User login
-
div[contains(@class, 'header__large-screen')]
div[contains(@class, 'read-next-article')]
div[contains(@class, 'main-prefix')]
div[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-primary')]
section[contains(@class, 'footer-nav-section-wrapper')]
footer[@id='footer']
section[contains(@class, 'nav-hidden')]
div[contains(@class, 'ce-card-content')]
nav[contains(@class, 'nav-ce-stack')]
div[contains(@class, 'view-medstat-quiz-listing-panes')]
div[contains(@class, 'pane-article-sidebar-latest-news')]


Consider adverse childhood experiences during the pandemic
We live in historic times. A worldwide pandemic is surging in the United States, with millions infected and the world’s highest death rate. Many of our hospitals are overwhelmed. Schools have been closed for months. Businesses are struggling, and unemployment is at record levels. The murder of George Floyd unleashed an outpouring of grief and rage over police brutality and structural racism.
It is ironic that this age of adversity emerged at the same time that efforts to assess and address childhood adversity are gaining momentum. The effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) have been well known for decades, but only recently have efforts at universal screening been initiated in primary care offices around the country. The multiple crises we face have made this work more pressing than ever. And
While there has long been awareness, especially among pediatricians, of the social determinants of health, it was only 1995 when Robert F. Anda, MD, and Vincent J. Felitti, MD, set about studying over 13,000 adult patients at Kaiser Permanente to understand the relationship between childhood trauma and chronic health problems in adulthood. In 1998 they published the results of this landmark study, establishing that childhood trauma was common and that it predicted chronic diseases and psychosocial problems in adulthood1.
They detailed 10 specific ACEs, and a patient’s ACE score was determined by how many of these experiences they had before they turned 18 years: neglect (emotional or physical), abuse (emotional, physical or sexual), and household dysfunction (parental divorce, incarceration of a parent, domestic violence, parental mental illness, or parental substance abuse). They found that more than half of adults studied had a score of at least 1, and 6% had scores of 4 or more. Those adults with an ACE score of 4 or more are twice as likely to be obese, twice as likely to smoke, and seven times as likely to abuse alcohol as the rest of the population. They are 4 times as likely to have emphysema, 5 times as likely to have depression, and 12 times as likely to attempt suicide. They have higher rates of heart disease, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. Those with ACE scores of 6 or more have their life expectancy shortened by an average of 20 years.
The value of knowing about these risk factors would seem self-evident; it would inform a patient’s health care from screening for cancer or heart disease, referral for mild depressive symptoms, and counseling about alcohol consumption. But this research did not lead to the establishment of routine screening for childhood adversity in primary care practices. There are multiple reasons for this, including growing pressure on physician time and discomfort with starting conversations about potentially traumatic material. But perhaps the greatest obstacle has been uncertainty about what to offer patients who screened in. What is the treatment for a high ACE score?
Even without treatments, we have learned much about childhood adversity since Dr. Anda and Dr. Felitti published their landmark study. Other more chronic adverse childhood experiences also contribute to adult health risk, such as poverty, homelessness, discrimination, community violence, parental chronic illness, or disability or placement in foster care. Having a high ACE score does not only affect health in adulthood. Children with an ACE score of 4 are 2 times as likely to have asthma2,3 and allergies3, 2 times as likely to be obese4, 3 times as likely to have headaches3 and dental problems5,6, 4 times as likely to have depression7,8, 5 times as likely to have ADHD8,9, 7 times as likely to have high rates of school absenteeism3 and aggression10, and over 30 times as likely to have learning or behavioral problems at school4. There is a growing body of knowledge about how chronic, severe stress in childhood affects can lead to pathological alterations in neuroendocrine and immune function. But this has not led to any concrete treatments that may be preventive or reparative.
Movement toward expanding screening nonetheless has accelerated. In California, Nadine Burke-Harris, MD, a pediatrician who studied ACEs and children’s health was named the state’s first Surgeon General in 2019 and spearheaded an effort to make screening for ACEs easier. Starting in 2020, MediCal will pay for annual screenings, and the state is offering training and resources on how to screen and what to do with the information to help patients and families.
The coronavirus pandemic has only highlighted the risks of childhood adversity. The burden of infection and mortality has been borne disproportionately by people of color and those with multiple chronic medical conditions (obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, etc.). While viruses do not discriminate, they are more likely to infect those with higher risk of exposure and to kill those who are physiologically vulnerable.
And the pandemic increases the risk for adversity for today’s children and families. When children cannot attend school, financially vulnerable parents may have to choose between supervising them or feeding them. Families who suddenly are all in a small apartment together without school or other outside supports may be at higher risk for domestic violence and child abuse. Unemployment and financial uncertainty will increase the rates of substance abuse and depression amongst parents. And the serious illness or death of a parent will be a more common event for children in the year ahead. One of these risk factors may increase the likelihood of others.
Beyond the obvious need for substantial policy changes focused on housing, education, and health care, And resilience can build on itself, as children face subsequent challenges with the support of caring connected adults.
The critical first step is asking. Then listen calmly and supportively, normalizing for parents and children how common these experiences are. Explain how they affect health and well-being. Explain that adversity and its consequences are not their fault. Then educate them about what is in their control: the skills they can practice to buffer against the consequences of adversity and build resilience. They sound simple, but still require effort and work. And the pandemic has created some difficulty (social distancing) and opportunity (more family time, fewer school demands).
Sleep
Help parents establish and protect consistent, restful sleep for their children. They can set a consistent bedtime and a calm routine, with screens all off at least 30 minutes before sleep and reading before sleep. Restful sleep is physiologically and psychologically protective to everyone in a family.
Movement
Beyond directly improving physical health, establishing habits of exercise – especially outside – every day can effectively manage ongoing stress, build skills of self-regulation, and help with sleep.
Find out what parents and their children like to do together (walking the dog, shooting hoops, even dancing) and help them devise ways to create family routines around exercise.
Nutrition
Food should be a source of pleasure, but stress can make food into a source of comfort or escape. Help parents to create realistic ways to consistently offer healthy family meals and discourage unhealthy habits.
Even small changes like water instead of soda can help, and there are nutritional and emotional benefits to eating a healthy breakfast or dinner together as a family.
Connections
Nourishing social connections are protective. Help parents think about protecting time to spend with their children for talking, playing games, or even singing.
They should support their children’s connections to other caring adults, through community organizations (church, community centers, or sports), and they should know who their children’s reliable friends are. Parents will benefit from these supports for themselves, which in turn will benefit the full family.
Self-awareness
Activities that cultivate mindfulness are protective. Parents can simply ask how their children are feeling, physically or emotionally, and be able to bear it when it is uncomfortable. Work towards nonjudgmental awareness of how they are feeling. Learning what is relaxing or recharging for them (exercise, music, a hot bath, a good book, time with a friend) will protect against defaulting into maladaptive coping such as escape, numbing, or avoidance.
Of course, if you learn about symptoms that suggest PTSD, depression, or addiction, you should help your patient connect with effective treatment. The difficulty of referring to a mental health provider does not mean you should not try and bring as many people onto the team and into the orbit of the child and family at risk. It may be easier to access some therapy given the new availability of telemedicine visits across many more systems of care. Although the heaviest burdens of adversity are not being borne equally, the fact that adversity is currently a shared experience makes this a moment of promise.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Swick and Dr. Jellinek had no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Am J Prev Med. 1998 May;14(4):245-58.
2. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;114: 379-84.
3. BMC Public Health. 2018. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5699-8.
4. Child Abuse Negl. 2011 Jun;35(6):408-13.
5. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2015;43:193-9.
6. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2018 Oct;46(5): 442-8.
7. Pediatrics 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-4016.
8. Matern Child Health J. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1007/s10995-015-1915-7.
9. Acad Pediatr. 2017 May-Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2016.08.013.
10. Pediatrics. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0597.
This article was updated 7/27/2020.
We live in historic times. A worldwide pandemic is surging in the United States, with millions infected and the world’s highest death rate. Many of our hospitals are overwhelmed. Schools have been closed for months. Businesses are struggling, and unemployment is at record levels. The murder of George Floyd unleashed an outpouring of grief and rage over police brutality and structural racism.
It is ironic that this age of adversity emerged at the same time that efforts to assess and address childhood adversity are gaining momentum. The effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) have been well known for decades, but only recently have efforts at universal screening been initiated in primary care offices around the country. The multiple crises we face have made this work more pressing than ever. And
While there has long been awareness, especially among pediatricians, of the social determinants of health, it was only 1995 when Robert F. Anda, MD, and Vincent J. Felitti, MD, set about studying over 13,000 adult patients at Kaiser Permanente to understand the relationship between childhood trauma and chronic health problems in adulthood. In 1998 they published the results of this landmark study, establishing that childhood trauma was common and that it predicted chronic diseases and psychosocial problems in adulthood1.
They detailed 10 specific ACEs, and a patient’s ACE score was determined by how many of these experiences they had before they turned 18 years: neglect (emotional or physical), abuse (emotional, physical or sexual), and household dysfunction (parental divorce, incarceration of a parent, domestic violence, parental mental illness, or parental substance abuse). They found that more than half of adults studied had a score of at least 1, and 6% had scores of 4 or more. Those adults with an ACE score of 4 or more are twice as likely to be obese, twice as likely to smoke, and seven times as likely to abuse alcohol as the rest of the population. They are 4 times as likely to have emphysema, 5 times as likely to have depression, and 12 times as likely to attempt suicide. They have higher rates of heart disease, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. Those with ACE scores of 6 or more have their life expectancy shortened by an average of 20 years.
The value of knowing about these risk factors would seem self-evident; it would inform a patient’s health care from screening for cancer or heart disease, referral for mild depressive symptoms, and counseling about alcohol consumption. But this research did not lead to the establishment of routine screening for childhood adversity in primary care practices. There are multiple reasons for this, including growing pressure on physician time and discomfort with starting conversations about potentially traumatic material. But perhaps the greatest obstacle has been uncertainty about what to offer patients who screened in. What is the treatment for a high ACE score?
Even without treatments, we have learned much about childhood adversity since Dr. Anda and Dr. Felitti published their landmark study. Other more chronic adverse childhood experiences also contribute to adult health risk, such as poverty, homelessness, discrimination, community violence, parental chronic illness, or disability or placement in foster care. Having a high ACE score does not only affect health in adulthood. Children with an ACE score of 4 are 2 times as likely to have asthma2,3 and allergies3, 2 times as likely to be obese4, 3 times as likely to have headaches3 and dental problems5,6, 4 times as likely to have depression7,8, 5 times as likely to have ADHD8,9, 7 times as likely to have high rates of school absenteeism3 and aggression10, and over 30 times as likely to have learning or behavioral problems at school4. There is a growing body of knowledge about how chronic, severe stress in childhood affects can lead to pathological alterations in neuroendocrine and immune function. But this has not led to any concrete treatments that may be preventive or reparative.
Movement toward expanding screening nonetheless has accelerated. In California, Nadine Burke-Harris, MD, a pediatrician who studied ACEs and children’s health was named the state’s first Surgeon General in 2019 and spearheaded an effort to make screening for ACEs easier. Starting in 2020, MediCal will pay for annual screenings, and the state is offering training and resources on how to screen and what to do with the information to help patients and families.
The coronavirus pandemic has only highlighted the risks of childhood adversity. The burden of infection and mortality has been borne disproportionately by people of color and those with multiple chronic medical conditions (obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, etc.). While viruses do not discriminate, they are more likely to infect those with higher risk of exposure and to kill those who are physiologically vulnerable.
And the pandemic increases the risk for adversity for today’s children and families. When children cannot attend school, financially vulnerable parents may have to choose between supervising them or feeding them. Families who suddenly are all in a small apartment together without school or other outside supports may be at higher risk for domestic violence and child abuse. Unemployment and financial uncertainty will increase the rates of substance abuse and depression amongst parents. And the serious illness or death of a parent will be a more common event for children in the year ahead. One of these risk factors may increase the likelihood of others.
Beyond the obvious need for substantial policy changes focused on housing, education, and health care, And resilience can build on itself, as children face subsequent challenges with the support of caring connected adults.
The critical first step is asking. Then listen calmly and supportively, normalizing for parents and children how common these experiences are. Explain how they affect health and well-being. Explain that adversity and its consequences are not their fault. Then educate them about what is in their control: the skills they can practice to buffer against the consequences of adversity and build resilience. They sound simple, but still require effort and work. And the pandemic has created some difficulty (social distancing) and opportunity (more family time, fewer school demands).
Sleep
Help parents establish and protect consistent, restful sleep for their children. They can set a consistent bedtime and a calm routine, with screens all off at least 30 minutes before sleep and reading before sleep. Restful sleep is physiologically and psychologically protective to everyone in a family.
Movement
Beyond directly improving physical health, establishing habits of exercise – especially outside – every day can effectively manage ongoing stress, build skills of self-regulation, and help with sleep.
Find out what parents and their children like to do together (walking the dog, shooting hoops, even dancing) and help them devise ways to create family routines around exercise.
Nutrition
Food should be a source of pleasure, but stress can make food into a source of comfort or escape. Help parents to create realistic ways to consistently offer healthy family meals and discourage unhealthy habits.
Even small changes like water instead of soda can help, and there are nutritional and emotional benefits to eating a healthy breakfast or dinner together as a family.
Connections
Nourishing social connections are protective. Help parents think about protecting time to spend with their children for talking, playing games, or even singing.
They should support their children’s connections to other caring adults, through community organizations (church, community centers, or sports), and they should know who their children’s reliable friends are. Parents will benefit from these supports for themselves, which in turn will benefit the full family.
Self-awareness
Activities that cultivate mindfulness are protective. Parents can simply ask how their children are feeling, physically or emotionally, and be able to bear it when it is uncomfortable. Work towards nonjudgmental awareness of how they are feeling. Learning what is relaxing or recharging for them (exercise, music, a hot bath, a good book, time with a friend) will protect against defaulting into maladaptive coping such as escape, numbing, or avoidance.
Of course, if you learn about symptoms that suggest PTSD, depression, or addiction, you should help your patient connect with effective treatment. The difficulty of referring to a mental health provider does not mean you should not try and bring as many people onto the team and into the orbit of the child and family at risk. It may be easier to access some therapy given the new availability of telemedicine visits across many more systems of care. Although the heaviest burdens of adversity are not being borne equally, the fact that adversity is currently a shared experience makes this a moment of promise.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Swick and Dr. Jellinek had no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Am J Prev Med. 1998 May;14(4):245-58.
2. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;114: 379-84.
3. BMC Public Health. 2018. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5699-8.
4. Child Abuse Negl. 2011 Jun;35(6):408-13.
5. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2015;43:193-9.
6. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2018 Oct;46(5): 442-8.
7. Pediatrics 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-4016.
8. Matern Child Health J. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1007/s10995-015-1915-7.
9. Acad Pediatr. 2017 May-Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2016.08.013.
10. Pediatrics. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0597.
This article was updated 7/27/2020.
We live in historic times. A worldwide pandemic is surging in the United States, with millions infected and the world’s highest death rate. Many of our hospitals are overwhelmed. Schools have been closed for months. Businesses are struggling, and unemployment is at record levels. The murder of George Floyd unleashed an outpouring of grief and rage over police brutality and structural racism.
It is ironic that this age of adversity emerged at the same time that efforts to assess and address childhood adversity are gaining momentum. The effects of adverse childhood experiences (ACEs) have been well known for decades, but only recently have efforts at universal screening been initiated in primary care offices around the country. The multiple crises we face have made this work more pressing than ever. And
While there has long been awareness, especially among pediatricians, of the social determinants of health, it was only 1995 when Robert F. Anda, MD, and Vincent J. Felitti, MD, set about studying over 13,000 adult patients at Kaiser Permanente to understand the relationship between childhood trauma and chronic health problems in adulthood. In 1998 they published the results of this landmark study, establishing that childhood trauma was common and that it predicted chronic diseases and psychosocial problems in adulthood1.
They detailed 10 specific ACEs, and a patient’s ACE score was determined by how many of these experiences they had before they turned 18 years: neglect (emotional or physical), abuse (emotional, physical or sexual), and household dysfunction (parental divorce, incarceration of a parent, domestic violence, parental mental illness, or parental substance abuse). They found that more than half of adults studied had a score of at least 1, and 6% had scores of 4 or more. Those adults with an ACE score of 4 or more are twice as likely to be obese, twice as likely to smoke, and seven times as likely to abuse alcohol as the rest of the population. They are 4 times as likely to have emphysema, 5 times as likely to have depression, and 12 times as likely to attempt suicide. They have higher rates of heart disease, autoimmune disorders, and cancer. Those with ACE scores of 6 or more have their life expectancy shortened by an average of 20 years.
The value of knowing about these risk factors would seem self-evident; it would inform a patient’s health care from screening for cancer or heart disease, referral for mild depressive symptoms, and counseling about alcohol consumption. But this research did not lead to the establishment of routine screening for childhood adversity in primary care practices. There are multiple reasons for this, including growing pressure on physician time and discomfort with starting conversations about potentially traumatic material. But perhaps the greatest obstacle has been uncertainty about what to offer patients who screened in. What is the treatment for a high ACE score?
Even without treatments, we have learned much about childhood adversity since Dr. Anda and Dr. Felitti published their landmark study. Other more chronic adverse childhood experiences also contribute to adult health risk, such as poverty, homelessness, discrimination, community violence, parental chronic illness, or disability or placement in foster care. Having a high ACE score does not only affect health in adulthood. Children with an ACE score of 4 are 2 times as likely to have asthma2,3 and allergies3, 2 times as likely to be obese4, 3 times as likely to have headaches3 and dental problems5,6, 4 times as likely to have depression7,8, 5 times as likely to have ADHD8,9, 7 times as likely to have high rates of school absenteeism3 and aggression10, and over 30 times as likely to have learning or behavioral problems at school4. There is a growing body of knowledge about how chronic, severe stress in childhood affects can lead to pathological alterations in neuroendocrine and immune function. But this has not led to any concrete treatments that may be preventive or reparative.
Movement toward expanding screening nonetheless has accelerated. In California, Nadine Burke-Harris, MD, a pediatrician who studied ACEs and children’s health was named the state’s first Surgeon General in 2019 and spearheaded an effort to make screening for ACEs easier. Starting in 2020, MediCal will pay for annual screenings, and the state is offering training and resources on how to screen and what to do with the information to help patients and families.
The coronavirus pandemic has only highlighted the risks of childhood adversity. The burden of infection and mortality has been borne disproportionately by people of color and those with multiple chronic medical conditions (obesity, cardiovascular disease, diabetes, etc.). While viruses do not discriminate, they are more likely to infect those with higher risk of exposure and to kill those who are physiologically vulnerable.
And the pandemic increases the risk for adversity for today’s children and families. When children cannot attend school, financially vulnerable parents may have to choose between supervising them or feeding them. Families who suddenly are all in a small apartment together without school or other outside supports may be at higher risk for domestic violence and child abuse. Unemployment and financial uncertainty will increase the rates of substance abuse and depression amongst parents. And the serious illness or death of a parent will be a more common event for children in the year ahead. One of these risk factors may increase the likelihood of others.
Beyond the obvious need for substantial policy changes focused on housing, education, and health care, And resilience can build on itself, as children face subsequent challenges with the support of caring connected adults.
The critical first step is asking. Then listen calmly and supportively, normalizing for parents and children how common these experiences are. Explain how they affect health and well-being. Explain that adversity and its consequences are not their fault. Then educate them about what is in their control: the skills they can practice to buffer against the consequences of adversity and build resilience. They sound simple, but still require effort and work. And the pandemic has created some difficulty (social distancing) and opportunity (more family time, fewer school demands).
Sleep
Help parents establish and protect consistent, restful sleep for their children. They can set a consistent bedtime and a calm routine, with screens all off at least 30 minutes before sleep and reading before sleep. Restful sleep is physiologically and psychologically protective to everyone in a family.
Movement
Beyond directly improving physical health, establishing habits of exercise – especially outside – every day can effectively manage ongoing stress, build skills of self-regulation, and help with sleep.
Find out what parents and their children like to do together (walking the dog, shooting hoops, even dancing) and help them devise ways to create family routines around exercise.
Nutrition
Food should be a source of pleasure, but stress can make food into a source of comfort or escape. Help parents to create realistic ways to consistently offer healthy family meals and discourage unhealthy habits.
Even small changes like water instead of soda can help, and there are nutritional and emotional benefits to eating a healthy breakfast or dinner together as a family.
Connections
Nourishing social connections are protective. Help parents think about protecting time to spend with their children for talking, playing games, or even singing.
They should support their children’s connections to other caring adults, through community organizations (church, community centers, or sports), and they should know who their children’s reliable friends are. Parents will benefit from these supports for themselves, which in turn will benefit the full family.
Self-awareness
Activities that cultivate mindfulness are protective. Parents can simply ask how their children are feeling, physically or emotionally, and be able to bear it when it is uncomfortable. Work towards nonjudgmental awareness of how they are feeling. Learning what is relaxing or recharging for them (exercise, music, a hot bath, a good book, time with a friend) will protect against defaulting into maladaptive coping such as escape, numbing, or avoidance.
Of course, if you learn about symptoms that suggest PTSD, depression, or addiction, you should help your patient connect with effective treatment. The difficulty of referring to a mental health provider does not mean you should not try and bring as many people onto the team and into the orbit of the child and family at risk. It may be easier to access some therapy given the new availability of telemedicine visits across many more systems of care. Although the heaviest burdens of adversity are not being borne equally, the fact that adversity is currently a shared experience makes this a moment of promise.
Dr. Swick is physician in chief at Ohana, Center for Child and Adolescent Behavioral Health, Community Hospital of the Monterey (Calif.) Peninsula. Dr. Jellinek is professor emeritus of psychiatry and pediatrics, Harvard Medical School, Boston. Dr. Swick and Dr. Jellinek had no relevant financial disclosures. Email them at [email protected].
References
1. Am J Prev Med. 1998 May;14(4):245-58.
2. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2015;114: 379-84.
3. BMC Public Health. 2018. doi: 10.1186/s12889-018-5699-8.
4. Child Abuse Negl. 2011 Jun;35(6):408-13.
5. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2015;43:193-9.
6. Community Dent Oral Epidemiol. 2018 Oct;46(5): 442-8.
7. Pediatrics 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-4016.
8. Matern Child Health J. 2016 Apr. doi: 10.1007/s10995-015-1915-7.
9. Acad Pediatr. 2017 May-Jun. doi: 10.1016/j.acap.2016.08.013.
10. Pediatrics. 2010 Apr. doi: 10.1542/peds.2009-0597.
This article was updated 7/27/2020.
Patients usually understand and agree with physicians’ notes
Overall, 93% of respondents said the notes accurately described the visit; only 6% reported that something important was missing, write Suzanne G. Leveille, RN, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, Boston, and colleagues in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
“I think it’s wonderful news,” commented Howard Levy, MD, PhD, who spearheaded the implementation of open notes at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “I’m thrilled with this report.”
Currently, 50 million Americans have access to their notes, the researchers report. Starting Nov. 2, 2020, the 21st Century Cures Act will require all US physicians to provide this access.
The regulation follows a movement to involve patients more actively in their care. Previous research has shown that access to visit notes improves patients’ feelings of control, helps them adhere to their medication regimens, and enables them to better understand their care plans.
Although physicians often feel that giving patients access to notes will lead to unnecessary conversations that will waste their time, previous studies have not borne that out. “Most clinical providers don’t notice a thing,” Levy told Medscape Medical News. “There was no change in the volume of work.”
Leveille and colleagues wanted to know how patients viewed the clarity, accuracy, and completeness of the notes they were reading and whether they had suggestions for improvements.
They surveyed all 136,815 adult outpatients affiliated with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts; the University of Washington Medicine, in Seattle; and the Geisinger Health System, based in Danville, Pennsylvania. These systems all offer patients access to physicians’ notes.
The researchers asked the patients to recall one note written by a doctor, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or mental health professional.
They received responses from 21,664 patients who had read at least one note. Of these, two thirds were women, three quarters were aged 45 years or older, and 85% were White.
Seventy-two percent had completed college. Although 85% reported being in good or excellent health, more of the respondents than nonrespondents had chronic health problems.
Ninety-seven percent of those with college educations understood their notes, compared with 92% of those who had not completed college, a finding that conflicted with the researchers’ expectations. “Good gracious, that’s wonderful,” Levy said. “In medicine we almost never get a 92% success rate in anything we do.”
Of the patients in fair or poor health, 88.6% said the note was accurate, compared with 94.4% of those in better health. Those in worse health were also more likely to say something important was missing.
When patients didn’t understand something, 35% searched the Internet, 27% asked a clinician, 7% asked a friend or family member, and 27% didn’t get help. (The researchers did not account for the other 4%.)
Of those patients whose note was written by a physician, 95% reported that the note accurately described the visit, compared with 92% of those whose note was written by a nurse practitioner and 90% of those whose note was written by a physician assistant.
Of patients reporting on a primary care note, 97% understood the note, compared with 94% of those reporting on a note from a visit to a specialist.
Ninety-three percent of those who understood their note were likely to recommend their clinician, compared with 77% of those who didn’t completely understand their note.
Asked how the notes could be improved, 3,812 people responded with comments of at least five words. These responses were included in the analysis.
Most commonly, patients wanted new information to be prominently featured at the top of the note, with clear instructions about next steps, referrals, and explanations of test results.
Often, they complained of old information or templates that felt impersonal. They stumbled over medical jargon and suggested links to glossaries. They bristled at such terms as “obese” and “patient denies.” Some wanted a way to comment on the notes.
Regarding the portals in which the notes were found, some patients said the notes were sometimes hard to find. Some said the notes were not posted quickly enough after the visits.
Levy said physicians should learn to write notes more succinctly, and he expects new regulations from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to encourage that. Previous regulations may have given physicians the impression that longer notes would allow them to bill at higher rates, he said. “The change in billing requirements will make it easier for healthcare providers to feel comfortable that they don’t have to restate information that had already been stated,” he said.
On the other hand, physicians should continue to use medical terminology, he said. “At times we use jargon, because it conveys rich, dense information in a few words,” he said. “That’s something that we should not have to give up.” Patients can research terms they don’t understand, he said.
Family physician Doug Iliff, MD, thinks it’s about time that his colleagues share their notes. He’s been doing it since he opened his solo practice in Topeka, Kansas, in 1984.
He still does it the way he always did, with carbonless copy paper. After each visit, he simply tears off the copy and hands it to the patient.
“It makes them know we’re on the same page,” he told Medscape Medical News. “It gives them confidence that I’m telling them what I really think.”
He has one comment on the work of Leveille and her colleagues. “Why are they studying this? Isn’t it obvious that it’s a good thing?”
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Peterson Center on Healthcare, and the Cambia Health Foundation. The study authors, Iliff, and Levy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, 93% of respondents said the notes accurately described the visit; only 6% reported that something important was missing, write Suzanne G. Leveille, RN, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, Boston, and colleagues in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
“I think it’s wonderful news,” commented Howard Levy, MD, PhD, who spearheaded the implementation of open notes at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “I’m thrilled with this report.”
Currently, 50 million Americans have access to their notes, the researchers report. Starting Nov. 2, 2020, the 21st Century Cures Act will require all US physicians to provide this access.
The regulation follows a movement to involve patients more actively in their care. Previous research has shown that access to visit notes improves patients’ feelings of control, helps them adhere to their medication regimens, and enables them to better understand their care plans.
Although physicians often feel that giving patients access to notes will lead to unnecessary conversations that will waste their time, previous studies have not borne that out. “Most clinical providers don’t notice a thing,” Levy told Medscape Medical News. “There was no change in the volume of work.”
Leveille and colleagues wanted to know how patients viewed the clarity, accuracy, and completeness of the notes they were reading and whether they had suggestions for improvements.
They surveyed all 136,815 adult outpatients affiliated with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts; the University of Washington Medicine, in Seattle; and the Geisinger Health System, based in Danville, Pennsylvania. These systems all offer patients access to physicians’ notes.
The researchers asked the patients to recall one note written by a doctor, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or mental health professional.
They received responses from 21,664 patients who had read at least one note. Of these, two thirds were women, three quarters were aged 45 years or older, and 85% were White.
Seventy-two percent had completed college. Although 85% reported being in good or excellent health, more of the respondents than nonrespondents had chronic health problems.
Ninety-seven percent of those with college educations understood their notes, compared with 92% of those who had not completed college, a finding that conflicted with the researchers’ expectations. “Good gracious, that’s wonderful,” Levy said. “In medicine we almost never get a 92% success rate in anything we do.”
Of the patients in fair or poor health, 88.6% said the note was accurate, compared with 94.4% of those in better health. Those in worse health were also more likely to say something important was missing.
When patients didn’t understand something, 35% searched the Internet, 27% asked a clinician, 7% asked a friend or family member, and 27% didn’t get help. (The researchers did not account for the other 4%.)
Of those patients whose note was written by a physician, 95% reported that the note accurately described the visit, compared with 92% of those whose note was written by a nurse practitioner and 90% of those whose note was written by a physician assistant.
Of patients reporting on a primary care note, 97% understood the note, compared with 94% of those reporting on a note from a visit to a specialist.
Ninety-three percent of those who understood their note were likely to recommend their clinician, compared with 77% of those who didn’t completely understand their note.
Asked how the notes could be improved, 3,812 people responded with comments of at least five words. These responses were included in the analysis.
Most commonly, patients wanted new information to be prominently featured at the top of the note, with clear instructions about next steps, referrals, and explanations of test results.
Often, they complained of old information or templates that felt impersonal. They stumbled over medical jargon and suggested links to glossaries. They bristled at such terms as “obese” and “patient denies.” Some wanted a way to comment on the notes.
Regarding the portals in which the notes were found, some patients said the notes were sometimes hard to find. Some said the notes were not posted quickly enough after the visits.
Levy said physicians should learn to write notes more succinctly, and he expects new regulations from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to encourage that. Previous regulations may have given physicians the impression that longer notes would allow them to bill at higher rates, he said. “The change in billing requirements will make it easier for healthcare providers to feel comfortable that they don’t have to restate information that had already been stated,” he said.
On the other hand, physicians should continue to use medical terminology, he said. “At times we use jargon, because it conveys rich, dense information in a few words,” he said. “That’s something that we should not have to give up.” Patients can research terms they don’t understand, he said.
Family physician Doug Iliff, MD, thinks it’s about time that his colleagues share their notes. He’s been doing it since he opened his solo practice in Topeka, Kansas, in 1984.
He still does it the way he always did, with carbonless copy paper. After each visit, he simply tears off the copy and hands it to the patient.
“It makes them know we’re on the same page,” he told Medscape Medical News. “It gives them confidence that I’m telling them what I really think.”
He has one comment on the work of Leveille and her colleagues. “Why are they studying this? Isn’t it obvious that it’s a good thing?”
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Peterson Center on Healthcare, and the Cambia Health Foundation. The study authors, Iliff, and Levy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Overall, 93% of respondents said the notes accurately described the visit; only 6% reported that something important was missing, write Suzanne G. Leveille, RN, PhD, of the University of Massachusetts, Boston, and colleagues in the Journal of General Internal Medicine.
“I think it’s wonderful news,” commented Howard Levy, MD, PhD, who spearheaded the implementation of open notes at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore. “I’m thrilled with this report.”
Currently, 50 million Americans have access to their notes, the researchers report. Starting Nov. 2, 2020, the 21st Century Cures Act will require all US physicians to provide this access.
The regulation follows a movement to involve patients more actively in their care. Previous research has shown that access to visit notes improves patients’ feelings of control, helps them adhere to their medication regimens, and enables them to better understand their care plans.
Although physicians often feel that giving patients access to notes will lead to unnecessary conversations that will waste their time, previous studies have not borne that out. “Most clinical providers don’t notice a thing,” Levy told Medscape Medical News. “There was no change in the volume of work.”
Leveille and colleagues wanted to know how patients viewed the clarity, accuracy, and completeness of the notes they were reading and whether they had suggestions for improvements.
They surveyed all 136,815 adult outpatients affiliated with Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center in Boston, Massachusetts; the University of Washington Medicine, in Seattle; and the Geisinger Health System, based in Danville, Pennsylvania. These systems all offer patients access to physicians’ notes.
The researchers asked the patients to recall one note written by a doctor, nurse practitioner, physician assistant, or mental health professional.
They received responses from 21,664 patients who had read at least one note. Of these, two thirds were women, three quarters were aged 45 years or older, and 85% were White.
Seventy-two percent had completed college. Although 85% reported being in good or excellent health, more of the respondents than nonrespondents had chronic health problems.
Ninety-seven percent of those with college educations understood their notes, compared with 92% of those who had not completed college, a finding that conflicted with the researchers’ expectations. “Good gracious, that’s wonderful,” Levy said. “In medicine we almost never get a 92% success rate in anything we do.”
Of the patients in fair or poor health, 88.6% said the note was accurate, compared with 94.4% of those in better health. Those in worse health were also more likely to say something important was missing.
When patients didn’t understand something, 35% searched the Internet, 27% asked a clinician, 7% asked a friend or family member, and 27% didn’t get help. (The researchers did not account for the other 4%.)
Of those patients whose note was written by a physician, 95% reported that the note accurately described the visit, compared with 92% of those whose note was written by a nurse practitioner and 90% of those whose note was written by a physician assistant.
Of patients reporting on a primary care note, 97% understood the note, compared with 94% of those reporting on a note from a visit to a specialist.
Ninety-three percent of those who understood their note were likely to recommend their clinician, compared with 77% of those who didn’t completely understand their note.
Asked how the notes could be improved, 3,812 people responded with comments of at least five words. These responses were included in the analysis.
Most commonly, patients wanted new information to be prominently featured at the top of the note, with clear instructions about next steps, referrals, and explanations of test results.
Often, they complained of old information or templates that felt impersonal. They stumbled over medical jargon and suggested links to glossaries. They bristled at such terms as “obese” and “patient denies.” Some wanted a way to comment on the notes.
Regarding the portals in which the notes were found, some patients said the notes were sometimes hard to find. Some said the notes were not posted quickly enough after the visits.
Levy said physicians should learn to write notes more succinctly, and he expects new regulations from the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services to encourage that. Previous regulations may have given physicians the impression that longer notes would allow them to bill at higher rates, he said. “The change in billing requirements will make it easier for healthcare providers to feel comfortable that they don’t have to restate information that had already been stated,” he said.
On the other hand, physicians should continue to use medical terminology, he said. “At times we use jargon, because it conveys rich, dense information in a few words,” he said. “That’s something that we should not have to give up.” Patients can research terms they don’t understand, he said.
Family physician Doug Iliff, MD, thinks it’s about time that his colleagues share their notes. He’s been doing it since he opened his solo practice in Topeka, Kansas, in 1984.
He still does it the way he always did, with carbonless copy paper. After each visit, he simply tears off the copy and hands it to the patient.
“It makes them know we’re on the same page,” he told Medscape Medical News. “It gives them confidence that I’m telling them what I really think.”
He has one comment on the work of Leveille and her colleagues. “Why are they studying this? Isn’t it obvious that it’s a good thing?”
The study was funded by the Robert Wood Johnson Foundation, the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, the Peterson Center on Healthcare, and the Cambia Health Foundation. The study authors, Iliff, and Levy have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Empagliflozin failed to improve exercise capacity in heart failure
Empagliflozin showed favorable effects on diuretic use and congestion symptoms in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), but the oral sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor did not improve the primary endpoint of improved exercise capacity in the EMPERIAL-Reduced trial, investigators reported at the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Discoveries virtual meeting.
In the matching EMPERIAL-Preserved trial, conducted in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), empagliflozin (Jardiance) produced modest improvements in diuretic use, as well as a reduction in unscheduled outpatient visits, compared with placebo-treated controls, although these trends failed to achieve statistical significance. And as in the EMPERIAL-Reduced trial, the SGLT2 inhibitor didn’t move the needle at all on the primary endpoint of improved exercise capacity as measured by 6-minute hall walk distance.
EMPERIAL-Reduced and -Preserved were identically designed, concurrent, phase 3, double-blind, 12-week randomized trials of empagliflozin versus placebo in 312 patients with HFrEF and 315 with HFpEF, defined in EMPERIAL-preserved as a left ventricular ejection fraction above 40%. The majority of participants had type 2 diabetes.
From a baseline median 6-minute walk distance of about 300 meters, the 6-minute walk distance at week 12 was actually 4.0 meters worse in the empagliflozin-treated HFrEF patients than it was in controls and a mere 4.0 meters better than with placebo in empagliflozin-treated patients with HFpEF, reported William T. Abraham, MD, professor of medicine, director of the division of cardiovascular medicine, and associate dean at Ohio State University, Columbus.
He indicated that the audience shouldn’t make too much of the failure to achieve the primary endpoint in the two trials in light of the studies’ major limitations: namely, their relatively small size for purposes of evaluating clinical outcomes and the relatively short 12-week duration.
“In many ways, I would say it’s remarkable that we can observe a positive signal, a favorable signal, in outcomes around congestion. In the case of HFrEF it’s statistically significant, and in HFpEF it’s a trend towards improvement. Of course, there are larger trials ongoing that may confirm these observations. Hopefully the EMPERIAL trials predict a good outcome for those ongoing trials,” Dr. Abraham said.
Piotr Ponikowski, MD, presented the study results for the secondary outcomes of congestion symptoms, diuretic use, and utilization of health care resources. In EMPERIAL-Reduced, intensification of diuretic therapy – often a prelude to acute decompensation and a trip to the hospital – occurred at a rate of 4.5% with empagliflozin and 16.1% with placebo, for a highly significant 73% relative risk reduction. Intensification of loop diuretics occurred in 2.6% of the empagliflozin group and 14.2% of controls, for a 82% risk reduction.
“That’s a pretty significant effect,” observed Dr. Ponikowski, professor of cardiology and head of the department of heart diseases at the Medical University of Wroclaw (Poland).
Moreover, a congestion symptoms score comprising a summary of orthopnea, jugular veinous distention, and edema improved by 47% after 12 weeks on empagliflozin, a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement that grew in magnitude over time and at 12 weeks was twice as large, compared with the reduction in placebo group, he added.
There was a trend for fewer unscheduled outpatient visits in the empagliflozin arm of EMPERIAL-Reduced with a rate of 10.4%, compared with 25.8% in controls; however, this 26% reduction in relative risk did not achieve statistical significance.
Intensification of loop diuretics occurred in 9% of EMPERIAL-Preserved participants on empagliflozin and 13.5% on placebo, but this 34% reduction in risk didn’t reach significance.
Adverse events in the EMPERIAL trials were similar across the active treatment and placebo arms. The benign safety profile was similar to what was seen in the earlier major clinical trials of empagliflozin for treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Session chair Stephane Heymans, MD, PhD, of the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands) noted that a substantial minority of patients in EMPERIAL-Reduced were on the combined neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan (Entresto), whereas far fewer were in EMPERIAL-Preserved. He wondered if this greater use of background sacubitril/valsartan could explain empagliflozin’s greater efficacy in EMPERIAL-Reduced.
Highly unlikely, according to the investigators.
“It looks like, as is the case with most of our heart failure therapies, that we do see incremental value here. If you met the criteria for these trials, it appears you derived benefit from empagliflozin regardless of whether you were on an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor or not. I think that speaks to the incremental benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors on top of current guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Abraham said.
Dr. Ponikowski observed that the same point was underscored in the DAPA-HF trial of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in patients with heart failure (DAPA-HF: N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 21;381[21]:1995-2008).
“You’ll see that the mortality and morbidity and quality-of-life benefit is in those treated with dapagliflozin with or without angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibition; so, regardless of background therapy. And the effect is especially clear in patients on both therapies,” the cardiologist said.
The EMPERIAL trials were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Abraham and Dr. Ponikowksi reported receiving consultant fees from the company for serving on the trials’ executive committee.
Empagliflozin showed favorable effects on diuretic use and congestion symptoms in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), but the oral sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor did not improve the primary endpoint of improved exercise capacity in the EMPERIAL-Reduced trial, investigators reported at the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Discoveries virtual meeting.
In the matching EMPERIAL-Preserved trial, conducted in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), empagliflozin (Jardiance) produced modest improvements in diuretic use, as well as a reduction in unscheduled outpatient visits, compared with placebo-treated controls, although these trends failed to achieve statistical significance. And as in the EMPERIAL-Reduced trial, the SGLT2 inhibitor didn’t move the needle at all on the primary endpoint of improved exercise capacity as measured by 6-minute hall walk distance.
EMPERIAL-Reduced and -Preserved were identically designed, concurrent, phase 3, double-blind, 12-week randomized trials of empagliflozin versus placebo in 312 patients with HFrEF and 315 with HFpEF, defined in EMPERIAL-preserved as a left ventricular ejection fraction above 40%. The majority of participants had type 2 diabetes.
From a baseline median 6-minute walk distance of about 300 meters, the 6-minute walk distance at week 12 was actually 4.0 meters worse in the empagliflozin-treated HFrEF patients than it was in controls and a mere 4.0 meters better than with placebo in empagliflozin-treated patients with HFpEF, reported William T. Abraham, MD, professor of medicine, director of the division of cardiovascular medicine, and associate dean at Ohio State University, Columbus.
He indicated that the audience shouldn’t make too much of the failure to achieve the primary endpoint in the two trials in light of the studies’ major limitations: namely, their relatively small size for purposes of evaluating clinical outcomes and the relatively short 12-week duration.
“In many ways, I would say it’s remarkable that we can observe a positive signal, a favorable signal, in outcomes around congestion. In the case of HFrEF it’s statistically significant, and in HFpEF it’s a trend towards improvement. Of course, there are larger trials ongoing that may confirm these observations. Hopefully the EMPERIAL trials predict a good outcome for those ongoing trials,” Dr. Abraham said.
Piotr Ponikowski, MD, presented the study results for the secondary outcomes of congestion symptoms, diuretic use, and utilization of health care resources. In EMPERIAL-Reduced, intensification of diuretic therapy – often a prelude to acute decompensation and a trip to the hospital – occurred at a rate of 4.5% with empagliflozin and 16.1% with placebo, for a highly significant 73% relative risk reduction. Intensification of loop diuretics occurred in 2.6% of the empagliflozin group and 14.2% of controls, for a 82% risk reduction.
“That’s a pretty significant effect,” observed Dr. Ponikowski, professor of cardiology and head of the department of heart diseases at the Medical University of Wroclaw (Poland).
Moreover, a congestion symptoms score comprising a summary of orthopnea, jugular veinous distention, and edema improved by 47% after 12 weeks on empagliflozin, a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement that grew in magnitude over time and at 12 weeks was twice as large, compared with the reduction in placebo group, he added.
There was a trend for fewer unscheduled outpatient visits in the empagliflozin arm of EMPERIAL-Reduced with a rate of 10.4%, compared with 25.8% in controls; however, this 26% reduction in relative risk did not achieve statistical significance.
Intensification of loop diuretics occurred in 9% of EMPERIAL-Preserved participants on empagliflozin and 13.5% on placebo, but this 34% reduction in risk didn’t reach significance.
Adverse events in the EMPERIAL trials were similar across the active treatment and placebo arms. The benign safety profile was similar to what was seen in the earlier major clinical trials of empagliflozin for treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Session chair Stephane Heymans, MD, PhD, of the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands) noted that a substantial minority of patients in EMPERIAL-Reduced were on the combined neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan (Entresto), whereas far fewer were in EMPERIAL-Preserved. He wondered if this greater use of background sacubitril/valsartan could explain empagliflozin’s greater efficacy in EMPERIAL-Reduced.
Highly unlikely, according to the investigators.
“It looks like, as is the case with most of our heart failure therapies, that we do see incremental value here. If you met the criteria for these trials, it appears you derived benefit from empagliflozin regardless of whether you were on an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor or not. I think that speaks to the incremental benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors on top of current guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Abraham said.
Dr. Ponikowski observed that the same point was underscored in the DAPA-HF trial of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in patients with heart failure (DAPA-HF: N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 21;381[21]:1995-2008).
“You’ll see that the mortality and morbidity and quality-of-life benefit is in those treated with dapagliflozin with or without angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibition; so, regardless of background therapy. And the effect is especially clear in patients on both therapies,” the cardiologist said.
The EMPERIAL trials were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Abraham and Dr. Ponikowksi reported receiving consultant fees from the company for serving on the trials’ executive committee.
Empagliflozin showed favorable effects on diuretic use and congestion symptoms in patients with heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF), but the oral sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor did not improve the primary endpoint of improved exercise capacity in the EMPERIAL-Reduced trial, investigators reported at the European Society of Cardiology Heart Failure Discoveries virtual meeting.
In the matching EMPERIAL-Preserved trial, conducted in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF), empagliflozin (Jardiance) produced modest improvements in diuretic use, as well as a reduction in unscheduled outpatient visits, compared with placebo-treated controls, although these trends failed to achieve statistical significance. And as in the EMPERIAL-Reduced trial, the SGLT2 inhibitor didn’t move the needle at all on the primary endpoint of improved exercise capacity as measured by 6-minute hall walk distance.
EMPERIAL-Reduced and -Preserved were identically designed, concurrent, phase 3, double-blind, 12-week randomized trials of empagliflozin versus placebo in 312 patients with HFrEF and 315 with HFpEF, defined in EMPERIAL-preserved as a left ventricular ejection fraction above 40%. The majority of participants had type 2 diabetes.
From a baseline median 6-minute walk distance of about 300 meters, the 6-minute walk distance at week 12 was actually 4.0 meters worse in the empagliflozin-treated HFrEF patients than it was in controls and a mere 4.0 meters better than with placebo in empagliflozin-treated patients with HFpEF, reported William T. Abraham, MD, professor of medicine, director of the division of cardiovascular medicine, and associate dean at Ohio State University, Columbus.
He indicated that the audience shouldn’t make too much of the failure to achieve the primary endpoint in the two trials in light of the studies’ major limitations: namely, their relatively small size for purposes of evaluating clinical outcomes and the relatively short 12-week duration.
“In many ways, I would say it’s remarkable that we can observe a positive signal, a favorable signal, in outcomes around congestion. In the case of HFrEF it’s statistically significant, and in HFpEF it’s a trend towards improvement. Of course, there are larger trials ongoing that may confirm these observations. Hopefully the EMPERIAL trials predict a good outcome for those ongoing trials,” Dr. Abraham said.
Piotr Ponikowski, MD, presented the study results for the secondary outcomes of congestion symptoms, diuretic use, and utilization of health care resources. In EMPERIAL-Reduced, intensification of diuretic therapy – often a prelude to acute decompensation and a trip to the hospital – occurred at a rate of 4.5% with empagliflozin and 16.1% with placebo, for a highly significant 73% relative risk reduction. Intensification of loop diuretics occurred in 2.6% of the empagliflozin group and 14.2% of controls, for a 82% risk reduction.
“That’s a pretty significant effect,” observed Dr. Ponikowski, professor of cardiology and head of the department of heart diseases at the Medical University of Wroclaw (Poland).
Moreover, a congestion symptoms score comprising a summary of orthopnea, jugular veinous distention, and edema improved by 47% after 12 weeks on empagliflozin, a statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement that grew in magnitude over time and at 12 weeks was twice as large, compared with the reduction in placebo group, he added.
There was a trend for fewer unscheduled outpatient visits in the empagliflozin arm of EMPERIAL-Reduced with a rate of 10.4%, compared with 25.8% in controls; however, this 26% reduction in relative risk did not achieve statistical significance.
Intensification of loop diuretics occurred in 9% of EMPERIAL-Preserved participants on empagliflozin and 13.5% on placebo, but this 34% reduction in risk didn’t reach significance.
Adverse events in the EMPERIAL trials were similar across the active treatment and placebo arms. The benign safety profile was similar to what was seen in the earlier major clinical trials of empagliflozin for treatment of type 2 diabetes.
Session chair Stephane Heymans, MD, PhD, of the University of Maastricht (the Netherlands) noted that a substantial minority of patients in EMPERIAL-Reduced were on the combined neprilysin inhibitor sacubitril and the angiotensin receptor blocker valsartan (Entresto), whereas far fewer were in EMPERIAL-Preserved. He wondered if this greater use of background sacubitril/valsartan could explain empagliflozin’s greater efficacy in EMPERIAL-Reduced.
Highly unlikely, according to the investigators.
“It looks like, as is the case with most of our heart failure therapies, that we do see incremental value here. If you met the criteria for these trials, it appears you derived benefit from empagliflozin regardless of whether you were on an angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitor or not. I think that speaks to the incremental benefit of SGLT2 inhibitors on top of current guideline-directed medical therapy,” Dr. Abraham said.
Dr. Ponikowski observed that the same point was underscored in the DAPA-HF trial of the SGLT2 inhibitor dapagliflozin (Farxiga) in patients with heart failure (DAPA-HF: N Engl J Med. 2019 Nov 21;381[21]:1995-2008).
“You’ll see that the mortality and morbidity and quality-of-life benefit is in those treated with dapagliflozin with or without angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibition; so, regardless of background therapy. And the effect is especially clear in patients on both therapies,” the cardiologist said.
The EMPERIAL trials were sponsored by Boehringer Ingelheim. Dr. Abraham and Dr. Ponikowksi reported receiving consultant fees from the company for serving on the trials’ executive committee.
FROM ESC HEART FAILURE 2020
Schools can reopen safely with precautions, experts say
The absence of in-person school has harmed children in ways beyond loss of academic learning, according to Josh Sharfstein, MD, vice dean for public health practice and community engagement at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. In addition to learning, school is a place where many children receive breakfast and lunch every day, as well as support services and the benefits of being in a safe and secure environment, Dr. Sharfstein said in a press briefing sponsored by Johns Hopkins University.
However, although it is an important priority for children to return to school, “we are in the midst of a pandemic that poses real risk,” he said.
In the press briefing, several experts shared ideas and considerations for safely reopening K-12 schools in the fall of 2020.
Data from other countries where schools have reopened, notably Austria and Denmark, have been reassuring about the lack of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among children in a school setting, said Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, an epidemiologist at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. However, other countries where schools have reopened successfully have reported low levels of viral transmission locally, and a responsible strategy for school reopening in the United States should follow a similar plan, she said. In areas where transmission and infection rates are increasing “it may not be safe to reopen,” but in areas where rates are declining or stable, schools could potentially reopen if they follow safety measures.
Dr. Nuzzo suggested that Considerations include protocols for handwashing and sanitation, and maintaining physical distance by creative use of outdoor classrooms (weather permitting) or other spaces within school buildings. Transportation to and from school also will be an issue to address, she noted.
None of the strategies being considered will completely eliminate risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in school settings, so allowing parents and students to opt out and choose distance learning will be important as well, said Dr. Nuzzo. In addition, schools may need to consider alternative roles for teachers and staff who don’t feel comfortable being in contact with students and fellow staff members. “All of these things are going to be hard,” Dr. Nuzzo acknowledged. “Hard should not be a deterrent,” to reopening schools, but “we acknowledge the resources that schools will need in order to do this.”
At present, all 50 states and the District of Columbia have released some type of plan for reopening schools, said Megan Collins, MD, MPH, codirector the Johns Hopkins Consortium for School-Based Health Solutions.
Dr. Collins and colleagues have developed a school reopening tracker, which is “a national snapshot of current reopening plans that have been released,” she said. The tracker is being updated continuously as plans evolve. The eSchool+ K-12 School Reopening Tracker identifies 12 reopening categories that states could potentially address in the plans. These categories are divided into Operational and Ethics/Equity. The operational categories include:
- Core academics
- SARS-CoV-2 protection
- Before and after school programs
- School access and transportation
- Student health services
- Food and nutrition.
Ethics/equity categories include the following:
- Parent choice
- Teacher and staff choice
- Children of poverty and systemic disadvantage
- Children with special needs/English as second language/gifted and twice exceptional
- Privacy
- Engagement and transparency.
As of July 15, 2020, 16 states (Arizona, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, New Mexico, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin) had addressed all 12 categories in their reopening plans, Dr. Collins said.
School reopening plans must take equity issues into account, said Annette Anderson, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins University School of Education.
Specifically, developing learning plans for special education students and others at the most risk for learning loss will be essential. “The digital divide has become a digital canyon” in some areas, Dr. Anderson noted, and schools need to rethink eligibility and work to provide access to devices for online learning for all students.
In addition, schools need to convince parents that schools are safe. She recommended that schools consider inviting parents and families to visit buildings in advance of reopening so they can see the safety measures, such as space between desks, cleaning stations, and other protective strategies.
The message to pediatricians and health care professionals when counseling families about returning individual children to school is to consider the risk to the child and the family directly in the context of the local plans, Dr. Sharfstein said during a question and answer session. “One school system’s plan is one school system’s plan,” he said, and added that families who are concerned about the risk should have an online option. However, “if you see a thoughtful approach” to reopening, with safety steps taken and parents informed, with protocols such as keeping small groups of children together to reduce transmission, “it is a pretty good trade-off,” and that is why the American Academy of Pediatrics currently favors children returning to school, he said.
The briefing participants had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
The absence of in-person school has harmed children in ways beyond loss of academic learning, according to Josh Sharfstein, MD, vice dean for public health practice and community engagement at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. In addition to learning, school is a place where many children receive breakfast and lunch every day, as well as support services and the benefits of being in a safe and secure environment, Dr. Sharfstein said in a press briefing sponsored by Johns Hopkins University.
However, although it is an important priority for children to return to school, “we are in the midst of a pandemic that poses real risk,” he said.
In the press briefing, several experts shared ideas and considerations for safely reopening K-12 schools in the fall of 2020.
Data from other countries where schools have reopened, notably Austria and Denmark, have been reassuring about the lack of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among children in a school setting, said Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, an epidemiologist at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. However, other countries where schools have reopened successfully have reported low levels of viral transmission locally, and a responsible strategy for school reopening in the United States should follow a similar plan, she said. In areas where transmission and infection rates are increasing “it may not be safe to reopen,” but in areas where rates are declining or stable, schools could potentially reopen if they follow safety measures.
Dr. Nuzzo suggested that Considerations include protocols for handwashing and sanitation, and maintaining physical distance by creative use of outdoor classrooms (weather permitting) or other spaces within school buildings. Transportation to and from school also will be an issue to address, she noted.
None of the strategies being considered will completely eliminate risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in school settings, so allowing parents and students to opt out and choose distance learning will be important as well, said Dr. Nuzzo. In addition, schools may need to consider alternative roles for teachers and staff who don’t feel comfortable being in contact with students and fellow staff members. “All of these things are going to be hard,” Dr. Nuzzo acknowledged. “Hard should not be a deterrent,” to reopening schools, but “we acknowledge the resources that schools will need in order to do this.”
At present, all 50 states and the District of Columbia have released some type of plan for reopening schools, said Megan Collins, MD, MPH, codirector the Johns Hopkins Consortium for School-Based Health Solutions.
Dr. Collins and colleagues have developed a school reopening tracker, which is “a national snapshot of current reopening plans that have been released,” she said. The tracker is being updated continuously as plans evolve. The eSchool+ K-12 School Reopening Tracker identifies 12 reopening categories that states could potentially address in the plans. These categories are divided into Operational and Ethics/Equity. The operational categories include:
- Core academics
- SARS-CoV-2 protection
- Before and after school programs
- School access and transportation
- Student health services
- Food and nutrition.
Ethics/equity categories include the following:
- Parent choice
- Teacher and staff choice
- Children of poverty and systemic disadvantage
- Children with special needs/English as second language/gifted and twice exceptional
- Privacy
- Engagement and transparency.
As of July 15, 2020, 16 states (Arizona, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, New Mexico, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin) had addressed all 12 categories in their reopening plans, Dr. Collins said.
School reopening plans must take equity issues into account, said Annette Anderson, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins University School of Education.
Specifically, developing learning plans for special education students and others at the most risk for learning loss will be essential. “The digital divide has become a digital canyon” in some areas, Dr. Anderson noted, and schools need to rethink eligibility and work to provide access to devices for online learning for all students.
In addition, schools need to convince parents that schools are safe. She recommended that schools consider inviting parents and families to visit buildings in advance of reopening so they can see the safety measures, such as space between desks, cleaning stations, and other protective strategies.
The message to pediatricians and health care professionals when counseling families about returning individual children to school is to consider the risk to the child and the family directly in the context of the local plans, Dr. Sharfstein said during a question and answer session. “One school system’s plan is one school system’s plan,” he said, and added that families who are concerned about the risk should have an online option. However, “if you see a thoughtful approach” to reopening, with safety steps taken and parents informed, with protocols such as keeping small groups of children together to reduce transmission, “it is a pretty good trade-off,” and that is why the American Academy of Pediatrics currently favors children returning to school, he said.
The briefing participants had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
The absence of in-person school has harmed children in ways beyond loss of academic learning, according to Josh Sharfstein, MD, vice dean for public health practice and community engagement at the Johns Hopkins Bloomberg School of Public Health, Baltimore. In addition to learning, school is a place where many children receive breakfast and lunch every day, as well as support services and the benefits of being in a safe and secure environment, Dr. Sharfstein said in a press briefing sponsored by Johns Hopkins University.
However, although it is an important priority for children to return to school, “we are in the midst of a pandemic that poses real risk,” he said.
In the press briefing, several experts shared ideas and considerations for safely reopening K-12 schools in the fall of 2020.
Data from other countries where schools have reopened, notably Austria and Denmark, have been reassuring about the lack of transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among children in a school setting, said Jennifer Nuzzo, DrPH, an epidemiologist at the Johns Hopkins Center for Health Security. However, other countries where schools have reopened successfully have reported low levels of viral transmission locally, and a responsible strategy for school reopening in the United States should follow a similar plan, she said. In areas where transmission and infection rates are increasing “it may not be safe to reopen,” but in areas where rates are declining or stable, schools could potentially reopen if they follow safety measures.
Dr. Nuzzo suggested that Considerations include protocols for handwashing and sanitation, and maintaining physical distance by creative use of outdoor classrooms (weather permitting) or other spaces within school buildings. Transportation to and from school also will be an issue to address, she noted.
None of the strategies being considered will completely eliminate risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection in school settings, so allowing parents and students to opt out and choose distance learning will be important as well, said Dr. Nuzzo. In addition, schools may need to consider alternative roles for teachers and staff who don’t feel comfortable being in contact with students and fellow staff members. “All of these things are going to be hard,” Dr. Nuzzo acknowledged. “Hard should not be a deterrent,” to reopening schools, but “we acknowledge the resources that schools will need in order to do this.”
At present, all 50 states and the District of Columbia have released some type of plan for reopening schools, said Megan Collins, MD, MPH, codirector the Johns Hopkins Consortium for School-Based Health Solutions.
Dr. Collins and colleagues have developed a school reopening tracker, which is “a national snapshot of current reopening plans that have been released,” she said. The tracker is being updated continuously as plans evolve. The eSchool+ K-12 School Reopening Tracker identifies 12 reopening categories that states could potentially address in the plans. These categories are divided into Operational and Ethics/Equity. The operational categories include:
- Core academics
- SARS-CoV-2 protection
- Before and after school programs
- School access and transportation
- Student health services
- Food and nutrition.
Ethics/equity categories include the following:
- Parent choice
- Teacher and staff choice
- Children of poverty and systemic disadvantage
- Children with special needs/English as second language/gifted and twice exceptional
- Privacy
- Engagement and transparency.
As of July 15, 2020, 16 states (Arizona, Colorado, Connecticut, Georgia, Maryland, Minnesota, New Mexico, North Carolina, North Dakota, Ohio, Rhode Island, Tennessee, Texas, Virginia, Washington, and Wisconsin) had addressed all 12 categories in their reopening plans, Dr. Collins said.
School reopening plans must take equity issues into account, said Annette Anderson, PhD, of the Johns Hopkins University School of Education.
Specifically, developing learning plans for special education students and others at the most risk for learning loss will be essential. “The digital divide has become a digital canyon” in some areas, Dr. Anderson noted, and schools need to rethink eligibility and work to provide access to devices for online learning for all students.
In addition, schools need to convince parents that schools are safe. She recommended that schools consider inviting parents and families to visit buildings in advance of reopening so they can see the safety measures, such as space between desks, cleaning stations, and other protective strategies.
The message to pediatricians and health care professionals when counseling families about returning individual children to school is to consider the risk to the child and the family directly in the context of the local plans, Dr. Sharfstein said during a question and answer session. “One school system’s plan is one school system’s plan,” he said, and added that families who are concerned about the risk should have an online option. However, “if you see a thoughtful approach” to reopening, with safety steps taken and parents informed, with protocols such as keeping small groups of children together to reduce transmission, “it is a pretty good trade-off,” and that is why the American Academy of Pediatrics currently favors children returning to school, he said.
The briefing participants had no relevant financial conflicts to disclose.
Why doctors keep monitoring kids who recover from mysterious COVID-linked illness
He’s a 5-year-old boy and would much rather talk about cartoons or the ideas for inventions that constantly pop into his head.
“Hold your horses, I think I know what I’m gonna make,” he said, holding up a finger in the middle of a conversation. “I’m gonna make something that lights up and attaches to things with glue, so if you don’t have a flashlight, you can just use it!”
In New York, at least 237 kids, including Israel, appear to have Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). And state officials continue to track the syndrome, but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention did not respond to repeated requests for information on how many children nationwide have been diagnosed so far with MIS-C.
A study published June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine reported on 186 patients in 26 states who had been diagnosed with MIS-C. A researcher writing in the same issue added reports from other countries, finding that about 1,000 children worldwide have been diagnosed with MIS-C.
Tracking the long-term health effects of MIS-C
Israel is friendly and energetic, but he’s also really good at sitting still. During a recent checkup at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, New York, he had no complaints about all the stickers and wires a health aide attached to him for an EKG. And when Marc Foca, MD, an infectious disease specialist, came by to listen to his heart and lungs, and prod his abdomen, Israel barely seemed to notice.
There were still some tests pending, but overall, Dr. Foca said, “Israel looks like a totally healthy 5-year-old.”
“Stay safe!” Israel called out, as Dr. Foca left. It’s his new sign-off, instead of goodbye. His mother, Janelle Moholland, explained Israel came up with it himself. And she’s also hoping that, after a harrowing couple of weeks in early May, Israel himself will “stay safe.”
That’s why they’ve been returning to Montefiore for the periodic checkups, even though Israel seems to have recovered fully from both COVID-19 and MIS-C.
MIS-C is relatively rare, and it apparently responds well to treatment, but it is new enough – and mysterious enough – that doctors here want to make sure the children who recover don’t experience any related health complications in the future.
“We’ve seen these kids get really sick, and get better and recover and go home, yet we don’t know what the long-term outcomes are,” said Nadine Choueiter, MD, a pediatric cardiologist at Montefiore. “So that’s why we will be seeing them.”
When Israel first got sick at the end of April, his illness didn’t exactly look like COVID-19. He had persistent high fevers, with his temperature reaching 104° F – but no problems breathing. He wasn’t eating. He was barely drinking. He wasn’t using the bathroom. He had abdominal pains. His eyes were red.
They went to the ED a couple of times and visited an urgent care center, but the doctors sent them home without testing him for the coronavirus. Ms. Moholland, 29, said she felt powerless.
“There was nothing I could do but make him comfortable,” she said. “I literally had to just trust in a higher power and just hope that He would come through for us. It taught me a lot about patience and faith.”
As Israel grew sicker, and they still had no answers, Ms. Moholland grew frustrated. “I wish his pediatrician and [the ED and urgent care staff] had done what they were supposed to do and given him a test” when Israel first got sick, Ms. Moholland said. “What harm would it have done? He suffered for about 10 or 11 days that could have been avoided.”
In a later interview, she talked with NPR about how COVID-19 has disproportionately affected the African American community because of a combination of underlying health conditions and lack of access to good health care. She said she felt she, too, had fallen victim to those disparities.
“It affects me, personally, because I am African American, but you just never know,” she said. “It’s hard. We’re living in uncertain times – very uncertain times.”
Finally, the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore admitted Israel – and the test she’d been trying to get for days confirmed he had the virus.
“I was literally in tears, like begging them not to discharge me because I knew he was not fine,” she recalled.
Israel was in shock, and by the time he got to the hospital, doctors were on the lookout for MIS-C, so they recognized his symptoms – which were distinct from most people with COVID-19.
Doctors gave Israel fluids and intravenous immunoglobulin, a substance obtained from donated human plasma, which is used to treat deficiencies in the immune system.
Immunoglobulin has been effective in children like Israel because MIS-C appears to be caused by an immune overreaction to the initial coronavirus infection, according to Dr. Choueiter.
“The immune system starts attacking the body itself, including the arteries of the heart,” she said.
In some MIS-C cases – though not Israel’s – the attack occurs in the coronary arteries, inflaming and dilating them. That also happens in a different syndrome affecting children, Kawasaki disease. About 5% of Kawasaki patients experience aneurysms – which can fatally rupture blood vessels – after the initial condition subsides.
Dr. Choueiter and colleagues want to make sure MIS-C patients don’t face similar risks. So far, they’re cautiously optimistic.
“We have not seen any new decrease in heart function or any new coronary artery dilations,” she said. “When we check their blood, their inflammatory markers are back to normal. For the parents, the child is back to baseline, and it’s as if this illness is a nightmare that’s long gone.”
For a Pennsylvania teen, the MIS-C diagnosis came much later
Not every child who develops MIS-C tests positive for the coronavirus, though many will test positive for antibodies to the coronavirus, indicating they had been infected previously. That was the case with Andrew Lis, a boy from Pennsylvania who was the first MIS-C patient seen at the Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del.
Andrew had been a healthy 14-year-old boy before he got sick. He and his twin brother love sports and video games. He said the first symptom was a bad headache. He developed a fever the next day, then constipation and intense stomach pain.
“It was terrible,” Andrew said. “It was unbearable. I couldn’t really move a lot.”
His mother, Ingrid Lis, said they were thinking appendicitis, not coronavirus, at first. In fact, she hesitated to take Andrew to the hospital, for fear of exposing him to the virus. But after Andrew stopped eating because of his headache and stomach discomfort, “I knew I couldn’t keep him home anymore,” Mrs. Lis said.
Andrew was admitted to the hospital April 12, but that was before reports of the mysterious syndrome had started trickling out of Europe.
Over about 5 days in the pediatric ICU, Andrew’s condition deteriorated rapidly, as doctors struggled to figure out what was wrong. Puzzled, they tried treatments for scarlet fever, strep throat, and toxic shock syndrome. Andrew’s body broke out in rashes, then his heart began failing and he was put on a ventilator. Andrew’s father, Ed Lis, said doctors told the family to brace for the worst: “We’ve got a healthy kid who a few days ago was just having these sort of strange symptoms. And now they’re telling us that we could lose him.”
Though Andrew’s symptoms were atypical for Kawasaki disease, doctors decided to give him the standard treatment for that condition – administering intravenous immunoglobulin, the same treatment Israel Shippy received.
“Within the 24 hours of the infusion, he was a different person,” Mrs. Lis said. Andrew was removed from the ventilator, and his appetite eventually returned. “That’s when we knew that we had turned that corner.”
It wasn’t until after Andrew’s discharge that his doctors learned about MIS-C from colleagues in Europe. They recommended the whole family be tested for antibodies to the coronavirus. Although Andrew tested positive, the rest of the family – both parents, Andrew’s twin brother and two older siblings – all tested negative. Andrew’s mother is still not sure how he was exposed since the family had been observing a strict lockdown since mid-March. Both she and her husband were working remotely from home, and she says they all wore masks and were conscientious about hand-washing when they ventured out for groceries. She thinks Andrew must have been exposed at least a month before his illness began.
And she’s puzzled why the rest of her close-knit family wasn’t infected as well. “We are a Latino family,” Mrs. Lis said. “We are very used to being together, clustering in the same room.” Even when Andrew was sick, she says, all six of them huddled in his bedroom to comfort him.
Meanwhile, Andrew has made a quick recovery. Not long after his discharge in April, he turned 15 and resumed an exercise routine involving running, push-ups, and sit-ups. A few weeks later, an ECG showed Andrew’s heart was “perfect,” Mr. Lis said. Still, doctors have asked Andrew to follow up with a cardiologist every 3 months.
An eye on the long-term effects
The medical team at Montefiore is tracking the 40 children they have already treated and discharged. With kids showing few symptoms in the immediate aftermath, Dr. Choueiter hopes the long-term trajectory after MIS-C will be similar to what happens after Kawasaki disease.
“Usually children who have had coronary artery dilations [from Kawasaki disease] that have resolved within the first 6 weeks of the illness do well long-term,” said Dr. Choueiter, who runs the Kawasaki disease program at Montefiore.
The Montefiore team is asking patients affected by MIS-C to return for a checkup 1 week after discharge, then after 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and a year. They will be evaluated by pediatric cardiologists, hematologists, rheumatologists and infectious disease specialists.
Montefiore and other children’s hospitals around the country are sharing information. Dr. Choueiter wants to establish an even longer-term monitoring program for MIS-C, comparable with registries that exist for other diseases.
Ms. Moholland is glad the hospital is being vigilant.
“The uncertainty of not knowing whether it could come back in his future is a little unsettling,” she said. “But I am hopeful.”
This story is part of a partnership that includes WNYC, NPR, and Kaiser Health News. A version of this article originally appeared on Kaiser Health News.
He’s a 5-year-old boy and would much rather talk about cartoons or the ideas for inventions that constantly pop into his head.
“Hold your horses, I think I know what I’m gonna make,” he said, holding up a finger in the middle of a conversation. “I’m gonna make something that lights up and attaches to things with glue, so if you don’t have a flashlight, you can just use it!”
In New York, at least 237 kids, including Israel, appear to have Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). And state officials continue to track the syndrome, but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention did not respond to repeated requests for information on how many children nationwide have been diagnosed so far with MIS-C.
A study published June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine reported on 186 patients in 26 states who had been diagnosed with MIS-C. A researcher writing in the same issue added reports from other countries, finding that about 1,000 children worldwide have been diagnosed with MIS-C.
Tracking the long-term health effects of MIS-C
Israel is friendly and energetic, but he’s also really good at sitting still. During a recent checkup at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, New York, he had no complaints about all the stickers and wires a health aide attached to him for an EKG. And when Marc Foca, MD, an infectious disease specialist, came by to listen to his heart and lungs, and prod his abdomen, Israel barely seemed to notice.
There were still some tests pending, but overall, Dr. Foca said, “Israel looks like a totally healthy 5-year-old.”
“Stay safe!” Israel called out, as Dr. Foca left. It’s his new sign-off, instead of goodbye. His mother, Janelle Moholland, explained Israel came up with it himself. And she’s also hoping that, after a harrowing couple of weeks in early May, Israel himself will “stay safe.”
That’s why they’ve been returning to Montefiore for the periodic checkups, even though Israel seems to have recovered fully from both COVID-19 and MIS-C.
MIS-C is relatively rare, and it apparently responds well to treatment, but it is new enough – and mysterious enough – that doctors here want to make sure the children who recover don’t experience any related health complications in the future.
“We’ve seen these kids get really sick, and get better and recover and go home, yet we don’t know what the long-term outcomes are,” said Nadine Choueiter, MD, a pediatric cardiologist at Montefiore. “So that’s why we will be seeing them.”
When Israel first got sick at the end of April, his illness didn’t exactly look like COVID-19. He had persistent high fevers, with his temperature reaching 104° F – but no problems breathing. He wasn’t eating. He was barely drinking. He wasn’t using the bathroom. He had abdominal pains. His eyes were red.
They went to the ED a couple of times and visited an urgent care center, but the doctors sent them home without testing him for the coronavirus. Ms. Moholland, 29, said she felt powerless.
“There was nothing I could do but make him comfortable,” she said. “I literally had to just trust in a higher power and just hope that He would come through for us. It taught me a lot about patience and faith.”
As Israel grew sicker, and they still had no answers, Ms. Moholland grew frustrated. “I wish his pediatrician and [the ED and urgent care staff] had done what they were supposed to do and given him a test” when Israel first got sick, Ms. Moholland said. “What harm would it have done? He suffered for about 10 or 11 days that could have been avoided.”
In a later interview, she talked with NPR about how COVID-19 has disproportionately affected the African American community because of a combination of underlying health conditions and lack of access to good health care. She said she felt she, too, had fallen victim to those disparities.
“It affects me, personally, because I am African American, but you just never know,” she said. “It’s hard. We’re living in uncertain times – very uncertain times.”
Finally, the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore admitted Israel – and the test she’d been trying to get for days confirmed he had the virus.
“I was literally in tears, like begging them not to discharge me because I knew he was not fine,” she recalled.
Israel was in shock, and by the time he got to the hospital, doctors were on the lookout for MIS-C, so they recognized his symptoms – which were distinct from most people with COVID-19.
Doctors gave Israel fluids and intravenous immunoglobulin, a substance obtained from donated human plasma, which is used to treat deficiencies in the immune system.
Immunoglobulin has been effective in children like Israel because MIS-C appears to be caused by an immune overreaction to the initial coronavirus infection, according to Dr. Choueiter.
“The immune system starts attacking the body itself, including the arteries of the heart,” she said.
In some MIS-C cases – though not Israel’s – the attack occurs in the coronary arteries, inflaming and dilating them. That also happens in a different syndrome affecting children, Kawasaki disease. About 5% of Kawasaki patients experience aneurysms – which can fatally rupture blood vessels – after the initial condition subsides.
Dr. Choueiter and colleagues want to make sure MIS-C patients don’t face similar risks. So far, they’re cautiously optimistic.
“We have not seen any new decrease in heart function or any new coronary artery dilations,” she said. “When we check their blood, their inflammatory markers are back to normal. For the parents, the child is back to baseline, and it’s as if this illness is a nightmare that’s long gone.”
For a Pennsylvania teen, the MIS-C diagnosis came much later
Not every child who develops MIS-C tests positive for the coronavirus, though many will test positive for antibodies to the coronavirus, indicating they had been infected previously. That was the case with Andrew Lis, a boy from Pennsylvania who was the first MIS-C patient seen at the Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del.
Andrew had been a healthy 14-year-old boy before he got sick. He and his twin brother love sports and video games. He said the first symptom was a bad headache. He developed a fever the next day, then constipation and intense stomach pain.
“It was terrible,” Andrew said. “It was unbearable. I couldn’t really move a lot.”
His mother, Ingrid Lis, said they were thinking appendicitis, not coronavirus, at first. In fact, she hesitated to take Andrew to the hospital, for fear of exposing him to the virus. But after Andrew stopped eating because of his headache and stomach discomfort, “I knew I couldn’t keep him home anymore,” Mrs. Lis said.
Andrew was admitted to the hospital April 12, but that was before reports of the mysterious syndrome had started trickling out of Europe.
Over about 5 days in the pediatric ICU, Andrew’s condition deteriorated rapidly, as doctors struggled to figure out what was wrong. Puzzled, they tried treatments for scarlet fever, strep throat, and toxic shock syndrome. Andrew’s body broke out in rashes, then his heart began failing and he was put on a ventilator. Andrew’s father, Ed Lis, said doctors told the family to brace for the worst: “We’ve got a healthy kid who a few days ago was just having these sort of strange symptoms. And now they’re telling us that we could lose him.”
Though Andrew’s symptoms were atypical for Kawasaki disease, doctors decided to give him the standard treatment for that condition – administering intravenous immunoglobulin, the same treatment Israel Shippy received.
“Within the 24 hours of the infusion, he was a different person,” Mrs. Lis said. Andrew was removed from the ventilator, and his appetite eventually returned. “That’s when we knew that we had turned that corner.”
It wasn’t until after Andrew’s discharge that his doctors learned about MIS-C from colleagues in Europe. They recommended the whole family be tested for antibodies to the coronavirus. Although Andrew tested positive, the rest of the family – both parents, Andrew’s twin brother and two older siblings – all tested negative. Andrew’s mother is still not sure how he was exposed since the family had been observing a strict lockdown since mid-March. Both she and her husband were working remotely from home, and she says they all wore masks and were conscientious about hand-washing when they ventured out for groceries. She thinks Andrew must have been exposed at least a month before his illness began.
And she’s puzzled why the rest of her close-knit family wasn’t infected as well. “We are a Latino family,” Mrs. Lis said. “We are very used to being together, clustering in the same room.” Even when Andrew was sick, she says, all six of them huddled in his bedroom to comfort him.
Meanwhile, Andrew has made a quick recovery. Not long after his discharge in April, he turned 15 and resumed an exercise routine involving running, push-ups, and sit-ups. A few weeks later, an ECG showed Andrew’s heart was “perfect,” Mr. Lis said. Still, doctors have asked Andrew to follow up with a cardiologist every 3 months.
An eye on the long-term effects
The medical team at Montefiore is tracking the 40 children they have already treated and discharged. With kids showing few symptoms in the immediate aftermath, Dr. Choueiter hopes the long-term trajectory after MIS-C will be similar to what happens after Kawasaki disease.
“Usually children who have had coronary artery dilations [from Kawasaki disease] that have resolved within the first 6 weeks of the illness do well long-term,” said Dr. Choueiter, who runs the Kawasaki disease program at Montefiore.
The Montefiore team is asking patients affected by MIS-C to return for a checkup 1 week after discharge, then after 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and a year. They will be evaluated by pediatric cardiologists, hematologists, rheumatologists and infectious disease specialists.
Montefiore and other children’s hospitals around the country are sharing information. Dr. Choueiter wants to establish an even longer-term monitoring program for MIS-C, comparable with registries that exist for other diseases.
Ms. Moholland is glad the hospital is being vigilant.
“The uncertainty of not knowing whether it could come back in his future is a little unsettling,” she said. “But I am hopeful.”
This story is part of a partnership that includes WNYC, NPR, and Kaiser Health News. A version of this article originally appeared on Kaiser Health News.
He’s a 5-year-old boy and would much rather talk about cartoons or the ideas for inventions that constantly pop into his head.
“Hold your horses, I think I know what I’m gonna make,” he said, holding up a finger in the middle of a conversation. “I’m gonna make something that lights up and attaches to things with glue, so if you don’t have a flashlight, you can just use it!”
In New York, at least 237 kids, including Israel, appear to have Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children (MIS-C). And state officials continue to track the syndrome, but the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention did not respond to repeated requests for information on how many children nationwide have been diagnosed so far with MIS-C.
A study published June 29 in the New England Journal of Medicine reported on 186 patients in 26 states who had been diagnosed with MIS-C. A researcher writing in the same issue added reports from other countries, finding that about 1,000 children worldwide have been diagnosed with MIS-C.
Tracking the long-term health effects of MIS-C
Israel is friendly and energetic, but he’s also really good at sitting still. During a recent checkup at the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore, New York, he had no complaints about all the stickers and wires a health aide attached to him for an EKG. And when Marc Foca, MD, an infectious disease specialist, came by to listen to his heart and lungs, and prod his abdomen, Israel barely seemed to notice.
There were still some tests pending, but overall, Dr. Foca said, “Israel looks like a totally healthy 5-year-old.”
“Stay safe!” Israel called out, as Dr. Foca left. It’s his new sign-off, instead of goodbye. His mother, Janelle Moholland, explained Israel came up with it himself. And she’s also hoping that, after a harrowing couple of weeks in early May, Israel himself will “stay safe.”
That’s why they’ve been returning to Montefiore for the periodic checkups, even though Israel seems to have recovered fully from both COVID-19 and MIS-C.
MIS-C is relatively rare, and it apparently responds well to treatment, but it is new enough – and mysterious enough – that doctors here want to make sure the children who recover don’t experience any related health complications in the future.
“We’ve seen these kids get really sick, and get better and recover and go home, yet we don’t know what the long-term outcomes are,” said Nadine Choueiter, MD, a pediatric cardiologist at Montefiore. “So that’s why we will be seeing them.”
When Israel first got sick at the end of April, his illness didn’t exactly look like COVID-19. He had persistent high fevers, with his temperature reaching 104° F – but no problems breathing. He wasn’t eating. He was barely drinking. He wasn’t using the bathroom. He had abdominal pains. His eyes were red.
They went to the ED a couple of times and visited an urgent care center, but the doctors sent them home without testing him for the coronavirus. Ms. Moholland, 29, said she felt powerless.
“There was nothing I could do but make him comfortable,” she said. “I literally had to just trust in a higher power and just hope that He would come through for us. It taught me a lot about patience and faith.”
As Israel grew sicker, and they still had no answers, Ms. Moholland grew frustrated. “I wish his pediatrician and [the ED and urgent care staff] had done what they were supposed to do and given him a test” when Israel first got sick, Ms. Moholland said. “What harm would it have done? He suffered for about 10 or 11 days that could have been avoided.”
In a later interview, she talked with NPR about how COVID-19 has disproportionately affected the African American community because of a combination of underlying health conditions and lack of access to good health care. She said she felt she, too, had fallen victim to those disparities.
“It affects me, personally, because I am African American, but you just never know,” she said. “It’s hard. We’re living in uncertain times – very uncertain times.”
Finally, the Children’s Hospital at Montefiore admitted Israel – and the test she’d been trying to get for days confirmed he had the virus.
“I was literally in tears, like begging them not to discharge me because I knew he was not fine,” she recalled.
Israel was in shock, and by the time he got to the hospital, doctors were on the lookout for MIS-C, so they recognized his symptoms – which were distinct from most people with COVID-19.
Doctors gave Israel fluids and intravenous immunoglobulin, a substance obtained from donated human plasma, which is used to treat deficiencies in the immune system.
Immunoglobulin has been effective in children like Israel because MIS-C appears to be caused by an immune overreaction to the initial coronavirus infection, according to Dr. Choueiter.
“The immune system starts attacking the body itself, including the arteries of the heart,” she said.
In some MIS-C cases – though not Israel’s – the attack occurs in the coronary arteries, inflaming and dilating them. That also happens in a different syndrome affecting children, Kawasaki disease. About 5% of Kawasaki patients experience aneurysms – which can fatally rupture blood vessels – after the initial condition subsides.
Dr. Choueiter and colleagues want to make sure MIS-C patients don’t face similar risks. So far, they’re cautiously optimistic.
“We have not seen any new decrease in heart function or any new coronary artery dilations,” she said. “When we check their blood, their inflammatory markers are back to normal. For the parents, the child is back to baseline, and it’s as if this illness is a nightmare that’s long gone.”
For a Pennsylvania teen, the MIS-C diagnosis came much later
Not every child who develops MIS-C tests positive for the coronavirus, though many will test positive for antibodies to the coronavirus, indicating they had been infected previously. That was the case with Andrew Lis, a boy from Pennsylvania who was the first MIS-C patient seen at the Nemours/Alfred I. duPont Hospital for Children in Wilmington, Del.
Andrew had been a healthy 14-year-old boy before he got sick. He and his twin brother love sports and video games. He said the first symptom was a bad headache. He developed a fever the next day, then constipation and intense stomach pain.
“It was terrible,” Andrew said. “It was unbearable. I couldn’t really move a lot.”
His mother, Ingrid Lis, said they were thinking appendicitis, not coronavirus, at first. In fact, she hesitated to take Andrew to the hospital, for fear of exposing him to the virus. But after Andrew stopped eating because of his headache and stomach discomfort, “I knew I couldn’t keep him home anymore,” Mrs. Lis said.
Andrew was admitted to the hospital April 12, but that was before reports of the mysterious syndrome had started trickling out of Europe.
Over about 5 days in the pediatric ICU, Andrew’s condition deteriorated rapidly, as doctors struggled to figure out what was wrong. Puzzled, they tried treatments for scarlet fever, strep throat, and toxic shock syndrome. Andrew’s body broke out in rashes, then his heart began failing and he was put on a ventilator. Andrew’s father, Ed Lis, said doctors told the family to brace for the worst: “We’ve got a healthy kid who a few days ago was just having these sort of strange symptoms. And now they’re telling us that we could lose him.”
Though Andrew’s symptoms were atypical for Kawasaki disease, doctors decided to give him the standard treatment for that condition – administering intravenous immunoglobulin, the same treatment Israel Shippy received.
“Within the 24 hours of the infusion, he was a different person,” Mrs. Lis said. Andrew was removed from the ventilator, and his appetite eventually returned. “That’s when we knew that we had turned that corner.”
It wasn’t until after Andrew’s discharge that his doctors learned about MIS-C from colleagues in Europe. They recommended the whole family be tested for antibodies to the coronavirus. Although Andrew tested positive, the rest of the family – both parents, Andrew’s twin brother and two older siblings – all tested negative. Andrew’s mother is still not sure how he was exposed since the family had been observing a strict lockdown since mid-March. Both she and her husband were working remotely from home, and she says they all wore masks and were conscientious about hand-washing when they ventured out for groceries. She thinks Andrew must have been exposed at least a month before his illness began.
And she’s puzzled why the rest of her close-knit family wasn’t infected as well. “We are a Latino family,” Mrs. Lis said. “We are very used to being together, clustering in the same room.” Even when Andrew was sick, she says, all six of them huddled in his bedroom to comfort him.
Meanwhile, Andrew has made a quick recovery. Not long after his discharge in April, he turned 15 and resumed an exercise routine involving running, push-ups, and sit-ups. A few weeks later, an ECG showed Andrew’s heart was “perfect,” Mr. Lis said. Still, doctors have asked Andrew to follow up with a cardiologist every 3 months.
An eye on the long-term effects
The medical team at Montefiore is tracking the 40 children they have already treated and discharged. With kids showing few symptoms in the immediate aftermath, Dr. Choueiter hopes the long-term trajectory after MIS-C will be similar to what happens after Kawasaki disease.
“Usually children who have had coronary artery dilations [from Kawasaki disease] that have resolved within the first 6 weeks of the illness do well long-term,” said Dr. Choueiter, who runs the Kawasaki disease program at Montefiore.
The Montefiore team is asking patients affected by MIS-C to return for a checkup 1 week after discharge, then after 1 month, 3 months, 6 months, and a year. They will be evaluated by pediatric cardiologists, hematologists, rheumatologists and infectious disease specialists.
Montefiore and other children’s hospitals around the country are sharing information. Dr. Choueiter wants to establish an even longer-term monitoring program for MIS-C, comparable with registries that exist for other diseases.
Ms. Moholland is glad the hospital is being vigilant.
“The uncertainty of not knowing whether it could come back in his future is a little unsettling,” she said. “But I am hopeful.”
This story is part of a partnership that includes WNYC, NPR, and Kaiser Health News. A version of this article originally appeared on Kaiser Health News.
Stillbirth incidence increases during COVID-19 pandemic
The incidence of stillbirth has increased since the COVID-19 pandemic began, according to a comparative study of pregnancy outcomes in a London hospital.
“The increase in stillbirths may have resulted from indirect effects such as reluctance to attend hospital when needed (e.g., with reduced fetal movements), fear of contracting infection, or not wanting to add to the National Health Service burden,” Asma Khalil, MD, of St George’s University of London and coauthors reported in JAMA.
To further assess reported changes in stillbirth and preterm delivery rates during the pandemic, the researchers began a retrospective study of pregnancy outcomes at St George’s University Hospital in London. They compared two periods: from Oct. 1, 2019, to Jan. 31, 2020 as the pre–COVID-19 period and from Feb. 1, 2020, to June 14, 2020 as the pandemic period. The median age of the mother at time of birth in both periods was 33 years. The prepandemic period had 1,681 births, and the pandemic period had 1,718 births.
Although there were found to be fewer nulliparous women and fewer women with hypertension in the pandemic period, the incidence of stillbirth in that period was significantly higher (n = 16 [9 per 1,000 births]) than in the prepandemic period (n = 4 [2 per 1,000 births]) (difference, 7 per 1,000 births; 95% confidence interval, 1.83-12.0; P = .01). The pandemic rate remained higher when late terminations for fetal abnormality were excluded (difference 6 per 1,000 births; 95% CI 1.54-10.1; P = .01).
None of the pregnant women who experienced stillbirth had COVID-19 symptoms, and none of the postmortems or placental exams indicated infection. There were no significant differences between the two periods in regard to births before 37 weeks’ gestation, births after 34 weeks’ gestation, neonatal unit admission, or cesarean delivery.
“It’s very important to highlight the effects of the pandemic on pregnant patients, even if they’re not infected with COVID-19,” Shannon Clark, MD, of the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston said in an interview.
She noted several COVID-related considerations that could have contributed to this increase: the reluctance of both low-risk and high-risk patients to enter a hospital setting during a pandemic, along with safety-centered changes made in antenatal services and care, which includes a reduced number of ultrasounds and screening exams.
“Checking a patient’s blood pressure, checking their weight changes, checking how the baby is growing,” she said. “They’re all simple things that just can’t be done via telemedicine.”
“We’ve thought a lot about the potential effects of getting COVID in pregnancy,” she added, “but it’s just as important to think about what might happen to those who don’t have it and are considered low risk otherwise.”
The study authors noted its limitations, including it being retrospective, analyzing a short time frame, and focusing on a single medical center. It also didn’t factor in the causes of the stillbirths, nor were the time periods precisely comparable, although they did add that “there is no seasonality to stillbirths in the UK.”
One doctor reported receiving grants outside of the submitted work. No other potential conflicts of interest were noted. Dr. Clark said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Khalil A et al. JAMA. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12746.
The incidence of stillbirth has increased since the COVID-19 pandemic began, according to a comparative study of pregnancy outcomes in a London hospital.
“The increase in stillbirths may have resulted from indirect effects such as reluctance to attend hospital when needed (e.g., with reduced fetal movements), fear of contracting infection, or not wanting to add to the National Health Service burden,” Asma Khalil, MD, of St George’s University of London and coauthors reported in JAMA.
To further assess reported changes in stillbirth and preterm delivery rates during the pandemic, the researchers began a retrospective study of pregnancy outcomes at St George’s University Hospital in London. They compared two periods: from Oct. 1, 2019, to Jan. 31, 2020 as the pre–COVID-19 period and from Feb. 1, 2020, to June 14, 2020 as the pandemic period. The median age of the mother at time of birth in both periods was 33 years. The prepandemic period had 1,681 births, and the pandemic period had 1,718 births.
Although there were found to be fewer nulliparous women and fewer women with hypertension in the pandemic period, the incidence of stillbirth in that period was significantly higher (n = 16 [9 per 1,000 births]) than in the prepandemic period (n = 4 [2 per 1,000 births]) (difference, 7 per 1,000 births; 95% confidence interval, 1.83-12.0; P = .01). The pandemic rate remained higher when late terminations for fetal abnormality were excluded (difference 6 per 1,000 births; 95% CI 1.54-10.1; P = .01).
None of the pregnant women who experienced stillbirth had COVID-19 symptoms, and none of the postmortems or placental exams indicated infection. There were no significant differences between the two periods in regard to births before 37 weeks’ gestation, births after 34 weeks’ gestation, neonatal unit admission, or cesarean delivery.
“It’s very important to highlight the effects of the pandemic on pregnant patients, even if they’re not infected with COVID-19,” Shannon Clark, MD, of the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston said in an interview.
She noted several COVID-related considerations that could have contributed to this increase: the reluctance of both low-risk and high-risk patients to enter a hospital setting during a pandemic, along with safety-centered changes made in antenatal services and care, which includes a reduced number of ultrasounds and screening exams.
“Checking a patient’s blood pressure, checking their weight changes, checking how the baby is growing,” she said. “They’re all simple things that just can’t be done via telemedicine.”
“We’ve thought a lot about the potential effects of getting COVID in pregnancy,” she added, “but it’s just as important to think about what might happen to those who don’t have it and are considered low risk otherwise.”
The study authors noted its limitations, including it being retrospective, analyzing a short time frame, and focusing on a single medical center. It also didn’t factor in the causes of the stillbirths, nor were the time periods precisely comparable, although they did add that “there is no seasonality to stillbirths in the UK.”
One doctor reported receiving grants outside of the submitted work. No other potential conflicts of interest were noted. Dr. Clark said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Khalil A et al. JAMA. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12746.
The incidence of stillbirth has increased since the COVID-19 pandemic began, according to a comparative study of pregnancy outcomes in a London hospital.
“The increase in stillbirths may have resulted from indirect effects such as reluctance to attend hospital when needed (e.g., with reduced fetal movements), fear of contracting infection, or not wanting to add to the National Health Service burden,” Asma Khalil, MD, of St George’s University of London and coauthors reported in JAMA.
To further assess reported changes in stillbirth and preterm delivery rates during the pandemic, the researchers began a retrospective study of pregnancy outcomes at St George’s University Hospital in London. They compared two periods: from Oct. 1, 2019, to Jan. 31, 2020 as the pre–COVID-19 period and from Feb. 1, 2020, to June 14, 2020 as the pandemic period. The median age of the mother at time of birth in both periods was 33 years. The prepandemic period had 1,681 births, and the pandemic period had 1,718 births.
Although there were found to be fewer nulliparous women and fewer women with hypertension in the pandemic period, the incidence of stillbirth in that period was significantly higher (n = 16 [9 per 1,000 births]) than in the prepandemic period (n = 4 [2 per 1,000 births]) (difference, 7 per 1,000 births; 95% confidence interval, 1.83-12.0; P = .01). The pandemic rate remained higher when late terminations for fetal abnormality were excluded (difference 6 per 1,000 births; 95% CI 1.54-10.1; P = .01).
None of the pregnant women who experienced stillbirth had COVID-19 symptoms, and none of the postmortems or placental exams indicated infection. There were no significant differences between the two periods in regard to births before 37 weeks’ gestation, births after 34 weeks’ gestation, neonatal unit admission, or cesarean delivery.
“It’s very important to highlight the effects of the pandemic on pregnant patients, even if they’re not infected with COVID-19,” Shannon Clark, MD, of the University of Texas Medical Branch in Galveston said in an interview.
She noted several COVID-related considerations that could have contributed to this increase: the reluctance of both low-risk and high-risk patients to enter a hospital setting during a pandemic, along with safety-centered changes made in antenatal services and care, which includes a reduced number of ultrasounds and screening exams.
“Checking a patient’s blood pressure, checking their weight changes, checking how the baby is growing,” she said. “They’re all simple things that just can’t be done via telemedicine.”
“We’ve thought a lot about the potential effects of getting COVID in pregnancy,” she added, “but it’s just as important to think about what might happen to those who don’t have it and are considered low risk otherwise.”
The study authors noted its limitations, including it being retrospective, analyzing a short time frame, and focusing on a single medical center. It also didn’t factor in the causes of the stillbirths, nor were the time periods precisely comparable, although they did add that “there is no seasonality to stillbirths in the UK.”
One doctor reported receiving grants outside of the submitted work. No other potential conflicts of interest were noted. Dr. Clark said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Khalil A et al. JAMA. 2020 Jul. doi: 10.1001/jama.2020.12746.
FROM JAMA
Doctors say their COVID-19 protocol saves lives; others want proof
As COVID-19 cases mounted in Texas in late June, a local Houston news station shadowed Joseph Varon, MD, making rounds in the intensive care unit at United Memorial Medical Center in Houston. An unseen newscaster tells viewers that Varon credits his success against COVID-19 so far to an experimental and “controversial” drug protocol consisting of vitamins, steroids, and blood thinners.
“This is war. There’s no time to double-blind anything,” Varon tells the camera. “This is working. And if it’s working, I’m going to keep on doing it.”
But response to the protocol among other critical care physicians is mixed, with several physicians, in interviews with Medscape Medical News, urging caution because the benefits and relative risks of the combined medications have not been tested in randomized control trials.
From the earliest days of the pandemic, there’s been tension between the need for rigorous scientific study to understand a novel disease, which takes time, and the need to treat seriously ill patients immediately. Some treatments, like hydroxychloroquine, were promoted without randomized clinical trial data and then later were shown to be ineffective or even potentially harmful when tested.
“This pandemic has shown us there’s lots of ideas out there and they need to be tested and a theoretical basis is insufficient,” says Daniel Kaul, MD, a professor of infectious disease at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The ups and downs with hydroxychloroquine offer a sobering example, he says. “I would argue we have an ethical obligation to do randomized controlled trials to see if our treatments work.”
Creating MATH+
MATH+ stands for methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin. The “+” holds a place for additional therapies like vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin. The protocol originated as a variation of the “HAT therapy,” a combination of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine, which critical care specialist Paul Marik, MD, created for treating critically ill patients with sepsis.
Over a few weeks, the protocol evolved as Marik, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, emailed with a small group of colleagues about treatments and their observations of SARS-CoV-2 in action, swapping in methylprednisolone and adding the anticoagulant heparin.
When Marik and colleagues created the protocol in early March, many healthcare organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were advising against steroids for COVID-19 patients. The MATH+ physicians decided they needed to spread a different message, and began publicizing the protocol with a website and a small communications team.
Marik says they tried to get their protocol in front of healthcare organizations – including the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health – but received no response. Marik went on Newt Gingrich’s podcast to discuss the protocol in the hopes it would make its way to the White House.
Senator Ron Johnson of Wisconsin saw the protocol and invited Pierre Kory, MD, MPA, who practices in Johnson’s home state, to testify remotely in front of the Senate Homeland Security Committee. Kory is a pulmonary critical care specialist about to start a new job at Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center in Milwaukee.
In his testimony, Kory shared his positive experience using the protocol to treat patients and expressed his dismay that national healthcare organizations came out against the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 from the early days of the pandemic based on what he called a “tragic error in analysis of medical data.” Although an analysis by national organizations suggested corticosteroids might be dangerous in COVID-19 patients, one of his colleagues came to the opposite conclusion, he said. But these organizations advised supportive care only, and against steroids. “We think that is a fatal and tragic flaw,” Kory said.
“The problem with the protocol early on was that it was heresy,” says Kory, referring to the protocol’s inclusion of corticosteroids before official treatment guidelines. During the height of the pandemic in New York this spring, Kory spent 5 weeks working in the ICU at Mount Sinai Beth Israel in Manhattan. Seeing patients flounder on supportive care, Kory says he used MATH+ successfully during his time in New York, using escalating and pulse doses of corticosteroids to stabilize rapidly deteriorating patients.
The website’s home page initially included an invitation for visitors to donate money to support “getting word of this effective treatment protocol out to physicians and hospitals around the world.” After Medscape Medical News brought up the donation prompt in questions, the physicians decided to remove all calls for donations from the website and social media, communications representative Betsy Ashton said. “Critics are misinterpreting this as some kind of fund-raising operation, when that could hardly be the case,” Ashton said in an email. “They are horrified that anyone would impugn their motives.”
Donations paid for the website designer, webmaster, and her work, Ashton said, and the physicians now have donors who will support publicizing the protocol without online calls for donations. “We have no commercial or vested interest,” Marik said. “I’m not going to make a single cent out of this and it’s obviously very time-consuming.”
The basis for the protocol
The protocol is based on common sense, an understanding of scientific literature, and an understanding of COVID-19, Marik says. The website includes links to past research trials and observational studies examining ascorbic acid and thiamine in critically ill patients and early looks at anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients.
They chose methylprednisolone as their corticosteroid based on the expertise of group member G. Umberto Meduri, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, Tennessee, who had found the steroid effective in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. On the MATH+ website, the physicians link to multiple observational studies posted on preprint servers in April and May that suggest methylprednisolone helped COVID-19 patients.
“What’s happened with time is all the elements have been validated by scientific studies, which makes this so cool,” says Marik. The RECOVERY Trial results in particular validated the push to use corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients, he says. But that study used a different steroid, dexamethasone, in much smaller doses than what MATH+ recommends. Revised guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends dexamethasone for severely ill patients, but says methylprednisolone and prednisone can be used as substitutes at equivalent doses.
Marik and Kory say that mortality rates for COVID-19 patients at their respective hospitals decreased after they began using the protocol. The physicians have been collecting observational data on their patients, but have not yet published any, and do not plan to conduct a randomized trial.
Several physicians who were not involved in the creation of the protocol say the evidence the physicians cite is not robust enough to warrant the promotion of MATH+ and call for randomized controlled trials. Coming up with a protocol is fine, says Kaul, but “you have to do the hard work of doing a randomized control trial to determine if those drugs given in those combinations work or not.”
“When I looked at it, I thought it was actually not very evidence based,” says Michelle Gong, MD, chief of the Division of Critical Care Medicine at Montefiore Health System in New York City. “It is not something I would recommend for my doctors to do outside of a clinical trial.”
The protocol authors push back against the necessity and feasibility of randomized control trials.
There is no time for a randomized control trial right now, says Jose Iglesias, DO, associate professor at Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine at Seton Hall and critical care specialist at Community Medical Center and Jersey Shore University Medical Center in New Jersey. “Time is limited. We’re busy bedside clinicians taking care of patients, and patients who are dying.”
Marik argues there is not equipoise: It wouldn’t be ethical to randomize patients in a placebo group when the physicians are confident the steroids will help. And the protocol is personalized for each patient, making the standardization required for a randomized control trial incredibly difficult, he says. He also cites “the people who are unwilling to accept our results and just think it’s too good to be true.”
Hugh Cassiere, MD, director of critical care medicine at Northwell Health’s North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said he finds it “very disturbing that this is being propagated.” In the context of a pandemic in which physicians from other specialties are helping out colleagues in ICUs and might follow the protocol uncritically, he worries, “this could potentially lead to harm.”
“I understand the intention; everybody wants to do something, these patients are so sick and the crisis so sharp that we all want to do something to make patients better,” Gong said. “But as physicians taking care of patients we need to make sure we separate the noise from the evidence.”
Peer review
The physicians who reviewed MATH+ for Medscape Medical News differed on which parts of the protocol they support and which parts they would change.
Dexamethasone should be the corticosteroid of choice over methylprednisolone, says Cassiere, because it has now been proven effective in the randomized RECOVERY Trial, which also tested dosing and a timetable for treatment.
But Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, thinks methylprednisolone may be effective, and that even higher doses over longer periods of time may stave off recurring pneumonia, based on his experience using the steroid to treat COVID-19 patients in New York.
“What I really like about this protocol is, these guys are very smart, they recommend the need to treat multiple different things at the same time,” says Parnia. COVID-19 is a complex condition, he notes: If physicians are only focused on solving one problem, like hypoxia, patients could still be dying from blood clots.
Despite general concerns about the protocol, Cassiere says he was excited about the inclusion of heparin. Given the extreme levels of clotting seen in COVID-19 patients, he would have included specific D-dimer levels to guide treatment and explored antiplatelet therapies like aspirin. Gong, however, cautioned that she had seen her patients on anticoagulants develop gastrointestinal bleeding, and reiterated the need for clinical evidence. (At least one clinical trial is currently testing the risks and benefits of heparin as an antithrombotic therapy for COVID-19 patients.)
Perhaps the most divisive part of the protocol is the inclusion of ascorbic acid. “That’s the civil war,” says Kory. “It’s the most polarizing medicine.” The authors of the MATH+ protocol were close colleagues before COVID-19 in part because of a mutual research interest in ascorbic acid, he says. Other physicians, including Cassiere, are extremely skeptical that ascorbic acid has any effect, citing recently published studies in the Journal of the American Medical Association that found ascorbic acid ineffective for treating sepsis.
The MATH+ creators say they are working on a literature review of the research behind the protocol, and they plan to write up the observational impacts of the protocol. Marik says he’s not optimistic about getting the findings published in a high-impact journal given the observational nature of the research; the relatively small number of patients treated at hospitals using the protocol (140 patients at Marik’s hospital in Virginia and 180 at Varon’s in Houston, according to Marik); and the vast number of COVID-19 papers being submitted to scientific journals right now.
“This is not a remedy with expensive designer drugs,” Marik said. “No one has any interest in treating patients with cheap, safe, readily available drugs.”
“I hope they’re right if they’re saying this combination of medicines dramatically decreases mortality,” says Taison Bell, MD, director of the medical intensive care unit and assistant professor of medicine at UVA Health in Charlottesville, Virginia.
But physicians have hurt patients in the past with medications they hoped would work, he says. “We have to make sure we’re balancing the risk and the harm with that benefit, and the only way to protect patients from those biases is by doing a randomized controlled trial.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 cases mounted in Texas in late June, a local Houston news station shadowed Joseph Varon, MD, making rounds in the intensive care unit at United Memorial Medical Center in Houston. An unseen newscaster tells viewers that Varon credits his success against COVID-19 so far to an experimental and “controversial” drug protocol consisting of vitamins, steroids, and blood thinners.
“This is war. There’s no time to double-blind anything,” Varon tells the camera. “This is working. And if it’s working, I’m going to keep on doing it.”
But response to the protocol among other critical care physicians is mixed, with several physicians, in interviews with Medscape Medical News, urging caution because the benefits and relative risks of the combined medications have not been tested in randomized control trials.
From the earliest days of the pandemic, there’s been tension between the need for rigorous scientific study to understand a novel disease, which takes time, and the need to treat seriously ill patients immediately. Some treatments, like hydroxychloroquine, were promoted without randomized clinical trial data and then later were shown to be ineffective or even potentially harmful when tested.
“This pandemic has shown us there’s lots of ideas out there and they need to be tested and a theoretical basis is insufficient,” says Daniel Kaul, MD, a professor of infectious disease at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The ups and downs with hydroxychloroquine offer a sobering example, he says. “I would argue we have an ethical obligation to do randomized controlled trials to see if our treatments work.”
Creating MATH+
MATH+ stands for methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin. The “+” holds a place for additional therapies like vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin. The protocol originated as a variation of the “HAT therapy,” a combination of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine, which critical care specialist Paul Marik, MD, created for treating critically ill patients with sepsis.
Over a few weeks, the protocol evolved as Marik, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, emailed with a small group of colleagues about treatments and their observations of SARS-CoV-2 in action, swapping in methylprednisolone and adding the anticoagulant heparin.
When Marik and colleagues created the protocol in early March, many healthcare organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were advising against steroids for COVID-19 patients. The MATH+ physicians decided they needed to spread a different message, and began publicizing the protocol with a website and a small communications team.
Marik says they tried to get their protocol in front of healthcare organizations – including the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health – but received no response. Marik went on Newt Gingrich’s podcast to discuss the protocol in the hopes it would make its way to the White House.
Senator Ron Johnson of Wisconsin saw the protocol and invited Pierre Kory, MD, MPA, who practices in Johnson’s home state, to testify remotely in front of the Senate Homeland Security Committee. Kory is a pulmonary critical care specialist about to start a new job at Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center in Milwaukee.
In his testimony, Kory shared his positive experience using the protocol to treat patients and expressed his dismay that national healthcare organizations came out against the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 from the early days of the pandemic based on what he called a “tragic error in analysis of medical data.” Although an analysis by national organizations suggested corticosteroids might be dangerous in COVID-19 patients, one of his colleagues came to the opposite conclusion, he said. But these organizations advised supportive care only, and against steroids. “We think that is a fatal and tragic flaw,” Kory said.
“The problem with the protocol early on was that it was heresy,” says Kory, referring to the protocol’s inclusion of corticosteroids before official treatment guidelines. During the height of the pandemic in New York this spring, Kory spent 5 weeks working in the ICU at Mount Sinai Beth Israel in Manhattan. Seeing patients flounder on supportive care, Kory says he used MATH+ successfully during his time in New York, using escalating and pulse doses of corticosteroids to stabilize rapidly deteriorating patients.
The website’s home page initially included an invitation for visitors to donate money to support “getting word of this effective treatment protocol out to physicians and hospitals around the world.” After Medscape Medical News brought up the donation prompt in questions, the physicians decided to remove all calls for donations from the website and social media, communications representative Betsy Ashton said. “Critics are misinterpreting this as some kind of fund-raising operation, when that could hardly be the case,” Ashton said in an email. “They are horrified that anyone would impugn their motives.”
Donations paid for the website designer, webmaster, and her work, Ashton said, and the physicians now have donors who will support publicizing the protocol without online calls for donations. “We have no commercial or vested interest,” Marik said. “I’m not going to make a single cent out of this and it’s obviously very time-consuming.”
The basis for the protocol
The protocol is based on common sense, an understanding of scientific literature, and an understanding of COVID-19, Marik says. The website includes links to past research trials and observational studies examining ascorbic acid and thiamine in critically ill patients and early looks at anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients.
They chose methylprednisolone as their corticosteroid based on the expertise of group member G. Umberto Meduri, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, Tennessee, who had found the steroid effective in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. On the MATH+ website, the physicians link to multiple observational studies posted on preprint servers in April and May that suggest methylprednisolone helped COVID-19 patients.
“What’s happened with time is all the elements have been validated by scientific studies, which makes this so cool,” says Marik. The RECOVERY Trial results in particular validated the push to use corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients, he says. But that study used a different steroid, dexamethasone, in much smaller doses than what MATH+ recommends. Revised guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends dexamethasone for severely ill patients, but says methylprednisolone and prednisone can be used as substitutes at equivalent doses.
Marik and Kory say that mortality rates for COVID-19 patients at their respective hospitals decreased after they began using the protocol. The physicians have been collecting observational data on their patients, but have not yet published any, and do not plan to conduct a randomized trial.
Several physicians who were not involved in the creation of the protocol say the evidence the physicians cite is not robust enough to warrant the promotion of MATH+ and call for randomized controlled trials. Coming up with a protocol is fine, says Kaul, but “you have to do the hard work of doing a randomized control trial to determine if those drugs given in those combinations work or not.”
“When I looked at it, I thought it was actually not very evidence based,” says Michelle Gong, MD, chief of the Division of Critical Care Medicine at Montefiore Health System in New York City. “It is not something I would recommend for my doctors to do outside of a clinical trial.”
The protocol authors push back against the necessity and feasibility of randomized control trials.
There is no time for a randomized control trial right now, says Jose Iglesias, DO, associate professor at Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine at Seton Hall and critical care specialist at Community Medical Center and Jersey Shore University Medical Center in New Jersey. “Time is limited. We’re busy bedside clinicians taking care of patients, and patients who are dying.”
Marik argues there is not equipoise: It wouldn’t be ethical to randomize patients in a placebo group when the physicians are confident the steroids will help. And the protocol is personalized for each patient, making the standardization required for a randomized control trial incredibly difficult, he says. He also cites “the people who are unwilling to accept our results and just think it’s too good to be true.”
Hugh Cassiere, MD, director of critical care medicine at Northwell Health’s North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said he finds it “very disturbing that this is being propagated.” In the context of a pandemic in which physicians from other specialties are helping out colleagues in ICUs and might follow the protocol uncritically, he worries, “this could potentially lead to harm.”
“I understand the intention; everybody wants to do something, these patients are so sick and the crisis so sharp that we all want to do something to make patients better,” Gong said. “But as physicians taking care of patients we need to make sure we separate the noise from the evidence.”
Peer review
The physicians who reviewed MATH+ for Medscape Medical News differed on which parts of the protocol they support and which parts they would change.
Dexamethasone should be the corticosteroid of choice over methylprednisolone, says Cassiere, because it has now been proven effective in the randomized RECOVERY Trial, which also tested dosing and a timetable for treatment.
But Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, thinks methylprednisolone may be effective, and that even higher doses over longer periods of time may stave off recurring pneumonia, based on his experience using the steroid to treat COVID-19 patients in New York.
“What I really like about this protocol is, these guys are very smart, they recommend the need to treat multiple different things at the same time,” says Parnia. COVID-19 is a complex condition, he notes: If physicians are only focused on solving one problem, like hypoxia, patients could still be dying from blood clots.
Despite general concerns about the protocol, Cassiere says he was excited about the inclusion of heparin. Given the extreme levels of clotting seen in COVID-19 patients, he would have included specific D-dimer levels to guide treatment and explored antiplatelet therapies like aspirin. Gong, however, cautioned that she had seen her patients on anticoagulants develop gastrointestinal bleeding, and reiterated the need for clinical evidence. (At least one clinical trial is currently testing the risks and benefits of heparin as an antithrombotic therapy for COVID-19 patients.)
Perhaps the most divisive part of the protocol is the inclusion of ascorbic acid. “That’s the civil war,” says Kory. “It’s the most polarizing medicine.” The authors of the MATH+ protocol were close colleagues before COVID-19 in part because of a mutual research interest in ascorbic acid, he says. Other physicians, including Cassiere, are extremely skeptical that ascorbic acid has any effect, citing recently published studies in the Journal of the American Medical Association that found ascorbic acid ineffective for treating sepsis.
The MATH+ creators say they are working on a literature review of the research behind the protocol, and they plan to write up the observational impacts of the protocol. Marik says he’s not optimistic about getting the findings published in a high-impact journal given the observational nature of the research; the relatively small number of patients treated at hospitals using the protocol (140 patients at Marik’s hospital in Virginia and 180 at Varon’s in Houston, according to Marik); and the vast number of COVID-19 papers being submitted to scientific journals right now.
“This is not a remedy with expensive designer drugs,” Marik said. “No one has any interest in treating patients with cheap, safe, readily available drugs.”
“I hope they’re right if they’re saying this combination of medicines dramatically decreases mortality,” says Taison Bell, MD, director of the medical intensive care unit and assistant professor of medicine at UVA Health in Charlottesville, Virginia.
But physicians have hurt patients in the past with medications they hoped would work, he says. “We have to make sure we’re balancing the risk and the harm with that benefit, and the only way to protect patients from those biases is by doing a randomized controlled trial.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
As COVID-19 cases mounted in Texas in late June, a local Houston news station shadowed Joseph Varon, MD, making rounds in the intensive care unit at United Memorial Medical Center in Houston. An unseen newscaster tells viewers that Varon credits his success against COVID-19 so far to an experimental and “controversial” drug protocol consisting of vitamins, steroids, and blood thinners.
“This is war. There’s no time to double-blind anything,” Varon tells the camera. “This is working. And if it’s working, I’m going to keep on doing it.”
But response to the protocol among other critical care physicians is mixed, with several physicians, in interviews with Medscape Medical News, urging caution because the benefits and relative risks of the combined medications have not been tested in randomized control trials.
From the earliest days of the pandemic, there’s been tension between the need for rigorous scientific study to understand a novel disease, which takes time, and the need to treat seriously ill patients immediately. Some treatments, like hydroxychloroquine, were promoted without randomized clinical trial data and then later were shown to be ineffective or even potentially harmful when tested.
“This pandemic has shown us there’s lots of ideas out there and they need to be tested and a theoretical basis is insufficient,” says Daniel Kaul, MD, a professor of infectious disease at the University of Michigan in Ann Arbor. The ups and downs with hydroxychloroquine offer a sobering example, he says. “I would argue we have an ethical obligation to do randomized controlled trials to see if our treatments work.”
Creating MATH+
MATH+ stands for methylprednisolone, ascorbic acid, thiamine, and heparin. The “+” holds a place for additional therapies like vitamin D, zinc, and melatonin. The protocol originated as a variation of the “HAT therapy,” a combination of hydrocortisone, ascorbic acid, and thiamine, which critical care specialist Paul Marik, MD, created for treating critically ill patients with sepsis.
Over a few weeks, the protocol evolved as Marik, chief of the division of pulmonary and critical care medicine at Eastern Virginia Medical School in Norfolk, emailed with a small group of colleagues about treatments and their observations of SARS-CoV-2 in action, swapping in methylprednisolone and adding the anticoagulant heparin.
When Marik and colleagues created the protocol in early March, many healthcare organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO) were advising against steroids for COVID-19 patients. The MATH+ physicians decided they needed to spread a different message, and began publicizing the protocol with a website and a small communications team.
Marik says they tried to get their protocol in front of healthcare organizations – including the WHO, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, and the National Institutes of Health – but received no response. Marik went on Newt Gingrich’s podcast to discuss the protocol in the hopes it would make its way to the White House.
Senator Ron Johnson of Wisconsin saw the protocol and invited Pierre Kory, MD, MPA, who practices in Johnson’s home state, to testify remotely in front of the Senate Homeland Security Committee. Kory is a pulmonary critical care specialist about to start a new job at Aurora St. Luke’s Medical Center in Milwaukee.
In his testimony, Kory shared his positive experience using the protocol to treat patients and expressed his dismay that national healthcare organizations came out against the use of corticosteroids for COVID-19 from the early days of the pandemic based on what he called a “tragic error in analysis of medical data.” Although an analysis by national organizations suggested corticosteroids might be dangerous in COVID-19 patients, one of his colleagues came to the opposite conclusion, he said. But these organizations advised supportive care only, and against steroids. “We think that is a fatal and tragic flaw,” Kory said.
“The problem with the protocol early on was that it was heresy,” says Kory, referring to the protocol’s inclusion of corticosteroids before official treatment guidelines. During the height of the pandemic in New York this spring, Kory spent 5 weeks working in the ICU at Mount Sinai Beth Israel in Manhattan. Seeing patients flounder on supportive care, Kory says he used MATH+ successfully during his time in New York, using escalating and pulse doses of corticosteroids to stabilize rapidly deteriorating patients.
The website’s home page initially included an invitation for visitors to donate money to support “getting word of this effective treatment protocol out to physicians and hospitals around the world.” After Medscape Medical News brought up the donation prompt in questions, the physicians decided to remove all calls for donations from the website and social media, communications representative Betsy Ashton said. “Critics are misinterpreting this as some kind of fund-raising operation, when that could hardly be the case,” Ashton said in an email. “They are horrified that anyone would impugn their motives.”
Donations paid for the website designer, webmaster, and her work, Ashton said, and the physicians now have donors who will support publicizing the protocol without online calls for donations. “We have no commercial or vested interest,” Marik said. “I’m not going to make a single cent out of this and it’s obviously very time-consuming.”
The basis for the protocol
The protocol is based on common sense, an understanding of scientific literature, and an understanding of COVID-19, Marik says. The website includes links to past research trials and observational studies examining ascorbic acid and thiamine in critically ill patients and early looks at anticoagulants in COVID-19 patients.
They chose methylprednisolone as their corticosteroid based on the expertise of group member G. Umberto Meduri, MD, professor of medicine at the University of Tennessee Health Science Center in Memphis, Tennessee, who had found the steroid effective in treating acute respiratory distress syndrome. On the MATH+ website, the physicians link to multiple observational studies posted on preprint servers in April and May that suggest methylprednisolone helped COVID-19 patients.
“What’s happened with time is all the elements have been validated by scientific studies, which makes this so cool,” says Marik. The RECOVERY Trial results in particular validated the push to use corticosteroids in COVID-19 patients, he says. But that study used a different steroid, dexamethasone, in much smaller doses than what MATH+ recommends. Revised guidance from the Infectious Diseases Society of America recommends dexamethasone for severely ill patients, but says methylprednisolone and prednisone can be used as substitutes at equivalent doses.
Marik and Kory say that mortality rates for COVID-19 patients at their respective hospitals decreased after they began using the protocol. The physicians have been collecting observational data on their patients, but have not yet published any, and do not plan to conduct a randomized trial.
Several physicians who were not involved in the creation of the protocol say the evidence the physicians cite is not robust enough to warrant the promotion of MATH+ and call for randomized controlled trials. Coming up with a protocol is fine, says Kaul, but “you have to do the hard work of doing a randomized control trial to determine if those drugs given in those combinations work or not.”
“When I looked at it, I thought it was actually not very evidence based,” says Michelle Gong, MD, chief of the Division of Critical Care Medicine at Montefiore Health System in New York City. “It is not something I would recommend for my doctors to do outside of a clinical trial.”
The protocol authors push back against the necessity and feasibility of randomized control trials.
There is no time for a randomized control trial right now, says Jose Iglesias, DO, associate professor at Hackensack Meridian School of Medicine at Seton Hall and critical care specialist at Community Medical Center and Jersey Shore University Medical Center in New Jersey. “Time is limited. We’re busy bedside clinicians taking care of patients, and patients who are dying.”
Marik argues there is not equipoise: It wouldn’t be ethical to randomize patients in a placebo group when the physicians are confident the steroids will help. And the protocol is personalized for each patient, making the standardization required for a randomized control trial incredibly difficult, he says. He also cites “the people who are unwilling to accept our results and just think it’s too good to be true.”
Hugh Cassiere, MD, director of critical care medicine at Northwell Health’s North Shore University Hospital in Manhasset, New York, said he finds it “very disturbing that this is being propagated.” In the context of a pandemic in which physicians from other specialties are helping out colleagues in ICUs and might follow the protocol uncritically, he worries, “this could potentially lead to harm.”
“I understand the intention; everybody wants to do something, these patients are so sick and the crisis so sharp that we all want to do something to make patients better,” Gong said. “But as physicians taking care of patients we need to make sure we separate the noise from the evidence.”
Peer review
The physicians who reviewed MATH+ for Medscape Medical News differed on which parts of the protocol they support and which parts they would change.
Dexamethasone should be the corticosteroid of choice over methylprednisolone, says Cassiere, because it has now been proven effective in the randomized RECOVERY Trial, which also tested dosing and a timetable for treatment.
But Sam Parnia, MD, PhD, associate professor of medicine and director of critical care and resuscitation research at NYU Langone, thinks methylprednisolone may be effective, and that even higher doses over longer periods of time may stave off recurring pneumonia, based on his experience using the steroid to treat COVID-19 patients in New York.
“What I really like about this protocol is, these guys are very smart, they recommend the need to treat multiple different things at the same time,” says Parnia. COVID-19 is a complex condition, he notes: If physicians are only focused on solving one problem, like hypoxia, patients could still be dying from blood clots.
Despite general concerns about the protocol, Cassiere says he was excited about the inclusion of heparin. Given the extreme levels of clotting seen in COVID-19 patients, he would have included specific D-dimer levels to guide treatment and explored antiplatelet therapies like aspirin. Gong, however, cautioned that she had seen her patients on anticoagulants develop gastrointestinal bleeding, and reiterated the need for clinical evidence. (At least one clinical trial is currently testing the risks and benefits of heparin as an antithrombotic therapy for COVID-19 patients.)
Perhaps the most divisive part of the protocol is the inclusion of ascorbic acid. “That’s the civil war,” says Kory. “It’s the most polarizing medicine.” The authors of the MATH+ protocol were close colleagues before COVID-19 in part because of a mutual research interest in ascorbic acid, he says. Other physicians, including Cassiere, are extremely skeptical that ascorbic acid has any effect, citing recently published studies in the Journal of the American Medical Association that found ascorbic acid ineffective for treating sepsis.
The MATH+ creators say they are working on a literature review of the research behind the protocol, and they plan to write up the observational impacts of the protocol. Marik says he’s not optimistic about getting the findings published in a high-impact journal given the observational nature of the research; the relatively small number of patients treated at hospitals using the protocol (140 patients at Marik’s hospital in Virginia and 180 at Varon’s in Houston, according to Marik); and the vast number of COVID-19 papers being submitted to scientific journals right now.
“This is not a remedy with expensive designer drugs,” Marik said. “No one has any interest in treating patients with cheap, safe, readily available drugs.”
“I hope they’re right if they’re saying this combination of medicines dramatically decreases mortality,” says Taison Bell, MD, director of the medical intensive care unit and assistant professor of medicine at UVA Health in Charlottesville, Virginia.
But physicians have hurt patients in the past with medications they hoped would work, he says. “We have to make sure we’re balancing the risk and the harm with that benefit, and the only way to protect patients from those biases is by doing a randomized controlled trial.”
This article first appeared on Medscape.com.
COVID-19 pandemic dictates reconsideration of pemphigus therapy
The Dedee F. Murrell, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Together with physicians from the Mayo Clinic, Alexandria (Egypt) University, and Tehran (Iran) University, she recently published updated expert guidance for treatment of this severe, potentially fatal mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease, in a letter to the editor in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. She presented some of the key recommendations at AAD 2020.
First off, rituximab (Rituxan), the only Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris and a biologic considered first-line therapy prepandemic, is ill-advised during the COVID-19 era. Its mechanism of benefit is through B-cell depletion. This is an irreversible effect, and reconstitution of B-cell immunity takes 6-12 months. The absence of this immunologic protection for such a long time poses potentially serious problems for pemphigus patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Also, the opportunity to administer intravenous infusions of the biologic becomes unpredictable during pandemic surges, when limitations on nonemergent medical care may be necessary, noted Dr. Murrell, professor of dermatology at the University of New South Wales and head of dermatology at St. George University Hospital, both in Sydney.
“We have taken the approach of postponing rituximab infusions temporarily, with the aim of delaying peak patient immunosuppression during peak COVID-19 incidence to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Murrell and coauthors wrote in the letter (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82[6]:e235-6).
The other traditional go-to therapy for pemphigus is corticosteroids. They’re effective, fast acting, and relatively inexpensive. But their nonselective immunosuppressive action boosts infection risk in general, and more specifically it increases the risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19 should a patient become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“A basic therapeutic principle with particular importance during the pandemic is that glucocorticoids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil, should be tapered to the lowest effective dose. In active COVID-19 infection, immunosuppressive steroid-sparing medications should be discontinued when possible, although glucocorticoid cessation often cannot be considered due to risk for adrenal insufficiency,” the authors continued.
“Effective as adjuvant treatment in both pemphigus and COVID-19,intravenous immunoglobulin supports immunity and therefore may be useful in this setting,” they wrote. It’s not immunosuppressive, and, they noted, there’s good-quality evidence from a Japanese randomized, double-blind, controlled trial that a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin is effective therapy for pemphigus (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009 Apr;60[4]:595-603).
Moreover, intravenous immunoglobulin is also reportedly effective in severe COVID-19 (Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 21. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102.).
Another option is to consider enrolling a patient with moderate or severe pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus in the ongoing pivotal phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled PEGASUS trial of rilzabrutinib, a promising oral reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The medication has a short half-life and a self-limited immunomodulatory effect. Moreover, the trial is set up for remote patient visits on an outpatient basis via teledermatology, so the 65-week study can continue despite the pandemic. Both newly diagnosed and relapsing patients are eligible for the trial, headed by Dr. Murrell. At AAD 2020 she reported encouraging results from a phase 2b trial of rilzabrutinib.
She is a consultant to Principia Biopharma, sponsor of the PEGASUS trial, and has received institutional research grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
The Dedee F. Murrell, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Together with physicians from the Mayo Clinic, Alexandria (Egypt) University, and Tehran (Iran) University, she recently published updated expert guidance for treatment of this severe, potentially fatal mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease, in a letter to the editor in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. She presented some of the key recommendations at AAD 2020.
First off, rituximab (Rituxan), the only Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris and a biologic considered first-line therapy prepandemic, is ill-advised during the COVID-19 era. Its mechanism of benefit is through B-cell depletion. This is an irreversible effect, and reconstitution of B-cell immunity takes 6-12 months. The absence of this immunologic protection for such a long time poses potentially serious problems for pemphigus patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Also, the opportunity to administer intravenous infusions of the biologic becomes unpredictable during pandemic surges, when limitations on nonemergent medical care may be necessary, noted Dr. Murrell, professor of dermatology at the University of New South Wales and head of dermatology at St. George University Hospital, both in Sydney.
“We have taken the approach of postponing rituximab infusions temporarily, with the aim of delaying peak patient immunosuppression during peak COVID-19 incidence to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Murrell and coauthors wrote in the letter (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82[6]:e235-6).
The other traditional go-to therapy for pemphigus is corticosteroids. They’re effective, fast acting, and relatively inexpensive. But their nonselective immunosuppressive action boosts infection risk in general, and more specifically it increases the risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19 should a patient become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“A basic therapeutic principle with particular importance during the pandemic is that glucocorticoids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil, should be tapered to the lowest effective dose. In active COVID-19 infection, immunosuppressive steroid-sparing medications should be discontinued when possible, although glucocorticoid cessation often cannot be considered due to risk for adrenal insufficiency,” the authors continued.
“Effective as adjuvant treatment in both pemphigus and COVID-19,intravenous immunoglobulin supports immunity and therefore may be useful in this setting,” they wrote. It’s not immunosuppressive, and, they noted, there’s good-quality evidence from a Japanese randomized, double-blind, controlled trial that a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin is effective therapy for pemphigus (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009 Apr;60[4]:595-603).
Moreover, intravenous immunoglobulin is also reportedly effective in severe COVID-19 (Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 21. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102.).
Another option is to consider enrolling a patient with moderate or severe pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus in the ongoing pivotal phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled PEGASUS trial of rilzabrutinib, a promising oral reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The medication has a short half-life and a self-limited immunomodulatory effect. Moreover, the trial is set up for remote patient visits on an outpatient basis via teledermatology, so the 65-week study can continue despite the pandemic. Both newly diagnosed and relapsing patients are eligible for the trial, headed by Dr. Murrell. At AAD 2020 she reported encouraging results from a phase 2b trial of rilzabrutinib.
She is a consultant to Principia Biopharma, sponsor of the PEGASUS trial, and has received institutional research grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
The Dedee F. Murrell, MD, said at the virtual annual meeting of the American Academy of Dermatology.
Together with physicians from the Mayo Clinic, Alexandria (Egypt) University, and Tehran (Iran) University, she recently published updated expert guidance for treatment of this severe, potentially fatal mucocutaneous autoimmune blistering disease, in a letter to the editor in the Journal of the American Academy of Dermatology. She presented some of the key recommendations at AAD 2020.
First off, rituximab (Rituxan), the only Food and Drug Administration–approved medication for moderate to severe pemphigus vulgaris and a biologic considered first-line therapy prepandemic, is ill-advised during the COVID-19 era. Its mechanism of benefit is through B-cell depletion. This is an irreversible effect, and reconstitution of B-cell immunity takes 6-12 months. The absence of this immunologic protection for such a long time poses potentially serious problems for pemphigus patients who become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
Also, the opportunity to administer intravenous infusions of the biologic becomes unpredictable during pandemic surges, when limitations on nonemergent medical care may be necessary, noted Dr. Murrell, professor of dermatology at the University of New South Wales and head of dermatology at St. George University Hospital, both in Sydney.
“We have taken the approach of postponing rituximab infusions temporarily, with the aim of delaying peak patient immunosuppression during peak COVID-19 incidence to reduce the risk of adverse outcomes,” Dr. Murrell and coauthors wrote in the letter (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2020 Jun;82[6]:e235-6).
The other traditional go-to therapy for pemphigus is corticosteroids. They’re effective, fast acting, and relatively inexpensive. But their nonselective immunosuppressive action boosts infection risk in general, and more specifically it increases the risk of developing severe forms of COVID-19 should a patient become infected with SARS-CoV-2.
“A basic therapeutic principle with particular importance during the pandemic is that glucocorticoids and steroid-sparing immunosuppressive agents, such as azathioprine and mycophenolate mofetil, should be tapered to the lowest effective dose. In active COVID-19 infection, immunosuppressive steroid-sparing medications should be discontinued when possible, although glucocorticoid cessation often cannot be considered due to risk for adrenal insufficiency,” the authors continued.
“Effective as adjuvant treatment in both pemphigus and COVID-19,intravenous immunoglobulin supports immunity and therefore may be useful in this setting,” they wrote. It’s not immunosuppressive, and, they noted, there’s good-quality evidence from a Japanese randomized, double-blind, controlled trial that a 5-day course of intravenous immunoglobulin is effective therapy for pemphigus (J Am Acad Dermatol. 2009 Apr;60[4]:595-603).
Moreover, intravenous immunoglobulin is also reportedly effective in severe COVID-19 (Open Forum Infect Dis. 2020 Mar 21. doi: 10.1093/ofid/ofaa102.).
Another option is to consider enrolling a patient with moderate or severe pemphigus vulgaris or foliaceus in the ongoing pivotal phase 3, international, double-blind, placebo-controlled PEGASUS trial of rilzabrutinib, a promising oral reversible Bruton tyrosine kinase inhibitor. The medication has a short half-life and a self-limited immunomodulatory effect. Moreover, the trial is set up for remote patient visits on an outpatient basis via teledermatology, so the 65-week study can continue despite the pandemic. Both newly diagnosed and relapsing patients are eligible for the trial, headed by Dr. Murrell. At AAD 2020 she reported encouraging results from a phase 2b trial of rilzabrutinib.
She is a consultant to Principia Biopharma, sponsor of the PEGASUS trial, and has received institutional research grants from numerous pharmaceutical companies.
FROM AAD 20
Prior beta-blockers predict extra burden of heart failure in women with ACS
In the analysis of more than 13,000 patients with ACS and no history of cardiovascular (CV) disease, the women who had taken beta-blockers for hypertension showed about a one-third increased risk for heart failure (HF) at the time of their ACS presentation.
The difference between women and men was especially pronounced among patients with ST-segment elevation MI, compared with those with non-STEMI.
No such relationship between sex and risk for HF with ACS was observed among the larger portion of the cohort that had not previously been treated with beta-blockers, according to a report published July 13 in Hypertension, with lead author Raffaele Bugiardini, MD, University of Bologna (Italy).
Mortality at 30 days was sharply higher for patients with than without HF at their ACS presentation, by more than 600% for women and more than 800% for men.
“Our study provides robust evidence of an interaction between sex and beta-blocker therapy and suggests an increased risk of HF among women presenting with incident myocardial infarction,” Dr. Bugiardini said in an interview.
Given their novelty, “our findings raise strong concern about the appropriate role of beta-blockers in the therapy of hypertension in women with no prior history of cardiovascular diseases. Beta-blocker use may be an acute precipitant of heart failure in women presenting with incident ACS as first manifestation of coronary heart disease.” Dr. Bugiardini and colleagues wrote.
“There is one main implication for clinical practice. Discontinuing a beta-blocker in an otherwise healthy woman with hypertension and no prior CV disease is not harmful and could be wise,” Dr. Bugiardini said. “Blood pressure in women may be regulated in a safer way, such as using other medications and, of course, through diet and exercise.”
Rationale for the study
Men and women “differ with respect to the risk, causes, and prognosis of HF,” Dr. Bugiardini and colleagues wrote, and current guidelines “do not differentiate between the use of beta-blockers in men and in women.”
However, they proposed, “because prior trials and meta-analyses enrolled nearly five men for every woman, any differences in the effect of beta-blockers among women would have been concealed by the effect of beta-blocker therapy among men.”
The current study looked at data from October 2010 to July 2018 in the ISACS ARCHIVES, ISACS-TC, and the EMMACE-3X registries, covering 13,764 patients from 12 European countries who had a history of hypertension and presented with confirmed ACS.
Of the combined cohort, 2,590 (19%) had been treated with beta-blockers prior to their ACS presentation. They were similar to those without a history of beta-blocker use with respect to baseline features and use of other medications in an adjusted analysis.
In the group with prior beta-blocker use, 21.3% of the women and 16.7% of the men had HF of Killip class 2 or higher, a 4.6% absolute difference that worked out to a relative risk of 1.35 (95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.65).
The corresponding rates for women and men without prior beta-blocker use were 17.2% and 16.1%, respectively, for an absolute difference of only 1.1% and an RR of1.09 (95% CI, 0.97-1.21).
The interaction between sex and beta-blocker therapy for the HF outcome was significant (P < .034). An analysis that excluded patients in cardiogenic shock at their ACS presentation produced similar results.
In an analysis only of patients with STEMI, the RR for HF in women versus men was 1.44 (95% CI, 1.12-1.84) among those with a history of beta-blocker use, and 1.11 (95% CI, 0.98-1.26) among those who hadn’t used the drugs. The interaction between sex and beta-blocker use was significant (P = .033).
No such significant interaction was seen for the subgroup with non-STEMI as their index ACS (P = .14).
Heart failure at ACS was the most powerful observed predictor of 30-day mortality in women and in men in multivariate analysis; the odds ratios were 7.54 (95% CI, 5.78-9.83) and 9.62 (95% CI, 7.67-12.07), respectively.
“Our study underscores the importance of sex analyses in clinical research studies, which may provide further actionable data,” Dr. Bugiardini stated. “Failure to include both sexes in therapeutic studies is a missed opportunity to uncover underlying sex-specific risks. The adverse effect of beta-blocker therapy in women with hypertension is a sex-specific risk.”
Not just a male disease
Part of the study’s conclusions are “really not that surprising, because we have known for a long time that women who have an MI are much more likely to develop HF than men, and we also know that HF raises mortality after MI,” Ileana L. Pina, MD, MPH, Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
But what surprised her was that women taking beta-blockers were at greater risk for HF. “This association needs to be proven in a prospective study and confirmed in another dataset,” said Dr. Pina, who was not involved with the current study. “The most important message is to remember that HF is not just a ‘male’ disease and to pay attention to the symptoms of women and not discount or relegate them to anxiety or gastric problems.”
The study was observational, Dr. Bugiardini noted, so “the results may have some variance and need confirmation. However, a sex-stratified, randomized, controlled trial of beta-blocker therapy in patients with hypertension but no prior history of coronary heart disease or HF may not be considered ethical, since it would be designed to confirm risk … and not benefit.”
“Further observational studies may give confirmation,” he added. “In the meantime, the Food and Drug Administration should alert health care professionals of the adverse events associated with beta-blocker use in women with hypertension and no prior history of CV disease, [because] prescribing beta-blockers to a woman with hypertension means exposing her to unnecessary risk.”
Dr. Bugiardini and the other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Pina reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the analysis of more than 13,000 patients with ACS and no history of cardiovascular (CV) disease, the women who had taken beta-blockers for hypertension showed about a one-third increased risk for heart failure (HF) at the time of their ACS presentation.
The difference between women and men was especially pronounced among patients with ST-segment elevation MI, compared with those with non-STEMI.
No such relationship between sex and risk for HF with ACS was observed among the larger portion of the cohort that had not previously been treated with beta-blockers, according to a report published July 13 in Hypertension, with lead author Raffaele Bugiardini, MD, University of Bologna (Italy).
Mortality at 30 days was sharply higher for patients with than without HF at their ACS presentation, by more than 600% for women and more than 800% for men.
“Our study provides robust evidence of an interaction between sex and beta-blocker therapy and suggests an increased risk of HF among women presenting with incident myocardial infarction,” Dr. Bugiardini said in an interview.
Given their novelty, “our findings raise strong concern about the appropriate role of beta-blockers in the therapy of hypertension in women with no prior history of cardiovascular diseases. Beta-blocker use may be an acute precipitant of heart failure in women presenting with incident ACS as first manifestation of coronary heart disease.” Dr. Bugiardini and colleagues wrote.
“There is one main implication for clinical practice. Discontinuing a beta-blocker in an otherwise healthy woman with hypertension and no prior CV disease is not harmful and could be wise,” Dr. Bugiardini said. “Blood pressure in women may be regulated in a safer way, such as using other medications and, of course, through diet and exercise.”
Rationale for the study
Men and women “differ with respect to the risk, causes, and prognosis of HF,” Dr. Bugiardini and colleagues wrote, and current guidelines “do not differentiate between the use of beta-blockers in men and in women.”
However, they proposed, “because prior trials and meta-analyses enrolled nearly five men for every woman, any differences in the effect of beta-blockers among women would have been concealed by the effect of beta-blocker therapy among men.”
The current study looked at data from October 2010 to July 2018 in the ISACS ARCHIVES, ISACS-TC, and the EMMACE-3X registries, covering 13,764 patients from 12 European countries who had a history of hypertension and presented with confirmed ACS.
Of the combined cohort, 2,590 (19%) had been treated with beta-blockers prior to their ACS presentation. They were similar to those without a history of beta-blocker use with respect to baseline features and use of other medications in an adjusted analysis.
In the group with prior beta-blocker use, 21.3% of the women and 16.7% of the men had HF of Killip class 2 or higher, a 4.6% absolute difference that worked out to a relative risk of 1.35 (95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.65).
The corresponding rates for women and men without prior beta-blocker use were 17.2% and 16.1%, respectively, for an absolute difference of only 1.1% and an RR of1.09 (95% CI, 0.97-1.21).
The interaction between sex and beta-blocker therapy for the HF outcome was significant (P < .034). An analysis that excluded patients in cardiogenic shock at their ACS presentation produced similar results.
In an analysis only of patients with STEMI, the RR for HF in women versus men was 1.44 (95% CI, 1.12-1.84) among those with a history of beta-blocker use, and 1.11 (95% CI, 0.98-1.26) among those who hadn’t used the drugs. The interaction between sex and beta-blocker use was significant (P = .033).
No such significant interaction was seen for the subgroup with non-STEMI as their index ACS (P = .14).
Heart failure at ACS was the most powerful observed predictor of 30-day mortality in women and in men in multivariate analysis; the odds ratios were 7.54 (95% CI, 5.78-9.83) and 9.62 (95% CI, 7.67-12.07), respectively.
“Our study underscores the importance of sex analyses in clinical research studies, which may provide further actionable data,” Dr. Bugiardini stated. “Failure to include both sexes in therapeutic studies is a missed opportunity to uncover underlying sex-specific risks. The adverse effect of beta-blocker therapy in women with hypertension is a sex-specific risk.”
Not just a male disease
Part of the study’s conclusions are “really not that surprising, because we have known for a long time that women who have an MI are much more likely to develop HF than men, and we also know that HF raises mortality after MI,” Ileana L. Pina, MD, MPH, Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
But what surprised her was that women taking beta-blockers were at greater risk for HF. “This association needs to be proven in a prospective study and confirmed in another dataset,” said Dr. Pina, who was not involved with the current study. “The most important message is to remember that HF is not just a ‘male’ disease and to pay attention to the symptoms of women and not discount or relegate them to anxiety or gastric problems.”
The study was observational, Dr. Bugiardini noted, so “the results may have some variance and need confirmation. However, a sex-stratified, randomized, controlled trial of beta-blocker therapy in patients with hypertension but no prior history of coronary heart disease or HF may not be considered ethical, since it would be designed to confirm risk … and not benefit.”
“Further observational studies may give confirmation,” he added. “In the meantime, the Food and Drug Administration should alert health care professionals of the adverse events associated with beta-blocker use in women with hypertension and no prior history of CV disease, [because] prescribing beta-blockers to a woman with hypertension means exposing her to unnecessary risk.”
Dr. Bugiardini and the other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Pina reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
In the analysis of more than 13,000 patients with ACS and no history of cardiovascular (CV) disease, the women who had taken beta-blockers for hypertension showed about a one-third increased risk for heart failure (HF) at the time of their ACS presentation.
The difference between women and men was especially pronounced among patients with ST-segment elevation MI, compared with those with non-STEMI.
No such relationship between sex and risk for HF with ACS was observed among the larger portion of the cohort that had not previously been treated with beta-blockers, according to a report published July 13 in Hypertension, with lead author Raffaele Bugiardini, MD, University of Bologna (Italy).
Mortality at 30 days was sharply higher for patients with than without HF at their ACS presentation, by more than 600% for women and more than 800% for men.
“Our study provides robust evidence of an interaction between sex and beta-blocker therapy and suggests an increased risk of HF among women presenting with incident myocardial infarction,” Dr. Bugiardini said in an interview.
Given their novelty, “our findings raise strong concern about the appropriate role of beta-blockers in the therapy of hypertension in women with no prior history of cardiovascular diseases. Beta-blocker use may be an acute precipitant of heart failure in women presenting with incident ACS as first manifestation of coronary heart disease.” Dr. Bugiardini and colleagues wrote.
“There is one main implication for clinical practice. Discontinuing a beta-blocker in an otherwise healthy woman with hypertension and no prior CV disease is not harmful and could be wise,” Dr. Bugiardini said. “Blood pressure in women may be regulated in a safer way, such as using other medications and, of course, through diet and exercise.”
Rationale for the study
Men and women “differ with respect to the risk, causes, and prognosis of HF,” Dr. Bugiardini and colleagues wrote, and current guidelines “do not differentiate between the use of beta-blockers in men and in women.”
However, they proposed, “because prior trials and meta-analyses enrolled nearly five men for every woman, any differences in the effect of beta-blockers among women would have been concealed by the effect of beta-blocker therapy among men.”
The current study looked at data from October 2010 to July 2018 in the ISACS ARCHIVES, ISACS-TC, and the EMMACE-3X registries, covering 13,764 patients from 12 European countries who had a history of hypertension and presented with confirmed ACS.
Of the combined cohort, 2,590 (19%) had been treated with beta-blockers prior to their ACS presentation. They were similar to those without a history of beta-blocker use with respect to baseline features and use of other medications in an adjusted analysis.
In the group with prior beta-blocker use, 21.3% of the women and 16.7% of the men had HF of Killip class 2 or higher, a 4.6% absolute difference that worked out to a relative risk of 1.35 (95% confidence interval, 1.10-1.65).
The corresponding rates for women and men without prior beta-blocker use were 17.2% and 16.1%, respectively, for an absolute difference of only 1.1% and an RR of1.09 (95% CI, 0.97-1.21).
The interaction between sex and beta-blocker therapy for the HF outcome was significant (P < .034). An analysis that excluded patients in cardiogenic shock at their ACS presentation produced similar results.
In an analysis only of patients with STEMI, the RR for HF in women versus men was 1.44 (95% CI, 1.12-1.84) among those with a history of beta-blocker use, and 1.11 (95% CI, 0.98-1.26) among those who hadn’t used the drugs. The interaction between sex and beta-blocker use was significant (P = .033).
No such significant interaction was seen for the subgroup with non-STEMI as their index ACS (P = .14).
Heart failure at ACS was the most powerful observed predictor of 30-day mortality in women and in men in multivariate analysis; the odds ratios were 7.54 (95% CI, 5.78-9.83) and 9.62 (95% CI, 7.67-12.07), respectively.
“Our study underscores the importance of sex analyses in clinical research studies, which may provide further actionable data,” Dr. Bugiardini stated. “Failure to include both sexes in therapeutic studies is a missed opportunity to uncover underlying sex-specific risks. The adverse effect of beta-blocker therapy in women with hypertension is a sex-specific risk.”
Not just a male disease
Part of the study’s conclusions are “really not that surprising, because we have known for a long time that women who have an MI are much more likely to develop HF than men, and we also know that HF raises mortality after MI,” Ileana L. Pina, MD, MPH, Wayne State University, Detroit, said in an interview.
But what surprised her was that women taking beta-blockers were at greater risk for HF. “This association needs to be proven in a prospective study and confirmed in another dataset,” said Dr. Pina, who was not involved with the current study. “The most important message is to remember that HF is not just a ‘male’ disease and to pay attention to the symptoms of women and not discount or relegate them to anxiety or gastric problems.”
The study was observational, Dr. Bugiardini noted, so “the results may have some variance and need confirmation. However, a sex-stratified, randomized, controlled trial of beta-blocker therapy in patients with hypertension but no prior history of coronary heart disease or HF may not be considered ethical, since it would be designed to confirm risk … and not benefit.”
“Further observational studies may give confirmation,” he added. “In the meantime, the Food and Drug Administration should alert health care professionals of the adverse events associated with beta-blocker use in women with hypertension and no prior history of CV disease, [because] prescribing beta-blockers to a woman with hypertension means exposing her to unnecessary risk.”
Dr. Bugiardini and the other authors had no disclosures. Dr. Pina reported no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
PCI or not, mortality climbs with post-ACS bleeding complications
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.
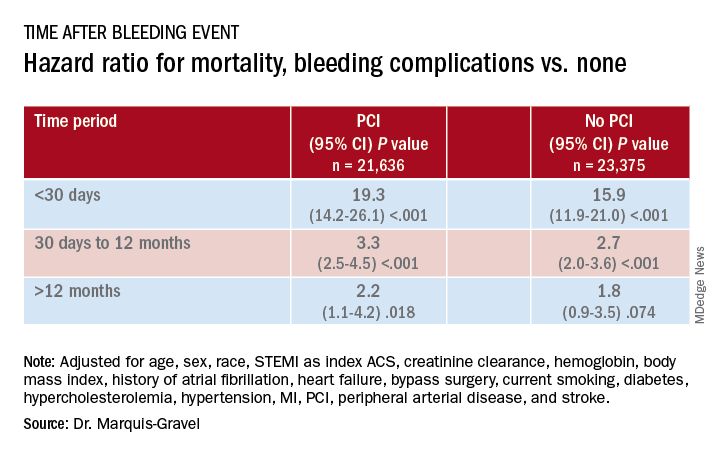
Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.

Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients with acute coronary syndromes (ACS) with later bleeding complications that were at least moderate in severity showed a 15-fold increased risk of dying within 30 days, compared with those without such bleeding, in a pooled analysis of four randomized antithrombotic-therapy trials.

Mortality 1 month to 1 year after a bleeding event was not as sharply increased, but there was still almost triple the risk seen in patients without bleeding complications.
In both cases, the risk increase was independent of whether percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) had been part of the management of ACS, concludes the study, published in the July 14 issue of the Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
“We showed that postdischarge bleeding was associated with a pretty bad prognosis, in terms of all-cause mortality, regardless of the index treatment – PCI or medical therapy,” lead author Guillaume Marquis-Gravel, MD, MSc, Duke Clinical Research Institute, Durham, N.C., said in an interview.
“Our data suggest that we should care about bleeding prevention in patients who had a previous ACS, regardless of the treatment strategy, as much as we care for prevention of future ischemic events,” said Dr. Marquis-Gravel, who is also an interventional cardiologist at the Montreal Heart Institute.
“This large-scale analysis clearly demonstrates that bleeding events occurring among ACS patients with coronary stents carry the same prognostic significance in magnitude and time course as among patients who do not undergo PCI,” observed Derek Chew, MBBS, MPH, PhD, of Flinders University, Adelaide, Australia, and Jack Wei Chieh Tan, MBBS, MBA, of National Heart Centre, Singapore, in an accompanying editorial.
“Therefore, at least in the later phases of planning antithrombotic therapy, when weighting bleeding risk in these conditions, these estimates should not be ‘discounted’ for the absence or presence of PCI during the initial ACS management,” they wrote.
A “proven assumption”
“A great deal of research has previously been conducted to tailor DAPT [dual-antiplatelet therapy] and to minimize bleeding risk following PCI based on the proven assumption that bleeding is associated with adverse clinical outcomes,” Dr. Marques-Gravel explained.
“The prognostic impact of postdischarge bleeding has not been studied thoroughly in patients with ACS who were only treated medically with DAPT without PCI.” Yet this population makes up a large proportion of the ACS population, and patients are “generally older and sicker” and therefore at increased risk for both ischemic and bleeding events, he said.
The researchers explored those issues in a post hoc pooled analysis of four randomized comparisons of antithrombotic strategies in patients with ACS: APPRAISE-2, PLATO, TRACER, and TRILOGY ACS. The analyses tracked bleeding events that took place from a landmark time of 7 days after presentation with ACS over a median follow-up of 1 year in 45,011 patients (31.3% female), 48% of whom were managed with PCI.
Those treated with PCI, compared with those medically managed only, tended to be younger, more often male, more likely to have ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI) as their ACS, and less likely to have cardiovascular comorbidities.
During the total follow-up of 48,717 person-years, the postdischarge rate of moderate, severe, or life-threatening bleeding defined by GUSTO criteria reached 2.6 events per 100 patient-years. A total of 2,149 patients died, and mortality was consistently higher in patients who had such bleeding complications. They showed an adjusted hazard ratio of 15.7 (95% confidence interval, 12.3-20.0) for mortality within 30 days, compared with patients without bleeds. Their HR for mortality at 30 days to 1 year was 2.7 (95% CI, 2.1-3.4).
The association between bleeding complications and mortality remained consistent, regardless of whether patients had undergone PCI for their ACS (interaction P = .240).
A pragmatic interpretation
Although an observational study can’t show causality between bleeding and mortality, Dr. Marquis-Gravel cautioned, “the fact that the majority of deaths occurred early after the bleeding event, within 30 days, is strongly suggestive of a causal relationship.”
He recommended a “pragmatic interpretation” of the study: “Bleeding avoidance strategies tested in PCI populations, including short-term DAPT or aspirin-free strategies, should also be considered in medically treated patients with ACS deemed at higher risk of bleeding.”
“It is clear that bleeding events after successful PCI for an ACS are independently associated with increased mortality and morbidity,” Debabrata Mukherjee, MD, of Texas Tech University, El Paso, said in an interview.
“Every effort should be made to minimize bleeding events with the use of appropriate access site for PCI, dosing, selection, and duration of antiplatelet and antithrombotic agents, and use of proton pump inhibitors when appropriate,” he said.
The clinical decision-making involved in this individualized approach “is often not easy,” said Dr. Mukherjee, who was not involved in the current study. “Integrating patients and clinical pharmacists in choosing optimal antithrombotic therapies post-MI is likely to be helpful” in the process.
Although “major bleeding following ACS increases the risk of mortality for both medically managed and PCI-managed patients with ACS, the vast majority of deaths, 90%, occur in those that have not had a bleed,” Mamas A. Mamas, DPhil, Keele University, Staffordshire, England, said in an interview.
“It is important to understand the causes of death in this population and think about how interventions may impact on this,” agreed Dr. Mamas, who was not involved in the study.
Dr. Marquis-Gravel reported receiving speaking fees and honoraria from Servier and Novartis; disclosures for the other authors are in the report. Dr. Chew reported receiving speaking fees and institutional grants in aid from Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, and Edwards Lifesciences. Dr. Tan discloses receiving speaking fees and educational grants from Amgen, Roche Diagnostics, AstraZeneca, Bayer, and Abbott Vascular. Dr. Mukherjee and Dr. Mamas report no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article originally appeared on Medscape.com.








