User login
Pleural Effusion and an Axillary Mass in a Woman With Hypertension
Editor's Note:
The Case Challenge series includes difficult-to-diagnose conditions, some of which are not frequently encountered by most clinicians but are nonetheless important to accurately recognize. Test your diagnostic and treatment skills using the following patient scenario and corresponding questions. If you have a case that you would like to suggest for a future Case Challenge, please contact us .
Background
A 58-year-old woman seeks medical attention after she discovered a new mass in her left axilla during a routine monthly breast self-examination while showering. She has not noted any changes in either of her breasts. The mass in her left axilla is not tender, and she has not felt any other abnormal masses, including in her right axilla. She reports no other symptoms and specifically has no pain anywhere in her body. She also does not have shortness of breath, fever, night sweats, fatigue, rash, or abdominal discomfort or bloating.
Fifteen years earlier, the patient was diagnosed with high-grade, stage 1 cervical cancer and underwent surgery and chemoradiation. She has been closely monitored since that time with physical examinations and abdominal CT, with no evidence of recurrent disease. The patient has not had any other surgical procedure, except for removal of two basal cell carcinomas on her neck 4 years ago. She has had yearly routine mammograms for at least the past 15 years.
The patient has hypertension, which has been well controlled with the same medications for the past 10 years. She also has a 25-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is currently managed with diet alone. She had a "silent myocardial infarction" sometime within the past 5 years but has had no cardiac symptoms and is not taking any cardiac medications. She smoked approximately one pack of cigarettes a day for less than 2 years when she was "in her teens" but has not had any tobacco products since that time.
Pancreatic cancer was diagnosed in the patient's father at age 49 years, and breast cancer was diagnosed in her aunt on her father's side at age 67 years. Her paternal grandmother is reported to have died in her 60s after diagnosis of a "cancer in her stomach." No further information is available regarding either the actual diagnosis or the medical care provided to this individual.
To the best of the patient's knowledge, her mother's side of the family and her two brothers have no history of cancer. She has no sisters. Her mother is in her 80s and has mild dementia. The patient is not aware of any member of her family having undergone genetic testing.
Physical Examination and Workup
The patient appears well and is in no acute distress. The patient is afebrile, with a blood pressure of 135/85 mm Hg, a respiratory rate of 16 breaths/min, and a pulse of 72 beats/min. Her weight is 148 lb (67 kg), and she has no reported recent weight loss.
Examination of the skin reveals no suspicious lesions. Scars from the previous removal of the basal cell carcinomas are noted, but no evidence suggests recurrence.
Results of the head and neck examination are unremarkable; specifically, no abnormal cervical lymphadenopathy is detected. The cardiac and chest examination results are normal. The lungs are clear to percussion and auscultation. The breast examination reveals no abnormal masses. The right axilla is unremarkable; however, a single 3 × 2 cm, nontender, firm, movable but partially fixed mass is noted in the left axilla.
The abdomen appears normal, with no ascites or enlargement of the liver. The pelvic examination reveals evidence of previous surgery and local radiation but no signs of recurrence of cervical cancer. The lymph nodes appear normal, except for the findings noted above. Results of the neurologic examination are unremarkable.
Complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte levels, renal function tests, and urinalysis are all normal. Liver function tests are normal except for a mildly elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level. The fecal occult blood test result is negative.
Chest radiography reveals a suspicious small left-sided pleural effusion. No other abnormalities are observed, and no prior chest radiographs are available to compare with the current findings.
Chest CT confirms the presence of a possible small pleural effusion, with no other abnormalities noted. The radiologist suggests it will not be possible to obtain fluid safely through an interventional procedure, owing to the limited (if any) amount of fluid present. Furthermore, the radiologist recommends PET/CT to look for other evidence of metastatic cancer in the lungs or elsewhere.
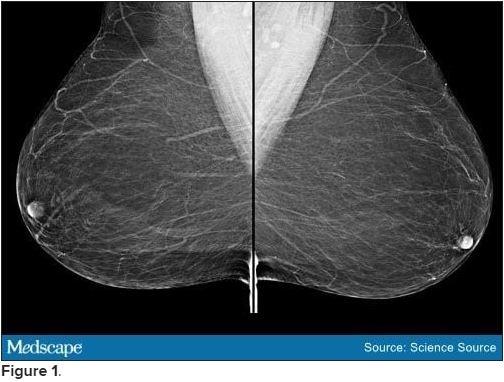
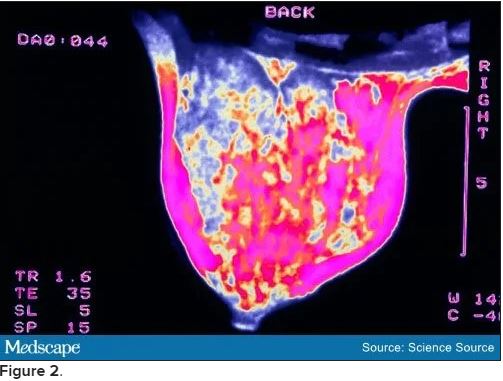
Bilateral mammograms reveal no suspicious abnormalities, and the results are unchanged from a previous examination 11 months earlier. Figure 1 shows a similar bilateral mammogram in another patient. Breast MRI shows no evidence of cancer. Figure 2 shows similar breast MRI findings in another patient.
CT of the abdomen and pelvis reveals no changes compared with a scan obtained 2 years earlier for follow-up of the previous diagnosis of cervical cancer. Specifically, no evidence suggests ascites or any pelvic masses.
An incisional biopsy sample is obtained from the left axillary mass. Light microscopy reveals a moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. Immunostaining shows the cancer to be cytokeratin (CK) 7 positive and CK 20 negative (CK 7+/CK 20-, thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) negative, thyroglobulin negative, napsin A negative, and mammaglobin positive. The tumor is estrogen receptor positive (2% staining), progesterone receptor negative, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative.
[polldaddy:10837180]
Discussion
The correct answer: Breast.
This case is a classic example of cancer of unknown primary site or origin (CUP). CUP represents approximately 5% of cancers diagnosed in the United States (50,000 to 60,000 cases each year), with various series reporting that the site of origin is not diagnosed in between 2% and 6% of all cancer cases.[1] Worldwide, the incidence of CUP is even higher, resulting from the limited availability of sophisticated (and expensive) diagnostic technology in many regions. The median age at diagnosis of CUP is 60 years, and men and women are equally likely to be affected.
A cancer is considered a CUP if, after routine clinical assessment, physical and laboratory examination, standard imaging studies, and routine pathologic evaluation (biopsy or surgical removal of a metastatic mass lesion), a site of origin cannot be defined. With the availability of more sophisticated imaging technologies (eg, MRI), the overall percentage of cancers that are defined as a CUP has been reduced. However, even at autopsy, the site of origin of such cancer is often unable to be determined if the location was unknown before the patient's death.
Several theories have been proposed for why a metastatic lesion becomes clinically evident despite the site of origin of the cancer remaining obscure. These include (1) very slow growth of the primary cancer compared with that of the metastasis; (2) spontaneous regression of the primary cancer; (3) a prominent vascular component of the cancer, which enhances the rate of spread; and (4) unique molecular events associated with the cancer, which result in rapid progression and the growth of metastatic lesions.
Approximately 60% of CUPs are adenocarcinomas (well or moderately well differentiated); 25%-30% are poorly differentiated (including poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas); 5% are completely undifferentiated, with no defining histologic features; 5% are squamous cell cancers; and approximately 1% are carcinomas, with evidence of neuroendocrine differentiation.[1]
Immunohistochemical staining of biopsy material can be helpful in narrowing the possible anatomical sites of origin. The results are particularly relevant in the selection of therapeutic strategies and in ensuring that a rare, potentially highly curable cancer is not missed (eg, lymphoma, germ cell tumor).[2]
A critical initial test is examination of several CK subtypes that are more likely to be expressed in certain carcinomas than in others. For example, the CK 7+/CK 20- staining seen in this patient is characteristic of breast and lung cancers (among others), whereas CK 7+/CK 20+ staining would be expected in pancreatic, gastric, and urothelial cancers. A CK 7-/CK 20+ finding would be more suggestive of colon or mucinous ovarian cancer. Furthermore, approximately 70% of lung adenocarcinomas are TTF-1 positive and 60%-80% are napsin A positive. The negative findings in this patient's case make the diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer less likely.
Examination for the presence (or absence) of well-established biomarkers for breast cancer can potentially be helpful in suggesting the site of origin or in helping to define subsequent therapy. These markers include estrogen and progesterone receptors and HER2 overexpression. An additional biomarker, mammaglobin, has been reported to be expressed in 48% of breast cancers but is absent in cancers of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, ovary, and head and neck region.[2]
Of note, mammaglobin was found to be expressed in this patient. Although only 2% of the cells were reported to stain for the estrogen receptor, this finding is still considered positive and supports breast cancer as the correct diagnosis.
Recognized relevant prognostic factors in CUP include baseline performance status, the number and location of metastatic lesions, and the response to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Unfortunately, the overall prognosis associated with a diagnosis of CUP is poor, with median survival in various series reported to be less than 6 months. However, important exceptions to this outcome include women who present with an isolated metastatic axillary mass, as described in this case.
Previous reports of axillary adenopathy as the initial presentation of cancer in women revealed that the majority had evidence of cancer in the breast at the time of subsequent mastectomy.[3,4] As a result, in the absence of other indications found during routine workup (eg, a single pulmonary lesion suggestive of a primary lung cancer, pathologic findings inconsistent with breast cancer), an isolated adenocarcinoma in the breast (with no evidence of metastatic cancer elsewhere) should be treated as either stage II or stage III breast cancer. Note that this recommendation specifically relates to female patients. If a male patient has CUP with an isolated axillary mass, it is generally assumed that the lung is the origin of the malignancy.
In a female patient with negative mammographic findings, breast MRI can be helpful. In one series, 28 of 40 women (70%) with evidence of cancer in the axilla and a normal mammogram were found to have a breast abnormality on MRI.[5] Of note, and of considerable relevance to subsequent disease management, five of the 12 women with negative findings in this series underwent surgery, and in four of the cases no cancer was found. Although the number of participants in this series is limited, the absence of an MRI abnormality in the patient in this case can reasonably be considered in her future treatment plans.
Specifically, it might be suggested in this case that treatment include surgical removal of the axillary mass (if possible) followed by radiation to this area and the breast (rather than performing a mastectomy). Alternatively, treatment might begin with chemotherapy (a neoadjuvant approach) followed by surgery to remove any residual axillary mass and local/regional radiation or local/regional radiation alone. Adjuvant chemotherapy and/or hormonal therapy would then be administered.
The presence of a possible small pleural effusion is a concern because it potentially indicates more widespread metastatic disease, as does the mild elevation of the serum alkaline phosphatase level (eg, suggesting metastatic disease in bone or the liver). In the absence of other evidence of tumor spread, PET would not be unreasonable. A negative scan for evidence of metastatic disease would support a "curative" approach to the management of local disease in the axilla and presumably the breast, whereas a finding of other metastatic sites would lead to the conclusion that treatment should probably be delivered with more palliative intent.
The family history of cancer (father, paternal aunt with breast cancer, paternal grandmother with possible ovarian cancer) is intriguing and would suggest a role for genetic counseling and possibly genetic testing (eg, for BRCA mutation).
The patient in this case underwent PET. The only abnormality observed was in the left axilla. The axillary mass was subsequently resected. This was followed by curative radiation to both the axilla and left breast, adjuvant chemotherapy, and 5 years of hormonal therapy. The patient has showed no evidence of recurrence 2 years after completion of the hormonal treatment.
[polldaddy:10841207]
Discussion
The correct answer: Lung
The lungs are generally assumed to be the site of origin of the cancer in a male patient who has CUP with an isolated axillary mass. In contrast, the majority of women with axillary adenopathy as the initial presentation of cancer were found to have evidence of cancer in the breast at the time of subsequent mastectomy.[3,4]
[polldaddy:10837187]
Discussion
The correct answer: MRI
Breast MRI can be helpful in a female patient with negative mammographic findings. In one series, MRI detected a breast abnormality in 28 of 40 women (70%) with evidence of cancer in the axilla and a normal mammogram.[5]
Editor's Note:
The Case Challenge series includes difficult-to-diagnose conditions, some of which are not frequently encountered by most clinicians but are nonetheless important to accurately recognize. Test your diagnostic and treatment skills using the following patient scenario and corresponding questions. If you have a case that you would like to suggest for a future Case Challenge, please contact us .
Background
A 58-year-old woman seeks medical attention after she discovered a new mass in her left axilla during a routine monthly breast self-examination while showering. She has not noted any changes in either of her breasts. The mass in her left axilla is not tender, and she has not felt any other abnormal masses, including in her right axilla. She reports no other symptoms and specifically has no pain anywhere in her body. She also does not have shortness of breath, fever, night sweats, fatigue, rash, or abdominal discomfort or bloating.
Fifteen years earlier, the patient was diagnosed with high-grade, stage 1 cervical cancer and underwent surgery and chemoradiation. She has been closely monitored since that time with physical examinations and abdominal CT, with no evidence of recurrent disease. The patient has not had any other surgical procedure, except for removal of two basal cell carcinomas on her neck 4 years ago. She has had yearly routine mammograms for at least the past 15 years.
The patient has hypertension, which has been well controlled with the same medications for the past 10 years. She also has a 25-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is currently managed with diet alone. She had a "silent myocardial infarction" sometime within the past 5 years but has had no cardiac symptoms and is not taking any cardiac medications. She smoked approximately one pack of cigarettes a day for less than 2 years when she was "in her teens" but has not had any tobacco products since that time.
Pancreatic cancer was diagnosed in the patient's father at age 49 years, and breast cancer was diagnosed in her aunt on her father's side at age 67 years. Her paternal grandmother is reported to have died in her 60s after diagnosis of a "cancer in her stomach." No further information is available regarding either the actual diagnosis or the medical care provided to this individual.
To the best of the patient's knowledge, her mother's side of the family and her two brothers have no history of cancer. She has no sisters. Her mother is in her 80s and has mild dementia. The patient is not aware of any member of her family having undergone genetic testing.
Physical Examination and Workup
The patient appears well and is in no acute distress. The patient is afebrile, with a blood pressure of 135/85 mm Hg, a respiratory rate of 16 breaths/min, and a pulse of 72 beats/min. Her weight is 148 lb (67 kg), and she has no reported recent weight loss.
Examination of the skin reveals no suspicious lesions. Scars from the previous removal of the basal cell carcinomas are noted, but no evidence suggests recurrence.
Results of the head and neck examination are unremarkable; specifically, no abnormal cervical lymphadenopathy is detected. The cardiac and chest examination results are normal. The lungs are clear to percussion and auscultation. The breast examination reveals no abnormal masses. The right axilla is unremarkable; however, a single 3 × 2 cm, nontender, firm, movable but partially fixed mass is noted in the left axilla.
The abdomen appears normal, with no ascites or enlargement of the liver. The pelvic examination reveals evidence of previous surgery and local radiation but no signs of recurrence of cervical cancer. The lymph nodes appear normal, except for the findings noted above. Results of the neurologic examination are unremarkable.
Complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte levels, renal function tests, and urinalysis are all normal. Liver function tests are normal except for a mildly elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level. The fecal occult blood test result is negative.
Chest radiography reveals a suspicious small left-sided pleural effusion. No other abnormalities are observed, and no prior chest radiographs are available to compare with the current findings.
Chest CT confirms the presence of a possible small pleural effusion, with no other abnormalities noted. The radiologist suggests it will not be possible to obtain fluid safely through an interventional procedure, owing to the limited (if any) amount of fluid present. Furthermore, the radiologist recommends PET/CT to look for other evidence of metastatic cancer in the lungs or elsewhere.
Bilateral mammograms reveal no suspicious abnormalities, and the results are unchanged from a previous examination 11 months earlier. Figure 1 shows a similar bilateral mammogram in another patient. Breast MRI shows no evidence of cancer. Figure 2 shows similar breast MRI findings in another patient.


CT of the abdomen and pelvis reveals no changes compared with a scan obtained 2 years earlier for follow-up of the previous diagnosis of cervical cancer. Specifically, no evidence suggests ascites or any pelvic masses.
An incisional biopsy sample is obtained from the left axillary mass. Light microscopy reveals a moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. Immunostaining shows the cancer to be cytokeratin (CK) 7 positive and CK 20 negative (CK 7+/CK 20-, thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) negative, thyroglobulin negative, napsin A negative, and mammaglobin positive. The tumor is estrogen receptor positive (2% staining), progesterone receptor negative, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative.
[polldaddy:10837180]
Discussion
The correct answer: Breast.
This case is a classic example of cancer of unknown primary site or origin (CUP). CUP represents approximately 5% of cancers diagnosed in the United States (50,000 to 60,000 cases each year), with various series reporting that the site of origin is not diagnosed in between 2% and 6% of all cancer cases.[1] Worldwide, the incidence of CUP is even higher, resulting from the limited availability of sophisticated (and expensive) diagnostic technology in many regions. The median age at diagnosis of CUP is 60 years, and men and women are equally likely to be affected.
A cancer is considered a CUP if, after routine clinical assessment, physical and laboratory examination, standard imaging studies, and routine pathologic evaluation (biopsy or surgical removal of a metastatic mass lesion), a site of origin cannot be defined. With the availability of more sophisticated imaging technologies (eg, MRI), the overall percentage of cancers that are defined as a CUP has been reduced. However, even at autopsy, the site of origin of such cancer is often unable to be determined if the location was unknown before the patient's death.
Several theories have been proposed for why a metastatic lesion becomes clinically evident despite the site of origin of the cancer remaining obscure. These include (1) very slow growth of the primary cancer compared with that of the metastasis; (2) spontaneous regression of the primary cancer; (3) a prominent vascular component of the cancer, which enhances the rate of spread; and (4) unique molecular events associated with the cancer, which result in rapid progression and the growth of metastatic lesions.
Approximately 60% of CUPs are adenocarcinomas (well or moderately well differentiated); 25%-30% are poorly differentiated (including poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas); 5% are completely undifferentiated, with no defining histologic features; 5% are squamous cell cancers; and approximately 1% are carcinomas, with evidence of neuroendocrine differentiation.[1]
Immunohistochemical staining of biopsy material can be helpful in narrowing the possible anatomical sites of origin. The results are particularly relevant in the selection of therapeutic strategies and in ensuring that a rare, potentially highly curable cancer is not missed (eg, lymphoma, germ cell tumor).[2]
A critical initial test is examination of several CK subtypes that are more likely to be expressed in certain carcinomas than in others. For example, the CK 7+/CK 20- staining seen in this patient is characteristic of breast and lung cancers (among others), whereas CK 7+/CK 20+ staining would be expected in pancreatic, gastric, and urothelial cancers. A CK 7-/CK 20+ finding would be more suggestive of colon or mucinous ovarian cancer. Furthermore, approximately 70% of lung adenocarcinomas are TTF-1 positive and 60%-80% are napsin A positive. The negative findings in this patient's case make the diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer less likely.
Examination for the presence (or absence) of well-established biomarkers for breast cancer can potentially be helpful in suggesting the site of origin or in helping to define subsequent therapy. These markers include estrogen and progesterone receptors and HER2 overexpression. An additional biomarker, mammaglobin, has been reported to be expressed in 48% of breast cancers but is absent in cancers of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, ovary, and head and neck region.[2]
Of note, mammaglobin was found to be expressed in this patient. Although only 2% of the cells were reported to stain for the estrogen receptor, this finding is still considered positive and supports breast cancer as the correct diagnosis.
Recognized relevant prognostic factors in CUP include baseline performance status, the number and location of metastatic lesions, and the response to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Unfortunately, the overall prognosis associated with a diagnosis of CUP is poor, with median survival in various series reported to be less than 6 months. However, important exceptions to this outcome include women who present with an isolated metastatic axillary mass, as described in this case.
Previous reports of axillary adenopathy as the initial presentation of cancer in women revealed that the majority had evidence of cancer in the breast at the time of subsequent mastectomy.[3,4] As a result, in the absence of other indications found during routine workup (eg, a single pulmonary lesion suggestive of a primary lung cancer, pathologic findings inconsistent with breast cancer), an isolated adenocarcinoma in the breast (with no evidence of metastatic cancer elsewhere) should be treated as either stage II or stage III breast cancer. Note that this recommendation specifically relates to female patients. If a male patient has CUP with an isolated axillary mass, it is generally assumed that the lung is the origin of the malignancy.
In a female patient with negative mammographic findings, breast MRI can be helpful. In one series, 28 of 40 women (70%) with evidence of cancer in the axilla and a normal mammogram were found to have a breast abnormality on MRI.[5] Of note, and of considerable relevance to subsequent disease management, five of the 12 women with negative findings in this series underwent surgery, and in four of the cases no cancer was found. Although the number of participants in this series is limited, the absence of an MRI abnormality in the patient in this case can reasonably be considered in her future treatment plans.
Specifically, it might be suggested in this case that treatment include surgical removal of the axillary mass (if possible) followed by radiation to this area and the breast (rather than performing a mastectomy). Alternatively, treatment might begin with chemotherapy (a neoadjuvant approach) followed by surgery to remove any residual axillary mass and local/regional radiation or local/regional radiation alone. Adjuvant chemotherapy and/or hormonal therapy would then be administered.
The presence of a possible small pleural effusion is a concern because it potentially indicates more widespread metastatic disease, as does the mild elevation of the serum alkaline phosphatase level (eg, suggesting metastatic disease in bone or the liver). In the absence of other evidence of tumor spread, PET would not be unreasonable. A negative scan for evidence of metastatic disease would support a "curative" approach to the management of local disease in the axilla and presumably the breast, whereas a finding of other metastatic sites would lead to the conclusion that treatment should probably be delivered with more palliative intent.
The family history of cancer (father, paternal aunt with breast cancer, paternal grandmother with possible ovarian cancer) is intriguing and would suggest a role for genetic counseling and possibly genetic testing (eg, for BRCA mutation).
The patient in this case underwent PET. The only abnormality observed was in the left axilla. The axillary mass was subsequently resected. This was followed by curative radiation to both the axilla and left breast, adjuvant chemotherapy, and 5 years of hormonal therapy. The patient has showed no evidence of recurrence 2 years after completion of the hormonal treatment.
[polldaddy:10841207]
Discussion
The correct answer: Lung
The lungs are generally assumed to be the site of origin of the cancer in a male patient who has CUP with an isolated axillary mass. In contrast, the majority of women with axillary adenopathy as the initial presentation of cancer were found to have evidence of cancer in the breast at the time of subsequent mastectomy.[3,4]
[polldaddy:10837187]
Discussion
The correct answer: MRI
Breast MRI can be helpful in a female patient with negative mammographic findings. In one series, MRI detected a breast abnormality in 28 of 40 women (70%) with evidence of cancer in the axilla and a normal mammogram.[5]
Editor's Note:
The Case Challenge series includes difficult-to-diagnose conditions, some of which are not frequently encountered by most clinicians but are nonetheless important to accurately recognize. Test your diagnostic and treatment skills using the following patient scenario and corresponding questions. If you have a case that you would like to suggest for a future Case Challenge, please contact us .
Background
A 58-year-old woman seeks medical attention after she discovered a new mass in her left axilla during a routine monthly breast self-examination while showering. She has not noted any changes in either of her breasts. The mass in her left axilla is not tender, and she has not felt any other abnormal masses, including in her right axilla. She reports no other symptoms and specifically has no pain anywhere in her body. She also does not have shortness of breath, fever, night sweats, fatigue, rash, or abdominal discomfort or bloating.
Fifteen years earlier, the patient was diagnosed with high-grade, stage 1 cervical cancer and underwent surgery and chemoradiation. She has been closely monitored since that time with physical examinations and abdominal CT, with no evidence of recurrent disease. The patient has not had any other surgical procedure, except for removal of two basal cell carcinomas on her neck 4 years ago. She has had yearly routine mammograms for at least the past 15 years.
The patient has hypertension, which has been well controlled with the same medications for the past 10 years. She also has a 25-year history of type 2 diabetes mellitus, which is currently managed with diet alone. She had a "silent myocardial infarction" sometime within the past 5 years but has had no cardiac symptoms and is not taking any cardiac medications. She smoked approximately one pack of cigarettes a day for less than 2 years when she was "in her teens" but has not had any tobacco products since that time.
Pancreatic cancer was diagnosed in the patient's father at age 49 years, and breast cancer was diagnosed in her aunt on her father's side at age 67 years. Her paternal grandmother is reported to have died in her 60s after diagnosis of a "cancer in her stomach." No further information is available regarding either the actual diagnosis or the medical care provided to this individual.
To the best of the patient's knowledge, her mother's side of the family and her two brothers have no history of cancer. She has no sisters. Her mother is in her 80s and has mild dementia. The patient is not aware of any member of her family having undergone genetic testing.
Physical Examination and Workup
The patient appears well and is in no acute distress. The patient is afebrile, with a blood pressure of 135/85 mm Hg, a respiratory rate of 16 breaths/min, and a pulse of 72 beats/min. Her weight is 148 lb (67 kg), and she has no reported recent weight loss.
Examination of the skin reveals no suspicious lesions. Scars from the previous removal of the basal cell carcinomas are noted, but no evidence suggests recurrence.
Results of the head and neck examination are unremarkable; specifically, no abnormal cervical lymphadenopathy is detected. The cardiac and chest examination results are normal. The lungs are clear to percussion and auscultation. The breast examination reveals no abnormal masses. The right axilla is unremarkable; however, a single 3 × 2 cm, nontender, firm, movable but partially fixed mass is noted in the left axilla.
The abdomen appears normal, with no ascites or enlargement of the liver. The pelvic examination reveals evidence of previous surgery and local radiation but no signs of recurrence of cervical cancer. The lymph nodes appear normal, except for the findings noted above. Results of the neurologic examination are unremarkable.
Complete blood cell count, serum electrolyte levels, renal function tests, and urinalysis are all normal. Liver function tests are normal except for a mildly elevated serum alkaline phosphatase level. The fecal occult blood test result is negative.
Chest radiography reveals a suspicious small left-sided pleural effusion. No other abnormalities are observed, and no prior chest radiographs are available to compare with the current findings.
Chest CT confirms the presence of a possible small pleural effusion, with no other abnormalities noted. The radiologist suggests it will not be possible to obtain fluid safely through an interventional procedure, owing to the limited (if any) amount of fluid present. Furthermore, the radiologist recommends PET/CT to look for other evidence of metastatic cancer in the lungs or elsewhere.
Bilateral mammograms reveal no suspicious abnormalities, and the results are unchanged from a previous examination 11 months earlier. Figure 1 shows a similar bilateral mammogram in another patient. Breast MRI shows no evidence of cancer. Figure 2 shows similar breast MRI findings in another patient.


CT of the abdomen and pelvis reveals no changes compared with a scan obtained 2 years earlier for follow-up of the previous diagnosis of cervical cancer. Specifically, no evidence suggests ascites or any pelvic masses.
An incisional biopsy sample is obtained from the left axillary mass. Light microscopy reveals a moderately well-differentiated adenocarcinoma. Immunostaining shows the cancer to be cytokeratin (CK) 7 positive and CK 20 negative (CK 7+/CK 20-, thyroid transcription factor 1 (TTF-1) negative, thyroglobulin negative, napsin A negative, and mammaglobin positive. The tumor is estrogen receptor positive (2% staining), progesterone receptor negative, and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) negative.
[polldaddy:10837180]
Discussion
The correct answer: Breast.
This case is a classic example of cancer of unknown primary site or origin (CUP). CUP represents approximately 5% of cancers diagnosed in the United States (50,000 to 60,000 cases each year), with various series reporting that the site of origin is not diagnosed in between 2% and 6% of all cancer cases.[1] Worldwide, the incidence of CUP is even higher, resulting from the limited availability of sophisticated (and expensive) diagnostic technology in many regions. The median age at diagnosis of CUP is 60 years, and men and women are equally likely to be affected.
A cancer is considered a CUP if, after routine clinical assessment, physical and laboratory examination, standard imaging studies, and routine pathologic evaluation (biopsy or surgical removal of a metastatic mass lesion), a site of origin cannot be defined. With the availability of more sophisticated imaging technologies (eg, MRI), the overall percentage of cancers that are defined as a CUP has been reduced. However, even at autopsy, the site of origin of such cancer is often unable to be determined if the location was unknown before the patient's death.
Several theories have been proposed for why a metastatic lesion becomes clinically evident despite the site of origin of the cancer remaining obscure. These include (1) very slow growth of the primary cancer compared with that of the metastasis; (2) spontaneous regression of the primary cancer; (3) a prominent vascular component of the cancer, which enhances the rate of spread; and (4) unique molecular events associated with the cancer, which result in rapid progression and the growth of metastatic lesions.
Approximately 60% of CUPs are adenocarcinomas (well or moderately well differentiated); 25%-30% are poorly differentiated (including poorly differentiated adenocarcinomas); 5% are completely undifferentiated, with no defining histologic features; 5% are squamous cell cancers; and approximately 1% are carcinomas, with evidence of neuroendocrine differentiation.[1]
Immunohistochemical staining of biopsy material can be helpful in narrowing the possible anatomical sites of origin. The results are particularly relevant in the selection of therapeutic strategies and in ensuring that a rare, potentially highly curable cancer is not missed (eg, lymphoma, germ cell tumor).[2]
A critical initial test is examination of several CK subtypes that are more likely to be expressed in certain carcinomas than in others. For example, the CK 7+/CK 20- staining seen in this patient is characteristic of breast and lung cancers (among others), whereas CK 7+/CK 20+ staining would be expected in pancreatic, gastric, and urothelial cancers. A CK 7-/CK 20+ finding would be more suggestive of colon or mucinous ovarian cancer. Furthermore, approximately 70% of lung adenocarcinomas are TTF-1 positive and 60%-80% are napsin A positive. The negative findings in this patient's case make the diagnosis of metastatic lung cancer less likely.
Examination for the presence (or absence) of well-established biomarkers for breast cancer can potentially be helpful in suggesting the site of origin or in helping to define subsequent therapy. These markers include estrogen and progesterone receptors and HER2 overexpression. An additional biomarker, mammaglobin, has been reported to be expressed in 48% of breast cancers but is absent in cancers of the lung, gastrointestinal tract, ovary, and head and neck region.[2]
Of note, mammaglobin was found to be expressed in this patient. Although only 2% of the cells were reported to stain for the estrogen receptor, this finding is still considered positive and supports breast cancer as the correct diagnosis.
Recognized relevant prognostic factors in CUP include baseline performance status, the number and location of metastatic lesions, and the response to cytotoxic chemotherapy.
Unfortunately, the overall prognosis associated with a diagnosis of CUP is poor, with median survival in various series reported to be less than 6 months. However, important exceptions to this outcome include women who present with an isolated metastatic axillary mass, as described in this case.
Previous reports of axillary adenopathy as the initial presentation of cancer in women revealed that the majority had evidence of cancer in the breast at the time of subsequent mastectomy.[3,4] As a result, in the absence of other indications found during routine workup (eg, a single pulmonary lesion suggestive of a primary lung cancer, pathologic findings inconsistent with breast cancer), an isolated adenocarcinoma in the breast (with no evidence of metastatic cancer elsewhere) should be treated as either stage II or stage III breast cancer. Note that this recommendation specifically relates to female patients. If a male patient has CUP with an isolated axillary mass, it is generally assumed that the lung is the origin of the malignancy.
In a female patient with negative mammographic findings, breast MRI can be helpful. In one series, 28 of 40 women (70%) with evidence of cancer in the axilla and a normal mammogram were found to have a breast abnormality on MRI.[5] Of note, and of considerable relevance to subsequent disease management, five of the 12 women with negative findings in this series underwent surgery, and in four of the cases no cancer was found. Although the number of participants in this series is limited, the absence of an MRI abnormality in the patient in this case can reasonably be considered in her future treatment plans.
Specifically, it might be suggested in this case that treatment include surgical removal of the axillary mass (if possible) followed by radiation to this area and the breast (rather than performing a mastectomy). Alternatively, treatment might begin with chemotherapy (a neoadjuvant approach) followed by surgery to remove any residual axillary mass and local/regional radiation or local/regional radiation alone. Adjuvant chemotherapy and/or hormonal therapy would then be administered.
The presence of a possible small pleural effusion is a concern because it potentially indicates more widespread metastatic disease, as does the mild elevation of the serum alkaline phosphatase level (eg, suggesting metastatic disease in bone or the liver). In the absence of other evidence of tumor spread, PET would not be unreasonable. A negative scan for evidence of metastatic disease would support a "curative" approach to the management of local disease in the axilla and presumably the breast, whereas a finding of other metastatic sites would lead to the conclusion that treatment should probably be delivered with more palliative intent.
The family history of cancer (father, paternal aunt with breast cancer, paternal grandmother with possible ovarian cancer) is intriguing and would suggest a role for genetic counseling and possibly genetic testing (eg, for BRCA mutation).
The patient in this case underwent PET. The only abnormality observed was in the left axilla. The axillary mass was subsequently resected. This was followed by curative radiation to both the axilla and left breast, adjuvant chemotherapy, and 5 years of hormonal therapy. The patient has showed no evidence of recurrence 2 years after completion of the hormonal treatment.
[polldaddy:10841207]
Discussion
The correct answer: Lung
The lungs are generally assumed to be the site of origin of the cancer in a male patient who has CUP with an isolated axillary mass. In contrast, the majority of women with axillary adenopathy as the initial presentation of cancer were found to have evidence of cancer in the breast at the time of subsequent mastectomy.[3,4]
[polldaddy:10837187]
Discussion
The correct answer: MRI
Breast MRI can be helpful in a female patient with negative mammographic findings. In one series, MRI detected a breast abnormality in 28 of 40 women (70%) with evidence of cancer in the axilla and a normal mammogram.[5]
Cell-free DNA improves response prediction in breast cancer
When the two techniques were in agreement, the accuracy of response prediction was 92.6% in the study, with a predictive value for complete response of 87.5% and a predictive value for absence of complete response of 94.7%, which was substantially better than either method alone.
“Our work identifies a new parameter that is easily combinable with MRI for a more accurate prediction of response following neoadjuvant treatment, with possible implications for current protocols for the evaluation of nodal residual disease,” researcher Francesco Ravera, MD, PhD, of the University of Genoa (Italy), said in a press release.
Dr. Ravera and colleagues presented their research in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract LB063).
Accurate response prediction is important because it guides subsequent surgical management, Dr. Ravera and colleagues noted. Pathological complete responders – generally about 25% of patients after neoadjuvant therapy – typically undergo a sentinel lymph node biopsy to ensure cancer hasn’t spread, while incomplete responders often have a complete axillary lymph node dissection.
Response is currently assessed by MRI, but accuracy is suboptimal, the researchers noted. A more accurate method might “allow the omission of sentinel lymph node biopsy in complete responders, which could be replaced by longitudinal radiologic monitoring. This would represent substantial progress in the pursuit of an effective, minimally invasive treatment,” Dr. Ravera said.
He and his colleagues turned to plasma cfDNA because it has shown potential for providing useful diagnostic, recurrence, and treatment response information in neoplastic patients.
When healthy cells die, they release similarly sized DNA fragments into the blood, but cancer cells release fragments of varying sizes. The heart of the research was using electrophoresis to assess the degree of fragmentation – called cfDNA integrity – in plasma samples from 38 patients after anthracycline/taxane-based regimens.
The researchers compared how well cfDNA, preoperative MRI, and the combination of the two methods predicted response according to surgical histology.
A total of 11 patients had pathological complete responses to neoadjuvant therapy.
The ratio of large 321-1,000 base pair sized fragments to smaller 150-220 base pair sized fragments, which the team dubbed the “cfDNA integrity index,” best predicted response. At a cutoff above 2.71, the index was 81.6% accurate in predicting pathological complete response, with a sensitivity of 81.8% and specificity of 81.5%.
The predictive power wasn’t much better than MRI, which was 77.1% accurate, with a sensitivity of 72.7% and a specificity of 81.5%.
The two techniques were concordant in their prediction in over two-thirds of patients. When the techniques agreed, accuracy was over 90%.
Prospective studies are needed to evaluate the cfDNA integrity index in combination with MRI, the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the University of Genoa and others. Dr. Ravera disclosed no conflicts of interest.
When the two techniques were in agreement, the accuracy of response prediction was 92.6% in the study, with a predictive value for complete response of 87.5% and a predictive value for absence of complete response of 94.7%, which was substantially better than either method alone.
“Our work identifies a new parameter that is easily combinable with MRI for a more accurate prediction of response following neoadjuvant treatment, with possible implications for current protocols for the evaluation of nodal residual disease,” researcher Francesco Ravera, MD, PhD, of the University of Genoa (Italy), said in a press release.
Dr. Ravera and colleagues presented their research in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract LB063).
Accurate response prediction is important because it guides subsequent surgical management, Dr. Ravera and colleagues noted. Pathological complete responders – generally about 25% of patients after neoadjuvant therapy – typically undergo a sentinel lymph node biopsy to ensure cancer hasn’t spread, while incomplete responders often have a complete axillary lymph node dissection.
Response is currently assessed by MRI, but accuracy is suboptimal, the researchers noted. A more accurate method might “allow the omission of sentinel lymph node biopsy in complete responders, which could be replaced by longitudinal radiologic monitoring. This would represent substantial progress in the pursuit of an effective, minimally invasive treatment,” Dr. Ravera said.
He and his colleagues turned to plasma cfDNA because it has shown potential for providing useful diagnostic, recurrence, and treatment response information in neoplastic patients.
When healthy cells die, they release similarly sized DNA fragments into the blood, but cancer cells release fragments of varying sizes. The heart of the research was using electrophoresis to assess the degree of fragmentation – called cfDNA integrity – in plasma samples from 38 patients after anthracycline/taxane-based regimens.
The researchers compared how well cfDNA, preoperative MRI, and the combination of the two methods predicted response according to surgical histology.
A total of 11 patients had pathological complete responses to neoadjuvant therapy.
The ratio of large 321-1,000 base pair sized fragments to smaller 150-220 base pair sized fragments, which the team dubbed the “cfDNA integrity index,” best predicted response. At a cutoff above 2.71, the index was 81.6% accurate in predicting pathological complete response, with a sensitivity of 81.8% and specificity of 81.5%.
The predictive power wasn’t much better than MRI, which was 77.1% accurate, with a sensitivity of 72.7% and a specificity of 81.5%.
The two techniques were concordant in their prediction in over two-thirds of patients. When the techniques agreed, accuracy was over 90%.
Prospective studies are needed to evaluate the cfDNA integrity index in combination with MRI, the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the University of Genoa and others. Dr. Ravera disclosed no conflicts of interest.
When the two techniques were in agreement, the accuracy of response prediction was 92.6% in the study, with a predictive value for complete response of 87.5% and a predictive value for absence of complete response of 94.7%, which was substantially better than either method alone.
“Our work identifies a new parameter that is easily combinable with MRI for a more accurate prediction of response following neoadjuvant treatment, with possible implications for current protocols for the evaluation of nodal residual disease,” researcher Francesco Ravera, MD, PhD, of the University of Genoa (Italy), said in a press release.
Dr. Ravera and colleagues presented their research in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 (Abstract LB063).
Accurate response prediction is important because it guides subsequent surgical management, Dr. Ravera and colleagues noted. Pathological complete responders – generally about 25% of patients after neoadjuvant therapy – typically undergo a sentinel lymph node biopsy to ensure cancer hasn’t spread, while incomplete responders often have a complete axillary lymph node dissection.
Response is currently assessed by MRI, but accuracy is suboptimal, the researchers noted. A more accurate method might “allow the omission of sentinel lymph node biopsy in complete responders, which could be replaced by longitudinal radiologic monitoring. This would represent substantial progress in the pursuit of an effective, minimally invasive treatment,” Dr. Ravera said.
He and his colleagues turned to plasma cfDNA because it has shown potential for providing useful diagnostic, recurrence, and treatment response information in neoplastic patients.
When healthy cells die, they release similarly sized DNA fragments into the blood, but cancer cells release fragments of varying sizes. The heart of the research was using electrophoresis to assess the degree of fragmentation – called cfDNA integrity – in plasma samples from 38 patients after anthracycline/taxane-based regimens.
The researchers compared how well cfDNA, preoperative MRI, and the combination of the two methods predicted response according to surgical histology.
A total of 11 patients had pathological complete responses to neoadjuvant therapy.
The ratio of large 321-1,000 base pair sized fragments to smaller 150-220 base pair sized fragments, which the team dubbed the “cfDNA integrity index,” best predicted response. At a cutoff above 2.71, the index was 81.6% accurate in predicting pathological complete response, with a sensitivity of 81.8% and specificity of 81.5%.
The predictive power wasn’t much better than MRI, which was 77.1% accurate, with a sensitivity of 72.7% and a specificity of 81.5%.
The two techniques were concordant in their prediction in over two-thirds of patients. When the techniques agreed, accuracy was over 90%.
Prospective studies are needed to evaluate the cfDNA integrity index in combination with MRI, the researchers concluded.
The study was sponsored by the University of Genoa and others. Dr. Ravera disclosed no conflicts of interest.
FROM AACR 2021
Quicker fertility rebound in young women with breast cancer
Researchers found that omitting cyclophosphamide from a regimen of epirubicin and paclitaxel increased the likelihood of an early return of menses, and there was a trend toward improved disease-free survival.
The phase 3 SPECTRUM trial involved 521 women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who had undergone definitive surgery at one of eight institutions in China. The average age of the patients was 34 years.
Cyclophosphamide is a standard component of adjuvant chemotherapy, but it’s strongly associated with premature ovarian failure and infertility.
“For the first time, we demonstrate that a cyclophosphamide-free regimen [can] increase the rate of menses recovery without compromising survival,” said the researchers, led by Ke-Da Yu, MD, PhD, of the Fudan University Shanghai (China) Cancer Center.
They also reported that, among the women who tried to conceive at a later date, there was a higher pregnancy success rate among those who did not take cyclophosphamide.
“Our findings can be extrapolated to patients with other subtypes of breast cancer, such as triple-negative or HER2-enriched, because the effect of paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide on menstrual resumption is not subtype specific,” the investigators commented.
The results were published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
This is the first prospective trial specifically designed to find an adjuvant breast cancer regimen less toxic to the ovaries. The “investigators ... should be applauded,” wrote Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, of the University of Genova (Italy), and Ann Partridge, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Although promising, there are a few caveats, the editorialists wrote. In a past trial of doxorubicin and docetaxel in lieu of a cyclophosphamide regimen, disease outcomes were inferior. There is also a question as to whether the SPECTRUM results apply to non-Asian women.
The editorialists also noted that enrollment in this trial ended in 2016, before it was recommended that ovarian suppression be used in conjunction with adjuvant chemotherapy to prevent premature menopause.
“[It’s] notable that the absolute benefit in reducing [premature ovarian insufficiency] rates with the use of a cyclophosphamide-free regimen is similar to the effect demonstrated with the administration of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy,” they commented. It’s possible that combining the two approaches might have an additive effect, but for now the possibility remains unknown.
In addition, the SPECTRUM trial predates the widespread use of genetic testing to guide treatment, the editorialists pointed out.
“Therefore, caution should be taken in adopting wholesale such regimens,” Dr. Lambertini and Dr. Partridge said.
Switch to paclitaxel
The research team was inspired by previous reports that swapping out cyclophosphamide for paclitaxel did not reduce adjuvant efficacy in the general breast cancer population.
The SPECTRUM trial randomly assigned 260 women to receive a cyclophosphamide-free regimen of epirubicin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks.
Another 261 women were randomly assigned to receive cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) and epirubicin (75 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks. These patients constituted the control group.
A year after completing chemotherapy, 63.1% of the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 48.3% of the control group, had resumed menses, defined as having two consecutive menstrual cycles or one cycle but with premenopausal levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (P < .001).
Another caveat of the study is that assessments of women who resumed menses were conducted at the 1-year point; rates may have been higher in the cyclophosphamide arm had the investigators conducted the assessments at 2 years, the editorialists said.
The 5-year disease-free survival was 84.7% in the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 78.3% in the control group, an absolute difference of 14.8% (P = .07).
Patients with node-positive disease appeared to benefit the most from cyclophosphamide sparing.
There were no statistically significant differences in overall or distant disease-free survival.
Higher pregnancy rates
Almost 18% of women in the experimental arm reported trying to conceive, and 9.6% of them did so. About 10% of women in the cyclophosphamide arm tried to conceive, and 2.7% did so (P = .03).
The median interval between randomization and pregnancy was 42 months.
For all of the women who became pregnant, endocrine therapy was interrupted. “Women who temporarily interrupt endocrine therapy due to pregnancy should be reminded to resume endocrine therapy following attempted or successful pregnancy,” the investigators wrote.
The patients were taking tamoxifen at least 5 years after receiving chemotherapy, most often as monotherapy. About 5% of the patients underwent up-front ovarian suppression with an aromatase inhibitor, which is a current standard option.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other organizations. The investigators and Dr. Partridge disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lambertini has consulted for and/or has received speakers fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers found that omitting cyclophosphamide from a regimen of epirubicin and paclitaxel increased the likelihood of an early return of menses, and there was a trend toward improved disease-free survival.
The phase 3 SPECTRUM trial involved 521 women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who had undergone definitive surgery at one of eight institutions in China. The average age of the patients was 34 years.
Cyclophosphamide is a standard component of adjuvant chemotherapy, but it’s strongly associated with premature ovarian failure and infertility.
“For the first time, we demonstrate that a cyclophosphamide-free regimen [can] increase the rate of menses recovery without compromising survival,” said the researchers, led by Ke-Da Yu, MD, PhD, of the Fudan University Shanghai (China) Cancer Center.
They also reported that, among the women who tried to conceive at a later date, there was a higher pregnancy success rate among those who did not take cyclophosphamide.
“Our findings can be extrapolated to patients with other subtypes of breast cancer, such as triple-negative or HER2-enriched, because the effect of paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide on menstrual resumption is not subtype specific,” the investigators commented.
The results were published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
This is the first prospective trial specifically designed to find an adjuvant breast cancer regimen less toxic to the ovaries. The “investigators ... should be applauded,” wrote Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, of the University of Genova (Italy), and Ann Partridge, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Although promising, there are a few caveats, the editorialists wrote. In a past trial of doxorubicin and docetaxel in lieu of a cyclophosphamide regimen, disease outcomes were inferior. There is also a question as to whether the SPECTRUM results apply to non-Asian women.
The editorialists also noted that enrollment in this trial ended in 2016, before it was recommended that ovarian suppression be used in conjunction with adjuvant chemotherapy to prevent premature menopause.
“[It’s] notable that the absolute benefit in reducing [premature ovarian insufficiency] rates with the use of a cyclophosphamide-free regimen is similar to the effect demonstrated with the administration of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy,” they commented. It’s possible that combining the two approaches might have an additive effect, but for now the possibility remains unknown.
In addition, the SPECTRUM trial predates the widespread use of genetic testing to guide treatment, the editorialists pointed out.
“Therefore, caution should be taken in adopting wholesale such regimens,” Dr. Lambertini and Dr. Partridge said.
Switch to paclitaxel
The research team was inspired by previous reports that swapping out cyclophosphamide for paclitaxel did not reduce adjuvant efficacy in the general breast cancer population.
The SPECTRUM trial randomly assigned 260 women to receive a cyclophosphamide-free regimen of epirubicin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks.
Another 261 women were randomly assigned to receive cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) and epirubicin (75 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks. These patients constituted the control group.
A year after completing chemotherapy, 63.1% of the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 48.3% of the control group, had resumed menses, defined as having two consecutive menstrual cycles or one cycle but with premenopausal levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (P < .001).
Another caveat of the study is that assessments of women who resumed menses were conducted at the 1-year point; rates may have been higher in the cyclophosphamide arm had the investigators conducted the assessments at 2 years, the editorialists said.
The 5-year disease-free survival was 84.7% in the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 78.3% in the control group, an absolute difference of 14.8% (P = .07).
Patients with node-positive disease appeared to benefit the most from cyclophosphamide sparing.
There were no statistically significant differences in overall or distant disease-free survival.
Higher pregnancy rates
Almost 18% of women in the experimental arm reported trying to conceive, and 9.6% of them did so. About 10% of women in the cyclophosphamide arm tried to conceive, and 2.7% did so (P = .03).
The median interval between randomization and pregnancy was 42 months.
For all of the women who became pregnant, endocrine therapy was interrupted. “Women who temporarily interrupt endocrine therapy due to pregnancy should be reminded to resume endocrine therapy following attempted or successful pregnancy,” the investigators wrote.
The patients were taking tamoxifen at least 5 years after receiving chemotherapy, most often as monotherapy. About 5% of the patients underwent up-front ovarian suppression with an aromatase inhibitor, which is a current standard option.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other organizations. The investigators and Dr. Partridge disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lambertini has consulted for and/or has received speakers fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Researchers found that omitting cyclophosphamide from a regimen of epirubicin and paclitaxel increased the likelihood of an early return of menses, and there was a trend toward improved disease-free survival.
The phase 3 SPECTRUM trial involved 521 women with estrogen receptor–positive, HER2-negative breast cancer who had undergone definitive surgery at one of eight institutions in China. The average age of the patients was 34 years.
Cyclophosphamide is a standard component of adjuvant chemotherapy, but it’s strongly associated with premature ovarian failure and infertility.
“For the first time, we demonstrate that a cyclophosphamide-free regimen [can] increase the rate of menses recovery without compromising survival,” said the researchers, led by Ke-Da Yu, MD, PhD, of the Fudan University Shanghai (China) Cancer Center.
They also reported that, among the women who tried to conceive at a later date, there was a higher pregnancy success rate among those who did not take cyclophosphamide.
“Our findings can be extrapolated to patients with other subtypes of breast cancer, such as triple-negative or HER2-enriched, because the effect of paclitaxel and cyclophosphamide on menstrual resumption is not subtype specific,” the investigators commented.
The results were published online in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute.
This is the first prospective trial specifically designed to find an adjuvant breast cancer regimen less toxic to the ovaries. The “investigators ... should be applauded,” wrote Matteo Lambertini, MD, PhD, of the University of Genova (Italy), and Ann Partridge, MD, of the Dana-Farber Cancer Institute in Boston, in an accompanying editorial.
Although promising, there are a few caveats, the editorialists wrote. In a past trial of doxorubicin and docetaxel in lieu of a cyclophosphamide regimen, disease outcomes were inferior. There is also a question as to whether the SPECTRUM results apply to non-Asian women.
The editorialists also noted that enrollment in this trial ended in 2016, before it was recommended that ovarian suppression be used in conjunction with adjuvant chemotherapy to prevent premature menopause.
“[It’s] notable that the absolute benefit in reducing [premature ovarian insufficiency] rates with the use of a cyclophosphamide-free regimen is similar to the effect demonstrated with the administration of a gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonist during cyclophosphamide-based chemotherapy,” they commented. It’s possible that combining the two approaches might have an additive effect, but for now the possibility remains unknown.
In addition, the SPECTRUM trial predates the widespread use of genetic testing to guide treatment, the editorialists pointed out.
“Therefore, caution should be taken in adopting wholesale such regimens,” Dr. Lambertini and Dr. Partridge said.
Switch to paclitaxel
The research team was inspired by previous reports that swapping out cyclophosphamide for paclitaxel did not reduce adjuvant efficacy in the general breast cancer population.
The SPECTRUM trial randomly assigned 260 women to receive a cyclophosphamide-free regimen of epirubicin (75 mg/m2) and paclitaxel (175 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks.
Another 261 women were randomly assigned to receive cyclophosphamide (600 mg/m2) and epirubicin (75 mg/m2) every 3 weeks for four cycles followed by weekly paclitaxel (80 mg/m2) for 12 weeks. These patients constituted the control group.
A year after completing chemotherapy, 63.1% of the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 48.3% of the control group, had resumed menses, defined as having two consecutive menstrual cycles or one cycle but with premenopausal levels of estradiol and follicle-stimulating hormone (P < .001).
Another caveat of the study is that assessments of women who resumed menses were conducted at the 1-year point; rates may have been higher in the cyclophosphamide arm had the investigators conducted the assessments at 2 years, the editorialists said.
The 5-year disease-free survival was 84.7% in the cyclophosphamide-free arm versus 78.3% in the control group, an absolute difference of 14.8% (P = .07).
Patients with node-positive disease appeared to benefit the most from cyclophosphamide sparing.
There were no statistically significant differences in overall or distant disease-free survival.
Higher pregnancy rates
Almost 18% of women in the experimental arm reported trying to conceive, and 9.6% of them did so. About 10% of women in the cyclophosphamide arm tried to conceive, and 2.7% did so (P = .03).
The median interval between randomization and pregnancy was 42 months.
For all of the women who became pregnant, endocrine therapy was interrupted. “Women who temporarily interrupt endocrine therapy due to pregnancy should be reminded to resume endocrine therapy following attempted or successful pregnancy,” the investigators wrote.
The patients were taking tamoxifen at least 5 years after receiving chemotherapy, most often as monotherapy. About 5% of the patients underwent up-front ovarian suppression with an aromatase inhibitor, which is a current standard option.
The study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China and other organizations. The investigators and Dr. Partridge disclosed no relevant financial relationships. Dr. Lambertini has consulted for and/or has received speakers fees from Roche, AstraZeneca, Lilly, Novartis, and other companies.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Ubrogepant safety and efficacy not affected by triptan therapy
according to a study published in Headache.
“The goal is to get migraine attacks under control as quickly as you can with as few adverse events as possible,” said lead author Andrew Blumenfeld, MD, director of the Headache Center of Southern California in Carlsbad, California. “Ubrogepant is very efficacious and well tolerated because it has few adverse events.”
Migraine disorder is the third most prevalent disease, and at least one person living in 25% of all U.S. households has the condition.
Clinicians have a wide range of medications at their disposal to treat migraines. These drug classes include triptans, ditans, NSAIDs, dihydroergotamine, and combination analgesics. Although numerous pharmacologic options are available to manage this patient population, an estimated 95% of patients who take oral medications to alleviate their migraine symptoms still fail to achieve relief with at least one acute episode.
Triptans remain a common option and first-line choice for acute migraine relief, but poor tolerability, among other factors, continue to limit their effectiveness. Moreover, their vasoconstrictive properties preclude their use in specific patient populations, such as those who have hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and cerebral vascular accident. These circumstances, combined with other unmet clinical needs in migraine, have prompted researchers to explore new options, including a newer class of drugs – CGRP receptor antagonists. An endogenous protein, CGRP, has inflammatory and pronociceptive properties that play an active role in contributing to migraine pathogenesis.
Efficacy analyzed by triptan response
To investigate the effects of anti-CGRP treatment in patients with migraine who have a previous history of triptan use, researchers conducted two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, single-attack trials, known as ACHIEVE I and ACHIEVE II.
Trial participants ranged in age from 18 to 75 years with a documented history of migraines with or without aura. In ACHIEVE I, investigators randomized 1,327 participants 1:1:1 to receive placebo, ubrogepant 50 mg, or ubrogepant 100 mg and placebo. Randomized patients in ACHIEVE II (n = 1,355) received placebo, ubrogepant 25 mg, or ubrogepant 50 mg to treat a single episode. During the screening process, researchers further placed patients in one of three groups based on their previous triptan use – triptan responder, triptan-insufficient responder, and triptan naive. Patients were further randomized based on their previous experience with triptans and whether they currently used them for migraine prevention. Patients participating in the study had up to 60 days to treat one qualifying migraine of moderate or severe nature at home.
The studies had two primary endpoints. The first was freedom from pain at the 2-hour mark following the initial dose, defined as decreased headache severity from moderate or severe at baseline to no pain. The other primary endpoint was the absence of most bothersome migraine-associated symptom (MBS) – photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea – 2 hours after the initial ubrogepant dose.
The pooled analysis collated data from 1,799 patients in both studies (placebo, n = 912; ubrogepant 50 mg, n = 887). Patients fell into the following categories: 682 triptan responders (placebo, n = 350; ubrogepant, n = 332); 451 triptan-insufficient responders (placebo, n = 223; ubrogepant, n = 228), and 666 triptan naive (placebo, n = 339; ubrogepant, n = 337).
Based on the data, approximately 25% of the patients enrolled in the study fell into the triptan-insufficient category. Of this subpopulation, about 80% of the patients in each treatment group experienced insufficient efficacy when using triptans. In each treatment group of insufficient responders, approximately 17% of patients cited tolerability issues, and 3% had contraindications that precluded them from triptan therapy.
The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and treatment-related TEAEs did not differ appreciably across historical triptan experience subgroups. The highest percentage of participants experiencing a treatment-related TEAE in the pooled ubrogepant 50-mg treatment group was found in the triptan-insufficient responders (10.4%), whereas the highest percentage in the placebo group was found in the triptan-naive subgroup (9.7%). No serious AEs (SAEs) were reported in any subgroup.
The researchers concluded that “ubrogepant efficacy and tolerability did not differ for the acute treatment of migraine in participants classified as triptan responders, triptan-insufficient responders, and triptan naive based on their historical experience with triptans.”
Payers limit use
Despite the promising data, payer hurdles limit ubrogepant’s use, said Stewart Tepper, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Tepper, a professor of neurology at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., was not involved in the study. “The study shows that ubrogepant will work as well as those who have not responded well to triptans, which is key,” Dr. Tepper said. “However, payers have set up step edits in which patients aren’t allowed to get ubrogepant unless they fail therapy with at least two triptans.”
Dr. Blumenfeld discounts the rationale behind requiring patients to try a second triptan after failing initial triptan therapy. “There are plenty of studies showing that if you fail one triptan, you’re likely to fail another,” he said. “Why would you put the patient on a different triptan when you could switch them to another drug with a different mechanism of action?”
The results showed that more patients in the ubrogepant 50-mg arm achieved pain freedom than those in the placebo arm within 2 hours after the initial dose in each group.
“Migraine is a very disabling condition, so you want to get the attack under control as quickly as possible while limiting the risk for potential side effects,” said Dr. Blumenfeld. “Ubrogepant is very efficacious and with very few adverse effects, but its use is limited because insurance companies require the failure of several triptans.”
One limitation of the study is that it is a subanalysis.
Dr. Blumenfeld has disclosed advisory board service, consulting, speaking, and authorship for AbbVie, Alder, Amgen, Biohaven, Lilly, Novartis, Teva, Theranica, and Zoscano.
according to a study published in Headache.
“The goal is to get migraine attacks under control as quickly as you can with as few adverse events as possible,” said lead author Andrew Blumenfeld, MD, director of the Headache Center of Southern California in Carlsbad, California. “Ubrogepant is very efficacious and well tolerated because it has few adverse events.”
Migraine disorder is the third most prevalent disease, and at least one person living in 25% of all U.S. households has the condition.
Clinicians have a wide range of medications at their disposal to treat migraines. These drug classes include triptans, ditans, NSAIDs, dihydroergotamine, and combination analgesics. Although numerous pharmacologic options are available to manage this patient population, an estimated 95% of patients who take oral medications to alleviate their migraine symptoms still fail to achieve relief with at least one acute episode.
Triptans remain a common option and first-line choice for acute migraine relief, but poor tolerability, among other factors, continue to limit their effectiveness. Moreover, their vasoconstrictive properties preclude their use in specific patient populations, such as those who have hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and cerebral vascular accident. These circumstances, combined with other unmet clinical needs in migraine, have prompted researchers to explore new options, including a newer class of drugs – CGRP receptor antagonists. An endogenous protein, CGRP, has inflammatory and pronociceptive properties that play an active role in contributing to migraine pathogenesis.
Efficacy analyzed by triptan response
To investigate the effects of anti-CGRP treatment in patients with migraine who have a previous history of triptan use, researchers conducted two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, single-attack trials, known as ACHIEVE I and ACHIEVE II.
Trial participants ranged in age from 18 to 75 years with a documented history of migraines with or without aura. In ACHIEVE I, investigators randomized 1,327 participants 1:1:1 to receive placebo, ubrogepant 50 mg, or ubrogepant 100 mg and placebo. Randomized patients in ACHIEVE II (n = 1,355) received placebo, ubrogepant 25 mg, or ubrogepant 50 mg to treat a single episode. During the screening process, researchers further placed patients in one of three groups based on their previous triptan use – triptan responder, triptan-insufficient responder, and triptan naive. Patients were further randomized based on their previous experience with triptans and whether they currently used them for migraine prevention. Patients participating in the study had up to 60 days to treat one qualifying migraine of moderate or severe nature at home.
The studies had two primary endpoints. The first was freedom from pain at the 2-hour mark following the initial dose, defined as decreased headache severity from moderate or severe at baseline to no pain. The other primary endpoint was the absence of most bothersome migraine-associated symptom (MBS) – photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea – 2 hours after the initial ubrogepant dose.
The pooled analysis collated data from 1,799 patients in both studies (placebo, n = 912; ubrogepant 50 mg, n = 887). Patients fell into the following categories: 682 triptan responders (placebo, n = 350; ubrogepant, n = 332); 451 triptan-insufficient responders (placebo, n = 223; ubrogepant, n = 228), and 666 triptan naive (placebo, n = 339; ubrogepant, n = 337).
Based on the data, approximately 25% of the patients enrolled in the study fell into the triptan-insufficient category. Of this subpopulation, about 80% of the patients in each treatment group experienced insufficient efficacy when using triptans. In each treatment group of insufficient responders, approximately 17% of patients cited tolerability issues, and 3% had contraindications that precluded them from triptan therapy.
The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and treatment-related TEAEs did not differ appreciably across historical triptan experience subgroups. The highest percentage of participants experiencing a treatment-related TEAE in the pooled ubrogepant 50-mg treatment group was found in the triptan-insufficient responders (10.4%), whereas the highest percentage in the placebo group was found in the triptan-naive subgroup (9.7%). No serious AEs (SAEs) were reported in any subgroup.
The researchers concluded that “ubrogepant efficacy and tolerability did not differ for the acute treatment of migraine in participants classified as triptan responders, triptan-insufficient responders, and triptan naive based on their historical experience with triptans.”
Payers limit use
Despite the promising data, payer hurdles limit ubrogepant’s use, said Stewart Tepper, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Tepper, a professor of neurology at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., was not involved in the study. “The study shows that ubrogepant will work as well as those who have not responded well to triptans, which is key,” Dr. Tepper said. “However, payers have set up step edits in which patients aren’t allowed to get ubrogepant unless they fail therapy with at least two triptans.”
Dr. Blumenfeld discounts the rationale behind requiring patients to try a second triptan after failing initial triptan therapy. “There are plenty of studies showing that if you fail one triptan, you’re likely to fail another,” he said. “Why would you put the patient on a different triptan when you could switch them to another drug with a different mechanism of action?”
The results showed that more patients in the ubrogepant 50-mg arm achieved pain freedom than those in the placebo arm within 2 hours after the initial dose in each group.
“Migraine is a very disabling condition, so you want to get the attack under control as quickly as possible while limiting the risk for potential side effects,” said Dr. Blumenfeld. “Ubrogepant is very efficacious and with very few adverse effects, but its use is limited because insurance companies require the failure of several triptans.”
One limitation of the study is that it is a subanalysis.
Dr. Blumenfeld has disclosed advisory board service, consulting, speaking, and authorship for AbbVie, Alder, Amgen, Biohaven, Lilly, Novartis, Teva, Theranica, and Zoscano.
according to a study published in Headache.
“The goal is to get migraine attacks under control as quickly as you can with as few adverse events as possible,” said lead author Andrew Blumenfeld, MD, director of the Headache Center of Southern California in Carlsbad, California. “Ubrogepant is very efficacious and well tolerated because it has few adverse events.”
Migraine disorder is the third most prevalent disease, and at least one person living in 25% of all U.S. households has the condition.
Clinicians have a wide range of medications at their disposal to treat migraines. These drug classes include triptans, ditans, NSAIDs, dihydroergotamine, and combination analgesics. Although numerous pharmacologic options are available to manage this patient population, an estimated 95% of patients who take oral medications to alleviate their migraine symptoms still fail to achieve relief with at least one acute episode.
Triptans remain a common option and first-line choice for acute migraine relief, but poor tolerability, among other factors, continue to limit their effectiveness. Moreover, their vasoconstrictive properties preclude their use in specific patient populations, such as those who have hypertension, peripheral vascular disease, and cerebral vascular accident. These circumstances, combined with other unmet clinical needs in migraine, have prompted researchers to explore new options, including a newer class of drugs – CGRP receptor antagonists. An endogenous protein, CGRP, has inflammatory and pronociceptive properties that play an active role in contributing to migraine pathogenesis.
Efficacy analyzed by triptan response
To investigate the effects of anti-CGRP treatment in patients with migraine who have a previous history of triptan use, researchers conducted two phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicenter, single-attack trials, known as ACHIEVE I and ACHIEVE II.
Trial participants ranged in age from 18 to 75 years with a documented history of migraines with or without aura. In ACHIEVE I, investigators randomized 1,327 participants 1:1:1 to receive placebo, ubrogepant 50 mg, or ubrogepant 100 mg and placebo. Randomized patients in ACHIEVE II (n = 1,355) received placebo, ubrogepant 25 mg, or ubrogepant 50 mg to treat a single episode. During the screening process, researchers further placed patients in one of three groups based on their previous triptan use – triptan responder, triptan-insufficient responder, and triptan naive. Patients were further randomized based on their previous experience with triptans and whether they currently used them for migraine prevention. Patients participating in the study had up to 60 days to treat one qualifying migraine of moderate or severe nature at home.
The studies had two primary endpoints. The first was freedom from pain at the 2-hour mark following the initial dose, defined as decreased headache severity from moderate or severe at baseline to no pain. The other primary endpoint was the absence of most bothersome migraine-associated symptom (MBS) – photophobia, phonophobia, or nausea – 2 hours after the initial ubrogepant dose.
The pooled analysis collated data from 1,799 patients in both studies (placebo, n = 912; ubrogepant 50 mg, n = 887). Patients fell into the following categories: 682 triptan responders (placebo, n = 350; ubrogepant, n = 332); 451 triptan-insufficient responders (placebo, n = 223; ubrogepant, n = 228), and 666 triptan naive (placebo, n = 339; ubrogepant, n = 337).
Based on the data, approximately 25% of the patients enrolled in the study fell into the triptan-insufficient category. Of this subpopulation, about 80% of the patients in each treatment group experienced insufficient efficacy when using triptans. In each treatment group of insufficient responders, approximately 17% of patients cited tolerability issues, and 3% had contraindications that precluded them from triptan therapy.
The incidence of treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) and treatment-related TEAEs did not differ appreciably across historical triptan experience subgroups. The highest percentage of participants experiencing a treatment-related TEAE in the pooled ubrogepant 50-mg treatment group was found in the triptan-insufficient responders (10.4%), whereas the highest percentage in the placebo group was found in the triptan-naive subgroup (9.7%). No serious AEs (SAEs) were reported in any subgroup.
The researchers concluded that “ubrogepant efficacy and tolerability did not differ for the acute treatment of migraine in participants classified as triptan responders, triptan-insufficient responders, and triptan naive based on their historical experience with triptans.”
Payers limit use
Despite the promising data, payer hurdles limit ubrogepant’s use, said Stewart Tepper, MD, who was asked to comment on the study. Dr. Tepper, a professor of neurology at the Geisel School of Medicine at Dartmouth, Hanover, N.H., was not involved in the study. “The study shows that ubrogepant will work as well as those who have not responded well to triptans, which is key,” Dr. Tepper said. “However, payers have set up step edits in which patients aren’t allowed to get ubrogepant unless they fail therapy with at least two triptans.”
Dr. Blumenfeld discounts the rationale behind requiring patients to try a second triptan after failing initial triptan therapy. “There are plenty of studies showing that if you fail one triptan, you’re likely to fail another,” he said. “Why would you put the patient on a different triptan when you could switch them to another drug with a different mechanism of action?”
The results showed that more patients in the ubrogepant 50-mg arm achieved pain freedom than those in the placebo arm within 2 hours after the initial dose in each group.
“Migraine is a very disabling condition, so you want to get the attack under control as quickly as possible while limiting the risk for potential side effects,” said Dr. Blumenfeld. “Ubrogepant is very efficacious and with very few adverse effects, but its use is limited because insurance companies require the failure of several triptans.”
One limitation of the study is that it is a subanalysis.
Dr. Blumenfeld has disclosed advisory board service, consulting, speaking, and authorship for AbbVie, Alder, Amgen, Biohaven, Lilly, Novartis, Teva, Theranica, and Zoscano.
FROM HEADACHE
Personalized cancer vaccine shows early promise across tumor types
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
The vaccine, PGV-001, was given to 13 patients with solid tumors or multiple myeloma who had a high risk of recurrence after surgery or autologous stem cell transplant.
At last follow-up, four patients were still alive without evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy, four were alive and receiving therapy, three had died, and two were lost to follow-up.
Thomas Marron, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai in New York presented these results in a poster at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2021: Week 1 ( Abstract LB048 ). Data in the abstract differ from the data presented.
“While cancer immunotherapy has revolutionized the treatment of cancer, we know that the majority of patients fail to achieve significant clinical response,” Dr. Marron said during his presentation. “One reason for this may be due to lack of preexisting primed T-cell response needed for PD-1 blockade to have a significant effect. To address this, personalized neoantigen vaccines may help prime an improved immune response against tumor cells.”
With this in mind, Dr. Marron and colleagues developed PGV-001, a vaccine consisting of patient-specific synthetic neoantigen peptides given to patients in the adjuvant setting.
Creating a personalized vaccine
The researchers synthesized PGV-001 for 15 patients with advanced malignancies. The patients first underwent tumor and germline DNA sequencing as well as HLA typing. Bulk RNA sequencing was performed on patients’ tumors as well.
Then, the researchers used a computational pipeline called OpenVax to identify candidate neoantigens. This pipeline, developed at Mount Sinai, identified and prioritized candidate neoantigens using predicted MHC class I binding affinity and neoantigen abundance.
OpenVax identified an average of 71.5 neoantigens per patient (range, 7-193). The goal was to synthesize a maximum of 10 peptides per patient, but two patients did not have an adequate number of neoantigens.
Vaccine administration
The peptides were administered over the course of 27 weeks along with poly-ICLC and a tetanus helper peptide. Before receiving their vaccine doses, patients with solid tumors had undergone curative-intent surgery, and those with multiple myeloma had undergone autologous stem cell transplant.
“Most experimental personalized cancer vaccines are administered in the metastatic setting, but prior research indicates that immunotherapies tend to be more effective in patients who have less cancer spread,” principal investigator Nina Bhardwaj, MD, PhD , of Mount Sinai, explained in a press release .
“We have, therefore, developed a neoantigen vaccine that is administered after standard-of-care adjuvant therapy, such as surgery in solid tumors and bone marrow transplant in multiple myeloma, when patients have minimal, typically microscopic, residual disease.”
Feasibility, safety, and immunogenicity
PGV-001 was synthesized for 15 patients and administered to 13 of them. Six of the 13 patients had head and neck squamous cell carcinoma, three had multiple myeloma, two had non–small cell lung cancer, one had breast cancer, and one had urothelial carcinoma.
Eleven patients received all 10 intended doses, and two patients received at least 8 doses.
“The vaccine was well tolerated, with only half of patients experiencing mild, grade 1 adverse events,” Dr. Marron said.
Transient injection site reactions occurred in four patients, and grade 1 fever was reported in one patient.
Immune monitoring is ongoing, but an initial analysis in one patient showed “robust responses” in CD4 and CD8 T cells by intracellular cytokine staining for interferon-gamma, tumor necrosis factor–alpha, and interleukin-2 after in vitro expansion in the presence of vaccine antigens, according to the researchers.
Dr. Marron noted that robust T-cell reactivity was seen at the completion of all 10 doses but was not seen after the 6th dose, and this supports the need for a prolonged dosing schedule.
Survival and subsequent therapy
At a mean follow-up of 880 days, four patients had no evidence of disease and had not received subsequent therapy. This includes one patient with stage IIIA non–small cell lung cancer, one with stage IVA HER-2 positive breast cancer, one with stage II urothelial carcinoma, and one with multiple myeloma.
Four patients were alive and receiving subsequent lines of therapy. Two of these patients had significant responses to anti–PD-1 therapy.
Three patients have died, two of whom had documented recurrence of their malignancy. The last two patients were lost to follow-up without documented recurrence.
“Our results demonstrate that the OpenVax pipeline is a viable approach to generate a safe, personalized cancer vaccine, which could potentially be used to treat a range of tumor types,” Dr. Bhardwaj said.
Trials combining neoantigens identified with the OpenVax platform are ongoing in patients with urothelial carcinoma and glioblastoma multiforme, Dr. Marron said.
The current study ( NCT02721043 ) is sponsored by Dr. Bhardwaj. Dr. Marron and Dr. Bhardwaj reported having no disclosures. Their colleagues disclosed relationships with Bristol Myers Squibb, Sema4, and Related Sciences.
FROM AACR 2021
Rankings of most common cancers to shift over next 20 years
The next 20 years will see a big shift in cancer type rankings, researchers predict.
At the moment, the most common cancers in the United States are breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, and melanoma.
the study authors predicted. Breast cancer will remain the top cancer to be diagnosed, lung cancer will drop from second to third, and colorectal cancer will remain at fourth.
These predicted rankings of cancer types by their total number of annual cases were published online April 7, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
The authors also rank cancer type by mortality. Currently, most cancer deaths are caused by lung cancer, followed by colorectal, pancreatic, and breast. By 2040, the most notable change in cancer deaths is that liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer, currently at sixth, will jump up to third.
Two decades from now, the ranking in terms of cancer deaths will be lung, pancreatic, liver and intrahepatic bile duct, and colorectal.
“Our findings reflect the shifting dynamics of cancer screening and treatment,” lead author Lola Rahib, PhD, a pancreatic cancer scientist at Cancer Commons, the advocacy nonprofit, commented in a press statement.
The new analysis used population-growth projections (based on 2010 U.S. Census data) and current population-based cancer incidence and death rates (from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 2014-2016) to calculate the changes in incidences and deaths to the year 2040.
The projected, estimated numbers are not ironclad, the researchers acknowledged.
“Our projections assume that the observed rates and trends [from recent years] don’t change over time,” Dr. Rahib said in an interview, but she pointed out that change may indeed happen.
“Any long-term projections should be considered with a grain of salt,” said Kim Miller, MPH, a surveillance research scientist at the American Cancer Society, who was approached for comment.
Dr. Miller explained that “cancer trends can sometimes rapidly change within a few years.” Projections just 2-4 years ahead are “extremely difficult” and those 20 years ahead are even more so, she added in an interview.
“We’re encouraged to see the projected decreases in deaths from lung, colorectal, and breast cancer in the coming years,” said coauthor Lynn Matrisian, PhD, MBA, chief science officer at the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. “It’s time to shift focus to some of the less commonly diagnosed cancers with the lowest survival rates, like pancreatic and liver cancer.”
Difference in opinion on prostate cancer
The huge fall in the incidence of prostate cancer that the authors predict will come about as a result of changes in prostate-specific antigen (PSA)–screening recommendations over the last 15 years, they suggested.
“The most recent change in 2018 recommends that men aged 55-69 can make their own decisions regarding screening, but previous changes recommended against PSA screening,” said Dr. Rahib.
“These changes in screening guidelines have influenced the number of diagnoses of prostate cancer in recent years and will continue to do so to 2040,” Dr. Rahib commented.
Dr. Miller casts doubt on this prediction.
Using data through 2017, “we have seen that the patterns in prostate cancer incidence are already shifting from the steep declines we saw in the early 2010s,” she said. “I would use caution when interpreting the overall trends for prostate, because this cancer in particular is dramatically affected by changes in recommendations for screening with the PSA test.”
Screening has also influenced colorectal cancer incidence, the authors pointed out, saying that the uptake of colorectal cancer screening is associated with a decrease in the number of colorectal cancers and deaths out to 2040, as a result of effectiveness of screening.
For breast cancer, the authors highlighted the fact that, although the number of breast cancers will continue to increase, the number of breast cancer deaths will decrease. That ongoing trend is most likely attributable to increased screening and advancements in treatment.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, Cancer Commons and the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. The study authors and Dr. Miller disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The next 20 years will see a big shift in cancer type rankings, researchers predict.
At the moment, the most common cancers in the United States are breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, and melanoma.
the study authors predicted. Breast cancer will remain the top cancer to be diagnosed, lung cancer will drop from second to third, and colorectal cancer will remain at fourth.
These predicted rankings of cancer types by their total number of annual cases were published online April 7, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
The authors also rank cancer type by mortality. Currently, most cancer deaths are caused by lung cancer, followed by colorectal, pancreatic, and breast. By 2040, the most notable change in cancer deaths is that liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer, currently at sixth, will jump up to third.
Two decades from now, the ranking in terms of cancer deaths will be lung, pancreatic, liver and intrahepatic bile duct, and colorectal.
“Our findings reflect the shifting dynamics of cancer screening and treatment,” lead author Lola Rahib, PhD, a pancreatic cancer scientist at Cancer Commons, the advocacy nonprofit, commented in a press statement.
The new analysis used population-growth projections (based on 2010 U.S. Census data) and current population-based cancer incidence and death rates (from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 2014-2016) to calculate the changes in incidences and deaths to the year 2040.
The projected, estimated numbers are not ironclad, the researchers acknowledged.
“Our projections assume that the observed rates and trends [from recent years] don’t change over time,” Dr. Rahib said in an interview, but she pointed out that change may indeed happen.
“Any long-term projections should be considered with a grain of salt,” said Kim Miller, MPH, a surveillance research scientist at the American Cancer Society, who was approached for comment.
Dr. Miller explained that “cancer trends can sometimes rapidly change within a few years.” Projections just 2-4 years ahead are “extremely difficult” and those 20 years ahead are even more so, she added in an interview.
“We’re encouraged to see the projected decreases in deaths from lung, colorectal, and breast cancer in the coming years,” said coauthor Lynn Matrisian, PhD, MBA, chief science officer at the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. “It’s time to shift focus to some of the less commonly diagnosed cancers with the lowest survival rates, like pancreatic and liver cancer.”
Difference in opinion on prostate cancer
The huge fall in the incidence of prostate cancer that the authors predict will come about as a result of changes in prostate-specific antigen (PSA)–screening recommendations over the last 15 years, they suggested.
“The most recent change in 2018 recommends that men aged 55-69 can make their own decisions regarding screening, but previous changes recommended against PSA screening,” said Dr. Rahib.
“These changes in screening guidelines have influenced the number of diagnoses of prostate cancer in recent years and will continue to do so to 2040,” Dr. Rahib commented.
Dr. Miller casts doubt on this prediction.
Using data through 2017, “we have seen that the patterns in prostate cancer incidence are already shifting from the steep declines we saw in the early 2010s,” she said. “I would use caution when interpreting the overall trends for prostate, because this cancer in particular is dramatically affected by changes in recommendations for screening with the PSA test.”
Screening has also influenced colorectal cancer incidence, the authors pointed out, saying that the uptake of colorectal cancer screening is associated with a decrease in the number of colorectal cancers and deaths out to 2040, as a result of effectiveness of screening.
For breast cancer, the authors highlighted the fact that, although the number of breast cancers will continue to increase, the number of breast cancer deaths will decrease. That ongoing trend is most likely attributable to increased screening and advancements in treatment.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, Cancer Commons and the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. The study authors and Dr. Miller disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
The next 20 years will see a big shift in cancer type rankings, researchers predict.
At the moment, the most common cancers in the United States are breast, lung, prostate, colorectal, and melanoma.
the study authors predicted. Breast cancer will remain the top cancer to be diagnosed, lung cancer will drop from second to third, and colorectal cancer will remain at fourth.
These predicted rankings of cancer types by their total number of annual cases were published online April 7, 2021, in JAMA Network Open.
The authors also rank cancer type by mortality. Currently, most cancer deaths are caused by lung cancer, followed by colorectal, pancreatic, and breast. By 2040, the most notable change in cancer deaths is that liver and intrahepatic bile duct cancer, currently at sixth, will jump up to third.
Two decades from now, the ranking in terms of cancer deaths will be lung, pancreatic, liver and intrahepatic bile duct, and colorectal.
“Our findings reflect the shifting dynamics of cancer screening and treatment,” lead author Lola Rahib, PhD, a pancreatic cancer scientist at Cancer Commons, the advocacy nonprofit, commented in a press statement.
The new analysis used population-growth projections (based on 2010 U.S. Census data) and current population-based cancer incidence and death rates (from Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results 2014-2016) to calculate the changes in incidences and deaths to the year 2040.
The projected, estimated numbers are not ironclad, the researchers acknowledged.
“Our projections assume that the observed rates and trends [from recent years] don’t change over time,” Dr. Rahib said in an interview, but she pointed out that change may indeed happen.
“Any long-term projections should be considered with a grain of salt,” said Kim Miller, MPH, a surveillance research scientist at the American Cancer Society, who was approached for comment.
Dr. Miller explained that “cancer trends can sometimes rapidly change within a few years.” Projections just 2-4 years ahead are “extremely difficult” and those 20 years ahead are even more so, she added in an interview.
“We’re encouraged to see the projected decreases in deaths from lung, colorectal, and breast cancer in the coming years,” said coauthor Lynn Matrisian, PhD, MBA, chief science officer at the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. “It’s time to shift focus to some of the less commonly diagnosed cancers with the lowest survival rates, like pancreatic and liver cancer.”
Difference in opinion on prostate cancer
The huge fall in the incidence of prostate cancer that the authors predict will come about as a result of changes in prostate-specific antigen (PSA)–screening recommendations over the last 15 years, they suggested.
“The most recent change in 2018 recommends that men aged 55-69 can make their own decisions regarding screening, but previous changes recommended against PSA screening,” said Dr. Rahib.
“These changes in screening guidelines have influenced the number of diagnoses of prostate cancer in recent years and will continue to do so to 2040,” Dr. Rahib commented.
Dr. Miller casts doubt on this prediction.
Using data through 2017, “we have seen that the patterns in prostate cancer incidence are already shifting from the steep declines we saw in the early 2010s,” she said. “I would use caution when interpreting the overall trends for prostate, because this cancer in particular is dramatically affected by changes in recommendations for screening with the PSA test.”
Screening has also influenced colorectal cancer incidence, the authors pointed out, saying that the uptake of colorectal cancer screening is associated with a decrease in the number of colorectal cancers and deaths out to 2040, as a result of effectiveness of screening.
For breast cancer, the authors highlighted the fact that, although the number of breast cancers will continue to increase, the number of breast cancer deaths will decrease. That ongoing trend is most likely attributable to increased screening and advancements in treatment.
The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health, National Cancer Institute, the Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas, Cancer Commons and the Pancreatic Cancer Action Network. The study authors and Dr. Miller disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Steroid-refractory pneumonitis from ICIs: Experience at major centers
Pneumonitis is an uncommon and potentially life-threatening complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. A fraction of patients with ICI-related pneumonitis fail to respond to initial therapy with high-dose systemic steroids.
The recently published experiences at two major cancer centers shed light on the outcomes from treatment and can provide some advice to clinicians for dealing with affected patients.
The Johns Hopkins experience
Because ICI-related pneumonitis typically improves within 48-72 hours of steroid therapy, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steroid-refractory pneumonitis is defined as pneumonitis that demonstrates no clinical improvement after high-dose corticosteroids for 2-14 days. If the immune toxicity–specialized, multidisciplinary management team implements additional immunosuppressive therapy, that is regarded as confirmatory evidence.
Aanika Balaji, a medical student at Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues retrospectively summarized the clinical course of 12 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis between 2011 and 2020. Clinical improvement with subsequent treatment was evidenced by reduction in either level of care or oxygen requirements.
Three-quarters of the patients were current or former smokers, and the same proportion had lung cancer. Most patients (91.6%) had received chemotherapy, 58.3% had prior chest radiotherapy, and 58.3% had achieved partial response or stable disease with an ICI.
Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis developed between 40 and 127 days (median, 85 days) after the first dose of ICI therapy. Subsequent immunosuppressive management included IVIg, infliximab, or the combination, in addition to ICU-level supportive care.
Among the seven patients who received IVIg alone, two patients (29%) achieved clinical improvement and hospital discharge. The remainder died.
The two patients treated with infliximab and the three patients treated with sequential IVIg and infliximab died. All deaths were attributed to ICI-related pneumonitis or infectious complications.
Overall, clinically relevant findings were:
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis was seen in 18.5% of patients referred for multidisciplinary care.
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis occurred at a median of 85 days into a patient’s ICI treatment.
- Some patients improved clinically after IVIg therapy, but mortality was high overall.
- Infliximab therapy, alone or in combination with IVIg, was ineffective.
The Memorial Sloan Kettering experience
Jason Beattie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues performed a retrospective study of patients who had pneumonitis after ICI therapy and/or received immune modulator therapy after corticosteroids in the setting of ICI cancer treatment.
Manual record review was performed to exclude cases of pneumonitis from other causes. The period reviewed was roughly contemporaneous with the Johns Hopkins series.
Patients with ICI-related pneumonitis were divided into “steroid refractory” (i.e., no response to high-dose corticosteroids) or “steroid resistant” (i.e., initial response, followed by worsening) categories.
The researchers identified 26 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis, all of whom had advanced malignancy (8 lung cancer, 4 malignant melanoma, 4 renal cell cancer, and 10 “other” cancers).
A majority of patients (85%) were current or former smokers, 73% had received ICI monotherapy, 35% had received prior chest radiation at a median interval of 4.9 months prior to pneumonitis onset, and 27% had preexisting pulmonary disease.
Twelve patients (46%) had steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis, and 14 (54%) had steroid-resistant ICI-related pneumonitis.
The two groups differed in time to pneumonitis onset (a median of 68 days in the refractory group and 182 days in the resistant group) and time to immune modulator therapy after beginning steroids (median 7 days and 2.9 months, respectively). In the steroid-refractory cases, pneumonitis was more severe.
In addition to corticosteroids, most patients received infliximab monotherapy or infliximab with mycophenolate mofetil. In contrast to the Johns Hopkins series, IVIg was not used in the Memorial Sloan Kettering cases.
Outcomes from immune modulators were graded based on clinical evidence (progress notes, oxygen requirements, level of care, radiologic information, etc.) of resolution of pneumonitis on imaging at least 8 weeks after cessation of steroids and immune modulator therapy, durable improvement for at least 8 weeks after immune modulator therapy, transient improvement followed by pneumonitis relapse or inadequate follow-up because of death or hospice referral, or no improvement.
Ten patients (38%) had durable improvement of ICI-related pneumonitis, of whom three (12%) had complete resolution. Two of the patients with complete resolution had steroid-refractory pneumonitis, both of whom had received infliximab followed by mycophenolate mofetil.
Among the seven patients with durable improvement, four remained alive on immune modulators. Time to resolution of pneumonitis was protracted, ranging from 2.3 months to 8.4 months in the steroid-refractory patients.
Durable response was less common with steroid-refractory (25%) than steroid-resistant (50%) disease, with a significant difference in 90-day survival of 25% and 71%, respectively.
Among the 13 (50%) patients with transient improvement in ICI-related pneumonitis, 8 ultimately died, either because of recurrent ICI-related pneumonitis or infection. All three patients with no improvement from immune modulators died.
The 90-day all-cause mortality was 50%, with durable pneumonitis improvement and freedom from severe infectious complications occurring in only about a third of patients.
Lessons for clinicians
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and the European Society of Medical Oncology have all published guidelines and recommendations for immunosuppression for steroid-refractory adverse events from ICIs.
Unfortunately, there is little experience with steroid-unresponsive ICI-related pneumonitis. The ideal sequence, dose, and duration of additional immune modulator therapy for ICI-related pneumonitis are unclear and may differ from the approaches to other immune-related toxicities.
This is important because, as suggested in an editorial by Margaret Gatti-Mays, MD, and James L. Gulley, MD, PhD, it is likely that ICI-related pneumonitis will be seen more in routine practice than in clinical trial populations. In addition, across all tumor types, ICI-related pneumonitis is the most common cause of ICI-associated death from toxicity.
The retrospective studies from Johns Hopkins and Memorial Sloan Kettering constitute the largest published experience with ICI-related pneumonitis and yield important clinical insights.
Uniform definitions of potentially important patient subgroups (e.g., steroid refractory vs. steroid resistant) are needed. The steroid-refractory and steroid-resistant subgroups have distinctly different clinical features and outcomes. Uniformity in the subgroup definitions would be a useful starting point from both clinical and research perspectives.
Preferred treatment choices need to be tested systematically in multi-institutional studies. Any potential impact of treatment for ICI-related pneumonitis on antitumor immune control should be identified.
Endpoints of interest need to be defined and measured prospectively. All-cause mortality after 90 days is important, but, as the authors of both reviews noted, there are vitally important narratives and differences in functionality that are completely concealed by restricting the focus to mortality.
Potential causal relationships with antecedent exposure to tobacco, radiation, intrathoracic tumor burden, or other factors need to be defined.
Clinicians need predictive biomarkers for ICI-related pneumonitis (e.g., in peripheral blood, pulmonary function testing, or bronchoscopy specimens). At-risk patients may benefit from early intervention.
The limitations of single-institution record reviews in guiding real-world patient management notwithstanding, these reviews illustrate the value of registries and prospective studies to guide the path forward. Taking these next steps will ensure for our patients that the success of immune-targeted therapy against their cancer never becomes a Pyrrhic victory.
The Johns Hopkins investigators and the editorialists reported having no disclosures. The Memorial Sloan Kettering investigators disclosed relationships with Targeted Oncology, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and many other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Pneumonitis is an uncommon and potentially life-threatening complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. A fraction of patients with ICI-related pneumonitis fail to respond to initial therapy with high-dose systemic steroids.
The recently published experiences at two major cancer centers shed light on the outcomes from treatment and can provide some advice to clinicians for dealing with affected patients.
The Johns Hopkins experience
Because ICI-related pneumonitis typically improves within 48-72 hours of steroid therapy, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steroid-refractory pneumonitis is defined as pneumonitis that demonstrates no clinical improvement after high-dose corticosteroids for 2-14 days. If the immune toxicity–specialized, multidisciplinary management team implements additional immunosuppressive therapy, that is regarded as confirmatory evidence.
Aanika Balaji, a medical student at Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues retrospectively summarized the clinical course of 12 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis between 2011 and 2020. Clinical improvement with subsequent treatment was evidenced by reduction in either level of care or oxygen requirements.
Three-quarters of the patients were current or former smokers, and the same proportion had lung cancer. Most patients (91.6%) had received chemotherapy, 58.3% had prior chest radiotherapy, and 58.3% had achieved partial response or stable disease with an ICI.
Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis developed between 40 and 127 days (median, 85 days) after the first dose of ICI therapy. Subsequent immunosuppressive management included IVIg, infliximab, or the combination, in addition to ICU-level supportive care.
Among the seven patients who received IVIg alone, two patients (29%) achieved clinical improvement and hospital discharge. The remainder died.
The two patients treated with infliximab and the three patients treated with sequential IVIg and infliximab died. All deaths were attributed to ICI-related pneumonitis or infectious complications.
Overall, clinically relevant findings were:
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis was seen in 18.5% of patients referred for multidisciplinary care.
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis occurred at a median of 85 days into a patient’s ICI treatment.
- Some patients improved clinically after IVIg therapy, but mortality was high overall.
- Infliximab therapy, alone or in combination with IVIg, was ineffective.
The Memorial Sloan Kettering experience
Jason Beattie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues performed a retrospective study of patients who had pneumonitis after ICI therapy and/or received immune modulator therapy after corticosteroids in the setting of ICI cancer treatment.
Manual record review was performed to exclude cases of pneumonitis from other causes. The period reviewed was roughly contemporaneous with the Johns Hopkins series.
Patients with ICI-related pneumonitis were divided into “steroid refractory” (i.e., no response to high-dose corticosteroids) or “steroid resistant” (i.e., initial response, followed by worsening) categories.
The researchers identified 26 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis, all of whom had advanced malignancy (8 lung cancer, 4 malignant melanoma, 4 renal cell cancer, and 10 “other” cancers).
A majority of patients (85%) were current or former smokers, 73% had received ICI monotherapy, 35% had received prior chest radiation at a median interval of 4.9 months prior to pneumonitis onset, and 27% had preexisting pulmonary disease.
Twelve patients (46%) had steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis, and 14 (54%) had steroid-resistant ICI-related pneumonitis.
The two groups differed in time to pneumonitis onset (a median of 68 days in the refractory group and 182 days in the resistant group) and time to immune modulator therapy after beginning steroids (median 7 days and 2.9 months, respectively). In the steroid-refractory cases, pneumonitis was more severe.
In addition to corticosteroids, most patients received infliximab monotherapy or infliximab with mycophenolate mofetil. In contrast to the Johns Hopkins series, IVIg was not used in the Memorial Sloan Kettering cases.
Outcomes from immune modulators were graded based on clinical evidence (progress notes, oxygen requirements, level of care, radiologic information, etc.) of resolution of pneumonitis on imaging at least 8 weeks after cessation of steroids and immune modulator therapy, durable improvement for at least 8 weeks after immune modulator therapy, transient improvement followed by pneumonitis relapse or inadequate follow-up because of death or hospice referral, or no improvement.
Ten patients (38%) had durable improvement of ICI-related pneumonitis, of whom three (12%) had complete resolution. Two of the patients with complete resolution had steroid-refractory pneumonitis, both of whom had received infliximab followed by mycophenolate mofetil.
Among the seven patients with durable improvement, four remained alive on immune modulators. Time to resolution of pneumonitis was protracted, ranging from 2.3 months to 8.4 months in the steroid-refractory patients.
Durable response was less common with steroid-refractory (25%) than steroid-resistant (50%) disease, with a significant difference in 90-day survival of 25% and 71%, respectively.
Among the 13 (50%) patients with transient improvement in ICI-related pneumonitis, 8 ultimately died, either because of recurrent ICI-related pneumonitis or infection. All three patients with no improvement from immune modulators died.
The 90-day all-cause mortality was 50%, with durable pneumonitis improvement and freedom from severe infectious complications occurring in only about a third of patients.
Lessons for clinicians
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and the European Society of Medical Oncology have all published guidelines and recommendations for immunosuppression for steroid-refractory adverse events from ICIs.
Unfortunately, there is little experience with steroid-unresponsive ICI-related pneumonitis. The ideal sequence, dose, and duration of additional immune modulator therapy for ICI-related pneumonitis are unclear and may differ from the approaches to other immune-related toxicities.
This is important because, as suggested in an editorial by Margaret Gatti-Mays, MD, and James L. Gulley, MD, PhD, it is likely that ICI-related pneumonitis will be seen more in routine practice than in clinical trial populations. In addition, across all tumor types, ICI-related pneumonitis is the most common cause of ICI-associated death from toxicity.
The retrospective studies from Johns Hopkins and Memorial Sloan Kettering constitute the largest published experience with ICI-related pneumonitis and yield important clinical insights.
Uniform definitions of potentially important patient subgroups (e.g., steroid refractory vs. steroid resistant) are needed. The steroid-refractory and steroid-resistant subgroups have distinctly different clinical features and outcomes. Uniformity in the subgroup definitions would be a useful starting point from both clinical and research perspectives.
Preferred treatment choices need to be tested systematically in multi-institutional studies. Any potential impact of treatment for ICI-related pneumonitis on antitumor immune control should be identified.
Endpoints of interest need to be defined and measured prospectively. All-cause mortality after 90 days is important, but, as the authors of both reviews noted, there are vitally important narratives and differences in functionality that are completely concealed by restricting the focus to mortality.
Potential causal relationships with antecedent exposure to tobacco, radiation, intrathoracic tumor burden, or other factors need to be defined.
Clinicians need predictive biomarkers for ICI-related pneumonitis (e.g., in peripheral blood, pulmonary function testing, or bronchoscopy specimens). At-risk patients may benefit from early intervention.
The limitations of single-institution record reviews in guiding real-world patient management notwithstanding, these reviews illustrate the value of registries and prospective studies to guide the path forward. Taking these next steps will ensure for our patients that the success of immune-targeted therapy against their cancer never becomes a Pyrrhic victory.
The Johns Hopkins investigators and the editorialists reported having no disclosures. The Memorial Sloan Kettering investigators disclosed relationships with Targeted Oncology, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and many other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Pneumonitis is an uncommon and potentially life-threatening complication of immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy. A fraction of patients with ICI-related pneumonitis fail to respond to initial therapy with high-dose systemic steroids.
The recently published experiences at two major cancer centers shed light on the outcomes from treatment and can provide some advice to clinicians for dealing with affected patients.
The Johns Hopkins experience
Because ICI-related pneumonitis typically improves within 48-72 hours of steroid therapy, at Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, steroid-refractory pneumonitis is defined as pneumonitis that demonstrates no clinical improvement after high-dose corticosteroids for 2-14 days. If the immune toxicity–specialized, multidisciplinary management team implements additional immunosuppressive therapy, that is regarded as confirmatory evidence.
Aanika Balaji, a medical student at Johns Hopkins University, and colleagues retrospectively summarized the clinical course of 12 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis between 2011 and 2020. Clinical improvement with subsequent treatment was evidenced by reduction in either level of care or oxygen requirements.
Three-quarters of the patients were current or former smokers, and the same proportion had lung cancer. Most patients (91.6%) had received chemotherapy, 58.3% had prior chest radiotherapy, and 58.3% had achieved partial response or stable disease with an ICI.
Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis developed between 40 and 127 days (median, 85 days) after the first dose of ICI therapy. Subsequent immunosuppressive management included IVIg, infliximab, or the combination, in addition to ICU-level supportive care.
Among the seven patients who received IVIg alone, two patients (29%) achieved clinical improvement and hospital discharge. The remainder died.
The two patients treated with infliximab and the three patients treated with sequential IVIg and infliximab died. All deaths were attributed to ICI-related pneumonitis or infectious complications.
Overall, clinically relevant findings were:
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis was seen in 18.5% of patients referred for multidisciplinary care.
- Steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis occurred at a median of 85 days into a patient’s ICI treatment.
- Some patients improved clinically after IVIg therapy, but mortality was high overall.
- Infliximab therapy, alone or in combination with IVIg, was ineffective.
The Memorial Sloan Kettering experience
Jason Beattie, MD, of Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center, New York, and colleagues performed a retrospective study of patients who had pneumonitis after ICI therapy and/or received immune modulator therapy after corticosteroids in the setting of ICI cancer treatment.
Manual record review was performed to exclude cases of pneumonitis from other causes. The period reviewed was roughly contemporaneous with the Johns Hopkins series.
Patients with ICI-related pneumonitis were divided into “steroid refractory” (i.e., no response to high-dose corticosteroids) or “steroid resistant” (i.e., initial response, followed by worsening) categories.
The researchers identified 26 patients with ICI-related pneumonitis, all of whom had advanced malignancy (8 lung cancer, 4 malignant melanoma, 4 renal cell cancer, and 10 “other” cancers).
A majority of patients (85%) were current or former smokers, 73% had received ICI monotherapy, 35% had received prior chest radiation at a median interval of 4.9 months prior to pneumonitis onset, and 27% had preexisting pulmonary disease.
Twelve patients (46%) had steroid-refractory ICI-related pneumonitis, and 14 (54%) had steroid-resistant ICI-related pneumonitis.
The two groups differed in time to pneumonitis onset (a median of 68 days in the refractory group and 182 days in the resistant group) and time to immune modulator therapy after beginning steroids (median 7 days and 2.9 months, respectively). In the steroid-refractory cases, pneumonitis was more severe.
In addition to corticosteroids, most patients received infliximab monotherapy or infliximab with mycophenolate mofetil. In contrast to the Johns Hopkins series, IVIg was not used in the Memorial Sloan Kettering cases.
Outcomes from immune modulators were graded based on clinical evidence (progress notes, oxygen requirements, level of care, radiologic information, etc.) of resolution of pneumonitis on imaging at least 8 weeks after cessation of steroids and immune modulator therapy, durable improvement for at least 8 weeks after immune modulator therapy, transient improvement followed by pneumonitis relapse or inadequate follow-up because of death or hospice referral, or no improvement.
Ten patients (38%) had durable improvement of ICI-related pneumonitis, of whom three (12%) had complete resolution. Two of the patients with complete resolution had steroid-refractory pneumonitis, both of whom had received infliximab followed by mycophenolate mofetil.
Among the seven patients with durable improvement, four remained alive on immune modulators. Time to resolution of pneumonitis was protracted, ranging from 2.3 months to 8.4 months in the steroid-refractory patients.
Durable response was less common with steroid-refractory (25%) than steroid-resistant (50%) disease, with a significant difference in 90-day survival of 25% and 71%, respectively.
Among the 13 (50%) patients with transient improvement in ICI-related pneumonitis, 8 ultimately died, either because of recurrent ICI-related pneumonitis or infection. All three patients with no improvement from immune modulators died.
The 90-day all-cause mortality was 50%, with durable pneumonitis improvement and freedom from severe infectious complications occurring in only about a third of patients.
Lessons for clinicians
The National Comprehensive Cancer Network, the Society for Immunotherapy of Cancer, and the European Society of Medical Oncology have all published guidelines and recommendations for immunosuppression for steroid-refractory adverse events from ICIs.
Unfortunately, there is little experience with steroid-unresponsive ICI-related pneumonitis. The ideal sequence, dose, and duration of additional immune modulator therapy for ICI-related pneumonitis are unclear and may differ from the approaches to other immune-related toxicities.
This is important because, as suggested in an editorial by Margaret Gatti-Mays, MD, and James L. Gulley, MD, PhD, it is likely that ICI-related pneumonitis will be seen more in routine practice than in clinical trial populations. In addition, across all tumor types, ICI-related pneumonitis is the most common cause of ICI-associated death from toxicity.
The retrospective studies from Johns Hopkins and Memorial Sloan Kettering constitute the largest published experience with ICI-related pneumonitis and yield important clinical insights.
Uniform definitions of potentially important patient subgroups (e.g., steroid refractory vs. steroid resistant) are needed. The steroid-refractory and steroid-resistant subgroups have distinctly different clinical features and outcomes. Uniformity in the subgroup definitions would be a useful starting point from both clinical and research perspectives.
Preferred treatment choices need to be tested systematically in multi-institutional studies. Any potential impact of treatment for ICI-related pneumonitis on antitumor immune control should be identified.
Endpoints of interest need to be defined and measured prospectively. All-cause mortality after 90 days is important, but, as the authors of both reviews noted, there are vitally important narratives and differences in functionality that are completely concealed by restricting the focus to mortality.
Potential causal relationships with antecedent exposure to tobacco, radiation, intrathoracic tumor burden, or other factors need to be defined.
Clinicians need predictive biomarkers for ICI-related pneumonitis (e.g., in peripheral blood, pulmonary function testing, or bronchoscopy specimens). At-risk patients may benefit from early intervention.
The limitations of single-institution record reviews in guiding real-world patient management notwithstanding, these reviews illustrate the value of registries and prospective studies to guide the path forward. Taking these next steps will ensure for our patients that the success of immune-targeted therapy against their cancer never becomes a Pyrrhic victory.
The Johns Hopkins investigators and the editorialists reported having no disclosures. The Memorial Sloan Kettering investigators disclosed relationships with Targeted Oncology, Merck, Array BioPharma, Novartis, and many other companies.
Dr. Lyss was a community-based medical oncologist and clinical researcher for more than 35 years before his recent retirement. His clinical and research interests were focused on breast and lung cancers, as well as expanding clinical trial access to medically underserved populations. He is based in St. Louis. He has no conflicts of interest.
Can exercise prevent cognitive decline in patients with early Parkinson’s disease?
, new research suggests. Investigators found that patients with Parkinson’s disease who were APOE epsilon4 carriers had greater cognitive decline compared with non-APOE epsilon4 carriers, but the findings also revealed higher physical activity appeared to slow cognitive decline in this higher risk group.
“The main finding of the current study is that higher physical activity was related to slower APOE epsilon4-associated cognitive decline in patients with early Parkinson’s disease, which was shown to be robust in sensitivity analyses,” wrote the researchers, led by Ryul Kim, MD, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
The study was published online March 31 in Neurology.
Unclear mechanism
The APOE epsilon4 allele is known to be a “major risk factor” for Alzheimer’s disease, but “accumulating evidence shows that this allele also has a potential role in cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease,” the authors noted.
Previous research shows physical activity has beneficial effects in patients with Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanisms underlying these effects are “not well understood.” Additional data suggest physical activity modifies the APOE epsilon4 effect on the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
“These observations led us to hypothesize that physical activity also plays a role in modulating the association between APOE [epsilon4] and cognition in Parkinson’s disease,” but no studies have yet reported on this interaction in patients with Parkinson’s disease, the authors noted.
To investigate, they drew on data from the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) – a cohort study conducted to identify Parkinson’s disease progression markers.
The current analysis included 173 patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease but not yet treated for the condition. The cohort’s mean age was 63.3 ± 10.0 years, age of Parkinson’s disease onset was 59.4 ± 10.0 years, and 68% were male. Of these participants, 46 were APOE epsilon4 carriers.
Dopamine transporter (DAT) activity was assessed using imaging at enrollment and again at years 2 and 4. Cognitive function was assessed at years 2, 3, and 4 using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test.
Protective effect
Although APOE epsilon4 carriers tended to be younger than noncarriers, the age of Parkinson’s disease onset did not differ between the 2 groups, and there were also no significant differences between the groups in demographic and clinical variables.
There were larger declines in MoCA scores in the APOE epsilon4 carriers versus the noncarriers (0.21 ± 1.40 and 0.08 ± 1.15 respectively).
The APOE epsilon4 allele was associated with a “steeper” rate of cognitive decline, compared with the non-APOE epsilon4 allele (estimate −1.33 [95% confidence interval, −2.12 to −0.47, P = .002).
There was a significant interaction of physical activity, APOE epsilon4, and time: Higher physical activity was associated with slower APOE epsilon4-related cognitive decline (estimate 0.007 [0.003 to 0.011, P = .001).
However, the researchers found no significant main effects of the APOE epsilon4 allele or physical activity on the change in the MoCA score.
“Considering that dopaminergic treatment may affect cognitive function, particularly in the early stage of Parkinson’s disease, we additionally included the levodopa daily equivalent dose (LEDD) and its interaction with time as covariates in the model,” the investigators noted.
They found that the interactive association between physical activity and the APOE epsilon4 allele on cognitive decline remained significant, even when participants who had normal cognitive performance at year 2 were included in the study population or when LEDD variables were included as covariates in the model.
Both high- and low-intensity exercise were significantly associated with slower APOE epsilon4-related cognitive decline.
There was no significant interaction between physical activity and APOE epsilon4 with changes in striatal DAT activities.
“Increased physical activity attenuated APOE epsilon4-related vulnerability to early cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” the authors noted, adding that the effect “did not appear to be mediated by striatal dopamine activity.”
They hypothesized that physical activity may “offer a greater protective effect” on cerebral amyloid accumulation in APOE epsilon4 carriers. It is also possible that physical activity will counteract the negative impact of the APOE epsilon4 allele through improved brain mechanism and decreased neuroinflammation.
‘The next blockbuster drug’
Commenting on the study in an interview, Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, director of the center of expertise for Parkinson & movement disorders, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands, said exercise might be seen as “the next blockbuster drug.”
Dr. Bloem, who was not involved in the study, noted there is “quite robust evidence now that exercise acts as symptomatic therapy, like a drug, alleviating sleep [disturbances], depression, constipation, and motor symptoms.”
The study “sheds new light on the idea of exercise as not only alleviating symptoms but actually as a potential disease modifier,” said Dr. Bloem, whose research has focused on the beneficial effects of a rigorous exercise program, combined with tablet-based gamificaton and a reward system in stabilizing motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease over time.
“The reward system created additional motivation for the patients with Parkinson’s disease who often experience depression and apathy that interfere with motivation,” he said.
The current study has important take-home messages for practicing clinicians. “Physicians should encourage exercise in patients, and patients should also take the lead themselves,” Dr. Bloem said. “It doesn’t matter what type of exercise you do, but it should have an aerobic component, should be safe so the patient doesn’t fall down, should have enough intensity to cause the patient to pant, and should be individualized and enjoyable so the patients stick to it,” he emphasized.
Dr. Bloem noted that yoga and mindfulness are also helpful. “If we’ve learned anything from the COVID-19 crisis, it’s that chronic stress is deleterious to all of us and particularly bad for people with PD, because you need dopamine to be able to handle stress, and the lack of dopamine in people with PD makes them deteriorate faster.”
The study was supported by a research grant of National Research Foundation by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) in Korea. The authors and Dr. Bloem have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests. Investigators found that patients with Parkinson’s disease who were APOE epsilon4 carriers had greater cognitive decline compared with non-APOE epsilon4 carriers, but the findings also revealed higher physical activity appeared to slow cognitive decline in this higher risk group.
“The main finding of the current study is that higher physical activity was related to slower APOE epsilon4-associated cognitive decline in patients with early Parkinson’s disease, which was shown to be robust in sensitivity analyses,” wrote the researchers, led by Ryul Kim, MD, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
The study was published online March 31 in Neurology.
Unclear mechanism
The APOE epsilon4 allele is known to be a “major risk factor” for Alzheimer’s disease, but “accumulating evidence shows that this allele also has a potential role in cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease,” the authors noted.
Previous research shows physical activity has beneficial effects in patients with Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanisms underlying these effects are “not well understood.” Additional data suggest physical activity modifies the APOE epsilon4 effect on the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
“These observations led us to hypothesize that physical activity also plays a role in modulating the association between APOE [epsilon4] and cognition in Parkinson’s disease,” but no studies have yet reported on this interaction in patients with Parkinson’s disease, the authors noted.
To investigate, they drew on data from the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) – a cohort study conducted to identify Parkinson’s disease progression markers.
The current analysis included 173 patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease but not yet treated for the condition. The cohort’s mean age was 63.3 ± 10.0 years, age of Parkinson’s disease onset was 59.4 ± 10.0 years, and 68% were male. Of these participants, 46 were APOE epsilon4 carriers.
Dopamine transporter (DAT) activity was assessed using imaging at enrollment and again at years 2 and 4. Cognitive function was assessed at years 2, 3, and 4 using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test.
Protective effect
Although APOE epsilon4 carriers tended to be younger than noncarriers, the age of Parkinson’s disease onset did not differ between the 2 groups, and there were also no significant differences between the groups in demographic and clinical variables.
There were larger declines in MoCA scores in the APOE epsilon4 carriers versus the noncarriers (0.21 ± 1.40 and 0.08 ± 1.15 respectively).
The APOE epsilon4 allele was associated with a “steeper” rate of cognitive decline, compared with the non-APOE epsilon4 allele (estimate −1.33 [95% confidence interval, −2.12 to −0.47, P = .002).
There was a significant interaction of physical activity, APOE epsilon4, and time: Higher physical activity was associated with slower APOE epsilon4-related cognitive decline (estimate 0.007 [0.003 to 0.011, P = .001).
However, the researchers found no significant main effects of the APOE epsilon4 allele or physical activity on the change in the MoCA score.
“Considering that dopaminergic treatment may affect cognitive function, particularly in the early stage of Parkinson’s disease, we additionally included the levodopa daily equivalent dose (LEDD) and its interaction with time as covariates in the model,” the investigators noted.
They found that the interactive association between physical activity and the APOE epsilon4 allele on cognitive decline remained significant, even when participants who had normal cognitive performance at year 2 were included in the study population or when LEDD variables were included as covariates in the model.
Both high- and low-intensity exercise were significantly associated with slower APOE epsilon4-related cognitive decline.
There was no significant interaction between physical activity and APOE epsilon4 with changes in striatal DAT activities.
“Increased physical activity attenuated APOE epsilon4-related vulnerability to early cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” the authors noted, adding that the effect “did not appear to be mediated by striatal dopamine activity.”
They hypothesized that physical activity may “offer a greater protective effect” on cerebral amyloid accumulation in APOE epsilon4 carriers. It is also possible that physical activity will counteract the negative impact of the APOE epsilon4 allele through improved brain mechanism and decreased neuroinflammation.
‘The next blockbuster drug’
Commenting on the study in an interview, Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, director of the center of expertise for Parkinson & movement disorders, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands, said exercise might be seen as “the next blockbuster drug.”
Dr. Bloem, who was not involved in the study, noted there is “quite robust evidence now that exercise acts as symptomatic therapy, like a drug, alleviating sleep [disturbances], depression, constipation, and motor symptoms.”
The study “sheds new light on the idea of exercise as not only alleviating symptoms but actually as a potential disease modifier,” said Dr. Bloem, whose research has focused on the beneficial effects of a rigorous exercise program, combined with tablet-based gamificaton and a reward system in stabilizing motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease over time.
“The reward system created additional motivation for the patients with Parkinson’s disease who often experience depression and apathy that interfere with motivation,” he said.
The current study has important take-home messages for practicing clinicians. “Physicians should encourage exercise in patients, and patients should also take the lead themselves,” Dr. Bloem said. “It doesn’t matter what type of exercise you do, but it should have an aerobic component, should be safe so the patient doesn’t fall down, should have enough intensity to cause the patient to pant, and should be individualized and enjoyable so the patients stick to it,” he emphasized.
Dr. Bloem noted that yoga and mindfulness are also helpful. “If we’ve learned anything from the COVID-19 crisis, it’s that chronic stress is deleterious to all of us and particularly bad for people with PD, because you need dopamine to be able to handle stress, and the lack of dopamine in people with PD makes them deteriorate faster.”
The study was supported by a research grant of National Research Foundation by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) in Korea. The authors and Dr. Bloem have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, new research suggests. Investigators found that patients with Parkinson’s disease who were APOE epsilon4 carriers had greater cognitive decline compared with non-APOE epsilon4 carriers, but the findings also revealed higher physical activity appeared to slow cognitive decline in this higher risk group.
“The main finding of the current study is that higher physical activity was related to slower APOE epsilon4-associated cognitive decline in patients with early Parkinson’s disease, which was shown to be robust in sensitivity analyses,” wrote the researchers, led by Ryul Kim, MD, Inha University Hospital, Incheon, Korea.
The study was published online March 31 in Neurology.
Unclear mechanism
The APOE epsilon4 allele is known to be a “major risk factor” for Alzheimer’s disease, but “accumulating evidence shows that this allele also has a potential role in cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease,” the authors noted.
Previous research shows physical activity has beneficial effects in patients with Parkinson’s disease, but the mechanisms underlying these effects are “not well understood.” Additional data suggest physical activity modifies the APOE epsilon4 effect on the development and progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
“These observations led us to hypothesize that physical activity also plays a role in modulating the association between APOE [epsilon4] and cognition in Parkinson’s disease,” but no studies have yet reported on this interaction in patients with Parkinson’s disease, the authors noted.
To investigate, they drew on data from the Parkinson’s Progression Markers Initiative (PPMI) – a cohort study conducted to identify Parkinson’s disease progression markers.
The current analysis included 173 patients recently diagnosed with Parkinson’s disease but not yet treated for the condition. The cohort’s mean age was 63.3 ± 10.0 years, age of Parkinson’s disease onset was 59.4 ± 10.0 years, and 68% were male. Of these participants, 46 were APOE epsilon4 carriers.
Dopamine transporter (DAT) activity was assessed using imaging at enrollment and again at years 2 and 4. Cognitive function was assessed at years 2, 3, and 4 using the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) test.
Protective effect
Although APOE epsilon4 carriers tended to be younger than noncarriers, the age of Parkinson’s disease onset did not differ between the 2 groups, and there were also no significant differences between the groups in demographic and clinical variables.
There were larger declines in MoCA scores in the APOE epsilon4 carriers versus the noncarriers (0.21 ± 1.40 and 0.08 ± 1.15 respectively).
The APOE epsilon4 allele was associated with a “steeper” rate of cognitive decline, compared with the non-APOE epsilon4 allele (estimate −1.33 [95% confidence interval, −2.12 to −0.47, P = .002).
There was a significant interaction of physical activity, APOE epsilon4, and time: Higher physical activity was associated with slower APOE epsilon4-related cognitive decline (estimate 0.007 [0.003 to 0.011, P = .001).
However, the researchers found no significant main effects of the APOE epsilon4 allele or physical activity on the change in the MoCA score.
“Considering that dopaminergic treatment may affect cognitive function, particularly in the early stage of Parkinson’s disease, we additionally included the levodopa daily equivalent dose (LEDD) and its interaction with time as covariates in the model,” the investigators noted.
They found that the interactive association between physical activity and the APOE epsilon4 allele on cognitive decline remained significant, even when participants who had normal cognitive performance at year 2 were included in the study population or when LEDD variables were included as covariates in the model.
Both high- and low-intensity exercise were significantly associated with slower APOE epsilon4-related cognitive decline.
There was no significant interaction between physical activity and APOE epsilon4 with changes in striatal DAT activities.
“Increased physical activity attenuated APOE epsilon4-related vulnerability to early cognitive decline in patients with Parkinson’s disease,” the authors noted, adding that the effect “did not appear to be mediated by striatal dopamine activity.”
They hypothesized that physical activity may “offer a greater protective effect” on cerebral amyloid accumulation in APOE epsilon4 carriers. It is also possible that physical activity will counteract the negative impact of the APOE epsilon4 allele through improved brain mechanism and decreased neuroinflammation.
‘The next blockbuster drug’
Commenting on the study in an interview, Bastiaan R. Bloem, MD, PhD, director of the center of expertise for Parkinson & movement disorders, Radboud University Medical Center, Nijmegen, Netherlands, said exercise might be seen as “the next blockbuster drug.”
Dr. Bloem, who was not involved in the study, noted there is “quite robust evidence now that exercise acts as symptomatic therapy, like a drug, alleviating sleep [disturbances], depression, constipation, and motor symptoms.”
The study “sheds new light on the idea of exercise as not only alleviating symptoms but actually as a potential disease modifier,” said Dr. Bloem, whose research has focused on the beneficial effects of a rigorous exercise program, combined with tablet-based gamificaton and a reward system in stabilizing motor symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease over time.
“The reward system created additional motivation for the patients with Parkinson’s disease who often experience depression and apathy that interfere with motivation,” he said.
The current study has important take-home messages for practicing clinicians. “Physicians should encourage exercise in patients, and patients should also take the lead themselves,” Dr. Bloem said. “It doesn’t matter what type of exercise you do, but it should have an aerobic component, should be safe so the patient doesn’t fall down, should have enough intensity to cause the patient to pant, and should be individualized and enjoyable so the patients stick to it,” he emphasized.
Dr. Bloem noted that yoga and mindfulness are also helpful. “If we’ve learned anything from the COVID-19 crisis, it’s that chronic stress is deleterious to all of us and particularly bad for people with PD, because you need dopamine to be able to handle stress, and the lack of dopamine in people with PD makes them deteriorate faster.”
The study was supported by a research grant of National Research Foundation by the Ministry of Science and ICT (MSIT) in Korea. The authors and Dr. Bloem have disclosed no relevant financial relationships.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Cancer screening stopped by pandemic: Repercussions to come?
Last year, cancer screening programs around the world ground to a halt as SARS-CoV-2 infection rates surged globally. The effect of this slowdown is now becoming clear.
Thousands of cancer diagnoses are “missing,” and oncologists worry that this will lead to more advanced cancers and higher mortality for years to come.
“I feel like this is an earthquake that’s rocked our health care system. My guess is that you’ll probably still see repercussions of this over the next couple of years at least,” said Sharon Chang, MD, an attending surgical oncologist in the Permanente Medical Group, Fremont, Calif.
She was senior author of a study that analyzed the effects of the slowdown in mammography screening as a result of California’s “shelter-in-place” order on March 17, 2020. In the 2 months that followed, there were 64% fewer breast cancer diagnoses at 21 Kaiser Permanente medical centers, compared with the same period in 2019 (250 vs. 703).
In effect, approximately 450 breast cancer patients had “disappeared,” said coauthor Annie Tang, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, East Bay surgery program.
“What surprised me most from our data was the sheer number of breast cancer patients that were missing,” Dr. Tang said in an interview.
A similar picture has emerged elsewhere.
In Boston, an estimated 1,438 cancerous and precancerous lesions “went missing” during the first 3 months of pandemic shutdown, according to a study from the Massachusetts General Brigham health care system.
In this study, the investigators assessed screening rates for five cancers – breast cancer (mammography), prostate cancer (prostate-specific antigen testing), colorectal cancer (colonoscopy), cervical cancer (Papanicolaou tests), and lung cancer (low-dose CT).
Screening rates during the first peak of the pandemic (March 2 to June 2, 2020) were compared with those during the preceding and following 3 months and during the same 3 months in 2019.
The results showed a pronounced drop in screening rates during the peak pandemic period, compared with the three control periods. Decreases occurred for all screening tests and ranged from –60% to –82%.
There were also significant decreases in cancer diagnoses resulting from the decreases in screening tests, ranging from –19% to –78%.
“Quantifying the actual problem made us realize how much work needs to be done to get us back to prepandemic numbers,” said senior author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, FACS, codirector of the Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s prostate cancer program.
In the Canadian province of Alberta, a similar decrease in cancer diagnoses occurred during the early days of the pandemic.
By the end of 2020, Alberta was “missing” approximately 2,000 cases of invasive cancers and 1,000 cases of noninvasive cancers, Doug Stewart, MD, senior medical director at the Cancer Strategic Clinical Network (SCN) of Alberta Health Services, told this news organization.
Dr. Stewart is able to track cancer diagnoses in Alberta almost in real time through a mandatory cancer registry. Within a month of shutdown, there was a 30% decrease in diagnoses of invasive cancers and a 50% decrease “in the kind of preinvasive cancers that, for the most part, are picked up by screening programs,” said Dr. Stewart.
After the health care system opened up again in the summer, Stewart said, noninvasive cancer diagnoses continued to be 20% lower than expected. There was a 10% shortfall in invasive cancer diagnoses.
The number of diagnoses had returned to normal by December 2020. However, Dr. Stewart is worried that this fact conceals a terrible truth.
The worry is over the backlog. Although the number of diagnoses is now similar to what it was before the pandemic, “people are presenting later, and maybe the cancer is more advanced,” he speculated.
His team at Alberta Health Services is assessing whether the cancers that are being diagnosed now are more advanced. Initial results are anticipated by late April 2021.
In the United Kingdom, there was a similar halt in cancer screening as a result of the country’s lockdown. Researchers now predict an uptick in cancer diagnoses.
Ajay Aggarwal, MD, PhD, consultant clinical oncologist and associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and colleagues have estimated that at least 3,500 deaths from breast, colorectal, esophageal, and lung cancer will occur during the next 5 years in England that could have been avoided had it not been for the lockdown measures necessitated by the pandemic.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Aggarwal warned that these numbers, which are from a modeling study published in August 2020, are “extremely conservative,” because the investigators considered diagnostic delays over only a 3-month period, the analysis involved only four cancers, and it did not reflect deferral of cancer treatment.
“It felt like it was the tip of the iceberg,” Dr. Aggarwal said. He warns that more recent data suggest that “diagnostic delays are probably worse than we predicted.”
He suspects that there is more at play than screening cancellations.
In another study conducted in the United Kingdom, data show “a falling edge of referrals” from primary care to cancer centers early in the pandemic. In that study, investigators analyzed real-time weekly hospital data from eight large British hospitals and found that urgent cancer referrals fell 70% at their lowest point.
“It really surprised me that the urgent referrals dropped so drastically,” said lead author Alvina Lai, PhD, a lecturer in health data analytics at University College London.
She attributed this in part to patients’ adherence to lockdown rules. “Patients are trying to follow government guidelines to stay home and not go to [general practitioners] unless necessary,” Dr. Lai explained in an interview.
Canada, like the United Kingdom, has a publicly funded health care system. Dr. Stewart came to a similar conclusion. “Some patients who have been diagnosed with cancer ... have told me it took them an extra couple of months to even contact the family doc, because they ... didn’t want to bother the family doctor with something that wasn’t COVID, this kind of guilt. They want to do something good for society. You know, most people are just really nice people, and they don’t want to bother the health care system if they don’t have COVID,” Dr. Stewart said.
Shelley Fuld Nasso, CEO of the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, a nonprofit organization based in Silver Spring, Md., agreed that screening shutdowns are not the only danger. “While we agree that screening is really important, we also want to make sure patients are following up with their physicians about symptoms that they have,” she said.
“Some of the speculation or concern about increased mortality for cancer is related to screening, but some of it is related to delayed diagnosis because of not following up on symptoms. ... What concerns me is not everyone has that ability or willingness to advocate for themselves,” she said.
Speaking at a press briefing held by the American Society for Radiation Oncology on March 30, Dr. Nasso related a case involving a patient who experienced severe arm pain. In a teleconsultation with her primary care physician, her condition was diagnosed as arthritis. She was subsequently diagnosed in the ED as having multiple myeloma.
Patients who “feel fine” may postpone their checkups to avoid going to the hospital and risking exposure to COVID-19.
“Some patients are still hesitant about returning for their mammograms or coming in if they feel a breast lump,” Dr. Tang said. “That fear of COVID-19 is still out there, and we don’t know how long patients are going to delay.”
In London, Dr. Aggarwal saw a similar response to the pandemic. “People were overestimating quite significantly what their risk of death was from acquiring COVID-19, and I think that balance was never [redressed] explicitly,” he said.
Public health initiatives to rebalance the messaging are now underway.
Public Health England and National Health Service England launched their Help Us Help You campaign in October 2020. The public information campaign urges people to speak to their doctors if they were “worried about a symptom that could be cancer.”
In Canada, the provincial government in Alberta has launched a public awareness campaign that conveys the message, “cancer has not gone away.”
“Cancer is still the No. 1 cause of potential life-years lost, despite COVID,” Dr. Stewart said. “We need to do what we can to make sure there’s no slippage in survival rates.”
Dr. Tang, Dr. Chang, Dr. Lai, Dr. Stewart, and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationship. Dr. Trinh has received personal fees from Astellas, Bayer, and Janssen and grants from Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, cancer screening programs around the world ground to a halt as SARS-CoV-2 infection rates surged globally. The effect of this slowdown is now becoming clear.
Thousands of cancer diagnoses are “missing,” and oncologists worry that this will lead to more advanced cancers and higher mortality for years to come.
“I feel like this is an earthquake that’s rocked our health care system. My guess is that you’ll probably still see repercussions of this over the next couple of years at least,” said Sharon Chang, MD, an attending surgical oncologist in the Permanente Medical Group, Fremont, Calif.
She was senior author of a study that analyzed the effects of the slowdown in mammography screening as a result of California’s “shelter-in-place” order on March 17, 2020. In the 2 months that followed, there were 64% fewer breast cancer diagnoses at 21 Kaiser Permanente medical centers, compared with the same period in 2019 (250 vs. 703).
In effect, approximately 450 breast cancer patients had “disappeared,” said coauthor Annie Tang, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, East Bay surgery program.
“What surprised me most from our data was the sheer number of breast cancer patients that were missing,” Dr. Tang said in an interview.
A similar picture has emerged elsewhere.
In Boston, an estimated 1,438 cancerous and precancerous lesions “went missing” during the first 3 months of pandemic shutdown, according to a study from the Massachusetts General Brigham health care system.
In this study, the investigators assessed screening rates for five cancers – breast cancer (mammography), prostate cancer (prostate-specific antigen testing), colorectal cancer (colonoscopy), cervical cancer (Papanicolaou tests), and lung cancer (low-dose CT).
Screening rates during the first peak of the pandemic (March 2 to June 2, 2020) were compared with those during the preceding and following 3 months and during the same 3 months in 2019.
The results showed a pronounced drop in screening rates during the peak pandemic period, compared with the three control periods. Decreases occurred for all screening tests and ranged from –60% to –82%.
There were also significant decreases in cancer diagnoses resulting from the decreases in screening tests, ranging from –19% to –78%.
“Quantifying the actual problem made us realize how much work needs to be done to get us back to prepandemic numbers,” said senior author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, FACS, codirector of the Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s prostate cancer program.
In the Canadian province of Alberta, a similar decrease in cancer diagnoses occurred during the early days of the pandemic.
By the end of 2020, Alberta was “missing” approximately 2,000 cases of invasive cancers and 1,000 cases of noninvasive cancers, Doug Stewart, MD, senior medical director at the Cancer Strategic Clinical Network (SCN) of Alberta Health Services, told this news organization.
Dr. Stewart is able to track cancer diagnoses in Alberta almost in real time through a mandatory cancer registry. Within a month of shutdown, there was a 30% decrease in diagnoses of invasive cancers and a 50% decrease “in the kind of preinvasive cancers that, for the most part, are picked up by screening programs,” said Dr. Stewart.
After the health care system opened up again in the summer, Stewart said, noninvasive cancer diagnoses continued to be 20% lower than expected. There was a 10% shortfall in invasive cancer diagnoses.
The number of diagnoses had returned to normal by December 2020. However, Dr. Stewart is worried that this fact conceals a terrible truth.
The worry is over the backlog. Although the number of diagnoses is now similar to what it was before the pandemic, “people are presenting later, and maybe the cancer is more advanced,” he speculated.
His team at Alberta Health Services is assessing whether the cancers that are being diagnosed now are more advanced. Initial results are anticipated by late April 2021.
In the United Kingdom, there was a similar halt in cancer screening as a result of the country’s lockdown. Researchers now predict an uptick in cancer diagnoses.
Ajay Aggarwal, MD, PhD, consultant clinical oncologist and associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and colleagues have estimated that at least 3,500 deaths from breast, colorectal, esophageal, and lung cancer will occur during the next 5 years in England that could have been avoided had it not been for the lockdown measures necessitated by the pandemic.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Aggarwal warned that these numbers, which are from a modeling study published in August 2020, are “extremely conservative,” because the investigators considered diagnostic delays over only a 3-month period, the analysis involved only four cancers, and it did not reflect deferral of cancer treatment.
“It felt like it was the tip of the iceberg,” Dr. Aggarwal said. He warns that more recent data suggest that “diagnostic delays are probably worse than we predicted.”
He suspects that there is more at play than screening cancellations.
In another study conducted in the United Kingdom, data show “a falling edge of referrals” from primary care to cancer centers early in the pandemic. In that study, investigators analyzed real-time weekly hospital data from eight large British hospitals and found that urgent cancer referrals fell 70% at their lowest point.
“It really surprised me that the urgent referrals dropped so drastically,” said lead author Alvina Lai, PhD, a lecturer in health data analytics at University College London.
She attributed this in part to patients’ adherence to lockdown rules. “Patients are trying to follow government guidelines to stay home and not go to [general practitioners] unless necessary,” Dr. Lai explained in an interview.
Canada, like the United Kingdom, has a publicly funded health care system. Dr. Stewart came to a similar conclusion. “Some patients who have been diagnosed with cancer ... have told me it took them an extra couple of months to even contact the family doc, because they ... didn’t want to bother the family doctor with something that wasn’t COVID, this kind of guilt. They want to do something good for society. You know, most people are just really nice people, and they don’t want to bother the health care system if they don’t have COVID,” Dr. Stewart said.
Shelley Fuld Nasso, CEO of the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, a nonprofit organization based in Silver Spring, Md., agreed that screening shutdowns are not the only danger. “While we agree that screening is really important, we also want to make sure patients are following up with their physicians about symptoms that they have,” she said.
“Some of the speculation or concern about increased mortality for cancer is related to screening, but some of it is related to delayed diagnosis because of not following up on symptoms. ... What concerns me is not everyone has that ability or willingness to advocate for themselves,” she said.
Speaking at a press briefing held by the American Society for Radiation Oncology on March 30, Dr. Nasso related a case involving a patient who experienced severe arm pain. In a teleconsultation with her primary care physician, her condition was diagnosed as arthritis. She was subsequently diagnosed in the ED as having multiple myeloma.
Patients who “feel fine” may postpone their checkups to avoid going to the hospital and risking exposure to COVID-19.
“Some patients are still hesitant about returning for their mammograms or coming in if they feel a breast lump,” Dr. Tang said. “That fear of COVID-19 is still out there, and we don’t know how long patients are going to delay.”
In London, Dr. Aggarwal saw a similar response to the pandemic. “People were overestimating quite significantly what their risk of death was from acquiring COVID-19, and I think that balance was never [redressed] explicitly,” he said.
Public health initiatives to rebalance the messaging are now underway.
Public Health England and National Health Service England launched their Help Us Help You campaign in October 2020. The public information campaign urges people to speak to their doctors if they were “worried about a symptom that could be cancer.”
In Canada, the provincial government in Alberta has launched a public awareness campaign that conveys the message, “cancer has not gone away.”
“Cancer is still the No. 1 cause of potential life-years lost, despite COVID,” Dr. Stewart said. “We need to do what we can to make sure there’s no slippage in survival rates.”
Dr. Tang, Dr. Chang, Dr. Lai, Dr. Stewart, and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationship. Dr. Trinh has received personal fees from Astellas, Bayer, and Janssen and grants from Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Last year, cancer screening programs around the world ground to a halt as SARS-CoV-2 infection rates surged globally. The effect of this slowdown is now becoming clear.
Thousands of cancer diagnoses are “missing,” and oncologists worry that this will lead to more advanced cancers and higher mortality for years to come.
“I feel like this is an earthquake that’s rocked our health care system. My guess is that you’ll probably still see repercussions of this over the next couple of years at least,” said Sharon Chang, MD, an attending surgical oncologist in the Permanente Medical Group, Fremont, Calif.
She was senior author of a study that analyzed the effects of the slowdown in mammography screening as a result of California’s “shelter-in-place” order on March 17, 2020. In the 2 months that followed, there were 64% fewer breast cancer diagnoses at 21 Kaiser Permanente medical centers, compared with the same period in 2019 (250 vs. 703).
In effect, approximately 450 breast cancer patients had “disappeared,” said coauthor Annie Tang, MD, a research fellow at the University of California, San Francisco, East Bay surgery program.
“What surprised me most from our data was the sheer number of breast cancer patients that were missing,” Dr. Tang said in an interview.
A similar picture has emerged elsewhere.
In Boston, an estimated 1,438 cancerous and precancerous lesions “went missing” during the first 3 months of pandemic shutdown, according to a study from the Massachusetts General Brigham health care system.
In this study, the investigators assessed screening rates for five cancers – breast cancer (mammography), prostate cancer (prostate-specific antigen testing), colorectal cancer (colonoscopy), cervical cancer (Papanicolaou tests), and lung cancer (low-dose CT).
Screening rates during the first peak of the pandemic (March 2 to June 2, 2020) were compared with those during the preceding and following 3 months and during the same 3 months in 2019.
The results showed a pronounced drop in screening rates during the peak pandemic period, compared with the three control periods. Decreases occurred for all screening tests and ranged from –60% to –82%.
There were also significant decreases in cancer diagnoses resulting from the decreases in screening tests, ranging from –19% to –78%.
“Quantifying the actual problem made us realize how much work needs to be done to get us back to prepandemic numbers,” said senior author Quoc-Dien Trinh, MD, FACS, codirector of the Dana Farber/Brigham and Women’s prostate cancer program.
In the Canadian province of Alberta, a similar decrease in cancer diagnoses occurred during the early days of the pandemic.
By the end of 2020, Alberta was “missing” approximately 2,000 cases of invasive cancers and 1,000 cases of noninvasive cancers, Doug Stewart, MD, senior medical director at the Cancer Strategic Clinical Network (SCN) of Alberta Health Services, told this news organization.
Dr. Stewart is able to track cancer diagnoses in Alberta almost in real time through a mandatory cancer registry. Within a month of shutdown, there was a 30% decrease in diagnoses of invasive cancers and a 50% decrease “in the kind of preinvasive cancers that, for the most part, are picked up by screening programs,” said Dr. Stewart.
After the health care system opened up again in the summer, Stewart said, noninvasive cancer diagnoses continued to be 20% lower than expected. There was a 10% shortfall in invasive cancer diagnoses.
The number of diagnoses had returned to normal by December 2020. However, Dr. Stewart is worried that this fact conceals a terrible truth.
The worry is over the backlog. Although the number of diagnoses is now similar to what it was before the pandemic, “people are presenting later, and maybe the cancer is more advanced,” he speculated.
His team at Alberta Health Services is assessing whether the cancers that are being diagnosed now are more advanced. Initial results are anticipated by late April 2021.
In the United Kingdom, there was a similar halt in cancer screening as a result of the country’s lockdown. Researchers now predict an uptick in cancer diagnoses.
Ajay Aggarwal, MD, PhD, consultant clinical oncologist and associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, and colleagues have estimated that at least 3,500 deaths from breast, colorectal, esophageal, and lung cancer will occur during the next 5 years in England that could have been avoided had it not been for the lockdown measures necessitated by the pandemic.
Speaking to this news organization, Dr. Aggarwal warned that these numbers, which are from a modeling study published in August 2020, are “extremely conservative,” because the investigators considered diagnostic delays over only a 3-month period, the analysis involved only four cancers, and it did not reflect deferral of cancer treatment.
“It felt like it was the tip of the iceberg,” Dr. Aggarwal said. He warns that more recent data suggest that “diagnostic delays are probably worse than we predicted.”
He suspects that there is more at play than screening cancellations.
In another study conducted in the United Kingdom, data show “a falling edge of referrals” from primary care to cancer centers early in the pandemic. In that study, investigators analyzed real-time weekly hospital data from eight large British hospitals and found that urgent cancer referrals fell 70% at their lowest point.
“It really surprised me that the urgent referrals dropped so drastically,” said lead author Alvina Lai, PhD, a lecturer in health data analytics at University College London.
She attributed this in part to patients’ adherence to lockdown rules. “Patients are trying to follow government guidelines to stay home and not go to [general practitioners] unless necessary,” Dr. Lai explained in an interview.
Canada, like the United Kingdom, has a publicly funded health care system. Dr. Stewart came to a similar conclusion. “Some patients who have been diagnosed with cancer ... have told me it took them an extra couple of months to even contact the family doc, because they ... didn’t want to bother the family doctor with something that wasn’t COVID, this kind of guilt. They want to do something good for society. You know, most people are just really nice people, and they don’t want to bother the health care system if they don’t have COVID,” Dr. Stewart said.
Shelley Fuld Nasso, CEO of the National Coalition for Cancer Survivorship, a nonprofit organization based in Silver Spring, Md., agreed that screening shutdowns are not the only danger. “While we agree that screening is really important, we also want to make sure patients are following up with their physicians about symptoms that they have,” she said.
“Some of the speculation or concern about increased mortality for cancer is related to screening, but some of it is related to delayed diagnosis because of not following up on symptoms. ... What concerns me is not everyone has that ability or willingness to advocate for themselves,” she said.
Speaking at a press briefing held by the American Society for Radiation Oncology on March 30, Dr. Nasso related a case involving a patient who experienced severe arm pain. In a teleconsultation with her primary care physician, her condition was diagnosed as arthritis. She was subsequently diagnosed in the ED as having multiple myeloma.
Patients who “feel fine” may postpone their checkups to avoid going to the hospital and risking exposure to COVID-19.
“Some patients are still hesitant about returning for their mammograms or coming in if they feel a breast lump,” Dr. Tang said. “That fear of COVID-19 is still out there, and we don’t know how long patients are going to delay.”
In London, Dr. Aggarwal saw a similar response to the pandemic. “People were overestimating quite significantly what their risk of death was from acquiring COVID-19, and I think that balance was never [redressed] explicitly,” he said.
Public health initiatives to rebalance the messaging are now underway.
Public Health England and National Health Service England launched their Help Us Help You campaign in October 2020. The public information campaign urges people to speak to their doctors if they were “worried about a symptom that could be cancer.”
In Canada, the provincial government in Alberta has launched a public awareness campaign that conveys the message, “cancer has not gone away.”
“Cancer is still the No. 1 cause of potential life-years lost, despite COVID,” Dr. Stewart said. “We need to do what we can to make sure there’s no slippage in survival rates.”
Dr. Tang, Dr. Chang, Dr. Lai, Dr. Stewart, and Dr. Aggarwal have disclosed no relevant financial relationship. Dr. Trinh has received personal fees from Astellas, Bayer, and Janssen and grants from Intuitive Surgical.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treating metastatic TNBC: Where are we now?
Treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), one of the more lethal breast cancer subtypes, remains a challenge. By definition, TNBC lacks the three telltale molecular signatures known to spur tumor growth: estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). A growing amount of literature shows that these frequently aggressive tumors harbor a rich array of molecular characteristics but no clear oncogenic driver.
“TNBC is incredibly heterogeneous, which makes it challenging to treat,” said Rita Nanda, MD, director of the breast oncology program and associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago. “We have subsets of TNBC that don’t respond to currently available therapies and, as of yet, have no identifiable therapeutic targets.”
Overall, about 40% of patients with TNBC show a pathologic complete response after first-line neoadjuvant chemotherapy – typically anthracycline and taxane-based agents. But for 50% of patients, chemotherapy leaves behind substantial residual cancer tissue. These patients subsequently face a 40%-80% risk for recurrence and progression to advanced disease.
When triple-negative disease metastasizes, survival rates plummet. The most recent data from the National Cancer Institute, which tracked patients by stage of diagnosis between 2010 and 2016, showed steep declines in 5-year survival as TNBC progressed from local (91.2%) to regional (65%) to advanced-stage disease (11.5%).
Experts have started to make headway identifying and targeting different molecular features of advanced TNBC. These approaches often focus on three key areas: targeting cell surface proteins or oncogenes, stimulating an anticancer immune response, or inhibiting an overactive signaling pathway.
“For a patient with metastatic breast cancer, finding a molecular target or an oncogenic driver is essential,” said Kelly McCann, MD, PhD, a hematologist/oncologist in the department of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. “Because TNBC encompasses many different molecular subsets of breast cancer, the development of effective new therapeutics is going to depend on subdividing TNBC into categories with more clear targets.”
A targeted strategy
The Food and Drug Administration’s approval of sacituzumab govitecan, the first antibody-drug conjugate to treat metastatic TNBC, marked an important addition to the TNBC drug armamentarium. “Sacituzumab govitecan is one of the most exciting drugs available for the treatment of metastatic disease,” Dr. Nanda said.
Sacituzumab govitecan, approved as third-line therapy for metastatic TNBC, works by targeting the cell surface protein TROP2, expressed in about 88% of TNBC tumors but rarely in healthy cells.
In the phase 1/2 ASCENT trial, the median progression-free survival was 5.5 months and overall survival was 13.0 months in 108 patients with metastatic TNBC who had received at least two therapies prior to sacituzumab govitecan.
A subsequent phase 3 trial showed progression-free survival of 5.6 months with sacituzumab govitecan and 1.7 months with physician’s choice of chemotherapy. The median overall survival was 12.1 months and 6.7 months, respectively.
But, according to the analysis, TROP2 expression did not necessarily predict who would benefit from sacituzumab govitecan. A biomarker study revealed that although patients with moderate to high TROP2 expression exhibited the strongest treatment response, those with low TROP2 expression also survived longer when given sacituzumab govitecan, compared with chemotherapy alone.
In other words, “patients did better on sacituzumab govitecan regardless of TROP2 expression, which suggests we do not have a good biomarker for identifying who will benefit,” Dr. Nanda said.
Two other investigational antibody-drug conjugates, trastuzumab deruxtecan and ladiratuzumab vedotin, show promise in the metastatic space as well. For instance, the recent phase 2 trial evaluating trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer reported treatment response in 44% of patients with HER2-low tumors.
Given that about 36.6% of TNBC tumors exhibit low levels of HER2 expression, “trastuzumab deruxtecan represents potential in treating HER2-low TNBC,” said Yuan Yuan, MD, PhD, medical oncologist at City of Hope, a comprehensive cancer center in Los Angeles County.
Early results from a phase 1b study showed that trastuzumab deruxtecan produced a response rate of 37% in patients with HER2-low breast cancer.
Investigators are now recruiting for an open-label phase 3 trial to determine whether trastuzumab deruxtecan extends survival in patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancers.
Immunotherapy advances
Immune checkpoint inhibitors represent another promising treatment avenue for metastatic TNBC. Pembrolizumab and atezolizumab, recently approved by the FDA, show moderate progression-free and overall survival benefits in patients with metastatic TNBC expressing PD-L1. Estimates of PD-L1 immune cells present in TNBC tumors vary widely, from about 20% to 65%.
Yet, data on which patients will benefit are not so clear-cut. “These drugs give us more choices and represent the fast-evolving therapeutic landscape in TNBC, but they also leave a lot of unanswered questions about PD-L1 as a biomarker,” Dr. Yuan said.
Take two recent phase 3 trials evaluating atezolizumab: IMpassion130 and IMpassion131. In IMpassion130, patients with PDL1–positive tumors exhibited significantly longer median overall survival on atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel (25.0 months) compared with nab-paclitaxel alone (15.5 months). As with the trend observed in the TROP2 data for sacituzumab govitecan, all patients survived longer on atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel regardless of PD-L1 status: 21.3 months vs. 17.6 months with nab-paclitaxel alone.
However, in IMpassion131, neither progression-free survival nor overall survival significantly improved in the PD-L1–positive group receiving atezolizumab plus paclitaxel compared with paclitaxel alone: Progression-free survival was 5.7 months vs. 6 months, respectively, and overall survival was 28.3 months vs. 22.1 months.
“It is unclear why this study failed to demonstrate a significant improvement in progression-free survival with the addition of atezolizumab to paclitaxel,” Dr. Nanda said. “Perhaps the negative finding has to do with how the trial was conducted, or perhaps the PD-L1 assay used is an unreliable biomarker of immunotherapy benefit.”
Continued efforts to understand TNBC
Given the diversity of metastatic TNBC and the absence of clear molecular targets, researchers are exploring a host of therapeutic strategies in addition to antibody-drug conjugates and immunotherapies.
On the oncogene front, researchers are investigating common mutations in TNBC. About 11% of TNBC tumors, for instance, carry germline mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. These tumors may be more likely to respond to platinum agents and PARP inhibitors, such as FDA-approved olaparib. In a phase 3 trial, patients with metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation who received olaparib exhibited a 2.8-month longer median progression-free survival and a 42% reduced risk for disease progression or death compared with those on standard chemotherapy.
When considering signaling pathways, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway has been the target of numerous clinical trials. Dysregulation of signaling through the PI3K and AKT signaling pathway occurs in 25%-30% of patients with advanced TNBC, and AKT inhibitors have been shown to extend survival in these patients. Data show, for instance, that adding capivasertib to first-line paclitaxel therapy in patients with metastatic TNBC led to longer overall survival – 19.1 months vs. 12.6 with placebo plus paclitaxel – with better survival results in patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN altered tumors.
But there’s more to learn about treating metastatic TNBC. “Relapses tend to occur early in TNBC, and some tumors are inherently resistant to chemotherapy from the get-go,” said Charles Shapiro, MD, medical oncologist, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Understanding the causes of drug response and resistance in patients with metastatic TNBC represents the holy grail.”
Dr. Nanda agreed, noting that advancing treatments for TNBC will hinge on identifying the key factors driving metastasis. “For TNBC, we are still trying to elucidate the best molecular targets, while at the same time trying to identify robust biomarkers to predict benefit from therapies we already have available,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), one of the more lethal breast cancer subtypes, remains a challenge. By definition, TNBC lacks the three telltale molecular signatures known to spur tumor growth: estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). A growing amount of literature shows that these frequently aggressive tumors harbor a rich array of molecular characteristics but no clear oncogenic driver.
“TNBC is incredibly heterogeneous, which makes it challenging to treat,” said Rita Nanda, MD, director of the breast oncology program and associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago. “We have subsets of TNBC that don’t respond to currently available therapies and, as of yet, have no identifiable therapeutic targets.”
Overall, about 40% of patients with TNBC show a pathologic complete response after first-line neoadjuvant chemotherapy – typically anthracycline and taxane-based agents. But for 50% of patients, chemotherapy leaves behind substantial residual cancer tissue. These patients subsequently face a 40%-80% risk for recurrence and progression to advanced disease.
When triple-negative disease metastasizes, survival rates plummet. The most recent data from the National Cancer Institute, which tracked patients by stage of diagnosis between 2010 and 2016, showed steep declines in 5-year survival as TNBC progressed from local (91.2%) to regional (65%) to advanced-stage disease (11.5%).
Experts have started to make headway identifying and targeting different molecular features of advanced TNBC. These approaches often focus on three key areas: targeting cell surface proteins or oncogenes, stimulating an anticancer immune response, or inhibiting an overactive signaling pathway.
“For a patient with metastatic breast cancer, finding a molecular target or an oncogenic driver is essential,” said Kelly McCann, MD, PhD, a hematologist/oncologist in the department of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. “Because TNBC encompasses many different molecular subsets of breast cancer, the development of effective new therapeutics is going to depend on subdividing TNBC into categories with more clear targets.”
A targeted strategy
The Food and Drug Administration’s approval of sacituzumab govitecan, the first antibody-drug conjugate to treat metastatic TNBC, marked an important addition to the TNBC drug armamentarium. “Sacituzumab govitecan is one of the most exciting drugs available for the treatment of metastatic disease,” Dr. Nanda said.
Sacituzumab govitecan, approved as third-line therapy for metastatic TNBC, works by targeting the cell surface protein TROP2, expressed in about 88% of TNBC tumors but rarely in healthy cells.
In the phase 1/2 ASCENT trial, the median progression-free survival was 5.5 months and overall survival was 13.0 months in 108 patients with metastatic TNBC who had received at least two therapies prior to sacituzumab govitecan.
A subsequent phase 3 trial showed progression-free survival of 5.6 months with sacituzumab govitecan and 1.7 months with physician’s choice of chemotherapy. The median overall survival was 12.1 months and 6.7 months, respectively.
But, according to the analysis, TROP2 expression did not necessarily predict who would benefit from sacituzumab govitecan. A biomarker study revealed that although patients with moderate to high TROP2 expression exhibited the strongest treatment response, those with low TROP2 expression also survived longer when given sacituzumab govitecan, compared with chemotherapy alone.
In other words, “patients did better on sacituzumab govitecan regardless of TROP2 expression, which suggests we do not have a good biomarker for identifying who will benefit,” Dr. Nanda said.
Two other investigational antibody-drug conjugates, trastuzumab deruxtecan and ladiratuzumab vedotin, show promise in the metastatic space as well. For instance, the recent phase 2 trial evaluating trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer reported treatment response in 44% of patients with HER2-low tumors.
Given that about 36.6% of TNBC tumors exhibit low levels of HER2 expression, “trastuzumab deruxtecan represents potential in treating HER2-low TNBC,” said Yuan Yuan, MD, PhD, medical oncologist at City of Hope, a comprehensive cancer center in Los Angeles County.
Early results from a phase 1b study showed that trastuzumab deruxtecan produced a response rate of 37% in patients with HER2-low breast cancer.
Investigators are now recruiting for an open-label phase 3 trial to determine whether trastuzumab deruxtecan extends survival in patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancers.
Immunotherapy advances
Immune checkpoint inhibitors represent another promising treatment avenue for metastatic TNBC. Pembrolizumab and atezolizumab, recently approved by the FDA, show moderate progression-free and overall survival benefits in patients with metastatic TNBC expressing PD-L1. Estimates of PD-L1 immune cells present in TNBC tumors vary widely, from about 20% to 65%.
Yet, data on which patients will benefit are not so clear-cut. “These drugs give us more choices and represent the fast-evolving therapeutic landscape in TNBC, but they also leave a lot of unanswered questions about PD-L1 as a biomarker,” Dr. Yuan said.
Take two recent phase 3 trials evaluating atezolizumab: IMpassion130 and IMpassion131. In IMpassion130, patients with PDL1–positive tumors exhibited significantly longer median overall survival on atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel (25.0 months) compared with nab-paclitaxel alone (15.5 months). As with the trend observed in the TROP2 data for sacituzumab govitecan, all patients survived longer on atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel regardless of PD-L1 status: 21.3 months vs. 17.6 months with nab-paclitaxel alone.
However, in IMpassion131, neither progression-free survival nor overall survival significantly improved in the PD-L1–positive group receiving atezolizumab plus paclitaxel compared with paclitaxel alone: Progression-free survival was 5.7 months vs. 6 months, respectively, and overall survival was 28.3 months vs. 22.1 months.
“It is unclear why this study failed to demonstrate a significant improvement in progression-free survival with the addition of atezolizumab to paclitaxel,” Dr. Nanda said. “Perhaps the negative finding has to do with how the trial was conducted, or perhaps the PD-L1 assay used is an unreliable biomarker of immunotherapy benefit.”
Continued efforts to understand TNBC
Given the diversity of metastatic TNBC and the absence of clear molecular targets, researchers are exploring a host of therapeutic strategies in addition to antibody-drug conjugates and immunotherapies.
On the oncogene front, researchers are investigating common mutations in TNBC. About 11% of TNBC tumors, for instance, carry germline mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. These tumors may be more likely to respond to platinum agents and PARP inhibitors, such as FDA-approved olaparib. In a phase 3 trial, patients with metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation who received olaparib exhibited a 2.8-month longer median progression-free survival and a 42% reduced risk for disease progression or death compared with those on standard chemotherapy.
When considering signaling pathways, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway has been the target of numerous clinical trials. Dysregulation of signaling through the PI3K and AKT signaling pathway occurs in 25%-30% of patients with advanced TNBC, and AKT inhibitors have been shown to extend survival in these patients. Data show, for instance, that adding capivasertib to first-line paclitaxel therapy in patients with metastatic TNBC led to longer overall survival – 19.1 months vs. 12.6 with placebo plus paclitaxel – with better survival results in patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN altered tumors.
But there’s more to learn about treating metastatic TNBC. “Relapses tend to occur early in TNBC, and some tumors are inherently resistant to chemotherapy from the get-go,” said Charles Shapiro, MD, medical oncologist, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Understanding the causes of drug response and resistance in patients with metastatic TNBC represents the holy grail.”
Dr. Nanda agreed, noting that advancing treatments for TNBC will hinge on identifying the key factors driving metastasis. “For TNBC, we are still trying to elucidate the best molecular targets, while at the same time trying to identify robust biomarkers to predict benefit from therapies we already have available,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Treating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC), one of the more lethal breast cancer subtypes, remains a challenge. By definition, TNBC lacks the three telltale molecular signatures known to spur tumor growth: estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2). A growing amount of literature shows that these frequently aggressive tumors harbor a rich array of molecular characteristics but no clear oncogenic driver.
“TNBC is incredibly heterogeneous, which makes it challenging to treat,” said Rita Nanda, MD, director of the breast oncology program and associate professor of medicine at the University of Chicago. “We have subsets of TNBC that don’t respond to currently available therapies and, as of yet, have no identifiable therapeutic targets.”
Overall, about 40% of patients with TNBC show a pathologic complete response after first-line neoadjuvant chemotherapy – typically anthracycline and taxane-based agents. But for 50% of patients, chemotherapy leaves behind substantial residual cancer tissue. These patients subsequently face a 40%-80% risk for recurrence and progression to advanced disease.
When triple-negative disease metastasizes, survival rates plummet. The most recent data from the National Cancer Institute, which tracked patients by stage of diagnosis between 2010 and 2016, showed steep declines in 5-year survival as TNBC progressed from local (91.2%) to regional (65%) to advanced-stage disease (11.5%).
Experts have started to make headway identifying and targeting different molecular features of advanced TNBC. These approaches often focus on three key areas: targeting cell surface proteins or oncogenes, stimulating an anticancer immune response, or inhibiting an overactive signaling pathway.
“For a patient with metastatic breast cancer, finding a molecular target or an oncogenic driver is essential,” said Kelly McCann, MD, PhD, a hematologist/oncologist in the department of medicine at the University of California, Los Angeles. “Because TNBC encompasses many different molecular subsets of breast cancer, the development of effective new therapeutics is going to depend on subdividing TNBC into categories with more clear targets.”
A targeted strategy
The Food and Drug Administration’s approval of sacituzumab govitecan, the first antibody-drug conjugate to treat metastatic TNBC, marked an important addition to the TNBC drug armamentarium. “Sacituzumab govitecan is one of the most exciting drugs available for the treatment of metastatic disease,” Dr. Nanda said.
Sacituzumab govitecan, approved as third-line therapy for metastatic TNBC, works by targeting the cell surface protein TROP2, expressed in about 88% of TNBC tumors but rarely in healthy cells.
In the phase 1/2 ASCENT trial, the median progression-free survival was 5.5 months and overall survival was 13.0 months in 108 patients with metastatic TNBC who had received at least two therapies prior to sacituzumab govitecan.
A subsequent phase 3 trial showed progression-free survival of 5.6 months with sacituzumab govitecan and 1.7 months with physician’s choice of chemotherapy. The median overall survival was 12.1 months and 6.7 months, respectively.
But, according to the analysis, TROP2 expression did not necessarily predict who would benefit from sacituzumab govitecan. A biomarker study revealed that although patients with moderate to high TROP2 expression exhibited the strongest treatment response, those with low TROP2 expression also survived longer when given sacituzumab govitecan, compared with chemotherapy alone.
In other words, “patients did better on sacituzumab govitecan regardless of TROP2 expression, which suggests we do not have a good biomarker for identifying who will benefit,” Dr. Nanda said.
Two other investigational antibody-drug conjugates, trastuzumab deruxtecan and ladiratuzumab vedotin, show promise in the metastatic space as well. For instance, the recent phase 2 trial evaluating trastuzumab deruxtecan in patients with HER2-positive breast cancer reported treatment response in 44% of patients with HER2-low tumors.
Given that about 36.6% of TNBC tumors exhibit low levels of HER2 expression, “trastuzumab deruxtecan represents potential in treating HER2-low TNBC,” said Yuan Yuan, MD, PhD, medical oncologist at City of Hope, a comprehensive cancer center in Los Angeles County.
Early results from a phase 1b study showed that trastuzumab deruxtecan produced a response rate of 37% in patients with HER2-low breast cancer.
Investigators are now recruiting for an open-label phase 3 trial to determine whether trastuzumab deruxtecan extends survival in patients with HER2-low metastatic breast cancers.
Immunotherapy advances
Immune checkpoint inhibitors represent another promising treatment avenue for metastatic TNBC. Pembrolizumab and atezolizumab, recently approved by the FDA, show moderate progression-free and overall survival benefits in patients with metastatic TNBC expressing PD-L1. Estimates of PD-L1 immune cells present in TNBC tumors vary widely, from about 20% to 65%.
Yet, data on which patients will benefit are not so clear-cut. “These drugs give us more choices and represent the fast-evolving therapeutic landscape in TNBC, but they also leave a lot of unanswered questions about PD-L1 as a biomarker,” Dr. Yuan said.
Take two recent phase 3 trials evaluating atezolizumab: IMpassion130 and IMpassion131. In IMpassion130, patients with PDL1–positive tumors exhibited significantly longer median overall survival on atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel (25.0 months) compared with nab-paclitaxel alone (15.5 months). As with the trend observed in the TROP2 data for sacituzumab govitecan, all patients survived longer on atezolizumab plus nab-paclitaxel regardless of PD-L1 status: 21.3 months vs. 17.6 months with nab-paclitaxel alone.
However, in IMpassion131, neither progression-free survival nor overall survival significantly improved in the PD-L1–positive group receiving atezolizumab plus paclitaxel compared with paclitaxel alone: Progression-free survival was 5.7 months vs. 6 months, respectively, and overall survival was 28.3 months vs. 22.1 months.
“It is unclear why this study failed to demonstrate a significant improvement in progression-free survival with the addition of atezolizumab to paclitaxel,” Dr. Nanda said. “Perhaps the negative finding has to do with how the trial was conducted, or perhaps the PD-L1 assay used is an unreliable biomarker of immunotherapy benefit.”
Continued efforts to understand TNBC
Given the diversity of metastatic TNBC and the absence of clear molecular targets, researchers are exploring a host of therapeutic strategies in addition to antibody-drug conjugates and immunotherapies.
On the oncogene front, researchers are investigating common mutations in TNBC. About 11% of TNBC tumors, for instance, carry germline mutations in BRCA1 and BRCA2. These tumors may be more likely to respond to platinum agents and PARP inhibitors, such as FDA-approved olaparib. In a phase 3 trial, patients with metastatic HER2-negative breast cancer and a germline BRCA mutation who received olaparib exhibited a 2.8-month longer median progression-free survival and a 42% reduced risk for disease progression or death compared with those on standard chemotherapy.
When considering signaling pathways, the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway has been the target of numerous clinical trials. Dysregulation of signaling through the PI3K and AKT signaling pathway occurs in 25%-30% of patients with advanced TNBC, and AKT inhibitors have been shown to extend survival in these patients. Data show, for instance, that adding capivasertib to first-line paclitaxel therapy in patients with metastatic TNBC led to longer overall survival – 19.1 months vs. 12.6 with placebo plus paclitaxel – with better survival results in patients with PIK3CA/AKT1/PTEN altered tumors.
But there’s more to learn about treating metastatic TNBC. “Relapses tend to occur early in TNBC, and some tumors are inherently resistant to chemotherapy from the get-go,” said Charles Shapiro, MD, medical oncologist, Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, New York. “Understanding the causes of drug response and resistance in patients with metastatic TNBC represents the holy grail.”
Dr. Nanda agreed, noting that advancing treatments for TNBC will hinge on identifying the key factors driving metastasis. “For TNBC, we are still trying to elucidate the best molecular targets, while at the same time trying to identify robust biomarkers to predict benefit from therapies we already have available,” she said.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.