User login
Sharon Worcester is an award-winning medical journalist for MDedge News. She has been with the company since 1996, first as the Southeast Bureau Chief (1996-2009) when the company was known as International Medical News Group, then as a freelance writer (2010-2015) before returning as a reporter in 2015. She previously worked as a daily newspaper reporter covering health and local government. Sharon currently reports primarily on oncology and hematology. She has a BA from Eckerd College and an MA in Mass Communication/Print Journalism from the University of Florida. Connect with her via LinkedIn and follow her on twitter @SW_MedReporter.
Dr. Louis Weiner: AACR presentations highlight new “transformative strategies”
ATLANTA – Several studies featured during a press briefing at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research highlight the types of “transformative strategies” currently being developed and implemented, according to Louis Weiner, MD.
“Had this been the AACR [meeting] 20 years ago ... each one of them would have been a main plenary presentation and would have been the talk of the meeting,” Dr. Weiner, director of the Georgetown Lombardi Cancer Center at Georgetown University, Washington, and press briefing moderator, said of the findings.
While they are well accepted as being high quality presentations of great value, they don’t cause the same amount of stir, he said, adding: “I wouldn’t say we’re jaded, but we’ve come to the point where we almost expect great results at these meetings, and isn’t that wonderful?”
In this video interview he discussed the findings of two of the studies, including the phase 2 UNITY-NHL study and a preclinical Lynch syndrome mouse model used to develop a potential cancer preventive vaccine.
The Lynch syndrome data “suggest the strong possibility that we might be able to immunize people and combine that treatment with standard nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents such as naproxen to delay or reduce the impact of Lynch syndrome.”
“This set of findings ... opens the door to investigators in many different areas of cancer research to explore whether or not there are common frameshift mutations that might create novel neoantigens that we can go after with vaccines – be they for therapeutic benefit or for prevention,” he said.
The UNITY-NHL study, which showed that umbralisib is active and well tolerated as single-agent therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma, suggests “it’s quite possible that [the phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta inhibitor] is going to become a very important element in the treatment of patients with marginal zone lymphomas, and obviously it can be then used in earlier stages of diseases since it’s well tolerated, and it may well have useful activity in other B-cell malignancies,” he said.
Dr. Weiner reported having no relevant disclosures.
ATLANTA – Several studies featured during a press briefing at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research highlight the types of “transformative strategies” currently being developed and implemented, according to Louis Weiner, MD.
“Had this been the AACR [meeting] 20 years ago ... each one of them would have been a main plenary presentation and would have been the talk of the meeting,” Dr. Weiner, director of the Georgetown Lombardi Cancer Center at Georgetown University, Washington, and press briefing moderator, said of the findings.
While they are well accepted as being high quality presentations of great value, they don’t cause the same amount of stir, he said, adding: “I wouldn’t say we’re jaded, but we’ve come to the point where we almost expect great results at these meetings, and isn’t that wonderful?”
In this video interview he discussed the findings of two of the studies, including the phase 2 UNITY-NHL study and a preclinical Lynch syndrome mouse model used to develop a potential cancer preventive vaccine.
The Lynch syndrome data “suggest the strong possibility that we might be able to immunize people and combine that treatment with standard nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents such as naproxen to delay or reduce the impact of Lynch syndrome.”
“This set of findings ... opens the door to investigators in many different areas of cancer research to explore whether or not there are common frameshift mutations that might create novel neoantigens that we can go after with vaccines – be they for therapeutic benefit or for prevention,” he said.
The UNITY-NHL study, which showed that umbralisib is active and well tolerated as single-agent therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma, suggests “it’s quite possible that [the phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta inhibitor] is going to become a very important element in the treatment of patients with marginal zone lymphomas, and obviously it can be then used in earlier stages of diseases since it’s well tolerated, and it may well have useful activity in other B-cell malignancies,” he said.
Dr. Weiner reported having no relevant disclosures.
ATLANTA – Several studies featured during a press briefing at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research highlight the types of “transformative strategies” currently being developed and implemented, according to Louis Weiner, MD.
“Had this been the AACR [meeting] 20 years ago ... each one of them would have been a main plenary presentation and would have been the talk of the meeting,” Dr. Weiner, director of the Georgetown Lombardi Cancer Center at Georgetown University, Washington, and press briefing moderator, said of the findings.
While they are well accepted as being high quality presentations of great value, they don’t cause the same amount of stir, he said, adding: “I wouldn’t say we’re jaded, but we’ve come to the point where we almost expect great results at these meetings, and isn’t that wonderful?”
In this video interview he discussed the findings of two of the studies, including the phase 2 UNITY-NHL study and a preclinical Lynch syndrome mouse model used to develop a potential cancer preventive vaccine.
The Lynch syndrome data “suggest the strong possibility that we might be able to immunize people and combine that treatment with standard nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents such as naproxen to delay or reduce the impact of Lynch syndrome.”
“This set of findings ... opens the door to investigators in many different areas of cancer research to explore whether or not there are common frameshift mutations that might create novel neoantigens that we can go after with vaccines – be they for therapeutic benefit or for prevention,” he said.
The UNITY-NHL study, which showed that umbralisib is active and well tolerated as single-agent therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma, suggests “it’s quite possible that [the phosphoinositide 3-kinase delta inhibitor] is going to become a very important element in the treatment of patients with marginal zone lymphomas, and obviously it can be then used in earlier stages of diseases since it’s well tolerated, and it may well have useful activity in other B-cell malignancies,” he said.
Dr. Weiner reported having no relevant disclosures.
REPORTING FROM AACR
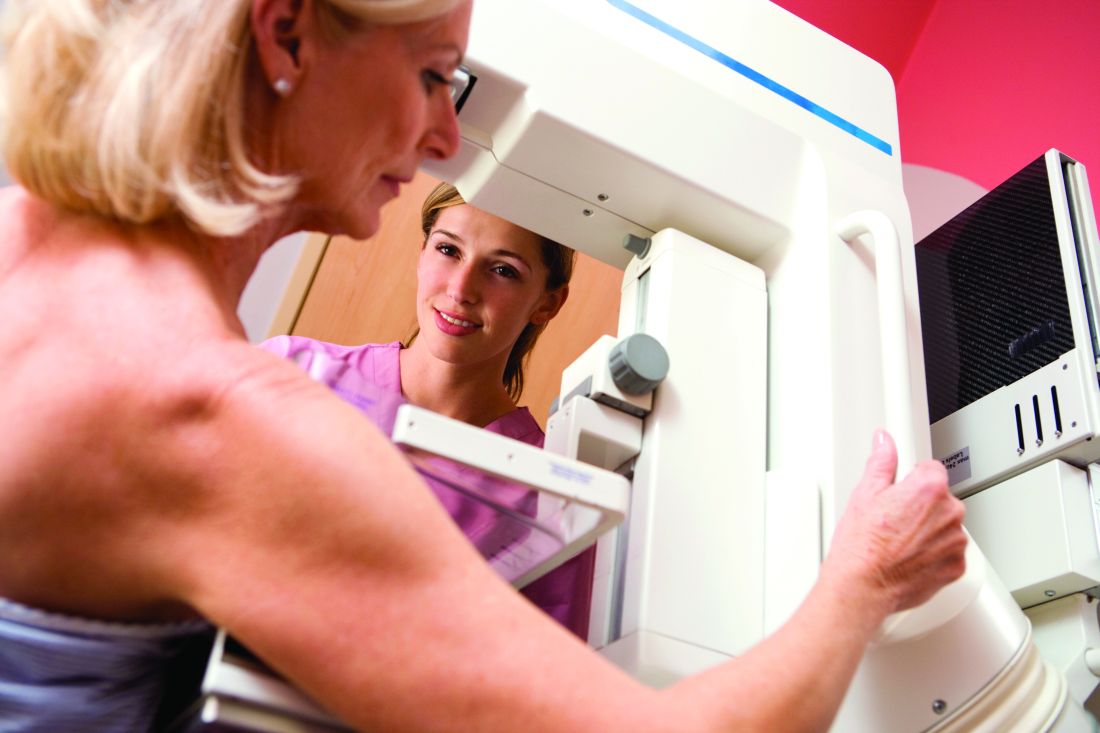
ACP: Average-risk women under 50 can postpone mammogram
(CBE) for screening in such women of any age, according to a new guideline from the American College of Physicians.
Further, clinicians should discuss whether to screen with mammography in average-risk women aged 40-49 years and consider potential harms and benefits, as well as patient preferences. Providers should discontinue screening average-risk women at age 75 years and women with a life expectancy of 10 years or less, Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, of the ACP and colleagues wrote on behalf of the ACP Clinical Guidelines Committee.
The ACP guidance also addresses the varying recommendations from other organizations on the age at which to start and stop screening and on screening intervals, noting that “areas of disagreement include screening in women aged 40 to 49 years, screening in women aged 75 years or older, and recommended screening intervals,” and stresses the importance of patient input.
“Women should be informed participants in personalized decisions about breast cancer screening,” the authors wrote, adding that those under age 50 years without a clear preference for screening should not be screened.
However, the evidence shows that most average-risk women with no symptoms will benefit from mammography every other year beginning at age 50 years, they said.
The statement, published online April 8 in the Annals of Internal Medicine, was derived from a review of seven existing English-language breast cancer screening guidelines and the evidence cited in those guidelines. It’s intended to be a resource for all clinicians.
It differs from the 2017 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines in that ACOG recommends CBE and does not address screening in those with a life expectancy of less than 10 years. It also differs from the 2016 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines, which make no recommendation on CBE and also do not address screening in those with a life expectancy of less than 10 years.
Other guidelines, such as those from the American College of Radiology, American Cancer Society (ACS), the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend CBE, and the World Health Organization guidelines recommend CBE in low resource settings.
“Although CBE continues to be used as part of the examination of symptomatic women, data are sparse on screening asymptomatic women using CBE alone or combined with mammography,” the ACP guideline authors wrote. “The ACS recommends against CBE in average-risk women of any age because of the lack of demonstrated benefit and the potential for false-positive results.”
The guidance, which does not apply to patients with prior abnormal screening results or those at higher breast cancer risk, also includes an evidence-driven “talking points with patients” section based on frequently asked questions.
An important goal of the ACP Clinical Guidelines Committee in developing the guidance is to reduce overdiagnosis and overtreatment, which affects about 20% of women diagnosed over a 10-year period.
The committee reviewed all national guidelines published in English between January 1, 2013, and November 15, 2017, in the National Guideline Clearinghouse or Guidelines International Network library, and it also selected other guidelines commonly used in clinical practice. The committee evaluated the quality of each by using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II (AGREE II) instrument.
Alex Krist, MD, the USPSTF vice-chairperson, offered support for the “shift toward shared decision making that is emerging” and added it’s “part of a larger movement toward empowering people with information not only about the potential benefits but also the potential harms of screening tests.”
“In its 2016 recommendation, the Task Force found that the value of mammography increases with age, with women ages 50-74 benefiting most from screening. For women in their 40s, the Task Force also found that mammography screening every two years can be effective,” he told this publication. “We recommend that the decision to start screening should be an individual one, taking into account a woman’s health history, preferences, and how she values the different potential benefits and harms.”
Dr. Krist further noted that the USPSTF, ACP, and many others “have all affirmed that mammography is an important tool to reduce breast cancer mortality and that the benefits of mammography increase with age.”
Likewise, Robert Smith, PhD, vice president of cancer screening for the ACS, noted that the ACP guidance generally aligns with ACS and USPSTF guidelines because all “support informed decision making starting at age 40, and screening every two years starting at age 50 (USPSTF) or 55 (ACS).”
“The fact that all guidelines are not totally in sync is not unexpected. ... The most important thing to recognize is that all of these guidelines stress that regular mammography plays an important role in breast cancer early detection, and women should be aware of its benefits and limitations, and also remain vigilant and report any breast changes,” he said.
The guidance authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Qaseem A et al., Ann Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.7326/M18-2147.
The ACP guidance statements provide “clarity and simplicity amidst the chaos of diverging guidelines,” Joann G. Elmore, MD, and Christoph I. Lee, MD, wrote in an editorial that accompanied the guideline (Ann Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.7326/M19-0726).
The four statements included in the guidance represent the convergence of differing recommendations, but they also highlight points for physicians to consider in shared decision making with patients, the editorial authors wrote.
Lacking, however, is advice on how clinicians should go about stopping screening in certain patients, they noted.
“We need reliable ways to determine life expectancy given comorbid conditions, as well as methods to appropriately manage the discussion about stopping screening. ... The cessation of routine screening is a highly uncomfortable situation for which we as clinicians currently have little guidance and few tools. At this crossroads of confusion, we need a clear path toward informed, tailored, risk-based screening for breast cancer,” they wrote adding that future guidance statements should “move beyond emphasizing variation across guidelines and instead provide more advice on how to implement high-value screening and deimplement low-value screening.”
Dr. Elmore is with the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Lee is with the University of Washington, Seattle.
The ACP guidance statements provide “clarity and simplicity amidst the chaos of diverging guidelines,” Joann G. Elmore, MD, and Christoph I. Lee, MD, wrote in an editorial that accompanied the guideline (Ann Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.7326/M19-0726).
The four statements included in the guidance represent the convergence of differing recommendations, but they also highlight points for physicians to consider in shared decision making with patients, the editorial authors wrote.
Lacking, however, is advice on how clinicians should go about stopping screening in certain patients, they noted.
“We need reliable ways to determine life expectancy given comorbid conditions, as well as methods to appropriately manage the discussion about stopping screening. ... The cessation of routine screening is a highly uncomfortable situation for which we as clinicians currently have little guidance and few tools. At this crossroads of confusion, we need a clear path toward informed, tailored, risk-based screening for breast cancer,” they wrote adding that future guidance statements should “move beyond emphasizing variation across guidelines and instead provide more advice on how to implement high-value screening and deimplement low-value screening.”
Dr. Elmore is with the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Lee is with the University of Washington, Seattle.
The ACP guidance statements provide “clarity and simplicity amidst the chaos of diverging guidelines,” Joann G. Elmore, MD, and Christoph I. Lee, MD, wrote in an editorial that accompanied the guideline (Ann Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.7326/M19-0726).
The four statements included in the guidance represent the convergence of differing recommendations, but they also highlight points for physicians to consider in shared decision making with patients, the editorial authors wrote.
Lacking, however, is advice on how clinicians should go about stopping screening in certain patients, they noted.
“We need reliable ways to determine life expectancy given comorbid conditions, as well as methods to appropriately manage the discussion about stopping screening. ... The cessation of routine screening is a highly uncomfortable situation for which we as clinicians currently have little guidance and few tools. At this crossroads of confusion, we need a clear path toward informed, tailored, risk-based screening for breast cancer,” they wrote adding that future guidance statements should “move beyond emphasizing variation across guidelines and instead provide more advice on how to implement high-value screening and deimplement low-value screening.”
Dr. Elmore is with the University of California, Los Angeles. Dr. Lee is with the University of Washington, Seattle.
(CBE) for screening in such women of any age, according to a new guideline from the American College of Physicians.
Further, clinicians should discuss whether to screen with mammography in average-risk women aged 40-49 years and consider potential harms and benefits, as well as patient preferences. Providers should discontinue screening average-risk women at age 75 years and women with a life expectancy of 10 years or less, Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, of the ACP and colleagues wrote on behalf of the ACP Clinical Guidelines Committee.
The ACP guidance also addresses the varying recommendations from other organizations on the age at which to start and stop screening and on screening intervals, noting that “areas of disagreement include screening in women aged 40 to 49 years, screening in women aged 75 years or older, and recommended screening intervals,” and stresses the importance of patient input.
“Women should be informed participants in personalized decisions about breast cancer screening,” the authors wrote, adding that those under age 50 years without a clear preference for screening should not be screened.
However, the evidence shows that most average-risk women with no symptoms will benefit from mammography every other year beginning at age 50 years, they said.
The statement, published online April 8 in the Annals of Internal Medicine, was derived from a review of seven existing English-language breast cancer screening guidelines and the evidence cited in those guidelines. It’s intended to be a resource for all clinicians.
It differs from the 2017 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines in that ACOG recommends CBE and does not address screening in those with a life expectancy of less than 10 years. It also differs from the 2016 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines, which make no recommendation on CBE and also do not address screening in those with a life expectancy of less than 10 years.
Other guidelines, such as those from the American College of Radiology, American Cancer Society (ACS), the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend CBE, and the World Health Organization guidelines recommend CBE in low resource settings.
“Although CBE continues to be used as part of the examination of symptomatic women, data are sparse on screening asymptomatic women using CBE alone or combined with mammography,” the ACP guideline authors wrote. “The ACS recommends against CBE in average-risk women of any age because of the lack of demonstrated benefit and the potential for false-positive results.”
The guidance, which does not apply to patients with prior abnormal screening results or those at higher breast cancer risk, also includes an evidence-driven “talking points with patients” section based on frequently asked questions.
An important goal of the ACP Clinical Guidelines Committee in developing the guidance is to reduce overdiagnosis and overtreatment, which affects about 20% of women diagnosed over a 10-year period.
The committee reviewed all national guidelines published in English between January 1, 2013, and November 15, 2017, in the National Guideline Clearinghouse or Guidelines International Network library, and it also selected other guidelines commonly used in clinical practice. The committee evaluated the quality of each by using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II (AGREE II) instrument.
Alex Krist, MD, the USPSTF vice-chairperson, offered support for the “shift toward shared decision making that is emerging” and added it’s “part of a larger movement toward empowering people with information not only about the potential benefits but also the potential harms of screening tests.”
“In its 2016 recommendation, the Task Force found that the value of mammography increases with age, with women ages 50-74 benefiting most from screening. For women in their 40s, the Task Force also found that mammography screening every two years can be effective,” he told this publication. “We recommend that the decision to start screening should be an individual one, taking into account a woman’s health history, preferences, and how she values the different potential benefits and harms.”
Dr. Krist further noted that the USPSTF, ACP, and many others “have all affirmed that mammography is an important tool to reduce breast cancer mortality and that the benefits of mammography increase with age.”
Likewise, Robert Smith, PhD, vice president of cancer screening for the ACS, noted that the ACP guidance generally aligns with ACS and USPSTF guidelines because all “support informed decision making starting at age 40, and screening every two years starting at age 50 (USPSTF) or 55 (ACS).”
“The fact that all guidelines are not totally in sync is not unexpected. ... The most important thing to recognize is that all of these guidelines stress that regular mammography plays an important role in breast cancer early detection, and women should be aware of its benefits and limitations, and also remain vigilant and report any breast changes,” he said.
The guidance authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Qaseem A et al., Ann Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.7326/M18-2147.
(CBE) for screening in such women of any age, according to a new guideline from the American College of Physicians.
Further, clinicians should discuss whether to screen with mammography in average-risk women aged 40-49 years and consider potential harms and benefits, as well as patient preferences. Providers should discontinue screening average-risk women at age 75 years and women with a life expectancy of 10 years or less, Amir Qaseem, MD, PhD, of the ACP and colleagues wrote on behalf of the ACP Clinical Guidelines Committee.
The ACP guidance also addresses the varying recommendations from other organizations on the age at which to start and stop screening and on screening intervals, noting that “areas of disagreement include screening in women aged 40 to 49 years, screening in women aged 75 years or older, and recommended screening intervals,” and stresses the importance of patient input.
“Women should be informed participants in personalized decisions about breast cancer screening,” the authors wrote, adding that those under age 50 years without a clear preference for screening should not be screened.
However, the evidence shows that most average-risk women with no symptoms will benefit from mammography every other year beginning at age 50 years, they said.
The statement, published online April 8 in the Annals of Internal Medicine, was derived from a review of seven existing English-language breast cancer screening guidelines and the evidence cited in those guidelines. It’s intended to be a resource for all clinicians.
It differs from the 2017 American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) guidelines in that ACOG recommends CBE and does not address screening in those with a life expectancy of less than 10 years. It also differs from the 2016 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) guidelines, which make no recommendation on CBE and also do not address screening in those with a life expectancy of less than 10 years.
Other guidelines, such as those from the American College of Radiology, American Cancer Society (ACS), the Canadian Task Force on Preventive Health Care, and the National Comprehensive Cancer Network, recommend CBE, and the World Health Organization guidelines recommend CBE in low resource settings.
“Although CBE continues to be used as part of the examination of symptomatic women, data are sparse on screening asymptomatic women using CBE alone or combined with mammography,” the ACP guideline authors wrote. “The ACS recommends against CBE in average-risk women of any age because of the lack of demonstrated benefit and the potential for false-positive results.”
The guidance, which does not apply to patients with prior abnormal screening results or those at higher breast cancer risk, also includes an evidence-driven “talking points with patients” section based on frequently asked questions.
An important goal of the ACP Clinical Guidelines Committee in developing the guidance is to reduce overdiagnosis and overtreatment, which affects about 20% of women diagnosed over a 10-year period.
The committee reviewed all national guidelines published in English between January 1, 2013, and November 15, 2017, in the National Guideline Clearinghouse or Guidelines International Network library, and it also selected other guidelines commonly used in clinical practice. The committee evaluated the quality of each by using the Appraisal of Guidelines for Research and Evaluation II (AGREE II) instrument.
Alex Krist, MD, the USPSTF vice-chairperson, offered support for the “shift toward shared decision making that is emerging” and added it’s “part of a larger movement toward empowering people with information not only about the potential benefits but also the potential harms of screening tests.”
“In its 2016 recommendation, the Task Force found that the value of mammography increases with age, with women ages 50-74 benefiting most from screening. For women in their 40s, the Task Force also found that mammography screening every two years can be effective,” he told this publication. “We recommend that the decision to start screening should be an individual one, taking into account a woman’s health history, preferences, and how she values the different potential benefits and harms.”
Dr. Krist further noted that the USPSTF, ACP, and many others “have all affirmed that mammography is an important tool to reduce breast cancer mortality and that the benefits of mammography increase with age.”
Likewise, Robert Smith, PhD, vice president of cancer screening for the ACS, noted that the ACP guidance generally aligns with ACS and USPSTF guidelines because all “support informed decision making starting at age 40, and screening every two years starting at age 50 (USPSTF) or 55 (ACS).”
“The fact that all guidelines are not totally in sync is not unexpected. ... The most important thing to recognize is that all of these guidelines stress that regular mammography plays an important role in breast cancer early detection, and women should be aware of its benefits and limitations, and also remain vigilant and report any breast changes,” he said.
The guidance authors reported having no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Qaseem A et al., Ann Intern Med. 2019. doi: 10.7326/M18-2147.
REPORTING FROM THE ANNALS OF INTERNAL MEDICINE
Preclinical findings highlight value of Lynch syndrome for cancer vaccine development
ATLANTA – Lynch syndrome serves as an excellent platform for the development of immunoprevention cancer vaccines, and findings from a preclinical Lynch syndrome mouse model support ongoing research, according to Steven M. Lipkin, MD, PhD.
A novel vaccine, which included peptides encoding four intestinal cancer frameshift peptide (FSP) neoantigens derived from coding microsatellite (cMS) mutations in the genes Nacad, Maz, Xirp1, and Senp6 elicited strong antigen-specific cellular immune responses in the model, Dr. Lipkin, the Gladys and Roland Harriman Professor of Medicine and vice chair for research in the Sanford and Joan Weill Department of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
CD4-specific T cell responses were detected for Maz, Nacad, and Senp6, and CD8-positive T cells were detected for Xirp1 and Nacad, he noted, explaining that the findings come in the wake of a recently completed clinical phase 1/2a trial that successfully demonstrated safety and immunogenicity of an FSP neoantigen-based vaccine in microsatellite unstable (MSI) colorectal cancer patients.
The current effort to further develop a cancer preventive vaccine against MSI cancers in Lynch syndrome using a preclinical mouse model involved a systematic database search to identify cMS sequences in the murine genome. Intestinal tumors obtained from Lynch syndrome mice were evaluated for mutations affecting these candidate cMS, and of 13 with a mutation frequency of 15% or higher, the 4 FSP neoantigens ultimately included in the vaccine elicited strong antigen-specific cellular immune responses.
Vaccination with peptides encoding these four intestinal cancer FSP neoantigens promoted antineoantigen immunity, reduced intestinal tumorigenicity, and prolonged overall survival, Dr. Lipkin said.
Further, based on preclinical data suggesting that naproxen in this setting might provide better risk-reducing effects, compared with aspirin (which has previously been shown to reduce colorectal cancer risk in Lynch syndrome patients), its addition to the vaccine did, indeed, improve response, he noted, explaining that naproxen worked as “sort of a super-aspirin,” that improved overall survival, compared with vaccine alone or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents alone.
In a video interview, Dr. Lipkin describes his research and its potential implications for the immunoprevention of Lynch syndrome and other cancers.
Vaccination with as few as four mutations that occur across Lynch syndrome tumors induced complete cures in some mice and delays in disease onset in others, he said.
“[This is] a very simple approach, very effective,” he added, noting that the T cells are now being studied to better understand the biology of the effects. “The idea of immunoprevention ... is actually very exciting and ... can be expanded beyond this.”
Lynch syndrome is a “great place to start,” because of the high rate of mutations, which are the most immunogenic types of mutations, he said.
“If we can get this basic paradigm to work, I think we can expand it to other types of mutations – for example, KRAS or BRAF, which are seen frequently in lung cancers, colon cancers, stomach cancers, pancreatic cancers, and others,” he said, noting that a proposal for a phase 1 clinical trial has been submitted.
ATLANTA – Lynch syndrome serves as an excellent platform for the development of immunoprevention cancer vaccines, and findings from a preclinical Lynch syndrome mouse model support ongoing research, according to Steven M. Lipkin, MD, PhD.
A novel vaccine, which included peptides encoding four intestinal cancer frameshift peptide (FSP) neoantigens derived from coding microsatellite (cMS) mutations in the genes Nacad, Maz, Xirp1, and Senp6 elicited strong antigen-specific cellular immune responses in the model, Dr. Lipkin, the Gladys and Roland Harriman Professor of Medicine and vice chair for research in the Sanford and Joan Weill Department of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
CD4-specific T cell responses were detected for Maz, Nacad, and Senp6, and CD8-positive T cells were detected for Xirp1 and Nacad, he noted, explaining that the findings come in the wake of a recently completed clinical phase 1/2a trial that successfully demonstrated safety and immunogenicity of an FSP neoantigen-based vaccine in microsatellite unstable (MSI) colorectal cancer patients.
The current effort to further develop a cancer preventive vaccine against MSI cancers in Lynch syndrome using a preclinical mouse model involved a systematic database search to identify cMS sequences in the murine genome. Intestinal tumors obtained from Lynch syndrome mice were evaluated for mutations affecting these candidate cMS, and of 13 with a mutation frequency of 15% or higher, the 4 FSP neoantigens ultimately included in the vaccine elicited strong antigen-specific cellular immune responses.
Vaccination with peptides encoding these four intestinal cancer FSP neoantigens promoted antineoantigen immunity, reduced intestinal tumorigenicity, and prolonged overall survival, Dr. Lipkin said.
Further, based on preclinical data suggesting that naproxen in this setting might provide better risk-reducing effects, compared with aspirin (which has previously been shown to reduce colorectal cancer risk in Lynch syndrome patients), its addition to the vaccine did, indeed, improve response, he noted, explaining that naproxen worked as “sort of a super-aspirin,” that improved overall survival, compared with vaccine alone or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents alone.
In a video interview, Dr. Lipkin describes his research and its potential implications for the immunoprevention of Lynch syndrome and other cancers.
Vaccination with as few as four mutations that occur across Lynch syndrome tumors induced complete cures in some mice and delays in disease onset in others, he said.
“[This is] a very simple approach, very effective,” he added, noting that the T cells are now being studied to better understand the biology of the effects. “The idea of immunoprevention ... is actually very exciting and ... can be expanded beyond this.”
Lynch syndrome is a “great place to start,” because of the high rate of mutations, which are the most immunogenic types of mutations, he said.
“If we can get this basic paradigm to work, I think we can expand it to other types of mutations – for example, KRAS or BRAF, which are seen frequently in lung cancers, colon cancers, stomach cancers, pancreatic cancers, and others,” he said, noting that a proposal for a phase 1 clinical trial has been submitted.
ATLANTA – Lynch syndrome serves as an excellent platform for the development of immunoprevention cancer vaccines, and findings from a preclinical Lynch syndrome mouse model support ongoing research, according to Steven M. Lipkin, MD, PhD.
A novel vaccine, which included peptides encoding four intestinal cancer frameshift peptide (FSP) neoantigens derived from coding microsatellite (cMS) mutations in the genes Nacad, Maz, Xirp1, and Senp6 elicited strong antigen-specific cellular immune responses in the model, Dr. Lipkin, the Gladys and Roland Harriman Professor of Medicine and vice chair for research in the Sanford and Joan Weill Department of Medicine, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
CD4-specific T cell responses were detected for Maz, Nacad, and Senp6, and CD8-positive T cells were detected for Xirp1 and Nacad, he noted, explaining that the findings come in the wake of a recently completed clinical phase 1/2a trial that successfully demonstrated safety and immunogenicity of an FSP neoantigen-based vaccine in microsatellite unstable (MSI) colorectal cancer patients.
The current effort to further develop a cancer preventive vaccine against MSI cancers in Lynch syndrome using a preclinical mouse model involved a systematic database search to identify cMS sequences in the murine genome. Intestinal tumors obtained from Lynch syndrome mice were evaluated for mutations affecting these candidate cMS, and of 13 with a mutation frequency of 15% or higher, the 4 FSP neoantigens ultimately included in the vaccine elicited strong antigen-specific cellular immune responses.
Vaccination with peptides encoding these four intestinal cancer FSP neoantigens promoted antineoantigen immunity, reduced intestinal tumorigenicity, and prolonged overall survival, Dr. Lipkin said.
Further, based on preclinical data suggesting that naproxen in this setting might provide better risk-reducing effects, compared with aspirin (which has previously been shown to reduce colorectal cancer risk in Lynch syndrome patients), its addition to the vaccine did, indeed, improve response, he noted, explaining that naproxen worked as “sort of a super-aspirin,” that improved overall survival, compared with vaccine alone or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory agents alone.
In a video interview, Dr. Lipkin describes his research and its potential implications for the immunoprevention of Lynch syndrome and other cancers.
Vaccination with as few as four mutations that occur across Lynch syndrome tumors induced complete cures in some mice and delays in disease onset in others, he said.
“[This is] a very simple approach, very effective,” he added, noting that the T cells are now being studied to better understand the biology of the effects. “The idea of immunoprevention ... is actually very exciting and ... can be expanded beyond this.”
Lynch syndrome is a “great place to start,” because of the high rate of mutations, which are the most immunogenic types of mutations, he said.
“If we can get this basic paradigm to work, I think we can expand it to other types of mutations – for example, KRAS or BRAF, which are seen frequently in lung cancers, colon cancers, stomach cancers, pancreatic cancers, and others,” he said, noting that a proposal for a phase 1 clinical trial has been submitted.
REPORTING FROM AACR 2019
UNITY-NHL: Interim findings show activity, tolerability of umbralisib for R/R MZL
ATLANTA – The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta inhibitor umbralisib is active and well tolerated as single-agent therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma, according to findings from the ongoing phase 2 UNITY-NHL study.
The best overall response rate (ORR) among 42 study participants with at least 9 months of follow-up was 52% by both independent review committee (IRC) and investigator assessment, and the complete response rate was 19%, Nathan H. Fowler, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The ORR by IRC assessment for those with extranodal, nodal, and splenic disease was 57%, 42%, and 43%, respectively, and for those with prior chemo-immunotherapy and those refractory to their last line of therapy, the ORR was 53% and 38%, respectively, said Dr. Fowler of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
The clinical benefit rate was 88%, and the median duration of response and progression-free survival (PFS) have not been reached; 12-month PFS is estimated at 66%, he added.
Patients in the marginal zone lymphoma cohort of the multicohort trial, which is evaluating umbralisib both as monotherapy and as part of various combinations in patients with previously treated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, received single agent umbralisib at a dose of 800 mg daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
“Most patients who have responded continue on drug,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Fowler also further discussed the findings to date with respect to response, adverse events, and future directions in the wake of the breakthrough therapy designation recently granted by the Food and Drug Administration for umbralisib based on these findings.
“Despite the fact that a lot of things work in the front line, when patients relapse, especially when they become refractory to rituximab, there are limited options available,” he said, noting that currently used treatments are associated with significant adverse event and short remission times. “We still need better options.”
ATLANTA – The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta inhibitor umbralisib is active and well tolerated as single-agent therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma, according to findings from the ongoing phase 2 UNITY-NHL study.
The best overall response rate (ORR) among 42 study participants with at least 9 months of follow-up was 52% by both independent review committee (IRC) and investigator assessment, and the complete response rate was 19%, Nathan H. Fowler, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The ORR by IRC assessment for those with extranodal, nodal, and splenic disease was 57%, 42%, and 43%, respectively, and for those with prior chemo-immunotherapy and those refractory to their last line of therapy, the ORR was 53% and 38%, respectively, said Dr. Fowler of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
The clinical benefit rate was 88%, and the median duration of response and progression-free survival (PFS) have not been reached; 12-month PFS is estimated at 66%, he added.
Patients in the marginal zone lymphoma cohort of the multicohort trial, which is evaluating umbralisib both as monotherapy and as part of various combinations in patients with previously treated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, received single agent umbralisib at a dose of 800 mg daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
“Most patients who have responded continue on drug,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Fowler also further discussed the findings to date with respect to response, adverse events, and future directions in the wake of the breakthrough therapy designation recently granted by the Food and Drug Administration for umbralisib based on these findings.
“Despite the fact that a lot of things work in the front line, when patients relapse, especially when they become refractory to rituximab, there are limited options available,” he said, noting that currently used treatments are associated with significant adverse event and short remission times. “We still need better options.”
ATLANTA – The phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) delta inhibitor umbralisib is active and well tolerated as single-agent therapy in patients with relapsed or refractory marginal zone lymphoma, according to findings from the ongoing phase 2 UNITY-NHL study.
The best overall response rate (ORR) among 42 study participants with at least 9 months of follow-up was 52% by both independent review committee (IRC) and investigator assessment, and the complete response rate was 19%, Nathan H. Fowler, MD, reported at the annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research.
The ORR by IRC assessment for those with extranodal, nodal, and splenic disease was 57%, 42%, and 43%, respectively, and for those with prior chemo-immunotherapy and those refractory to their last line of therapy, the ORR was 53% and 38%, respectively, said Dr. Fowler of MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
The clinical benefit rate was 88%, and the median duration of response and progression-free survival (PFS) have not been reached; 12-month PFS is estimated at 66%, he added.
Patients in the marginal zone lymphoma cohort of the multicohort trial, which is evaluating umbralisib both as monotherapy and as part of various combinations in patients with previously treated non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma, received single agent umbralisib at a dose of 800 mg daily until disease progression or unacceptable toxicity.
“Most patients who have responded continue on drug,” he said in a video interview.
Dr. Fowler also further discussed the findings to date with respect to response, adverse events, and future directions in the wake of the breakthrough therapy designation recently granted by the Food and Drug Administration for umbralisib based on these findings.
“Despite the fact that a lot of things work in the front line, when patients relapse, especially when they become refractory to rituximab, there are limited options available,” he said, noting that currently used treatments are associated with significant adverse event and short remission times. “We still need better options.”
REPORTING FROM AACR 2019
Tisotumab vedotin shows promise in recurrent, metastatic cervical cancer
HONOLULU – The novel antibody-drug conjugate tisotumab vedotin (TV) shows encouraging activity and tolerability in heavily pretreated recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, according to findings from the phase 1/2a innovaTV 201 trial.
The investigator-assessed overall response rate (ORR) among 55 patients enrolled in the cervical cancer expansion portion of the study was 35%, and the confirmed response rate was 22%, including one complete response lasting 46 weeks, David S. Hong, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
The median duration of response in confirmed responders was 6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4.1 months, and 6-month PFS was 40%, said Dr. Hong, deputy chair, department of investigational cancer therapeutics, division of cancer medicine, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“Overall, the independent review and investigator review were highly correlated,” he noted.
Study participants had recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer that progressed on standard therapy, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status scores of 0-1. Most had received at least two prior therapies.
As established in the phase 1 dose-escalation portion of the study, TV in the expansion phase was given at a dose of 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks until disease progression, toxicity, or withdrawal.
Median follow-up was 3.5 months and the median number of doses received was four; the treatment had acceptable tolerability, Dr. Hong said, noting that no treatment-related deaths occurred, and only 13% of patients had a dose reduction caused by an adverse event (AE).
The most common AE occurring in more than 20% of patients was epistaxis; most cases were grade 1. AEs of special interest and possibly related to the TV mechanism of action included neuropathy, bleeding-related events, and ocular events.
While there were a few cases of vaginal bleeding, they were believed to be caused by underlying disease, he noted.
The ocular events noted early in phase 1 of the study included mainly dry eyes and conjunctivitis, but a plan to mitigate these events, which involved the use of steroid eye drops, cooling eye masks, and dose reductions, reduced their incidence.
There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events related to the agent, he said, noting that most patients came off study because of disease progression.
The prognosis for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer is very poor, with a 5-year survival rate of only about 17%, Dr. Hong said, adding that data on the overall response and survival after the first line of therapy are somewhat limited.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) received Food and Drug Administration approval based on second-line setting data from the Keynote-158 trial showing a median ORR of just 14% and median PFS of just 2.1 months in programmed death-ligand 1–positive cervical cancer, he noted.
“Tissue factor (TF) is a protein expressed in cervical cancer, as well as ... a broad range of solid tumors. It is associated with high tumor stage, metastasis, and poor prognosis,” he explained. “TV is a first-in-class antibody-drug conjugate that’s a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting tissue factor.”
The drug, which has multiple mechanisms of action, is conjugated to the microtubule disrupting agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) via a protease-cleavable linker. Findings regarding its safety and tolerability in cervical cancer and a number of other tumors were published recently in The Lancet.
Dr. Hong’s presentation focused on the cervical cancer cohort.
The median PFS in innovaTV 201 compares favorably with that for pembrolizumab and supports continued investigation of TV, he said, noting that phase 2 studies of TV alone and in combination with other agents for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, as well as for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, are ongoing.
The innovaTV 201 trial is sponsored by Genmab A/S. Dr. Hong reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Hong DS et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 19.
HONOLULU – The novel antibody-drug conjugate tisotumab vedotin (TV) shows encouraging activity and tolerability in heavily pretreated recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, according to findings from the phase 1/2a innovaTV 201 trial.
The investigator-assessed overall response rate (ORR) among 55 patients enrolled in the cervical cancer expansion portion of the study was 35%, and the confirmed response rate was 22%, including one complete response lasting 46 weeks, David S. Hong, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
The median duration of response in confirmed responders was 6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4.1 months, and 6-month PFS was 40%, said Dr. Hong, deputy chair, department of investigational cancer therapeutics, division of cancer medicine, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“Overall, the independent review and investigator review were highly correlated,” he noted.
Study participants had recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer that progressed on standard therapy, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status scores of 0-1. Most had received at least two prior therapies.
As established in the phase 1 dose-escalation portion of the study, TV in the expansion phase was given at a dose of 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks until disease progression, toxicity, or withdrawal.
Median follow-up was 3.5 months and the median number of doses received was four; the treatment had acceptable tolerability, Dr. Hong said, noting that no treatment-related deaths occurred, and only 13% of patients had a dose reduction caused by an adverse event (AE).
The most common AE occurring in more than 20% of patients was epistaxis; most cases were grade 1. AEs of special interest and possibly related to the TV mechanism of action included neuropathy, bleeding-related events, and ocular events.
While there were a few cases of vaginal bleeding, they were believed to be caused by underlying disease, he noted.
The ocular events noted early in phase 1 of the study included mainly dry eyes and conjunctivitis, but a plan to mitigate these events, which involved the use of steroid eye drops, cooling eye masks, and dose reductions, reduced their incidence.
There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events related to the agent, he said, noting that most patients came off study because of disease progression.
The prognosis for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer is very poor, with a 5-year survival rate of only about 17%, Dr. Hong said, adding that data on the overall response and survival after the first line of therapy are somewhat limited.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) received Food and Drug Administration approval based on second-line setting data from the Keynote-158 trial showing a median ORR of just 14% and median PFS of just 2.1 months in programmed death-ligand 1–positive cervical cancer, he noted.
“Tissue factor (TF) is a protein expressed in cervical cancer, as well as ... a broad range of solid tumors. It is associated with high tumor stage, metastasis, and poor prognosis,” he explained. “TV is a first-in-class antibody-drug conjugate that’s a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting tissue factor.”
The drug, which has multiple mechanisms of action, is conjugated to the microtubule disrupting agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) via a protease-cleavable linker. Findings regarding its safety and tolerability in cervical cancer and a number of other tumors were published recently in The Lancet.
Dr. Hong’s presentation focused on the cervical cancer cohort.
The median PFS in innovaTV 201 compares favorably with that for pembrolizumab and supports continued investigation of TV, he said, noting that phase 2 studies of TV alone and in combination with other agents for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, as well as for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, are ongoing.
The innovaTV 201 trial is sponsored by Genmab A/S. Dr. Hong reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Hong DS et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 19.
HONOLULU – The novel antibody-drug conjugate tisotumab vedotin (TV) shows encouraging activity and tolerability in heavily pretreated recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, according to findings from the phase 1/2a innovaTV 201 trial.
The investigator-assessed overall response rate (ORR) among 55 patients enrolled in the cervical cancer expansion portion of the study was 35%, and the confirmed response rate was 22%, including one complete response lasting 46 weeks, David S. Hong, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
The median duration of response in confirmed responders was 6 months, median progression-free survival (PFS) was 4.1 months, and 6-month PFS was 40%, said Dr. Hong, deputy chair, department of investigational cancer therapeutics, division of cancer medicine, the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“Overall, the independent review and investigator review were highly correlated,” he noted.
Study participants had recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer that progressed on standard therapy, and Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status scores of 0-1. Most had received at least two prior therapies.
As established in the phase 1 dose-escalation portion of the study, TV in the expansion phase was given at a dose of 2 mg/kg every 3 weeks until disease progression, toxicity, or withdrawal.
Median follow-up was 3.5 months and the median number of doses received was four; the treatment had acceptable tolerability, Dr. Hong said, noting that no treatment-related deaths occurred, and only 13% of patients had a dose reduction caused by an adverse event (AE).
The most common AE occurring in more than 20% of patients was epistaxis; most cases were grade 1. AEs of special interest and possibly related to the TV mechanism of action included neuropathy, bleeding-related events, and ocular events.
While there were a few cases of vaginal bleeding, they were believed to be caused by underlying disease, he noted.
The ocular events noted early in phase 1 of the study included mainly dry eyes and conjunctivitis, but a plan to mitigate these events, which involved the use of steroid eye drops, cooling eye masks, and dose reductions, reduced their incidence.
There were no grade 4 or 5 adverse events related to the agent, he said, noting that most patients came off study because of disease progression.
The prognosis for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer is very poor, with a 5-year survival rate of only about 17%, Dr. Hong said, adding that data on the overall response and survival after the first line of therapy are somewhat limited.
Pembrolizumab (Keytruda) received Food and Drug Administration approval based on second-line setting data from the Keynote-158 trial showing a median ORR of just 14% and median PFS of just 2.1 months in programmed death-ligand 1–positive cervical cancer, he noted.
“Tissue factor (TF) is a protein expressed in cervical cancer, as well as ... a broad range of solid tumors. It is associated with high tumor stage, metastasis, and poor prognosis,” he explained. “TV is a first-in-class antibody-drug conjugate that’s a fully human monoclonal antibody targeting tissue factor.”
The drug, which has multiple mechanisms of action, is conjugated to the microtubule disrupting agent monomethyl auristatin E (MMAE) via a protease-cleavable linker. Findings regarding its safety and tolerability in cervical cancer and a number of other tumors were published recently in The Lancet.
Dr. Hong’s presentation focused on the cervical cancer cohort.
The median PFS in innovaTV 201 compares favorably with that for pembrolizumab and supports continued investigation of TV, he said, noting that phase 2 studies of TV alone and in combination with other agents for recurrent or metastatic cervical cancer, as well as for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer, are ongoing.
The innovaTV 201 trial is sponsored by Genmab A/S. Dr. Hong reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Hong DS et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 19.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2019
Study explores third-line trabectedin plus PLD for BRCA1/2 ovarian cancer
HONOLULU – Adding trabectedin to pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) significantly prolongs overall and progression-free survival in BRCA1/2-mutated patients with advanced-relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer after two prior lines of platinum-based therapy, according to prespecified subgroup analyses of a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial.
Patients with a platinum-free interval (PFI) of 6-12 months also experienced significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS), and those with both a BRCA mutation and PFI of 6-12 months experienced significantly improved overall survival (OS) and PFS with combined trabectedin and PLD vs. PLD alone, Bradley J. Monk, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Of 576 patients enrolled in the ET743-OVC-3006 trial, 289 received the combination regimen, and 287 received PLD alone. The study completed enrollment but was discontinued on January 18, 2018, after an interim analysis showed the futility threshold for OS and observed toxicity in the combination therapy group was exceeded.
OS was 21.5 and 22.2 months (hazard ratio = 1.13) in the combination and monotherapy groups, respectively. However, the subgroups analysis of patients with a germline BRCA1/2 mutation showed a median OS of 34.2 months with combination therapy and 20.9 months with PLD monotherapy, for a median survival benefit with combination therapy of 13.3 months (HR = 0.54), said Dr. Monk, professor and director of the division of gynecologic oncology at Creighton University School of Medicine, St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Ariz.
A subgroup of 60 patients with both a BRCA mutation and a PFI of 6-12 months had even greater improvement in OS with combination therapy when compared with PLD monotherapy (31.5 vs. 14.9 months; HR = 0.37). An effect on PFS was also detected in this subgroup (10.1 vs. 6.1 months; HR = 0.48), he said.
No difference in PFS was found in the overall unselected study population, Dr. Monk said, but among all patients with 6-12-month PFI alone, combination therapy led to significantly longer PFS than with monotherapy (7.5 vs. 5.5 months; HR = 0.72, P = .0388) and a positive trend in OS for the combination group (24.8 vs. 17.4 months; HR = 0.69; P = .565).
“I get it – this suffers from multiple comparisons, and this [analysis] in particular was ad hoc,” he said.
Still, given historical findings with respect to trabectedin in combination with PLD, the findings are provocative, he said.
Trabectedin is “a complicated anticancer cytotoxic medication” approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 based on findings of treatment benefit in liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma (including uterine leiomyosarcoma), he explained.
The agent has also been studied widely in other tumors, including in ovarian cancer. In the OVA-301 trial, for example, Dr. Monk and his colleagues looked at trabectedin in the second-line setting in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
That trial, which met its primary endpoint of an overall PFS benefit with trabectedin and generated the hypothesis that the agent might have particular benefit in BRCA-mutated patients, led to regulatory approval of trabectedin in Europe and elsewhere as an option for treatment in patients with partially platinum-sensitive recurrences – but not in the United States, he said.
Since OVA-301 did not lead to FDA approval, he and his colleagues designed the current study to look more closely at trabectedin with and without PLD, using the same dosing regimens as in OVA-301, but in the third-line setting and using OS as the primary endpoint.
Based on the intriguing OVA-301 findings in BRCA-mutated patients, the BRCA1/2-mutated subgroup analysis in the ET743-OVC-3006 trial was prespecified, he noted.
Study participants were women with advanced-relapsed epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancer who responded to two prior lines of platinum-based therapy and who were at least 6 months platinum-free. They were randomly assigned 1:1 to trabectedin plus PLD or PLD alone. Dosing in the combination arm was 1.1 mg/m2 of intravenous trabectedin over 3 hours and 30 mg/m2 of IV PLD given over 90 minutes every 3 weeks, and in the monotherapy arm PLD was given at a dose of 50 mg/m2 IV over 90 minutes every 4 weeks.
The groups were well balanced with respect to age, race, and performance status, and each included “a smattering of histological subtypes,” he said.
Of the 576 enrolled, 155 were BRCA1 or BRCA2-positive, with about two-thirds carrying a BRCA1 mutation.
Very few were exposed to bevacizumab or poly(ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors, as the study was initiated before those were developed.
Adverse events (AEs) of all grades occurred at similar rates in the two arms and occurred in most patients. Most were drug-related, but grade 3-4 AE rates were higher in the combination arm (79% vs. 54%). Drug-related AEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 32.5% and 16% of the combination and monotherapy arm patients, respectively, Dr. Monk said.
“Most of those treatment-related AEs were cytopenia and/or transaminitis. There were also almost twice as many deaths in the combination arm: 3.5% vs. 1.6%,” he said, adding that the deaths were thought to be related to tumor progression rather than to the drugs.
Although the addition of trabectedin to PLD did not prolong OS, compared with PLD alone in unselected patients with advanced, third-line, recurrent ovarian cancer, the combination does appear to benefit patients with germline BRCA mutations, a 6-12 month platinum-free interval, or both, he said, concluding that “the results of this phase 3 subanalysis are consistent with the previous observations in OVA-301 that trabectedin alone or with PLD displays selective antitumor activity in this BRCA subgroup.
“It adds more toxicity, but no new safety signals were identified,” he added.
Asked during a panel discussion if he thinks these results mark “then end of the road” for trabectedin, Dr. Monk said he does not.
“I don’t think we should be penalized because we enrolled all those non-BRCA patients. When you look at the BRCA cohort I think there is an opportunity to get this to our patients,” he said, noting that “the major challenge” is that those patients had not been given a PARP inhibitor. “So I think that there might be an opportunity for licensing, but the confirmatory trial would have to [look at whether] the drug still works after failure of a PARP.”
The ET743-OVC-3006 trial was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Monk reported financial relationships (consulting, honoraria/reimbursement, and/or speaker’s bureau participation) with Janssen/Johnson & Johnson and more than 20 other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Monk B et al., SGO 2019: Abstract 20.
HONOLULU – Adding trabectedin to pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) significantly prolongs overall and progression-free survival in BRCA1/2-mutated patients with advanced-relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer after two prior lines of platinum-based therapy, according to prespecified subgroup analyses of a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial.
Patients with a platinum-free interval (PFI) of 6-12 months also experienced significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS), and those with both a BRCA mutation and PFI of 6-12 months experienced significantly improved overall survival (OS) and PFS with combined trabectedin and PLD vs. PLD alone, Bradley J. Monk, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Of 576 patients enrolled in the ET743-OVC-3006 trial, 289 received the combination regimen, and 287 received PLD alone. The study completed enrollment but was discontinued on January 18, 2018, after an interim analysis showed the futility threshold for OS and observed toxicity in the combination therapy group was exceeded.
OS was 21.5 and 22.2 months (hazard ratio = 1.13) in the combination and monotherapy groups, respectively. However, the subgroups analysis of patients with a germline BRCA1/2 mutation showed a median OS of 34.2 months with combination therapy and 20.9 months with PLD monotherapy, for a median survival benefit with combination therapy of 13.3 months (HR = 0.54), said Dr. Monk, professor and director of the division of gynecologic oncology at Creighton University School of Medicine, St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Ariz.
A subgroup of 60 patients with both a BRCA mutation and a PFI of 6-12 months had even greater improvement in OS with combination therapy when compared with PLD monotherapy (31.5 vs. 14.9 months; HR = 0.37). An effect on PFS was also detected in this subgroup (10.1 vs. 6.1 months; HR = 0.48), he said.
No difference in PFS was found in the overall unselected study population, Dr. Monk said, but among all patients with 6-12-month PFI alone, combination therapy led to significantly longer PFS than with monotherapy (7.5 vs. 5.5 months; HR = 0.72, P = .0388) and a positive trend in OS for the combination group (24.8 vs. 17.4 months; HR = 0.69; P = .565).
“I get it – this suffers from multiple comparisons, and this [analysis] in particular was ad hoc,” he said.
Still, given historical findings with respect to trabectedin in combination with PLD, the findings are provocative, he said.
Trabectedin is “a complicated anticancer cytotoxic medication” approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 based on findings of treatment benefit in liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma (including uterine leiomyosarcoma), he explained.
The agent has also been studied widely in other tumors, including in ovarian cancer. In the OVA-301 trial, for example, Dr. Monk and his colleagues looked at trabectedin in the second-line setting in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
That trial, which met its primary endpoint of an overall PFS benefit with trabectedin and generated the hypothesis that the agent might have particular benefit in BRCA-mutated patients, led to regulatory approval of trabectedin in Europe and elsewhere as an option for treatment in patients with partially platinum-sensitive recurrences – but not in the United States, he said.
Since OVA-301 did not lead to FDA approval, he and his colleagues designed the current study to look more closely at trabectedin with and without PLD, using the same dosing regimens as in OVA-301, but in the third-line setting and using OS as the primary endpoint.
Based on the intriguing OVA-301 findings in BRCA-mutated patients, the BRCA1/2-mutated subgroup analysis in the ET743-OVC-3006 trial was prespecified, he noted.
Study participants were women with advanced-relapsed epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancer who responded to two prior lines of platinum-based therapy and who were at least 6 months platinum-free. They were randomly assigned 1:1 to trabectedin plus PLD or PLD alone. Dosing in the combination arm was 1.1 mg/m2 of intravenous trabectedin over 3 hours and 30 mg/m2 of IV PLD given over 90 minutes every 3 weeks, and in the monotherapy arm PLD was given at a dose of 50 mg/m2 IV over 90 minutes every 4 weeks.
The groups were well balanced with respect to age, race, and performance status, and each included “a smattering of histological subtypes,” he said.
Of the 576 enrolled, 155 were BRCA1 or BRCA2-positive, with about two-thirds carrying a BRCA1 mutation.
Very few were exposed to bevacizumab or poly(ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors, as the study was initiated before those were developed.
Adverse events (AEs) of all grades occurred at similar rates in the two arms and occurred in most patients. Most were drug-related, but grade 3-4 AE rates were higher in the combination arm (79% vs. 54%). Drug-related AEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 32.5% and 16% of the combination and monotherapy arm patients, respectively, Dr. Monk said.
“Most of those treatment-related AEs were cytopenia and/or transaminitis. There were also almost twice as many deaths in the combination arm: 3.5% vs. 1.6%,” he said, adding that the deaths were thought to be related to tumor progression rather than to the drugs.
Although the addition of trabectedin to PLD did not prolong OS, compared with PLD alone in unselected patients with advanced, third-line, recurrent ovarian cancer, the combination does appear to benefit patients with germline BRCA mutations, a 6-12 month platinum-free interval, or both, he said, concluding that “the results of this phase 3 subanalysis are consistent with the previous observations in OVA-301 that trabectedin alone or with PLD displays selective antitumor activity in this BRCA subgroup.
“It adds more toxicity, but no new safety signals were identified,” he added.
Asked during a panel discussion if he thinks these results mark “then end of the road” for trabectedin, Dr. Monk said he does not.
“I don’t think we should be penalized because we enrolled all those non-BRCA patients. When you look at the BRCA cohort I think there is an opportunity to get this to our patients,” he said, noting that “the major challenge” is that those patients had not been given a PARP inhibitor. “So I think that there might be an opportunity for licensing, but the confirmatory trial would have to [look at whether] the drug still works after failure of a PARP.”
The ET743-OVC-3006 trial was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Monk reported financial relationships (consulting, honoraria/reimbursement, and/or speaker’s bureau participation) with Janssen/Johnson & Johnson and more than 20 other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Monk B et al., SGO 2019: Abstract 20.
HONOLULU – Adding trabectedin to pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (PLD) significantly prolongs overall and progression-free survival in BRCA1/2-mutated patients with advanced-relapsed epithelial ovarian cancer after two prior lines of platinum-based therapy, according to prespecified subgroup analyses of a randomized, open-label, phase 3 trial.
Patients with a platinum-free interval (PFI) of 6-12 months also experienced significantly improved progression-free survival (PFS), and those with both a BRCA mutation and PFI of 6-12 months experienced significantly improved overall survival (OS) and PFS with combined trabectedin and PLD vs. PLD alone, Bradley J. Monk, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Of 576 patients enrolled in the ET743-OVC-3006 trial, 289 received the combination regimen, and 287 received PLD alone. The study completed enrollment but was discontinued on January 18, 2018, after an interim analysis showed the futility threshold for OS and observed toxicity in the combination therapy group was exceeded.
OS was 21.5 and 22.2 months (hazard ratio = 1.13) in the combination and monotherapy groups, respectively. However, the subgroups analysis of patients with a germline BRCA1/2 mutation showed a median OS of 34.2 months with combination therapy and 20.9 months with PLD monotherapy, for a median survival benefit with combination therapy of 13.3 months (HR = 0.54), said Dr. Monk, professor and director of the division of gynecologic oncology at Creighton University School of Medicine, St. Joseph’s Hospital and Medical Center, Phoenix, Ariz.
A subgroup of 60 patients with both a BRCA mutation and a PFI of 6-12 months had even greater improvement in OS with combination therapy when compared with PLD monotherapy (31.5 vs. 14.9 months; HR = 0.37). An effect on PFS was also detected in this subgroup (10.1 vs. 6.1 months; HR = 0.48), he said.
No difference in PFS was found in the overall unselected study population, Dr. Monk said, but among all patients with 6-12-month PFI alone, combination therapy led to significantly longer PFS than with monotherapy (7.5 vs. 5.5 months; HR = 0.72, P = .0388) and a positive trend in OS for the combination group (24.8 vs. 17.4 months; HR = 0.69; P = .565).
“I get it – this suffers from multiple comparisons, and this [analysis] in particular was ad hoc,” he said.
Still, given historical findings with respect to trabectedin in combination with PLD, the findings are provocative, he said.
Trabectedin is “a complicated anticancer cytotoxic medication” approved by the Food and Drug Administration in 2015 based on findings of treatment benefit in liposarcoma and leiomyosarcoma (including uterine leiomyosarcoma), he explained.
The agent has also been studied widely in other tumors, including in ovarian cancer. In the OVA-301 trial, for example, Dr. Monk and his colleagues looked at trabectedin in the second-line setting in patients with recurrent ovarian cancer.
That trial, which met its primary endpoint of an overall PFS benefit with trabectedin and generated the hypothesis that the agent might have particular benefit in BRCA-mutated patients, led to regulatory approval of trabectedin in Europe and elsewhere as an option for treatment in patients with partially platinum-sensitive recurrences – but not in the United States, he said.
Since OVA-301 did not lead to FDA approval, he and his colleagues designed the current study to look more closely at trabectedin with and without PLD, using the same dosing regimens as in OVA-301, but in the third-line setting and using OS as the primary endpoint.
Based on the intriguing OVA-301 findings in BRCA-mutated patients, the BRCA1/2-mutated subgroup analysis in the ET743-OVC-3006 trial was prespecified, he noted.
Study participants were women with advanced-relapsed epithelial ovarian, primary peritoneal, or fallopian tube cancer who responded to two prior lines of platinum-based therapy and who were at least 6 months platinum-free. They were randomly assigned 1:1 to trabectedin plus PLD or PLD alone. Dosing in the combination arm was 1.1 mg/m2 of intravenous trabectedin over 3 hours and 30 mg/m2 of IV PLD given over 90 minutes every 3 weeks, and in the monotherapy arm PLD was given at a dose of 50 mg/m2 IV over 90 minutes every 4 weeks.
The groups were well balanced with respect to age, race, and performance status, and each included “a smattering of histological subtypes,” he said.
Of the 576 enrolled, 155 were BRCA1 or BRCA2-positive, with about two-thirds carrying a BRCA1 mutation.
Very few were exposed to bevacizumab or poly(ADP ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors, as the study was initiated before those were developed.
Adverse events (AEs) of all grades occurred at similar rates in the two arms and occurred in most patients. Most were drug-related, but grade 3-4 AE rates were higher in the combination arm (79% vs. 54%). Drug-related AEs leading to treatment discontinuation occurred in 32.5% and 16% of the combination and monotherapy arm patients, respectively, Dr. Monk said.
“Most of those treatment-related AEs were cytopenia and/or transaminitis. There were also almost twice as many deaths in the combination arm: 3.5% vs. 1.6%,” he said, adding that the deaths were thought to be related to tumor progression rather than to the drugs.
Although the addition of trabectedin to PLD did not prolong OS, compared with PLD alone in unselected patients with advanced, third-line, recurrent ovarian cancer, the combination does appear to benefit patients with germline BRCA mutations, a 6-12 month platinum-free interval, or both, he said, concluding that “the results of this phase 3 subanalysis are consistent with the previous observations in OVA-301 that trabectedin alone or with PLD displays selective antitumor activity in this BRCA subgroup.
“It adds more toxicity, but no new safety signals were identified,” he added.
Asked during a panel discussion if he thinks these results mark “then end of the road” for trabectedin, Dr. Monk said he does not.
“I don’t think we should be penalized because we enrolled all those non-BRCA patients. When you look at the BRCA cohort I think there is an opportunity to get this to our patients,” he said, noting that “the major challenge” is that those patients had not been given a PARP inhibitor. “So I think that there might be an opportunity for licensing, but the confirmatory trial would have to [look at whether] the drug still works after failure of a PARP.”
The ET743-OVC-3006 trial was sponsored by Janssen Research & Development. Dr. Monk reported financial relationships (consulting, honoraria/reimbursement, and/or speaker’s bureau participation) with Janssen/Johnson & Johnson and more than 20 other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Monk B et al., SGO 2019: Abstract 20.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2019
Study: Racial disparities in gyn-onc trial enrollment persist
HONOLULU – Racial disparities in phase 1 gynecologic oncology clinical trial enrollment is nothing new, but the gap between African American and Caucasian enrollment widened in recent years, according to a review of studies conducted since 1985.
The literature review identified 357 relevant phase 1 studies involving 9,492 patients published between 1985 and 2018. However, only 83 of the studies (23%) included a racial breakdown; of the 2,483 patients in those 83 trials, 79% were Caucasian, 5% were African American, and 16% were of “other” race, Elias Awad reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Ovarian cancer was the most common tumor type studied, but among studies listing a racial breakdown, endometrial cancer studies had the highest enrollment of African American patients at 12%, said Mr. Awad, a 4th-year medical student at the University of South Alabama, Mobile. The remaining studies all had less than 10% participation of black patients.
“Also of note is that other races exceeded black patients in 55% of trials across all tumor types,” he said. “Despite the focus on increasing diversity in clinical trials over the years, the percentage of black patients has declined 1.8-fold from 11% in 1995-1999 to 6% in 2015-2018.”
Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age-adjusted incidence for race, expected and observed ratios of racial participation were calculated – and were found to be less than expected for each tumor site, Mr. Awad said.
For example, the enrollment ratio in ovarian cancer studies was 0.04:1 for black and white patients, respectively, while the ratios for endometrial and cervical cancer were 0.004:1 and 0.025:1, respectively.
These ratios represent a 1,750% lower than expected enrollment of black patients in ovarian cancer trials, 2,080% lower than expected enrollment for endometrial cancer trials, and 5,300% lower than expected enrollment for cervical cancer, he said.
This lack of minority participation in early-phase clinical trials likely contributes to cancer health disparities, Mr. Awad added, explaining that the underrepresentation of minorities in trials results in agents that work in majority populations.
“Thus, it is paramount to have therapeutic agents specifically effective in minority populations,” he said. “Considering that phase 1 trials are the entry point for therapeutic success, these results further compound the lack of adequate clinical trials for our black patients who continue to suffer the consequences of these inequities.
“Accordingly, it is time to enact strategies to enhance equity in the enrollment of black patients on clinical trials in order to assist in eliminating racial disparities in gynecologic malignancies,” he concluded.
Mr. Awad reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Awad E et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 22.
HONOLULU – Racial disparities in phase 1 gynecologic oncology clinical trial enrollment is nothing new, but the gap between African American and Caucasian enrollment widened in recent years, according to a review of studies conducted since 1985.
The literature review identified 357 relevant phase 1 studies involving 9,492 patients published between 1985 and 2018. However, only 83 of the studies (23%) included a racial breakdown; of the 2,483 patients in those 83 trials, 79% were Caucasian, 5% were African American, and 16% were of “other” race, Elias Awad reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Ovarian cancer was the most common tumor type studied, but among studies listing a racial breakdown, endometrial cancer studies had the highest enrollment of African American patients at 12%, said Mr. Awad, a 4th-year medical student at the University of South Alabama, Mobile. The remaining studies all had less than 10% participation of black patients.
“Also of note is that other races exceeded black patients in 55% of trials across all tumor types,” he said. “Despite the focus on increasing diversity in clinical trials over the years, the percentage of black patients has declined 1.8-fold from 11% in 1995-1999 to 6% in 2015-2018.”
Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age-adjusted incidence for race, expected and observed ratios of racial participation were calculated – and were found to be less than expected for each tumor site, Mr. Awad said.
For example, the enrollment ratio in ovarian cancer studies was 0.04:1 for black and white patients, respectively, while the ratios for endometrial and cervical cancer were 0.004:1 and 0.025:1, respectively.
These ratios represent a 1,750% lower than expected enrollment of black patients in ovarian cancer trials, 2,080% lower than expected enrollment for endometrial cancer trials, and 5,300% lower than expected enrollment for cervical cancer, he said.
This lack of minority participation in early-phase clinical trials likely contributes to cancer health disparities, Mr. Awad added, explaining that the underrepresentation of minorities in trials results in agents that work in majority populations.
“Thus, it is paramount to have therapeutic agents specifically effective in minority populations,” he said. “Considering that phase 1 trials are the entry point for therapeutic success, these results further compound the lack of adequate clinical trials for our black patients who continue to suffer the consequences of these inequities.
“Accordingly, it is time to enact strategies to enhance equity in the enrollment of black patients on clinical trials in order to assist in eliminating racial disparities in gynecologic malignancies,” he concluded.
Mr. Awad reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Awad E et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 22.
HONOLULU – Racial disparities in phase 1 gynecologic oncology clinical trial enrollment is nothing new, but the gap between African American and Caucasian enrollment widened in recent years, according to a review of studies conducted since 1985.
The literature review identified 357 relevant phase 1 studies involving 9,492 patients published between 1985 and 2018. However, only 83 of the studies (23%) included a racial breakdown; of the 2,483 patients in those 83 trials, 79% were Caucasian, 5% were African American, and 16% were of “other” race, Elias Awad reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Ovarian cancer was the most common tumor type studied, but among studies listing a racial breakdown, endometrial cancer studies had the highest enrollment of African American patients at 12%, said Mr. Awad, a 4th-year medical student at the University of South Alabama, Mobile. The remaining studies all had less than 10% participation of black patients.
“Also of note is that other races exceeded black patients in 55% of trials across all tumor types,” he said. “Despite the focus on increasing diversity in clinical trials over the years, the percentage of black patients has declined 1.8-fold from 11% in 1995-1999 to 6% in 2015-2018.”
Based on Centers for Disease Control and Prevention age-adjusted incidence for race, expected and observed ratios of racial participation were calculated – and were found to be less than expected for each tumor site, Mr. Awad said.
For example, the enrollment ratio in ovarian cancer studies was 0.04:1 for black and white patients, respectively, while the ratios for endometrial and cervical cancer were 0.004:1 and 0.025:1, respectively.
These ratios represent a 1,750% lower than expected enrollment of black patients in ovarian cancer trials, 2,080% lower than expected enrollment for endometrial cancer trials, and 5,300% lower than expected enrollment for cervical cancer, he said.
This lack of minority participation in early-phase clinical trials likely contributes to cancer health disparities, Mr. Awad added, explaining that the underrepresentation of minorities in trials results in agents that work in majority populations.
“Thus, it is paramount to have therapeutic agents specifically effective in minority populations,” he said. “Considering that phase 1 trials are the entry point for therapeutic success, these results further compound the lack of adequate clinical trials for our black patients who continue to suffer the consequences of these inequities.
“Accordingly, it is time to enact strategies to enhance equity in the enrollment of black patients on clinical trials in order to assist in eliminating racial disparities in gynecologic malignancies,” he concluded.
Mr. Awad reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: Awad E et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 22.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2019
ARIEL3 analysis: Rucaparib PFS benefit in recurrent OC occurs across age groups
HONOLULU – The improved progression-free survival and reduced risk of disease progression seen with maintenance rucaparib versus placebo in women with recurrent ovarian cancer in the pivotal ARIEL3 study occurred across age subgroups, according to a post hoc exploratory analysis of data from the phase 3 study.
In general, the safety profile of the first-in-class poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor was consistent across age groups, as well, but rates of dose modifications and treatment discontinuations varied slightly by age subgroup in the rucaparib (Rubraca)and placebo arms, Jonathan A. Ledermann, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
No clear trend emerged with respect to those differences, said Dr. Ledermann, a professor of medical oncology at University College of London Cancer Institute and UCL Hospitals.
Initial results from the randomized, placebo-controlled study were published in 2017 and showed a significant progression-free survival (PFS) benefit with 600 mg of maintenance rucaparib vs. placebo (10.8 vs. 5.4 months, respectively, in the intention-to-treat population). For the current analysis, outcomes were assessed for the ITT population across three baseline age-based subgroups: those under age 65 years, those aged 65-74 years, and those 75 years or older.
Investigator-assessed PFS – the primary endpoint of ARIEL3 – for the rucaparib vs. placebo groups was 11.1 vs. 5.4 months among 237 and 117 patients under age 65 years in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.33); 8.3 vs. 5.3 for 113 and 64 patients aged 65-74 years, respectively (HR, 0.43); and 9.2 and 5.5 months in 25 and 8 patients aged 75 and older (HR, 0.47), he said.
“The hazard ratios are comparable across all three age cohorts,” Dr. Ledermann said.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any grade occurring in at least 35% of patients included nausea, asthenia, vomiting, dysgeusia, constipation, anemia, ALT/AST increase, diarrhea, abdominal pain, thrombocytopenia, and pruritus.
The rates of these events were similar across age groups, although slight, nonsignificant numerical increases in grade 3 toxicities occurred with increasing age, he noted.
“If we look at dose interruption and dose reduction rates – again, broadly similar, [but with] a slight trend toward an increase in older age groups,” he said.
Dose modifications related to TEAEs, however, occurred in 65.5% of rucaparib and 9.4% of placebo patients aged under 65 years, compared with 82.3% and 12.5% of those aged 65-74, and 83.3% and 12.5% of those aged 75 or older, respectively. Discontinuations because of TEAEs occurred in 13.6% and 1.7% in those under age 65 years vs. 19.5% and 3.1% in those aged 65-74 years, and 20.8% and 0% of those aged 75 years or older in the groups, respectively.
Of note, the age subgroups and the treatment and placebo groups were well balanced except more of those under age 65 years had a deleterious germline or somatic BRCA mutation (96 and 49 in the rucaparib and placebo arms, respectively) than did patients aged 65-74 years (29 and 15, respectively), and patients aged 75 years and older (5 and 2, respectively).
ARIEL3 was funded by Clovis Oncology. Dr. Ledermann reported financial relationships (consulting, grant receipt, honorarial reimbursement, and/or speakers bureau fees) with AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Roche, and MSD/Merck.
SOURCE: Ledermann J et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 4.
HONOLULU – The improved progression-free survival and reduced risk of disease progression seen with maintenance rucaparib versus placebo in women with recurrent ovarian cancer in the pivotal ARIEL3 study occurred across age subgroups, according to a post hoc exploratory analysis of data from the phase 3 study.
In general, the safety profile of the first-in-class poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor was consistent across age groups, as well, but rates of dose modifications and treatment discontinuations varied slightly by age subgroup in the rucaparib (Rubraca)and placebo arms, Jonathan A. Ledermann, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
No clear trend emerged with respect to those differences, said Dr. Ledermann, a professor of medical oncology at University College of London Cancer Institute and UCL Hospitals.
Initial results from the randomized, placebo-controlled study were published in 2017 and showed a significant progression-free survival (PFS) benefit with 600 mg of maintenance rucaparib vs. placebo (10.8 vs. 5.4 months, respectively, in the intention-to-treat population). For the current analysis, outcomes were assessed for the ITT population across three baseline age-based subgroups: those under age 65 years, those aged 65-74 years, and those 75 years or older.
Investigator-assessed PFS – the primary endpoint of ARIEL3 – for the rucaparib vs. placebo groups was 11.1 vs. 5.4 months among 237 and 117 patients under age 65 years in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.33); 8.3 vs. 5.3 for 113 and 64 patients aged 65-74 years, respectively (HR, 0.43); and 9.2 and 5.5 months in 25 and 8 patients aged 75 and older (HR, 0.47), he said.
“The hazard ratios are comparable across all three age cohorts,” Dr. Ledermann said.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any grade occurring in at least 35% of patients included nausea, asthenia, vomiting, dysgeusia, constipation, anemia, ALT/AST increase, diarrhea, abdominal pain, thrombocytopenia, and pruritus.
The rates of these events were similar across age groups, although slight, nonsignificant numerical increases in grade 3 toxicities occurred with increasing age, he noted.
“If we look at dose interruption and dose reduction rates – again, broadly similar, [but with] a slight trend toward an increase in older age groups,” he said.
Dose modifications related to TEAEs, however, occurred in 65.5% of rucaparib and 9.4% of placebo patients aged under 65 years, compared with 82.3% and 12.5% of those aged 65-74, and 83.3% and 12.5% of those aged 75 or older, respectively. Discontinuations because of TEAEs occurred in 13.6% and 1.7% in those under age 65 years vs. 19.5% and 3.1% in those aged 65-74 years, and 20.8% and 0% of those aged 75 years or older in the groups, respectively.
Of note, the age subgroups and the treatment and placebo groups were well balanced except more of those under age 65 years had a deleterious germline or somatic BRCA mutation (96 and 49 in the rucaparib and placebo arms, respectively) than did patients aged 65-74 years (29 and 15, respectively), and patients aged 75 years and older (5 and 2, respectively).
ARIEL3 was funded by Clovis Oncology. Dr. Ledermann reported financial relationships (consulting, grant receipt, honorarial reimbursement, and/or speakers bureau fees) with AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Roche, and MSD/Merck.
SOURCE: Ledermann J et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 4.
HONOLULU – The improved progression-free survival and reduced risk of disease progression seen with maintenance rucaparib versus placebo in women with recurrent ovarian cancer in the pivotal ARIEL3 study occurred across age subgroups, according to a post hoc exploratory analysis of data from the phase 3 study.
In general, the safety profile of the first-in-class poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitor was consistent across age groups, as well, but rates of dose modifications and treatment discontinuations varied slightly by age subgroup in the rucaparib (Rubraca)and placebo arms, Jonathan A. Ledermann, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
No clear trend emerged with respect to those differences, said Dr. Ledermann, a professor of medical oncology at University College of London Cancer Institute and UCL Hospitals.
Initial results from the randomized, placebo-controlled study were published in 2017 and showed a significant progression-free survival (PFS) benefit with 600 mg of maintenance rucaparib vs. placebo (10.8 vs. 5.4 months, respectively, in the intention-to-treat population). For the current analysis, outcomes were assessed for the ITT population across three baseline age-based subgroups: those under age 65 years, those aged 65-74 years, and those 75 years or older.
Investigator-assessed PFS – the primary endpoint of ARIEL3 – for the rucaparib vs. placebo groups was 11.1 vs. 5.4 months among 237 and 117 patients under age 65 years in the groups, respectively (hazard ratio, 0.33); 8.3 vs. 5.3 for 113 and 64 patients aged 65-74 years, respectively (HR, 0.43); and 9.2 and 5.5 months in 25 and 8 patients aged 75 and older (HR, 0.47), he said.
“The hazard ratios are comparable across all three age cohorts,” Dr. Ledermann said.
Treatment-emergent adverse events (TEAEs) of any grade occurring in at least 35% of patients included nausea, asthenia, vomiting, dysgeusia, constipation, anemia, ALT/AST increase, diarrhea, abdominal pain, thrombocytopenia, and pruritus.
The rates of these events were similar across age groups, although slight, nonsignificant numerical increases in grade 3 toxicities occurred with increasing age, he noted.
“If we look at dose interruption and dose reduction rates – again, broadly similar, [but with] a slight trend toward an increase in older age groups,” he said.
Dose modifications related to TEAEs, however, occurred in 65.5% of rucaparib and 9.4% of placebo patients aged under 65 years, compared with 82.3% and 12.5% of those aged 65-74, and 83.3% and 12.5% of those aged 75 or older, respectively. Discontinuations because of TEAEs occurred in 13.6% and 1.7% in those under age 65 years vs. 19.5% and 3.1% in those aged 65-74 years, and 20.8% and 0% of those aged 75 years or older in the groups, respectively.
Of note, the age subgroups and the treatment and placebo groups were well balanced except more of those under age 65 years had a deleterious germline or somatic BRCA mutation (96 and 49 in the rucaparib and placebo arms, respectively) than did patients aged 65-74 years (29 and 15, respectively), and patients aged 75 years and older (5 and 2, respectively).
ARIEL3 was funded by Clovis Oncology. Dr. Ledermann reported financial relationships (consulting, grant receipt, honorarial reimbursement, and/or speakers bureau fees) with AstraZeneca, Clovis Oncology, Pfizer, Seattle Genetics, Roche, and MSD/Merck.
SOURCE: Ledermann J et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 4.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2019
Neratinib shows promise in HER2-mutant cervical cancer
HONOLULU – Treatment with the pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor neratinib leads to durable responses and disease control in heavily pretreated metastatic patients with HER2-mutant cervical cancer, preliminary efficacy results from the phase 2 SUMMIT basket trial suggest.
Of 11 trial subjects evaluable for efficacy, 3 (27%) had objective confirmed responses and 6 others had stable disease for at least 16 weeks (clinical benefit rate, 55%). Median progression-free survival was 7 months, Anishka D’Souza, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Study subjects included HER2-mutant metastatic cervical cancer patients. Most (89%) had adenocarcinoma and 11% had squamous cell carcinoma, said Dr. D’Souza of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
The median number of total prior regimens was two, with a range of one to four, she said. Patients received oral neratinib at a dose of 240 mg once daily.
The treatment was generally well tolerated; the most common adverse event was diarrhea, with only one grade 3/4 case occurring, she said, noting that high-dose loperamide prophylaxis was mandatory during cycle 1 because of the high incidence of diarrhea.
Though preliminary, the findings are notable as somatic HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, observed in about 5% of metastatic cervical cancer cases, are associated with poor prognosis, she explained, noting that there are limited treatment options and few long-term durable responses.
“There is a great need for additional treatment options,” she said.
Neratinib has been shown to have single-agent clinical activity in multiple HER2‑mutant cancers, so Dr. D’Souza and her colleagues are assessing its safety and efficacy as either monotherapy or in combination with other treatments across multiple tumor types. The current analysis focuses on the cohort of patients who received neratinib monotherapy.
Neratinib use in this cohort led to durable responses and disease control in heavily pretreated metastatic patients with HER2-mutant cervical cancer, she said, adding that “this is an ongoing study and we are continuing to enroll patients to expand our dataset.”
Dr. D’Souza reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: D’Souza A et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 18.
HONOLULU – Treatment with the pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor neratinib leads to durable responses and disease control in heavily pretreated metastatic patients with HER2-mutant cervical cancer, preliminary efficacy results from the phase 2 SUMMIT basket trial suggest.
Of 11 trial subjects evaluable for efficacy, 3 (27%) had objective confirmed responses and 6 others had stable disease for at least 16 weeks (clinical benefit rate, 55%). Median progression-free survival was 7 months, Anishka D’Souza, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Study subjects included HER2-mutant metastatic cervical cancer patients. Most (89%) had adenocarcinoma and 11% had squamous cell carcinoma, said Dr. D’Souza of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
The median number of total prior regimens was two, with a range of one to four, she said. Patients received oral neratinib at a dose of 240 mg once daily.
The treatment was generally well tolerated; the most common adverse event was diarrhea, with only one grade 3/4 case occurring, she said, noting that high-dose loperamide prophylaxis was mandatory during cycle 1 because of the high incidence of diarrhea.
Though preliminary, the findings are notable as somatic HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, observed in about 5% of metastatic cervical cancer cases, are associated with poor prognosis, she explained, noting that there are limited treatment options and few long-term durable responses.
“There is a great need for additional treatment options,” she said.
Neratinib has been shown to have single-agent clinical activity in multiple HER2‑mutant cancers, so Dr. D’Souza and her colleagues are assessing its safety and efficacy as either monotherapy or in combination with other treatments across multiple tumor types. The current analysis focuses on the cohort of patients who received neratinib monotherapy.
Neratinib use in this cohort led to durable responses and disease control in heavily pretreated metastatic patients with HER2-mutant cervical cancer, she said, adding that “this is an ongoing study and we are continuing to enroll patients to expand our dataset.”
Dr. D’Souza reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: D’Souza A et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 18.
HONOLULU – Treatment with the pan-HER tyrosine kinase inhibitor neratinib leads to durable responses and disease control in heavily pretreated metastatic patients with HER2-mutant cervical cancer, preliminary efficacy results from the phase 2 SUMMIT basket trial suggest.
Of 11 trial subjects evaluable for efficacy, 3 (27%) had objective confirmed responses and 6 others had stable disease for at least 16 weeks (clinical benefit rate, 55%). Median progression-free survival was 7 months, Anishka D’Souza, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer.
Study subjects included HER2-mutant metastatic cervical cancer patients. Most (89%) had adenocarcinoma and 11% had squamous cell carcinoma, said Dr. D’Souza of the University of Southern California, Los Angeles.
The median number of total prior regimens was two, with a range of one to four, she said. Patients received oral neratinib at a dose of 240 mg once daily.
The treatment was generally well tolerated; the most common adverse event was diarrhea, with only one grade 3/4 case occurring, she said, noting that high-dose loperamide prophylaxis was mandatory during cycle 1 because of the high incidence of diarrhea.
Though preliminary, the findings are notable as somatic HER2 (ERBB2) mutations, observed in about 5% of metastatic cervical cancer cases, are associated with poor prognosis, she explained, noting that there are limited treatment options and few long-term durable responses.
“There is a great need for additional treatment options,” she said.
Neratinib has been shown to have single-agent clinical activity in multiple HER2‑mutant cancers, so Dr. D’Souza and her colleagues are assessing its safety and efficacy as either monotherapy or in combination with other treatments across multiple tumor types. The current analysis focuses on the cohort of patients who received neratinib monotherapy.
Neratinib use in this cohort led to durable responses and disease control in heavily pretreated metastatic patients with HER2-mutant cervical cancer, she said, adding that “this is an ongoing study and we are continuing to enroll patients to expand our dataset.”
Dr. D’Souza reported having no financial disclosures.
SOURCE: D’Souza A et al. SGO 2019, Abstract 18.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2019
WISP: Early data provide further support for ISDO in women at high OC risk
HONOLULU – Women at high risk for ovarian cancer who undergo risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) or interval salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy (ISDO) experience significant reductions in cancer distress, according to preliminary findings from the WISP (Women Choosing Surgical Prevention) study.
However, those who choose RRSO experience worse menopausal symptoms and higher rates of regret, Karen H. Lu, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer. Of 183 women enrolled to date in the prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter study, 91 underwent RRSO and 92 underwent ISDO at a median age of 40.9 and 37.5 years, respectively. Significant decreases in cancer-related distress as measured using the Impact of Event scale were seen in both groups at 6-month follow-up after surgery: The mean scores in the RRSO arm were 19.6 at baseline and 10.9 at 6 months, and in the ISDO arm they were 20.8 and 14.0, respectively.
The decrease in scores at 6 months did not differ significantly between study arms, but women in the RRSO arm had a significantly increased incidence of hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and weight gain after surgery, said Dr. Lu, professor and chair in the department of gynecologic oncology and reproductive medicine and the J. Taylor Wharton Distinguished Chair in Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“There was a significant difference in quality of life physical scores in RRSO versus the salpingectomy arm,” she said, adding that no difference was seen between the groups in quality of life mental scores.
The level of decision regret was significantly higher in the women who underwent RRSO (scores,14.1 vs. 8.7 on the 100-point scale), she noted.
“We hypothesized that use of HRT [hormone replacement therapy] after RRSO may have accounted for this difference, and looked at the two subsets,” she said. “Within the RRSO group, 25% did not go on HRT, and while higher than ISDO scores, these scores did not account for the large difference in decision regret.”
About half of the women had a history of breast cancer.
“Clinically, this agrees with what we see in that women with a prior history of breast cancer have less angst about undergoing RRSO,” she said, adding that 75% of women in the RRSO arm did go on HRT, and “these women represent the majority of our ‘previvors’ – healthy women with no history of cancer who struggle with the RRSO decision and who are able to take HRT.”
“Interestingly, compared to ISDO, RRSO women on HRT had the highest decisional regret,” she said.
An analysis of numerous possible predictors of decisional regret showed that only baseline depression score was a significant independent predictor, she noted.
Study participants are premenopausal women aged 30-50 years who have a high risk of ovarian cancer because of a pathogenic germline mutation in an ovarian cancer predisposition gene, and a normal CA125 and transvaginal ultrasound within 6 months before enrollment. All receive scripted counseling about the recommended age for oophorectomy and can choose their study arm. Planned enrollment at nine participating U.S. centers is 270 women.
The RRSO and ISDO arms at current enrollment are statistically similar with respect to mutation type, education level, breast cancer history, and first/second-degree ovarian cancer, but significantly more women in the ISDO arm had undergone risk-reducing mastectomy (51% vs. 35%), Dr. Lu noted, adding that to date no ovarian cancers have been identified at initial surgery, between surgeries, or at the time of completion oophorectomy in the ISDO patients – although only two women in that arm have undergone completion oophorectomy.
In the RRSO arm, one high-grade serous tubal intraepithelial neoplasia (STIC) was found at the time of surgery in a PALB2 mutation carrier.
“We believe this is the first report of a STIC in a PALB2 carrier. This woman was 39 years old with a strong family history of breast and ovarian cancer,” she said.
The findings suggest that “for these high-risk women who underwent ISDO ... the option encouraged them to undergo limited but potentially lifesaving surgical prophylaxis at an earlier age rather than wait to undergo full surgical prophylaxis at the upper-accepted age limit due to fear of early menopause,” Dr. Lu said.
Safety continues to be closely monitored in this study and the use of ISDO outside of the clinical trial setting is not recommended, she added, noting that an expansion of both WISP and the TUBA trial, for which preliminary results showing similar outcomes were also presented at the SGO meeting, is planned.
Dr. Lu reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Lu KH et al. SGO 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract 3.
HONOLULU – Women at high risk for ovarian cancer who undergo risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) or interval salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy (ISDO) experience significant reductions in cancer distress, according to preliminary findings from the WISP (Women Choosing Surgical Prevention) study.
However, those who choose RRSO experience worse menopausal symptoms and higher rates of regret, Karen H. Lu, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer. Of 183 women enrolled to date in the prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter study, 91 underwent RRSO and 92 underwent ISDO at a median age of 40.9 and 37.5 years, respectively. Significant decreases in cancer-related distress as measured using the Impact of Event scale were seen in both groups at 6-month follow-up after surgery: The mean scores in the RRSO arm were 19.6 at baseline and 10.9 at 6 months, and in the ISDO arm they were 20.8 and 14.0, respectively.
The decrease in scores at 6 months did not differ significantly between study arms, but women in the RRSO arm had a significantly increased incidence of hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and weight gain after surgery, said Dr. Lu, professor and chair in the department of gynecologic oncology and reproductive medicine and the J. Taylor Wharton Distinguished Chair in Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“There was a significant difference in quality of life physical scores in RRSO versus the salpingectomy arm,” she said, adding that no difference was seen between the groups in quality of life mental scores.
The level of decision regret was significantly higher in the women who underwent RRSO (scores,14.1 vs. 8.7 on the 100-point scale), she noted.
“We hypothesized that use of HRT [hormone replacement therapy] after RRSO may have accounted for this difference, and looked at the two subsets,” she said. “Within the RRSO group, 25% did not go on HRT, and while higher than ISDO scores, these scores did not account for the large difference in decision regret.”
About half of the women had a history of breast cancer.
“Clinically, this agrees with what we see in that women with a prior history of breast cancer have less angst about undergoing RRSO,” she said, adding that 75% of women in the RRSO arm did go on HRT, and “these women represent the majority of our ‘previvors’ – healthy women with no history of cancer who struggle with the RRSO decision and who are able to take HRT.”
“Interestingly, compared to ISDO, RRSO women on HRT had the highest decisional regret,” she said.
An analysis of numerous possible predictors of decisional regret showed that only baseline depression score was a significant independent predictor, she noted.
Study participants are premenopausal women aged 30-50 years who have a high risk of ovarian cancer because of a pathogenic germline mutation in an ovarian cancer predisposition gene, and a normal CA125 and transvaginal ultrasound within 6 months before enrollment. All receive scripted counseling about the recommended age for oophorectomy and can choose their study arm. Planned enrollment at nine participating U.S. centers is 270 women.
The RRSO and ISDO arms at current enrollment are statistically similar with respect to mutation type, education level, breast cancer history, and first/second-degree ovarian cancer, but significantly more women in the ISDO arm had undergone risk-reducing mastectomy (51% vs. 35%), Dr. Lu noted, adding that to date no ovarian cancers have been identified at initial surgery, between surgeries, or at the time of completion oophorectomy in the ISDO patients – although only two women in that arm have undergone completion oophorectomy.
In the RRSO arm, one high-grade serous tubal intraepithelial neoplasia (STIC) was found at the time of surgery in a PALB2 mutation carrier.
“We believe this is the first report of a STIC in a PALB2 carrier. This woman was 39 years old with a strong family history of breast and ovarian cancer,” she said.
The findings suggest that “for these high-risk women who underwent ISDO ... the option encouraged them to undergo limited but potentially lifesaving surgical prophylaxis at an earlier age rather than wait to undergo full surgical prophylaxis at the upper-accepted age limit due to fear of early menopause,” Dr. Lu said.
Safety continues to be closely monitored in this study and the use of ISDO outside of the clinical trial setting is not recommended, she added, noting that an expansion of both WISP and the TUBA trial, for which preliminary results showing similar outcomes were also presented at the SGO meeting, is planned.
Dr. Lu reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Lu KH et al. SGO 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract 3.
HONOLULU – Women at high risk for ovarian cancer who undergo risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) or interval salpingectomy with delayed oophorectomy (ISDO) experience significant reductions in cancer distress, according to preliminary findings from the WISP (Women Choosing Surgical Prevention) study.
However, those who choose RRSO experience worse menopausal symptoms and higher rates of regret, Karen H. Lu, MD, reported at the Society of Gynecologic Oncology’s Annual Meeting on Women’s Cancer. Of 183 women enrolled to date in the prospective, nonrandomized, multicenter study, 91 underwent RRSO and 92 underwent ISDO at a median age of 40.9 and 37.5 years, respectively. Significant decreases in cancer-related distress as measured using the Impact of Event scale were seen in both groups at 6-month follow-up after surgery: The mean scores in the RRSO arm were 19.6 at baseline and 10.9 at 6 months, and in the ISDO arm they were 20.8 and 14.0, respectively.
The decrease in scores at 6 months did not differ significantly between study arms, but women in the RRSO arm had a significantly increased incidence of hot flashes, night sweats, vaginal dryness, and weight gain after surgery, said Dr. Lu, professor and chair in the department of gynecologic oncology and reproductive medicine and the J. Taylor Wharton Distinguished Chair in Gynecologic Oncology at the University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, Houston.
“There was a significant difference in quality of life physical scores in RRSO versus the salpingectomy arm,” she said, adding that no difference was seen between the groups in quality of life mental scores.
The level of decision regret was significantly higher in the women who underwent RRSO (scores,14.1 vs. 8.7 on the 100-point scale), she noted.
“We hypothesized that use of HRT [hormone replacement therapy] after RRSO may have accounted for this difference, and looked at the two subsets,” she said. “Within the RRSO group, 25% did not go on HRT, and while higher than ISDO scores, these scores did not account for the large difference in decision regret.”
About half of the women had a history of breast cancer.
“Clinically, this agrees with what we see in that women with a prior history of breast cancer have less angst about undergoing RRSO,” she said, adding that 75% of women in the RRSO arm did go on HRT, and “these women represent the majority of our ‘previvors’ – healthy women with no history of cancer who struggle with the RRSO decision and who are able to take HRT.”
“Interestingly, compared to ISDO, RRSO women on HRT had the highest decisional regret,” she said.
An analysis of numerous possible predictors of decisional regret showed that only baseline depression score was a significant independent predictor, she noted.
Study participants are premenopausal women aged 30-50 years who have a high risk of ovarian cancer because of a pathogenic germline mutation in an ovarian cancer predisposition gene, and a normal CA125 and transvaginal ultrasound within 6 months before enrollment. All receive scripted counseling about the recommended age for oophorectomy and can choose their study arm. Planned enrollment at nine participating U.S. centers is 270 women.
The RRSO and ISDO arms at current enrollment are statistically similar with respect to mutation type, education level, breast cancer history, and first/second-degree ovarian cancer, but significantly more women in the ISDO arm had undergone risk-reducing mastectomy (51% vs. 35%), Dr. Lu noted, adding that to date no ovarian cancers have been identified at initial surgery, between surgeries, or at the time of completion oophorectomy in the ISDO patients – although only two women in that arm have undergone completion oophorectomy.
In the RRSO arm, one high-grade serous tubal intraepithelial neoplasia (STIC) was found at the time of surgery in a PALB2 mutation carrier.
“We believe this is the first report of a STIC in a PALB2 carrier. This woman was 39 years old with a strong family history of breast and ovarian cancer,” she said.
The findings suggest that “for these high-risk women who underwent ISDO ... the option encouraged them to undergo limited but potentially lifesaving surgical prophylaxis at an earlier age rather than wait to undergo full surgical prophylaxis at the upper-accepted age limit due to fear of early menopause,” Dr. Lu said.
Safety continues to be closely monitored in this study and the use of ISDO outside of the clinical trial setting is not recommended, she added, noting that an expansion of both WISP and the TUBA trial, for which preliminary results showing similar outcomes were also presented at the SGO meeting, is planned.
Dr. Lu reported having no disclosures.
SOURCE: Lu KH et al. SGO 2019, Late-Breaking Abstract 3.
REPORTING FROM SGO 2019