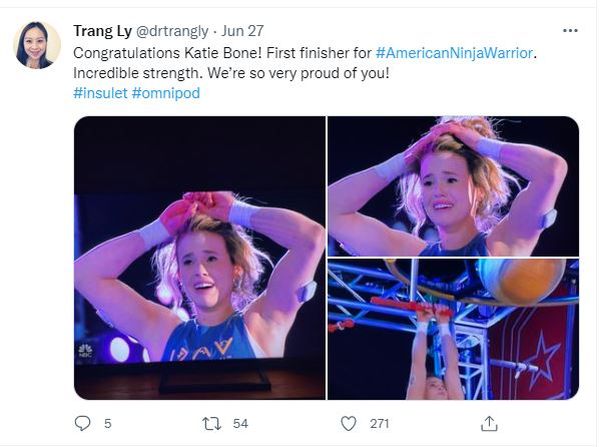User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Meet a champion climber with type 1 diabetes
Managing type 1 diabetes is never easy. But if you ask 16-year-old climbing star Katie Bone, she’ll tell you that she will never let this disease get in the way of her goals.
“My motto is the same one as Bethany Hamilton’s – the surfer who lost her arm in a shark attack: ‘I don’t need easy, I just need possible,” said Ms. Bone, who lives in Albuquerque and has been a competitive rock climber since she was 8 years old. “That really stuck with me.”
Just watching her compete on NBC’s hit reality show American Ninja Warrior in June is proof of that. Not only did the nationally ranked climber fly through the obstacles with grace and grit, but she proudly showed off her two monitoring devices: a glucose monitor on one arm and a tubeless insulin pump on the other.
“I specifically decided to keep my devices visible when I went on the show,” she said. “It’s part of my life, and I wanted to show that I’m not ashamed to wear medical devices.”
Still, it has been a long journey since Bone was diagnosed in 2017. She was just 11 years old at the time and had recently done a climbing competition when she started feeling ill.
“I didn’t perform well,” she said. “I needed to go to the bathroom a lot and felt really nauseous. Three days later, we ended up in urgent care.”
When her doctor first told her she had diabetes, she started crying.
“My grandma had type 1 and was extremely sick and died from complications,” she said. “That was all I knew about diabetes, and it was scary to think my life could be like that.”
But her outlook brightened when her doctor assured her that she could keep climbing.
“When I was told that I could keep competing, a switch flipped for me and I made a decision that nothing would hold me back,” she says.
But every day isn’t easy.
“It’s sometimes really hard to manage my diabetes during competitions,” she said. “When we climb, for example, we’re not allowed to have our phones, and I manage my [glucose monitor] through my phone. This means accommodations have to be made for me.”
And managing her diabetes can be unpredictable at times.
“If my blood sugar is low or high, I might be put last in a competition,” she said. “That messes up my warm-up and my mental game. It’s a never-ending battle.”
Ultimately, Ms. Bone’s goal is to inspire others and advocate for diabetes awareness. She says she’s been overwhelmed by viewer responses to her appearance on the show.
“I heard from so many parents and kids,” she said. “I want the world to know that wearing a pump on your arm only makes you more amazing.”
She also draws inspiration from others with diabetes.
“Everyone with this disease is a role model for me, since everyone is fighting their own battles,” she said. “Diabetes is different for everyone, and seeing how people can do what they do despite the diagnosis has been incredibly inspiring.”
For now, the rising high school junior plans to continue training and competing.
“My goal is to make the 2024 Olympic climbing team in Paris,” she said. “I’ve always wanted to compete in the Olympics since I was a little kid. Nothing can stop me.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Managing type 1 diabetes is never easy. But if you ask 16-year-old climbing star Katie Bone, she’ll tell you that she will never let this disease get in the way of her goals.
“My motto is the same one as Bethany Hamilton’s – the surfer who lost her arm in a shark attack: ‘I don’t need easy, I just need possible,” said Ms. Bone, who lives in Albuquerque and has been a competitive rock climber since she was 8 years old. “That really stuck with me.”
Just watching her compete on NBC’s hit reality show American Ninja Warrior in June is proof of that. Not only did the nationally ranked climber fly through the obstacles with grace and grit, but she proudly showed off her two monitoring devices: a glucose monitor on one arm and a tubeless insulin pump on the other.
“I specifically decided to keep my devices visible when I went on the show,” she said. “It’s part of my life, and I wanted to show that I’m not ashamed to wear medical devices.”
Still, it has been a long journey since Bone was diagnosed in 2017. She was just 11 years old at the time and had recently done a climbing competition when she started feeling ill.
“I didn’t perform well,” she said. “I needed to go to the bathroom a lot and felt really nauseous. Three days later, we ended up in urgent care.”
When her doctor first told her she had diabetes, she started crying.
“My grandma had type 1 and was extremely sick and died from complications,” she said. “That was all I knew about diabetes, and it was scary to think my life could be like that.”
But her outlook brightened when her doctor assured her that she could keep climbing.
“When I was told that I could keep competing, a switch flipped for me and I made a decision that nothing would hold me back,” she says.
But every day isn’t easy.
“It’s sometimes really hard to manage my diabetes during competitions,” she said. “When we climb, for example, we’re not allowed to have our phones, and I manage my [glucose monitor] through my phone. This means accommodations have to be made for me.”
And managing her diabetes can be unpredictable at times.
“If my blood sugar is low or high, I might be put last in a competition,” she said. “That messes up my warm-up and my mental game. It’s a never-ending battle.”
Ultimately, Ms. Bone’s goal is to inspire others and advocate for diabetes awareness. She says she’s been overwhelmed by viewer responses to her appearance on the show.
“I heard from so many parents and kids,” she said. “I want the world to know that wearing a pump on your arm only makes you more amazing.”
She also draws inspiration from others with diabetes.
“Everyone with this disease is a role model for me, since everyone is fighting their own battles,” she said. “Diabetes is different for everyone, and seeing how people can do what they do despite the diagnosis has been incredibly inspiring.”
For now, the rising high school junior plans to continue training and competing.
“My goal is to make the 2024 Olympic climbing team in Paris,” she said. “I’ve always wanted to compete in the Olympics since I was a little kid. Nothing can stop me.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Managing type 1 diabetes is never easy. But if you ask 16-year-old climbing star Katie Bone, she’ll tell you that she will never let this disease get in the way of her goals.
“My motto is the same one as Bethany Hamilton’s – the surfer who lost her arm in a shark attack: ‘I don’t need easy, I just need possible,” said Ms. Bone, who lives in Albuquerque and has been a competitive rock climber since she was 8 years old. “That really stuck with me.”
Just watching her compete on NBC’s hit reality show American Ninja Warrior in June is proof of that. Not only did the nationally ranked climber fly through the obstacles with grace and grit, but she proudly showed off her two monitoring devices: a glucose monitor on one arm and a tubeless insulin pump on the other.
“I specifically decided to keep my devices visible when I went on the show,” she said. “It’s part of my life, and I wanted to show that I’m not ashamed to wear medical devices.”
Still, it has been a long journey since Bone was diagnosed in 2017. She was just 11 years old at the time and had recently done a climbing competition when she started feeling ill.
“I didn’t perform well,” she said. “I needed to go to the bathroom a lot and felt really nauseous. Three days later, we ended up in urgent care.”
When her doctor first told her she had diabetes, she started crying.
“My grandma had type 1 and was extremely sick and died from complications,” she said. “That was all I knew about diabetes, and it was scary to think my life could be like that.”
But her outlook brightened when her doctor assured her that she could keep climbing.
“When I was told that I could keep competing, a switch flipped for me and I made a decision that nothing would hold me back,” she says.
But every day isn’t easy.
“It’s sometimes really hard to manage my diabetes during competitions,” she said. “When we climb, for example, we’re not allowed to have our phones, and I manage my [glucose monitor] through my phone. This means accommodations have to be made for me.”
And managing her diabetes can be unpredictable at times.
“If my blood sugar is low or high, I might be put last in a competition,” she said. “That messes up my warm-up and my mental game. It’s a never-ending battle.”
Ultimately, Ms. Bone’s goal is to inspire others and advocate for diabetes awareness. She says she’s been overwhelmed by viewer responses to her appearance on the show.
“I heard from so many parents and kids,” she said. “I want the world to know that wearing a pump on your arm only makes you more amazing.”
She also draws inspiration from others with diabetes.
“Everyone with this disease is a role model for me, since everyone is fighting their own battles,” she said. “Diabetes is different for everyone, and seeing how people can do what they do despite the diagnosis has been incredibly inspiring.”
For now, the rising high school junior plans to continue training and competing.
“My goal is to make the 2024 Olympic climbing team in Paris,” she said. “I’ve always wanted to compete in the Olympics since I was a little kid. Nothing can stop me.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Short walks after meals can cut diabetes risk
Taking a brief walk after eating can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a recent study published in Sports Medicine (2022 Aug;52:1765-87).
Light walking after a meal – even for 2-5 minutes – can reduce blood sugar and insulin levels, the researchers found.
Blood sugar levels spike after eating, and the insulin produced to control them can lead to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, the researchers explained.
“With standing and walking, there are contractions of your muscles” that use glucose and lower blood sugar levels, Aidan Buffey, the lead study author and a PhD student in physical education and sport sciences at the University of Limerick (Ireland), told The Times.
“If you can do physical activity before the glucose peak, typically 60-90 minutes [after eating], that is when you’re going to have the benefit of not having the glucose spike,” he said.
Mr. Buffey and colleagues looked at seven studies to understand what would happen if you used standing or easy walking to interrupt prolonged sitting.
In five of the studies, none of the participants had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The other two studies included people with and without diabetes. The people in the studies were asked to either stand or walk for 2-5 minutes every 20-30 minutes over the course of a full day.
All seven studies showed that standing after a meal is better than sitting, and taking a short walk offered even better health benefits. Those who stood up for a short period of time after a meal had improved blood sugar levels but not insulin, while those who took a brief walk after a meal had lower blood sugar and insulin levels. Those who walked also had blood sugar levels that rose and fell more gradually, which is critical for managing diabetes.
Going for a walk, doing housework, or finding other ways to move your body within 60-90 minutes after eating could offer the best results, the study authors concluded.
These “mini-walks” could also be useful during the workday to break up prolonged periods of sitting at a desk.
“People are not going to get up and run on a treadmill or run around the office,” Mr. Buffey told The New York Times.
But making mini-walks a normal thing during the workday could be easy and acceptable at the office, he said. Even if people can’t take walks, standing up will help somewhat.
“Each small thing you do will have benefits, even if it is a small step,” Kershaw Patel, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Houston Methodist Hospital, told the newspaper. Dr. Patel wasn’t involved with the study.
“It’s a gradual effect of more activity, better health,” he said. “Each incremental step, each incremental stand or brisk walk appears to have a benefit.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Taking a brief walk after eating can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a recent study published in Sports Medicine (2022 Aug;52:1765-87).
Light walking after a meal – even for 2-5 minutes – can reduce blood sugar and insulin levels, the researchers found.
Blood sugar levels spike after eating, and the insulin produced to control them can lead to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, the researchers explained.
“With standing and walking, there are contractions of your muscles” that use glucose and lower blood sugar levels, Aidan Buffey, the lead study author and a PhD student in physical education and sport sciences at the University of Limerick (Ireland), told The Times.
“If you can do physical activity before the glucose peak, typically 60-90 minutes [after eating], that is when you’re going to have the benefit of not having the glucose spike,” he said.
Mr. Buffey and colleagues looked at seven studies to understand what would happen if you used standing or easy walking to interrupt prolonged sitting.
In five of the studies, none of the participants had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The other two studies included people with and without diabetes. The people in the studies were asked to either stand or walk for 2-5 minutes every 20-30 minutes over the course of a full day.
All seven studies showed that standing after a meal is better than sitting, and taking a short walk offered even better health benefits. Those who stood up for a short period of time after a meal had improved blood sugar levels but not insulin, while those who took a brief walk after a meal had lower blood sugar and insulin levels. Those who walked also had blood sugar levels that rose and fell more gradually, which is critical for managing diabetes.
Going for a walk, doing housework, or finding other ways to move your body within 60-90 minutes after eating could offer the best results, the study authors concluded.
These “mini-walks” could also be useful during the workday to break up prolonged periods of sitting at a desk.
“People are not going to get up and run on a treadmill or run around the office,” Mr. Buffey told The New York Times.
But making mini-walks a normal thing during the workday could be easy and acceptable at the office, he said. Even if people can’t take walks, standing up will help somewhat.
“Each small thing you do will have benefits, even if it is a small step,” Kershaw Patel, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Houston Methodist Hospital, told the newspaper. Dr. Patel wasn’t involved with the study.
“It’s a gradual effect of more activity, better health,” he said. “Each incremental step, each incremental stand or brisk walk appears to have a benefit.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Taking a brief walk after eating can help lower the risk of type 2 diabetes, according to a recent study published in Sports Medicine (2022 Aug;52:1765-87).
Light walking after a meal – even for 2-5 minutes – can reduce blood sugar and insulin levels, the researchers found.
Blood sugar levels spike after eating, and the insulin produced to control them can lead to diabetes and cardiovascular issues, the researchers explained.
“With standing and walking, there are contractions of your muscles” that use glucose and lower blood sugar levels, Aidan Buffey, the lead study author and a PhD student in physical education and sport sciences at the University of Limerick (Ireland), told The Times.
“If you can do physical activity before the glucose peak, typically 60-90 minutes [after eating], that is when you’re going to have the benefit of not having the glucose spike,” he said.
Mr. Buffey and colleagues looked at seven studies to understand what would happen if you used standing or easy walking to interrupt prolonged sitting.
In five of the studies, none of the participants had prediabetes or type 2 diabetes. The other two studies included people with and without diabetes. The people in the studies were asked to either stand or walk for 2-5 minutes every 20-30 minutes over the course of a full day.
All seven studies showed that standing after a meal is better than sitting, and taking a short walk offered even better health benefits. Those who stood up for a short period of time after a meal had improved blood sugar levels but not insulin, while those who took a brief walk after a meal had lower blood sugar and insulin levels. Those who walked also had blood sugar levels that rose and fell more gradually, which is critical for managing diabetes.
Going for a walk, doing housework, or finding other ways to move your body within 60-90 minutes after eating could offer the best results, the study authors concluded.
These “mini-walks” could also be useful during the workday to break up prolonged periods of sitting at a desk.
“People are not going to get up and run on a treadmill or run around the office,” Mr. Buffey told The New York Times.
But making mini-walks a normal thing during the workday could be easy and acceptable at the office, he said. Even if people can’t take walks, standing up will help somewhat.
“Each small thing you do will have benefits, even if it is a small step,” Kershaw Patel, MD, a preventive cardiologist at Houston Methodist Hospital, told the newspaper. Dr. Patel wasn’t involved with the study.
“It’s a gradual effect of more activity, better health,” he said. “Each incremental step, each incremental stand or brisk walk appears to have a benefit.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Saddled with med school debt, yet left out of loan forgiveness plans
In a recently obtained plan by Politico, the Biden administration is zeroing in on a broad student loan forgiveness plan to be released imminently. The plan would broadly forgive $10,000 in federal student loans, including graduate and PLUS loans. However, there’s a rub: The plan restricts the forgiveness to those with incomes below $150,000.
This would unfairly exclude many in health care from receiving this forgiveness, an egregious oversight given how much health care providers have sacrificed during the pandemic.
What was proposed?
Previously, it was reported that the Biden administration was considering this same amount of forgiveness, but with plans to exclude borrowers by either career or income. Student loan payments have been on an extended CARES Act forbearance since March 2020, with payment resumption planned for Aug. 31. The administration has said that they would deliver a plan for further extensions before this date and have repeatedly teased including forgiveness.
Forgiveness for some ...
Forgiving $10,000 of federal student loans would relieve some 15 million borrowers of student debt, roughly one-third of the 45 million borrowers with debt.
This would provide a massive boost to these borrowers (who disproportionately are female, low-income, and non-White), many of whom were targeted by predatory institutions whose education didn’t offer any actual tangible benefit to their earnings. While this is a group that absolutely ought to have their loans forgiven, drawing an income line inappropriately restricts those in health care from receiving any forgiveness.
... But not for others
Someone making an annual gross income of $150,000 is in the 80th percentile of earners in the United States (for comparison, the top 1% took home more than $505,000 in 2021). What student loan borrowers make up the remaining 20%? Overwhelmingly, health care providers occupy that tier: physicians, dentists, veterinarians, and advanced-practice nurses.
These schools leave their graduates with some of the highest student loan burdens, with veterinarians, dentists, and physicians having the highest debt-to-income ratios of any professional careers.
Flat forgiveness is regressive
Forgiving any student debt is the right direction. Too may have fallen victim to an industry without quality control, appropriate regulation, or price control. Quite the opposite, the blank-check model of student loan financing has led to an arms race as it comes to capital improvements in university spending.
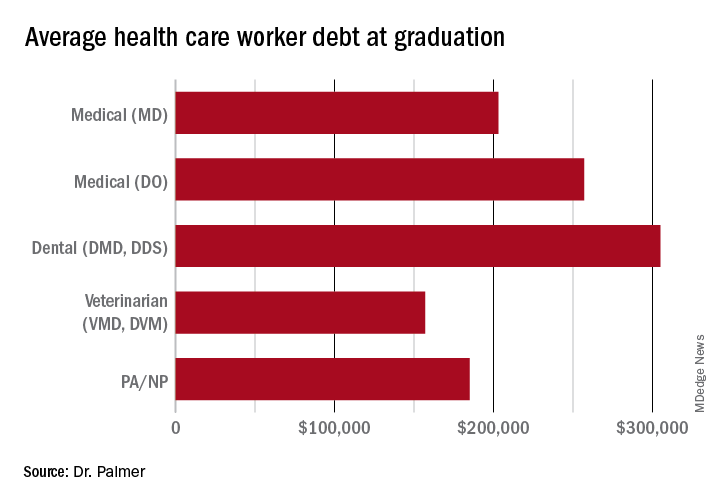
The price of medical schools has risen more than four times as fast as inflation over the past 30 years, with dental and veterinary schools and nursing education showing similarly exaggerated price increases. Trainees in these fields are more likely to have taken on six-figure debt, with average debt loads at graduation in the table below. While $10,000 will move the proverbial needle less for these borrowers, does that mean they should be excluded?
Health care workers’ income declines during the pandemic
Now, over 2½ years since the start of the COVID pandemic, multiple reports have demonstrated that health care workers have suffered a loss in income. This loss in income was never compensated for, as the Paycheck Protection Program and the individual economic stimuli typically excluded doctors and high earners.
COVID and the hazard tax
As a provider during the COVID-19 pandemic, I didn’t ask for hazard pay. I supported those who did but recognized their requests were more ceremonial than they were likely to be successful.
However, I flatly reject the idea that my fellow health care practitioners are not deserving of student loan forgiveness simply based on an arbitrary income threshold. Health care providers are saddled with high debt burden, have suffered lost income, and have given of themselves during a devastating pandemic, where more than 1 million perished in the United States.
Bottom line
Health care workers should not be excluded from student loan forgiveness. Sadly, the Biden administration has signaled that they are dropping career-based exclusions in favor of more broadly harmful income-based forgiveness restrictions. This will disproportionately harm physicians and other health care workers.
These practitioners have suffered financially as a result of working through the COVID pandemic; should they also be forced to shoulder another financial injury by being excluded from student loan forgiveness?
Dr. Palmer is the chief operating officer and cofounder of Panacea Financial. He is also a practicing pediatric hospitalist at Boston Children’s Hospital and is on faculty at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recently obtained plan by Politico, the Biden administration is zeroing in on a broad student loan forgiveness plan to be released imminently. The plan would broadly forgive $10,000 in federal student loans, including graduate and PLUS loans. However, there’s a rub: The plan restricts the forgiveness to those with incomes below $150,000.
This would unfairly exclude many in health care from receiving this forgiveness, an egregious oversight given how much health care providers have sacrificed during the pandemic.
What was proposed?
Previously, it was reported that the Biden administration was considering this same amount of forgiveness, but with plans to exclude borrowers by either career or income. Student loan payments have been on an extended CARES Act forbearance since March 2020, with payment resumption planned for Aug. 31. The administration has said that they would deliver a plan for further extensions before this date and have repeatedly teased including forgiveness.
Forgiveness for some ...
Forgiving $10,000 of federal student loans would relieve some 15 million borrowers of student debt, roughly one-third of the 45 million borrowers with debt.
This would provide a massive boost to these borrowers (who disproportionately are female, low-income, and non-White), many of whom were targeted by predatory institutions whose education didn’t offer any actual tangible benefit to their earnings. While this is a group that absolutely ought to have their loans forgiven, drawing an income line inappropriately restricts those in health care from receiving any forgiveness.
... But not for others
Someone making an annual gross income of $150,000 is in the 80th percentile of earners in the United States (for comparison, the top 1% took home more than $505,000 in 2021). What student loan borrowers make up the remaining 20%? Overwhelmingly, health care providers occupy that tier: physicians, dentists, veterinarians, and advanced-practice nurses.
These schools leave their graduates with some of the highest student loan burdens, with veterinarians, dentists, and physicians having the highest debt-to-income ratios of any professional careers.
Flat forgiveness is regressive
Forgiving any student debt is the right direction. Too may have fallen victim to an industry without quality control, appropriate regulation, or price control. Quite the opposite, the blank-check model of student loan financing has led to an arms race as it comes to capital improvements in university spending.

The price of medical schools has risen more than four times as fast as inflation over the past 30 years, with dental and veterinary schools and nursing education showing similarly exaggerated price increases. Trainees in these fields are more likely to have taken on six-figure debt, with average debt loads at graduation in the table below. While $10,000 will move the proverbial needle less for these borrowers, does that mean they should be excluded?
Health care workers’ income declines during the pandemic
Now, over 2½ years since the start of the COVID pandemic, multiple reports have demonstrated that health care workers have suffered a loss in income. This loss in income was never compensated for, as the Paycheck Protection Program and the individual economic stimuli typically excluded doctors and high earners.
COVID and the hazard tax
As a provider during the COVID-19 pandemic, I didn’t ask for hazard pay. I supported those who did but recognized their requests were more ceremonial than they were likely to be successful.
However, I flatly reject the idea that my fellow health care practitioners are not deserving of student loan forgiveness simply based on an arbitrary income threshold. Health care providers are saddled with high debt burden, have suffered lost income, and have given of themselves during a devastating pandemic, where more than 1 million perished in the United States.
Bottom line
Health care workers should not be excluded from student loan forgiveness. Sadly, the Biden administration has signaled that they are dropping career-based exclusions in favor of more broadly harmful income-based forgiveness restrictions. This will disproportionately harm physicians and other health care workers.
These practitioners have suffered financially as a result of working through the COVID pandemic; should they also be forced to shoulder another financial injury by being excluded from student loan forgiveness?
Dr. Palmer is the chief operating officer and cofounder of Panacea Financial. He is also a practicing pediatric hospitalist at Boston Children’s Hospital and is on faculty at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
In a recently obtained plan by Politico, the Biden administration is zeroing in on a broad student loan forgiveness plan to be released imminently. The plan would broadly forgive $10,000 in federal student loans, including graduate and PLUS loans. However, there’s a rub: The plan restricts the forgiveness to those with incomes below $150,000.
This would unfairly exclude many in health care from receiving this forgiveness, an egregious oversight given how much health care providers have sacrificed during the pandemic.
What was proposed?
Previously, it was reported that the Biden administration was considering this same amount of forgiveness, but with plans to exclude borrowers by either career or income. Student loan payments have been on an extended CARES Act forbearance since March 2020, with payment resumption planned for Aug. 31. The administration has said that they would deliver a plan for further extensions before this date and have repeatedly teased including forgiveness.
Forgiveness for some ...
Forgiving $10,000 of federal student loans would relieve some 15 million borrowers of student debt, roughly one-third of the 45 million borrowers with debt.
This would provide a massive boost to these borrowers (who disproportionately are female, low-income, and non-White), many of whom were targeted by predatory institutions whose education didn’t offer any actual tangible benefit to their earnings. While this is a group that absolutely ought to have their loans forgiven, drawing an income line inappropriately restricts those in health care from receiving any forgiveness.
... But not for others
Someone making an annual gross income of $150,000 is in the 80th percentile of earners in the United States (for comparison, the top 1% took home more than $505,000 in 2021). What student loan borrowers make up the remaining 20%? Overwhelmingly, health care providers occupy that tier: physicians, dentists, veterinarians, and advanced-practice nurses.
These schools leave their graduates with some of the highest student loan burdens, with veterinarians, dentists, and physicians having the highest debt-to-income ratios of any professional careers.
Flat forgiveness is regressive
Forgiving any student debt is the right direction. Too may have fallen victim to an industry without quality control, appropriate regulation, or price control. Quite the opposite, the blank-check model of student loan financing has led to an arms race as it comes to capital improvements in university spending.

The price of medical schools has risen more than four times as fast as inflation over the past 30 years, with dental and veterinary schools and nursing education showing similarly exaggerated price increases. Trainees in these fields are more likely to have taken on six-figure debt, with average debt loads at graduation in the table below. While $10,000 will move the proverbial needle less for these borrowers, does that mean they should be excluded?
Health care workers’ income declines during the pandemic
Now, over 2½ years since the start of the COVID pandemic, multiple reports have demonstrated that health care workers have suffered a loss in income. This loss in income was never compensated for, as the Paycheck Protection Program and the individual economic stimuli typically excluded doctors and high earners.
COVID and the hazard tax
As a provider during the COVID-19 pandemic, I didn’t ask for hazard pay. I supported those who did but recognized their requests were more ceremonial than they were likely to be successful.
However, I flatly reject the idea that my fellow health care practitioners are not deserving of student loan forgiveness simply based on an arbitrary income threshold. Health care providers are saddled with high debt burden, have suffered lost income, and have given of themselves during a devastating pandemic, where more than 1 million perished in the United States.
Bottom line
Health care workers should not be excluded from student loan forgiveness. Sadly, the Biden administration has signaled that they are dropping career-based exclusions in favor of more broadly harmful income-based forgiveness restrictions. This will disproportionately harm physicians and other health care workers.
These practitioners have suffered financially as a result of working through the COVID pandemic; should they also be forced to shoulder another financial injury by being excluded from student loan forgiveness?
Dr. Palmer is the chief operating officer and cofounder of Panacea Financial. He is also a practicing pediatric hospitalist at Boston Children’s Hospital and is on faculty at Harvard Medical School, also in Boston.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Regular fasting linked to less severe COVID: Study
, according to the findings of a new study.
The study was done on men and women in Utah who were, on average, in their 60s and got COVID before vaccines were available.
Roughly one in three people in Utah fast from time to time – higher than in other states. This is partly because more than 60% of people in Utah belong to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, and roughly 40% of them fast – typically skipping two meals in a row.
Those who fasted, on average, for a day a month over the past 40 years were not less likely to get COVID, but they were less likely to be hospitalized or die from the virus.
“Intermittent fasting has already shown to lower inflammation and improve cardiovascular health,” lead study author Benjamin Horne, PhD, of Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“In this study, we’re finding additional benefits when it comes to battling an infection of COVID-19 in patients who have been fasting for decades,” he said.
The study was published in BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health.
Intermittent fasting not a substitute for a COVID-19 vaccine
Importantly, intermittent fasting shouldn’t be seen as a substitute for getting a COVID vaccine, the researchers stressed. Rather, periodic fasting might be a health habit to consider, since it is also linked to a lower risk of diabetes and heart disease, for example.
But anyone who wants to consider intermittent fasting should consult their doctor first, Dr. Horne stressed, especially if they are elderly, pregnant, or have diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease.
Fasting didn’t prevent COVID-19 but made it less severe
In their study, the team looked at data from 1,524 adults who were seen in the cardiac catheterization lab at Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute, completed a survey, and had a test for the virus that causes COVID-19 from March 16, 2020, to Feb. 25, 2021.
Of these patients, 205 tested positive for COVID, and of these, 73 reported that they had fasted regularly at least once a month.
Similar numbers of patients got COVID-19 whether they had, or had not, fasted regularly (14%, versus 13%).
But among those who tested positive for the virus, fewer patients were hospitalized for COVID or died during the study follow-up if they had fasted regularly (11%) than if they had not fasted regularly (29%).
Even when the analyses were adjusted for age, smoking, alcohol use, ethnicity, history of heart disease, and other factors, periodic fasting was still an independent predictor of a lower risk of hospitalization or death.
Several things may explain the findings, the researchers suggested.
A loss of appetite is a typical response to infection, they noted.
Fasting reduces inflammation, and after 12-14 hours of fasting, the body switches from using glucose in the blood to using ketones, including linoleic acid.
“There’s a pocket on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 that linoleic acid fits into – and can make the virus less able to attach to other cells,” Dr. Horne said.
Intermittent fasting also promotes autophagy, he noted, which is “the body’s recycling system that helps your body destroy and recycle damaged and infected cells.”
The researchers concluded that intermittent fasting plans should be investigated in further research “as a complementary therapy to vaccines to reduce COVID-19 severity, both during the pandemic and post pandemic, since repeat vaccinations cannot be performed every few months indefinitely for the entire world and vaccine access is limited in many nations.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to the findings of a new study.
The study was done on men and women in Utah who were, on average, in their 60s and got COVID before vaccines were available.
Roughly one in three people in Utah fast from time to time – higher than in other states. This is partly because more than 60% of people in Utah belong to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, and roughly 40% of them fast – typically skipping two meals in a row.
Those who fasted, on average, for a day a month over the past 40 years were not less likely to get COVID, but they were less likely to be hospitalized or die from the virus.
“Intermittent fasting has already shown to lower inflammation and improve cardiovascular health,” lead study author Benjamin Horne, PhD, of Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“In this study, we’re finding additional benefits when it comes to battling an infection of COVID-19 in patients who have been fasting for decades,” he said.
The study was published in BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health.
Intermittent fasting not a substitute for a COVID-19 vaccine
Importantly, intermittent fasting shouldn’t be seen as a substitute for getting a COVID vaccine, the researchers stressed. Rather, periodic fasting might be a health habit to consider, since it is also linked to a lower risk of diabetes and heart disease, for example.
But anyone who wants to consider intermittent fasting should consult their doctor first, Dr. Horne stressed, especially if they are elderly, pregnant, or have diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease.
Fasting didn’t prevent COVID-19 but made it less severe
In their study, the team looked at data from 1,524 adults who were seen in the cardiac catheterization lab at Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute, completed a survey, and had a test for the virus that causes COVID-19 from March 16, 2020, to Feb. 25, 2021.
Of these patients, 205 tested positive for COVID, and of these, 73 reported that they had fasted regularly at least once a month.
Similar numbers of patients got COVID-19 whether they had, or had not, fasted regularly (14%, versus 13%).
But among those who tested positive for the virus, fewer patients were hospitalized for COVID or died during the study follow-up if they had fasted regularly (11%) than if they had not fasted regularly (29%).
Even when the analyses were adjusted for age, smoking, alcohol use, ethnicity, history of heart disease, and other factors, periodic fasting was still an independent predictor of a lower risk of hospitalization or death.
Several things may explain the findings, the researchers suggested.
A loss of appetite is a typical response to infection, they noted.
Fasting reduces inflammation, and after 12-14 hours of fasting, the body switches from using glucose in the blood to using ketones, including linoleic acid.
“There’s a pocket on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 that linoleic acid fits into – and can make the virus less able to attach to other cells,” Dr. Horne said.
Intermittent fasting also promotes autophagy, he noted, which is “the body’s recycling system that helps your body destroy and recycle damaged and infected cells.”
The researchers concluded that intermittent fasting plans should be investigated in further research “as a complementary therapy to vaccines to reduce COVID-19 severity, both during the pandemic and post pandemic, since repeat vaccinations cannot be performed every few months indefinitely for the entire world and vaccine access is limited in many nations.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
, according to the findings of a new study.
The study was done on men and women in Utah who were, on average, in their 60s and got COVID before vaccines were available.
Roughly one in three people in Utah fast from time to time – higher than in other states. This is partly because more than 60% of people in Utah belong to the Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, and roughly 40% of them fast – typically skipping two meals in a row.
Those who fasted, on average, for a day a month over the past 40 years were not less likely to get COVID, but they were less likely to be hospitalized or die from the virus.
“Intermittent fasting has already shown to lower inflammation and improve cardiovascular health,” lead study author Benjamin Horne, PhD, of Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute in Salt Lake City, said in a statement.
“In this study, we’re finding additional benefits when it comes to battling an infection of COVID-19 in patients who have been fasting for decades,” he said.
The study was published in BMJ Nutrition, Prevention & Health.
Intermittent fasting not a substitute for a COVID-19 vaccine
Importantly, intermittent fasting shouldn’t be seen as a substitute for getting a COVID vaccine, the researchers stressed. Rather, periodic fasting might be a health habit to consider, since it is also linked to a lower risk of diabetes and heart disease, for example.
But anyone who wants to consider intermittent fasting should consult their doctor first, Dr. Horne stressed, especially if they are elderly, pregnant, or have diabetes, heart disease, or kidney disease.
Fasting didn’t prevent COVID-19 but made it less severe
In their study, the team looked at data from 1,524 adults who were seen in the cardiac catheterization lab at Intermountain Medical Center Heart Institute, completed a survey, and had a test for the virus that causes COVID-19 from March 16, 2020, to Feb. 25, 2021.
Of these patients, 205 tested positive for COVID, and of these, 73 reported that they had fasted regularly at least once a month.
Similar numbers of patients got COVID-19 whether they had, or had not, fasted regularly (14%, versus 13%).
But among those who tested positive for the virus, fewer patients were hospitalized for COVID or died during the study follow-up if they had fasted regularly (11%) than if they had not fasted regularly (29%).
Even when the analyses were adjusted for age, smoking, alcohol use, ethnicity, history of heart disease, and other factors, periodic fasting was still an independent predictor of a lower risk of hospitalization or death.
Several things may explain the findings, the researchers suggested.
A loss of appetite is a typical response to infection, they noted.
Fasting reduces inflammation, and after 12-14 hours of fasting, the body switches from using glucose in the blood to using ketones, including linoleic acid.
“There’s a pocket on the surface of SARS-CoV-2 that linoleic acid fits into – and can make the virus less able to attach to other cells,” Dr. Horne said.
Intermittent fasting also promotes autophagy, he noted, which is “the body’s recycling system that helps your body destroy and recycle damaged and infected cells.”
The researchers concluded that intermittent fasting plans should be investigated in further research “as a complementary therapy to vaccines to reduce COVID-19 severity, both during the pandemic and post pandemic, since repeat vaccinations cannot be performed every few months indefinitely for the entire world and vaccine access is limited in many nations.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
FROM BMJ NUTRITION, PREVENTION & HEALTH
Long COVID’s grip will likely tighten as infections continue
COVID-19 is far from done in the United States, with more than 111,000 new cases being recorded a day in the second week of August, according to Johns Hopkins University, and 625 deaths being reported every day. , a condition that already has affected between 7.7 million and 23 million Americans, according to U.S. government estimates.
“It is evident that long COVID is real, that it already impacts a substantial number of people, and that this number may continue to grow as new infections occur,” the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) said in a research action plan released Aug. 4.
“We are heading towards a big problem on our hands,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs Hospital in St. Louis. “It’s like if we are falling in a plane, hurtling towards the ground. It doesn’t matter at what speed we are falling; what matters is that we are all falling, and falling fast. It’s a real problem. We needed to bring attention to this, yesterday,” he said.
Bryan Lau, PhD, professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-lead of a long COVID study there, says whether it’s 5% of the 92 million officially recorded U.S. COVID-19 cases, or 30% – on the higher end of estimates – that means anywhere between 4.5 million and 27 million Americans will have the effects of long COVID.
Other experts put the estimates even higher.
“If we conservatively assume 100 million working-age adults have been infected, that implies 10 to 33 million may have long COVID,” Alice Burns, PhD, associate director for the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Program on Medicaid and the Uninsured, wrote in an analysis.
And even the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only a fraction of cases have been recorded.
That, in turn, means tens of millions of people who struggle to work, to get to school, and to take care of their families – and who will be making demands on an already stressed U.S. health care system.
The HHS said in its Aug. 4 report that long COVID could keep 1 million people a day out of work, with a loss of $50 billion in annual pay.
Dr. Lau said health workers and policymakers are woefully unprepared.
“If you have a family unit, and the mom or dad can’t work, or has trouble taking their child to activities, where does the question of support come into play? Where is there potential for food issues, or housing issues?” he asked. “I see the potential for the burden to be extremely large in that capacity.”
Dr. Lau said he has yet to see any strong estimates of how many cases of long COVID might develop. Because a person has to get COVID-19 to ultimately get long COVID, the two are linked. In other words, as COVID-19 cases rise, so will cases of long COVID, and vice versa.
Evidence from the Kaiser Family Foundation analysis suggests a significant impact on employment: Surveys showed more than half of adults with long COVID who worked before becoming infected are either out of work or working fewer hours. Conditions associated with long COVID – such as fatigue, malaise, or problems concentrating – limit people’s ability to work, even if they have jobs that allow for accommodations.
Two surveys of people with long COVID who had worked before becoming infected showed that between 22% and 27% of them were out of work after getting long COVID. In comparison, among all working-age adults in 2019, only 7% were out of work. Given the sheer number of working-age adults with long COVID, the effects on employment may be profound and are likely to involve more people over time. One study estimates that long COVID already accounts for 15% of unfilled jobs.
The most severe symptoms of long COVID include brain fog and heart complications, known to persist for weeks for months after a COVID-19 infection.
A study from the University of Norway published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases found 53% of people tested had at least one symptom of thinking problems 13 months after infection with COVID-19. According to the HHS’ latest report on long COVID, people with thinking problems, heart conditions, mobility issues, and other symptoms are going to need a considerable amount of care. Many will need lengthy periods of rehabilitation.
Dr. Al-Aly worries that long COVID has already severely affected the labor force and the job market, all while burdening the country’s health care system.
“While there are variations in how individuals respond and cope with long COVID, the unifying thread is that with the level of disability it causes, more people will be struggling to keep up with the demands of the workforce and more people will be out on disability than ever before,” he said.
Studies from Johns Hopkins and the University of Washington estimate that 5%-30% of people could get long COVID in the future. Projections beyond that are hazy.
“So far, all the studies we have done on long COVID have been reactionary. Much of the activism around long COVID has been patient led. We are seeing more and more people with lasting symptoms. We need our research to catch up,” Dr. Lau said.
Theo Vos, MD, PhD, professor of health sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, said the main reasons for the huge range of predictions are the variety of methods used, as well as differences in sample size. Also, much long COVID data is self-reported, making it difficult for epidemiologists to track.
“With self-reported data, you can’t plug people into a machine and say this is what they have or this is what they don’t have. At the population level, the only thing you can do is ask questions. There is no systematic way to define long COVID,” he said.
Dr. Vos’s most recent study, which is being peer-reviewed and revised, found that most people with long COVID have symptoms similar to those seen in other autoimmune diseases. But sometimes the immune system can overreact, causing the more severe symptoms, such as brain fog and heart problems, associated with long COVID.
One reason that researchers struggle to come up with numbers, said Dr. Al-Aly, is the rapid rise of new variants. These variants appear to sometimes cause less severe disease than previous ones, but it’s not clear whether that means different risks for long COVID.
“There’s a wide diversity in severity. Someone can have long COVID and be fully functional, while others are not functional at all. We still have a long way to go before we figure out why,” Dr. Lau said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 is far from done in the United States, with more than 111,000 new cases being recorded a day in the second week of August, according to Johns Hopkins University, and 625 deaths being reported every day. , a condition that already has affected between 7.7 million and 23 million Americans, according to U.S. government estimates.
“It is evident that long COVID is real, that it already impacts a substantial number of people, and that this number may continue to grow as new infections occur,” the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) said in a research action plan released Aug. 4.
“We are heading towards a big problem on our hands,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs Hospital in St. Louis. “It’s like if we are falling in a plane, hurtling towards the ground. It doesn’t matter at what speed we are falling; what matters is that we are all falling, and falling fast. It’s a real problem. We needed to bring attention to this, yesterday,” he said.
Bryan Lau, PhD, professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-lead of a long COVID study there, says whether it’s 5% of the 92 million officially recorded U.S. COVID-19 cases, or 30% – on the higher end of estimates – that means anywhere between 4.5 million and 27 million Americans will have the effects of long COVID.
Other experts put the estimates even higher.
“If we conservatively assume 100 million working-age adults have been infected, that implies 10 to 33 million may have long COVID,” Alice Burns, PhD, associate director for the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Program on Medicaid and the Uninsured, wrote in an analysis.
And even the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only a fraction of cases have been recorded.
That, in turn, means tens of millions of people who struggle to work, to get to school, and to take care of their families – and who will be making demands on an already stressed U.S. health care system.
The HHS said in its Aug. 4 report that long COVID could keep 1 million people a day out of work, with a loss of $50 billion in annual pay.
Dr. Lau said health workers and policymakers are woefully unprepared.
“If you have a family unit, and the mom or dad can’t work, or has trouble taking their child to activities, where does the question of support come into play? Where is there potential for food issues, or housing issues?” he asked. “I see the potential for the burden to be extremely large in that capacity.”
Dr. Lau said he has yet to see any strong estimates of how many cases of long COVID might develop. Because a person has to get COVID-19 to ultimately get long COVID, the two are linked. In other words, as COVID-19 cases rise, so will cases of long COVID, and vice versa.
Evidence from the Kaiser Family Foundation analysis suggests a significant impact on employment: Surveys showed more than half of adults with long COVID who worked before becoming infected are either out of work or working fewer hours. Conditions associated with long COVID – such as fatigue, malaise, or problems concentrating – limit people’s ability to work, even if they have jobs that allow for accommodations.
Two surveys of people with long COVID who had worked before becoming infected showed that between 22% and 27% of them were out of work after getting long COVID. In comparison, among all working-age adults in 2019, only 7% were out of work. Given the sheer number of working-age adults with long COVID, the effects on employment may be profound and are likely to involve more people over time. One study estimates that long COVID already accounts for 15% of unfilled jobs.
The most severe symptoms of long COVID include brain fog and heart complications, known to persist for weeks for months after a COVID-19 infection.
A study from the University of Norway published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases found 53% of people tested had at least one symptom of thinking problems 13 months after infection with COVID-19. According to the HHS’ latest report on long COVID, people with thinking problems, heart conditions, mobility issues, and other symptoms are going to need a considerable amount of care. Many will need lengthy periods of rehabilitation.
Dr. Al-Aly worries that long COVID has already severely affected the labor force and the job market, all while burdening the country’s health care system.
“While there are variations in how individuals respond and cope with long COVID, the unifying thread is that with the level of disability it causes, more people will be struggling to keep up with the demands of the workforce and more people will be out on disability than ever before,” he said.
Studies from Johns Hopkins and the University of Washington estimate that 5%-30% of people could get long COVID in the future. Projections beyond that are hazy.
“So far, all the studies we have done on long COVID have been reactionary. Much of the activism around long COVID has been patient led. We are seeing more and more people with lasting symptoms. We need our research to catch up,” Dr. Lau said.
Theo Vos, MD, PhD, professor of health sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, said the main reasons for the huge range of predictions are the variety of methods used, as well as differences in sample size. Also, much long COVID data is self-reported, making it difficult for epidemiologists to track.
“With self-reported data, you can’t plug people into a machine and say this is what they have or this is what they don’t have. At the population level, the only thing you can do is ask questions. There is no systematic way to define long COVID,” he said.
Dr. Vos’s most recent study, which is being peer-reviewed and revised, found that most people with long COVID have symptoms similar to those seen in other autoimmune diseases. But sometimes the immune system can overreact, causing the more severe symptoms, such as brain fog and heart problems, associated with long COVID.
One reason that researchers struggle to come up with numbers, said Dr. Al-Aly, is the rapid rise of new variants. These variants appear to sometimes cause less severe disease than previous ones, but it’s not clear whether that means different risks for long COVID.
“There’s a wide diversity in severity. Someone can have long COVID and be fully functional, while others are not functional at all. We still have a long way to go before we figure out why,” Dr. Lau said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 is far from done in the United States, with more than 111,000 new cases being recorded a day in the second week of August, according to Johns Hopkins University, and 625 deaths being reported every day. , a condition that already has affected between 7.7 million and 23 million Americans, according to U.S. government estimates.
“It is evident that long COVID is real, that it already impacts a substantial number of people, and that this number may continue to grow as new infections occur,” the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) said in a research action plan released Aug. 4.
“We are heading towards a big problem on our hands,” says Ziyad Al-Aly, MD, chief of research and development at the Veterans Affairs Hospital in St. Louis. “It’s like if we are falling in a plane, hurtling towards the ground. It doesn’t matter at what speed we are falling; what matters is that we are all falling, and falling fast. It’s a real problem. We needed to bring attention to this, yesterday,” he said.
Bryan Lau, PhD, professor of epidemiology at Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore, and co-lead of a long COVID study there, says whether it’s 5% of the 92 million officially recorded U.S. COVID-19 cases, or 30% – on the higher end of estimates – that means anywhere between 4.5 million and 27 million Americans will have the effects of long COVID.
Other experts put the estimates even higher.
“If we conservatively assume 100 million working-age adults have been infected, that implies 10 to 33 million may have long COVID,” Alice Burns, PhD, associate director for the Kaiser Family Foundation’s Program on Medicaid and the Uninsured, wrote in an analysis.
And even the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention says only a fraction of cases have been recorded.
That, in turn, means tens of millions of people who struggle to work, to get to school, and to take care of their families – and who will be making demands on an already stressed U.S. health care system.
The HHS said in its Aug. 4 report that long COVID could keep 1 million people a day out of work, with a loss of $50 billion in annual pay.
Dr. Lau said health workers and policymakers are woefully unprepared.
“If you have a family unit, and the mom or dad can’t work, or has trouble taking their child to activities, where does the question of support come into play? Where is there potential for food issues, or housing issues?” he asked. “I see the potential for the burden to be extremely large in that capacity.”
Dr. Lau said he has yet to see any strong estimates of how many cases of long COVID might develop. Because a person has to get COVID-19 to ultimately get long COVID, the two are linked. In other words, as COVID-19 cases rise, so will cases of long COVID, and vice versa.
Evidence from the Kaiser Family Foundation analysis suggests a significant impact on employment: Surveys showed more than half of adults with long COVID who worked before becoming infected are either out of work or working fewer hours. Conditions associated with long COVID – such as fatigue, malaise, or problems concentrating – limit people’s ability to work, even if they have jobs that allow for accommodations.
Two surveys of people with long COVID who had worked before becoming infected showed that between 22% and 27% of them were out of work after getting long COVID. In comparison, among all working-age adults in 2019, only 7% were out of work. Given the sheer number of working-age adults with long COVID, the effects on employment may be profound and are likely to involve more people over time. One study estimates that long COVID already accounts for 15% of unfilled jobs.
The most severe symptoms of long COVID include brain fog and heart complications, known to persist for weeks for months after a COVID-19 infection.
A study from the University of Norway published in Open Forum Infectious Diseases found 53% of people tested had at least one symptom of thinking problems 13 months after infection with COVID-19. According to the HHS’ latest report on long COVID, people with thinking problems, heart conditions, mobility issues, and other symptoms are going to need a considerable amount of care. Many will need lengthy periods of rehabilitation.
Dr. Al-Aly worries that long COVID has already severely affected the labor force and the job market, all while burdening the country’s health care system.
“While there are variations in how individuals respond and cope with long COVID, the unifying thread is that with the level of disability it causes, more people will be struggling to keep up with the demands of the workforce and more people will be out on disability than ever before,” he said.
Studies from Johns Hopkins and the University of Washington estimate that 5%-30% of people could get long COVID in the future. Projections beyond that are hazy.
“So far, all the studies we have done on long COVID have been reactionary. Much of the activism around long COVID has been patient led. We are seeing more and more people with lasting symptoms. We need our research to catch up,” Dr. Lau said.
Theo Vos, MD, PhD, professor of health sciences at University of Washington, Seattle, said the main reasons for the huge range of predictions are the variety of methods used, as well as differences in sample size. Also, much long COVID data is self-reported, making it difficult for epidemiologists to track.
“With self-reported data, you can’t plug people into a machine and say this is what they have or this is what they don’t have. At the population level, the only thing you can do is ask questions. There is no systematic way to define long COVID,” he said.
Dr. Vos’s most recent study, which is being peer-reviewed and revised, found that most people with long COVID have symptoms similar to those seen in other autoimmune diseases. But sometimes the immune system can overreact, causing the more severe symptoms, such as brain fog and heart problems, associated with long COVID.
One reason that researchers struggle to come up with numbers, said Dr. Al-Aly, is the rapid rise of new variants. These variants appear to sometimes cause less severe disease than previous ones, but it’s not clear whether that means different risks for long COVID.
“There’s a wide diversity in severity. Someone can have long COVID and be fully functional, while others are not functional at all. We still have a long way to go before we figure out why,” Dr. Lau said.
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
Stressed about weight gain? Well, stress causes weight gain
Stress, meet weight gain. Weight gain, meet stress
You’re not eating differently and you’re keeping active, but your waistline is expanding. How is that happening? Since eating healthy and exercising shouldn’t make you gain weight, there may be a hidden factor getting in your way. Stress. The one thing that can have a grip on your circadian rhythm stronger than any bodybuilder.
Investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine published two mouse studies that suggest stress and other factors that throw the body’s circadian clocks out of rhythm may contribute to weight gain.
In the first study, the researchers imitated disruptive condition effects like high cortisol exposure and chronic stress by implanting pellets under the skin that released glucocorticoid at a constant rate for 21 days. Mice that received the pellets had twice as much white and brown fat, as well as much higher insulin levels, regardless of their unchanged and still-healthy diet.
In the second study, they used tagged proteins as markers to monitor the daily fluctuations of a protein that regulates fat cell production and circadian gene expression in mouse fat cell precursors. The results showed “that fat cell precursors commit to becoming fat cells only during the circadian cycle phase corresponding to evening in humans,” they said in a written statement.
“Every cell in our body has an intrinsic cell clock, just like the fat cells, and we have a master clock in our brain, which controls hormone secretion,” said senior author Mary Teruel of Cornell University. “A lot of forces are working against a healthy metabolism when we are out of circadian rhythm. The more we understand, the more likely we will be able to do something about it.”
So if you’re stressing out that the scale is or isn’t moving in the direction you want, you could be standing in your own way. Take a chill pill.
Who can smell cancer? The locust nose
If you need to smell some gas, there’s nothing better than a nose. Just ask a scientist: “Noses are still state of the art,” said Debajit Saha, PhD, of Michigan State University. “There’s really nothing like them when it comes to gas sensing.”
And when it comes to noses, dogs are best, right? After all, there’s a reason we don’t have bomb-sniffing wombats and drug-sniffing ostriches. Dogs are better. Better, but not perfect. And if they’re not perfect, then human technology can do better.
Enter the electronic nose. Which is better than dogs … except that it isn’t. “People have been working on ‘electronic noses’ for more than 15 years, but they’re still not close to achieving what biology can do seamlessly,” Dr. Saha explained in a statement from the university.
Which brings us back to dogs. If you want to detect early-stage cancer using smell, you go to the dogs, right? Nope.
Here’s Christopher Contag, PhD, also of Michigan State, who recruited Dr. Saha to the university: “I told him, ‘When you come here, we’ll detect cancer. I’m sure your locusts can do it.’ ”
Yes, locusts. Dr. Contag and his research team were looking at mouth cancers and noticed that different cell lines had different appearances. Then they discovered that those different-looking cell lines produced different metabolites, some of which were volatile.
Enter Dr. Saha’s locusts. They were able to tell the difference between normal cells and cancer cells and could even distinguish between the different cell lines. And how they were able to share this information? Not voluntarily, that’s for sure. The researchers attached electrodes to the insects’ brains and recorded their responses to gas samples from both healthy and cancer cells. Those brain signals were then used to create chemical profiles of the different cells. Piece of cake.
The whole getting-electrodes-attached-to-their-brains thing seemed at least a bit ethically ambiguous, so we contacted the locusts’ PR office, which offered some positive spin: “Humans get their early cancer detection and we get that whole swarms-that-devour-entire-countrysides thing off our backs. Win win.”
Bad news for vampires everywhere
Pop culture has been extraordinarily kind to the vampire. A few hundred years ago, vampires were demon-possessed, often-inhuman monsters. Now? They’re suave, sophisticated, beautiful, and oh-so dramatic and angst-filled about their “curse.” Drink a little human blood, live and look young forever. Such monsters they are.
It does make sense in a morbid sort of way. An old person receiving the blood of the young does seem like a good idea for rejuvenation, right? A team of Ukrainian researchers sought to find out, conducting a study in which older mice were linked with young mice via heterochronic parabiosis. For 3 months, old-young mice pairs were surgically connected and shared blood. After 3 months, the mice were disconnected from each other and the effects of the blood link were studied.
For all the vampire enthusiasts out there, we have bad news and worse news. The bad news first: The older mice received absolutely no benefit from heterochronic parabiosis. No youthfulness, no increased lifespan, nothing. The worse news is that the younger mice were adversely affected by the older blood. They aged more and experienced a shortened lifespan, even after the connection was severed. The old blood, according to the investigators, contains factors capable of inducing aging in younger mice, but the opposite is not true. Further research into aging, they added, should focus on suppressing the aging factors in older blood.
Of note, the paper was written by doctors who are currently refugees, fleeing the war in Ukraine. We don’t want to speculate on the true cause of the war, but we’re onto you, Putin. We know you wanted the vampire research for yourself, but it won’t work. Your dream of becoming Vlad “Dracula” Putin will never come to pass.
Hearing is not always believing
Have you ever heard yourself on a voice mail, or from a recording you did at work? No matter how good you sound, you still might feel like the recording sounds nothing like you. It may even cause low self-esteem for those who don’t like how their voice sounds or don’t recognize it when it’s played back to them.
Since one possible symptom of schizophrenia is not recognizing one’s own speech and having a false sense of control over actions, and those with schizophrenia may hallucinate or hear voices, not being able to recognize their own voices may be alarming.
A recent study on the sense of agency, or sense of control, involved having volunteers speak with different pitches in their voices and then having it played back to them to gauge their reactions.
“Our results demonstrate that hearing one’s own voice is a critical factor to increased self-agency over speech. In other words, we do not strongly feel that ‘I’ am generating the speech if we hear someone else’s voice as an outcome of the speech. Our study provides empirical evidence of the tight link between the sense of agency and self-voice identity,” lead author Ryu Ohata, PhD, of the University of Tokyo, said in a written statement.
As social interaction becomes more digital through platforms such as FaceTime, Zoom, and voicemail, especially since the pandemic has promoted social distancing, it makes sense that people may be more aware and more surprised by how they sound on recordings.
So, if you ever promised someone something that you don’t want to do, and they play it back to you from the recording you made, maybe you can just say you don’t recognize the voice. And if it’s not you, then you don’t have to do it.
Stress, meet weight gain. Weight gain, meet stress
You’re not eating differently and you’re keeping active, but your waistline is expanding. How is that happening? Since eating healthy and exercising shouldn’t make you gain weight, there may be a hidden factor getting in your way. Stress. The one thing that can have a grip on your circadian rhythm stronger than any bodybuilder.
Investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine published two mouse studies that suggest stress and other factors that throw the body’s circadian clocks out of rhythm may contribute to weight gain.
In the first study, the researchers imitated disruptive condition effects like high cortisol exposure and chronic stress by implanting pellets under the skin that released glucocorticoid at a constant rate for 21 days. Mice that received the pellets had twice as much white and brown fat, as well as much higher insulin levels, regardless of their unchanged and still-healthy diet.
In the second study, they used tagged proteins as markers to monitor the daily fluctuations of a protein that regulates fat cell production and circadian gene expression in mouse fat cell precursors. The results showed “that fat cell precursors commit to becoming fat cells only during the circadian cycle phase corresponding to evening in humans,” they said in a written statement.
“Every cell in our body has an intrinsic cell clock, just like the fat cells, and we have a master clock in our brain, which controls hormone secretion,” said senior author Mary Teruel of Cornell University. “A lot of forces are working against a healthy metabolism when we are out of circadian rhythm. The more we understand, the more likely we will be able to do something about it.”
So if you’re stressing out that the scale is or isn’t moving in the direction you want, you could be standing in your own way. Take a chill pill.
Who can smell cancer? The locust nose
If you need to smell some gas, there’s nothing better than a nose. Just ask a scientist: “Noses are still state of the art,” said Debajit Saha, PhD, of Michigan State University. “There’s really nothing like them when it comes to gas sensing.”
And when it comes to noses, dogs are best, right? After all, there’s a reason we don’t have bomb-sniffing wombats and drug-sniffing ostriches. Dogs are better. Better, but not perfect. And if they’re not perfect, then human technology can do better.
Enter the electronic nose. Which is better than dogs … except that it isn’t. “People have been working on ‘electronic noses’ for more than 15 years, but they’re still not close to achieving what biology can do seamlessly,” Dr. Saha explained in a statement from the university.
Which brings us back to dogs. If you want to detect early-stage cancer using smell, you go to the dogs, right? Nope.
Here’s Christopher Contag, PhD, also of Michigan State, who recruited Dr. Saha to the university: “I told him, ‘When you come here, we’ll detect cancer. I’m sure your locusts can do it.’ ”
Yes, locusts. Dr. Contag and his research team were looking at mouth cancers and noticed that different cell lines had different appearances. Then they discovered that those different-looking cell lines produced different metabolites, some of which were volatile.
Enter Dr. Saha’s locusts. They were able to tell the difference between normal cells and cancer cells and could even distinguish between the different cell lines. And how they were able to share this information? Not voluntarily, that’s for sure. The researchers attached electrodes to the insects’ brains and recorded their responses to gas samples from both healthy and cancer cells. Those brain signals were then used to create chemical profiles of the different cells. Piece of cake.
The whole getting-electrodes-attached-to-their-brains thing seemed at least a bit ethically ambiguous, so we contacted the locusts’ PR office, which offered some positive spin: “Humans get their early cancer detection and we get that whole swarms-that-devour-entire-countrysides thing off our backs. Win win.”
Bad news for vampires everywhere
Pop culture has been extraordinarily kind to the vampire. A few hundred years ago, vampires were demon-possessed, often-inhuman monsters. Now? They’re suave, sophisticated, beautiful, and oh-so dramatic and angst-filled about their “curse.” Drink a little human blood, live and look young forever. Such monsters they are.
It does make sense in a morbid sort of way. An old person receiving the blood of the young does seem like a good idea for rejuvenation, right? A team of Ukrainian researchers sought to find out, conducting a study in which older mice were linked with young mice via heterochronic parabiosis. For 3 months, old-young mice pairs were surgically connected and shared blood. After 3 months, the mice were disconnected from each other and the effects of the blood link were studied.
For all the vampire enthusiasts out there, we have bad news and worse news. The bad news first: The older mice received absolutely no benefit from heterochronic parabiosis. No youthfulness, no increased lifespan, nothing. The worse news is that the younger mice were adversely affected by the older blood. They aged more and experienced a shortened lifespan, even after the connection was severed. The old blood, according to the investigators, contains factors capable of inducing aging in younger mice, but the opposite is not true. Further research into aging, they added, should focus on suppressing the aging factors in older blood.
Of note, the paper was written by doctors who are currently refugees, fleeing the war in Ukraine. We don’t want to speculate on the true cause of the war, but we’re onto you, Putin. We know you wanted the vampire research for yourself, but it won’t work. Your dream of becoming Vlad “Dracula” Putin will never come to pass.
Hearing is not always believing
Have you ever heard yourself on a voice mail, or from a recording you did at work? No matter how good you sound, you still might feel like the recording sounds nothing like you. It may even cause low self-esteem for those who don’t like how their voice sounds or don’t recognize it when it’s played back to them.
Since one possible symptom of schizophrenia is not recognizing one’s own speech and having a false sense of control over actions, and those with schizophrenia may hallucinate or hear voices, not being able to recognize their own voices may be alarming.
A recent study on the sense of agency, or sense of control, involved having volunteers speak with different pitches in their voices and then having it played back to them to gauge their reactions.
“Our results demonstrate that hearing one’s own voice is a critical factor to increased self-agency over speech. In other words, we do not strongly feel that ‘I’ am generating the speech if we hear someone else’s voice as an outcome of the speech. Our study provides empirical evidence of the tight link between the sense of agency and self-voice identity,” lead author Ryu Ohata, PhD, of the University of Tokyo, said in a written statement.
As social interaction becomes more digital through platforms such as FaceTime, Zoom, and voicemail, especially since the pandemic has promoted social distancing, it makes sense that people may be more aware and more surprised by how they sound on recordings.
So, if you ever promised someone something that you don’t want to do, and they play it back to you from the recording you made, maybe you can just say you don’t recognize the voice. And if it’s not you, then you don’t have to do it.
Stress, meet weight gain. Weight gain, meet stress
You’re not eating differently and you’re keeping active, but your waistline is expanding. How is that happening? Since eating healthy and exercising shouldn’t make you gain weight, there may be a hidden factor getting in your way. Stress. The one thing that can have a grip on your circadian rhythm stronger than any bodybuilder.
Investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine published two mouse studies that suggest stress and other factors that throw the body’s circadian clocks out of rhythm may contribute to weight gain.
In the first study, the researchers imitated disruptive condition effects like high cortisol exposure and chronic stress by implanting pellets under the skin that released glucocorticoid at a constant rate for 21 days. Mice that received the pellets had twice as much white and brown fat, as well as much higher insulin levels, regardless of their unchanged and still-healthy diet.
In the second study, they used tagged proteins as markers to monitor the daily fluctuations of a protein that regulates fat cell production and circadian gene expression in mouse fat cell precursors. The results showed “that fat cell precursors commit to becoming fat cells only during the circadian cycle phase corresponding to evening in humans,” they said in a written statement.
“Every cell in our body has an intrinsic cell clock, just like the fat cells, and we have a master clock in our brain, which controls hormone secretion,” said senior author Mary Teruel of Cornell University. “A lot of forces are working against a healthy metabolism when we are out of circadian rhythm. The more we understand, the more likely we will be able to do something about it.”
So if you’re stressing out that the scale is or isn’t moving in the direction you want, you could be standing in your own way. Take a chill pill.
Who can smell cancer? The locust nose
If you need to smell some gas, there’s nothing better than a nose. Just ask a scientist: “Noses are still state of the art,” said Debajit Saha, PhD, of Michigan State University. “There’s really nothing like them when it comes to gas sensing.”
And when it comes to noses, dogs are best, right? After all, there’s a reason we don’t have bomb-sniffing wombats and drug-sniffing ostriches. Dogs are better. Better, but not perfect. And if they’re not perfect, then human technology can do better.
Enter the electronic nose. Which is better than dogs … except that it isn’t. “People have been working on ‘electronic noses’ for more than 15 years, but they’re still not close to achieving what biology can do seamlessly,” Dr. Saha explained in a statement from the university.
Which brings us back to dogs. If you want to detect early-stage cancer using smell, you go to the dogs, right? Nope.
Here’s Christopher Contag, PhD, also of Michigan State, who recruited Dr. Saha to the university: “I told him, ‘When you come here, we’ll detect cancer. I’m sure your locusts can do it.’ ”
Yes, locusts. Dr. Contag and his research team were looking at mouth cancers and noticed that different cell lines had different appearances. Then they discovered that those different-looking cell lines produced different metabolites, some of which were volatile.
Enter Dr. Saha’s locusts. They were able to tell the difference between normal cells and cancer cells and could even distinguish between the different cell lines. And how they were able to share this information? Not voluntarily, that’s for sure. The researchers attached electrodes to the insects’ brains and recorded their responses to gas samples from both healthy and cancer cells. Those brain signals were then used to create chemical profiles of the different cells. Piece of cake.
The whole getting-electrodes-attached-to-their-brains thing seemed at least a bit ethically ambiguous, so we contacted the locusts’ PR office, which offered some positive spin: “Humans get their early cancer detection and we get that whole swarms-that-devour-entire-countrysides thing off our backs. Win win.”
Bad news for vampires everywhere
Pop culture has been extraordinarily kind to the vampire. A few hundred years ago, vampires were demon-possessed, often-inhuman monsters. Now? They’re suave, sophisticated, beautiful, and oh-so dramatic and angst-filled about their “curse.” Drink a little human blood, live and look young forever. Such monsters they are.
It does make sense in a morbid sort of way. An old person receiving the blood of the young does seem like a good idea for rejuvenation, right? A team of Ukrainian researchers sought to find out, conducting a study in which older mice were linked with young mice via heterochronic parabiosis. For 3 months, old-young mice pairs were surgically connected and shared blood. After 3 months, the mice were disconnected from each other and the effects of the blood link were studied.
For all the vampire enthusiasts out there, we have bad news and worse news. The bad news first: The older mice received absolutely no benefit from heterochronic parabiosis. No youthfulness, no increased lifespan, nothing. The worse news is that the younger mice were adversely affected by the older blood. They aged more and experienced a shortened lifespan, even after the connection was severed. The old blood, according to the investigators, contains factors capable of inducing aging in younger mice, but the opposite is not true. Further research into aging, they added, should focus on suppressing the aging factors in older blood.
Of note, the paper was written by doctors who are currently refugees, fleeing the war in Ukraine. We don’t want to speculate on the true cause of the war, but we’re onto you, Putin. We know you wanted the vampire research for yourself, but it won’t work. Your dream of becoming Vlad “Dracula” Putin will never come to pass.
Hearing is not always believing
Have you ever heard yourself on a voice mail, or from a recording you did at work? No matter how good you sound, you still might feel like the recording sounds nothing like you. It may even cause low self-esteem for those who don’t like how their voice sounds or don’t recognize it when it’s played back to them.
Since one possible symptom of schizophrenia is not recognizing one’s own speech and having a false sense of control over actions, and those with schizophrenia may hallucinate or hear voices, not being able to recognize their own voices may be alarming.
A recent study on the sense of agency, or sense of control, involved having volunteers speak with different pitches in their voices and then having it played back to them to gauge their reactions.
“Our results demonstrate that hearing one’s own voice is a critical factor to increased self-agency over speech. In other words, we do not strongly feel that ‘I’ am generating the speech if we hear someone else’s voice as an outcome of the speech. Our study provides empirical evidence of the tight link between the sense of agency and self-voice identity,” lead author Ryu Ohata, PhD, of the University of Tokyo, said in a written statement.
As social interaction becomes more digital through platforms such as FaceTime, Zoom, and voicemail, especially since the pandemic has promoted social distancing, it makes sense that people may be more aware and more surprised by how they sound on recordings.
So, if you ever promised someone something that you don’t want to do, and they play it back to you from the recording you made, maybe you can just say you don’t recognize the voice. And if it’s not you, then you don’t have to do it.
Cardiorespiratory fitness key to longevity for all?
Cardiorespiratory fitness emerged as a stronger predictor of all-cause mortality than did any traditional risk factor across the spectrum of age, sex, and race in a modeling study that included more than 750,000 U.S. veterans.
In addition, mortality risk was cut in half if individuals achieved a moderate cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) level – that is, by meeting the current U.S. physical activity recommendations of 150 minutes per week, the authors note.
Furthermore, contrary to some previous research, “extremely high” fitness was not associated with an increased risk for mortality in the study, published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“This study has been 15 years in the making,” lead author Peter Kokkinos, PhD, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J., and the VA Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization. “We waited until we had the computer power and the right people to really assess this. We wanted to be very liberal in excluding patients we thought might contaminate the results, such as those with cardiovascular disease in the 6 months prior to a stress test.”
Figuring the time was right, the team analyzed data from the VA’s Exercise Testing and Health Outcomes Study (ETHOS) on individuals aged 30-95 years who underwent exercise treadmill tests between 1999 and 2020.
After exclusions, 750,302 individuals (from among 822,995) were included: 6.5% were women; 73.7% were White individuals; 19% were African American individuals; 4.7% were Hispanic individuals; and 2.1% were Native American, Asian, or Hawaiian individuals. Septuagenarians made up 14.7% of the cohort, and octogenarians made up 3.6%.
CRF categories for age and sex were determined by the peak metabolic equivalent of task (MET) achieved during the treadmill test. One MET is the energy spent at rest – that is the basal metabolic rate.
Although some physicians may resist putting patients through a stress test, “the amount of information we get from it is incredible,” Dr. Kokkinos noted. “We get blood pressure, we get heart rate, we get a response if you’re not doing exercise. This tells us a lot more than having you sit around so we can measure resting heart rate and blood pressure.”
Lowest mortality at 14.0 METs
During a median follow-up of 10.2 years (7,803,861 person-years), 23% of participants died, for an average of 22.4 events per 1,000 person-years.
Higher exercise capacity was inversely related to mortality risk across the cohort and within each age category. Specifically, every 1 MET increase in exercise capacity yielded an adjusted hazard ratio for mortality of 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.85-0.87; P < .001) for the entire cohort and similar HRs by sex and race.
The mortality risk for the least-fit individuals (20th percentile) was fourfold higher than for extremely fit individuals (HR, 4.09; 95% CI, 3.90-4.20), with the lowest mortality risk at about 14.0 METs for both men (HR, 0.24; 95% CI, 0.23-0.25) and women (HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.17-0.29). Extremely high CRF did not increase the risk.
In addition, at 20 years of follow-up, about 80% of men and 95% of women in the highest CRF category (98th percentile) were alive vs. less than 40% of men and approximately 75% of women in the least fit CRF category.
“We know CRF declines by 1% per year after age 30,” Dr. Kokkinos said. “But the age-related decline is cut in half if you are fit, meaning that an expected 10% decline over a decade will be only a 5% decline if you stay active. We cannot stop or reverse the decline, but we can kind of put the brakes on, and that’s a reason for clinicians to continue to encourage fitness.”
Indeed, “improving CRF should be considered a target in CVD prevention, similar to improving lipids, blood sugar, blood pressure, and weight,” Carl J. Lavie, MD, Ochsner Health, New Orleans, and colleagues affirm in a related editorial.
‘A difficult battle’
But that may not happen any time soon. “Unfortunately, despite having been recognized in an American Heart Association scientific statement as a clinical vital sign, aerobic fitness is undervalued and underutilized,” Claudio Gil Araújo, MD, PhD, research director of the Exercise Medicine Clinic-CLINIMEX, Rio de Janeiro, told this news organization.
Dr. Araújo led a recent study showing that the ability to stand on one leg for at least 10 seconds is strongly linked to the risk for death over the next 7 years.
Although physicians should be encouraging fitness, he said that “a substantial part of health professionals are physically unfit and feel uncomfortable talking about and prescribing exercise for their patients. Also, physicians tend to be better trained in treating diseases (using medications and/or prescribing procedures) than in preventing diseases by stimulating adoption of healthy habits. So, this a long road and a difficult battle.”
Nonetheless, he added, “Darwin said a long time ago that only the fittest will survive. If Darwin could read this study, he would surely smile.”
No commercial funding or conflicts of interest related to the study were reported. Dr. Lavie previously served as a speaker and consultant for PAI Health on their PAI (Personalized Activity Intelligence) applications.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiorespiratory fitness emerged as a stronger predictor of all-cause mortality than did any traditional risk factor across the spectrum of age, sex, and race in a modeling study that included more than 750,000 U.S. veterans.
In addition, mortality risk was cut in half if individuals achieved a moderate cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) level – that is, by meeting the current U.S. physical activity recommendations of 150 minutes per week, the authors note.
Furthermore, contrary to some previous research, “extremely high” fitness was not associated with an increased risk for mortality in the study, published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“This study has been 15 years in the making,” lead author Peter Kokkinos, PhD, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J., and the VA Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization. “We waited until we had the computer power and the right people to really assess this. We wanted to be very liberal in excluding patients we thought might contaminate the results, such as those with cardiovascular disease in the 6 months prior to a stress test.”
Figuring the time was right, the team analyzed data from the VA’s Exercise Testing and Health Outcomes Study (ETHOS) on individuals aged 30-95 years who underwent exercise treadmill tests between 1999 and 2020.
After exclusions, 750,302 individuals (from among 822,995) were included: 6.5% were women; 73.7% were White individuals; 19% were African American individuals; 4.7% were Hispanic individuals; and 2.1% were Native American, Asian, or Hawaiian individuals. Septuagenarians made up 14.7% of the cohort, and octogenarians made up 3.6%.
CRF categories for age and sex were determined by the peak metabolic equivalent of task (MET) achieved during the treadmill test. One MET is the energy spent at rest – that is the basal metabolic rate.
Although some physicians may resist putting patients through a stress test, “the amount of information we get from it is incredible,” Dr. Kokkinos noted. “We get blood pressure, we get heart rate, we get a response if you’re not doing exercise. This tells us a lot more than having you sit around so we can measure resting heart rate and blood pressure.”
Lowest mortality at 14.0 METs
During a median follow-up of 10.2 years (7,803,861 person-years), 23% of participants died, for an average of 22.4 events per 1,000 person-years.
Higher exercise capacity was inversely related to mortality risk across the cohort and within each age category. Specifically, every 1 MET increase in exercise capacity yielded an adjusted hazard ratio for mortality of 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.85-0.87; P < .001) for the entire cohort and similar HRs by sex and race.
The mortality risk for the least-fit individuals (20th percentile) was fourfold higher than for extremely fit individuals (HR, 4.09; 95% CI, 3.90-4.20), with the lowest mortality risk at about 14.0 METs for both men (HR, 0.24; 95% CI, 0.23-0.25) and women (HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.17-0.29). Extremely high CRF did not increase the risk.
In addition, at 20 years of follow-up, about 80% of men and 95% of women in the highest CRF category (98th percentile) were alive vs. less than 40% of men and approximately 75% of women in the least fit CRF category.
“We know CRF declines by 1% per year after age 30,” Dr. Kokkinos said. “But the age-related decline is cut in half if you are fit, meaning that an expected 10% decline over a decade will be only a 5% decline if you stay active. We cannot stop or reverse the decline, but we can kind of put the brakes on, and that’s a reason for clinicians to continue to encourage fitness.”
Indeed, “improving CRF should be considered a target in CVD prevention, similar to improving lipids, blood sugar, blood pressure, and weight,” Carl J. Lavie, MD, Ochsner Health, New Orleans, and colleagues affirm in a related editorial.
‘A difficult battle’
But that may not happen any time soon. “Unfortunately, despite having been recognized in an American Heart Association scientific statement as a clinical vital sign, aerobic fitness is undervalued and underutilized,” Claudio Gil Araújo, MD, PhD, research director of the Exercise Medicine Clinic-CLINIMEX, Rio de Janeiro, told this news organization.
Dr. Araújo led a recent study showing that the ability to stand on one leg for at least 10 seconds is strongly linked to the risk for death over the next 7 years.
Although physicians should be encouraging fitness, he said that “a substantial part of health professionals are physically unfit and feel uncomfortable talking about and prescribing exercise for their patients. Also, physicians tend to be better trained in treating diseases (using medications and/or prescribing procedures) than in preventing diseases by stimulating adoption of healthy habits. So, this a long road and a difficult battle.”
Nonetheless, he added, “Darwin said a long time ago that only the fittest will survive. If Darwin could read this study, he would surely smile.”
No commercial funding or conflicts of interest related to the study were reported. Dr. Lavie previously served as a speaker and consultant for PAI Health on their PAI (Personalized Activity Intelligence) applications.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Cardiorespiratory fitness emerged as a stronger predictor of all-cause mortality than did any traditional risk factor across the spectrum of age, sex, and race in a modeling study that included more than 750,000 U.S. veterans.
In addition, mortality risk was cut in half if individuals achieved a moderate cardiorespiratory fitness (CRF) level – that is, by meeting the current U.S. physical activity recommendations of 150 minutes per week, the authors note.
Furthermore, contrary to some previous research, “extremely high” fitness was not associated with an increased risk for mortality in the study, published online in the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“This study has been 15 years in the making,” lead author Peter Kokkinos, PhD, Rutgers University, New Brunswick, N.J., and the VA Medical Center, Washington, told this news organization. “We waited until we had the computer power and the right people to really assess this. We wanted to be very liberal in excluding patients we thought might contaminate the results, such as those with cardiovascular disease in the 6 months prior to a stress test.”
Figuring the time was right, the team analyzed data from the VA’s Exercise Testing and Health Outcomes Study (ETHOS) on individuals aged 30-95 years who underwent exercise treadmill tests between 1999 and 2020.
After exclusions, 750,302 individuals (from among 822,995) were included: 6.5% were women; 73.7% were White individuals; 19% were African American individuals; 4.7% were Hispanic individuals; and 2.1% were Native American, Asian, or Hawaiian individuals. Septuagenarians made up 14.7% of the cohort, and octogenarians made up 3.6%.
CRF categories for age and sex were determined by the peak metabolic equivalent of task (MET) achieved during the treadmill test. One MET is the energy spent at rest – that is the basal metabolic rate.
Although some physicians may resist putting patients through a stress test, “the amount of information we get from it is incredible,” Dr. Kokkinos noted. “We get blood pressure, we get heart rate, we get a response if you’re not doing exercise. This tells us a lot more than having you sit around so we can measure resting heart rate and blood pressure.”
Lowest mortality at 14.0 METs
During a median follow-up of 10.2 years (7,803,861 person-years), 23% of participants died, for an average of 22.4 events per 1,000 person-years.
Higher exercise capacity was inversely related to mortality risk across the cohort and within each age category. Specifically, every 1 MET increase in exercise capacity yielded an adjusted hazard ratio for mortality of 0.86 (95% confidence interval, 0.85-0.87; P < .001) for the entire cohort and similar HRs by sex and race.
The mortality risk for the least-fit individuals (20th percentile) was fourfold higher than for extremely fit individuals (HR, 4.09; 95% CI, 3.90-4.20), with the lowest mortality risk at about 14.0 METs for both men (HR, 0.24; 95% CI, 0.23-0.25) and women (HR, 0.23; 95% CI, 0.17-0.29). Extremely high CRF did not increase the risk.
In addition, at 20 years of follow-up, about 80% of men and 95% of women in the highest CRF category (98th percentile) were alive vs. less than 40% of men and approximately 75% of women in the least fit CRF category.
“We know CRF declines by 1% per year after age 30,” Dr. Kokkinos said. “But the age-related decline is cut in half if you are fit, meaning that an expected 10% decline over a decade will be only a 5% decline if you stay active. We cannot stop or reverse the decline, but we can kind of put the brakes on, and that’s a reason for clinicians to continue to encourage fitness.”
Indeed, “improving CRF should be considered a target in CVD prevention, similar to improving lipids, blood sugar, blood pressure, and weight,” Carl J. Lavie, MD, Ochsner Health, New Orleans, and colleagues affirm in a related editorial.
‘A difficult battle’
But that may not happen any time soon. “Unfortunately, despite having been recognized in an American Heart Association scientific statement as a clinical vital sign, aerobic fitness is undervalued and underutilized,” Claudio Gil Araújo, MD, PhD, research director of the Exercise Medicine Clinic-CLINIMEX, Rio de Janeiro, told this news organization.
Dr. Araújo led a recent study showing that the ability to stand on one leg for at least 10 seconds is strongly linked to the risk for death over the next 7 years.
Although physicians should be encouraging fitness, he said that “a substantial part of health professionals are physically unfit and feel uncomfortable talking about and prescribing exercise for their patients. Also, physicians tend to be better trained in treating diseases (using medications and/or prescribing procedures) than in preventing diseases by stimulating adoption of healthy habits. So, this a long road and a difficult battle.”
Nonetheless, he added, “Darwin said a long time ago that only the fittest will survive. If Darwin could read this study, he would surely smile.”
No commercial funding or conflicts of interest related to the study were reported. Dr. Lavie previously served as a speaker and consultant for PAI Health on their PAI (Personalized Activity Intelligence) applications.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN COLLEGE OF CARDIOLOGY
NAFLD linked with increased heart failure risk
The risk of developing incident heart failure is 1.5-times higher in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) during a median follow-up of 10 years, according to a new meta-analysis.
The risk appears to increase with greater liver disease severity and was independent of age, sex, ethnicity, obesity, and the presence of diabetes, hypertension, and other common cardiovascular risk factors.
“Health care professionals should be aware that the risk of new-onset heart failure is moderately higher in patients with NAFLD,” senior author Giovanni Targher, MD, said in an interview.
“Because of the link between the two conditions, more careful surveillance of these patients will be needed,” said Dr. Targher, who is an associate professor of diabetes and endocrinology at the University of Verona (Italy). “In particular, the results of this meta-analysis highlight the need for a patient-centered, multidisciplinary, and holistic approach to manage both liver disease and cardiovascular risk in patients with NAFLD.”
The study was published online in Gut.
Risk calculations
NAFLD has become one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide (affecting up to about 30% of the world’s adults), and is expected to rise sharply in the next decade, the study authors write. The disease is linked with liver-related conditions, such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as complications in other organs.
Previous meta-analyses have found an association between NAFLD and a higher risk of heart failure, though the analyses included a relatively small number of studies and a relatively modest sample size, Dr. Targher and colleagues write.
Since then, several new cohort studies have examined the association, which inspired a new meta-analysis.
The research team analyzed 11 observational cohort studies with aggregate data on more than 11 million middle-aged people from different countries, including nearly 3 million with NAFLD and nearly 98,000 cases of incident heart failure over a median follow-up of 10 years.
In the studies, NAFLD was diagnosed by serum liver enzyme levels, serum biomarkers or scores, diagnostic codes, imaging techniques, or liver histology. Four studies were conducted in the United States, three were conducted in South Korea, and four were carried out in Europe, including Finland, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
Dr. Targher and colleagues found that the presence of NAFLD was associated with a moderately higher risk of new-onset heart failure, with a pooled random-effects hazard ratio of 1.5. The risk was independent of age, sex, ethnicity, adiposity measures, diabetes, hypertension, and other typical cardiovascular risk factors.
The association between NAFLD and heart failure risk was consistent even when the comparison was stratified by study country, follow-up length, modality of heart failure diagnosis, and modality of NAFLD diagnosis.
In addition, sensitivity analyses didn’t change the results, and a funnel plot suggested that publication bias was unlikely.
“Accumulating evidence supports that NAFLD is part of a multisystem disease that adversely affects several extrahepatic organs, including the heart,” Dr. Targher said.
“NAFLD not only promotes accelerated coronary atherosclerosis but also confers a higher risk of myocardial abnormalities (cardiac remodeling and hypertrophy) and certain arrhythmias (mostly atrial fibrillation), which may precede and promote the development of new-onset heart failure over time,” he said.
Future research
Dr. Targher and colleagues also found that the risk of incident heart failure appeared to further increase with more advanced liver disease, particularly with higher levels of liver fibrosis, as assessed by noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers or histology. With only two cohort studies that examined the association, the authors judged there was insufficient data available to combine the studies into a meta-analysis.
But the observations are consistent with other recent meta-analyses that reported a significant association between the presence and severity of NAFLD and the risk of developing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease, or other non-liver complications.
“It’s reassuring that the observations that have come from single studies hold true when you look at the totality of evidence,” Ambarish Pandey, MD, a cardiologist and assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, told this news organization.
Dr. Pandey, who wasn’t involved with this study, conducted one of the recent meta-analyses that found a 1.6-times increased risk of heart failure associated with NAFLD, as well as a further increased risk with more advanced liver disease.
Now Dr. Pandey and colleagues are studying the underlying mechanisms for the link between NAFLD and heart failure risk, including cardiac structure and function, biomarkers of injury and stress, and how proportions of liver fat influence risk. Additional studies should investigate whether resolving NAFLD could reduce the risk of heart failure, he said.
“It’s really important to look for patients with NAFLD in primary care and think about cardiovascular disease in our liver patients,” he said. “Early strategies to implement the prevention of heart failure would go a long way in reducing long-term risks for these patients.”
The study authors did not declare a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors. Dr. Targher and Dr. Pandey report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of developing incident heart failure is 1.5-times higher in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) during a median follow-up of 10 years, according to a new meta-analysis.
The risk appears to increase with greater liver disease severity and was independent of age, sex, ethnicity, obesity, and the presence of diabetes, hypertension, and other common cardiovascular risk factors.
“Health care professionals should be aware that the risk of new-onset heart failure is moderately higher in patients with NAFLD,” senior author Giovanni Targher, MD, said in an interview.
“Because of the link between the two conditions, more careful surveillance of these patients will be needed,” said Dr. Targher, who is an associate professor of diabetes and endocrinology at the University of Verona (Italy). “In particular, the results of this meta-analysis highlight the need for a patient-centered, multidisciplinary, and holistic approach to manage both liver disease and cardiovascular risk in patients with NAFLD.”
The study was published online in Gut.
Risk calculations
NAFLD has become one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide (affecting up to about 30% of the world’s adults), and is expected to rise sharply in the next decade, the study authors write. The disease is linked with liver-related conditions, such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as complications in other organs.
Previous meta-analyses have found an association between NAFLD and a higher risk of heart failure, though the analyses included a relatively small number of studies and a relatively modest sample size, Dr. Targher and colleagues write.
Since then, several new cohort studies have examined the association, which inspired a new meta-analysis.
The research team analyzed 11 observational cohort studies with aggregate data on more than 11 million middle-aged people from different countries, including nearly 3 million with NAFLD and nearly 98,000 cases of incident heart failure over a median follow-up of 10 years.
In the studies, NAFLD was diagnosed by serum liver enzyme levels, serum biomarkers or scores, diagnostic codes, imaging techniques, or liver histology. Four studies were conducted in the United States, three were conducted in South Korea, and four were carried out in Europe, including Finland, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
Dr. Targher and colleagues found that the presence of NAFLD was associated with a moderately higher risk of new-onset heart failure, with a pooled random-effects hazard ratio of 1.5. The risk was independent of age, sex, ethnicity, adiposity measures, diabetes, hypertension, and other typical cardiovascular risk factors.
The association between NAFLD and heart failure risk was consistent even when the comparison was stratified by study country, follow-up length, modality of heart failure diagnosis, and modality of NAFLD diagnosis.
In addition, sensitivity analyses didn’t change the results, and a funnel plot suggested that publication bias was unlikely.
“Accumulating evidence supports that NAFLD is part of a multisystem disease that adversely affects several extrahepatic organs, including the heart,” Dr. Targher said.
“NAFLD not only promotes accelerated coronary atherosclerosis but also confers a higher risk of myocardial abnormalities (cardiac remodeling and hypertrophy) and certain arrhythmias (mostly atrial fibrillation), which may precede and promote the development of new-onset heart failure over time,” he said.
Future research
Dr. Targher and colleagues also found that the risk of incident heart failure appeared to further increase with more advanced liver disease, particularly with higher levels of liver fibrosis, as assessed by noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers or histology. With only two cohort studies that examined the association, the authors judged there was insufficient data available to combine the studies into a meta-analysis.
But the observations are consistent with other recent meta-analyses that reported a significant association between the presence and severity of NAFLD and the risk of developing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease, or other non-liver complications.
“It’s reassuring that the observations that have come from single studies hold true when you look at the totality of evidence,” Ambarish Pandey, MD, a cardiologist and assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, told this news organization.
Dr. Pandey, who wasn’t involved with this study, conducted one of the recent meta-analyses that found a 1.6-times increased risk of heart failure associated with NAFLD, as well as a further increased risk with more advanced liver disease.
Now Dr. Pandey and colleagues are studying the underlying mechanisms for the link between NAFLD and heart failure risk, including cardiac structure and function, biomarkers of injury and stress, and how proportions of liver fat influence risk. Additional studies should investigate whether resolving NAFLD could reduce the risk of heart failure, he said.
“It’s really important to look for patients with NAFLD in primary care and think about cardiovascular disease in our liver patients,” he said. “Early strategies to implement the prevention of heart failure would go a long way in reducing long-term risks for these patients.”
The study authors did not declare a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors. Dr. Targher and Dr. Pandey report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The risk of developing incident heart failure is 1.5-times higher in people with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) during a median follow-up of 10 years, according to a new meta-analysis.
The risk appears to increase with greater liver disease severity and was independent of age, sex, ethnicity, obesity, and the presence of diabetes, hypertension, and other common cardiovascular risk factors.
“Health care professionals should be aware that the risk of new-onset heart failure is moderately higher in patients with NAFLD,” senior author Giovanni Targher, MD, said in an interview.
“Because of the link between the two conditions, more careful surveillance of these patients will be needed,” said Dr. Targher, who is an associate professor of diabetes and endocrinology at the University of Verona (Italy). “In particular, the results of this meta-analysis highlight the need for a patient-centered, multidisciplinary, and holistic approach to manage both liver disease and cardiovascular risk in patients with NAFLD.”
The study was published online in Gut.
Risk calculations
NAFLD has become one of the most common causes of chronic liver disease worldwide (affecting up to about 30% of the world’s adults), and is expected to rise sharply in the next decade, the study authors write. The disease is linked with liver-related conditions, such as nonalcoholic steatohepatitis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, as well as complications in other organs.
Previous meta-analyses have found an association between NAFLD and a higher risk of heart failure, though the analyses included a relatively small number of studies and a relatively modest sample size, Dr. Targher and colleagues write.
Since then, several new cohort studies have examined the association, which inspired a new meta-analysis.
The research team analyzed 11 observational cohort studies with aggregate data on more than 11 million middle-aged people from different countries, including nearly 3 million with NAFLD and nearly 98,000 cases of incident heart failure over a median follow-up of 10 years.
In the studies, NAFLD was diagnosed by serum liver enzyme levels, serum biomarkers or scores, diagnostic codes, imaging techniques, or liver histology. Four studies were conducted in the United States, three were conducted in South Korea, and four were carried out in Europe, including Finland, Sweden, and the United Kingdom.
Dr. Targher and colleagues found that the presence of NAFLD was associated with a moderately higher risk of new-onset heart failure, with a pooled random-effects hazard ratio of 1.5. The risk was independent of age, sex, ethnicity, adiposity measures, diabetes, hypertension, and other typical cardiovascular risk factors.
The association between NAFLD and heart failure risk was consistent even when the comparison was stratified by study country, follow-up length, modality of heart failure diagnosis, and modality of NAFLD diagnosis.
In addition, sensitivity analyses didn’t change the results, and a funnel plot suggested that publication bias was unlikely.
“Accumulating evidence supports that NAFLD is part of a multisystem disease that adversely affects several extrahepatic organs, including the heart,” Dr. Targher said.
“NAFLD not only promotes accelerated coronary atherosclerosis but also confers a higher risk of myocardial abnormalities (cardiac remodeling and hypertrophy) and certain arrhythmias (mostly atrial fibrillation), which may precede and promote the development of new-onset heart failure over time,” he said.
Future research
Dr. Targher and colleagues also found that the risk of incident heart failure appeared to further increase with more advanced liver disease, particularly with higher levels of liver fibrosis, as assessed by noninvasive fibrosis biomarkers or histology. With only two cohort studies that examined the association, the authors judged there was insufficient data available to combine the studies into a meta-analysis.
But the observations are consistent with other recent meta-analyses that reported a significant association between the presence and severity of NAFLD and the risk of developing adverse cardiovascular outcomes, atrial fibrillation, chronic kidney disease, or other non-liver complications.
“It’s reassuring that the observations that have come from single studies hold true when you look at the totality of evidence,” Ambarish Pandey, MD, a cardiologist and assistant professor of internal medicine at the University of Texas Southwestern Medical Center, Dallas, told this news organization.
Dr. Pandey, who wasn’t involved with this study, conducted one of the recent meta-analyses that found a 1.6-times increased risk of heart failure associated with NAFLD, as well as a further increased risk with more advanced liver disease.
Now Dr. Pandey and colleagues are studying the underlying mechanisms for the link between NAFLD and heart failure risk, including cardiac structure and function, biomarkers of injury and stress, and how proportions of liver fat influence risk. Additional studies should investigate whether resolving NAFLD could reduce the risk of heart failure, he said.
“It’s really important to look for patients with NAFLD in primary care and think about cardiovascular disease in our liver patients,” he said. “Early strategies to implement the prevention of heart failure would go a long way in reducing long-term risks for these patients.”
The study authors did not declare a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial, or nonprofit sectors. Dr. Targher and Dr. Pandey report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM GUT
Updates on treatment/prevention of VTE in cancer patients
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Updated clinical practice guidelines for the treatment and prevention of venous thromboembolism for patients with cancer, including those with cancer and COVID-19, have been released by the International Initiative on Thrombosis and Cancer (ITAC), an academic working group of VTE experts.
“Because patients with cancer have a baseline increased risk of VTE, compared with patients without cancer, the combination of both COVID-19 and cancer – and its effect on VTE risk and treatment – is of concern,” said the authors, led by Dominique Farge, MD, PhD, Nord Universite de Paris.
they added.
The new guidelines were published online in The Lancet Oncology.
“Cancer-associated VTE remains an important clinical problem, associated with increased morbidity and mortality,” Dr. Farge and colleagues observed.
“The ITAC guidelines’ companion free web-based mobile application will assist the practicing clinician with decision making at various levels to provide optimal care of patients with cancer to treat and prevent VTE,” they emphasized. More information is available at itaccme.com.
Cancer patients with COVID
The new section of the guidelines notes that the treatment and prevention of VTE for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2 remain the same as for patients without COVID.
Whether or not cancer patients with COVID-19 are hospitalized, have been discharged, or are ambulatory, they should be assessed for the risk of VTE, as should any other patient. For cancer patients with COVID-19 who are hospitalized, pharmacologic prophylaxis should be given at the same dose and anticoagulant type as for hospitalized cancer patients who do not have COVID-19.
Following discharge, VTE prophylaxis is not advised for cancer patients infected with SARS-CoV-2, and routine primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE for ambulatory patients with COVID-19 is also not recommended, the authors noted.
Initial treatment of established VTE
Initial treatment of established VTE for up to 10 days of anticoagulation should include low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) when creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“A regimen of LMWH, taken once per day, is recommended unless a twice-per-day regimen is required because of patients’ characteristics,” the authors noted. These characteristics include a high risk of bleeding, moderate renal failure, and the need for technical intervention, including surgery.
If a twice-a-day regimen is required, only enoxaparin at a dose of 1 mg/kg twice daily can be used, the authors cautioned.
For patients with a low risk of gastrointestinal or genitourinary bleeding, rivaroxaban (Xarelto) or apixaban (Eliquis) can be given in the first 10 days, as well as edoxaban (Lixiana). The latter should be started after at least 5 days of parenteral anticoagulation, provided creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min.
“Unfractionated heparin as well as fondaparinux (GlaxoSmithKline) can be also used for the initial treatment of established VTE when LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants are contraindicated,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Thrombolysis can be considered on a case-by-case basis, although physicians must pay attention to specific contraindications, especially bleeding risk.
“In the initial treatment of VTE, inferior vena cava filters might be considered when anticoagulant treatment is contraindicated or, in the case of pulmonary embolism, when recurrence occurs under optimal anticoagulation,” the authors noted.
Maintenance VTE treatment
For maintenance therapy, which the authors define as early maintenance for up to 6 months and long-term maintenance beyond 6 months, they point out that LMWHs are preferred over vitamin K antagonists for the treatment of VTE when the creatinine clearance is again at least 30 mL/min.
Any of the direct oral anticoagulants (DOAs) – edoxaban, rivaroxaban, or apixaban – is also recommended for the same patients, provided there is no risk of inducing a strong drug-drug interaction or GI absorption is impaired.
However, the DOAs should be used with caution for patients with GI malignancies, especially upper GI cancers, because data show there is an increased risk of GI bleeding with both edoxaban and rivaroxaban.
“LMWH or direct oral anticoagulants should be used for a minimum of 6 months to treat established VTE in patients with cancer,” the authors wrote.
“After 6 months, termination or continuation of anticoagulation (LMWH, direct oral anticoagulants, or vitamin K antagonists) should be based on individual evaluation of the benefit-risk ratio,” they added.
Treatment of VTE recurrence
The guideline authors explain that three options can be considered in the event of VTE recurrence. These include an increase in the LMWH dose by 20%-25%, or a switch to a DOA, or, if patients are taking a DOA, a switch to an LMWH. If the patient is taking a vitamin K antagonist, it can be switched to either an LMWH or a DOA.
For treatment of catheter-related thrombosis, anticoagulant treatment is recommended for a minimum of 3 months and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. In this setting, the LMWHs are recommended.
The central venous catheter can be kept in place if it is functional, well positioned, and is not infected, provided there is good resolution of symptoms under close surveillance while anticoagulants are being administered.
In surgically treated patients, the LMWH, given once a day, to patients with a serum creatinine concentration of at least 30 mL/min can be used to prevent VTE. Alternatively, VTE can be prevented by the use low-dose unfractionated heparin, given three times a day.
“Pharmacological prophylaxis should be started 2-12 h preoperatively and continued for at least 7–10 days,” Dr. Farge and colleagues advised. In this setting, there is insufficient evidence to support the use of fondaparinux or a DOA as an alternative to an LMWH for the prophylaxis of postoperative VTE. “Use of the highest prophylactic dose of LMWH to prevent postoperative VTE in patients with cancer is recommended,” the authors advised.
Furthermore, extended prophylaxis of at least 4 weeks with LMWH is advised to prevent postoperative VTE after major abdominal or pelvic surgery. Mechanical methods are not recommended except when pharmacologic methods are contraindicated. Inferior vena cava filters are also not recommended for routine prophylaxis.
Patients with reduced mobility
For medically treated hospitalized patients with cancer whose mobility is reduced, the authors recommend prophylaxis with either an LMWH or fondaparinux, provided their creatinine clearance is at least 30 mL/min. These patients can also be treated with unfractionated heparin, they add.
In contrast, DOAs are not recommended – at least not routinely – in this setting, the authors cautioned. Primary pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE with either LMWH or DOAs – either rivaroxaban or apixaban – is indicated in ambulatory patients with locally advanced or metastatic pancreatic cancer who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy, provided they are at low risk of bleeding.
However, primary pharmacologic prophylaxis with LMWH is not recommended outside of a clinical trial for patients with locally advanced or metastatic lung cancer who are undergoing systemic anticancer therapy, even for patients who are at low risk of bleeding.
For ambulatory patients who are receiving systemic anticancer therapy and who are at intermediate risk of VTE, primary prophylaxis with rivaroxaban or apixaban is recommended for those with myeloma who are receiving immunomodulatory therapy plus steroids or other systemic therapies.
In this setting, oral anticoagulants should consist of a vitamin K antagonist, given at low or therapeutic doses, or apixaban, given at prophylactic doses. Alternatively, LMWH, given at prophylactic doses, or low-dose aspirin, given at a dose of 100 mg/day, can be used.
Catheter-related thrombosis
Use of anticoagulation for routine prophylaxis of catheter-related thrombosis is not recommended. Catheters should be inserted on the right side in the jugular vein, and the distal extremity of the central catheter should be located at the junction of the superior vena cava and the right atrium. “In patients requiring central venous catheters, we suggest the use of implanted ports over peripheral inserted central catheter lines,” the authors noted.
The authors described a number of unique situations regarding the treatment of VTE. These situations include patients with a brain tumor, for whom treatment of established VTE should favor either LMWH or a DOA. The authors also recommended the use of LMWH or unfractionated heparin, started postoperatively, for the prevention of VTE for patients undergoing neurosurgery.
In contrast, pharmacologic prophylaxis of VTE in medically treated patients with a brain tumor who are not undergoing neurosurgery is not recommended. “In the presence of severe renal failure...we suggest using unfractionated heparin followed by early vitamin K antagonists (possibly from day 1) or LMWH adjusted to anti-Xa concentration of the treatment of established VTE,” Dr. Farge and colleagues wrote.
Anticoagulant treatment is also recommended for a minimum of 3 months for children with symptomatic catheter-related thrombosis and as long as the central venous catheter is in place. For children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia who are undergoing induction chemotherapy, LMWH is also recommended as thromboprophylaxis.
For children who require a central venous catheter, the authors suggested that physicians use implanted ports over peripherally inserted central lines.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE LANCET ONCOLOGY
CV admissions on the rise in Americans with cancer
Although cardiovascular disease (CVD) is known to often strike the mortal blow in patients with cancer, a national analysis puts in stark relief the burden of CV-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable population.
, whereas admissions fell 10.9% among those without cancer.
Admissions increased steadily across all cancer types, except prostate cancer, with heart failure being the most common reason for admission.
“Hospital admissions is really important because we know that the size of this group is increasing, given that they live longer and many of the treatments that we offer cause cardiovascular disease or increase the risk of having cardiovascular events. So, from a health care planning perspective, I think it’s really important to see what the burden is likely to be in the next few years,” senior author Mamas Mamas, MD, Keele University, England, told this news organization.
For physicians and the wider population, he said, the findings underscore the need to shift the conversation from saying that patients with cancer are at increased CVD risk to asking how to mitigate this risk. “Because I would say that this increase in cardiovascular admissions, that’s a failure from a preventative perspective.”
The study was published in the European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes.
Individual cancer types
The researchers, led by Ofer Kobo, MD, also with Keele University, used the National Inpatient Sample to identify 42.5 million weighted cases of CV admissions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation (AFib) or atrial flutter, and intracranial hemorrhage from January 2004 to December 2017. Of these, 1.9 million had a record of cancer.
Patients with cancer were older; had a higher prevalence of valvular disease, anemia, and coagulopathy; and had a lower prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity than did patients without cancer.
The most common cancer type was hematologic cancers (26.1%), followed by lung (18.7%), gastrointestinal (12.4%), prostate (11.6%), breast (6.7%), and other in 24.4%.
The admission rate increased across all six admission causes – between 7% for AMI and ischemic stroke and 46% for AFib.
Heart failure was the chief reason for admission among all patients. Annual rates per 100,000 U.S. population increased in patients with cancer (from 13.6 to 16.6; P for trend = .02) and declined in those without (from 352.2 to 349.8; P for trend < .001).
“In the past, patients would be started on medications, and perhaps the importance of monitoring [left ventricular] LV function wasn’t as widely known, whereas now we’re much more aggressive in looking at it and much more aggressive at trying to prevent it,” Dr. Mamas said. “But even with this greater identification and attempting to modify regimens, we’re still getting quite substantial increases in heart failure admissions in this population. And what really surprised me is that it wasn’t just in the breast cancer population, but it was nearly across the board.”
He noted that patients are at highest risk from CV events within the first 2 years of cancer diagnosis. “So that’s really the time where you’ve got to be really aggressive in looking and working up their cardiovascular profile.”
Patients with hematologic cancers (9.7-13.5), lung (7.4-8.9), and gastrointestinal cancer (4.6-6.3) had the highest crude admission rates of CV hospitalizations per 100,000 U.S. population.
The CV admission rate went up from 2.5 to 3.7 per 100,000 U.S. population for breast cancer, and in prostate cancer, the rate dropped from 5.8 to 4.8 per 100,000 U.S. population.
Of note, patients with hematologic cancers also had the highest rate of heart failure hospitalization across all cancer types, which, coupled with their increasing admission rates, likely reflects their exposure to a “constellation of cardiotoxic therapies” as well as pathologic processes related to the cancers themselves, the authors suggest.
In-hospital mortality rates were higher among patients with cancer than those without, ranging from 5% for patients with breast cancer to 9.6% for patients with lung cancer versus 4.2% for those without cancer.
Among patients with cancer, the odds ratio for mortality was highest in those admitted with AFib (4.43), followed by pulmonary embolism (2.36), AMI (2.31), ischemic stroke (2.29), and heart failure (2.24).
In line with prior work and general population trends, in-hospital deaths in primary CV admissions trended lower among patients with cancer over the study period.
Mitigating risk
Commenting on the study, Joerg Herrmann, MD, director of the cardio-oncology clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the data are “extremely important” because they reflect admissions during a new era of cancer therapy. “Targeted therapies all came out about the turn of the millennium, so we’re not really looking at cancer patients treated with only old and ancient strategies.”
This may be one reason for the increased admissions, but because the study lacked information on specific cancer treatments and the date of cancer diagnosis, it’s not possible to tease out whether the uptick is related to cardiotoxicity or because the oncology outcomes have improved so much that this is a growing population, he said.
One clear implication, however, is that whoever is working on the hospital service will see more patients with a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Herrmann observed.
“Though some may have tried to maybe not get involved with this topic as much, it really calls for some broader scope to get familiar with this very entity,” he said. “And that plays out, in particular, in those patients with a diagnosis of active cancer.”
Dr. Herrmann and colleagues previously reported that patients with active leukemia or lymphoma who were hospitalized with acute coronary syndrome were less likely to receive guideline-directed therapies, even at the Mayo Clinic.
Similarly, a 2020 report by Dr. Mamas and colleagues found that patients with a variety of active cancers derived similar benefit from primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment–elevation MI as those without cancer but received the treatment less commonly.
Although there’s a greater appreciation that patients with cancer benefit equally from aggressive treatment, much more can be done to mitigate CV risk, Dr. Mamas noted. Valuable coronary information captured by MRI and CT done as part of the cancer investigation is often overlooked. For example, “we know that breast calcification and vascular calcification in the breast are very strong predictors of cardiovascular outcomes and yet people aren’t using this information.”
There are numerous shared risk factors in the development of cancer and coronary artery disease, and patients with cancer often have much worse CV risk profiles but aren’t routinely risk stratified from a CV perspective, he said.
Dr. Mamas said that his team is also studying whether CVD risk prediction tools like the Framingham Risk Score, which were derived from noncancer populations, work as well in patients with cancer. “Often, when you look at the performance of these tools in populations that weren’t covered, they’re much worse.”
“A lot of cancer survivors worry about the recurrence of their cancer and will religiously go and have repeated scans, religiously check themselves, and have all these investigations but don’t think about the actual risk that is greater for them, which is cardiovascular risk,” he said.
The authors report no study funding or relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although cardiovascular disease (CVD) is known to often strike the mortal blow in patients with cancer, a national analysis puts in stark relief the burden of CV-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable population.
, whereas admissions fell 10.9% among those without cancer.
Admissions increased steadily across all cancer types, except prostate cancer, with heart failure being the most common reason for admission.
“Hospital admissions is really important because we know that the size of this group is increasing, given that they live longer and many of the treatments that we offer cause cardiovascular disease or increase the risk of having cardiovascular events. So, from a health care planning perspective, I think it’s really important to see what the burden is likely to be in the next few years,” senior author Mamas Mamas, MD, Keele University, England, told this news organization.
For physicians and the wider population, he said, the findings underscore the need to shift the conversation from saying that patients with cancer are at increased CVD risk to asking how to mitigate this risk. “Because I would say that this increase in cardiovascular admissions, that’s a failure from a preventative perspective.”
The study was published in the European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes.
Individual cancer types
The researchers, led by Ofer Kobo, MD, also with Keele University, used the National Inpatient Sample to identify 42.5 million weighted cases of CV admissions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation (AFib) or atrial flutter, and intracranial hemorrhage from January 2004 to December 2017. Of these, 1.9 million had a record of cancer.
Patients with cancer were older; had a higher prevalence of valvular disease, anemia, and coagulopathy; and had a lower prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity than did patients without cancer.
The most common cancer type was hematologic cancers (26.1%), followed by lung (18.7%), gastrointestinal (12.4%), prostate (11.6%), breast (6.7%), and other in 24.4%.
The admission rate increased across all six admission causes – between 7% for AMI and ischemic stroke and 46% for AFib.
Heart failure was the chief reason for admission among all patients. Annual rates per 100,000 U.S. population increased in patients with cancer (from 13.6 to 16.6; P for trend = .02) and declined in those without (from 352.2 to 349.8; P for trend < .001).
“In the past, patients would be started on medications, and perhaps the importance of monitoring [left ventricular] LV function wasn’t as widely known, whereas now we’re much more aggressive in looking at it and much more aggressive at trying to prevent it,” Dr. Mamas said. “But even with this greater identification and attempting to modify regimens, we’re still getting quite substantial increases in heart failure admissions in this population. And what really surprised me is that it wasn’t just in the breast cancer population, but it was nearly across the board.”
He noted that patients are at highest risk from CV events within the first 2 years of cancer diagnosis. “So that’s really the time where you’ve got to be really aggressive in looking and working up their cardiovascular profile.”
Patients with hematologic cancers (9.7-13.5), lung (7.4-8.9), and gastrointestinal cancer (4.6-6.3) had the highest crude admission rates of CV hospitalizations per 100,000 U.S. population.
The CV admission rate went up from 2.5 to 3.7 per 100,000 U.S. population for breast cancer, and in prostate cancer, the rate dropped from 5.8 to 4.8 per 100,000 U.S. population.
Of note, patients with hematologic cancers also had the highest rate of heart failure hospitalization across all cancer types, which, coupled with their increasing admission rates, likely reflects their exposure to a “constellation of cardiotoxic therapies” as well as pathologic processes related to the cancers themselves, the authors suggest.
In-hospital mortality rates were higher among patients with cancer than those without, ranging from 5% for patients with breast cancer to 9.6% for patients with lung cancer versus 4.2% for those without cancer.
Among patients with cancer, the odds ratio for mortality was highest in those admitted with AFib (4.43), followed by pulmonary embolism (2.36), AMI (2.31), ischemic stroke (2.29), and heart failure (2.24).
In line with prior work and general population trends, in-hospital deaths in primary CV admissions trended lower among patients with cancer over the study period.
Mitigating risk
Commenting on the study, Joerg Herrmann, MD, director of the cardio-oncology clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the data are “extremely important” because they reflect admissions during a new era of cancer therapy. “Targeted therapies all came out about the turn of the millennium, so we’re not really looking at cancer patients treated with only old and ancient strategies.”
This may be one reason for the increased admissions, but because the study lacked information on specific cancer treatments and the date of cancer diagnosis, it’s not possible to tease out whether the uptick is related to cardiotoxicity or because the oncology outcomes have improved so much that this is a growing population, he said.
One clear implication, however, is that whoever is working on the hospital service will see more patients with a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Herrmann observed.
“Though some may have tried to maybe not get involved with this topic as much, it really calls for some broader scope to get familiar with this very entity,” he said. “And that plays out, in particular, in those patients with a diagnosis of active cancer.”
Dr. Herrmann and colleagues previously reported that patients with active leukemia or lymphoma who were hospitalized with acute coronary syndrome were less likely to receive guideline-directed therapies, even at the Mayo Clinic.
Similarly, a 2020 report by Dr. Mamas and colleagues found that patients with a variety of active cancers derived similar benefit from primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment–elevation MI as those without cancer but received the treatment less commonly.
Although there’s a greater appreciation that patients with cancer benefit equally from aggressive treatment, much more can be done to mitigate CV risk, Dr. Mamas noted. Valuable coronary information captured by MRI and CT done as part of the cancer investigation is often overlooked. For example, “we know that breast calcification and vascular calcification in the breast are very strong predictors of cardiovascular outcomes and yet people aren’t using this information.”
There are numerous shared risk factors in the development of cancer and coronary artery disease, and patients with cancer often have much worse CV risk profiles but aren’t routinely risk stratified from a CV perspective, he said.
Dr. Mamas said that his team is also studying whether CVD risk prediction tools like the Framingham Risk Score, which were derived from noncancer populations, work as well in patients with cancer. “Often, when you look at the performance of these tools in populations that weren’t covered, they’re much worse.”
“A lot of cancer survivors worry about the recurrence of their cancer and will religiously go and have repeated scans, religiously check themselves, and have all these investigations but don’t think about the actual risk that is greater for them, which is cardiovascular risk,” he said.
The authors report no study funding or relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Although cardiovascular disease (CVD) is known to often strike the mortal blow in patients with cancer, a national analysis puts in stark relief the burden of CV-related hospitalizations in this vulnerable population.
, whereas admissions fell 10.9% among those without cancer.
Admissions increased steadily across all cancer types, except prostate cancer, with heart failure being the most common reason for admission.
“Hospital admissions is really important because we know that the size of this group is increasing, given that they live longer and many of the treatments that we offer cause cardiovascular disease or increase the risk of having cardiovascular events. So, from a health care planning perspective, I think it’s really important to see what the burden is likely to be in the next few years,” senior author Mamas Mamas, MD, Keele University, England, told this news organization.
For physicians and the wider population, he said, the findings underscore the need to shift the conversation from saying that patients with cancer are at increased CVD risk to asking how to mitigate this risk. “Because I would say that this increase in cardiovascular admissions, that’s a failure from a preventative perspective.”
The study was published in the European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes.
Individual cancer types
The researchers, led by Ofer Kobo, MD, also with Keele University, used the National Inpatient Sample to identify 42.5 million weighted cases of CV admissions for acute myocardial infarction (AMI), pulmonary embolism, ischemic stroke, heart failure, atrial fibrillation (AFib) or atrial flutter, and intracranial hemorrhage from January 2004 to December 2017. Of these, 1.9 million had a record of cancer.
Patients with cancer were older; had a higher prevalence of valvular disease, anemia, and coagulopathy; and had a lower prevalence of hypertension, diabetes mellitus, and obesity than did patients without cancer.
The most common cancer type was hematologic cancers (26.1%), followed by lung (18.7%), gastrointestinal (12.4%), prostate (11.6%), breast (6.7%), and other in 24.4%.
The admission rate increased across all six admission causes – between 7% for AMI and ischemic stroke and 46% for AFib.
Heart failure was the chief reason for admission among all patients. Annual rates per 100,000 U.S. population increased in patients with cancer (from 13.6 to 16.6; P for trend = .02) and declined in those without (from 352.2 to 349.8; P for trend < .001).
“In the past, patients would be started on medications, and perhaps the importance of monitoring [left ventricular] LV function wasn’t as widely known, whereas now we’re much more aggressive in looking at it and much more aggressive at trying to prevent it,” Dr. Mamas said. “But even with this greater identification and attempting to modify regimens, we’re still getting quite substantial increases in heart failure admissions in this population. And what really surprised me is that it wasn’t just in the breast cancer population, but it was nearly across the board.”
He noted that patients are at highest risk from CV events within the first 2 years of cancer diagnosis. “So that’s really the time where you’ve got to be really aggressive in looking and working up their cardiovascular profile.”
Patients with hematologic cancers (9.7-13.5), lung (7.4-8.9), and gastrointestinal cancer (4.6-6.3) had the highest crude admission rates of CV hospitalizations per 100,000 U.S. population.
The CV admission rate went up from 2.5 to 3.7 per 100,000 U.S. population for breast cancer, and in prostate cancer, the rate dropped from 5.8 to 4.8 per 100,000 U.S. population.
Of note, patients with hematologic cancers also had the highest rate of heart failure hospitalization across all cancer types, which, coupled with their increasing admission rates, likely reflects their exposure to a “constellation of cardiotoxic therapies” as well as pathologic processes related to the cancers themselves, the authors suggest.
In-hospital mortality rates were higher among patients with cancer than those without, ranging from 5% for patients with breast cancer to 9.6% for patients with lung cancer versus 4.2% for those without cancer.
Among patients with cancer, the odds ratio for mortality was highest in those admitted with AFib (4.43), followed by pulmonary embolism (2.36), AMI (2.31), ischemic stroke (2.29), and heart failure (2.24).
In line with prior work and general population trends, in-hospital deaths in primary CV admissions trended lower among patients with cancer over the study period.
Mitigating risk
Commenting on the study, Joerg Herrmann, MD, director of the cardio-oncology clinic at Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minn., said that the data are “extremely important” because they reflect admissions during a new era of cancer therapy. “Targeted therapies all came out about the turn of the millennium, so we’re not really looking at cancer patients treated with only old and ancient strategies.”
This may be one reason for the increased admissions, but because the study lacked information on specific cancer treatments and the date of cancer diagnosis, it’s not possible to tease out whether the uptick is related to cardiotoxicity or because the oncology outcomes have improved so much that this is a growing population, he said.
One clear implication, however, is that whoever is working on the hospital service will see more patients with a cancer diagnosis, Dr. Herrmann observed.
“Though some may have tried to maybe not get involved with this topic as much, it really calls for some broader scope to get familiar with this very entity,” he said. “And that plays out, in particular, in those patients with a diagnosis of active cancer.”
Dr. Herrmann and colleagues previously reported that patients with active leukemia or lymphoma who were hospitalized with acute coronary syndrome were less likely to receive guideline-directed therapies, even at the Mayo Clinic.
Similarly, a 2020 report by Dr. Mamas and colleagues found that patients with a variety of active cancers derived similar benefit from primary percutaneous coronary intervention for ST-segment–elevation MI as those without cancer but received the treatment less commonly.
Although there’s a greater appreciation that patients with cancer benefit equally from aggressive treatment, much more can be done to mitigate CV risk, Dr. Mamas noted. Valuable coronary information captured by MRI and CT done as part of the cancer investigation is often overlooked. For example, “we know that breast calcification and vascular calcification in the breast are very strong predictors of cardiovascular outcomes and yet people aren’t using this information.”
There are numerous shared risk factors in the development of cancer and coronary artery disease, and patients with cancer often have much worse CV risk profiles but aren’t routinely risk stratified from a CV perspective, he said.
Dr. Mamas said that his team is also studying whether CVD risk prediction tools like the Framingham Risk Score, which were derived from noncancer populations, work as well in patients with cancer. “Often, when you look at the performance of these tools in populations that weren’t covered, they’re much worse.”
“A lot of cancer survivors worry about the recurrence of their cancer and will religiously go and have repeated scans, religiously check themselves, and have all these investigations but don’t think about the actual risk that is greater for them, which is cardiovascular risk,” he said.
The authors report no study funding or relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM European Heart Journal: Quality of Care & Clinical Outcomes