User login
Trial of mesh vs. hysterectomy for prolapse yields inconclusive results
Transvaginal mesh hysteropexy for symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse may not significantly reduce treatment failure after 3 years, compared with vaginal hysterectomy with uterosacral ligament suspension, according to randomized trial results.
Nevertheless, “the point estimate favored hysteropexy,” the study authors wrote in JAMA. The 36-month cumulative treatment failure outcomes – defined as retreatment of prolapse, prolapse beyond the hymen, or prolapse symptoms – were 33% for patients who underwent hysteropexy, compared with 42% for patients who underwent hysterectomy. In addition, mean operative time was 45 minutes less for patients who underwent hysteropexy.
The publication follows the Food and Drug Administration’s ruling in April 2019 that manufacturers must cease marketing transvaginal mesh kits for repair of anterior or apical compartment prolapse. The investigators plan to continue evaluating patient outcomes to 5 years, and they noted that longer follow-up may lead to different conclusions.
From a class II device to class III
Surgical repair of uterovaginal prolapse is common. Although vaginal hysterectomy is the procedure of choice for many surgeons, “uterine-sparing suspension techniques ... are increasing in usage,” wrote Charles W. Nager, MD, chair and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, and coauthors. However, few high-quality, long-term studies have compared apical transvaginal mesh with native tissue procedures.
The FDA first approved a mesh device for transvaginal repair of prolapse in 2002. In 2008, the agency notified clinicians and patients about an increase in adverse event reports related to vaginal mesh. It later advised that mesh for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse does not conclusively improve clinical outcomes and that serious adverse events are not rare.
In 2016, the FDA reclassified surgical mesh to repair pelvic organ prolapse transvaginally as high risk, citing safety concerns such as severe pelvic pain and organ perforation. And in April 2019, the FDA ordered companies to stop selling transvaginal mesh intended for pelvic organ prolapse repair. “Even though these products can no longer be used in patients moving forward, [manufacturers] are required to continue follow-up” of patients in post–market surveillance studies, the FDA said in a statement.
An FDA panel had concluded that 3-year outcomes for prolapse repair with mesh should be better than the outcomes for repair with native tissue, and that the procedures should have comparable safety profiles.
The SUPeR trial
To compare the efficacy and adverse events of vaginal hysterectomy with suture apical suspension and transvaginal mesh hysteropexy, Dr. Nager and colleagues conducted the Study of Uterine Prolapse Procedures Randomized (SUPeR) trial.
Researchers enrolled 183 postmenopausal women with symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse undergoing surgical intervention at nine sites between April 2013 and February 2015. Investigators randomized 93 women to undergo vaginal mesh hysteropexy and 90 to undergo vaginal hysterectomy with uterosacral ligament suspension. Hysteropexy used the UpholdLITE transvaginal mesh support system (Boston Scientific). Uterosacral ligament suspension required one permanent and one delayed absorbable suture on each side. The primary analysis included data from 175 patients.
Compared with hysterectomy, hysteropexy resulted in an adjusted hazard ratio of treatment failure of 0.62 after 3 years, which was not statistically significant (P = .06). The 95% confidence interval of 0.38-1.02 “was wide and only slightly crossed the null value,” the researchers said. “The remaining uncertainty is too great” to establish or rule out the benefit of vaginal mesh hysteropexy.
Mean operative time was about 45 minutes shorter in the hysteropexy group versus the hysterectomy group (111.5 minutes vs. 156.7 minutes). Adverse events in the hysteropexy versus hysterectomy groups included mesh exposure (8% vs. 0%), ureteral kinking managed intraoperatively (0% vs. 7%), excessive granulation tissue after 12 weeks (1% vs. 11%), and suture exposure after 12 weeks (3% vs. 21%).
“Both groups reported improvements in sexual function, and dyspareunia and pain and de novo dyspareunia rates were low,” Dr. Nager and colleagues wrote. “All other complications with long-term sequelae were not different between groups.”
“Patients in the current study are being followed up for 60 months and the results and conclusions at 36 months could change with extended follow-up,” they added.
A role for mesh?
“The report ... by Nager and colleagues is particularly timely and important,” Cynthia A. Brincat, MD, PhD, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Dr. Brincat is affiliated with the division of female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
Although the mesh exposures, granulation tissue, or suture exposures during the trial did not require reoperation, “management of these adverse events was not described,” the editorialist noted. “Clinically important differences could exist between the management of these reported adverse events.”
Based on the findings, gynecologic surgeons “will need to reconsider several important questions regarding the repair of pelvic organ prolapse. For instance, is hysterectomy a necessary component for the repair? What is the role of mesh, and can its use reduce the use of otherwise unnecessary procedures (i.e., hysterectomy) without increasing risk to patients?” she wrote. Other questions center on what constitutes operative failure and how surgeons should augment prolapse repair.
“This study also provides a potential new and well-defined role for the use of mesh in pelvic prolapse surgery, with no significant difference, and perhaps some benefit (i.e., no hysterectomy), compared with a native tissue repair,” Dr. Brincat wrote. “The study also provides useful information for shared decision-making discussions between patients and gynecologic surgeons with respect to selection of procedures and use of mesh for treatment of women with symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse undergoing vaginal surgery.”
The trial was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Women’s Health. Boston Scientific provided support through an unrestricted grant. One author reported stock ownership in a medical device company, and others reported grants from medical device companies outside the submitted work. Dr. Brincat reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Nager CW et al. JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1054-65; Brincat CA. JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1047-8.
Transvaginal mesh hysteropexy for symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse may not significantly reduce treatment failure after 3 years, compared with vaginal hysterectomy with uterosacral ligament suspension, according to randomized trial results.
Nevertheless, “the point estimate favored hysteropexy,” the study authors wrote in JAMA. The 36-month cumulative treatment failure outcomes – defined as retreatment of prolapse, prolapse beyond the hymen, or prolapse symptoms – were 33% for patients who underwent hysteropexy, compared with 42% for patients who underwent hysterectomy. In addition, mean operative time was 45 minutes less for patients who underwent hysteropexy.
The publication follows the Food and Drug Administration’s ruling in April 2019 that manufacturers must cease marketing transvaginal mesh kits for repair of anterior or apical compartment prolapse. The investigators plan to continue evaluating patient outcomes to 5 years, and they noted that longer follow-up may lead to different conclusions.
From a class II device to class III
Surgical repair of uterovaginal prolapse is common. Although vaginal hysterectomy is the procedure of choice for many surgeons, “uterine-sparing suspension techniques ... are increasing in usage,” wrote Charles W. Nager, MD, chair and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, and coauthors. However, few high-quality, long-term studies have compared apical transvaginal mesh with native tissue procedures.
The FDA first approved a mesh device for transvaginal repair of prolapse in 2002. In 2008, the agency notified clinicians and patients about an increase in adverse event reports related to vaginal mesh. It later advised that mesh for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse does not conclusively improve clinical outcomes and that serious adverse events are not rare.
In 2016, the FDA reclassified surgical mesh to repair pelvic organ prolapse transvaginally as high risk, citing safety concerns such as severe pelvic pain and organ perforation. And in April 2019, the FDA ordered companies to stop selling transvaginal mesh intended for pelvic organ prolapse repair. “Even though these products can no longer be used in patients moving forward, [manufacturers] are required to continue follow-up” of patients in post–market surveillance studies, the FDA said in a statement.
An FDA panel had concluded that 3-year outcomes for prolapse repair with mesh should be better than the outcomes for repair with native tissue, and that the procedures should have comparable safety profiles.
The SUPeR trial
To compare the efficacy and adverse events of vaginal hysterectomy with suture apical suspension and transvaginal mesh hysteropexy, Dr. Nager and colleagues conducted the Study of Uterine Prolapse Procedures Randomized (SUPeR) trial.
Researchers enrolled 183 postmenopausal women with symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse undergoing surgical intervention at nine sites between April 2013 and February 2015. Investigators randomized 93 women to undergo vaginal mesh hysteropexy and 90 to undergo vaginal hysterectomy with uterosacral ligament suspension. Hysteropexy used the UpholdLITE transvaginal mesh support system (Boston Scientific). Uterosacral ligament suspension required one permanent and one delayed absorbable suture on each side. The primary analysis included data from 175 patients.
Compared with hysterectomy, hysteropexy resulted in an adjusted hazard ratio of treatment failure of 0.62 after 3 years, which was not statistically significant (P = .06). The 95% confidence interval of 0.38-1.02 “was wide and only slightly crossed the null value,” the researchers said. “The remaining uncertainty is too great” to establish or rule out the benefit of vaginal mesh hysteropexy.
Mean operative time was about 45 minutes shorter in the hysteropexy group versus the hysterectomy group (111.5 minutes vs. 156.7 minutes). Adverse events in the hysteropexy versus hysterectomy groups included mesh exposure (8% vs. 0%), ureteral kinking managed intraoperatively (0% vs. 7%), excessive granulation tissue after 12 weeks (1% vs. 11%), and suture exposure after 12 weeks (3% vs. 21%).
“Both groups reported improvements in sexual function, and dyspareunia and pain and de novo dyspareunia rates were low,” Dr. Nager and colleagues wrote. “All other complications with long-term sequelae were not different between groups.”
“Patients in the current study are being followed up for 60 months and the results and conclusions at 36 months could change with extended follow-up,” they added.
A role for mesh?
“The report ... by Nager and colleagues is particularly timely and important,” Cynthia A. Brincat, MD, PhD, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Dr. Brincat is affiliated with the division of female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
Although the mesh exposures, granulation tissue, or suture exposures during the trial did not require reoperation, “management of these adverse events was not described,” the editorialist noted. “Clinically important differences could exist between the management of these reported adverse events.”
Based on the findings, gynecologic surgeons “will need to reconsider several important questions regarding the repair of pelvic organ prolapse. For instance, is hysterectomy a necessary component for the repair? What is the role of mesh, and can its use reduce the use of otherwise unnecessary procedures (i.e., hysterectomy) without increasing risk to patients?” she wrote. Other questions center on what constitutes operative failure and how surgeons should augment prolapse repair.
“This study also provides a potential new and well-defined role for the use of mesh in pelvic prolapse surgery, with no significant difference, and perhaps some benefit (i.e., no hysterectomy), compared with a native tissue repair,” Dr. Brincat wrote. “The study also provides useful information for shared decision-making discussions between patients and gynecologic surgeons with respect to selection of procedures and use of mesh for treatment of women with symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse undergoing vaginal surgery.”
The trial was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Women’s Health. Boston Scientific provided support through an unrestricted grant. One author reported stock ownership in a medical device company, and others reported grants from medical device companies outside the submitted work. Dr. Brincat reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Nager CW et al. JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1054-65; Brincat CA. JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1047-8.
Transvaginal mesh hysteropexy for symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse may not significantly reduce treatment failure after 3 years, compared with vaginal hysterectomy with uterosacral ligament suspension, according to randomized trial results.
Nevertheless, “the point estimate favored hysteropexy,” the study authors wrote in JAMA. The 36-month cumulative treatment failure outcomes – defined as retreatment of prolapse, prolapse beyond the hymen, or prolapse symptoms – were 33% for patients who underwent hysteropexy, compared with 42% for patients who underwent hysterectomy. In addition, mean operative time was 45 minutes less for patients who underwent hysteropexy.
The publication follows the Food and Drug Administration’s ruling in April 2019 that manufacturers must cease marketing transvaginal mesh kits for repair of anterior or apical compartment prolapse. The investigators plan to continue evaluating patient outcomes to 5 years, and they noted that longer follow-up may lead to different conclusions.
From a class II device to class III
Surgical repair of uterovaginal prolapse is common. Although vaginal hysterectomy is the procedure of choice for many surgeons, “uterine-sparing suspension techniques ... are increasing in usage,” wrote Charles W. Nager, MD, chair and professor of obstetrics, gynecology, and reproductive sciences at the University of California, San Diego, and coauthors. However, few high-quality, long-term studies have compared apical transvaginal mesh with native tissue procedures.
The FDA first approved a mesh device for transvaginal repair of prolapse in 2002. In 2008, the agency notified clinicians and patients about an increase in adverse event reports related to vaginal mesh. It later advised that mesh for the treatment of pelvic organ prolapse does not conclusively improve clinical outcomes and that serious adverse events are not rare.
In 2016, the FDA reclassified surgical mesh to repair pelvic organ prolapse transvaginally as high risk, citing safety concerns such as severe pelvic pain and organ perforation. And in April 2019, the FDA ordered companies to stop selling transvaginal mesh intended for pelvic organ prolapse repair. “Even though these products can no longer be used in patients moving forward, [manufacturers] are required to continue follow-up” of patients in post–market surveillance studies, the FDA said in a statement.
An FDA panel had concluded that 3-year outcomes for prolapse repair with mesh should be better than the outcomes for repair with native tissue, and that the procedures should have comparable safety profiles.
The SUPeR trial
To compare the efficacy and adverse events of vaginal hysterectomy with suture apical suspension and transvaginal mesh hysteropexy, Dr. Nager and colleagues conducted the Study of Uterine Prolapse Procedures Randomized (SUPeR) trial.
Researchers enrolled 183 postmenopausal women with symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse undergoing surgical intervention at nine sites between April 2013 and February 2015. Investigators randomized 93 women to undergo vaginal mesh hysteropexy and 90 to undergo vaginal hysterectomy with uterosacral ligament suspension. Hysteropexy used the UpholdLITE transvaginal mesh support system (Boston Scientific). Uterosacral ligament suspension required one permanent and one delayed absorbable suture on each side. The primary analysis included data from 175 patients.
Compared with hysterectomy, hysteropexy resulted in an adjusted hazard ratio of treatment failure of 0.62 after 3 years, which was not statistically significant (P = .06). The 95% confidence interval of 0.38-1.02 “was wide and only slightly crossed the null value,” the researchers said. “The remaining uncertainty is too great” to establish or rule out the benefit of vaginal mesh hysteropexy.
Mean operative time was about 45 minutes shorter in the hysteropexy group versus the hysterectomy group (111.5 minutes vs. 156.7 minutes). Adverse events in the hysteropexy versus hysterectomy groups included mesh exposure (8% vs. 0%), ureteral kinking managed intraoperatively (0% vs. 7%), excessive granulation tissue after 12 weeks (1% vs. 11%), and suture exposure after 12 weeks (3% vs. 21%).
“Both groups reported improvements in sexual function, and dyspareunia and pain and de novo dyspareunia rates were low,” Dr. Nager and colleagues wrote. “All other complications with long-term sequelae were not different between groups.”
“Patients in the current study are being followed up for 60 months and the results and conclusions at 36 months could change with extended follow-up,” they added.
A role for mesh?
“The report ... by Nager and colleagues is particularly timely and important,” Cynthia A. Brincat, MD, PhD, wrote in an accompanying editorial. Dr. Brincat is affiliated with the division of female pelvic medicine and reconstructive surgery at Rush Medical College, Chicago.
Although the mesh exposures, granulation tissue, or suture exposures during the trial did not require reoperation, “management of these adverse events was not described,” the editorialist noted. “Clinically important differences could exist between the management of these reported adverse events.”
Based on the findings, gynecologic surgeons “will need to reconsider several important questions regarding the repair of pelvic organ prolapse. For instance, is hysterectomy a necessary component for the repair? What is the role of mesh, and can its use reduce the use of otherwise unnecessary procedures (i.e., hysterectomy) without increasing risk to patients?” she wrote. Other questions center on what constitutes operative failure and how surgeons should augment prolapse repair.
“This study also provides a potential new and well-defined role for the use of mesh in pelvic prolapse surgery, with no significant difference, and perhaps some benefit (i.e., no hysterectomy), compared with a native tissue repair,” Dr. Brincat wrote. “The study also provides useful information for shared decision-making discussions between patients and gynecologic surgeons with respect to selection of procedures and use of mesh for treatment of women with symptomatic uterovaginal prolapse undergoing vaginal surgery.”
The trial was funded by the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development and the National Institutes of Health Office of Research on Women’s Health. Boston Scientific provided support through an unrestricted grant. One author reported stock ownership in a medical device company, and others reported grants from medical device companies outside the submitted work. Dr. Brincat reported no conflicts of interest.
SOURCES: Nager CW et al. JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1054-65; Brincat CA. JAMA. 2019 Sep 17;322(11):1047-8.
FROM JAMA
Benralizumab trials cast doubt on eosinophil depletion’s role in COPD treatment
and eosinophilic inflammation, according to results from two phase 3 trials. The data were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Benralizumab, an interleukin-5 receptor alpha–directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody, is approved for the treatment of patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. To assess whether the treatment may prevent COPD exacerbations, Gerard J. Criner, MD, chair and professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University in Philadelphia and colleagues conducted two randomized, double-blind, parallel-group studies: GALATHEA and TERRANOVA. Researchers enrolled patients with frequent moderate or severe COPD exacerbations and blood eosinophil counts of at least 220 per mm3.
A 56-week treatment period
“An eosinophil threshold of 220 per mm3 was selected on the basis of the phase 2 trial of benralizumab in patients with COPD, in which modeling of annual exacerbations according to baseline blood eosinophil count indicated that patients with eosinophil counts above a similar threshold were more likely to have a response to benralizumab,” the authors wrote. “The doses selected were 30 mg, the approved dose for asthma treatment; 100 mg, to inform the safety margin; and 10 mg (in TERRANOVA), to evaluate the dose-efficacy relationship.”
Patients received placebo or benralizumab via subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks for the first three doses, then every 8 weeks for the rest of the 56-week treatment period. The primary end point was the annualized COPD exacerbation rate ratio (benralizumab vs. placebo) at week 56.
The primary analysis populations included 1,120 patients in GALATHEA and 1,545 patients in TERRANOVA. Most patients were white men, and the average age was 65 years. The percentages of patients with current asthma (5.4% in GALATHEA and 3.3% in TERRANOVA) or past asthma (8.3% in GALATHEA and 6.1% in TERRANOVA) were low.
In GALATHEA, the estimated annualized exacerbation rates were 1.19 per year in the 30-mg benralizumab group, 1.03 per year in the 100-mg benralizumab group, and 1.24 per year in the placebo group. Compared with placebo, the rate ratio was 0.96 for 30 mg of benralizumab and 0.83 for 100 mg of benralizumab.
In TERRANOVA, the estimated annualized exacerbation rates for 10 mg, 30 mg, and 100 mg of benralizumab and for placebo were 0.99 per year, 1.21 per year, 1.09 per year, and 1.17 per year, respectively. The corresponding rate ratios were 0.85, 1.04, and 0.93. “At 56 weeks, none of the annualized COPD exacerbation rate ratios for any dose of benralizumab as compared with placebo reached significance in either trial,” the researchers said. “Types and frequencies of adverse events were similar with benralizumab and placebo.”
Depletion of eosinophils in blood and sputum
By week 4, benralizumab substantially depleted blood eosinophils. In addition, treatment substantially depleted sputum eosinophils by week 24. “However, in contrast to the results in benralizumab-treated patients with severe eosinophilic asthma, this eosinophil depletion did not correspond to a significant difference in the rate of exacerbations. This finding, together with the effect on eosinophils – with minimal effect on the COPD exacerbation rate – that was observed in the mepolizumab trials, suggests that eosinophil depletion is unlikely to ameliorate exacerbation outcomes for the majority of patients with COPD,” Dr. Criner and his coauthors concluded. “Future investigation is required to identify additional clinical factors or biomarkers that may characterize the patients with COPD who are most likely to benefit from anti–interleukin-5 receptor antibody therapy.”
The trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca, which manufactures benralizumab (Fasenra), and by Kyowa Hakko Kirin. One author is supported by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. The authors’ disclosures included grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Criner GJ et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;382(11):1023-34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905248.
and eosinophilic inflammation, according to results from two phase 3 trials. The data were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Benralizumab, an interleukin-5 receptor alpha–directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody, is approved for the treatment of patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. To assess whether the treatment may prevent COPD exacerbations, Gerard J. Criner, MD, chair and professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University in Philadelphia and colleagues conducted two randomized, double-blind, parallel-group studies: GALATHEA and TERRANOVA. Researchers enrolled patients with frequent moderate or severe COPD exacerbations and blood eosinophil counts of at least 220 per mm3.
A 56-week treatment period
“An eosinophil threshold of 220 per mm3 was selected on the basis of the phase 2 trial of benralizumab in patients with COPD, in which modeling of annual exacerbations according to baseline blood eosinophil count indicated that patients with eosinophil counts above a similar threshold were more likely to have a response to benralizumab,” the authors wrote. “The doses selected were 30 mg, the approved dose for asthma treatment; 100 mg, to inform the safety margin; and 10 mg (in TERRANOVA), to evaluate the dose-efficacy relationship.”
Patients received placebo or benralizumab via subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks for the first three doses, then every 8 weeks for the rest of the 56-week treatment period. The primary end point was the annualized COPD exacerbation rate ratio (benralizumab vs. placebo) at week 56.
The primary analysis populations included 1,120 patients in GALATHEA and 1,545 patients in TERRANOVA. Most patients were white men, and the average age was 65 years. The percentages of patients with current asthma (5.4% in GALATHEA and 3.3% in TERRANOVA) or past asthma (8.3% in GALATHEA and 6.1% in TERRANOVA) were low.
In GALATHEA, the estimated annualized exacerbation rates were 1.19 per year in the 30-mg benralizumab group, 1.03 per year in the 100-mg benralizumab group, and 1.24 per year in the placebo group. Compared with placebo, the rate ratio was 0.96 for 30 mg of benralizumab and 0.83 for 100 mg of benralizumab.
In TERRANOVA, the estimated annualized exacerbation rates for 10 mg, 30 mg, and 100 mg of benralizumab and for placebo were 0.99 per year, 1.21 per year, 1.09 per year, and 1.17 per year, respectively. The corresponding rate ratios were 0.85, 1.04, and 0.93. “At 56 weeks, none of the annualized COPD exacerbation rate ratios for any dose of benralizumab as compared with placebo reached significance in either trial,” the researchers said. “Types and frequencies of adverse events were similar with benralizumab and placebo.”
Depletion of eosinophils in blood and sputum
By week 4, benralizumab substantially depleted blood eosinophils. In addition, treatment substantially depleted sputum eosinophils by week 24. “However, in contrast to the results in benralizumab-treated patients with severe eosinophilic asthma, this eosinophil depletion did not correspond to a significant difference in the rate of exacerbations. This finding, together with the effect on eosinophils – with minimal effect on the COPD exacerbation rate – that was observed in the mepolizumab trials, suggests that eosinophil depletion is unlikely to ameliorate exacerbation outcomes for the majority of patients with COPD,” Dr. Criner and his coauthors concluded. “Future investigation is required to identify additional clinical factors or biomarkers that may characterize the patients with COPD who are most likely to benefit from anti–interleukin-5 receptor antibody therapy.”
The trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca, which manufactures benralizumab (Fasenra), and by Kyowa Hakko Kirin. One author is supported by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. The authors’ disclosures included grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Criner GJ et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;382(11):1023-34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905248.
and eosinophilic inflammation, according to results from two phase 3 trials. The data were published in the New England Journal of Medicine.
Benralizumab, an interleukin-5 receptor alpha–directed cytolytic monoclonal antibody, is approved for the treatment of patients with severe eosinophilic asthma. To assess whether the treatment may prevent COPD exacerbations, Gerard J. Criner, MD, chair and professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at Temple University in Philadelphia and colleagues conducted two randomized, double-blind, parallel-group studies: GALATHEA and TERRANOVA. Researchers enrolled patients with frequent moderate or severe COPD exacerbations and blood eosinophil counts of at least 220 per mm3.
A 56-week treatment period
“An eosinophil threshold of 220 per mm3 was selected on the basis of the phase 2 trial of benralizumab in patients with COPD, in which modeling of annual exacerbations according to baseline blood eosinophil count indicated that patients with eosinophil counts above a similar threshold were more likely to have a response to benralizumab,” the authors wrote. “The doses selected were 30 mg, the approved dose for asthma treatment; 100 mg, to inform the safety margin; and 10 mg (in TERRANOVA), to evaluate the dose-efficacy relationship.”
Patients received placebo or benralizumab via subcutaneous injection every 4 weeks for the first three doses, then every 8 weeks for the rest of the 56-week treatment period. The primary end point was the annualized COPD exacerbation rate ratio (benralizumab vs. placebo) at week 56.
The primary analysis populations included 1,120 patients in GALATHEA and 1,545 patients in TERRANOVA. Most patients were white men, and the average age was 65 years. The percentages of patients with current asthma (5.4% in GALATHEA and 3.3% in TERRANOVA) or past asthma (8.3% in GALATHEA and 6.1% in TERRANOVA) were low.
In GALATHEA, the estimated annualized exacerbation rates were 1.19 per year in the 30-mg benralizumab group, 1.03 per year in the 100-mg benralizumab group, and 1.24 per year in the placebo group. Compared with placebo, the rate ratio was 0.96 for 30 mg of benralizumab and 0.83 for 100 mg of benralizumab.
In TERRANOVA, the estimated annualized exacerbation rates for 10 mg, 30 mg, and 100 mg of benralizumab and for placebo were 0.99 per year, 1.21 per year, 1.09 per year, and 1.17 per year, respectively. The corresponding rate ratios were 0.85, 1.04, and 0.93. “At 56 weeks, none of the annualized COPD exacerbation rate ratios for any dose of benralizumab as compared with placebo reached significance in either trial,” the researchers said. “Types and frequencies of adverse events were similar with benralizumab and placebo.”
Depletion of eosinophils in blood and sputum
By week 4, benralizumab substantially depleted blood eosinophils. In addition, treatment substantially depleted sputum eosinophils by week 24. “However, in contrast to the results in benralizumab-treated patients with severe eosinophilic asthma, this eosinophil depletion did not correspond to a significant difference in the rate of exacerbations. This finding, together with the effect on eosinophils – with minimal effect on the COPD exacerbation rate – that was observed in the mepolizumab trials, suggests that eosinophil depletion is unlikely to ameliorate exacerbation outcomes for the majority of patients with COPD,” Dr. Criner and his coauthors concluded. “Future investigation is required to identify additional clinical factors or biomarkers that may characterize the patients with COPD who are most likely to benefit from anti–interleukin-5 receptor antibody therapy.”
The trials were sponsored by AstraZeneca, which manufactures benralizumab (Fasenra), and by Kyowa Hakko Kirin. One author is supported by the National Institute for Health Research Manchester Biomedical Research Centre. The authors’ disclosures included grants and personal fees from AstraZeneca and other pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Criner GJ et al. N Engl J Med. 2019;382(11):1023-34. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1905248.
FROM THE NEW ENGLAND JOURNAL OF MEDICINE
Can a novel steroidal anti-inflammatory drug benefit patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy?
Daily treatment with vamorolone at doses of 2.0 mg/kg per day and 6.0 mg/kg per day suggested possible efficacy in a 24-week study, researchers said. The exploratory study included 48 boys who had completed a phase 2a trial.
The treatment was safe and well tolerated, and patients who received 2.0 mg/kg per day had significantly improved muscle function, as assessed by time to stand, compared with natural history controls, according to the results, which were published in Neurology.
In addition, the novel drug may reduce “safety concerns typically seen with traditional glucocorticoids,” wrote Eric P. Hoffman, PhD, and coauthors. Dr. Hoffman is president and CEO of ReveraGen BioPharma in Rockville, Md., which is developing the drug, and associate dean for research in the school of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences at Binghamton (N.Y.) University.
In preclinical studies, vamorolone retained anti-inflammatory efficacy while reducing adverse effects, compared with prednisolone, in a manner that is “consistent with vamorolone blocking [nuclear factor-kappa beta]–associated proinflammatory signals as a ligand/receptor monomeric state instead of the traditional molecular models of ligand/receptor dimeric complexes,” the authors said.
Phase 1 and phase 2a studies suggest that the drug may have an improved safety profile. To assess possible efficacy and define optimal doses, the investigators conducted the 24-week extension study. Participants were boys aged 4 years to younger than 7 years who had never been treated with glucocorticoids. They received 0.25, 0.75, 2.0, or 6.0 mg/kg per day vamorolone in an oral suspension formulation. Twelve boys received each dose level.
“Vamorolone was well tolerated ... with no adverse events leading to reduction of drug dosing or withdrawal from the trial,” they said. “The [timed stand from supine] primary outcome measure in vamorolone-treated patients with DMD supports efficacy of the 2.0-mg/kg/d dose ... at 24 weeks,” they said. A secondary outcome measure, the 6-minute walk test, supports efficacy at this dose at 12 and 24 weeks of treatment.
Furthermore, the data indicate that the 2.0-mg/kg per day dose may be associated with less weight gain and improved bone turnover and insulin resistance biomarkers, relative to prednisone therapy. “There was evidence of adrenal suppression in a subset of boys with DMD treated with 2.0 mg/kg/d vamorolone, with 18% of patients showing reduced morning cortisol levels,” the authors said. “Future studies of vamorolone will include adrenocorticotropic hormone–challenge tests to further explore adrenal function.”
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of vamorolone is underway. Investigators are testing two doses of vamorolone (2.0 and 6.0 mg/kg per day) versus placebo and prednisone (0.75 mg/kg per day). Researchers plan to enroll 120 patients, with 30 patients in each arm.
ReveraGen BioPharma received funds for the present study from Actelion Pharmaceuticals, U.S. and European government agencies, and nonprofit foundations. Dr. Hoffman and some of his collaborators are cofounders of ReveraGen. Other coauthors received support from the company.
SOURCE: Hoffman EP et al. Neurology. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008168.
Daily treatment with vamorolone at doses of 2.0 mg/kg per day and 6.0 mg/kg per day suggested possible efficacy in a 24-week study, researchers said. The exploratory study included 48 boys who had completed a phase 2a trial.
The treatment was safe and well tolerated, and patients who received 2.0 mg/kg per day had significantly improved muscle function, as assessed by time to stand, compared with natural history controls, according to the results, which were published in Neurology.
In addition, the novel drug may reduce “safety concerns typically seen with traditional glucocorticoids,” wrote Eric P. Hoffman, PhD, and coauthors. Dr. Hoffman is president and CEO of ReveraGen BioPharma in Rockville, Md., which is developing the drug, and associate dean for research in the school of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences at Binghamton (N.Y.) University.
In preclinical studies, vamorolone retained anti-inflammatory efficacy while reducing adverse effects, compared with prednisolone, in a manner that is “consistent with vamorolone blocking [nuclear factor-kappa beta]–associated proinflammatory signals as a ligand/receptor monomeric state instead of the traditional molecular models of ligand/receptor dimeric complexes,” the authors said.
Phase 1 and phase 2a studies suggest that the drug may have an improved safety profile. To assess possible efficacy and define optimal doses, the investigators conducted the 24-week extension study. Participants were boys aged 4 years to younger than 7 years who had never been treated with glucocorticoids. They received 0.25, 0.75, 2.0, or 6.0 mg/kg per day vamorolone in an oral suspension formulation. Twelve boys received each dose level.
“Vamorolone was well tolerated ... with no adverse events leading to reduction of drug dosing or withdrawal from the trial,” they said. “The [timed stand from supine] primary outcome measure in vamorolone-treated patients with DMD supports efficacy of the 2.0-mg/kg/d dose ... at 24 weeks,” they said. A secondary outcome measure, the 6-minute walk test, supports efficacy at this dose at 12 and 24 weeks of treatment.
Furthermore, the data indicate that the 2.0-mg/kg per day dose may be associated with less weight gain and improved bone turnover and insulin resistance biomarkers, relative to prednisone therapy. “There was evidence of adrenal suppression in a subset of boys with DMD treated with 2.0 mg/kg/d vamorolone, with 18% of patients showing reduced morning cortisol levels,” the authors said. “Future studies of vamorolone will include adrenocorticotropic hormone–challenge tests to further explore adrenal function.”
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of vamorolone is underway. Investigators are testing two doses of vamorolone (2.0 and 6.0 mg/kg per day) versus placebo and prednisone (0.75 mg/kg per day). Researchers plan to enroll 120 patients, with 30 patients in each arm.
ReveraGen BioPharma received funds for the present study from Actelion Pharmaceuticals, U.S. and European government agencies, and nonprofit foundations. Dr. Hoffman and some of his collaborators are cofounders of ReveraGen. Other coauthors received support from the company.
SOURCE: Hoffman EP et al. Neurology. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008168.
Daily treatment with vamorolone at doses of 2.0 mg/kg per day and 6.0 mg/kg per day suggested possible efficacy in a 24-week study, researchers said. The exploratory study included 48 boys who had completed a phase 2a trial.
The treatment was safe and well tolerated, and patients who received 2.0 mg/kg per day had significantly improved muscle function, as assessed by time to stand, compared with natural history controls, according to the results, which were published in Neurology.
In addition, the novel drug may reduce “safety concerns typically seen with traditional glucocorticoids,” wrote Eric P. Hoffman, PhD, and coauthors. Dr. Hoffman is president and CEO of ReveraGen BioPharma in Rockville, Md., which is developing the drug, and associate dean for research in the school of pharmacy and pharmaceutical sciences at Binghamton (N.Y.) University.
In preclinical studies, vamorolone retained anti-inflammatory efficacy while reducing adverse effects, compared with prednisolone, in a manner that is “consistent with vamorolone blocking [nuclear factor-kappa beta]–associated proinflammatory signals as a ligand/receptor monomeric state instead of the traditional molecular models of ligand/receptor dimeric complexes,” the authors said.
Phase 1 and phase 2a studies suggest that the drug may have an improved safety profile. To assess possible efficacy and define optimal doses, the investigators conducted the 24-week extension study. Participants were boys aged 4 years to younger than 7 years who had never been treated with glucocorticoids. They received 0.25, 0.75, 2.0, or 6.0 mg/kg per day vamorolone in an oral suspension formulation. Twelve boys received each dose level.
“Vamorolone was well tolerated ... with no adverse events leading to reduction of drug dosing or withdrawal from the trial,” they said. “The [timed stand from supine] primary outcome measure in vamorolone-treated patients with DMD supports efficacy of the 2.0-mg/kg/d dose ... at 24 weeks,” they said. A secondary outcome measure, the 6-minute walk test, supports efficacy at this dose at 12 and 24 weeks of treatment.
Furthermore, the data indicate that the 2.0-mg/kg per day dose may be associated with less weight gain and improved bone turnover and insulin resistance biomarkers, relative to prednisone therapy. “There was evidence of adrenal suppression in a subset of boys with DMD treated with 2.0 mg/kg/d vamorolone, with 18% of patients showing reduced morning cortisol levels,” the authors said. “Future studies of vamorolone will include adrenocorticotropic hormone–challenge tests to further explore adrenal function.”
A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial of vamorolone is underway. Investigators are testing two doses of vamorolone (2.0 and 6.0 mg/kg per day) versus placebo and prednisone (0.75 mg/kg per day). Researchers plan to enroll 120 patients, with 30 patients in each arm.
ReveraGen BioPharma received funds for the present study from Actelion Pharmaceuticals, U.S. and European government agencies, and nonprofit foundations. Dr. Hoffman and some of his collaborators are cofounders of ReveraGen. Other coauthors received support from the company.
SOURCE: Hoffman EP et al. Neurology. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008168.
FROM NEUROLOGY
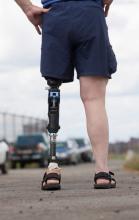
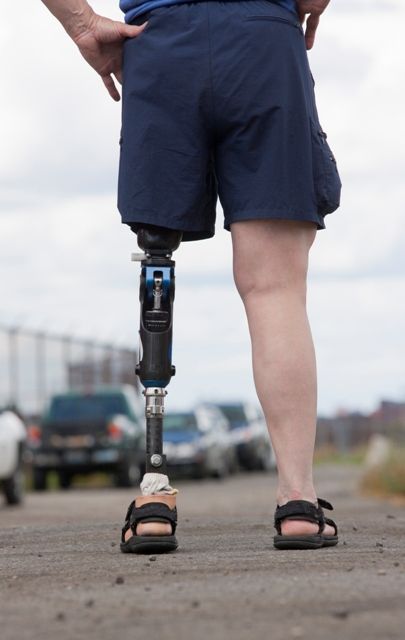
Sensory feedback may smooth walking with a prosthetic leg
A prosthetic leg that elicits the sensation of knee motion and the feeling of the sole of the foot touching the ground may improve walking performance and reduce phantom limb pain, according to a proof-of-concept study with two patients.
With the bionic leg system, the patients performed better during clinically important tests indoors and outdoors, study author Stanisa Raspopovic, PhD, explained during a press briefing about the research. The findings were published in Nature Medicine.
The results indicate that the use of sensory feedback “could be common practice” in prosthetic devices in the future, he said. Dr. Raspopovic is a researcher at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich and a founder of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Neural prosthetics allow the nervous system and external devices to interact. These brain-machine interfaces may improve quality of life for patients with brain or spinal cord injuries, degenerative disease, or loss of limbs.
“Conventional leg prostheses do not convey sensory information about motion or interaction with the ground to above-knee amputees, thereby reducing confidence and walking speed in the users,” the study authors wrote. Users may also have high levels of mental and physical fatigue, and the lack of physiologic feedback from the extremity to the brain may contribute to the generation of phantom limb pain.
To evaluate whether neural sensory feedback restoration could address these issues, investigators conducted a study with two patients who had undergone transfemoral amputations as a result of traumatic events. The patients were implanted with four intraneural stimulation electrodes in the remaining tibial nerve. The prosthetic leg device included sensors to represent foot touch and pressure and knee joint angle. The sensors transmitted sensory signals to the nervous system through the stimulation electrodes in the tibial nerve.
When the patients walked outdoors over a path traced in the sand, “participants’ speeds were significantly higher when sensory feedback was provided,” the authors wrote. One participant walked 3.56 m/min faster, and the other walked 5.68 m/min faster.
The participants also rated their confidence in the prosthesis on a scale from 0 to 10. For patient 1, self-rated confidence improved from 4.85 to 7.71 with the device. Patient 2 reported a confidence level that climbed from 2.7 to 5.55.
When tested indoors, both patients reached a 0.5 km/hour higher speed on the treadmill when stimulation was provided and both had a lower mean rate of oxygen uptake during the sensory feedback trials, the study authors reported.
Levels of phantom limb pain also decreased significantly after 10-minute stimulation sessions, but not during control sessions.
Longer studies with more patients are required, and fully implantable devices without transcutaneous cables need to be developed, the authors wrote.
Grants from the European Research Council, European Commission, and Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research. Dr. Raspopovic and two coauthors hold shares of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, a start-up company dealing with the commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs.
SOURCE: Petrini FM et al. Nat Med. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0567-3.
A prosthetic leg that elicits the sensation of knee motion and the feeling of the sole of the foot touching the ground may improve walking performance and reduce phantom limb pain, according to a proof-of-concept study with two patients.
With the bionic leg system, the patients performed better during clinically important tests indoors and outdoors, study author Stanisa Raspopovic, PhD, explained during a press briefing about the research. The findings were published in Nature Medicine.
The results indicate that the use of sensory feedback “could be common practice” in prosthetic devices in the future, he said. Dr. Raspopovic is a researcher at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich and a founder of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Neural prosthetics allow the nervous system and external devices to interact. These brain-machine interfaces may improve quality of life for patients with brain or spinal cord injuries, degenerative disease, or loss of limbs.
“Conventional leg prostheses do not convey sensory information about motion or interaction with the ground to above-knee amputees, thereby reducing confidence and walking speed in the users,” the study authors wrote. Users may also have high levels of mental and physical fatigue, and the lack of physiologic feedback from the extremity to the brain may contribute to the generation of phantom limb pain.
To evaluate whether neural sensory feedback restoration could address these issues, investigators conducted a study with two patients who had undergone transfemoral amputations as a result of traumatic events. The patients were implanted with four intraneural stimulation electrodes in the remaining tibial nerve. The prosthetic leg device included sensors to represent foot touch and pressure and knee joint angle. The sensors transmitted sensory signals to the nervous system through the stimulation electrodes in the tibial nerve.
When the patients walked outdoors over a path traced in the sand, “participants’ speeds were significantly higher when sensory feedback was provided,” the authors wrote. One participant walked 3.56 m/min faster, and the other walked 5.68 m/min faster.
The participants also rated their confidence in the prosthesis on a scale from 0 to 10. For patient 1, self-rated confidence improved from 4.85 to 7.71 with the device. Patient 2 reported a confidence level that climbed from 2.7 to 5.55.
When tested indoors, both patients reached a 0.5 km/hour higher speed on the treadmill when stimulation was provided and both had a lower mean rate of oxygen uptake during the sensory feedback trials, the study authors reported.
Levels of phantom limb pain also decreased significantly after 10-minute stimulation sessions, but not during control sessions.
Longer studies with more patients are required, and fully implantable devices without transcutaneous cables need to be developed, the authors wrote.
Grants from the European Research Council, European Commission, and Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research. Dr. Raspopovic and two coauthors hold shares of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, a start-up company dealing with the commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs.
SOURCE: Petrini FM et al. Nat Med. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0567-3.
A prosthetic leg that elicits the sensation of knee motion and the feeling of the sole of the foot touching the ground may improve walking performance and reduce phantom limb pain, according to a proof-of-concept study with two patients.
With the bionic leg system, the patients performed better during clinically important tests indoors and outdoors, study author Stanisa Raspopovic, PhD, explained during a press briefing about the research. The findings were published in Nature Medicine.
The results indicate that the use of sensory feedback “could be common practice” in prosthetic devices in the future, he said. Dr. Raspopovic is a researcher at Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Zürich and a founder of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, which is based in Lausanne, Switzerland.
Neural prosthetics allow the nervous system and external devices to interact. These brain-machine interfaces may improve quality of life for patients with brain or spinal cord injuries, degenerative disease, or loss of limbs.
“Conventional leg prostheses do not convey sensory information about motion or interaction with the ground to above-knee amputees, thereby reducing confidence and walking speed in the users,” the study authors wrote. Users may also have high levels of mental and physical fatigue, and the lack of physiologic feedback from the extremity to the brain may contribute to the generation of phantom limb pain.
To evaluate whether neural sensory feedback restoration could address these issues, investigators conducted a study with two patients who had undergone transfemoral amputations as a result of traumatic events. The patients were implanted with four intraneural stimulation electrodes in the remaining tibial nerve. The prosthetic leg device included sensors to represent foot touch and pressure and knee joint angle. The sensors transmitted sensory signals to the nervous system through the stimulation electrodes in the tibial nerve.
When the patients walked outdoors over a path traced in the sand, “participants’ speeds were significantly higher when sensory feedback was provided,” the authors wrote. One participant walked 3.56 m/min faster, and the other walked 5.68 m/min faster.
The participants also rated their confidence in the prosthesis on a scale from 0 to 10. For patient 1, self-rated confidence improved from 4.85 to 7.71 with the device. Patient 2 reported a confidence level that climbed from 2.7 to 5.55.
When tested indoors, both patients reached a 0.5 km/hour higher speed on the treadmill when stimulation was provided and both had a lower mean rate of oxygen uptake during the sensory feedback trials, the study authors reported.
Levels of phantom limb pain also decreased significantly after 10-minute stimulation sessions, but not during control sessions.
Longer studies with more patients are required, and fully implantable devices without transcutaneous cables need to be developed, the authors wrote.
Grants from the European Research Council, European Commission, and Swiss National Science Foundation funded the research. Dr. Raspopovic and two coauthors hold shares of SensArs Neuroprosthetics, a start-up company dealing with the commercialization of neurocontrolled artificial limbs.
SOURCE: Petrini FM et al. Nat Med. 2019 Sep 9. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0567-3.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE
Less CPAP time linked to exacerbation in COPD/OSA overlap syndrome
and all‐cause mortality, according to a retrospective cohort study.
“These factors should be taken into account when considering the management and prognosis of these patients,” the researchers said in the Clinical Respiratory Journal.
Prior studies have found that patients with COPD and OSA – that is, with overlap syndrome – “have a substantially greater risk of morbidity and mortality, compared to those with either COPD or OSA alone,” said Philippe E. Jaoude, MD, and Ali A. El Solh, MD, both of the Veterans Affairs Western New York Healthcare System in Buffalo and the University at Buffalo.
To identify factors associated with COPD exacerbation and all‐cause mortality in patients with overlap syndrome, Dr. Jaoude and Dr. El Solh reviewed the electronic health records of patients with simultaneous COPD and OSA. They compared patients with overlap syndrome who had an acute exacerbation of COPD during a 42-month period with a control group of patients with overlap syndrome who did not have exacerbations during that time. Patients with exacerbations and controls were matched 1:1 by age and body mass index.
Eligible patients were aged 42-90 years, had objectively confirmed COPD, and had documented OSA by in-laboratory polysomnography (that is, at least five obstructive apneas and hypopneas per hour). The investigators defined a COPD exacerbation as a sustained worsening of a patient’s respiratory condition that warranted additional treatment.
Of 225 eligible patients, 92 had at least one COPD exacerbation between March 2014 and September 2017. Patients with COPD exacerbation and controls had a mean age of about 68 years. The group of patients with exacerbation had a higher percentage of active smokers (21% vs. 9%) and had poorer lung function (mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second percent predicted: 55.2% vs. 64.5%).
“Although the rate of CPAP adherence between the two groups was not significantly different, the average time of CPAP use was significantly higher in patients with no recorded exacerbation,” the researchers reported – 285.4 min/night versus 238.2 min/night.
In all, 146 patients (79.4%) survived, and 38 patients (20.6%) died during the study period. The crude mortality rate was significantly higher in the group with COPD exacerbations (14% vs. 7%).
“Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified the independent risk factors associated with COPD exacerbations as active smoking, worse airflow limitation, and lower CPAP utilization,” they said. “As for all-cause mortality, a higher burden of comorbidities, worse airflow limitation, and lower time of CPAP use were independently associated with poor outcome.”
The researchers noted that they cannot rule out the possibility that patients who were adherent to CPAP were systematically different from those who were not.
The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jaoude P et al. Clin Respir J. 2019 Aug 22. doi: 10.1111/crj.13079.
and all‐cause mortality, according to a retrospective cohort study.
“These factors should be taken into account when considering the management and prognosis of these patients,” the researchers said in the Clinical Respiratory Journal.
Prior studies have found that patients with COPD and OSA – that is, with overlap syndrome – “have a substantially greater risk of morbidity and mortality, compared to those with either COPD or OSA alone,” said Philippe E. Jaoude, MD, and Ali A. El Solh, MD, both of the Veterans Affairs Western New York Healthcare System in Buffalo and the University at Buffalo.
To identify factors associated with COPD exacerbation and all‐cause mortality in patients with overlap syndrome, Dr. Jaoude and Dr. El Solh reviewed the electronic health records of patients with simultaneous COPD and OSA. They compared patients with overlap syndrome who had an acute exacerbation of COPD during a 42-month period with a control group of patients with overlap syndrome who did not have exacerbations during that time. Patients with exacerbations and controls were matched 1:1 by age and body mass index.
Eligible patients were aged 42-90 years, had objectively confirmed COPD, and had documented OSA by in-laboratory polysomnography (that is, at least five obstructive apneas and hypopneas per hour). The investigators defined a COPD exacerbation as a sustained worsening of a patient’s respiratory condition that warranted additional treatment.
Of 225 eligible patients, 92 had at least one COPD exacerbation between March 2014 and September 2017. Patients with COPD exacerbation and controls had a mean age of about 68 years. The group of patients with exacerbation had a higher percentage of active smokers (21% vs. 9%) and had poorer lung function (mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second percent predicted: 55.2% vs. 64.5%).
“Although the rate of CPAP adherence between the two groups was not significantly different, the average time of CPAP use was significantly higher in patients with no recorded exacerbation,” the researchers reported – 285.4 min/night versus 238.2 min/night.
In all, 146 patients (79.4%) survived, and 38 patients (20.6%) died during the study period. The crude mortality rate was significantly higher in the group with COPD exacerbations (14% vs. 7%).
“Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified the independent risk factors associated with COPD exacerbations as active smoking, worse airflow limitation, and lower CPAP utilization,” they said. “As for all-cause mortality, a higher burden of comorbidities, worse airflow limitation, and lower time of CPAP use were independently associated with poor outcome.”
The researchers noted that they cannot rule out the possibility that patients who were adherent to CPAP were systematically different from those who were not.
The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jaoude P et al. Clin Respir J. 2019 Aug 22. doi: 10.1111/crj.13079.
and all‐cause mortality, according to a retrospective cohort study.
“These factors should be taken into account when considering the management and prognosis of these patients,” the researchers said in the Clinical Respiratory Journal.
Prior studies have found that patients with COPD and OSA – that is, with overlap syndrome – “have a substantially greater risk of morbidity and mortality, compared to those with either COPD or OSA alone,” said Philippe E. Jaoude, MD, and Ali A. El Solh, MD, both of the Veterans Affairs Western New York Healthcare System in Buffalo and the University at Buffalo.
To identify factors associated with COPD exacerbation and all‐cause mortality in patients with overlap syndrome, Dr. Jaoude and Dr. El Solh reviewed the electronic health records of patients with simultaneous COPD and OSA. They compared patients with overlap syndrome who had an acute exacerbation of COPD during a 42-month period with a control group of patients with overlap syndrome who did not have exacerbations during that time. Patients with exacerbations and controls were matched 1:1 by age and body mass index.
Eligible patients were aged 42-90 years, had objectively confirmed COPD, and had documented OSA by in-laboratory polysomnography (that is, at least five obstructive apneas and hypopneas per hour). The investigators defined a COPD exacerbation as a sustained worsening of a patient’s respiratory condition that warranted additional treatment.
Of 225 eligible patients, 92 had at least one COPD exacerbation between March 2014 and September 2017. Patients with COPD exacerbation and controls had a mean age of about 68 years. The group of patients with exacerbation had a higher percentage of active smokers (21% vs. 9%) and had poorer lung function (mean forced expiratory volume in 1 second percent predicted: 55.2% vs. 64.5%).
“Although the rate of CPAP adherence between the two groups was not significantly different, the average time of CPAP use was significantly higher in patients with no recorded exacerbation,” the researchers reported – 285.4 min/night versus 238.2 min/night.
In all, 146 patients (79.4%) survived, and 38 patients (20.6%) died during the study period. The crude mortality rate was significantly higher in the group with COPD exacerbations (14% vs. 7%).
“Multivariate logistic regression analysis identified the independent risk factors associated with COPD exacerbations as active smoking, worse airflow limitation, and lower CPAP utilization,” they said. “As for all-cause mortality, a higher burden of comorbidities, worse airflow limitation, and lower time of CPAP use were independently associated with poor outcome.”
The researchers noted that they cannot rule out the possibility that patients who were adherent to CPAP were systematically different from those who were not.
The authors had no conflicts of interest.
SOURCE: Jaoude P et al. Clin Respir J. 2019 Aug 22. doi: 10.1111/crj.13079.
FROM CLINICAL RESPIRATORY JOURNAL
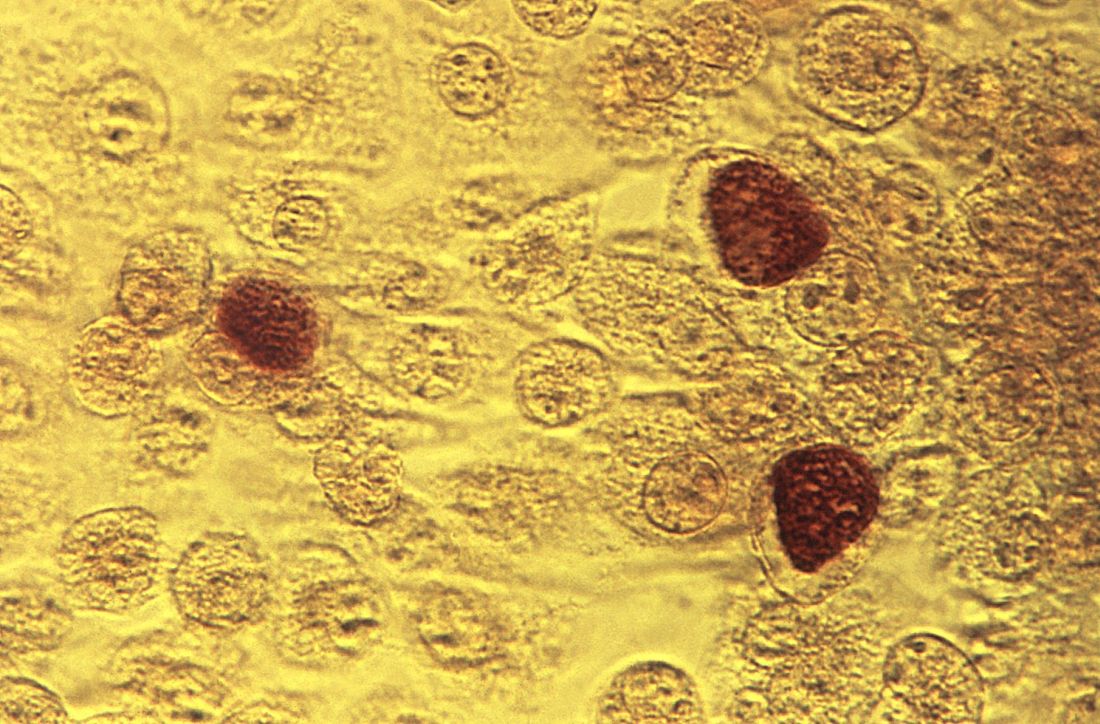
Chlamydia trachomatis is associated with adverse reproductive health outcomes
compared with women who have tested negative for C. trachomatis or who have not been tested for the bacterium, according to a retrospective cohort study.
The risk of PID increases with repeat chlamydial infections, and the use of antibiotics that are effective against C. trachomatis does not decrease the risk of subsequent PID, the researchers reported in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Prior studies have yielded different estimates of the risk of reproductive complications after chlamydia infection, said Casper den Heijer, MD, PhD, a researcher at Utrecht Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Heerlen, the Netherlands, and colleagues. To assess the risk of PID, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility in women with a previous C. trachomatis diagnosis, Dr. den Heijer and coauthors conducted a retrospective study of women aged 12-25 years at baseline in the Clinical Practice Research Datalink GOLD database. Their analysis included data from women living in England between 2000 and 2013. The investigators used Cox proportional hazard models to evaluate the risk of adverse outcomes.
The researchers analyzed data from 857,324 women with a mean follow-up of 7.5 years. Patients’ mean age at baseline was 15 years. In all, the participants had 8,346 occurrences of PID, 2,484 occurrences of ectopic pregnancy, and 2,066 occurrences of female infertility.
For PID, incidence rates per 1,000 person-years were 1.1 among women untested for C. trachomatis, 1.4 among women who tested negative, and 5.4 among women who tested positive. For ectopic pregnancy, the incidence rates were 0.3 for untested women, 0.4 for negatively tested women, and 1.2 for positively tested women. Infertility incidence rates were 0.3 for untested women, 0.3 for negatively tested women, and 0.9 for positively tested women.
Compared with women who tested negative for C. trachomatis, women who tested positive had an increased risk of PID (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.36), ectopic pregnancy (aHR, 1.87), and female infertility (aHR, 1.85). Untested women had a lower risk for PID, compared with women who tested negative (aHR, 0.57).
C. trachomatis–effective antibiotic use was associated with higher PID risk, and that risk increased as the women used more of the antibiotic prescriptions, Dr. den Heijer and associates said. This occurred in all three groups of women. A possible explanation for this association between the antibiotics and higher PID risk could be that PID can be caused by other infectious diseases that could be treated with C. trachomatis–effective antibiotics.
While the study relied on primary care data, genitourinary medicine clinics diagnose and treat “a sizable proportion” of sexually transmitted infections in the United Kingdom, the authors noted. This limitation means that the study underestimates the number of C. trachomatis diagnoses in the cohort, they said.
Nonetheless, “Our results confirm the reproductive health burden of [C. trachomatis] and show the need for adequate public health interventions,” Dr. den Heijer and associates concluded.
Iris Krishna, MD, said in an interview, “This is a well-designed population-based retrospective cohort study evaluating the incidence of PID, ectopic pregnancy, and female infertility amongst more than 850,000 women in a primary care setting with a previous diagnosis of C. trachomatis, compared with women who have tested negative for C. trachomatis and women who have not been tested for C. trachomatis. This study also evaluated the impact of antibiotic use on PID.”
Dr. Krishna, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University in Atlanta, continued, “This study demonstrates an association between C. trachomatis infection and adverse reproductive health outcomes. It highlights the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment of C. trachomatis to reduce the risk of both short- and long-term reproductive health complications, as well as highlighting the importance of preventing recurrent C. trachomatis infections. It also emphasizes the importance of targeted screening for high-risk groups and appropriate follow-up to ensure that optimal antibiotic treatment is provided, especially amongst women who have recently used C. trachomatis–effective antibiotics.
“The finding of progression to PID despite C. trachomatis-effective antibiotic use indicates a more complex relationship where perhaps host immunological factors or effects of antibiotics on the vaginal microbiome may play a role and requires further study,” concluded Dr. Krishna. She was not involved in the current study, and was asked to comment on the findings.
The study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Dr. den Heijer had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Krishna said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: den Heijer CDJ et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 24. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz429.
compared with women who have tested negative for C. trachomatis or who have not been tested for the bacterium, according to a retrospective cohort study.
The risk of PID increases with repeat chlamydial infections, and the use of antibiotics that are effective against C. trachomatis does not decrease the risk of subsequent PID, the researchers reported in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Prior studies have yielded different estimates of the risk of reproductive complications after chlamydia infection, said Casper den Heijer, MD, PhD, a researcher at Utrecht Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Heerlen, the Netherlands, and colleagues. To assess the risk of PID, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility in women with a previous C. trachomatis diagnosis, Dr. den Heijer and coauthors conducted a retrospective study of women aged 12-25 years at baseline in the Clinical Practice Research Datalink GOLD database. Their analysis included data from women living in England between 2000 and 2013. The investigators used Cox proportional hazard models to evaluate the risk of adverse outcomes.
The researchers analyzed data from 857,324 women with a mean follow-up of 7.5 years. Patients’ mean age at baseline was 15 years. In all, the participants had 8,346 occurrences of PID, 2,484 occurrences of ectopic pregnancy, and 2,066 occurrences of female infertility.
For PID, incidence rates per 1,000 person-years were 1.1 among women untested for C. trachomatis, 1.4 among women who tested negative, and 5.4 among women who tested positive. For ectopic pregnancy, the incidence rates were 0.3 for untested women, 0.4 for negatively tested women, and 1.2 for positively tested women. Infertility incidence rates were 0.3 for untested women, 0.3 for negatively tested women, and 0.9 for positively tested women.
Compared with women who tested negative for C. trachomatis, women who tested positive had an increased risk of PID (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.36), ectopic pregnancy (aHR, 1.87), and female infertility (aHR, 1.85). Untested women had a lower risk for PID, compared with women who tested negative (aHR, 0.57).
C. trachomatis–effective antibiotic use was associated with higher PID risk, and that risk increased as the women used more of the antibiotic prescriptions, Dr. den Heijer and associates said. This occurred in all three groups of women. A possible explanation for this association between the antibiotics and higher PID risk could be that PID can be caused by other infectious diseases that could be treated with C. trachomatis–effective antibiotics.
While the study relied on primary care data, genitourinary medicine clinics diagnose and treat “a sizable proportion” of sexually transmitted infections in the United Kingdom, the authors noted. This limitation means that the study underestimates the number of C. trachomatis diagnoses in the cohort, they said.
Nonetheless, “Our results confirm the reproductive health burden of [C. trachomatis] and show the need for adequate public health interventions,” Dr. den Heijer and associates concluded.
Iris Krishna, MD, said in an interview, “This is a well-designed population-based retrospective cohort study evaluating the incidence of PID, ectopic pregnancy, and female infertility amongst more than 850,000 women in a primary care setting with a previous diagnosis of C. trachomatis, compared with women who have tested negative for C. trachomatis and women who have not been tested for C. trachomatis. This study also evaluated the impact of antibiotic use on PID.”
Dr. Krishna, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University in Atlanta, continued, “This study demonstrates an association between C. trachomatis infection and adverse reproductive health outcomes. It highlights the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment of C. trachomatis to reduce the risk of both short- and long-term reproductive health complications, as well as highlighting the importance of preventing recurrent C. trachomatis infections. It also emphasizes the importance of targeted screening for high-risk groups and appropriate follow-up to ensure that optimal antibiotic treatment is provided, especially amongst women who have recently used C. trachomatis–effective antibiotics.
“The finding of progression to PID despite C. trachomatis-effective antibiotic use indicates a more complex relationship where perhaps host immunological factors or effects of antibiotics on the vaginal microbiome may play a role and requires further study,” concluded Dr. Krishna. She was not involved in the current study, and was asked to comment on the findings.
The study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Dr. den Heijer had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Krishna said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: den Heijer CDJ et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 24. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz429.
compared with women who have tested negative for C. trachomatis or who have not been tested for the bacterium, according to a retrospective cohort study.
The risk of PID increases with repeat chlamydial infections, and the use of antibiotics that are effective against C. trachomatis does not decrease the risk of subsequent PID, the researchers reported in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
Prior studies have yielded different estimates of the risk of reproductive complications after chlamydia infection, said Casper den Heijer, MD, PhD, a researcher at Utrecht Institute of Pharmaceutical Sciences in Heerlen, the Netherlands, and colleagues. To assess the risk of PID, ectopic pregnancy, and infertility in women with a previous C. trachomatis diagnosis, Dr. den Heijer and coauthors conducted a retrospective study of women aged 12-25 years at baseline in the Clinical Practice Research Datalink GOLD database. Their analysis included data from women living in England between 2000 and 2013. The investigators used Cox proportional hazard models to evaluate the risk of adverse outcomes.
The researchers analyzed data from 857,324 women with a mean follow-up of 7.5 years. Patients’ mean age at baseline was 15 years. In all, the participants had 8,346 occurrences of PID, 2,484 occurrences of ectopic pregnancy, and 2,066 occurrences of female infertility.
For PID, incidence rates per 1,000 person-years were 1.1 among women untested for C. trachomatis, 1.4 among women who tested negative, and 5.4 among women who tested positive. For ectopic pregnancy, the incidence rates were 0.3 for untested women, 0.4 for negatively tested women, and 1.2 for positively tested women. Infertility incidence rates were 0.3 for untested women, 0.3 for negatively tested women, and 0.9 for positively tested women.
Compared with women who tested negative for C. trachomatis, women who tested positive had an increased risk of PID (adjusted hazard ratio, 2.36), ectopic pregnancy (aHR, 1.87), and female infertility (aHR, 1.85). Untested women had a lower risk for PID, compared with women who tested negative (aHR, 0.57).
C. trachomatis–effective antibiotic use was associated with higher PID risk, and that risk increased as the women used more of the antibiotic prescriptions, Dr. den Heijer and associates said. This occurred in all three groups of women. A possible explanation for this association between the antibiotics and higher PID risk could be that PID can be caused by other infectious diseases that could be treated with C. trachomatis–effective antibiotics.
While the study relied on primary care data, genitourinary medicine clinics diagnose and treat “a sizable proportion” of sexually transmitted infections in the United Kingdom, the authors noted. This limitation means that the study underestimates the number of C. trachomatis diagnoses in the cohort, they said.
Nonetheless, “Our results confirm the reproductive health burden of [C. trachomatis] and show the need for adequate public health interventions,” Dr. den Heijer and associates concluded.
Iris Krishna, MD, said in an interview, “This is a well-designed population-based retrospective cohort study evaluating the incidence of PID, ectopic pregnancy, and female infertility amongst more than 850,000 women in a primary care setting with a previous diagnosis of C. trachomatis, compared with women who have tested negative for C. trachomatis and women who have not been tested for C. trachomatis. This study also evaluated the impact of antibiotic use on PID.”
Dr. Krishna, assistant professor of gynecology and obstetrics in the division of maternal-fetal medicine at Emory University in Atlanta, continued, “This study demonstrates an association between C. trachomatis infection and adverse reproductive health outcomes. It highlights the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment of C. trachomatis to reduce the risk of both short- and long-term reproductive health complications, as well as highlighting the importance of preventing recurrent C. trachomatis infections. It also emphasizes the importance of targeted screening for high-risk groups and appropriate follow-up to ensure that optimal antibiotic treatment is provided, especially amongst women who have recently used C. trachomatis–effective antibiotics.
“The finding of progression to PID despite C. trachomatis-effective antibiotic use indicates a more complex relationship where perhaps host immunological factors or effects of antibiotics on the vaginal microbiome may play a role and requires further study,” concluded Dr. Krishna. She was not involved in the current study, and was asked to comment on the findings.
The study was supported by the Netherlands Organization for Health Research and Development. Dr. den Heijer had no relevant disclosures. Dr. Krishna said she had no relevant financial disclosures.
SOURCE: den Heijer CDJ et al. Clin Infect Dis. 2019 Aug 24. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz429.
FROM CLINICAL INFECTIOUS DISEASES
FDA approves istradefylline for Parkinson’s disease
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 27 approved Nourianz (istradefylline) tablets as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing off episodes. During off episodes, patients’ medications do not work well, and symptoms such as tremor and difficulty walking increase.
The effectiveness of Nourianz for this indication was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included 1,143 participants. In all four studies, patients treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily off time, compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse reactions to istradefylline with an incidence of 5% or greater and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%, for Nourianz 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%). In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with Nourianz 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared with no patients who received placebo.
In addition,one patient treated with Nourianz 40 mg experienced impulse control disorder, compared with no patients who received Nourianz 20 mg or placebo.
If hallucinations, psychotic behavior, or impulsive or compulsive behavior occurs, a dosage reduction or stoppage should be considered, according to the FDA. Use of Nourianz during pregnancy is not recommended, and women of childbearing potential should be advised to use contraception during treatment.
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily, and clinicians should avoid use of Nourianz with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Istradefylline is the first adenosine A2A receptor antagonist for use in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, and the drug provides patients with a novel nondopaminergic daily oral treatment option, according to a news release from Kyowa Kirin, the company that markets the drug.
Since 2013, istradefylline has been marketed at Nouriast in Japan, where it is indicated for the wearing-off phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease who take preparations containing levodopa.
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 27 approved Nourianz (istradefylline) tablets as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing off episodes. During off episodes, patients’ medications do not work well, and symptoms such as tremor and difficulty walking increase.
The effectiveness of Nourianz for this indication was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included 1,143 participants. In all four studies, patients treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily off time, compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse reactions to istradefylline with an incidence of 5% or greater and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%, for Nourianz 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%). In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with Nourianz 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared with no patients who received placebo.
In addition,one patient treated with Nourianz 40 mg experienced impulse control disorder, compared with no patients who received Nourianz 20 mg or placebo.
If hallucinations, psychotic behavior, or impulsive or compulsive behavior occurs, a dosage reduction or stoppage should be considered, according to the FDA. Use of Nourianz during pregnancy is not recommended, and women of childbearing potential should be advised to use contraception during treatment.
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily, and clinicians should avoid use of Nourianz with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Istradefylline is the first adenosine A2A receptor antagonist for use in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, and the drug provides patients with a novel nondopaminergic daily oral treatment option, according to a news release from Kyowa Kirin, the company that markets the drug.
Since 2013, istradefylline has been marketed at Nouriast in Japan, where it is indicated for the wearing-off phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease who take preparations containing levodopa.
The Food and Drug Administration on Aug. 27 approved Nourianz (istradefylline) tablets as an add-on treatment to levodopa/carbidopa in adult patients with Parkinson’s disease experiencing off episodes. During off episodes, patients’ medications do not work well, and symptoms such as tremor and difficulty walking increase.
The effectiveness of Nourianz for this indication was shown in four 12-week placebo-controlled clinical studies that included 1,143 participants. In all four studies, patients treated with Nourianz experienced a statistically significant decrease from baseline in daily off time, compared with patients who received placebo.
The most common adverse reactions to istradefylline with an incidence of 5% or greater and occurring more frequently than with placebo were dyskinesia (15%, 17%, and 8%, for Nourianz 20 mg, 40 mg, and placebo, respectively), dizziness (3%, 6%, and 4%), constipation (5%, 6%, and 3%), nausea (4%, 6%, and 5%), hallucination (2%, 6%, and 3%), and insomnia (1%, 6%, and 4%). In clinical trials, 1% of patients treated with Nourianz 20 mg or 40 mg discontinued treatment because of dyskinesia, compared with no patients who received placebo.
In addition,one patient treated with Nourianz 40 mg experienced impulse control disorder, compared with no patients who received Nourianz 20 mg or placebo.
If hallucinations, psychotic behavior, or impulsive or compulsive behavior occurs, a dosage reduction or stoppage should be considered, according to the FDA. Use of Nourianz during pregnancy is not recommended, and women of childbearing potential should be advised to use contraception during treatment.
The maximum recommended dosage in patients taking strong CYP3A4 inhibitors is 20 mg once daily, and clinicians should avoid use of Nourianz with strong CYP3A4 inducers.
Istradefylline is the first adenosine A2A receptor antagonist for use in Parkinson’s disease in the United States, and the drug provides patients with a novel nondopaminergic daily oral treatment option, according to a news release from Kyowa Kirin, the company that markets the drug.
Since 2013, istradefylline has been marketed at Nouriast in Japan, where it is indicated for the wearing-off phenomenon in patients with Parkinson’s disease who take preparations containing levodopa.
AAN guideline encourages vaccinations for MS patients
according to an American Academy of Neurology practice guideline.
A summary of the guideline on vaccine-preventable infections and immunization in MS was published online Aug. 28 in Neurology. The new effort updates a 2002 guideline on this topic and incorporates new evidence, vaccines, and disease-modifying therapies (DMTs). The guideline was endorsed by the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers and by the Multiple Sclerosis Association of America.
To create the guideline, lead author Mauricio F. Farez, MD, of the Raúl Carrea Institute for Neurological Research (FLENI) in Buenos Aires and colleagues on the 17-member guideline panel performed a systematic review of the evidence and reached consensus on recommendations using a modified Delphi voting process. The review included randomized, controlled trials; cohort studies; and case-control studies published between 1990 and March 2018.
“Immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agents used to treat MS may suppress or modulate normal immune function. These drugs may increase susceptibility to infections and may reduce vaccine effectiveness because of a decreased ability to mount an immune response,” the authors said.
Based on its review of the evidence, principles of care, and inferences, the authors made the following eight recommendations:
- Clinicians should discuss with patients the evidence regarding immunization in MS (Level B). In addition, clinicians should examine patients’ opinions, preferences, and questions regarding immunizations (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend that patients with MS follow all local vaccine standards in the absence of specific contraindications (Level B).
- Clinicians should consider local risks of vaccine-preventable diseases when counseling patients (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend that patients with MS receive the influenza vaccination if there is no specific contraindication, such as a previous severe reaction (Level B).
- When treatment with an immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agent is considered, clinicians should counsel patients about infection risks associated with the specific medication and the treatment-specific vaccination guidance in the medication’s prescribing instructions (Level B). In addition, physicians should assess patients’ vaccination status before prescribing immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapy and vaccinate patients according to local regulatory standards and treatment-specific infectious risks at least 4-6 weeks before initiating therapy, as advised by the prescribing information (Level B). Furthermore, clinicians may discuss the advantages of vaccination soon after MS diagnosis, regardless of initial therapeutic plans, to prevent delays should immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies be initiated in the future (Level C, based on variation in patient preferences).
- Clinicians must screen for certain infections (such as hepatitis, tuberculosis, and varicella zoster virus) according to a medication’s prescribing information before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating treatment (Level A) and should treat patients who have latent infections before MS treatment according to the medication prescribing information (Level B, based on feasibility and cost relative to benefit). Further, in high-risk populations or in countries with a high burden of infectious disease, clinicians must screen for latent infections before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating medications, even when such screening is not specifically mentioned in the prescribing information (Level A). Clinicians should consult infectious disease or other specialists about treating patients with latent infection before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating medications (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend against live-attenuated vaccines in people with MS who receive immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies or have recently discontinued these therapies (Level B, based on importance of outcomes). When the risk of infection is high, clinicians may recommend live-attenuated vaccines if killed vaccines are unavailable (Level C, based on variation in patient preferences, benefit relative to harm, and importance of outcomes).
- If a patient with MS is experiencing a relapse, clinicians should delay vaccination until the relapse has clinically resolved or is no longer active, often many weeks after relapse onset (Level B).
Personal and population-level benefits
“There is no evidence that vaccination increases the risk of MS exacerbation, although the literature is sparse,” the authors said. “In addition to conferring personal benefits, vaccination of the MS patient population contributes to the well-established phenomenon of herd immunity for the communities in which patients with MS live,” the authors wrote.
Because influenza infection has known risks of exacerbation and morbidity, whereas influenza vaccine has no identified risks of exacerbation, “benefits of influenza vaccination outweigh the risks in most scenarios, although patients with MS receiving some [immunosuppressive or immunomodulating] treatments (fingolimod [Gilenya], glatiramer acetate [Copaxone], and mitoxantrone) may have a reduced response to influenza vaccination,” the authors said. Studies in patients with diseases other than MS suggest that rituximab (Rituxan) also may be associated with reduced influenza vaccine responsiveness.
Immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory medications including alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), fingolimod, mitoxantrone, natalizumab (Tysabri), ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), rituximab, and teriflunomide (Aubagio) have been associated with severe occurrences or recurrences of vaccine-preventable infections, and many package inserts approved by the Food and Drug Administration provide guidance regarding immunization with live vaccines and treatment.
Prescribing information for alemtuzumab, fingolimod, ocrelizumab, and teriflunomide recommends against the use of live vaccines during and immediately preceding treatment. Furthermore, the prescribing information recommends waiting 2-6 months after treatment to immunize with live vaccines, depending on the half-life of the specific therapy.
“The guideline panel identified no evidence that vaccines increase the risk of relapse or worsen relapse severity, but studies are limited,” Dr. Farez and colleagues wrote. “Experts remain concerned that vaccines may worsen relapse severity if given to patients who are actively experiencing an MS relapse.” In addition, use of glucocorticoids may raise concerns about the safety of live-virus vaccines. “Immunization is not typically an urgent need and, in most cases, can be temporarily delayed without a marked increase in infection risk,” the guideline says.
Few high-quality studies
Data were lacking or insufficient to assess whether most vaccine-preventable diseases increase the risk of MS exacerbations. “It is probable that individuals with active MS exacerbations have higher odds of varicella zoster virus viral DNA present in peripheral blood mononuclear cells than individuals with MS in remission,” the guideline says.
Human papillomavirus, pertussis, and tetanus toxoid vaccinations probably are associated with a lower likelihood of a subsequent MS diagnosis, and smallpox vaccination is possibly associated with a lower likelihood of a subsequent MS diagnosis, the review found.
Studies included in the systematic review did not address whether live-attenuated vaccines are as effective in patients with MS as they are in the general population. With regard to the effectiveness of inactivated vaccines, patients with MS possibly are less likely to have a sufficient response to influenza vaccination, compared with controls.
The systematic review “found few high-quality studies to inform recommendations,” the authors said. “As more [immunosuppressive or immunomodulating] agents are developed to manage chronic diseases such as MS, long-term prospective cohort studies are required to evaluate both the safety and effectiveness of immunizations in MS.”
Dr. Farez has received funding for travel from Teva Argentina, Novartis Argentina, and Merck Serono Argentina and has received research support from Biogen. Coauthors’ disclosures included financial ties to pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Farez M et al. Neurology. 2019 Aug 28. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008157.
according to an American Academy of Neurology practice guideline.
A summary of the guideline on vaccine-preventable infections and immunization in MS was published online Aug. 28 in Neurology. The new effort updates a 2002 guideline on this topic and incorporates new evidence, vaccines, and disease-modifying therapies (DMTs). The guideline was endorsed by the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers and by the Multiple Sclerosis Association of America.
To create the guideline, lead author Mauricio F. Farez, MD, of the Raúl Carrea Institute for Neurological Research (FLENI) in Buenos Aires and colleagues on the 17-member guideline panel performed a systematic review of the evidence and reached consensus on recommendations using a modified Delphi voting process. The review included randomized, controlled trials; cohort studies; and case-control studies published between 1990 and March 2018.
“Immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agents used to treat MS may suppress or modulate normal immune function. These drugs may increase susceptibility to infections and may reduce vaccine effectiveness because of a decreased ability to mount an immune response,” the authors said.
Based on its review of the evidence, principles of care, and inferences, the authors made the following eight recommendations:
- Clinicians should discuss with patients the evidence regarding immunization in MS (Level B). In addition, clinicians should examine patients’ opinions, preferences, and questions regarding immunizations (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend that patients with MS follow all local vaccine standards in the absence of specific contraindications (Level B).
- Clinicians should consider local risks of vaccine-preventable diseases when counseling patients (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend that patients with MS receive the influenza vaccination if there is no specific contraindication, such as a previous severe reaction (Level B).
- When treatment with an immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agent is considered, clinicians should counsel patients about infection risks associated with the specific medication and the treatment-specific vaccination guidance in the medication’s prescribing instructions (Level B). In addition, physicians should assess patients’ vaccination status before prescribing immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapy and vaccinate patients according to local regulatory standards and treatment-specific infectious risks at least 4-6 weeks before initiating therapy, as advised by the prescribing information (Level B). Furthermore, clinicians may discuss the advantages of vaccination soon after MS diagnosis, regardless of initial therapeutic plans, to prevent delays should immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies be initiated in the future (Level C, based on variation in patient preferences).
- Clinicians must screen for certain infections (such as hepatitis, tuberculosis, and varicella zoster virus) according to a medication’s prescribing information before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating treatment (Level A) and should treat patients who have latent infections before MS treatment according to the medication prescribing information (Level B, based on feasibility and cost relative to benefit). Further, in high-risk populations or in countries with a high burden of infectious disease, clinicians must screen for latent infections before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating medications, even when such screening is not specifically mentioned in the prescribing information (Level A). Clinicians should consult infectious disease or other specialists about treating patients with latent infection before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating medications (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend against live-attenuated vaccines in people with MS who receive immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies or have recently discontinued these therapies (Level B, based on importance of outcomes). When the risk of infection is high, clinicians may recommend live-attenuated vaccines if killed vaccines are unavailable (Level C, based on variation in patient preferences, benefit relative to harm, and importance of outcomes).
- If a patient with MS is experiencing a relapse, clinicians should delay vaccination until the relapse has clinically resolved or is no longer active, often many weeks after relapse onset (Level B).
Personal and population-level benefits
“There is no evidence that vaccination increases the risk of MS exacerbation, although the literature is sparse,” the authors said. “In addition to conferring personal benefits, vaccination of the MS patient population contributes to the well-established phenomenon of herd immunity for the communities in which patients with MS live,” the authors wrote.
Because influenza infection has known risks of exacerbation and morbidity, whereas influenza vaccine has no identified risks of exacerbation, “benefits of influenza vaccination outweigh the risks in most scenarios, although patients with MS receiving some [immunosuppressive or immunomodulating] treatments (fingolimod [Gilenya], glatiramer acetate [Copaxone], and mitoxantrone) may have a reduced response to influenza vaccination,” the authors said. Studies in patients with diseases other than MS suggest that rituximab (Rituxan) also may be associated with reduced influenza vaccine responsiveness.
Immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory medications including alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), fingolimod, mitoxantrone, natalizumab (Tysabri), ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), rituximab, and teriflunomide (Aubagio) have been associated with severe occurrences or recurrences of vaccine-preventable infections, and many package inserts approved by the Food and Drug Administration provide guidance regarding immunization with live vaccines and treatment.
Prescribing information for alemtuzumab, fingolimod, ocrelizumab, and teriflunomide recommends against the use of live vaccines during and immediately preceding treatment. Furthermore, the prescribing information recommends waiting 2-6 months after treatment to immunize with live vaccines, depending on the half-life of the specific therapy.
“The guideline panel identified no evidence that vaccines increase the risk of relapse or worsen relapse severity, but studies are limited,” Dr. Farez and colleagues wrote. “Experts remain concerned that vaccines may worsen relapse severity if given to patients who are actively experiencing an MS relapse.” In addition, use of glucocorticoids may raise concerns about the safety of live-virus vaccines. “Immunization is not typically an urgent need and, in most cases, can be temporarily delayed without a marked increase in infection risk,” the guideline says.
Few high-quality studies
Data were lacking or insufficient to assess whether most vaccine-preventable diseases increase the risk of MS exacerbations. “It is probable that individuals with active MS exacerbations have higher odds of varicella zoster virus viral DNA present in peripheral blood mononuclear cells than individuals with MS in remission,” the guideline says.
Human papillomavirus, pertussis, and tetanus toxoid vaccinations probably are associated with a lower likelihood of a subsequent MS diagnosis, and smallpox vaccination is possibly associated with a lower likelihood of a subsequent MS diagnosis, the review found.
Studies included in the systematic review did not address whether live-attenuated vaccines are as effective in patients with MS as they are in the general population. With regard to the effectiveness of inactivated vaccines, patients with MS possibly are less likely to have a sufficient response to influenza vaccination, compared with controls.
The systematic review “found few high-quality studies to inform recommendations,” the authors said. “As more [immunosuppressive or immunomodulating] agents are developed to manage chronic diseases such as MS, long-term prospective cohort studies are required to evaluate both the safety and effectiveness of immunizations in MS.”
Dr. Farez has received funding for travel from Teva Argentina, Novartis Argentina, and Merck Serono Argentina and has received research support from Biogen. Coauthors’ disclosures included financial ties to pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Farez M et al. Neurology. 2019 Aug 28. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008157.
according to an American Academy of Neurology practice guideline.
A summary of the guideline on vaccine-preventable infections and immunization in MS was published online Aug. 28 in Neurology. The new effort updates a 2002 guideline on this topic and incorporates new evidence, vaccines, and disease-modifying therapies (DMTs). The guideline was endorsed by the Consortium of Multiple Sclerosis Centers and by the Multiple Sclerosis Association of America.
To create the guideline, lead author Mauricio F. Farez, MD, of the Raúl Carrea Institute for Neurological Research (FLENI) in Buenos Aires and colleagues on the 17-member guideline panel performed a systematic review of the evidence and reached consensus on recommendations using a modified Delphi voting process. The review included randomized, controlled trials; cohort studies; and case-control studies published between 1990 and March 2018.
“Immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agents used to treat MS may suppress or modulate normal immune function. These drugs may increase susceptibility to infections and may reduce vaccine effectiveness because of a decreased ability to mount an immune response,” the authors said.
Based on its review of the evidence, principles of care, and inferences, the authors made the following eight recommendations:
- Clinicians should discuss with patients the evidence regarding immunization in MS (Level B). In addition, clinicians should examine patients’ opinions, preferences, and questions regarding immunizations (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend that patients with MS follow all local vaccine standards in the absence of specific contraindications (Level B).
- Clinicians should consider local risks of vaccine-preventable diseases when counseling patients (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend that patients with MS receive the influenza vaccination if there is no specific contraindication, such as a previous severe reaction (Level B).
- When treatment with an immunosuppressive or immunomodulating agent is considered, clinicians should counsel patients about infection risks associated with the specific medication and the treatment-specific vaccination guidance in the medication’s prescribing instructions (Level B). In addition, physicians should assess patients’ vaccination status before prescribing immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapy and vaccinate patients according to local regulatory standards and treatment-specific infectious risks at least 4-6 weeks before initiating therapy, as advised by the prescribing information (Level B). Furthermore, clinicians may discuss the advantages of vaccination soon after MS diagnosis, regardless of initial therapeutic plans, to prevent delays should immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies be initiated in the future (Level C, based on variation in patient preferences).
- Clinicians must screen for certain infections (such as hepatitis, tuberculosis, and varicella zoster virus) according to a medication’s prescribing information before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating treatment (Level A) and should treat patients who have latent infections before MS treatment according to the medication prescribing information (Level B, based on feasibility and cost relative to benefit). Further, in high-risk populations or in countries with a high burden of infectious disease, clinicians must screen for latent infections before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating medications, even when such screening is not specifically mentioned in the prescribing information (Level A). Clinicians should consult infectious disease or other specialists about treating patients with latent infection before starting immunosuppressive or immunomodulating medications (Level B).
- Clinicians should recommend against live-attenuated vaccines in people with MS who receive immunosuppressive or immunomodulating therapies or have recently discontinued these therapies (Level B, based on importance of outcomes). When the risk of infection is high, clinicians may recommend live-attenuated vaccines if killed vaccines are unavailable (Level C, based on variation in patient preferences, benefit relative to harm, and importance of outcomes).
- If a patient with MS is experiencing a relapse, clinicians should delay vaccination until the relapse has clinically resolved or is no longer active, often many weeks after relapse onset (Level B).
Personal and population-level benefits
“There is no evidence that vaccination increases the risk of MS exacerbation, although the literature is sparse,” the authors said. “In addition to conferring personal benefits, vaccination of the MS patient population contributes to the well-established phenomenon of herd immunity for the communities in which patients with MS live,” the authors wrote.
Because influenza infection has known risks of exacerbation and morbidity, whereas influenza vaccine has no identified risks of exacerbation, “benefits of influenza vaccination outweigh the risks in most scenarios, although patients with MS receiving some [immunosuppressive or immunomodulating] treatments (fingolimod [Gilenya], glatiramer acetate [Copaxone], and mitoxantrone) may have a reduced response to influenza vaccination,” the authors said. Studies in patients with diseases other than MS suggest that rituximab (Rituxan) also may be associated with reduced influenza vaccine responsiveness.
Immunosuppressive or immunomodulatory medications including alemtuzumab (Lemtrada), dimethyl fumarate (Tecfidera), fingolimod, mitoxantrone, natalizumab (Tysabri), ocrelizumab (Ocrevus), rituximab, and teriflunomide (Aubagio) have been associated with severe occurrences or recurrences of vaccine-preventable infections, and many package inserts approved by the Food and Drug Administration provide guidance regarding immunization with live vaccines and treatment.
Prescribing information for alemtuzumab, fingolimod, ocrelizumab, and teriflunomide recommends against the use of live vaccines during and immediately preceding treatment. Furthermore, the prescribing information recommends waiting 2-6 months after treatment to immunize with live vaccines, depending on the half-life of the specific therapy.
“The guideline panel identified no evidence that vaccines increase the risk of relapse or worsen relapse severity, but studies are limited,” Dr. Farez and colleagues wrote. “Experts remain concerned that vaccines may worsen relapse severity if given to patients who are actively experiencing an MS relapse.” In addition, use of glucocorticoids may raise concerns about the safety of live-virus vaccines. “Immunization is not typically an urgent need and, in most cases, can be temporarily delayed without a marked increase in infection risk,” the guideline says.
Few high-quality studies
Data were lacking or insufficient to assess whether most vaccine-preventable diseases increase the risk of MS exacerbations. “It is probable that individuals with active MS exacerbations have higher odds of varicella zoster virus viral DNA present in peripheral blood mononuclear cells than individuals with MS in remission,” the guideline says.
Human papillomavirus, pertussis, and tetanus toxoid vaccinations probably are associated with a lower likelihood of a subsequent MS diagnosis, and smallpox vaccination is possibly associated with a lower likelihood of a subsequent MS diagnosis, the review found.
Studies included in the systematic review did not address whether live-attenuated vaccines are as effective in patients with MS as they are in the general population. With regard to the effectiveness of inactivated vaccines, patients with MS possibly are less likely to have a sufficient response to influenza vaccination, compared with controls.
The systematic review “found few high-quality studies to inform recommendations,” the authors said. “As more [immunosuppressive or immunomodulating] agents are developed to manage chronic diseases such as MS, long-term prospective cohort studies are required to evaluate both the safety and effectiveness of immunizations in MS.”
Dr. Farez has received funding for travel from Teva Argentina, Novartis Argentina, and Merck Serono Argentina and has received research support from Biogen. Coauthors’ disclosures included financial ties to pharmaceutical companies.
SOURCE: Farez M et al. Neurology. 2019 Aug 28. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000008157.
FROM NEUROLOGY
Blood test may reveal brain injury
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
researchers reported Aug. 26 in BMJ Paediatrics Open.
“GFAP outperformed UCH-L1 in detecting concussion in both children and adults within 4 hours of injury,” reported lead author Linda Papa, MD, and collaborators. Dr. Papa is an emergency medicine doctor at Orlando Health. “UCH-L1 was expressed at much higher levels than GFAP in those with nonconcussive trauma, particularly in children. Elevations of these biomarkers in nonconcussive head trauma suggest possible subconcussive brain injury. GFAP could be potentially useful to detect concussion for up to a week post injury.”
In 2018 the Food and Drug Administration approved the use of these biomarkers to guide CT scan ordering in adults with mild to moderate traumatic brain injury, but investigators have not established their ability to detect concussion in children or adults. Clinicians lack an objective measure to diagnose concussion acutely.
To assess the ability of GFAP and UCH-L1 to detect concussion, Dr. Papa and colleagues conducted a prospective cohort study. The researchers enrolled trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. They included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and who presented within 4 hours of injury. Investigators screened for concussion symptoms, obtained biomarker data from 712 trauma patients, and conducted repeated blood sampling in adults.
They grouped patients by those with concussion (n = 371), those with head trauma without overt signs of concussion (n = 149), and those with peripheral trauma without head trauma or concussion (n = 192). The study included 175 children. Injury mechanisms included car crashes, falls, bicycle accidents, and sports injuries.
Patients with concussion had significantly higher GFAP concentrations, compared with patients with body trauma and patients with nonconcussive head trauma. UCH-L1 levels did not significantly differ between patients with concussion and head trauma controls, however.
“Based on these results, the potential utility of GFAP to distinguish concussion from body trauma controls over 7 days postinjury was fair to excellent,” with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves (AUCs) of 0.75-0.89, the researchers said. “UCH-L1’s ability was guarded and variable with AUCs from poor to good depending on timing of samples.” UCH-L1 demonstrated AUCs that ranged from 0.54 to 0.78; earlier samples performed better.
GFAP elevations in head trauma controls “may represent milder forms of concussion that do not elicit typical signs or symptoms associated with concussion,” the authors wrote. “These injuries may be irrelevant, or they may represent important trauma that is just below the level of clinical detection and referred to as subconcussive trauma. ... Biomarkers (such as GFAP and UCH-L1) could provide a more objective measure of injury and potentially identify those at risk for neurocognitive problems.”
The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers, and coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
SOURCE: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
FROM BMJ PAEDIATRICS OPEN
Key clinical point: Levels of glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L1 (UCH-L1) are lowest in patients with nonconcussive body trauma, higher in patients with nonconcussive head trauma, and highest in patients with concussion.
Major finding: GFAP was fair to excellent at distinguishing concussion from body trauma, with area under the receiver operating characteristics curves of 0.75-0.89.
Study details: A prospective cohort study of 712 trauma patients of all ages at three level I trauma centers in the United States. The study included patients with and without head trauma who had a Glasgow Coma Scale score of 15 and presented within 4 hours of injury.
Disclosures: The study was supported by the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke. Dr. Papa is an unpaid scientific consultant for Banyan Biomarkers, which developed kits to measure the biomarkers. Coauthors receive contract research funding from Banyan Biomarkers.
Source: Papa L et al. BMJ Paediatr Open. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1136/bmjpo-2019-000473.
Genotype may affect lifestyle’s influence on dementia risk
But among people at high genetic risk for dementia, these potentially modifiable factors – not smoking, not having depression or diabetes, getting regular physical activity, avoiding social isolation, and following a healthy diet – may not have protective associations, according to research published in Nature Medicine.
Recent analyses have indicated that eliminating known modifiable risk factors for dementia at a population level could prevent one-third of dementia cases, but prevention trials “have yielded inconsistent results so far,” wrote first author Silvan Licher, MD, of the department of epidemiology at Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam (the Netherlands) and his colleagues.
“Prior studies have mostly focused on the risk of dementia associated with an individual protective factor, yet the combination of multiple factors may yield more beneficial effects than the individual parts,” they wrote. “Combining data about a number of factors is also important because it takes into account the multifactorial nature of late-life dementia. We used data from the Rotterdam Study to determine to what extent a favorable profile based on modifiable risk factors is associated with a lower risk of dementia among individuals at low, intermediate, or high genetic risk.”
Grouped by APOE genotype
Patients who were apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 allele (APOE4) carriers (i.e., APOE2 and 4, APOE3 and 4, or two APOE4) were classified as having high genetic risk (n = 1,747). Other APOE genotypes were considered intermediate risk (n = 3,718 with two APOE3 alleles) or low risk (n = 887 with either two APOE2 alleles or APOE2 and 3).
The researchers measured six potentially modifiable lifestyle or health factors that “have been implicated in a lower risk of dementia.” Modifiable risk scores ranged from 0 to 6. Participants were classified as having an unfavorable profile (0-2 protective factors), an intermediate profile (3-4 protective factors), or a favorable profile (5-6 factors).
The researchers calculated the relative risk of developing dementia using a Cox proportional hazards model and the absolutely risk using competing risk models.
In all, 56.2% of the participants were women, the average age was about 69 years, and patient characteristics were similar across the categories of APOE risk. APOE4 carriers received dementia diagnoses at a younger age, more often had a parental history of dementia, and had higher total cholesterol levels, compared with noncarriers. In all, 915 people received a dementia diagnosis, of whom 739 received a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The other 2,644 participants died free from dementia. The median follow-up was 14.1 years.
“Dementia risk was significantly higher among participants at high or intermediate APOE risk, compared with those at low APOE risk,” the researchers said. In addition, the risk of dementia increased in participants who had fewer protective factors. Those with 0-2 protective factors had a 29% higher risk of dementia, compared with participants with 5 or 6 protective factors, after adjusting for age, sex, level of education, parental history of dementia, history of stroke, systolic blood pressure, and total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Lifestyle benefits tended to be greater in younger participants
“APOE genotype significantly modified the association between protective factors and dementia,” the authors said. Compared with participants with protective modifiable risk profiles, participants with unfavorable modifiable risk profiles had greater risk for dementia in the low–APOE risk group (hazard ratio, 2.51) and intermediate–APOE risk group (HR, 1.39), but not in the high–APOE risk group.
“Protective associations of favorable risk profiles against dementia tended to be stronger in younger individuals than in older individuals and were most pronounced for younger individuals at low APOE risk,” Dr. Licher and colleagues said. In a sensitivity analysis that used a polygenic risk score for Alzheimer’s disease based on 27 variants other than APOE to determine participants’ genetic risk, the patterns were “attenuated yet largely comparable,” they wrote. Patterns also remained consistent when the researchers used an ideal cardiovascular health score to indicate modifiable health profiles.
“Our results confirm that individuals with a favorable profile have a lower risk of dementia than those with intermediate or unfavorable profiles based on modifiable risk factors,” they said. Unlike in a subgroup analysis of data from the FINGER study, however, “this study found that a favorable profile could not offset high APOE risk.”
The findings may have implications for clinical trial design and suggest that APOE4 carriers may need to be targeted earlier in the disease process to influence their risk for dementia.
“On the positive side, results from this study show that avoiding an unhealthy lifestyle could potentially prevent or postpone the onset of dementia in most individuals in the population (73%), namely those at low and intermediate genetic risk,” the investigators wrote. “Among these, the majority were categorized has having a favorable profile (66%), yet room for improvement is still substantial.”
The study lacked data on hearing impairment and did not capture shifts to more adverse or optimal lifestyles during follow-up. In addition, the results are based on relatively small samples in each risk category, and the estimates had wide confidence intervals. The population was older and mostly of European descent, which limits the generalizability of the findings, the authors noted.
Lifestyle factors may benefit only people with low genetic risk
“The authors’ key finding was that modifiable lifestyle risk factors were able to reduce dementia risk only in people who did not have an APOE4 allele and hence were at lower genetic risk,” said Kenneth Rockwood, MD, professor of geriatric medicine and neurology at Dalhousie University in Halifax, N.S., and his coauthors, in an accompanying editorial.
The findings contrast with those of another recent population-based study using data from the UK Biobank (JAMA. 2019;322[5]:430-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9879), which suggested that modifiable factors affect dementia risk regardless of genetic risk.
Together, these studies “tell us that ... we must better understand outcomes in those most at risk,” they said. “We might begin by recognizing that aging is essential, rather than incidental, to dementia disease expression.” Future research should focus on people living with frailty, who often are excluded from trials and are at high risk for dementia. Older adults who develop delirium also may be an ideal target group of patients at increased risk for dementia.
“Reducing the extent of disease expression in people prone to developing dementia late in life is difficult. Studies investigating whether dementia can be prevented at all, such as the Rotterdam study, and then whether it can be prevented in the people at greatest risk, can be commended for their clear-eyed approach,” Dr. Rockwood and colleagues said.
The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and University, as well as a variety of Dutch organizations, institutes, and government ministries, and the European Commission. The authors had no competing interests.
Dr. Rockwood is president and chief science officer of DGI Clinical, which has contracts with pharmaceutical and device manufacturers related to individualized outcome measurement.
SOURCES: Licher S et al. Nat Med. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0547-7; and Rockwood K et al. Nat Med. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0575-3.
The study by Dr. Licher and associates shows a clinically significant impact of a healthy lifestyle in reducing dementia. But what is surprising is that the effect was not seen in genetically higher-risk people.
If anything, the results strengthen our recommendations to people interested in lowering their risk for dementia with lifestyle modification. Bear in mind that APOE testing is not done routinely, so the vast majority of our patients do not know their APOE genotype. Since a healthy lifestyle can benefit the majority of the population (around 75%), even if it is less or ineffective in the APOE4 carrier group (about 25% of the population), it is certainly something to recommend. Of course, health care professionals already recommend heart healthy habits, which have an equivalent benefit, and sadly, adherence is relatively low. Adding that lifestyle modification may help prevent dementia might improve patient compliance. Starting healthy lifestyles as early in life as possible may be the key. It is less effective if we wait until we already have memory loss.
Finally, the study results regard relative risk, a concept that many fail to fully grasp. A person can still get dementia in any of the categories, including the “best one” (low genetic and lifestyle risk). It’s a matter of the odds being better or worse, but there is no guarantee of a positive or negative outcome.
Richard J. Caselli, MD, is professor of neurology at the Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale and associate director and clinical core director of the Arizona Alzheimer’s Disease Center, Phoenix. He made these comments in an interview.
The study by Dr. Licher and associates shows a clinically significant impact of a healthy lifestyle in reducing dementia. But what is surprising is that the effect was not seen in genetically higher-risk people.
If anything, the results strengthen our recommendations to people interested in lowering their risk for dementia with lifestyle modification. Bear in mind that APOE testing is not done routinely, so the vast majority of our patients do not know their APOE genotype. Since a healthy lifestyle can benefit the majority of the population (around 75%), even if it is less or ineffective in the APOE4 carrier group (about 25% of the population), it is certainly something to recommend. Of course, health care professionals already recommend heart healthy habits, which have an equivalent benefit, and sadly, adherence is relatively low. Adding that lifestyle modification may help prevent dementia might improve patient compliance. Starting healthy lifestyles as early in life as possible may be the key. It is less effective if we wait until we already have memory loss.
Finally, the study results regard relative risk, a concept that many fail to fully grasp. A person can still get dementia in any of the categories, including the “best one” (low genetic and lifestyle risk). It’s a matter of the odds being better or worse, but there is no guarantee of a positive or negative outcome.
Richard J. Caselli, MD, is professor of neurology at the Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale and associate director and clinical core director of the Arizona Alzheimer’s Disease Center, Phoenix. He made these comments in an interview.
The study by Dr. Licher and associates shows a clinically significant impact of a healthy lifestyle in reducing dementia. But what is surprising is that the effect was not seen in genetically higher-risk people.
If anything, the results strengthen our recommendations to people interested in lowering their risk for dementia with lifestyle modification. Bear in mind that APOE testing is not done routinely, so the vast majority of our patients do not know their APOE genotype. Since a healthy lifestyle can benefit the majority of the population (around 75%), even if it is less or ineffective in the APOE4 carrier group (about 25% of the population), it is certainly something to recommend. Of course, health care professionals already recommend heart healthy habits, which have an equivalent benefit, and sadly, adherence is relatively low. Adding that lifestyle modification may help prevent dementia might improve patient compliance. Starting healthy lifestyles as early in life as possible may be the key. It is less effective if we wait until we already have memory loss.
Finally, the study results regard relative risk, a concept that many fail to fully grasp. A person can still get dementia in any of the categories, including the “best one” (low genetic and lifestyle risk). It’s a matter of the odds being better or worse, but there is no guarantee of a positive or negative outcome.
Richard J. Caselli, MD, is professor of neurology at the Mayo Clinic Arizona in Scottsdale and associate director and clinical core director of the Arizona Alzheimer’s Disease Center, Phoenix. He made these comments in an interview.
But among people at high genetic risk for dementia, these potentially modifiable factors – not smoking, not having depression or diabetes, getting regular physical activity, avoiding social isolation, and following a healthy diet – may not have protective associations, according to research published in Nature Medicine.
Recent analyses have indicated that eliminating known modifiable risk factors for dementia at a population level could prevent one-third of dementia cases, but prevention trials “have yielded inconsistent results so far,” wrote first author Silvan Licher, MD, of the department of epidemiology at Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam (the Netherlands) and his colleagues.
“Prior studies have mostly focused on the risk of dementia associated with an individual protective factor, yet the combination of multiple factors may yield more beneficial effects than the individual parts,” they wrote. “Combining data about a number of factors is also important because it takes into account the multifactorial nature of late-life dementia. We used data from the Rotterdam Study to determine to what extent a favorable profile based on modifiable risk factors is associated with a lower risk of dementia among individuals at low, intermediate, or high genetic risk.”
Grouped by APOE genotype
Patients who were apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 allele (APOE4) carriers (i.e., APOE2 and 4, APOE3 and 4, or two APOE4) were classified as having high genetic risk (n = 1,747). Other APOE genotypes were considered intermediate risk (n = 3,718 with two APOE3 alleles) or low risk (n = 887 with either two APOE2 alleles or APOE2 and 3).
The researchers measured six potentially modifiable lifestyle or health factors that “have been implicated in a lower risk of dementia.” Modifiable risk scores ranged from 0 to 6. Participants were classified as having an unfavorable profile (0-2 protective factors), an intermediate profile (3-4 protective factors), or a favorable profile (5-6 factors).
The researchers calculated the relative risk of developing dementia using a Cox proportional hazards model and the absolutely risk using competing risk models.
In all, 56.2% of the participants were women, the average age was about 69 years, and patient characteristics were similar across the categories of APOE risk. APOE4 carriers received dementia diagnoses at a younger age, more often had a parental history of dementia, and had higher total cholesterol levels, compared with noncarriers. In all, 915 people received a dementia diagnosis, of whom 739 received a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The other 2,644 participants died free from dementia. The median follow-up was 14.1 years.
“Dementia risk was significantly higher among participants at high or intermediate APOE risk, compared with those at low APOE risk,” the researchers said. In addition, the risk of dementia increased in participants who had fewer protective factors. Those with 0-2 protective factors had a 29% higher risk of dementia, compared with participants with 5 or 6 protective factors, after adjusting for age, sex, level of education, parental history of dementia, history of stroke, systolic blood pressure, and total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Lifestyle benefits tended to be greater in younger participants
“APOE genotype significantly modified the association between protective factors and dementia,” the authors said. Compared with participants with protective modifiable risk profiles, participants with unfavorable modifiable risk profiles had greater risk for dementia in the low–APOE risk group (hazard ratio, 2.51) and intermediate–APOE risk group (HR, 1.39), but not in the high–APOE risk group.
“Protective associations of favorable risk profiles against dementia tended to be stronger in younger individuals than in older individuals and were most pronounced for younger individuals at low APOE risk,” Dr. Licher and colleagues said. In a sensitivity analysis that used a polygenic risk score for Alzheimer’s disease based on 27 variants other than APOE to determine participants’ genetic risk, the patterns were “attenuated yet largely comparable,” they wrote. Patterns also remained consistent when the researchers used an ideal cardiovascular health score to indicate modifiable health profiles.
“Our results confirm that individuals with a favorable profile have a lower risk of dementia than those with intermediate or unfavorable profiles based on modifiable risk factors,” they said. Unlike in a subgroup analysis of data from the FINGER study, however, “this study found that a favorable profile could not offset high APOE risk.”
The findings may have implications for clinical trial design and suggest that APOE4 carriers may need to be targeted earlier in the disease process to influence their risk for dementia.
“On the positive side, results from this study show that avoiding an unhealthy lifestyle could potentially prevent or postpone the onset of dementia in most individuals in the population (73%), namely those at low and intermediate genetic risk,” the investigators wrote. “Among these, the majority were categorized has having a favorable profile (66%), yet room for improvement is still substantial.”
The study lacked data on hearing impairment and did not capture shifts to more adverse or optimal lifestyles during follow-up. In addition, the results are based on relatively small samples in each risk category, and the estimates had wide confidence intervals. The population was older and mostly of European descent, which limits the generalizability of the findings, the authors noted.
Lifestyle factors may benefit only people with low genetic risk
“The authors’ key finding was that modifiable lifestyle risk factors were able to reduce dementia risk only in people who did not have an APOE4 allele and hence were at lower genetic risk,” said Kenneth Rockwood, MD, professor of geriatric medicine and neurology at Dalhousie University in Halifax, N.S., and his coauthors, in an accompanying editorial.
The findings contrast with those of another recent population-based study using data from the UK Biobank (JAMA. 2019;322[5]:430-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9879), which suggested that modifiable factors affect dementia risk regardless of genetic risk.
Together, these studies “tell us that ... we must better understand outcomes in those most at risk,” they said. “We might begin by recognizing that aging is essential, rather than incidental, to dementia disease expression.” Future research should focus on people living with frailty, who often are excluded from trials and are at high risk for dementia. Older adults who develop delirium also may be an ideal target group of patients at increased risk for dementia.
“Reducing the extent of disease expression in people prone to developing dementia late in life is difficult. Studies investigating whether dementia can be prevented at all, such as the Rotterdam study, and then whether it can be prevented in the people at greatest risk, can be commended for their clear-eyed approach,” Dr. Rockwood and colleagues said.
The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and University, as well as a variety of Dutch organizations, institutes, and government ministries, and the European Commission. The authors had no competing interests.
Dr. Rockwood is president and chief science officer of DGI Clinical, which has contracts with pharmaceutical and device manufacturers related to individualized outcome measurement.
SOURCES: Licher S et al. Nat Med. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0547-7; and Rockwood K et al. Nat Med. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0575-3.
But among people at high genetic risk for dementia, these potentially modifiable factors – not smoking, not having depression or diabetes, getting regular physical activity, avoiding social isolation, and following a healthy diet – may not have protective associations, according to research published in Nature Medicine.
Recent analyses have indicated that eliminating known modifiable risk factors for dementia at a population level could prevent one-third of dementia cases, but prevention trials “have yielded inconsistent results so far,” wrote first author Silvan Licher, MD, of the department of epidemiology at Erasmus University Medical Center Rotterdam (the Netherlands) and his colleagues.
“Prior studies have mostly focused on the risk of dementia associated with an individual protective factor, yet the combination of multiple factors may yield more beneficial effects than the individual parts,” they wrote. “Combining data about a number of factors is also important because it takes into account the multifactorial nature of late-life dementia. We used data from the Rotterdam Study to determine to what extent a favorable profile based on modifiable risk factors is associated with a lower risk of dementia among individuals at low, intermediate, or high genetic risk.”
Grouped by APOE genotype
Patients who were apolipoprotein E epsilon-4 allele (APOE4) carriers (i.e., APOE2 and 4, APOE3 and 4, or two APOE4) were classified as having high genetic risk (n = 1,747). Other APOE genotypes were considered intermediate risk (n = 3,718 with two APOE3 alleles) or low risk (n = 887 with either two APOE2 alleles or APOE2 and 3).
The researchers measured six potentially modifiable lifestyle or health factors that “have been implicated in a lower risk of dementia.” Modifiable risk scores ranged from 0 to 6. Participants were classified as having an unfavorable profile (0-2 protective factors), an intermediate profile (3-4 protective factors), or a favorable profile (5-6 factors).
The researchers calculated the relative risk of developing dementia using a Cox proportional hazards model and the absolutely risk using competing risk models.
In all, 56.2% of the participants were women, the average age was about 69 years, and patient characteristics were similar across the categories of APOE risk. APOE4 carriers received dementia diagnoses at a younger age, more often had a parental history of dementia, and had higher total cholesterol levels, compared with noncarriers. In all, 915 people received a dementia diagnosis, of whom 739 received a diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. The other 2,644 participants died free from dementia. The median follow-up was 14.1 years.
“Dementia risk was significantly higher among participants at high or intermediate APOE risk, compared with those at low APOE risk,” the researchers said. In addition, the risk of dementia increased in participants who had fewer protective factors. Those with 0-2 protective factors had a 29% higher risk of dementia, compared with participants with 5 or 6 protective factors, after adjusting for age, sex, level of education, parental history of dementia, history of stroke, systolic blood pressure, and total and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol.
Lifestyle benefits tended to be greater in younger participants
“APOE genotype significantly modified the association between protective factors and dementia,” the authors said. Compared with participants with protective modifiable risk profiles, participants with unfavorable modifiable risk profiles had greater risk for dementia in the low–APOE risk group (hazard ratio, 2.51) and intermediate–APOE risk group (HR, 1.39), but not in the high–APOE risk group.
“Protective associations of favorable risk profiles against dementia tended to be stronger in younger individuals than in older individuals and were most pronounced for younger individuals at low APOE risk,” Dr. Licher and colleagues said. In a sensitivity analysis that used a polygenic risk score for Alzheimer’s disease based on 27 variants other than APOE to determine participants’ genetic risk, the patterns were “attenuated yet largely comparable,” they wrote. Patterns also remained consistent when the researchers used an ideal cardiovascular health score to indicate modifiable health profiles.
“Our results confirm that individuals with a favorable profile have a lower risk of dementia than those with intermediate or unfavorable profiles based on modifiable risk factors,” they said. Unlike in a subgroup analysis of data from the FINGER study, however, “this study found that a favorable profile could not offset high APOE risk.”
The findings may have implications for clinical trial design and suggest that APOE4 carriers may need to be targeted earlier in the disease process to influence their risk for dementia.
“On the positive side, results from this study show that avoiding an unhealthy lifestyle could potentially prevent or postpone the onset of dementia in most individuals in the population (73%), namely those at low and intermediate genetic risk,” the investigators wrote. “Among these, the majority were categorized has having a favorable profile (66%), yet room for improvement is still substantial.”
The study lacked data on hearing impairment and did not capture shifts to more adverse or optimal lifestyles during follow-up. In addition, the results are based on relatively small samples in each risk category, and the estimates had wide confidence intervals. The population was older and mostly of European descent, which limits the generalizability of the findings, the authors noted.
Lifestyle factors may benefit only people with low genetic risk
“The authors’ key finding was that modifiable lifestyle risk factors were able to reduce dementia risk only in people who did not have an APOE4 allele and hence were at lower genetic risk,” said Kenneth Rockwood, MD, professor of geriatric medicine and neurology at Dalhousie University in Halifax, N.S., and his coauthors, in an accompanying editorial.
The findings contrast with those of another recent population-based study using data from the UK Biobank (JAMA. 2019;322[5]:430-7. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.9879), which suggested that modifiable factors affect dementia risk regardless of genetic risk.
Together, these studies “tell us that ... we must better understand outcomes in those most at risk,” they said. “We might begin by recognizing that aging is essential, rather than incidental, to dementia disease expression.” Future research should focus on people living with frailty, who often are excluded from trials and are at high risk for dementia. Older adults who develop delirium also may be an ideal target group of patients at increased risk for dementia.
“Reducing the extent of disease expression in people prone to developing dementia late in life is difficult. Studies investigating whether dementia can be prevented at all, such as the Rotterdam study, and then whether it can be prevented in the people at greatest risk, can be commended for their clear-eyed approach,” Dr. Rockwood and colleagues said.
The Rotterdam Study is funded by Erasmus Medical Center and University, as well as a variety of Dutch organizations, institutes, and government ministries, and the European Commission. The authors had no competing interests.
Dr. Rockwood is president and chief science officer of DGI Clinical, which has contracts with pharmaceutical and device manufacturers related to individualized outcome measurement.
SOURCES: Licher S et al. Nat Med. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0547-7; and Rockwood K et al. Nat Med. 2019 Aug 26. doi: 10.1038/s41591-019-0575-3.
FROM NATURE MEDICINE