User login
Federal Government Funds Program for Hepatitis C Care and Cure
, according to an HHS press release.
The program, known as the Hepatitis C Elimination Initiative Pilot, will be administered by the Substance and Mental Health Administration. “This program is designed to support communities severely affected by homelessness and to gain insights on effective ways to identify patients, complete treatment, cure infections, and reduce reinfection by hepatitis C,” according to the press release.
The upfront investment in hepatitis C management is projected to not only save lives, but also to save community health care costs in the long-term, according to the press release.
“This is a vigorous pilot program that provides the first steps toward the large goal of eliminating hepatitis C in the United States population,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, in an interview.
Hepatitis C affects more than two million individuals in the US, and is often complicated by social and medical issues such as homelessness, substance abuse, and mental health issues, said Schaffner. Fortunately, hepatitis C can be treated with oral medications that cure the chronic viral infection, thereby ending ongoing liver injury and interrupting person-to-person transmission of the virus by sharing needles, he said.
Given that the population most affected with hepatitis C also is often homeless, with possible mental health issues and sharing of needles for illicit drug use, challenges in reaching this population include assuring them that the care they receive though this and other programs is nonjudgemental and helpful, Schaffner told GI & Hepatology News.
The oral medications that now can cure the chronic hepatitis C viral infections must be taken over a period of weeks, and patients who lead socially disorganized lives often need assistance to assure that the medicine is taken as intended, so trained and sensitive personnel who are committed to helping this population are needed to make treatment programs succeed, he said.
Looking ahead, “the purpose of the pilot studies that will be funded by this program is to explore various approaches to determine which are more successful in bringing patients in to be evaluated and then to complete treatment,” Schaffner added.
State and community-based organizations are among the entities eligible to apply for the program. Potential applicants can find information about the program and application materials on the SAMSHA website.
Schaffner had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
, according to an HHS press release.
The program, known as the Hepatitis C Elimination Initiative Pilot, will be administered by the Substance and Mental Health Administration. “This program is designed to support communities severely affected by homelessness and to gain insights on effective ways to identify patients, complete treatment, cure infections, and reduce reinfection by hepatitis C,” according to the press release.
The upfront investment in hepatitis C management is projected to not only save lives, but also to save community health care costs in the long-term, according to the press release.
“This is a vigorous pilot program that provides the first steps toward the large goal of eliminating hepatitis C in the United States population,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, in an interview.
Hepatitis C affects more than two million individuals in the US, and is often complicated by social and medical issues such as homelessness, substance abuse, and mental health issues, said Schaffner. Fortunately, hepatitis C can be treated with oral medications that cure the chronic viral infection, thereby ending ongoing liver injury and interrupting person-to-person transmission of the virus by sharing needles, he said.
Given that the population most affected with hepatitis C also is often homeless, with possible mental health issues and sharing of needles for illicit drug use, challenges in reaching this population include assuring them that the care they receive though this and other programs is nonjudgemental and helpful, Schaffner told GI & Hepatology News.
The oral medications that now can cure the chronic hepatitis C viral infections must be taken over a period of weeks, and patients who lead socially disorganized lives often need assistance to assure that the medicine is taken as intended, so trained and sensitive personnel who are committed to helping this population are needed to make treatment programs succeed, he said.
Looking ahead, “the purpose of the pilot studies that will be funded by this program is to explore various approaches to determine which are more successful in bringing patients in to be evaluated and then to complete treatment,” Schaffner added.
State and community-based organizations are among the entities eligible to apply for the program. Potential applicants can find information about the program and application materials on the SAMSHA website.
Schaffner had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
, according to an HHS press release.
The program, known as the Hepatitis C Elimination Initiative Pilot, will be administered by the Substance and Mental Health Administration. “This program is designed to support communities severely affected by homelessness and to gain insights on effective ways to identify patients, complete treatment, cure infections, and reduce reinfection by hepatitis C,” according to the press release.
The upfront investment in hepatitis C management is projected to not only save lives, but also to save community health care costs in the long-term, according to the press release.
“This is a vigorous pilot program that provides the first steps toward the large goal of eliminating hepatitis C in the United States population,” said William Schaffner, MD, professor of infectious diseases at Vanderbilt University Medical Center, Nashville, Tennessee, in an interview.
Hepatitis C affects more than two million individuals in the US, and is often complicated by social and medical issues such as homelessness, substance abuse, and mental health issues, said Schaffner. Fortunately, hepatitis C can be treated with oral medications that cure the chronic viral infection, thereby ending ongoing liver injury and interrupting person-to-person transmission of the virus by sharing needles, he said.
Given that the population most affected with hepatitis C also is often homeless, with possible mental health issues and sharing of needles for illicit drug use, challenges in reaching this population include assuring them that the care they receive though this and other programs is nonjudgemental and helpful, Schaffner told GI & Hepatology News.
The oral medications that now can cure the chronic hepatitis C viral infections must be taken over a period of weeks, and patients who lead socially disorganized lives often need assistance to assure that the medicine is taken as intended, so trained and sensitive personnel who are committed to helping this population are needed to make treatment programs succeed, he said.
Looking ahead, “the purpose of the pilot studies that will be funded by this program is to explore various approaches to determine which are more successful in bringing patients in to be evaluated and then to complete treatment,” Schaffner added.
State and community-based organizations are among the entities eligible to apply for the program. Potential applicants can find information about the program and application materials on the SAMSHA website.
Schaffner had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com .
Novel Peptides Expressed in HIV Could Drive Treatment
Genetic sequencing of peptides in rebound virus in individuals with HIV who had analytic treatment interruptions (ATIs) confirmed the peptides’ expression in HIV-1 infection, according to data presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
Previous research has shown that HIV-specific CD8 T-cell responses directed against five genetically conserved HIV-1 protein regions (Gag, Pol, Vif, Vpr, and Env) are associated with viral control, Josefina Marín-Rojas, PhD, Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, and colleagues wrote in their abstract.
However, data on whether these peptides are expressed in rebound virus among individuals with HIV who experienced ATI are limited, they wrote.
The researchers applied an immunoinformatics analysis pipeline (IMAP) to select 182 peptides (IMAP-peptides) from structurally important and mutation-intolerant regions of HIV-1 proteins, senior author Sarah Palmer, PhD, co-director of the Centre for Virus Research at the Westmead Institute for Medical Research and professor in the Faculty of Medicine and Health at the University of Sydney, said in an interview.
“Our studies indicate if the immune system targets these structurally important and mutation-intolerant regions of HIV-1 proteins, this can contribute to virological control in the absence of HIV-1 therapy,” she explained.
The researchers reviewed data from the PULSE clinical trial, which included 68 men who have sex with men living with HIV in Australia. The men underwent three consecutive ATIs. A total of seven participants’ transiently controlled HIV rebound during the third ATI. The researchers examined whether the IMAP peptides were present in the HIV-1 RNA sequences of the rebound virus in four noncontrollers (patients who had viral rebound in all three ATIs) and five of the seven transient controllers who showed viral control during the third ATI.
The technique of near full-length HIV-1 RNA sequencing of rebound virus from three noncontrollers and two transient controllers identified the Gag, Pol, Vif, Vpr, and Env IMAP-peptides in 52%-100% of the viral sequences obtained from these participants across three ATI timepoints.
“We assumed that cells from people living with HIV that experience virological control after treatment interruption would have the immune response to our IMAP-peptides that we observed; however, we are amazed and encouraged by the level and extent of this immune response,” Palmer told this news organization.
The researchers also compared CD8 T-cell response between the IMAP peptides and a control peptide pool without the IMAP peptides.
The CD8 T-cells from three transient controllers had a 15- to 53-fold higher effector response to the IMAP-peptides than the CD8 T-cells from two noncontrollers, the researchers wrote in their abstract. The relative response to the IMAP-peptides in noncontrollers was 20 times lower than that to the control peptides, but the IMAP-peptide response in the transient controllers group was similar to that in the control group, the authors noted.
The results highlight the potential of IMAP in developing treatment strategies. Although the results are too preliminary to impact clinical practice at this time, the findings from the current study could lead to the development of an mRNA vaccine to clear HIV-infected cells from people living with HIV, Palmer told this news organization.
“Our next steps include developing and testing mRNA vaccine constructs that contain our IMAP-peptides to assess the immune response of cells from people living with HIV to these vaccines,” Palmer said. “From there we will conduct studies of the most promising mRNA vaccine constructs in a humanized mouse model,” she said.
Data Enhance Understanding of Immunity
The current study may provide information that can significantly impact understanding of the immune responses to HIV, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
“The investigators looked at highly conserved regions of multiple HIV proteins,” said Cennimo, who was not involved in the study. “Conserved regions and antibody responses to them may play a role in controlling HIV viral replication and rebound,” Cennimo told this news organization. “The investigators showed these regions were present in rebounding viremia, and individuals that exhibited greater immune recognition of these regions suppressed rebound viremia longer, and perhaps targeting these regions could impact HIV prevention or cure strategies,” he said.
Secondarily, the study showed the success of the novel technique (IMAP) to identify conserved peptides, said Cennimo. The technique could potentially be applied to other viruses that mutate to escape host response, he said.The study was funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for AIDS Research, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Sandra and David Ansley. The researchers and Cennimo disclosed no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic sequencing of peptides in rebound virus in individuals with HIV who had analytic treatment interruptions (ATIs) confirmed the peptides’ expression in HIV-1 infection, according to data presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
Previous research has shown that HIV-specific CD8 T-cell responses directed against five genetically conserved HIV-1 protein regions (Gag, Pol, Vif, Vpr, and Env) are associated with viral control, Josefina Marín-Rojas, PhD, Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, and colleagues wrote in their abstract.
However, data on whether these peptides are expressed in rebound virus among individuals with HIV who experienced ATI are limited, they wrote.
The researchers applied an immunoinformatics analysis pipeline (IMAP) to select 182 peptides (IMAP-peptides) from structurally important and mutation-intolerant regions of HIV-1 proteins, senior author Sarah Palmer, PhD, co-director of the Centre for Virus Research at the Westmead Institute for Medical Research and professor in the Faculty of Medicine and Health at the University of Sydney, said in an interview.
“Our studies indicate if the immune system targets these structurally important and mutation-intolerant regions of HIV-1 proteins, this can contribute to virological control in the absence of HIV-1 therapy,” she explained.
The researchers reviewed data from the PULSE clinical trial, which included 68 men who have sex with men living with HIV in Australia. The men underwent three consecutive ATIs. A total of seven participants’ transiently controlled HIV rebound during the third ATI. The researchers examined whether the IMAP peptides were present in the HIV-1 RNA sequences of the rebound virus in four noncontrollers (patients who had viral rebound in all three ATIs) and five of the seven transient controllers who showed viral control during the third ATI.
The technique of near full-length HIV-1 RNA sequencing of rebound virus from three noncontrollers and two transient controllers identified the Gag, Pol, Vif, Vpr, and Env IMAP-peptides in 52%-100% of the viral sequences obtained from these participants across three ATI timepoints.
“We assumed that cells from people living with HIV that experience virological control after treatment interruption would have the immune response to our IMAP-peptides that we observed; however, we are amazed and encouraged by the level and extent of this immune response,” Palmer told this news organization.
The researchers also compared CD8 T-cell response between the IMAP peptides and a control peptide pool without the IMAP peptides.
The CD8 T-cells from three transient controllers had a 15- to 53-fold higher effector response to the IMAP-peptides than the CD8 T-cells from two noncontrollers, the researchers wrote in their abstract. The relative response to the IMAP-peptides in noncontrollers was 20 times lower than that to the control peptides, but the IMAP-peptide response in the transient controllers group was similar to that in the control group, the authors noted.
The results highlight the potential of IMAP in developing treatment strategies. Although the results are too preliminary to impact clinical practice at this time, the findings from the current study could lead to the development of an mRNA vaccine to clear HIV-infected cells from people living with HIV, Palmer told this news organization.
“Our next steps include developing and testing mRNA vaccine constructs that contain our IMAP-peptides to assess the immune response of cells from people living with HIV to these vaccines,” Palmer said. “From there we will conduct studies of the most promising mRNA vaccine constructs in a humanized mouse model,” she said.
Data Enhance Understanding of Immunity
The current study may provide information that can significantly impact understanding of the immune responses to HIV, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
“The investigators looked at highly conserved regions of multiple HIV proteins,” said Cennimo, who was not involved in the study. “Conserved regions and antibody responses to them may play a role in controlling HIV viral replication and rebound,” Cennimo told this news organization. “The investigators showed these regions were present in rebounding viremia, and individuals that exhibited greater immune recognition of these regions suppressed rebound viremia longer, and perhaps targeting these regions could impact HIV prevention or cure strategies,” he said.
Secondarily, the study showed the success of the novel technique (IMAP) to identify conserved peptides, said Cennimo. The technique could potentially be applied to other viruses that mutate to escape host response, he said.The study was funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for AIDS Research, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Sandra and David Ansley. The researchers and Cennimo disclosed no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Genetic sequencing of peptides in rebound virus in individuals with HIV who had analytic treatment interruptions (ATIs) confirmed the peptides’ expression in HIV-1 infection, according to data presented at the International AIDS Society Conference on HIV Science.
Previous research has shown that HIV-specific CD8 T-cell responses directed against five genetically conserved HIV-1 protein regions (Gag, Pol, Vif, Vpr, and Env) are associated with viral control, Josefina Marín-Rojas, PhD, Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, and colleagues wrote in their abstract.
However, data on whether these peptides are expressed in rebound virus among individuals with HIV who experienced ATI are limited, they wrote.
The researchers applied an immunoinformatics analysis pipeline (IMAP) to select 182 peptides (IMAP-peptides) from structurally important and mutation-intolerant regions of HIV-1 proteins, senior author Sarah Palmer, PhD, co-director of the Centre for Virus Research at the Westmead Institute for Medical Research and professor in the Faculty of Medicine and Health at the University of Sydney, said in an interview.
“Our studies indicate if the immune system targets these structurally important and mutation-intolerant regions of HIV-1 proteins, this can contribute to virological control in the absence of HIV-1 therapy,” she explained.
The researchers reviewed data from the PULSE clinical trial, which included 68 men who have sex with men living with HIV in Australia. The men underwent three consecutive ATIs. A total of seven participants’ transiently controlled HIV rebound during the third ATI. The researchers examined whether the IMAP peptides were present in the HIV-1 RNA sequences of the rebound virus in four noncontrollers (patients who had viral rebound in all three ATIs) and five of the seven transient controllers who showed viral control during the third ATI.
The technique of near full-length HIV-1 RNA sequencing of rebound virus from three noncontrollers and two transient controllers identified the Gag, Pol, Vif, Vpr, and Env IMAP-peptides in 52%-100% of the viral sequences obtained from these participants across three ATI timepoints.
“We assumed that cells from people living with HIV that experience virological control after treatment interruption would have the immune response to our IMAP-peptides that we observed; however, we are amazed and encouraged by the level and extent of this immune response,” Palmer told this news organization.
The researchers also compared CD8 T-cell response between the IMAP peptides and a control peptide pool without the IMAP peptides.
The CD8 T-cells from three transient controllers had a 15- to 53-fold higher effector response to the IMAP-peptides than the CD8 T-cells from two noncontrollers, the researchers wrote in their abstract. The relative response to the IMAP-peptides in noncontrollers was 20 times lower than that to the control peptides, but the IMAP-peptide response in the transient controllers group was similar to that in the control group, the authors noted.
The results highlight the potential of IMAP in developing treatment strategies. Although the results are too preliminary to impact clinical practice at this time, the findings from the current study could lead to the development of an mRNA vaccine to clear HIV-infected cells from people living with HIV, Palmer told this news organization.
“Our next steps include developing and testing mRNA vaccine constructs that contain our IMAP-peptides to assess the immune response of cells from people living with HIV to these vaccines,” Palmer said. “From there we will conduct studies of the most promising mRNA vaccine constructs in a humanized mouse model,” she said.
Data Enhance Understanding of Immunity
The current study may provide information that can significantly impact understanding of the immune responses to HIV, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics in the Division of Infectious Disease at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
“The investigators looked at highly conserved regions of multiple HIV proteins,” said Cennimo, who was not involved in the study. “Conserved regions and antibody responses to them may play a role in controlling HIV viral replication and rebound,” Cennimo told this news organization. “The investigators showed these regions were present in rebounding viremia, and individuals that exhibited greater immune recognition of these regions suppressed rebound viremia longer, and perhaps targeting these regions could impact HIV prevention or cure strategies,” he said.
Secondarily, the study showed the success of the novel technique (IMAP) to identify conserved peptides, said Cennimo. The technique could potentially be applied to other viruses that mutate to escape host response, he said.The study was funded by the U.S. National Institutes of Health, the Foundation for AIDS Research, the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council, and Sandra and David Ansley. The researchers and Cennimo disclosed no financial conflicts of interest.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
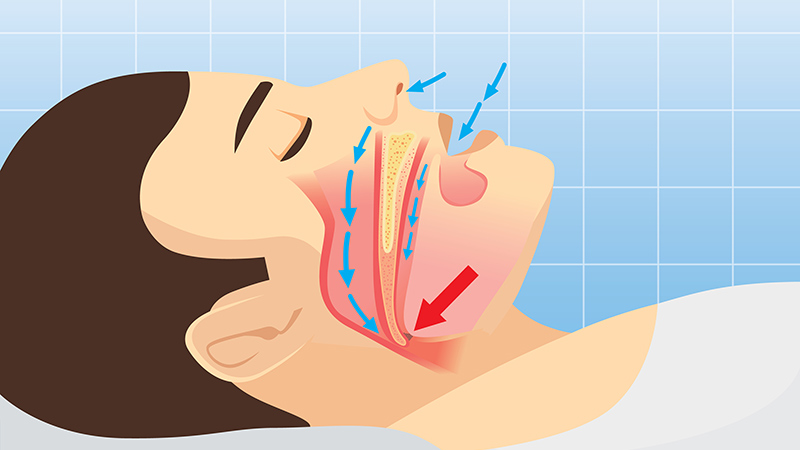
Stay Alert to Sleep Apnea Burden in the Military
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) was associated with a significantly increased risk for adverse health outcomes and health care resource use among military personnel in the US, according to data from about 120,000 active-duty service members.
OSA and other clinical sleep disorders are common among military personnel, driven in part by demanding, nontraditional work schedules that can exacerbate sleep problems, but OSA’s impact in this population has not been well-studied, Emerson M. Wickwire, PhD, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in a new paper published in Chest.
In the current health economic climate of increasing costs and limited resources, the economic aspects of sleep disorders have never been more important, Wickwire said in an interview. The data in this study are the first to quantify the health and utilization burden of OSA in the US military and can support military decision-makers regarding allocation of scarce resources, he said.
To assess the burden of OSA in the military, they reviewed fully de-identified data from 59,203 active-duty military personnel with diagnoses of OSA and compared them with 59,203 active-duty military personnel without OSA. The participants ranged in age from 18 to 64 years; 7.4% were women and 64.5% were white individuals. Study outcomes included new diagnoses of physical and psychological health conditions, as well as health care resource use in the first year after the index date.
About one third of the participants were in the Army (38.7%), 25.6% were in the Air Force, 23.5% were in the Navy, 5.8% were in the Marines, 5.7% were in the Coast Guard, and 0.7% were in the Public Health Service.
Over the 1-year study period, military personnel with OSA diagnoses were significantly more likely to experience new physical and psychological adverse events than control individuals without OSA, based on proportional hazards models. The physical conditions with the greatest increased risk in the OSA group were traumatic brain injury and cardiovascular disease (which included acute myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, ischemic heart disease, and peripheral procedures), with hazard ratios (HRs) 3.27 and 2.32, respectively. The psychological conditions with the greatest increased risk in the OSA group vs control individuals were posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and anxiety (HR, 4.41, and HR, 3.35, respectively).
Individuals with OSA also showed increased use of healthcare resources compared with control individuals without OSA, with an additional 170,511 outpatient visits, 66 inpatient visits, and 1,852 emergency department visits.
Don’t Discount OSA in Military Personnel
“From a clinical perspective, these findings underscore the importance of recognizing OSA as a critical risk factor for a wide array of physical and psychological health outcomes,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The results highlight the need for more clinical attention to patient screening, triage, and delivery of care, but efforts are limited by the documented shortage of sleep specialists in the military health system, they noted.
Key limitations of the study include the use of an administrative claims data source, which did not include clinical information such as disease severity or daytime symptoms, and the nonrandomized, observational study design, Wickwire told this news organization.
Looking ahead, the researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, are launching a new trial to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of telehealth visits for military beneficiaries diagnosed with OSA as a way to manage the shortage of sleep specialists in the military health system, according to a press release from the University of Maryland.
“Although the association between poor sleep and traumatic stress is well-known, present results highlight striking associations between sleep apnea and posttraumatic stress disorder, traumatic brain injury, and musculoskeletal injuries, which are key outcomes from the military perspective,” Wickwire told this news organization.
“Our most important clinical recommendation is for healthcare providers to be on alert for signs and symptoms of OSA, including snoring, daytime sleepiness, and morning dry mouth,” said Wickwire. “Primary care and mental health providers should be especially attuned,” he added.
Results Not Surprising, but Research Gaps Remain
“The sleep health of active-duty military personnel is not only vital for optimal military performance but also impacts the health of Veterans after separation from the military,” said Q. Afifa Shamim-Uzzaman, MD, an associate professor and a sleep medicine specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, in an interview.
The current study identifies increased utilization of healthcare resources by active-duty personnel with sleep apnea, and outcomes were not surprising, said Shamim-Uzzaman, who is employed by the Veterans’ Health Administration, but was not involved in the current study.
The association between untreated OSA and medical and psychological comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mood disorders such as depression and anxiety is well-known, Shamim-Uzzaman said. “Patients with depression who also have sleep disturbances are at higher risk for suicide — the strength of this association is such that it led the Veterans’ Health Administration to mandate suicide screening for Veterans seen in its sleep clinics,” he added.
“We also know that untreated OSA is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, slowed reaction times, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents, all of which can contribute to sustaining injuries such as traumatic brain injury,” said Shamim-Uzzaman. “Emerging evidence also suggests that sleep disruption prior to exposure to trauma increases the risk of developing PTSD. Therefore, it is not surprising that patients with sleep apnea would have higher healthcare utilization for non-OSA conditions than those without sleep apnea,” he noted.
In clinical practice, the study underscores the importance of identifying and managing sleep health in military personnel, who frequently work nontraditional schedules with long, sustained shifts in grueling conditions not conducive to healthy sleep, Shamim-Uzzaman told this news organization. “Although the harsh work environments that our active-duty military endure come part and parcel with the job, clinicians caring for these individuals should ask specifically about their sleep and working schedules to optimize sleep as best as possible; this should include, but not be limited to, screening and testing for sleep disordered breathing and insomnia,” he said.
The current study has several limitations, including the inability to control for smoking or alcohol use, which are common in military personnel and associated with increased morbidity, said Shamim-Uzzaman. The study also did not assess the impact of other confounding factors, such as sleep duration and daytime sleepiness, that could impact the results, especially the association of OSA and traumatic brain injury, he noted. “More research is needed to assess the impact of these factors as well as the effect of treatment of OSA on comorbidities and healthcare utilization,” he said.
This study was supported by the Military Health Services Research Program.
Wickwire’s institution had received research funding from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation, Department of Defense, Merck, National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging, ResMed, the ResMed Foundation, and the SRS Foundation. Wickwire disclosed serving as a scientific consultant to Axsome Therapeutics, Dayzz, Eisai, EnsoData, Idorsia, Merck, Nox Health, Primasun, Purdue, and ResMed and is an equity shareholder in Well Tap.
Shamim-Uzzaman is an employee of the Veterans’ Health Administration.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) was associated with a significantly increased risk for adverse health outcomes and health care resource use among military personnel in the US, according to data from about 120,000 active-duty service members.
OSA and other clinical sleep disorders are common among military personnel, driven in part by demanding, nontraditional work schedules that can exacerbate sleep problems, but OSA’s impact in this population has not been well-studied, Emerson M. Wickwire, PhD, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in a new paper published in Chest.
In the current health economic climate of increasing costs and limited resources, the economic aspects of sleep disorders have never been more important, Wickwire said in an interview. The data in this study are the first to quantify the health and utilization burden of OSA in the US military and can support military decision-makers regarding allocation of scarce resources, he said.
To assess the burden of OSA in the military, they reviewed fully de-identified data from 59,203 active-duty military personnel with diagnoses of OSA and compared them with 59,203 active-duty military personnel without OSA. The participants ranged in age from 18 to 64 years; 7.4% were women and 64.5% were white individuals. Study outcomes included new diagnoses of physical and psychological health conditions, as well as health care resource use in the first year after the index date.
About one third of the participants were in the Army (38.7%), 25.6% were in the Air Force, 23.5% were in the Navy, 5.8% were in the Marines, 5.7% were in the Coast Guard, and 0.7% were in the Public Health Service.
Over the 1-year study period, military personnel with OSA diagnoses were significantly more likely to experience new physical and psychological adverse events than control individuals without OSA, based on proportional hazards models. The physical conditions with the greatest increased risk in the OSA group were traumatic brain injury and cardiovascular disease (which included acute myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, ischemic heart disease, and peripheral procedures), with hazard ratios (HRs) 3.27 and 2.32, respectively. The psychological conditions with the greatest increased risk in the OSA group vs control individuals were posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and anxiety (HR, 4.41, and HR, 3.35, respectively).
Individuals with OSA also showed increased use of healthcare resources compared with control individuals without OSA, with an additional 170,511 outpatient visits, 66 inpatient visits, and 1,852 emergency department visits.
Don’t Discount OSA in Military Personnel
“From a clinical perspective, these findings underscore the importance of recognizing OSA as a critical risk factor for a wide array of physical and psychological health outcomes,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The results highlight the need for more clinical attention to patient screening, triage, and delivery of care, but efforts are limited by the documented shortage of sleep specialists in the military health system, they noted.
Key limitations of the study include the use of an administrative claims data source, which did not include clinical information such as disease severity or daytime symptoms, and the nonrandomized, observational study design, Wickwire told this news organization.
Looking ahead, the researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, are launching a new trial to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of telehealth visits for military beneficiaries diagnosed with OSA as a way to manage the shortage of sleep specialists in the military health system, according to a press release from the University of Maryland.
“Although the association between poor sleep and traumatic stress is well-known, present results highlight striking associations between sleep apnea and posttraumatic stress disorder, traumatic brain injury, and musculoskeletal injuries, which are key outcomes from the military perspective,” Wickwire told this news organization.
“Our most important clinical recommendation is for healthcare providers to be on alert for signs and symptoms of OSA, including snoring, daytime sleepiness, and morning dry mouth,” said Wickwire. “Primary care and mental health providers should be especially attuned,” he added.
Results Not Surprising, but Research Gaps Remain
“The sleep health of active-duty military personnel is not only vital for optimal military performance but also impacts the health of Veterans after separation from the military,” said Q. Afifa Shamim-Uzzaman, MD, an associate professor and a sleep medicine specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, in an interview.
The current study identifies increased utilization of healthcare resources by active-duty personnel with sleep apnea, and outcomes were not surprising, said Shamim-Uzzaman, who is employed by the Veterans’ Health Administration, but was not involved in the current study.
The association between untreated OSA and medical and psychological comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mood disorders such as depression and anxiety is well-known, Shamim-Uzzaman said. “Patients with depression who also have sleep disturbances are at higher risk for suicide — the strength of this association is such that it led the Veterans’ Health Administration to mandate suicide screening for Veterans seen in its sleep clinics,” he added.
“We also know that untreated OSA is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, slowed reaction times, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents, all of which can contribute to sustaining injuries such as traumatic brain injury,” said Shamim-Uzzaman. “Emerging evidence also suggests that sleep disruption prior to exposure to trauma increases the risk of developing PTSD. Therefore, it is not surprising that patients with sleep apnea would have higher healthcare utilization for non-OSA conditions than those without sleep apnea,” he noted.
In clinical practice, the study underscores the importance of identifying and managing sleep health in military personnel, who frequently work nontraditional schedules with long, sustained shifts in grueling conditions not conducive to healthy sleep, Shamim-Uzzaman told this news organization. “Although the harsh work environments that our active-duty military endure come part and parcel with the job, clinicians caring for these individuals should ask specifically about their sleep and working schedules to optimize sleep as best as possible; this should include, but not be limited to, screening and testing for sleep disordered breathing and insomnia,” he said.
The current study has several limitations, including the inability to control for smoking or alcohol use, which are common in military personnel and associated with increased morbidity, said Shamim-Uzzaman. The study also did not assess the impact of other confounding factors, such as sleep duration and daytime sleepiness, that could impact the results, especially the association of OSA and traumatic brain injury, he noted. “More research is needed to assess the impact of these factors as well as the effect of treatment of OSA on comorbidities and healthcare utilization,” he said.
This study was supported by the Military Health Services Research Program.
Wickwire’s institution had received research funding from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation, Department of Defense, Merck, National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging, ResMed, the ResMed Foundation, and the SRS Foundation. Wickwire disclosed serving as a scientific consultant to Axsome Therapeutics, Dayzz, Eisai, EnsoData, Idorsia, Merck, Nox Health, Primasun, Purdue, and ResMed and is an equity shareholder in Well Tap.
Shamim-Uzzaman is an employee of the Veterans’ Health Administration.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) was associated with a significantly increased risk for adverse health outcomes and health care resource use among military personnel in the US, according to data from about 120,000 active-duty service members.
OSA and other clinical sleep disorders are common among military personnel, driven in part by demanding, nontraditional work schedules that can exacerbate sleep problems, but OSA’s impact in this population has not been well-studied, Emerson M. Wickwire, PhD, of the University of Maryland School of Medicine, Baltimore, and colleagues wrote in a new paper published in Chest.
In the current health economic climate of increasing costs and limited resources, the economic aspects of sleep disorders have never been more important, Wickwire said in an interview. The data in this study are the first to quantify the health and utilization burden of OSA in the US military and can support military decision-makers regarding allocation of scarce resources, he said.
To assess the burden of OSA in the military, they reviewed fully de-identified data from 59,203 active-duty military personnel with diagnoses of OSA and compared them with 59,203 active-duty military personnel without OSA. The participants ranged in age from 18 to 64 years; 7.4% were women and 64.5% were white individuals. Study outcomes included new diagnoses of physical and psychological health conditions, as well as health care resource use in the first year after the index date.
About one third of the participants were in the Army (38.7%), 25.6% were in the Air Force, 23.5% were in the Navy, 5.8% were in the Marines, 5.7% were in the Coast Guard, and 0.7% were in the Public Health Service.
Over the 1-year study period, military personnel with OSA diagnoses were significantly more likely to experience new physical and psychological adverse events than control individuals without OSA, based on proportional hazards models. The physical conditions with the greatest increased risk in the OSA group were traumatic brain injury and cardiovascular disease (which included acute myocardial infarction, atrial fibrillation, ischemic heart disease, and peripheral procedures), with hazard ratios (HRs) 3.27 and 2.32, respectively. The psychological conditions with the greatest increased risk in the OSA group vs control individuals were posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and anxiety (HR, 4.41, and HR, 3.35, respectively).
Individuals with OSA also showed increased use of healthcare resources compared with control individuals without OSA, with an additional 170,511 outpatient visits, 66 inpatient visits, and 1,852 emergency department visits.
Don’t Discount OSA in Military Personnel
“From a clinical perspective, these findings underscore the importance of recognizing OSA as a critical risk factor for a wide array of physical and psychological health outcomes,” the researchers wrote in their discussion.
The results highlight the need for more clinical attention to patient screening, triage, and delivery of care, but efforts are limited by the documented shortage of sleep specialists in the military health system, they noted.
Key limitations of the study include the use of an administrative claims data source, which did not include clinical information such as disease severity or daytime symptoms, and the nonrandomized, observational study design, Wickwire told this news organization.
Looking ahead, the researchers at the University of Maryland School of Medicine and the Uniformed Services University, Bethesda, Maryland, are launching a new trial to assess the clinical effectiveness and cost-effectiveness of telehealth visits for military beneficiaries diagnosed with OSA as a way to manage the shortage of sleep specialists in the military health system, according to a press release from the University of Maryland.
“Although the association between poor sleep and traumatic stress is well-known, present results highlight striking associations between sleep apnea and posttraumatic stress disorder, traumatic brain injury, and musculoskeletal injuries, which are key outcomes from the military perspective,” Wickwire told this news organization.
“Our most important clinical recommendation is for healthcare providers to be on alert for signs and symptoms of OSA, including snoring, daytime sleepiness, and morning dry mouth,” said Wickwire. “Primary care and mental health providers should be especially attuned,” he added.
Results Not Surprising, but Research Gaps Remain
“The sleep health of active-duty military personnel is not only vital for optimal military performance but also impacts the health of Veterans after separation from the military,” said Q. Afifa Shamim-Uzzaman, MD, an associate professor and a sleep medicine specialist at the University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, Michigan, in an interview.
The current study identifies increased utilization of healthcare resources by active-duty personnel with sleep apnea, and outcomes were not surprising, said Shamim-Uzzaman, who is employed by the Veterans’ Health Administration, but was not involved in the current study.
The association between untreated OSA and medical and psychological comorbidities such as cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and mood disorders such as depression and anxiety is well-known, Shamim-Uzzaman said. “Patients with depression who also have sleep disturbances are at higher risk for suicide — the strength of this association is such that it led the Veterans’ Health Administration to mandate suicide screening for Veterans seen in its sleep clinics,” he added.
“We also know that untreated OSA is associated with excessive daytime sleepiness, slowed reaction times, and increased risk of motor vehicle accidents, all of which can contribute to sustaining injuries such as traumatic brain injury,” said Shamim-Uzzaman. “Emerging evidence also suggests that sleep disruption prior to exposure to trauma increases the risk of developing PTSD. Therefore, it is not surprising that patients with sleep apnea would have higher healthcare utilization for non-OSA conditions than those without sleep apnea,” he noted.
In clinical practice, the study underscores the importance of identifying and managing sleep health in military personnel, who frequently work nontraditional schedules with long, sustained shifts in grueling conditions not conducive to healthy sleep, Shamim-Uzzaman told this news organization. “Although the harsh work environments that our active-duty military endure come part and parcel with the job, clinicians caring for these individuals should ask specifically about their sleep and working schedules to optimize sleep as best as possible; this should include, but not be limited to, screening and testing for sleep disordered breathing and insomnia,” he said.
The current study has several limitations, including the inability to control for smoking or alcohol use, which are common in military personnel and associated with increased morbidity, said Shamim-Uzzaman. The study also did not assess the impact of other confounding factors, such as sleep duration and daytime sleepiness, that could impact the results, especially the association of OSA and traumatic brain injury, he noted. “More research is needed to assess the impact of these factors as well as the effect of treatment of OSA on comorbidities and healthcare utilization,” he said.
This study was supported by the Military Health Services Research Program.
Wickwire’s institution had received research funding from the American Academy of Sleep Medicine Foundation, Department of Defense, Merck, National Institutes of Health/National Institute on Aging, ResMed, the ResMed Foundation, and the SRS Foundation. Wickwire disclosed serving as a scientific consultant to Axsome Therapeutics, Dayzz, Eisai, EnsoData, Idorsia, Merck, Nox Health, Primasun, Purdue, and ResMed and is an equity shareholder in Well Tap.
Shamim-Uzzaman is an employee of the Veterans’ Health Administration.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Experts Recommend Medication for Pediatric MASLD Management
, according to a new joint perspective paper.
Pediatric MASLD is the number-one cause of chronic liver disease in children and the number-one reason for liver transplant listing in young adults aged 18-40 years, said corresponding author Jennifer A. Panganiban, MD, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia.
The paper, published in Obesity Pillars, represents “a call to action that has been long overdue,” Panganiban told GI & Hepatology News.
The goal of the authors was to bring global awareness to the recent changes in the pediatric MASLD landscape — especially in medication use — and to empower clinicians treating the disease, she explained.
The recommendations are based on a combination of the latest published evidence and clinical expertise from eight hepatologists/gastroenterologists and two physicians from the Obesity Medicine Association, Centennial, Colorado.
One of the major barriers to MASLD management in children is suboptimal screening resulting in underdiagnosis, said Panganiban. “Unfortunately, only up to 30% of children are being screened in their pediatrician’s office.”
The new guideline outlines the patient care process from screening, referral to a subspecialist, and workup; however, the primary focus is on treatment with medication options that were previously not available or underutilized, she said.
Successful and Sustainable Weight Loss
Adiposity and weight gain make MASLD worse, but weight reduction has been shown to improve the condition, the authors noted. Previous strategies for curbing MASLD in children with obesity have focused mainly on lifestyle changes, but with limited success.
Nevertheless, the authors recommend continuing physical activity and nutrition as treatments for MASLD in children, with a plan tailored specifically to the patient.
In addition, however, they suggest that anti-obesity medications started early in the disease may help reduce costs and improve future outcomes.
Although glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have not yet been studied specifically for pediatric MASLD, data from studies of pediatric obesity, diabetes, and other retrospective studies are encouraging, the authors wrote.
The GLP-1 RAs liraglutide and semaglutide are both approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for managing obesity in children and adolescents aged 12 years or older, they noted. And a recent phase 3a randomized trial showed that liraglutide, not yet approved for children younger than 12 years, led to a mean change in body mass index of 5.8% from baseline to 56 weeks in children aged 6-11 years with obesity.
GLP-1 RAs not only are effective for weight management but also improve other metabolic dysfunction indicators including cholesterol and blood pressure, which makes these medications an even more beneficial option for individuals with obesity and MASLD, Panganiban and colleagues wrote.
For example, a recent single-center study of 111 children with MASLD (mean age, 15 years) showed a significant improvement in alanine aminotransferase levels with the use of GLP-1 RAs, although body mass index and weight were unchanged.
Regaining weight after discontinuing GLP-1 RAs is the main barrier to their use for MASLD, the authors noted. In addition, GLP-1 RAs are contraindicated in some situations, such as in those with a history of serious hypersensitivity, and in patients with a personal or family history of either medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 based on animal studies showing an association with the medications and thyroid C–cell tumors.
Other FDA-approved medication options for obesity in children include metformin, topiramate, and phentermine, as well as bupropion, lisdexamfetamine, and setmelanotide, the authors said.
Resmetirom, a thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist, which is another significant breakthrough in MASLD for adults, has not yet been tested or approved for pediatric use.
In addition to medications, metabolic bariatric surgery has shown effectiveness in children with obesity and/or MASLD by reducing liver fat and reversing fibrosis, as shown in the Teen-LABS study, the authors wrote. However, long-term data on fibrosis reversal are limited, and cost and access remain barriers.
More Research Needed
The joint expert review is intended as an educational tool that may require updates and should not be interpreted as rules for individual patient care, the authors cautioned. And physical activity and nutrition remain the primary treatment of MASLD and should be continued in conjunction with other treatment modalities, they emphasized.
Looking ahead, research is needed to develop accurate and reliable noninvasive biomarkers to diagnose and assess obesity treatment efficacy, Panganiban told GI & Hepatology News.
Also needed are multicenter randomized control trials in children with obesity involving different medications that have been successful in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis/fibrosis in adults, such as GLP-1 RAs or resmetirom, she added.
Educating Clinicians on Early Identification
When obesity occurs in childhood, it starts a process of additional complications that arise in earlier ages in adults, said Saul J. Karpen, MD, chief scientific officer at the Stravitz-Sanyal Institute for Liver Disease and Metabolic Health, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia, in an interview.“Given the epidemic of obesity, altered diets, and reduced physical activities during younger ages, it is not easy to identify which children are at greater risk of MASLD,” said Karpen.
“It requires insight from the care providers and often imaging, a blood test, or a referral to a pediatric hepatologist, and not every region has easy access to such expertise,” Karpen said.
The new review is important because it highlights the fact that obesity and its consequences are not limited to adulthood, and that educated clinicians are in a position to get an early start on treatment in children, Karpen noted.
The guideline received no outside funding. Panganiban and Karpen had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new joint perspective paper.
Pediatric MASLD is the number-one cause of chronic liver disease in children and the number-one reason for liver transplant listing in young adults aged 18-40 years, said corresponding author Jennifer A. Panganiban, MD, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia.
The paper, published in Obesity Pillars, represents “a call to action that has been long overdue,” Panganiban told GI & Hepatology News.
The goal of the authors was to bring global awareness to the recent changes in the pediatric MASLD landscape — especially in medication use — and to empower clinicians treating the disease, she explained.
The recommendations are based on a combination of the latest published evidence and clinical expertise from eight hepatologists/gastroenterologists and two physicians from the Obesity Medicine Association, Centennial, Colorado.
One of the major barriers to MASLD management in children is suboptimal screening resulting in underdiagnosis, said Panganiban. “Unfortunately, only up to 30% of children are being screened in their pediatrician’s office.”
The new guideline outlines the patient care process from screening, referral to a subspecialist, and workup; however, the primary focus is on treatment with medication options that were previously not available or underutilized, she said.
Successful and Sustainable Weight Loss
Adiposity and weight gain make MASLD worse, but weight reduction has been shown to improve the condition, the authors noted. Previous strategies for curbing MASLD in children with obesity have focused mainly on lifestyle changes, but with limited success.
Nevertheless, the authors recommend continuing physical activity and nutrition as treatments for MASLD in children, with a plan tailored specifically to the patient.
In addition, however, they suggest that anti-obesity medications started early in the disease may help reduce costs and improve future outcomes.
Although glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have not yet been studied specifically for pediatric MASLD, data from studies of pediatric obesity, diabetes, and other retrospective studies are encouraging, the authors wrote.
The GLP-1 RAs liraglutide and semaglutide are both approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for managing obesity in children and adolescents aged 12 years or older, they noted. And a recent phase 3a randomized trial showed that liraglutide, not yet approved for children younger than 12 years, led to a mean change in body mass index of 5.8% from baseline to 56 weeks in children aged 6-11 years with obesity.
GLP-1 RAs not only are effective for weight management but also improve other metabolic dysfunction indicators including cholesterol and blood pressure, which makes these medications an even more beneficial option for individuals with obesity and MASLD, Panganiban and colleagues wrote.
For example, a recent single-center study of 111 children with MASLD (mean age, 15 years) showed a significant improvement in alanine aminotransferase levels with the use of GLP-1 RAs, although body mass index and weight were unchanged.
Regaining weight after discontinuing GLP-1 RAs is the main barrier to their use for MASLD, the authors noted. In addition, GLP-1 RAs are contraindicated in some situations, such as in those with a history of serious hypersensitivity, and in patients with a personal or family history of either medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 based on animal studies showing an association with the medications and thyroid C–cell tumors.
Other FDA-approved medication options for obesity in children include metformin, topiramate, and phentermine, as well as bupropion, lisdexamfetamine, and setmelanotide, the authors said.
Resmetirom, a thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist, which is another significant breakthrough in MASLD for adults, has not yet been tested or approved for pediatric use.
In addition to medications, metabolic bariatric surgery has shown effectiveness in children with obesity and/or MASLD by reducing liver fat and reversing fibrosis, as shown in the Teen-LABS study, the authors wrote. However, long-term data on fibrosis reversal are limited, and cost and access remain barriers.
More Research Needed
The joint expert review is intended as an educational tool that may require updates and should not be interpreted as rules for individual patient care, the authors cautioned. And physical activity and nutrition remain the primary treatment of MASLD and should be continued in conjunction with other treatment modalities, they emphasized.
Looking ahead, research is needed to develop accurate and reliable noninvasive biomarkers to diagnose and assess obesity treatment efficacy, Panganiban told GI & Hepatology News.
Also needed are multicenter randomized control trials in children with obesity involving different medications that have been successful in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis/fibrosis in adults, such as GLP-1 RAs or resmetirom, she added.
Educating Clinicians on Early Identification
When obesity occurs in childhood, it starts a process of additional complications that arise in earlier ages in adults, said Saul J. Karpen, MD, chief scientific officer at the Stravitz-Sanyal Institute for Liver Disease and Metabolic Health, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia, in an interview.“Given the epidemic of obesity, altered diets, and reduced physical activities during younger ages, it is not easy to identify which children are at greater risk of MASLD,” said Karpen.
“It requires insight from the care providers and often imaging, a blood test, or a referral to a pediatric hepatologist, and not every region has easy access to such expertise,” Karpen said.
The new review is important because it highlights the fact that obesity and its consequences are not limited to adulthood, and that educated clinicians are in a position to get an early start on treatment in children, Karpen noted.
The guideline received no outside funding. Panganiban and Karpen had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new joint perspective paper.
Pediatric MASLD is the number-one cause of chronic liver disease in children and the number-one reason for liver transplant listing in young adults aged 18-40 years, said corresponding author Jennifer A. Panganiban, MD, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, Philadelphia.
The paper, published in Obesity Pillars, represents “a call to action that has been long overdue,” Panganiban told GI & Hepatology News.
The goal of the authors was to bring global awareness to the recent changes in the pediatric MASLD landscape — especially in medication use — and to empower clinicians treating the disease, she explained.
The recommendations are based on a combination of the latest published evidence and clinical expertise from eight hepatologists/gastroenterologists and two physicians from the Obesity Medicine Association, Centennial, Colorado.
One of the major barriers to MASLD management in children is suboptimal screening resulting in underdiagnosis, said Panganiban. “Unfortunately, only up to 30% of children are being screened in their pediatrician’s office.”
The new guideline outlines the patient care process from screening, referral to a subspecialist, and workup; however, the primary focus is on treatment with medication options that were previously not available or underutilized, she said.
Successful and Sustainable Weight Loss
Adiposity and weight gain make MASLD worse, but weight reduction has been shown to improve the condition, the authors noted. Previous strategies for curbing MASLD in children with obesity have focused mainly on lifestyle changes, but with limited success.
Nevertheless, the authors recommend continuing physical activity and nutrition as treatments for MASLD in children, with a plan tailored specifically to the patient.
In addition, however, they suggest that anti-obesity medications started early in the disease may help reduce costs and improve future outcomes.
Although glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RAs) have not yet been studied specifically for pediatric MASLD, data from studies of pediatric obesity, diabetes, and other retrospective studies are encouraging, the authors wrote.
The GLP-1 RAs liraglutide and semaglutide are both approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for managing obesity in children and adolescents aged 12 years or older, they noted. And a recent phase 3a randomized trial showed that liraglutide, not yet approved for children younger than 12 years, led to a mean change in body mass index of 5.8% from baseline to 56 weeks in children aged 6-11 years with obesity.
GLP-1 RAs not only are effective for weight management but also improve other metabolic dysfunction indicators including cholesterol and blood pressure, which makes these medications an even more beneficial option for individuals with obesity and MASLD, Panganiban and colleagues wrote.
For example, a recent single-center study of 111 children with MASLD (mean age, 15 years) showed a significant improvement in alanine aminotransferase levels with the use of GLP-1 RAs, although body mass index and weight were unchanged.
Regaining weight after discontinuing GLP-1 RAs is the main barrier to their use for MASLD, the authors noted. In addition, GLP-1 RAs are contraindicated in some situations, such as in those with a history of serious hypersensitivity, and in patients with a personal or family history of either medullary thyroid carcinoma or multiple endocrine neoplasia syndrome type 2 based on animal studies showing an association with the medications and thyroid C–cell tumors.
Other FDA-approved medication options for obesity in children include metformin, topiramate, and phentermine, as well as bupropion, lisdexamfetamine, and setmelanotide, the authors said.
Resmetirom, a thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonist, which is another significant breakthrough in MASLD for adults, has not yet been tested or approved for pediatric use.
In addition to medications, metabolic bariatric surgery has shown effectiveness in children with obesity and/or MASLD by reducing liver fat and reversing fibrosis, as shown in the Teen-LABS study, the authors wrote. However, long-term data on fibrosis reversal are limited, and cost and access remain barriers.
More Research Needed
The joint expert review is intended as an educational tool that may require updates and should not be interpreted as rules for individual patient care, the authors cautioned. And physical activity and nutrition remain the primary treatment of MASLD and should be continued in conjunction with other treatment modalities, they emphasized.
Looking ahead, research is needed to develop accurate and reliable noninvasive biomarkers to diagnose and assess obesity treatment efficacy, Panganiban told GI & Hepatology News.
Also needed are multicenter randomized control trials in children with obesity involving different medications that have been successful in the treatment of metabolic dysfunction–associated steatohepatitis/fibrosis in adults, such as GLP-1 RAs or resmetirom, she added.
Educating Clinicians on Early Identification
When obesity occurs in childhood, it starts a process of additional complications that arise in earlier ages in adults, said Saul J. Karpen, MD, chief scientific officer at the Stravitz-Sanyal Institute for Liver Disease and Metabolic Health, Virginia Commonwealth University, Richmond, Virginia, in an interview.“Given the epidemic of obesity, altered diets, and reduced physical activities during younger ages, it is not easy to identify which children are at greater risk of MASLD,” said Karpen.
“It requires insight from the care providers and often imaging, a blood test, or a referral to a pediatric hepatologist, and not every region has easy access to such expertise,” Karpen said.
The new review is important because it highlights the fact that obesity and its consequences are not limited to adulthood, and that educated clinicians are in a position to get an early start on treatment in children, Karpen noted.
The guideline received no outside funding. Panganiban and Karpen had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Elemental Diet Eases Symptoms in Microbiome Gastro Disorders
, according to a new study.
“Elemental diets have long shown promise for treating gastrointestinal disorders like Crohn’s disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth), and IMO (intestinal methanogen overgrowth), but poor palatability has limited their use,” lead author Ali Rezaie, MD, medical director of the Gastrointestinal (GI) Motility Program and director of Bioinformatics at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told GI & Hepatology News.
Elemental diets are specialized formulas tailored to meet an individual’s specific nutritional needs and daily requirements for vitamins, minerals, fat, free amino acids, and carbohydrates.
In SIBO and IMO specifically, only about half the patients respond to antibiotics, and many require repeat treatments, which underscores the need for effective nonantibiotic alternatives, said Rezaie. “This is the first prospective trial using a PED, aiming to make this approach both viable and accessible for patients,” he noted.
Assessing a Novel Diet in IMO and SIBO
In the study, which was recently published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Rezaie and colleagues enrolled 30 adults with IMO (40%), SIBO (20%), or both (40%). The mean participant age was 45 years, and 63% were women.
All participants completed 2 weeks of a PED, transitioned to 2-3 days of a bland diet, and then resumed their regular diets for 2 weeks.
The diet consisted of multiple 300-calorie packets, adjusted for individual caloric needs. Participants could consume additional packets for hunger but were prohibited from eating other foods. There was no restriction on water intake.
The primary endpoint was changes in stool microbiome after the PED and reintroduction of regular food. Secondary endpoints included lactose breath test normalization to determine bacterial overgrowth in the gut, symptom response, and adverse events.
Researchers collected 29 stool samples at baseline, 27 post-PED, and 27 at study conclusion (2 weeks post-diet).
Key Outcomes
Although the stool samples’ alpha diversity decreased after the PED, the difference was not statistically significant at the end of the study. However, 30 bacterial families showed significant differences in relative abundance post-PED.
Daily symptom severity improved significantly during the second week of the diet compared with baseline, with reduction in abdominal discomfort, bloating, distention, constipation, and flatulence. Further significant improvements in measures such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, urgency, and brain fog were observed after reintroducing regular food.
“We observed 73% breath test normalization and 83% global symptom relief — with 100% adherence and tolerance to 2 weeks of exclusive PED,” Rezaie told GI & Hepatology News. No serious adverse events occurred during the study, he added.
Lactose breath test normalization rates post-PED were 58% in patients with IMO, 100% in patients with SIBO, and 75% in those with both conditions.
The extent of patient response to PED was notable, given that 83% had failed prior treatments, Rezaie said.
“While we expected benefit based on palatability improvements and prior retrospective data, the rapid reduction in methane and hydrogen gas — and the sustained microbiome modulation even after reintroducing a regular diet — exceeded expectations,” he said. A significant reduction in visceral fat was another novel finding.
“This study reinforces the power of diet as a therapeutic tool,” Rezaie said, adding that the results show that elemental diets can be palatable, thereby improving patient adherence, tolerance, and, eventually, effectiveness. This is particularly valuable for patients with SIBO and IMO who do not tolerate or respond to antibiotics, prefer nonpharmacologic options, or experience recurrent symptoms after antibiotic treatment.
Limitations and Next Steps
Study limitations included the lack of a placebo group with a sham diet, the short follow-up after reintroducing a regular diet, and the inability to assess microbial gene function.
However, the results support the safety, tolerance, and benefit of a PED in patients with IMO/SIBO. Personalized dietary interventions that support the growth of beneficial bacteria may be an effective approach to treating these disorders, Rezaie and colleagues noted in their publication.
Although the current study is a promising first step, longer-term studies are needed to evaluate the durability of microbiome and symptom improvements, Rezaie said.
Making the Most of Microbiome Manipulation
Elemental diets may help modulate the gut microbiome while reducing immune activation, making them attractive for microbiome-targeted gastrointestinal therapies, Jatin Roper, MD, a gastroenterologist at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, told GI & Hepatology News.
“Antibiotics are only effective in half of SIBO cases and often require retreatment, so better therapies are needed,” said Roper, who was not affiliated with the study. He added that its findings confirmed the researchers’ hypothesis that a PED can be both safe and effective in patients with SIBO.
Roper noted the 83% symptom improvement as the study’s most unexpected and encouraging finding, as it represents a substantial improvement compared with standard antibiotic therapy. “It is also surprising that the tolerance rate of the elemental diet in this study was 100%,” he said.
However, diet palatability remains a major barrier in real-world practice.
“Adherence rates are likely to be far lower than in trials in which patients are closely monitored, and this challenge will not be easily overcome,” he added.
The study’s limitations, including the lack of metagenomic analysis and a placebo group, are important to address in future research, Roper said. In particular, controlled trials of elemental diets are needed to determine whether microbiome changes are directly responsible for symptom improvement.
The study was supported in part by Good LFE and the John and Geraldine Cusenza Foundation. Rezaie disclosed serving as a consultant/speaker for Bausch Health and having equity in Dieta Health, Gemelli Biotech, and Good LFE. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new study.
“Elemental diets have long shown promise for treating gastrointestinal disorders like Crohn’s disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth), and IMO (intestinal methanogen overgrowth), but poor palatability has limited their use,” lead author Ali Rezaie, MD, medical director of the Gastrointestinal (GI) Motility Program and director of Bioinformatics at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told GI & Hepatology News.
Elemental diets are specialized formulas tailored to meet an individual’s specific nutritional needs and daily requirements for vitamins, minerals, fat, free amino acids, and carbohydrates.
In SIBO and IMO specifically, only about half the patients respond to antibiotics, and many require repeat treatments, which underscores the need for effective nonantibiotic alternatives, said Rezaie. “This is the first prospective trial using a PED, aiming to make this approach both viable and accessible for patients,” he noted.
Assessing a Novel Diet in IMO and SIBO
In the study, which was recently published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Rezaie and colleagues enrolled 30 adults with IMO (40%), SIBO (20%), or both (40%). The mean participant age was 45 years, and 63% were women.
All participants completed 2 weeks of a PED, transitioned to 2-3 days of a bland diet, and then resumed their regular diets for 2 weeks.
The diet consisted of multiple 300-calorie packets, adjusted for individual caloric needs. Participants could consume additional packets for hunger but were prohibited from eating other foods. There was no restriction on water intake.
The primary endpoint was changes in stool microbiome after the PED and reintroduction of regular food. Secondary endpoints included lactose breath test normalization to determine bacterial overgrowth in the gut, symptom response, and adverse events.
Researchers collected 29 stool samples at baseline, 27 post-PED, and 27 at study conclusion (2 weeks post-diet).
Key Outcomes
Although the stool samples’ alpha diversity decreased after the PED, the difference was not statistically significant at the end of the study. However, 30 bacterial families showed significant differences in relative abundance post-PED.
Daily symptom severity improved significantly during the second week of the diet compared with baseline, with reduction in abdominal discomfort, bloating, distention, constipation, and flatulence. Further significant improvements in measures such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, urgency, and brain fog were observed after reintroducing regular food.
“We observed 73% breath test normalization and 83% global symptom relief — with 100% adherence and tolerance to 2 weeks of exclusive PED,” Rezaie told GI & Hepatology News. No serious adverse events occurred during the study, he added.
Lactose breath test normalization rates post-PED were 58% in patients with IMO, 100% in patients with SIBO, and 75% in those with both conditions.
The extent of patient response to PED was notable, given that 83% had failed prior treatments, Rezaie said.
“While we expected benefit based on palatability improvements and prior retrospective data, the rapid reduction in methane and hydrogen gas — and the sustained microbiome modulation even after reintroducing a regular diet — exceeded expectations,” he said. A significant reduction in visceral fat was another novel finding.
“This study reinforces the power of diet as a therapeutic tool,” Rezaie said, adding that the results show that elemental diets can be palatable, thereby improving patient adherence, tolerance, and, eventually, effectiveness. This is particularly valuable for patients with SIBO and IMO who do not tolerate or respond to antibiotics, prefer nonpharmacologic options, or experience recurrent symptoms after antibiotic treatment.
Limitations and Next Steps
Study limitations included the lack of a placebo group with a sham diet, the short follow-up after reintroducing a regular diet, and the inability to assess microbial gene function.
However, the results support the safety, tolerance, and benefit of a PED in patients with IMO/SIBO. Personalized dietary interventions that support the growth of beneficial bacteria may be an effective approach to treating these disorders, Rezaie and colleagues noted in their publication.
Although the current study is a promising first step, longer-term studies are needed to evaluate the durability of microbiome and symptom improvements, Rezaie said.
Making the Most of Microbiome Manipulation
Elemental diets may help modulate the gut microbiome while reducing immune activation, making them attractive for microbiome-targeted gastrointestinal therapies, Jatin Roper, MD, a gastroenterologist at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, told GI & Hepatology News.
“Antibiotics are only effective in half of SIBO cases and often require retreatment, so better therapies are needed,” said Roper, who was not affiliated with the study. He added that its findings confirmed the researchers’ hypothesis that a PED can be both safe and effective in patients with SIBO.
Roper noted the 83% symptom improvement as the study’s most unexpected and encouraging finding, as it represents a substantial improvement compared with standard antibiotic therapy. “It is also surprising that the tolerance rate of the elemental diet in this study was 100%,” he said.
However, diet palatability remains a major barrier in real-world practice.
“Adherence rates are likely to be far lower than in trials in which patients are closely monitored, and this challenge will not be easily overcome,” he added.
The study’s limitations, including the lack of metagenomic analysis and a placebo group, are important to address in future research, Roper said. In particular, controlled trials of elemental diets are needed to determine whether microbiome changes are directly responsible for symptom improvement.
The study was supported in part by Good LFE and the John and Geraldine Cusenza Foundation. Rezaie disclosed serving as a consultant/speaker for Bausch Health and having equity in Dieta Health, Gemelli Biotech, and Good LFE. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
, according to a new study.
“Elemental diets have long shown promise for treating gastrointestinal disorders like Crohn’s disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, SIBO (small intestinal bacterial overgrowth), and IMO (intestinal methanogen overgrowth), but poor palatability has limited their use,” lead author Ali Rezaie, MD, medical director of the Gastrointestinal (GI) Motility Program and director of Bioinformatics at Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, told GI & Hepatology News.
Elemental diets are specialized formulas tailored to meet an individual’s specific nutritional needs and daily requirements for vitamins, minerals, fat, free amino acids, and carbohydrates.
In SIBO and IMO specifically, only about half the patients respond to antibiotics, and many require repeat treatments, which underscores the need for effective nonantibiotic alternatives, said Rezaie. “This is the first prospective trial using a PED, aiming to make this approach both viable and accessible for patients,” he noted.
Assessing a Novel Diet in IMO and SIBO
In the study, which was recently published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology, Rezaie and colleagues enrolled 30 adults with IMO (40%), SIBO (20%), or both (40%). The mean participant age was 45 years, and 63% were women.
All participants completed 2 weeks of a PED, transitioned to 2-3 days of a bland diet, and then resumed their regular diets for 2 weeks.
The diet consisted of multiple 300-calorie packets, adjusted for individual caloric needs. Participants could consume additional packets for hunger but were prohibited from eating other foods. There was no restriction on water intake.
The primary endpoint was changes in stool microbiome after the PED and reintroduction of regular food. Secondary endpoints included lactose breath test normalization to determine bacterial overgrowth in the gut, symptom response, and adverse events.
Researchers collected 29 stool samples at baseline, 27 post-PED, and 27 at study conclusion (2 weeks post-diet).
Key Outcomes
Although the stool samples’ alpha diversity decreased after the PED, the difference was not statistically significant at the end of the study. However, 30 bacterial families showed significant differences in relative abundance post-PED.
Daily symptom severity improved significantly during the second week of the diet compared with baseline, with reduction in abdominal discomfort, bloating, distention, constipation, and flatulence. Further significant improvements in measures such as abdominal pain, diarrhea, fatigue, urgency, and brain fog were observed after reintroducing regular food.
“We observed 73% breath test normalization and 83% global symptom relief — with 100% adherence and tolerance to 2 weeks of exclusive PED,” Rezaie told GI & Hepatology News. No serious adverse events occurred during the study, he added.
Lactose breath test normalization rates post-PED were 58% in patients with IMO, 100% in patients with SIBO, and 75% in those with both conditions.
The extent of patient response to PED was notable, given that 83% had failed prior treatments, Rezaie said.
“While we expected benefit based on palatability improvements and prior retrospective data, the rapid reduction in methane and hydrogen gas — and the sustained microbiome modulation even after reintroducing a regular diet — exceeded expectations,” he said. A significant reduction in visceral fat was another novel finding.
“This study reinforces the power of diet as a therapeutic tool,” Rezaie said, adding that the results show that elemental diets can be palatable, thereby improving patient adherence, tolerance, and, eventually, effectiveness. This is particularly valuable for patients with SIBO and IMO who do not tolerate or respond to antibiotics, prefer nonpharmacologic options, or experience recurrent symptoms after antibiotic treatment.
Limitations and Next Steps
Study limitations included the lack of a placebo group with a sham diet, the short follow-up after reintroducing a regular diet, and the inability to assess microbial gene function.
However, the results support the safety, tolerance, and benefit of a PED in patients with IMO/SIBO. Personalized dietary interventions that support the growth of beneficial bacteria may be an effective approach to treating these disorders, Rezaie and colleagues noted in their publication.
Although the current study is a promising first step, longer-term studies are needed to evaluate the durability of microbiome and symptom improvements, Rezaie said.
Making the Most of Microbiome Manipulation
Elemental diets may help modulate the gut microbiome while reducing immune activation, making them attractive for microbiome-targeted gastrointestinal therapies, Jatin Roper, MD, a gastroenterologist at Duke University, Durham, North Carolina, told GI & Hepatology News.
“Antibiotics are only effective in half of SIBO cases and often require retreatment, so better therapies are needed,” said Roper, who was not affiliated with the study. He added that its findings confirmed the researchers’ hypothesis that a PED can be both safe and effective in patients with SIBO.
Roper noted the 83% symptom improvement as the study’s most unexpected and encouraging finding, as it represents a substantial improvement compared with standard antibiotic therapy. “It is also surprising that the tolerance rate of the elemental diet in this study was 100%,” he said.
However, diet palatability remains a major barrier in real-world practice.
“Adherence rates are likely to be far lower than in trials in which patients are closely monitored, and this challenge will not be easily overcome,” he added.
The study’s limitations, including the lack of metagenomic analysis and a placebo group, are important to address in future research, Roper said. In particular, controlled trials of elemental diets are needed to determine whether microbiome changes are directly responsible for symptom improvement.
The study was supported in part by Good LFE and the John and Geraldine Cusenza Foundation. Rezaie disclosed serving as a consultant/speaker for Bausch Health and having equity in Dieta Health, Gemelli Biotech, and Good LFE. Roper had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
FROM CLINICAL GASTROENTEROLOGY AND HEPATOLOGY
Could Statins Prevent Hepatocellular Carcinoma?
, emerging research, including several large cohort studies, suggested.
The most recent study, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, showed a lower incidence of hepatic decompensation among statin users in a registry for adults aged 40 years or older with baseline chronic liver disease.
“Our findings support the idea that statins may offer benefits beyond lipid-lowering in patients with [chronic liver disease], and clinicians may be more confident in prescribing statins when indicated,” even in these patients, said corresponding Co-author Raymond T. Chung, MD, gastroenterology investigator at Mass General Research Institute, Boston, in an interview.
“While prior studies have suggested an association between statin use and reduced hepatocellular carcinoma risk, our study aimed to build on that evidence by using a large, real-world, hospital-based cohort inclusive of all etiologies of chronic liver disease,” Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
Chung, along with Jonggi Choi, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues, reviewed data from the Research Patient Data Registry from 2000 to 2023 for 16,501 participantsaged 40 years or older with baseline chronic liver disease and baseline Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) scores ≥ 1.3.
The study population had a mean age of 59.7 years, and 40.9% were women. The researchers divided the population into statin users (n = 3610) and nonusers (n = 12,891). Statin use was defined as a cumulative defined daily dose ≥ 30 mg.
The primary outcome was the cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation.
At 10 years follow-up, statin users showed a significantly reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma vs nonusers (3.8% vs 8.0%; P < .001) as well as a significantly reduced incidence of hepatic decompensation (10.6% vs 19.5%; P < .001).
Incorporating FIB-4 scores, a surrogate marker for liver fibrosis, also showed that statin users were less likely to experience fibrosis progression, offering a potential mechanism of action for the observed reduction in adverse liver outcomes, Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
“Similar trends have been observed in prior observational studies, but our findings now support a real effect of statin use on fibrosis progression,” he said. “However, what strengthened our study was that the association remained consistent across multiple subgroups and sensitivity analyses.”
Another study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology showed a reduced risk of developing severe liver disease in a Swedish cohort of noncirrhotic adults with chronic liver disease who used statins (n = 3862) compared with control patients with chronic liver disease (matched 1:1) and who did not use statins (hazard ratio [HR], 0.60).
In that study, Rajani Sharma, MD, and colleagues found a protective association in both prefibrosis and fibrosis stages at diagnosis, and statin use was associated with reduced rates of progression to both cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.62 and 0.44, respectively).
Exciting and Necessary Research
The research by Choi and colleagues is “exciting,” said Bubu Banini, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in digestive diseases at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, in an interview.
Liver cancer prevalence has risen over the past few decades in the United States and worldwide, and the 5-year overall survival rate of liver cancer is less than 20%, Banini told GI & Hepatology News.
Clinicians often withhold statins out of fear of liver injury in persons with chronic liver disease; however, a takeaway from this study is that for persons with chronic liver disease who have indications for statin use, the medication should not be withheld, she said.
Of course, prospective studies are needed to replicate the results, Banini added.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to adjust for all potential confounding variables, lack of data on post-index treatments, and the use of wide, cumulative, defined daily dose categories to ensure statistical power, the researchers noted.
“Moving forward, randomized controlled trials are essential to establish a causal relationship and clarify the molecular and clinical pathways through which statins exert hepatoprotective effects,” Chung added.
Randomized controlled trials are also needed to determine whether statins can actually reduce the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation in patients with chronic liver disease, and cost-effectiveness analyses may be essential for translating this evidence into clinical guidelines, he added.
Statins and HCC Risk in the General Population
A large cohort study, published in JAMA Network Open by Mara Sophie Vell, PhD, and colleagues, showed an association between reduced risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and statin use in the general population and in those at increased risk for liver disease.
The study, which included data for individuals aged 37-73 years from the UK Biobank, found a 15% reduced risk for new-onset liver disease and a 28% reduced risk for liver-related death among regular statin users than among nonusers (HR, 0.85 and 0.72, respectively).
In addition, regular statin users showed a 74% reduced risk (P = .003) of developing hepatocellular carcinoma compared with those not using statins. The researchers identified a particular impact on liver disease risk reduction among men, individuals with diabetes, and patients with high levels of liver scarring at baseline based on the FIB-4 index.
A meta-analysis of 24 studies, previously published in the journal Cancers, showed a significant reduction of 46% in hepatocellular carcinoma risk among statins users compared with nonusers.
The researchers found this risk reduction was significant in subgroups of patients with diabetes, liver cirrhosis, and those on antiviral therapy, and they suggested that the antiangiogenic, immunomodulatory, antiproliferative, and antifibrotic properties of statins may contribute to their potential to reduce tumor growth or hepatocellular carcinoma development.
The meta-analysis authors noted that although most studies have reported a low risk for statin-induced hepatotoxicity, clinicians should proceed with caution in some patients with existing cirrhosis.
“If the patients are diagnosed with decompensated cirrhosis, then statins should be prescribed with caution at low doses,” they wrote.
Advocating statin use solely for chemoprevention may be premature based on observational data, Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
“However, in patients with [chronic liver disease] who already meet indications for statin therapy, the potential added benefit of reducing liver-related complications strengthens the rationale for their use,” he said. Future randomized clinical trials will be key to defining the risk-benefit profile in this context.
The study by Choi and colleagues was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
The study by Sharma and colleagues was supported by the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City; researchers were supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council, Center for Innovative Medicine, the Swedish Cancer Society, and the National Institutes of Health.
The study by Vell and colleagues had no outside funding.
The study by Mohaimenul Islam and colleagues was supported by the Ministry of Education and Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Chung and Banini had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, emerging research, including several large cohort studies, suggested.
The most recent study, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, showed a lower incidence of hepatic decompensation among statin users in a registry for adults aged 40 years or older with baseline chronic liver disease.
“Our findings support the idea that statins may offer benefits beyond lipid-lowering in patients with [chronic liver disease], and clinicians may be more confident in prescribing statins when indicated,” even in these patients, said corresponding Co-author Raymond T. Chung, MD, gastroenterology investigator at Mass General Research Institute, Boston, in an interview.
“While prior studies have suggested an association between statin use and reduced hepatocellular carcinoma risk, our study aimed to build on that evidence by using a large, real-world, hospital-based cohort inclusive of all etiologies of chronic liver disease,” Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
Chung, along with Jonggi Choi, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues, reviewed data from the Research Patient Data Registry from 2000 to 2023 for 16,501 participantsaged 40 years or older with baseline chronic liver disease and baseline Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) scores ≥ 1.3.
The study population had a mean age of 59.7 years, and 40.9% were women. The researchers divided the population into statin users (n = 3610) and nonusers (n = 12,891). Statin use was defined as a cumulative defined daily dose ≥ 30 mg.
The primary outcome was the cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation.
At 10 years follow-up, statin users showed a significantly reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma vs nonusers (3.8% vs 8.0%; P < .001) as well as a significantly reduced incidence of hepatic decompensation (10.6% vs 19.5%; P < .001).
Incorporating FIB-4 scores, a surrogate marker for liver fibrosis, also showed that statin users were less likely to experience fibrosis progression, offering a potential mechanism of action for the observed reduction in adverse liver outcomes, Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
“Similar trends have been observed in prior observational studies, but our findings now support a real effect of statin use on fibrosis progression,” he said. “However, what strengthened our study was that the association remained consistent across multiple subgroups and sensitivity analyses.”
Another study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology showed a reduced risk of developing severe liver disease in a Swedish cohort of noncirrhotic adults with chronic liver disease who used statins (n = 3862) compared with control patients with chronic liver disease (matched 1:1) and who did not use statins (hazard ratio [HR], 0.60).
In that study, Rajani Sharma, MD, and colleagues found a protective association in both prefibrosis and fibrosis stages at diagnosis, and statin use was associated with reduced rates of progression to both cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.62 and 0.44, respectively).
Exciting and Necessary Research
The research by Choi and colleagues is “exciting,” said Bubu Banini, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in digestive diseases at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, in an interview.
Liver cancer prevalence has risen over the past few decades in the United States and worldwide, and the 5-year overall survival rate of liver cancer is less than 20%, Banini told GI & Hepatology News.
Clinicians often withhold statins out of fear of liver injury in persons with chronic liver disease; however, a takeaway from this study is that for persons with chronic liver disease who have indications for statin use, the medication should not be withheld, she said.
Of course, prospective studies are needed to replicate the results, Banini added.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to adjust for all potential confounding variables, lack of data on post-index treatments, and the use of wide, cumulative, defined daily dose categories to ensure statistical power, the researchers noted.
“Moving forward, randomized controlled trials are essential to establish a causal relationship and clarify the molecular and clinical pathways through which statins exert hepatoprotective effects,” Chung added.
Randomized controlled trials are also needed to determine whether statins can actually reduce the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation in patients with chronic liver disease, and cost-effectiveness analyses may be essential for translating this evidence into clinical guidelines, he added.
Statins and HCC Risk in the General Population
A large cohort study, published in JAMA Network Open by Mara Sophie Vell, PhD, and colleagues, showed an association between reduced risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and statin use in the general population and in those at increased risk for liver disease.
The study, which included data for individuals aged 37-73 years from the UK Biobank, found a 15% reduced risk for new-onset liver disease and a 28% reduced risk for liver-related death among regular statin users than among nonusers (HR, 0.85 and 0.72, respectively).
In addition, regular statin users showed a 74% reduced risk (P = .003) of developing hepatocellular carcinoma compared with those not using statins. The researchers identified a particular impact on liver disease risk reduction among men, individuals with diabetes, and patients with high levels of liver scarring at baseline based on the FIB-4 index.
A meta-analysis of 24 studies, previously published in the journal Cancers, showed a significant reduction of 46% in hepatocellular carcinoma risk among statins users compared with nonusers.
The researchers found this risk reduction was significant in subgroups of patients with diabetes, liver cirrhosis, and those on antiviral therapy, and they suggested that the antiangiogenic, immunomodulatory, antiproliferative, and antifibrotic properties of statins may contribute to their potential to reduce tumor growth or hepatocellular carcinoma development.
The meta-analysis authors noted that although most studies have reported a low risk for statin-induced hepatotoxicity, clinicians should proceed with caution in some patients with existing cirrhosis.
“If the patients are diagnosed with decompensated cirrhosis, then statins should be prescribed with caution at low doses,” they wrote.
Advocating statin use solely for chemoprevention may be premature based on observational data, Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
“However, in patients with [chronic liver disease] who already meet indications for statin therapy, the potential added benefit of reducing liver-related complications strengthens the rationale for their use,” he said. Future randomized clinical trials will be key to defining the risk-benefit profile in this context.
The study by Choi and colleagues was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
The study by Sharma and colleagues was supported by the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City; researchers were supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council, Center for Innovative Medicine, the Swedish Cancer Society, and the National Institutes of Health.
The study by Vell and colleagues had no outside funding.
The study by Mohaimenul Islam and colleagues was supported by the Ministry of Education and Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Chung and Banini had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
, emerging research, including several large cohort studies, suggested.
The most recent study, published in JAMA Internal Medicine, showed a lower incidence of hepatic decompensation among statin users in a registry for adults aged 40 years or older with baseline chronic liver disease.
“Our findings support the idea that statins may offer benefits beyond lipid-lowering in patients with [chronic liver disease], and clinicians may be more confident in prescribing statins when indicated,” even in these patients, said corresponding Co-author Raymond T. Chung, MD, gastroenterology investigator at Mass General Research Institute, Boston, in an interview.
“While prior studies have suggested an association between statin use and reduced hepatocellular carcinoma risk, our study aimed to build on that evidence by using a large, real-world, hospital-based cohort inclusive of all etiologies of chronic liver disease,” Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
Chung, along with Jonggi Choi, MD, of the University of Ulsan College of Medicine, Seoul, South Korea, and colleagues, reviewed data from the Research Patient Data Registry from 2000 to 2023 for 16,501 participantsaged 40 years or older with baseline chronic liver disease and baseline Fibrosis-4 (FIB-4) scores ≥ 1.3.
The study population had a mean age of 59.7 years, and 40.9% were women. The researchers divided the population into statin users (n = 3610) and nonusers (n = 12,891). Statin use was defined as a cumulative defined daily dose ≥ 30 mg.
The primary outcome was the cumulative incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation.
At 10 years follow-up, statin users showed a significantly reduced incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma vs nonusers (3.8% vs 8.0%; P < .001) as well as a significantly reduced incidence of hepatic decompensation (10.6% vs 19.5%; P < .001).
Incorporating FIB-4 scores, a surrogate marker for liver fibrosis, also showed that statin users were less likely to experience fibrosis progression, offering a potential mechanism of action for the observed reduction in adverse liver outcomes, Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
“Similar trends have been observed in prior observational studies, but our findings now support a real effect of statin use on fibrosis progression,” he said. “However, what strengthened our study was that the association remained consistent across multiple subgroups and sensitivity analyses.”
Another study published in Clinical Gastroenterology and Hepatology showed a reduced risk of developing severe liver disease in a Swedish cohort of noncirrhotic adults with chronic liver disease who used statins (n = 3862) compared with control patients with chronic liver disease (matched 1:1) and who did not use statins (hazard ratio [HR], 0.60).
In that study, Rajani Sharma, MD, and colleagues found a protective association in both prefibrosis and fibrosis stages at diagnosis, and statin use was associated with reduced rates of progression to both cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma (HR, 0.62 and 0.44, respectively).
Exciting and Necessary Research
The research by Choi and colleagues is “exciting,” said Bubu Banini, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in digestive diseases at Yale School of Medicine, New Haven, Connecticut, in an interview.
Liver cancer prevalence has risen over the past few decades in the United States and worldwide, and the 5-year overall survival rate of liver cancer is less than 20%, Banini told GI & Hepatology News.
Clinicians often withhold statins out of fear of liver injury in persons with chronic liver disease; however, a takeaway from this study is that for persons with chronic liver disease who have indications for statin use, the medication should not be withheld, she said.
Of course, prospective studies are needed to replicate the results, Banini added.
The study findings were limited by several factors, including the inability to adjust for all potential confounding variables, lack of data on post-index treatments, and the use of wide, cumulative, defined daily dose categories to ensure statistical power, the researchers noted.
“Moving forward, randomized controlled trials are essential to establish a causal relationship and clarify the molecular and clinical pathways through which statins exert hepatoprotective effects,” Chung added.
Randomized controlled trials are also needed to determine whether statins can actually reduce the risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatic decompensation in patients with chronic liver disease, and cost-effectiveness analyses may be essential for translating this evidence into clinical guidelines, he added.
Statins and HCC Risk in the General Population
A large cohort study, published in JAMA Network Open by Mara Sophie Vell, PhD, and colleagues, showed an association between reduced risk for hepatocellular carcinoma and statin use in the general population and in those at increased risk for liver disease.
The study, which included data for individuals aged 37-73 years from the UK Biobank, found a 15% reduced risk for new-onset liver disease and a 28% reduced risk for liver-related death among regular statin users than among nonusers (HR, 0.85 and 0.72, respectively).
In addition, regular statin users showed a 74% reduced risk (P = .003) of developing hepatocellular carcinoma compared with those not using statins. The researchers identified a particular impact on liver disease risk reduction among men, individuals with diabetes, and patients with high levels of liver scarring at baseline based on the FIB-4 index.
A meta-analysis of 24 studies, previously published in the journal Cancers, showed a significant reduction of 46% in hepatocellular carcinoma risk among statins users compared with nonusers.
The researchers found this risk reduction was significant in subgroups of patients with diabetes, liver cirrhosis, and those on antiviral therapy, and they suggested that the antiangiogenic, immunomodulatory, antiproliferative, and antifibrotic properties of statins may contribute to their potential to reduce tumor growth or hepatocellular carcinoma development.
The meta-analysis authors noted that although most studies have reported a low risk for statin-induced hepatotoxicity, clinicians should proceed with caution in some patients with existing cirrhosis.
“If the patients are diagnosed with decompensated cirrhosis, then statins should be prescribed with caution at low doses,” they wrote.
Advocating statin use solely for chemoprevention may be premature based on observational data, Chung told GI & Hepatology News.
“However, in patients with [chronic liver disease] who already meet indications for statin therapy, the potential added benefit of reducing liver-related complications strengthens the rationale for their use,” he said. Future randomized clinical trials will be key to defining the risk-benefit profile in this context.
The study by Choi and colleagues was supported by the National Institutes of Health.
The study by Sharma and colleagues was supported by the Karolinska Institutet, Stockholm, Sweden, and the Columbia University Irving Medical Center, New York City; researchers were supported by grants from the Swedish Research Council, Center for Innovative Medicine, the Swedish Cancer Society, and the National Institutes of Health.
The study by Vell and colleagues had no outside funding.
The study by Mohaimenul Islam and colleagues was supported by the Ministry of Education and Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan.
Chung and Banini had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Patients With Asthma and COPD At Increased Cancer Risk From Microplastics
Individuals with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were more vulnerable than healthy controls to epithelial cell changes caused by microplastics exposure, based on data from a new simulation study.
Microplastic fibers present in the ambient air can be inhaled into the lungs and promote a range of complications including oxidative stress, local injury, and cytotoxicity, but data on the effects of microplastic fibers on individuals with obstructive lung diseases are limited, wrote Magdalena Poplinska-Goryca, MD, of the Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland, and colleagues.
In a study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers identified 10 adults aged ≥ 18 years with asthma, eight adults aged ≥ 40 years with COPD, and 11 healthy adult controls. Individuals with more serious conditions such as severe asthma or COPD, unstable or uncontrolled disease, concomitant malignancies, or chronic or acute lung disease were excluded.
The researchers obtained nasal epithelial cells from all participants, and exposed these cells to microplastic fibers created by the researchers in a laboratory setting. Overall, asthmatic and COPD airway epithelial cells showed a different reaction to microplastic fibers stimulation compared to healthy epithelial cells. The most significant response was associated with Th2 inflammation, modulation of stress response, and carcinogenesis. No differences in cytotoxic or minor inflammatory effects on epithelial cells of patients with asthma or COPD were noted compared with healthy controls.
In addition, flow cytometric analysis showed increased CD24+ epithelial cells in asthma patients compared to controls after microplastics exposure.
“Many of the gene candidates selected from RNA-Seq analysis are related to cancer (upregulated in many cancer types according to the literature), and the activation of CD24 on primarily ciliated asthmatic epithelial cells after microplastic stimulation further supports this theory,” the researchers wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of nasal rather than bronchial epithelial cells, which would have yielded more information, the researchers noted. Also, patients with severe asthma and COPD were excluded, they said, because of the impact of oral steroid and antibiotic use by this patient group on epithelial cell immunology that could bias the results of epithelial response to microplastic fiber exposure.
However, the results suggest that “the structural impairment of the airway epithelium in obstructive diseases enhances the impact of microplastic particles compared to healthy epithelium,” the researchers concluded.
Current and Future Implications
The current study is important in addressing the increasing environmental presence of microplastics and their potential impact on respiratory health, said Seyedmohammad Pourshahid, MD, assistant professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, in an interview.
“By examining how microplastics interact with airway epithelial cells, particularly in individuals with asthma and COPD, the research aims to elucidate mechanisms that could contribute to disease progression or exacerbation,” he said.
“The study’s findings that microplastics did not induce a strong inflammatory response, unlike other pollutants such as PM2.5, were unexpected; instead, microplastics appeared to influence pathways related to airway remodeling and oxidative stress,” Pourshahid noted. “This suggests that microplastics may affect respiratory health through mechanisms distinct from traditional pollutants,” he said.
“While preliminary, this research highlights the potential role of environmental microplastic exposure in respiratory diseases,” Pourshahid told this news organization. “Clinicians should be aware of emerging environmental factors that could impact patient health, especially in individuals with asthma and COPD. This awareness may inform patient education and advocacy for reducing exposure to airborne microplastics,” he said.
More studies are needed to explore the long-term effects of microplastic exposure on respiratory health, particularly in vulnerable populations, said Pourshahid. Research with in vivo models is necessary to confirm the findings and assess potential clinical implications to confirm these findings and assess potential clinical implications, he said. “Understanding the prevalence and sources of daily microplastic exposure can inform public health strategies to mitigate risks,” he added.
The study was supported by the Jakub Potocki Foundation. Paplińska-Goryca and Pourshahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were more vulnerable than healthy controls to epithelial cell changes caused by microplastics exposure, based on data from a new simulation study.
Microplastic fibers present in the ambient air can be inhaled into the lungs and promote a range of complications including oxidative stress, local injury, and cytotoxicity, but data on the effects of microplastic fibers on individuals with obstructive lung diseases are limited, wrote Magdalena Poplinska-Goryca, MD, of the Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland, and colleagues.
In a study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers identified 10 adults aged ≥ 18 years with asthma, eight adults aged ≥ 40 years with COPD, and 11 healthy adult controls. Individuals with more serious conditions such as severe asthma or COPD, unstable or uncontrolled disease, concomitant malignancies, or chronic or acute lung disease were excluded.
The researchers obtained nasal epithelial cells from all participants, and exposed these cells to microplastic fibers created by the researchers in a laboratory setting. Overall, asthmatic and COPD airway epithelial cells showed a different reaction to microplastic fibers stimulation compared to healthy epithelial cells. The most significant response was associated with Th2 inflammation, modulation of stress response, and carcinogenesis. No differences in cytotoxic or minor inflammatory effects on epithelial cells of patients with asthma or COPD were noted compared with healthy controls.
In addition, flow cytometric analysis showed increased CD24+ epithelial cells in asthma patients compared to controls after microplastics exposure.
“Many of the gene candidates selected from RNA-Seq analysis are related to cancer (upregulated in many cancer types according to the literature), and the activation of CD24 on primarily ciliated asthmatic epithelial cells after microplastic stimulation further supports this theory,” the researchers wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of nasal rather than bronchial epithelial cells, which would have yielded more information, the researchers noted. Also, patients with severe asthma and COPD were excluded, they said, because of the impact of oral steroid and antibiotic use by this patient group on epithelial cell immunology that could bias the results of epithelial response to microplastic fiber exposure.
However, the results suggest that “the structural impairment of the airway epithelium in obstructive diseases enhances the impact of microplastic particles compared to healthy epithelium,” the researchers concluded.
Current and Future Implications
The current study is important in addressing the increasing environmental presence of microplastics and their potential impact on respiratory health, said Seyedmohammad Pourshahid, MD, assistant professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, in an interview.
“By examining how microplastics interact with airway epithelial cells, particularly in individuals with asthma and COPD, the research aims to elucidate mechanisms that could contribute to disease progression or exacerbation,” he said.
“The study’s findings that microplastics did not induce a strong inflammatory response, unlike other pollutants such as PM2.5, were unexpected; instead, microplastics appeared to influence pathways related to airway remodeling and oxidative stress,” Pourshahid noted. “This suggests that microplastics may affect respiratory health through mechanisms distinct from traditional pollutants,” he said.
“While preliminary, this research highlights the potential role of environmental microplastic exposure in respiratory diseases,” Pourshahid told this news organization. “Clinicians should be aware of emerging environmental factors that could impact patient health, especially in individuals with asthma and COPD. This awareness may inform patient education and advocacy for reducing exposure to airborne microplastics,” he said.
More studies are needed to explore the long-term effects of microplastic exposure on respiratory health, particularly in vulnerable populations, said Pourshahid. Research with in vivo models is necessary to confirm the findings and assess potential clinical implications to confirm these findings and assess potential clinical implications, he said. “Understanding the prevalence and sources of daily microplastic exposure can inform public health strategies to mitigate risks,” he added.
The study was supported by the Jakub Potocki Foundation. Paplińska-Goryca and Pourshahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Individuals with asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) were more vulnerable than healthy controls to epithelial cell changes caused by microplastics exposure, based on data from a new simulation study.
Microplastic fibers present in the ambient air can be inhaled into the lungs and promote a range of complications including oxidative stress, local injury, and cytotoxicity, but data on the effects of microplastic fibers on individuals with obstructive lung diseases are limited, wrote Magdalena Poplinska-Goryca, MD, of the Medical University of Warsaw, Warsaw, Poland, and colleagues.
In a study published in Scientific Reports, the researchers identified 10 adults aged ≥ 18 years with asthma, eight adults aged ≥ 40 years with COPD, and 11 healthy adult controls. Individuals with more serious conditions such as severe asthma or COPD, unstable or uncontrolled disease, concomitant malignancies, or chronic or acute lung disease were excluded.
The researchers obtained nasal epithelial cells from all participants, and exposed these cells to microplastic fibers created by the researchers in a laboratory setting. Overall, asthmatic and COPD airway epithelial cells showed a different reaction to microplastic fibers stimulation compared to healthy epithelial cells. The most significant response was associated with Th2 inflammation, modulation of stress response, and carcinogenesis. No differences in cytotoxic or minor inflammatory effects on epithelial cells of patients with asthma or COPD were noted compared with healthy controls.
In addition, flow cytometric analysis showed increased CD24+ epithelial cells in asthma patients compared to controls after microplastics exposure.
“Many of the gene candidates selected from RNA-Seq analysis are related to cancer (upregulated in many cancer types according to the literature), and the activation of CD24 on primarily ciliated asthmatic epithelial cells after microplastic stimulation further supports this theory,” the researchers wrote.
The findings were limited by several factors including the use of nasal rather than bronchial epithelial cells, which would have yielded more information, the researchers noted. Also, patients with severe asthma and COPD were excluded, they said, because of the impact of oral steroid and antibiotic use by this patient group on epithelial cell immunology that could bias the results of epithelial response to microplastic fiber exposure.
However, the results suggest that “the structural impairment of the airway epithelium in obstructive diseases enhances the impact of microplastic particles compared to healthy epithelium,” the researchers concluded.
Current and Future Implications
The current study is important in addressing the increasing environmental presence of microplastics and their potential impact on respiratory health, said Seyedmohammad Pourshahid, MD, assistant professor of thoracic medicine and surgery at the Lewis Katz School of Medicine at Temple University, Philadelphia, in an interview.
“By examining how microplastics interact with airway epithelial cells, particularly in individuals with asthma and COPD, the research aims to elucidate mechanisms that could contribute to disease progression or exacerbation,” he said.
“The study’s findings that microplastics did not induce a strong inflammatory response, unlike other pollutants such as PM2.5, were unexpected; instead, microplastics appeared to influence pathways related to airway remodeling and oxidative stress,” Pourshahid noted. “This suggests that microplastics may affect respiratory health through mechanisms distinct from traditional pollutants,” he said.
“While preliminary, this research highlights the potential role of environmental microplastic exposure in respiratory diseases,” Pourshahid told this news organization. “Clinicians should be aware of emerging environmental factors that could impact patient health, especially in individuals with asthma and COPD. This awareness may inform patient education and advocacy for reducing exposure to airborne microplastics,” he said.
More studies are needed to explore the long-term effects of microplastic exposure on respiratory health, particularly in vulnerable populations, said Pourshahid. Research with in vivo models is necessary to confirm the findings and assess potential clinical implications to confirm these findings and assess potential clinical implications, he said. “Understanding the prevalence and sources of daily microplastic exposure can inform public health strategies to mitigate risks,” he added.
The study was supported by the Jakub Potocki Foundation. Paplińska-Goryca and Pourshahid had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article first appeared on Medscape.com.
Early-Onset Asthma May Slow Memory Development
Children with asthma scored significantly lower than those without asthma on measures of episodic memory, based on longitudinal data from nearly 500 individuals.
Animal models have shown associations between asthma and memory problems, but data for children are lacking, wrote Nicholas J. Christopher-Hayes, MA, of the University of California, Davis, and colleagues.
“Asthma is very frequent among children, and there is mounting evidence from rodent models that asthma may result in neural injury in the hippocampus, which in turn may cause memory loss,” Christopher-Hayes said in an interview. “Although there is also a good amount of research with older adults, very little research has been done with children, the period that is most frequently linked to asthma onset,” he said. Therefore, the researchers leveraged a large national study on child development to examine development of memory as a function of asthma exposure.
In this study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers conducted both a longitudinal and cross-sectional analysis of data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study, which began in 2015. Children were enrolled at ages 9-10 years with a follow-up assessment 1-2 years later.
The participants were categorized as early childhood-onset asthma (asthma at baseline and follow-up), later childhood-onset asthma (asthma at follow-up only), or no asthma history. The primary outcome of the longitudinal analysis was episodic memory. Approximately half of the participants were boys, and slightly more than half were White.
Overall, those with early-onset asthma showed significantly lower rates of longitudinal memory improvements at follow-up compared with the comparison group (P < .01).
Developmental memory improvement in children with later-onset asthma was not significantly different from the control individuals.
Secondary outcomes included processing speed and inhibition, and attention. In a cross-sectional analysis with a larger sample of 2062 children from the same database (1031 with any asthma), those with asthma scored significantly lower on measures not only of episodic memory but also processing speed and inhibition/attention than children with no asthma, with P values of .04, .01, and .02, respectively.
The results were limited by several factors, including the reliance on parent reports for indicators of asthma and the lack of data on the potential effect of prescription corticosteroid use on neurocognitive development, the researchers noted.
The mechanism behind the association remains unclear; the inflammation associated with asthma may disrupt neural processing and manifest as cognitive dysfunction, as has been seen in rodent models of asthma, the researchers wrote. “It is possible that associations between asthma and developmental trajectories emerge earlier for memory, perhaps due to its sensitivity to subtle hippocampal injury,” they noted.
Longer follow-up studies are needed to fully understand how childhood asthma predicts memory declines or difficulties in childhood and beyond, said Christopher-Hayes. “We also need additional studies to understand why children who were diagnosed earlier and had asthma for longer seem to be particularly affected,” he said.
The results of this study were consistent with previous findings and therefore not surprising, senior author Simona Ghetti, PhD, a professor of psychology at the University of California, Davis, said in an interview. However, the finding that the extent of exposure to asthma was associated with slower memory improvement in childhood was striking, she said. That children with an earlier asthma onset who had disease indicators for a longer period showed a slower development of memory over time, suggests that asthma exposure may affect the developmental trajectory of memory, Ghetti noted.
“Recommendations to clinicians are premature because we need a better understanding of the boundary conditions, such as the minimal level of asthma exposure that might generate memory difficulties,” said Ghetti.
“Nevertheless, our results underscore the importance of looking at asthma as a potential source of cognitive difficulty in children,” she said.
Asthma’s Extensive Effect
Evidence is mounting that a diagnosis of asthma may have implications outside the pulmonary system, Diego J. Maselli, MD, professor and chief of the Division of Pulmonary Diseases & Critical Care at UT Health, San Antonio, said in an interview.
“Asthmatics may be at risk of nasal polyps, allergic rhinitis, and other allergic conditions, but there is emerging of evidence inflammation associated with asthma may affect other organ systems,” said Maselli, who was not involved in the study.
“For example, chronic inflammation in asthmatics may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Although less is known about the effects of asthma on the nervous system, animal models suggest that inflammation associated with asthma may result in neuronal injury and potential effects on memory, said Maselli.
The findings of this study provide evidence of potential detrimental effects on the memory of children with asthma but should be interpreted with caution, Maselli said. “Children with chronic medical conditions may have an inherent disadvantage compared with their peers due to the burden of their disease, medication utilization and side effects, absenteeism from school, physical limitations, and other disease-specific circumstances,” he noted.
“Uncontrolled asthma, in particular, has strong links to low socioeconomic factors that are closely tied to access to adequate medical care, nutrition, educational institutions, and other relevant contributors to normal cognitive development,” Maselli said. Although the authors account for some of these socioeconomic factors by evaluating income and race, other variables may have influenced the results, he added.
Overall, this study’s findings suggested that the diagnosis of asthma in children may be associated with memory deficits and may influence neurodevelopment; however, more research is needed to determine whether the findings are replicated in other cohorts, said Maselli. “In particular, evaluating the effects of the severity of asthma and different asthma endotypes would be crucial to identify children with a higher risk of memory or cognitive deficits and confirm these associations,” he said.
This study was funded by the Memory and Plasticity Program at the University of California, Davis, and by a Learning, Memory, and Plasticity Training Program Fellowship grant from the National Institutes of Health. The researchers and Maselli had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with asthma scored significantly lower than those without asthma on measures of episodic memory, based on longitudinal data from nearly 500 individuals.
Animal models have shown associations between asthma and memory problems, but data for children are lacking, wrote Nicholas J. Christopher-Hayes, MA, of the University of California, Davis, and colleagues.
“Asthma is very frequent among children, and there is mounting evidence from rodent models that asthma may result in neural injury in the hippocampus, which in turn may cause memory loss,” Christopher-Hayes said in an interview. “Although there is also a good amount of research with older adults, very little research has been done with children, the period that is most frequently linked to asthma onset,” he said. Therefore, the researchers leveraged a large national study on child development to examine development of memory as a function of asthma exposure.
In this study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers conducted both a longitudinal and cross-sectional analysis of data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study, which began in 2015. Children were enrolled at ages 9-10 years with a follow-up assessment 1-2 years later.
The participants were categorized as early childhood-onset asthma (asthma at baseline and follow-up), later childhood-onset asthma (asthma at follow-up only), or no asthma history. The primary outcome of the longitudinal analysis was episodic memory. Approximately half of the participants were boys, and slightly more than half were White.
Overall, those with early-onset asthma showed significantly lower rates of longitudinal memory improvements at follow-up compared with the comparison group (P < .01).
Developmental memory improvement in children with later-onset asthma was not significantly different from the control individuals.
Secondary outcomes included processing speed and inhibition, and attention. In a cross-sectional analysis with a larger sample of 2062 children from the same database (1031 with any asthma), those with asthma scored significantly lower on measures not only of episodic memory but also processing speed and inhibition/attention than children with no asthma, with P values of .04, .01, and .02, respectively.
The results were limited by several factors, including the reliance on parent reports for indicators of asthma and the lack of data on the potential effect of prescription corticosteroid use on neurocognitive development, the researchers noted.
The mechanism behind the association remains unclear; the inflammation associated with asthma may disrupt neural processing and manifest as cognitive dysfunction, as has been seen in rodent models of asthma, the researchers wrote. “It is possible that associations between asthma and developmental trajectories emerge earlier for memory, perhaps due to its sensitivity to subtle hippocampal injury,” they noted.
Longer follow-up studies are needed to fully understand how childhood asthma predicts memory declines or difficulties in childhood and beyond, said Christopher-Hayes. “We also need additional studies to understand why children who were diagnosed earlier and had asthma for longer seem to be particularly affected,” he said.
The results of this study were consistent with previous findings and therefore not surprising, senior author Simona Ghetti, PhD, a professor of psychology at the University of California, Davis, said in an interview. However, the finding that the extent of exposure to asthma was associated with slower memory improvement in childhood was striking, she said. That children with an earlier asthma onset who had disease indicators for a longer period showed a slower development of memory over time, suggests that asthma exposure may affect the developmental trajectory of memory, Ghetti noted.
“Recommendations to clinicians are premature because we need a better understanding of the boundary conditions, such as the minimal level of asthma exposure that might generate memory difficulties,” said Ghetti.
“Nevertheless, our results underscore the importance of looking at asthma as a potential source of cognitive difficulty in children,” she said.
Asthma’s Extensive Effect
Evidence is mounting that a diagnosis of asthma may have implications outside the pulmonary system, Diego J. Maselli, MD, professor and chief of the Division of Pulmonary Diseases & Critical Care at UT Health, San Antonio, said in an interview.
“Asthmatics may be at risk of nasal polyps, allergic rhinitis, and other allergic conditions, but there is emerging of evidence inflammation associated with asthma may affect other organ systems,” said Maselli, who was not involved in the study.
“For example, chronic inflammation in asthmatics may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Although less is known about the effects of asthma on the nervous system, animal models suggest that inflammation associated with asthma may result in neuronal injury and potential effects on memory, said Maselli.
The findings of this study provide evidence of potential detrimental effects on the memory of children with asthma but should be interpreted with caution, Maselli said. “Children with chronic medical conditions may have an inherent disadvantage compared with their peers due to the burden of their disease, medication utilization and side effects, absenteeism from school, physical limitations, and other disease-specific circumstances,” he noted.
“Uncontrolled asthma, in particular, has strong links to low socioeconomic factors that are closely tied to access to adequate medical care, nutrition, educational institutions, and other relevant contributors to normal cognitive development,” Maselli said. Although the authors account for some of these socioeconomic factors by evaluating income and race, other variables may have influenced the results, he added.
Overall, this study’s findings suggested that the diagnosis of asthma in children may be associated with memory deficits and may influence neurodevelopment; however, more research is needed to determine whether the findings are replicated in other cohorts, said Maselli. “In particular, evaluating the effects of the severity of asthma and different asthma endotypes would be crucial to identify children with a higher risk of memory or cognitive deficits and confirm these associations,” he said.
This study was funded by the Memory and Plasticity Program at the University of California, Davis, and by a Learning, Memory, and Plasticity Training Program Fellowship grant from the National Institutes of Health. The researchers and Maselli had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Children with asthma scored significantly lower than those without asthma on measures of episodic memory, based on longitudinal data from nearly 500 individuals.
Animal models have shown associations between asthma and memory problems, but data for children are lacking, wrote Nicholas J. Christopher-Hayes, MA, of the University of California, Davis, and colleagues.
“Asthma is very frequent among children, and there is mounting evidence from rodent models that asthma may result in neural injury in the hippocampus, which in turn may cause memory loss,” Christopher-Hayes said in an interview. “Although there is also a good amount of research with older adults, very little research has been done with children, the period that is most frequently linked to asthma onset,” he said. Therefore, the researchers leveraged a large national study on child development to examine development of memory as a function of asthma exposure.
In this study published in JAMA Network Open, the researchers conducted both a longitudinal and cross-sectional analysis of data from the Adolescent Brain Cognitive Development Study, which began in 2015. Children were enrolled at ages 9-10 years with a follow-up assessment 1-2 years later.
The participants were categorized as early childhood-onset asthma (asthma at baseline and follow-up), later childhood-onset asthma (asthma at follow-up only), or no asthma history. The primary outcome of the longitudinal analysis was episodic memory. Approximately half of the participants were boys, and slightly more than half were White.
Overall, those with early-onset asthma showed significantly lower rates of longitudinal memory improvements at follow-up compared with the comparison group (P < .01).
Developmental memory improvement in children with later-onset asthma was not significantly different from the control individuals.
Secondary outcomes included processing speed and inhibition, and attention. In a cross-sectional analysis with a larger sample of 2062 children from the same database (1031 with any asthma), those with asthma scored significantly lower on measures not only of episodic memory but also processing speed and inhibition/attention than children with no asthma, with P values of .04, .01, and .02, respectively.
The results were limited by several factors, including the reliance on parent reports for indicators of asthma and the lack of data on the potential effect of prescription corticosteroid use on neurocognitive development, the researchers noted.
The mechanism behind the association remains unclear; the inflammation associated with asthma may disrupt neural processing and manifest as cognitive dysfunction, as has been seen in rodent models of asthma, the researchers wrote. “It is possible that associations between asthma and developmental trajectories emerge earlier for memory, perhaps due to its sensitivity to subtle hippocampal injury,” they noted.
Longer follow-up studies are needed to fully understand how childhood asthma predicts memory declines or difficulties in childhood and beyond, said Christopher-Hayes. “We also need additional studies to understand why children who were diagnosed earlier and had asthma for longer seem to be particularly affected,” he said.
The results of this study were consistent with previous findings and therefore not surprising, senior author Simona Ghetti, PhD, a professor of psychology at the University of California, Davis, said in an interview. However, the finding that the extent of exposure to asthma was associated with slower memory improvement in childhood was striking, she said. That children with an earlier asthma onset who had disease indicators for a longer period showed a slower development of memory over time, suggests that asthma exposure may affect the developmental trajectory of memory, Ghetti noted.
“Recommendations to clinicians are premature because we need a better understanding of the boundary conditions, such as the minimal level of asthma exposure that might generate memory difficulties,” said Ghetti.
“Nevertheless, our results underscore the importance of looking at asthma as a potential source of cognitive difficulty in children,” she said.
Asthma’s Extensive Effect
Evidence is mounting that a diagnosis of asthma may have implications outside the pulmonary system, Diego J. Maselli, MD, professor and chief of the Division of Pulmonary Diseases & Critical Care at UT Health, San Antonio, said in an interview.
“Asthmatics may be at risk of nasal polyps, allergic rhinitis, and other allergic conditions, but there is emerging of evidence inflammation associated with asthma may affect other organ systems,” said Maselli, who was not involved in the study.
“For example, chronic inflammation in asthmatics may increase the risk of cardiovascular disease,” he said.
Although less is known about the effects of asthma on the nervous system, animal models suggest that inflammation associated with asthma may result in neuronal injury and potential effects on memory, said Maselli.
The findings of this study provide evidence of potential detrimental effects on the memory of children with asthma but should be interpreted with caution, Maselli said. “Children with chronic medical conditions may have an inherent disadvantage compared with their peers due to the burden of their disease, medication utilization and side effects, absenteeism from school, physical limitations, and other disease-specific circumstances,” he noted.
“Uncontrolled asthma, in particular, has strong links to low socioeconomic factors that are closely tied to access to adequate medical care, nutrition, educational institutions, and other relevant contributors to normal cognitive development,” Maselli said. Although the authors account for some of these socioeconomic factors by evaluating income and race, other variables may have influenced the results, he added.
Overall, this study’s findings suggested that the diagnosis of asthma in children may be associated with memory deficits and may influence neurodevelopment; however, more research is needed to determine whether the findings are replicated in other cohorts, said Maselli. “In particular, evaluating the effects of the severity of asthma and different asthma endotypes would be crucial to identify children with a higher risk of memory or cognitive deficits and confirm these associations,” he said.
This study was funded by the Memory and Plasticity Program at the University of California, Davis, and by a Learning, Memory, and Plasticity Training Program Fellowship grant from the National Institutes of Health. The researchers and Maselli had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Highly Contagious Norovirus Cases Spike This Season
Current data from the CDC’s NoroSTAT monitoring system show 495 reported outbreaks during the period from August 1, 2024, to December 11, 2024, compared with 363 outbreaks during the same period last year. In addition, the total number of norovirus outbreaks in the current season are higher than those reported in the seasonal years: 2012-2020 and 2021-2024.
Circulating strains of norovirus change over time, which can affect disease burden and potential disease severity, Sara Mirza, MD, an epidemiologist in the CDC’s Division of Viral Diseases, said in an interview.
The numbers for the 2024 norovirus season (considered approximately November to April) have reached or exceeded the case numbers seen before the COVID-19 pandemic, Mirza said.
The increase in cases may be caused in part by a new predominant strain of norovirus. “For the fall/winter of 2024-2025 season, genogroup 2, genotype 17, known as GII.17, has become the most detected genotype (strain) in the US among laboratory confirmed outbreaks reported to CDC,” said Mirza. “At this time, there is no indication that GII.17 causes more severe illness or affects one population more than another, but we are continuing to conduct surveillance to assess,” she added.
Clinical Takeaways
“Norovirus affects all ages, but young children and older adults are most at risk from more severe outcomes,” said Mirza.
“Clinicians treating older patients for acute gastroenteritis should be aware of these elevated risks and be sure to include norovirus as a potentially serious diagnosis, particularly in vulnerable patients with other diseases and those living in congregate settings, such as nursing homes,” she said.
When treating a patient with norovirus during an outbreak, use soap and water for hand hygiene after caring for patients with suspected or confirmed norovirus gastroenteritis, said Mirza. If norovirus infection is suspected, PPE use is recommended for individuals in the patient care area, she added.
Although state, local, and territorial health departments are not required to report individual cases of norovirus to the CDC, healthcare providers are encouraged to report all outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis, including suspected outbreaks of norovirus, to the appropriate state, local, or territorial health department, said Mirza. “Health departments are encouraged to report all suspected and confirmed norovirus outbreaks through the National Outbreak Reporting System and CaliciNet,” she added.
“Infection control measures, such as thorough hand washing, cleaning and disinfecting surfaces with bleach, and patient isolation and contact precautions in congregate or healthcare settings are the best ways to prevent norovirus and keep it from spreading to others,” Mirza said.
Remind patients that alcohol-based hand sanitizer is ineffective against norovirus, because the virus’s protective protein shell prevents the alcohol from penetrating and inactivating the virus, Mirza emphasized. “Soap and water work to remove germs from hands,” she said.
Cruise Ship Considerations
Cruise ships continue to be sources of increased risk for norovirus, according the CDC. The CDC’s Vessel Sanitation Program (VSP) was created to help the cruise industry prevent public health issues such as norovirus outbreaks, and to provide guidance for actions to take in the event of outbreaks.
For example, the most recently reported outbreak of norovirus on a cruise ship reported to the VSP was January 4, 2025, and occurred on a Holland America cruise from December 30, 2024, through January 8, 2025. Overall, 4.0% of passengers and 1.0% of crew members reported illness. Following VSP guidance, the ship reported increased cleaning and disinfection procedures and the collection of stool specimens for testing, and isolation of ill passengers and crew.
Clinical Perspective
In clinical practice, the number of norovirus cases is significantly exceeding previous years, and the trend seems to be consistent nationwide, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
“Norovirus is incredibly contagious and spreads very quickly, which is how you get entire cruise ships infected at once,” he said. Norovirus is notoriously difficult to disinfect or kill, he added.
One possible contributor to the surge in cases is increased travel, especially during the holiday season, when people are coming together and sharing food, Cennimo noted. “We have seen many infections such as pneumonia return to levels approaching the period before the COVID-19 pandemic,” he said.
For norovirus prevention, strict attention to sanitation and handwashing is a must at home or when traveling, said Cennimo. For clinicians, it is important to report outbreaks of GI illness so appropriate control measures can be taken, he said.
Visit the CDC’s website on norovirus prevention for more information.
Mirza and Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Current data from the CDC’s NoroSTAT monitoring system show 495 reported outbreaks during the period from August 1, 2024, to December 11, 2024, compared with 363 outbreaks during the same period last year. In addition, the total number of norovirus outbreaks in the current season are higher than those reported in the seasonal years: 2012-2020 and 2021-2024.
Circulating strains of norovirus change over time, which can affect disease burden and potential disease severity, Sara Mirza, MD, an epidemiologist in the CDC’s Division of Viral Diseases, said in an interview.
The numbers for the 2024 norovirus season (considered approximately November to April) have reached or exceeded the case numbers seen before the COVID-19 pandemic, Mirza said.
The increase in cases may be caused in part by a new predominant strain of norovirus. “For the fall/winter of 2024-2025 season, genogroup 2, genotype 17, known as GII.17, has become the most detected genotype (strain) in the US among laboratory confirmed outbreaks reported to CDC,” said Mirza. “At this time, there is no indication that GII.17 causes more severe illness or affects one population more than another, but we are continuing to conduct surveillance to assess,” she added.
Clinical Takeaways
“Norovirus affects all ages, but young children and older adults are most at risk from more severe outcomes,” said Mirza.
“Clinicians treating older patients for acute gastroenteritis should be aware of these elevated risks and be sure to include norovirus as a potentially serious diagnosis, particularly in vulnerable patients with other diseases and those living in congregate settings, such as nursing homes,” she said.
When treating a patient with norovirus during an outbreak, use soap and water for hand hygiene after caring for patients with suspected or confirmed norovirus gastroenteritis, said Mirza. If norovirus infection is suspected, PPE use is recommended for individuals in the patient care area, she added.
Although state, local, and territorial health departments are not required to report individual cases of norovirus to the CDC, healthcare providers are encouraged to report all outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis, including suspected outbreaks of norovirus, to the appropriate state, local, or territorial health department, said Mirza. “Health departments are encouraged to report all suspected and confirmed norovirus outbreaks through the National Outbreak Reporting System and CaliciNet,” she added.
“Infection control measures, such as thorough hand washing, cleaning and disinfecting surfaces with bleach, and patient isolation and contact precautions in congregate or healthcare settings are the best ways to prevent norovirus and keep it from spreading to others,” Mirza said.
Remind patients that alcohol-based hand sanitizer is ineffective against norovirus, because the virus’s protective protein shell prevents the alcohol from penetrating and inactivating the virus, Mirza emphasized. “Soap and water work to remove germs from hands,” she said.
Cruise Ship Considerations
Cruise ships continue to be sources of increased risk for norovirus, according the CDC. The CDC’s Vessel Sanitation Program (VSP) was created to help the cruise industry prevent public health issues such as norovirus outbreaks, and to provide guidance for actions to take in the event of outbreaks.
For example, the most recently reported outbreak of norovirus on a cruise ship reported to the VSP was January 4, 2025, and occurred on a Holland America cruise from December 30, 2024, through January 8, 2025. Overall, 4.0% of passengers and 1.0% of crew members reported illness. Following VSP guidance, the ship reported increased cleaning and disinfection procedures and the collection of stool specimens for testing, and isolation of ill passengers and crew.
Clinical Perspective
In clinical practice, the number of norovirus cases is significantly exceeding previous years, and the trend seems to be consistent nationwide, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
“Norovirus is incredibly contagious and spreads very quickly, which is how you get entire cruise ships infected at once,” he said. Norovirus is notoriously difficult to disinfect or kill, he added.
One possible contributor to the surge in cases is increased travel, especially during the holiday season, when people are coming together and sharing food, Cennimo noted. “We have seen many infections such as pneumonia return to levels approaching the period before the COVID-19 pandemic,” he said.
For norovirus prevention, strict attention to sanitation and handwashing is a must at home or when traveling, said Cennimo. For clinicians, it is important to report outbreaks of GI illness so appropriate control measures can be taken, he said.
Visit the CDC’s website on norovirus prevention for more information.
Mirza and Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
Current data from the CDC’s NoroSTAT monitoring system show 495 reported outbreaks during the period from August 1, 2024, to December 11, 2024, compared with 363 outbreaks during the same period last year. In addition, the total number of norovirus outbreaks in the current season are higher than those reported in the seasonal years: 2012-2020 and 2021-2024.
Circulating strains of norovirus change over time, which can affect disease burden and potential disease severity, Sara Mirza, MD, an epidemiologist in the CDC’s Division of Viral Diseases, said in an interview.
The numbers for the 2024 norovirus season (considered approximately November to April) have reached or exceeded the case numbers seen before the COVID-19 pandemic, Mirza said.
The increase in cases may be caused in part by a new predominant strain of norovirus. “For the fall/winter of 2024-2025 season, genogroup 2, genotype 17, known as GII.17, has become the most detected genotype (strain) in the US among laboratory confirmed outbreaks reported to CDC,” said Mirza. “At this time, there is no indication that GII.17 causes more severe illness or affects one population more than another, but we are continuing to conduct surveillance to assess,” she added.
Clinical Takeaways
“Norovirus affects all ages, but young children and older adults are most at risk from more severe outcomes,” said Mirza.
“Clinicians treating older patients for acute gastroenteritis should be aware of these elevated risks and be sure to include norovirus as a potentially serious diagnosis, particularly in vulnerable patients with other diseases and those living in congregate settings, such as nursing homes,” she said.
When treating a patient with norovirus during an outbreak, use soap and water for hand hygiene after caring for patients with suspected or confirmed norovirus gastroenteritis, said Mirza. If norovirus infection is suspected, PPE use is recommended for individuals in the patient care area, she added.
Although state, local, and territorial health departments are not required to report individual cases of norovirus to the CDC, healthcare providers are encouraged to report all outbreaks of acute gastroenteritis, including suspected outbreaks of norovirus, to the appropriate state, local, or territorial health department, said Mirza. “Health departments are encouraged to report all suspected and confirmed norovirus outbreaks through the National Outbreak Reporting System and CaliciNet,” she added.
“Infection control measures, such as thorough hand washing, cleaning and disinfecting surfaces with bleach, and patient isolation and contact precautions in congregate or healthcare settings are the best ways to prevent norovirus and keep it from spreading to others,” Mirza said.
Remind patients that alcohol-based hand sanitizer is ineffective against norovirus, because the virus’s protective protein shell prevents the alcohol from penetrating and inactivating the virus, Mirza emphasized. “Soap and water work to remove germs from hands,” she said.
Cruise Ship Considerations
Cruise ships continue to be sources of increased risk for norovirus, according the CDC. The CDC’s Vessel Sanitation Program (VSP) was created to help the cruise industry prevent public health issues such as norovirus outbreaks, and to provide guidance for actions to take in the event of outbreaks.
For example, the most recently reported outbreak of norovirus on a cruise ship reported to the VSP was January 4, 2025, and occurred on a Holland America cruise from December 30, 2024, through January 8, 2025. Overall, 4.0% of passengers and 1.0% of crew members reported illness. Following VSP guidance, the ship reported increased cleaning and disinfection procedures and the collection of stool specimens for testing, and isolation of ill passengers and crew.
Clinical Perspective
In clinical practice, the number of norovirus cases is significantly exceeding previous years, and the trend seems to be consistent nationwide, David J. Cennimo, MD, associate professor of medicine and pediatrics at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School, Newark, New Jersey, said in an interview.
“Norovirus is incredibly contagious and spreads very quickly, which is how you get entire cruise ships infected at once,” he said. Norovirus is notoriously difficult to disinfect or kill, he added.
One possible contributor to the surge in cases is increased travel, especially during the holiday season, when people are coming together and sharing food, Cennimo noted. “We have seen many infections such as pneumonia return to levels approaching the period before the COVID-19 pandemic,” he said.
For norovirus prevention, strict attention to sanitation and handwashing is a must at home or when traveling, said Cennimo. For clinicians, it is important to report outbreaks of GI illness so appropriate control measures can be taken, he said.
Visit the CDC’s website on norovirus prevention for more information.
Mirza and Cennimo had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
First Human Bird Flu Death Confirmed in US; Overall Risk Remains Low
The first human patient in the United States with a confirmed case of avian influenza has died, according to a press release from the Louisiana Department of Health. The individual was older than 65 years and had underlying medical conditions and remains the only known human case in the state.
The patient contracted highly pathogenic avian influenza, also known as H5N1, through exposure to wild birds and a noncommercial backyard flock, according to the release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) conducted genetic sequencing of specimens of the virus collected from the Louisiana patient. The agency compared the sequences with sequences from dairy cows, wild birds, and poultry in various areas of the United States that were infected with the H5N1 virus.
The Louisiana patient was infected with the D1.1 genotype of the H5N1 virus. Although D1.1 is related to other D1.1 viruses found in recent human cases in Washington State and British Columbia, Canada, it is distinct from the widely spreading B3.13 genotype that has caused H5N1 outbreaks in dairy cows, poultry, and other animals and has been linked to sporadic human cases in the United States, according to the CDC.
Despite evidence of some changes in the virus between the Louisiana patient and samples from poultry on the patient’s property, “these changes would be more concerning if found in animal hosts or in early stages of infection,” according to the CDC. The CDC and the Louisiana Department of Health are conducting additional sequencing to facilitate further analysis.
In the meantime, the risk to the general public for H5N1 remains low, but individuals who work with or have recreational exposure to birds, poultry, or cows remain at increased risk.
The CDC and the Louisiana Department of Health advise individuals to reduce the risk for H5N1 exposure by avoiding direct contact with wild birds or other animals infected or possibly infected with the virus, avoiding any contact with dead animals, and keeping pets away from sick or dead animals and their feces. Additional safety measures include avoiding uncooked food products such as unpasteurized raw milk or cheese from animals with suspected or confirmed infections and reporting sick or dead birds or animals to the US Department of Agriculture by calling 1-866-536-7593 or the Louisiana Department of Agriculture and Forestry Diagnostic Lab by calling 318-927-3441.
The CDC advises clinicians to consider H5N1 in patients presenting with conjunctivitis or signs of acute respiratory illness and a history of high-risk exposure, including handling sick or dead animals, notably birds and livestock, within 10 days before the onset of symptoms. Other risk factors include consuming uncooked or undercooked food, direct contact with areas contaminated with feces, direct contact with unpasteurized milk or other dairy products or with parts of potentially infected animals, and prolonged exposure to infected animals in a confined space.
Clinical symptoms also may include gastrointestinal complaints such as diarrhea, as well as fatigue, arthralgia, and headache. Patients with more severe H5N1 may experience shortness of breath, altered mental state, and seizures, and serious complications of the virus include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiorgan failure, and sepsis, according to the CDC.
Clinicians who suspect H5N1 cases should contact their local public health departments. The CDC offers additional advice on evaluating and managing patients with novel influenza A viruses.
A Clinician’s Take
“Some symptoms of avian flu include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, fatigue, body aches or eye redness or irritation,” Shirin A. Mazumder, MD, associate professor and infectious disease specialist at The University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, said in an interview. “The timing to the development of symptoms after exposure is typically within 10 days. Avian influenza should be considered when individuals develop symptoms with a relevant exposure history,” she said.
Whenever possible, avoidance of sick or dead birds and other animals is ideal, but for those who must have contact with sick or dead birds, poultry, or other animals, personal protective equipment (PPE) including a respirator, goggles, and disposable gloves is recommended, said Mazumder.
“For those working in high-exposure settings, additional PPE including boots or boot covers, hair cover, and fluid-resistant coveralls are recommended,” she said. “Other protective measures include avoiding touching surfaces or materials contaminated with feces, mucus, and saliva from infected animals and avoid[ing] the consumption of raw milk, raw milk products, and undercooked meat from infected animals,” she added.
Hunters handling wild game should dress birds in the field, practice good hand hygiene, and use a respirator or well-fitting mask and gloves when handling the animals to help prevent disease, said Mazumder.
In addition, those working with confirmed or suspected H5N1 cases should monitor themselves for symptoms, said Mazumder. “Those who become ill within 10 days of exposure to an infected animal or source should isolate from household members and avoid going to work or school until infection is excluded. It is important to reach out to a healthcare professional if you think you may have been exposed or if you think you are infected,” she said.
There is no currently available vaccine for H5N1 infection, but oseltamivir can be used for chemoprophylaxis and treatment, said Mazumder. “The seasonal flu vaccine does not protect against avian influenza; however, it is still important to ensure that you are up to date on the latest flu vaccine to prevent the possibility of a coinfection with seasonal flu and avian flu,” she emphasized.
More research is needed to better understand how the influenza virus is transmitted, said Mazumder. “The potential for the virus to evolve and mutate, and how it affects different hosts, are all factors that can impact public health decisions,” she said. “In addition, further research into finding a vaccine and improving surveillance methods are necessary for disease prevention,” she said.
Mazumder had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The first human patient in the United States with a confirmed case of avian influenza has died, according to a press release from the Louisiana Department of Health. The individual was older than 65 years and had underlying medical conditions and remains the only known human case in the state.
The patient contracted highly pathogenic avian influenza, also known as H5N1, through exposure to wild birds and a noncommercial backyard flock, according to the release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) conducted genetic sequencing of specimens of the virus collected from the Louisiana patient. The agency compared the sequences with sequences from dairy cows, wild birds, and poultry in various areas of the United States that were infected with the H5N1 virus.
The Louisiana patient was infected with the D1.1 genotype of the H5N1 virus. Although D1.1 is related to other D1.1 viruses found in recent human cases in Washington State and British Columbia, Canada, it is distinct from the widely spreading B3.13 genotype that has caused H5N1 outbreaks in dairy cows, poultry, and other animals and has been linked to sporadic human cases in the United States, according to the CDC.
Despite evidence of some changes in the virus between the Louisiana patient and samples from poultry on the patient’s property, “these changes would be more concerning if found in animal hosts or in early stages of infection,” according to the CDC. The CDC and the Louisiana Department of Health are conducting additional sequencing to facilitate further analysis.
In the meantime, the risk to the general public for H5N1 remains low, but individuals who work with or have recreational exposure to birds, poultry, or cows remain at increased risk.
The CDC and the Louisiana Department of Health advise individuals to reduce the risk for H5N1 exposure by avoiding direct contact with wild birds or other animals infected or possibly infected with the virus, avoiding any contact with dead animals, and keeping pets away from sick or dead animals and their feces. Additional safety measures include avoiding uncooked food products such as unpasteurized raw milk or cheese from animals with suspected or confirmed infections and reporting sick or dead birds or animals to the US Department of Agriculture by calling 1-866-536-7593 or the Louisiana Department of Agriculture and Forestry Diagnostic Lab by calling 318-927-3441.
The CDC advises clinicians to consider H5N1 in patients presenting with conjunctivitis or signs of acute respiratory illness and a history of high-risk exposure, including handling sick or dead animals, notably birds and livestock, within 10 days before the onset of symptoms. Other risk factors include consuming uncooked or undercooked food, direct contact with areas contaminated with feces, direct contact with unpasteurized milk or other dairy products or with parts of potentially infected animals, and prolonged exposure to infected animals in a confined space.
Clinical symptoms also may include gastrointestinal complaints such as diarrhea, as well as fatigue, arthralgia, and headache. Patients with more severe H5N1 may experience shortness of breath, altered mental state, and seizures, and serious complications of the virus include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiorgan failure, and sepsis, according to the CDC.
Clinicians who suspect H5N1 cases should contact their local public health departments. The CDC offers additional advice on evaluating and managing patients with novel influenza A viruses.
A Clinician’s Take
“Some symptoms of avian flu include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, fatigue, body aches or eye redness or irritation,” Shirin A. Mazumder, MD, associate professor and infectious disease specialist at The University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, said in an interview. “The timing to the development of symptoms after exposure is typically within 10 days. Avian influenza should be considered when individuals develop symptoms with a relevant exposure history,” she said.
Whenever possible, avoidance of sick or dead birds and other animals is ideal, but for those who must have contact with sick or dead birds, poultry, or other animals, personal protective equipment (PPE) including a respirator, goggles, and disposable gloves is recommended, said Mazumder.
“For those working in high-exposure settings, additional PPE including boots or boot covers, hair cover, and fluid-resistant coveralls are recommended,” she said. “Other protective measures include avoiding touching surfaces or materials contaminated with feces, mucus, and saliva from infected animals and avoid[ing] the consumption of raw milk, raw milk products, and undercooked meat from infected animals,” she added.
Hunters handling wild game should dress birds in the field, practice good hand hygiene, and use a respirator or well-fitting mask and gloves when handling the animals to help prevent disease, said Mazumder.
In addition, those working with confirmed or suspected H5N1 cases should monitor themselves for symptoms, said Mazumder. “Those who become ill within 10 days of exposure to an infected animal or source should isolate from household members and avoid going to work or school until infection is excluded. It is important to reach out to a healthcare professional if you think you may have been exposed or if you think you are infected,” she said.
There is no currently available vaccine for H5N1 infection, but oseltamivir can be used for chemoprophylaxis and treatment, said Mazumder. “The seasonal flu vaccine does not protect against avian influenza; however, it is still important to ensure that you are up to date on the latest flu vaccine to prevent the possibility of a coinfection with seasonal flu and avian flu,” she emphasized.
More research is needed to better understand how the influenza virus is transmitted, said Mazumder. “The potential for the virus to evolve and mutate, and how it affects different hosts, are all factors that can impact public health decisions,” she said. “In addition, further research into finding a vaccine and improving surveillance methods are necessary for disease prevention,” she said.
Mazumder had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.
The first human patient in the United States with a confirmed case of avian influenza has died, according to a press release from the Louisiana Department of Health. The individual was older than 65 years and had underlying medical conditions and remains the only known human case in the state.
The patient contracted highly pathogenic avian influenza, also known as H5N1, through exposure to wild birds and a noncommercial backyard flock, according to the release.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) conducted genetic sequencing of specimens of the virus collected from the Louisiana patient. The agency compared the sequences with sequences from dairy cows, wild birds, and poultry in various areas of the United States that were infected with the H5N1 virus.
The Louisiana patient was infected with the D1.1 genotype of the H5N1 virus. Although D1.1 is related to other D1.1 viruses found in recent human cases in Washington State and British Columbia, Canada, it is distinct from the widely spreading B3.13 genotype that has caused H5N1 outbreaks in dairy cows, poultry, and other animals and has been linked to sporadic human cases in the United States, according to the CDC.
Despite evidence of some changes in the virus between the Louisiana patient and samples from poultry on the patient’s property, “these changes would be more concerning if found in animal hosts or in early stages of infection,” according to the CDC. The CDC and the Louisiana Department of Health are conducting additional sequencing to facilitate further analysis.
In the meantime, the risk to the general public for H5N1 remains low, but individuals who work with or have recreational exposure to birds, poultry, or cows remain at increased risk.
The CDC and the Louisiana Department of Health advise individuals to reduce the risk for H5N1 exposure by avoiding direct contact with wild birds or other animals infected or possibly infected with the virus, avoiding any contact with dead animals, and keeping pets away from sick or dead animals and their feces. Additional safety measures include avoiding uncooked food products such as unpasteurized raw milk or cheese from animals with suspected or confirmed infections and reporting sick or dead birds or animals to the US Department of Agriculture by calling 1-866-536-7593 or the Louisiana Department of Agriculture and Forestry Diagnostic Lab by calling 318-927-3441.
The CDC advises clinicians to consider H5N1 in patients presenting with conjunctivitis or signs of acute respiratory illness and a history of high-risk exposure, including handling sick or dead animals, notably birds and livestock, within 10 days before the onset of symptoms. Other risk factors include consuming uncooked or undercooked food, direct contact with areas contaminated with feces, direct contact with unpasteurized milk or other dairy products or with parts of potentially infected animals, and prolonged exposure to infected animals in a confined space.
Clinical symptoms also may include gastrointestinal complaints such as diarrhea, as well as fatigue, arthralgia, and headache. Patients with more severe H5N1 may experience shortness of breath, altered mental state, and seizures, and serious complications of the virus include pneumonia, acute respiratory distress syndrome, multiorgan failure, and sepsis, according to the CDC.
Clinicians who suspect H5N1 cases should contact their local public health departments. The CDC offers additional advice on evaluating and managing patients with novel influenza A viruses.
A Clinician’s Take
“Some symptoms of avian flu include fever, cough, sore throat, runny nose, fatigue, body aches or eye redness or irritation,” Shirin A. Mazumder, MD, associate professor and infectious disease specialist at The University of Tennessee Health Science Center, Memphis, said in an interview. “The timing to the development of symptoms after exposure is typically within 10 days. Avian influenza should be considered when individuals develop symptoms with a relevant exposure history,” she said.
Whenever possible, avoidance of sick or dead birds and other animals is ideal, but for those who must have contact with sick or dead birds, poultry, or other animals, personal protective equipment (PPE) including a respirator, goggles, and disposable gloves is recommended, said Mazumder.
“For those working in high-exposure settings, additional PPE including boots or boot covers, hair cover, and fluid-resistant coveralls are recommended,” she said. “Other protective measures include avoiding touching surfaces or materials contaminated with feces, mucus, and saliva from infected animals and avoid[ing] the consumption of raw milk, raw milk products, and undercooked meat from infected animals,” she added.
Hunters handling wild game should dress birds in the field, practice good hand hygiene, and use a respirator or well-fitting mask and gloves when handling the animals to help prevent disease, said Mazumder.
In addition, those working with confirmed or suspected H5N1 cases should monitor themselves for symptoms, said Mazumder. “Those who become ill within 10 days of exposure to an infected animal or source should isolate from household members and avoid going to work or school until infection is excluded. It is important to reach out to a healthcare professional if you think you may have been exposed or if you think you are infected,” she said.
There is no currently available vaccine for H5N1 infection, but oseltamivir can be used for chemoprophylaxis and treatment, said Mazumder. “The seasonal flu vaccine does not protect against avian influenza; however, it is still important to ensure that you are up to date on the latest flu vaccine to prevent the possibility of a coinfection with seasonal flu and avian flu,” she emphasized.
More research is needed to better understand how the influenza virus is transmitted, said Mazumder. “The potential for the virus to evolve and mutate, and how it affects different hosts, are all factors that can impact public health decisions,” she said. “In addition, further research into finding a vaccine and improving surveillance methods are necessary for disease prevention,” she said.
Mazumder had no financial conflicts to disclose.
A version of this article appeared on Medscape.com.