User login
Clinical Psychiatry News is the online destination and multimedia properties of Clinica Psychiatry News, the independent news publication for psychiatrists. Since 1971, Clinical Psychiatry News has been the leading source of news and commentary about clinical developments in psychiatry as well as health care policy and regulations that affect the physician's practice.
Dear Drupal User: You're seeing this because you're logged in to Drupal, and not redirected to MDedge.com/psychiatry.
Depression
adolescent depression
adolescent major depressive disorder
adolescent schizophrenia
adolescent with major depressive disorder
animals
autism
baby
brexpiprazole
child
child bipolar
child depression
child schizophrenia
children with bipolar disorder
children with depression
children with major depressive disorder
compulsive behaviors
cure
elderly bipolar
elderly depression
elderly major depressive disorder
elderly schizophrenia
elderly with dementia
first break
first episode
gambling
gaming
geriatric depression
geriatric major depressive disorder
geriatric schizophrenia
infant
ketamine
kid
major depressive disorder
major depressive disorder in adolescents
major depressive disorder in children
parenting
pediatric
pediatric bipolar
pediatric depression
pediatric major depressive disorder
pediatric schizophrenia
pregnancy
pregnant
rexulti
skin care
suicide
teen
wine
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
footer[@id='footer']
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-article-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-home-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-pub-topic-cpn')]
div[contains(@class, 'panel-panel-inner')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-node-field-article-topics')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
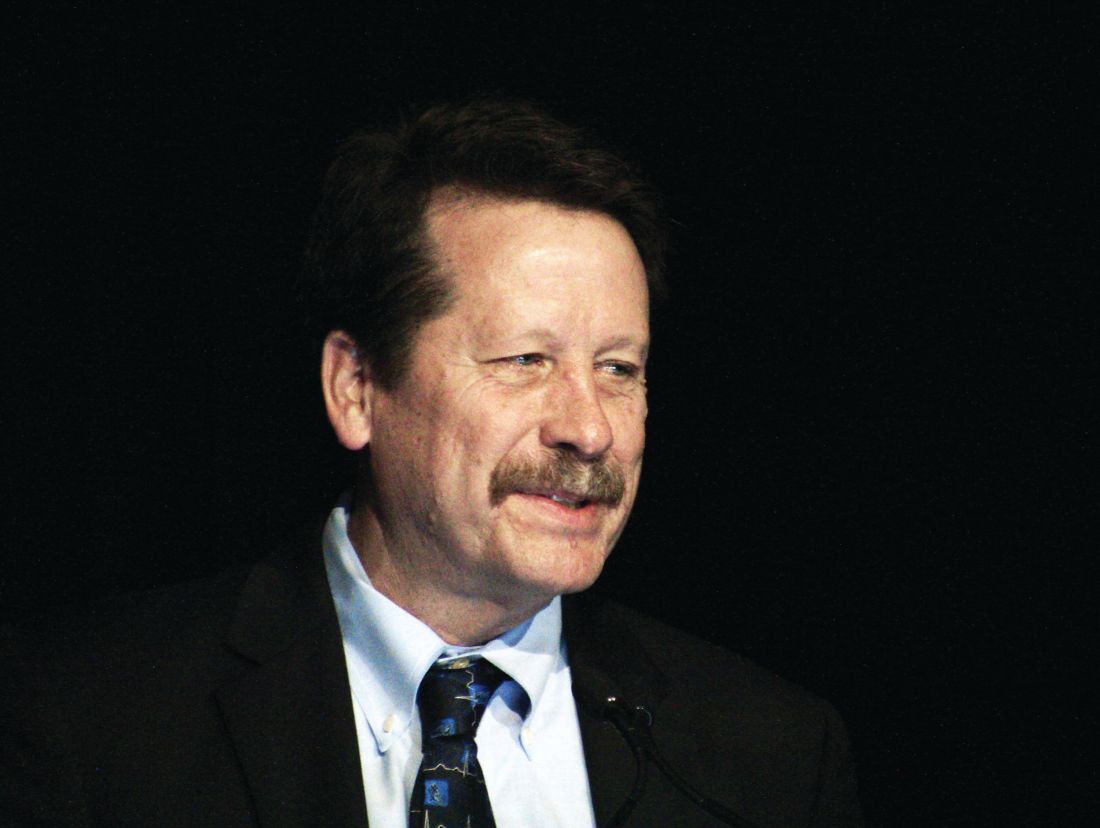
Califf plans work on opioids, accelerated approvals on return to FDA
Robert M. Califf, MD, plans to take a close look at federal policies on opioid prescriptions in his expected second turn as the top U.S. regulator of medical products, as well as keep closer tabs on the performance of drugs cleared with accelerated approvals.
Dr. Califf on Tuesday fielded questions at a Senate hearing about his nomination by President Joe Biden to serve as administrator of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, a role in which he served in the Obama administration. He also spoke about the need to bolster the nation’s ability to maintain an adequate supply of key medical products, including drugs.
Members of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, which is handling Dr. Califf’s nomination, were largely cordial and supportive during the hearing. Sen. Patty Murray (D-Wash.), the committee chair, and the panel’s top Republican, Sen. Richard Burr of North Carolina, addressed Dr. Califf during the hearing as if he would soon serve again as the FDA’s leader. Both were among the senators who voted 89-4 to confirm Dr. Califf in a February 2016 vote.
Dr. Califf “was previously confirmed to lead FDA in an overwhelming bipartisan vote, and I look forward to working with him again to ensure FDA continues to protect families across the country, uphold the gold standard of safety and effectiveness, and put science and data first,” Sen. Murray said.
Less enthusiastic about Dr. Califf was Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-VT), who was among the seven senators who did not vote on Dr. Califf’s nomination in 2016.
Sen. Sanders objected in 2016 to Dr. Califf’s ties to the pharmaceutical industry, and he did so again Tuesday. A noted leader in conducting clinical trials, Dr. Califf has worked with many drugmakers. But at the hearing, Dr. Califf said he concurs with Sen. Sanders on an idea strongly opposed by the pharmaceutical industry.
In response to Sen. Sanders’ question, Dr. Califf said he already is “on record as being in favor of Medicare negotiating with the industry on prices.”
The FDA would not take direct part in negotiations, as this work would be handled by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Democrats want to give Medicare some negotiating authority through their sweeping Build Back Better Act.
People in the United States are dismayed over both the cost of prescription drugs and the widespread distribution of prescription painkillers that helped fuel the current opioid epidemic, Sen. Sanders told Dr. Califf. Many people will be concerned about an FDA commissioner who has benefited from close ties to the industry, Sen. Sanders said.
“How are they going to believe that you’re going to be an independent and strong voice against this enormously powerful, special interest?” Sen. Sanders asked.
“I’m totally with you on the concept that the price of pharmaceuticals is way too high in this country,” Dr. Califf said in reply.
Dr. Califf was paid $2.7 million in salary and bonus by Verily Life Sciences, the biomedical research organization operated by Alphabet, parent company of Google, according to his federal financial disclosure. He also reported holding board positions with pharmaceutical companies AmyriAD and Centessa Pharmaceuticals.
Bloomberg Government reported that Dr. Califf has ties to about 16 other research organizations and biotech companies. Bloomberg Government also said that, in his earlier FDA service, Dr. Califf kept a whiteboard in his office that listed all the activities and projects that required his recusal, citing as a source Howard Sklamberg, who was a deputy commissioner under Dr. Califf.
“He was very, very, very careful,” Mr. Sklamberg, who’s now an attorney at Arnold & Porter LLP, told Bloomberg Government.
‘Work to do’ on opioids
Senators looped back repeatedly to the topic of opioids during Dr. Califf’s hearing, reflecting deep concerns about the FDA’s efforts to warn of the risks of prescription painkillers.
There were an estimated 100,306 drug overdose deaths in the United States in the 12 months ending in April, an increase of 28.5% from the 78,056 deaths during the same period the year before, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Califf said he plans to focus on what information the FDA conveys to the public about the risks of prescription painkillers, including a look at what the labels for these products say.
“I am committed to do a comprehensive review of the status of opioids, early in my tenure,” Dr. Califf said.
Dr. Califf indicated that physicians are still too quick to provide excess doses of these medicines, despite years of efforts to restrain their use. He said he knows relatives who were given 30-day prescriptions for opioids after minor surgery.
“So I know we have work to do,” Dr. Califf said.
Concerns about the FDA’s previous work in managing opioids has led to protests from a few Democratic senators about the prospect of President Biden nominating the acting FDA commissioner, Janet Woodcock, MD, for the permanent post.
At the hearing, Sen. Ben Ray Luján (D-NM) raised the case of the FDA’s approval of the powerful Zohydro painkiller. The agency approved that drug despite an 11-2 vote against it by the FDA’s Anesthetic and Analgesic Drug Products Advisory Committee.
Sen. Luján asked Dr. Califf what he would do if an FDA advisory committee voted “overwhelmingly” against recommending approval of a medicine, as happened in the Zohydro case.
While not mentioned by Sen. Luján in this exchange during the hearing with Dr. Califf, the FDA staff’s rejection of recommendations of advisory committees has been a growing concern among researchers.
The agency last year approved aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen), a drug for Alzheimer’s disease, dismissing the advice of its Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee. That decision triggered the resignation of several members of the panel. The FDA staff also earlier rejected the conclusion the majority of members of the same advisory committee offered in 2016 on eteplirsen (Exondys 51, Sarepta), a drug for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Dr. Califf told Sen. Luján he had done recent research into how often the FDA staff does not concur with the recommendations of an advisory committee. He said the FDA takes a different course of action in about 25% of cases. In about three-quarters of those cases, the FDA staff opts for a “more stringent” approach regarding allowing the public access to the drug, as opposed to a more generous one as seen in the Zohydro, Aduhelm, and Exondys 51 cases.
Still, Dr. Califf said that when there’s an 11-2 advisory committee vote against recommendation of a product, “the leaders at FDA really need to take a close look” at what’s happening.
Question on accelerated approvals
The FDA’s approval of aducanumab drew attention to a debate already underway about conditional clearances known as accelerated approvals.
The FDA has used this path since the 1990s to speed access to drugs for serious conditions. The trade-off for early access is that the agency sometimes makes the wrong call based on initial findings, and clears a medicine later found not to benefit patients as expected.
The FDA’s cancer division is in the midst of public efforts to address cases where drugmakers have not been able to deliver studies that support accelerated approvals of their oncology drugs. In addition, the Office of Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services announced in August that it is reviewing the FDA’s handling of the accelerated approval process.
At Tuesday’s hearing, Sen. Burr grilled Dr. Califf about how he would respond to calls to change how the FDA handles the accelerated-approval process.
“Can you commit to me and to patients who may rely on cutting-edge treatments that you will not support efforts to narrow this pathway or raise the bar for drugs to be approved under those pathways?” Burr asked Califf.
Dr. Califf responded by saying he was “a fan of accelerated approval – for the right conditions.”
Earlier, in his opening statement, Dr. Califf had said his mother benefited directly from the accelerated approval of new drugs for multiple myeloma. Dr. Califf told Sen. Burr that he had spent “countless hours with patient groups” and understands the need to speed the approval of medicines for serious diseases.
But the FDA also has to make sure it holds up its end of the bargain struck with accelerated approvals. This involves checking on how these medicines work once they are marketed.
“We’re accepting that there’s more uncertainty,” Dr. Califf said. “That means we’ve got to have a better system to evaluate these products as they’re used on the market. And I think there are ways that we can do that now. Technology is making this possible in ways that it just was not possible before.”
Worries about the medical supply chain
Sen. Susan Collins (R-Maine) asked Dr. Califf about the vulnerability of the U.S. medical system to disruptions of the supply chain. She raised concerns about China’s dominance in antibiotic manufacturing as an example. She asked if Congress could do more to encourage domestic manufacturing of medical supplies, such as by offering tax incentives.
Dr. Califf told Sen. Collins he shared her concern about the U.S. manufacturing of ingredients used in both branded and generic drugs. He said he recently has served on a committee of the National Academy of Medicine that is examining supply chain issues.
This committee will soon release a report with specific recommendations, Dr. Califf said.
“We don’t have enough competitive entities in what’s become sort of a commodity business” of drug manufacturing, Dr. Califf said. “So we need a number of steps to make the system more resilient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Robert M. Califf, MD, plans to take a close look at federal policies on opioid prescriptions in his expected second turn as the top U.S. regulator of medical products, as well as keep closer tabs on the performance of drugs cleared with accelerated approvals.
Dr. Califf on Tuesday fielded questions at a Senate hearing about his nomination by President Joe Biden to serve as administrator of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, a role in which he served in the Obama administration. He also spoke about the need to bolster the nation’s ability to maintain an adequate supply of key medical products, including drugs.
Members of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, which is handling Dr. Califf’s nomination, were largely cordial and supportive during the hearing. Sen. Patty Murray (D-Wash.), the committee chair, and the panel’s top Republican, Sen. Richard Burr of North Carolina, addressed Dr. Califf during the hearing as if he would soon serve again as the FDA’s leader. Both were among the senators who voted 89-4 to confirm Dr. Califf in a February 2016 vote.
Dr. Califf “was previously confirmed to lead FDA in an overwhelming bipartisan vote, and I look forward to working with him again to ensure FDA continues to protect families across the country, uphold the gold standard of safety and effectiveness, and put science and data first,” Sen. Murray said.
Less enthusiastic about Dr. Califf was Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-VT), who was among the seven senators who did not vote on Dr. Califf’s nomination in 2016.
Sen. Sanders objected in 2016 to Dr. Califf’s ties to the pharmaceutical industry, and he did so again Tuesday. A noted leader in conducting clinical trials, Dr. Califf has worked with many drugmakers. But at the hearing, Dr. Califf said he concurs with Sen. Sanders on an idea strongly opposed by the pharmaceutical industry.
In response to Sen. Sanders’ question, Dr. Califf said he already is “on record as being in favor of Medicare negotiating with the industry on prices.”
The FDA would not take direct part in negotiations, as this work would be handled by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Democrats want to give Medicare some negotiating authority through their sweeping Build Back Better Act.
People in the United States are dismayed over both the cost of prescription drugs and the widespread distribution of prescription painkillers that helped fuel the current opioid epidemic, Sen. Sanders told Dr. Califf. Many people will be concerned about an FDA commissioner who has benefited from close ties to the industry, Sen. Sanders said.
“How are they going to believe that you’re going to be an independent and strong voice against this enormously powerful, special interest?” Sen. Sanders asked.
“I’m totally with you on the concept that the price of pharmaceuticals is way too high in this country,” Dr. Califf said in reply.
Dr. Califf was paid $2.7 million in salary and bonus by Verily Life Sciences, the biomedical research organization operated by Alphabet, parent company of Google, according to his federal financial disclosure. He also reported holding board positions with pharmaceutical companies AmyriAD and Centessa Pharmaceuticals.
Bloomberg Government reported that Dr. Califf has ties to about 16 other research organizations and biotech companies. Bloomberg Government also said that, in his earlier FDA service, Dr. Califf kept a whiteboard in his office that listed all the activities and projects that required his recusal, citing as a source Howard Sklamberg, who was a deputy commissioner under Dr. Califf.
“He was very, very, very careful,” Mr. Sklamberg, who’s now an attorney at Arnold & Porter LLP, told Bloomberg Government.
‘Work to do’ on opioids
Senators looped back repeatedly to the topic of opioids during Dr. Califf’s hearing, reflecting deep concerns about the FDA’s efforts to warn of the risks of prescription painkillers.
There were an estimated 100,306 drug overdose deaths in the United States in the 12 months ending in April, an increase of 28.5% from the 78,056 deaths during the same period the year before, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Califf said he plans to focus on what information the FDA conveys to the public about the risks of prescription painkillers, including a look at what the labels for these products say.
“I am committed to do a comprehensive review of the status of opioids, early in my tenure,” Dr. Califf said.
Dr. Califf indicated that physicians are still too quick to provide excess doses of these medicines, despite years of efforts to restrain their use. He said he knows relatives who were given 30-day prescriptions for opioids after minor surgery.
“So I know we have work to do,” Dr. Califf said.
Concerns about the FDA’s previous work in managing opioids has led to protests from a few Democratic senators about the prospect of President Biden nominating the acting FDA commissioner, Janet Woodcock, MD, for the permanent post.
At the hearing, Sen. Ben Ray Luján (D-NM) raised the case of the FDA’s approval of the powerful Zohydro painkiller. The agency approved that drug despite an 11-2 vote against it by the FDA’s Anesthetic and Analgesic Drug Products Advisory Committee.
Sen. Luján asked Dr. Califf what he would do if an FDA advisory committee voted “overwhelmingly” against recommending approval of a medicine, as happened in the Zohydro case.
While not mentioned by Sen. Luján in this exchange during the hearing with Dr. Califf, the FDA staff’s rejection of recommendations of advisory committees has been a growing concern among researchers.
The agency last year approved aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen), a drug for Alzheimer’s disease, dismissing the advice of its Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee. That decision triggered the resignation of several members of the panel. The FDA staff also earlier rejected the conclusion the majority of members of the same advisory committee offered in 2016 on eteplirsen (Exondys 51, Sarepta), a drug for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Dr. Califf told Sen. Luján he had done recent research into how often the FDA staff does not concur with the recommendations of an advisory committee. He said the FDA takes a different course of action in about 25% of cases. In about three-quarters of those cases, the FDA staff opts for a “more stringent” approach regarding allowing the public access to the drug, as opposed to a more generous one as seen in the Zohydro, Aduhelm, and Exondys 51 cases.
Still, Dr. Califf said that when there’s an 11-2 advisory committee vote against recommendation of a product, “the leaders at FDA really need to take a close look” at what’s happening.
Question on accelerated approvals
The FDA’s approval of aducanumab drew attention to a debate already underway about conditional clearances known as accelerated approvals.
The FDA has used this path since the 1990s to speed access to drugs for serious conditions. The trade-off for early access is that the agency sometimes makes the wrong call based on initial findings, and clears a medicine later found not to benefit patients as expected.
The FDA’s cancer division is in the midst of public efforts to address cases where drugmakers have not been able to deliver studies that support accelerated approvals of their oncology drugs. In addition, the Office of Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services announced in August that it is reviewing the FDA’s handling of the accelerated approval process.
At Tuesday’s hearing, Sen. Burr grilled Dr. Califf about how he would respond to calls to change how the FDA handles the accelerated-approval process.
“Can you commit to me and to patients who may rely on cutting-edge treatments that you will not support efforts to narrow this pathway or raise the bar for drugs to be approved under those pathways?” Burr asked Califf.
Dr. Califf responded by saying he was “a fan of accelerated approval – for the right conditions.”
Earlier, in his opening statement, Dr. Califf had said his mother benefited directly from the accelerated approval of new drugs for multiple myeloma. Dr. Califf told Sen. Burr that he had spent “countless hours with patient groups” and understands the need to speed the approval of medicines for serious diseases.
But the FDA also has to make sure it holds up its end of the bargain struck with accelerated approvals. This involves checking on how these medicines work once they are marketed.
“We’re accepting that there’s more uncertainty,” Dr. Califf said. “That means we’ve got to have a better system to evaluate these products as they’re used on the market. And I think there are ways that we can do that now. Technology is making this possible in ways that it just was not possible before.”
Worries about the medical supply chain
Sen. Susan Collins (R-Maine) asked Dr. Califf about the vulnerability of the U.S. medical system to disruptions of the supply chain. She raised concerns about China’s dominance in antibiotic manufacturing as an example. She asked if Congress could do more to encourage domestic manufacturing of medical supplies, such as by offering tax incentives.
Dr. Califf told Sen. Collins he shared her concern about the U.S. manufacturing of ingredients used in both branded and generic drugs. He said he recently has served on a committee of the National Academy of Medicine that is examining supply chain issues.
This committee will soon release a report with specific recommendations, Dr. Califf said.
“We don’t have enough competitive entities in what’s become sort of a commodity business” of drug manufacturing, Dr. Califf said. “So we need a number of steps to make the system more resilient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Robert M. Califf, MD, plans to take a close look at federal policies on opioid prescriptions in his expected second turn as the top U.S. regulator of medical products, as well as keep closer tabs on the performance of drugs cleared with accelerated approvals.
Dr. Califf on Tuesday fielded questions at a Senate hearing about his nomination by President Joe Biden to serve as administrator of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, a role in which he served in the Obama administration. He also spoke about the need to bolster the nation’s ability to maintain an adequate supply of key medical products, including drugs.
Members of the Senate Health, Education, Labor and Pensions Committee, which is handling Dr. Califf’s nomination, were largely cordial and supportive during the hearing. Sen. Patty Murray (D-Wash.), the committee chair, and the panel’s top Republican, Sen. Richard Burr of North Carolina, addressed Dr. Califf during the hearing as if he would soon serve again as the FDA’s leader. Both were among the senators who voted 89-4 to confirm Dr. Califf in a February 2016 vote.
Dr. Califf “was previously confirmed to lead FDA in an overwhelming bipartisan vote, and I look forward to working with him again to ensure FDA continues to protect families across the country, uphold the gold standard of safety and effectiveness, and put science and data first,” Sen. Murray said.
Less enthusiastic about Dr. Califf was Sen. Bernie Sanders (I-VT), who was among the seven senators who did not vote on Dr. Califf’s nomination in 2016.
Sen. Sanders objected in 2016 to Dr. Califf’s ties to the pharmaceutical industry, and he did so again Tuesday. A noted leader in conducting clinical trials, Dr. Califf has worked with many drugmakers. But at the hearing, Dr. Califf said he concurs with Sen. Sanders on an idea strongly opposed by the pharmaceutical industry.
In response to Sen. Sanders’ question, Dr. Califf said he already is “on record as being in favor of Medicare negotiating with the industry on prices.”
The FDA would not take direct part in negotiations, as this work would be handled by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services. Democrats want to give Medicare some negotiating authority through their sweeping Build Back Better Act.
People in the United States are dismayed over both the cost of prescription drugs and the widespread distribution of prescription painkillers that helped fuel the current opioid epidemic, Sen. Sanders told Dr. Califf. Many people will be concerned about an FDA commissioner who has benefited from close ties to the industry, Sen. Sanders said.
“How are they going to believe that you’re going to be an independent and strong voice against this enormously powerful, special interest?” Sen. Sanders asked.
“I’m totally with you on the concept that the price of pharmaceuticals is way too high in this country,” Dr. Califf said in reply.
Dr. Califf was paid $2.7 million in salary and bonus by Verily Life Sciences, the biomedical research organization operated by Alphabet, parent company of Google, according to his federal financial disclosure. He also reported holding board positions with pharmaceutical companies AmyriAD and Centessa Pharmaceuticals.
Bloomberg Government reported that Dr. Califf has ties to about 16 other research organizations and biotech companies. Bloomberg Government also said that, in his earlier FDA service, Dr. Califf kept a whiteboard in his office that listed all the activities and projects that required his recusal, citing as a source Howard Sklamberg, who was a deputy commissioner under Dr. Califf.
“He was very, very, very careful,” Mr. Sklamberg, who’s now an attorney at Arnold & Porter LLP, told Bloomberg Government.
‘Work to do’ on opioids
Senators looped back repeatedly to the topic of opioids during Dr. Califf’s hearing, reflecting deep concerns about the FDA’s efforts to warn of the risks of prescription painkillers.
There were an estimated 100,306 drug overdose deaths in the United States in the 12 months ending in April, an increase of 28.5% from the 78,056 deaths during the same period the year before, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Dr. Califf said he plans to focus on what information the FDA conveys to the public about the risks of prescription painkillers, including a look at what the labels for these products say.
“I am committed to do a comprehensive review of the status of opioids, early in my tenure,” Dr. Califf said.
Dr. Califf indicated that physicians are still too quick to provide excess doses of these medicines, despite years of efforts to restrain their use. He said he knows relatives who were given 30-day prescriptions for opioids after minor surgery.
“So I know we have work to do,” Dr. Califf said.
Concerns about the FDA’s previous work in managing opioids has led to protests from a few Democratic senators about the prospect of President Biden nominating the acting FDA commissioner, Janet Woodcock, MD, for the permanent post.
At the hearing, Sen. Ben Ray Luján (D-NM) raised the case of the FDA’s approval of the powerful Zohydro painkiller. The agency approved that drug despite an 11-2 vote against it by the FDA’s Anesthetic and Analgesic Drug Products Advisory Committee.
Sen. Luján asked Dr. Califf what he would do if an FDA advisory committee voted “overwhelmingly” against recommending approval of a medicine, as happened in the Zohydro case.
While not mentioned by Sen. Luján in this exchange during the hearing with Dr. Califf, the FDA staff’s rejection of recommendations of advisory committees has been a growing concern among researchers.
The agency last year approved aducanumab (Aduhelm, Biogen), a drug for Alzheimer’s disease, dismissing the advice of its Peripheral and Central Nervous System Drugs Advisory Committee. That decision triggered the resignation of several members of the panel. The FDA staff also earlier rejected the conclusion the majority of members of the same advisory committee offered in 2016 on eteplirsen (Exondys 51, Sarepta), a drug for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.
Dr. Califf told Sen. Luján he had done recent research into how often the FDA staff does not concur with the recommendations of an advisory committee. He said the FDA takes a different course of action in about 25% of cases. In about three-quarters of those cases, the FDA staff opts for a “more stringent” approach regarding allowing the public access to the drug, as opposed to a more generous one as seen in the Zohydro, Aduhelm, and Exondys 51 cases.
Still, Dr. Califf said that when there’s an 11-2 advisory committee vote against recommendation of a product, “the leaders at FDA really need to take a close look” at what’s happening.
Question on accelerated approvals
The FDA’s approval of aducanumab drew attention to a debate already underway about conditional clearances known as accelerated approvals.
The FDA has used this path since the 1990s to speed access to drugs for serious conditions. The trade-off for early access is that the agency sometimes makes the wrong call based on initial findings, and clears a medicine later found not to benefit patients as expected.
The FDA’s cancer division is in the midst of public efforts to address cases where drugmakers have not been able to deliver studies that support accelerated approvals of their oncology drugs. In addition, the Office of Inspector General of the U.S. Department of Health & Human Services announced in August that it is reviewing the FDA’s handling of the accelerated approval process.
At Tuesday’s hearing, Sen. Burr grilled Dr. Califf about how he would respond to calls to change how the FDA handles the accelerated-approval process.
“Can you commit to me and to patients who may rely on cutting-edge treatments that you will not support efforts to narrow this pathway or raise the bar for drugs to be approved under those pathways?” Burr asked Califf.
Dr. Califf responded by saying he was “a fan of accelerated approval – for the right conditions.”
Earlier, in his opening statement, Dr. Califf had said his mother benefited directly from the accelerated approval of new drugs for multiple myeloma. Dr. Califf told Sen. Burr that he had spent “countless hours with patient groups” and understands the need to speed the approval of medicines for serious diseases.
But the FDA also has to make sure it holds up its end of the bargain struck with accelerated approvals. This involves checking on how these medicines work once they are marketed.
“We’re accepting that there’s more uncertainty,” Dr. Califf said. “That means we’ve got to have a better system to evaluate these products as they’re used on the market. And I think there are ways that we can do that now. Technology is making this possible in ways that it just was not possible before.”
Worries about the medical supply chain
Sen. Susan Collins (R-Maine) asked Dr. Califf about the vulnerability of the U.S. medical system to disruptions of the supply chain. She raised concerns about China’s dominance in antibiotic manufacturing as an example. She asked if Congress could do more to encourage domestic manufacturing of medical supplies, such as by offering tax incentives.
Dr. Califf told Sen. Collins he shared her concern about the U.S. manufacturing of ingredients used in both branded and generic drugs. He said he recently has served on a committee of the National Academy of Medicine that is examining supply chain issues.
This committee will soon release a report with specific recommendations, Dr. Califf said.
“We don’t have enough competitive entities in what’s become sort of a commodity business” of drug manufacturing, Dr. Califf said. “So we need a number of steps to make the system more resilient.”
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Is prescribing stimulants OK for comorbid opioid use disorder, ADHD?
A growing number of patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) have a diagnosis of comorbid attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), raising issues about whether it’s appropriate to prescribe stimulants in this patient population.
One new study showed that from 2007-2017, there was a threefold increase in OUD and comorbid ADHD and that a significant number of these patients received prescription stimulants.
“This is the beginning stages of looking at whether or not there are risks of prescribing stimulants to patients who are on medications for opioid use disorder,” investigator Tae Woo (Ted) Park, MD, assistant professor, department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, told this news organization.
“More and more people are being identified with ADHD, and we need to do more research on the best way to manage this patient group,” Dr. Park added.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Biological connection?
Dr. Park is not convinced there is “an actual biological connection” between ADHD and OUD, noting that there are many reasons why patients with ADHD may be more prone to developing such a disorder.
Perhaps they did not get an ADHD diagnosis as a child, “which led to impairment in their ability to be successful at school and then in a job,” which in turn predisposed them to having a substance use disorder, said Dr. Park.
From previous research and his own clinical experience, ADHD can significantly affect quality of life and “cause increased impairment” in patients with a substance use disorder, he added.
Interestingly, there’s evidence suggesting patients treated for ADHD early in life are less likely to develop a substance use disorder later on, he said.
The “gold standard” treatment for ADHD is a prescription stimulant, which carries its own addiction risks. “So the issue is about whether or not to prescribe risky medications and how to weigh the risks and benefits,” said Dr. Park.
From a private health insurance database, researchers examined records for patients aged 18-64 years who were receiving medication for OUD, including buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone, from 2007-2017.
In the study sample, about 17,000 individuals were receiving stimulants, and 156,000 were not receiving these drugs. The largest percentage of participants in both groups was in the age-18-to-25 category.
About 35% of those receiving stimulants had ADHD, and about the same percentage had a mood disorder diagnosis.
Percentage of co-occurring ADHD and OUD increased from more than 4% in 2007 to more than 14% in 2017. The prevalence of stimulant use plus medication for OUD also increased during that time.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses may reflect growing identification of the condition, Dr. Park noted. As the opioid problem became more apparent and additional treatments made available, “there were more health care contacts, more assessments, and more diagnoses, including of ADHD,” he said.
Risks versus benefits
Stimulants may also be risky in patients with OUD. Results from another study presented at the AAAP meeting showed these drugs were associated with an increased chance of poisoning in patients receiving buprenorphine.
However, Dr. Park is skeptical the combination of stimulants and buprenorphine “leads to a biological risk of overdose.” He used a hypothetical scenario where other factors play into the connection: A patient gets a prescription stimulant, becomes addicted, then starts using street or illicit stimulants, which leads to a relapse on opioids, and then to an overdose.
Dr. Park noted that the same study that found an increased poisoning risk in stimulant users also found that patients tend to stay on buprenorphine treatment, providing protection against overdose.
“So there are risks and benefits of prescribing these medications, and it becomes tricky to know whether to prescribe them or not,” he said.
While stimulants are by far the best treatment for ADHD, atomoxetine (Strattera), a nonstimulant medication with antidepressant effects is another option, Dr. Park said.
He added that a limitation of his study was that very few individuals in the database received methadone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A growing number of patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) have a diagnosis of comorbid attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), raising issues about whether it’s appropriate to prescribe stimulants in this patient population.
One new study showed that from 2007-2017, there was a threefold increase in OUD and comorbid ADHD and that a significant number of these patients received prescription stimulants.
“This is the beginning stages of looking at whether or not there are risks of prescribing stimulants to patients who are on medications for opioid use disorder,” investigator Tae Woo (Ted) Park, MD, assistant professor, department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, told this news organization.
“More and more people are being identified with ADHD, and we need to do more research on the best way to manage this patient group,” Dr. Park added.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Biological connection?
Dr. Park is not convinced there is “an actual biological connection” between ADHD and OUD, noting that there are many reasons why patients with ADHD may be more prone to developing such a disorder.
Perhaps they did not get an ADHD diagnosis as a child, “which led to impairment in their ability to be successful at school and then in a job,” which in turn predisposed them to having a substance use disorder, said Dr. Park.
From previous research and his own clinical experience, ADHD can significantly affect quality of life and “cause increased impairment” in patients with a substance use disorder, he added.
Interestingly, there’s evidence suggesting patients treated for ADHD early in life are less likely to develop a substance use disorder later on, he said.
The “gold standard” treatment for ADHD is a prescription stimulant, which carries its own addiction risks. “So the issue is about whether or not to prescribe risky medications and how to weigh the risks and benefits,” said Dr. Park.
From a private health insurance database, researchers examined records for patients aged 18-64 years who were receiving medication for OUD, including buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone, from 2007-2017.
In the study sample, about 17,000 individuals were receiving stimulants, and 156,000 were not receiving these drugs. The largest percentage of participants in both groups was in the age-18-to-25 category.
About 35% of those receiving stimulants had ADHD, and about the same percentage had a mood disorder diagnosis.
Percentage of co-occurring ADHD and OUD increased from more than 4% in 2007 to more than 14% in 2017. The prevalence of stimulant use plus medication for OUD also increased during that time.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses may reflect growing identification of the condition, Dr. Park noted. As the opioid problem became more apparent and additional treatments made available, “there were more health care contacts, more assessments, and more diagnoses, including of ADHD,” he said.
Risks versus benefits
Stimulants may also be risky in patients with OUD. Results from another study presented at the AAAP meeting showed these drugs were associated with an increased chance of poisoning in patients receiving buprenorphine.
However, Dr. Park is skeptical the combination of stimulants and buprenorphine “leads to a biological risk of overdose.” He used a hypothetical scenario where other factors play into the connection: A patient gets a prescription stimulant, becomes addicted, then starts using street or illicit stimulants, which leads to a relapse on opioids, and then to an overdose.
Dr. Park noted that the same study that found an increased poisoning risk in stimulant users also found that patients tend to stay on buprenorphine treatment, providing protection against overdose.
“So there are risks and benefits of prescribing these medications, and it becomes tricky to know whether to prescribe them or not,” he said.
While stimulants are by far the best treatment for ADHD, atomoxetine (Strattera), a nonstimulant medication with antidepressant effects is another option, Dr. Park said.
He added that a limitation of his study was that very few individuals in the database received methadone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A growing number of patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) have a diagnosis of comorbid attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), raising issues about whether it’s appropriate to prescribe stimulants in this patient population.
One new study showed that from 2007-2017, there was a threefold increase in OUD and comorbid ADHD and that a significant number of these patients received prescription stimulants.
“This is the beginning stages of looking at whether or not there are risks of prescribing stimulants to patients who are on medications for opioid use disorder,” investigator Tae Woo (Ted) Park, MD, assistant professor, department of psychiatry, University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine, told this news organization.
“More and more people are being identified with ADHD, and we need to do more research on the best way to manage this patient group,” Dr. Park added.
The findings were presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Addiction Psychiatry.
Biological connection?
Dr. Park is not convinced there is “an actual biological connection” between ADHD and OUD, noting that there are many reasons why patients with ADHD may be more prone to developing such a disorder.
Perhaps they did not get an ADHD diagnosis as a child, “which led to impairment in their ability to be successful at school and then in a job,” which in turn predisposed them to having a substance use disorder, said Dr. Park.
From previous research and his own clinical experience, ADHD can significantly affect quality of life and “cause increased impairment” in patients with a substance use disorder, he added.
Interestingly, there’s evidence suggesting patients treated for ADHD early in life are less likely to develop a substance use disorder later on, he said.
The “gold standard” treatment for ADHD is a prescription stimulant, which carries its own addiction risks. “So the issue is about whether or not to prescribe risky medications and how to weigh the risks and benefits,” said Dr. Park.
From a private health insurance database, researchers examined records for patients aged 18-64 years who were receiving medication for OUD, including buprenorphine, methadone, or naltrexone, from 2007-2017.
In the study sample, about 17,000 individuals were receiving stimulants, and 156,000 were not receiving these drugs. The largest percentage of participants in both groups was in the age-18-to-25 category.
About 35% of those receiving stimulants had ADHD, and about the same percentage had a mood disorder diagnosis.
Percentage of co-occurring ADHD and OUD increased from more than 4% in 2007 to more than 14% in 2017. The prevalence of stimulant use plus medication for OUD also increased during that time.
The increase in ADHD diagnoses may reflect growing identification of the condition, Dr. Park noted. As the opioid problem became more apparent and additional treatments made available, “there were more health care contacts, more assessments, and more diagnoses, including of ADHD,” he said.
Risks versus benefits
Stimulants may also be risky in patients with OUD. Results from another study presented at the AAAP meeting showed these drugs were associated with an increased chance of poisoning in patients receiving buprenorphine.
However, Dr. Park is skeptical the combination of stimulants and buprenorphine “leads to a biological risk of overdose.” He used a hypothetical scenario where other factors play into the connection: A patient gets a prescription stimulant, becomes addicted, then starts using street or illicit stimulants, which leads to a relapse on opioids, and then to an overdose.
Dr. Park noted that the same study that found an increased poisoning risk in stimulant users also found that patients tend to stay on buprenorphine treatment, providing protection against overdose.
“So there are risks and benefits of prescribing these medications, and it becomes tricky to know whether to prescribe them or not,” he said.
While stimulants are by far the best treatment for ADHD, atomoxetine (Strattera), a nonstimulant medication with antidepressant effects is another option, Dr. Park said.
He added that a limitation of his study was that very few individuals in the database received methadone.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM AAAP 2021
Ginger for migraine: A new review
in patients who do not want to use or don’t have access to prescription medications, new data suggest.
Conducted by investigators at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India, the review showed ginger root can relieve migraine-related pain, nausea, and vomiting. However, the evidence does not support ginger’s use as a first-line therapy for acute migraine or for migraine prevention.
Study author Chittaranjan Andrade, MD, professor of clinical psychopharmacology and neurotoxicology at the institute, said in an interview that the evidence base is still “too small” to support formal clinical recommendations. However, he added, ginger can be considered as a viable “home-remedy option” for acute migraine.
The review was published online Dec. 2 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Potential uses
Used for centuries in traditional medicine, much of the preclinical and clinical research has examined the potential of raw ginger, ginger extracts, and ginger constituents to prevent and treat a wide range of medical conditions. These include nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, chemotherapy, postoperative states, motion sickness, and other diseases and disorders, said Dr. Andrade.
Ginger has “long been recommended as an effective home remedy for the acute treatment of migraine, relieving both headache and the associated nausea,” Dr. Andrade noted.
One recommended recipe is stirring half a teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of water and drinking the “ginger juice,” while another is to drink hot tea made from a teaspoon of freshly ground ginger.
“Patients with a number of common ailments, including migraine, are sometimes caught without medicines; or they may have poor access to medicines,” Dr. Andrade said. “I came across a reference to the use of ginger for migraine in a book on home remedies and I thought that if the research literature supports the use of ginger for migraine episodes, such patients could benefit.”
Large treatment gap
The review and meta-analysis included three randomized controlled trials with 227 patients looking at ginger versus placebo for the treatment.
One of the studies investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a specific proprietary formulation of ginger, combined with feverfew, while two trials were independent of industry.
Of these two, one examined the benefit of add-on dry ginger extract (400 mg; 5% active gingerols) in 50 patients who were also taking ketoprofen to treat migraine episodes, while the other examined the 3-month efficacy of daily dry ginger extract for migraine prophylaxis in 107 patients.
The two studies that examined the therapeutic efficacy of ginger versus placebo showed ginger reduced mean pain scores at 2 hours (mean difference, –1.27 [95% confidence interval, –1.46 to 1,07]) and also increased the proportion of patients who were pain free at 2 hours (RR, 1.79 [1.04 to 3.09]). In addition, compared to placebo, ginger halved the risk of migraine-related nausea and vomiting in all of the studies and was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
One RCT investigated prophylactic efficacy and found it to be more effective than placebo in bringing a ≥ 50% reduction in the frequency of monthly migraine episodes (in 42% versus 39% of patients, respectively), but the difference was not deemed statistically significant. In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in days of pain, severe pain, days requiring use of analgesics, number of migraine episodes, and maximum duration of migraine episodes.
Dr. Andrade noted that ginger has many chemical constituents, including phenolic compounds, terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, and organic acids of which 6-shogaol, 6-gingerol, and 10-dehydrogingerdione “may be important.”
It also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, lowering prostaglandins, and reducing several serum lipid and glycemic measures. Additionally, it has “putative” vasculoprotective effects, he added.
“Ginger has a large number of chemical constituents and we do not know which of these, separately or in combination, will help relieve migraine,” he said. “We won’t know the answer unless clinical trials are conducted with the individual constituents rather than with ginger extract.” He compared this to the study of omega-3 fatty acids rather than fish and nuts for various neuropsychiatric or cardiovascular indications.
Nevertheless, given the high global prevalence of migraine and the “large treatment gap [of migraine] in primary care,” it could be common for many affected patients to experience episodes of migraine headache “without recourse to recommended pharmacologic relief,” he noted. “In such cases, the availability of a simple home remedy, such as ginger, could be helpful.”
‘Good additional tool’
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jessica Ailani, MD, director, MedStar Georgetown Headache Center and professor of clinical neurology, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, said that for “people with migraine who are seeking treatment with minimal side effects that they can obtain without counsel of a health care provider, ginger is a good additional tool to have.”
Dr. Ailani, vice cochair of strategic planning in the MedStar department of neurology, who was not involved with the study, said that clinicians can “consider suggesting ginger to patients with migraine that have associated nausea who are interested in nonpharmacologic ways to treat symptoms.”
Since there are “many other effective ways to treat migraine,” she advises “conversing with the patient about speed of onset of efficacy, along with tolerability, and return of migraine symptoms as important factors to evaluate when choosing and staying with a treatment.”
Also commenting on the study for this news organization, Nada Hindiyeh, MD, clinical associate professor, department of neurology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called it a “nice summary of the objective research available for the use of ginger in acute and preventive treatment of migraine.”
Although there is insufficient literature evaluating ginger alone in migraine treatment, so “no definitive conclusions can be drawn,” since it appears to be safe and “somewhat helpful for migraine-associated nausea and vomiting and possibly in frequency of migraine reduction, it remains a considerable alternative for those seeking nonprescription options,” said Dr. Hindiyeh, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Andrade publishes an e-newsletter supported by Sun Pharmaceuticals, with payments made to charities. He has received payments for developing educational materials for scientific initiatives and programs. Dr. Ailani reports honoraria for independent consulting from various pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial grants to her institution from the American Migraine Foundation, Allergan, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Satsuma, and Zosano. Dr. Hindiyeh discloses no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in patients who do not want to use or don’t have access to prescription medications, new data suggest.
Conducted by investigators at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India, the review showed ginger root can relieve migraine-related pain, nausea, and vomiting. However, the evidence does not support ginger’s use as a first-line therapy for acute migraine or for migraine prevention.
Study author Chittaranjan Andrade, MD, professor of clinical psychopharmacology and neurotoxicology at the institute, said in an interview that the evidence base is still “too small” to support formal clinical recommendations. However, he added, ginger can be considered as a viable “home-remedy option” for acute migraine.
The review was published online Dec. 2 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Potential uses
Used for centuries in traditional medicine, much of the preclinical and clinical research has examined the potential of raw ginger, ginger extracts, and ginger constituents to prevent and treat a wide range of medical conditions. These include nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, chemotherapy, postoperative states, motion sickness, and other diseases and disorders, said Dr. Andrade.
Ginger has “long been recommended as an effective home remedy for the acute treatment of migraine, relieving both headache and the associated nausea,” Dr. Andrade noted.
One recommended recipe is stirring half a teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of water and drinking the “ginger juice,” while another is to drink hot tea made from a teaspoon of freshly ground ginger.
“Patients with a number of common ailments, including migraine, are sometimes caught without medicines; or they may have poor access to medicines,” Dr. Andrade said. “I came across a reference to the use of ginger for migraine in a book on home remedies and I thought that if the research literature supports the use of ginger for migraine episodes, such patients could benefit.”
Large treatment gap
The review and meta-analysis included three randomized controlled trials with 227 patients looking at ginger versus placebo for the treatment.
One of the studies investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a specific proprietary formulation of ginger, combined with feverfew, while two trials were independent of industry.
Of these two, one examined the benefit of add-on dry ginger extract (400 mg; 5% active gingerols) in 50 patients who were also taking ketoprofen to treat migraine episodes, while the other examined the 3-month efficacy of daily dry ginger extract for migraine prophylaxis in 107 patients.
The two studies that examined the therapeutic efficacy of ginger versus placebo showed ginger reduced mean pain scores at 2 hours (mean difference, –1.27 [95% confidence interval, –1.46 to 1,07]) and also increased the proportion of patients who were pain free at 2 hours (RR, 1.79 [1.04 to 3.09]). In addition, compared to placebo, ginger halved the risk of migraine-related nausea and vomiting in all of the studies and was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
One RCT investigated prophylactic efficacy and found it to be more effective than placebo in bringing a ≥ 50% reduction in the frequency of monthly migraine episodes (in 42% versus 39% of patients, respectively), but the difference was not deemed statistically significant. In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in days of pain, severe pain, days requiring use of analgesics, number of migraine episodes, and maximum duration of migraine episodes.
Dr. Andrade noted that ginger has many chemical constituents, including phenolic compounds, terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, and organic acids of which 6-shogaol, 6-gingerol, and 10-dehydrogingerdione “may be important.”
It also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, lowering prostaglandins, and reducing several serum lipid and glycemic measures. Additionally, it has “putative” vasculoprotective effects, he added.
“Ginger has a large number of chemical constituents and we do not know which of these, separately or in combination, will help relieve migraine,” he said. “We won’t know the answer unless clinical trials are conducted with the individual constituents rather than with ginger extract.” He compared this to the study of omega-3 fatty acids rather than fish and nuts for various neuropsychiatric or cardiovascular indications.
Nevertheless, given the high global prevalence of migraine and the “large treatment gap [of migraine] in primary care,” it could be common for many affected patients to experience episodes of migraine headache “without recourse to recommended pharmacologic relief,” he noted. “In such cases, the availability of a simple home remedy, such as ginger, could be helpful.”
‘Good additional tool’
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jessica Ailani, MD, director, MedStar Georgetown Headache Center and professor of clinical neurology, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, said that for “people with migraine who are seeking treatment with minimal side effects that they can obtain without counsel of a health care provider, ginger is a good additional tool to have.”
Dr. Ailani, vice cochair of strategic planning in the MedStar department of neurology, who was not involved with the study, said that clinicians can “consider suggesting ginger to patients with migraine that have associated nausea who are interested in nonpharmacologic ways to treat symptoms.”
Since there are “many other effective ways to treat migraine,” she advises “conversing with the patient about speed of onset of efficacy, along with tolerability, and return of migraine symptoms as important factors to evaluate when choosing and staying with a treatment.”
Also commenting on the study for this news organization, Nada Hindiyeh, MD, clinical associate professor, department of neurology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called it a “nice summary of the objective research available for the use of ginger in acute and preventive treatment of migraine.”
Although there is insufficient literature evaluating ginger alone in migraine treatment, so “no definitive conclusions can be drawn,” since it appears to be safe and “somewhat helpful for migraine-associated nausea and vomiting and possibly in frequency of migraine reduction, it remains a considerable alternative for those seeking nonprescription options,” said Dr. Hindiyeh, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Andrade publishes an e-newsletter supported by Sun Pharmaceuticals, with payments made to charities. He has received payments for developing educational materials for scientific initiatives and programs. Dr. Ailani reports honoraria for independent consulting from various pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial grants to her institution from the American Migraine Foundation, Allergan, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Satsuma, and Zosano. Dr. Hindiyeh discloses no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
in patients who do not want to use or don’t have access to prescription medications, new data suggest.
Conducted by investigators at the National Institute of Mental Health and Neurosciences, Bangalore, India, the review showed ginger root can relieve migraine-related pain, nausea, and vomiting. However, the evidence does not support ginger’s use as a first-line therapy for acute migraine or for migraine prevention.
Study author Chittaranjan Andrade, MD, professor of clinical psychopharmacology and neurotoxicology at the institute, said in an interview that the evidence base is still “too small” to support formal clinical recommendations. However, he added, ginger can be considered as a viable “home-remedy option” for acute migraine.
The review was published online Dec. 2 in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry.
Potential uses
Used for centuries in traditional medicine, much of the preclinical and clinical research has examined the potential of raw ginger, ginger extracts, and ginger constituents to prevent and treat a wide range of medical conditions. These include nausea and vomiting associated with pregnancy, chemotherapy, postoperative states, motion sickness, and other diseases and disorders, said Dr. Andrade.
Ginger has “long been recommended as an effective home remedy for the acute treatment of migraine, relieving both headache and the associated nausea,” Dr. Andrade noted.
One recommended recipe is stirring half a teaspoon of ground ginger into a glass of water and drinking the “ginger juice,” while another is to drink hot tea made from a teaspoon of freshly ground ginger.
“Patients with a number of common ailments, including migraine, are sometimes caught without medicines; or they may have poor access to medicines,” Dr. Andrade said. “I came across a reference to the use of ginger for migraine in a book on home remedies and I thought that if the research literature supports the use of ginger for migraine episodes, such patients could benefit.”
Large treatment gap
The review and meta-analysis included three randomized controlled trials with 227 patients looking at ginger versus placebo for the treatment.
One of the studies investigated the therapeutic efficacy of a specific proprietary formulation of ginger, combined with feverfew, while two trials were independent of industry.
Of these two, one examined the benefit of add-on dry ginger extract (400 mg; 5% active gingerols) in 50 patients who were also taking ketoprofen to treat migraine episodes, while the other examined the 3-month efficacy of daily dry ginger extract for migraine prophylaxis in 107 patients.
The two studies that examined the therapeutic efficacy of ginger versus placebo showed ginger reduced mean pain scores at 2 hours (mean difference, –1.27 [95% confidence interval, –1.46 to 1,07]) and also increased the proportion of patients who were pain free at 2 hours (RR, 1.79 [1.04 to 3.09]). In addition, compared to placebo, ginger halved the risk of migraine-related nausea and vomiting in all of the studies and was not associated with an increased risk of adverse events.
One RCT investigated prophylactic efficacy and found it to be more effective than placebo in bringing a ≥ 50% reduction in the frequency of monthly migraine episodes (in 42% versus 39% of patients, respectively), but the difference was not deemed statistically significant. In addition, there were no significant differences between the groups in days of pain, severe pain, days requiring use of analgesics, number of migraine episodes, and maximum duration of migraine episodes.
Dr. Andrade noted that ginger has many chemical constituents, including phenolic compounds, terpenes, polysaccharides, lipids, and organic acids of which 6-shogaol, 6-gingerol, and 10-dehydrogingerdione “may be important.”
It also has antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, lowering prostaglandins, and reducing several serum lipid and glycemic measures. Additionally, it has “putative” vasculoprotective effects, he added.
“Ginger has a large number of chemical constituents and we do not know which of these, separately or in combination, will help relieve migraine,” he said. “We won’t know the answer unless clinical trials are conducted with the individual constituents rather than with ginger extract.” He compared this to the study of omega-3 fatty acids rather than fish and nuts for various neuropsychiatric or cardiovascular indications.
Nevertheless, given the high global prevalence of migraine and the “large treatment gap [of migraine] in primary care,” it could be common for many affected patients to experience episodes of migraine headache “without recourse to recommended pharmacologic relief,” he noted. “In such cases, the availability of a simple home remedy, such as ginger, could be helpful.”
‘Good additional tool’
Commenting on the study for this news organization, Jessica Ailani, MD, director, MedStar Georgetown Headache Center and professor of clinical neurology, MedStar Georgetown University Hospital, Washington, said that for “people with migraine who are seeking treatment with minimal side effects that they can obtain without counsel of a health care provider, ginger is a good additional tool to have.”
Dr. Ailani, vice cochair of strategic planning in the MedStar department of neurology, who was not involved with the study, said that clinicians can “consider suggesting ginger to patients with migraine that have associated nausea who are interested in nonpharmacologic ways to treat symptoms.”
Since there are “many other effective ways to treat migraine,” she advises “conversing with the patient about speed of onset of efficacy, along with tolerability, and return of migraine symptoms as important factors to evaluate when choosing and staying with a treatment.”
Also commenting on the study for this news organization, Nada Hindiyeh, MD, clinical associate professor, department of neurology, Stanford (Calif.) University, called it a “nice summary of the objective research available for the use of ginger in acute and preventive treatment of migraine.”
Although there is insufficient literature evaluating ginger alone in migraine treatment, so “no definitive conclusions can be drawn,” since it appears to be safe and “somewhat helpful for migraine-associated nausea and vomiting and possibly in frequency of migraine reduction, it remains a considerable alternative for those seeking nonprescription options,” said Dr. Hindiyeh, who was not involved with the study.
Dr. Andrade publishes an e-newsletter supported by Sun Pharmaceuticals, with payments made to charities. He has received payments for developing educational materials for scientific initiatives and programs. Dr. Ailani reports honoraria for independent consulting from various pharmaceutical companies and clinical trial grants to her institution from the American Migraine Foundation, Allergan, Biohaven, Eli Lilly, Satsuma, and Zosano. Dr. Hindiyeh discloses no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHIATRY
A pandemic silver lining? Dramatic drop in teen drug use
Illicit drug use among U.S. teenagers dropped sharply in 2021, likely because of stay-at-home orders and other restrictions on social activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The latest findings, from the Monitoring the Future survey, represent the largest 1-year decrease in overall illicit drug use reported since the survey began in 1975.
“We have never seen such dramatic decreases in drug use among teens in just a 1-year period,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), said in a news release.
“These data are unprecedented and highlight one unexpected potential consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused seismic shifts in the day-to-day lives of adolescents,” said Dr. Volkow.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey is conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and funded by NIDA, to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States.
This year’s self-reported survey included 32,260 students in grades 8, 10, and 12 across 319 public and private schools.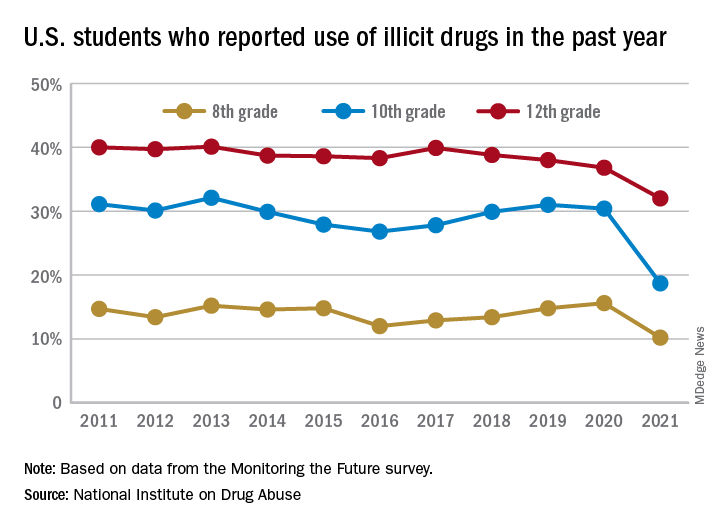
Compared with 2020, the percentage of students reporting any illicit drug use (other than marijuana) in 2021 decreased significantly for 8th graders (down 5.4%), 10th graders (down 11.7%), and 12th graders (down 4.8%).
For alcohol, about 47% of 12th graders and 29% of 10th graders said they drank alcohol in 2021, down significantly from 55% and 41%, respectively, in 2020. The percentage of 8th graders who said they drank alcohol remained stable (17% in 2021 and 20% in 2020).
For teen vaping, about 27% of 12th graders and 20% of 10th graders said they had vaped nicotine in 2021, down significantly from nearly 35% and 31%, respectively, in 2020. Fewer 8th graders also vaped nicotine in 2021 compared with 2020 (12% vs. 17%).
For marijuana, use dropped significantly for all three grades in 2021 compared with 2020. About 31% of 12th graders and 17% of 10th graders said they used marijuana in 2021, down from 35% and 28% in 2020. Among 8th graders, 7% used marijuana in 2021, down from 11% in 2020.
The latest survey also shows significant declines in use of a range of other drugs for many of the age cohorts, including cocaine, hallucinogens, and nonmedical use of amphetamines, tranquilizers, and prescription opioids.
“We knew that this year’s data would illuminate how the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted substance use among young people, and in the coming years, we will find out whether those impacts are long-lasting as we continue tracking the drug use patterns of these unique cohorts of adolescents,” Richard A. Miech, PhD, who heads the Monitoring the Future study at the University of Michigan, said in the news release.
“Moving forward, it will be crucial to identify the pivotal elements of this past year that contributed to decreased drug use – whether related to drug availability, family involvement, differences in peer pressure, or other factors – and harness them to inform future prevention efforts,” Dr. Volkow added.
In 2021, students across all age groups reported moderate increases in feelings of boredom, anxiety, depression, loneliness, worry, difficulty sleeping, and other negative mental health indicators since the beginning of the pandemic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Illicit drug use among U.S. teenagers dropped sharply in 2021, likely because of stay-at-home orders and other restrictions on social activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The latest findings, from the Monitoring the Future survey, represent the largest 1-year decrease in overall illicit drug use reported since the survey began in 1975.
“We have never seen such dramatic decreases in drug use among teens in just a 1-year period,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), said in a news release.
“These data are unprecedented and highlight one unexpected potential consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused seismic shifts in the day-to-day lives of adolescents,” said Dr. Volkow.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey is conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and funded by NIDA, to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States.
This year’s self-reported survey included 32,260 students in grades 8, 10, and 12 across 319 public and private schools.
Compared with 2020, the percentage of students reporting any illicit drug use (other than marijuana) in 2021 decreased significantly for 8th graders (down 5.4%), 10th graders (down 11.7%), and 12th graders (down 4.8%).
For alcohol, about 47% of 12th graders and 29% of 10th graders said they drank alcohol in 2021, down significantly from 55% and 41%, respectively, in 2020. The percentage of 8th graders who said they drank alcohol remained stable (17% in 2021 and 20% in 2020).
For teen vaping, about 27% of 12th graders and 20% of 10th graders said they had vaped nicotine in 2021, down significantly from nearly 35% and 31%, respectively, in 2020. Fewer 8th graders also vaped nicotine in 2021 compared with 2020 (12% vs. 17%).
For marijuana, use dropped significantly for all three grades in 2021 compared with 2020. About 31% of 12th graders and 17% of 10th graders said they used marijuana in 2021, down from 35% and 28% in 2020. Among 8th graders, 7% used marijuana in 2021, down from 11% in 2020.
The latest survey also shows significant declines in use of a range of other drugs for many of the age cohorts, including cocaine, hallucinogens, and nonmedical use of amphetamines, tranquilizers, and prescription opioids.
“We knew that this year’s data would illuminate how the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted substance use among young people, and in the coming years, we will find out whether those impacts are long-lasting as we continue tracking the drug use patterns of these unique cohorts of adolescents,” Richard A. Miech, PhD, who heads the Monitoring the Future study at the University of Michigan, said in the news release.
“Moving forward, it will be crucial to identify the pivotal elements of this past year that contributed to decreased drug use – whether related to drug availability, family involvement, differences in peer pressure, or other factors – and harness them to inform future prevention efforts,” Dr. Volkow added.
In 2021, students across all age groups reported moderate increases in feelings of boredom, anxiety, depression, loneliness, worry, difficulty sleeping, and other negative mental health indicators since the beginning of the pandemic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Illicit drug use among U.S. teenagers dropped sharply in 2021, likely because of stay-at-home orders and other restrictions on social activities due to the COVID-19 pandemic.
The latest findings, from the Monitoring the Future survey, represent the largest 1-year decrease in overall illicit drug use reported since the survey began in 1975.
“We have never seen such dramatic decreases in drug use among teens in just a 1-year period,” Nora Volkow, MD, director of the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA), said in a news release.
“These data are unprecedented and highlight one unexpected potential consequence of the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused seismic shifts in the day-to-day lives of adolescents,” said Dr. Volkow.
The annual Monitoring the Future survey is conducted by researchers at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, and funded by NIDA, to assess drug and alcohol use and related attitudes among adolescent students across the United States.
This year’s self-reported survey included 32,260 students in grades 8, 10, and 12 across 319 public and private schools.
Compared with 2020, the percentage of students reporting any illicit drug use (other than marijuana) in 2021 decreased significantly for 8th graders (down 5.4%), 10th graders (down 11.7%), and 12th graders (down 4.8%).
For alcohol, about 47% of 12th graders and 29% of 10th graders said they drank alcohol in 2021, down significantly from 55% and 41%, respectively, in 2020. The percentage of 8th graders who said they drank alcohol remained stable (17% in 2021 and 20% in 2020).
For teen vaping, about 27% of 12th graders and 20% of 10th graders said they had vaped nicotine in 2021, down significantly from nearly 35% and 31%, respectively, in 2020. Fewer 8th graders also vaped nicotine in 2021 compared with 2020 (12% vs. 17%).
For marijuana, use dropped significantly for all three grades in 2021 compared with 2020. About 31% of 12th graders and 17% of 10th graders said they used marijuana in 2021, down from 35% and 28% in 2020. Among 8th graders, 7% used marijuana in 2021, down from 11% in 2020.
The latest survey also shows significant declines in use of a range of other drugs for many of the age cohorts, including cocaine, hallucinogens, and nonmedical use of amphetamines, tranquilizers, and prescription opioids.
“We knew that this year’s data would illuminate how the COVID-19 pandemic may have impacted substance use among young people, and in the coming years, we will find out whether those impacts are long-lasting as we continue tracking the drug use patterns of these unique cohorts of adolescents,” Richard A. Miech, PhD, who heads the Monitoring the Future study at the University of Michigan, said in the news release.
“Moving forward, it will be crucial to identify the pivotal elements of this past year that contributed to decreased drug use – whether related to drug availability, family involvement, differences in peer pressure, or other factors – and harness them to inform future prevention efforts,” Dr. Volkow added.
In 2021, students across all age groups reported moderate increases in feelings of boredom, anxiety, depression, loneliness, worry, difficulty sleeping, and other negative mental health indicators since the beginning of the pandemic.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Even COVID-19 can’t stop a true optimist
Squeezing a little lemonade out of COVID-19
We like to think of ourselves as optimists here at LOTME. A glass is half full, the sky is partly sunny, and our motto is “Always look on the bright side of insanity.” Then again, our motto before that was “LOTME: Where science meets stupid,” so what do we know?
Anyway, it’s that upbeat, can-do attitude that allows us to say something positive – two somethings, actually – about the insanity that is COVID-19.
Our journey to the bright side begins, oddly enough, in the courtroom. Seems that our old friend, the face mask, is something of a lie-detector aid for juries. The authors of a recent literature review of studies on deception “found that facial expressions and other forms of nonverbal behaviour are an unreliable indicator of deceit,” according to a statement from the University of Portsmouth, where the analysis was conducted.
The one study that directly examined the role of face coverings in court proceedings showed that, “by taking away the distraction of nonverbal behaviours, observers had to rely on speech content, which turned out to be better for detecting lies,” the university said.
The second stage of our positivity trek brings us to the National Trends in Disability Employment monthly update, where we see a fourth consecutive month of gains for people with disabilities despite the larger trend of declines among those without disabilities.
Here are some numbers from the Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability to tell the story: From October to November, the employment-to-population ratio increased 4.2% for working-age people with disabilities, compared with 0.4% for people without disabilities. At the same time, the labor force participation rate rose 2.4% for working-age people with disabilities and just 0.1% for working-age people without disabilities.
Both indicators surpassed their historic highs, Andrew Houtenville, PhD, director of the Institute on Disability, said in the update. “These gains suggest that the restructuring resulting from the pandemic may be benefiting people with disabilities. Ironically, it may have taken a pandemic to shake the labor market loose for people with disabilities.”
And that is how a world-class optimist turns one gigantic lemon into lemonade.
Cut the cheese for better sleep
So, we’ve already talked about the TikTok lettuce tea hack that’s supposed to help us sleep better. Well, there’s another food that could have the opposite effect.
According to an article from the BBC, cheese has something of a reputation. Ever since the 1960s, when a researcher noted that one patient’s nightmares stopped after he quit eating an ounce or two of cheddar each night, there’s been speculation that cheese gives you weird dreams. Another study in 2005 suggested certain types of cheese cause certain types of dreams. Blue cheese for vivid dreams and cheddar cheese for celebrity cameos.
But is there any truth to it at all?
Regardless of what we eat, going to bed hungry could cause vivid dreams, according to research by Tore Nielsen, director of the University of Montreal’s dream and nightmare lab. The 2015 study showed that high lactose could have an effect on dreams.
In that study, 17% of participants said their dreams were influenced by what they ate, but the kicker was that dairy products were the foods most reported as causing the weird dreams, the BBC noted.
“It’s likely an indirect effect in that lactose produces symptoms like gas, bloating and diarrhoea and influences dreams, as dreams draw on somatic sources like this. And if you have certain kinds of intolerances, you still may be likely to eat those foods sometimes,” Mr. Nielsen told the BBC.
There’s also the theory that it’s all in the timing of consumption. Are you the type of person to sneak a slice of cheese from the fridge late at night? (Nods.) Same.
“One reason cheese and nightmares come about is that eating later before bed is more likely to disrupt sleep, and cheese can be hard to digest,” said Charlotte Gupta, a research fellow at Central Queensland University in Australia and a coauthor of a 2020 review on how diet affects our sleep.
So as tempting as it is, maybe skip sprinkling Parmesan cheese shreds into your mouth at the open fridge before bed.
Teeing up against Parkinson’s
For the nearly 1 million people in the United States with Parkinson’s disease, tai chi is one of the best ways to alleviate the symptoms. The average Parkinson’s patient, however, is going to be on the older side and more likely to view the martial art as some sort of communist plot. And would you participate in a communist plot? We don’t think so.
One group of researchers saw that patients weren’t keeping up with their therapy and decided to try a different activity, something that older people would be more likely to stick with. Something a bit more stereotypical. No, not shuffleboard. They tried golf.
“Golf is popular – the most popular sport for people over the age of 55 – which might encourage people to try it and stick with it,” study author Anne-Marie A. Wills, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in a Study Finds report.
In a small study, the investigators had a group of patients with Parkinson’s regularly go to a driving range for 10 weeks to hit golf balls (all expenses paid too, and that’s a big deal for golf), while another group continued with their tai chi.
At the end of the study, the 8 patients who went to the driving range had significantly better results in a Parkinson’s mobility test than those of the 12 patients in the tai chi group. In addition, the golf-group participants said they were more likely to continue with their therapy than were those who did tai chi.
Despite the small size of the study, the research team said the results certainly warrant further research. After all, the best sort of therapy is the kind that actually gets done. And golf just gets in your head. The eternal quest to add distance, to straighten out that annoying slice, to stop thinning half your chips, to make those annoying 4-footers. ... Maybe that’s just us.
Squeezing a little lemonade out of COVID-19
We like to think of ourselves as optimists here at LOTME. A glass is half full, the sky is partly sunny, and our motto is “Always look on the bright side of insanity.” Then again, our motto before that was “LOTME: Where science meets stupid,” so what do we know?
Anyway, it’s that upbeat, can-do attitude that allows us to say something positive – two somethings, actually – about the insanity that is COVID-19.
Our journey to the bright side begins, oddly enough, in the courtroom. Seems that our old friend, the face mask, is something of a lie-detector aid for juries. The authors of a recent literature review of studies on deception “found that facial expressions and other forms of nonverbal behaviour are an unreliable indicator of deceit,” according to a statement from the University of Portsmouth, where the analysis was conducted.
The one study that directly examined the role of face coverings in court proceedings showed that, “by taking away the distraction of nonverbal behaviours, observers had to rely on speech content, which turned out to be better for detecting lies,” the university said.
The second stage of our positivity trek brings us to the National Trends in Disability Employment monthly update, where we see a fourth consecutive month of gains for people with disabilities despite the larger trend of declines among those without disabilities.
Here are some numbers from the Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability to tell the story: From October to November, the employment-to-population ratio increased 4.2% for working-age people with disabilities, compared with 0.4% for people without disabilities. At the same time, the labor force participation rate rose 2.4% for working-age people with disabilities and just 0.1% for working-age people without disabilities.
Both indicators surpassed their historic highs, Andrew Houtenville, PhD, director of the Institute on Disability, said in the update. “These gains suggest that the restructuring resulting from the pandemic may be benefiting people with disabilities. Ironically, it may have taken a pandemic to shake the labor market loose for people with disabilities.”
And that is how a world-class optimist turns one gigantic lemon into lemonade.
Cut the cheese for better sleep
So, we’ve already talked about the TikTok lettuce tea hack that’s supposed to help us sleep better. Well, there’s another food that could have the opposite effect.
According to an article from the BBC, cheese has something of a reputation. Ever since the 1960s, when a researcher noted that one patient’s nightmares stopped after he quit eating an ounce or two of cheddar each night, there’s been speculation that cheese gives you weird dreams. Another study in 2005 suggested certain types of cheese cause certain types of dreams. Blue cheese for vivid dreams and cheddar cheese for celebrity cameos.
But is there any truth to it at all?
Regardless of what we eat, going to bed hungry could cause vivid dreams, according to research by Tore Nielsen, director of the University of Montreal’s dream and nightmare lab. The 2015 study showed that high lactose could have an effect on dreams.
In that study, 17% of participants said their dreams were influenced by what they ate, but the kicker was that dairy products were the foods most reported as causing the weird dreams, the BBC noted.
“It’s likely an indirect effect in that lactose produces symptoms like gas, bloating and diarrhoea and influences dreams, as dreams draw on somatic sources like this. And if you have certain kinds of intolerances, you still may be likely to eat those foods sometimes,” Mr. Nielsen told the BBC.
There’s also the theory that it’s all in the timing of consumption. Are you the type of person to sneak a slice of cheese from the fridge late at night? (Nods.) Same.
“One reason cheese and nightmares come about is that eating later before bed is more likely to disrupt sleep, and cheese can be hard to digest,” said Charlotte Gupta, a research fellow at Central Queensland University in Australia and a coauthor of a 2020 review on how diet affects our sleep.
So as tempting as it is, maybe skip sprinkling Parmesan cheese shreds into your mouth at the open fridge before bed.
Teeing up against Parkinson’s
For the nearly 1 million people in the United States with Parkinson’s disease, tai chi is one of the best ways to alleviate the symptoms. The average Parkinson’s patient, however, is going to be on the older side and more likely to view the martial art as some sort of communist plot. And would you participate in a communist plot? We don’t think so.
One group of researchers saw that patients weren’t keeping up with their therapy and decided to try a different activity, something that older people would be more likely to stick with. Something a bit more stereotypical. No, not shuffleboard. They tried golf.
“Golf is popular – the most popular sport for people over the age of 55 – which might encourage people to try it and stick with it,” study author Anne-Marie A. Wills, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in a Study Finds report.
In a small study, the investigators had a group of patients with Parkinson’s regularly go to a driving range for 10 weeks to hit golf balls (all expenses paid too, and that’s a big deal for golf), while another group continued with their tai chi.
At the end of the study, the 8 patients who went to the driving range had significantly better results in a Parkinson’s mobility test than those of the 12 patients in the tai chi group. In addition, the golf-group participants said they were more likely to continue with their therapy than were those who did tai chi.
Despite the small size of the study, the research team said the results certainly warrant further research. After all, the best sort of therapy is the kind that actually gets done. And golf just gets in your head. The eternal quest to add distance, to straighten out that annoying slice, to stop thinning half your chips, to make those annoying 4-footers. ... Maybe that’s just us.
Squeezing a little lemonade out of COVID-19
We like to think of ourselves as optimists here at LOTME. A glass is half full, the sky is partly sunny, and our motto is “Always look on the bright side of insanity.” Then again, our motto before that was “LOTME: Where science meets stupid,” so what do we know?
Anyway, it’s that upbeat, can-do attitude that allows us to say something positive – two somethings, actually – about the insanity that is COVID-19.
Our journey to the bright side begins, oddly enough, in the courtroom. Seems that our old friend, the face mask, is something of a lie-detector aid for juries. The authors of a recent literature review of studies on deception “found that facial expressions and other forms of nonverbal behaviour are an unreliable indicator of deceit,” according to a statement from the University of Portsmouth, where the analysis was conducted.
The one study that directly examined the role of face coverings in court proceedings showed that, “by taking away the distraction of nonverbal behaviours, observers had to rely on speech content, which turned out to be better for detecting lies,” the university said.
The second stage of our positivity trek brings us to the National Trends in Disability Employment monthly update, where we see a fourth consecutive month of gains for people with disabilities despite the larger trend of declines among those without disabilities.
Here are some numbers from the Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability to tell the story: From October to November, the employment-to-population ratio increased 4.2% for working-age people with disabilities, compared with 0.4% for people without disabilities. At the same time, the labor force participation rate rose 2.4% for working-age people with disabilities and just 0.1% for working-age people without disabilities.
Both indicators surpassed their historic highs, Andrew Houtenville, PhD, director of the Institute on Disability, said in the update. “These gains suggest that the restructuring resulting from the pandemic may be benefiting people with disabilities. Ironically, it may have taken a pandemic to shake the labor market loose for people with disabilities.”
And that is how a world-class optimist turns one gigantic lemon into lemonade.
Cut the cheese for better sleep
So, we’ve already talked about the TikTok lettuce tea hack that’s supposed to help us sleep better. Well, there’s another food that could have the opposite effect.
According to an article from the BBC, cheese has something of a reputation. Ever since the 1960s, when a researcher noted that one patient’s nightmares stopped after he quit eating an ounce or two of cheddar each night, there’s been speculation that cheese gives you weird dreams. Another study in 2005 suggested certain types of cheese cause certain types of dreams. Blue cheese for vivid dreams and cheddar cheese for celebrity cameos.
But is there any truth to it at all?
Regardless of what we eat, going to bed hungry could cause vivid dreams, according to research by Tore Nielsen, director of the University of Montreal’s dream and nightmare lab. The 2015 study showed that high lactose could have an effect on dreams.
In that study, 17% of participants said their dreams were influenced by what they ate, but the kicker was that dairy products were the foods most reported as causing the weird dreams, the BBC noted.
“It’s likely an indirect effect in that lactose produces symptoms like gas, bloating and diarrhoea and influences dreams, as dreams draw on somatic sources like this. And if you have certain kinds of intolerances, you still may be likely to eat those foods sometimes,” Mr. Nielsen told the BBC.
There’s also the theory that it’s all in the timing of consumption. Are you the type of person to sneak a slice of cheese from the fridge late at night? (Nods.) Same.
“One reason cheese and nightmares come about is that eating later before bed is more likely to disrupt sleep, and cheese can be hard to digest,” said Charlotte Gupta, a research fellow at Central Queensland University in Australia and a coauthor of a 2020 review on how diet affects our sleep.
So as tempting as it is, maybe skip sprinkling Parmesan cheese shreds into your mouth at the open fridge before bed.
Teeing up against Parkinson’s
For the nearly 1 million people in the United States with Parkinson’s disease, tai chi is one of the best ways to alleviate the symptoms. The average Parkinson’s patient, however, is going to be on the older side and more likely to view the martial art as some sort of communist plot. And would you participate in a communist plot? We don’t think so.
One group of researchers saw that patients weren’t keeping up with their therapy and decided to try a different activity, something that older people would be more likely to stick with. Something a bit more stereotypical. No, not shuffleboard. They tried golf.
“Golf is popular – the most popular sport for people over the age of 55 – which might encourage people to try it and stick with it,” study author Anne-Marie A. Wills, MD, of Massachusetts General Hospital, Boston, said in a Study Finds report.
In a small study, the investigators had a group of patients with Parkinson’s regularly go to a driving range for 10 weeks to hit golf balls (all expenses paid too, and that’s a big deal for golf), while another group continued with their tai chi.
At the end of the study, the 8 patients who went to the driving range had significantly better results in a Parkinson’s mobility test than those of the 12 patients in the tai chi group. In addition, the golf-group participants said they were more likely to continue with their therapy than were those who did tai chi.
Despite the small size of the study, the research team said the results certainly warrant further research. After all, the best sort of therapy is the kind that actually gets done. And golf just gets in your head. The eternal quest to add distance, to straighten out that annoying slice, to stop thinning half your chips, to make those annoying 4-footers. ... Maybe that’s just us.
More evidence ties some antipsychotics to increased breast cancer risk
New research provides more evidence that antipsychotics that raise prolactin levels are tied to a significantly increased risk for breast cancer.
The relative risk for breast cancer was 62% higher in women who took category 1 antipsychotic medications associated with high prolactin levels. These include haloperidol (Haldol), paliperidone (Invega), and risperidone (Risperdal). Additionally, the risk was 54% higher in those taking category 2 antipsychotics that have mid-range effects on prolactin. These include iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
In contrast, category 3 antipsychotics which have a lesser effect on prolactin levels were not associated with any increase in breast cancer risk. These drugs include aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), clozapine (multiple brands), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
While the “absolute” breast cancer risk for these drugs is unclear, “we can make the case that high circulating prolactin levels are associated with breast cancer risk. This follows what is already known about prolactin from prior studies, notably the nurses’ health studies,” Tahir Rahman, MD, associate professor of psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, told this news organization.
“We don’t want to alarm patients taking antipsychotic drugs for life-threatening mental health problems, but we also think it is time for doctors to track prolactin levels and vigilantly monitor their patients who are being treated with antipsychotics,” Dr. Rahman added in a news release.
The study was published online Dec. 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Test prolactin levels
Using administrative claims data, the researchers evaluated breast cancer risk in women aged 18-64 exposed to antipsychotic medications compared with anticonvulsants and/or lithium.
They identified 914 cases of invasive breast cancer among 540,737 women.
Roughly 52% of the study population filled at least one prescription for a category 3 antipsychotic agent, whereas 15% filled at least one prescription for a category 1 agent; 49% of women filled at least one prescription for an anticonvulsant medication during the study period.
Exposure to all antipsychotics was independently associated with a 35% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.14-1.61), the study team found.
Compared with anticonvulsants or lithium, the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased for high prolactin (category 1) antipsychotics (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.30-2.03) and for mid-prolactin (category 2) drugs (aHR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99), with no increased risk for category 3 antipsychotics.
“Our research is obviously of interest for preventing breast cancer in antipsychotic-treated patients. Checking a blood prolactin level is cheap and easy [and a high level is] fairly simple to mitigate,” said Dr. Rahman.
A matter of debate
Reached for comment, Christoph Correll, MD, professor of psychiatry and molecular medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said, “The potential elevation of breast cancer risk depending on the dose and time of treatment with antipsychotic medications with varying degrees of prolactin-raising properties has been a topic of research and matter of debate.”
This new study “adds another data point indicating that antipsychotics that are associated on average with a higher prolactin-raising effect than other antipsychotics may increase the risk of breast cancer in women to some degree,” said Dr. Correll, who was not involved with the study.
However, he cautioned that “naturalistic data are always vulnerable to residual confounding, for example, unmeasured effects that could also at least partially explain the results, and the follow-up time of only 4 years (maximum 6 years) in this study was relatively short.
“Nevertheless, given availability of many different antipsychotics with varying degrees of prolactin-raising potential, in women requiring antipsychotic treatment, less prolactin-raising antipsychotics may be preferable,” Dr. Correll said.
“In women receiving prolactin-raising antipsychotics for medium- and longer-term maintenance therapy, prolactin levels should be monitored,” he added.
When an elevated prolactin level is detected, this should be addressed “either via dose reduction, a switch to an alternative antipsychotic that does not raise prolactin levels significantly, or the addition of a partial or full D2 agonist when the prolactin-raising antipsychotic should be continued based on individualized risk assessment,” Dr. Correll advised.
This work was supported by an award from the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center; the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health; the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research; and the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Correll has received royalties from UpToDate and is a stock option holder of LB Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides more evidence that antipsychotics that raise prolactin levels are tied to a significantly increased risk for breast cancer.
The relative risk for breast cancer was 62% higher in women who took category 1 antipsychotic medications associated with high prolactin levels. These include haloperidol (Haldol), paliperidone (Invega), and risperidone (Risperdal). Additionally, the risk was 54% higher in those taking category 2 antipsychotics that have mid-range effects on prolactin. These include iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
In contrast, category 3 antipsychotics which have a lesser effect on prolactin levels were not associated with any increase in breast cancer risk. These drugs include aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), clozapine (multiple brands), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
While the “absolute” breast cancer risk for these drugs is unclear, “we can make the case that high circulating prolactin levels are associated with breast cancer risk. This follows what is already known about prolactin from prior studies, notably the nurses’ health studies,” Tahir Rahman, MD, associate professor of psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, told this news organization.
“We don’t want to alarm patients taking antipsychotic drugs for life-threatening mental health problems, but we also think it is time for doctors to track prolactin levels and vigilantly monitor their patients who are being treated with antipsychotics,” Dr. Rahman added in a news release.
The study was published online Dec. 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Test prolactin levels
Using administrative claims data, the researchers evaluated breast cancer risk in women aged 18-64 exposed to antipsychotic medications compared with anticonvulsants and/or lithium.
They identified 914 cases of invasive breast cancer among 540,737 women.
Roughly 52% of the study population filled at least one prescription for a category 3 antipsychotic agent, whereas 15% filled at least one prescription for a category 1 agent; 49% of women filled at least one prescription for an anticonvulsant medication during the study period.
Exposure to all antipsychotics was independently associated with a 35% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.14-1.61), the study team found.
Compared with anticonvulsants or lithium, the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased for high prolactin (category 1) antipsychotics (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.30-2.03) and for mid-prolactin (category 2) drugs (aHR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99), with no increased risk for category 3 antipsychotics.
“Our research is obviously of interest for preventing breast cancer in antipsychotic-treated patients. Checking a blood prolactin level is cheap and easy [and a high level is] fairly simple to mitigate,” said Dr. Rahman.
A matter of debate
Reached for comment, Christoph Correll, MD, professor of psychiatry and molecular medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said, “The potential elevation of breast cancer risk depending on the dose and time of treatment with antipsychotic medications with varying degrees of prolactin-raising properties has been a topic of research and matter of debate.”
This new study “adds another data point indicating that antipsychotics that are associated on average with a higher prolactin-raising effect than other antipsychotics may increase the risk of breast cancer in women to some degree,” said Dr. Correll, who was not involved with the study.
However, he cautioned that “naturalistic data are always vulnerable to residual confounding, for example, unmeasured effects that could also at least partially explain the results, and the follow-up time of only 4 years (maximum 6 years) in this study was relatively short.
“Nevertheless, given availability of many different antipsychotics with varying degrees of prolactin-raising potential, in women requiring antipsychotic treatment, less prolactin-raising antipsychotics may be preferable,” Dr. Correll said.
“In women receiving prolactin-raising antipsychotics for medium- and longer-term maintenance therapy, prolactin levels should be monitored,” he added.
When an elevated prolactin level is detected, this should be addressed “either via dose reduction, a switch to an alternative antipsychotic that does not raise prolactin levels significantly, or the addition of a partial or full D2 agonist when the prolactin-raising antipsychotic should be continued based on individualized risk assessment,” Dr. Correll advised.
This work was supported by an award from the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center; the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health; the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research; and the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Correll has received royalties from UpToDate and is a stock option holder of LB Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
New research provides more evidence that antipsychotics that raise prolactin levels are tied to a significantly increased risk for breast cancer.
The relative risk for breast cancer was 62% higher in women who took category 1 antipsychotic medications associated with high prolactin levels. These include haloperidol (Haldol), paliperidone (Invega), and risperidone (Risperdal). Additionally, the risk was 54% higher in those taking category 2 antipsychotics that have mid-range effects on prolactin. These include iloperidone (Fanapt), lurasidone (Latuda), and olanzapine (Zyprexa).
In contrast, category 3 antipsychotics which have a lesser effect on prolactin levels were not associated with any increase in breast cancer risk. These drugs include aripiprazole (Abilify), asenapine (Saphris), brexpiprazole (Rexulti), cariprazine (Vraylar), clozapine (multiple brands), quetiapine (Seroquel), and ziprasidone (Geodon).
While the “absolute” breast cancer risk for these drugs is unclear, “we can make the case that high circulating prolactin levels are associated with breast cancer risk. This follows what is already known about prolactin from prior studies, notably the nurses’ health studies,” Tahir Rahman, MD, associate professor of psychiatry, Washington University School of Medicine, St. Louis, told this news organization.
“We don’t want to alarm patients taking antipsychotic drugs for life-threatening mental health problems, but we also think it is time for doctors to track prolactin levels and vigilantly monitor their patients who are being treated with antipsychotics,” Dr. Rahman added in a news release.
The study was published online Dec. 3 in the Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology.
Test prolactin levels
Using administrative claims data, the researchers evaluated breast cancer risk in women aged 18-64 exposed to antipsychotic medications compared with anticonvulsants and/or lithium.
They identified 914 cases of invasive breast cancer among 540,737 women.
Roughly 52% of the study population filled at least one prescription for a category 3 antipsychotic agent, whereas 15% filled at least one prescription for a category 1 agent; 49% of women filled at least one prescription for an anticonvulsant medication during the study period.
Exposure to all antipsychotics was independently associated with a 35% increased risk for breast cancer (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.35; 95% CI, 1.14-1.61), the study team found.
Compared with anticonvulsants or lithium, the risk for breast cancer was significantly increased for high prolactin (category 1) antipsychotics (adjusted hazard ratio, 1.62; 95% CI, 1.30-2.03) and for mid-prolactin (category 2) drugs (aHR 1.54; 95% CI, 1.19-1.99), with no increased risk for category 3 antipsychotics.
“Our research is obviously of interest for preventing breast cancer in antipsychotic-treated patients. Checking a blood prolactin level is cheap and easy [and a high level is] fairly simple to mitigate,” said Dr. Rahman.
A matter of debate
Reached for comment, Christoph Correll, MD, professor of psychiatry and molecular medicine, Zucker School of Medicine at Hofstra/Northwell, Hempstead, New York, said, “The potential elevation of breast cancer risk depending on the dose and time of treatment with antipsychotic medications with varying degrees of prolactin-raising properties has been a topic of research and matter of debate.”
This new study “adds another data point indicating that antipsychotics that are associated on average with a higher prolactin-raising effect than other antipsychotics may increase the risk of breast cancer in women to some degree,” said Dr. Correll, who was not involved with the study.
However, he cautioned that “naturalistic data are always vulnerable to residual confounding, for example, unmeasured effects that could also at least partially explain the results, and the follow-up time of only 4 years (maximum 6 years) in this study was relatively short.
“Nevertheless, given availability of many different antipsychotics with varying degrees of prolactin-raising potential, in women requiring antipsychotic treatment, less prolactin-raising antipsychotics may be preferable,” Dr. Correll said.
“In women receiving prolactin-raising antipsychotics for medium- and longer-term maintenance therapy, prolactin levels should be monitored,” he added.
When an elevated prolactin level is detected, this should be addressed “either via dose reduction, a switch to an alternative antipsychotic that does not raise prolactin levels significantly, or the addition of a partial or full D2 agonist when the prolactin-raising antipsychotic should be continued based on individualized risk assessment,” Dr. Correll advised.
This work was supported by an award from the Alvin J. Siteman Cancer Center; the National Cancer Institute and the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences of the National Institutes of Health; the Taylor Family Institute for Innovative Psychiatric Research; and the Center for Brain Research in Mood Disorders. The authors have disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Correll has received royalties from UpToDate and is a stock option holder of LB Pharma.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM THE JOURNAL OF CLINICAL PSYCHOPHARMACOLOGY
More Americans skipping medical care because of cost, survey says
That’s the highest reported number since the pandemic began and a tripling from March to October.
Even 20% of the country’s highest-income households – earning more than $120,000 per year – said they’ve also skipped care. That’s an increase of about seven times for higher-income families since March.
“Americans tend to think there is a group of lower-income people, and they have worse health care than the rest of us, and the rest of us, we’re okay,” Tim Lash, chief strategy officer for West Health, a nonprofit focused on lowering health care costs, told CBS News.
“What we are seeing now in this survey is this group of people who are identifying themselves as struggling with health care costs is growing,” he said.
As part of the 2021 Healthcare in America Report, researchers surveyed more than 6,000 people in September and October about their concerns and experiences with affording health care and treatment. About half of respondents said health care in America has gotten worse because of the pandemic, and more than half said they’re more worried about medical costs than before.
What’s more, many Americans put off routine doctor visits at the beginning of the pandemic, and now that they’re beginning to schedule appointments again, they’re facing major costs, the survey found. Some expenses have increased in the past year, including prescription medications.
The rising costs have led many people to skip care or treatment, which can have major consequences. About 1 in 20 adults said they know a friend or family member who died during the past year because they couldn’t afford medical care, the survey found. And about 20% of adults said they or someone in their household had a health issue that grew worse after postponing care because of price.
About 23% of survey respondents said that paying for health care represents a major financial burden, which increases to a third of respondents who earn less than $48,000 per year. Out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles and insurance premiums have increased, which have taken up larger portions of people’s budgets.
“We often overlook the side effect of costs, and it’s quite toxic – there is a financial toxicity that exists in health care,” Mr. Lash said. “We know when you skip treatment, that can have an impact on mortality.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
That’s the highest reported number since the pandemic began and a tripling from March to October.
Even 20% of the country’s highest-income households – earning more than $120,000 per year – said they’ve also skipped care. That’s an increase of about seven times for higher-income families since March.
“Americans tend to think there is a group of lower-income people, and they have worse health care than the rest of us, and the rest of us, we’re okay,” Tim Lash, chief strategy officer for West Health, a nonprofit focused on lowering health care costs, told CBS News.
“What we are seeing now in this survey is this group of people who are identifying themselves as struggling with health care costs is growing,” he said.
As part of the 2021 Healthcare in America Report, researchers surveyed more than 6,000 people in September and October about their concerns and experiences with affording health care and treatment. About half of respondents said health care in America has gotten worse because of the pandemic, and more than half said they’re more worried about medical costs than before.
What’s more, many Americans put off routine doctor visits at the beginning of the pandemic, and now that they’re beginning to schedule appointments again, they’re facing major costs, the survey found. Some expenses have increased in the past year, including prescription medications.
The rising costs have led many people to skip care or treatment, which can have major consequences. About 1 in 20 adults said they know a friend or family member who died during the past year because they couldn’t afford medical care, the survey found. And about 20% of adults said they or someone in their household had a health issue that grew worse after postponing care because of price.
About 23% of survey respondents said that paying for health care represents a major financial burden, which increases to a third of respondents who earn less than $48,000 per year. Out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles and insurance premiums have increased, which have taken up larger portions of people’s budgets.
“We often overlook the side effect of costs, and it’s quite toxic – there is a financial toxicity that exists in health care,” Mr. Lash said. “We know when you skip treatment, that can have an impact on mortality.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
That’s the highest reported number since the pandemic began and a tripling from March to October.
Even 20% of the country’s highest-income households – earning more than $120,000 per year – said they’ve also skipped care. That’s an increase of about seven times for higher-income families since March.
“Americans tend to think there is a group of lower-income people, and they have worse health care than the rest of us, and the rest of us, we’re okay,” Tim Lash, chief strategy officer for West Health, a nonprofit focused on lowering health care costs, told CBS News.
“What we are seeing now in this survey is this group of people who are identifying themselves as struggling with health care costs is growing,” he said.
As part of the 2021 Healthcare in America Report, researchers surveyed more than 6,000 people in September and October about their concerns and experiences with affording health care and treatment. About half of respondents said health care in America has gotten worse because of the pandemic, and more than half said they’re more worried about medical costs than before.
What’s more, many Americans put off routine doctor visits at the beginning of the pandemic, and now that they’re beginning to schedule appointments again, they’re facing major costs, the survey found. Some expenses have increased in the past year, including prescription medications.
The rising costs have led many people to skip care or treatment, which can have major consequences. About 1 in 20 adults said they know a friend or family member who died during the past year because they couldn’t afford medical care, the survey found. And about 20% of adults said they or someone in their household had a health issue that grew worse after postponing care because of price.
About 23% of survey respondents said that paying for health care represents a major financial burden, which increases to a third of respondents who earn less than $48,000 per year. Out-of-pocket costs such as deductibles and insurance premiums have increased, which have taken up larger portions of people’s budgets.
“We often overlook the side effect of costs, and it’s quite toxic – there is a financial toxicity that exists in health care,” Mr. Lash said. “We know when you skip treatment, that can have an impact on mortality.”
A version of this article first appeared on WebMD.com.
COVID-19 asymptomatic infection rate remains high
Based on data from a meta-analysis of 95 studies that included nearly 30,000,000 individuals, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections was 0.25% in the tested population and 40.5% among confirmed cases.
, wrote Qiuyue Ma, PhD, and colleagues of Peking University, Beijing.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open the researchers identified 44 cross-sectional studies, 41 cohort studies, seven case series, and three case series on transmission studies. A total of 74 studies were conducted in developed countries, including those in Europe, North America, and Asia. Approximately one-third (37) of the studies were conducted among health care workers or in-hospital patients, 17 among nursing home staff or residents, and 14 among community residents. In addition, 13 studies involved pregnant women, eight involved air or cruise ship travelers, and six involved close contacts of individuals with confirmed infections.
The meta-analysis included 29,776,306 tested individuals; 11,516 of them had asymptomatic infections.
Overall, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the tested population was 0.25%. In an analysis of different study populations, the percentage was higher in nursing home residents or staff (4.52%), air or cruise ship travelers (2.02%), and pregnant women (2.34%), compared against the pooled percentage.
The pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the confirmed population was 40.50%, and this percentage was higher in pregnant women (54.11%), air or cruise ship travelers (52.91%), and nursing home residents or staff (47.53%).
The pooled percentage in the tested population was higher than the overall percentage when the mean age of the study population was 60 years or older (3.69%). By contrast, in the confirmed population, the pooled percentage was higher than the overall percentage when the study population was younger than 20 years (60.2%) or aged 20 to 39 years (49.5%).
The researchers noted in their discussion that the varying percentage of asymptomatic individuals according to community prevalence might impact the heterogeneity of the included studies. They also noted the high number of studies conducted in nursing home populations, groups in which asymptomatic individuals were more likely to be tested.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for missed studies that were not published at the time of the meta-analysis, as well as the exclusion of studies written in Chinese, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of follow-up on presymptomatic and covert infections, and the focus on specific populations, factors that may limit the degree to which the results can be generalized.
However, the results highlight the need to screen for asymptomatic infections, especially in countries where COVID-19 has been better controlled, the researchers said. Management strategies for asymptomatic infections, when identified, should include isolation and contact tracing similar to strategies used with confirmed cases, they added.
More testing needed to catch cases early
“During the initial phase of [the] COVID-19 pandemic, testing was not widely available in the United States or the rest of the world,” Setu Patolia, MD, of Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Missouri, said in an interview. Much of the world still lacks access to COVID-19 testing, and early in the pandemic only severely symptomatic patients were tested, he said. “With new variants, particularly the Omicron variant, which may have mild or minimally symptomatic disease, asymptomatic carriers play an important role in propagation of the pandemic,” he explained. “It is important to know the asymptomatic carrier rate among the general population for the future control of [the] pandemic,” he added.
Dr. Patolia said he was surprised by the study finding that one in 400 people in the general population could be asymptomatic carriers of COVID-19.
“Also, nursing home patients are more at risk of complications of COVID, and I expected that they would have a higher rate of symptomatic disease as compared to [the] general population,” said Dr. Patolia. He was also surprised by the high rate of asymptomatic infections in travelers.
“Physicians should be more aware about the asymptomatic carrier rate, particularly in travelers and nursing home patients,” he noted. “Travelers carry high risk of transferring infection from one region to another region of the world, and physicians should advise them to get tested despite the absence of symptoms,” Dr. Patolia emphasized. “Similarly, once any nursing home patient has been diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians should be more careful with the rest of the nursing home patients and test them despite the absence of the symptoms,” he added.
Dr. Patolia also recommended that pregnant women wear masks to help prevent disease transmission when visiting a doctor’s office or labor unit.
Looking ahead, there is a need for cheaper at-home testing kits so that all vulnerable populations can be tested fast and frequently, Dr. Patolia said.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Patolia has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Based on data from a meta-analysis of 95 studies that included nearly 30,000,000 individuals, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections was 0.25% in the tested population and 40.5% among confirmed cases.
, wrote Qiuyue Ma, PhD, and colleagues of Peking University, Beijing.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open the researchers identified 44 cross-sectional studies, 41 cohort studies, seven case series, and three case series on transmission studies. A total of 74 studies were conducted in developed countries, including those in Europe, North America, and Asia. Approximately one-third (37) of the studies were conducted among health care workers or in-hospital patients, 17 among nursing home staff or residents, and 14 among community residents. In addition, 13 studies involved pregnant women, eight involved air or cruise ship travelers, and six involved close contacts of individuals with confirmed infections.
The meta-analysis included 29,776,306 tested individuals; 11,516 of them had asymptomatic infections.
Overall, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the tested population was 0.25%. In an analysis of different study populations, the percentage was higher in nursing home residents or staff (4.52%), air or cruise ship travelers (2.02%), and pregnant women (2.34%), compared against the pooled percentage.
The pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the confirmed population was 40.50%, and this percentage was higher in pregnant women (54.11%), air or cruise ship travelers (52.91%), and nursing home residents or staff (47.53%).
The pooled percentage in the tested population was higher than the overall percentage when the mean age of the study population was 60 years or older (3.69%). By contrast, in the confirmed population, the pooled percentage was higher than the overall percentage when the study population was younger than 20 years (60.2%) or aged 20 to 39 years (49.5%).
The researchers noted in their discussion that the varying percentage of asymptomatic individuals according to community prevalence might impact the heterogeneity of the included studies. They also noted the high number of studies conducted in nursing home populations, groups in which asymptomatic individuals were more likely to be tested.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for missed studies that were not published at the time of the meta-analysis, as well as the exclusion of studies written in Chinese, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of follow-up on presymptomatic and covert infections, and the focus on specific populations, factors that may limit the degree to which the results can be generalized.
However, the results highlight the need to screen for asymptomatic infections, especially in countries where COVID-19 has been better controlled, the researchers said. Management strategies for asymptomatic infections, when identified, should include isolation and contact tracing similar to strategies used with confirmed cases, they added.
More testing needed to catch cases early
“During the initial phase of [the] COVID-19 pandemic, testing was not widely available in the United States or the rest of the world,” Setu Patolia, MD, of Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Missouri, said in an interview. Much of the world still lacks access to COVID-19 testing, and early in the pandemic only severely symptomatic patients were tested, he said. “With new variants, particularly the Omicron variant, which may have mild or minimally symptomatic disease, asymptomatic carriers play an important role in propagation of the pandemic,” he explained. “It is important to know the asymptomatic carrier rate among the general population for the future control of [the] pandemic,” he added.
Dr. Patolia said he was surprised by the study finding that one in 400 people in the general population could be asymptomatic carriers of COVID-19.
“Also, nursing home patients are more at risk of complications of COVID, and I expected that they would have a higher rate of symptomatic disease as compared to [the] general population,” said Dr. Patolia. He was also surprised by the high rate of asymptomatic infections in travelers.
“Physicians should be more aware about the asymptomatic carrier rate, particularly in travelers and nursing home patients,” he noted. “Travelers carry high risk of transferring infection from one region to another region of the world, and physicians should advise them to get tested despite the absence of symptoms,” Dr. Patolia emphasized. “Similarly, once any nursing home patient has been diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians should be more careful with the rest of the nursing home patients and test them despite the absence of the symptoms,” he added.
Dr. Patolia also recommended that pregnant women wear masks to help prevent disease transmission when visiting a doctor’s office or labor unit.
Looking ahead, there is a need for cheaper at-home testing kits so that all vulnerable populations can be tested fast and frequently, Dr. Patolia said.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Patolia has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Based on data from a meta-analysis of 95 studies that included nearly 30,000,000 individuals, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic COVID-19 infections was 0.25% in the tested population and 40.5% among confirmed cases.
, wrote Qiuyue Ma, PhD, and colleagues of Peking University, Beijing.
In a study published in JAMA Network Open the researchers identified 44 cross-sectional studies, 41 cohort studies, seven case series, and three case series on transmission studies. A total of 74 studies were conducted in developed countries, including those in Europe, North America, and Asia. Approximately one-third (37) of the studies were conducted among health care workers or in-hospital patients, 17 among nursing home staff or residents, and 14 among community residents. In addition, 13 studies involved pregnant women, eight involved air or cruise ship travelers, and six involved close contacts of individuals with confirmed infections.
The meta-analysis included 29,776,306 tested individuals; 11,516 of them had asymptomatic infections.
Overall, the pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the tested population was 0.25%. In an analysis of different study populations, the percentage was higher in nursing home residents or staff (4.52%), air or cruise ship travelers (2.02%), and pregnant women (2.34%), compared against the pooled percentage.
The pooled percentage of asymptomatic infections among the confirmed population was 40.50%, and this percentage was higher in pregnant women (54.11%), air or cruise ship travelers (52.91%), and nursing home residents or staff (47.53%).
The pooled percentage in the tested population was higher than the overall percentage when the mean age of the study population was 60 years or older (3.69%). By contrast, in the confirmed population, the pooled percentage was higher than the overall percentage when the study population was younger than 20 years (60.2%) or aged 20 to 39 years (49.5%).
The researchers noted in their discussion that the varying percentage of asymptomatic individuals according to community prevalence might impact the heterogeneity of the included studies. They also noted the high number of studies conducted in nursing home populations, groups in which asymptomatic individuals were more likely to be tested.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the potential for missed studies that were not published at the time of the meta-analysis, as well as the exclusion of studies written in Chinese, the researchers noted. Other limitations included lack of follow-up on presymptomatic and covert infections, and the focus on specific populations, factors that may limit the degree to which the results can be generalized.
However, the results highlight the need to screen for asymptomatic infections, especially in countries where COVID-19 has been better controlled, the researchers said. Management strategies for asymptomatic infections, when identified, should include isolation and contact tracing similar to strategies used with confirmed cases, they added.
More testing needed to catch cases early
“During the initial phase of [the] COVID-19 pandemic, testing was not widely available in the United States or the rest of the world,” Setu Patolia, MD, of Saint Louis University School of Medicine, Missouri, said in an interview. Much of the world still lacks access to COVID-19 testing, and early in the pandemic only severely symptomatic patients were tested, he said. “With new variants, particularly the Omicron variant, which may have mild or minimally symptomatic disease, asymptomatic carriers play an important role in propagation of the pandemic,” he explained. “It is important to know the asymptomatic carrier rate among the general population for the future control of [the] pandemic,” he added.
Dr. Patolia said he was surprised by the study finding that one in 400 people in the general population could be asymptomatic carriers of COVID-19.
“Also, nursing home patients are more at risk of complications of COVID, and I expected that they would have a higher rate of symptomatic disease as compared to [the] general population,” said Dr. Patolia. He was also surprised by the high rate of asymptomatic infections in travelers.
“Physicians should be more aware about the asymptomatic carrier rate, particularly in travelers and nursing home patients,” he noted. “Travelers carry high risk of transferring infection from one region to another region of the world, and physicians should advise them to get tested despite the absence of symptoms,” Dr. Patolia emphasized. “Similarly, once any nursing home patient has been diagnosed with COVID-19, physicians should be more careful with the rest of the nursing home patients and test them despite the absence of the symptoms,” he added.
Dr. Patolia also recommended that pregnant women wear masks to help prevent disease transmission when visiting a doctor’s office or labor unit.
Looking ahead, there is a need for cheaper at-home testing kits so that all vulnerable populations can be tested fast and frequently, Dr. Patolia said.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China. The researchers had no financial conflicts to disclose. Dr. Patolia has disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Case report: ECT for delirious mania
Delirious mania is a diagnostic term used in variety of settings, including the emergency department and inpatient psychiatry, but it does not have formal criteria established in the DSM-5. Delirious mania was first described in the 1800s and was referred to as “Bell’s Mania.”
As the late Max Fink, MD, wrote in the journal Bipolar Disorders (2002 Feb 23. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-561.1999.10112.x), delirious mania is considered to be a syndrome of the acute onset of the excitement, grandiosity, emotional lability, delusions, and insomnia characteristic of mania, and the disorientation and altered consciousness characteristic of delirium.
Such patients can be considered as having a component of bipolar I disorder, comprising mania with psychotic features. Delirious mania is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality, and demonstrates limited response to conventional treatment guidelines. Therefore, early detection and decisive treatment are imperative. The concurrence of delirium and mania is not unusual, yet currently there are no universal accepted treatment guidelines for delirious mania (BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 21. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-65). The purpose of this case report is to inspire and support community psychiatric clinicians in managing such complex cases and to improve behavioral health care outcomes. To protect our patient’s identity, we changed several key identifiers.
The treatment plan emerges
This case is of a middle-aged man with an established diagnosis of bipolar disorder. He was referred to the ED because of worsening manic symptoms marked by mood lability, pressured speech, grandiose delusions, tangential thought processes, poor insight, and impaired sleep.
Laboratory studies in the ED revealed hyponatremia and serum sodium of 126meq/l (ref. range: 135-146). The patient’s toxicology screen was positive for benzodiazepines. He was stabilized on the medical floor and then transitioned to inpatient psychiatry.
Before his admission to psychiatry, the patient’s medications were alprazolam 1 mg at bed time, bupropion 100 mg twice daily, loxapine 25 mg morning and 50 mg at bed time, olanzapine 20 mg at bedtime and 5 mg twice daily, risperidone 2 mg twice daily and oxcarbazepine 900 mg twice daily.
The bupropion was discontinued because of manic behavior, and the patient’s dose of oxcarbazepine was lowered from 900 mg twice daily to 450 mg twice daily because of hyponatremia. Our team continued to administer risperidone, olanzapine, loxapine, and alprazolam to the patient. However, he was agitated and disorganized on the psychiatry floor. In addition, we noticed that the patient exhibited confusion, disorientation, an inability to connect with reality, and periods of profound agitation.
The patient was frequently restrained physically, and medications were administered to him for safety and containment. The use of benzodiazepines and anticholinergics was minimized. However, we noticed that the patient acted paranoid, disinhibited, and combative, and he became difficult to restrain. He seemed to have a high pain tolerance, responded to internal stimuli, and began hallucinating and displaying aggressive behavior toward staff persons.
It became apparent that the patient’s circadian rhythm had been altered. He slept for only a couple of hours during the day. During the course of treatment, in one incidence, the patient became agitated and charged at a nurse. Subsequently, the patient hit his head on a wall and fell – suffering a head strike and lacerations.
The team conducted investigations, including labs and neuroimaging, to make sure that the patient was OK. His CT head scan proved unremarkable. Liver function tests revealed mild transaminitis. His TSH, folate, B12, and B1 levels were normal.
We then placed the patient in a single room with continuous behavior monitoring. His recovery seemed to take a long time with trials of different antipsychotic medications, including olanzapine, loxapine, risperidone, and paliperidone. Because of his poor response to medications, the team considered using electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
However, the patient was unable to give informed consent for ECT because of his impaired mental status. At this point, our team submitted a substitute treatment plan that included ECT to the court for approval, and the court approved our plan.
After receiving approximately four bilateral ECT procedures three times a week, the patient’s condition started to improve gradually. He received total of 11 procedures.
Our patient became alert to time, place, and person, and his circadian rhythm normalized. Soon, his delirium cleared, and he demonstrated marked improvement in both insight into his illness and behavioral control. His grandiose delusions were still present, but he was easily redirectable. In addition, our patient demonstrated improved reality testing. He was able to be discharged home following medication adjustments and with community supports within a few short weeks of receiving ECT.
As Bo-Shyan Lee, MD, and associates reported (BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 21;12:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-65), delirious mania is closely related to catatonia. Although there are different definitions for delirium and catatonia, even the most lethal form of catatonia meets the criteria for delirium. ECT is a well established first-line treatment for catatonia. This tool has been shown to be highly effective in the treatment of delirious mania. Delirious mania can be life-threatening and should be managed aggressively. The most common causes of death are heart failure from arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and respiratory failure. ECT is a safe treatment, and, as Dr. Fink argued, the mortality rate is even less than that associated with normal pregnancies (World J Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Jan;2[1]:1-8). In light of the safety and effectiveness of ECT, we think the tool should be considered not only in university hospital settings but as an early intervention in community settings. This case warrants further research in exploring hyperactive delirium and delirious mania.
Dr. Lamba is BR-2 unit medical director at BayRidge Hospital in Lynn, Mass. Ms. Kennedy is an attending clinician at BayRidge. Dr. Vu is medical director at BayRidge. He also serves as associate chief of psychiatry at Beverly (Mass.) Hospital and at Addison Gilbert Hospital in Gloucester, Mass. Dr. Lamba, Ms. Kennedy, and Dr. Vu have no disclosures.
Delirious mania is a diagnostic term used in variety of settings, including the emergency department and inpatient psychiatry, but it does not have formal criteria established in the DSM-5. Delirious mania was first described in the 1800s and was referred to as “Bell’s Mania.”
As the late Max Fink, MD, wrote in the journal Bipolar Disorders (2002 Feb 23. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-561.1999.10112.x), delirious mania is considered to be a syndrome of the acute onset of the excitement, grandiosity, emotional lability, delusions, and insomnia characteristic of mania, and the disorientation and altered consciousness characteristic of delirium.
Such patients can be considered as having a component of bipolar I disorder, comprising mania with psychotic features. Delirious mania is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality, and demonstrates limited response to conventional treatment guidelines. Therefore, early detection and decisive treatment are imperative. The concurrence of delirium and mania is not unusual, yet currently there are no universal accepted treatment guidelines for delirious mania (BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 21. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-65). The purpose of this case report is to inspire and support community psychiatric clinicians in managing such complex cases and to improve behavioral health care outcomes. To protect our patient’s identity, we changed several key identifiers.
The treatment plan emerges
This case is of a middle-aged man with an established diagnosis of bipolar disorder. He was referred to the ED because of worsening manic symptoms marked by mood lability, pressured speech, grandiose delusions, tangential thought processes, poor insight, and impaired sleep.
Laboratory studies in the ED revealed hyponatremia and serum sodium of 126meq/l (ref. range: 135-146). The patient’s toxicology screen was positive for benzodiazepines. He was stabilized on the medical floor and then transitioned to inpatient psychiatry.
Before his admission to psychiatry, the patient’s medications were alprazolam 1 mg at bed time, bupropion 100 mg twice daily, loxapine 25 mg morning and 50 mg at bed time, olanzapine 20 mg at bedtime and 5 mg twice daily, risperidone 2 mg twice daily and oxcarbazepine 900 mg twice daily.
The bupropion was discontinued because of manic behavior, and the patient’s dose of oxcarbazepine was lowered from 900 mg twice daily to 450 mg twice daily because of hyponatremia. Our team continued to administer risperidone, olanzapine, loxapine, and alprazolam to the patient. However, he was agitated and disorganized on the psychiatry floor. In addition, we noticed that the patient exhibited confusion, disorientation, an inability to connect with reality, and periods of profound agitation.
The patient was frequently restrained physically, and medications were administered to him for safety and containment. The use of benzodiazepines and anticholinergics was minimized. However, we noticed that the patient acted paranoid, disinhibited, and combative, and he became difficult to restrain. He seemed to have a high pain tolerance, responded to internal stimuli, and began hallucinating and displaying aggressive behavior toward staff persons.
It became apparent that the patient’s circadian rhythm had been altered. He slept for only a couple of hours during the day. During the course of treatment, in one incidence, the patient became agitated and charged at a nurse. Subsequently, the patient hit his head on a wall and fell – suffering a head strike and lacerations.
The team conducted investigations, including labs and neuroimaging, to make sure that the patient was OK. His CT head scan proved unremarkable. Liver function tests revealed mild transaminitis. His TSH, folate, B12, and B1 levels were normal.
We then placed the patient in a single room with continuous behavior monitoring. His recovery seemed to take a long time with trials of different antipsychotic medications, including olanzapine, loxapine, risperidone, and paliperidone. Because of his poor response to medications, the team considered using electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
However, the patient was unable to give informed consent for ECT because of his impaired mental status. At this point, our team submitted a substitute treatment plan that included ECT to the court for approval, and the court approved our plan.
After receiving approximately four bilateral ECT procedures three times a week, the patient’s condition started to improve gradually. He received total of 11 procedures.
Our patient became alert to time, place, and person, and his circadian rhythm normalized. Soon, his delirium cleared, and he demonstrated marked improvement in both insight into his illness and behavioral control. His grandiose delusions were still present, but he was easily redirectable. In addition, our patient demonstrated improved reality testing. He was able to be discharged home following medication adjustments and with community supports within a few short weeks of receiving ECT.
As Bo-Shyan Lee, MD, and associates reported (BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 21;12:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-65), delirious mania is closely related to catatonia. Although there are different definitions for delirium and catatonia, even the most lethal form of catatonia meets the criteria for delirium. ECT is a well established first-line treatment for catatonia. This tool has been shown to be highly effective in the treatment of delirious mania. Delirious mania can be life-threatening and should be managed aggressively. The most common causes of death are heart failure from arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and respiratory failure. ECT is a safe treatment, and, as Dr. Fink argued, the mortality rate is even less than that associated with normal pregnancies (World J Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Jan;2[1]:1-8). In light of the safety and effectiveness of ECT, we think the tool should be considered not only in university hospital settings but as an early intervention in community settings. This case warrants further research in exploring hyperactive delirium and delirious mania.
Dr. Lamba is BR-2 unit medical director at BayRidge Hospital in Lynn, Mass. Ms. Kennedy is an attending clinician at BayRidge. Dr. Vu is medical director at BayRidge. He also serves as associate chief of psychiatry at Beverly (Mass.) Hospital and at Addison Gilbert Hospital in Gloucester, Mass. Dr. Lamba, Ms. Kennedy, and Dr. Vu have no disclosures.
Delirious mania is a diagnostic term used in variety of settings, including the emergency department and inpatient psychiatry, but it does not have formal criteria established in the DSM-5. Delirious mania was first described in the 1800s and was referred to as “Bell’s Mania.”
As the late Max Fink, MD, wrote in the journal Bipolar Disorders (2002 Feb 23. doi: 10.1034/j.1399-561.1999.10112.x), delirious mania is considered to be a syndrome of the acute onset of the excitement, grandiosity, emotional lability, delusions, and insomnia characteristic of mania, and the disorientation and altered consciousness characteristic of delirium.
Such patients can be considered as having a component of bipolar I disorder, comprising mania with psychotic features. Delirious mania is associated with higher rates of morbidity and mortality, and demonstrates limited response to conventional treatment guidelines. Therefore, early detection and decisive treatment are imperative. The concurrence of delirium and mania is not unusual, yet currently there are no universal accepted treatment guidelines for delirious mania (BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 21. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-65). The purpose of this case report is to inspire and support community psychiatric clinicians in managing such complex cases and to improve behavioral health care outcomes. To protect our patient’s identity, we changed several key identifiers.
The treatment plan emerges
This case is of a middle-aged man with an established diagnosis of bipolar disorder. He was referred to the ED because of worsening manic symptoms marked by mood lability, pressured speech, grandiose delusions, tangential thought processes, poor insight, and impaired sleep.
Laboratory studies in the ED revealed hyponatremia and serum sodium of 126meq/l (ref. range: 135-146). The patient’s toxicology screen was positive for benzodiazepines. He was stabilized on the medical floor and then transitioned to inpatient psychiatry.
Before his admission to psychiatry, the patient’s medications were alprazolam 1 mg at bed time, bupropion 100 mg twice daily, loxapine 25 mg morning and 50 mg at bed time, olanzapine 20 mg at bedtime and 5 mg twice daily, risperidone 2 mg twice daily and oxcarbazepine 900 mg twice daily.
The bupropion was discontinued because of manic behavior, and the patient’s dose of oxcarbazepine was lowered from 900 mg twice daily to 450 mg twice daily because of hyponatremia. Our team continued to administer risperidone, olanzapine, loxapine, and alprazolam to the patient. However, he was agitated and disorganized on the psychiatry floor. In addition, we noticed that the patient exhibited confusion, disorientation, an inability to connect with reality, and periods of profound agitation.
The patient was frequently restrained physically, and medications were administered to him for safety and containment. The use of benzodiazepines and anticholinergics was minimized. However, we noticed that the patient acted paranoid, disinhibited, and combative, and he became difficult to restrain. He seemed to have a high pain tolerance, responded to internal stimuli, and began hallucinating and displaying aggressive behavior toward staff persons.
It became apparent that the patient’s circadian rhythm had been altered. He slept for only a couple of hours during the day. During the course of treatment, in one incidence, the patient became agitated and charged at a nurse. Subsequently, the patient hit his head on a wall and fell – suffering a head strike and lacerations.
The team conducted investigations, including labs and neuroimaging, to make sure that the patient was OK. His CT head scan proved unremarkable. Liver function tests revealed mild transaminitis. His TSH, folate, B12, and B1 levels were normal.
We then placed the patient in a single room with continuous behavior monitoring. His recovery seemed to take a long time with trials of different antipsychotic medications, including olanzapine, loxapine, risperidone, and paliperidone. Because of his poor response to medications, the team considered using electroconvulsive therapy (ECT).
However, the patient was unable to give informed consent for ECT because of his impaired mental status. At this point, our team submitted a substitute treatment plan that included ECT to the court for approval, and the court approved our plan.
After receiving approximately four bilateral ECT procedures three times a week, the patient’s condition started to improve gradually. He received total of 11 procedures.
Our patient became alert to time, place, and person, and his circadian rhythm normalized. Soon, his delirium cleared, and he demonstrated marked improvement in both insight into his illness and behavioral control. His grandiose delusions were still present, but he was easily redirectable. In addition, our patient demonstrated improved reality testing. He was able to be discharged home following medication adjustments and with community supports within a few short weeks of receiving ECT.
As Bo-Shyan Lee, MD, and associates reported (BMC Psychiatry. 2012 Jun 21;12:65. doi: 10.1186/1471-244X-12-65), delirious mania is closely related to catatonia. Although there are different definitions for delirium and catatonia, even the most lethal form of catatonia meets the criteria for delirium. ECT is a well established first-line treatment for catatonia. This tool has been shown to be highly effective in the treatment of delirious mania. Delirious mania can be life-threatening and should be managed aggressively. The most common causes of death are heart failure from arrhythmias, cardiac arrest, and respiratory failure. ECT is a safe treatment, and, as Dr. Fink argued, the mortality rate is even less than that associated with normal pregnancies (World J Biol Psychiatry. 2001 Jan;2[1]:1-8). In light of the safety and effectiveness of ECT, we think the tool should be considered not only in university hospital settings but as an early intervention in community settings. This case warrants further research in exploring hyperactive delirium and delirious mania.
Dr. Lamba is BR-2 unit medical director at BayRidge Hospital in Lynn, Mass. Ms. Kennedy is an attending clinician at BayRidge. Dr. Vu is medical director at BayRidge. He also serves as associate chief of psychiatry at Beverly (Mass.) Hospital and at Addison Gilbert Hospital in Gloucester, Mass. Dr. Lamba, Ms. Kennedy, and Dr. Vu have no disclosures.
Physician gender pay gap isn’t news; health inequity is rampant
A recent study examined projected career earnings between the genders in a largely community-based physician population, finding a difference of about $2 million in career earnings. That a gender pay gap exists in medicine is not news – but the manner in which this study was done, the investigators’ ability to control for a number of confounding variables, and the size of the study group (over 80,000) are newsworthy.
Some of the key findings include that gender pay gaps start with your first job, and you never close the gap, even as you gain experience and efficiency. Also, the more highly remunerated your specialty, the larger the gap. The gender pay gap joins a growing list of inequities within health care. Although physician compensation is not the most important, given that nearly all physicians are well-paid, and we have much more significant inequities that lead to direct patient harm, the reasons for this discrepancy warrant further consideration.
When I was first being educated about social inequity as part of work in social determinants of health, I made the error of using “inequality” and “inequity” interchangeably. The subtle yet important difference between the two terms was quickly described to me. Inequality is a gastroenterologist getting paid more money to do a colonoscopy than a family physician. Inequity is a female gastroenterologist getting paid less than a male gastroenterologist. Global Health Europe boldly identifies that “inequity is the result of failure.” In looking at the inequity inherent in the gender pay gap, I consider what failed and why.
I’m currently making a major career change, leaving an executive leadership position to return to full-time clinical practice. There is a significant pay decrease that will accompany this change because I am in a primary care specialty. Beyond that, I am considering two employment contracts from different systems to do a similar clinical role.
One of the questions my husband asked was which will pay more over the long run. This is difficult to discern because the compensation formula each health system uses is different, even though they are based on standard national benchmarking data. It is possible that women, in general, are like I am and look for factors other than compensation to make a job decision – assuming, like I do, that it will be close enough to not matter or is generally fair. In fact, while compensation is most certainly a consideration for me, once I determined that it was likely to be in the same ballpark, I stopped comparing. Even as the sole breadwinner in our family, I take this (probably faulty) approach.
It’s time to reconsider how we pay physicians
Women may be more likely to gloss over compensation details that men evaluate and negotiate carefully. To change this, women must first take responsibility for being an active, informed, and engaged part of compensation negotiations. In addition, employers who value gender pay equity must negotiate in good faith, keeping in mind the well-described vulnerabilities in discussions about pay. Finally, male and female mentors and leaders should actively coach female physicians on how to approach these conversations with confidence and skill.
In primary care, female physicians spend, on average, about 15% more time with their patients during a visit. Despite spending as much time in clinic seeing patients per week, they see fewer patients, thereby generating less revenue. For compensation plans that are based on productivity, the extra time spent costs money. In this case, it costs the female physicians lost compensation.
The way in which women are more likely to practice medicine, which includes the amount of time they spend with patients, may affect clinical outcomes without directly increasing productivity. A 2017 study demonstrated that elderly patients had lower rates of mortality and readmission when cared for by a female rather than a male physician. These findings require health systems to critically evaluate what compensation plans value and to promote an appropriate balance between quality of care, quantity of care, and style of care.
Although I’ve seen gender pay inequity as blatant as two different salaries for physicians doing the same work – one male and one female – I think this is uncommon. Like many forms of inequity, the outputs are often related to a failed system rather than solely a series of individual failures. Making compensation formulas gender-blind is an important step – but it is only the first step, not the last. Recognizing that the structure of a compensation formula may be biased toward a style of medical practice more likely to be espoused by one gender is necessary as well.
The data, including the findings of this recent study, clearly identify the gender pay gap that exists in medicine, as it does in many other fields, and that it is not explainable solely by differences in specialties, work hours, family status, or title.
To address the inequity, it is imperative that women engage with employers and leaders to both understand and develop skills around effective and appropriate compensation negotiation. Recognizing that compensation plans, especially those built on productivity models, may fail to place adequate value on gender-specific practice styles.
Jennifer Frank is a family physician, physician leader, wife, and mother in Northeast Wisconsin.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent study examined projected career earnings between the genders in a largely community-based physician population, finding a difference of about $2 million in career earnings. That a gender pay gap exists in medicine is not news – but the manner in which this study was done, the investigators’ ability to control for a number of confounding variables, and the size of the study group (over 80,000) are newsworthy.
Some of the key findings include that gender pay gaps start with your first job, and you never close the gap, even as you gain experience and efficiency. Also, the more highly remunerated your specialty, the larger the gap. The gender pay gap joins a growing list of inequities within health care. Although physician compensation is not the most important, given that nearly all physicians are well-paid, and we have much more significant inequities that lead to direct patient harm, the reasons for this discrepancy warrant further consideration.
When I was first being educated about social inequity as part of work in social determinants of health, I made the error of using “inequality” and “inequity” interchangeably. The subtle yet important difference between the two terms was quickly described to me. Inequality is a gastroenterologist getting paid more money to do a colonoscopy than a family physician. Inequity is a female gastroenterologist getting paid less than a male gastroenterologist. Global Health Europe boldly identifies that “inequity is the result of failure.” In looking at the inequity inherent in the gender pay gap, I consider what failed and why.
I’m currently making a major career change, leaving an executive leadership position to return to full-time clinical practice. There is a significant pay decrease that will accompany this change because I am in a primary care specialty. Beyond that, I am considering two employment contracts from different systems to do a similar clinical role.
One of the questions my husband asked was which will pay more over the long run. This is difficult to discern because the compensation formula each health system uses is different, even though they are based on standard national benchmarking data. It is possible that women, in general, are like I am and look for factors other than compensation to make a job decision – assuming, like I do, that it will be close enough to not matter or is generally fair. In fact, while compensation is most certainly a consideration for me, once I determined that it was likely to be in the same ballpark, I stopped comparing. Even as the sole breadwinner in our family, I take this (probably faulty) approach.
It’s time to reconsider how we pay physicians
Women may be more likely to gloss over compensation details that men evaluate and negotiate carefully. To change this, women must first take responsibility for being an active, informed, and engaged part of compensation negotiations. In addition, employers who value gender pay equity must negotiate in good faith, keeping in mind the well-described vulnerabilities in discussions about pay. Finally, male and female mentors and leaders should actively coach female physicians on how to approach these conversations with confidence and skill.
In primary care, female physicians spend, on average, about 15% more time with their patients during a visit. Despite spending as much time in clinic seeing patients per week, they see fewer patients, thereby generating less revenue. For compensation plans that are based on productivity, the extra time spent costs money. In this case, it costs the female physicians lost compensation.
The way in which women are more likely to practice medicine, which includes the amount of time they spend with patients, may affect clinical outcomes without directly increasing productivity. A 2017 study demonstrated that elderly patients had lower rates of mortality and readmission when cared for by a female rather than a male physician. These findings require health systems to critically evaluate what compensation plans value and to promote an appropriate balance between quality of care, quantity of care, and style of care.
Although I’ve seen gender pay inequity as blatant as two different salaries for physicians doing the same work – one male and one female – I think this is uncommon. Like many forms of inequity, the outputs are often related to a failed system rather than solely a series of individual failures. Making compensation formulas gender-blind is an important step – but it is only the first step, not the last. Recognizing that the structure of a compensation formula may be biased toward a style of medical practice more likely to be espoused by one gender is necessary as well.
The data, including the findings of this recent study, clearly identify the gender pay gap that exists in medicine, as it does in many other fields, and that it is not explainable solely by differences in specialties, work hours, family status, or title.
To address the inequity, it is imperative that women engage with employers and leaders to both understand and develop skills around effective and appropriate compensation negotiation. Recognizing that compensation plans, especially those built on productivity models, may fail to place adequate value on gender-specific practice styles.
Jennifer Frank is a family physician, physician leader, wife, and mother in Northeast Wisconsin.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
A recent study examined projected career earnings between the genders in a largely community-based physician population, finding a difference of about $2 million in career earnings. That a gender pay gap exists in medicine is not news – but the manner in which this study was done, the investigators’ ability to control for a number of confounding variables, and the size of the study group (over 80,000) are newsworthy.
Some of the key findings include that gender pay gaps start with your first job, and you never close the gap, even as you gain experience and efficiency. Also, the more highly remunerated your specialty, the larger the gap. The gender pay gap joins a growing list of inequities within health care. Although physician compensation is not the most important, given that nearly all physicians are well-paid, and we have much more significant inequities that lead to direct patient harm, the reasons for this discrepancy warrant further consideration.
When I was first being educated about social inequity as part of work in social determinants of health, I made the error of using “inequality” and “inequity” interchangeably. The subtle yet important difference between the two terms was quickly described to me. Inequality is a gastroenterologist getting paid more money to do a colonoscopy than a family physician. Inequity is a female gastroenterologist getting paid less than a male gastroenterologist. Global Health Europe boldly identifies that “inequity is the result of failure.” In looking at the inequity inherent in the gender pay gap, I consider what failed and why.
I’m currently making a major career change, leaving an executive leadership position to return to full-time clinical practice. There is a significant pay decrease that will accompany this change because I am in a primary care specialty. Beyond that, I am considering two employment contracts from different systems to do a similar clinical role.
One of the questions my husband asked was which will pay more over the long run. This is difficult to discern because the compensation formula each health system uses is different, even though they are based on standard national benchmarking data. It is possible that women, in general, are like I am and look for factors other than compensation to make a job decision – assuming, like I do, that it will be close enough to not matter or is generally fair. In fact, while compensation is most certainly a consideration for me, once I determined that it was likely to be in the same ballpark, I stopped comparing. Even as the sole breadwinner in our family, I take this (probably faulty) approach.
It’s time to reconsider how we pay physicians
Women may be more likely to gloss over compensation details that men evaluate and negotiate carefully. To change this, women must first take responsibility for being an active, informed, and engaged part of compensation negotiations. In addition, employers who value gender pay equity must negotiate in good faith, keeping in mind the well-described vulnerabilities in discussions about pay. Finally, male and female mentors and leaders should actively coach female physicians on how to approach these conversations with confidence and skill.
In primary care, female physicians spend, on average, about 15% more time with their patients during a visit. Despite spending as much time in clinic seeing patients per week, they see fewer patients, thereby generating less revenue. For compensation plans that are based on productivity, the extra time spent costs money. In this case, it costs the female physicians lost compensation.
The way in which women are more likely to practice medicine, which includes the amount of time they spend with patients, may affect clinical outcomes without directly increasing productivity. A 2017 study demonstrated that elderly patients had lower rates of mortality and readmission when cared for by a female rather than a male physician. These findings require health systems to critically evaluate what compensation plans value and to promote an appropriate balance between quality of care, quantity of care, and style of care.
Although I’ve seen gender pay inequity as blatant as two different salaries for physicians doing the same work – one male and one female – I think this is uncommon. Like many forms of inequity, the outputs are often related to a failed system rather than solely a series of individual failures. Making compensation formulas gender-blind is an important step – but it is only the first step, not the last. Recognizing that the structure of a compensation formula may be biased toward a style of medical practice more likely to be espoused by one gender is necessary as well.
The data, including the findings of this recent study, clearly identify the gender pay gap that exists in medicine, as it does in many other fields, and that it is not explainable solely by differences in specialties, work hours, family status, or title.
To address the inequity, it is imperative that women engage with employers and leaders to both understand and develop skills around effective and appropriate compensation negotiation. Recognizing that compensation plans, especially those built on productivity models, may fail to place adequate value on gender-specific practice styles.
Jennifer Frank is a family physician, physician leader, wife, and mother in Northeast Wisconsin.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.











