User login
Ultrasound’s role in detecting enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis remains debatable
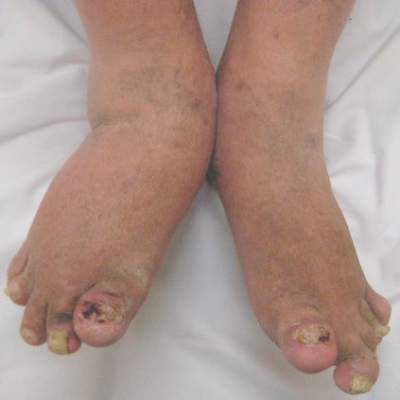
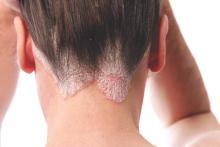
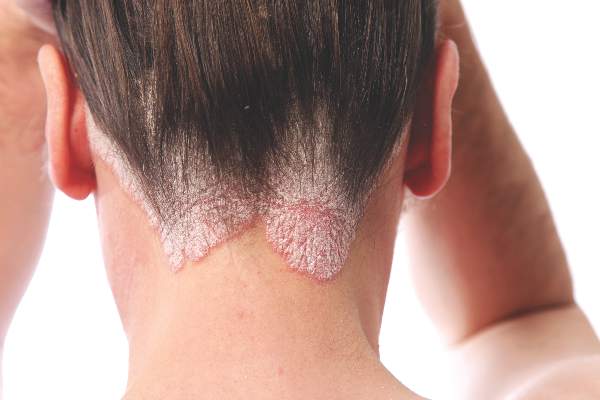
MIAMI – Ultrasound-detected enthesitis was associated with both destructive and bone formation lesions on radiography of peripheral and axial joints in a study of 222 patients with psoriatic arthritis. But its lack of correlation to clinically detected enthesitis in this study and in others has made its clinical usefulness somewhat controversial.
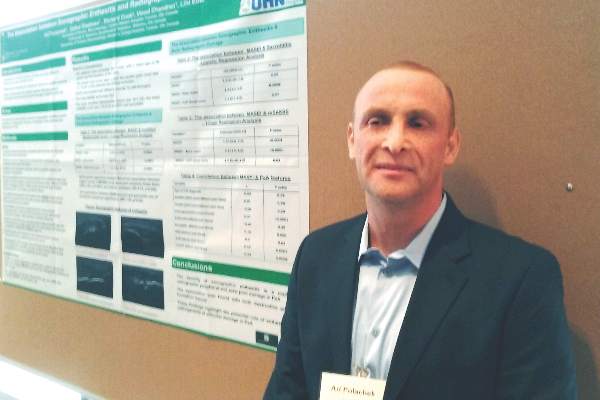
“This is not first time we see this result in the literature,” Ari Polachek, MD, said when presenting the research at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA). The findings suggest ultrasound reveals something different than a physical examination does, and because it’s more sensitive and specific, ultrasound is more accurate, he said.
Diagnostic disagreement
Some differing opinions arose during a discussion after Dr. Polachek’s presentation. “When you look at the enthesitis measures [with ultrasound] ... you don’t necessarily measure the same enthesitis points you measure in clinical practice,” said Dafna D. Gladman, MD, a senior scientist at Toronto Western Hospital’s Krembil Research Institute and a rheumatologist at the University of Toronto. “We have to be careful. I don’t think we should immediately cancel the relationship between the ultrasound and clinical exam.”
“Well, I disagree entirely,” said Philip Helliwell, DM, PhD, senior lecturer in rheumatology at the University of Leeds, England, and president of GRAPPA. “We have looked at the Leeds [Enthesitis Index] with ultrasound and MRI and found no significant relationship at all.” Although Dr. Helliwell said there is a possible role for ultrasound to detect enthesitis in the Achilles, “We are fooling ourselves if we are measuring enthesitis as a pathologic entity. I don’t really know what we’re measuring when we do these scores.”
“My message is you do not need to scan every patient,” Dr. Polachek said in an interview. If a physician remains unsure about the physical exam results, it can be useful. Dr. Polachek, who completed his medical training in Israel, added: “In Israel, we say that ultrasound is ‘the final judge.’ ”
Association with radiographic joint findings
The investigators achieved their study aim: demonstrating that the severity of sonographic enthesitis is a marker of radiographic peripheral and axial joint damage in psoriatic arthritis. They found an association for both destructive and bone formation lesions.
“These findings highlight the potential role of enthesitis in the pathogenesis of articular damage in psoriatic arthritis,” said Dr. Polachek, clinical and research fellow at the University of Toronto.
The researchers assessed 12 entheseal sites with ultrasound. They used the Madrid Sonography Enthesitis Index scoring system (MASEI) to determine the global extent of enthesitis in each patient. In addition, they used the modified Steinbrocker score to assess peripheral joint damage, and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) to assess spinal damage. Patients also underwent a clinical exam and were asked about their medical history.
Multivariate analysis revealed a significant association between higher MASEI score and joint ankylosis (odds ratio, 2.09; P = .0001) and arthritis mutilans (OR, 1.73; P = .005). The total MASEI score was associated with the modified Steinbrocker score (OR, 9.3; P less than .0001) in a logistic regression analysis; total MASEI also significantly correlated with the mSASSS measure of spinal damage (OR, 1.55; P less than .0001) in a linear regression analysis.
Participants had a mean age of 56 years and a 17-year mean duration of psoriatic arthritis. They presented with a mean of 2.4 tender joints and 1.1 swollen joints. At study entry, their mean scores were 15.6 on MASEI, 18.1 on modified Steinbrocker, and 1.72 on mSASSS.
The strengths of the study included a large number of participants and control of multiple possible confounders (age, sex, body mass index, duration of psoriatic arthritis, and use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologics). It is limited by its cross-sectional design, which rules out inferences of causality.
Clinical confirmation
“Traditionally, patients came in with a tender joint, and we might not see anything. Now I can put the sensor down and say they have inflammation,” Dr. Polachek said. In such cases, he may suggest more aggressive treatment. However, if an asymptomatic patient has ultrasound findings, “right now the recommendation is not to do anything. Otherwise, it could be overtreatment.”
“This is the future,” Dr. Polachek said. “I started doing ultrasound myself – it’s a game changer.”
Dr. Polachek has received funding from Janssen and the Krembil Research Institute.
MIAMI – Ultrasound-detected enthesitis was associated with both destructive and bone formation lesions on radiography of peripheral and axial joints in a study of 222 patients with psoriatic arthritis. But its lack of correlation to clinically detected enthesitis in this study and in others has made its clinical usefulness somewhat controversial.
“This is not first time we see this result in the literature,” Ari Polachek, MD, said when presenting the research at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA). The findings suggest ultrasound reveals something different than a physical examination does, and because it’s more sensitive and specific, ultrasound is more accurate, he said.
Diagnostic disagreement
Some differing opinions arose during a discussion after Dr. Polachek’s presentation. “When you look at the enthesitis measures [with ultrasound] ... you don’t necessarily measure the same enthesitis points you measure in clinical practice,” said Dafna D. Gladman, MD, a senior scientist at Toronto Western Hospital’s Krembil Research Institute and a rheumatologist at the University of Toronto. “We have to be careful. I don’t think we should immediately cancel the relationship between the ultrasound and clinical exam.”
“Well, I disagree entirely,” said Philip Helliwell, DM, PhD, senior lecturer in rheumatology at the University of Leeds, England, and president of GRAPPA. “We have looked at the Leeds [Enthesitis Index] with ultrasound and MRI and found no significant relationship at all.” Although Dr. Helliwell said there is a possible role for ultrasound to detect enthesitis in the Achilles, “We are fooling ourselves if we are measuring enthesitis as a pathologic entity. I don’t really know what we’re measuring when we do these scores.”
“My message is you do not need to scan every patient,” Dr. Polachek said in an interview. If a physician remains unsure about the physical exam results, it can be useful. Dr. Polachek, who completed his medical training in Israel, added: “In Israel, we say that ultrasound is ‘the final judge.’ ”
Association with radiographic joint findings
The investigators achieved their study aim: demonstrating that the severity of sonographic enthesitis is a marker of radiographic peripheral and axial joint damage in psoriatic arthritis. They found an association for both destructive and bone formation lesions.
“These findings highlight the potential role of enthesitis in the pathogenesis of articular damage in psoriatic arthritis,” said Dr. Polachek, clinical and research fellow at the University of Toronto.
The researchers assessed 12 entheseal sites with ultrasound. They used the Madrid Sonography Enthesitis Index scoring system (MASEI) to determine the global extent of enthesitis in each patient. In addition, they used the modified Steinbrocker score to assess peripheral joint damage, and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) to assess spinal damage. Patients also underwent a clinical exam and were asked about their medical history.
Multivariate analysis revealed a significant association between higher MASEI score and joint ankylosis (odds ratio, 2.09; P = .0001) and arthritis mutilans (OR, 1.73; P = .005). The total MASEI score was associated with the modified Steinbrocker score (OR, 9.3; P less than .0001) in a logistic regression analysis; total MASEI also significantly correlated with the mSASSS measure of spinal damage (OR, 1.55; P less than .0001) in a linear regression analysis.
Participants had a mean age of 56 years and a 17-year mean duration of psoriatic arthritis. They presented with a mean of 2.4 tender joints and 1.1 swollen joints. At study entry, their mean scores were 15.6 on MASEI, 18.1 on modified Steinbrocker, and 1.72 on mSASSS.
The strengths of the study included a large number of participants and control of multiple possible confounders (age, sex, body mass index, duration of psoriatic arthritis, and use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologics). It is limited by its cross-sectional design, which rules out inferences of causality.
Clinical confirmation
“Traditionally, patients came in with a tender joint, and we might not see anything. Now I can put the sensor down and say they have inflammation,” Dr. Polachek said. In such cases, he may suggest more aggressive treatment. However, if an asymptomatic patient has ultrasound findings, “right now the recommendation is not to do anything. Otherwise, it could be overtreatment.”
“This is the future,” Dr. Polachek said. “I started doing ultrasound myself – it’s a game changer.”
Dr. Polachek has received funding from Janssen and the Krembil Research Institute.
MIAMI – Ultrasound-detected enthesitis was associated with both destructive and bone formation lesions on radiography of peripheral and axial joints in a study of 222 patients with psoriatic arthritis. But its lack of correlation to clinically detected enthesitis in this study and in others has made its clinical usefulness somewhat controversial.
“This is not first time we see this result in the literature,” Ari Polachek, MD, said when presenting the research at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA). The findings suggest ultrasound reveals something different than a physical examination does, and because it’s more sensitive and specific, ultrasound is more accurate, he said.
Diagnostic disagreement
Some differing opinions arose during a discussion after Dr. Polachek’s presentation. “When you look at the enthesitis measures [with ultrasound] ... you don’t necessarily measure the same enthesitis points you measure in clinical practice,” said Dafna D. Gladman, MD, a senior scientist at Toronto Western Hospital’s Krembil Research Institute and a rheumatologist at the University of Toronto. “We have to be careful. I don’t think we should immediately cancel the relationship between the ultrasound and clinical exam.”
“Well, I disagree entirely,” said Philip Helliwell, DM, PhD, senior lecturer in rheumatology at the University of Leeds, England, and president of GRAPPA. “We have looked at the Leeds [Enthesitis Index] with ultrasound and MRI and found no significant relationship at all.” Although Dr. Helliwell said there is a possible role for ultrasound to detect enthesitis in the Achilles, “We are fooling ourselves if we are measuring enthesitis as a pathologic entity. I don’t really know what we’re measuring when we do these scores.”
“My message is you do not need to scan every patient,” Dr. Polachek said in an interview. If a physician remains unsure about the physical exam results, it can be useful. Dr. Polachek, who completed his medical training in Israel, added: “In Israel, we say that ultrasound is ‘the final judge.’ ”
Association with radiographic joint findings
The investigators achieved their study aim: demonstrating that the severity of sonographic enthesitis is a marker of radiographic peripheral and axial joint damage in psoriatic arthritis. They found an association for both destructive and bone formation lesions.
“These findings highlight the potential role of enthesitis in the pathogenesis of articular damage in psoriatic arthritis,” said Dr. Polachek, clinical and research fellow at the University of Toronto.
The researchers assessed 12 entheseal sites with ultrasound. They used the Madrid Sonography Enthesitis Index scoring system (MASEI) to determine the global extent of enthesitis in each patient. In addition, they used the modified Steinbrocker score to assess peripheral joint damage, and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) to assess spinal damage. Patients also underwent a clinical exam and were asked about their medical history.
Multivariate analysis revealed a significant association between higher MASEI score and joint ankylosis (odds ratio, 2.09; P = .0001) and arthritis mutilans (OR, 1.73; P = .005). The total MASEI score was associated with the modified Steinbrocker score (OR, 9.3; P less than .0001) in a logistic regression analysis; total MASEI also significantly correlated with the mSASSS measure of spinal damage (OR, 1.55; P less than .0001) in a linear regression analysis.
Participants had a mean age of 56 years and a 17-year mean duration of psoriatic arthritis. They presented with a mean of 2.4 tender joints and 1.1 swollen joints. At study entry, their mean scores were 15.6 on MASEI, 18.1 on modified Steinbrocker, and 1.72 on mSASSS.
The strengths of the study included a large number of participants and control of multiple possible confounders (age, sex, body mass index, duration of psoriatic arthritis, and use of disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs and biologics). It is limited by its cross-sectional design, which rules out inferences of causality.
Clinical confirmation
“Traditionally, patients came in with a tender joint, and we might not see anything. Now I can put the sensor down and say they have inflammation,” Dr. Polachek said. In such cases, he may suggest more aggressive treatment. However, if an asymptomatic patient has ultrasound findings, “right now the recommendation is not to do anything. Otherwise, it could be overtreatment.”
“This is the future,” Dr. Polachek said. “I started doing ultrasound myself – it’s a game changer.”
Dr. Polachek has received funding from Janssen and the Krembil Research Institute.
AT 2016 GRAPPA
Key clinical point: Ultrasound can diagnose enthesitis in psoriatic arthritis, but findings differ from physical exam.
Major finding: Multivariate analysis revealed a significant association between higher MASEI score and joint ankylosis (OR, 2.09; P = .0001) and arthritis mutilans (OR, 1.73; P = .005).
Data source: Cross-sectional study of 222 patients with psoriatic arthritis.
Disclosures: Dr. Polachek has received funding from Janssen and the Krembil Research Institute.
Psoriatic flare assessment tool in validation stage
MIAMI – Reaching a consensus on measurement and assessment of flare in psoriatic arthritis remains challenging, especially with no widely accepted definition and differing opinions among patients and physicians. But getting standard evaluation of flare under control is critical for both clinical and research outcomes.
Through a series of patient interviews, physician surveys, and lessons learned in rheumatoid arthritis, the GRAPPA Flare Project is close to a validated flare instrument. A 10-question flare assessment tool is now in the final validation stage, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Flare is a clearly personal experience and varies from patient to patient. It’s clear that physicians and patients have clearly different ideas of what flare is. Bringing those two worlds together was a challenge,” Philip Helliwell, MD, of Leeds (England) University and GRAPPA president, said at the meeting.
“Some societies – I’m not going to mention any names – have gone down the route of a definition of flare linked to disease activity measures. We have not done this,” Dr. Helliwell said.
Instead, the Flare Project is taking a patient-driven and physician-reviewed approach. Investigators cast a wide net, identifying 79 factors important to patients in six major domains: skin, joint, emotional, participation, fatigue, and unclassified. The results were published in 2015 (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2015 Aug;54[8]:1448-53). Through a Delphi survey, physicians reviewed these considerations. Then GRAPPA identified items important to both patients and physicians and developed a preliminary flare instrument.
Unlike most assessment tools for psoriatic disease, the new instrument includes patient-reported emotional well-being. Niti Goel, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said that physicians do not always ask patients about the psychological impact of their disease, so the tool “could provide additional information.”
Another goal of the project is to provide standard answers to some of the common questions related to psoriatic arthritis, including: What exactly is a flare? Does the definition truly capture the worsening of disease? Are there different types of flares? Is flare different if you start from a point of high disease activity? What self-management and other interventions are effective for flare?
GRAPPA adopted a definition of flare developed from rheumatoid arthritis, stating that flare is any worsening of disease activity that would, if persistent, in most cases lead to initiation or change of therapy (J Rheumatol. 2009 Oct;36[10]:2335-41).
“It took [them] some time to get to that definition,” Dr. Helliwell said. “We know from rheumatoid arthritis that there is a lot more to a flare than joint swelling and pain.”
The GRAPPA flare tool is now in the validation stage, Dr. Helliwell said, and will be tested in several studies, including a prospective multicenter study where the 10-item questionnaire will be administered to patients.
A meeting attendee commented that the patient and physician global scales are sufficient and asked: “Is there really a need for a flare instrument?”
“I accept what you are saying, but I would also retort that knowledge is power, and the more information we get, the more we know about what we are doing,” Dr. Helliwell said. “We are going to collect all our information – physician global, patient global, composite disease measures – everything within that study.”
Dr. Helliwell and Dr. Goel reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
MIAMI – Reaching a consensus on measurement and assessment of flare in psoriatic arthritis remains challenging, especially with no widely accepted definition and differing opinions among patients and physicians. But getting standard evaluation of flare under control is critical for both clinical and research outcomes.
Through a series of patient interviews, physician surveys, and lessons learned in rheumatoid arthritis, the GRAPPA Flare Project is close to a validated flare instrument. A 10-question flare assessment tool is now in the final validation stage, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Flare is a clearly personal experience and varies from patient to patient. It’s clear that physicians and patients have clearly different ideas of what flare is. Bringing those two worlds together was a challenge,” Philip Helliwell, MD, of Leeds (England) University and GRAPPA president, said at the meeting.
“Some societies – I’m not going to mention any names – have gone down the route of a definition of flare linked to disease activity measures. We have not done this,” Dr. Helliwell said.
Instead, the Flare Project is taking a patient-driven and physician-reviewed approach. Investigators cast a wide net, identifying 79 factors important to patients in six major domains: skin, joint, emotional, participation, fatigue, and unclassified. The results were published in 2015 (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2015 Aug;54[8]:1448-53). Through a Delphi survey, physicians reviewed these considerations. Then GRAPPA identified items important to both patients and physicians and developed a preliminary flare instrument.
Unlike most assessment tools for psoriatic disease, the new instrument includes patient-reported emotional well-being. Niti Goel, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said that physicians do not always ask patients about the psychological impact of their disease, so the tool “could provide additional information.”
Another goal of the project is to provide standard answers to some of the common questions related to psoriatic arthritis, including: What exactly is a flare? Does the definition truly capture the worsening of disease? Are there different types of flares? Is flare different if you start from a point of high disease activity? What self-management and other interventions are effective for flare?
GRAPPA adopted a definition of flare developed from rheumatoid arthritis, stating that flare is any worsening of disease activity that would, if persistent, in most cases lead to initiation or change of therapy (J Rheumatol. 2009 Oct;36[10]:2335-41).
“It took [them] some time to get to that definition,” Dr. Helliwell said. “We know from rheumatoid arthritis that there is a lot more to a flare than joint swelling and pain.”
The GRAPPA flare tool is now in the validation stage, Dr. Helliwell said, and will be tested in several studies, including a prospective multicenter study where the 10-item questionnaire will be administered to patients.
A meeting attendee commented that the patient and physician global scales are sufficient and asked: “Is there really a need for a flare instrument?”
“I accept what you are saying, but I would also retort that knowledge is power, and the more information we get, the more we know about what we are doing,” Dr. Helliwell said. “We are going to collect all our information – physician global, patient global, composite disease measures – everything within that study.”
Dr. Helliwell and Dr. Goel reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
MIAMI – Reaching a consensus on measurement and assessment of flare in psoriatic arthritis remains challenging, especially with no widely accepted definition and differing opinions among patients and physicians. But getting standard evaluation of flare under control is critical for both clinical and research outcomes.
Through a series of patient interviews, physician surveys, and lessons learned in rheumatoid arthritis, the GRAPPA Flare Project is close to a validated flare instrument. A 10-question flare assessment tool is now in the final validation stage, according to a presentation at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
“Flare is a clearly personal experience and varies from patient to patient. It’s clear that physicians and patients have clearly different ideas of what flare is. Bringing those two worlds together was a challenge,” Philip Helliwell, MD, of Leeds (England) University and GRAPPA president, said at the meeting.
“Some societies – I’m not going to mention any names – have gone down the route of a definition of flare linked to disease activity measures. We have not done this,” Dr. Helliwell said.
Instead, the Flare Project is taking a patient-driven and physician-reviewed approach. Investigators cast a wide net, identifying 79 factors important to patients in six major domains: skin, joint, emotional, participation, fatigue, and unclassified. The results were published in 2015 (Rheumatology [Oxford]. 2015 Aug;54[8]:1448-53). Through a Delphi survey, physicians reviewed these considerations. Then GRAPPA identified items important to both patients and physicians and developed a preliminary flare instrument.
Unlike most assessment tools for psoriatic disease, the new instrument includes patient-reported emotional well-being. Niti Goel, MD, of Duke University, Durham, N.C., said that physicians do not always ask patients about the psychological impact of their disease, so the tool “could provide additional information.”
Another goal of the project is to provide standard answers to some of the common questions related to psoriatic arthritis, including: What exactly is a flare? Does the definition truly capture the worsening of disease? Are there different types of flares? Is flare different if you start from a point of high disease activity? What self-management and other interventions are effective for flare?
GRAPPA adopted a definition of flare developed from rheumatoid arthritis, stating that flare is any worsening of disease activity that would, if persistent, in most cases lead to initiation or change of therapy (J Rheumatol. 2009 Oct;36[10]:2335-41).
“It took [them] some time to get to that definition,” Dr. Helliwell said. “We know from rheumatoid arthritis that there is a lot more to a flare than joint swelling and pain.”
The GRAPPA flare tool is now in the validation stage, Dr. Helliwell said, and will be tested in several studies, including a prospective multicenter study where the 10-item questionnaire will be administered to patients.
A meeting attendee commented that the patient and physician global scales are sufficient and asked: “Is there really a need for a flare instrument?”
“I accept what you are saying, but I would also retort that knowledge is power, and the more information we get, the more we know about what we are doing,” Dr. Helliwell said. “We are going to collect all our information – physician global, patient global, composite disease measures – everything within that study.”
Dr. Helliwell and Dr. Goel reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM 2016 GRAPPA ANNUAL MEETING
Psoriatic arthritis patients face more endocrine comorbidities
MIAMI – Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease, and osteoporosis occur more frequently in people with psoriatic arthritis than in controls, a large cohort study reveals. Prevalence of these endocrine conditions was greater in a group of 3,161 patients with psoriatic arthritis, compared with 31,610 matched controls.
“We recommend that physicians should be aware of comorbid associations to provide comprehensive medical care to patients with psoriatic arthritis,” said Amir Haddad, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Carmel Medical Center in Haifa, Israel.
Dr. Haddad and his colleagues, however, found no significant differences in the prevalence of hyperthyroidism, hypo- and hyperparathyroidism, hyperprolactinemia, Addison’s disease, diabetes insipidus, pituitary adenoma, or acromegaly between groups in this retrospective, cross-sectional study.
They identified 1,474 men and 1,687 women diagnosed with psoriatic disease from 2000 to 2013 using the Clalit health services database in Israel. This group was a mean of 58 years old and 53% were women. Each patient was matched with 10 age- and gender-matched controls without psoriatic disease for the study.
“This is, to our knowledge, one of the largest real-life cohorts of psoriatic patient registries,” Dr. Haddad said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
In the psoriatic arthritis group versus controls, diabetes mellitus prevalence was 27.9% vs. 20.7%; for hypothyroidism it was 12.7% vs. 8.6%; and for Cushing’s disease it was 0.3% vs. 0.1%. All these differences were statically significant (P less than 0.0001). Osteoporosis prevalence also differed significantly between the psoriatic arthritis and control groups: 13.2% vs. 9.1% (P less than 0.001).
Greater awareness of nonskin and nonjoint comorbidities is important, Dr. Haddad said, because it can influence choice of therapy and management of patients with psoriatic arthritis.
The investigators also conducted univariate and multivariate regression analyses. Compared with controls, the results suggest psoriatic arthritis patients have a higher risk for diabetes mellitus (odds ratio, 1.48), hypothyroidism (OR, 1.56), and osteoporosis (OR, 1.52). The risk for Cushing’s disease was notably higher (OR, 5.31) in the univariate analysis.
Risks for these endocrine conditions remained higher for the psoriatic arthritis patients in a multivariate regression analysis as well. For example, risk for diabetes mellitus (OR, 1.30) remained after adjusting for age, gender, smoking, obesity, and steroid use. Risk of hypothyroidism (OR, 1.61) remained after adjusting for age and gender; risk of osteoporosis (OR, 1.50) after adjusting for age, gender, steroid use, and smoking; and risk of Cushing’s disease (OR, 3.79) after adjustment for age, gender, and steroid use.
The large, population-based cohort is a strength of the study. “We are now going back to see how many of these patients were seen by rheumatologists,” Dr. Haddad said. A lack of association with disease burden is a potential limitation, he added.
Thirty percent of patients were treated with biologics and about 67% with steroids. “That number treated with steroids seems high,” a meeting attendee commented. Dr. Haddad explained that it is the percentage ever treated with steroids, not necessarily currently on steroids.
In a separate session at the GRAPPA meeting addressing psoriatic disease treatment recommendations, an attendee asked about specific recommendations for comorbidities. For now, GRAPPA plans to include comorbidities within its overall recommendations, as it did in its most recent update, released in January 2016. A limited amount of data is a primary reason.
“As the evidence on comorbidities gets better, we may someday have separate recommendations for comorbidities,” said Laura Coates, MD, a clinical lecturer in rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England).
“The comorbidities are very important,” said Arthur F. Kavanaugh, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego. “That’s trickier and deals with the international nature of GRAPPA. It’s hard to say, ‘Go see this specialist,’ because that might not be standard of care in that country.”
Dr. Haddad, Dr. Coates, and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
MIAMI – Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease, and osteoporosis occur more frequently in people with psoriatic arthritis than in controls, a large cohort study reveals. Prevalence of these endocrine conditions was greater in a group of 3,161 patients with psoriatic arthritis, compared with 31,610 matched controls.
“We recommend that physicians should be aware of comorbid associations to provide comprehensive medical care to patients with psoriatic arthritis,” said Amir Haddad, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Carmel Medical Center in Haifa, Israel.
Dr. Haddad and his colleagues, however, found no significant differences in the prevalence of hyperthyroidism, hypo- and hyperparathyroidism, hyperprolactinemia, Addison’s disease, diabetes insipidus, pituitary adenoma, or acromegaly between groups in this retrospective, cross-sectional study.
They identified 1,474 men and 1,687 women diagnosed with psoriatic disease from 2000 to 2013 using the Clalit health services database in Israel. This group was a mean of 58 years old and 53% were women. Each patient was matched with 10 age- and gender-matched controls without psoriatic disease for the study.
“This is, to our knowledge, one of the largest real-life cohorts of psoriatic patient registries,” Dr. Haddad said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
In the psoriatic arthritis group versus controls, diabetes mellitus prevalence was 27.9% vs. 20.7%; for hypothyroidism it was 12.7% vs. 8.6%; and for Cushing’s disease it was 0.3% vs. 0.1%. All these differences were statically significant (P less than 0.0001). Osteoporosis prevalence also differed significantly between the psoriatic arthritis and control groups: 13.2% vs. 9.1% (P less than 0.001).
Greater awareness of nonskin and nonjoint comorbidities is important, Dr. Haddad said, because it can influence choice of therapy and management of patients with psoriatic arthritis.
The investigators also conducted univariate and multivariate regression analyses. Compared with controls, the results suggest psoriatic arthritis patients have a higher risk for diabetes mellitus (odds ratio, 1.48), hypothyroidism (OR, 1.56), and osteoporosis (OR, 1.52). The risk for Cushing’s disease was notably higher (OR, 5.31) in the univariate analysis.
Risks for these endocrine conditions remained higher for the psoriatic arthritis patients in a multivariate regression analysis as well. For example, risk for diabetes mellitus (OR, 1.30) remained after adjusting for age, gender, smoking, obesity, and steroid use. Risk of hypothyroidism (OR, 1.61) remained after adjusting for age and gender; risk of osteoporosis (OR, 1.50) after adjusting for age, gender, steroid use, and smoking; and risk of Cushing’s disease (OR, 3.79) after adjustment for age, gender, and steroid use.
The large, population-based cohort is a strength of the study. “We are now going back to see how many of these patients were seen by rheumatologists,” Dr. Haddad said. A lack of association with disease burden is a potential limitation, he added.
Thirty percent of patients were treated with biologics and about 67% with steroids. “That number treated with steroids seems high,” a meeting attendee commented. Dr. Haddad explained that it is the percentage ever treated with steroids, not necessarily currently on steroids.
In a separate session at the GRAPPA meeting addressing psoriatic disease treatment recommendations, an attendee asked about specific recommendations for comorbidities. For now, GRAPPA plans to include comorbidities within its overall recommendations, as it did in its most recent update, released in January 2016. A limited amount of data is a primary reason.
“As the evidence on comorbidities gets better, we may someday have separate recommendations for comorbidities,” said Laura Coates, MD, a clinical lecturer in rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England).
“The comorbidities are very important,” said Arthur F. Kavanaugh, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego. “That’s trickier and deals with the international nature of GRAPPA. It’s hard to say, ‘Go see this specialist,’ because that might not be standard of care in that country.”
Dr. Haddad, Dr. Coates, and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
MIAMI – Diabetes mellitus, hypothyroidism, Cushing’s disease, and osteoporosis occur more frequently in people with psoriatic arthritis than in controls, a large cohort study reveals. Prevalence of these endocrine conditions was greater in a group of 3,161 patients with psoriatic arthritis, compared with 31,610 matched controls.
“We recommend that physicians should be aware of comorbid associations to provide comprehensive medical care to patients with psoriatic arthritis,” said Amir Haddad, MD, of the department of rheumatology at Carmel Medical Center in Haifa, Israel.
Dr. Haddad and his colleagues, however, found no significant differences in the prevalence of hyperthyroidism, hypo- and hyperparathyroidism, hyperprolactinemia, Addison’s disease, diabetes insipidus, pituitary adenoma, or acromegaly between groups in this retrospective, cross-sectional study.
They identified 1,474 men and 1,687 women diagnosed with psoriatic disease from 2000 to 2013 using the Clalit health services database in Israel. This group was a mean of 58 years old and 53% were women. Each patient was matched with 10 age- and gender-matched controls without psoriatic disease for the study.
“This is, to our knowledge, one of the largest real-life cohorts of psoriatic patient registries,” Dr. Haddad said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
In the psoriatic arthritis group versus controls, diabetes mellitus prevalence was 27.9% vs. 20.7%; for hypothyroidism it was 12.7% vs. 8.6%; and for Cushing’s disease it was 0.3% vs. 0.1%. All these differences were statically significant (P less than 0.0001). Osteoporosis prevalence also differed significantly between the psoriatic arthritis and control groups: 13.2% vs. 9.1% (P less than 0.001).
Greater awareness of nonskin and nonjoint comorbidities is important, Dr. Haddad said, because it can influence choice of therapy and management of patients with psoriatic arthritis.
The investigators also conducted univariate and multivariate regression analyses. Compared with controls, the results suggest psoriatic arthritis patients have a higher risk for diabetes mellitus (odds ratio, 1.48), hypothyroidism (OR, 1.56), and osteoporosis (OR, 1.52). The risk for Cushing’s disease was notably higher (OR, 5.31) in the univariate analysis.
Risks for these endocrine conditions remained higher for the psoriatic arthritis patients in a multivariate regression analysis as well. For example, risk for diabetes mellitus (OR, 1.30) remained after adjusting for age, gender, smoking, obesity, and steroid use. Risk of hypothyroidism (OR, 1.61) remained after adjusting for age and gender; risk of osteoporosis (OR, 1.50) after adjusting for age, gender, steroid use, and smoking; and risk of Cushing’s disease (OR, 3.79) after adjustment for age, gender, and steroid use.
The large, population-based cohort is a strength of the study. “We are now going back to see how many of these patients were seen by rheumatologists,” Dr. Haddad said. A lack of association with disease burden is a potential limitation, he added.
Thirty percent of patients were treated with biologics and about 67% with steroids. “That number treated with steroids seems high,” a meeting attendee commented. Dr. Haddad explained that it is the percentage ever treated with steroids, not necessarily currently on steroids.
In a separate session at the GRAPPA meeting addressing psoriatic disease treatment recommendations, an attendee asked about specific recommendations for comorbidities. For now, GRAPPA plans to include comorbidities within its overall recommendations, as it did in its most recent update, released in January 2016. A limited amount of data is a primary reason.
“As the evidence on comorbidities gets better, we may someday have separate recommendations for comorbidities,” said Laura Coates, MD, a clinical lecturer in rheumatology at the University of Leeds (England).
“The comorbidities are very important,” said Arthur F. Kavanaugh, MD, professor of medicine at the University of California, San Diego. “That’s trickier and deals with the international nature of GRAPPA. It’s hard to say, ‘Go see this specialist,’ because that might not be standard of care in that country.”
Dr. Haddad, Dr. Coates, and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
AT 2016 GRAPPA ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:Patients with psoriatic disease had a significantly higher prevalence of diabetes mellitus and some other endocrine comorbidities.
Major finding: In a univariate analysis, the risk for Cushing’s disease was notably higher among psoriatic arthritis patients, compared with controls (odds ratio, 5.31).
Data source: Retrospective, cross-sectional comparison of 3,161 patients with psoriatic arthritis and 31,610 matched controls.
Disclosures: Dr. Haddad, Dr. Coates, and Dr. Kavanaugh reported having no relevant financial disclosures.
Weight loss boosts TNFi’s psoriatic arthritis efficacy
DENVER – Weight loss enhances responsiveness of patients with psoriatic arthritis to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and should be part of routine care when using these drugs in this setting, Lianne Gensler, MD, said at an educational symposium organized by the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network.
She cited results from a randomized study conducted in Naples, Italy, with 138 patients and published in 2014, which showed the greater the weight loss of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) during their first 6 months on treatment with a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor, the greater their rate of achieving minimal disease activity by the end of the first 6 months.
Patients achieving a 5%-10% weight loss in the first 6 months on TNF-inhibitor treatment had a nearly fourfold increased rate of minimally active disease, compared with patients who had anything less than a 5% weight loss (including patients who may have had no weight change or gained weight). Those who lost more than 10% of their starting weight had a nearly sevenfold higher rate of achieving minimal disease activity, compared with those who had anything less than a 5% weight loss (Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 June;73[6]:1157-62).
“I use this result in my routine practice when starting patients on a TNF inhibitor or when patients are not responding to TNF-inhibitor treatment,” said Dr. Gensler, director of the ankylosing spondylitis clinic at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It’s a patient-centered approach to improving outcomes,” she said at the symposium, also organized by the Group for the Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
The 2015 guidelines (Arthritis Rheum. 2016 May;68[5]:1060-71) for managing psoriasis and PsA from GRAPPA cite the Naples data to recommend that all PsA patients be encouraged to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight, she noted.
The evidence that weight can affect TNF-inhibitor response in PsA patients first dates to a prior report from the same Naples group, which prospectively followed 270 PsA patients starting a TNF-inhibitor regimen, including 135 obese patients and 135 at normal weight. After 12 months, 36% of patients had minimal disease activity. The obese patients were nearly fivefold more likely to not achieve minimal disease activity during the first 12 months on treatment, compared with the normal-weight patients (Arthritis Care Res. 2013 Jan;65[1]:141-7). Obesity also was linked with a significantly increased risk that patients who achieved minimal disease activity after 1 year would relapse by 2-year follow-up.
“These studies have provided a new reason for [PsA] patients to lose weight,” agreed Atul A. Deodhar, MD, professor of medicine and medical director of the rheumatology clinics at the Oregon Health and Science University in Portland. “Before we counseled patients to lose weight for other reasons. Now there is a rheumatologic reason.”
Smoking cessation is another lifestyle step recently shown to improve TNF-inhibitor response in PsA patients, Dr. Deodhar added. For example, results from a recent Danish study of 1,388 PsA patients enrolled in the Danish national registry showed that smokers had significantly worse responses, compared with nonsmokers, during their first 6 months on a TNF-inhibitor regimen (Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Dec;74[12]:2130-6).
Both weight loss and smoking cessation “have a powerful effect. I use these results in my practice to counsel patients to stop smoking and lose weight [for] those going on a TNF inhibitor, or when a TNF inhibitor is not working,” Dr. Deodhar said in an interview.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
DENVER – Weight loss enhances responsiveness of patients with psoriatic arthritis to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and should be part of routine care when using these drugs in this setting, Lianne Gensler, MD, said at an educational symposium organized by the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network.
She cited results from a randomized study conducted in Naples, Italy, with 138 patients and published in 2014, which showed the greater the weight loss of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) during their first 6 months on treatment with a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor, the greater their rate of achieving minimal disease activity by the end of the first 6 months.
Patients achieving a 5%-10% weight loss in the first 6 months on TNF-inhibitor treatment had a nearly fourfold increased rate of minimally active disease, compared with patients who had anything less than a 5% weight loss (including patients who may have had no weight change or gained weight). Those who lost more than 10% of their starting weight had a nearly sevenfold higher rate of achieving minimal disease activity, compared with those who had anything less than a 5% weight loss (Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 June;73[6]:1157-62).
“I use this result in my routine practice when starting patients on a TNF inhibitor or when patients are not responding to TNF-inhibitor treatment,” said Dr. Gensler, director of the ankylosing spondylitis clinic at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It’s a patient-centered approach to improving outcomes,” she said at the symposium, also organized by the Group for the Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
The 2015 guidelines (Arthritis Rheum. 2016 May;68[5]:1060-71) for managing psoriasis and PsA from GRAPPA cite the Naples data to recommend that all PsA patients be encouraged to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight, she noted.
The evidence that weight can affect TNF-inhibitor response in PsA patients first dates to a prior report from the same Naples group, which prospectively followed 270 PsA patients starting a TNF-inhibitor regimen, including 135 obese patients and 135 at normal weight. After 12 months, 36% of patients had minimal disease activity. The obese patients were nearly fivefold more likely to not achieve minimal disease activity during the first 12 months on treatment, compared with the normal-weight patients (Arthritis Care Res. 2013 Jan;65[1]:141-7). Obesity also was linked with a significantly increased risk that patients who achieved minimal disease activity after 1 year would relapse by 2-year follow-up.
“These studies have provided a new reason for [PsA] patients to lose weight,” agreed Atul A. Deodhar, MD, professor of medicine and medical director of the rheumatology clinics at the Oregon Health and Science University in Portland. “Before we counseled patients to lose weight for other reasons. Now there is a rheumatologic reason.”
Smoking cessation is another lifestyle step recently shown to improve TNF-inhibitor response in PsA patients, Dr. Deodhar added. For example, results from a recent Danish study of 1,388 PsA patients enrolled in the Danish national registry showed that smokers had significantly worse responses, compared with nonsmokers, during their first 6 months on a TNF-inhibitor regimen (Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Dec;74[12]:2130-6).
Both weight loss and smoking cessation “have a powerful effect. I use these results in my practice to counsel patients to stop smoking and lose weight [for] those going on a TNF inhibitor, or when a TNF inhibitor is not working,” Dr. Deodhar said in an interview.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
DENVER – Weight loss enhances responsiveness of patients with psoriatic arthritis to tumor necrosis factor inhibitors and should be part of routine care when using these drugs in this setting, Lianne Gensler, MD, said at an educational symposium organized by the Spondyloarthritis Research and Treatment Network.
She cited results from a randomized study conducted in Naples, Italy, with 138 patients and published in 2014, which showed the greater the weight loss of patients with psoriatic arthritis (PsA) during their first 6 months on treatment with a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor, the greater their rate of achieving minimal disease activity by the end of the first 6 months.
Patients achieving a 5%-10% weight loss in the first 6 months on TNF-inhibitor treatment had a nearly fourfold increased rate of minimally active disease, compared with patients who had anything less than a 5% weight loss (including patients who may have had no weight change or gained weight). Those who lost more than 10% of their starting weight had a nearly sevenfold higher rate of achieving minimal disease activity, compared with those who had anything less than a 5% weight loss (Ann Rheum Dis. 2014 June;73[6]:1157-62).
“I use this result in my routine practice when starting patients on a TNF inhibitor or when patients are not responding to TNF-inhibitor treatment,” said Dr. Gensler, director of the ankylosing spondylitis clinic at the University of California, San Francisco.
“It’s a patient-centered approach to improving outcomes,” she said at the symposium, also organized by the Group for the Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis (GRAPPA).
The 2015 guidelines (Arthritis Rheum. 2016 May;68[5]:1060-71) for managing psoriasis and PsA from GRAPPA cite the Naples data to recommend that all PsA patients be encouraged to achieve and maintain a healthy body weight, she noted.
The evidence that weight can affect TNF-inhibitor response in PsA patients first dates to a prior report from the same Naples group, which prospectively followed 270 PsA patients starting a TNF-inhibitor regimen, including 135 obese patients and 135 at normal weight. After 12 months, 36% of patients had minimal disease activity. The obese patients were nearly fivefold more likely to not achieve minimal disease activity during the first 12 months on treatment, compared with the normal-weight patients (Arthritis Care Res. 2013 Jan;65[1]:141-7). Obesity also was linked with a significantly increased risk that patients who achieved minimal disease activity after 1 year would relapse by 2-year follow-up.
“These studies have provided a new reason for [PsA] patients to lose weight,” agreed Atul A. Deodhar, MD, professor of medicine and medical director of the rheumatology clinics at the Oregon Health and Science University in Portland. “Before we counseled patients to lose weight for other reasons. Now there is a rheumatologic reason.”
Smoking cessation is another lifestyle step recently shown to improve TNF-inhibitor response in PsA patients, Dr. Deodhar added. For example, results from a recent Danish study of 1,388 PsA patients enrolled in the Danish national registry showed that smokers had significantly worse responses, compared with nonsmokers, during their first 6 months on a TNF-inhibitor regimen (Ann Rheum Dis. 2015 Dec;74[12]:2130-6).
Both weight loss and smoking cessation “have a powerful effect. I use these results in my practice to counsel patients to stop smoking and lose weight [for] those going on a TNF inhibitor, or when a TNF inhibitor is not working,” Dr. Deodhar said in an interview.
On Twitter @mitchelzoler
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM A SPARTAN-GRAPPA SYMPOSIUM
Benefits, challenges emerge in evolution of rheumatology-dermatology clinics
MIAMI – Combined rheumatology-dermatology clinics to help people with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and other relevant overlapping conditions continue to evolve, with evidence suggesting advantages and challenges for both patients and physicians.
Physicians like the improved communication and greater collaboration but still have reservations about billing and scheduling, according to preliminary results of a survey conducted by the Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic Multicenter Advancement Network (PPACMAN). For patients, the advantages go beyond convenience, according to a 1-year study of outcomes at a Rhode Island Hospital–Brown University combined clinic in Providence.
“The goal of the combined clinics survey is to gauge strengths, barriers, and challenges to creating these models, to learn from one another to improve current clinical care, and to support propagation of these models,” said Joseph F. Merola, MD, at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
Multiple clinic models
The clinic setups differ. In those settings where rheumatologists and dermatologists see patients on the same day, approximately three-quarters provide care together in the same room. The remaining clinics see patients through serial visits. Another 30% of respondents said dermatologists and rheumatologists generally see patients in a combined clinic on different days.
“Rheumatologists said it is a satisfying and rewarding endeavor, they form closer ties with colleagues, and it allows early, improved communication,” said Dr. Merola, a rheumatologist and dermatologist who is co-director of the Center for Skin and Related Musculoskeletal Diseases, a combined clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Some common benefits, each cited by more than 80% of respondents, include a prompt and accurate diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis, the ability of physicians to learn from each other, and multiple training opportunities for residents and fellows. In fact, 72% said their combined clinic has rheumatology fellows, 82% have dermatology residents, and 27% incorporate internal medicine trainees.
Other than rheumatologists and dermatologists, 31% said their clinic has dedicated nursing, 15% have a cardiologist, and 15% have a psychiatrist.
A majority of physicians (92%) said they bill through their own department. At a subsequent roundtable discussion, Dr. Merola noted that patients pay separate copays at the combined clinic. “We’ve had some complaints from patients. They don’t like having two copayments.”
“You have to tell patients in advance,” suggested Soumya M. Reddy, MD, a rheumatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York and co-director of its Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Center.
Common conditions and challenges
Not surprisingly, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis are the most common conditions treated in these clinics, followed by lupus and dermatomyositis. Most clinics see patients either once weekly or once monthly.
A major concern expressed by 75% surrounds scheduling. More than half, 58%, worry about demonstrating value to their institution. Only a minority, 17%, responded that achieving consensus on patient management is a challenge.
In general, rheumatology evaluations take more time than dermatology assessments, presenting a challenge for scheduling and maximizing physician time. “You don’t really want the dermatologist sitting there for 20 minutes not really doing a lot,” said Alison Ehrlich, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University in Washington.
The solution at Brigham and Women’s Hospital is to staff the clinic with two dermatologists and one rheumatologist. The two dermatologists see about 20 patients each in a half-day; the rheumatologist probably treats about 6 to 8 of those 40 patients, Dr. Merola said. At George Washington, Dr. Ehrlich sees patients along with the rheumatologist, leaves the room to treat other patients, later consults with her colleague, and they go back in together as necessary.
“The patients are incredibly appreciative” of the combined clinic, Dr. Ehrlich said. “They really love it.”
The survey is ongoing. The preliminary responses above are based on 17 responses, a 52% response rate. Of the respondents, 10 are dermatologists, 6 are rheumatologists, and 1 is dual trained. Since the meeting, Dr. Merola indicated that another two dermatologists and three rheumatologists have responded to the survey.
The Brown University experience
Charis Gn, MD, and colleagues studied outcomes for 167 patients treated at a combined clinic at Rhode Island Hospital. The ultimate goal of the clinic is “to identify patients with psoriatic arthritis early on,” Dr. Gn said at a poster presentation at the GRAPPA annual meeting. “We wanted to see what kind of outcomes [we get] for patients who see rheumatology and dermatology.”
About one-third of patients left the clinic with changes in diagnosis. About 1 in 5 patients with psoriasis were diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis as well. For the psoriasis patients newly diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis, 80% had an escalation in treatment, said Dr. Gn, an internal medicine resident.
Of the 41 patients with psoriasis, 17 (41%) had a treatment escalation. The same was true for 15 (79%) of the 19 patients with psoriatic arthritis post-evaluation.
Regarding the combined clinic, “it’s shown to be very beneficial for patients with psoriatic arthritis,” Dr. Gn said.
The record review from July 2014 to February 2016 shows the clinic also serves patients with cutaneous lupus, dermatomyositis, pyoderma gangrenosum, vasculitis, and rheumatoid arthritis, among others.
The presenters had no relevant disclosures.
MIAMI – Combined rheumatology-dermatology clinics to help people with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and other relevant overlapping conditions continue to evolve, with evidence suggesting advantages and challenges for both patients and physicians.
Physicians like the improved communication and greater collaboration but still have reservations about billing and scheduling, according to preliminary results of a survey conducted by the Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic Multicenter Advancement Network (PPACMAN). For patients, the advantages go beyond convenience, according to a 1-year study of outcomes at a Rhode Island Hospital–Brown University combined clinic in Providence.
“The goal of the combined clinics survey is to gauge strengths, barriers, and challenges to creating these models, to learn from one another to improve current clinical care, and to support propagation of these models,” said Joseph F. Merola, MD, at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
Multiple clinic models
The clinic setups differ. In those settings where rheumatologists and dermatologists see patients on the same day, approximately three-quarters provide care together in the same room. The remaining clinics see patients through serial visits. Another 30% of respondents said dermatologists and rheumatologists generally see patients in a combined clinic on different days.
“Rheumatologists said it is a satisfying and rewarding endeavor, they form closer ties with colleagues, and it allows early, improved communication,” said Dr. Merola, a rheumatologist and dermatologist who is co-director of the Center for Skin and Related Musculoskeletal Diseases, a combined clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Some common benefits, each cited by more than 80% of respondents, include a prompt and accurate diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis, the ability of physicians to learn from each other, and multiple training opportunities for residents and fellows. In fact, 72% said their combined clinic has rheumatology fellows, 82% have dermatology residents, and 27% incorporate internal medicine trainees.
Other than rheumatologists and dermatologists, 31% said their clinic has dedicated nursing, 15% have a cardiologist, and 15% have a psychiatrist.
A majority of physicians (92%) said they bill through their own department. At a subsequent roundtable discussion, Dr. Merola noted that patients pay separate copays at the combined clinic. “We’ve had some complaints from patients. They don’t like having two copayments.”
“You have to tell patients in advance,” suggested Soumya M. Reddy, MD, a rheumatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York and co-director of its Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Center.
Common conditions and challenges
Not surprisingly, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis are the most common conditions treated in these clinics, followed by lupus and dermatomyositis. Most clinics see patients either once weekly or once monthly.
A major concern expressed by 75% surrounds scheduling. More than half, 58%, worry about demonstrating value to their institution. Only a minority, 17%, responded that achieving consensus on patient management is a challenge.
In general, rheumatology evaluations take more time than dermatology assessments, presenting a challenge for scheduling and maximizing physician time. “You don’t really want the dermatologist sitting there for 20 minutes not really doing a lot,” said Alison Ehrlich, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University in Washington.
The solution at Brigham and Women’s Hospital is to staff the clinic with two dermatologists and one rheumatologist. The two dermatologists see about 20 patients each in a half-day; the rheumatologist probably treats about 6 to 8 of those 40 patients, Dr. Merola said. At George Washington, Dr. Ehrlich sees patients along with the rheumatologist, leaves the room to treat other patients, later consults with her colleague, and they go back in together as necessary.
“The patients are incredibly appreciative” of the combined clinic, Dr. Ehrlich said. “They really love it.”
The survey is ongoing. The preliminary responses above are based on 17 responses, a 52% response rate. Of the respondents, 10 are dermatologists, 6 are rheumatologists, and 1 is dual trained. Since the meeting, Dr. Merola indicated that another two dermatologists and three rheumatologists have responded to the survey.
The Brown University experience
Charis Gn, MD, and colleagues studied outcomes for 167 patients treated at a combined clinic at Rhode Island Hospital. The ultimate goal of the clinic is “to identify patients with psoriatic arthritis early on,” Dr. Gn said at a poster presentation at the GRAPPA annual meeting. “We wanted to see what kind of outcomes [we get] for patients who see rheumatology and dermatology.”
About one-third of patients left the clinic with changes in diagnosis. About 1 in 5 patients with psoriasis were diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis as well. For the psoriasis patients newly diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis, 80% had an escalation in treatment, said Dr. Gn, an internal medicine resident.
Of the 41 patients with psoriasis, 17 (41%) had a treatment escalation. The same was true for 15 (79%) of the 19 patients with psoriatic arthritis post-evaluation.
Regarding the combined clinic, “it’s shown to be very beneficial for patients with psoriatic arthritis,” Dr. Gn said.
The record review from July 2014 to February 2016 shows the clinic also serves patients with cutaneous lupus, dermatomyositis, pyoderma gangrenosum, vasculitis, and rheumatoid arthritis, among others.
The presenters had no relevant disclosures.
MIAMI – Combined rheumatology-dermatology clinics to help people with psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and other relevant overlapping conditions continue to evolve, with evidence suggesting advantages and challenges for both patients and physicians.
Physicians like the improved communication and greater collaboration but still have reservations about billing and scheduling, according to preliminary results of a survey conducted by the Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Clinic Multicenter Advancement Network (PPACMAN). For patients, the advantages go beyond convenience, according to a 1-year study of outcomes at a Rhode Island Hospital–Brown University combined clinic in Providence.
“The goal of the combined clinics survey is to gauge strengths, barriers, and challenges to creating these models, to learn from one another to improve current clinical care, and to support propagation of these models,” said Joseph F. Merola, MD, at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
Multiple clinic models
The clinic setups differ. In those settings where rheumatologists and dermatologists see patients on the same day, approximately three-quarters provide care together in the same room. The remaining clinics see patients through serial visits. Another 30% of respondents said dermatologists and rheumatologists generally see patients in a combined clinic on different days.
“Rheumatologists said it is a satisfying and rewarding endeavor, they form closer ties with colleagues, and it allows early, improved communication,” said Dr. Merola, a rheumatologist and dermatologist who is co-director of the Center for Skin and Related Musculoskeletal Diseases, a combined clinic at Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston.
Some common benefits, each cited by more than 80% of respondents, include a prompt and accurate diagnosis of psoriatic arthritis, the ability of physicians to learn from each other, and multiple training opportunities for residents and fellows. In fact, 72% said their combined clinic has rheumatology fellows, 82% have dermatology residents, and 27% incorporate internal medicine trainees.
Other than rheumatologists and dermatologists, 31% said their clinic has dedicated nursing, 15% have a cardiologist, and 15% have a psychiatrist.
A majority of physicians (92%) said they bill through their own department. At a subsequent roundtable discussion, Dr. Merola noted that patients pay separate copays at the combined clinic. “We’ve had some complaints from patients. They don’t like having two copayments.”
“You have to tell patients in advance,” suggested Soumya M. Reddy, MD, a rheumatologist at NYU Langone Medical Center in New York and co-director of its Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Center.
Common conditions and challenges
Not surprisingly, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis are the most common conditions treated in these clinics, followed by lupus and dermatomyositis. Most clinics see patients either once weekly or once monthly.
A major concern expressed by 75% surrounds scheduling. More than half, 58%, worry about demonstrating value to their institution. Only a minority, 17%, responded that achieving consensus on patient management is a challenge.
In general, rheumatology evaluations take more time than dermatology assessments, presenting a challenge for scheduling and maximizing physician time. “You don’t really want the dermatologist sitting there for 20 minutes not really doing a lot,” said Alison Ehrlich, MD, professor and chair of dermatology at George Washington University in Washington.
The solution at Brigham and Women’s Hospital is to staff the clinic with two dermatologists and one rheumatologist. The two dermatologists see about 20 patients each in a half-day; the rheumatologist probably treats about 6 to 8 of those 40 patients, Dr. Merola said. At George Washington, Dr. Ehrlich sees patients along with the rheumatologist, leaves the room to treat other patients, later consults with her colleague, and they go back in together as necessary.
“The patients are incredibly appreciative” of the combined clinic, Dr. Ehrlich said. “They really love it.”
The survey is ongoing. The preliminary responses above are based on 17 responses, a 52% response rate. Of the respondents, 10 are dermatologists, 6 are rheumatologists, and 1 is dual trained. Since the meeting, Dr. Merola indicated that another two dermatologists and three rheumatologists have responded to the survey.
The Brown University experience
Charis Gn, MD, and colleagues studied outcomes for 167 patients treated at a combined clinic at Rhode Island Hospital. The ultimate goal of the clinic is “to identify patients with psoriatic arthritis early on,” Dr. Gn said at a poster presentation at the GRAPPA annual meeting. “We wanted to see what kind of outcomes [we get] for patients who see rheumatology and dermatology.”
About one-third of patients left the clinic with changes in diagnosis. About 1 in 5 patients with psoriasis were diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis as well. For the psoriasis patients newly diagnosed with psoriatic arthritis, 80% had an escalation in treatment, said Dr. Gn, an internal medicine resident.
Of the 41 patients with psoriasis, 17 (41%) had a treatment escalation. The same was true for 15 (79%) of the 19 patients with psoriatic arthritis post-evaluation.
Regarding the combined clinic, “it’s shown to be very beneficial for patients with psoriatic arthritis,” Dr. Gn said.
The record review from July 2014 to February 2016 shows the clinic also serves patients with cutaneous lupus, dermatomyositis, pyoderma gangrenosum, vasculitis, and rheumatoid arthritis, among others.
The presenters had no relevant disclosures.
AT 2016 GRAPPA ANNUAL MEETING
Psoriasiform eruptions in Kawasaki disease reveal distinct phenotype
A comparison of psoriasis-like eruptions in Kawasaki disease (KD) with classic psoriasis shows a distinct phenotype with greater remission, report Ellen S. Haddock, AB, MBA and coauthors from the School of Medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Investigators performed a retrospective study of 11 KD cases with a psoriasiform eruption matched by gender, age, and ethnicity with psoriasis-only and KD-only controls. Genotyping was performed in 10 cases for a deletion of two late cornified envelope genes associated with pediatric-onset psoriasis.
KD-associated eruptions were similar to classic psoriasis in presentation, but with less frequent diaper area involvement, more crust, more serious exudate, and significantly higher remission (91% vs. 23%; P less than .001), the authors noted.
The findings indicate that despite similarities to classic psoriasis, “this appears to be a distinct phenotype with significantly greater propensity for remission,” the authors concluded.
Read the full article in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A comparison of psoriasis-like eruptions in Kawasaki disease (KD) with classic psoriasis shows a distinct phenotype with greater remission, report Ellen S. Haddock, AB, MBA and coauthors from the School of Medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Investigators performed a retrospective study of 11 KD cases with a psoriasiform eruption matched by gender, age, and ethnicity with psoriasis-only and KD-only controls. Genotyping was performed in 10 cases for a deletion of two late cornified envelope genes associated with pediatric-onset psoriasis.
KD-associated eruptions were similar to classic psoriasis in presentation, but with less frequent diaper area involvement, more crust, more serious exudate, and significantly higher remission (91% vs. 23%; P less than .001), the authors noted.
The findings indicate that despite similarities to classic psoriasis, “this appears to be a distinct phenotype with significantly greater propensity for remission,” the authors concluded.
Read the full article in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
A comparison of psoriasis-like eruptions in Kawasaki disease (KD) with classic psoriasis shows a distinct phenotype with greater remission, report Ellen S. Haddock, AB, MBA and coauthors from the School of Medicine at the University of California, San Diego.
Investigators performed a retrospective study of 11 KD cases with a psoriasiform eruption matched by gender, age, and ethnicity with psoriasis-only and KD-only controls. Genotyping was performed in 10 cases for a deletion of two late cornified envelope genes associated with pediatric-onset psoriasis.
KD-associated eruptions were similar to classic psoriasis in presentation, but with less frequent diaper area involvement, more crust, more serious exudate, and significantly higher remission (91% vs. 23%; P less than .001), the authors noted.
The findings indicate that despite similarities to classic psoriasis, “this appears to be a distinct phenotype with significantly greater propensity for remission,” the authors concluded.
Read the full article in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF THE AMERICAN ACADEMY OF DERMATOLOGY
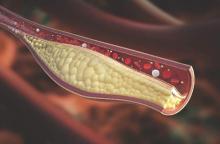
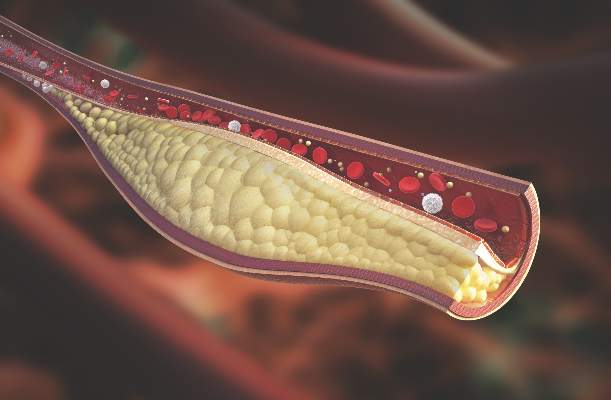
Psoriatic arthritis patients have elevated risk for coronary artery plaque
MIAMI – Patients with psoriatic arthritis had a higher prevalence and greater extent of coronary artery plaque in a pilot study comparison with healthy control patients that may point to increased risk independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
In the study, coronary artery plaque as assessed by cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) occurred in 39 (78%) of 50 patients with psoriatic arthritis, a significantly higher rate than that observed for healthy controls (11 of 25, 44%).
Investigators not only measured plaque volume, but also assessed the type of plaque: calcified, noncalcified, or mixed. Mixed plaque predominated. This could be important because “noncalcified and mixed carry higher risk for rupture and later cardiovascular events,” Agnes Szentpetery, MD, a research fellow at St. Vincent’s University Hospital in Dublin, said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
She and her colleagues also found more clinically significant stenosis among the 50 participants with psoriatic arthritis, compared with 25 healthy controls matched for age, sex, smoking status, and presence of metabolic syndrome. “This pilot study is the first to assess coronary plaques in asymptomatic patients with psoriatic arthritis with CCTA,” Dr. Szentpetery said.
Total plaque volume was higher in the psoriatic arthritis group versus controls, and higher in the left main artery for psoriatic arthritis patients, both with and without metabolic syndrome.
The study points to increased risk independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. For example, CCTA revealed no difference in plaque volume between patients with and without metabolic disease. In addition, a previous study suggests “the burden of carotid artery plaques is higher in patients with psoriatic arthritis compared to those with psoriasis alone,” Dr. Szentpetery said, citing a cross-sectional study comparing 125 people with psoriasis to 114 others with psoriatic arthritis (Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 May;72[5]:715-20).
Perhaps not surprisingly, inflammation could be driving the association between psoriatic and cardiovascular disease risk. Other investigators suggest chronic, low-grade inflammation leads to atherosclerosis through a maladaptive immune response and altered lipid metabolism, for example (Nat Med. 2011 Nov;17[11]:1410-22).
In the current study, the patients with psoriatic arthritis had well-established disease, occurring for a mean duration of 19 years. Mean age was 58 years, and 54% were men. Approximately 60% were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, two-thirds were taking biologics, and about one-third were on combination treatment. Controls were similar demographically with a mean age of 57 years, and 52% were men.
Interestingly, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores did not correlate with increased risk. During discussion after the presentation of the study, a researcher unaffiliated with the study offered an answer. “It could be their skin disease was controlled by the biologics. You had 67% on biologics,” said Nehal Mehta, MD, Clinical Research Scholar in the section of inflammation and cardiometabolic disease at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “We at the NIH see a strong correlation between PASI and coronary artery disease risk.”
“We know methotrexate and anti-TNF agents can have a protective effect on atherosclerosis, but we did not look at this specifically,” Dr. Szentpetery said. Overall, PASI scores were relatively low in the study population, she added, which “may explain why we did not see the correlation with PASI scores.”
Dr. Szentpetery and Dr. Mehta had no relevant financial disclosures.
MIAMI – Patients with psoriatic arthritis had a higher prevalence and greater extent of coronary artery plaque in a pilot study comparison with healthy control patients that may point to increased risk independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
In the study, coronary artery plaque as assessed by cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) occurred in 39 (78%) of 50 patients with psoriatic arthritis, a significantly higher rate than that observed for healthy controls (11 of 25, 44%).
Investigators not only measured plaque volume, but also assessed the type of plaque: calcified, noncalcified, or mixed. Mixed plaque predominated. This could be important because “noncalcified and mixed carry higher risk for rupture and later cardiovascular events,” Agnes Szentpetery, MD, a research fellow at St. Vincent’s University Hospital in Dublin, said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
She and her colleagues also found more clinically significant stenosis among the 50 participants with psoriatic arthritis, compared with 25 healthy controls matched for age, sex, smoking status, and presence of metabolic syndrome. “This pilot study is the first to assess coronary plaques in asymptomatic patients with psoriatic arthritis with CCTA,” Dr. Szentpetery said.
Total plaque volume was higher in the psoriatic arthritis group versus controls, and higher in the left main artery for psoriatic arthritis patients, both with and without metabolic syndrome.
The study points to increased risk independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. For example, CCTA revealed no difference in plaque volume between patients with and without metabolic disease. In addition, a previous study suggests “the burden of carotid artery plaques is higher in patients with psoriatic arthritis compared to those with psoriasis alone,” Dr. Szentpetery said, citing a cross-sectional study comparing 125 people with psoriasis to 114 others with psoriatic arthritis (Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 May;72[5]:715-20).
Perhaps not surprisingly, inflammation could be driving the association between psoriatic and cardiovascular disease risk. Other investigators suggest chronic, low-grade inflammation leads to atherosclerosis through a maladaptive immune response and altered lipid metabolism, for example (Nat Med. 2011 Nov;17[11]:1410-22).
In the current study, the patients with psoriatic arthritis had well-established disease, occurring for a mean duration of 19 years. Mean age was 58 years, and 54% were men. Approximately 60% were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, two-thirds were taking biologics, and about one-third were on combination treatment. Controls were similar demographically with a mean age of 57 years, and 52% were men.
Interestingly, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores did not correlate with increased risk. During discussion after the presentation of the study, a researcher unaffiliated with the study offered an answer. “It could be their skin disease was controlled by the biologics. You had 67% on biologics,” said Nehal Mehta, MD, Clinical Research Scholar in the section of inflammation and cardiometabolic disease at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “We at the NIH see a strong correlation between PASI and coronary artery disease risk.”
“We know methotrexate and anti-TNF agents can have a protective effect on atherosclerosis, but we did not look at this specifically,” Dr. Szentpetery said. Overall, PASI scores were relatively low in the study population, she added, which “may explain why we did not see the correlation with PASI scores.”
Dr. Szentpetery and Dr. Mehta had no relevant financial disclosures.
MIAMI – Patients with psoriatic arthritis had a higher prevalence and greater extent of coronary artery plaque in a pilot study comparison with healthy control patients that may point to increased risk independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors.
In the study, coronary artery plaque as assessed by cardiac computed tomography angiography (CCTA) occurred in 39 (78%) of 50 patients with psoriatic arthritis, a significantly higher rate than that observed for healthy controls (11 of 25, 44%).
Investigators not only measured plaque volume, but also assessed the type of plaque: calcified, noncalcified, or mixed. Mixed plaque predominated. This could be important because “noncalcified and mixed carry higher risk for rupture and later cardiovascular events,” Agnes Szentpetery, MD, a research fellow at St. Vincent’s University Hospital in Dublin, said at the annual meeting of the Group for Research and Assessment of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis.
She and her colleagues also found more clinically significant stenosis among the 50 participants with psoriatic arthritis, compared with 25 healthy controls matched for age, sex, smoking status, and presence of metabolic syndrome. “This pilot study is the first to assess coronary plaques in asymptomatic patients with psoriatic arthritis with CCTA,” Dr. Szentpetery said.
Total plaque volume was higher in the psoriatic arthritis group versus controls, and higher in the left main artery for psoriatic arthritis patients, both with and without metabolic syndrome.
The study points to increased risk independent of traditional cardiovascular risk factors. For example, CCTA revealed no difference in plaque volume between patients with and without metabolic disease. In addition, a previous study suggests “the burden of carotid artery plaques is higher in patients with psoriatic arthritis compared to those with psoriasis alone,” Dr. Szentpetery said, citing a cross-sectional study comparing 125 people with psoriasis to 114 others with psoriatic arthritis (Ann Rheum Dis. 2013 May;72[5]:715-20).
Perhaps not surprisingly, inflammation could be driving the association between psoriatic and cardiovascular disease risk. Other investigators suggest chronic, low-grade inflammation leads to atherosclerosis through a maladaptive immune response and altered lipid metabolism, for example (Nat Med. 2011 Nov;17[11]:1410-22).
In the current study, the patients with psoriatic arthritis had well-established disease, occurring for a mean duration of 19 years. Mean age was 58 years, and 54% were men. Approximately 60% were taking disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, two-thirds were taking biologics, and about one-third were on combination treatment. Controls were similar demographically with a mean age of 57 years, and 52% were men.
Interestingly, Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI) scores did not correlate with increased risk. During discussion after the presentation of the study, a researcher unaffiliated with the study offered an answer. “It could be their skin disease was controlled by the biologics. You had 67% on biologics,” said Nehal Mehta, MD, Clinical Research Scholar in the section of inflammation and cardiometabolic disease at the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute. “We at the NIH see a strong correlation between PASI and coronary artery disease risk.”
“We know methotrexate and anti-TNF agents can have a protective effect on atherosclerosis, but we did not look at this specifically,” Dr. Szentpetery said. Overall, PASI scores were relatively low in the study population, she added, which “may explain why we did not see the correlation with PASI scores.”
Dr. Szentpetery and Dr. Mehta had no relevant financial disclosures.
AT 2016 GRAPPA ANNUAL MEETING
Key clinical point:Imaging reveals a higher rate and greater extent of coronary plaque in people with psoriatic arthritis versus healthy controls.
Major finding: 78% of people with PsA had coronary artery plaque versus 44% of controls, a significant difference.
Data source: Comparison of 50 people with PsA versus 25 healthy controls undergoing CCTA.
Disclosures: Dr. Szentpetery and Dr. Mehta had no relevant disclosures.
Brodalumab approval recommended, despite possible suicide signal
A Food and Drug Administration advisory committee has unanimously supported approval of the monoclonal antibody brodalumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, with the majority recommending risk management options beyond labeling to address concerns about the six completed suicides among patients treated with brodalumab in clinical trials.
Though no members of the FDA’s Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee disputed the drug’s efficacy for plaque psoriasis, the possibility of a signal for suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB) among the brodalumab group prompted the committee’s chair, Michael Bigby, M.D., to remark, “The big problem is that you have six completed suicides. … I would say it’s a fairly big number for a randomized controlled trial. Patients and clinicians need to be aware of this as a fact.”
Dr. Bigby, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, headed the 18-member panel, which included dermatologists, psychiatrists, and cardiologists. Fourteen members voted in favor of approval with risk management measures beyond labeling; four members voted for approval with labeling alone.
Brodalumab targets interleukin-17 receptors, inhibiting IL-17 uptake and thus blocking the pathway responsible for the cutaneous and systemic signs and symptoms of psoriasis. The pivotal phase III brodalumab studies, AMAGINE-1, -2, and -3, enrolled a total of 4,373 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. AMAGINE-1 enrolled 661 patients in a 1:1:1 ratio to a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study that included two doses of brodalumab: 210 mg and 140 mg. The placebo-controlled phase of the study ran for 12 weeks, followed by a withdrawal and retreatment phase, and after 52 weeks, by an open label long-term extension phase.
AMAGINE-2 (1,831 patients) and AMAGINE-3 (1,881 patients) were identically designed studies that pitted both doses of brodalumab against an active comparator, ustekinumab (Stelara), as well as placebo, in a 2:2:1:1 ratio. This double-blind phase of the study also lasted 12 weeks. During weeks 12-52, patients on the brodalumab arms continued, with an exploration of wider-dose intervals for the 140-mg dose. Patients also continued with ustekinumab, with a rescue option to transition to brodalumab 210 mg. The placebo group could continue on brodalumab 210 mg as well. These two studies also had an open label long-term extension phase.
At the 12-week mark in AMAGINE-1, 41.9% of patients achieved the coprimary endpoint of 100% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 100) score, compared with 0.5% of those on placebo (P less than .001). AMAGINE-2 and -3 saw 44.4% and 36.7% of the brodalumab 210-mg arms achieving PASI 100 at the 12-week mark, respectively. These figures were significantly higher than the 21.7% and 18.5% reaching PASI 100 on ustekinumab (P less than .001), as well as significantly higher than the less than 1% of patients in the placebo arm who reached that endpoint.
At the end of 52 weeks, 51% of those on brodalumab 210 mg had completely clear skin, compared with 28.1% of the patients receiving ustekinumab (P less than .001).
The safety analysis for brodalumab showed that the most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and arthralgia; of these, the last two were considered adverse drug reactions. At 52 weeks, those on brodalumab had a slightly greater risk of having nonserious fungal infections than did those on ustekinumab. Overall, however, there was no difference between the brodalumab and ustekinumab arms at week 52 for treatment-emergent adverse events or for serious adverse events.
A cluster of SIB events occurred in 2013 and 2014 during the clinical trials, and the sponsor consulted the FDA. Additional monitoring for suicidal ideation and depression via the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) were implemented at a point where 84% of trial patients were already in the uncontrolled open label extension stage of the trial; in addition, a retrospective data review searched for suicidal ideation and attempts before the implementation of these two tools.
A total of six brodalumab patients completed suicide in all clinical trials, including those for psoriatic arthritis and RA. Suicides included two during the 12- to 52-week follow-up and four during the long-term follow-up phase. Another 29 patients attempted suicide, had intentional self-injury, or had suicidal ideation during these phases of the study, for a total of 35 SIB events. (SIB includes completed suicide, suicide attempt, suicide behavior, and suicide ideation.)*
The significance of the number of completed suicides was difficult to ascertain, given the increased baseline prevalence of depression and related illnesses among patients with psoriasis. Compared with the general population, individuals with psoriasis have hazard ratios of 1.39, 1.31, and 1.44 for depression, anxiety, and suicidality, according to a cohort study cited by Robert Levin, M.D. , director of the division of pharmacovigilance I at the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER).
In addition, monitoring for suicidal ideation and attempts was stepped up during the course of the clinical trials. Brodalumab’s sponsor, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, noted that the rates of suicidal ideation and attempts increased after implementation of the C-SSRS, while other neuropsychiatric symptoms remained stable or declined during the course of the studies. “This makes us think this is ascertainment bias,” said Valeant consultant Lauren Marangell, M.D., a psychiatrist and president of Brain Health Consultants.
Dr. Marangell also reported that, after stratification for preexisting psychiatric comorbidities and risk factors, “there is no question that the rate of SIB is higher in both arms with patients with baseline risk factors.” The FDA’s data analysis showed an 18-fold increase in the rate of SIB for brodalumab arm participants with a prior history of suicidality.
During its presentation, Valeant also pointed out that patients with histories of drug and alcohol abuse, depression, and suicidality were not specifically excluded from the clinical trials. This differentiates the brodalumab program from other biologic studies, “making the studies more characteristic of the real world,” said R.K. Pillai, Ph.D., Valeant vice president.
Dr. Levin’s analysis, one of several independent analyses conducted by different FDA divisions, found that the data were inconclusive. “We currently can’t conclude whether or not these are drug-related risks,” he said. Considering the critical severity of suicide as an outcome, “we must consider the application and regulatory actions carefully.”
Jean Kim, M.D., medical officer in CDER’s division of psychiatry products (DPP), noted that the number of suicides seen in the brodalumab trials “is higher than typically seen in DPP’s large psychiatric drug trials, which involve populations with higher psychiatric morbidity than patients with psoriasis.”
Patients with psoriasis are also known to have a baseline elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, and no committee member felt the brodalumab data showed any additional signal for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) beyond what would be suspected in this population. “I don’t right now see a safety signal for MACE,” said panelist Michael Blaha, M.D., a cardiologist and director of clinical research at Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Heart Disease, Baltimore. He noted, however, that research is ongoing to elucidate the relationship between cytokine levels and MACE. “This question about whether cytokines raise or reduce rates for [cardiovascular] events is an open one.”
One of the dermatologists on the committee, Lynn Drake, M.D., said that her decision making was influenced by the disease burden psoriasis inflicts on the patients she sees in her daily practice. “These patients are ill. People tend to think it’s just skin disease. It is not just skin disease. … I’d hate to see our patients deprived of a drug that might help alleviate their symptoms,” said Dr. Drake.
Though committee members voiced some disagreement about whether a patient registry should be established, and if it should be voluntary, they were in agreement that patients and prescribers both be aware of the potential risks of brodalumab, without making any risk management strategy so burdensome that appropriate patients would be deterred from considering the medication. Psoriasis, Dr. Drake said, “is a devastating disease. We need this in our armamentarium.”
The proposed dosing for brodalumab is 210 mg injected subcutaneously weekly for 3 weeks, followed by 210 mg every 2 weeks thereafter.
The FDA usually follows the recommendations of its advisory committees. The panelists had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
*A previous version of this article misstated the number of patients who experienced SIB events.
A Food and Drug Administration advisory committee has unanimously supported approval of the monoclonal antibody brodalumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, with the majority recommending risk management options beyond labeling to address concerns about the six completed suicides among patients treated with brodalumab in clinical trials.
Though no members of the FDA’s Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee disputed the drug’s efficacy for plaque psoriasis, the possibility of a signal for suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB) among the brodalumab group prompted the committee’s chair, Michael Bigby, M.D., to remark, “The big problem is that you have six completed suicides. … I would say it’s a fairly big number for a randomized controlled trial. Patients and clinicians need to be aware of this as a fact.”
Dr. Bigby, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, headed the 18-member panel, which included dermatologists, psychiatrists, and cardiologists. Fourteen members voted in favor of approval with risk management measures beyond labeling; four members voted for approval with labeling alone.
Brodalumab targets interleukin-17 receptors, inhibiting IL-17 uptake and thus blocking the pathway responsible for the cutaneous and systemic signs and symptoms of psoriasis. The pivotal phase III brodalumab studies, AMAGINE-1, -2, and -3, enrolled a total of 4,373 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. AMAGINE-1 enrolled 661 patients in a 1:1:1 ratio to a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study that included two doses of brodalumab: 210 mg and 140 mg. The placebo-controlled phase of the study ran for 12 weeks, followed by a withdrawal and retreatment phase, and after 52 weeks, by an open label long-term extension phase.
AMAGINE-2 (1,831 patients) and AMAGINE-3 (1,881 patients) were identically designed studies that pitted both doses of brodalumab against an active comparator, ustekinumab (Stelara), as well as placebo, in a 2:2:1:1 ratio. This double-blind phase of the study also lasted 12 weeks. During weeks 12-52, patients on the brodalumab arms continued, with an exploration of wider-dose intervals for the 140-mg dose. Patients also continued with ustekinumab, with a rescue option to transition to brodalumab 210 mg. The placebo group could continue on brodalumab 210 mg as well. These two studies also had an open label long-term extension phase.
At the 12-week mark in AMAGINE-1, 41.9% of patients achieved the coprimary endpoint of 100% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 100) score, compared with 0.5% of those on placebo (P less than .001). AMAGINE-2 and -3 saw 44.4% and 36.7% of the brodalumab 210-mg arms achieving PASI 100 at the 12-week mark, respectively. These figures were significantly higher than the 21.7% and 18.5% reaching PASI 100 on ustekinumab (P less than .001), as well as significantly higher than the less than 1% of patients in the placebo arm who reached that endpoint.
At the end of 52 weeks, 51% of those on brodalumab 210 mg had completely clear skin, compared with 28.1% of the patients receiving ustekinumab (P less than .001).
The safety analysis for brodalumab showed that the most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and arthralgia; of these, the last two were considered adverse drug reactions. At 52 weeks, those on brodalumab had a slightly greater risk of having nonserious fungal infections than did those on ustekinumab. Overall, however, there was no difference between the brodalumab and ustekinumab arms at week 52 for treatment-emergent adverse events or for serious adverse events.
A cluster of SIB events occurred in 2013 and 2014 during the clinical trials, and the sponsor consulted the FDA. Additional monitoring for suicidal ideation and depression via the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) were implemented at a point where 84% of trial patients were already in the uncontrolled open label extension stage of the trial; in addition, a retrospective data review searched for suicidal ideation and attempts before the implementation of these two tools.
A total of six brodalumab patients completed suicide in all clinical trials, including those for psoriatic arthritis and RA. Suicides included two during the 12- to 52-week follow-up and four during the long-term follow-up phase. Another 29 patients attempted suicide, had intentional self-injury, or had suicidal ideation during these phases of the study, for a total of 35 SIB events. (SIB includes completed suicide, suicide attempt, suicide behavior, and suicide ideation.)*
The significance of the number of completed suicides was difficult to ascertain, given the increased baseline prevalence of depression and related illnesses among patients with psoriasis. Compared with the general population, individuals with psoriasis have hazard ratios of 1.39, 1.31, and 1.44 for depression, anxiety, and suicidality, according to a cohort study cited by Robert Levin, M.D. , director of the division of pharmacovigilance I at the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER).
In addition, monitoring for suicidal ideation and attempts was stepped up during the course of the clinical trials. Brodalumab’s sponsor, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, noted that the rates of suicidal ideation and attempts increased after implementation of the C-SSRS, while other neuropsychiatric symptoms remained stable or declined during the course of the studies. “This makes us think this is ascertainment bias,” said Valeant consultant Lauren Marangell, M.D., a psychiatrist and president of Brain Health Consultants.
Dr. Marangell also reported that, after stratification for preexisting psychiatric comorbidities and risk factors, “there is no question that the rate of SIB is higher in both arms with patients with baseline risk factors.” The FDA’s data analysis showed an 18-fold increase in the rate of SIB for brodalumab arm participants with a prior history of suicidality.
During its presentation, Valeant also pointed out that patients with histories of drug and alcohol abuse, depression, and suicidality were not specifically excluded from the clinical trials. This differentiates the brodalumab program from other biologic studies, “making the studies more characteristic of the real world,” said R.K. Pillai, Ph.D., Valeant vice president.
Dr. Levin’s analysis, one of several independent analyses conducted by different FDA divisions, found that the data were inconclusive. “We currently can’t conclude whether or not these are drug-related risks,” he said. Considering the critical severity of suicide as an outcome, “we must consider the application and regulatory actions carefully.”
Jean Kim, M.D., medical officer in CDER’s division of psychiatry products (DPP), noted that the number of suicides seen in the brodalumab trials “is higher than typically seen in DPP’s large psychiatric drug trials, which involve populations with higher psychiatric morbidity than patients with psoriasis.”
Patients with psoriasis are also known to have a baseline elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, and no committee member felt the brodalumab data showed any additional signal for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) beyond what would be suspected in this population. “I don’t right now see a safety signal for MACE,” said panelist Michael Blaha, M.D., a cardiologist and director of clinical research at Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Heart Disease, Baltimore. He noted, however, that research is ongoing to elucidate the relationship between cytokine levels and MACE. “This question about whether cytokines raise or reduce rates for [cardiovascular] events is an open one.”
One of the dermatologists on the committee, Lynn Drake, M.D., said that her decision making was influenced by the disease burden psoriasis inflicts on the patients she sees in her daily practice. “These patients are ill. People tend to think it’s just skin disease. It is not just skin disease. … I’d hate to see our patients deprived of a drug that might help alleviate their symptoms,” said Dr. Drake.
Though committee members voiced some disagreement about whether a patient registry should be established, and if it should be voluntary, they were in agreement that patients and prescribers both be aware of the potential risks of brodalumab, without making any risk management strategy so burdensome that appropriate patients would be deterred from considering the medication. Psoriasis, Dr. Drake said, “is a devastating disease. We need this in our armamentarium.”
The proposed dosing for brodalumab is 210 mg injected subcutaneously weekly for 3 weeks, followed by 210 mg every 2 weeks thereafter.
The FDA usually follows the recommendations of its advisory committees. The panelists had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
*A previous version of this article misstated the number of patients who experienced SIB events.
A Food and Drug Administration advisory committee has unanimously supported approval of the monoclonal antibody brodalumab for the treatment of moderate to severe plaque psoriasis, with the majority recommending risk management options beyond labeling to address concerns about the six completed suicides among patients treated with brodalumab in clinical trials.
Though no members of the FDA’s Dermatologic and Ophthalmic Drugs Advisory Committee disputed the drug’s efficacy for plaque psoriasis, the possibility of a signal for suicidal ideation and behavior (SIB) among the brodalumab group prompted the committee’s chair, Michael Bigby, M.D., to remark, “The big problem is that you have six completed suicides. … I would say it’s a fairly big number for a randomized controlled trial. Patients and clinicians need to be aware of this as a fact.”
Dr. Bigby, professor of dermatology at Harvard Medical School, Boston, headed the 18-member panel, which included dermatologists, psychiatrists, and cardiologists. Fourteen members voted in favor of approval with risk management measures beyond labeling; four members voted for approval with labeling alone.
Brodalumab targets interleukin-17 receptors, inhibiting IL-17 uptake and thus blocking the pathway responsible for the cutaneous and systemic signs and symptoms of psoriasis. The pivotal phase III brodalumab studies, AMAGINE-1, -2, and -3, enrolled a total of 4,373 patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis. AMAGINE-1 enrolled 661 patients in a 1:1:1 ratio to a randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled study that included two doses of brodalumab: 210 mg and 140 mg. The placebo-controlled phase of the study ran for 12 weeks, followed by a withdrawal and retreatment phase, and after 52 weeks, by an open label long-term extension phase.
AMAGINE-2 (1,831 patients) and AMAGINE-3 (1,881 patients) were identically designed studies that pitted both doses of brodalumab against an active comparator, ustekinumab (Stelara), as well as placebo, in a 2:2:1:1 ratio. This double-blind phase of the study also lasted 12 weeks. During weeks 12-52, patients on the brodalumab arms continued, with an exploration of wider-dose intervals for the 140-mg dose. Patients also continued with ustekinumab, with a rescue option to transition to brodalumab 210 mg. The placebo group could continue on brodalumab 210 mg as well. These two studies also had an open label long-term extension phase.
At the 12-week mark in AMAGINE-1, 41.9% of patients achieved the coprimary endpoint of 100% reduction in the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index (PASI 100) score, compared with 0.5% of those on placebo (P less than .001). AMAGINE-2 and -3 saw 44.4% and 36.7% of the brodalumab 210-mg arms achieving PASI 100 at the 12-week mark, respectively. These figures were significantly higher than the 21.7% and 18.5% reaching PASI 100 on ustekinumab (P less than .001), as well as significantly higher than the less than 1% of patients in the placebo arm who reached that endpoint.
At the end of 52 weeks, 51% of those on brodalumab 210 mg had completely clear skin, compared with 28.1% of the patients receiving ustekinumab (P less than .001).
The safety analysis for brodalumab showed that the most common adverse events were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, and arthralgia; of these, the last two were considered adverse drug reactions. At 52 weeks, those on brodalumab had a slightly greater risk of having nonserious fungal infections than did those on ustekinumab. Overall, however, there was no difference between the brodalumab and ustekinumab arms at week 52 for treatment-emergent adverse events or for serious adverse events.
A cluster of SIB events occurred in 2013 and 2014 during the clinical trials, and the sponsor consulted the FDA. Additional monitoring for suicidal ideation and depression via the Columbia Suicide Severity Rating Scale (C-SSRS) and the Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ) were implemented at a point where 84% of trial patients were already in the uncontrolled open label extension stage of the trial; in addition, a retrospective data review searched for suicidal ideation and attempts before the implementation of these two tools.
A total of six brodalumab patients completed suicide in all clinical trials, including those for psoriatic arthritis and RA. Suicides included two during the 12- to 52-week follow-up and four during the long-term follow-up phase. Another 29 patients attempted suicide, had intentional self-injury, or had suicidal ideation during these phases of the study, for a total of 35 SIB events. (SIB includes completed suicide, suicide attempt, suicide behavior, and suicide ideation.)*
The significance of the number of completed suicides was difficult to ascertain, given the increased baseline prevalence of depression and related illnesses among patients with psoriasis. Compared with the general population, individuals with psoriasis have hazard ratios of 1.39, 1.31, and 1.44 for depression, anxiety, and suicidality, according to a cohort study cited by Robert Levin, M.D. , director of the division of pharmacovigilance I at the FDA’s Center for Drug Evaluation and Research (CDER).
In addition, monitoring for suicidal ideation and attempts was stepped up during the course of the clinical trials. Brodalumab’s sponsor, Valeant Pharmaceuticals, noted that the rates of suicidal ideation and attempts increased after implementation of the C-SSRS, while other neuropsychiatric symptoms remained stable or declined during the course of the studies. “This makes us think this is ascertainment bias,” said Valeant consultant Lauren Marangell, M.D., a psychiatrist and president of Brain Health Consultants.
Dr. Marangell also reported that, after stratification for preexisting psychiatric comorbidities and risk factors, “there is no question that the rate of SIB is higher in both arms with patients with baseline risk factors.” The FDA’s data analysis showed an 18-fold increase in the rate of SIB for brodalumab arm participants with a prior history of suicidality.
During its presentation, Valeant also pointed out that patients with histories of drug and alcohol abuse, depression, and suicidality were not specifically excluded from the clinical trials. This differentiates the brodalumab program from other biologic studies, “making the studies more characteristic of the real world,” said R.K. Pillai, Ph.D., Valeant vice president.
Dr. Levin’s analysis, one of several independent analyses conducted by different FDA divisions, found that the data were inconclusive. “We currently can’t conclude whether or not these are drug-related risks,” he said. Considering the critical severity of suicide as an outcome, “we must consider the application and regulatory actions carefully.”
Jean Kim, M.D., medical officer in CDER’s division of psychiatry products (DPP), noted that the number of suicides seen in the brodalumab trials “is higher than typically seen in DPP’s large psychiatric drug trials, which involve populations with higher psychiatric morbidity than patients with psoriasis.”
Patients with psoriasis are also known to have a baseline elevated risk of cardiovascular disease, and no committee member felt the brodalumab data showed any additional signal for major adverse cardiovascular events (MACEs) beyond what would be suspected in this population. “I don’t right now see a safety signal for MACE,” said panelist Michael Blaha, M.D., a cardiologist and director of clinical research at Johns Hopkins Ciccarone Center for Prevention of Heart Disease, Baltimore. He noted, however, that research is ongoing to elucidate the relationship between cytokine levels and MACE. “This question about whether cytokines raise or reduce rates for [cardiovascular] events is an open one.”
One of the dermatologists on the committee, Lynn Drake, M.D., said that her decision making was influenced by the disease burden psoriasis inflicts on the patients she sees in her daily practice. “These patients are ill. People tend to think it’s just skin disease. It is not just skin disease. … I’d hate to see our patients deprived of a drug that might help alleviate their symptoms,” said Dr. Drake.
Though committee members voiced some disagreement about whether a patient registry should be established, and if it should be voluntary, they were in agreement that patients and prescribers both be aware of the potential risks of brodalumab, without making any risk management strategy so burdensome that appropriate patients would be deterred from considering the medication. Psoriasis, Dr. Drake said, “is a devastating disease. We need this in our armamentarium.”
The proposed dosing for brodalumab is 210 mg injected subcutaneously weekly for 3 weeks, followed by 210 mg every 2 weeks thereafter.
The FDA usually follows the recommendations of its advisory committees. The panelists had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
*A previous version of this article misstated the number of patients who experienced SIB events.
FROM AN FDA ADVISORY COMMITTEE HEARING
Consider home phototherapy for some pediatric patients
MINNEAPOLIS, MINN. – For a select subset of pediatric dermatology patients, home phototherapy may represent a safe, effective, and even affordable alternative to office visits. Some families whose children are in treatment for vitiligo, psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis may find that the expense and learning curve of administering treatment at home are worthwhile, but dermatologists must select those families carefully.
Leslie Castelo-Soccio, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric dermatology at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, gave an overview of medical phototherapy for childhood skin diseases at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
For vitiligo, narrow-band UVB’s (NBUVB) effectiveness is maximized if treatment is begun relatively early, and if results are going to happen, they’ll show up fairly quickly. “If there’s no response after six months, stop the therapy,” Dr. Castelo-Soccio said.
Although the literature shows NBUVB to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis, Dr. Castelo-Soccio noted that most pediatric atopic dermatitis studies have been small and retrospective and conducted in a population with severe disease.
Regarding psoriasis in children, the literature shows “higher numbers of patients with near-complete or complete response,” she said.
The experience of NBUVB for pediatric dermatologic conditions at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia supports the idea that “the best responses are seen after at least 40 treatments,” and that 6 months is enough time to see whether a patient will respond. The best responders at her institution are children with facial vitiligo. “Of course, you get a better response with compliance,” she noted.
The experience of her patients falls in line with the data about side effects, in which the most common adverse events are reactivation of HSV and burning.
Families ask about cancer risk, but “there are no published data on the risk of skin cancer in long-term phototherapy in children,” she said. At this point, the best pediatric dermatologists can do is to extrapolate risk from data on phototherapy for neonatal jaundice, but even those data are inconclusive, she said.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio noted that it’s pretty common for families to request home treatment: “When you start talking to patients about phototherapy, the thing I always get questions about is, ‘Why can’t I do it at home?’ ” She prefers to initiate treatment in the clinic and then assess suitability for home therapy after a relationship has been established.
The ideal patient, said Dr. Castelo-Soccio, is one whose family has been diligent about coming to appointments and who otherwise demonstrates excellent compliance.
At first blush, the cost of acquiring a home device – often in the $2,000 range – might seem prohibitive for many families. The upfront cost may be worth it for some, since office visits involve copayments and lost time from school and work for multiple treatments weekly over a period of months. A big commute to the doctor’s office for treatment may further tip the scales toward home treatment. “I wouldn’t hesitate to offer this option to the right family,” she said.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio said she’s had some limited success getting insurance reimbursement for home phototherapy, especially if success has already been seen with office-based treatment.
NBUVB therapy has limitations, though. Some that have particular relevance for the pediatric population involve the challenges of safe delivery, including using appropriate eye wear and ensuring lack of movement. Each of these problems can be even more of a challenge at home, reinforcing the need to select appropriate patients for home phototherapy, she added.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio said she provides information about all of the various phototherapy devices to her patients and their parents, letting them make the choice. “All of the companies are really good about helping with paperwork” to apply for insurance reimbursement, she said. Options range from the bulkiest and most expensive – a full phototherapy box – to three-panel arrays, single panels, hand-foot devices, and even hand-held devices. The latter can be had for less than $1,000 and may be best suited for targeting smaller areas.
Features to look for in home phototherapy devices include a dosimeter accuracy sensor, which adjusts the treatment time to deliver the same dose, even if dust or aging lamps reduce output. User-friendly timers also are helpful for families, said Dr. Castelo-Soccio. A safety lock-out will allow only a certain number of treatments before the unit must be reset by the physician and is a reassuring feature. Each activation counts as a treatment, however, so families and physicians must be aware that if a hand-held unit is used to treat multiple small lesions in different body areas, a single treatment session will involve many device activations, each of which will be registered as a treatment.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
MINNEAPOLIS, MINN. – For a select subset of pediatric dermatology patients, home phototherapy may represent a safe, effective, and even affordable alternative to office visits. Some families whose children are in treatment for vitiligo, psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis may find that the expense and learning curve of administering treatment at home are worthwhile, but dermatologists must select those families carefully.
Leslie Castelo-Soccio, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric dermatology at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, gave an overview of medical phototherapy for childhood skin diseases at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
For vitiligo, narrow-band UVB’s (NBUVB) effectiveness is maximized if treatment is begun relatively early, and if results are going to happen, they’ll show up fairly quickly. “If there’s no response after six months, stop the therapy,” Dr. Castelo-Soccio said.
Although the literature shows NBUVB to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis, Dr. Castelo-Soccio noted that most pediatric atopic dermatitis studies have been small and retrospective and conducted in a population with severe disease.
Regarding psoriasis in children, the literature shows “higher numbers of patients with near-complete or complete response,” she said.
The experience of NBUVB for pediatric dermatologic conditions at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia supports the idea that “the best responses are seen after at least 40 treatments,” and that 6 months is enough time to see whether a patient will respond. The best responders at her institution are children with facial vitiligo. “Of course, you get a better response with compliance,” she noted.
The experience of her patients falls in line with the data about side effects, in which the most common adverse events are reactivation of HSV and burning.
Families ask about cancer risk, but “there are no published data on the risk of skin cancer in long-term phototherapy in children,” she said. At this point, the best pediatric dermatologists can do is to extrapolate risk from data on phototherapy for neonatal jaundice, but even those data are inconclusive, she said.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio noted that it’s pretty common for families to request home treatment: “When you start talking to patients about phototherapy, the thing I always get questions about is, ‘Why can’t I do it at home?’ ” She prefers to initiate treatment in the clinic and then assess suitability for home therapy after a relationship has been established.
The ideal patient, said Dr. Castelo-Soccio, is one whose family has been diligent about coming to appointments and who otherwise demonstrates excellent compliance.
At first blush, the cost of acquiring a home device – often in the $2,000 range – might seem prohibitive for many families. The upfront cost may be worth it for some, since office visits involve copayments and lost time from school and work for multiple treatments weekly over a period of months. A big commute to the doctor’s office for treatment may further tip the scales toward home treatment. “I wouldn’t hesitate to offer this option to the right family,” she said.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio said she’s had some limited success getting insurance reimbursement for home phototherapy, especially if success has already been seen with office-based treatment.
NBUVB therapy has limitations, though. Some that have particular relevance for the pediatric population involve the challenges of safe delivery, including using appropriate eye wear and ensuring lack of movement. Each of these problems can be even more of a challenge at home, reinforcing the need to select appropriate patients for home phototherapy, she added.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio said she provides information about all of the various phototherapy devices to her patients and their parents, letting them make the choice. “All of the companies are really good about helping with paperwork” to apply for insurance reimbursement, she said. Options range from the bulkiest and most expensive – a full phototherapy box – to three-panel arrays, single panels, hand-foot devices, and even hand-held devices. The latter can be had for less than $1,000 and may be best suited for targeting smaller areas.
Features to look for in home phototherapy devices include a dosimeter accuracy sensor, which adjusts the treatment time to deliver the same dose, even if dust or aging lamps reduce output. User-friendly timers also are helpful for families, said Dr. Castelo-Soccio. A safety lock-out will allow only a certain number of treatments before the unit must be reset by the physician and is a reassuring feature. Each activation counts as a treatment, however, so families and physicians must be aware that if a hand-held unit is used to treat multiple small lesions in different body areas, a single treatment session will involve many device activations, each of which will be registered as a treatment.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
MINNEAPOLIS, MINN. – For a select subset of pediatric dermatology patients, home phototherapy may represent a safe, effective, and even affordable alternative to office visits. Some families whose children are in treatment for vitiligo, psoriasis, and atopic dermatitis may find that the expense and learning curve of administering treatment at home are worthwhile, but dermatologists must select those families carefully.
Leslie Castelo-Soccio, MD, PhD, professor of pediatric dermatology at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, gave an overview of medical phototherapy for childhood skin diseases at the annual meeting of the Society for Pediatric Dermatology.
For vitiligo, narrow-band UVB’s (NBUVB) effectiveness is maximized if treatment is begun relatively early, and if results are going to happen, they’ll show up fairly quickly. “If there’s no response after six months, stop the therapy,” Dr. Castelo-Soccio said.
Although the literature shows NBUVB to be effective in treating atopic dermatitis, Dr. Castelo-Soccio noted that most pediatric atopic dermatitis studies have been small and retrospective and conducted in a population with severe disease.
Regarding psoriasis in children, the literature shows “higher numbers of patients with near-complete or complete response,” she said.
The experience of NBUVB for pediatric dermatologic conditions at the Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia supports the idea that “the best responses are seen after at least 40 treatments,” and that 6 months is enough time to see whether a patient will respond. The best responders at her institution are children with facial vitiligo. “Of course, you get a better response with compliance,” she noted.
The experience of her patients falls in line with the data about side effects, in which the most common adverse events are reactivation of HSV and burning.
Families ask about cancer risk, but “there are no published data on the risk of skin cancer in long-term phototherapy in children,” she said. At this point, the best pediatric dermatologists can do is to extrapolate risk from data on phototherapy for neonatal jaundice, but even those data are inconclusive, she said.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio noted that it’s pretty common for families to request home treatment: “When you start talking to patients about phototherapy, the thing I always get questions about is, ‘Why can’t I do it at home?’ ” She prefers to initiate treatment in the clinic and then assess suitability for home therapy after a relationship has been established.
The ideal patient, said Dr. Castelo-Soccio, is one whose family has been diligent about coming to appointments and who otherwise demonstrates excellent compliance.
At first blush, the cost of acquiring a home device – often in the $2,000 range – might seem prohibitive for many families. The upfront cost may be worth it for some, since office visits involve copayments and lost time from school and work for multiple treatments weekly over a period of months. A big commute to the doctor’s office for treatment may further tip the scales toward home treatment. “I wouldn’t hesitate to offer this option to the right family,” she said.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio said she’s had some limited success getting insurance reimbursement for home phototherapy, especially if success has already been seen with office-based treatment.
NBUVB therapy has limitations, though. Some that have particular relevance for the pediatric population involve the challenges of safe delivery, including using appropriate eye wear and ensuring lack of movement. Each of these problems can be even more of a challenge at home, reinforcing the need to select appropriate patients for home phototherapy, she added.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio said she provides information about all of the various phototherapy devices to her patients and their parents, letting them make the choice. “All of the companies are really good about helping with paperwork” to apply for insurance reimbursement, she said. Options range from the bulkiest and most expensive – a full phototherapy box – to three-panel arrays, single panels, hand-foot devices, and even hand-held devices. The latter can be had for less than $1,000 and may be best suited for targeting smaller areas.
Features to look for in home phototherapy devices include a dosimeter accuracy sensor, which adjusts the treatment time to deliver the same dose, even if dust or aging lamps reduce output. User-friendly timers also are helpful for families, said Dr. Castelo-Soccio. A safety lock-out will allow only a certain number of treatments before the unit must be reset by the physician and is a reassuring feature. Each activation counts as a treatment, however, so families and physicians must be aware that if a hand-held unit is used to treat multiple small lesions in different body areas, a single treatment session will involve many device activations, each of which will be registered as a treatment.
Dr. Castelo-Soccio had no relevant financial disclosures.
On Twitter @karioakes
EXPERT ANALYSIS FROM THE SPD ANNUAL MEETING
Cochrane review: Topical steroid–vitamin D combination best for scalp psoriasis
As a treatment for scalp psoriasis, the combination of a topical steroid and topical vitamin D was marginally better than topical steroids alone, but both approaches have a similar safety profile, according to a Cochrane review.
The systematic review included 59 randomized controlled trials of topical treatments for scalp psoriasis, representing a total of 11,561 participants of all ages, most of whom were followed for less than 6 months, according to Justin Schlager, MD, of the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, and coauthors (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016. Issue 2. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009687.pub2).
In the analysis, topical steroid monotherapy was significantly better than topical vitamin D for clearance, as assessed by the Investigator’s Global Assessment of Disease Severity (risk ratio, 1.82; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-2.18). But the combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed a small but statistically significant advantage over steroids alone (RR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.08-1.36) and an even greater advantage over vitamin D alone (RR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.87-2.78).
Similarly, for treatment response, the combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed the greatest benefit in terms of treatment response when compared with steroid monotherapy (RR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.06-1.25) – an additional benefit the authors observed was small – and when compared with vitamin D alone (RR, 2.31; 95% CI, 1.75-3.04).
But for monotherapy, corticosteroids were more than twice as effective as vitamin D alone for treatment response (RR, 2.09; 95% CI, 1.80-2.41). The analysis also showed that corticosteroids of moderate, high, and very high potency were similarly effective.
Steroids were associated with a significantly lower risk of withdrawal because of adverse events than vitamin D (RR, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.11-0.42). Patients using topical steroids reported adverse events such as a burning sensation or irritation at the site of application, while patients taking vitamin D reported side effects such as pruritus, candidiasis, dermatitis, and erythema, although in both cases these were mostly limited to the application site.
The combination of vitamin D and topical steroid had a lower risk of withdrawals because of adverse events than vitamin D alone, but showed a similar rate to topical steroids alone.
“Given the similar safety profile and only slim benefit of the two-compound combination over the steroid alone, monotherapy with generic topical corticosteroids may be fully acceptable for short-term therapy,” the authors wrote. The authors noted that data on patients’ quality of life was poor across all the studies included in the analysis and called for future trials to address this gap, and more long-term assessments.
“Regardless of the type of psoriasis, up to 79% of people with the condition present with scalp involvement, which has frequently been the first site to show symptoms of the disease,” they pointed out.
Thirty of the 59 studies were either conducted or sponsored by the manufacturer of the study medication, and the authors described the overall quality of the studies as “moderate.” Thirty-three studies were double blind, 14 were single blind, two had “third-party” blinding, six were open-label, and four did not report blinding information.
The study was supported by the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil; the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil; and the National Institute for Health Research, United Kingdom. Six authors and one clinical referee declared speakers’ fees, research grants, and funding from the pharmaceutical industry. One author had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
As a treatment for scalp psoriasis, the combination of a topical steroid and topical vitamin D was marginally better than topical steroids alone, but both approaches have a similar safety profile, according to a Cochrane review.
The systematic review included 59 randomized controlled trials of topical treatments for scalp psoriasis, representing a total of 11,561 participants of all ages, most of whom were followed for less than 6 months, according to Justin Schlager, MD, of the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, and coauthors (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016. Issue 2. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009687.pub2).
In the analysis, topical steroid monotherapy was significantly better than topical vitamin D for clearance, as assessed by the Investigator’s Global Assessment of Disease Severity (risk ratio, 1.82; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-2.18). But the combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed a small but statistically significant advantage over steroids alone (RR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.08-1.36) and an even greater advantage over vitamin D alone (RR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.87-2.78).
Similarly, for treatment response, the combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed the greatest benefit in terms of treatment response when compared with steroid monotherapy (RR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.06-1.25) – an additional benefit the authors observed was small – and when compared with vitamin D alone (RR, 2.31; 95% CI, 1.75-3.04).
But for monotherapy, corticosteroids were more than twice as effective as vitamin D alone for treatment response (RR, 2.09; 95% CI, 1.80-2.41). The analysis also showed that corticosteroids of moderate, high, and very high potency were similarly effective.
Steroids were associated with a significantly lower risk of withdrawal because of adverse events than vitamin D (RR, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.11-0.42). Patients using topical steroids reported adverse events such as a burning sensation or irritation at the site of application, while patients taking vitamin D reported side effects such as pruritus, candidiasis, dermatitis, and erythema, although in both cases these were mostly limited to the application site.
The combination of vitamin D and topical steroid had a lower risk of withdrawals because of adverse events than vitamin D alone, but showed a similar rate to topical steroids alone.
“Given the similar safety profile and only slim benefit of the two-compound combination over the steroid alone, monotherapy with generic topical corticosteroids may be fully acceptable for short-term therapy,” the authors wrote. The authors noted that data on patients’ quality of life was poor across all the studies included in the analysis and called for future trials to address this gap, and more long-term assessments.
“Regardless of the type of psoriasis, up to 79% of people with the condition present with scalp involvement, which has frequently been the first site to show symptoms of the disease,” they pointed out.
Thirty of the 59 studies were either conducted or sponsored by the manufacturer of the study medication, and the authors described the overall quality of the studies as “moderate.” Thirty-three studies were double blind, 14 were single blind, two had “third-party” blinding, six were open-label, and four did not report blinding information.
The study was supported by the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil; the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil; and the National Institute for Health Research, United Kingdom. Six authors and one clinical referee declared speakers’ fees, research grants, and funding from the pharmaceutical industry. One author had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
As a treatment for scalp psoriasis, the combination of a topical steroid and topical vitamin D was marginally better than topical steroids alone, but both approaches have a similar safety profile, according to a Cochrane review.
The systematic review included 59 randomized controlled trials of topical treatments for scalp psoriasis, representing a total of 11,561 participants of all ages, most of whom were followed for less than 6 months, according to Justin Schlager, MD, of the Charité – Universitätsmedizin Berlin, and coauthors (Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016. Issue 2. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD009687.pub2).
In the analysis, topical steroid monotherapy was significantly better than topical vitamin D for clearance, as assessed by the Investigator’s Global Assessment of Disease Severity (risk ratio, 1.82; 95% confidence interval, 1.52-2.18). But the combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed a small but statistically significant advantage over steroids alone (RR, 1.22; 95% CI, 1.08-1.36) and an even greater advantage over vitamin D alone (RR, 2.28; 95% CI, 1.87-2.78).
Similarly, for treatment response, the combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed the greatest benefit in terms of treatment response when compared with steroid monotherapy (RR, 1.15; 95% CI, 1.06-1.25) – an additional benefit the authors observed was small – and when compared with vitamin D alone (RR, 2.31; 95% CI, 1.75-3.04).
But for monotherapy, corticosteroids were more than twice as effective as vitamin D alone for treatment response (RR, 2.09; 95% CI, 1.80-2.41). The analysis also showed that corticosteroids of moderate, high, and very high potency were similarly effective.
Steroids were associated with a significantly lower risk of withdrawal because of adverse events than vitamin D (RR, 0.22; 95% CI, 0.11-0.42). Patients using topical steroids reported adverse events such as a burning sensation or irritation at the site of application, while patients taking vitamin D reported side effects such as pruritus, candidiasis, dermatitis, and erythema, although in both cases these were mostly limited to the application site.
The combination of vitamin D and topical steroid had a lower risk of withdrawals because of adverse events than vitamin D alone, but showed a similar rate to topical steroids alone.
“Given the similar safety profile and only slim benefit of the two-compound combination over the steroid alone, monotherapy with generic topical corticosteroids may be fully acceptable for short-term therapy,” the authors wrote. The authors noted that data on patients’ quality of life was poor across all the studies included in the analysis and called for future trials to address this gap, and more long-term assessments.
“Regardless of the type of psoriasis, up to 79% of people with the condition present with scalp involvement, which has frequently been the first site to show symptoms of the disease,” they pointed out.
Thirty of the 59 studies were either conducted or sponsored by the manufacturer of the study medication, and the authors described the overall quality of the studies as “moderate.” Thirty-three studies were double blind, 14 were single blind, two had “third-party” blinding, six were open-label, and four did not report blinding information.
The study was supported by the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil; the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil; and the National Institute for Health Research, United Kingdom. Six authors and one clinical referee declared speakers’ fees, research grants, and funding from the pharmaceutical industry. One author had no conflicts of interest to disclose.
FROM THE COCHRANE DATABASE OF SYSTEMATIC REVIEWS
Key clinical point: The combination of a topical steroid and topical vitamin D is marginally better but with a similar safety profile to steroids alone as a treatment for psoriasis on the scalp.
Major finding: The combination of a topical steroid and vitamin D showed a small but statistically significant advantage over steroids alone, and a greater advantage over vitamin D alone.
Data source: A systematic review of 59 randomized controlled studies in 11,561 patients.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the Universidade Federal de São Paulo, Brazil; the Universidade Federal do Rio Grande do Norte, Brazil; and the National Institute for Health Research, United Kingdom. Six authors and one clinical referee declared speakers’ fees, research grants, and funding from the pharmaceutical industry. One author had no conflicts of interest to disclose.