User login
Cardiology News is an independent news source that provides cardiologists with timely and relevant news and commentary about clinical developments and the impact of health care policy on cardiology and the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is the online destination and multimedia properties of Cardiology News, the independent news publication for cardiologists. Cardiology news is the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in cardiology as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the cardiologist's practice. Cardiology News Digital Network is owned by Frontline Medical Communications.
Cut in AFib burden gains traction as gauge of ablation success: PULSED-AF
suggests a new analysis.
It’s the first study tying those outcomes to residual AFib burden after ablation achieved using the emerging pulsed-field ablation (PFA) technology, say researchers. These associations are already established for cath ablation using traditional radiofrequency energy or cryoablation.
The new findings come from a secondary analysis of the recently published PULSED-AF study, which highlighted the ablation efficacy of Medtronic’s investigational PulseSelect PFA system in patients with either paroxysmal AFib (PAF) or persistent AFib.
The trial had entered 300 adult candidates for catheter ablation of recurrent, symptomatic PAF or persistent AFib at 41 centers in Australia, Canada, Europe, Japan, and the United States.
After ablation, 69% of PAF patients and 62% of those who had persistent AFib showed no sign of atrial arrhythmia (AA) over 12 months, based on the trial’s method for estimating AA burden.
Residual AA burden less than 10% was seen in 87% and 82% of those initially with PAF and persistent AFib, respectively. Burdens in that lowest range, compared with greater AA burden, predicted a “clinically meaningful” improvement in QoL scores in PAF patients.
Those who entered the study with persistent AFib showed such improvement – defined as a more than 19-point gain on the Atrial Fibrillation Effect on Quality-of-Life Questionnaire – regardless of postablation AA burden.
Moreover, patients initially with either type of AFib and residual burdens in the lowest range went on to have fewer cardioversions and repeat ablations (P < .01), Atul Verma, MD, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
Dr. Verma, the trial’s principal investigator, is also lead author on the same-day publication of the secondary analysis in Heart Rhythm.
Binary endpoint lacks relevance
The PULSED-AF primary analysis defined ablation efficacy partly as freedom from AA recurrence lasting at least 30 seconds, with or without symptoms, a traditional AFib-ablation trial endpoint that is nonetheless considered clinically unhelpful.
The secondary analysis recasts that binary endpoint as degree of reduction in AFib burden, a continuous variable. That potentially allows AFib ablation efficacy to be assessed in a more nuanced way likely to be more meaningful to patients and the health care system, observed Dr. Verma and colleagues.
The “30-second endpoint” is limited in clinical usefulness and “doesn’t mean much to the patient,” he said at a press conference on the analysis before formally presenting it at the HRS sessions.
Recent AFib ablation trials have explored AA burden as possibly a superior way to assess the procedure’s success “but also to see if it’s better correlated with quality of life and health care outcomes,” Dr. Verma said. “So that’s exactly what we’ve tried to do here using the PULSED-AF data.”
In the secondary analysis, he said, patients’ rate of freedom from the 30-second endpoint was about 70%, but “more than 85% of them had an AFib burden of less than 10%.”
“This efficacy endpoint of 30 seconds of atrial arrhythmia has been challenged and has been seen clinically as insignificant,” agreed Rajeev Pathak, MBBS, PhD, of Australian National University and director of cardiac electrophysiology at Canberra (Australia) Hospital.
In AFib radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation studies “there is clear disconnect between these 30-second episodes of atrial arrhythmias we see and the clinical relevance of health care utilization and quality of life,” said Dr. Pathak, invited discussant for Dr. Verma’s presentation at the sessions.
Now an AFib ablation trial using PFA catheters has yielded similar results, finding AA burden to be “a more objective and relevant measure of success,” he said. “A 30-second endpoint is arbitrary, lacks significance, and is highly dependent on the monitoring strategy.”
The more you look, the more you see
The new secondary analysis included a demonstration that success rates based on the 30-second endpoint indeed vary depending on how subsequent arrhythmias are monitored.
As described by Dr. Verma, PULSED-AF data were assessed for the 30-second endpoint captured using three separate intermittent monitoring strategies that it and other recent ablation trials have used:
- Strategy A: Transtelephonic monitoring weekly and in the event of symptoms, plus 24-hour Holter monitoring at 6 and 12 months and 12-lead ECG at 3, 6, and 12 months
- Strategy B: Transtelephonic monitoring weekly and at symptoms for 3-6 months followed by monthly and at symptoms from 6 to 12 months, plus 24-hour Holter monitoring at 6 and 12 months, plus 12-lead ECG at 3, 6, and 12 months
- Strategy C: The median of two 24-hour Holter monitoring sessions per patient over 12 months
As Dr. Verma reported, rates of freedom from the 30-second endpoint climbed with successive monitoring strategies. The rates for PAF and persistent AFib patients, respectively, were: Strategy A – 70% and 62%, Strategy B – 71% and 68%, Strategy C – 91% and 86%.
“If you’re using the ‘freedom-from-30-seconds’ endpoint, the results that you are going to get are highly dependent on the monitoring strategy,” Dr. Verma said. “The more you look, the more you see.”
Valid estimation of burden
For the main PULSED-AF secondary analysis, the investigators defined AA burden according to findings on either Holter monitoring or the 12-lead ECG. “So as not to bias these results,” Dr. Verma said, “for every patient, we picked the method that gave us the highest atrial arrhythmia burden.”
Ideally, Dr. Verma said in an interview, arrhythmia burden would be determined using devices such as implantable loop recorders. “The problem is, this is expensive and not practical” in both clinical practice and many trials, so PULSED-AF investigators went with the intermittent monitoring strategy to estimate burdens.
Their method appears valid, he said, given that the study identified a statistically relevant 10% AA burden cut off for predicting quality of life improvement or less health care resource use.
“If their residual atrial arrhythmia burden was greater than 10%, they did not have a statistically significant improvement in quality of life,” Dr. Verma observed. And “very few” of them had cardioversions or repeat ablation.
“I couldn’t agree more” that residual AA burden is preferable to the 30-second endpoint for gauging AFib ablation success, Kenneth Ellenbogen, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, said in an interview. Dr. Ellenbogen is also director of clinical cardiac electrophysiology and pacing at VCU Health Pauley Heart Center and not associated with PULSED-AF.
That AA burden was linked to health care resource use in the study “is absolutely brilliant,” he said, “because that’s what the bean counters really want at the end of the day. And as doctors we care about patients feeling better – improving quality of life.”
PULSED-AF was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Verma disclosed financial relationships with Bayer, Biosense Webster, Medtronic, Thermedical, Kardium, and Galaxy Medical, as well as and research grants from Adagio Medical. Dr. Ellenbogen disclosed financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Kestra, Hylomorph, Biotronik, MediLynx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Abbott, Biosense Webster, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Medpace, and Elsevier. Dr. Pathak disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a new analysis.
It’s the first study tying those outcomes to residual AFib burden after ablation achieved using the emerging pulsed-field ablation (PFA) technology, say researchers. These associations are already established for cath ablation using traditional radiofrequency energy or cryoablation.
The new findings come from a secondary analysis of the recently published PULSED-AF study, which highlighted the ablation efficacy of Medtronic’s investigational PulseSelect PFA system in patients with either paroxysmal AFib (PAF) or persistent AFib.
The trial had entered 300 adult candidates for catheter ablation of recurrent, symptomatic PAF or persistent AFib at 41 centers in Australia, Canada, Europe, Japan, and the United States.
After ablation, 69% of PAF patients and 62% of those who had persistent AFib showed no sign of atrial arrhythmia (AA) over 12 months, based on the trial’s method for estimating AA burden.
Residual AA burden less than 10% was seen in 87% and 82% of those initially with PAF and persistent AFib, respectively. Burdens in that lowest range, compared with greater AA burden, predicted a “clinically meaningful” improvement in QoL scores in PAF patients.
Those who entered the study with persistent AFib showed such improvement – defined as a more than 19-point gain on the Atrial Fibrillation Effect on Quality-of-Life Questionnaire – regardless of postablation AA burden.
Moreover, patients initially with either type of AFib and residual burdens in the lowest range went on to have fewer cardioversions and repeat ablations (P < .01), Atul Verma, MD, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
Dr. Verma, the trial’s principal investigator, is also lead author on the same-day publication of the secondary analysis in Heart Rhythm.
Binary endpoint lacks relevance
The PULSED-AF primary analysis defined ablation efficacy partly as freedom from AA recurrence lasting at least 30 seconds, with or without symptoms, a traditional AFib-ablation trial endpoint that is nonetheless considered clinically unhelpful.
The secondary analysis recasts that binary endpoint as degree of reduction in AFib burden, a continuous variable. That potentially allows AFib ablation efficacy to be assessed in a more nuanced way likely to be more meaningful to patients and the health care system, observed Dr. Verma and colleagues.
The “30-second endpoint” is limited in clinical usefulness and “doesn’t mean much to the patient,” he said at a press conference on the analysis before formally presenting it at the HRS sessions.
Recent AFib ablation trials have explored AA burden as possibly a superior way to assess the procedure’s success “but also to see if it’s better correlated with quality of life and health care outcomes,” Dr. Verma said. “So that’s exactly what we’ve tried to do here using the PULSED-AF data.”
In the secondary analysis, he said, patients’ rate of freedom from the 30-second endpoint was about 70%, but “more than 85% of them had an AFib burden of less than 10%.”
“This efficacy endpoint of 30 seconds of atrial arrhythmia has been challenged and has been seen clinically as insignificant,” agreed Rajeev Pathak, MBBS, PhD, of Australian National University and director of cardiac electrophysiology at Canberra (Australia) Hospital.
In AFib radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation studies “there is clear disconnect between these 30-second episodes of atrial arrhythmias we see and the clinical relevance of health care utilization and quality of life,” said Dr. Pathak, invited discussant for Dr. Verma’s presentation at the sessions.
Now an AFib ablation trial using PFA catheters has yielded similar results, finding AA burden to be “a more objective and relevant measure of success,” he said. “A 30-second endpoint is arbitrary, lacks significance, and is highly dependent on the monitoring strategy.”
The more you look, the more you see
The new secondary analysis included a demonstration that success rates based on the 30-second endpoint indeed vary depending on how subsequent arrhythmias are monitored.
As described by Dr. Verma, PULSED-AF data were assessed for the 30-second endpoint captured using three separate intermittent monitoring strategies that it and other recent ablation trials have used:
- Strategy A: Transtelephonic monitoring weekly and in the event of symptoms, plus 24-hour Holter monitoring at 6 and 12 months and 12-lead ECG at 3, 6, and 12 months
- Strategy B: Transtelephonic monitoring weekly and at symptoms for 3-6 months followed by monthly and at symptoms from 6 to 12 months, plus 24-hour Holter monitoring at 6 and 12 months, plus 12-lead ECG at 3, 6, and 12 months
- Strategy C: The median of two 24-hour Holter monitoring sessions per patient over 12 months
As Dr. Verma reported, rates of freedom from the 30-second endpoint climbed with successive monitoring strategies. The rates for PAF and persistent AFib patients, respectively, were: Strategy A – 70% and 62%, Strategy B – 71% and 68%, Strategy C – 91% and 86%.
“If you’re using the ‘freedom-from-30-seconds’ endpoint, the results that you are going to get are highly dependent on the monitoring strategy,” Dr. Verma said. “The more you look, the more you see.”
Valid estimation of burden
For the main PULSED-AF secondary analysis, the investigators defined AA burden according to findings on either Holter monitoring or the 12-lead ECG. “So as not to bias these results,” Dr. Verma said, “for every patient, we picked the method that gave us the highest atrial arrhythmia burden.”
Ideally, Dr. Verma said in an interview, arrhythmia burden would be determined using devices such as implantable loop recorders. “The problem is, this is expensive and not practical” in both clinical practice and many trials, so PULSED-AF investigators went with the intermittent monitoring strategy to estimate burdens.
Their method appears valid, he said, given that the study identified a statistically relevant 10% AA burden cut off for predicting quality of life improvement or less health care resource use.
“If their residual atrial arrhythmia burden was greater than 10%, they did not have a statistically significant improvement in quality of life,” Dr. Verma observed. And “very few” of them had cardioversions or repeat ablation.
“I couldn’t agree more” that residual AA burden is preferable to the 30-second endpoint for gauging AFib ablation success, Kenneth Ellenbogen, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, said in an interview. Dr. Ellenbogen is also director of clinical cardiac electrophysiology and pacing at VCU Health Pauley Heart Center and not associated with PULSED-AF.
That AA burden was linked to health care resource use in the study “is absolutely brilliant,” he said, “because that’s what the bean counters really want at the end of the day. And as doctors we care about patients feeling better – improving quality of life.”
PULSED-AF was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Verma disclosed financial relationships with Bayer, Biosense Webster, Medtronic, Thermedical, Kardium, and Galaxy Medical, as well as and research grants from Adagio Medical. Dr. Ellenbogen disclosed financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Kestra, Hylomorph, Biotronik, MediLynx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Abbott, Biosense Webster, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Medpace, and Elsevier. Dr. Pathak disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
suggests a new analysis.
It’s the first study tying those outcomes to residual AFib burden after ablation achieved using the emerging pulsed-field ablation (PFA) technology, say researchers. These associations are already established for cath ablation using traditional radiofrequency energy or cryoablation.
The new findings come from a secondary analysis of the recently published PULSED-AF study, which highlighted the ablation efficacy of Medtronic’s investigational PulseSelect PFA system in patients with either paroxysmal AFib (PAF) or persistent AFib.
The trial had entered 300 adult candidates for catheter ablation of recurrent, symptomatic PAF or persistent AFib at 41 centers in Australia, Canada, Europe, Japan, and the United States.
After ablation, 69% of PAF patients and 62% of those who had persistent AFib showed no sign of atrial arrhythmia (AA) over 12 months, based on the trial’s method for estimating AA burden.
Residual AA burden less than 10% was seen in 87% and 82% of those initially with PAF and persistent AFib, respectively. Burdens in that lowest range, compared with greater AA burden, predicted a “clinically meaningful” improvement in QoL scores in PAF patients.
Those who entered the study with persistent AFib showed such improvement – defined as a more than 19-point gain on the Atrial Fibrillation Effect on Quality-of-Life Questionnaire – regardless of postablation AA burden.
Moreover, patients initially with either type of AFib and residual burdens in the lowest range went on to have fewer cardioversions and repeat ablations (P < .01), Atul Verma, MD, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, reported at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society.
Dr. Verma, the trial’s principal investigator, is also lead author on the same-day publication of the secondary analysis in Heart Rhythm.
Binary endpoint lacks relevance
The PULSED-AF primary analysis defined ablation efficacy partly as freedom from AA recurrence lasting at least 30 seconds, with or without symptoms, a traditional AFib-ablation trial endpoint that is nonetheless considered clinically unhelpful.
The secondary analysis recasts that binary endpoint as degree of reduction in AFib burden, a continuous variable. That potentially allows AFib ablation efficacy to be assessed in a more nuanced way likely to be more meaningful to patients and the health care system, observed Dr. Verma and colleagues.
The “30-second endpoint” is limited in clinical usefulness and “doesn’t mean much to the patient,” he said at a press conference on the analysis before formally presenting it at the HRS sessions.
Recent AFib ablation trials have explored AA burden as possibly a superior way to assess the procedure’s success “but also to see if it’s better correlated with quality of life and health care outcomes,” Dr. Verma said. “So that’s exactly what we’ve tried to do here using the PULSED-AF data.”
In the secondary analysis, he said, patients’ rate of freedom from the 30-second endpoint was about 70%, but “more than 85% of them had an AFib burden of less than 10%.”
“This efficacy endpoint of 30 seconds of atrial arrhythmia has been challenged and has been seen clinically as insignificant,” agreed Rajeev Pathak, MBBS, PhD, of Australian National University and director of cardiac electrophysiology at Canberra (Australia) Hospital.
In AFib radiofrequency ablation and cryoablation studies “there is clear disconnect between these 30-second episodes of atrial arrhythmias we see and the clinical relevance of health care utilization and quality of life,” said Dr. Pathak, invited discussant for Dr. Verma’s presentation at the sessions.
Now an AFib ablation trial using PFA catheters has yielded similar results, finding AA burden to be “a more objective and relevant measure of success,” he said. “A 30-second endpoint is arbitrary, lacks significance, and is highly dependent on the monitoring strategy.”
The more you look, the more you see
The new secondary analysis included a demonstration that success rates based on the 30-second endpoint indeed vary depending on how subsequent arrhythmias are monitored.
As described by Dr. Verma, PULSED-AF data were assessed for the 30-second endpoint captured using three separate intermittent monitoring strategies that it and other recent ablation trials have used:
- Strategy A: Transtelephonic monitoring weekly and in the event of symptoms, plus 24-hour Holter monitoring at 6 and 12 months and 12-lead ECG at 3, 6, and 12 months
- Strategy B: Transtelephonic monitoring weekly and at symptoms for 3-6 months followed by monthly and at symptoms from 6 to 12 months, plus 24-hour Holter monitoring at 6 and 12 months, plus 12-lead ECG at 3, 6, and 12 months
- Strategy C: The median of two 24-hour Holter monitoring sessions per patient over 12 months
As Dr. Verma reported, rates of freedom from the 30-second endpoint climbed with successive monitoring strategies. The rates for PAF and persistent AFib patients, respectively, were: Strategy A – 70% and 62%, Strategy B – 71% and 68%, Strategy C – 91% and 86%.
“If you’re using the ‘freedom-from-30-seconds’ endpoint, the results that you are going to get are highly dependent on the monitoring strategy,” Dr. Verma said. “The more you look, the more you see.”
Valid estimation of burden
For the main PULSED-AF secondary analysis, the investigators defined AA burden according to findings on either Holter monitoring or the 12-lead ECG. “So as not to bias these results,” Dr. Verma said, “for every patient, we picked the method that gave us the highest atrial arrhythmia burden.”
Ideally, Dr. Verma said in an interview, arrhythmia burden would be determined using devices such as implantable loop recorders. “The problem is, this is expensive and not practical” in both clinical practice and many trials, so PULSED-AF investigators went with the intermittent monitoring strategy to estimate burdens.
Their method appears valid, he said, given that the study identified a statistically relevant 10% AA burden cut off for predicting quality of life improvement or less health care resource use.
“If their residual atrial arrhythmia burden was greater than 10%, they did not have a statistically significant improvement in quality of life,” Dr. Verma observed. And “very few” of them had cardioversions or repeat ablation.
“I couldn’t agree more” that residual AA burden is preferable to the 30-second endpoint for gauging AFib ablation success, Kenneth Ellenbogen, MD, Virginia Commonwealth University Medical Center, Richmond, said in an interview. Dr. Ellenbogen is also director of clinical cardiac electrophysiology and pacing at VCU Health Pauley Heart Center and not associated with PULSED-AF.
That AA burden was linked to health care resource use in the study “is absolutely brilliant,” he said, “because that’s what the bean counters really want at the end of the day. And as doctors we care about patients feeling better – improving quality of life.”
PULSED-AF was funded by Medtronic. Dr. Verma disclosed financial relationships with Bayer, Biosense Webster, Medtronic, Thermedical, Kardium, and Galaxy Medical, as well as and research grants from Adagio Medical. Dr. Ellenbogen disclosed financial relationships with Boston Scientific, Medtronic, Kestra, Hylomorph, Biotronik, MediLynx, Impulse Dynamics USA, Abbott, Biosense Webster, Milestone Pharmaceuticals, Sanofi, Medpace, and Elsevier. Dr. Pathak disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HRS 2023
Earlier anticoagulation safe in stroke with AFib: ELAN
, a new study suggests.
The ELAN trial found that starting DOAC treatment earlier was not associated with an increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) but rather was linked to a lower rate of ischemic events.
“We conclude that there is no reason to delay DOAC treatment in these patients. Our results suggest that early DOAC treatment is reasonable; it is unlikely to cause harm, and it is probably better at reducing ischemic events,” lead investigator of the study, Urs Fischer, MD, professor of neurology at University Hospital Basel (Switzerland), commented in an interview.
“This trial will change clinical practice in that we can feel much more reassured that starting DOAC treatment early in these patients will not cause harm,” he said.
Senior investigator Jesse Dawson, MD, professor of stroke medicine at Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow, added: “This issue of timing of DOAC treatment causes a lot of anxiety in our daily workload. Clinicians are scared of causing an ICH, so they tend to wait. These results will ease a lot of that anxiety.”
Dr. Fischer presented the results of the ELAN trial at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) in Munich. The trial was also simultaneously published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
He explained that patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke who are found to have atrial fibrillation need to be started on anticoagulation to reduce the risk for a recurrent stroke. But there are no clear guidelines on when to start anticoagulation in these patients at present, with concerns that starting very early may increase the risk for hemorrhagic transformation and ICH.
Based on observations that patients with larger strokes have a higher risk for ICH in the early post-stroke period, some guidelines advise different times for starting anticoagulation for different stroke severities: 1 day for a transient ischemic attack, 3 days for a minor stroke, 6 days for a moderate stroke, and 12 days for a severe stroke – known as the 1-, 3-, 6-, 12-day rule.
“But this is not based on evidence – just on expert opinion,” Dr. Fischer noted. “The ELAN trial was conducted to obtain more solid information on optimal timing for starting anticoagulation and whether we can safely start a DOAC earlier than these guidelines currently advise.”
For the trial, which was conducted in 15 countries, 2,013 patients with an acute ischemic stroke and found to have AFib were randomly selected to start DOAC treatment earlier or later.
The later-treatment strategy followed the current approach of starting treatment at day 3 or 4 after a minor stroke, day 6 or 7 after a moderate stroke, or day 12, 13, or 14 after a major stroke, whereas the earlier-treatment group started DOAC treatment within 48 hours after a minor or moderate stroke or on day 6 or 7 after a major stroke.
In terms of stroke severity, which was defined on imaging-based criteria, 37% of patients had a minor stroke, 40% had a moderate stroke, and 23% had a major stroke.
The primary outcome was a composite of recurrent ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, major extracranial bleeding, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, or vascular death within 30 days after randomization.
Results showed that this occurred in 2.9% in the early-treatment group and 4.1% in the later-treatment group (risk difference, –1.18 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, –2.84-0.47) by 30 days.
Recurrent ischemic stroke occurred in 1.4% in the early-treatment group and 2.5% in the later-treatment group (odds ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.29-1.07). Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in two participants (0.2%) in both groups by 30 days.
The rates of the outcomes increased only slightly more at 90 days than at 30 days, “findings that suggest there was not an excessive risk associated with early anticoagulation through that period,” the researchers report in the NEJM paper.
“Early treatment initiation can therefore be supported if indicated or if desired,” they conclude.
“The most important finding was that among 2,000 patients randomized, there was a very low rate of bleeding complications and no increase in any bleeding complication in the early DOAC group. This has been a major worry about starting anticoagulation early,” Dr. Fischer commented.
“These are very practical findings in that we can keep things simple,” Dr. Dawson added. “If the patient has a big stroke, anticoagulation with a DOAC can now be started at 6 days. For everyone else, we can start DOAC treatment as soon as possible without fear of causing harm. So, we can now confidently give patients with a minor or moderate stroke, as defined by imaging, a beneficial treatment as soon as we establish they are having an ischemic stroke and have AFib.”
Dr. Dawson pointed out that about 25% of patients with ischemic stroke are found to have AFib on admission ECG, and in another 4%-5%, AFib is found in the first 48 hours. “These are the patients we are targeting in this study.”
The researchers note that the trial did not have a statistical superiority or noninferiority design but rather aimed to estimate the treatment effects of early initiation versus later initiation of DOACs.
“This trial was slightly different in that we weren’t testing a strict statistical hypothesis because we didn’t have any data with which to formulate what sort of effect size to aim for, so we performed a qualitative trial to look at what the event rates were with the two approaches,” Dr. Fischer explained. “Our main findings are that ICH rates were not increased with early DOAC treatment and that ischemic event rates were numerically reduced, but because we didn’t have strict statistical limits, we can only say this is a high probability but not a certainty.”
Dr. Dawson added: “We can say from these results that there is a high level of probability that early DOAC treatment does not cause harm and a reasonable probability that it reduces risks of a recurrent stroke or other ischemic event.”
The researchers give an estimate of the effect size for the primary composite endpoint, which combines the major ischemic and bleeding events, ranging from a 2.8% lower risk to a 0.5% higher risk with early DOAC treatment.
“So, it is very likely that the composite endpoint would be lower,” Dr. Dawson said.
Dr. Fischer noted that a previous study (TIMING) tried to address the issue of earlier versus later anticoagulation in these patients but was stopped early after 880 patients had been enrolled because of slow recruitment.
“Results from this study failed to show superiority of early versus late DOAC treatment but they did suggest noninferiority, and they also found no increase in major bleeding complications, which is an added reassurance,” he commented.
Another trial looking at early versus late anticoagulation in these patients, OPTIMAS, is ongoing in the United Kingdom and is aiming to randomize 3,500 patients.
Imaging-based assessment of stroke severity
In the ELAN trial, the definition of stroke severity was based on imaging rather than on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS).
“We took a cautious approach by using imaging to define stroke severity. So, when using these results in clinical practice, it is important that patients are selected for the timing of DOAC treatment based on the imaging results,” Dr. Dawson explained. “This is very straightforward, as the size of the stroke can be seen clearly on the routine CT imaging that all patients receive up front. This is a very pragmatic and simple protocol. And advanced imaging is not required.”
He noted that though clinicians tend to use the NIHSS clinical symptom score to define mild, moderate, and severe stroke, the imaging approach is actually more accurate when determining the risk for bleeding and ICH. And though imaging results often correlate with NIHSS scores, there can be some exceptions.
Commenting on the ELAN trial results at the ESOC meeting, Georgios Tsivgoulis, MD, professor of neurology, University of Athens, said that the trial showed that early administration of DOACs in these patients was safe and did not increase the rate of ICH.
“There was a very low ICH rate with only two events in each group. And then there was above a 1% reduction in the composite outcome including ischemic vascular events and bleeding,” he noted.
“This is important because there are many thousands of patients with acute ischemic stroke and AFib, and now we have a large study showing we can treat them with a DOAC early, and this appears to be safe and it appears also be more effective in terms of outcome events,” Dr. Tsivgoulis said.
But he highlighted one important caveat: The majority of patients had mild or moderate stroke.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
The ELAN trial found that starting DOAC treatment earlier was not associated with an increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) but rather was linked to a lower rate of ischemic events.
“We conclude that there is no reason to delay DOAC treatment in these patients. Our results suggest that early DOAC treatment is reasonable; it is unlikely to cause harm, and it is probably better at reducing ischemic events,” lead investigator of the study, Urs Fischer, MD, professor of neurology at University Hospital Basel (Switzerland), commented in an interview.
“This trial will change clinical practice in that we can feel much more reassured that starting DOAC treatment early in these patients will not cause harm,” he said.
Senior investigator Jesse Dawson, MD, professor of stroke medicine at Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow, added: “This issue of timing of DOAC treatment causes a lot of anxiety in our daily workload. Clinicians are scared of causing an ICH, so they tend to wait. These results will ease a lot of that anxiety.”
Dr. Fischer presented the results of the ELAN trial at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) in Munich. The trial was also simultaneously published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
He explained that patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke who are found to have atrial fibrillation need to be started on anticoagulation to reduce the risk for a recurrent stroke. But there are no clear guidelines on when to start anticoagulation in these patients at present, with concerns that starting very early may increase the risk for hemorrhagic transformation and ICH.
Based on observations that patients with larger strokes have a higher risk for ICH in the early post-stroke period, some guidelines advise different times for starting anticoagulation for different stroke severities: 1 day for a transient ischemic attack, 3 days for a minor stroke, 6 days for a moderate stroke, and 12 days for a severe stroke – known as the 1-, 3-, 6-, 12-day rule.
“But this is not based on evidence – just on expert opinion,” Dr. Fischer noted. “The ELAN trial was conducted to obtain more solid information on optimal timing for starting anticoagulation and whether we can safely start a DOAC earlier than these guidelines currently advise.”
For the trial, which was conducted in 15 countries, 2,013 patients with an acute ischemic stroke and found to have AFib were randomly selected to start DOAC treatment earlier or later.
The later-treatment strategy followed the current approach of starting treatment at day 3 or 4 after a minor stroke, day 6 or 7 after a moderate stroke, or day 12, 13, or 14 after a major stroke, whereas the earlier-treatment group started DOAC treatment within 48 hours after a minor or moderate stroke or on day 6 or 7 after a major stroke.
In terms of stroke severity, which was defined on imaging-based criteria, 37% of patients had a minor stroke, 40% had a moderate stroke, and 23% had a major stroke.
The primary outcome was a composite of recurrent ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, major extracranial bleeding, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, or vascular death within 30 days after randomization.
Results showed that this occurred in 2.9% in the early-treatment group and 4.1% in the later-treatment group (risk difference, –1.18 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, –2.84-0.47) by 30 days.
Recurrent ischemic stroke occurred in 1.4% in the early-treatment group and 2.5% in the later-treatment group (odds ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.29-1.07). Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in two participants (0.2%) in both groups by 30 days.
The rates of the outcomes increased only slightly more at 90 days than at 30 days, “findings that suggest there was not an excessive risk associated with early anticoagulation through that period,” the researchers report in the NEJM paper.
“Early treatment initiation can therefore be supported if indicated or if desired,” they conclude.
“The most important finding was that among 2,000 patients randomized, there was a very low rate of bleeding complications and no increase in any bleeding complication in the early DOAC group. This has been a major worry about starting anticoagulation early,” Dr. Fischer commented.
“These are very practical findings in that we can keep things simple,” Dr. Dawson added. “If the patient has a big stroke, anticoagulation with a DOAC can now be started at 6 days. For everyone else, we can start DOAC treatment as soon as possible without fear of causing harm. So, we can now confidently give patients with a minor or moderate stroke, as defined by imaging, a beneficial treatment as soon as we establish they are having an ischemic stroke and have AFib.”
Dr. Dawson pointed out that about 25% of patients with ischemic stroke are found to have AFib on admission ECG, and in another 4%-5%, AFib is found in the first 48 hours. “These are the patients we are targeting in this study.”
The researchers note that the trial did not have a statistical superiority or noninferiority design but rather aimed to estimate the treatment effects of early initiation versus later initiation of DOACs.
“This trial was slightly different in that we weren’t testing a strict statistical hypothesis because we didn’t have any data with which to formulate what sort of effect size to aim for, so we performed a qualitative trial to look at what the event rates were with the two approaches,” Dr. Fischer explained. “Our main findings are that ICH rates were not increased with early DOAC treatment and that ischemic event rates were numerically reduced, but because we didn’t have strict statistical limits, we can only say this is a high probability but not a certainty.”
Dr. Dawson added: “We can say from these results that there is a high level of probability that early DOAC treatment does not cause harm and a reasonable probability that it reduces risks of a recurrent stroke or other ischemic event.”
The researchers give an estimate of the effect size for the primary composite endpoint, which combines the major ischemic and bleeding events, ranging from a 2.8% lower risk to a 0.5% higher risk with early DOAC treatment.
“So, it is very likely that the composite endpoint would be lower,” Dr. Dawson said.
Dr. Fischer noted that a previous study (TIMING) tried to address the issue of earlier versus later anticoagulation in these patients but was stopped early after 880 patients had been enrolled because of slow recruitment.
“Results from this study failed to show superiority of early versus late DOAC treatment but they did suggest noninferiority, and they also found no increase in major bleeding complications, which is an added reassurance,” he commented.
Another trial looking at early versus late anticoagulation in these patients, OPTIMAS, is ongoing in the United Kingdom and is aiming to randomize 3,500 patients.
Imaging-based assessment of stroke severity
In the ELAN trial, the definition of stroke severity was based on imaging rather than on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS).
“We took a cautious approach by using imaging to define stroke severity. So, when using these results in clinical practice, it is important that patients are selected for the timing of DOAC treatment based on the imaging results,” Dr. Dawson explained. “This is very straightforward, as the size of the stroke can be seen clearly on the routine CT imaging that all patients receive up front. This is a very pragmatic and simple protocol. And advanced imaging is not required.”
He noted that though clinicians tend to use the NIHSS clinical symptom score to define mild, moderate, and severe stroke, the imaging approach is actually more accurate when determining the risk for bleeding and ICH. And though imaging results often correlate with NIHSS scores, there can be some exceptions.
Commenting on the ELAN trial results at the ESOC meeting, Georgios Tsivgoulis, MD, professor of neurology, University of Athens, said that the trial showed that early administration of DOACs in these patients was safe and did not increase the rate of ICH.
“There was a very low ICH rate with only two events in each group. And then there was above a 1% reduction in the composite outcome including ischemic vascular events and bleeding,” he noted.
“This is important because there are many thousands of patients with acute ischemic stroke and AFib, and now we have a large study showing we can treat them with a DOAC early, and this appears to be safe and it appears also be more effective in terms of outcome events,” Dr. Tsivgoulis said.
But he highlighted one important caveat: The majority of patients had mild or moderate stroke.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
The ELAN trial found that starting DOAC treatment earlier was not associated with an increased risk for intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) but rather was linked to a lower rate of ischemic events.
“We conclude that there is no reason to delay DOAC treatment in these patients. Our results suggest that early DOAC treatment is reasonable; it is unlikely to cause harm, and it is probably better at reducing ischemic events,” lead investigator of the study, Urs Fischer, MD, professor of neurology at University Hospital Basel (Switzerland), commented in an interview.
“This trial will change clinical practice in that we can feel much more reassured that starting DOAC treatment early in these patients will not cause harm,” he said.
Senior investigator Jesse Dawson, MD, professor of stroke medicine at Queen Elizabeth University Hospital, Glasgow, added: “This issue of timing of DOAC treatment causes a lot of anxiety in our daily workload. Clinicians are scared of causing an ICH, so they tend to wait. These results will ease a lot of that anxiety.”
Dr. Fischer presented the results of the ELAN trial at the European Stroke Organisation Conference (ESOC) in Munich. The trial was also simultaneously published online in The New England Journal of Medicine.
He explained that patients presenting with acute ischemic stroke who are found to have atrial fibrillation need to be started on anticoagulation to reduce the risk for a recurrent stroke. But there are no clear guidelines on when to start anticoagulation in these patients at present, with concerns that starting very early may increase the risk for hemorrhagic transformation and ICH.
Based on observations that patients with larger strokes have a higher risk for ICH in the early post-stroke period, some guidelines advise different times for starting anticoagulation for different stroke severities: 1 day for a transient ischemic attack, 3 days for a minor stroke, 6 days for a moderate stroke, and 12 days for a severe stroke – known as the 1-, 3-, 6-, 12-day rule.
“But this is not based on evidence – just on expert opinion,” Dr. Fischer noted. “The ELAN trial was conducted to obtain more solid information on optimal timing for starting anticoagulation and whether we can safely start a DOAC earlier than these guidelines currently advise.”
For the trial, which was conducted in 15 countries, 2,013 patients with an acute ischemic stroke and found to have AFib were randomly selected to start DOAC treatment earlier or later.
The later-treatment strategy followed the current approach of starting treatment at day 3 or 4 after a minor stroke, day 6 or 7 after a moderate stroke, or day 12, 13, or 14 after a major stroke, whereas the earlier-treatment group started DOAC treatment within 48 hours after a minor or moderate stroke or on day 6 or 7 after a major stroke.
In terms of stroke severity, which was defined on imaging-based criteria, 37% of patients had a minor stroke, 40% had a moderate stroke, and 23% had a major stroke.
The primary outcome was a composite of recurrent ischemic stroke, systemic embolism, major extracranial bleeding, symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage, or vascular death within 30 days after randomization.
Results showed that this occurred in 2.9% in the early-treatment group and 4.1% in the later-treatment group (risk difference, –1.18 percentage points; 95% confidence interval, –2.84-0.47) by 30 days.
Recurrent ischemic stroke occurred in 1.4% in the early-treatment group and 2.5% in the later-treatment group (odds ratio, 0.57; 95% CI, 0.29-1.07). Symptomatic intracranial hemorrhage occurred in two participants (0.2%) in both groups by 30 days.
The rates of the outcomes increased only slightly more at 90 days than at 30 days, “findings that suggest there was not an excessive risk associated with early anticoagulation through that period,” the researchers report in the NEJM paper.
“Early treatment initiation can therefore be supported if indicated or if desired,” they conclude.
“The most important finding was that among 2,000 patients randomized, there was a very low rate of bleeding complications and no increase in any bleeding complication in the early DOAC group. This has been a major worry about starting anticoagulation early,” Dr. Fischer commented.
“These are very practical findings in that we can keep things simple,” Dr. Dawson added. “If the patient has a big stroke, anticoagulation with a DOAC can now be started at 6 days. For everyone else, we can start DOAC treatment as soon as possible without fear of causing harm. So, we can now confidently give patients with a minor or moderate stroke, as defined by imaging, a beneficial treatment as soon as we establish they are having an ischemic stroke and have AFib.”
Dr. Dawson pointed out that about 25% of patients with ischemic stroke are found to have AFib on admission ECG, and in another 4%-5%, AFib is found in the first 48 hours. “These are the patients we are targeting in this study.”
The researchers note that the trial did not have a statistical superiority or noninferiority design but rather aimed to estimate the treatment effects of early initiation versus later initiation of DOACs.
“This trial was slightly different in that we weren’t testing a strict statistical hypothesis because we didn’t have any data with which to formulate what sort of effect size to aim for, so we performed a qualitative trial to look at what the event rates were with the two approaches,” Dr. Fischer explained. “Our main findings are that ICH rates were not increased with early DOAC treatment and that ischemic event rates were numerically reduced, but because we didn’t have strict statistical limits, we can only say this is a high probability but not a certainty.”
Dr. Dawson added: “We can say from these results that there is a high level of probability that early DOAC treatment does not cause harm and a reasonable probability that it reduces risks of a recurrent stroke or other ischemic event.”
The researchers give an estimate of the effect size for the primary composite endpoint, which combines the major ischemic and bleeding events, ranging from a 2.8% lower risk to a 0.5% higher risk with early DOAC treatment.
“So, it is very likely that the composite endpoint would be lower,” Dr. Dawson said.
Dr. Fischer noted that a previous study (TIMING) tried to address the issue of earlier versus later anticoagulation in these patients but was stopped early after 880 patients had been enrolled because of slow recruitment.
“Results from this study failed to show superiority of early versus late DOAC treatment but they did suggest noninferiority, and they also found no increase in major bleeding complications, which is an added reassurance,” he commented.
Another trial looking at early versus late anticoagulation in these patients, OPTIMAS, is ongoing in the United Kingdom and is aiming to randomize 3,500 patients.
Imaging-based assessment of stroke severity
In the ELAN trial, the definition of stroke severity was based on imaging rather than on the National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS).
“We took a cautious approach by using imaging to define stroke severity. So, when using these results in clinical practice, it is important that patients are selected for the timing of DOAC treatment based on the imaging results,” Dr. Dawson explained. “This is very straightforward, as the size of the stroke can be seen clearly on the routine CT imaging that all patients receive up front. This is a very pragmatic and simple protocol. And advanced imaging is not required.”
He noted that though clinicians tend to use the NIHSS clinical symptom score to define mild, moderate, and severe stroke, the imaging approach is actually more accurate when determining the risk for bleeding and ICH. And though imaging results often correlate with NIHSS scores, there can be some exceptions.
Commenting on the ELAN trial results at the ESOC meeting, Georgios Tsivgoulis, MD, professor of neurology, University of Athens, said that the trial showed that early administration of DOACs in these patients was safe and did not increase the rate of ICH.
“There was a very low ICH rate with only two events in each group. And then there was above a 1% reduction in the composite outcome including ischemic vascular events and bleeding,” he noted.
“This is important because there are many thousands of patients with acute ischemic stroke and AFib, and now we have a large study showing we can treat them with a DOAC early, and this appears to be safe and it appears also be more effective in terms of outcome events,” Dr. Tsivgoulis said.
But he highlighted one important caveat: The majority of patients had mild or moderate stroke.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESOC 2023
Half of deaths from homozygous FH occur before age 32 years
MANNHEIM, GERMANY –
The researchers looked at almost 40 patients from the HoFH International Clinical Collaborators (HICC) registry who had died before data entry, finding that they had a mean age of diagnosis of 12 years.
Even those who received treatment had high LDL cholesterol levels, and 70% developed atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) at a median age of 28 years.
Worryingly, the results showed that the median age at death was 32 years. Results were presented at the annual congress of the European Atherosclerosis Society.
Patients with HoFH “have severe atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk,” said study presenter Janneke Mulder, a PhD candidate at the department of internal medicine, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“Therefore, early diagnosis and initiation of treatments, and also a combination of treatments, is really crucial,” she added.
Call to action
Approached for comment, Maciej Banach, MD, PhD, full professor of cardiology, Polish Mother’s Memorial Hospital Research Institute, Lodz, and Secretary of the EAS, described the results as “terrifying.”
He said in an interview that they are a “call to action,” especially given that so few patients in the study received intensive combination lipid-lowering therapy despite having a baseline LDL cholesterol level that was “very, very high.”
Banach underlined that patients who receive triple lipid-lowering therapy with a high-intensity statin, ezetimibe (Nustendi), and a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, could expect, based on current evidence, to see their LDL cholesterol levels reduced by 85% and be on target.
“Obviously, this is kind of academic,” because in the real-world “this 85% is not observed very often,” but it offers a target for steep reductions in cholesterol levels.
“This is something that we should focus on for these patients from the beginning,” said Dr. Banach, either with a stepwise approach “or for experts in pediatric HoFH, “maybe immediately.”
He emphasized that clinicians have everything at hand to “be both effective in the early diagnosis of HoFH, the earlier the better, and obviously to be effective with its treatment.”
“We should do something to prolong the lives of those people,” because the current results are “terrifying,” Dr. Banach added.
Rare genetic condition
Presenting her findings, Ms. Mulder began by highlighting that HoFH is a “rare genetic condition that occurs due to mutations in cholesterol metabolism.”
This, she continued, leads to “severely increased LDL cholesterol levels, and consequently to very premature cardiovascular disease,” with patients potentially experiencing their first cardiovascular event before age 20 years.
Ms. Mulder pointed out that, although there have been case series in the literature on HoFH, they have had “limited numbers” and patients have typically spent decades being treated at the same lipid management clinic.
To broaden the understanding of the clinical characteristics and management of patients dying with HoFH, the team examined data from the HICC registry, which is “the largest contemporary database of homozygous FH patients,” Ms. Mulder said.
It includes 751 patients with HoFH from 88 centers in 38 countries who were alive in 2010 or later. Data entry was between 2016 and 2020. The current analysis focused on 37 patients who had already died by the time they were included on the registry.
Of those, 49% were women, 38% were of White ethnicity, and 43% were from high-income countries.
The median age at diagnosis was 12 years, Ms. Mulder said, explaining that this is similar to that seen in other studies. The majority (86%) underwent genetic testing, and 92% presented with xanthomas.
Ms. Mulder also noted that, at their final clinical evaluation, which was conducted a median age of 18 years after their initial diagnosis, 43% of patients were recorded as current or former smokers.
In terms of their lipid-lowering therapy, 94% were taking a statin, whereas 68% were on ezetimibe, and 23% were undergoing apheresis.
Ms. Mulder said that the median number of lipid-lowering therapies per patient was two, and that “sadly ... 26% of the deceased patients had only one or no treatment.”
Therefore, perhaps unsurprisingly even those patients who were receiving treatment had LDL cholesterol levels that were “too high,” at 9.4 mmol/L versus 15.6 mmol/L among those who were untreated.
There was a high prevalence of ASCVD, at 70% overall, or 41% for aortic stenosis, 30% for myocardial infarction, 30% for angina pectoris, and 22% each for aortic valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting. In addition, 19% underwent percutaneous coronary intervention.
The median age of onset for ASCVD was 28 years. Ms. Mulder pointed out, however, that, as data were not available for all patients, “this might be an underestimation.” About 70% of patients experienced recurrent ASCVD.
There was a wide range in the age at which patients with HoFH died, although the median was, “strikingly,” 32 years, Ms. Mulder said. Death was confirmed as stemming from cardiovascular causes in 76% of cases.
During the postpresentation discussion, session chair Antonio J. Vallejo-Vaz, PhD, from the Research Group of Clinical Epidemiology and Vascular Risk, Institute of Biomedicine of Seville (Spain), highlighted that, if 38% of the patients were of White ethnicity, then the remainder must therefore be from other ethnic groups.
“There could be potential issues with accessibility to lipid centers” for these patients, which could affect the findings, noted Dr. Vallejo-Vaz, who is also chief scientist of the EAS Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Studies Collaboration.
Ms. Mulder agreed, replying that their results, though already striking, may be an underestimation because the patients were all from either high or middle-income countries, “so it would be good to have some data on low-income countries.”
She was also asked about two patients who died at a much older age than did the others, at ages 70 years and 86 years, respectively, and whether they had, for example, a protective genetic mutation.
Ms. Mulder said that they do not yet know, but they are planning an extended case series on these and other long-lived patients so that they can be investigated further.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MANNHEIM, GERMANY –
The researchers looked at almost 40 patients from the HoFH International Clinical Collaborators (HICC) registry who had died before data entry, finding that they had a mean age of diagnosis of 12 years.
Even those who received treatment had high LDL cholesterol levels, and 70% developed atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) at a median age of 28 years.
Worryingly, the results showed that the median age at death was 32 years. Results were presented at the annual congress of the European Atherosclerosis Society.
Patients with HoFH “have severe atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk,” said study presenter Janneke Mulder, a PhD candidate at the department of internal medicine, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“Therefore, early diagnosis and initiation of treatments, and also a combination of treatments, is really crucial,” she added.
Call to action
Approached for comment, Maciej Banach, MD, PhD, full professor of cardiology, Polish Mother’s Memorial Hospital Research Institute, Lodz, and Secretary of the EAS, described the results as “terrifying.”
He said in an interview that they are a “call to action,” especially given that so few patients in the study received intensive combination lipid-lowering therapy despite having a baseline LDL cholesterol level that was “very, very high.”
Banach underlined that patients who receive triple lipid-lowering therapy with a high-intensity statin, ezetimibe (Nustendi), and a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, could expect, based on current evidence, to see their LDL cholesterol levels reduced by 85% and be on target.
“Obviously, this is kind of academic,” because in the real-world “this 85% is not observed very often,” but it offers a target for steep reductions in cholesterol levels.
“This is something that we should focus on for these patients from the beginning,” said Dr. Banach, either with a stepwise approach “or for experts in pediatric HoFH, “maybe immediately.”
He emphasized that clinicians have everything at hand to “be both effective in the early diagnosis of HoFH, the earlier the better, and obviously to be effective with its treatment.”
“We should do something to prolong the lives of those people,” because the current results are “terrifying,” Dr. Banach added.
Rare genetic condition
Presenting her findings, Ms. Mulder began by highlighting that HoFH is a “rare genetic condition that occurs due to mutations in cholesterol metabolism.”
This, she continued, leads to “severely increased LDL cholesterol levels, and consequently to very premature cardiovascular disease,” with patients potentially experiencing their first cardiovascular event before age 20 years.
Ms. Mulder pointed out that, although there have been case series in the literature on HoFH, they have had “limited numbers” and patients have typically spent decades being treated at the same lipid management clinic.
To broaden the understanding of the clinical characteristics and management of patients dying with HoFH, the team examined data from the HICC registry, which is “the largest contemporary database of homozygous FH patients,” Ms. Mulder said.
It includes 751 patients with HoFH from 88 centers in 38 countries who were alive in 2010 or later. Data entry was between 2016 and 2020. The current analysis focused on 37 patients who had already died by the time they were included on the registry.
Of those, 49% were women, 38% were of White ethnicity, and 43% were from high-income countries.
The median age at diagnosis was 12 years, Ms. Mulder said, explaining that this is similar to that seen in other studies. The majority (86%) underwent genetic testing, and 92% presented with xanthomas.
Ms. Mulder also noted that, at their final clinical evaluation, which was conducted a median age of 18 years after their initial diagnosis, 43% of patients were recorded as current or former smokers.
In terms of their lipid-lowering therapy, 94% were taking a statin, whereas 68% were on ezetimibe, and 23% were undergoing apheresis.
Ms. Mulder said that the median number of lipid-lowering therapies per patient was two, and that “sadly ... 26% of the deceased patients had only one or no treatment.”
Therefore, perhaps unsurprisingly even those patients who were receiving treatment had LDL cholesterol levels that were “too high,” at 9.4 mmol/L versus 15.6 mmol/L among those who were untreated.
There was a high prevalence of ASCVD, at 70% overall, or 41% for aortic stenosis, 30% for myocardial infarction, 30% for angina pectoris, and 22% each for aortic valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting. In addition, 19% underwent percutaneous coronary intervention.
The median age of onset for ASCVD was 28 years. Ms. Mulder pointed out, however, that, as data were not available for all patients, “this might be an underestimation.” About 70% of patients experienced recurrent ASCVD.
There was a wide range in the age at which patients with HoFH died, although the median was, “strikingly,” 32 years, Ms. Mulder said. Death was confirmed as stemming from cardiovascular causes in 76% of cases.
During the postpresentation discussion, session chair Antonio J. Vallejo-Vaz, PhD, from the Research Group of Clinical Epidemiology and Vascular Risk, Institute of Biomedicine of Seville (Spain), highlighted that, if 38% of the patients were of White ethnicity, then the remainder must therefore be from other ethnic groups.
“There could be potential issues with accessibility to lipid centers” for these patients, which could affect the findings, noted Dr. Vallejo-Vaz, who is also chief scientist of the EAS Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Studies Collaboration.
Ms. Mulder agreed, replying that their results, though already striking, may be an underestimation because the patients were all from either high or middle-income countries, “so it would be good to have some data on low-income countries.”
She was also asked about two patients who died at a much older age than did the others, at ages 70 years and 86 years, respectively, and whether they had, for example, a protective genetic mutation.
Ms. Mulder said that they do not yet know, but they are planning an extended case series on these and other long-lived patients so that they can be investigated further.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
MANNHEIM, GERMANY –
The researchers looked at almost 40 patients from the HoFH International Clinical Collaborators (HICC) registry who had died before data entry, finding that they had a mean age of diagnosis of 12 years.
Even those who received treatment had high LDL cholesterol levels, and 70% developed atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) at a median age of 28 years.
Worryingly, the results showed that the median age at death was 32 years. Results were presented at the annual congress of the European Atherosclerosis Society.
Patients with HoFH “have severe atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk,” said study presenter Janneke Mulder, a PhD candidate at the department of internal medicine, Erasmus University Medical Center, Rotterdam, the Netherlands.
“Therefore, early diagnosis and initiation of treatments, and also a combination of treatments, is really crucial,” she added.
Call to action
Approached for comment, Maciej Banach, MD, PhD, full professor of cardiology, Polish Mother’s Memorial Hospital Research Institute, Lodz, and Secretary of the EAS, described the results as “terrifying.”
He said in an interview that they are a “call to action,” especially given that so few patients in the study received intensive combination lipid-lowering therapy despite having a baseline LDL cholesterol level that was “very, very high.”
Banach underlined that patients who receive triple lipid-lowering therapy with a high-intensity statin, ezetimibe (Nustendi), and a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9 inhibitor, could expect, based on current evidence, to see their LDL cholesterol levels reduced by 85% and be on target.
“Obviously, this is kind of academic,” because in the real-world “this 85% is not observed very often,” but it offers a target for steep reductions in cholesterol levels.
“This is something that we should focus on for these patients from the beginning,” said Dr. Banach, either with a stepwise approach “or for experts in pediatric HoFH, “maybe immediately.”
He emphasized that clinicians have everything at hand to “be both effective in the early diagnosis of HoFH, the earlier the better, and obviously to be effective with its treatment.”
“We should do something to prolong the lives of those people,” because the current results are “terrifying,” Dr. Banach added.
Rare genetic condition
Presenting her findings, Ms. Mulder began by highlighting that HoFH is a “rare genetic condition that occurs due to mutations in cholesterol metabolism.”
This, she continued, leads to “severely increased LDL cholesterol levels, and consequently to very premature cardiovascular disease,” with patients potentially experiencing their first cardiovascular event before age 20 years.
Ms. Mulder pointed out that, although there have been case series in the literature on HoFH, they have had “limited numbers” and patients have typically spent decades being treated at the same lipid management clinic.
To broaden the understanding of the clinical characteristics and management of patients dying with HoFH, the team examined data from the HICC registry, which is “the largest contemporary database of homozygous FH patients,” Ms. Mulder said.
It includes 751 patients with HoFH from 88 centers in 38 countries who were alive in 2010 or later. Data entry was between 2016 and 2020. The current analysis focused on 37 patients who had already died by the time they were included on the registry.
Of those, 49% were women, 38% were of White ethnicity, and 43% were from high-income countries.
The median age at diagnosis was 12 years, Ms. Mulder said, explaining that this is similar to that seen in other studies. The majority (86%) underwent genetic testing, and 92% presented with xanthomas.
Ms. Mulder also noted that, at their final clinical evaluation, which was conducted a median age of 18 years after their initial diagnosis, 43% of patients were recorded as current or former smokers.
In terms of their lipid-lowering therapy, 94% were taking a statin, whereas 68% were on ezetimibe, and 23% were undergoing apheresis.
Ms. Mulder said that the median number of lipid-lowering therapies per patient was two, and that “sadly ... 26% of the deceased patients had only one or no treatment.”
Therefore, perhaps unsurprisingly even those patients who were receiving treatment had LDL cholesterol levels that were “too high,” at 9.4 mmol/L versus 15.6 mmol/L among those who were untreated.
There was a high prevalence of ASCVD, at 70% overall, or 41% for aortic stenosis, 30% for myocardial infarction, 30% for angina pectoris, and 22% each for aortic valve replacement and coronary artery bypass grafting. In addition, 19% underwent percutaneous coronary intervention.
The median age of onset for ASCVD was 28 years. Ms. Mulder pointed out, however, that, as data were not available for all patients, “this might be an underestimation.” About 70% of patients experienced recurrent ASCVD.
There was a wide range in the age at which patients with HoFH died, although the median was, “strikingly,” 32 years, Ms. Mulder said. Death was confirmed as stemming from cardiovascular causes in 76% of cases.
During the postpresentation discussion, session chair Antonio J. Vallejo-Vaz, PhD, from the Research Group of Clinical Epidemiology and Vascular Risk, Institute of Biomedicine of Seville (Spain), highlighted that, if 38% of the patients were of White ethnicity, then the remainder must therefore be from other ethnic groups.
“There could be potential issues with accessibility to lipid centers” for these patients, which could affect the findings, noted Dr. Vallejo-Vaz, who is also chief scientist of the EAS Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Studies Collaboration.
Ms. Mulder agreed, replying that their results, though already striking, may be an underestimation because the patients were all from either high or middle-income countries, “so it would be good to have some data on low-income countries.”
She was also asked about two patients who died at a much older age than did the others, at ages 70 years and 86 years, respectively, and whether they had, for example, a protective genetic mutation.
Ms. Mulder said that they do not yet know, but they are planning an extended case series on these and other long-lived patients so that they can be investigated further.
No funding or relevant financial relationships were declared.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
People still want their medical intelligence in human form
Doctors or AI? Lukewarm vote of confidence goes to …
Well, we’ve got some good news for the physicians out there, and we’ve got some bad news. Which do you want first? Okay, we’re mostly hearing good news, so here goes: Most people would choose a human doctor over artificial intelligence for the diagnosis and treatment of their medical conditions.
And the bad news? In the survey we’re talking about, “most” was 53%, so not exactly a huge victory for the carbon-based life forms. Yup, about 47% of the 2,472 respondents said they would prefer an AI-based clinic over a human specialist, and that number went up if individuals were told that their primary care physicians were on board with AI, “or otherwise nudged to consider AI as good,” the research team said in a written statement released by the University of Arizona, Tucson.
They went on to add that “this signaled the significance of the human physician in guiding a patient’s decision.” So patients will still need their doctors in the future to … um … this is a bit awkward … tell them how good the AI is?
And yes, we know that ChatGPT is already doing the same thing to journalists, but could it write a medical-humor column? Not a chance. Probably can’t even tell a joke.
How do ghosts get rid of wrinkles? Boo-tox. There, let’s see ChatGPT do that.
Explaining the joke makes it funnier, right?
Here at LOTME headquarters, we live by one simple rule, passed down directly from the Buddha himself: “Never let a good presurgical assessment of refractory epilepsy go to waste. Also, don’t believe everything you read on the Internet.”
This human-created joke has been brought to you by the leading theory of humor, which states that comedy stems from our brain reacting to an incongruous part of reality in a positive way. These positive emotions light up our neurons in a specific fashion, and boom, comedy is achieved.
Previous studies into the science of comedy have typically used functional MRI to analyze the brain while it was gripped in the throes of a comedic reaction. Unfortunately, fMRI cannot detect the entirety of the electromagnetic spectrum generated by the brain during these moments, so observing scientists have been, quite literally, missing out on some of the joke. And that’s where a new study from France comes in.
In the study, the researchers showed a group of patients with epilepsy who were hooked up to deep brain electrodes and a high-tech neuroimaging machine – part of the aforementioned presurgical assessment – a 3-minute excerpt from a Charlie Chaplin movie and analyzed their brain activity. Why Charlie Chaplin? Simple. Slapstick is perhaps the most accessible form of comedy across cultures. We can all appreciate a man getting hit in the head with a coconut. The world’s oldest bar joke or whatever this is? Not so much.
During the funniest scenes, all study participants showed increased high-frequency gamma waves (indicating high cognitive engagement) and a decrease in low-frequency waves (indicating reduced inattention and introspection). During unfunny scenes, such as transition moments, the opposite occurred. Importantly, this inverse relationship occurred in the temporal lobe but not in other regions, supporting previous research that indicated humor was mainly processed in the temporal lobe.
The investigators suggested future research should focus on longer videos with more complex forms of comedy, such as jokes, irony, sarcasm, or reference humor. So, uh, a guy getting hit in the head with two coconuts? That’s high-brow stuff right there.
Hot take: Humans aren’t that special
We humans have always prided ourselves on being different from “the animals” in an exceptional way. News flash! We aren’t. We may be the apex predator, but new research shows that humans, as part of the animal kingdom, just aren’t special.
Not special? How can they say that? Are gorillas doing open-heart surgery? Do wolverines tell jokes? At a more basic level, though, the way we operate as mammals in societies is not unique or even new. Elephants are known to mourn their deceased and to have funeral-like practices, ants invented agriculture, and we’re certainly not the only species that has figured out how to use tools.
This new research just demonstrates another way we aren’t exceptional, and that’s in our mating practices and outcomes.
“Humans appear to resemble mammals that live in monogamous partnerships and to some extent, those classified as cooperative breeders, where breeding individuals have to rely on the help of others to raise their offspring,” Monique Borgerhoff Mulder, PhD, professor emerita of anthropology at the University of California, Davis, said in a written statement.
The research team, which consisted of over 100 investigators, looked at 90 human populations based on data from over 80,000 people globally and compared the human data with 49 different nonhuman mammal species. In polygynous societies in which men take several wives, they found, women have more access to resources like food, shelter, and parenting help. Monogamy, on the other hand, “can drive significant inequalities among women,” Dr. Borgerhoff Mulder said, by promoting large differences in the number of children couples produce.
Human day-to-day behavior and child-rearing habits – one parent taking a daughter to ballet class and fixing dinner so the other parent can get to exercise class before picking up the son from soccer practice – may have us thinking that we are part of an evolved society, but really we are not much different than other mammals that hunt, forage for food, and rear and teach their children, the researchers suggested.
So, yes, humans can travel to the moon, create a vaccine for smallpox, and hit other humans with coconuts, but when it comes to simply having offspring or raising them, we’re not all that special. Get over it.
Doctors or AI? Lukewarm vote of confidence goes to …
Well, we’ve got some good news for the physicians out there, and we’ve got some bad news. Which do you want first? Okay, we’re mostly hearing good news, so here goes: Most people would choose a human doctor over artificial intelligence for the diagnosis and treatment of their medical conditions.
And the bad news? In the survey we’re talking about, “most” was 53%, so not exactly a huge victory for the carbon-based life forms. Yup, about 47% of the 2,472 respondents said they would prefer an AI-based clinic over a human specialist, and that number went up if individuals were told that their primary care physicians were on board with AI, “or otherwise nudged to consider AI as good,” the research team said in a written statement released by the University of Arizona, Tucson.
They went on to add that “this signaled the significance of the human physician in guiding a patient’s decision.” So patients will still need their doctors in the future to … um … this is a bit awkward … tell them how good the AI is?
And yes, we know that ChatGPT is already doing the same thing to journalists, but could it write a medical-humor column? Not a chance. Probably can’t even tell a joke.
How do ghosts get rid of wrinkles? Boo-tox. There, let’s see ChatGPT do that.
Explaining the joke makes it funnier, right?
Here at LOTME headquarters, we live by one simple rule, passed down directly from the Buddha himself: “Never let a good presurgical assessment of refractory epilepsy go to waste. Also, don’t believe everything you read on the Internet.”
This human-created joke has been brought to you by the leading theory of humor, which states that comedy stems from our brain reacting to an incongruous part of reality in a positive way. These positive emotions light up our neurons in a specific fashion, and boom, comedy is achieved.
Previous studies into the science of comedy have typically used functional MRI to analyze the brain while it was gripped in the throes of a comedic reaction. Unfortunately, fMRI cannot detect the entirety of the electromagnetic spectrum generated by the brain during these moments, so observing scientists have been, quite literally, missing out on some of the joke. And that’s where a new study from France comes in.
In the study, the researchers showed a group of patients with epilepsy who were hooked up to deep brain electrodes and a high-tech neuroimaging machine – part of the aforementioned presurgical assessment – a 3-minute excerpt from a Charlie Chaplin movie and analyzed their brain activity. Why Charlie Chaplin? Simple. Slapstick is perhaps the most accessible form of comedy across cultures. We can all appreciate a man getting hit in the head with a coconut. The world’s oldest bar joke or whatever this is? Not so much.
During the funniest scenes, all study participants showed increased high-frequency gamma waves (indicating high cognitive engagement) and a decrease in low-frequency waves (indicating reduced inattention and introspection). During unfunny scenes, such as transition moments, the opposite occurred. Importantly, this inverse relationship occurred in the temporal lobe but not in other regions, supporting previous research that indicated humor was mainly processed in the temporal lobe.
The investigators suggested future research should focus on longer videos with more complex forms of comedy, such as jokes, irony, sarcasm, or reference humor. So, uh, a guy getting hit in the head with two coconuts? That’s high-brow stuff right there.
Hot take: Humans aren’t that special
We humans have always prided ourselves on being different from “the animals” in an exceptional way. News flash! We aren’t. We may be the apex predator, but new research shows that humans, as part of the animal kingdom, just aren’t special.
Not special? How can they say that? Are gorillas doing open-heart surgery? Do wolverines tell jokes? At a more basic level, though, the way we operate as mammals in societies is not unique or even new. Elephants are known to mourn their deceased and to have funeral-like practices, ants invented agriculture, and we’re certainly not the only species that has figured out how to use tools.
This new research just demonstrates another way we aren’t exceptional, and that’s in our mating practices and outcomes.
“Humans appear to resemble mammals that live in monogamous partnerships and to some extent, those classified as cooperative breeders, where breeding individuals have to rely on the help of others to raise their offspring,” Monique Borgerhoff Mulder, PhD, professor emerita of anthropology at the University of California, Davis, said in a written statement.
The research team, which consisted of over 100 investigators, looked at 90 human populations based on data from over 80,000 people globally and compared the human data with 49 different nonhuman mammal species. In polygynous societies in which men take several wives, they found, women have more access to resources like food, shelter, and parenting help. Monogamy, on the other hand, “can drive significant inequalities among women,” Dr. Borgerhoff Mulder said, by promoting large differences in the number of children couples produce.
Human day-to-day behavior and child-rearing habits – one parent taking a daughter to ballet class and fixing dinner so the other parent can get to exercise class before picking up the son from soccer practice – may have us thinking that we are part of an evolved society, but really we are not much different than other mammals that hunt, forage for food, and rear and teach their children, the researchers suggested.
So, yes, humans can travel to the moon, create a vaccine for smallpox, and hit other humans with coconuts, but when it comes to simply having offspring or raising them, we’re not all that special. Get over it.
Doctors or AI? Lukewarm vote of confidence goes to …
Well, we’ve got some good news for the physicians out there, and we’ve got some bad news. Which do you want first? Okay, we’re mostly hearing good news, so here goes: Most people would choose a human doctor over artificial intelligence for the diagnosis and treatment of their medical conditions.
And the bad news? In the survey we’re talking about, “most” was 53%, so not exactly a huge victory for the carbon-based life forms. Yup, about 47% of the 2,472 respondents said they would prefer an AI-based clinic over a human specialist, and that number went up if individuals were told that their primary care physicians were on board with AI, “or otherwise nudged to consider AI as good,” the research team said in a written statement released by the University of Arizona, Tucson.
They went on to add that “this signaled the significance of the human physician in guiding a patient’s decision.” So patients will still need their doctors in the future to … um … this is a bit awkward … tell them how good the AI is?
And yes, we know that ChatGPT is already doing the same thing to journalists, but could it write a medical-humor column? Not a chance. Probably can’t even tell a joke.
How do ghosts get rid of wrinkles? Boo-tox. There, let’s see ChatGPT do that.
Explaining the joke makes it funnier, right?
Here at LOTME headquarters, we live by one simple rule, passed down directly from the Buddha himself: “Never let a good presurgical assessment of refractory epilepsy go to waste. Also, don’t believe everything you read on the Internet.”
This human-created joke has been brought to you by the leading theory of humor, which states that comedy stems from our brain reacting to an incongruous part of reality in a positive way. These positive emotions light up our neurons in a specific fashion, and boom, comedy is achieved.
Previous studies into the science of comedy have typically used functional MRI to analyze the brain while it was gripped in the throes of a comedic reaction. Unfortunately, fMRI cannot detect the entirety of the electromagnetic spectrum generated by the brain during these moments, so observing scientists have been, quite literally, missing out on some of the joke. And that’s where a new study from France comes in.
In the study, the researchers showed a group of patients with epilepsy who were hooked up to deep brain electrodes and a high-tech neuroimaging machine – part of the aforementioned presurgical assessment – a 3-minute excerpt from a Charlie Chaplin movie and analyzed their brain activity. Why Charlie Chaplin? Simple. Slapstick is perhaps the most accessible form of comedy across cultures. We can all appreciate a man getting hit in the head with a coconut. The world’s oldest bar joke or whatever this is? Not so much.
During the funniest scenes, all study participants showed increased high-frequency gamma waves (indicating high cognitive engagement) and a decrease in low-frequency waves (indicating reduced inattention and introspection). During unfunny scenes, such as transition moments, the opposite occurred. Importantly, this inverse relationship occurred in the temporal lobe but not in other regions, supporting previous research that indicated humor was mainly processed in the temporal lobe.
The investigators suggested future research should focus on longer videos with more complex forms of comedy, such as jokes, irony, sarcasm, or reference humor. So, uh, a guy getting hit in the head with two coconuts? That’s high-brow stuff right there.
Hot take: Humans aren’t that special
We humans have always prided ourselves on being different from “the animals” in an exceptional way. News flash! We aren’t. We may be the apex predator, but new research shows that humans, as part of the animal kingdom, just aren’t special.
Not special? How can they say that? Are gorillas doing open-heart surgery? Do wolverines tell jokes? At a more basic level, though, the way we operate as mammals in societies is not unique or even new. Elephants are known to mourn their deceased and to have funeral-like practices, ants invented agriculture, and we’re certainly not the only species that has figured out how to use tools.
This new research just demonstrates another way we aren’t exceptional, and that’s in our mating practices and outcomes.
“Humans appear to resemble mammals that live in monogamous partnerships and to some extent, those classified as cooperative breeders, where breeding individuals have to rely on the help of others to raise their offspring,” Monique Borgerhoff Mulder, PhD, professor emerita of anthropology at the University of California, Davis, said in a written statement.
The research team, which consisted of over 100 investigators, looked at 90 human populations based on data from over 80,000 people globally and compared the human data with 49 different nonhuman mammal species. In polygynous societies in which men take several wives, they found, women have more access to resources like food, shelter, and parenting help. Monogamy, on the other hand, “can drive significant inequalities among women,” Dr. Borgerhoff Mulder said, by promoting large differences in the number of children couples produce.
Human day-to-day behavior and child-rearing habits – one parent taking a daughter to ballet class and fixing dinner so the other parent can get to exercise class before picking up the son from soccer practice – may have us thinking that we are part of an evolved society, but really we are not much different than other mammals that hunt, forage for food, and rear and teach their children, the researchers suggested.
So, yes, humans can travel to the moon, create a vaccine for smallpox, and hit other humans with coconuts, but when it comes to simply having offspring or raising them, we’re not all that special. Get over it.
First in utero cerebrovascular surgery success
The team from Boston Children’s Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital used ultrasound guidance to repair the vein of Galen malformation, which causes excessively high blood flow, resulting in both neurologic and cardiac complications.
The surgery was performed in a fetus at 34 weeks’ gestational age, with remarkable results. Since birth, the baby girl, who was identified in utero as being at high risk of suffering serious complications of the malformation, has required no medication to treat heart failure and no postnatal surgery.
Repeated echocardiograms after birth displayed marked improvement in cardiac output, and brain MRI showed no brain injury and a normal neurologic exam.
“This is incredibly exciting. The hope is that this baby, and others with this condition who receive this in utero surgery in future, will go on to have a normal life,” lead researcher Darren B. Orbach, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“We were thrilled to see that the aggressive decline usually seen after birth simply did not appear. We are pleased to report that at 6 weeks, the infant is progressing remarkably well, on no medications, eating normally, gaining weight and is back home. There are no signs of any negative effects on the brain,” he added.
Dr. Orbach, codirector of the Cerebrovascular Surgery & Interventions Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues described this first case report of the in utero vein of Galen malformation repair in a research letter, published online in the journal Stroke.
Vein of Galen malformation
Dr. Orbach explained that vein of Galen malformation, which occurs in around 1 in every 60,000 births, is a cerebrovascular anomaly in which the arterial system is directly connected to the venous system rather than to capillaries that are necessary to slow blood flow and deliver oxygen to surrounding brain tissue.
“The arterial and venous systems are fundamentally very different. The arterial system is high pressure, high flow; while the venous system is low pressure, low flow. They shouldn’t be directly connected,” he noted.
The vein of Galen malformation is the most extreme version of such an anomaly. Developing in early gestation, it is associated with a large increase in blood flow through the brain which grows over time and can sometimes result in twice the total cardiac output of the body or even more, Dr. Orbach said.
The placenta is believed to be protective as most babies don’t have overt physiologic problems in utero, but they can run into crisis after birth, with the abnormally high blood flow causing an immense stress to the heart.
Babies typically present with heart failure as their first major symptom soon after birth, Dr. Orbach said. “Although the anatomical problem is in the brain, the clinical manifestation is high-output heart failure. The heart is trying to do double its normal work, pumping the blood to the malformation and immediately back to the heart and that blood is not performing any useful function.
“These newborns can get very sick. They need multiple medications to support their cardiovascular system and we need to do procedures to try and reduce the blood flow,” he explained.
Brain injury is also a common problem. “The brain circulation is very abnormal. The blood is being shunted through the malformation rather than circulating through the brain tissue which can become ischemic,” Dr. Orbach commented.
“The babies who get sick would have a very high mortality (up to 90%) without expert care. Even those who do receive expert care at a specialty center have a mortality rate of 30% to 40% and those who survive have a high risk of neurologic and cognitive impairment,” he added.
The current treatment for babies born with the condition involves transarterial embolization, by which a catheter is inserted into the arterial system to enable the malformation to be occluded by various techniques.
But Dr. Orbach pointed out that some babies are born too sick to have the postnatal intervention. “The heart failure and brain injury is so overwhelming that no matter what we do, we cannot reverse it, and these babies normally do not survive. What we are doing with the fetal surgery is trying to help those babies who cannot be treated with the current postnatal approach,” he said.
The first stage of this research involved trying to identify these very-high-risk babies in utero, and the researchers found that on fetal MRI a particular measurement of one of the venous sinuses that drains the main malformation was a good predictor of how the baby would fare after birth. The babies predicted to do poorly from this test are the targets for the fetal surgery.
The technique used for the postnatal intervention is too technically challenging to perform in utero. “So we have developed a different approach for the in utero surgery that involves navigating into the accepting vein in the malformation with a needle under ultrasound guidance, and then packing the vein with metal coils to dramatically reduce the blood flow,” Dr. Orbach explained.
This procedure was performed in this first patient on March 15. The surgery was part of a clinical trial that is planned to include 20 cases in total.
“The immediate goal is to see whether we can transform those fetuses who are at very high risk of getting sick after birth into babies who do well in the [neonatal] ICU and are able to be sent home for elective treatment at a few months of age,” Dr. Orbach noted. “The study is continuing as it is vital that we continue and show efficacy and safety in other patients as well,” he added.
Dr. Orbach said the results of this first case were extremely encouraging. “Each stage was exciting – the technical success of the procedure, and then seeing the [blood] flow diminish on the ultrasound right there during the procedure; then the next day we did a fetal echocardiogram, and we could see that the abnormal cardiac output was dramatically reduced, and a fetal MRI scan also showed the malformation was already coming down in size.”
The baby was born prematurely 2 days after the procedure because of ruptured membranes with a birth weight of 1.9 kg (4.2 lb). She has not required any cardiovascular support or postnatal embolization.
“We were waiting with bated breath until the baby was born to see how she did clinically. I was trying to be conservative in my expectations, but it was quickly apparent that she was going to do great,” he said. Now at home, she has some oxygen treatment for the first few weeks, “but right now her neurological status is completely intact and essentially she looks like any other baby,” Dr. Orbach commented.
It is not yet known whether the infant will need any additional procedures. “We will follow her closely and make a decision on whether further treatment is needed based on whether the malformation is growing or not,” Dr. Orbach said. Longer term follow-up will also assess secondary problems sometimes seen, such as learning problems and seizures.
Although other fetal surgeries are now routinely performed, this is believed to be the first in utero surgery aimed at the cerebrovascular system.
“There were a lot of uncertainties,” Dr. Orbach said. “We didn’t even know if we would be able to see our instruments on ultrasound.” To model the procedure, the researchers had a phantom fetal skull and brain constructed with a vein of Galen malformation, which was key to obtaining Food and Drug Administration approval for the study.
If the study shows success in the other patients too, the technique could be rolled out to other centers. “There definitely needs to be fetal surgery and neurointerventional teams familiar with vein of Galen malformation in place, and ready to manage complications after delivery regardless of outcome. But we are not the only center with those capabilities, so if our trial pans out, yes, the hope is that other teams in specialist children’s hospitals around the world could do this too,” he added.
Pioneering work
Commenting on the case report in an American Heart Association press release, Colin Derdeyn, MD, a neurointerventional radiologist at University of Iowa Health Care, Iowa City, who performs vein of Galen malformation embolizations on neonates, said: “The key advance here is to intervene before the physiologic events of birth can cause life-threatening heart failure.”
Dr. Derdeyn, who is a past chair of the American Heart Association’s Stroke Council, cautioned that one successful case is not enough experience to conclude that the risks of this procedure are worth the benefits.
But, he added: “The positive hemodynamic changes that they observed in utero and after birth – reduction in flow, reduction in size of the draining vein, reversal of the abnormal reversed flow in the aorta – are really encouraging. These are some of the most exciting and surprising aspects of this case report. This is pioneering work being done in a very careful and responsible way.”
The study was funded by a grant from the Sage Schermerhorn Chair for Image-Guided Therapy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The team from Boston Children’s Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital used ultrasound guidance to repair the vein of Galen malformation, which causes excessively high blood flow, resulting in both neurologic and cardiac complications.
The surgery was performed in a fetus at 34 weeks’ gestational age, with remarkable results. Since birth, the baby girl, who was identified in utero as being at high risk of suffering serious complications of the malformation, has required no medication to treat heart failure and no postnatal surgery.
Repeated echocardiograms after birth displayed marked improvement in cardiac output, and brain MRI showed no brain injury and a normal neurologic exam.
“This is incredibly exciting. The hope is that this baby, and others with this condition who receive this in utero surgery in future, will go on to have a normal life,” lead researcher Darren B. Orbach, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“We were thrilled to see that the aggressive decline usually seen after birth simply did not appear. We are pleased to report that at 6 weeks, the infant is progressing remarkably well, on no medications, eating normally, gaining weight and is back home. There are no signs of any negative effects on the brain,” he added.
Dr. Orbach, codirector of the Cerebrovascular Surgery & Interventions Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues described this first case report of the in utero vein of Galen malformation repair in a research letter, published online in the journal Stroke.
Vein of Galen malformation
Dr. Orbach explained that vein of Galen malformation, which occurs in around 1 in every 60,000 births, is a cerebrovascular anomaly in which the arterial system is directly connected to the venous system rather than to capillaries that are necessary to slow blood flow and deliver oxygen to surrounding brain tissue.
“The arterial and venous systems are fundamentally very different. The arterial system is high pressure, high flow; while the venous system is low pressure, low flow. They shouldn’t be directly connected,” he noted.
The vein of Galen malformation is the most extreme version of such an anomaly. Developing in early gestation, it is associated with a large increase in blood flow through the brain which grows over time and can sometimes result in twice the total cardiac output of the body or even more, Dr. Orbach said.
The placenta is believed to be protective as most babies don’t have overt physiologic problems in utero, but they can run into crisis after birth, with the abnormally high blood flow causing an immense stress to the heart.
Babies typically present with heart failure as their first major symptom soon after birth, Dr. Orbach said. “Although the anatomical problem is in the brain, the clinical manifestation is high-output heart failure. The heart is trying to do double its normal work, pumping the blood to the malformation and immediately back to the heart and that blood is not performing any useful function.
“These newborns can get very sick. They need multiple medications to support their cardiovascular system and we need to do procedures to try and reduce the blood flow,” he explained.
Brain injury is also a common problem. “The brain circulation is very abnormal. The blood is being shunted through the malformation rather than circulating through the brain tissue which can become ischemic,” Dr. Orbach commented.
“The babies who get sick would have a very high mortality (up to 90%) without expert care. Even those who do receive expert care at a specialty center have a mortality rate of 30% to 40% and those who survive have a high risk of neurologic and cognitive impairment,” he added.
The current treatment for babies born with the condition involves transarterial embolization, by which a catheter is inserted into the arterial system to enable the malformation to be occluded by various techniques.
But Dr. Orbach pointed out that some babies are born too sick to have the postnatal intervention. “The heart failure and brain injury is so overwhelming that no matter what we do, we cannot reverse it, and these babies normally do not survive. What we are doing with the fetal surgery is trying to help those babies who cannot be treated with the current postnatal approach,” he said.
The first stage of this research involved trying to identify these very-high-risk babies in utero, and the researchers found that on fetal MRI a particular measurement of one of the venous sinuses that drains the main malformation was a good predictor of how the baby would fare after birth. The babies predicted to do poorly from this test are the targets for the fetal surgery.
The technique used for the postnatal intervention is too technically challenging to perform in utero. “So we have developed a different approach for the in utero surgery that involves navigating into the accepting vein in the malformation with a needle under ultrasound guidance, and then packing the vein with metal coils to dramatically reduce the blood flow,” Dr. Orbach explained.
This procedure was performed in this first patient on March 15. The surgery was part of a clinical trial that is planned to include 20 cases in total.
“The immediate goal is to see whether we can transform those fetuses who are at very high risk of getting sick after birth into babies who do well in the [neonatal] ICU and are able to be sent home for elective treatment at a few months of age,” Dr. Orbach noted. “The study is continuing as it is vital that we continue and show efficacy and safety in other patients as well,” he added.
Dr. Orbach said the results of this first case were extremely encouraging. “Each stage was exciting – the technical success of the procedure, and then seeing the [blood] flow diminish on the ultrasound right there during the procedure; then the next day we did a fetal echocardiogram, and we could see that the abnormal cardiac output was dramatically reduced, and a fetal MRI scan also showed the malformation was already coming down in size.”
The baby was born prematurely 2 days after the procedure because of ruptured membranes with a birth weight of 1.9 kg (4.2 lb). She has not required any cardiovascular support or postnatal embolization.
“We were waiting with bated breath until the baby was born to see how she did clinically. I was trying to be conservative in my expectations, but it was quickly apparent that she was going to do great,” he said. Now at home, she has some oxygen treatment for the first few weeks, “but right now her neurological status is completely intact and essentially she looks like any other baby,” Dr. Orbach commented.
It is not yet known whether the infant will need any additional procedures. “We will follow her closely and make a decision on whether further treatment is needed based on whether the malformation is growing or not,” Dr. Orbach said. Longer term follow-up will also assess secondary problems sometimes seen, such as learning problems and seizures.
Although other fetal surgeries are now routinely performed, this is believed to be the first in utero surgery aimed at the cerebrovascular system.
“There were a lot of uncertainties,” Dr. Orbach said. “We didn’t even know if we would be able to see our instruments on ultrasound.” To model the procedure, the researchers had a phantom fetal skull and brain constructed with a vein of Galen malformation, which was key to obtaining Food and Drug Administration approval for the study.
If the study shows success in the other patients too, the technique could be rolled out to other centers. “There definitely needs to be fetal surgery and neurointerventional teams familiar with vein of Galen malformation in place, and ready to manage complications after delivery regardless of outcome. But we are not the only center with those capabilities, so if our trial pans out, yes, the hope is that other teams in specialist children’s hospitals around the world could do this too,” he added.
Pioneering work
Commenting on the case report in an American Heart Association press release, Colin Derdeyn, MD, a neurointerventional radiologist at University of Iowa Health Care, Iowa City, who performs vein of Galen malformation embolizations on neonates, said: “The key advance here is to intervene before the physiologic events of birth can cause life-threatening heart failure.”
Dr. Derdeyn, who is a past chair of the American Heart Association’s Stroke Council, cautioned that one successful case is not enough experience to conclude that the risks of this procedure are worth the benefits.
But, he added: “The positive hemodynamic changes that they observed in utero and after birth – reduction in flow, reduction in size of the draining vein, reversal of the abnormal reversed flow in the aorta – are really encouraging. These are some of the most exciting and surprising aspects of this case report. This is pioneering work being done in a very careful and responsible way.”
The study was funded by a grant from the Sage Schermerhorn Chair for Image-Guided Therapy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The team from Boston Children’s Hospital and Brigham and Women’s Hospital used ultrasound guidance to repair the vein of Galen malformation, which causes excessively high blood flow, resulting in both neurologic and cardiac complications.
The surgery was performed in a fetus at 34 weeks’ gestational age, with remarkable results. Since birth, the baby girl, who was identified in utero as being at high risk of suffering serious complications of the malformation, has required no medication to treat heart failure and no postnatal surgery.
Repeated echocardiograms after birth displayed marked improvement in cardiac output, and brain MRI showed no brain injury and a normal neurologic exam.
“This is incredibly exciting. The hope is that this baby, and others with this condition who receive this in utero surgery in future, will go on to have a normal life,” lead researcher Darren B. Orbach, MD, PhD, said in an interview.
“We were thrilled to see that the aggressive decline usually seen after birth simply did not appear. We are pleased to report that at 6 weeks, the infant is progressing remarkably well, on no medications, eating normally, gaining weight and is back home. There are no signs of any negative effects on the brain,” he added.
Dr. Orbach, codirector of the Cerebrovascular Surgery & Interventions Center at Boston Children’s Hospital, and colleagues described this first case report of the in utero vein of Galen malformation repair in a research letter, published online in the journal Stroke.
Vein of Galen malformation
Dr. Orbach explained that vein of Galen malformation, which occurs in around 1 in every 60,000 births, is a cerebrovascular anomaly in which the arterial system is directly connected to the venous system rather than to capillaries that are necessary to slow blood flow and deliver oxygen to surrounding brain tissue.
“The arterial and venous systems are fundamentally very different. The arterial system is high pressure, high flow; while the venous system is low pressure, low flow. They shouldn’t be directly connected,” he noted.
The vein of Galen malformation is the most extreme version of such an anomaly. Developing in early gestation, it is associated with a large increase in blood flow through the brain which grows over time and can sometimes result in twice the total cardiac output of the body or even more, Dr. Orbach said.
The placenta is believed to be protective as most babies don’t have overt physiologic problems in utero, but they can run into crisis after birth, with the abnormally high blood flow causing an immense stress to the heart.
Babies typically present with heart failure as their first major symptom soon after birth, Dr. Orbach said. “Although the anatomical problem is in the brain, the clinical manifestation is high-output heart failure. The heart is trying to do double its normal work, pumping the blood to the malformation and immediately back to the heart and that blood is not performing any useful function.
“These newborns can get very sick. They need multiple medications to support their cardiovascular system and we need to do procedures to try and reduce the blood flow,” he explained.
Brain injury is also a common problem. “The brain circulation is very abnormal. The blood is being shunted through the malformation rather than circulating through the brain tissue which can become ischemic,” Dr. Orbach commented.
“The babies who get sick would have a very high mortality (up to 90%) without expert care. Even those who do receive expert care at a specialty center have a mortality rate of 30% to 40% and those who survive have a high risk of neurologic and cognitive impairment,” he added.
The current treatment for babies born with the condition involves transarterial embolization, by which a catheter is inserted into the arterial system to enable the malformation to be occluded by various techniques.
But Dr. Orbach pointed out that some babies are born too sick to have the postnatal intervention. “The heart failure and brain injury is so overwhelming that no matter what we do, we cannot reverse it, and these babies normally do not survive. What we are doing with the fetal surgery is trying to help those babies who cannot be treated with the current postnatal approach,” he said.
The first stage of this research involved trying to identify these very-high-risk babies in utero, and the researchers found that on fetal MRI a particular measurement of one of the venous sinuses that drains the main malformation was a good predictor of how the baby would fare after birth. The babies predicted to do poorly from this test are the targets for the fetal surgery.
The technique used for the postnatal intervention is too technically challenging to perform in utero. “So we have developed a different approach for the in utero surgery that involves navigating into the accepting vein in the malformation with a needle under ultrasound guidance, and then packing the vein with metal coils to dramatically reduce the blood flow,” Dr. Orbach explained.
This procedure was performed in this first patient on March 15. The surgery was part of a clinical trial that is planned to include 20 cases in total.
“The immediate goal is to see whether we can transform those fetuses who are at very high risk of getting sick after birth into babies who do well in the [neonatal] ICU and are able to be sent home for elective treatment at a few months of age,” Dr. Orbach noted. “The study is continuing as it is vital that we continue and show efficacy and safety in other patients as well,” he added.
Dr. Orbach said the results of this first case were extremely encouraging. “Each stage was exciting – the technical success of the procedure, and then seeing the [blood] flow diminish on the ultrasound right there during the procedure; then the next day we did a fetal echocardiogram, and we could see that the abnormal cardiac output was dramatically reduced, and a fetal MRI scan also showed the malformation was already coming down in size.”
The baby was born prematurely 2 days after the procedure because of ruptured membranes with a birth weight of 1.9 kg (4.2 lb). She has not required any cardiovascular support or postnatal embolization.
“We were waiting with bated breath until the baby was born to see how she did clinically. I was trying to be conservative in my expectations, but it was quickly apparent that she was going to do great,” he said. Now at home, she has some oxygen treatment for the first few weeks, “but right now her neurological status is completely intact and essentially she looks like any other baby,” Dr. Orbach commented.
It is not yet known whether the infant will need any additional procedures. “We will follow her closely and make a decision on whether further treatment is needed based on whether the malformation is growing or not,” Dr. Orbach said. Longer term follow-up will also assess secondary problems sometimes seen, such as learning problems and seizures.
Although other fetal surgeries are now routinely performed, this is believed to be the first in utero surgery aimed at the cerebrovascular system.
“There were a lot of uncertainties,” Dr. Orbach said. “We didn’t even know if we would be able to see our instruments on ultrasound.” To model the procedure, the researchers had a phantom fetal skull and brain constructed with a vein of Galen malformation, which was key to obtaining Food and Drug Administration approval for the study.
If the study shows success in the other patients too, the technique could be rolled out to other centers. “There definitely needs to be fetal surgery and neurointerventional teams familiar with vein of Galen malformation in place, and ready to manage complications after delivery regardless of outcome. But we are not the only center with those capabilities, so if our trial pans out, yes, the hope is that other teams in specialist children’s hospitals around the world could do this too,” he added.
Pioneering work
Commenting on the case report in an American Heart Association press release, Colin Derdeyn, MD, a neurointerventional radiologist at University of Iowa Health Care, Iowa City, who performs vein of Galen malformation embolizations on neonates, said: “The key advance here is to intervene before the physiologic events of birth can cause life-threatening heart failure.”
Dr. Derdeyn, who is a past chair of the American Heart Association’s Stroke Council, cautioned that one successful case is not enough experience to conclude that the risks of this procedure are worth the benefits.
But, he added: “The positive hemodynamic changes that they observed in utero and after birth – reduction in flow, reduction in size of the draining vein, reversal of the abnormal reversed flow in the aorta – are really encouraging. These are some of the most exciting and surprising aspects of this case report. This is pioneering work being done in a very careful and responsible way.”
The study was funded by a grant from the Sage Schermerhorn Chair for Image-Guided Therapy.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM STROKE
CardioMEMS boosts QoL, curbs HF hospitalizations: MONITOR-HF
In the first randomized clinical trial of remote pulmonary artery pressure–guided monitoring and management of chronic heart failure (HF) in Europe, the intervention “substantially” improved quality of life (QoL) and reduced HF hospitalizations, new data show.
The CardioMEMS-HF system (Abbot Laboratories) used in the trial, called MONITOR-HF, remotely monitors changes in pulmonary artery pressure and provides an early warning of worsening HF.
Jasper Brugts, MD, PhD, of Erasmus MC University Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in an interview, “The concordance on outcomes of the three CardioMEMS trials across different eras, evolving GDMT [guideline-directed medical therapy], different conditions (pandemic), and different health care systems is reassuring and supportive of technologies such as CardioMEMS to improve patient monitoring to prevent HF hospitalizations and improve QoL.”
Dr. Brugts presented the study at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2023 sessions.
(11 vs. 17), in comparison with standard of care, Dr. Brugts told meeting attendees.
Furthermore, CardioMEMS monitors hypervolemia as well as hypovolemia, enabling “fine-tuning of diuretics.”
The presentation drew such applause that one chairperson described it as “close to a standing ovation.” The study was published simultaneously in The Lancet.
Aggregate evidence
Early clinical evidence of the benefits of remote monitoring with the CardioMEMS-HF system was provided by the CHAMPION trial, which included patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III heart failure.
Results of the subsequent GUIDE-HF trial, which aimed to test a broader population of patients with NYHA class II–IV heart failure and either increased N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations or hospitalization, were inconclusive.
However, a pre–COVID-19 impact analysis of GUIDE-HF indicated a possible benefit, which was primarily driven by a lower HF hospitalization rate, compared with the control group. That finding was the basis for an expanded indication for the system from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The 2022 FDA indication permits the use of CardioMEMS for patients with NYHA class II HF and for those with worsening HF, as assessed by elevated natriuretic peptide levels.
From United States to Europe
Aware that most CardioMEMS data came from U.S. trials, the investigators embarked on the current trial, MONITOR-HF, an open-label, randomized trial in 25 centers in the Netherlands. Eligible patients had chronic NYHA class III HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, and had previously undergone hospitalization for HF.
A total of 348 patients were randomly assigned to either CardioMEMS-HF or standard of care (SoC) between 2019 and 2022.The median age of the patients was 69 years, and the median ejection fraction was 30%.
All patients were scheduled to be seen by their clinician at 3 months, 6 months, and every 6 months thereafter for up to 48 months.
The primary endpoint was the mean difference in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) summary score at 12 months
That difference between groups was 7.13 (+7.05 in the CardioMEMS group and –0.08 in the SoC group).
In the responder analysis, the odds ratio of an improvement of at least 5 points in the KCCQ overall summary score was 1.69 in the CardioMEMS group vs. the SoC group; the OR of a deterioration of at least 5 points was 0.45.
Subgroup analyses showed no relevant heterogeneity in the treatment effect on total HF hospitalizations and, notably, no significant interaction in patients with an EF below 40% and an EF above 40%.
There was a significant reduction in the median NT-proBNP change from baseline only in the remote monitoring group (800 pg/mL) and a smaller, nonsignificant difference with SoC.
Both groups received highly appropriate background guideline–directed medical therapy throughout the study. There were no significant between-group differences at 12 months.
Freedom from device-related or system-related complications and sensor failure were 97.7% and 98.8%, respectively.
Two sensor failures occurred during a mean follow-up 1.8 years. The percentage of failures was comparable to CHAMPION and GUIDE-HF trials.
The trial was not powered to assess a mortality benefit.
Pick the right patients
“As in the U.S. trials, there will be side effects, so select the right patients, because [remote monitoring] is not without risk,” Dr. Brugts told meeting attendees.
That point also was made by Christiane E. Angermann of University and University Hospital Würzburg, Germany, in a related editorial in The Lancet.
“To reproduce these results on a large scale in real-life health care, diligent patient selection should identify those at high risk of heart failure–related hospitalization who agree with the concept of daily data collection and are able and motivated to comply with treatment recommendations even if asymptomatic,” Dr. Angermann writes.
“Without direct interaction between health care providers and patients, and timely treatment modification triggered by abnormal monitoring results, the care cycle might break and the potential benefits from early detection of decompensation would be lost.”
Val Rakita, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, a specialist in advanced heart failure and main implanter of the CardioMEMS device at Temple University Hospital, commented on the study for this article.
“This study confirms the previous data that the device is very safe and effective in preventing HF hospitalizations and improving patients’ quality of life, even in a different population with more modern background guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Nevertheless, he noted, “Studies have yet to confirm a mortality benefit, despite logic telling us that preventing heart failure hospitalizations should also improve patient survival. More studies are needed to see if a survival benefit can be proven over a longer follow-up period.”
Overall, he said, “Remote monitoring allows more precise management of medications, prevention of hospitalizations, and improvement in quality of life, and I am an advocate for it in my practice.”
Not everyone is an advocate, however. In a commentary published last year, John M. Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates in Louisville, Ky., said the expanded FDA indication for the device is the result of “dubious trial analysis, spin, lax regulation, and the growth of low-value care.”
Others also have questioned the device’s value in the clinic.
But at least for now, as Dr. Angermann writes, “Scientific evidence supports the use of the CardioMEMS-HF system to enhance remote patient management in heart failure care. For more widespread application, technological advancements are desirable to provide more comfort for patients and reusable external device components, thereby improving care experience and saving resources.”
The MONITOR-HF trial is funded by the Dutch Ministry of Health and Health Care institute. Dr. Brugts has an independent research grant from Abbott (investigator-sponsored study) and has had speaker engagements or has participated in advisory boards for Abbott and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Angermann has received personal fees from Abbott for serving as chair of the steering committee for the CardioMEMS European Monitoring Study for Heart Failure (MEMS-HF) and consulting fees, honoraria, and travel costs from Abbott. Dr. Rakita has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first randomized clinical trial of remote pulmonary artery pressure–guided monitoring and management of chronic heart failure (HF) in Europe, the intervention “substantially” improved quality of life (QoL) and reduced HF hospitalizations, new data show.
The CardioMEMS-HF system (Abbot Laboratories) used in the trial, called MONITOR-HF, remotely monitors changes in pulmonary artery pressure and provides an early warning of worsening HF.
Jasper Brugts, MD, PhD, of Erasmus MC University Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in an interview, “The concordance on outcomes of the three CardioMEMS trials across different eras, evolving GDMT [guideline-directed medical therapy], different conditions (pandemic), and different health care systems is reassuring and supportive of technologies such as CardioMEMS to improve patient monitoring to prevent HF hospitalizations and improve QoL.”
Dr. Brugts presented the study at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2023 sessions.
(11 vs. 17), in comparison with standard of care, Dr. Brugts told meeting attendees.
Furthermore, CardioMEMS monitors hypervolemia as well as hypovolemia, enabling “fine-tuning of diuretics.”
The presentation drew such applause that one chairperson described it as “close to a standing ovation.” The study was published simultaneously in The Lancet.
Aggregate evidence
Early clinical evidence of the benefits of remote monitoring with the CardioMEMS-HF system was provided by the CHAMPION trial, which included patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III heart failure.
Results of the subsequent GUIDE-HF trial, which aimed to test a broader population of patients with NYHA class II–IV heart failure and either increased N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations or hospitalization, were inconclusive.
However, a pre–COVID-19 impact analysis of GUIDE-HF indicated a possible benefit, which was primarily driven by a lower HF hospitalization rate, compared with the control group. That finding was the basis for an expanded indication for the system from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The 2022 FDA indication permits the use of CardioMEMS for patients with NYHA class II HF and for those with worsening HF, as assessed by elevated natriuretic peptide levels.
From United States to Europe
Aware that most CardioMEMS data came from U.S. trials, the investigators embarked on the current trial, MONITOR-HF, an open-label, randomized trial in 25 centers in the Netherlands. Eligible patients had chronic NYHA class III HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, and had previously undergone hospitalization for HF.
A total of 348 patients were randomly assigned to either CardioMEMS-HF or standard of care (SoC) between 2019 and 2022.The median age of the patients was 69 years, and the median ejection fraction was 30%.
All patients were scheduled to be seen by their clinician at 3 months, 6 months, and every 6 months thereafter for up to 48 months.
The primary endpoint was the mean difference in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) summary score at 12 months
That difference between groups was 7.13 (+7.05 in the CardioMEMS group and –0.08 in the SoC group).
In the responder analysis, the odds ratio of an improvement of at least 5 points in the KCCQ overall summary score was 1.69 in the CardioMEMS group vs. the SoC group; the OR of a deterioration of at least 5 points was 0.45.
Subgroup analyses showed no relevant heterogeneity in the treatment effect on total HF hospitalizations and, notably, no significant interaction in patients with an EF below 40% and an EF above 40%.
There was a significant reduction in the median NT-proBNP change from baseline only in the remote monitoring group (800 pg/mL) and a smaller, nonsignificant difference with SoC.
Both groups received highly appropriate background guideline–directed medical therapy throughout the study. There were no significant between-group differences at 12 months.
Freedom from device-related or system-related complications and sensor failure were 97.7% and 98.8%, respectively.
Two sensor failures occurred during a mean follow-up 1.8 years. The percentage of failures was comparable to CHAMPION and GUIDE-HF trials.
The trial was not powered to assess a mortality benefit.
Pick the right patients
“As in the U.S. trials, there will be side effects, so select the right patients, because [remote monitoring] is not without risk,” Dr. Brugts told meeting attendees.
That point also was made by Christiane E. Angermann of University and University Hospital Würzburg, Germany, in a related editorial in The Lancet.
“To reproduce these results on a large scale in real-life health care, diligent patient selection should identify those at high risk of heart failure–related hospitalization who agree with the concept of daily data collection and are able and motivated to comply with treatment recommendations even if asymptomatic,” Dr. Angermann writes.
“Without direct interaction between health care providers and patients, and timely treatment modification triggered by abnormal monitoring results, the care cycle might break and the potential benefits from early detection of decompensation would be lost.”
Val Rakita, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, a specialist in advanced heart failure and main implanter of the CardioMEMS device at Temple University Hospital, commented on the study for this article.
“This study confirms the previous data that the device is very safe and effective in preventing HF hospitalizations and improving patients’ quality of life, even in a different population with more modern background guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Nevertheless, he noted, “Studies have yet to confirm a mortality benefit, despite logic telling us that preventing heart failure hospitalizations should also improve patient survival. More studies are needed to see if a survival benefit can be proven over a longer follow-up period.”
Overall, he said, “Remote monitoring allows more precise management of medications, prevention of hospitalizations, and improvement in quality of life, and I am an advocate for it in my practice.”
Not everyone is an advocate, however. In a commentary published last year, John M. Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates in Louisville, Ky., said the expanded FDA indication for the device is the result of “dubious trial analysis, spin, lax regulation, and the growth of low-value care.”
Others also have questioned the device’s value in the clinic.
But at least for now, as Dr. Angermann writes, “Scientific evidence supports the use of the CardioMEMS-HF system to enhance remote patient management in heart failure care. For more widespread application, technological advancements are desirable to provide more comfort for patients and reusable external device components, thereby improving care experience and saving resources.”
The MONITOR-HF trial is funded by the Dutch Ministry of Health and Health Care institute. Dr. Brugts has an independent research grant from Abbott (investigator-sponsored study) and has had speaker engagements or has participated in advisory boards for Abbott and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Angermann has received personal fees from Abbott for serving as chair of the steering committee for the CardioMEMS European Monitoring Study for Heart Failure (MEMS-HF) and consulting fees, honoraria, and travel costs from Abbott. Dr. Rakita has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the first randomized clinical trial of remote pulmonary artery pressure–guided monitoring and management of chronic heart failure (HF) in Europe, the intervention “substantially” improved quality of life (QoL) and reduced HF hospitalizations, new data show.
The CardioMEMS-HF system (Abbot Laboratories) used in the trial, called MONITOR-HF, remotely monitors changes in pulmonary artery pressure and provides an early warning of worsening HF.
Jasper Brugts, MD, PhD, of Erasmus MC University Medical Centre, Rotterdam, the Netherlands, said in an interview, “The concordance on outcomes of the three CardioMEMS trials across different eras, evolving GDMT [guideline-directed medical therapy], different conditions (pandemic), and different health care systems is reassuring and supportive of technologies such as CardioMEMS to improve patient monitoring to prevent HF hospitalizations and improve QoL.”
Dr. Brugts presented the study at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2023 sessions.
(11 vs. 17), in comparison with standard of care, Dr. Brugts told meeting attendees.
Furthermore, CardioMEMS monitors hypervolemia as well as hypovolemia, enabling “fine-tuning of diuretics.”
The presentation drew such applause that one chairperson described it as “close to a standing ovation.” The study was published simultaneously in The Lancet.
Aggregate evidence
Early clinical evidence of the benefits of remote monitoring with the CardioMEMS-HF system was provided by the CHAMPION trial, which included patients with New York Heart Association (NYHA) class III heart failure.
Results of the subsequent GUIDE-HF trial, which aimed to test a broader population of patients with NYHA class II–IV heart failure and either increased N-terminal-pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) concentrations or hospitalization, were inconclusive.
However, a pre–COVID-19 impact analysis of GUIDE-HF indicated a possible benefit, which was primarily driven by a lower HF hospitalization rate, compared with the control group. That finding was the basis for an expanded indication for the system from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
The 2022 FDA indication permits the use of CardioMEMS for patients with NYHA class II HF and for those with worsening HF, as assessed by elevated natriuretic peptide levels.
From United States to Europe
Aware that most CardioMEMS data came from U.S. trials, the investigators embarked on the current trial, MONITOR-HF, an open-label, randomized trial in 25 centers in the Netherlands. Eligible patients had chronic NYHA class III HF, irrespective of ejection fraction, and had previously undergone hospitalization for HF.
A total of 348 patients were randomly assigned to either CardioMEMS-HF or standard of care (SoC) between 2019 and 2022.The median age of the patients was 69 years, and the median ejection fraction was 30%.
All patients were scheduled to be seen by their clinician at 3 months, 6 months, and every 6 months thereafter for up to 48 months.
The primary endpoint was the mean difference in the Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire (KCCQ) summary score at 12 months
That difference between groups was 7.13 (+7.05 in the CardioMEMS group and –0.08 in the SoC group).
In the responder analysis, the odds ratio of an improvement of at least 5 points in the KCCQ overall summary score was 1.69 in the CardioMEMS group vs. the SoC group; the OR of a deterioration of at least 5 points was 0.45.
Subgroup analyses showed no relevant heterogeneity in the treatment effect on total HF hospitalizations and, notably, no significant interaction in patients with an EF below 40% and an EF above 40%.
There was a significant reduction in the median NT-proBNP change from baseline only in the remote monitoring group (800 pg/mL) and a smaller, nonsignificant difference with SoC.
Both groups received highly appropriate background guideline–directed medical therapy throughout the study. There were no significant between-group differences at 12 months.
Freedom from device-related or system-related complications and sensor failure were 97.7% and 98.8%, respectively.
Two sensor failures occurred during a mean follow-up 1.8 years. The percentage of failures was comparable to CHAMPION and GUIDE-HF trials.
The trial was not powered to assess a mortality benefit.
Pick the right patients
“As in the U.S. trials, there will be side effects, so select the right patients, because [remote monitoring] is not without risk,” Dr. Brugts told meeting attendees.
That point also was made by Christiane E. Angermann of University and University Hospital Würzburg, Germany, in a related editorial in The Lancet.
“To reproduce these results on a large scale in real-life health care, diligent patient selection should identify those at high risk of heart failure–related hospitalization who agree with the concept of daily data collection and are able and motivated to comply with treatment recommendations even if asymptomatic,” Dr. Angermann writes.
“Without direct interaction between health care providers and patients, and timely treatment modification triggered by abnormal monitoring results, the care cycle might break and the potential benefits from early detection of decompensation would be lost.”
Val Rakita, MD, assistant professor of medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, a specialist in advanced heart failure and main implanter of the CardioMEMS device at Temple University Hospital, commented on the study for this article.
“This study confirms the previous data that the device is very safe and effective in preventing HF hospitalizations and improving patients’ quality of life, even in a different population with more modern background guideline-directed medical therapy.”
Nevertheless, he noted, “Studies have yet to confirm a mortality benefit, despite logic telling us that preventing heart failure hospitalizations should also improve patient survival. More studies are needed to see if a survival benefit can be proven over a longer follow-up period.”
Overall, he said, “Remote monitoring allows more precise management of medications, prevention of hospitalizations, and improvement in quality of life, and I am an advocate for it in my practice.”
Not everyone is an advocate, however. In a commentary published last year, John M. Mandrola, MD, a cardiac electrophysiologist at Baptist Medical Associates in Louisville, Ky., said the expanded FDA indication for the device is the result of “dubious trial analysis, spin, lax regulation, and the growth of low-value care.”
Others also have questioned the device’s value in the clinic.
But at least for now, as Dr. Angermann writes, “Scientific evidence supports the use of the CardioMEMS-HF system to enhance remote patient management in heart failure care. For more widespread application, technological advancements are desirable to provide more comfort for patients and reusable external device components, thereby improving care experience and saving resources.”
The MONITOR-HF trial is funded by the Dutch Ministry of Health and Health Care institute. Dr. Brugts has an independent research grant from Abbott (investigator-sponsored study) and has had speaker engagements or has participated in advisory boards for Abbott and other pharmaceutical companies. Dr. Angermann has received personal fees from Abbott for serving as chair of the steering committee for the CardioMEMS European Monitoring Study for Heart Failure (MEMS-HF) and consulting fees, honoraria, and travel costs from Abbott. Dr. Rakita has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2023
Losing weight may bolster AFib ablation’s chances for success: LEAF interim results
, a new analysis suggests.
The finding comes from a small study that entered such patients with paroxysmal and especially persistent AFib who were candidates for ablation. Those shedding at least 3% of body weight in the months before the procedure while engaged in a structured risk-factor modification (RFM) program were “dramatically” more likely to be AFib-free 6 months later.
The improved ablation efficacy, compared with results in similar patients who didn’t lose as much weight, was most pronounced among those whose AFib had been the persistent form, reported investigators at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society, held in New Orleans.
Of note, ablations in the study were consistently limited, as much as possible, to standard pulmonary-vein isolation (PVI).
Associations between AFib and obesity and other behavioral and lifestyle-related risk factors are well recognized, but the limited studies of their effect on AFib ablation success have been inconsistent. The current analysis, the group says, points specifically to preablation weight loss as means to improving AFib-ablation outcomes.
“Adjunctive therapy focused on weight loss should be incorporated in the treatment plan for obese patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation,” Jeffrey J. Goldberger, MD, MBA, of the University of Miami, said when presenting the new results at the HRS sessions.
Such a plan is entirely consistent with recent guidelines and especially a 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) consensus statement, but is inconsistently and perhaps even seldom realized in clinical practice.
Dramatic increase in success
Even modest weight loss before ablation may help, proposed Dr. Goldberger, who directs his institution’s Center for Atrial Fibrillation. Decreases for the greater-weight-loss group actually averaged less than 6% of baseline body weight.
Yet it was apparently enough to improve ablation outcomes significantly: Eighty-eight percent were free of AFib 6 months after the procedure, compared with 61% for patients who lost less than 3% of their preablation weight.
For improving ablation success, he said, “We’re talking about a moderate amount of weight loss. These patients are not going from being obese to being thin. They’re still quite overweight.”
In an analysis limited to the four-fifths of patients with persistent AFib, “we saw the same pattern,” Dr. Goldberger said at a media presentation prior to his formal report at the HRS sessions.
Moreover, that subgroup’s benefit persisted out to 12 months, at which time 42% and 81% of patients with less and greater weight loss, respectively, were free of AFib. That represents, he said, “a really tremendous – dramatic, actually – increase in success of pulmonary vein isolation in those who lost weight.”
“We’ve known for a long time that weight loss is important for preventing atrial fibrillation or increasing the success rates of the different treatments we use,” Cynthia M. Tracy, MD, said in an interview. “Probably in some studies, weight loss has been as effective as antiarrhythmics.”
A loss of 3% body weight “is not a lot,” she said. In the current analysis, “It’s notable that it made that much difference with even a fairly modest amount of weight loss.”
Now when asked, “ ‘How much do I have to lose before you’ll consider doing my ablation?’ we have a bit more concrete data to give patients and doctors as to what amount might be beneficial,” said Dr. Tracy of George Washington University Hospital, Washington, who is not associated with the study.
Evolving view of AFib
The findings are emblematic of the profession’s evolving view of AFib and its management, Dr. Goldberger observed at the press conference. Should clinicians think of AFib as similar to “a disease like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome,” in which the patient usually has a successful ablation, and then “we expect that to last in perpetuity with no further interventions?”
Or, he said, “is atrial fibrillation more a disease like coronary artery disease, where even if they have an intervention, the disease process is still ongoing and requires long-term disease management? I think it’s pretty clear that we’re dealing with the latter case.”
Dr. Goldberger’s report was an interim analysis of an ongoing randomized trial called LEAF (Liraglutide Effect on Atrial Fibrillation), which is comparing patients with AFib assigned to “take” vs. “not take” the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide, an antidiabetic (Victoza) and weight-loss (Saxenda) drug. The trial aims to assess the drug’s apparent ability to shrink atrial epicardial adipose tissue which, Dr. Goldberger said, is thought to contribute to AFib development and influence AFib-ablation outcomes.
It’s unknown and a limitation of the current analysis, he said, whether the observed link between improved preablation–weight ablation success “is specifically related to weight loss, liraglutide treatment, or both.”
As the invited discussant for Dr. Goldberger’s presentation, David Frankel, MD, observed that studies have been inconsistent on whether substantial weight loss may improve the results of AFib rhythm-control therapy.
Those finding such an association, including LEAF and the influential LEGACY study, differed from others showing a null effect by including “a comprehensive risk factor management” program, observed Dr. Frankel, of the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Heart and Vascular Center, Philadelphia.
Rather than focusing solely on weight loss or sleep apnea as AFib risk factors, he said, the studies linking weight loss to AFib rhythm control also included “hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking cessation, and alcohol reduction,” Dr. Frankel said. “So it seems clear that to significantly impact AF recurrence, we need to focus on all these contributors to metabolic syndrome.”
Comprehensive risk-factor management
LEAF entered patients with AFib, 79% of whom had persistent AF and the rest paroxysmal AF, who followed the RFM program and were randomly assigned also to take liraglutide or placebo. The “nurse-practitioner-led” RFM program, conducted both in-clinic and online, featured “established goals for each patient” using AHA diet and lifestyle recommendations, an exercise prescription, dietary counseling, evaluation and treatment of sleep apnea, and measures to control any diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or hypertension, Dr. Goldberger said. And patients “were counseled on alcohol reduction and smoking cessation as necessary.”
After 3 months, 29 and 30 patients – regardless of randomization assignment – had lost < 3% and at least 3% of baseline body weight, respectively.
Catheter ablation achieved PVI in all patients. A 3-month blanking period followed, after which they went off antiarrhythmic meds.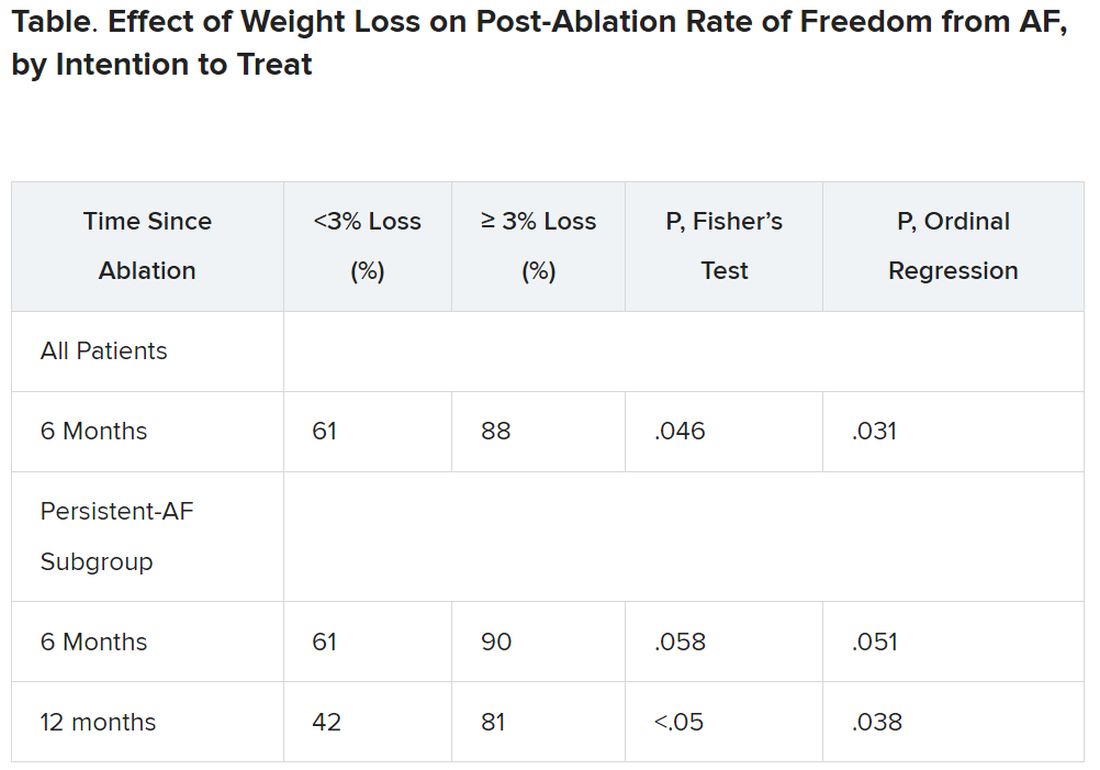
It’s very difficult for patients to lose 10% or more of body weight, “and it would not happen overnight,” Dr. Tracy observed. “These are symptomatic patients, for the most part, if they get referred to an electrophysiologist. So you don’t want to defer them indefinitely.”
The current findings, she said, point to “a more realistic target,” suggesting that weight loss of at least 3% should improve AFib ablation’s chances for success.
Dr. Goldberger disclosed ties to Medtronic. Dr. Frankel disclosed ties to Medtronic, Stryker, Biosense Webster, and Boston Scientific. Dr. Tracy reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new analysis suggests.
The finding comes from a small study that entered such patients with paroxysmal and especially persistent AFib who were candidates for ablation. Those shedding at least 3% of body weight in the months before the procedure while engaged in a structured risk-factor modification (RFM) program were “dramatically” more likely to be AFib-free 6 months later.
The improved ablation efficacy, compared with results in similar patients who didn’t lose as much weight, was most pronounced among those whose AFib had been the persistent form, reported investigators at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society, held in New Orleans.
Of note, ablations in the study were consistently limited, as much as possible, to standard pulmonary-vein isolation (PVI).
Associations between AFib and obesity and other behavioral and lifestyle-related risk factors are well recognized, but the limited studies of their effect on AFib ablation success have been inconsistent. The current analysis, the group says, points specifically to preablation weight loss as means to improving AFib-ablation outcomes.
“Adjunctive therapy focused on weight loss should be incorporated in the treatment plan for obese patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation,” Jeffrey J. Goldberger, MD, MBA, of the University of Miami, said when presenting the new results at the HRS sessions.
Such a plan is entirely consistent with recent guidelines and especially a 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) consensus statement, but is inconsistently and perhaps even seldom realized in clinical practice.
Dramatic increase in success
Even modest weight loss before ablation may help, proposed Dr. Goldberger, who directs his institution’s Center for Atrial Fibrillation. Decreases for the greater-weight-loss group actually averaged less than 6% of baseline body weight.
Yet it was apparently enough to improve ablation outcomes significantly: Eighty-eight percent were free of AFib 6 months after the procedure, compared with 61% for patients who lost less than 3% of their preablation weight.
For improving ablation success, he said, “We’re talking about a moderate amount of weight loss. These patients are not going from being obese to being thin. They’re still quite overweight.”
In an analysis limited to the four-fifths of patients with persistent AFib, “we saw the same pattern,” Dr. Goldberger said at a media presentation prior to his formal report at the HRS sessions.
Moreover, that subgroup’s benefit persisted out to 12 months, at which time 42% and 81% of patients with less and greater weight loss, respectively, were free of AFib. That represents, he said, “a really tremendous – dramatic, actually – increase in success of pulmonary vein isolation in those who lost weight.”
“We’ve known for a long time that weight loss is important for preventing atrial fibrillation or increasing the success rates of the different treatments we use,” Cynthia M. Tracy, MD, said in an interview. “Probably in some studies, weight loss has been as effective as antiarrhythmics.”
A loss of 3% body weight “is not a lot,” she said. In the current analysis, “It’s notable that it made that much difference with even a fairly modest amount of weight loss.”
Now when asked, “ ‘How much do I have to lose before you’ll consider doing my ablation?’ we have a bit more concrete data to give patients and doctors as to what amount might be beneficial,” said Dr. Tracy of George Washington University Hospital, Washington, who is not associated with the study.
Evolving view of AFib
The findings are emblematic of the profession’s evolving view of AFib and its management, Dr. Goldberger observed at the press conference. Should clinicians think of AFib as similar to “a disease like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome,” in which the patient usually has a successful ablation, and then “we expect that to last in perpetuity with no further interventions?”
Or, he said, “is atrial fibrillation more a disease like coronary artery disease, where even if they have an intervention, the disease process is still ongoing and requires long-term disease management? I think it’s pretty clear that we’re dealing with the latter case.”
Dr. Goldberger’s report was an interim analysis of an ongoing randomized trial called LEAF (Liraglutide Effect on Atrial Fibrillation), which is comparing patients with AFib assigned to “take” vs. “not take” the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide, an antidiabetic (Victoza) and weight-loss (Saxenda) drug. The trial aims to assess the drug’s apparent ability to shrink atrial epicardial adipose tissue which, Dr. Goldberger said, is thought to contribute to AFib development and influence AFib-ablation outcomes.
It’s unknown and a limitation of the current analysis, he said, whether the observed link between improved preablation–weight ablation success “is specifically related to weight loss, liraglutide treatment, or both.”
As the invited discussant for Dr. Goldberger’s presentation, David Frankel, MD, observed that studies have been inconsistent on whether substantial weight loss may improve the results of AFib rhythm-control therapy.
Those finding such an association, including LEAF and the influential LEGACY study, differed from others showing a null effect by including “a comprehensive risk factor management” program, observed Dr. Frankel, of the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Heart and Vascular Center, Philadelphia.
Rather than focusing solely on weight loss or sleep apnea as AFib risk factors, he said, the studies linking weight loss to AFib rhythm control also included “hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking cessation, and alcohol reduction,” Dr. Frankel said. “So it seems clear that to significantly impact AF recurrence, we need to focus on all these contributors to metabolic syndrome.”
Comprehensive risk-factor management
LEAF entered patients with AFib, 79% of whom had persistent AF and the rest paroxysmal AF, who followed the RFM program and were randomly assigned also to take liraglutide or placebo. The “nurse-practitioner-led” RFM program, conducted both in-clinic and online, featured “established goals for each patient” using AHA diet and lifestyle recommendations, an exercise prescription, dietary counseling, evaluation and treatment of sleep apnea, and measures to control any diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or hypertension, Dr. Goldberger said. And patients “were counseled on alcohol reduction and smoking cessation as necessary.”
After 3 months, 29 and 30 patients – regardless of randomization assignment – had lost < 3% and at least 3% of baseline body weight, respectively.
Catheter ablation achieved PVI in all patients. A 3-month blanking period followed, after which they went off antiarrhythmic meds.
It’s very difficult for patients to lose 10% or more of body weight, “and it would not happen overnight,” Dr. Tracy observed. “These are symptomatic patients, for the most part, if they get referred to an electrophysiologist. So you don’t want to defer them indefinitely.”
The current findings, she said, point to “a more realistic target,” suggesting that weight loss of at least 3% should improve AFib ablation’s chances for success.
Dr. Goldberger disclosed ties to Medtronic. Dr. Frankel disclosed ties to Medtronic, Stryker, Biosense Webster, and Boston Scientific. Dr. Tracy reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new analysis suggests.
The finding comes from a small study that entered such patients with paroxysmal and especially persistent AFib who were candidates for ablation. Those shedding at least 3% of body weight in the months before the procedure while engaged in a structured risk-factor modification (RFM) program were “dramatically” more likely to be AFib-free 6 months later.
The improved ablation efficacy, compared with results in similar patients who didn’t lose as much weight, was most pronounced among those whose AFib had been the persistent form, reported investigators at the annual scientific sessions of the Heart Rhythm Society, held in New Orleans.
Of note, ablations in the study were consistently limited, as much as possible, to standard pulmonary-vein isolation (PVI).
Associations between AFib and obesity and other behavioral and lifestyle-related risk factors are well recognized, but the limited studies of their effect on AFib ablation success have been inconsistent. The current analysis, the group says, points specifically to preablation weight loss as means to improving AFib-ablation outcomes.
“Adjunctive therapy focused on weight loss should be incorporated in the treatment plan for obese patients undergoing ablation for atrial fibrillation,” Jeffrey J. Goldberger, MD, MBA, of the University of Miami, said when presenting the new results at the HRS sessions.
Such a plan is entirely consistent with recent guidelines and especially a 2020 American Heart Association (AHA) consensus statement, but is inconsistently and perhaps even seldom realized in clinical practice.
Dramatic increase in success
Even modest weight loss before ablation may help, proposed Dr. Goldberger, who directs his institution’s Center for Atrial Fibrillation. Decreases for the greater-weight-loss group actually averaged less than 6% of baseline body weight.
Yet it was apparently enough to improve ablation outcomes significantly: Eighty-eight percent were free of AFib 6 months after the procedure, compared with 61% for patients who lost less than 3% of their preablation weight.
For improving ablation success, he said, “We’re talking about a moderate amount of weight loss. These patients are not going from being obese to being thin. They’re still quite overweight.”
In an analysis limited to the four-fifths of patients with persistent AFib, “we saw the same pattern,” Dr. Goldberger said at a media presentation prior to his formal report at the HRS sessions.
Moreover, that subgroup’s benefit persisted out to 12 months, at which time 42% and 81% of patients with less and greater weight loss, respectively, were free of AFib. That represents, he said, “a really tremendous – dramatic, actually – increase in success of pulmonary vein isolation in those who lost weight.”
“We’ve known for a long time that weight loss is important for preventing atrial fibrillation or increasing the success rates of the different treatments we use,” Cynthia M. Tracy, MD, said in an interview. “Probably in some studies, weight loss has been as effective as antiarrhythmics.”
A loss of 3% body weight “is not a lot,” she said. In the current analysis, “It’s notable that it made that much difference with even a fairly modest amount of weight loss.”
Now when asked, “ ‘How much do I have to lose before you’ll consider doing my ablation?’ we have a bit more concrete data to give patients and doctors as to what amount might be beneficial,” said Dr. Tracy of George Washington University Hospital, Washington, who is not associated with the study.
Evolving view of AFib
The findings are emblematic of the profession’s evolving view of AFib and its management, Dr. Goldberger observed at the press conference. Should clinicians think of AFib as similar to “a disease like Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome,” in which the patient usually has a successful ablation, and then “we expect that to last in perpetuity with no further interventions?”
Or, he said, “is atrial fibrillation more a disease like coronary artery disease, where even if they have an intervention, the disease process is still ongoing and requires long-term disease management? I think it’s pretty clear that we’re dealing with the latter case.”
Dr. Goldberger’s report was an interim analysis of an ongoing randomized trial called LEAF (Liraglutide Effect on Atrial Fibrillation), which is comparing patients with AFib assigned to “take” vs. “not take” the GLP-1 receptor agonist liraglutide, an antidiabetic (Victoza) and weight-loss (Saxenda) drug. The trial aims to assess the drug’s apparent ability to shrink atrial epicardial adipose tissue which, Dr. Goldberger said, is thought to contribute to AFib development and influence AFib-ablation outcomes.
It’s unknown and a limitation of the current analysis, he said, whether the observed link between improved preablation–weight ablation success “is specifically related to weight loss, liraglutide treatment, or both.”
As the invited discussant for Dr. Goldberger’s presentation, David Frankel, MD, observed that studies have been inconsistent on whether substantial weight loss may improve the results of AFib rhythm-control therapy.
Those finding such an association, including LEAF and the influential LEGACY study, differed from others showing a null effect by including “a comprehensive risk factor management” program, observed Dr. Frankel, of the Hospital of the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Heart and Vascular Center, Philadelphia.
Rather than focusing solely on weight loss or sleep apnea as AFib risk factors, he said, the studies linking weight loss to AFib rhythm control also included “hypertension, diabetes, hyperlipidemia, smoking cessation, and alcohol reduction,” Dr. Frankel said. “So it seems clear that to significantly impact AF recurrence, we need to focus on all these contributors to metabolic syndrome.”
Comprehensive risk-factor management
LEAF entered patients with AFib, 79% of whom had persistent AF and the rest paroxysmal AF, who followed the RFM program and were randomly assigned also to take liraglutide or placebo. The “nurse-practitioner-led” RFM program, conducted both in-clinic and online, featured “established goals for each patient” using AHA diet and lifestyle recommendations, an exercise prescription, dietary counseling, evaluation and treatment of sleep apnea, and measures to control any diabetes, hyperlipidemia, or hypertension, Dr. Goldberger said. And patients “were counseled on alcohol reduction and smoking cessation as necessary.”
After 3 months, 29 and 30 patients – regardless of randomization assignment – had lost < 3% and at least 3% of baseline body weight, respectively.
Catheter ablation achieved PVI in all patients. A 3-month blanking period followed, after which they went off antiarrhythmic meds.
It’s very difficult for patients to lose 10% or more of body weight, “and it would not happen overnight,” Dr. Tracy observed. “These are symptomatic patients, for the most part, if they get referred to an electrophysiologist. So you don’t want to defer them indefinitely.”
The current findings, she said, point to “a more realistic target,” suggesting that weight loss of at least 3% should improve AFib ablation’s chances for success.
Dr. Goldberger disclosed ties to Medtronic. Dr. Frankel disclosed ties to Medtronic, Stryker, Biosense Webster, and Boston Scientific. Dr. Tracy reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM HEART RHYTHM 2023
Novel antibody safe, promising for ATTR in phase 1 trial
, a new study suggests.
Currently, the only drug approved to treat ATTR is tafamidis, which improves survival and reduces hospitalizations, but does not reverse disease symptoms, the authors noted.
NI006 is a recombinant human anti-ATTR antibody given by infusion that was developed to trigger removal of ATTR by the body’s phagocytic immune cells.
Use of the drug was not associated with serious drug-related adverse events, though mild and moderate adverse events did occur.
Median N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and troponin T levels also seemed to be reduced over the study period.
Given the success of the antibody in this initial 40-patient trial, a larger phase-3 placebo-controlled trial is planned and expected to launch in the second half of 2023, said lead author Pablo Garcia-Pavia, MD, of Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro and the Spanish National Cardiovascular Research Institute, Madrid.
However, “The design of appropriate phase-3 trials to demonstrate efficacy of drugs for ATTR-CM is becoming more complicated and challenging,” he said.
“Increased awareness of the disease and advances in cardiac imaging techniques have led to recognition of a larger number of patients with ATTR-CM who have a different clinical profile and a different prognosis than the patients who were diagnosed in previous years and were enrolled in the initial trials of stabilizers,” Dr. Garcia-Pavia added.
“Moreover, the availability of tafamidis, and hopefully soon other medications to treat ATTR-CM has complicated the design of new clinical trials because of the heterogenicity of treatments that patients might receive,” he said. “Therefore, it is critical to plan the design very well.”
Dr. Garcia-Pavia presented the findings on NI006 at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2023 sessions. The study was published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
No serious adverse events
For the phase-1, double-blind, multicenter study, the investigators randomly assigned (2:1 ratio) 40 patients (median age, 72 years; 98% men) with wild-type or variant ATTR cardiomyopathy and chronic heart failure to receive IV infusions of either NI006, at one of six doses ranging from 0.3 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg of body weight, or placebo every 4 weeks for 4 months.
After the four infusions, participants were enrolled in an open-label extension phase in which they received eight NI006 infusions with stepwise increases in the dose.
Participants had a confirmed diagnosis of ATTR-CM; left ventricular wall thickness of at least 14 mm; left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 40%; New York Heart Association class I, II, or III; estimated glomerular filtration rate of more than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2; and an NT-proBNP level of 600 to 6,000 pg/mL.
Most (36) were receiving tafamidis, with a median treatment duration of 7 months; other ATTR-specific drugs were not permitted. Patients randomly assigned to receive NI006 seemed to have more advanced disease compared with those assigned to placebo.
Adherence to the trial protocol was high: Thirty-four patients received the four scheduled infusions during the ascending-dose phase, and 34 of 35 patients who completed this phase subsequently enrolled in the open-label extension.
No apparent drug-related serious adverse events were reported. However, during the ascending-dose phase, 38 patients had at least one adverse event, most of which were mild or moderate; of the 191 total events, 124 were grade 1 and 60 were grade 2 (most commonly heart failure and arrhythmias). Three patients had cytokine release syndrome; all three completed treatment through the extension phase.
Musculoskeletal events increased with ascending doses of NI006, which led two patients to withdraw from the trial.
At doses of at least 10 mg/kg, cardiac tracer uptake on scintigraphy and extracellular volume on cardiac MRI, both of which are imaging-based surrogate markers of cardiac amyloid load, appeared to be reduced over 12 months.
Because NI006 stimulates the patient’s own immune system to eliminate cardiac amyloid fibrils, one session chair at the meeting wondered whether NI006 represented the “rise of immunology in cardiology,” and whether biologics might follow.
Another questioned how removing amyloid might affect cardiac function. The echocardiographic findings gathered so far don’t indicate dysfunction, “but this is a small trial, and we need more data,” Dr. Garcia-Pavia said.
Tempered excitement
In a comment, Ronald Witteles, MD, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University, and founder/codirector of the Stanford Amyloid Center, said that “antibody-based amyloid removal strategies are not currently clinically available and represent a fundamentally different mechanism to treat the disease from what we currently have.
“While the data are encouraging and will generate excitement for later-phase studies, we’re talking about small numbers of patients and nothing definitive should be drawn from this data,” said Dr. Witteles, deputy editor of JACC: CardioOncology.
“The biggest caveat is that similar approaches of antibody removal of amyloid deposits for other forms of amyloidosis — most notably AL amyloidosis (amyloid light chain or primary amyloidosis) – have failed in late-phase trials. Although there is reason to believe that ATTR amyloidosis may be more amenable to improvements with amyloid fibril removal than AL amyloidosis, the unimpressive results in other forms of amyloidosis still do temper the excitement to a degree.”
Like Dr. Garcia-Pavia, Dr. Witteles said, “Ultimately, we are going to need to see a phase 3 clinical trial which shows that NI006 – on top of standard-of-care treatment – improves hard outcomes in the disease. As treatment options likely expand in the coming years, that is likely to be a harder and harder bar to reach.”
Furthermore, although the safety profile was favorable overall, it “wasn’t entirely clean,” given cytokine release syndrome in three patients, a lowering of platelet counts in a couple of patients, and musculoskeletal side effects that triggered two to withdraw from the study. “Unless that changes,” he said, “that will be a barrier for some patients.”
Overall, he noted, “With the vast majority of patients being able to be diagnosed noninvasively, and with treatment options now available, we have seen a true explosion in the number of patients being diagnosed.
“But we also know that the large majority ... are still not getting diagnosed or are having huge delays in diagnosis. As such, the biggest thing we can do for patients with the disease is to continue to educate people about it,” Dr. Witteles concluded.
The study was funded by Neurimmune. Dr. Garcia-Pavia disclosed ties to Alexion, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Attralus, BridgeBio, General Electric, Intellia, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Neurimmune, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. Dr. Witteles reported ties to Alexion, Alnylam, AstraZeneca, BridgeBio, Intellia, Ionis, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
Currently, the only drug approved to treat ATTR is tafamidis, which improves survival and reduces hospitalizations, but does not reverse disease symptoms, the authors noted.
NI006 is a recombinant human anti-ATTR antibody given by infusion that was developed to trigger removal of ATTR by the body’s phagocytic immune cells.
Use of the drug was not associated with serious drug-related adverse events, though mild and moderate adverse events did occur.
Median N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and troponin T levels also seemed to be reduced over the study period.
Given the success of the antibody in this initial 40-patient trial, a larger phase-3 placebo-controlled trial is planned and expected to launch in the second half of 2023, said lead author Pablo Garcia-Pavia, MD, of Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro and the Spanish National Cardiovascular Research Institute, Madrid.
However, “The design of appropriate phase-3 trials to demonstrate efficacy of drugs for ATTR-CM is becoming more complicated and challenging,” he said.
“Increased awareness of the disease and advances in cardiac imaging techniques have led to recognition of a larger number of patients with ATTR-CM who have a different clinical profile and a different prognosis than the patients who were diagnosed in previous years and were enrolled in the initial trials of stabilizers,” Dr. Garcia-Pavia added.
“Moreover, the availability of tafamidis, and hopefully soon other medications to treat ATTR-CM has complicated the design of new clinical trials because of the heterogenicity of treatments that patients might receive,” he said. “Therefore, it is critical to plan the design very well.”
Dr. Garcia-Pavia presented the findings on NI006 at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2023 sessions. The study was published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
No serious adverse events
For the phase-1, double-blind, multicenter study, the investigators randomly assigned (2:1 ratio) 40 patients (median age, 72 years; 98% men) with wild-type or variant ATTR cardiomyopathy and chronic heart failure to receive IV infusions of either NI006, at one of six doses ranging from 0.3 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg of body weight, or placebo every 4 weeks for 4 months.
After the four infusions, participants were enrolled in an open-label extension phase in which they received eight NI006 infusions with stepwise increases in the dose.
Participants had a confirmed diagnosis of ATTR-CM; left ventricular wall thickness of at least 14 mm; left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 40%; New York Heart Association class I, II, or III; estimated glomerular filtration rate of more than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2; and an NT-proBNP level of 600 to 6,000 pg/mL.
Most (36) were receiving tafamidis, with a median treatment duration of 7 months; other ATTR-specific drugs were not permitted. Patients randomly assigned to receive NI006 seemed to have more advanced disease compared with those assigned to placebo.
Adherence to the trial protocol was high: Thirty-four patients received the four scheduled infusions during the ascending-dose phase, and 34 of 35 patients who completed this phase subsequently enrolled in the open-label extension.
No apparent drug-related serious adverse events were reported. However, during the ascending-dose phase, 38 patients had at least one adverse event, most of which were mild or moderate; of the 191 total events, 124 were grade 1 and 60 were grade 2 (most commonly heart failure and arrhythmias). Three patients had cytokine release syndrome; all three completed treatment through the extension phase.
Musculoskeletal events increased with ascending doses of NI006, which led two patients to withdraw from the trial.
At doses of at least 10 mg/kg, cardiac tracer uptake on scintigraphy and extracellular volume on cardiac MRI, both of which are imaging-based surrogate markers of cardiac amyloid load, appeared to be reduced over 12 months.
Because NI006 stimulates the patient’s own immune system to eliminate cardiac amyloid fibrils, one session chair at the meeting wondered whether NI006 represented the “rise of immunology in cardiology,” and whether biologics might follow.
Another questioned how removing amyloid might affect cardiac function. The echocardiographic findings gathered so far don’t indicate dysfunction, “but this is a small trial, and we need more data,” Dr. Garcia-Pavia said.
Tempered excitement
In a comment, Ronald Witteles, MD, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University, and founder/codirector of the Stanford Amyloid Center, said that “antibody-based amyloid removal strategies are not currently clinically available and represent a fundamentally different mechanism to treat the disease from what we currently have.
“While the data are encouraging and will generate excitement for later-phase studies, we’re talking about small numbers of patients and nothing definitive should be drawn from this data,” said Dr. Witteles, deputy editor of JACC: CardioOncology.
“The biggest caveat is that similar approaches of antibody removal of amyloid deposits for other forms of amyloidosis — most notably AL amyloidosis (amyloid light chain or primary amyloidosis) – have failed in late-phase trials. Although there is reason to believe that ATTR amyloidosis may be more amenable to improvements with amyloid fibril removal than AL amyloidosis, the unimpressive results in other forms of amyloidosis still do temper the excitement to a degree.”
Like Dr. Garcia-Pavia, Dr. Witteles said, “Ultimately, we are going to need to see a phase 3 clinical trial which shows that NI006 – on top of standard-of-care treatment – improves hard outcomes in the disease. As treatment options likely expand in the coming years, that is likely to be a harder and harder bar to reach.”
Furthermore, although the safety profile was favorable overall, it “wasn’t entirely clean,” given cytokine release syndrome in three patients, a lowering of platelet counts in a couple of patients, and musculoskeletal side effects that triggered two to withdraw from the study. “Unless that changes,” he said, “that will be a barrier for some patients.”
Overall, he noted, “With the vast majority of patients being able to be diagnosed noninvasively, and with treatment options now available, we have seen a true explosion in the number of patients being diagnosed.
“But we also know that the large majority ... are still not getting diagnosed or are having huge delays in diagnosis. As such, the biggest thing we can do for patients with the disease is to continue to educate people about it,” Dr. Witteles concluded.
The study was funded by Neurimmune. Dr. Garcia-Pavia disclosed ties to Alexion, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Attralus, BridgeBio, General Electric, Intellia, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Neurimmune, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. Dr. Witteles reported ties to Alexion, Alnylam, AstraZeneca, BridgeBio, Intellia, Ionis, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, a new study suggests.
Currently, the only drug approved to treat ATTR is tafamidis, which improves survival and reduces hospitalizations, but does not reverse disease symptoms, the authors noted.
NI006 is a recombinant human anti-ATTR antibody given by infusion that was developed to trigger removal of ATTR by the body’s phagocytic immune cells.
Use of the drug was not associated with serious drug-related adverse events, though mild and moderate adverse events did occur.
Median N-terminal pro–B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) and troponin T levels also seemed to be reduced over the study period.
Given the success of the antibody in this initial 40-patient trial, a larger phase-3 placebo-controlled trial is planned and expected to launch in the second half of 2023, said lead author Pablo Garcia-Pavia, MD, of Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro and the Spanish National Cardiovascular Research Institute, Madrid.
However, “The design of appropriate phase-3 trials to demonstrate efficacy of drugs for ATTR-CM is becoming more complicated and challenging,” he said.
“Increased awareness of the disease and advances in cardiac imaging techniques have led to recognition of a larger number of patients with ATTR-CM who have a different clinical profile and a different prognosis than the patients who were diagnosed in previous years and were enrolled in the initial trials of stabilizers,” Dr. Garcia-Pavia added.
“Moreover, the availability of tafamidis, and hopefully soon other medications to treat ATTR-CM has complicated the design of new clinical trials because of the heterogenicity of treatments that patients might receive,” he said. “Therefore, it is critical to plan the design very well.”
Dr. Garcia-Pavia presented the findings on NI006 at the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology (HFA-ESC) 2023 sessions. The study was published simultaneously in the New England Journal of Medicine.
No serious adverse events
For the phase-1, double-blind, multicenter study, the investigators randomly assigned (2:1 ratio) 40 patients (median age, 72 years; 98% men) with wild-type or variant ATTR cardiomyopathy and chronic heart failure to receive IV infusions of either NI006, at one of six doses ranging from 0.3 mg/kg to 60 mg/kg of body weight, or placebo every 4 weeks for 4 months.
After the four infusions, participants were enrolled in an open-label extension phase in which they received eight NI006 infusions with stepwise increases in the dose.
Participants had a confirmed diagnosis of ATTR-CM; left ventricular wall thickness of at least 14 mm; left ventricular ejection fraction of at least 40%; New York Heart Association class I, II, or III; estimated glomerular filtration rate of more than 30 mL/min per 1.73 m2; and an NT-proBNP level of 600 to 6,000 pg/mL.
Most (36) were receiving tafamidis, with a median treatment duration of 7 months; other ATTR-specific drugs were not permitted. Patients randomly assigned to receive NI006 seemed to have more advanced disease compared with those assigned to placebo.
Adherence to the trial protocol was high: Thirty-four patients received the four scheduled infusions during the ascending-dose phase, and 34 of 35 patients who completed this phase subsequently enrolled in the open-label extension.
No apparent drug-related serious adverse events were reported. However, during the ascending-dose phase, 38 patients had at least one adverse event, most of which were mild or moderate; of the 191 total events, 124 were grade 1 and 60 were grade 2 (most commonly heart failure and arrhythmias). Three patients had cytokine release syndrome; all three completed treatment through the extension phase.
Musculoskeletal events increased with ascending doses of NI006, which led two patients to withdraw from the trial.
At doses of at least 10 mg/kg, cardiac tracer uptake on scintigraphy and extracellular volume on cardiac MRI, both of which are imaging-based surrogate markers of cardiac amyloid load, appeared to be reduced over 12 months.
Because NI006 stimulates the patient’s own immune system to eliminate cardiac amyloid fibrils, one session chair at the meeting wondered whether NI006 represented the “rise of immunology in cardiology,” and whether biologics might follow.
Another questioned how removing amyloid might affect cardiac function. The echocardiographic findings gathered so far don’t indicate dysfunction, “but this is a small trial, and we need more data,” Dr. Garcia-Pavia said.
Tempered excitement
In a comment, Ronald Witteles, MD, professor of cardiovascular medicine, Stanford (Calif.) University, and founder/codirector of the Stanford Amyloid Center, said that “antibody-based amyloid removal strategies are not currently clinically available and represent a fundamentally different mechanism to treat the disease from what we currently have.
“While the data are encouraging and will generate excitement for later-phase studies, we’re talking about small numbers of patients and nothing definitive should be drawn from this data,” said Dr. Witteles, deputy editor of JACC: CardioOncology.
“The biggest caveat is that similar approaches of antibody removal of amyloid deposits for other forms of amyloidosis — most notably AL amyloidosis (amyloid light chain or primary amyloidosis) – have failed in late-phase trials. Although there is reason to believe that ATTR amyloidosis may be more amenable to improvements with amyloid fibril removal than AL amyloidosis, the unimpressive results in other forms of amyloidosis still do temper the excitement to a degree.”
Like Dr. Garcia-Pavia, Dr. Witteles said, “Ultimately, we are going to need to see a phase 3 clinical trial which shows that NI006 – on top of standard-of-care treatment – improves hard outcomes in the disease. As treatment options likely expand in the coming years, that is likely to be a harder and harder bar to reach.”
Furthermore, although the safety profile was favorable overall, it “wasn’t entirely clean,” given cytokine release syndrome in three patients, a lowering of platelet counts in a couple of patients, and musculoskeletal side effects that triggered two to withdraw from the study. “Unless that changes,” he said, “that will be a barrier for some patients.”
Overall, he noted, “With the vast majority of patients being able to be diagnosed noninvasively, and with treatment options now available, we have seen a true explosion in the number of patients being diagnosed.
“But we also know that the large majority ... are still not getting diagnosed or are having huge delays in diagnosis. As such, the biggest thing we can do for patients with the disease is to continue to educate people about it,” Dr. Witteles concluded.
The study was funded by Neurimmune. Dr. Garcia-Pavia disclosed ties to Alexion, Alnylam Pharmaceuticals, AstraZeneca, Attralus, BridgeBio, General Electric, Intellia, Ionis Pharmaceuticals, Neurimmune, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer. Dr. Witteles reported ties to Alexion, Alnylam, AstraZeneca, BridgeBio, Intellia, Ionis, Janssen, Novo Nordisk, and Pfizer.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2023
Coronary artery calcium score bests polygenic risk score in CHD prediction
As a predictor of coronary heart disease (CHD) events, the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score on computed tomography had better risk discrimination than the polygenic risk score, a binational study found. And when added to classic cardiovascular risk factors, the CAC score significantly improved risk classification while the polygenic risk factor score did not.
These findings emerged from two large cohorts of middle-aged and older White adults from the United States and the Netherlands in the first head-to-head comparison of these two approaches. Led by Sadiya S. Kahn, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine (cardiology) and preventive medicine (epidemiology) at Northwestern University, Chicago, the study was published online in JAMA.
There has been much interest in using both genetic factors and CT imaging to better identify individuals at risk for heart disease. “Each approach has advantages and disadvantages, and we wanted to better understand the comparative predictive utility to provide support for what the preferred approach should be,” Dr. Kahn said in an interview. “We focused on middle-aged to older adults for whom current risk prediction equations are relevant in estimating risk with the Pooled Cohort Equation, or PCE.”
The superiority of the CT-imaged coronary artery risk score may be because of its direct visualization of calcification in the arteries and the subclinical disease burden rather than a focus on common genetic variants, Dr. Kahn explained. “In addition, prior studies have demonstrated that genetics, or inherited risk, is not destiny, so this score may not perform as well for risk discrimination as the traditional risk factors themselves along with CT.”
The study
Study participants came from the U.S. Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, n = 1,991) and the Dutch Rotterdam Study (RS, n = 1,217). Ages ranged from 45 to 79, with the medians in the two cohorts 61 and 68 years, respectively. Slightly more than half of participants in both groups were female.
Traditional risk factors were used to calculate CHD risk with pooled cohort equations, while computed tomography was used to determine the CAC score and genotyped samples for a validated polygenic risk score.
Both scores were significantly associated with 10-year risk of incident CHD.
The median predicted atherosclerotic disease risk based on traditional risk factors was 6.99% in MESA and 5.93% in RS. During the total available follow-up in MESA (median, 16.0 years) and RS (median, 14.2 years), incident CHD occurred in 187 participants (9.4%) and 98 participants (8.1%), respectively.
C (concordance) statistics for the two scores showed the superiority of the CAC. This statistic measures a model’s ability to rank patients from high to low risk, with a value of 1 being perfect risk fit or concordance and 0.70 or more indicating good concordance and risk discrimination. The CAC score had a C statistic of 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.79) vs. 0.69 for the polygenic risk score (95% CI, 0.63-0.71).
When each score was added to PCEs, the C statistics changed as follows: CAC score, 0.09 (95% CI, 0.06-0.13); polygenic risk score, 0.02 (95% CI, 0.00-0.04); and 0.10 (95% CI, 0.07-0.14) for both.
Net reclassification significantly improved with the CAC plus PCEs by the following values: 0.19 (95% CI, 0.06-0.28). The change was not significant, however, with the polygenic risk score plus PCEs: 0.04 (95% CI, –0.05-0.10).
In the clinical setting, Dr. Kahn said, “The use of CT in patients who are at intermediate risk for heart disease can be helpful in refining risk estimation and guiding recommendations for lipid-lowering therapy. Polygenic risk scores are not helpful in middle-aged to older adults above and beyond traditional risk factors for predicting risk of heart disease.”
This study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. MESA is supported by the NHLBI. The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University Rotterdam; the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research; the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development; the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly; the Netherlands Genomics Initiative; the Ministry of Education, Culture and Science, the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sports; the European Commission (DG XII); and the Municipality of Rotterdam. Dr. Khan reported grants from the NHLBI and the NIH during the study and outside of the submitted work. Several coauthors reported grant support from, variously, the NIH, the NHLBI, and the American Heart Association.
As a predictor of coronary heart disease (CHD) events, the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score on computed tomography had better risk discrimination than the polygenic risk score, a binational study found. And when added to classic cardiovascular risk factors, the CAC score significantly improved risk classification while the polygenic risk factor score did not.
These findings emerged from two large cohorts of middle-aged and older White adults from the United States and the Netherlands in the first head-to-head comparison of these two approaches. Led by Sadiya S. Kahn, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine (cardiology) and preventive medicine (epidemiology) at Northwestern University, Chicago, the study was published online in JAMA.
There has been much interest in using both genetic factors and CT imaging to better identify individuals at risk for heart disease. “Each approach has advantages and disadvantages, and we wanted to better understand the comparative predictive utility to provide support for what the preferred approach should be,” Dr. Kahn said in an interview. “We focused on middle-aged to older adults for whom current risk prediction equations are relevant in estimating risk with the Pooled Cohort Equation, or PCE.”
The superiority of the CT-imaged coronary artery risk score may be because of its direct visualization of calcification in the arteries and the subclinical disease burden rather than a focus on common genetic variants, Dr. Kahn explained. “In addition, prior studies have demonstrated that genetics, or inherited risk, is not destiny, so this score may not perform as well for risk discrimination as the traditional risk factors themselves along with CT.”
The study
Study participants came from the U.S. Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, n = 1,991) and the Dutch Rotterdam Study (RS, n = 1,217). Ages ranged from 45 to 79, with the medians in the two cohorts 61 and 68 years, respectively. Slightly more than half of participants in both groups were female.
Traditional risk factors were used to calculate CHD risk with pooled cohort equations, while computed tomography was used to determine the CAC score and genotyped samples for a validated polygenic risk score.
Both scores were significantly associated with 10-year risk of incident CHD.
The median predicted atherosclerotic disease risk based on traditional risk factors was 6.99% in MESA and 5.93% in RS. During the total available follow-up in MESA (median, 16.0 years) and RS (median, 14.2 years), incident CHD occurred in 187 participants (9.4%) and 98 participants (8.1%), respectively.
C (concordance) statistics for the two scores showed the superiority of the CAC. This statistic measures a model’s ability to rank patients from high to low risk, with a value of 1 being perfect risk fit or concordance and 0.70 or more indicating good concordance and risk discrimination. The CAC score had a C statistic of 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.79) vs. 0.69 for the polygenic risk score (95% CI, 0.63-0.71).
When each score was added to PCEs, the C statistics changed as follows: CAC score, 0.09 (95% CI, 0.06-0.13); polygenic risk score, 0.02 (95% CI, 0.00-0.04); and 0.10 (95% CI, 0.07-0.14) for both.
Net reclassification significantly improved with the CAC plus PCEs by the following values: 0.19 (95% CI, 0.06-0.28). The change was not significant, however, with the polygenic risk score plus PCEs: 0.04 (95% CI, –0.05-0.10).
In the clinical setting, Dr. Kahn said, “The use of CT in patients who are at intermediate risk for heart disease can be helpful in refining risk estimation and guiding recommendations for lipid-lowering therapy. Polygenic risk scores are not helpful in middle-aged to older adults above and beyond traditional risk factors for predicting risk of heart disease.”
This study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. MESA is supported by the NHLBI. The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University Rotterdam; the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research; the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development; the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly; the Netherlands Genomics Initiative; the Ministry of Education, Culture and Science, the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sports; the European Commission (DG XII); and the Municipality of Rotterdam. Dr. Khan reported grants from the NHLBI and the NIH during the study and outside of the submitted work. Several coauthors reported grant support from, variously, the NIH, the NHLBI, and the American Heart Association.
As a predictor of coronary heart disease (CHD) events, the coronary artery calcium (CAC) score on computed tomography had better risk discrimination than the polygenic risk score, a binational study found. And when added to classic cardiovascular risk factors, the CAC score significantly improved risk classification while the polygenic risk factor score did not.
These findings emerged from two large cohorts of middle-aged and older White adults from the United States and the Netherlands in the first head-to-head comparison of these two approaches. Led by Sadiya S. Kahn, MD, MSc, an assistant professor of medicine (cardiology) and preventive medicine (epidemiology) at Northwestern University, Chicago, the study was published online in JAMA.
There has been much interest in using both genetic factors and CT imaging to better identify individuals at risk for heart disease. “Each approach has advantages and disadvantages, and we wanted to better understand the comparative predictive utility to provide support for what the preferred approach should be,” Dr. Kahn said in an interview. “We focused on middle-aged to older adults for whom current risk prediction equations are relevant in estimating risk with the Pooled Cohort Equation, or PCE.”
The superiority of the CT-imaged coronary artery risk score may be because of its direct visualization of calcification in the arteries and the subclinical disease burden rather than a focus on common genetic variants, Dr. Kahn explained. “In addition, prior studies have demonstrated that genetics, or inherited risk, is not destiny, so this score may not perform as well for risk discrimination as the traditional risk factors themselves along with CT.”
The study
Study participants came from the U.S. Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis (MESA, n = 1,991) and the Dutch Rotterdam Study (RS, n = 1,217). Ages ranged from 45 to 79, with the medians in the two cohorts 61 and 68 years, respectively. Slightly more than half of participants in both groups were female.
Traditional risk factors were used to calculate CHD risk with pooled cohort equations, while computed tomography was used to determine the CAC score and genotyped samples for a validated polygenic risk score.
Both scores were significantly associated with 10-year risk of incident CHD.
The median predicted atherosclerotic disease risk based on traditional risk factors was 6.99% in MESA and 5.93% in RS. During the total available follow-up in MESA (median, 16.0 years) and RS (median, 14.2 years), incident CHD occurred in 187 participants (9.4%) and 98 participants (8.1%), respectively.
C (concordance) statistics for the two scores showed the superiority of the CAC. This statistic measures a model’s ability to rank patients from high to low risk, with a value of 1 being perfect risk fit or concordance and 0.70 or more indicating good concordance and risk discrimination. The CAC score had a C statistic of 0.76 (95% confidence interval, 0.71-0.79) vs. 0.69 for the polygenic risk score (95% CI, 0.63-0.71).
When each score was added to PCEs, the C statistics changed as follows: CAC score, 0.09 (95% CI, 0.06-0.13); polygenic risk score, 0.02 (95% CI, 0.00-0.04); and 0.10 (95% CI, 0.07-0.14) for both.
Net reclassification significantly improved with the CAC plus PCEs by the following values: 0.19 (95% CI, 0.06-0.28). The change was not significant, however, with the polygenic risk score plus PCEs: 0.04 (95% CI, –0.05-0.10).
In the clinical setting, Dr. Kahn said, “The use of CT in patients who are at intermediate risk for heart disease can be helpful in refining risk estimation and guiding recommendations for lipid-lowering therapy. Polygenic risk scores are not helpful in middle-aged to older adults above and beyond traditional risk factors for predicting risk of heart disease.”
This study was supported by the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. MESA is supported by the NHLBI. The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and Erasmus University Rotterdam; the Netherlands Organization for Scientific Research; the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development; the Research Institute for Diseases in the Elderly; the Netherlands Genomics Initiative; the Ministry of Education, Culture and Science, the Ministry of Health, Welfare and Sports; the European Commission (DG XII); and the Municipality of Rotterdam. Dr. Khan reported grants from the NHLBI and the NIH during the study and outside of the submitted work. Several coauthors reported grant support from, variously, the NIH, the NHLBI, and the American Heart Association.
FROM JAMA
Noninferior to DES, novel bioadaptable stent may improve target vessel physiology
Stent is not a “me-too” device
Moving in a very different direction from past coronary stent designs, at 12 months in a randomized controlled trial.
“The device restored vessel motion, which we think is the reason that we saw plaque stabilization and regression,” reported Shigero Saito, MD, director of the catheterization laboratory at Shonan Kamakura (Japan) General Hospital.
The principal features of the bioadaptable design are cobalt-chromium metal helical strands to provide indefinite scaffolding support coupled with a biodegradable sirolimus-containing poly(D,L-lacti-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) topcoat and a biodegradable poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) bottom coat to “uncage” the vessel once these materials are resorbed, said Dr. Saito.
Twelve-month data from the randomized BIOADAPTOR trial, presented as a late breaker at the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions, provide the first evidence that this uncaging of the vessel is an advantage.
Compared head-to-head in a contemporary drug-eluting stent (DES) in a randomized trial, the bioadaptable stent, as predicted in prior studies, “improved hemodynamics and supported plaque stabilization and positive remodeling,” said Dr. Saito.
In BIOADAPTOR, 445 patients in Japan, Germany, Belgium, and New Zealand were randomized to the novel stent, called DynamX, or to the Resolute Onyx. The trial has a planned follow-up of 5 years.
While the primary endpoint at 12 months was noninferiority for target lesion failure (TLF), it was a series of secondary imaging endpoints that suggest an important impact of uncaging the vessel. This includes better vessel function potentially relevant to resistance to restenosis.
As a result of numerically lower TLF in the DynamX group (1.8% vs. 2.8%), the new device easily demonstrated noninferiority at a high level of significance (P < .001). A numerical advantage for most events, including cardiovascular death (0% vs. 0.9%) and target-vessel myocardial infarction (1.4% vs. 1.9%), favored the novel device, but event rates were low in both arms and none of these differences were statistically significant.
However, the secondary imaging analyses at 12 months suggested major differences between the two devices from “uncaging” the vessel.
These differences included a highly significant improvement at 12 months in vessel pulsatility (P < .001) within the DynamX stent relative to the Onyx stent in all measured segments (proximal, mid, and distal).
In addition, compliance remained suppressed relative to both the proximal (P < .001) and distal (P < .001) vessels of patients fitted with Onyx device. Conversely, there was no significant relative difference in this measure among those fitted with the DynamX device.
At 12 months, the plaque volume change behind the stent of noncalcified lesions increased 9% in the Onyx group but was reduced 4% in the DynamX group (P = .028).
While there was a 13% gain overall in percent diameter stenosis within the stent of patients receiving the DynamX device, it was consistently lower than that observed in the Onyx group. This difference was only a trend overall (12.7% vs. 17.3%; P = .051), but the advantage reached significance, favoring DynamX, for the left anterior descending (LAD) artery (12.1% vs. 19.0%; P = .006), small vessels (13.0% vs. 18.3%; P = .045), and long lesions (13.0% vs. 22.9%; P = .008).
The same relative advantage for DynamX was seen on late lumen loss at 6 months. In this case, the overall advantage of DynamX (0.09 vs. 0.25; P = .038) did reach significance, and there was an advantage for the LAD (–0.02 vs. 0.24; P = .007) and long lesions (–0.06 vs. 0.38; P = .016). The difference did not reach significance for small vessels (0.08 vs. 0.26; P = .121).
All of these advantages on the secondary endpoints can be directly attributed to the effect of uncaging the vessel, according to Dr. Saito, who said this new design “addresses the shortcomings” of both previous drug-eluting and biodegradable stents.
Pointing out that the nonplateauing of late events has persisted regardless of stent design after “more than 20 years of innovation in design and materials,” Dr. Saito said all current stents have weaknesses. While biodegradable stents have not improved long-term outcomes relative to DES “as a result of loss of long-term vessel dynamic support,” DES are flawed due to “permanent caging of the vessel and loss of vessel motion and function.”
This novel hybrid design, employing both metal and biodegradable components, “is a completely different concept,” said Ron Waksman, MD, associate director, division of cardiology, Medstar Hospital Center, Washington. He was particularly impressed by the improvements in pulsatility and compliance in target vessels along with the favorable effects on plaque volume.
“The reduction in plaque volume is something we have not seen before. Usually we see the opposite,” Dr. Waksman said.
“Clearly, the Bioadaptor device is not a me-too stent,” he said. He was not surprised that there was no difference in hard outcomes given both the small sample size and the fact that the advantages of uncaging the vessel are likely to accrue over time.
“We need to look at what happens after 1 year. We still have not seen the potential of this device,” he said, adding he was “impressed” by the features of this novel concept. However, he suggested the advantages remain theoretical from the clinical standpoint, advising Dr. Saito that “you still need to demonstrate the clinical benefits.”
Dr. Saito reports a financial relationship with Elixir Medical, which funded the BIOADAPTOR trial. Dr. Waksman reports financial relationships with 19 pharmaceutical companies including those that manufacture cardiovascular stents.
Stent is not a “me-too” device
Stent is not a “me-too” device
Moving in a very different direction from past coronary stent designs, at 12 months in a randomized controlled trial.
“The device restored vessel motion, which we think is the reason that we saw plaque stabilization and regression,” reported Shigero Saito, MD, director of the catheterization laboratory at Shonan Kamakura (Japan) General Hospital.
The principal features of the bioadaptable design are cobalt-chromium metal helical strands to provide indefinite scaffolding support coupled with a biodegradable sirolimus-containing poly(D,L-lacti-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) topcoat and a biodegradable poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) bottom coat to “uncage” the vessel once these materials are resorbed, said Dr. Saito.
Twelve-month data from the randomized BIOADAPTOR trial, presented as a late breaker at the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions, provide the first evidence that this uncaging of the vessel is an advantage.
Compared head-to-head in a contemporary drug-eluting stent (DES) in a randomized trial, the bioadaptable stent, as predicted in prior studies, “improved hemodynamics and supported plaque stabilization and positive remodeling,” said Dr. Saito.
In BIOADAPTOR, 445 patients in Japan, Germany, Belgium, and New Zealand were randomized to the novel stent, called DynamX, or to the Resolute Onyx. The trial has a planned follow-up of 5 years.
While the primary endpoint at 12 months was noninferiority for target lesion failure (TLF), it was a series of secondary imaging endpoints that suggest an important impact of uncaging the vessel. This includes better vessel function potentially relevant to resistance to restenosis.
As a result of numerically lower TLF in the DynamX group (1.8% vs. 2.8%), the new device easily demonstrated noninferiority at a high level of significance (P < .001). A numerical advantage for most events, including cardiovascular death (0% vs. 0.9%) and target-vessel myocardial infarction (1.4% vs. 1.9%), favored the novel device, but event rates were low in both arms and none of these differences were statistically significant.
However, the secondary imaging analyses at 12 months suggested major differences between the two devices from “uncaging” the vessel.
These differences included a highly significant improvement at 12 months in vessel pulsatility (P < .001) within the DynamX stent relative to the Onyx stent in all measured segments (proximal, mid, and distal).
In addition, compliance remained suppressed relative to both the proximal (P < .001) and distal (P < .001) vessels of patients fitted with Onyx device. Conversely, there was no significant relative difference in this measure among those fitted with the DynamX device.
At 12 months, the plaque volume change behind the stent of noncalcified lesions increased 9% in the Onyx group but was reduced 4% in the DynamX group (P = .028).
While there was a 13% gain overall in percent diameter stenosis within the stent of patients receiving the DynamX device, it was consistently lower than that observed in the Onyx group. This difference was only a trend overall (12.7% vs. 17.3%; P = .051), but the advantage reached significance, favoring DynamX, for the left anterior descending (LAD) artery (12.1% vs. 19.0%; P = .006), small vessels (13.0% vs. 18.3%; P = .045), and long lesions (13.0% vs. 22.9%; P = .008).
The same relative advantage for DynamX was seen on late lumen loss at 6 months. In this case, the overall advantage of DynamX (0.09 vs. 0.25; P = .038) did reach significance, and there was an advantage for the LAD (–0.02 vs. 0.24; P = .007) and long lesions (–0.06 vs. 0.38; P = .016). The difference did not reach significance for small vessels (0.08 vs. 0.26; P = .121).
All of these advantages on the secondary endpoints can be directly attributed to the effect of uncaging the vessel, according to Dr. Saito, who said this new design “addresses the shortcomings” of both previous drug-eluting and biodegradable stents.
Pointing out that the nonplateauing of late events has persisted regardless of stent design after “more than 20 years of innovation in design and materials,” Dr. Saito said all current stents have weaknesses. While biodegradable stents have not improved long-term outcomes relative to DES “as a result of loss of long-term vessel dynamic support,” DES are flawed due to “permanent caging of the vessel and loss of vessel motion and function.”
This novel hybrid design, employing both metal and biodegradable components, “is a completely different concept,” said Ron Waksman, MD, associate director, division of cardiology, Medstar Hospital Center, Washington. He was particularly impressed by the improvements in pulsatility and compliance in target vessels along with the favorable effects on plaque volume.
“The reduction in plaque volume is something we have not seen before. Usually we see the opposite,” Dr. Waksman said.
“Clearly, the Bioadaptor device is not a me-too stent,” he said. He was not surprised that there was no difference in hard outcomes given both the small sample size and the fact that the advantages of uncaging the vessel are likely to accrue over time.
“We need to look at what happens after 1 year. We still have not seen the potential of this device,” he said, adding he was “impressed” by the features of this novel concept. However, he suggested the advantages remain theoretical from the clinical standpoint, advising Dr. Saito that “you still need to demonstrate the clinical benefits.”
Dr. Saito reports a financial relationship with Elixir Medical, which funded the BIOADAPTOR trial. Dr. Waksman reports financial relationships with 19 pharmaceutical companies including those that manufacture cardiovascular stents.
Moving in a very different direction from past coronary stent designs, at 12 months in a randomized controlled trial.
“The device restored vessel motion, which we think is the reason that we saw plaque stabilization and regression,” reported Shigero Saito, MD, director of the catheterization laboratory at Shonan Kamakura (Japan) General Hospital.
The principal features of the bioadaptable design are cobalt-chromium metal helical strands to provide indefinite scaffolding support coupled with a biodegradable sirolimus-containing poly(D,L-lacti-co-glycolic acid) (PLGA) topcoat and a biodegradable poly-L-lactic acid (PLLA) bottom coat to “uncage” the vessel once these materials are resorbed, said Dr. Saito.
Twelve-month data from the randomized BIOADAPTOR trial, presented as a late breaker at the annual meeting of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions, provide the first evidence that this uncaging of the vessel is an advantage.
Compared head-to-head in a contemporary drug-eluting stent (DES) in a randomized trial, the bioadaptable stent, as predicted in prior studies, “improved hemodynamics and supported plaque stabilization and positive remodeling,” said Dr. Saito.
In BIOADAPTOR, 445 patients in Japan, Germany, Belgium, and New Zealand were randomized to the novel stent, called DynamX, or to the Resolute Onyx. The trial has a planned follow-up of 5 years.
While the primary endpoint at 12 months was noninferiority for target lesion failure (TLF), it was a series of secondary imaging endpoints that suggest an important impact of uncaging the vessel. This includes better vessel function potentially relevant to resistance to restenosis.
As a result of numerically lower TLF in the DynamX group (1.8% vs. 2.8%), the new device easily demonstrated noninferiority at a high level of significance (P < .001). A numerical advantage for most events, including cardiovascular death (0% vs. 0.9%) and target-vessel myocardial infarction (1.4% vs. 1.9%), favored the novel device, but event rates were low in both arms and none of these differences were statistically significant.
However, the secondary imaging analyses at 12 months suggested major differences between the two devices from “uncaging” the vessel.
These differences included a highly significant improvement at 12 months in vessel pulsatility (P < .001) within the DynamX stent relative to the Onyx stent in all measured segments (proximal, mid, and distal).
In addition, compliance remained suppressed relative to both the proximal (P < .001) and distal (P < .001) vessels of patients fitted with Onyx device. Conversely, there was no significant relative difference in this measure among those fitted with the DynamX device.
At 12 months, the plaque volume change behind the stent of noncalcified lesions increased 9% in the Onyx group but was reduced 4% in the DynamX group (P = .028).
While there was a 13% gain overall in percent diameter stenosis within the stent of patients receiving the DynamX device, it was consistently lower than that observed in the Onyx group. This difference was only a trend overall (12.7% vs. 17.3%; P = .051), but the advantage reached significance, favoring DynamX, for the left anterior descending (LAD) artery (12.1% vs. 19.0%; P = .006), small vessels (13.0% vs. 18.3%; P = .045), and long lesions (13.0% vs. 22.9%; P = .008).
The same relative advantage for DynamX was seen on late lumen loss at 6 months. In this case, the overall advantage of DynamX (0.09 vs. 0.25; P = .038) did reach significance, and there was an advantage for the LAD (–0.02 vs. 0.24; P = .007) and long lesions (–0.06 vs. 0.38; P = .016). The difference did not reach significance for small vessels (0.08 vs. 0.26; P = .121).
All of these advantages on the secondary endpoints can be directly attributed to the effect of uncaging the vessel, according to Dr. Saito, who said this new design “addresses the shortcomings” of both previous drug-eluting and biodegradable stents.
Pointing out that the nonplateauing of late events has persisted regardless of stent design after “more than 20 years of innovation in design and materials,” Dr. Saito said all current stents have weaknesses. While biodegradable stents have not improved long-term outcomes relative to DES “as a result of loss of long-term vessel dynamic support,” DES are flawed due to “permanent caging of the vessel and loss of vessel motion and function.”
This novel hybrid design, employing both metal and biodegradable components, “is a completely different concept,” said Ron Waksman, MD, associate director, division of cardiology, Medstar Hospital Center, Washington. He was particularly impressed by the improvements in pulsatility and compliance in target vessels along with the favorable effects on plaque volume.
“The reduction in plaque volume is something we have not seen before. Usually we see the opposite,” Dr. Waksman said.
“Clearly, the Bioadaptor device is not a me-too stent,” he said. He was not surprised that there was no difference in hard outcomes given both the small sample size and the fact that the advantages of uncaging the vessel are likely to accrue over time.
“We need to look at what happens after 1 year. We still have not seen the potential of this device,” he said, adding he was “impressed” by the features of this novel concept. However, he suggested the advantages remain theoretical from the clinical standpoint, advising Dr. Saito that “you still need to demonstrate the clinical benefits.”
Dr. Saito reports a financial relationship with Elixir Medical, which funded the BIOADAPTOR trial. Dr. Waksman reports financial relationships with 19 pharmaceutical companies including those that manufacture cardiovascular stents.
FROM EUROPCR 2023