree that freshly baked cookies taste good, but what about lima beans? And what about mosquitoes? What tastes good to a mosquito?
The answer? Blood. Blood tastes good to a mosquito. That really wasn’t a very hard question, was it? You did know the answer, didn’t you? They don’t care about cookies, and they certainly don’t care about lima beans. It’s blood that they love.
That brings us back to subjectivity, because it is possible for blood to taste even better. The secret ingredient is dengue … and Zika.
A study just published in Cell demonstrates that mice infected with dengue and Zika viruses release a volatile compound called acetophenone. “We found that flavivirus [like dengue and Zika] can utilize the increased release of acetophenone to help itself achieve its lifecycles more effectively by making their hosts more attractive to mosquito vectors,” senior author Gong Cheng of Tsinghua University, Beijing, said in a written statement.
How do they do it? The viruses, he explained, promote the proliferation of acetophenone-producing skin bacteria. “As a result, some bacteria overreplicate and produce more acetophenone. Suddenly, these sick individuals smell as delicious to mosquitoes as a tray of freshly baked cookies to a group of five-year-old children,” the statement said.
And how do you stop a group of tiny, flying 5-year-olds? That’s right, with acne medication. Really? You knew that one but not the blood one before? The investigators fed isotretinoin to the infected mice, which led to reduced acetophenone release from skin bacteria and made the animals no more attractive to the mosquitoes than their uninfected counterparts.
The investigators are planning to take the next step – feeding isotretinoin to people with dengue and Zika – having gotten the official fictional taste-test approval of celebrity chef Gordon Ramsay, who said, “You’re going to feed this #$^% to sick people? ARE YOU &%*$@#& KIDDING ME?”
Okay, so maybe approval isn’t quite the right word.
Welcome to bladders of the rich and famous!
Don’t you hate it when you’re driving out to your multimillion-dollar second home in the Hamptons and traffic is so bad you absolutely have to find a place to “rest” along the way? But wouldn’t you know it, there just isn’t anywhere to stop! Geez, how do we live?
That’s where David Shusterman, MD, a urologist in New York City and a true American hero, comes in. He’s identified a market and positioned himself as the king of both bladder surgery and “bladder Botox” for the wealthy New Yorkers who regularly make long journeys from the city out to their second homes in the Hamptons. Traffic has increased dramatically on Long Island roads in recent years, and the journey can now taking upward of 4 hours. Some people just can’t make it that long without a bathroom break, and there are very few places to stop along the way.
Dr. Shusterman understands the plight of the Hamptons vacationer, as he told Insider.com: “I can’t tell you how many arguments I personally get into – I’ve lost three friends because I’m the driver and refuse to stop for them.” A tragedy worthy of Shakespeare himself.
During the summer season, Dr. Shusterman performs about 10 prostate artery embolizations a week, an hour-long procedure that shrinks the prostate, which is great for 50- to 60-year-old men with enlarged prostates that cause more frequent bathroom trips. He also performs Botox injections into the bladder once or twice a week for women, which reduces the need to urinate for roughly 6 months. The perfect amount of time to get them through the summer season.
These procedures are sometimes covered by insurance but can cost as much as $20,000 if paid out of pocket. That’s a lot of money to us, but if you’re the sort of person who has a second home in the Hamptons, $20,000 is chump change, especially if it means you won’t have to go 2 entire minutes out of your way to use a gas-station bathroom. Then again, having seen a more than a few gas-station bathrooms in our time, maybe they have a point.
Ditch the apples. Go for the avocados
We’ve all heard about “an apple a day,” but instead of apples you might want to go with avocados.
Avocados are generally thought to be a healthy fat. A study just published in the Journal of the American Heart Association proves that they actually don’t do anything for your waistline but will work wonders on your cholesterol level. The study involved 923 participants who were considered overweight/obese split into two groups: One was asked to consume an avocado a day, and the other continued their usual diets and were asked to consume fewer than two avocados a month.
At the end of the 6 months, the researchers found total cholesterol decreased by an additional 2.9 mg/dL and LDL cholesterol by 2.5 mg/dL in those who ate one avocado every day, compared with the usual-diet group. And even though avocados have a lot of calories, there was no clinical evidence that it impacted weight gain or any cardiometabolic risk factors, according to a statement from Penn State University.
Avocados, then, can be considered a guilt-free food. The findings from this study suggest it can give a substantial boost to your overall quality of diet, in turn lessening your risk of developing type 2 diabetes and some cancers, Kristina Peterson, PhD, assistant professor of nutritional sciences at Texas Tech University, said in the statement.
So get creative with your avocado recipes. You can only eat so much guacamole.
Your nose knows a good friend for you
You’ve probably noticed how dogs sniff other dogs and people before becoming friends. It would be pretty comical if people did the same thing, right? Just walked up to strangers and started sniffing them like dogs?
Well, apparently humans do go by smell when it comes to making friends, and they prefer people who smell like them. Maybe you’ve noticed that your friends look like you, share your values, and think the same way as you. You’re probably right, seeing as previous research has pointed to this.
For the current study, done to show how smell affects human behavior, researchers recruited people who befriended each other quickly, before knowing much about each other. They assumed that the relationships between these same-sex, nonromantic “click friends” relied more on physiological traits, including smell. After collecting samples from the click friends, researchers used an eNose to scan chemical signatures. In another experiment, human volunteers sniffed samples to determine if any were similar. Both experiments showed that click friends had more similar smells than pairs of random people.
“This is not to say that we act like goats or shrews – humans likely rely on other, far more dominant cues in their social decision-making. Nevertheless, our study’s results do suggest that our nose plays a bigger role than previously thought in our choice of friends,” said senior author Noam Sobel, PhD, of the Weizmann Institute of Science in Rehovot, Israel.
Lead author Inbal Ravreby, a graduate student at the institute, put it this way: “These results imply that, as the saying goes, there is chemistry in social chemistry.”
‘Not their fault:’ Obesity warrants long-term management
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s important to remember and to think about the first time when patients with obesity come to see us: What have they faced? What have been their struggles? What shame and blame and bias have they faced?
One of the first things that I do when a patient comes to see me is invite them to share their weight journey with me. I ask them to tell me about their struggles, about what’s worked and what hasn’t worked, what they would like, and what their health goals are.
As they share their stories, I look for the opportunity to share with them that obesity is not their fault, but that it’s biology driving their body to carry extra weight and their body is super smart. Neither their body nor their brain want them to starve.
Our bodies evolved during a time where there was food scarcity and the potential of famine. We have a complex system that was designed to make sure that we always held on to extra weight, specifically extra fat, because that’s how we store energy. In the current obesogenic environment, what happens is our bodies carry extra weight, or specifically, extra fat.
Again, I say to them, this is biology. Your body’s doing exactly what it was designed to do. Your body’s very smart, but now we have to figure out how to help your body want to carry less fat because it is impacting your health. This is not your fault. Having obesity is not your fault any more than having diabetes or hypertension is anyone’s fault. Now it’s time for all of us to use highly effective tools that target the pathophysiology of obesity.
When a patient comes to me for weight management or to help them treat their obesity, I listen to them, and I look for clues as to what might help that specific patient. Every patient deserves to have individualized treatment. One medicine may be right for one person, another medicine may be right for another, and surgery may be right for another patient. I really try to listen and hear what that patient is telling me.
What we as providers really need is tools – different options – to be able to provide for our patients and basically present them with different options, and then guide them toward the best therapy for them. Whether it’s semaglutide or tirzepatide potentially in the future, these types of medications are excellent options for our patients. They’re highly effective tools with safe profiles.
A question that I often get from providers or patients is, “Well, Doctor, I’ve lost the weight now. How long should I take this medicine? Can I stop it now?”
Then, we have a conversation, and we actually usually have this conversation even before we start the medicine. Basically, we talk about the fact that obesity is a chronic disease. There’s no cure for obesity. Because it’s a chronic disease, we need to treat it like we would treat any other chronic disease.
The example that I often use is, if you have a patient who has hypertension and you start them on an antihypertensive medication, what happens? Their blood pressure goes down. It improves. Now, if their blood pressure is improved with a specific antihypertensive, would you stop that medicine? What would happen if you stopped that antihypertensive? Well, their blood pressure would go up, and we wouldn’t be surprised.
In the same way, if you have a patient who has obesity and you start that patient on an antiobesity medication, and their weight decreases, and their body fat mass at that point decreases, what would happen if you stop that medicine? They lost the weight, but you stop the medicine. Well, their weight gain comes back. They regain the weight.
We should not be surprised that weight gain occurs when we stop the treatment. That really underscores the fact that treatment needs to be continued. If a patient is started on an antiobesity medication and they lose weight, that medication needs to be continued to maintain that weight loss.
Basically, we eat food and our body responds by releasing these hormones. The hormones are made in our gut and in our pancreas and these hormones inform our brain. Are we hungry? Are we full? Where are we with our homeostatic set point of fat mass? Based on that, our brain is like the sensor or the thermostat.
Obesity is a chronic, treatable disease. We should treat obesity as we treat any other chronic disease, with effective and safe approaches that target underlying disease mechanisms. These results in the SURMOUNT-1 trial underscore that tirzepatide may be doing just that. Remarkably, 9 in 10 individuals with obesity lost weight while taking tirzepatide. These results are impressive. They’re an important step forward in potentially expanding effective therapeutic options for people with obesity.
Dr. Jastreboff is an associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of weight management and obesity prevention at Yale Stress Center. She reported conducting trials with Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals; serving on scientific advisory boards for Ely Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and WW; and consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim and Scholar Rock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s important to remember and to think about the first time when patients with obesity come to see us: What have they faced? What have been their struggles? What shame and blame and bias have they faced?
One of the first things that I do when a patient comes to see me is invite them to share their weight journey with me. I ask them to tell me about their struggles, about what’s worked and what hasn’t worked, what they would like, and what their health goals are.
As they share their stories, I look for the opportunity to share with them that obesity is not their fault, but that it’s biology driving their body to carry extra weight and their body is super smart. Neither their body nor their brain want them to starve.
Our bodies evolved during a time where there was food scarcity and the potential of famine. We have a complex system that was designed to make sure that we always held on to extra weight, specifically extra fat, because that’s how we store energy. In the current obesogenic environment, what happens is our bodies carry extra weight, or specifically, extra fat.
Again, I say to them, this is biology. Your body’s doing exactly what it was designed to do. Your body’s very smart, but now we have to figure out how to help your body want to carry less fat because it is impacting your health. This is not your fault. Having obesity is not your fault any more than having diabetes or hypertension is anyone’s fault. Now it’s time for all of us to use highly effective tools that target the pathophysiology of obesity.
When a patient comes to me for weight management or to help them treat their obesity, I listen to them, and I look for clues as to what might help that specific patient. Every patient deserves to have individualized treatment. One medicine may be right for one person, another medicine may be right for another, and surgery may be right for another patient. I really try to listen and hear what that patient is telling me.
What we as providers really need is tools – different options – to be able to provide for our patients and basically present them with different options, and then guide them toward the best therapy for them. Whether it’s semaglutide or tirzepatide potentially in the future, these types of medications are excellent options for our patients. They’re highly effective tools with safe profiles.
A question that I often get from providers or patients is, “Well, Doctor, I’ve lost the weight now. How long should I take this medicine? Can I stop it now?”
Then, we have a conversation, and we actually usually have this conversation even before we start the medicine. Basically, we talk about the fact that obesity is a chronic disease. There’s no cure for obesity. Because it’s a chronic disease, we need to treat it like we would treat any other chronic disease.
The example that I often use is, if you have a patient who has hypertension and you start them on an antihypertensive medication, what happens? Their blood pressure goes down. It improves. Now, if their blood pressure is improved with a specific antihypertensive, would you stop that medicine? What would happen if you stopped that antihypertensive? Well, their blood pressure would go up, and we wouldn’t be surprised.
In the same way, if you have a patient who has obesity and you start that patient on an antiobesity medication, and their weight decreases, and their body fat mass at that point decreases, what would happen if you stop that medicine? They lost the weight, but you stop the medicine. Well, their weight gain comes back. They regain the weight.
We should not be surprised that weight gain occurs when we stop the treatment. That really underscores the fact that treatment needs to be continued. If a patient is started on an antiobesity medication and they lose weight, that medication needs to be continued to maintain that weight loss.
Basically, we eat food and our body responds by releasing these hormones. The hormones are made in our gut and in our pancreas and these hormones inform our brain. Are we hungry? Are we full? Where are we with our homeostatic set point of fat mass? Based on that, our brain is like the sensor or the thermostat.
Obesity is a chronic, treatable disease. We should treat obesity as we treat any other chronic disease, with effective and safe approaches that target underlying disease mechanisms. These results in the SURMOUNT-1 trial underscore that tirzepatide may be doing just that. Remarkably, 9 in 10 individuals with obesity lost weight while taking tirzepatide. These results are impressive. They’re an important step forward in potentially expanding effective therapeutic options for people with obesity.
Dr. Jastreboff is an associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of weight management and obesity prevention at Yale Stress Center. She reported conducting trials with Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals; serving on scientific advisory boards for Ely Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and WW; and consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim and Scholar Rock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
This transcript has been edited for clarity.
It’s important to remember and to think about the first time when patients with obesity come to see us: What have they faced? What have been their struggles? What shame and blame and bias have they faced?
One of the first things that I do when a patient comes to see me is invite them to share their weight journey with me. I ask them to tell me about their struggles, about what’s worked and what hasn’t worked, what they would like, and what their health goals are.
As they share their stories, I look for the opportunity to share with them that obesity is not their fault, but that it’s biology driving their body to carry extra weight and their body is super smart. Neither their body nor their brain want them to starve.
Our bodies evolved during a time where there was food scarcity and the potential of famine. We have a complex system that was designed to make sure that we always held on to extra weight, specifically extra fat, because that’s how we store energy. In the current obesogenic environment, what happens is our bodies carry extra weight, or specifically, extra fat.
Again, I say to them, this is biology. Your body’s doing exactly what it was designed to do. Your body’s very smart, but now we have to figure out how to help your body want to carry less fat because it is impacting your health. This is not your fault. Having obesity is not your fault any more than having diabetes or hypertension is anyone’s fault. Now it’s time for all of us to use highly effective tools that target the pathophysiology of obesity.
When a patient comes to me for weight management or to help them treat their obesity, I listen to them, and I look for clues as to what might help that specific patient. Every patient deserves to have individualized treatment. One medicine may be right for one person, another medicine may be right for another, and surgery may be right for another patient. I really try to listen and hear what that patient is telling me.
What we as providers really need is tools – different options – to be able to provide for our patients and basically present them with different options, and then guide them toward the best therapy for them. Whether it’s semaglutide or tirzepatide potentially in the future, these types of medications are excellent options for our patients. They’re highly effective tools with safe profiles.
A question that I often get from providers or patients is, “Well, Doctor, I’ve lost the weight now. How long should I take this medicine? Can I stop it now?”
Then, we have a conversation, and we actually usually have this conversation even before we start the medicine. Basically, we talk about the fact that obesity is a chronic disease. There’s no cure for obesity. Because it’s a chronic disease, we need to treat it like we would treat any other chronic disease.
The example that I often use is, if you have a patient who has hypertension and you start them on an antihypertensive medication, what happens? Their blood pressure goes down. It improves. Now, if their blood pressure is improved with a specific antihypertensive, would you stop that medicine? What would happen if you stopped that antihypertensive? Well, their blood pressure would go up, and we wouldn’t be surprised.
In the same way, if you have a patient who has obesity and you start that patient on an antiobesity medication, and their weight decreases, and their body fat mass at that point decreases, what would happen if you stop that medicine? They lost the weight, but you stop the medicine. Well, their weight gain comes back. They regain the weight.
We should not be surprised that weight gain occurs when we stop the treatment. That really underscores the fact that treatment needs to be continued. If a patient is started on an antiobesity medication and they lose weight, that medication needs to be continued to maintain that weight loss.
Basically, we eat food and our body responds by releasing these hormones. The hormones are made in our gut and in our pancreas and these hormones inform our brain. Are we hungry? Are we full? Where are we with our homeostatic set point of fat mass? Based on that, our brain is like the sensor or the thermostat.
Obesity is a chronic, treatable disease. We should treat obesity as we treat any other chronic disease, with effective and safe approaches that target underlying disease mechanisms. These results in the SURMOUNT-1 trial underscore that tirzepatide may be doing just that. Remarkably, 9 in 10 individuals with obesity lost weight while taking tirzepatide. These results are impressive. They’re an important step forward in potentially expanding effective therapeutic options for people with obesity.
Dr. Jastreboff is an associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Yale University, New Haven, Conn., and director of weight management and obesity prevention at Yale Stress Center. She reported conducting trials with Eli Lilly, Novo Nordisk, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals; serving on scientific advisory boards for Ely Lilly, Intellihealth, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Rhythm Pharmaceuticals, and WW; and consulting for Boehringer Ingelheim and Scholar Rock.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Access to certified stroke centers divided by race, income
Hospitals in low-income and rural areas of the United States are much less likely to adopt stroke certification than hospitals in high-income and urban communities, a new study shows.
Further, other results showed that, after adjustment for population and hospital size, access to stroke-certified hospitals is significantly lower in Black, racially segregated communities.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Noting that stroke-certified hospitals provide higher-quality stroke care, the authors, led by Yu-Chu Shen, PhD, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif., conclude that: “Our findings suggest that structural inequities in stroke care may be an important consideration in eliminating stroke disparities for vulnerable populations.”
In an audio interview on the JAMA Neurology website, senior author Renee Y. Hsia, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said: “Our findings show there are clear disparities in which communities are getting access to stroke certified hospitals.”
She called for more help for hospitals in underserved areas to obtain stroke certification.
Dr. Hsia explained that hospitals can seek certification at their own expense and that although stroke care is expensive, it is also lucrative in terms of reimbursement. So it tends to be the private for-profit hospitals that seek these certifications. “If you are a county hospital on a really tight budget, you’re not going to have the extra cash on hand to be applying for stroke certification,” she commented.
This can result in an increase in hospitals with stroke certification – but not in the areas that need it the most.
Dr. Hsia points out that this has happened in cardiac care. One study showed a 44% increase in hospitals providing percutaneous coronary intervention over a 10-year period, but the percentage of the population that had better access increased by less than 1%.
“In general, in the United States we have a mentality that ‘more is better,’ and because there is no government regulation in health care, any time a hospital applies for these specialized services we just generally think that’s a good thing. But this might not always be the case,” Dr. Hsia noted. “We have a very market-based approach, and this doesn’t lead to equity. It leads to profit maximization, and that is not synonymous with what’s good for patients or populations.”
She suggested that in future the process of certification should include some consideration of how it will affect population-based equity.
“Rather than rubber stamping an application just because hospitals have certain resources, we need to ask what the benefit is of providing this service,” Dr. Hsia said. “Does this community really need it? If not, maybe we should invest these resources into helping a hospital in a community that needs it more.”
Dr. Hsia explained that she and her colleagues conducted their study to investigate whether there were structural issues that might be contributing to disparities in stroke care.
“We like to think emergency stroke care is equitable. Anyone can call 911 or go the emergency room. But, actually, there is a big disparity on who receives what type of care,” she said. “We know Black patients are less likely to receive thrombolytics and mechanical thrombectomy compared to White patents. And wealthy patients are more likely to receive thrombectomy compared to patients from the poorest zip codes.”
She said there is a tendency to think this is a result of some sort of bias on the part of health care professionals. “We wanted to look deep down in the system and whether the built environment of health care supply and geographic distribution of services contributed to access and treatment inequities.”
The study combined a dataset of hospital stroke certification from all general acute nonfederal hospitals in the continental United States from January 2009 to December 2019. National, hospital, and census data were used to identify historically underserved communities by racial and ethnic composition, income distribution, and rurality.
A total of 4,984 hospitals were assessed. Results showed that over the 11-year study period, the number of hospitals with stroke certification grew from 961 (19%) to 1,763 (36%).
Without controlling for population and hospital size, hospitals in predominantly Black, racially segregated areas were 1.67-fold more likely to adopt stroke care of any level than those in predominantly non-Black, racially segregated areas (hazard ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-1.97).
However, after adjustment for population and hospital size, the likelihood of adopting stroke care among hospitals serving Black, racially segregated communities was significantly lower than among those serving non-Black, racially segregated communities (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.62-0.89).
“In other words, on a per-capita basis, a hospital serving a predominantly Black, racially segregated community was 26% less likely to adopt stroke certification of any level than a hospital in a predominantly non-Black, racially segregated community,” the authors state.
In terms of socioeconomic factors, hospitals serving low-income, economically integrated (HR, 0.23) and low-income, economically segregated (HR, 0.29) areas were far less likely to adopt any level of stroke care certification than hospitals serving high-income areas, regardless of income segregation.
Rural hospitals were also much less likely to adopt any level of stroke care than urban hospitals (HR, 0.10).
“Our results suggest that it might be necessary to incentivize hospitals operating in underserved communities to seek stroke certification or to entice hospitals with higher propensity to adopt stroke care to operate in such communities so access at the per-patient level becomes more equitable,” the authors say.
This project was supported by the Pilot Project Award from the National Bureau of Economic Research Center for Aging and Health Research, funded by the National Institute on Aging and by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Shen and Dr. Hsia have received grants from the National Institute of Aging and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals in low-income and rural areas of the United States are much less likely to adopt stroke certification than hospitals in high-income and urban communities, a new study shows.
Further, other results showed that, after adjustment for population and hospital size, access to stroke-certified hospitals is significantly lower in Black, racially segregated communities.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Noting that stroke-certified hospitals provide higher-quality stroke care, the authors, led by Yu-Chu Shen, PhD, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif., conclude that: “Our findings suggest that structural inequities in stroke care may be an important consideration in eliminating stroke disparities for vulnerable populations.”
In an audio interview on the JAMA Neurology website, senior author Renee Y. Hsia, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said: “Our findings show there are clear disparities in which communities are getting access to stroke certified hospitals.”
She called for more help for hospitals in underserved areas to obtain stroke certification.
Dr. Hsia explained that hospitals can seek certification at their own expense and that although stroke care is expensive, it is also lucrative in terms of reimbursement. So it tends to be the private for-profit hospitals that seek these certifications. “If you are a county hospital on a really tight budget, you’re not going to have the extra cash on hand to be applying for stroke certification,” she commented.
This can result in an increase in hospitals with stroke certification – but not in the areas that need it the most.
Dr. Hsia points out that this has happened in cardiac care. One study showed a 44% increase in hospitals providing percutaneous coronary intervention over a 10-year period, but the percentage of the population that had better access increased by less than 1%.
“In general, in the United States we have a mentality that ‘more is better,’ and because there is no government regulation in health care, any time a hospital applies for these specialized services we just generally think that’s a good thing. But this might not always be the case,” Dr. Hsia noted. “We have a very market-based approach, and this doesn’t lead to equity. It leads to profit maximization, and that is not synonymous with what’s good for patients or populations.”
She suggested that in future the process of certification should include some consideration of how it will affect population-based equity.
“Rather than rubber stamping an application just because hospitals have certain resources, we need to ask what the benefit is of providing this service,” Dr. Hsia said. “Does this community really need it? If not, maybe we should invest these resources into helping a hospital in a community that needs it more.”
Dr. Hsia explained that she and her colleagues conducted their study to investigate whether there were structural issues that might be contributing to disparities in stroke care.
“We like to think emergency stroke care is equitable. Anyone can call 911 or go the emergency room. But, actually, there is a big disparity on who receives what type of care,” she said. “We know Black patients are less likely to receive thrombolytics and mechanical thrombectomy compared to White patents. And wealthy patients are more likely to receive thrombectomy compared to patients from the poorest zip codes.”
She said there is a tendency to think this is a result of some sort of bias on the part of health care professionals. “We wanted to look deep down in the system and whether the built environment of health care supply and geographic distribution of services contributed to access and treatment inequities.”
The study combined a dataset of hospital stroke certification from all general acute nonfederal hospitals in the continental United States from January 2009 to December 2019. National, hospital, and census data were used to identify historically underserved communities by racial and ethnic composition, income distribution, and rurality.
A total of 4,984 hospitals were assessed. Results showed that over the 11-year study period, the number of hospitals with stroke certification grew from 961 (19%) to 1,763 (36%).
Without controlling for population and hospital size, hospitals in predominantly Black, racially segregated areas were 1.67-fold more likely to adopt stroke care of any level than those in predominantly non-Black, racially segregated areas (hazard ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-1.97).
However, after adjustment for population and hospital size, the likelihood of adopting stroke care among hospitals serving Black, racially segregated communities was significantly lower than among those serving non-Black, racially segregated communities (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.62-0.89).
“In other words, on a per-capita basis, a hospital serving a predominantly Black, racially segregated community was 26% less likely to adopt stroke certification of any level than a hospital in a predominantly non-Black, racially segregated community,” the authors state.
In terms of socioeconomic factors, hospitals serving low-income, economically integrated (HR, 0.23) and low-income, economically segregated (HR, 0.29) areas were far less likely to adopt any level of stroke care certification than hospitals serving high-income areas, regardless of income segregation.
Rural hospitals were also much less likely to adopt any level of stroke care than urban hospitals (HR, 0.10).
“Our results suggest that it might be necessary to incentivize hospitals operating in underserved communities to seek stroke certification or to entice hospitals with higher propensity to adopt stroke care to operate in such communities so access at the per-patient level becomes more equitable,” the authors say.
This project was supported by the Pilot Project Award from the National Bureau of Economic Research Center for Aging and Health Research, funded by the National Institute on Aging and by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Shen and Dr. Hsia have received grants from the National Institute of Aging and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Hospitals in low-income and rural areas of the United States are much less likely to adopt stroke certification than hospitals in high-income and urban communities, a new study shows.
Further, other results showed that, after adjustment for population and hospital size, access to stroke-certified hospitals is significantly lower in Black, racially segregated communities.
The study was published online in JAMA Neurology.
Noting that stroke-certified hospitals provide higher-quality stroke care, the authors, led by Yu-Chu Shen, PhD, Naval Postgraduate School, Monterey, Calif., conclude that: “Our findings suggest that structural inequities in stroke care may be an important consideration in eliminating stroke disparities for vulnerable populations.”
In an audio interview on the JAMA Neurology website, senior author Renee Y. Hsia, MD, University of California, San Francisco, said: “Our findings show there are clear disparities in which communities are getting access to stroke certified hospitals.”
She called for more help for hospitals in underserved areas to obtain stroke certification.
Dr. Hsia explained that hospitals can seek certification at their own expense and that although stroke care is expensive, it is also lucrative in terms of reimbursement. So it tends to be the private for-profit hospitals that seek these certifications. “If you are a county hospital on a really tight budget, you’re not going to have the extra cash on hand to be applying for stroke certification,” she commented.
This can result in an increase in hospitals with stroke certification – but not in the areas that need it the most.
Dr. Hsia points out that this has happened in cardiac care. One study showed a 44% increase in hospitals providing percutaneous coronary intervention over a 10-year period, but the percentage of the population that had better access increased by less than 1%.
“In general, in the United States we have a mentality that ‘more is better,’ and because there is no government regulation in health care, any time a hospital applies for these specialized services we just generally think that’s a good thing. But this might not always be the case,” Dr. Hsia noted. “We have a very market-based approach, and this doesn’t lead to equity. It leads to profit maximization, and that is not synonymous with what’s good for patients or populations.”
She suggested that in future the process of certification should include some consideration of how it will affect population-based equity.
“Rather than rubber stamping an application just because hospitals have certain resources, we need to ask what the benefit is of providing this service,” Dr. Hsia said. “Does this community really need it? If not, maybe we should invest these resources into helping a hospital in a community that needs it more.”
Dr. Hsia explained that she and her colleagues conducted their study to investigate whether there were structural issues that might be contributing to disparities in stroke care.
“We like to think emergency stroke care is equitable. Anyone can call 911 or go the emergency room. But, actually, there is a big disparity on who receives what type of care,” she said. “We know Black patients are less likely to receive thrombolytics and mechanical thrombectomy compared to White patents. And wealthy patients are more likely to receive thrombectomy compared to patients from the poorest zip codes.”
She said there is a tendency to think this is a result of some sort of bias on the part of health care professionals. “We wanted to look deep down in the system and whether the built environment of health care supply and geographic distribution of services contributed to access and treatment inequities.”
The study combined a dataset of hospital stroke certification from all general acute nonfederal hospitals in the continental United States from January 2009 to December 2019. National, hospital, and census data were used to identify historically underserved communities by racial and ethnic composition, income distribution, and rurality.
A total of 4,984 hospitals were assessed. Results showed that over the 11-year study period, the number of hospitals with stroke certification grew from 961 (19%) to 1,763 (36%).
Without controlling for population and hospital size, hospitals in predominantly Black, racially segregated areas were 1.67-fold more likely to adopt stroke care of any level than those in predominantly non-Black, racially segregated areas (hazard ratio, 1.67; 95% confidence interval, 1.41-1.97).
However, after adjustment for population and hospital size, the likelihood of adopting stroke care among hospitals serving Black, racially segregated communities was significantly lower than among those serving non-Black, racially segregated communities (HR, 0.74; 95% CI, 0.62-0.89).
“In other words, on a per-capita basis, a hospital serving a predominantly Black, racially segregated community was 26% less likely to adopt stroke certification of any level than a hospital in a predominantly non-Black, racially segregated community,” the authors state.
In terms of socioeconomic factors, hospitals serving low-income, economically integrated (HR, 0.23) and low-income, economically segregated (HR, 0.29) areas were far less likely to adopt any level of stroke care certification than hospitals serving high-income areas, regardless of income segregation.
Rural hospitals were also much less likely to adopt any level of stroke care than urban hospitals (HR, 0.10).
“Our results suggest that it might be necessary to incentivize hospitals operating in underserved communities to seek stroke certification or to entice hospitals with higher propensity to adopt stroke care to operate in such communities so access at the per-patient level becomes more equitable,” the authors say.
This project was supported by the Pilot Project Award from the National Bureau of Economic Research Center for Aging and Health Research, funded by the National Institute on Aging and by the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences, National Institutes of Health. Dr. Shen and Dr. Hsia have received grants from the National Institute of Aging and the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New AHA checklist: Only one in five adults has optimal heart health
About 80% of American adults have low to moderate cardiovascular (CV) health based on the American Heart Association checklist for optimal heart health, which now includes healthy sleep as an essential component for heart health.
With the addition of sleep, “Life’s Essential 8” replaces the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” checklist.
“The new metric of sleep duration reflects the latest research findings: Sleep impacts overall health, and people who have healthier sleep patterns manage health factors such as weight, blood pressure, or risk for type 2 diabetes more effectively,” AHA President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a news release.
“In addition, advances in ways to measure sleep, such as with wearable devices, now offer people the ability to reliably and routinely monitor their sleep habits at home,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The AHA Presidential Advisory – Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct on Cardiovascular Health – was published online in the journal Circulation.
A companion paper published simultaneously in Circulation reports the first study using Life’s Essential 8.
Overall, the results show that CV health of the U.S. population is “suboptimal, and we see important differences across age and sociodemographic groups,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Refining Life’s Simple 7
The AHA first defined the seven metrics for optimal CV health in 2010. After 12 years and more than 2,400 scientific papers on the topic, new discoveries in CV health and ways to measure it provided an opportunity to revisit each health component in more detail and provide updates as needed, the AHA explains.
“We felt it was the right time to conduct a comprehensive review of the latest research to refine the existing metrics and consider any new metrics that add value to assessing cardiovascular health for all people,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Four of the original metrics have been redefined for consistency with newer clinical guidelines or compatibility with new measurement tools, and the scoring system can now also be applied to anyone ages 2 and older. Here is a snapshot of Life’s Essential 8 metrics, including updates.
1. Diet (updated)
The tool includes a new guide to assess diet quality for adults and children at the individual and population level. At the population level, dietary assessment is based on daily intake of elements in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating pattern. For individuals, the Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans (MEPA) is used to assess and monitor cardiovascular health.
2. Physical activity (no changes)
Physical activity continues to be measured by the total number of minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week, as defined by the U.S. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (2nd edition). The optimal level is 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate physical activity or more per week or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity for adults; 420 minutes (7 hours) or more per week for children ages 6 and older; and age-specific modifications for younger children.
3. Nicotine exposure (updated)
Use of inhaled nicotine-delivery systems, which includes e-cigarettes or vaping devices, has been added since the previous metric monitored only traditional, combustible cigarettes. This reflects use by adults and youth and their implications on long-term health. Second-hand smoke exposure for children and adults has also been added.
4. Sleep duration (new)
Sleep duration is associated with CV health. Measured by average hours of sleep per night, the ideal level is 7-9 hours daily for adults. Ideal daily sleep ranges for children are 10-16 hours per 24 hours for ages 5 and younger; 9-12 hours for ages 6-12 years; and 8-10 hours for ages 13-18 years.
5. Body mass index (no changes)
The AHA acknowledges that body mass index (BMI) is an imperfect metric. Yet, because it’s easily calculated and widely available, BMI continues as a “reasonable” gauge to assess weight categories that may lead to health problems. BMI of 18.5-24.9 is associated with the highest levels of CV health. The AHA notes that BMI ranges and the subsequent health risks associated with them may differ among people from diverse racial or ethnic backgrounds or ancestry. This aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations to adjust BMI ranges for people of Asian or Pacific Islander ancestry because recent evidence indicates their risk of conditions such as CVD or type 2 diabetes is higher at a lower BMI.
6. Blood lipids (updated)
The metric for blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) is updated to use non-HDL cholesterol as the preferred number to monitor, rather than total cholesterol. This shift is made because non-HDL cholesterol can be measured without fasting beforehand (thereby increasing its availability at any time of day and implementation at more appointments) and reliably calculated among all people.
7. Blood glucose (updated)
This metric is expanded to include the option of hemoglobin A1c readings or blood glucose levels for people with or without type 1 or 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
8. Blood pressure (no changes)
Blood pressure criteria remain unchanged from 2017 guidance that established levels less than 120/80 mm Hg as optimal, and defined hypertension as 130-139 mm Hg systolic pressure or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic pressure.
‘Concerning’ new data
Results of the first study using Life’s Essential 8 show that the overall CV health of the U.S. population is “well below ideal,” with 80% of adults scoring at a low or moderate level, the researchers report.
Data for the analysis came from 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys (NHANES) of more than 13,500 adults aged 20-79 years and nearly 9,900 children aged 2-19 years. Among the key findings:
- The average CV health score based on Life’s Essential 8 was 64.7 for adults and 65.5 for children – in the moderate range on the 0-100 scale.
- Only 0.45% of adults had a perfect score of 100; 20% had high CV health (score of 80 or higher), 63% moderate (score of 50-79), and 18% had low CV health (score of less than 50).
- Adult women had higher average CV health scores (67) compared with men (62.5).
- In general, adults scored lowest in the areas of diet, physical activity, and BMI.
- CV health scores were generally lower at older ages.
- Non-Hispanic Asian Americans had a higher average CV health score than other racial/ethnic groups. Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest average CV health score, followed, in order, by Hispanic (other than Mexican), Mexican, and non-Hispanic Blacks.
- Children’s diet scores were low, at an average of 40.6.
- Adult sociodemographic groups varied notably in CV health scores for diet, nicotine exposure, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
“These data represent the first look at the cardiovascular health of the U.S. population using the AHA’s new Life’s Essential 8 scoring algorithm,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
“Life’s Essential 8 is a major step forward in our ability to identify when cardiovascular health can be preserved and when it is suboptimal. It should energize efforts to improve cardiovascular health for all people and at every life stage,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
“Analyses like this can help policymakers, communities, clinicians, and the public to understand the opportunities to intervene to improve and maintain optimal cardiovascular health across the life course,” he said.
This research had no commercial funding. The authors have no reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About 80% of American adults have low to moderate cardiovascular (CV) health based on the American Heart Association checklist for optimal heart health, which now includes healthy sleep as an essential component for heart health.
With the addition of sleep, “Life’s Essential 8” replaces the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” checklist.
“The new metric of sleep duration reflects the latest research findings: Sleep impacts overall health, and people who have healthier sleep patterns manage health factors such as weight, blood pressure, or risk for type 2 diabetes more effectively,” AHA President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a news release.
“In addition, advances in ways to measure sleep, such as with wearable devices, now offer people the ability to reliably and routinely monitor their sleep habits at home,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The AHA Presidential Advisory – Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct on Cardiovascular Health – was published online in the journal Circulation.
A companion paper published simultaneously in Circulation reports the first study using Life’s Essential 8.
Overall, the results show that CV health of the U.S. population is “suboptimal, and we see important differences across age and sociodemographic groups,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Refining Life’s Simple 7
The AHA first defined the seven metrics for optimal CV health in 2010. After 12 years and more than 2,400 scientific papers on the topic, new discoveries in CV health and ways to measure it provided an opportunity to revisit each health component in more detail and provide updates as needed, the AHA explains.
“We felt it was the right time to conduct a comprehensive review of the latest research to refine the existing metrics and consider any new metrics that add value to assessing cardiovascular health for all people,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Four of the original metrics have been redefined for consistency with newer clinical guidelines or compatibility with new measurement tools, and the scoring system can now also be applied to anyone ages 2 and older. Here is a snapshot of Life’s Essential 8 metrics, including updates.
1. Diet (updated)
The tool includes a new guide to assess diet quality for adults and children at the individual and population level. At the population level, dietary assessment is based on daily intake of elements in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating pattern. For individuals, the Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans (MEPA) is used to assess and monitor cardiovascular health.
2. Physical activity (no changes)
Physical activity continues to be measured by the total number of minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week, as defined by the U.S. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (2nd edition). The optimal level is 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate physical activity or more per week or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity for adults; 420 minutes (7 hours) or more per week for children ages 6 and older; and age-specific modifications for younger children.
3. Nicotine exposure (updated)
Use of inhaled nicotine-delivery systems, which includes e-cigarettes or vaping devices, has been added since the previous metric monitored only traditional, combustible cigarettes. This reflects use by adults and youth and their implications on long-term health. Second-hand smoke exposure for children and adults has also been added.
4. Sleep duration (new)
Sleep duration is associated with CV health. Measured by average hours of sleep per night, the ideal level is 7-9 hours daily for adults. Ideal daily sleep ranges for children are 10-16 hours per 24 hours for ages 5 and younger; 9-12 hours for ages 6-12 years; and 8-10 hours for ages 13-18 years.
5. Body mass index (no changes)
The AHA acknowledges that body mass index (BMI) is an imperfect metric. Yet, because it’s easily calculated and widely available, BMI continues as a “reasonable” gauge to assess weight categories that may lead to health problems. BMI of 18.5-24.9 is associated with the highest levels of CV health. The AHA notes that BMI ranges and the subsequent health risks associated with them may differ among people from diverse racial or ethnic backgrounds or ancestry. This aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations to adjust BMI ranges for people of Asian or Pacific Islander ancestry because recent evidence indicates their risk of conditions such as CVD or type 2 diabetes is higher at a lower BMI.
6. Blood lipids (updated)
The metric for blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) is updated to use non-HDL cholesterol as the preferred number to monitor, rather than total cholesterol. This shift is made because non-HDL cholesterol can be measured without fasting beforehand (thereby increasing its availability at any time of day and implementation at more appointments) and reliably calculated among all people.
7. Blood glucose (updated)
This metric is expanded to include the option of hemoglobin A1c readings or blood glucose levels for people with or without type 1 or 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
8. Blood pressure (no changes)
Blood pressure criteria remain unchanged from 2017 guidance that established levels less than 120/80 mm Hg as optimal, and defined hypertension as 130-139 mm Hg systolic pressure or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic pressure.
‘Concerning’ new data
Results of the first study using Life’s Essential 8 show that the overall CV health of the U.S. population is “well below ideal,” with 80% of adults scoring at a low or moderate level, the researchers report.
Data for the analysis came from 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys (NHANES) of more than 13,500 adults aged 20-79 years and nearly 9,900 children aged 2-19 years. Among the key findings:
- The average CV health score based on Life’s Essential 8 was 64.7 for adults and 65.5 for children – in the moderate range on the 0-100 scale.
- Only 0.45% of adults had a perfect score of 100; 20% had high CV health (score of 80 or higher), 63% moderate (score of 50-79), and 18% had low CV health (score of less than 50).
- Adult women had higher average CV health scores (67) compared with men (62.5).
- In general, adults scored lowest in the areas of diet, physical activity, and BMI.
- CV health scores were generally lower at older ages.
- Non-Hispanic Asian Americans had a higher average CV health score than other racial/ethnic groups. Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest average CV health score, followed, in order, by Hispanic (other than Mexican), Mexican, and non-Hispanic Blacks.
- Children’s diet scores were low, at an average of 40.6.
- Adult sociodemographic groups varied notably in CV health scores for diet, nicotine exposure, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
“These data represent the first look at the cardiovascular health of the U.S. population using the AHA’s new Life’s Essential 8 scoring algorithm,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
“Life’s Essential 8 is a major step forward in our ability to identify when cardiovascular health can be preserved and when it is suboptimal. It should energize efforts to improve cardiovascular health for all people and at every life stage,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
“Analyses like this can help policymakers, communities, clinicians, and the public to understand the opportunities to intervene to improve and maintain optimal cardiovascular health across the life course,” he said.
This research had no commercial funding. The authors have no reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
About 80% of American adults have low to moderate cardiovascular (CV) health based on the American Heart Association checklist for optimal heart health, which now includes healthy sleep as an essential component for heart health.
With the addition of sleep, “Life’s Essential 8” replaces the AHA’s “Life’s Simple 7” checklist.
“The new metric of sleep duration reflects the latest research findings: Sleep impacts overall health, and people who have healthier sleep patterns manage health factors such as weight, blood pressure, or risk for type 2 diabetes more effectively,” AHA President Donald M. Lloyd-Jones, MD, said in a news release.
“In addition, advances in ways to measure sleep, such as with wearable devices, now offer people the ability to reliably and routinely monitor their sleep habits at home,” said Dr. Lloyd-Jones, chair of the department of preventive medicine at Northwestern University in Chicago.
The AHA Presidential Advisory – Life’s Essential 8: Updating and Enhancing the American Heart Association’s Construct on Cardiovascular Health – was published online in the journal Circulation.
A companion paper published simultaneously in Circulation reports the first study using Life’s Essential 8.
Overall, the results show that CV health of the U.S. population is “suboptimal, and we see important differences across age and sociodemographic groups,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Refining Life’s Simple 7
The AHA first defined the seven metrics for optimal CV health in 2010. After 12 years and more than 2,400 scientific papers on the topic, new discoveries in CV health and ways to measure it provided an opportunity to revisit each health component in more detail and provide updates as needed, the AHA explains.
“We felt it was the right time to conduct a comprehensive review of the latest research to refine the existing metrics and consider any new metrics that add value to assessing cardiovascular health for all people,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
Four of the original metrics have been redefined for consistency with newer clinical guidelines or compatibility with new measurement tools, and the scoring system can now also be applied to anyone ages 2 and older. Here is a snapshot of Life’s Essential 8 metrics, including updates.
1. Diet (updated)
The tool includes a new guide to assess diet quality for adults and children at the individual and population level. At the population level, dietary assessment is based on daily intake of elements in the Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension (DASH) eating pattern. For individuals, the Mediterranean Eating Pattern for Americans (MEPA) is used to assess and monitor cardiovascular health.
2. Physical activity (no changes)
Physical activity continues to be measured by the total number of minutes of moderate or vigorous physical activity per week, as defined by the U.S. Physical Activity Guidelines for Americans (2nd edition). The optimal level is 150 minutes (2.5 hours) of moderate physical activity or more per week or 75 minutes per week of vigorous-intensity physical activity for adults; 420 minutes (7 hours) or more per week for children ages 6 and older; and age-specific modifications for younger children.
3. Nicotine exposure (updated)
Use of inhaled nicotine-delivery systems, which includes e-cigarettes or vaping devices, has been added since the previous metric monitored only traditional, combustible cigarettes. This reflects use by adults and youth and their implications on long-term health. Second-hand smoke exposure for children and adults has also been added.
4. Sleep duration (new)
Sleep duration is associated with CV health. Measured by average hours of sleep per night, the ideal level is 7-9 hours daily for adults. Ideal daily sleep ranges for children are 10-16 hours per 24 hours for ages 5 and younger; 9-12 hours for ages 6-12 years; and 8-10 hours for ages 13-18 years.
5. Body mass index (no changes)
The AHA acknowledges that body mass index (BMI) is an imperfect metric. Yet, because it’s easily calculated and widely available, BMI continues as a “reasonable” gauge to assess weight categories that may lead to health problems. BMI of 18.5-24.9 is associated with the highest levels of CV health. The AHA notes that BMI ranges and the subsequent health risks associated with them may differ among people from diverse racial or ethnic backgrounds or ancestry. This aligns with the World Health Organization recommendations to adjust BMI ranges for people of Asian or Pacific Islander ancestry because recent evidence indicates their risk of conditions such as CVD or type 2 diabetes is higher at a lower BMI.
6. Blood lipids (updated)
The metric for blood lipids (cholesterol and triglycerides) is updated to use non-HDL cholesterol as the preferred number to monitor, rather than total cholesterol. This shift is made because non-HDL cholesterol can be measured without fasting beforehand (thereby increasing its availability at any time of day and implementation at more appointments) and reliably calculated among all people.
7. Blood glucose (updated)
This metric is expanded to include the option of hemoglobin A1c readings or blood glucose levels for people with or without type 1 or 2 diabetes or prediabetes.
8. Blood pressure (no changes)
Blood pressure criteria remain unchanged from 2017 guidance that established levels less than 120/80 mm Hg as optimal, and defined hypertension as 130-139 mm Hg systolic pressure or 80-89 mm Hg diastolic pressure.
‘Concerning’ new data
Results of the first study using Life’s Essential 8 show that the overall CV health of the U.S. population is “well below ideal,” with 80% of adults scoring at a low or moderate level, the researchers report.
Data for the analysis came from 2013-2018 U.S. National Health and Nutrition Examination surveys (NHANES) of more than 13,500 adults aged 20-79 years and nearly 9,900 children aged 2-19 years. Among the key findings:
- The average CV health score based on Life’s Essential 8 was 64.7 for adults and 65.5 for children – in the moderate range on the 0-100 scale.
- Only 0.45% of adults had a perfect score of 100; 20% had high CV health (score of 80 or higher), 63% moderate (score of 50-79), and 18% had low CV health (score of less than 50).
- Adult women had higher average CV health scores (67) compared with men (62.5).
- In general, adults scored lowest in the areas of diet, physical activity, and BMI.
- CV health scores were generally lower at older ages.
- Non-Hispanic Asian Americans had a higher average CV health score than other racial/ethnic groups. Non-Hispanic Whites had the second highest average CV health score, followed, in order, by Hispanic (other than Mexican), Mexican, and non-Hispanic Blacks.
- Children’s diet scores were low, at an average of 40.6.
- Adult sociodemographic groups varied notably in CV health scores for diet, nicotine exposure, blood glucose, and blood pressure.
“These data represent the first look at the cardiovascular health of the U.S. population using the AHA’s new Life’s Essential 8 scoring algorithm,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones said.
“Life’s Essential 8 is a major step forward in our ability to identify when cardiovascular health can be preserved and when it is suboptimal. It should energize efforts to improve cardiovascular health for all people and at every life stage,” Dr. Lloyd-Jones added.
“Analyses like this can help policymakers, communities, clinicians, and the public to understand the opportunities to intervene to improve and maintain optimal cardiovascular health across the life course,” he said.
This research had no commercial funding. The authors have no reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION
Physicians react: Compensation isn’t worth the hassles. What’s the solution?
How satisfied are physicians that they are fairly compensated for their dedication, skills, and time? That’s a subject that seems to steer many physicians to heated emotions and to a variety of issues with today’s medical field – not all of which directly affect their pay.
Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2022: “Incomes Gain, Pay Gaps Remain” generally shows encouraging trends. Physician income rose from a year earlier, when it stagnated as COVID-19 restrictions led patients to stay home and medical practices to cut hours or close. And for the first time in Medscape’s 11 years of reporting on physician compensation, average income rose for every medical specialty surveyed.
Heartening findings, right? Yet the tone of comments to the report was anything but peppy. One physician even complained his plumber earns more than he does.
A family physician lamented that he has “made less in the past 3 years, with more hassles and work” and he “can’t wait to retire next year.” Meanwhile, he complained, the U.S. health system is “the costliest, yet wasteful, with worse outcomes; reactive, not preventative; and has the costliest drugs and social issues.”
Do NPs and PAs encroach on your income?
The conversation about fair compensation launched some commenters into a discussion about competition from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Some physicians expressed wariness at best, and anger at worst, about NPs and PAs evolving beyond traditional doctor support roles into certain direct patient support.
One-fourth of respondents in the compensation report said their income was negatively affected by competition from NPs, PAs, and other nonphysician providers. For example, with states like Arkansas expanding independent practice for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), one commenter complained, “we are no longer needed.”
Added another physician, “primary care, especially internal medicine, is just going away for doctors. We wasted, by all accounts, 4 full years of our working lives because NPs are ‘just as good.’ ”
Greater independence for NPs and PAs strengthens the hands of health insurers and “will end up hastening the demise of primary care as we have known it,” another reader predicted. Other physicians’ takes: “For the institution, it’s much cheaper to hire NPs than to hire doctors” and “overall, physician negotiating power will decrease in the future.”
Medicare reimbursement rates grate
Although 7 in 10 respondents in the compensation report said they would continue to accept new Medicare or Medicaid patients, comments reveal resentment about the practical need to work with Medicare and its resentment rates.
“An open question to Medicare: Are you doing the dumbest thing possible by paying low wages and giving huge administrative burdens for internal medicine on purpose?” one physician wrote. “Or are you really that short-sighted?”
Another reader cited an analysis from the American College of Surgeons of Medicare’s 1998 surgical CPT codes. If Medicare had left those codes alone beyond annual inflation adjustments, the study found, reimbursement rates by 2019 would be half of what they became.
Another way of looking at the code reimbursement increases is a 50% pay cut over 20 years for doctors and medical practices, that reader insisted. “The rising cost of employee wages, particularly of the last two-and-a-half years of COVID-19, combined with the effective pay cuts over the last 20 years, equals time to quit!”
Another commenter concurred. “In the 1990s, most full-time docs were making almost double what you see [in the report], and everything cost almost half of what it does now. So, MD purchasing power is between half and one-quarter of what it was in the early 1990s.”
Are self-pay models better?
Do physicians have a better chance at consistently fair income under a self-pay practice that avoids dealing with insurance companies?
One commenter hypothesized that psychiatrists once trailed internists in income but today earn more because many “quit working for insurance and went to a cash business 15 years ago.” Many family physicians did something similar by switching to a direct primary care model, he said.
This physician said he has done the same “with great results” for patients as well: shorter office visits, faster booking of appointments, no deductibles owed. Best of all, “I love practicing medicine again, and my patients love the great health care they receive.”
Another commenter agreed. “Two words: cash practice.” But another objected, “I guess only the very rich can afford to cover your business costs.”
Regardless of the payment model, another physician argued for private practice over employed positions. “Save on the bureaucratic expenses. Go back to private practice and get rid of electronic records.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How satisfied are physicians that they are fairly compensated for their dedication, skills, and time? That’s a subject that seems to steer many physicians to heated emotions and to a variety of issues with today’s medical field – not all of which directly affect their pay.
Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2022: “Incomes Gain, Pay Gaps Remain” generally shows encouraging trends. Physician income rose from a year earlier, when it stagnated as COVID-19 restrictions led patients to stay home and medical practices to cut hours or close. And for the first time in Medscape’s 11 years of reporting on physician compensation, average income rose for every medical specialty surveyed.
Heartening findings, right? Yet the tone of comments to the report was anything but peppy. One physician even complained his plumber earns more than he does.
A family physician lamented that he has “made less in the past 3 years, with more hassles and work” and he “can’t wait to retire next year.” Meanwhile, he complained, the U.S. health system is “the costliest, yet wasteful, with worse outcomes; reactive, not preventative; and has the costliest drugs and social issues.”
Do NPs and PAs encroach on your income?
The conversation about fair compensation launched some commenters into a discussion about competition from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Some physicians expressed wariness at best, and anger at worst, about NPs and PAs evolving beyond traditional doctor support roles into certain direct patient support.
One-fourth of respondents in the compensation report said their income was negatively affected by competition from NPs, PAs, and other nonphysician providers. For example, with states like Arkansas expanding independent practice for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), one commenter complained, “we are no longer needed.”
Added another physician, “primary care, especially internal medicine, is just going away for doctors. We wasted, by all accounts, 4 full years of our working lives because NPs are ‘just as good.’ ”
Greater independence for NPs and PAs strengthens the hands of health insurers and “will end up hastening the demise of primary care as we have known it,” another reader predicted. Other physicians’ takes: “For the institution, it’s much cheaper to hire NPs than to hire doctors” and “overall, physician negotiating power will decrease in the future.”
Medicare reimbursement rates grate
Although 7 in 10 respondents in the compensation report said they would continue to accept new Medicare or Medicaid patients, comments reveal resentment about the practical need to work with Medicare and its resentment rates.
“An open question to Medicare: Are you doing the dumbest thing possible by paying low wages and giving huge administrative burdens for internal medicine on purpose?” one physician wrote. “Or are you really that short-sighted?”
Another reader cited an analysis from the American College of Surgeons of Medicare’s 1998 surgical CPT codes. If Medicare had left those codes alone beyond annual inflation adjustments, the study found, reimbursement rates by 2019 would be half of what they became.
Another way of looking at the code reimbursement increases is a 50% pay cut over 20 years for doctors and medical practices, that reader insisted. “The rising cost of employee wages, particularly of the last two-and-a-half years of COVID-19, combined with the effective pay cuts over the last 20 years, equals time to quit!”
Another commenter concurred. “In the 1990s, most full-time docs were making almost double what you see [in the report], and everything cost almost half of what it does now. So, MD purchasing power is between half and one-quarter of what it was in the early 1990s.”
Are self-pay models better?
Do physicians have a better chance at consistently fair income under a self-pay practice that avoids dealing with insurance companies?
One commenter hypothesized that psychiatrists once trailed internists in income but today earn more because many “quit working for insurance and went to a cash business 15 years ago.” Many family physicians did something similar by switching to a direct primary care model, he said.
This physician said he has done the same “with great results” for patients as well: shorter office visits, faster booking of appointments, no deductibles owed. Best of all, “I love practicing medicine again, and my patients love the great health care they receive.”
Another commenter agreed. “Two words: cash practice.” But another objected, “I guess only the very rich can afford to cover your business costs.”
Regardless of the payment model, another physician argued for private practice over employed positions. “Save on the bureaucratic expenses. Go back to private practice and get rid of electronic records.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
How satisfied are physicians that they are fairly compensated for their dedication, skills, and time? That’s a subject that seems to steer many physicians to heated emotions and to a variety of issues with today’s medical field – not all of which directly affect their pay.
Medscape’s Physician Compensation Report 2022: “Incomes Gain, Pay Gaps Remain” generally shows encouraging trends. Physician income rose from a year earlier, when it stagnated as COVID-19 restrictions led patients to stay home and medical practices to cut hours or close. And for the first time in Medscape’s 11 years of reporting on physician compensation, average income rose for every medical specialty surveyed.
Heartening findings, right? Yet the tone of comments to the report was anything but peppy. One physician even complained his plumber earns more than he does.
A family physician lamented that he has “made less in the past 3 years, with more hassles and work” and he “can’t wait to retire next year.” Meanwhile, he complained, the U.S. health system is “the costliest, yet wasteful, with worse outcomes; reactive, not preventative; and has the costliest drugs and social issues.”
Do NPs and PAs encroach on your income?
The conversation about fair compensation launched some commenters into a discussion about competition from nurse practitioners (NPs) and physician assistants (PAs). Some physicians expressed wariness at best, and anger at worst, about NPs and PAs evolving beyond traditional doctor support roles into certain direct patient support.
One-fourth of respondents in the compensation report said their income was negatively affected by competition from NPs, PAs, and other nonphysician providers. For example, with states like Arkansas expanding independent practice for certified registered nurse anesthetists (CRNAs), one commenter complained, “we are no longer needed.”
Added another physician, “primary care, especially internal medicine, is just going away for doctors. We wasted, by all accounts, 4 full years of our working lives because NPs are ‘just as good.’ ”
Greater independence for NPs and PAs strengthens the hands of health insurers and “will end up hastening the demise of primary care as we have known it,” another reader predicted. Other physicians’ takes: “For the institution, it’s much cheaper to hire NPs than to hire doctors” and “overall, physician negotiating power will decrease in the future.”
Medicare reimbursement rates grate
Although 7 in 10 respondents in the compensation report said they would continue to accept new Medicare or Medicaid patients, comments reveal resentment about the practical need to work with Medicare and its resentment rates.
“An open question to Medicare: Are you doing the dumbest thing possible by paying low wages and giving huge administrative burdens for internal medicine on purpose?” one physician wrote. “Or are you really that short-sighted?”
Another reader cited an analysis from the American College of Surgeons of Medicare’s 1998 surgical CPT codes. If Medicare had left those codes alone beyond annual inflation adjustments, the study found, reimbursement rates by 2019 would be half of what they became.
Another way of looking at the code reimbursement increases is a 50% pay cut over 20 years for doctors and medical practices, that reader insisted. “The rising cost of employee wages, particularly of the last two-and-a-half years of COVID-19, combined with the effective pay cuts over the last 20 years, equals time to quit!”
Another commenter concurred. “In the 1990s, most full-time docs were making almost double what you see [in the report], and everything cost almost half of what it does now. So, MD purchasing power is between half and one-quarter of what it was in the early 1990s.”
Are self-pay models better?
Do physicians have a better chance at consistently fair income under a self-pay practice that avoids dealing with insurance companies?
One commenter hypothesized that psychiatrists once trailed internists in income but today earn more because many “quit working for insurance and went to a cash business 15 years ago.” Many family physicians did something similar by switching to a direct primary care model, he said.
This physician said he has done the same “with great results” for patients as well: shorter office visits, faster booking of appointments, no deductibles owed. Best of all, “I love practicing medicine again, and my patients love the great health care they receive.”
Another commenter agreed. “Two words: cash practice.” But another objected, “I guess only the very rich can afford to cover your business costs.”
Regardless of the payment model, another physician argued for private practice over employed positions. “Save on the bureaucratic expenses. Go back to private practice and get rid of electronic records.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Heart attack care not equal for women and people of color
Radiating chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness. Everyone knows the telltale signs of a myocardial infarction. Yet a new study shows that despite this widespread recognition, heart attacks aren’t attended to quickly across the board. Historically, the study says, women and people of color wait longer to access emergency care for a heart attack.
Researchers from the University of California, San Francisco published these findings in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. The study used the Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development dataset to gather information on 453,136 cases of heart attack in California between 2005 and 2015. They found that over time, differences in timely treatment between the demographics narrowed, but the gap still existed.
The study defined timely treatment as receiving care for a heart attack within 3 days of admission to a hospital. Women and people of color were found to wait 3 days or more to receive care than their White male counterparts. A disparity of this sort can cause ripples of health effects across society, ripples that doctors should be aware of, says lead author Juan Carlos Montoy, MD. Dr. Montoy was “sadly surprised by our findings that disparities for women and for Black patients only decreased slightly or not at all over time.”
In the study, the team separated the dataset between the two primary types of heart attack: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), caused by blood vessel blockage, and non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), caused by a narrowing or temporary blockage of the artery.
Regardless of the type of heart attack, the standard first step in treatment is a coronary angiogram. After finding out where blood flow is disrupted using the angiogram, a physician can proceed with treatment.
But when looking back, the team found that it took a while for many patients to receive this first step in treatment. In 2005, 50% of men and 35.7% of women with STEMI and 45% of men and 33.1% of women with NSTEMI had a timely angiography. In the same year, 46% of White patients and 31.2% of Black patients with STEMI underwent timely angiography.
By 2015, timely treatment increased across the board, but there were still discrepancies, with 76.7% of men and 66.8% of women with STEMI undergoing timely angiography and 56.3% of men and 45.9% of women with NSTEMI undergoing timely angiography. Also in 2015, 75.2% of White patients and 69.2% of Black patients underwent timely angiography for STEMI.
Although differences in care decreased between the demographics, the gap still exists. Whereas this dataset only extends to 2015, this trend may still persist today, says Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, who was not involved in the study. Therefore, physicians need to consider this bias when treating patients. “The bottom line is that we continue to have much work to do to achieve equality in managing not only medical conditions but treating people who have them equally,” Dr. Glatter said.
“Raising awareness of ongoing inequality in care related to gender and ethnic disparities is critical to drive change in our institutions,” he emphasized. “We simply cannot accept the status quo.”
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Glatter and the authors declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Radiating chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness. Everyone knows the telltale signs of a myocardial infarction. Yet a new study shows that despite this widespread recognition, heart attacks aren’t attended to quickly across the board. Historically, the study says, women and people of color wait longer to access emergency care for a heart attack.
Researchers from the University of California, San Francisco published these findings in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. The study used the Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development dataset to gather information on 453,136 cases of heart attack in California between 2005 and 2015. They found that over time, differences in timely treatment between the demographics narrowed, but the gap still existed.
The study defined timely treatment as receiving care for a heart attack within 3 days of admission to a hospital. Women and people of color were found to wait 3 days or more to receive care than their White male counterparts. A disparity of this sort can cause ripples of health effects across society, ripples that doctors should be aware of, says lead author Juan Carlos Montoy, MD. Dr. Montoy was “sadly surprised by our findings that disparities for women and for Black patients only decreased slightly or not at all over time.”
In the study, the team separated the dataset between the two primary types of heart attack: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), caused by blood vessel blockage, and non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), caused by a narrowing or temporary blockage of the artery.
Regardless of the type of heart attack, the standard first step in treatment is a coronary angiogram. After finding out where blood flow is disrupted using the angiogram, a physician can proceed with treatment.
But when looking back, the team found that it took a while for many patients to receive this first step in treatment. In 2005, 50% of men and 35.7% of women with STEMI and 45% of men and 33.1% of women with NSTEMI had a timely angiography. In the same year, 46% of White patients and 31.2% of Black patients with STEMI underwent timely angiography.
By 2015, timely treatment increased across the board, but there were still discrepancies, with 76.7% of men and 66.8% of women with STEMI undergoing timely angiography and 56.3% of men and 45.9% of women with NSTEMI undergoing timely angiography. Also in 2015, 75.2% of White patients and 69.2% of Black patients underwent timely angiography for STEMI.
Although differences in care decreased between the demographics, the gap still exists. Whereas this dataset only extends to 2015, this trend may still persist today, says Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, who was not involved in the study. Therefore, physicians need to consider this bias when treating patients. “The bottom line is that we continue to have much work to do to achieve equality in managing not only medical conditions but treating people who have them equally,” Dr. Glatter said.
“Raising awareness of ongoing inequality in care related to gender and ethnic disparities is critical to drive change in our institutions,” he emphasized. “We simply cannot accept the status quo.”
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Glatter and the authors declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Radiating chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea, lightheadedness. Everyone knows the telltale signs of a myocardial infarction. Yet a new study shows that despite this widespread recognition, heart attacks aren’t attended to quickly across the board. Historically, the study says, women and people of color wait longer to access emergency care for a heart attack.
Researchers from the University of California, San Francisco published these findings in the Annals of Emergency Medicine. The study used the Office of Statewide Health Planning and Development dataset to gather information on 453,136 cases of heart attack in California between 2005 and 2015. They found that over time, differences in timely treatment between the demographics narrowed, but the gap still existed.
The study defined timely treatment as receiving care for a heart attack within 3 days of admission to a hospital. Women and people of color were found to wait 3 days or more to receive care than their White male counterparts. A disparity of this sort can cause ripples of health effects across society, ripples that doctors should be aware of, says lead author Juan Carlos Montoy, MD. Dr. Montoy was “sadly surprised by our findings that disparities for women and for Black patients only decreased slightly or not at all over time.”
In the study, the team separated the dataset between the two primary types of heart attack: ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), caused by blood vessel blockage, and non–ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (NSTEMI), caused by a narrowing or temporary blockage of the artery.
Regardless of the type of heart attack, the standard first step in treatment is a coronary angiogram. After finding out where blood flow is disrupted using the angiogram, a physician can proceed with treatment.
But when looking back, the team found that it took a while for many patients to receive this first step in treatment. In 2005, 50% of men and 35.7% of women with STEMI and 45% of men and 33.1% of women with NSTEMI had a timely angiography. In the same year, 46% of White patients and 31.2% of Black patients with STEMI underwent timely angiography.
By 2015, timely treatment increased across the board, but there were still discrepancies, with 76.7% of men and 66.8% of women with STEMI undergoing timely angiography and 56.3% of men and 45.9% of women with NSTEMI undergoing timely angiography. Also in 2015, 75.2% of White patients and 69.2% of Black patients underwent timely angiography for STEMI.
Although differences in care decreased between the demographics, the gap still exists. Whereas this dataset only extends to 2015, this trend may still persist today, says Robert Glatter, MD, an emergency medicine physician at Lenox Hill Hospital, New York, who was not involved in the study. Therefore, physicians need to consider this bias when treating patients. “The bottom line is that we continue to have much work to do to achieve equality in managing not only medical conditions but treating people who have them equally,” Dr. Glatter said.
“Raising awareness of ongoing inequality in care related to gender and ethnic disparities is critical to drive change in our institutions,” he emphasized. “We simply cannot accept the status quo.”
The study was funded by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health. Dr. Glatter and the authors declared no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ANNALS OF EMERGENCY MEDICINE
How much health insurers pay for almost everything is about to go public
perhaps helping answer a question that has long dogged those who buy insurance: Are we getting the best deal we can?
As of July 1, health insurers and self-insured employers must post on websites just about every price they’ve negotiated with providers for health care services, item by item. About the only thing excluded are the prices paid for prescription drugs, except those administered in hospitals or doctors’ offices.
The federally required data release could affect future prices or even how employers contract for health care. Many will see for the first time how well their insurers are doing, compared with others.
The new rules are far broader than those that went into effect in 2021 requiring hospitals to post their negotiated rates for the public to see. Now insurers must post the amounts paid for “every physician in network, every hospital, every surgery center, every nursing facility,” said Jeffrey Leibach, a partner at the consulting firm Guidehouse.
“When you start doing the math, you’re talking trillions of records,” he said. The fines the federal government could impose for noncompliance are also heftier than the penalties that hospitals face.
Federal officials learned from the hospital experience and gave insurers more direction on what was expected, said Mr. Leibach. Insurers or self-insured employers could be fined as much as $100 a day for each violation, for each affected enrollee if they fail to provide the data.
“Get your calculator out: All of a sudden you are in the millions pretty fast,” Mr. Leibach said.
Determined consumers, especially those with high-deductible health plans, may try to dig in right away and use the data to try comparing what they will have to pay at different hospitals, clinics, or doctor offices for specific services.
But each database’s enormous size may mean that most people “will find it very hard to use the data in a nuanced way,” said Katherine Baicker, dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.
At least at first.
Entrepreneurs are expected to quickly translate the information into more user-friendly formats so it can be incorporated into new or existing services that estimate costs for patients. And starting Jan. 1, the rules require insurers to provide online tools that will help people get up-front cost estimates for about 500 so-called “shoppable” services, meaning medical care they can schedule ahead of time.
Once those things happen, “you’ll at least have the options in front of you,” said Chris Severn, CEO of Turquoise Health, an online company that has posted price information made available under the rules for hospitals, although many hospitals have yet to comply.
With the addition of the insurers’ data, sites like his will be able to drill down further into cost variation from one place to another or among insurers.
“If you’re going to get an x-ray, you will be able to see that you can do it for $250 at this hospital, $75 at the imaging center down the road, or your specialist can do it in office for $25,” he said.
Everyone will know everyone else’s business: for example, how much insurers Aetna and Humana pay the same surgery center for a knee replacement.
The requirements stem from the Affordable Care Act and a 2019 executive order by then-President Donald Trump.
“These plans are supposed to be acting on behalf of employers in negotiating good rates, and the little insight we have on that shows it has not happened,” said Elizabeth Mitchell, president and CEO of the Purchaser Business Group on Health, an affiliation of employers who offer job-based health benefits to workers. “I do believe the dynamics are going to change.”
Other observers are more circumspect.
“Maybe at best this will reduce the wide variance of prices out there,” said Zack Cooper, director of health policy at the Yale University Institution for Social and Policy Studies, New Haven, Conn. “But it won’t be unleashing a consumer revolution.”
Still, the biggest value of the July data release may well be to shed light on how successful insurers have been at negotiating prices. It comes on the heels of research that has shown tremendous variation in what is paid for health care. A recent study by Rand, for example, shows that employers that offer job-based insurance plans paid, on average, 224% more than Medicare for the same services.
Tens of thousands of employers who buy insurance coverage for their workers will get this more-complete pricing picture – and may not like what they see.
“What we’re learning from the hospital data is that insurers are really bad at negotiating,” said Gerard Anderson, a professor in the department of health policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, Baltimore, citing research that found that negotiated rates for hospital care can be higher than what the facilities accept from patients who are not using insurance and are paying cash.
That could add to the frustration that Ms. Mitchell and others say employers have with the current health insurance system. More might try to contract with providers directly, only using insurance companies for claims processing.
Other employers may bring their insurers back to the bargaining table.
“For the first time, an employer will be able to go to an insurance company and say: ‘You have not negotiated a good-enough deal, and we know that because we can see the same provider has negotiated a better deal with another company,’ ” said James Gelfand, president of the ERISA Industry Committee, a trade group of self-insured employers.
If that happens, he added, “patients will be able to save money.”
That’s not necessarily a given, however.
Because this kind of public release of pricing data hasn’t been tried widely in health care before, how it will affect future spending remains uncertain. If insurers are pushed back to the bargaining table or providers see where they stand relative to their peers, prices could drop. However, some providers could raise their prices if they see they are charging less than their peers.
“Downward pressure may not be a given,” said Kelley Schultz, vice president of commercial policy for AHIP, the industry’s trade lobby.
Ms. Baicker said that, even after the data is out, rates will continue to be heavily influenced by local conditions, such as the size of an insurer or employer – providers often give bigger discounts, for example, to the insurers or self-insured employers that can send them the most patients. The number of hospitals in a region also matters – if an area has only one, for instance, that usually means the facility can demand higher rates.
Another unknown: Will insurers meet the deadline and provide usable data?
Ms. Schultz, at AHIP, said the industry is well on the way, partly because the original deadline was extended by 6 months. She expects insurers to do better than the hospital industry. “We saw a lot of hospitals that just decided not to post files or make them difficult to find,” she said.
So far, more than 300 noncompliant hospitals received warning letters from the government. But they could face fines of $300 a day fines for failing to comply, which is less than what insurers potentially face, although the federal government has recently upped the ante to up to $5,500 a day for the largest facilities.
Even after the pricing data is public, “I don’t think things will change overnight,” said Mr. Leibach. “Patients are still going to make care decisions based on their doctors and referrals, a lot of reasons other than price.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
perhaps helping answer a question that has long dogged those who buy insurance: Are we getting the best deal we can?
As of July 1, health insurers and self-insured employers must post on websites just about every price they’ve negotiated with providers for health care services, item by item. About the only thing excluded are the prices paid for prescription drugs, except those administered in hospitals or doctors’ offices.
The federally required data release could affect future prices or even how employers contract for health care. Many will see for the first time how well their insurers are doing, compared with others.
The new rules are far broader than those that went into effect in 2021 requiring hospitals to post their negotiated rates for the public to see. Now insurers must post the amounts paid for “every physician in network, every hospital, every surgery center, every nursing facility,” said Jeffrey Leibach, a partner at the consulting firm Guidehouse.
“When you start doing the math, you’re talking trillions of records,” he said. The fines the federal government could impose for noncompliance are also heftier than the penalties that hospitals face.
Federal officials learned from the hospital experience and gave insurers more direction on what was expected, said Mr. Leibach. Insurers or self-insured employers could be fined as much as $100 a day for each violation, for each affected enrollee if they fail to provide the data.
“Get your calculator out: All of a sudden you are in the millions pretty fast,” Mr. Leibach said.
Determined consumers, especially those with high-deductible health plans, may try to dig in right away and use the data to try comparing what they will have to pay at different hospitals, clinics, or doctor offices for specific services.
But each database’s enormous size may mean that most people “will find it very hard to use the data in a nuanced way,” said Katherine Baicker, dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.
At least at first.
Entrepreneurs are expected to quickly translate the information into more user-friendly formats so it can be incorporated into new or existing services that estimate costs for patients. And starting Jan. 1, the rules require insurers to provide online tools that will help people get up-front cost estimates for about 500 so-called “shoppable” services, meaning medical care they can schedule ahead of time.
Once those things happen, “you’ll at least have the options in front of you,” said Chris Severn, CEO of Turquoise Health, an online company that has posted price information made available under the rules for hospitals, although many hospitals have yet to comply.
With the addition of the insurers’ data, sites like his will be able to drill down further into cost variation from one place to another or among insurers.
“If you’re going to get an x-ray, you will be able to see that you can do it for $250 at this hospital, $75 at the imaging center down the road, or your specialist can do it in office for $25,” he said.
Everyone will know everyone else’s business: for example, how much insurers Aetna and Humana pay the same surgery center for a knee replacement.
The requirements stem from the Affordable Care Act and a 2019 executive order by then-President Donald Trump.
“These plans are supposed to be acting on behalf of employers in negotiating good rates, and the little insight we have on that shows it has not happened,” said Elizabeth Mitchell, president and CEO of the Purchaser Business Group on Health, an affiliation of employers who offer job-based health benefits to workers. “I do believe the dynamics are going to change.”
Other observers are more circumspect.
“Maybe at best this will reduce the wide variance of prices out there,” said Zack Cooper, director of health policy at the Yale University Institution for Social and Policy Studies, New Haven, Conn. “But it won’t be unleashing a consumer revolution.”
Still, the biggest value of the July data release may well be to shed light on how successful insurers have been at negotiating prices. It comes on the heels of research that has shown tremendous variation in what is paid for health care. A recent study by Rand, for example, shows that employers that offer job-based insurance plans paid, on average, 224% more than Medicare for the same services.
Tens of thousands of employers who buy insurance coverage for their workers will get this more-complete pricing picture – and may not like what they see.
“What we’re learning from the hospital data is that insurers are really bad at negotiating,” said Gerard Anderson, a professor in the department of health policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, Baltimore, citing research that found that negotiated rates for hospital care can be higher than what the facilities accept from patients who are not using insurance and are paying cash.
That could add to the frustration that Ms. Mitchell and others say employers have with the current health insurance system. More might try to contract with providers directly, only using insurance companies for claims processing.
Other employers may bring their insurers back to the bargaining table.
“For the first time, an employer will be able to go to an insurance company and say: ‘You have not negotiated a good-enough deal, and we know that because we can see the same provider has negotiated a better deal with another company,’ ” said James Gelfand, president of the ERISA Industry Committee, a trade group of self-insured employers.
If that happens, he added, “patients will be able to save money.”
That’s not necessarily a given, however.
Because this kind of public release of pricing data hasn’t been tried widely in health care before, how it will affect future spending remains uncertain. If insurers are pushed back to the bargaining table or providers see where they stand relative to their peers, prices could drop. However, some providers could raise their prices if they see they are charging less than their peers.
“Downward pressure may not be a given,” said Kelley Schultz, vice president of commercial policy for AHIP, the industry’s trade lobby.
Ms. Baicker said that, even after the data is out, rates will continue to be heavily influenced by local conditions, such as the size of an insurer or employer – providers often give bigger discounts, for example, to the insurers or self-insured employers that can send them the most patients. The number of hospitals in a region also matters – if an area has only one, for instance, that usually means the facility can demand higher rates.
Another unknown: Will insurers meet the deadline and provide usable data?
Ms. Schultz, at AHIP, said the industry is well on the way, partly because the original deadline was extended by 6 months. She expects insurers to do better than the hospital industry. “We saw a lot of hospitals that just decided not to post files or make them difficult to find,” she said.
So far, more than 300 noncompliant hospitals received warning letters from the government. But they could face fines of $300 a day fines for failing to comply, which is less than what insurers potentially face, although the federal government has recently upped the ante to up to $5,500 a day for the largest facilities.
Even after the pricing data is public, “I don’t think things will change overnight,” said Mr. Leibach. “Patients are still going to make care decisions based on their doctors and referrals, a lot of reasons other than price.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
perhaps helping answer a question that has long dogged those who buy insurance: Are we getting the best deal we can?
As of July 1, health insurers and self-insured employers must post on websites just about every price they’ve negotiated with providers for health care services, item by item. About the only thing excluded are the prices paid for prescription drugs, except those administered in hospitals or doctors’ offices.
The federally required data release could affect future prices or even how employers contract for health care. Many will see for the first time how well their insurers are doing, compared with others.
The new rules are far broader than those that went into effect in 2021 requiring hospitals to post their negotiated rates for the public to see. Now insurers must post the amounts paid for “every physician in network, every hospital, every surgery center, every nursing facility,” said Jeffrey Leibach, a partner at the consulting firm Guidehouse.
“When you start doing the math, you’re talking trillions of records,” he said. The fines the federal government could impose for noncompliance are also heftier than the penalties that hospitals face.
Federal officials learned from the hospital experience and gave insurers more direction on what was expected, said Mr. Leibach. Insurers or self-insured employers could be fined as much as $100 a day for each violation, for each affected enrollee if they fail to provide the data.
“Get your calculator out: All of a sudden you are in the millions pretty fast,” Mr. Leibach said.
Determined consumers, especially those with high-deductible health plans, may try to dig in right away and use the data to try comparing what they will have to pay at different hospitals, clinics, or doctor offices for specific services.
But each database’s enormous size may mean that most people “will find it very hard to use the data in a nuanced way,” said Katherine Baicker, dean of the University of Chicago Harris School of Public Policy.
At least at first.
Entrepreneurs are expected to quickly translate the information into more user-friendly formats so it can be incorporated into new or existing services that estimate costs for patients. And starting Jan. 1, the rules require insurers to provide online tools that will help people get up-front cost estimates for about 500 so-called “shoppable” services, meaning medical care they can schedule ahead of time.
Once those things happen, “you’ll at least have the options in front of you,” said Chris Severn, CEO of Turquoise Health, an online company that has posted price information made available under the rules for hospitals, although many hospitals have yet to comply.
With the addition of the insurers’ data, sites like his will be able to drill down further into cost variation from one place to another or among insurers.
“If you’re going to get an x-ray, you will be able to see that you can do it for $250 at this hospital, $75 at the imaging center down the road, or your specialist can do it in office for $25,” he said.
Everyone will know everyone else’s business: for example, how much insurers Aetna and Humana pay the same surgery center for a knee replacement.
The requirements stem from the Affordable Care Act and a 2019 executive order by then-President Donald Trump.
“These plans are supposed to be acting on behalf of employers in negotiating good rates, and the little insight we have on that shows it has not happened,” said Elizabeth Mitchell, president and CEO of the Purchaser Business Group on Health, an affiliation of employers who offer job-based health benefits to workers. “I do believe the dynamics are going to change.”
Other observers are more circumspect.
“Maybe at best this will reduce the wide variance of prices out there,” said Zack Cooper, director of health policy at the Yale University Institution for Social and Policy Studies, New Haven, Conn. “But it won’t be unleashing a consumer revolution.”
Still, the biggest value of the July data release may well be to shed light on how successful insurers have been at negotiating prices. It comes on the heels of research that has shown tremendous variation in what is paid for health care. A recent study by Rand, for example, shows that employers that offer job-based insurance plans paid, on average, 224% more than Medicare for the same services.
Tens of thousands of employers who buy insurance coverage for their workers will get this more-complete pricing picture – and may not like what they see.
“What we’re learning from the hospital data is that insurers are really bad at negotiating,” said Gerard Anderson, a professor in the department of health policy at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg, Baltimore, citing research that found that negotiated rates for hospital care can be higher than what the facilities accept from patients who are not using insurance and are paying cash.
That could add to the frustration that Ms. Mitchell and others say employers have with the current health insurance system. More might try to contract with providers directly, only using insurance companies for claims processing.
Other employers may bring their insurers back to the bargaining table.
“For the first time, an employer will be able to go to an insurance company and say: ‘You have not negotiated a good-enough deal, and we know that because we can see the same provider has negotiated a better deal with another company,’ ” said James Gelfand, president of the ERISA Industry Committee, a trade group of self-insured employers.
If that happens, he added, “patients will be able to save money.”
That’s not necessarily a given, however.
Because this kind of public release of pricing data hasn’t been tried widely in health care before, how it will affect future spending remains uncertain. If insurers are pushed back to the bargaining table or providers see where they stand relative to their peers, prices could drop. However, some providers could raise their prices if they see they are charging less than their peers.
“Downward pressure may not be a given,” said Kelley Schultz, vice president of commercial policy for AHIP, the industry’s trade lobby.
Ms. Baicker said that, even after the data is out, rates will continue to be heavily influenced by local conditions, such as the size of an insurer or employer – providers often give bigger discounts, for example, to the insurers or self-insured employers that can send them the most patients. The number of hospitals in a region also matters – if an area has only one, for instance, that usually means the facility can demand higher rates.
Another unknown: Will insurers meet the deadline and provide usable data?
Ms. Schultz, at AHIP, said the industry is well on the way, partly because the original deadline was extended by 6 months. She expects insurers to do better than the hospital industry. “We saw a lot of hospitals that just decided not to post files or make them difficult to find,” she said.
So far, more than 300 noncompliant hospitals received warning letters from the government. But they could face fines of $300 a day fines for failing to comply, which is less than what insurers potentially face, although the federal government has recently upped the ante to up to $5,500 a day for the largest facilities.
Even after the pricing data is public, “I don’t think things will change overnight,” said Mr. Leibach. “Patients are still going to make care decisions based on their doctors and referrals, a lot of reasons other than price.”
KHN (Kaiser Health News) is a national newsroom that produces in-depth journalism about health issues. Together with Policy Analysis and Polling, KHN is one of the three major operating programs at KFF (Kaiser Family Foundation). KFF is an endowed nonprofit organization providing information on health issues to the nation.
New biomarker data add to concerns over REDUCE-IT trial
A new analysis of the REDUCE-IT study has reignited concerns that the benefit shown by the high-dose fish oil product in the study, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), may have been related to harms caused by the placebo mineral oil.
Results show that allocation to icosapent ethyl had minimal effects on a series of biomarkers associated with atherosclerotic disease, whereas levels of these biomarkers increased among those allocated to mineral oil.
At 12 months, the median percent increases from baseline in the mineral oil group were 1.5% for homocysteine, 2.2% for lipoprotein(a), 10.9% for oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, 16.2% for interleukin (IL)-6, 18.5% for lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, 21.9% for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and 28.9% for IL-1β. The changes were similar at 24 months. However, in the icosapent ethyl group, there were minimal changes in these biomarkers at 12 and 24 months.
The study was published online in Circulation.
The authors, led by Paul Ridker, MD, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, do not voice much opinion on what the results mean, concluding that “the effect of these findings on the interpretation of the REDUCE-IT trial results remains unclear and will require further investigation.”
They also say that a second icosapent ethyl trial using a nonmineral oil comparator “would help resolve ongoing controversy.”
However, the authors are a mixed group; Dr. Ridker and some of his coauthors were not part of the original REDUCE-IT trial, whereas other coauthors were members of the REDUCE-IT steering committee, and one was an employee of Amarin.
Lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, Deepak Bhatt, MD, also from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, who is the senior author of the current study, played down the new findings, saying they did not offer much new incremental information on mechanistic insight.
“These are small degrees of biomarker increases on an absolute level we are seeing with the placebo that would not be expected to produce harm,” Dr. Bhatt told this news organization. He also said the Circulation peer-review process had removed some of the discussion, which could lead to some “misinterpretation” of the authors’ views.
Dr. Ridker was unavailable for further comment.
The publication of this study has inevitably poured fuel on the fire regarding the controversy that has long dogged the REDUCE-IT trial, with questions about the large reduction in event rates seen with icosapent ethyl without an obvious mechanistic explanation.
‘Smoking gun’
One of the loudest critics of the study, Steve Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, described the new findings as “the closest thing I’ve seen to a smoking gun in medicine for a long, long time.”
“The result of this new analysis shows that mineral oil increases virtually every inflammatory and lipid marker that they measured,” he commented.
“There are a lot of theories, but the bottom line is that something really bad happened in the mineral-oil group, which makes icosapent ethyl look efficacious. In my view, this needs to be reviewed by the FDA for consideration of removing the label claim for cardiovascular benefit.”
Other experts in the field not directly involved in the study voiced concern about these new findings, adding to calls for another trial.
In a Twitter thread on the issue, Harlan Krumholz, MD, describes the Circulation publication as “an exceptionally important article,” adding that it is “time to rethink this drug.”
“My point is ... once you know you have non-neutral comparator and the effect on risk biomarkers is far from trivial ... then you have introduced substantial uncertainty about the trial result, as conveyed by the authors ... and no one can say what would happen with a neutral comparator,” Dr. Krumholz writes.
In an accompanying editorial in Circulation, Robert Harrington, MD, professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, concludes that “the hard reality is that we are left with uncertainties and the questions raised by use of the mineral oil as placebo can only be answered by another randomized controlled trial.”
“My main points are that the chosen placebo was not inert (an essential characteristic for an active control–placebo comparison), that the biomarker data show elevations in multiple markers involved with inflammatory pathways associated with atherosclerosis, and that these data create enough uncertainty in the trial interpretation that the best recourse to answer the criticisms is to do another trial with a truly inert placebo,” Dr. Harrington said in an interview.
He added that Dr. Bhatt’s point that the changes in biomarkers are too small to really matter clinically may be right. “But for me, the uncertainties mean that I have less confidence in the true magnitude of the treatment effect than I would have if there were no changes in the inflammatory markers.”
In Circulation, the authors say it is unclear why multiple biomarkers increased over time among REDUCE-IT participants allocated to mineral oil. They note that no substantive changes in these biomarkers were observed in the placebo groups over periods of 3-5 years in other trials, including JUPITER, CIRT, CANTOS, SPIRE, and the STRENGTH trials, which evaluated a different high-dose omega-3 oil product but used corn oil as the placebo.
“The core design of REDUCE-IT does not make it possible to resolve convincingly whether any adverse effects associated with mineral oil use as a comparator may have affected clinical outcomes,” they write.
They point out that regulatory agencies evaluating REDUCE-IT estimated that approximately 3% of the net clinical benefit observed with icosapent ethyl might have been a consequence of adverse biomarker effects on LDL cholesterol and hsCRP attributable to mineral oil. But in the context of an overall 25% relative risk reduction in first events and a 30% reduction in total ischemic events observed, a potential bias of this magnitude, even if doubled in size, would be unlikely to fully attenuate the overall benefit of icosapent ethyl observed.
They add that they are not aware of a method to assess what the potential magnitude might be of a combination of the multiple effects.
New data do not change the debate
“We did a large, well-powered randomized trial, and this paper shouldn’t change anything in how that trial should be interpreted,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
He claims the new biomarkers evaluated in the study are correlated with LDL and CRP, data which have already been reported and analyzed so have limited relevance.
“It’s not really independent biomarker information; this is what we would expect to see when we see small increases in LDL and CRP. So, I don’t think this new information fundamentally changes the debate,” he said.
Dr. Bhatt also pointed out that the study highlights relative increases rather than absolute increases in the biomarkers, making it seem more alarming than is actually the case.
“The paper makes it seem like that there are large increases in these other biomarkers, but the values reported are relative increases and the absolute increases were actually rather small. In many cases, the changes reported are less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay used,” he noted.
He added: “Even if one is unable to get around the placebo issue in the REDUCE-IT trial, there will always be the JELIS trial – a randomized trial with no placebo showing a 19% relative risk reduction. While the biomarker data may be interesting, what really matters in the end is clinical events. And significant reductions in two independent trials should be enough.”
Dr. Bhatt says the REDUCE-IT steering committee does not believe another trial is needed. “Maybe a different population would be good – such as primary prevention, patients without elevated triglycerides – but just repeating REDUCE- IT with a different placebo would be a waste of resources,” he commented.
But Dr. Nissen refuted Dr. Bhatt’s claims.
“These biomarkers are not in the same pathways as LDL and CRP, and these are not small increases. In the CANTOS trial, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-1β beta showed a significant benefit. The increase in interleukin-1β now reported in REDUCE-IT is exactly the opposite of CANTOS,” he pointed out.
“The FDA did not know about these additional biomarkers when it reviewed the data on LDL and CRP. Now we have new information. It needs to be looked at again,” Dr. Nissen added.
Funding for the study was provided by Amarin Pharma. Dr. Bhatt was the lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial. Dr. Nissen was the lead investigator the STRENGTH trial. Further disclosures of the authors can be found in Circulation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis of the REDUCE-IT study has reignited concerns that the benefit shown by the high-dose fish oil product in the study, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), may have been related to harms caused by the placebo mineral oil.
Results show that allocation to icosapent ethyl had minimal effects on a series of biomarkers associated with atherosclerotic disease, whereas levels of these biomarkers increased among those allocated to mineral oil.
At 12 months, the median percent increases from baseline in the mineral oil group were 1.5% for homocysteine, 2.2% for lipoprotein(a), 10.9% for oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, 16.2% for interleukin (IL)-6, 18.5% for lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, 21.9% for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and 28.9% for IL-1β. The changes were similar at 24 months. However, in the icosapent ethyl group, there were minimal changes in these biomarkers at 12 and 24 months.
The study was published online in Circulation.
The authors, led by Paul Ridker, MD, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, do not voice much opinion on what the results mean, concluding that “the effect of these findings on the interpretation of the REDUCE-IT trial results remains unclear and will require further investigation.”
They also say that a second icosapent ethyl trial using a nonmineral oil comparator “would help resolve ongoing controversy.”
However, the authors are a mixed group; Dr. Ridker and some of his coauthors were not part of the original REDUCE-IT trial, whereas other coauthors were members of the REDUCE-IT steering committee, and one was an employee of Amarin.
Lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, Deepak Bhatt, MD, also from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, who is the senior author of the current study, played down the new findings, saying they did not offer much new incremental information on mechanistic insight.
“These are small degrees of biomarker increases on an absolute level we are seeing with the placebo that would not be expected to produce harm,” Dr. Bhatt told this news organization. He also said the Circulation peer-review process had removed some of the discussion, which could lead to some “misinterpretation” of the authors’ views.
Dr. Ridker was unavailable for further comment.
The publication of this study has inevitably poured fuel on the fire regarding the controversy that has long dogged the REDUCE-IT trial, with questions about the large reduction in event rates seen with icosapent ethyl without an obvious mechanistic explanation.
‘Smoking gun’
One of the loudest critics of the study, Steve Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, described the new findings as “the closest thing I’ve seen to a smoking gun in medicine for a long, long time.”
“The result of this new analysis shows that mineral oil increases virtually every inflammatory and lipid marker that they measured,” he commented.
“There are a lot of theories, but the bottom line is that something really bad happened in the mineral-oil group, which makes icosapent ethyl look efficacious. In my view, this needs to be reviewed by the FDA for consideration of removing the label claim for cardiovascular benefit.”
Other experts in the field not directly involved in the study voiced concern about these new findings, adding to calls for another trial.
In a Twitter thread on the issue, Harlan Krumholz, MD, describes the Circulation publication as “an exceptionally important article,” adding that it is “time to rethink this drug.”
“My point is ... once you know you have non-neutral comparator and the effect on risk biomarkers is far from trivial ... then you have introduced substantial uncertainty about the trial result, as conveyed by the authors ... and no one can say what would happen with a neutral comparator,” Dr. Krumholz writes.
In an accompanying editorial in Circulation, Robert Harrington, MD, professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, concludes that “the hard reality is that we are left with uncertainties and the questions raised by use of the mineral oil as placebo can only be answered by another randomized controlled trial.”
“My main points are that the chosen placebo was not inert (an essential characteristic for an active control–placebo comparison), that the biomarker data show elevations in multiple markers involved with inflammatory pathways associated with atherosclerosis, and that these data create enough uncertainty in the trial interpretation that the best recourse to answer the criticisms is to do another trial with a truly inert placebo,” Dr. Harrington said in an interview.
He added that Dr. Bhatt’s point that the changes in biomarkers are too small to really matter clinically may be right. “But for me, the uncertainties mean that I have less confidence in the true magnitude of the treatment effect than I would have if there were no changes in the inflammatory markers.”
In Circulation, the authors say it is unclear why multiple biomarkers increased over time among REDUCE-IT participants allocated to mineral oil. They note that no substantive changes in these biomarkers were observed in the placebo groups over periods of 3-5 years in other trials, including JUPITER, CIRT, CANTOS, SPIRE, and the STRENGTH trials, which evaluated a different high-dose omega-3 oil product but used corn oil as the placebo.
“The core design of REDUCE-IT does not make it possible to resolve convincingly whether any adverse effects associated with mineral oil use as a comparator may have affected clinical outcomes,” they write.
They point out that regulatory agencies evaluating REDUCE-IT estimated that approximately 3% of the net clinical benefit observed with icosapent ethyl might have been a consequence of adverse biomarker effects on LDL cholesterol and hsCRP attributable to mineral oil. But in the context of an overall 25% relative risk reduction in first events and a 30% reduction in total ischemic events observed, a potential bias of this magnitude, even if doubled in size, would be unlikely to fully attenuate the overall benefit of icosapent ethyl observed.
They add that they are not aware of a method to assess what the potential magnitude might be of a combination of the multiple effects.
New data do not change the debate
“We did a large, well-powered randomized trial, and this paper shouldn’t change anything in how that trial should be interpreted,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
He claims the new biomarkers evaluated in the study are correlated with LDL and CRP, data which have already been reported and analyzed so have limited relevance.
“It’s not really independent biomarker information; this is what we would expect to see when we see small increases in LDL and CRP. So, I don’t think this new information fundamentally changes the debate,” he said.
Dr. Bhatt also pointed out that the study highlights relative increases rather than absolute increases in the biomarkers, making it seem more alarming than is actually the case.
“The paper makes it seem like that there are large increases in these other biomarkers, but the values reported are relative increases and the absolute increases were actually rather small. In many cases, the changes reported are less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay used,” he noted.
He added: “Even if one is unable to get around the placebo issue in the REDUCE-IT trial, there will always be the JELIS trial – a randomized trial with no placebo showing a 19% relative risk reduction. While the biomarker data may be interesting, what really matters in the end is clinical events. And significant reductions in two independent trials should be enough.”
Dr. Bhatt says the REDUCE-IT steering committee does not believe another trial is needed. “Maybe a different population would be good – such as primary prevention, patients without elevated triglycerides – but just repeating REDUCE- IT with a different placebo would be a waste of resources,” he commented.
But Dr. Nissen refuted Dr. Bhatt’s claims.
“These biomarkers are not in the same pathways as LDL and CRP, and these are not small increases. In the CANTOS trial, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-1β beta showed a significant benefit. The increase in interleukin-1β now reported in REDUCE-IT is exactly the opposite of CANTOS,” he pointed out.
“The FDA did not know about these additional biomarkers when it reviewed the data on LDL and CRP. Now we have new information. It needs to be looked at again,” Dr. Nissen added.
Funding for the study was provided by Amarin Pharma. Dr. Bhatt was the lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial. Dr. Nissen was the lead investigator the STRENGTH trial. Further disclosures of the authors can be found in Circulation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A new analysis of the REDUCE-IT study has reignited concerns that the benefit shown by the high-dose fish oil product in the study, icosapent ethyl (Vascepa, Amarin), may have been related to harms caused by the placebo mineral oil.
Results show that allocation to icosapent ethyl had minimal effects on a series of biomarkers associated with atherosclerotic disease, whereas levels of these biomarkers increased among those allocated to mineral oil.
At 12 months, the median percent increases from baseline in the mineral oil group were 1.5% for homocysteine, 2.2% for lipoprotein(a), 10.9% for oxidized low-density-lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, 16.2% for interleukin (IL)-6, 18.5% for lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2, 21.9% for high-sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and 28.9% for IL-1β. The changes were similar at 24 months. However, in the icosapent ethyl group, there were minimal changes in these biomarkers at 12 and 24 months.
The study was published online in Circulation.
The authors, led by Paul Ridker, MD, Brigham & Women’s Hospital, Boston, do not voice much opinion on what the results mean, concluding that “the effect of these findings on the interpretation of the REDUCE-IT trial results remains unclear and will require further investigation.”
They also say that a second icosapent ethyl trial using a nonmineral oil comparator “would help resolve ongoing controversy.”
However, the authors are a mixed group; Dr. Ridker and some of his coauthors were not part of the original REDUCE-IT trial, whereas other coauthors were members of the REDUCE-IT steering committee, and one was an employee of Amarin.
Lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial, Deepak Bhatt, MD, also from Brigham & Women’s Hospital, who is the senior author of the current study, played down the new findings, saying they did not offer much new incremental information on mechanistic insight.
“These are small degrees of biomarker increases on an absolute level we are seeing with the placebo that would not be expected to produce harm,” Dr. Bhatt told this news organization. He also said the Circulation peer-review process had removed some of the discussion, which could lead to some “misinterpretation” of the authors’ views.
Dr. Ridker was unavailable for further comment.
The publication of this study has inevitably poured fuel on the fire regarding the controversy that has long dogged the REDUCE-IT trial, with questions about the large reduction in event rates seen with icosapent ethyl without an obvious mechanistic explanation.
‘Smoking gun’
One of the loudest critics of the study, Steve Nissen, MD, Cleveland Clinic, described the new findings as “the closest thing I’ve seen to a smoking gun in medicine for a long, long time.”
“The result of this new analysis shows that mineral oil increases virtually every inflammatory and lipid marker that they measured,” he commented.
“There are a lot of theories, but the bottom line is that something really bad happened in the mineral-oil group, which makes icosapent ethyl look efficacious. In my view, this needs to be reviewed by the FDA for consideration of removing the label claim for cardiovascular benefit.”
Other experts in the field not directly involved in the study voiced concern about these new findings, adding to calls for another trial.
In a Twitter thread on the issue, Harlan Krumholz, MD, describes the Circulation publication as “an exceptionally important article,” adding that it is “time to rethink this drug.”
“My point is ... once you know you have non-neutral comparator and the effect on risk biomarkers is far from trivial ... then you have introduced substantial uncertainty about the trial result, as conveyed by the authors ... and no one can say what would happen with a neutral comparator,” Dr. Krumholz writes.
In an accompanying editorial in Circulation, Robert Harrington, MD, professor of medicine at Stanford (Calif.) University, concludes that “the hard reality is that we are left with uncertainties and the questions raised by use of the mineral oil as placebo can only be answered by another randomized controlled trial.”
“My main points are that the chosen placebo was not inert (an essential characteristic for an active control–placebo comparison), that the biomarker data show elevations in multiple markers involved with inflammatory pathways associated with atherosclerosis, and that these data create enough uncertainty in the trial interpretation that the best recourse to answer the criticisms is to do another trial with a truly inert placebo,” Dr. Harrington said in an interview.
He added that Dr. Bhatt’s point that the changes in biomarkers are too small to really matter clinically may be right. “But for me, the uncertainties mean that I have less confidence in the true magnitude of the treatment effect than I would have if there were no changes in the inflammatory markers.”
In Circulation, the authors say it is unclear why multiple biomarkers increased over time among REDUCE-IT participants allocated to mineral oil. They note that no substantive changes in these biomarkers were observed in the placebo groups over periods of 3-5 years in other trials, including JUPITER, CIRT, CANTOS, SPIRE, and the STRENGTH trials, which evaluated a different high-dose omega-3 oil product but used corn oil as the placebo.
“The core design of REDUCE-IT does not make it possible to resolve convincingly whether any adverse effects associated with mineral oil use as a comparator may have affected clinical outcomes,” they write.
They point out that regulatory agencies evaluating REDUCE-IT estimated that approximately 3% of the net clinical benefit observed with icosapent ethyl might have been a consequence of adverse biomarker effects on LDL cholesterol and hsCRP attributable to mineral oil. But in the context of an overall 25% relative risk reduction in first events and a 30% reduction in total ischemic events observed, a potential bias of this magnitude, even if doubled in size, would be unlikely to fully attenuate the overall benefit of icosapent ethyl observed.
They add that they are not aware of a method to assess what the potential magnitude might be of a combination of the multiple effects.
New data do not change the debate
“We did a large, well-powered randomized trial, and this paper shouldn’t change anything in how that trial should be interpreted,” Dr. Bhatt said in an interview.
He claims the new biomarkers evaluated in the study are correlated with LDL and CRP, data which have already been reported and analyzed so have limited relevance.
“It’s not really independent biomarker information; this is what we would expect to see when we see small increases in LDL and CRP. So, I don’t think this new information fundamentally changes the debate,” he said.
Dr. Bhatt also pointed out that the study highlights relative increases rather than absolute increases in the biomarkers, making it seem more alarming than is actually the case.
“The paper makes it seem like that there are large increases in these other biomarkers, but the values reported are relative increases and the absolute increases were actually rather small. In many cases, the changes reported are less than the lower limit of quantification of the assay used,” he noted.
He added: “Even if one is unable to get around the placebo issue in the REDUCE-IT trial, there will always be the JELIS trial – a randomized trial with no placebo showing a 19% relative risk reduction. While the biomarker data may be interesting, what really matters in the end is clinical events. And significant reductions in two independent trials should be enough.”
Dr. Bhatt says the REDUCE-IT steering committee does not believe another trial is needed. “Maybe a different population would be good – such as primary prevention, patients without elevated triglycerides – but just repeating REDUCE- IT with a different placebo would be a waste of resources,” he commented.
But Dr. Nissen refuted Dr. Bhatt’s claims.
“These biomarkers are not in the same pathways as LDL and CRP, and these are not small increases. In the CANTOS trial, a monoclonal antibody against interleukin-1β beta showed a significant benefit. The increase in interleukin-1β now reported in REDUCE-IT is exactly the opposite of CANTOS,” he pointed out.
“The FDA did not know about these additional biomarkers when it reviewed the data on LDL and CRP. Now we have new information. It needs to be looked at again,” Dr. Nissen added.
Funding for the study was provided by Amarin Pharma. Dr. Bhatt was the lead investigator of the REDUCE-IT trial. Dr. Nissen was the lead investigator the STRENGTH trial. Further disclosures of the authors can be found in Circulation.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CIRCULATION