User login
The overall prevalence of genital human papillomavirus (HPV) among adults aged 18-59 years was 42.5% in 2013-2014, with more than half of that representing infection with high-risk types, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
Prevalence of the 14 HPV types (out of 37 total) considered to be high risk was almost 23% in 2013-2014. Men were significantly more likely than women to have any genital HPV (45% vs. 40%) and high-risk genital HPV (25% vs. 20%), the NCHS reported.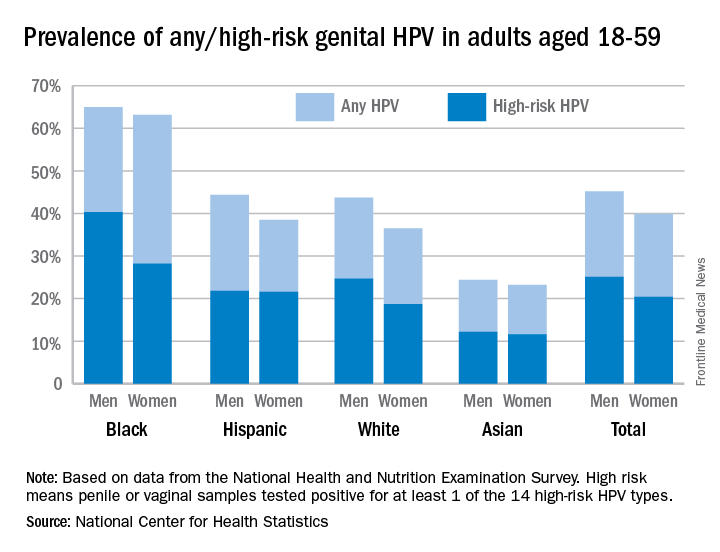
Oral rinse samples were collected as well for adults aged 18-69 years, and the overall prevalence was 7.3% for any oral HPV and 4% for high-risk HPV in 2011-2014. Prevalence among men was significantly higher than among women for all oral HPV (11.5% vs. 3.3%) and for high-risk HPV (6.8% vs. 1.2%), the NCHS said.
The overall prevalence of genital human papillomavirus (HPV) among adults aged 18-59 years was 42.5% in 2013-2014, with more than half of that representing infection with high-risk types, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
Prevalence of the 14 HPV types (out of 37 total) considered to be high risk was almost 23% in 2013-2014. Men were significantly more likely than women to have any genital HPV (45% vs. 40%) and high-risk genital HPV (25% vs. 20%), the NCHS reported.
Oral rinse samples were collected as well for adults aged 18-69 years, and the overall prevalence was 7.3% for any oral HPV and 4% for high-risk HPV in 2011-2014. Prevalence among men was significantly higher than among women for all oral HPV (11.5% vs. 3.3%) and for high-risk HPV (6.8% vs. 1.2%), the NCHS said.
The overall prevalence of genital human papillomavirus (HPV) among adults aged 18-59 years was 42.5% in 2013-2014, with more than half of that representing infection with high-risk types, according to the National Center for Health Statistics.
Prevalence of the 14 HPV types (out of 37 total) considered to be high risk was almost 23% in 2013-2014. Men were significantly more likely than women to have any genital HPV (45% vs. 40%) and high-risk genital HPV (25% vs. 20%), the NCHS reported.
Oral rinse samples were collected as well for adults aged 18-69 years, and the overall prevalence was 7.3% for any oral HPV and 4% for high-risk HPV in 2011-2014. Prevalence among men was significantly higher than among women for all oral HPV (11.5% vs. 3.3%) and for high-risk HPV (6.8% vs. 1.2%), the NCHS said.